We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.

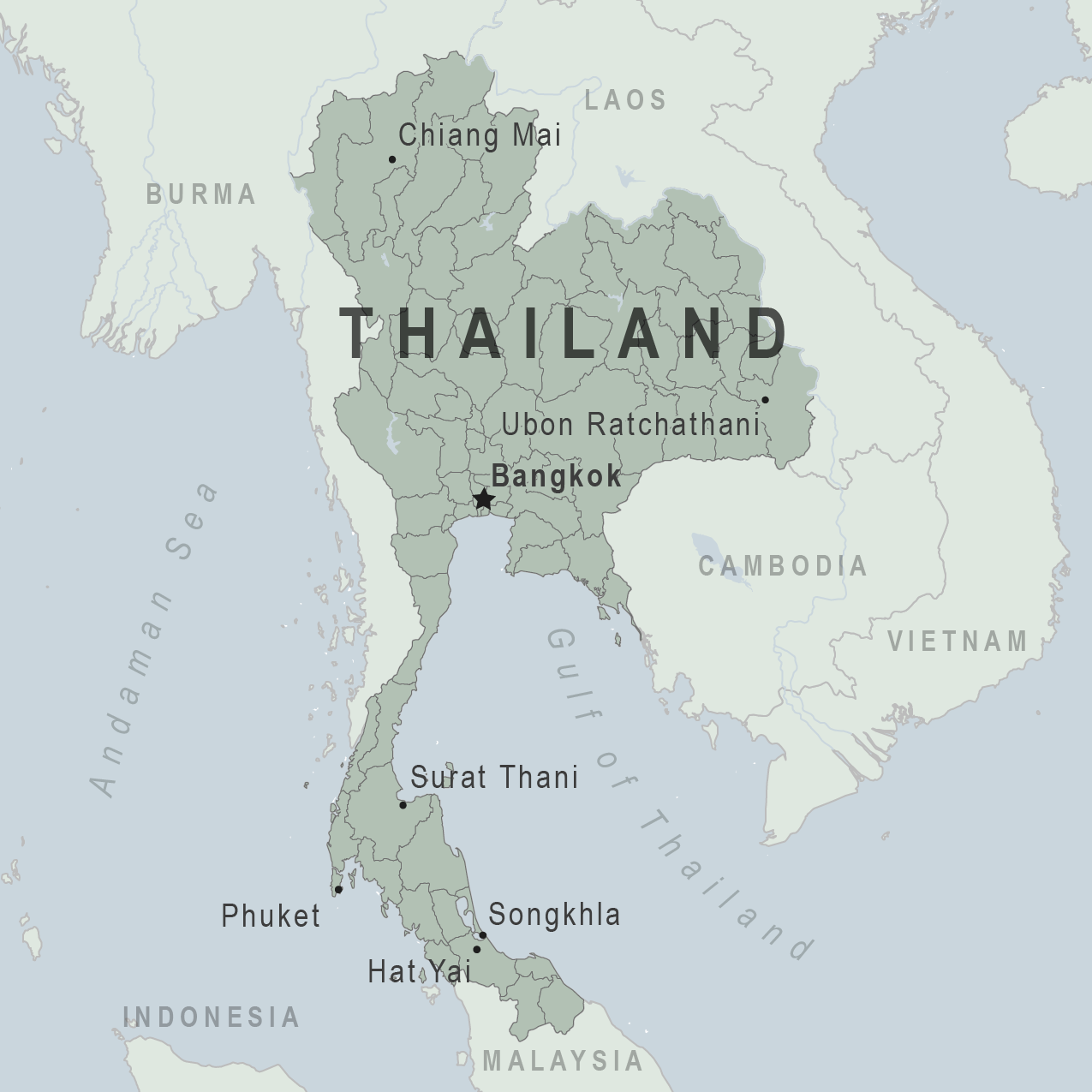
Thailand Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
There are no notices currently in effect for Thailand.
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
There is no longer active cholera transmission and vaccine is not recommended.
Cholera - CDC Yellow Book
Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Thailand.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers younger than 60 years old traveling to Thailand. Unvaccinated travelers 60 years and older may get vaccinated before traveling to Thailand.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
Japanese Encephalitis
Recommended for travelers who
- Are moving to an area with Japanese encephalitis to live
- Spend long periods of time, such as a month or more, in areas with Japanese encephalitis
- Frequently travel to areas with Japanese encephalitis
Consider vaccination for travelers
- Spending less than a month in areas with Japanese encephalitis but will be doing activities that increase risk of infection, such as visiting rural areas, hiking or camping, or staying in places without air conditioning, screens, or bed nets
- Going to areas with Japanese encephalitis who are uncertain of their activities or how long they will be there
Not recommended for travelers planning short-term travel to urban areas or travel to areas with no clear Japanese encephalitis season.
Japanese encephalitis - CDC Yellow Book
Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine for US Children
CDC recommends that travelers going to certain areas of Thailand take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for Thailand.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
Rabid dogs are commonly found in Thailand. However, if you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other mammal while in Thailand, rabies treatment is often available.
Consider rabies vaccination before your trip if your activities mean you will be around dogs or wildlife.
Travelers more likely to encounter rabid animals include
- Campers, adventure travelers, or cave explorers (spelunkers)
- Veterinarians, animal handlers, field biologists, or laboratory workers handling animal specimens
- Visitors to rural areas
Since children are more likely to be bitten or scratched by a dog or other animals, consider rabies vaccination for children traveling to Thailand.
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
Yellow Fever
Required for travelers ≥9 months old arriving from countries with risk for YF virus transmission; this includes >12-hour airport transits or layovers in countries with risk for YF virus transmission. 1
Yellow Fever - CDC Yellow Book
Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
Clinical Guidance
Avoid bug bites.
Chikungunya
- Mosquito bite
- Avoid Bug Bites
- Mosquito bite
Leishmaniasis
- Sand fly bite
- An infected pregnant woman can spread it to her unborn baby
Airborne & droplet
Avian/bird flu.
- Being around, touching, or working with infected poultry, such as visiting poultry farms or live-animal markets
- Avoid domestic and wild poultry
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Thailand, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene | Healthy Water
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Thailand. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Some diseases in Thailand—such as dengue, Zika, and filariasis—are spread by bugs and cannot be prevented with a vaccine. Follow the insect avoidance measures described above to prevent these and other illnesses.
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Thailand include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Leptospirosis, a bacterial infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Thailand. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Thailand’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in some parts of Thailand. If you are going to a risk area, fill your malaria prescription before you leave, and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Thailand may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Thailand, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
For information traffic safety and road conditions in Thailand, see Travel and Transportation on US Department of State's country-specific information for Thailand .
Traffic flows on the left side of the road in Thailand.
- Always pay close attention to the flow of traffic, especially when crossing the street.
- LOOK RIGHT for approaching traffic.
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
To call for emergency services while in Thailand, dial 1669 for an ambulance, 199 for the fire department, and 191 for the police. Write these numbers down to carry with you on your trip.
Learn as much as you can about Thailand before you travel there. A good place to start is the country-specific information on Thailand from the US Department of State.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Thailand for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution, update may 10, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Learn about your destination
Take 90 seconds for safer travel.
Travel Advisory Levels
Enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:

Search Smartraveller

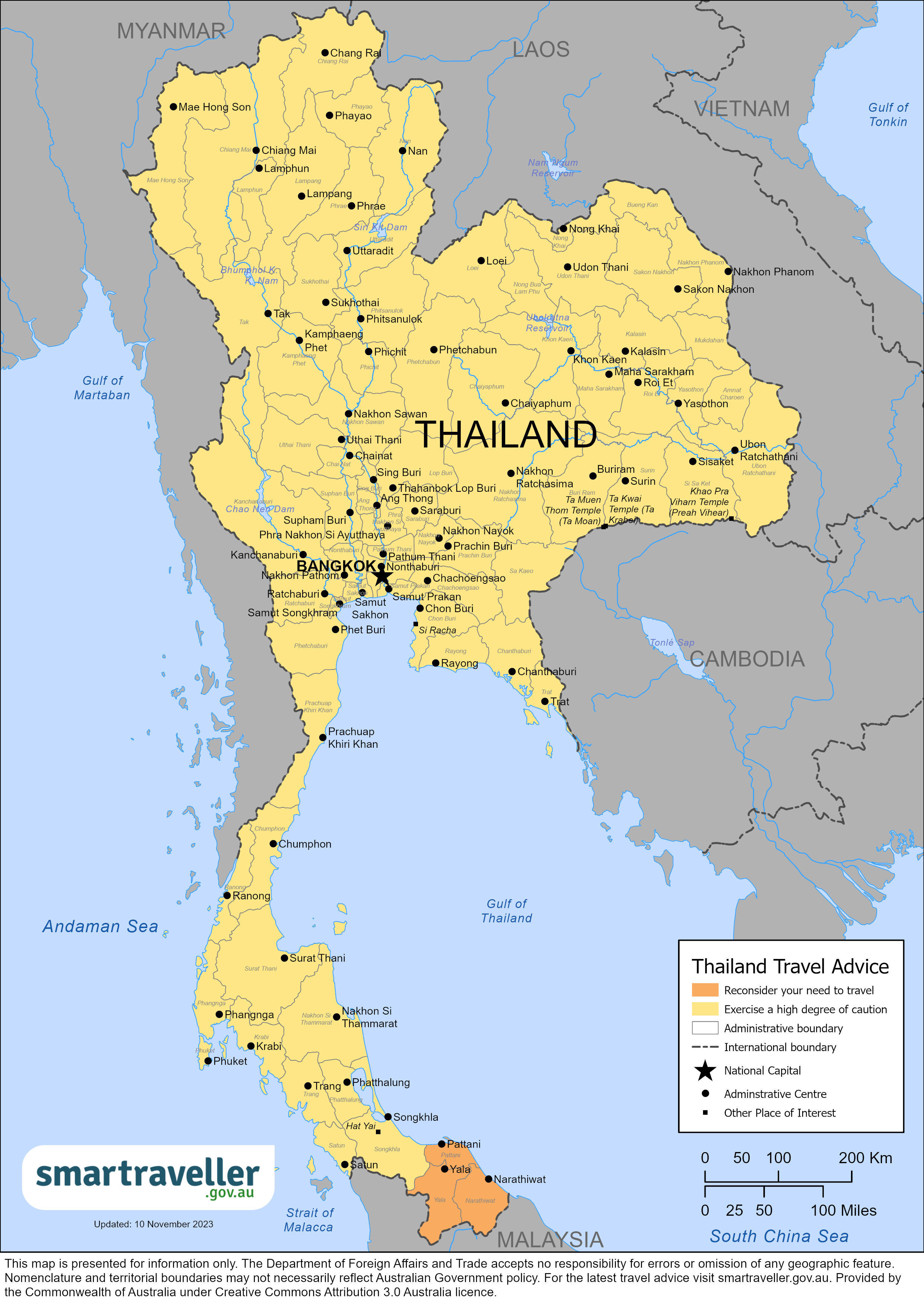
Latest update
Exercise a high degree of caution in Thailand overall due to security and safety risks.
Higher levels apply in some areas.
Thailand (PDF 998.61 KB)
Asia (PDF 2.21 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Fire and rescue services, medical emergencies.
Call 1669 for medical emergencies and rescue services.
Call 1724 for an ambulance in Bangkok. 1669 Nationwide.
Call 191 for police.
Call 1155 for the tourist police.
Advice levels
Exercise a high degree of caution in Thailand overall due to security and safety risks.
Reconsider your need to travel to Yala, Pattani and Narathiwat provinces.
Reconsider your need to travel to:
- Yala province,
- Pattani province, and
- Narathiwat province
due to ongoing risks of low-level insurgent activity, including terrorism.
See Safety .
- Road accidents are a significant cause of injury. Be alert at all times on the roads.
- Floods and severe weather can disrupt essential services during the wet season (June to November). Follow the advice of local officials.
- Scams, credit card fraud and ATM fraud are common.
- Sexual assault, assault, robbery and drink spiking can happen to tourists. Never leave your drink unattended. Stay with people you trust at parties, in bars, nightclubs and taxis.
- Anti-government protests have previously occurred in Bangkok and other areas of Thailand. The security environment can be unpredictable and turn violent. Those attending protests can face arrest or other legal consequences. Monitor local media for information on protest locations and avoid public gatherings. Take official warnings seriously and follow the advice of local authorities.
- There's an ongoing risk of terrorist attack in Thailand. Popular tourist areas may be the target of terrorist attacks. Thai authorities have warned of possible bombings on symbolic dates or holidays. Be alert to possible threats. Take official warnings seriously and follow the advice of local authorities.
- Reconsider your need to travel to the 3 most southern provinces of the Thailand-Malaysia border: Yala, Pattani and Narathiwat. Low-level insurgent activity continues to occur in these areas.
- Border areas near Cambodia, Myanmar and Malaysia are dangerous due to violence, armed conflict and landmines. Pay close attention to your personal security.
Full travel advice: Safety
- Travellers have been arrested for carrying medicine they bought at a Thai pharmacy without a prescription. Get medical advice before buying medicine.
- Insect-borne diseases include malaria, Zika virus, dengue, chikungunya, Japanese encephalitis and filariasis. Use insect repellent. Ensure your accommodation is insect-proof as possible.
- Animals in parts of Thailand can carry rabies. Don't ever feed, pat or tease monkeys. If you're bitten or scratched by a dog, monkey or other animal, get treatment immediately.
- Thailand has high levels of air pollution. Air pollution can make bronchial, sinus or asthma conditions worse. Check air quality levels on the World Air Quality Index .
- Medical tourism is common. Avoid discount and uncertified medical establishments. Their standards can be poor. Research medical service providers and choose with care.
Full travel advice: Health
- Penalties for drug offences are severe. They include the death penalty.
- Commercial surrogacy is illegal. E-cigarettes, e-baraku, vaporisers and refills are illegal. Smoking on some beaches is illegal. Travel without carrying identification is illegal.
- Penalties for breaking the law can apply to anyone aged under 18 years. Penalties for children can include detention in a juvenile or adult prison.
- Thailand has the death penalty for serious crimes, including murder, attempted murder and rape. Crimes against the state and offences against the monarchy can also attract the death penalty. Take care not to cause offence about the monarchy, including on social media.
Full travel advice: Local laws
You can get a visa exemption for up to 30 days on arrival (restricted to 2 entries per calendar year). The visa exemption is strictly for tourism purposes only. If your travel is not for tourism purposes, contact the nearest Royal Thai Embassy or Consulate-General to apply for the appropriate visa.
- You may be subject to biometric screening at points of entry, and restrictions may change at short notice. Check with your airline, the International Air Transport Association (IATA) or the nearest Thai Embassy for the latest information.
- You can transit between international flights in Bangkok's Suvarnabhumi Airport . Ensure that your connecting flight is booked on the same itinerary and ticket. You must remain in the transiting area in the airport.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter tells you what the Australian Government can and can't do to help when you're overseas.
- For consular help, contact the Australian Embassy, Bangkok , or the Australian Consulate-General, Phuket .
- To stay up to date with local information, follow the Embassy's social media accounts.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Civil unrest and political tension, security situation .
The security situation can be unpredictable in Thailand. Large protests have occurred in Bangkok and other areas. In previous years, large political protests and government crowd control operations have resulted in violence.
More incidents are possible.
To stay safe during periods of unrest:
- avoid demonstrations, processions and public gatherings
- follow media and other sources
- take official warnings seriously
- follow the advice of local authorities
- If you see a suspicious package, stay clear and report it to Police
More information:
- Demonstrations and civil unrest
Thailand-Cambodia border
Thailand and Cambodia have an ongoing border dispute. There's a risk of landmines and unexploded weapons near the Thai-Cambodian border area.
Be extra careful at tourist areas, including:
- the Preah Vihear temple - Khao Pra Viharn in Thailand
- the Ta Kwai temple - Ta Krabei in Cambodia
- the Ta Muen Thom temple - Ta Moan in Cambodia
Tourist attractions and border crossings in this area may close with little or no notice.
Thailand-Myanmar border
Fighting and armed theft can occur along the Thai-Myanmar border. This includes:
- fighting between the Burmese military and armed ethnic opposition groups
- clashes between Thai security forces and armed criminal groups, such as drug traffickers
Armed clashes between the military and opposition groups inside Myanmar may lead to border closures.
If you try to cross the border illegally, you may be detained and deported.
Bandits may target you if you travel through national parks in this border region.
If you travel to this region:
- monitor the news
- watch out for other signs of unrest
- pay close attention to your personal security
Thailand-Malaysia border
Reconsider your need to travel to or from the three most southern provinces:
Violence includes attacks and bombings, with deaths and injuries. Since 2004, over 6500 people have been killed and many more injured in these provinces.
Bombings are often coordinated to target people who respond to the first explosion.
Over the past few years, multiple coordinated explosions have occurred in the southern border provinces, and low-level insurgent activity continues.
If you travel to or stay in these provinces, you could get caught up in violence directed at others.
Attacks can happen at any time.
Terrorism is a threat worldwide.
Attacks, including bombings and shootings, are possible anytime. They can happen anywhere, including Bangkok and Phuket.
Popular tourist areas may be the target of terrorist attacks.
Thai authorities have warned of possible bombings on symbolic dates or holidays.
Possible targets for future attacks include:
- shopping malls, markets and banks
- hotels and beach resorts
- restaurants, bars and nightclubs
- schools and places of worship
- outdoor recreation events
Other targets include public buildings, public transport, airports and sea ports.
To reduce your risk of being involved in a terrorist attack:
- have a clear exit plan in case there's a security incident
- be alert to possible threats
- report suspicious activity or items to police
- monitor the media for threats
If there is an attack, leave the area as soon as it's safe. Avoid the affected area in case of secondary attacks.
Gun-related violence can occur at any time. On 3 October 2023, 3 people were killed and 4 injured in a shooting at the Siam Paragon mall in Bangkok. On 6 October 2022, 36 people were killed in a shooting and stabbing incident in Nong Bua Lamphu province.
Sexual assault and violent crime
Travellers may experience sexual assault , other assault and robbery .
Be extra careful in tourist spots such as Khao San Road in Bangkok and the night-time entertainment zones in Bangkok, Pattaya and Phuket.
Be aware of drink-spiking. Don't drink homemade or local cocktails. They can contain narcotics or poison. You're at higher risk of sexual assault and theft if you get drugged.
Never leave your drink unattended.
Stay with people you trust at parties, in bars, nightclubs and taxis.
Get urgent medical attention if you think you or someone else has been drugged.
If you're a victim of violent crime, including rape, get immediate medical attention.
Under Thai law, courts will only accept the results of a medical examination from some government hospitals. After you've been examined by a government hospital, you can receive medical attention at a private hospital. Please contact the Australian Embassy Bangkok, Consulate-General Phuket, or Consular Emergency Centre in Canberra for assistance.
- Partying safely
Petty crime
Money and passports have been stolen from budget hotel and hostel rooms, and from bags on public transport. Thieves also target luggage stored on trains and below buses.
Bags have been snatched by thieves on motorcycles or sliced open with razor blades.
To reduce your risk of theft:
- don't leave valuables in luggage stowed under buses or away from you on trains
- be wary of motorcycles approaching from behind as you walk on the footpath
- hold bags and backpacks in front of you
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you're connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
More information:
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
Kidnapping
Kidnapping can happen anywhere, anytime, including in destinations that are typically at lower risk.
The Australian Government's longstanding policy is that it doesn't make payments or concessions to kidnappers.
- Kidnapping
Tours and adventure activities
Transport and tour operators don't always follow safety and maintenance standards. This includes for:
- scuba diving
- elephant safaris
- bungee jumping
If you plan to do an adventure activity :
- check if your travel insurance policy covers it
- ask about and insist on minimum safety requirements
- always use available safety gear, such as life jackets or seatbelts
If proper safety equipment isn't available, use another provider.
Climate and natural disasters
Thailand experiences natural disasters and severe weather , including:
- earthquakes
Severe weather events are likely to disrupt transport, electricity and communications.
To stay safe during severe weather:
- check media and weather reports
- check in with your tour operator
- don't enter areas affected by flooding or landslides
If there is a natural disaster:
- secure your passport in a safe, waterproof place
- keep in contact with friends and family
- monitor the media and other local sources of information
- Register with the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System to receive alerts on major disasters.
Storms and floods
Severe storms and widespread seasonal flooding can occur without warning. This includes flash floods.
The wet season in north and central Thailand is from May to October.
In Koh Samui and the south-east of the peninsula, the wet season is from November to March.
- Thai Meteorological Department
- Mekong River Commission — flood levels for the Mekong River
Earthquakes and tsunamis
Earthquakes occur in Thailand.
Tsunamis are more likely in Thailand because of the risk of earthquakes.
Check with the US Tsunami Warning Centre for updates on seismic activity and tsunamis.
If you're near the coast, move to high ground straight away if advised, or if you:
- feel a strong earthquake that makes it hard to stand up
- feel a weak, rolling earthquake that lasts a minute or more
- see a sudden rise or fall in sea level
- hear loud and unusual noises from the sea
Don't wait for official warnings such as alarms or sirens. Once on high ground, monitor local media.
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
- what activities and care your policy covers, including in terms of health and travel disruptions
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away
Physical and mental health
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
If you plan to bring medication, check if it's legal in Thailand. Take enough legal medicine for your trip.
Get medical advice before buying medicine in Thailand. Travellers have been arrested for carrying medicine they bought at a Thai pharmacy without a prescription.
Carry a copy of your prescription or a letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medication is
- your required dosage
- that it's for personal use
- Medications
Health risks
Insect-borne illnesses.
Zika virus is a risk in Thailand. If you are pregnant, defer non-essential travel to affected areas. Speak to your doctor before you travel. Several cases have been reported, including in Bangkok.
The Department of Health and Aged Care's Zika virus bulletin has advice for all travellers on how to reduce Zika virus risks. There's no vaccine for Zika virus.
Malaria is a risk throughout the year in rural areas. The worst affected areas are near the borders with Cambodia, Laos and Myanmar.
Dengue occurs in Thailand. It's common during the rainy season:
- November to March in Koh Samui and the south-east of Thailand
- May to October in the rest of Thailand, including Phuket
Dengue peaks in July and August although it is prevalent throughout the year. There's no vaccine or specific treatment for dengue.
Other insect-borne diseases include:
- chikungunya
- Japanese encephalitis
To protect yourself from disease:
- make sure your accommodation is insect-proof
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
- consider taking medicine to prevent malaria
- get vaccinated against Japanese encephalitis
- Infectious diseases
Animals in parts of Thailand can carry rabies .
Rabies is deadly. Humans can get rabies from mammals, such as:
- other animals
Don't ever feed, pat or tease monkeys, even if you're encouraged to.
If you're bitten or scratched by a dog, monkey or other animal, get treatment as soon as possible.
Smoke haze and air pollution
Thailand has high levels of air pollution. It can reach hazardous levels. Bangkok and Chiang Mai can be particularly bad.
Air pollution can make bronchial, sinus or asthma conditions worse.
Smoke haze is an issue across the north and north-east of Thailand from March to April.
Check air quality levels on the World Air Quality Index .
Get advice from your doctor before you travel.
Medical care
Medical facilities.
The standard of medical facilities varies.
In an emergency, we recommend you contact an ambulance on 1669.
Private hospitals in major cities have high standards of medical care. Services can be limited in other areas.
Hospitals and doctors often need to confirm your insurance before they'll treat you, even in an emergency. Otherwise you may need to pay cash up-front. Costs can be very high.
Hospitals in Bangkok and other large cities can treat serious illnesses and accidents. In other areas, you may need to be moved to a place with better facilities. Medical evacuation can be very expensive.
Decompression chambers are located near popular dive sites in:
Medical tourism
Medical tourism , including for cosmetic and sex-change operations, is common.
Standards at discount and uncertified medical establishments can be poor. Serious and life-threatening complications can result.
Some hospitals and clinics have refused to compensate patients:
- who aren't satisfied with the results of cosmetic surgery
- who are harmed during surgery
- who die during surgery
Do your research. Choose your medical service providers with care.
Don't use discount or uncertified medical service providers.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
If you're arrested or jailed , the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
Penalties for drug offences are severe. They include the death penalty.
Possession of even small quantities of drugs for recreational purposes can lead to long jail sentences and deportation.
Thai authorities may conduct spot-checks for illegal drugs in tourist areas.
Travellers have been targeted for narcotic tests. Under Thai law, authorities have the right to demand urine samples from people suspected of taking illegal drugs.
If you're asked to submit a urine sample, ask to do it at a police station. You can also ask to contact the Tourist Police. Call 1155 for English-speaking officers.
Private recreational use of cannabis is legal if the THC content is below 0.2% in weight. Cannabis use in public places remains illegal, and smoking outside is considered a public nuisance, and offenders risk fines and arrest. It is still illegal to sell or supply any extracts of cannabis containing more than 0.2% of THC.
While cannabis is decriminalised in Thailand, be aware of the next destination you are travelling to, where it may be illegal, including when transiting. This may include residual amounts of illicit drugs in your system (such as in your blood or saliva) or on items you are carrying.
Follow directions from local authorities.
- Carrying or using drugs
Surrogacy laws
Commercial surrogacy is illegal.
- Going overseas for international surrogacy
- Going overseas to adopt a child
E-cigarettes
E-cigarettes, e-baraku, and other related vaporisers, including refills, are prohibited. You can't import or transfer them through Thailand, even for personal use.
Producing or selling these items is illegal. You face either 10 years of imprisonment or a fine up to THB1 million, or both.
Penalties for breaking the law can be severe.
These penalties can also apply to anyone aged under 18 years who is subject to Thai juvenile judicial processes. Penalties can include detention in a juvenile or adult prison.
The death penalty can apply to:
- attempted murder
- crimes against the state, including treason
- some offences against the monarchy
Insulting the monarchy, or defacing images of the monarchy - including on a bank note bearing the King's image - can lead to prison terms of up to 15 years.
Take care not to cause offence when posting, commenting or liking items about the monarchy, including on social media.
In Thailand, it's illegal to:
- travel without carrying identification
- gamble - other than at a few major race tracks
- make a false statement to police, including about an insurance claim
It is also illegal to smoke on beaches in tourist areas, including:
- Prachuap Khiri Khan
- Songkhla
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
- Staying within the law and respecting customs
Dual citizenship
Thai-Australian dual nationals may be liable to complete military conscription.
If you're a dual national, contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Thailand before you travel.
- Dual nationals
Local customs
Respect local customs and take care to not offend. Deliberately ignoring local customs can cause grave offence.
Do not show the soles of your feet or touch the top of a person's head. These are insulting in Thai culture.
If in doubt, ask for local advice.
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. Contact the nearest Embassy or consulate of Thailand, the Royal Thai Embassy Canberra or Royal Thai Consulate-General Sydney . See the official website of the Tourism Authority of Thailand for the latest details about visas, currency, customs and quarantine rules.
Visas overstays
If you overstay your visa, you'll need to pay a fine before you can leave. You can also be:
- banned from re-entering Thailand
Thai authorities can blacklist you, which means you can never return to Thailand.
Penalties for not paying the fine include long prison sentences. Conditions at Immigration Detention Centres are harsh.
- Thai Immigration Bureau
Border measures
International passengers can transit Suvarnabhumi Airport , Bangkok.
You may be subject to biometric screening at points of entry. Clarify entry requirements with your airline, International Air Transport Association (IATA) or your nearest Thai Embassy.
Departure from Thailand
Travellers should refer to the relevant airline or travel provider for information about departing Thailand.
- Royal Thai Embassy , Canberra
- Thai government's Facebook page
Some countries won't let you enter unless your passport is valid for 6 months after you plan to leave that country. This can apply even if you're just transiting or stopping over.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
You can end up stranded if your passport is not valid for more than 6 months.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
Don't give your passport to third parties - like a jet ski or motorcycle rental businesses - as a guarantee. Companies may hold on to the passport and ask for payment for damages.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
Passport with ‘X’ gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can't guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
- LGBTQIA+ travellers
The currency of Thailand is the Thai Baht (THB).
You can convert Australian dollars for THB in tourist areas, major cities and towns.
ATMs are available in cities and regional centres.
Most hotels, restaurants and higher-end shops accept international credit cards.
Card skimming occurs. See Safety
Local travel
Driver's permit.
To drive a car or motorcycle in Thailand, you'll need a valid Australian driver's licence for the type of vehicle you're using.
To drive a motorbike, you'll need a valid motorcycle licence. Some rental companies will tell you otherwise.
You are required to have an International Driving Permit (IDP).
Don't drive any vehicles not covered by your Australian licence.
The Department of Land Transport issues Thai driver’s licences. Contact them to confirm:
- your eligibility
- what documents you need to apply
The legal driving age in Thailand is 18.
Road travel
Thailand has one of the highest traffic-related fatality rates in the world. Motorcyclists are most at risk.
Road accidents are common, including in resort areas such as Phuket, Pattaya and Koh Samui.
Driving in Thailand is dangerous due to:
- reckless passing
- ignoring traffic laws
Be extra careful during holidays, such as Songkran (Thai New Year). Alcohol use and congestion are worse during these times.
Don't drink and drive.
If you're walking, use overhead walkways. Look in both directions before crossing streets, even at marked crossways.
- Driving or riding
Motorcycles
Under Thai law, motorcycle riders and passengers must wear a helmet. However, hire companies or motorcycle taxis rarely provide helmets. You may need to shop around to hire a helmet.
Australians are regularly injured or die in motorbike accidents in Thailand. Alcohol is often involved.
If you're in an accident, police may detain or arrest you until compensation is agreed. This can often cost thousands of dollars.
Many vehicle hire companies don't have insurance.
If you have a motorcycle accident, you could be responsible for any damages, loss or costs associated with injury to others. The embassy can't help you negotiate on compensation demands.
Lawyers who can represent you are available from:
- Australian Embassy and Consulates-General in Thailand
- the Consular Emergency Centre in Canberra
If you plan to hire a motorbike, make sure:
- your insurance policy covers it
- you have a valid motorcycle licence
- the hiring company has comprehensive and third-party insurance
- you know the excess you would need to pay if you have an accident
- you always wear a helmet
Don't drink and drive, or drink and ride.
Never give your passport as a deposit or guarantee.
Taxis, tuktuks and motorcycle taxis
Official, metered taxis are generally safe and convenient. Be alert to possible scams and safety risks.
Be aware of apparently friendly taxi or tuktuk drivers who offer you cheap tours. They will take you to shops where they receive a commission. You may be overcharged or sold worthless goods or gems.
Before you get in an unmetered taxi, tuktuk or motorcycle taxi, agree on the fare and the route.
Make sure your bags are secure when you're travelling in a tuktuk or motorcycle taxi.
Never put yourself in danger by confronting a taxi, tuktuk or motorcycle taxi driver. Call the Tourist Police on 1155 if you need help.
Be careful when opening taxi doors. Look out for other vehicles, pedestrians and cyclists.
Ferry and speedboat travel can be dangerous. Serious incidents involving tourists have occurred and people have died.
If you plan on travelling by boat or ferry:
- check safety standards are in place
- check there is enough safety equipment for everyone
- wear your life jacket at all times
- avoid travelling after dark
- don't get on overcrowded boats
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check Thailand's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network.
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
Call 1724 for an ambulance in Bangkok.
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
Australian Embassy, Bangkok
181 Wireless Road Lumphini, Pathumwan Bangkok, Thailand. 10330 Phone: (+66 2) 344 6300 Fax: (+66 2) 344 6593 Website: thailand.embassy.gov.au Email: [email protected] Facebook: Australia in Thailand X: @AusAmbBKK
Check the Embassy website for details about opening hours and any temporary closures.
Australian Consulate-General, Phuket
6th Floor CCM Complex 77/77 Chalermprakiat Rama 9 Road (Bypass Road) Muang Phuket, Thailand, 83000 Phone: (+66 76) 317 700 Fax: (+66 76) 317 743 Website: phuket.consulate.gov.au E-mail: [email protected]
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Thailand?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Thailand travel advice
Latest updates: Editorial change
Last updated: May 23, 2024 08:00 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, thailand - exercise a high degree of caution.
Exercise a high degree of caution in Thailand due to ongoing political tensions and sporadic demonstrations in Bangkok and elsewhere in the country.
Southern provinces of Narathiwat, Pattani, Songkhla and Yala - Avoid all travel
Back to top

Southern provinces of Narathiwat, Pattani, Songkhla and Yala
Separatist insurgents periodically perpetrate criminally and politically motivated attacks in the southernmost provinces of Narathiwat, Pattani, Songkhla and Yala.
These deadly attacks include shootings, bombings and arson, and are usually directed at military, government and security buildings and personnel. They have also occurred in a variety of public places.
Martial law and heavily enhanced security measures are in place in Narathiwat, Pattani, Yala, and Sadao District in Songkhla.
Increased enforcement powers allow authorities to:
- detain suspects without charge
- conduct searches
- seize objects or documents
- impose curfews
You risk becoming a collateral victim of an attack if you travel in these provinces.
Myanmar border areas in the provinces of Mae Hong Son and Tak
Exercise a high degree of caution when travelling to the Thailand–Myanmar border areas in the provinces of Mae Hong Son and Tak.
Occasional violence, banditry and clashes between government forces and drug traffickers occur.
Border crossing points may be closed without notice. Cross at designated border crossing points only, with the required travel documentation.
Preah Vihear Temple area and surrounding border region
Thailand and Cambodia have an ongoing border dispute in the region. There are reports of landmines in the Preah Vihear temple area.
Exercise a high degree of caution if you are travelling to any other Thai–Cambodian border areas.
Political tensions
Political instability in Thailand has created a volatile and unpredictable security environment throughout the country, particularly in Bangkok.
Legal provisions may allow the military to retain and exercise sweeping powers that could include the right to:
- prevent public gatherings
- censor media
- set up checkpoints
- restrict movement
- search for weapons
- exercise force in response to violence
Such measures could be enforced at any time. Some television, radio stations and web sites may be unavailable, and access to social media services may be intermittently suspended.
Petty crime, such as purse snatching, pickpocketing and theft, is common. Thieves sometimes use razors to cut purses and bags open to remove their contents.
- Don’t leave bags unattended
- Ensure that your personal belongings, including your passport and travel documents, are secure at all times, especially in tourist areas, crowded markets and bus or train stations
- Avoid walking in dark alleys or isolated areas
Thefts occur on cross-country buses and vans. Personal belongings, including passports, have been stolen from luggage compartments under buses, especially on long-distance journeys. Use only reputable transportation companies.
Break-ins occur at budget guesthouses, sometimes while guests are asleep in their rooms.
Be careful at night in entertainment areas throughout the country, including in Koh Pha Ngan and Koh Tao, particularly during full moon parties, Songkran, and other events in popular tourist locations. Robberies and assaults (including sexual assaults) can occur during these events. Passport thefts and losses are common.
Violent crime against foreigners occurs occasionally.
You should report all criminal incidents to the Thai police in the jurisdiction where the incident occurred before leaving Thailand.
Many Canadians fall victim to a variety of scams while visiting Thailand. You should report all incidents to the tourist police.
Credit card and ATM fraud
Credit card and ATM fraud occurs. Be cautious when using debit or credit cards:
- pay careful attention when your cards are being handled by others
- use ATMs located in well-lit public areas or inside a bank or business
- avoid using card readers with an irregular or unusual feature
- cover the keypad with one hand when entering your PIN
- check for any unauthorized transactions on your account statements
Rental scams
Rental companies have at times accused renters of causing damage upon return of the equipment. In some cases, renters who refused to pay were harassed and threatened, and their passports (left as collateral) were withheld. Some companies have also stolen the motorcycle and then claimed compensation from the renter.
Before renting a motorcycle or personal watercraft, read all rental contracts thoroughly to ensure that the vehicle is insured to cover damage and theft. Take photos of existing damage on rented vehicles as proof of pre-existing damage.
You must never use your Canadian passport as collateral for rental. If your passport is inaccessible or stolen because of such a situation, you may be subject to investigation by Passport Canada and may receive limited passport services.
Only rent from reputable companies.
Entertainment venues
Some bars, nightclubs and entertainment venues may try to charge exorbitant prices. Discussions about overcharging may lead to threats of violence.
- Confirm the prices before consumption
- Avoid running a tab
- Avoid leaving your credit card with bar or restaurant staff
Travel agencies
When dealing with travel agencies, ensure that the company is a reputable tour organization before providing payment.
Investment fraud
If you plan on buying property or making other investments in Thailand seek legal advice in Canada and Thailand. Do so before making commitments. Related disputes could take time and be costly to resolve.
Gems and jewellery purchases
In scams involving gems and jewellery, merchants sell lower-quality items at inflated prices with promises that the items can be resold at a profit. The guarantees that merchants offer are not always honoured.
Carefully consider all purchases if you are not knowledgeable about gems and jewellery. The Government of Canada cannot assist in obtaining refunds for purchases made.
Overseas fraud
Spiked food and drinks
Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers. Be wary of accepting snacks, beverages, gum or cigarettes from new acquaintances. These items may contain drugs that could put you at risk of sexual assault and robbery.
Seek immediate medical attention if you suspect that you have been drugged.
Women’s safety
Sexual assaults against foreign women have occurred. Be particularly vigilant during full moon parties, Songkran, and other events in popular tourist locations.
If you are victim of a sexual assault, you should seek medical attention and report the situation immediately to local authorities and the nearest Canadian office.
Advice for women travellers
There is a threat of terrorism in Thailand. Although infrequent outside of the southern provinces of Narathiwat, Pattani, Songkhla and Yala, small-scale bomb attacks have occurred in public places. Further attacks are possible.
Targets could include:
- government buildings, including schools
- places of worship
- airports and other transportation hubs and networks
- public areas such as tourist attractions, restaurants, bars, coffee shops, shopping centres, markets, hotels and other sites frequented by foreigners
Always be aware of your surroundings when in public places.
Demonstrations
Large demonstrations are taking place regularly in Bangkok and across the country. There are social tensions, and demonstrations are likely to continue.
Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. They can also disrupt traffic and public transportation when they block major roads and intersections and may cause the closure of mass transit stations.
Maintain a high level of personal security awareness at all times.
Demonstration sites in Bangkok include:
- the areas around the Victory Monument
- Thammasat University
- the Bangkok Arts and Cultural Centre
- the Democracy Monument
- Ratchaprasong intersection
Other areas of the city may also be affected by protests and associated movements. Demonstrations have also taken place in other cities.
- Avoid military installations and concentrations of security personnel
- Expect a heightened security presence in several areas
- Carry identification documents at all time
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Water activities
Deaths have occurred due to contact with poisonous jellyfish off Koh Lanta, Koh Pha Ngan, Koh Phi Phi, Krabi and Phuket.
Riptides in coastal areas can be strong, including in the popular destinations of Cha-am/Hua Hin, Koh Samui, Pattaya, Phuket and Rayong. There have been several deaths due to drowning.
Diving schools and rescue services may not adhere to international standards.
- Rent water sports equipment only from operators affiliated with major international training organizations
- Exercise extreme caution when swimming or practising water activities
- Heed flag warnings and don’t swim when a red flag is displayed
- If stung by a jellyfish, seek immediate medical assistance
Water safety abroad
Adventure tourism
If you undertake adventure sports, such as zip-lining, rock climbing, speleology, elephant trekking or parasailing, choose a well-established and reputable company that has insurance.
Tour operators may not adhere to international standards. If you have any doubt concerning the safety of the installation or equipment, don’t use them. Ensure that your travel insurance covers the recreational activities you choose.
If engaging in adventure tourism:
- never do so alone
- always hire an experienced guide from a reputable company
- buy travel insurance that includes helicopter rescue and medical evacuation
- ensure that your physical condition is good enough to meet the challenges of your activity
- don’t venture off marked trails
- ensure that you’re properly equipped
- ensure that you’re well informed about weather and other conditions that may pose a hazard
- inform a family member or friend of your itinerary
- obtain detailed information on each activity before setting out
Chemical pesticide poisoning
There have been cases of poisoning linked to the use of chemical pesticides, including phosphine. Seek immediate medical assistance if you believe that you have been exposed to a chemical pesticide and are experiencing unusual symptoms.
Seek information on whether or not chemical pesticides are used in your accommodations.
Road safety
Accidents involving vehicles and pedestrians are extremely frequent in Thailand.
Hazardous road conditions, adverse weather conditions, local disregard for traffic laws and drunk driving result in frequent accidents.
Some vehicles may drive against the flow of traffic and on the sidewalks, particularly motorcycles.
Drunk driving and accidents are much more frequent around the western New Year (January 1) and Thai New Year (Songkran, mid-April). Be particularly vigilant when driving during these holiday periods.
Slow-moving trucks limit speed and visibility. Avoid driving on mountain roads at night, especially during the rainy season (June to October). Paved roads connect major cities, but most have only two lanes. Some roads can become impassable, particularly during the rainy season.
Pedestrians and cyclists should be particularly careful. You should always use elevated walkways/pedestrian bridges whenever possible, especially in Bangkok.
Motorcycles
Motorcycle accidents are common and are responsible for the majority of road deaths. Rental scooters and motorcycles are often poorly maintained, making them unsafe to their riders and others on the road.
Helmets are mandatory for motorcycle riders (including passengers), but many helmets don’t meet international safety standards.
Insurance claims could be denied if you were driving without a motorcycle licence.
Avoid driving or riding motorcycles in Thailand, even if you are an experienced motorcyclist
Public transportation
Use licensed taxis from official taxi stands, limousine services or a trusted ride-sharing app.
If arriving by air, arrange to be picked up by hotel shuttle services, use a trusted ride-sharing app, the airport rail-link service or official airport buses.
Unlicensed vehicles (bearing black and white licence plates) are not correctly insured to carry passengers and may not use meters. Many taxis may not be equipped with backseat seatbelts.
Don’t share a taxi with strangers.
Disputes with taxis operators, tuk-tuks (motorized rickshaws), etc., occur and have occasionally resulted in violence or intimidation. Should a dispute occur and you feel threatened, seek local police's assistance to settle the matter.
Marine transportation
Passenger boats accidents have occurred due to overloading and poor maintenance of some vessels. Vessels often lack adequate safety equipment.
Don’t board vessels that appear overloaded or unseaworthy.
In the past, rail lines in the far south have been the targets of sabotage and armed attacks.
Train accidents in recent years have caused injuries and deaths.
Pirate attacks and armed robbery against ships occur in coastal waters. Mariners should take appropriate precautions.
Live piracy report - International Maritime Bureau
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Thai authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid at least 6 months upon entry into Thailand.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: not required for stays of up to 30 days Business visa: required Student visa: required Working visa: required
If you’re travelling to Thailand for tourism with a regular Canadian passport, you can obtain a 30-day visa upon arrival.
If you obtain a multiple-entry tourist visa, you can stay for up to 60 days. The visa is valid for 6 months and must be obtained before travelling.
If you wish to stay longer than 60 days or work or study in Thailand, you must obtain the appropriate visa from a Thai embassy or consulate. Local authorities are actively monitoring and enforcing compliance with visa regulations.
Those applying for non-immigrant visas of category "O-A" need to show proof of a valid health insurance meeting specific criteria.
Guidelines Non-Immigrant Visa (O-A) - Thai General Insurance Association
Other entry requirements
Thai Border officials may ask you to show them a return or onward ticket and proof that you have sufficient funds to support yourself for the duration of your stay.
If you are unable to do so, you may be denied entry.
Entry stamp
You must get an entry stamp from an immigration officer at the point of entry into Thailand. Don’t get your visa, visa extension or entry stamp from visa shops or travel agents in Thailand.
A passport that has been altered or that contains counterfeit visas, and entry/exit stamps is deemed invalid. Offenders can expect jail sentences, fines and deportation, and may also be prohibited from entering Thailand in the future.
Length of stay
The date indicated on your Thai entry stamp determines how long you may stay in the country, even if your visa shows a different date.
All foreigners staying in Thailand longer than 3 months must notify Thailand’s immigration bureau of their residence every 90 days.
The Royal Thai Police perform random visa checks and strict penalties are enforced for overstaying. Canadians overstaying their visa have been arrested and detained until deportation. Deportation procedures are at the foreigner’s own expense and can be lengthy. Detention conditions in immigration detention centres are poor.
If you overstay, regardless of whether you leave Thailand voluntarily or are deported, you may be banned from re-entering Thailand for 1 to 10 years.
Notification of stay longer than 90 days - Thailand’s immigration bureau
Dual citizenship
If you are a dual citizen, you must enter and exit Thailand with the same nationality passport.
Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- Zika virus: Advice for travellers - 31 August, 2023
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is no risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is required if you are coming from or have transited through an airport of a country where yellow fever occurs.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is not recommended.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada * It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Japanese encephalitis is a viral infection that can cause swelling of the brain. It is spread to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito. Risk is very low for most travellers. Travellers at relatively higher risk may want to consider vaccination for JE prior to travelling.
Travellers are at higher risk if they will be:
- travelling long term (e.g. more than 30 days)
- making multiple trips to endemic areas
- staying for extended periods in rural areas
- visiting an area suffering a JE outbreak
- engaging in activities involving high contact with mosquitos (e.g., entomologists)
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes. There is a risk of malaria in certain areas and/or during a certain time of year in this destination.
Antimalarial medication may be recommended depending on your itinerary and the time of year you are travelling. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times: • Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin. • Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows. • Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area. • Wear permethrin-treated clothing. If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
In this destination, rabies is carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by an animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. Rabies treatment is often available in this destination.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Cholera is a risk in parts of this country. Most travellers are at very low risk.
To protect against cholera, all travellers should practise safe food and water precautions .
Travellers at higher risk of getting cholera include those:
- visiting, working or living in areas with limited access to safe food, water and proper sanitation
- visiting areas where outbreaks are occurring
Vaccination may be recommended for high-risk travellers, and should be discussed with a health care professional.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
- In this country, dengue is a risk to travellers. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue.
Zika virus is a risk in this country.
Zika virus is primarily spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can also be sexually transmitted. Zika virus can cause serious birth defects.
During your trip:
- Prevent mosquito bites at all times.
- Use condoms correctly or avoid sexual contact, particularly if you are pregnant.
If you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy, you should discuss the potential risks of travelling to this destination with your health care provider. You may choose to avoid or postpone travel.
For more information, see Zika virus: Pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Human cases of avian influenza have been reported in this destination. Avian influenza is a viral infection that can spread quickly and easily among birds and in rare cases it can infect mammals, including people. The risk is low for most travellers.
Avoid contact with birds, including wild, farm, and backyard birds (alive or dead) and surfaces that may have bird droppings on them. Ensure all poultry dishes, including eggs and wild game, are properly cooked.
Travellers with a higher risk of exposure include those:
- visiting live bird/animal markets or poultry farms
- working with poultry (such as chickens, turkeys, domestic ducks)
- hunting, de-feathering, field dressing and butchering wild birds and wild mammals
- working with wild birds for activities such as research, conservation, or rehabilitation
- working with wild mammals, especially those that eat wild birds (e.g., foxes)
All eligible people are encouraged to get the seasonal influenza shot, which will protect them against human influenza viruses. While the seasonal influenza shot does not prevent infection with avian influenza, it can reduce the chance of getting sick with human and avian influenza viruses at the same time.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Tuberculosis is an infection caused by bacteria and usually affects the lungs.
For most travellers the risk of tuberculosis is low.
Travellers who may be at high risk while travelling in regions with risk of tuberculosis should discuss pre- and post-travel options with a health care professional.
High-risk travellers include those visiting or working in prisons, refugee camps, homeless shelters, or hospitals, or travellers visiting friends and relatives.
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that attacks and impairs the immune system, resulting in a chronic, progressive illness known as AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome).
High risk activities include anything which puts you in contact with blood or body fluids, such as unprotected sex and exposure to unsterilized needles for medications or other substances (for example, steroids and drugs), tattooing, body-piercing or acupuncture.
Medical services and facilities
Excellent healthcare is available in major cities, particularly in private hospitals and clinics. Quality of care varies significantly in rural areas.
Establishments may require confirmation of health insurance coverage, a guarantee of payment or an upfront deposit before admitting patients.
Psychiatric or psychological facilities and services in Thailand may not meet international standards. Canadians with mental illness have been committed to state facilities, detained and deported.
Medical evacuation can be very expensive and you may need it in case of serious illness or injury.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Overview of the criminal law system in Thailand
Identification
You must carry identification at all times. Carry a photocopy of your passport bio-data page and Thai visa or entry stamp.
Police may still require that you produce the original document. If you fail to do so, you could be detained.
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs, including cannabis, are very severe. Convicted offenders can expect heavy fines, jail sentences or even the death penalty.
Police regularly perform spot checks to search for illegal drugs, particularly in and around entertainment venues. Uniformed or undercover police may conduct physical searches and may screen your belongings. You may be asked to provide a urine sample.
If you carry prescription drugs or other medicines, keep them in clearly marked, original packaging.
Certain prescription drugs are frequently sold without prescription in entertainment areas and coastal resorts, including on the street. You should never buy controlled drugs without prescription or on the street. These may be counterfeit or could contain illegal substances. If you purchase these drugs, you could be subject to scrutiny or detained.
The legal drinking age in Thailand is 20.
It is illegal to promote the consumption of alcohol. You could be fined or taken to court for posting on social media any pictures that include alcoholic beverages or people consuming alcohol.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
It is prohibited to import, possess or use e-cigarettes, vaporisers, e-baraku (e-hashish) and their refills. Convicted offenders can expect heavy fines or jail sentences of up to 10 years.
A smoking ban is in effect on several beaches across the country and is punishable by a 100,000-baht fine and up to 1 year in prison.
Check with local authorities and look for no-smoking signs before smoking on a beach.
Gambling, with some exceptions, is illegal.
Lèse-majesté
Actions or words that are considered offensive or insulting to the king or the royal family are illegal and may result in criminal prosecution and lengthy prison sentences.
Don’t make any public statement, including online, that could be perceived as critical of:
- the monarchy
- the political situation in Thailand
- the Royal Thai Army
Restricted goods
There are strict regulations regarding the importation and exportation of images of the Buddha, counterfeit goods, pornographic material and other items.
Consult the complete list of restricted and prohibited items before travelling.
Restricted goods - Thai Customs
Feeding fish
Feeding fish in the ocean is illegal and punishable by a 100000-baht fine and up to 1 year in prison.
Do not feed fish in the ocean and avoid boat tour operators who encourage tourists to do so.
Traffic drives on the left.
You must be at least 18 years old to drive a car in Thailand.
You must carry an international driving permit or a Thai driver’s licence to drive in Thailand.
It is illegal to operate a motorcycle without a valid Thai motorcycle licence or an international driving permit with a motorcycle endorsement.
Helmets are mandatory for motorcycle riders (including passengers), but many helmets do not meet international safety standards.
Carry your identification card, driver’s licence and vehicle registration book at all times.
International Driving Permit
Housing foreign citizens
All hosts, including hotel staff and homeowners, must notify local authorities that they are housing foreign citizens within 24 hours of the arrival of these foreigners.
Commercial surrogacy
Commercial surrogacy is illegal in Thailand.
If you’re planning to visit Thailand for the purpose of commissioning surrogacy arrangements, you should consider the potential challenges involved in pursuing international surrogacy and seek specialist legal advice on Thai and Canadian laws prior to making any arrangements.
It is also recommended that you consult with Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) on current policies regarding citizenship through descent and the issuance of Canadian travel documents.
Dual citizenship is not legally recognized in Thailand.
If local authorities consider you a citizen of Thailand, they may refuse to grant you access to Canadian consular services. This will prevent us from providing you with those services.
Travellers with dual citizenship
Compulsory military service
Male Thai citizens are subject to compulsory military service when they reach the age of 21. If you’re a dual Canadian–Thai citizen, you may be subject to this requirement.
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and Thailand.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Thailand by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Thailand to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children’s Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country’s judicial affairs.
- International Child Abduction: A Guidebook for Left-Behind Parents
- Travelling with children
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Emergency Watch and Response Centre
The currency of Thailand is the Thai baht (THB).
Seismic activity
Thailand is located in an active seismic zone and is prone to earthquakes and tsunamis.
In case of an earthquake or a tsunami alert, follow the instructions of local authorities.
Tsunami alerts - U.S. Tsunami Warning System
The rainy (or monsoon) season extends from June to October. Seasonal flooding can hamper overland travel and reduce the provision of essential services. Roads may become impassable and bridges damaged.
Jungle treks are not advisable during the rainy season due to the possibility of mudslides. Flash flooding in caves has caused fatalities.
- Weather warnings - Thai Meteorological department
- Mekong river levels - Mekong River Commission
- Tornadoes, cyclones, hurricanes, typhoons and monsoons
Air pollution
Air pollution fluctuates greatly and can be hazardous in urban areas, including Bangkok and Chiang Mai. Seasonal smog during the dry season is recurrent. In the northern provinces, including Chiang Mai, air quality can also be affected by agricultural burning.
You should monitor air pollution levels, especially if you suffer from respiratory ailments or if you have a pre-existing medical condition.
Local authorities recommend that children, seniors and pregnant women wear anti-pollution masks, and minimize outdoor activities, when air pollution levels are high.
Air pollution in Thailand – World Air Quality Index
Local services
In case of emergency, dial:
- police: 191
- tourist police: 1155
- medical assistance: 1669
- firefighters: 199
General services
The Tourism Authority of Thailand offers general advice for tourists. Dial 1672 and press 9 for English.
Consular assistance
Online appointment requests
Thailand, Cambodia, Laos
For emergency consular assistance, call the Embassy of Canada to Thailand, in Bangkok, and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.

Tamil Nadu gov't issues advisory to youth seeking jobs overseas amid rise in employment scams
T he Tamil Nadu government on Sunday, May 26, appealed to youth seeking employment abroad, particularly in South East Asian countries, to thoroughly verify the antecedents of recruitment agents and companies before applying for a job.
The advisory was issued in the wake of rescue of 83 Tamil youngsters from Cambodia, Thailand and Myanmar, where they were taken on tourist visas under the pretext of providing jobs in the Information Technology (IT) sector and later were forced to engage in 'illegal online activities'.
Citing reports of Indian nationals being lured by unregistered agents with high paying jobs in Laos, the Non-Resident Tamil's Welfare department in an official release on Sunday, May 26, said the candidates were taken illegally across the border into Laos from Thailand and were held captive to work under 'harsh and restrictive conditions.
At times, they were held hostage by criminal syndicates involved in illegal activities, and forced to work in strenuous conditions and subjected to "physical and mental torture".
The government also explained that Visa on Arrival in Thailand or Laos for Indian nationals does not allow employment in those countries and tourist visa is to be used only for tourism purposes.
"Please note that those convicted of human trafficking crimes have been sentenced up to 18 years in prison in Laos," the release said.
The government advised people not to get "enticed" and "entrapped" in such fraudulent or exploitative job offers and appealed them to stay alert on employment scams.
Candidates need to thoroughly verify recruitment agents and the companies they will be working for before going abroad, it said.
Indians should travel only with an employment visa and a proper employment contract.
They should also verify the authenticity of the visa through the Indian Embassy in the respective countries and the embassies of those countries in India, the government said.

Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
beta This is a test version of the layout of this page. Take the survey to help us improve it
- Help and services around the world
- UK help and services in Thailand
Travelling to Thailand
Includes travel advice and how to get married abroad.
Subscriptions
- Get emails for this topic Travelling to Thailand
Getting married or registering a civil partnership abroad
Requirements, paperwork and processes for weddings and civil partnerships overseas - registration, restrictions, fees
Rape and sexual assault in Thailand: information for victims
Information for British nationals who are victims of rape and sexual assault in Thailand.
Reduce your risk from terrorism while abroad
How to minimise your risk, and what to do if there's a terrorist attack.
Thailand travel advice
FCDO travel advice for Thailand. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .

This website is managed by Siam Legal International - a law firm in Thailand

Travel to Thailand from the US
Updated on October 26, 2023, Bangkok, Thailand
Travel to Thailand from US can be done now without any restrictions. You should exercise normal precautions however when in public. All travel restrictions previously implemented have been lifted.
Thailand has always been a favorite destination for US holiday goers. Delicious food, diverse culture, and stunning beaches have drawn people year after year. Since Thailand is famous among foreign travelers, the Thai government was quick to remove any travel restrictions and remove any entry requirements.
US Citizens should consult with the State Department for travel advisories and with the Royal Thai Embassy Washington DC for the most current visa information, if you plan to stay long term in Thailand. Short term traveler on holiday are allowed to stay for 30 days with the visa exemption scheme.
Traveling to Thailand has become even easier for 2023: No restrictions in place. Check for any travel advisory before your departure.

Required Documents for Travel to Thailand
Please have the following documents ready.
- Passport with at least six month validity
- Visa or visa exemption qualification
- Buy Thailand Travel Insurance
- Boarding pass to be presented at Passport Control
- Hotel booking confirmation if asked by Immigration Officer
- Note: Vaccination record no longer required
Incorrect documents will delay the entry screening by rules from the Thai immigration bureau and its Thai immigration officials.
Buy Your Insurance Now
If you are an American citizen who is ready to get away, these are the major changes that will affect travelers:
- Foreigners do not need to show proof of Covid Insurance.
- All mandatory hotel quarantine has been removed.
- Thailand Pass is no longer required for foreign travelers entering Thailand.
- Vaccinated travelers do not need to provide proof of vaccination before arriving.
- Unvaccinated travelers: No restrictions
- Airlines and Thai Immigration no longer request proof of travel insurance to Thailand
- Wearing masks is no longer compulsory
- The TM6 arrival card has been temporarily removed when entering Thailand.
Things are easier, but remember travelers still need to be responsible when abroad and remember to exercise normal precautions regarding public health for protection against Covid 19. Read on to learn how you can enjoy a worry-free holiday in Thailand. If you feel unwell it is best to visit a medical professional at a Thai clinic or hospital. Without travel insurance, you will be required to pay at your own expense. Remember to hold Thai currency for such emergency situations.
Visas for US Citizens
United states of america – a visa exempt country.
If you ask people about traveling to Thailand, you will often hear the word VISA. US Citizens are fortunate because USA is included in Thailand’s Visa Exemption list.
American citizens can enter Thailand as a tourist for up to 30 days without needing a pre-approved Thai visa. Visitors from the USA can organize a 30-day period of stay when landing at one of Thailand’s international airports. This 30-day stay is often referred to as a “Visa on arrival”.
If 30 days is not long enough after two years of isolation There are many options for American citizens to visit (or move to) Thailand on a longer-term basis with a Thai Visa. US Citizens must obtain a Thai visa for stays longer than 30 days.
Long Term Visas for Americans
Tourist visa.
Foreigners can apply for a Tourist Visa from the Thai embassy or consulate. Normally, it is a 60-day tourist visa that can be extended for additional 30 days.
Thailand Elite Visa
If you wish to make Thailand easily accessible for many years to come or are perhaps thinking of relocating permanently, it is worth having a look at the Thai Elite Visa.
The Thai Elite Visa allows American citizens to live in Thailand for 5, 10, 15, or even 20 years. Thai Elite members do not need to worry about some of the eligibility criteria that are needed when applying for other long-term visas.
The Thai Elite visa is exclusive and offers a host of benefits to holders. If you want to enjoy “Thai life” for the long term, you can read more about the Thailand Elite Visa .
Non-Immigrant Visa
Foreigners may also apply for a wide range of non-immigrant visas:
- Non-immigrant B Visa – for conducting business or employment
- Non-immigrant O visa – for visiting Thai spouse and family
- Non-immigrant ED visa – for students of recognized institutions in Thailand and their Parents or Legal guardian
- Non-immigrant O retirement visa – for those who wish to retire in Thailand
- Non-immigrant OA and OX visa – for those who wish to obtain a Thailand retirement visa for long stay (it differs from type O visa)
The above visas can be organized with a local Thai Embassy or Consulate in the USA. The paperwork can be quite involved, but there are companies that can help. Check if e visas are available for your desired type of non-immigrant visa.
Foreign nationals are prohibited from employment unless they applied for a Thai work permit.
Siam Legal International is a reputable law firm in Thailand that has offered visa assistance to Americans for years. They are well versed in Thai immigration policies and processes.
Whether you are looking to study, conduct business, seek medical treatment, or even retire in Thailand , Siam Legal can help streamline your application process for a long-term stay in Thailand. You can reach Siam Legal at www.siam-legal.com .
How to get to Thailand in 2023
Entering thailand from us.
Thailand Pass is no longer required from July 1. Americans do not need to register in systems, provide documents for COVID 19 vaccinations, or seek pre-approval before traveling to Thailand. When American citizens visit Thailand, they need to look at their vaccination status and plan accordingly.
Vaccinated Travelers – Vaccinated travelers from the US do not need to complete any Covid tests before leaving America. No vaccination certificate is required. Children under 18 have no restrictions for entry.
Unvaccinated Travelers – Will I be denied entry if I am unvaccinated? No, unvaccinated travelers from the US do not need to complete any Covid tests before leaving America. No vaccination certificate is required
With the removal of Thailand Pass post COVID-19 restrictions, airlines and immigration officers no longer conduct random checks of passengers to confirm Covid requirements are met. No need to have your Vaccination or Covid Test certificate available for show. All travel restrictions have been removed and are no longer in effect.
Airlines and Booking Flights
Flights from the United States to Thailand are available from many airlines. The following airlines are operating and are available for travelers to book flights from the United States to Thailand:
- All Nippon Airlines
- Cathay Pacific
- Qatar Airways
- Etihad Airways
- Japan Airlines
- Singapore Airlines
- KLM Royal Dutch Airlines
All mandatory quarantine was removed from July 1, 2022. On social media, you may hear the term “sealed flights”. These are no longer required, so US citizens are free to enter Thailand at any international airport and then transit domestically anywhere in Thailand.
The Thailand Pass was removed and is no longer in effect. Airlines no longer are required to check passengers’ documents before boarding.
Organize Your Travel Insurance
Since the change of July 1, 2022, the common question asked about travel is, “Do I need Travel Insurance?”
The fact is that from July 1, 2022, Thailand does not require foreign visitors to have insurance with Covid cover. Travelers do not need to provide any proof of insurance in order to enter Thailand.
Before Covid, seasoned travelers understood the benefits of comprehensive travel insurance. Covid has not changed this. Though travel restrictions have eased, Covid is still a problem, and if diagnosed with Covid while traveling, an American citizen will still be required to isolate in a hotel or quarantine in a medical facility. This can ruin any holiday, especially if you need to budget for potential medical expenses.
The important thing to know about insurance and Thailand is that foreigners are not eligible for any form of free medical care. No matter the circumstance, if an American needs medical attention, they need to pay for it. Depending on the severity, this could amount to thousands of dollars in out-of-pocket costs.
Travel Insurance to Thailand is something that is better to have and not need, then need and not have. Your Thailand travel insurance doesn’t just cover Covid. Comprehensive travel insurance will also cover:
- Medical emergencies
- Personal injury & accidents
- Missed or delayed flights
- Damage to belongings
- Loss of luggage
There are multiple reasons to protect yourself when traveling. Many visitors to Thailand choose AXA Insurance Thailand. It is a trusted company that offers comprehensive insurance to travelers from around the world. Their policies are straightforward with good coverage.
Some advantages to AXA Insurance are:
- Recognized and trusted by Thai authorities and medical facilities.
- Easy to apply online and approved in minutes.
- Competitive pricing and cover.
- Has no 14 day waiting period and covers Covid-related incidents, including asymptomatic cases.
- Provides customers with a convenient 1-Page Certificate of insurance. This certificate contains all relevant information needed by medical professionals or if making a claim.
To see the cover offered and organize your insurance to Thailand in minutes. Visit AXA Thailand .
Finding Accommodation in Thailand
Thailand is popular as a holiday destination because of its diverse geography. People can visit and lounge of a beach, go diving on the islands, or visit the mountains and lose themselves in nature.
There is accommodation everywhere, and US travelers can spend a night somewhere beautiful for less than a meal back home. Common travel destinations are Bangkok, Phuket, Chiang Mai, Pattaya, Koh Samui and Hua Hin .
After July 1, 2022, visitors are welcome to book any accommodation. There is no need to book SHA+ hotels or quarantine packages. SHA+ quarantine packages have been removed from most booking sites.
Now that Thailand Pass is removed, visitors don’t need to provide any proof of a hotel booking before entering Thailand. But after a long flight, it’s nice to have at least your first night’s accommodation organized. It is good to see what is around in your travel area, and if you are a “planner”, you can use hotels to help decide places to visit.
To find and compare the best hotels available in Thailand, visit Agoda . They allow free booking and cancellation, confirm bookings with hotels and their web page is easy to navigate and compare hotels. You can book any accommodation in Thailand, and many hotels are offering competitive prices to welcome holiday makers back.
Arriving in Thailand – Best Practices
So what can you expect when landing in Thailand? Travel to Thailand is back to normal. Americans are again being welcomed by Thai locals and post-Covid experiences are being created.
Here are a few things that will help you enjoy your trip and show respect to local Thai people.
Wearing Masks
From July 1, 2022, masks are no longer compulsory, but still recommended when in public places. You see that many Thai people (and visitors) still wear masks when out and about. It is recommended to wear a mask when visiting restaurants, tourist areas or public venues. You will not get in trouble for not wearing a mask. It’s a case of “do as the locals do”. It is about respect and consideration.
TM6 Arrival Cards
The Thai government has temporarily removed the need for visitors to complete the blue arrival card known as TM6. Their aim is to ease congestion at airports and remove another form that holiday makers need to complete. This initiative is in a testing phase, but it is hoped that the removal of TM6 will be successful and the change will become permanent.
Paperwork to Prepare
Though Thailand Pass is removed, and travelers do not need to provide proof before entry, it is recommended that passport holders prepare a few documents before arrival in Thailand.
- A copy of your Travel Insurance
- Hotel booking or address of stay
- Boarding Pass with your flight number and travel date clearly identified
- Thai Visa, if you stay in Thailand is over 30 days.
- Covid-19 medical and vaccination records are optional
These documents can be presented in digital form, but airlines, Immigration and Health Officers will appreciate the extra effort if you print them.
COVID 19 Insurance: https://u.axa.co.th/Sawasdee_Siamlegal

Book Your Hotels for Thailand: https://www.agoda.com/?cid=1897011
Do’s and don’ts when visiting thailand.

Thailand is a country with rich cultural traditions and a strong sense of social etiquette. Here are some dos and don’ts to keep in mind when visiting:
- Show Respect to the Monarchy : Thai people have a deep respect for their royal family, and it’s important for visitors to show the same respect. Never speak ill of the monarchy.
- Wai Properly : The ‘Wai’ is a traditional Thai greeting involving a slight bow, with the palms pressed together in a prayer-like fashion. It’s a sign of respect and is commonly used when greeting, thanking, or apologizing.
- Respect Buddhist Monks : Monks are highly respected in Thailand. Always give them space, and do not touch them if you are a woman.
- Remove Your Shoes : Take off your shoes when entering someone’s home and even in certain shops or guesthouses.
- Dress Appropriately : Dress modestly, especially when visiting temples. Shoulders and knees should be covered.
- Stay Calm : Keep your cool, even in frustrating situations. Raising your voice or showing anger is considered losing face, and it’s highly frowned upon. Be patient with drivers of metered taxis. Always use the meter and exit if they refuse to do so.
- Use Polite Language : Use ‘ka’ (for women) or ‘krup’ (for men) at the end of sentences to be polite.
- Practice Good Table Manners : Wait for the eldest person to start eating first, and try a bit of everything.
- Be Respectful with Your Feet : Feet are considered the lowest part of the body in Thai culture. Do not point them at people or religious objects.
- Support Sustainable Tourism : Engage in responsible and sustainable tourism practices to help preserve the country’s natural and cultural heritage.
- Don’t Touch Someone’s Head : The head is considered the most sacred part of the body, and it should not be touched.
- Don’t Point Your Feet : As mentioned before, feet are considered lowly, so don’t point them at people or religious objects.
- Don’t Show Public Displays of Affection : Keep public displays of affection to a minimum as they can be considered disrespectful.
- Don’t Take Photos in Restricted Areas : Be mindful of signs that prohibit photography, especially in religious or sacred sites.
- Don’t Engage in Illegal Activities : This includes drug use and purchasing counterfeit goods. Don’t remove Buddha images from the country.
- Don’t Disrespect Religious Objects or Sites : Always show respect at temples and other religious sites.
- Don’t Touch Artifacts or Relics : In museums and historical sites, refrain from touching artifacts unless explicitly allowed.
- Don’t Feed the Monkeys : If you encounter monkeys, do not feed them as it can lead to aggressive behavior.
- Don’t Litter : Dispose of your trash responsibly and avoid using single-use plastics.
- Don’t Engage in PDA at Religious Sites : Even more so than in public, avoid public displays of affection at temples and other religious sites.
By following these guidelines, you can help ensure that your visit to Thailand is enjoyable and respectful of the local culture and traditions.
Summary for Travel to Thailand for US Citizens
Thailand is fully open and no travel restrictions are currently in place. Any future travel advisory will be posted on Thai Embassy Washington DC website. Remember that US Citizens can stay in Thailand for up to 30 days without a Thai Visa. Entry restrictions are subject to change. For further information regarding Thailand Thailand restrictions: https://www.thaiembassy.com/travel-to-thailand/thailand-travel-restrictions-2023
If you need a travel insurance for your trip, you may book from here: https://u.axa.co.th/Sawasdee_Siamlegal
Related Posts

How to Travel to Thailand in 2024

Best Places to Retire in Thailand for Couples

How to Retire in Thailand for Couples

Thailand Travel Restrictions 2023
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This form collects your name, email and content so that we can keep track of the comments placed on the website. By submitting this form, you accepted and agreed on our privacy policy and terms .
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
Thailand's entry requirements from 1 July 2022. Thailand Pass removed, Also lifting an US$10,000 health insurance requirement, thus welcoming all travellers with proof of either a certificate of vaccination or a pre-arrival negative RT-PCR or professional ATK test result. Learn More & Suggestion. Traveller's Journey.
Still current at: 25 May 2024 Updated: 19 January 2024 Latest update: Information that while cannabis is legal in Thailand, be aware of the next place you are travelling to, where it may be ...
Visa requirements. British passport holders arriving by air or land can enter Thailand for 30 days without a visa (visa exemption). If you intend to stay longer (for work, study or other reasons ...
The official site of Tourism Authority of Thailand. Amazing Thailand, Travel information, Travel guide, maps, hotels, accommodation, attractions, events & festivals, food, culture, shopping information to help you plan your Thailand vacations.
Last updated: May 17, 2023. The CDC's Order requiring proof of vaccination for non-U.S. citizen nonimmigrants to travel to the United States is no longer in effect. For more information see Requirement for Proof of COVID-19 Vaccination for Air Passengers. Check the CDC website for additional information and Frequently Asked Questions.
Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 443 Sri Ayudhya Road Bangkok 10400. Office Hours : Monday - Friday, 08.30 - 16.30. (Except public and offcial holidays) This website had been designed to be as accessible as possible to all and is certified by the WCAG 2.0 standard (Level AA) ** Best viewed with Chrome Version 76 up **. COVID-19.
Plan your trip to Thailand with ease. Find out how to apply for a certificate of entry, check the latest travel updates, and explore the country's attractions.
Foreigners under the Visa Exemption may enter Thailand without a visa for up to 30 days and travelers under the Visa on Arrival program may stay in Thailand for up to 15 days. Travelers under the Visa Exemption and the Visa on Arrival must apply for Thailand Pass before traveling to Thailand. April 07, 2020 at Thai Immigration Office Chaengwattana.
After months of strict travel restrictions due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Thailand is gearing up for a return to normalcy by easing some travel restrictions and quarantine requirements and allowing normal tourists to enter the country. Vaccinated travelers are allowed to travel to Thailand without quarantine under the Phuket Sandbox and the Samui Plus Sandbox programs.
FCDO travel advice for Thailand. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
The U.S. and Thailand established relations in 1818 and signed a Treaty of Amity and Commerce in 1833, formalizing diplomatic relations. An interim military government has ruled Thailand, a constitutional monarchy, since a May 2014 military coup which deposed an elected civilian government. The U.S. has urged the restoration of elected civilian ...
The COVID-19 pandemic wreaked havoc on the world. International travel ground to a halt and countries were forced to implement strict processes and entry requirements to halt the spread of the virus. Thailand introduced quarantine measures and Thailand Pass. Thailand Pass required visitors to register details like vaccination status, flight, and hotel bookings, and confirmation
For information traffic safety and road conditions in Thailand, see Travel and Transportation on US Department of State's country-specific information for Thailand. Traffic flows on the left side of the road in Thailand. Always pay close attention to the flow of traffic, especially when crossing the street. LOOK RIGHT for approaching traffic. Hide
The basics. Thailand has recorded more than 32,000 deaths and over 4.67 million cases of Covid-19 as of September 26, 2022. Ad Feedback. On average, around 700 Covid-19 cases are reported per day ...
At least 8 weeks before your trip check: Health risks in Thailand include: See the 'Other risks' section of the TravelHealthPro Thailand guide for more on health risks. To avoid mosquito-borne ...
Thailand Travel Advisory: Level 1: Exercise Normal Precautions: July 24, 2023: Timor-Leste Travel Advisory: Level 2: Exercise Increased Caution: July 24, 2023: ... You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
The legal driving age in Thailand is 18. Road travel. Thailand has one of the highest traffic-related fatality rates in the world. Motorcyclists are most at risk. Road accidents are common, including in resort areas such as Phuket, Pattaya and Koh Samui. Driving in Thailand is dangerous due to: speeding; reckless passing; ignoring traffic laws
Thailand Travel Updates for May 1, 2022 Thailand is easing its entry requirements and Thailand Pass process from the 1st of May, 2022. How a traveler enters Thailand will. Thailand Travel Updates; Facebook. This website is managed by Siam Legal International - a law firm in Thailand.
Your passport must be valid at least 6 months upon entry into Thailand. Passport for official travel. Different entry rules may apply. Official travel. Passport with "X" gender identifier. While the Government of Canada issues passports with an "X" gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries.
The government also explained that Visa on Arrival in Thailand or Laos for Indian nationals does not allow employment in those countries and tourist visa is to be used only for tourism purposes.
Thailand travel advice. FCDO travel advice for Thailand. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences. Includes travel advice and how to get married abroad.
The early 20th century teak industry left northern Thailand scarred but also peppered with magnificent examples of local architecture, seen on its 'teak trail' that starts in Chiang Mai.
The Thai Elite Visa allows American citizens to live in Thailand for 5, 10, 15, or even 20 years. Thai Elite members do not need to worry about some of the eligibility criteria that are needed when applying for other long-term visas. The Thai Elite visa is exclusive and offers a host of benefits to holders.
India's highest recorded temperature on Monday was 47.4C (117F) at Najafgarh in Delhi, according to the bureau. The weather has been 5C hotter than normal in several parts of the nation and the ...