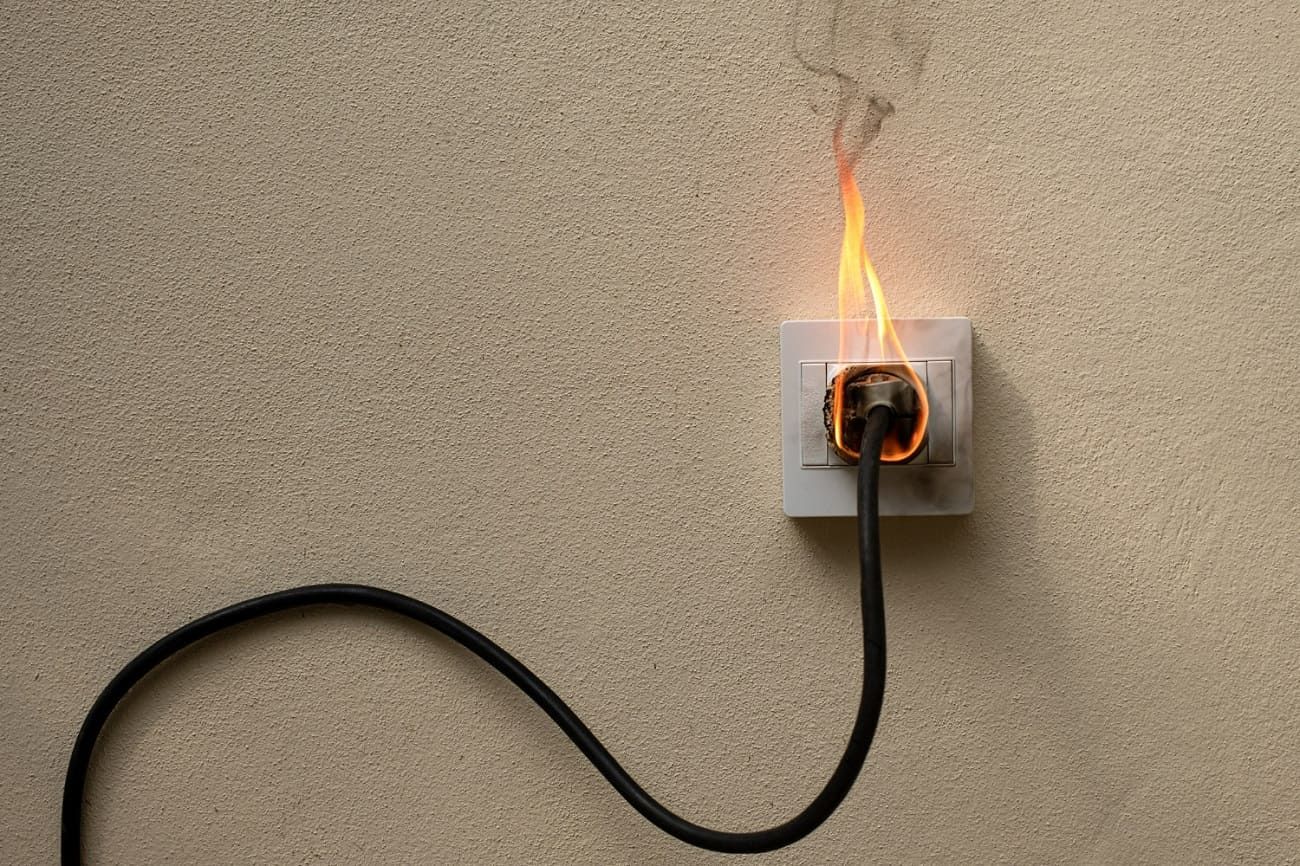
Electrical Repair
Ceiling Fan Repair
Electrical Panel Repair
Emergency Electrician
Lighting Repair Service

Installations
Carbon Monoxide and Smoke Detector Installation
Exhaust Fan Installation Service
Home Backup Generator Services
EV Charger Installation and Service
Outlet Installation
Ballast and Bulb Replacement
Commercial Specialty Lighting
Lighting Controls
Retrofit Lighting
Bathroom and Kitchen Lighting
Chandelier Installation
Motion Sensors
Track and Accent Lighting
Landscape Lighting
Recessed Lighting Installation
Electrical Safety
Electrical Code Updates
GFCI Outlet Installation & Replacement
Circuit Breaker Replacement
Home Wiring Updates
Dedicated Computer Circuits

Beginner’s Guide to Identifying a Tripped Circuit Breaker
Key highlights.
- Understanding the different types of circuit breakers and their functions
- Common reasons for circuit breaker trips: overloaded circuits, short circuits, and ground faults
- Steps to troubleshoot and reset a tripped circuit breaker
- When to call in professional help for persistent tripping or serious electrical issues
- Tips for maintaining your circuit breaker panel to prevent future trips
- FAQs: Why does a circuit breaker keep tripping? Can I replace a circuit breaker myself? How to know if a circuit breaker is faulty? What’s the difference between a circuit breaker and a fuse? Why did my circuit breaker trip? What to do when a tripped breaker is found? What causes a circuit breaker to trip? How to prevent frequent tripping? Can frequent tripping indicate a larger electrical issue in the home? When to call a professional to fix a tripped circuit breaker
Introduction
Hey there! Ever had that moment when all the lights suddenly go out in your home? Yeah, this can be a bit annoying, especially when the big Basketball game is about to start or when you are rushing to get the kids ready for school in the morning! Well, chances are, your circuit breaker decided to take a little break. But don’t worry, it’s actually a safety feature designed to prevent any electrical disasters.
Think of it like your circuit breaker playing superhero, swooping in to save the day when there’s too much electrical action going on. It’s there to protect you from overloads, short circuits, and ground faults, kind of like your own personal electric guardian angel.
Now, I get it, dealing with a tripped circuit breaker can be a bit of a hassle. But fear you’re your Tripp your personal electrical guide from the Doctor Electric Team is here to guide you through the process with some friendly tips and tricks. Consider this your beginner’s guide to tackling those annoying tripped circuit breakers like a pro. So, let’s dive in and get your power back on in no time!
Understanding Circuit Breakers: The Basics
Before we get into finding a tripped circuit breaker, let’s talk about what they are. A circuit breaker is like a traffic cop for electricity in your home’s electrical panel, also called a service panel or breaker box. It controls the electricity flow, keeping your electrical system safe from overloads and problems. If a circuit breaker trips, it’s like it puts up a “stop” sign for electricity to prevent damage or dangerous situations.
What is a Circuit Breaker?
Think of a circuit breaker as your electrical system’s guardian. It’s like a super cool switch that can be turned on or off manually or even flips itself off automatically when it senses weird stuff happening with the electricity.
If the electricity flow gets too intense for the circuit breaker to handle, it does its magic and disconnects the circuit. This way, it prevents the electrical wires and your fancy appliances from getting all hot and bothered or worse, damaged.
Circuit breakers are like the superheroes of your home’s electrical system, making sure everything stays safe and sound, and avoiding those nasty electrical fires and accidents.
Types of Circuit Breakers and Their Functions
Let’s talk about the different types of circuit breakers. Knowing what they do can help you pick the right one for your electrical needs Here are some common types of circuit breakers:
- Magnetic Circuit Breakers: Picture this: a superhero with electromagnetism as their superpower! These circuit breakers use electromagnetic force to trip when the electrical current goes above the limit they’re designed for. They’re like the Flash, super-fast in detecting and reacting to electrical surges.
- Thermal Circuit Breakers: These circuit breakers have metal strips that act as their sensors. When there’s an overload or a fault, the strips heat up, bend, and cut off the power. It’s like a safety valve that keeps the temperature from getting too hot in your electrical system.
- Thermal-Magnetic Circuit Breakers: Think of these circuit breakers as the ultimate protectors. They combine the powers of both magnetic and thermal circuit breakers, providing double the defense against overloads and short circuits. They’re like the Avengers of the circuit breaker world, ready to tackle any electrical challenge.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI): GFCIs are the safety experts when it comes to preventing shocks. They’re designed to detect imbalances in electrical current and quickly interrupt the flow of electricity if it’s taking an unintended path, like through water or a person. They’re like invisible shields protecting us from electrical hazards, especially in areas like bathrooms and kitchens.

Common Reasons for Circuit Breaker Trips
Circuit breakers can sometimes get a little jumpy and trip for various reasons. Let’s explore some of the most common causes and how to prevent them:
Overloaded Circuit: When you cram too many appliances or devices into one outlet, it can cause the circuit to get overloaded and trip the breaker. It’s like a traffic jam in your electrical system. The solution? Spread out your power-hungry friends by using different outlets or try to limit the number of appliances on one circuit.
Short Circuit: Ever seen sparks fly when you plug in a faulty appliance? That’s a short circuit. It happens when the “hot” wire (the one that carries electricity) touches the “neutral” wire (the one that returns electricity). It’s like a shortcut that electricity takes, causing a surge and tripping the breaker. Unplug the faulty appliance and call an electrician if it keeps happening.
Ground Fault: If electricity takes a detour through an unintended path, like a person or water, it’s called a ground fault. It’s like a sneaky escape route for electricity. This can trip the breaker to prevent electrical shocks or fires. If you suspect a ground fault, consult with a qualified electrician for help.
Overloaded Circuits: Recognizing the Signs
An overloaded circuit occurs when you have too many electrical devices or appliances drawing power from a single circuit. This can lead to a tripped circuit breaker and potential hazards. Here are some signs that you may have an overloaded circuit:
- Frequently tripping circuit breaker: If your circuit breaker trips frequently, especially when using certain appliances or devices, it could be a sign of an overloaded circuit.
- Flickering or dimming lights: When you turn on multiple appliances or devices, you may notice your lights flickering or dimming. This indicates that the circuit is struggling to handle the power load.
- Warm electrical outlets: If your electrical outlets feel warm to the touch or emit a burning smell, it could be a sign of an overloaded circuit. This can be dangerous and should be addressed promptly.
To avoid overloading your circuits, distribute the electrical load evenly among different circuits in your home. Consider using power strips with built-in circuit breakers to protect against overloads and ensure that you’re not exceeding the capacity of the circuit. If you frequently experience circuit breaker trips due to an overloaded circuit, it may be necessary to consult a licensed electrician to assess and upgrade your electrical system.
Short Circuits: Identifying and Preventing Risks
A short circuit occurs when a hot wire comes into contact with another hot wire or a neutral wire, causing a surge of electricity. This can be caused by wiring issues, damaged appliances, or faulty electrical connections. Here’s how to identify and prevent short circuits:
- Signs of a short circuit: If you notice sparks, a burning smell, or a sudden loss of power without tripping the circuit breaker, it could be a sign of a short circuit.
- Inspect the wiring: Check for any visible signs of damage, such as frayed wires, loose connections, or exposed conductors. Damaged or deteriorating wiring can increase the risk of short circuits.
- Avoid overloading outlets: Do not plug too many devices into a single outlet, as this can increase the risk of a short circuit. Use power strips with built-in surge protectors to distribute the load evenly.
- Use proper electrical insulation: Ensure that all wires are properly insulated and protected to prevent contact with other wires or surfaces.
- Seek professional help: If you suspect a short circuit or are unsure about the safety of the wiring in your home, it is recommended to consult a licensed electrician who can identify and resolve the issue safely.
Preventing short circuits is essential for the safety of your home and family. Regularly inspect your electrical system, address any wiring issues promptly, and avoid overloading outlets to minimize the risk of short circuits.
Ground Faults: Safety Measures and Solutions
Ground faults occur when electricity flows through an unintended path, such as water or a person. This can result in electrical shocks and fires. Here are some safety measures and solutions to prevent ground faults:
- Install Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs): GFCIs are designed to detect ground faults and quickly interrupt the flow of electricity, protecting against electrical shocks. Install GFCI outlets in areas where water is present, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor outlets.
- Test GFCIs regularly: GFCIs have a built-in test button to ensure they are working correctly. Test them monthly by pressing the test button and verifying that the power is cut off. Reset them afterward to restore power.
- Avoid using electrical devices near water: Keep electrical devices away from water sources to reduce the risk of ground faults. This includes using extension cords and appliances in wet areas.
- Inspect and maintain electrical wiring: Regularly inspect the wiring in your home for signs of wear, damage, or aging. Replace any damaged or worn-out wiring to minimize the risk of ground faults.
- Consult a licensed electrician: If you experience frequent ground faults or are unsure about the safety of your electrical system, it is recommended to consult a licensed electrician for professional inspection and repairs.
By implementing these safety measures and solutions, you can protect yourself and your home from ground faults and ensure the electrical system operates safely.
Beginner’s Guide: Preparing to Troubleshoot Your Circuit Breaker
Before attempting to troubleshoot a tripped circuit breaker, it’s important to prioritize safety. Dealing with electricity can be hazardous, so it’s crucial to take the necessary precautions. Here are some important safety measures to keep in mind when preparing to troubleshoot your circuit breaker:
- Turn off all appliances and devices connected to the circuit that tripped to prevent power surges or electrical shocks.
- Identify the location of your electrical panel or breaker box, usually found in the basement, garage, or utility closet.
- Familiarize yourself with the different circuit breakers in your panel and their corresponding circuits.
- If you’re unsure or uncomfortable working with electrical systems, it’s always best to contact a licensed electrician for assistance.
By prioritizing safety and taking the necessary precautions, you can troubleshoot your tripped circuit breaker effectively and minimize the risk of accidents or further electrical issues.
Safety First: What You’ll Need
To ensure a safe and successful troubleshooting process, it’s important to gather the necessary tools and equipment. Here’s what you’ll need:
- Flashlight: A flashlight will help you see clearly in the electrical panel, especially if it’s located in a dimly lit area.
- Non-contact voltage tester: This tool allows you to check if a circuit is live or if there’s still electricity flowing through it without making direct contact.
- Screwdriver: You may need a screwdriver to remove the cover of the electrical panel and access the circuit breakers.
- Safety gloves and goggles: It’s essential to protect yourself from electrical shocks and debris. Wear safety gloves and goggles to minimize the risk of injury.
- Knowledge of your electrical system: Understand which circuit breakers correspond to specific areas of your home before troubleshooting. If you’re unsure, consult a licensed electrician for guidance.
Keep in mind that electrical work can be dangerous, and if you’re not confident in your abilities or uncomfortable working with your electrical system, it’s always best to consult a licensed electrician to ensure your safety and avoid potential hazards.
Identifying Your Circuit Breaker Panel
Your circuit breaker panel, also known as the breaker box, is the central hub for controlling the electrical circuits in your home. It’s important to locate and identify your circuit breaker panel before troubleshooting a tripped breaker. Here’s how to find it:
- Look for a metal box: Circuit breaker panels are typically housed in a metal box mounted on a wall. Common locations include basements, garages, utility closets, or other designated electrical rooms.
- Check for labels or markings: The circuit breaker panel may have labels or markings indicating which breakers correspond to specific areas of your home, such as kitchen, living room, or bedroom.
- Open the panel cover: Once you’ve located the circuit breaker panel, use a screwdriver to remove the cover and access the circuit breakers.
It’s important to exercise caution when working with your circuit breaker panel. If you’re unsure or uncomfortable, it’s recommended to contact a licensed electrician for assistance in identifying your circuit breaker panel.
Step-by-Step Guide to Resetting a Tripped Circuit Breaker
Resetting a tripped circuit breaker is a simple process that can be done by following a few easy steps. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you reset a tripped circuit breaker safely and effectively:
Step 1: Locating the Tripped Breaker
Step 2: ensuring safety before proceeding, step 3: resetting the circuit breaker, step 4: identifying the cause of the trip.
By following these steps, you can reset a tripped circuit breaker and restore power to the affected circuit. However, it’s important to identify the cause of the trip to prevent further issues and ensure the safety of your electrical system.
The first step in resetting a tripped circuit breaker is to locate the specific breaker that has tripped. Here’s how to do it:
- Locate your electrical panel or circuit breaker box, usually found in a basement, garage, or utility closet.
- Open the panel cover using a screwdriver, exposing the circuit breakers.
- Visually inspect the circuit breakers and look for one that is in the middle position or slightly shifted from the “on” position. This indicates a tripped breaker.
Once you have identified the tripped breaker, make a note of its location and proceed to the next step to ensure safety before resetting it.
Before resetting a tripped circuit breaker, it’s crucial to take safety measures to avoid electrical hazards. Follow these steps to ensure safety before proceeding:
- Turn off all appliances and devices connected to the tripped circuit to prevent power surges.
- If there is a power outage in your home, make sure to determine the cause. If it’s only a specific circuit that has lost power, it’s likely due to a tripped breaker.
- If you’re unsure or uncomfortable working with your electrical system, it’s recommended to contact a licensed electrician for assistance.
By following these safety measures, you can minimize the risk of electrical shocks or accidents while troubleshooting a tripped circuit breaker.
Once you have taken the necessary safety precautions, you can proceed to reset the tripped circuit breaker. Follow these steps to reset the circuit breaker:
- Locate the tripped breaker, which will be in the middle position or slightly shifted from the “on” position.
- Firmly push the tripped breaker to the “off” position and then back to the “on” position.
- If the breaker stays in the “on” position without tripping or feeling loose, it has been successfully reset.
If the breaker does not reset or continues to trip, there may be a more serious issue that requires professional attention. In such cases, it’s recommended to contact a licensed electrician to diagnose and resolve the problem.
After resetting the tripped circuit breaker, it’s important to identify the cause of the trip to prevent future occurrences. Here are some common causes of circuit breaker trips and how to determine the cause:
By identifying the cause of the trip, you can take appropriate measures to address the issue and prevent future circuit breaker trips. However, if you’re unsure or unable to determine the cause, it’s best to consult a licensed electrician for professional assistance.
When to Call in the Professionals
While resetting a tripped circuit breaker can often be done by homeowners, there are certain situations where it’s best to call in a professional electrician. Here are some instances when you should consider contacting a licensed electrician:
- Persistent Tripping: If your circuit breaker trips frequently, even after resetting it, there may be an underlying electrical problem that requires professional attention.
- Serious Electrical Issues: If you notice signs of serious electrical issues, such as burning smells, charred outlets, or flickering lights, it’s important to have a professional electrician assess and address the problem.
- Lack of Electrical Expertise: If you’re unsure about your electrical knowledge or uncomfortable working with your electrical system, it’s always safer to rely on the expertise of a licensed electrician.
Calling in a professional electrician ensures that the issue is properly diagnosed, resolved, and that your electrical system is safe and up to code.
Persistent Tripping: Knowing When It’s Beyond DIY
If your circuit breaker trips frequently, even after resetting it, it may indicate an underlying electrical problem that requires the expertise of a licensed electrician. Here are some signs that the issue may be beyond DIY troubleshooting:
- Tripping on Multiple Circuits: If the circuit breaker trips on different circuits throughout your home, it could indicate a more widespread problem in the electrical system.
- Tripping Without Overloaded Circuits: If the circuit breaker trips even when the electrical load is within the rated capacity, it suggests a fault in the system.
- Intermittent Tripping: If the circuit breaker trips intermittently or randomly, it can be a sign of a loose connection, damaged wiring, or other electrical faults.
In these situations, it’s best to contact a licensed electrician who has the expertise to diagnose and resolve complex electrical issues. They can ensure the safety of your electrical system and provide appropriate solutions.
Signs of Serious Electrical Issues
Certain signs indicate serious electrical issues that should not be ignored. If you notice any of these signs, it’s crucial to contact a licensed electrician for immediate assistance:
- Burning Smell: A persistent burning smell, especially around outlets or electrical panels, could indicate overheating or electrical arcing, which can lead to fires.
- Charred Outlets or Switches: If you find discolored or charred outlets, switches, or wiring, it suggests excessive heat buildup and potential fire hazards.
- Flickering or Dimming Lights: If your lights flicker or dim without an apparent cause, it may indicate loose connections or faulty wiring, which can lead to electrical failures or fires.
- Electrical Work: If you’ve recently had electrical work done and experience unusual electrical issues afterward, it’s essential to have a professional electrician inspect the work for potential problems.
Ignoring these signs of serious electrical issues can pose significant safety risks. It’s important to contact a licensed electrician promptly to evaluate and address the underlying problems.
Maintaining Your Circuit Breaker Panel
Proper maintenance of your circuit breaker panel is essential to ensure its optimal performance and prevent unnecessary trips. Here are some maintenance tips to keep in mind:
- Regular Checks: Periodically inspect your circuit breaker panel for signs of damage, such as loose connections, corrosion, or overheating. Address any issues promptly.
- Balancing Loads: Distribute the electrical load evenly across different circuits to avoid overloading and tripping.
- Updating Old Circuit Breakers: If you have an older home with outdated circuit breakers, consider upgrading them to newer models with higher capacities and enhanced safety features.
By following these maintenance tips, you can prolong the lifespan of your circuit breaker panel, reduce the risk of trips, and ensure the safety of your electrical system.
Regular Checks and Balancing Loads
Regular checks and balancing the electrical load in your home are essential for maintaining the performance and safety of your circuit breaker panel. Here’s what you can do:
- Regular Checks: Periodically inspect your circuit breaker panel for any signs of damage or wear, such as loose connections, corrosion, or charred components. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage or hazards.
- Balancing Loads: Distribute the electrical load evenly across different circuits in your home. Avoid overloading a single circuit by plugging in too many appliances or devices. Consider using power strips with surge protectors to distribute the load.
- Amperage Rating: Understand the amperage rating of your circuit breakers and the maximum load they can handle. Avoid exceeding the amperage rating to prevent tripping and potential damage to the circuit breaker or electrical system.
By performing regular checks and balancing the electrical load, you can ensure that your circuit breaker panel operates efficiently and minimize the risk of trips and electrical hazards.
Updating Old Circuit Breakers
If you live in an older home with outdated circuit breakers, it may be necessary to update them to ensure the safety and efficiency of your electrical system. Here’s why you should consider updating old circuit breakers:
- Enhanced Safety: Newer circuit breakers come with improved safety features, such as arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs) and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), which provide enhanced protection against electrical hazards.
- Higher Capacities: Older circuit breakers may have lower amperage ratings and may not be able to handle the electrical demands of modern appliances and devices. Upgrading to higher-capacity circuit breakers can prevent overloading and tripping.
- Code Compliance: Electrical codes and standards evolve over time. Updating your circuit breakers ensures that your electrical system complies with current codes and regulations, providing peace of mind and safety.
When updating circuit breakers, it’s important to consult a licensed electrician who can assess your electrical system and recommend the appropriate upgrades for your specific needs.
Remember, safety first when dealing with circuit breakers. Understanding the basics and common reasons for trips can help you troubleshoot effectively. Always prioritize safety and know when to seek professional help. Regular maintenance and updates are key to preventing future issues. If you’re unsure or face persistent tripping, don’t hesitate to get in touch with a professional for assistance. Your home’s electrical system is essential for your safety, so ensure it’s always well-maintained. Stay safe and informed!
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does my circuit breaker keep tripping.
Circuit breakers can trip due to various reasons, including an overloaded circuit, a short circuit, or a ground fault. These trips are safety measures to protect your electrical system from damage or hazards. Identifying and addressing the cause of the trips can help prevent recurring issues.
Can I replace a circuit breaker myself?
While some homeowners may have the knowledge and skills to replace a circuit breaker, it’s recommended to consult a licensed electrician for safety reasons. Working with electricity can be dangerous, and a professional electrician can ensure that the replacement is done correctly and safely.
How do I know if my circuit breaker is faulty?
If you’re experiencing frequent circuit breaker trips, flickering lights, or other electrical issues, it could indicate a faulty circuit breaker. A licensed electrician can inspect and test the breaker to determine if it needs to be replaced.
What’s the difference between a circuit breaker and a fuse?
Circuit breakers and fuses both protect electrical circuits from overloads and faults. However, while circuit breakers can be reset and reused, fuses need to be replaced after they trip. Circuit breakers are more commonly used in modern electrical panels.
Why Did My Circuit Breaker Trip?
Circuit breakers can trip due to electrical overloads, short circuits, or ground faults. These trips occur to protect your electrical system from damage or hazards. Identifying the cause of the trip can help prevent future occurrences.
What should be done when a tripped breaker is found?
When you find a tripped breaker, it’s important to follow the proper procedure for resetting it. Turn off all appliances connected to the circuit, locate the tripped breaker, reset it by moving the switch to the “off” and then “on” position, and ensure that the cause of the trip is identified and resolved.
What causes a circuit breaker to trip?
Circuit breakers can trip due to various reasons, including an overloaded circuit, loose electrical connections, or electrical faults. These trips occur to protect your electrical system from damage or hazards.
How can you prevent circuit breakers from frequently tripping in the future?
To prevent circuit breakers from frequently tripping, distribute the electrical load evenly across different circuits, avoid overloading circuits, and implement proper circuit management. Consider upgrading your electrical system if necessary.
Can frequent tripping of a circuit breaker indicate a larger electrical issue in the home?
Frequent tripping of a circuit breaker can indicate a larger electrical issue, such as overloaded circuits or faulty wiring. It is advisable to have a licensed electrician conduct an electrical inspection to identify and address any underlying problems.
When should you call a professional to fix a tripped circuit breaker?
You should call a professional electrician if you’re uncomfortable working with your electrical system, if you experience persistent circuit breaker trips, or if you notice signs of serious electrical issues. A professional electrician has the expertise to diagnose and resolve complex electrical problems safely.
Recent Posts
- Beginner’s Guide to Identifying a Tripped Circuit Breaker March 14, 2024
Service Areas Sidebar
- Electrician in Berea, KY
- Electrician in Richmond, KY
- Electrician in Lexington, KY
- Electrician in Frankfort, KY
- Electrician in Georgetown, KY
- Electrician in Jessamine County, KY
- Electrician in Versailles, KY
- Electrician in Winchester, KY
- Electrician in Nicholasville, KY
Latest Projects
No results found.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
WhatsApp Our Local Electrician To Get a Fast Response & Quote For Your Electrical Needs.

What Causes Circuit Breakers To Trip?
- June 1, 2024
If your circuit breakers are often tripping, there’s no need to worry. This is a typical issue. Below, you’ll find reasons why this occurs and tips for avoiding it going forward. Get a handle on your circuit breaker issues!
Table of Contents
Understanding Circuit Breaker Tripping
Circuit breakers are protection devices for electrical circuits. When too much current passes, the breaker trips, stopping the flow of electricity and preventing damage. This can be caused by faulty wiring, too many appliances on one circuit, or a ground fault.
Overloading can cause tripping. This happens when too many devices are connected to a single circuit. Heat builds up in the wires, which can start fires or cause damage. To prevent this, distribute loads across multiple circuits and don’t connect too many appliances to one outlet.
Short circuits also lead to tripping. This happens when two wires with opposite charges come in contact or when a wire touches something grounded. This causes an immediate surge in current that triggers the breaker. Check for exposed wires or insulation damage, and call an electrician if you spot any signs of trouble.
Ground faults can also cause tripping. This happens when there’s an unintentional connection between a live wire and a conductive surface. Install GFCIs to avoid this.
In short, know what causes circuit breakers to trip. Identify potential hazards like overloading, short circuits, and ground faults. Take steps to prevent accidents and ensure your electrical equipment is safe. If you’re unsure how to handle electrical problems, call a licensed electrician.
Overloading Causes
Circuit breakers trip to stop overheating, electrical fires, and damage to electrical parts. Plugging in too many devices can cause the circuit to become overloaded, so the breaker trips to cut off the power.
Short circuits are like a blind date gone wrong. They can be explosive, and often end in disaster. This happens when a hot wire comes into contact with a neutral or insulation/water. This throws off the electric balance, causing danger and tripping.
Short Circuit Causes
A short circuit happens when a low-resistance path appears between two points in the circuit that aren’t usually connected. This can cause too much current to flow, making a circuit breaker trip. Insulation or wiring damage, faulty appliances, and circuit overload are the most common reasons for a short circuit. It’s critical to identify and fix the root cause quickly to avoid electrical fires and other dangers .
When too much power passes through a circuit, the circuit breaker will automatically turn off. It’s designed to protect wiring and guard against electrical accidents . But if the breaker trips regularly, there may be underlying issues that need investigation and repair. Often times, this means upgrading or replacing components.
Sometimes short circuits are caused by human error or wear and tear. But they may also come from design or installation problems. Planning and upkeep from local electricians can keep electrical systems running safely and appropriately for a long time. If your circuit breaker is tripping a lot, get an experienced technician to review your system and suggest solutions that match your needs and budget .
Overheating Causes
Circuit breakers are essential safety features. They stop electrical fires and protect your appliances. When overloaded, too much current flows, producing heat. This causes the breaker to trip!
Other factors can cause overheating. Damaged insulation on wires increases resistance. Loose connections add resistance and heat. High temperatures and poor ventilation worsen the situation.
It’s important to maintain and service the electrical system. Checks of all components will make sure they work efficiently. To avoid tripping, prevent overheating. This will reduce energy consumption and safeguard equipment. So, let’s learn about circuit breakers and how they deal with overloads!
Circuit Breaker Types
Circuit breakers are essential for any electrical system. They prevent overloaded and faulted circuits . There are different types of circuit breakers suitable for specific electrical loads.
See the table below for the different types of circuit breakers and their functions:
It is crucial to select the right type of breaker. Each one has its own advantages in specific situations. For instance, thermal circuit breakers are perfect for small appliances like hair dryers or irons . Meanwhile, magnetic circuit breakers are great for bigger loads such as air conditioners or refrigerators .
Remember, circuit breakers are like Beyoncé – they can handle a lot, but have their limits.
Circuit Breaker Ratings and Specifications
Circuit breakers are designed to protect electrical circuits from overloads. To ensure that circuits and appliances are safe, the ratings and specifications of circuit breakers need to be understood.
If a circuit breaker trips often, it may mean there’s an issue. It’s best to get professional help in these cases. Time to go on a hunt for your electrical wiring!
Troubleshooting Circuit Breaker Tripping
Circuit breakers can flip out for multiple reasons, like overloads , short circuits , and ground faults .
Overloads happen when too much electricity passes through the circuit, creating too much heat and tripping the breaker. Short circuits are when two or more wires touch, resulting in extra current. Ground faults occur when the power takes an unexpected route, like through a person’s body.
To figure out why your circuit breaker is tripping, it’s important to figure out what is going on and act accordingly. Inspections and maintenance can also help avoid future tripping.
Stop your circuit breaker from misbehaving with these prevention tips!
Preventing Circuit Breaker Tripping
A circuit breaker tripping can be prevented with understanding. When circuits are overloaded, breakers trip to avoid overheating and potential fires. Here are 3 steps that can help you prevent circuit breakers tripping:
- Know the electrical load – work out how many appliances & devices are connected to one circuit. Don’t overload them by spreading high-energy equipment across multiple circuits .
- Look after your appliances – ensure all your appliances & devices are in good condition, with no damaged cords or frayed wires.
- Upgrade your system – if you’re tripping breakers often you may need to upgrade the electrical system with higher capacity breakers or more circuits.
Plus, investing in surge protectors can also assist in preventing circuit overload and subsequent tripping of breakers. By following these steps you can make sure your home’s electricity runs safely and without interruption due to circuit breakers tripping.
Remember: these precautions will keep you from tripping more than just your circuit breakers!
Safety Precautions
Safety must be taken seriously when dealing with circuit breakers . Always switch off the main power supply before beginning work. Wear protective gear such as insulated gloves and boots to stay safe from electrocution. Never touch wires or components inside the box without proper training. Keep the area around the breaker box free from any flammable substances. Inspect breakers for damage or wear regularly .
Label each circuit breaker correctly . Test them frequently for functionality. This will help identify circuits quickly in case of an emergency. These precautions and practices ensure safety while dealing with circuit breakers. When in doubt, blame it on the circuit breaker – it’s always a good scapegoat for electrical woes!
Circuit breakers are essential components of any electrical system. They stop too much current flowing and thus, protect against potential fires . The most common cause for tripping is overload. But, other causes like short circuits and ground faults can also cause the breaker to trip. When it trips, there is something wrong that needs to be fixed right away.
Short circuits occur when two wires touch each other. This creates a low resistance path which allows a lot of current to flow with no load. Ground faults occur when the hot wire touches something incorrectly wired or with a damaged cord.
To prevent tripping, regular maintenance of the electrical system is needed. Keeping appliances in good condition, replacing worn-out cords and fixtures, and periodically checking for loose wires all help reduce the chances of tripping. In summary, understanding why the breaker trips and taking precautionary measures will keep you safe and save you repair costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what causes a circuit breaker to trip.
There are several possible causes, including overheating due to circuit overload, short circuits, ground faults, and age-related wear and tear.
2. How can I prevent my circuit breaker from tripping?
You can avoid overloading your circuit by keeping the number of electrical appliances used on one circuit to a minimum, regularly checking wires for signs of wear and tear, and not using too many extension cords.
3. What should I do if my circuit breaker keeps tripping?
If your circuit breaker is constantly tripping, it is important to identify and fix the underlying issue. Contact an electrician to inspect and repair any faulty wiring or electrical devices.
4. Can a circuit breaker trip without an overload?
Yes, a circuit breaker can trip due to a short circuit or a ground fault, which may occur without an overload.
5. How do I reset a tripped circuit breaker?
To reset a tripped circuit breaker, turn it off and then back on again. Make sure to identify and correct the underlying issue that caused the trip before restoring power.
6. What is the lifespan of a circuit breaker?
The lifespan of a circuit breaker can vary depending on usage and other factors. However, most circuit breakers last between 10 and 30 years.
Related posts:
- What Causes Power Outages?
- How Do I Know If A Sparking Outlet Is Dangerous?
- Electrical Safety Check When Buying A House in Puchong
- Does Your DB Board Need Repair Or Replacement?
- About Team Austin
- Club Austin
- Service Area
- Explore Partnership Opportunities
- Plumbing Services
- Drain Cleaning
- Sump, Sewage & Grinder Pump Services
- Air Conditioning
- Water Heaters
- Air Duct Cleaning
- Wells & Pumps
- Water Conditioning
- Emergency Services
Mon – Fri: 7 AM – 5 PM
Why Do Circuit Breakers Trip? Common Reasons + Next Steps

No power at certain outlets? You may find your circuit breaker tripped. But why? And is it safe to turn back on? Our Master Tradesman responds.
Is it safe to reset a circuit breaker?
It is safe to reset a circuit breaker only if the breaker was tripped by an overloaded circuit, which we will get to later in this article. Resetting a breaker repeatedly can become a safety hazard due to arcing. If your circuit breaker is tripped and won’t reset, you will need a qualified electrician to investigate and troubleshoot the cause of the problem.
How to reset a tripped circuit breaker
A tripped breaker doesn’t always look tripped. Most breakers have a red or orange indicator showing that it has been tripped. Here are a few things to know before resetting the tripped circuit.
SAFETY TIP: Touch the electric panel using only one hand
- A breaker handle that is pointed to the outer edge of an electrical panel is off
- A breaker handle that is pointed towards the centerline of the electrical panel is on
- A breaker handle that is in the center is tripped
Follow these steps to reset a tripped breaker:
- First, slide the breaker handle all the way towards the outside edge of the panel
- Next, slide the breaker panel towards the center of the electrical panel
- The handle should stay on
- If you hear it the breaker trip again or if it returns to the center, call for service
How does a circuit breaker work?
A home’s circuit breaker serves a very important purpose by installing shut offs or cutting the power to circuits in the home. Without a working circuit breaker, routine and normal electrical failures could turn into a fire or cause electrocution. The inner workings of the circuit breaker are quite complicated, but this electrical safety device works by instantly shutting off the power to prevent electrical hazards and fires that can result from overloaded circuits or shorts in electric wires.
- An average home has 15-25 circuits
- Some circuits in a home are dedicated, which means only one electrical consuming appliance is on that circuit. Common examples with dedicated circuits would be electric ovens, well pumps, water heaters and air conditioners.
- Each circuit in the home is protected by a circuit breaker
- The circuit breaker in the electric panel also serves as a handy on/off switch for the area of the house it serves
- Circuit breakers should be labeled so you know the general area served by the breaker
The main circuit breaker: What can cause it to trip?
Sitting above all of the individual circuit breakers in a panel is the main circuit breaker. This breaker is one that controls the power to the entire home and any subpanels in the home after the main breaker. The main breaker also acts as a throttle, limiting the amount of total electricity usage of your home. Lightning strikes and other power surges coming from the electric grid are typically causes of a main breaker tripping, but on rare occasions an issue inside the breaker panel can cause issues with the main breaker.
Next steps if the main breaker is tripped
Whole home surge protectors are a great investment if you commonly find the main breaker of your home tripped. They can also prevent electrical emergencies and emergency repairs. These surge protectors work to absorb the power surge so further damage to the electrical system and your home’s electrons is prevented.
Failed Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers have a useful life of around 30 years and are under use and strain anytime there is a load on the electrical current that they serve. Circuit breakers also get warm and over time the mechanism inside the breaker wears and will eventually fail or trip for no reason. Common causes of a faulty breaker are overuse of the breaker (turning on and off a circuit often) and an overloaded circuit that doesn’t quite trip the breaker. If you have simultaneous use of high draw electrical motors and frequent overload happening on a circuit, this will cause failure as well.
- Water damage causes breaker failure
- Frequent usage of the breaker will cause wear
- Constant overload on the circuit will eventually cause the breaker to fail
- Loose wire connections at the breaker or inside the panel can cause overheating and fire
- Failed breakers can make it seem like you have a circuit overload or shorts even if you don’t
What to do if your circuit breaker is faulty
Replacement of a circuit breaker should only be done by a qualified electrician and is very dangerous. Because of this, if you suspect a failed circuit breaker, you should call Austin Plumbing, Heating, Air & Electric for evaluation and repair.
Overloaded Circuits
By far the most common cause of tripped circuit breakers is an overload in that circuit. Each electrical load that is on a circuit (outlet, light, appliance) has a total potential power draw while the circuit is being used. Wire also has load ratings. The circuit breaker’s job is to sense the load on the circuit and to interrupt or trip if the load gets too high. The reason for this is to protect the wire from starting on fire or getting hot and causing safety issues. When too much power travels through the circuit, danger increases.
Overloads are very common and usually easy to identify. If the circuit tripped when you started using an electrical appliance, then it’s likely that a combination of all of the electrical devices being used caused a simple overload.
Next steps if you have an overloaded circuit
Unplug or turn off the electric component that you think caused the system to overload and reset the breaker. If the breaker resets and everything seems fine, then you chalk up this breaker trip to an overloaded circuit breaker. If on the other hand the breaker trips again, something else may be going on.
The key to resolving an overloaded breaker is to lessen the load on it and the circuit it serves. Ways to do this include finding alternative places to plug in appliances, such as vacuums, and if you have several plugs running to the same outlet, consider using outlets in different areas of the home.
Short Circuits
A short circuit, or a dead short as many electricians call it, is a condition where two hot wires are touching together or touching something else metal. These short circuits can happen in jacketed wire, in electrical junction boxes, inside the panel or in the electrical appliance or equipment. Almost all residential home wiring utilizes three wires in order to make electricity work properly. One wire is live or also called hot (and covered with a black jacket), the second wire (covered with a white jacket) is called the neutral wire, and a bare copper ground wire.
What happens when the hot wire touches something it shouldn’t? This eliminates the electrical resistance and allows too much current to flow through the wire, which overloads the circuit breaker.
Many parts of the electrical system can be to blame for a short circuit, but loose wire connections, failed appliance cords, and damage to internal home wiring are among common causes we find.
Short circuits are dangerous because of the sparks that occur. It is quite common to see smoke, and the potential for a house fire due to a short circuit is high. If you happen to be touching the metal that the hot wire is shorting to, you run the risk of being burnt and electrocuted. If you see char marks on any electrical component, use caution!!!
Next steps for a short circuit
Because of the danger associated with a short circuit, a professional electrician should be called in to troubleshoot the root cause of the short.
Grounded Fault Surge
A ground fault surge is a specific type of short circuit that occurs when the black hot wire touches the ground wire or something metal in the electrical or plumbing system that ground wire is connected to.
Grounded faults are caused by the same thing that causes many shorts. Either the insulation on the wire is damaged or a connection gets loose allowing the hot wire to touch the ground.
From a safety point of view, ground faults can be more dangerous than short circuits, especially when the fault is caused by water. Modern homes and modern electrical code requires electrical outlets near water be protected with a special type of ground fault interrupter called a GFCI. GFCI stands for Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter. The code says that any outlet within six feet from a source of water must use a GFCI outlet. GFCI’s are commonly found in bathrooms, outdoor receptacles, kitchens, near sump pumps and in garages and basements.
GFCI’s provide an extra level of protection against grounded fault surges and are a critical safety component of modern electrical systems.
How to handle a tripped GFCI
GFCI receptacles are equipped with a reset. If you find the GFCI tripped, try simply resetting the outlet to see if that works. If pressing the reset button or test button several times does not restore the problem, call Team Austin for help.
Aged or Damaged Wire
The wire that carries the current from your electrical panel to the electrical appliance (aka load) has to be properly sized, properly insulated and installed correctly to prevent circuit breaker tripping and other electrical issues in the home. In very old homes, the wire insulation becomes degraded and brittle, which can cause various types of electrical shorts. As we learned earlier, this will cause the breakers to trip. Over the years as the electrical industry has improved, the flow of electricity with the quality of wire, wire nuts and other fasteners has also gotten better. If you have an old electrical system that has worn significantly and you continually have tripped breakers, you may consider a whole home rewire.
Next steps for aged or damaged wire
If you simply have damaged wire in a small area, the electrical pros at Austin Plumbing, Heating, Air & Electric can repair it in a cost effective manner. However, an aged or obsolete electrical system that involves rewiring a whole home or a section of the home will require design and a comprehensive plan for the best outcome. Both wire repairs and wire replacement is best suited for licensed electricians.
SE Wisconsin’s Electrical Experts & Full Trades Service
Austin Plumbing, Heating, Air & Electric has been solving the comfort, power and water problems of SE Wisconsin for over 80 years. If you’re having troubles with your electrical system or any other system in your home, you can trust the professional electricians at Team Austin for upfront pricing, honest recommendations and electrical repairs and replacements that will stand the test of time. Learn more about our electrical services on our electrical services main page or call 262-367-3808.
Table of Contents
— Air Conditioning
— Wells & Pumps
— Water Conditioning

10 Signs Your AC Needs a Repair (Or Replacement)
How Long Do Circuit Breakers Last?

The Ultimate Guide to Water Softener Troubleshooting: 20 Tips & Tricks

What Size Generator Does My Home Need?

The Actual Cost to Install an Automatic Whole-House Generator

Well Inspector? Or Septic Pumper in Disguise? Why Wisconsin Home Buyers Should NEVER Let Sellers’ Agents Pay for Well Inspections

1335 Martin Luther King Jr Ave
Dunedin, fl 34698, (727) 648-6101.

1335 Martin Luther King Jr Ave, Dunedin, FL 34698
CALL US: (727) 648-6101

What Does a Circuit Breaker Tripping Mean?
when there's a circuit breaker tripping, it can indicate that the circuit breaker detects an electrical issue, and it shouldn't be ignored..

The pandemic-induced surge in home electricity use is real. Consider that, according to the National Bureau of Economic Research, American spending on home power consump tion skyrocketed by $6 billion!
With more usage comes more problems, and circuit breaker issues are among the most common. When there's a circuit breaker tripping, it can indicate that the circuit breaker detects an electrical issue, and it shouldn't be ignored.
Circuit Breaker Tripping 101
Most circuit breaker issues center around circuit overload. Circuit breakers are a vital part of your home's electrical system since they are designed to prevent costly and damaging surges in electrical current.
The breaker, working in tandem with a fuse, serves as an electrical unit's internal sensing mechanism. At the slightest sense of excess current, the circuit breaker will "trip," triggering a cease in all electrical activity within the circuit.
Not only can such a smart mechanism help with preventing damage to wires and other electrical components, but circuit breakers can also save lives by preventing electrical fires. According to the National Fire Protection Association, electrical failures were the second leading cause of home fires between 2012-2016.
So why do circuit breakers trip? Here are the three most common reasons for circuit breaker tripping and how you can go about fixing a circuit breaker.
1) Circuit Overload
By far, the m ost common reason a circuit trips is because it's overloaded. Even running a circuit at its electrical capacity can cause home appliances to burn out or a circuit to trip. Ideally, you want to run a circuit below its capacity to keep it from tripping and to prevent any damage from occurring.
The most familiar example of circuit overload is an over-stuffed power outlet. When you have a dozen gadgets all demanding electrical current to work, eventually that single outlet's capacity will experience overload, and the circuit will trip.
Knowing what each electrical outlet in your house can handle is key to preventing circuit overload. Even a single high-current appliance like a washing machine cannot plug into just any outlet. Understanding your power outlets is critical for a safer home.
Before you head to your circuit breaker box or call your electrician, notice what was plugged in at the outlet where the tripped circuit occurred. You may have overloaded it.
2) Short Circuit
Similar to an overload, when a circuit "shorts," it responds to more current than it can bear. But a short circuit is far more dangerous.
A short circuit occurs when a "hot" or active wire comes into contact with either another active wire or a neutral wire. The touching wires cause a spike in current that can likewise trip your circuit breaker. Most often, the causes for short circuits are mechanical issues like:
- Loose Connections
- Improper Wiring
- Damaged Wires
Faulty components, like switches, plugs, cords, appliances, or lighting fixtures, are often culprits of short circuits. Short circuits can occur if you screw or nail into drywall and penetrate an electrical wire.
Remember that short circuits may involve faulty circuit wiring, but the device you're plugging in can cause the problem as well. Keep this in mind, especially if you're using older devices or gadgets that have been out of commission for years, as these can be more prone to short circuits, independent of what's going on in the outlet.
Due to their volatile nature, short circuits are some of the biggest causes of electrical fires, so be extra attentive and don't hesitate to call a professional. As a general rule, most people should never DIY electrical issues in their homes.
3) Ground Fault Surge
Ground fault surges are similar to short circuits because they involve a sudden spike in current, creating an overload. Ground faults occur when an active wire comes into contact with the ground wire. The contact can come directly or indirectly via the metal housing that connects to the ground wire.
Copper grounding wires are especially prone to ground fault surges. Copper is the most conductive material in everyday use when it comes to home electrical systems. When a hot wire touches the ground wire's copper coating, it results in superconductivity that overwhelms the circuit. A similar result can come from an active wire touching a ground's metal outlet box.
Understanding and Fixing Circuit Breaker Issues
So how should you go about troubleshooting a circuit breaker issue? Even though you should leave anything remotely technical to a professional, there are a few things you can do to investigate circuit breaker trip meaning.
First thing's first. Make sure you and your family are safe. Check for signs of excess heat or burning—smell for what could be smoke from an electrical fire. If you sense any signs of a fire, evacuate and call 911.
Check for any discoloration around an outlet. Also, make a note of any sparks or popping noises coming from the outlet. Any of these could be a sign of a ground fault surge or a short, in which case simply flipping the circuit breaker switch won't help. And remember, the older the outlet, the more likely it is to experience problems.
Look for any signs of damage to your devices. Remember that the problem could be coming, not from your home's outlet, but from what you plugged in.
If there are no signs of a blown circuit, try going to your circuit breaker service panel. You may be familiar with this metal box, often located in a garage or utility room. Flip the switch of the house area that tripped, and see if that "resets" the circuit.
Fixing a Circuit Breaker
If a simple flipping of the switch doesn't work, it's time to call a professional electrician. The seasoned team at Buell Electric can assess the problem and fix a circuit breaker, which may involve repairs or upgrades.
Circuit breaker tripping may be as innocent as overloading an outlet, but it can point to more serious problems as well. The best way to know for sure is to contact us today.
Newer Post >
Buell Electric's Blog

Shedding Light on Your Home: Finding the Right Electrician in Tampa

How Electricians Keep Up with Changing Technology in the Industry

The Importance of Regular Electrical Maintenance For Your Business

Marine Electrical Standards and Regulations You Need to Know

The Benefits of Installing a Smart Home System

Understanding the Different Types of Electrical Wiring in Your Home

How to Prepare Your Home for an Electrical Emergency

5 Reasons Your Ceiling Fan Installation Should be Left to the Pros

5 Tips for Hiring Residential Electrical Services

8 Common Outdoor Lighting Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
[email protected]
Mon-fri 9:00 am - 5:00 pm sat-sun 10:00 am - 5:00 pm privacy page, connect with us:.

Mon-Fri 9:00 AM - 5:00 PM Sat-Sun 10:00 AM - 5:00 PM
All Rights Reserved | Buell Electric, Inc.

- svg]:stroke-accent-900"> 826K
- svg]:stroke-accent-900"> 622K
- svg]:stroke-accent-900"> 246K
- svg]:stroke-accent-900"> 45K
Why Is My Circuit Breaker Tripping? 4 Potential Problems and Solutions
By Glenda Taylor , Bob Vila , Evelyn Auer
Updated on Dec 21, 2023 8:55 PM EST
6 minute read
We may earn revenue from the products available on this page and participate in affiliate programs. Learn More ›
Q: Every few hours—sometimes minutes!—my living room and one side of my kitchen lose electrical power. I’ll check the breaker panel and, sure enough, a circuit breaker has tripped…again. Should I call an electrician, or is there a simple DIY fix I can try first?
A: While it’s frustrating when a circuit breaker keeps tripping, they are important safety mechanisms. Designed to shut off the electrical current when something goes wrong, circuit breakers are one of the best ways of protecting a home from an electrical fire. “When a circuit breaker trips, typically it is because we use too much electricity, which causes it to overload and turn off,” says Christopher Haas, expert electrician and owner of Haas & Sons Electric in Millersville, Maryland. For those who need an electrical panels 101 refresher course or aren’t sure how to reset circuit breakers, each breaker has an on/off switch and controls a separate electrical circuit in the home. When a breaker trips, its switch automatically flips “off,” and it must be manually turned back on to restore electricity to the circuit. For those wondering, “Is it dangerous if a circuit breaker keeps tripping?” the answer is that it can be, depending on the source of the problem. An electrician can ultimately deal with the root issue, but a little sleuthing will reveal whether it’s something that’s easily remedied.
In many cases, the cause of a circuit breaking tripping is an overloaded circuit.
A circuit overloads when more electrical current is being drawn through the wires than they can handle, tripping the circuit breaker. If this happens, there may be a few additional signs:
- Buzzing noises coming from outlets
- Devices charging slowly
- Electrical outlets not working
- Flickering lights
- Scorch marks on outlets and light switches
If a circuit breaker keeps tripping in one room, homeowners can test for circuit overload by turning off all the switches in the affected area and unplugging all appliances and devices. After the breaker is flipped back on, the devices can be turned back on one at a time, with homeowners waiting a few minutes in between to see if the circuit remains on. If the breaker trips before all the appliances are turned on, the experiment can be repeated, this time turning them on in a different order. It may be necessary to do this several times to find out how many appliances can be operated at once before the circuit overloads.
“As a short-term solution, you can unplug unnecessary appliances to prevent tripping circuit breakers. You may still get some trips, but you can limit them by unplugging devices that you don’t need to use,” advises Dan Mock, vice president of operations at Mister Sparky , an electrical company with 90 locations in the U.S. The best long-term solution, however, is to pay an electrician for the cost to rewire the house and add additional circuits. The cost to replace an electrical panel is about $1,274 on average.
Other times, the issue may be caused by a short circuit.
A “short” circuit means that two wires that should not be coming into contact are inadvertently touching, triggering a sudden surge of electricity through the wires. A short can occur in an outlet, a switch, or within an appliance if wires are loose or have been chewed through by mice or pets. Some signs of a short circuit include:
- Popping sounds
- Discolored outlets or switches
- Burning smells
Testing to see if an appliance has a short is similar to testing for an overloaded circuit. When an appliance that has a short in its wiring is turned on, it will immediately trip the circuit. Homeowners can also try plugging it into an outlet in a different room. If the breaker for that room trips, there’s a short in the appliance (if it’s unclear what breaker goes to what room, the breaker can be identified with one of the best circuit breaker finders ). Electrical shorts can be a major fire hazard, so it’s a good idea to call a licensed electrician for this circuit breaker repair. It’s wise to stop using the outlet or appliance until a pro takes care of the problem.
Another potential cause of a circuit breaker tripping is a ground fault.
A ground fault occurs when the electricity running through a home’s wiring diverts from the wiring loop and travels to the ground, usually due to faulty wiring or water infiltration in an outlet or switch box. Water is a conductor, which is why walking through puddles is often listed as something not to do in a power outage in case of downed power lines. Once water makes contact with wires, electricity can jump from the wiring loop and follow the water trail. This creates a surge in electricity leading to a tripped circuit breaker. If a person comes in contact with the electricity that is on its way to the ground, this can result in electrocution. Homeowners may notice a few signs of a ground fault, including:
- Tripped GFCI (ground fault circuit interrupter) outlets;
- A burning smell coming from an outlet; and
- Lights flickering.
Newer electrical breakers have features designed to protect against the danger of ground faults. According to Haas, “Ground fault breakers sense electricity going to earth as opposed to going through the wires of the circuit. You’ll find [these] for bathrooms, kitchens, garages, exteriors, and basements.” GFCI outlets are another safety feature that shut off the electric current within a fraction of a second of sensing a ground fault.
If a ground fault is the problem, the cause of the errant water must be discovered and repaired, and any damaged wiring must also be replaced. It’s also a good idea to install GFCI outlets in rooms where water is commonly used. A GFCI outlet costs $210 on average.
Sometimes a bad or worn-out circuit breaker can be the culprit.
In some cases, the circuit breaker itself may be faulty. Breakers that are old, damaged, or were installed incorrectly may trip frequently for no apparent reason. Alternatively, faulty breakers may not trip when they are supposed to, leaving the home at risk of electrical fire. Some signs of a bad circuit breaker include:
- The circuit breaker getting hot and tripping frequently;
- The circuit breaker won’t reset;
- It has been over 10 years since the breaker was last serviced; and
- The breaker has scorch marks.
An important electrical safety tip to keep in mind is that resetting a breaker over and over again can cause what is called an arc flash, which is a small electrical explosion that can be deadly. If resetting the breaker once does not remedy the issue, it’s a good idea for the homeowner to hire an electrician near them who knows how to replace a circuit breaker safely. Mock warns, “Don’t take any chances with circuit breakers. Instead, call a licensed electrician who knows the safe ways to replace breaker boxes, upgrade circuits, and diagnose potential electrical problems in your home.” Wiring a breaker box is a job to leave to an experienced electrician.
A professional electrician can help determine the specific cause of a frequently tripping circuit breaker.
Most circuit breaker problems—aside from those explained in the sections above—will need to be inspected and addressed by a licensed electrician. According to the Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI) , each year “thousands of people in the United States are critically injured and electrocuted as a result of electrical fires, accidents, [or] electrocution in their own homes.” While homeowners may be tempted to save on electrician costs by attempting circuit breaker replacement or repair themselves, electrical work is not suitable for casual DIYers. “Yes, you have to pay, but you can save many hours of head-scratching by hiring an electrician. Electricians will also have all the right tools for diagnosing and repairing the circuit,” Haas adds. “Lastly, they will come with a warranty/guarantee should something arise, and they will typically return at no additional cost.”
Anker’s New Home Battery Tower Is a Sleek, Modular Step Toward Complete Energy Independence Anker’s New Home Battery Tower Is a Sleek, Modular Step Toward Complete Energy Independence
By Chase Brush
The Government Is Paying People to Upgrade Their Home Comfort, Here’s Why The Government Is Paying People to Upgrade Their Home Comfort, Here’s Why
By Tony Carrick
- Join Insider
Follow This Old House online:
Site search, why do circuit breakers trip.
Master electrician Heath Eastman shows host Kevin O’Connor everything he needs to know about why and how breakers trip.
Heath Eastman talks about circuit breakers. Heath shows Kevin O’Connor that while resetting these breakers is simple, these are complex devices that monitor and protect circuits. First, the two talk about the different sizes of breakers before moving on to the different types. Finally, Heath shows Kevin how to test certain breakers to ensure they’re working properly.
Circuit breakers exist to protect people, appliances, and homes from dangerous electrical current. However, few people understand why the trip and how they operate. Master electrician Heath Eastman shows host Kevin O’Connor why this happens, and even explains a few different types of breakers.
All About Electrical Systems
Breakers protect circuits.
When electricity comes into the house, it flows through the electrical service panel. From there, the electricity flows out through different branches in the house, each controlled by a circuit breaker. Should a branch begin to overload and overheat, the breaker will trip to prevent damage.
Breaker Sizes
There are two main sizes of breakers in a house: 15 amp and 20 amp. The amp rating explains how much current the breaker can handle before it will trip, and each requires a certain size of wire. Fifteen-amp breakers require a 14-gauge wire, while 20-amp breakers require a 12-gauge wire.
How They Work
A 15-amp breaker won’t necessarily trip the moment it experiences a spike above 15 amps. Many devices draw more amps upon start-up, and these breakers allow those temporary spikes. However, should the breaker sense elevated amperage for longer than is typical, it will trip to prevent the circuit from overheating.
GFCIs and AFCIs
Beyond circuit overload protection, there are other types of breakers that offer additional coverage. These include GFCI breakers and relatively-new AFCI breakers .
GFCI (ground fault circuit interrupter) breakers need to experience the same amount of current going out as coming back through the circuit. If the breaker experiences a drop in returning current, it assumes that the circuit is leaking, whether it be through a water source or a person. When this imbalance occurs, the GFCI trips immediately.
AFCI (arc fault circuit interrupter) breakers sense when the circuit, a device, or an appliance is arcing (the current is jumping from the circuit and onto something else or someone). When the breaker recognizes the arc signature, it trips immediately. These breakers are relatively new and look similar to GFCI breakers, but they’re becoming a code requirement in most locations.
How to Test Breakers
Homeowners, electricians, and inspectors can test their breakers. There are devices that users can plug into an outlet and replicate an error. These devices, known as AFCI/GFCI testers, can trip the breaker altogether or replicate a ground or arc fault, triggering the breaker. This is one of the best ways to ensure that a breaker is working properly.
When to Call a Professional
If a circuit is continuously tripping, or you know that it should be tripping and isn’t, be sure to call in a professional. An electrician will be able to determine the cause of the issue and make sure your circuit breakers and electrical system are safe.
Heath explains what a circuit breaker is, why they trip and how it protects a home. A circuit breaker is a device, installed in the electrical panel, that controls whether power can be sent from the panel through a circuit. Heath explains this ability is controlled by a switch that can be operated either manually—like when a person wants to interrupt power for service—or automatically, like a breaker trip.
He says power overloads, current “leaks”, and arcs are the three reasons that would cause a breaker to trip. A Power overload happens when a device is calling for more power than a receptacle , or a circuit is designed to provide. Current “leaks” are caused when current strays from the circuit for whatever reason, though it happens most commonly when moisture is present. Arcs can happen when the wire breaks down over time (due to overloads but also due to other factors, like animals chewing the wire and other decay) but what Heath sees the most is human error.
If a specific receptacle is consistently tripping the breaker, Heath advises to have a licensed electrician identify the problem to ensure the work is done safely.
Next Up In Electrical
- How to Label a Circuit Breaker
- Simple Guide for Selecting a Home Generator
- All About Portable Power Stations
- Simple Guide to Installing a Generator Hook-Up
- How to Build a Utility Cover
- Understanding Smoke and Carbon Monoxide Detectors

Sign up for the Newsletter
Get the latest This Old House news, trusted tips, tricks, and DIY Smarts projects from our experts–straight to your inbox.

- Navien Heating Systems
- Rheem Heating Systems
- Air conditioning
- Ductless mini-splits
- Air Filtration
- Drain Cleaning
- Plumbing Fixtures
- Toilet Repairs
- Pipe Repairs
- Water Heaters
- Water Treatment
- Sewer and Water Line Service
- Drainpipe and Septic Treatment
- Toxic Fume Detectors
- Electrical safety equipment
- Smart Devices for home automation
- Home Lighting
- Mass Save Program Information Page
- Mass Save Heat Pump Rebates
- Mass Save Insulation Rebates
- Area Served
- (978) 539-7172

Why Do Circuit Breakers Trip? The Most Common Reasons
Circuit breakers are vital components of your home's electrical system, protecting you from potential hazards and electrical emergencies. However, dealing with constantly tripping breakers can be frustrating. It is crucial to understand why circuit breakers trip and the possible causes behind these issues. In this comprehensive guide, we will breakdown how circuit breakers work, common causes of tripped breakers, and the importance of electrical safety in your home.
How Circuit Breakers Work
Every electrical circuit in your home is connected to a circuit breaker, which acts as a safety device. When a circuit experiences an overload, short circuit, or other electrical issue, the breaker instantly shuts off the power to that specific circuit, preventing potential fires or electrocution. This mechanism safeguards individual circuits and ensures uninterrupted power supply throughout your home. Understanding the functionality of circuit breakers is essential for maintaining a safe electrical system.
Common Causes of Tripped Circuit Breakers
Overloaded circuits:.
The most frequent cause of a tripped circuit breaker is an overloaded circuit. Each circuit is designed to handle a specific electrical load. If the load exceeds this limit, the breaker trips to prevent overheating and potential fire hazards. Overloading can occur when multiple high-power appliances or devices are connected to a single circuit simultaneously, pushing it beyond its capacity.
Short Circuits:
Short circuits occur when a hot wire comes into contact with a neutral wire, a ground wire, or any conductive material. This contact creates a low-resistance pathway, allowing excessive current flow and triggering the breaker. Short circuits are often caused by damaged wiring, loose connections, or faulty appliances, posing both fire and electrocution risks.
Ground Fault Surges:
A ground fault surge is a specific type of short circuit that occurs when the hot wire touches the ground wire or a metal electrical box. It can be caused by damaged insulation, faulty wiring, or water entering outlets. Ground fault surges are particularly dangerous as they can lead to electrocution. Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlets provide additional protection by detecting ground faults and automatically cutting off power to prevent accidents.
Old or Faulty Circuit Breakers:
In some cases, circuit breakers may trip due to their age, faults, or incorrect wiring. If your breakers or electrical panel are outdated or malfunctioning, they may trigger unnecessary trips. While rare, this possibility should be considered if other causes have been ruled out.
Electrical Safety Precautions
Maintaining electrical safety in your home is crucial to protect your family and property. Here are some important precautions to follow:
Avoid Overloading Circuits:
Distribute electrical loads evenly across circuits and avoid plugging multiple high-power appliances into a single outlet or circuit.
Proper Appliance Usage:
Follow manufacturer instructions for appliance installation, use, and maintenance. Avoid using damaged or frayed cords, and unplug appliances when not in use.
Regular Inspections:
Conduct periodic inspections of your electrical system, including outlets, switches, and wiring. Look for signs of wear, damage, or discoloration.
Professional Assistance:
If you experience frequent circuit breaker trips or notice any electrical issues, it is best to consult a licensed electrician. They can diagnose problems, perform repairs, and ensure your electrical system is up to code.
Call On The Electrical Experts at Home Mechanics
Understanding why circuit breakers trip and taking necessary electrical safety precautions are vital for maintaining a secure home environment. Overloaded circuits, short circuits, ground fault surges, and faulty breakers are common causes of tripped breakers. By properly distributing electrical loads, using appliances correctly, conducting regular inspections, and seeking professional assistance when needed, you can mitigate potential hazards and ensure the smooth functioning of your electrical system. Prioritizing electrical safety will provide peace of mind and protect your home and loved ones from electrical emergencies. Our team of professional electricians can diagnose and repair any electrical problems you may be having, contact us to schedule your service visit today!
Whether you require simply deplete cleaning or a whole pipes registration.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate.
Why call Home Mechanics?
Home comfort with comfortable savings.
Be sure to take advantage of all the ways to reduce costs and increase savings! We'll be sure to help.
- Rebates & Incentives
- Free Home Energy Assessment
- Energy Efficient Devices
- 0% Financing
- Federal Tax Credits
- Lower Energy Bills
" * " indicates required fields
Breaker principal de circuito eléctrico: Tipos, funcionamiento y mantenimiento

El breaker principal de circuito eléctrico (Main Breaker) es una parte esencial de cualquier sistema eléctrico residencial o comercial. Este dispositivo de protección cumple una función crucial al salvaguardar el sistema eléctrico y los dispositivos conectados contra sobrecargas y cortocircuitos, garantizando así la seguridad de las personas y la integridad de los equipos.
Te contamos en detalle qué es un breaker principal de circuito eléctrico, cómo funciona, por qué es importante y qué consideraciones deben tenerse en cuenta al instalar o mantener este componente vital en un sistema eléctrico. Además, discutiremos las diferentes opciones disponibles en el mercado y proporcionaremos recomendaciones prácticas para su uso adecuado y seguro.

Funcionamiento del breaker principal de circuito eléctrico
El funcionamiento del breaker principal de circuito eléctrico se basa en el principio de interrupción del flujo de corriente eléctrica cuando se detecta una sobrecarga o un cortocircuito en el sistema eléctrico. Este dispositivo consta de varios componentes clave que trabajan en conjunto para lograr esta función de protección.
El breaker principal funciona como la puerta de entrada de la electricidad a la vivienda. Cuando se encuentra en la posición "ON", permite el flujo de corriente eléctrica a través del sistema eléctrico.
Interruptor automático
El breaker principal actúa como un interruptor automático que puede abrir o cerrar el circuito eléctrico según las condiciones de carga y las señales de protección detectadas. Cuando la corriente eléctrica excede un nivel seguro o se presenta un cortocircuito, el interruptor se activa automáticamente para interrumpir el flujo de electricidad.
Elemento de disparo
Este componente es sensible a las variaciones de corriente y actúa como el sensor del breaker. Cuando la corriente eléctrica supera el límite preestablecido, el elemento de disparo se activa, generando una señal que desencadena la apertura del interruptor automático.
Mecanismo de apertura y cierre
El breaker principal está equipado con un mecanismo que permite abrir y cerrar el circuito eléctrico de manera rápida y confiable. Cuando se activa el elemento de disparo, este mecanismo se acciona para abrir el interruptor y detener el flujo de corriente, evitando así daños mayores en el sistema eléctrico y en los dispositivos conectados.
Capacidad de reinicio
Después de que se ha activado para interrumpir el flujo de corriente, el breaker principal tiene la capacidad de reiniciarse manualmente una vez que se han corregido las condiciones que causaron la activación. Esto proporciona una funcionalidad conveniente y permite restablecer el suministro eléctrico sin la necesidad de reemplazar el dispositivo.

Función del breaker principal o Main Breaker
El breaker principal de circuito eléctrico desempeña un papel fundamental en la protección y seguridad de cualquier instalación eléctrica.
Protección contra sobrecargas
Las sobrecargas eléctricas pueden ocurrir debido a la conexión de demasiados dispositivos en un circuito o al funcionamiento anormal de equipos eléctricos. Sin un breaker principal, estas sobrecargas podrían provocar daños graves en los cables, equipos y dispositivos conectados, así como un riesgo de incendio.
El manbreaker (como suele llamarse coloquialmente) actúa como una barrera de protección al interrumpir automáticamente el flujo de corriente cuando se detecta una sobrecarga, evitando así posibles daños y peligros.
Prevención de cortocircuitos
Los cortocircuitos son otro peligro potencial en cualquier sistema eléctrico. Ocurren cuando hay un camino de baja resistencia entre los conductores eléctricos, lo que puede resultar en una corriente eléctrica excesiva y un sobrecalentamiento rápido.
Los cortocircuitos pueden ser extremadamente peligrosos y causar daños graves en el sistema eléctrico e incluso iniciar incendios. El breaker principal detecta estos cortocircuitos y los interrumpe rápidamente para evitar consecuencias catastróficas.
Seguridad de las personas
Además de proteger el sistema eléctrico y los equipos, el breaker principal también juega un papel crucial en la seguridad de las personas que interactúan con la instalación eléctrica. Al cortar el suministro eléctrico en caso de una situación de riesgo, como una sobrecarga o un cortocircuito, el breaker principal ayuda a prevenir descargas eléctricas que podrían resultar en lesiones graves o incluso fatales.
Cumplimiento de normativas y códigos de seguridad
En muchos países, los códigos de construcción y las normativas eléctricas requieren la instalación de un breaker principal en todas las instalaciones eléctricas. Cumplir con estas normativas no solo es necesario para garantizar la seguridad de las personas y la propiedad, sino que también puede ser un requisito legal.

Consideraciones al instalar o mantener un breaker principal
Instalar y mantener adecuadamente un breaker principal de circuito eléctrico es fundamental para garantizar su correcto funcionamiento y la protección eficaz del sistema eléctrico.
Capacidad de carga adecuada
Es crucial seleccionar un breaker principal con la capacidad de carga adecuada para el sistema eléctrico en el que se instalará. Esto significa elegir un breaker que pueda manejar la corriente máxima esperada sin activarse innecesariamente ni quedarse corto en caso de una sobrecarga real.
Se deben considerar factores como el tamaño de la instalación, la carga eléctrica máxima y las necesidades de seguridad del sistema.
Compatibilidad con el panel eléctrico
Antes de la instalación, asegúrate de que el breaker principal sea compatible con el panel eléctrico existente. Verifica las especificaciones del fabricante y asegúrate de que el breaker encaje correctamente en el panel y cumpla con los requisitos de voltaje y amperaje.
Ubicación y acceso
El breaker principal debe instalarse en una ubicación fácilmente accesible y bien ventilada para facilitar su inspección, mantenimiento y operación. Evita colocar objetos u obstrucciones que dificulten el acceso al breaker en caso de una emergencia eléctrica.
En la mayoría de las viviendas, el breaker principal se encuentra en el cuadro eléctrico, también conocido como caja de distribución o panel de interruptores. Este cuadro suele estar ubicado en la marquesina, parqueo del edificio, o cerca de la puerta principal de la vivienda.
Mantenimiento regular
Es importante realizar inspecciones y mantenimiento periódicos del breaker principal para garantizar su funcionamiento óptimo. Esto puede incluir la limpieza de contactos, la verificación de la integridad de los componentes y la prueba de su funcionamiento con dispositivos de prueba adecuados.
Reemplazo en caso de daño o desgaste
Si se detecta algún signo de daño o desgaste en el breaker principal, como grietas en la carcasa, conexiones sueltas o mal funcionamiento, es crucial reemplazarlo de inmediato. No intentes reparar un breaker dañado, ya que esto podría comprometer su capacidad de protección y seguridad.

Tipos de breakers eléctrico y sus características
Cuando se trata de seleccionar un breaker principal de circuito eléctrico, es importante considerar los diferentes tipos disponibles y sus características únicas.
Breaker principal termomagnético
- Este tipo de breaker utiliza dos métodos de protección: térmico y magnético. El elemento térmico responde a las sobrecargas prolongadas, mientras que el elemento magnético detecta las corrientes de cortocircuito.
- Son versátiles y se utilizan en una amplia gama de aplicaciones, desde residenciales hasta industriales.
- Proporcionan una protección confiable contra sobrecargas y cortocircuitos, lo que los hace ideales para aplicaciones donde se requiere una protección completa.
Breaker principal de arco eléctrico
- Estos breakers están diseñados específicamente para proteger contra los peligros asociados con los arcos eléctricos, que pueden ocurrir debido a conexiones sueltas, cables dañados o condiciones ambientales adversas.
- Incorporan tecnología avanzada para detectar y extinguir arcos eléctricos de manera rápida y efectiva, minimizando el riesgo de incendios y daños en el equipo.
- Son ideales para aplicaciones donde existe un alto riesgo de formación de arcos eléctricos, como en instalaciones industriales o comerciales con equipos sensibles.
Breaker principal de corriente residual (GFCI o RCD)
- Estos breakers están diseñados para proteger contra descargas eléctricas al detectar la pérdida de corriente en un circuito, como cuando una persona entra en contacto con la electricidad.
- Actúan rápidamente para desconectar el circuito en caso de una fuga de corriente, lo que reduce significativamente el riesgo de descargas eléctricas y lesiones.
- Son obligatorios en áreas donde existe un alto riesgo de descargas eléctricas, como baños, cocinas, áreas exteriores y entornos industriales.
Clasificación según el número de circuitos eléctricos que controlan
Además de los tipos comunes de breakers principales de circuito eléctrico, también podemos clasificarlos según el número de circuitos eléctricos que controlan.
Breakers unipolares
Estos breakers controlan un solo circuito eléctrico.
Son adecuados para aplicaciones donde se necesita proteger un solo circuito, como la iluminación de una habitación o los tomacorrientes de una pared. Son comúnmente utilizados en instalaciones residenciales y comerciales.
Breakers bipolares
Estos breakers controlan dos circuitos eléctricos simultáneamente.
Son útiles en aplicaciones donde se requiere una protección independiente para dos circuitos, como en sistemas eléctricos que alimentan electrodomésticos de alto consumo o en sistemas que requieren circuitos separados para equipos sensibles.
Al considerar los diferentes tipos de breakers principales de circuito eléctrico, es importante tener en cuenta tanto su función de protección como el número de circuitos que pueden controlar, para seleccionar el tipo más adecuado según las necesidades específicas de la instalación eléctrica.
Electricidad

Elevadores para casa: Guía detallada de tipos, costos y beneficios

¿Qué hacer cuando tu refrigerador no enfría?

Proceso de instalación de acometida eléctrica residencial
- Air Conditioning
- Electrician
- Garage Door Installation
- Garage Door Repair
- Heating & Furnace
- HVAC Contractors
- Landscaping
- Pest Control
- Experiences
- Homeowner Login
- Join As a Pro
What Causes a Tripped Breaker?
Are you looking to hire a:.
- Carpentry Pro
- Landscaping Pro
- Plumbing Pro
- Remodeling Pro
- Roofing Pro
- HVAC Contractors Pro

- If the circuit breaker in your home trips, restart it by flipping the tripped switch to the off position and then back to on. If your breaker trips again, call an electrician to come and service the breaker.
- One of the most common reasons for a tripped breaker is loose electrical connections. Aluminum wires tend to expand and contract, thereby loosening over time.
- Another common cause for your breaker to trip is a direct electrical short in the wiring or equipment. You can tell if this is the problem if the breaker trips instantly once the unit tries to start. If this happens, call an electrician to service it immediately.
- There are times when a breaker trips due to the compressor having trouble starting. The compressor might be old, weak or just tight. While you can buy a Hard Start Kit, the problem may be easily fixed by replacing a bad capacitor, which helps start the compressor.
The reason your breaker trips in the first place is to protect your equipment, wiring and home. Do not ignore the situation, as it could result in high voltage and amperage, leading to melted wires and even possibly a fire. Remember a circuit breaker should not feel hot to the touch. Utilize the backs of your fingers to check the temperature of the breaker; if it is room temperature or warm, then it is safe; but if it is hot, that could be a sign of a problem. Contact a professional electrician .
Related Articles

Looking for a Pro? Call us at (866) 441-6648

Electrical Average Costs
- Rewire a House $13,125
- Install a Smart House System $2,117
- Hire an Electrician $320/service call
Electricians Experiences

Look To Your Electrician For Advice On The Best Lighting System

Parking Lot Lights Restored So Employees Can Reach Cars Safely

We Needed A New Bathroom Vent Fan To Get Our House Renter-Ready
Top cities covered by our electricians.
- Service Needed Select Service Needed Additions / Remodels / Major Renovations Air Conditioning & Heating Appliances Asphalt Paving Builders (New Home) Carpentry, Decks & Porches Carpet - Install / Clean Cleaning Services Concrete, Brick & Stone Countertops - Install / Repairs Doors Driveways, Patios, Walks, Floors Drywall Electrical / Generators Fences Flooring Garage - Build/Remodel Garage Doors, Openers Gutters Handyman Services Heating & Cooling Home Security Insulation Landscaping & Lawn Care Major Renovations Painting & Staining Pest Control / Termites Plumbing / Water Heaters / Gas Piping Recovery Services (Water, Fire, Etc) Roofing Septic System Services Siding Tile & Stone Tree Removal And Trimming Windows Other / Miscellaneous
5+ Reasons Why Your Breaker Keeps Tripping – And How to Fix It
Your breaker may trip due to circuit overload, short circuits, ground faults, outdated wiring, or a faulty breaker. Follow tips to fix each issue and ensure safety.

Your circuit breaker will trip once in a while if it detects an electrical fault. After all, that’s what it’s designed to do. Without the breaker, you could be putting yourself, loved ones, and property at risk of electrocutions and fires. But what if the breaker keeps tripping and leaves you in pitch darkness?
Before you call an electrician, consider implementing the tips below. You’ll discover the root causes and what to do if your breaker keeps tripping.
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases. Thanks!
Why Does My Breaker Keep Tripping?
If your breaker frequently trips, examine your electric power system to determine if the issue results from one of the following causes.
Hey hey! Don’t forget to subscribe to get our best content 🙂
Type your email…
Circuit Overload
Have you checked whether you’re dealing with an overloaded circuit? A circuit overload occurs when the wires receive more electrical current than they can handle.
Each circuit has a maximum current it can handle. The breaker will trip if it detects that the current exceeds the circuit’s capacity.
Often, a circuit overload happens if you’ve plugged multiple appliances, including high-power devices, into the circuit. You might notice that power goes out in your kitchen or living room when the breaker trips. That’s a telltale that a single circuit in either of the rooms is powering multiple appliances.
- Disconnect all the devices and reset the breaker.
- Before connecting an appliance, allow your electric power system to rest for a few minutes. Plug in your devices one at a time.
- If it trips again as you plug in the devices, relocate the appliances to other outlets.
- If the breaker continues to trip, call an electrician to troubleshoot the problem.
Short Circuit
A short circuit might be another reason why your breaker keeps tripping. Unlike circuit overloads, short circuits have more potential to cause fires.
A short circuit happens when a live or “hot” wire touches a neutral wire. When the two wires touch, they cause a sudden surge of current through the wires. This surge leads to a circuit overload, which causes the breaker to trip. If your circuit breaker fails to trip, it can put your property at risk of fire.
To know whether the culprit is a short circuit, you can look for sparks, smoke, burning smells, or popping sounds. A short circuit will occur in a switch, outlet, or within the circuit breaker due to the following reasons:
- Slipped wires
- Damaged wires
- Loose connections
Do you know what to do if your breaker keeps tripping? Unless you have professional experience, avoid trying to fix a short circuit in your electric power system. The affected cables can instigate fire and further damage. You may also get electrocuted. Call your electrician to fix the problem.
Ground Faults
When it comes to ground faults, a live or “hot” wire touches a ground wire or the breaker’s outer casing. This contact causes a sudden surge of current passing through the breaker. The breaker will trip if it detects more electricity than it can handle.
Ground faults occur when water enters the appliance or an outlet. If it touches the hot wire, the current changes its route and follows the water path. This might cause electrocution if you touch the water with bare hands or feet.
Thankfully, the National Electrical Code (NEC) requires buildings to install Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlets . These outlets can detect ground faults and cut off the current.

- Find where the water is coming from and fix it. If it’s damaged roofing directing rainwater into the box, call a roofer to fix it.
- Replace damaged wiring. Call your electrician to replace the damaged wiring to avoid causing further damage.
- If you’ve not installed GFCI outlets, call a licensed electrician to install them for you.
Outdated Wiring
Outdated wiring is prevalent in older homes. If you live in an old house, you’re likely to have a breaker that keeps tripping. The electric power system in that home can only handle low-power devices. If you plug in modern appliances, you might experience frequent breaker trips due to circuit overload.
Old aluminum wires might melt when the circuit overloads. The melting cables might burn the plastic casing, causing a fire.
If you check the insulation in one of your outdated wires, you might find it deteriorating. When this insulation touches a conductor, it can cause a ground fault.
According to the National Fire Prevention Association (NFPA), faulty wiring leading to electrical failure is one of the main causes of fires in residential areas. The wiring can be outdated if you live in a house over 40 years old. Outdated and faulty wiring will likely cause a fire during overloads or short circuits.
The only way to fix outdated wiring is to have it replaced. Find a professional who’ll inspect the wiring and upgrade it.
A Bad Circuit Breaker
If your breaker doesn’t stop tripping even after fixing some or all of the above causes, then your breaker might be faulty. Sometimes, a breaker will trip even when it’s newly installed. This might be due to an undersized breaker, manufacturer’s defect, or loss of efficiency. If one of these is the case, your breaker will trip even if there are no overloading, short circuits, or ground faults.
When inspecting your old wiring, check whether you’re working with an old breaker. It may no longer produce electricity for your modern appliances if it’s old. You should also check whether the breaker is tripping due to a lack of maintenance.
Avoid tampering with your faulty breaker, especially if you don’t have the necessary skills. Call a certified electrician to diagnose the problem and fix it. If your breaker is old or beyond repair, they can replace it.
How To Reset a Tripped Breaker
If your breaker won’t stop tripping, resetting it is the first thing you might consider. Resetting the circuit breaker is a great way to determine what causes the tripping.
To reset your breaker:
- Locate the appliance’s handle or switch and move it to the “OFF” position.
- Before this, ensure you’ve unplugged all the devices.
- Move the switch to the “ON” position.
When turning the switch on, the breaker might produce sparks that might cause a fire or electrocution. To be safe, avoid standing near and directly facing the panel. You can stand at the side or a few steps back. After resetting, allow the breaker to rest for a few minutes before plugging in your devices. Now you know what to do if your breaker keeps tripping.
The following are some of the most common questions people have asked about circuit breakers.
How can you tell if your circuit breaker has gone bad?
The following symptoms should help you know that your circuit breaker has gone bad:
- Frequent tripping
- Unable to reset
- Burnt smell
- Scorch marks on its box
- Visibly damaged breaker
- Worn-out breaker
- Hot circuit breaker
What causes the breaker not to reset?
A breaker might fail to reset if it has gone bad. The breaker won’t reset if you’ve plugged in too many devices that consume a lot of power.
What is the average life of a circuit breaker?
The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) states that the lifespan of breakers is between 30-40 years . Factors such as fluctuating voltages and poor power ratings can affect the life of your breaker.

Jeff (pen name for privacy) is our primary contributor. Previously, he has worked at 84 Lumber as a manager trainee and contractor sales rep. Before that, he worked for a local plumbing firm doing everything from rough-ins to septic repair and more.
Similar Posts

9 Surprising Reasons Electrical Wire Costs Add Up

7 Best Outdoor Light Bulbs for Exceptional Illumination

5 Reasons Canless Recessed Lighting Is Ideal for Your Home

5 Best Electrical Tape Substitute Options for Safe Wiring

3+ Key Differences Between Limit Switches and Proximity Switches

10 Essential Tips to Pull Wire Through Conduit Easily
Discover more from journeyman hq.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
Why Circuit Breakers Trip and What To Do About It
by Exquisite Electric | Last updated Nov 26, 2023 | Blog
Have you ever wonder why your circuit breakers trip?
We when a circuit breaker in your electrical panel trips, it happens for a reason. , but simply resetting the breaker won’t solve the underlying issue and may end up causing bigger problems in the future. in this article, we will discuss 3 common reasons why your electrical circuit breakers trip and what you can do about it..
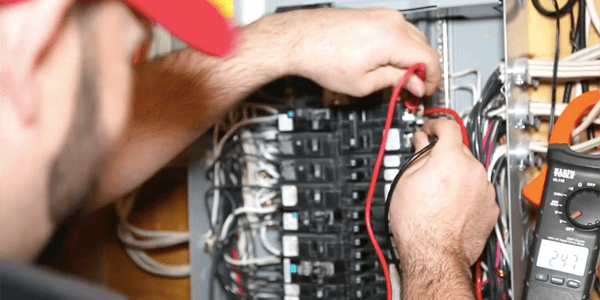
Post Takeaways:
- Circuit Breakers trip for a reason. Don’t reset them unless you know why they tripped in the first place
- Most if the time breakers trip because of an overloaded circuit
- Wires can touch and cause a short for a number of reasons, including loose connections or improper installation
- Ground faults are often the result of the wire’s insulation breaking down or improper installation
- Ignoring the underlying problem and resetting the breakers could result in fire, hazard conditions, or electrocution risk
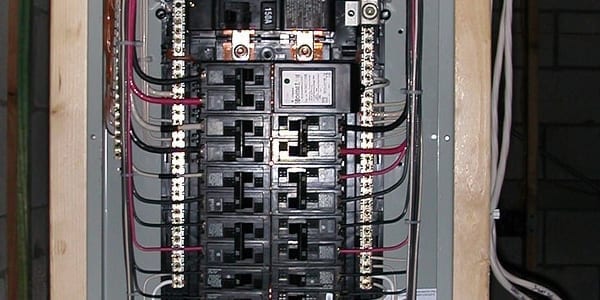
What is a ‘Trip’?
“Why are my circuit breakers tripping?”
This is a question we often hear when customers call us for help. Without performing an inspection it’s hard to know what the cause is, BUT a breaker ‘trips’ because it senses an abnormal power draw and shuts off the electrical flow.
By shutting off the circuit, your panel prevents overheating and a potentially electrical fire. So, if you have to reset the breaker frequently, you may have a bigger issue that needs attention.
So, What Causes a Circuit Breaker to Trip?
There are three main reasons why your circuit breaker trips: an overloaded circuit , a short circuit , or a ground fault .
Circuit Breaker Safety
At Exquisite Electric, we don’t recommend resetting any breakers without understanding why the circuit breaker tripped and shut off power in the first place.
Ignoring the underlying problem and resetting the breakers could result in fire, hazard conditions, or electrocution risk.
Be Safe. Call a professional e lectrician for help.
1. An Overloaded Circuit is Causing the Breaker to Trip
The most common reason for a breaker to trip is an overloaded circuit.
Usually, having too many appliances running on the same circuit is what causes the problem. These appliances are generally high power devices, such as air conditioners, hairdryers, or heaters.
In addition, if one of those appliances becomes overheated, it can cause the whole circuit to overheat, causing the breaker to shut off power.

How To Connect a ShuntTrip?

You Might Also Like
8 comments:.
This comment has been removed by the author.
The information you have published here is really awesome, as it contains some great knowledge which is very essential for me. Thanks for posting it. Smoke Detector Alarm
It is a proficient article that you have shared here about electrical contractors in penzance I got some unique and valuable information from your article. Thankful to you for sharing this article here.
I generally check this kind of article and I found your article which is related to my interest. Genuinely it is good and instructive information. Thankful to you for sharing an article like this testing and tagging Melbourne
Cool stuff you have got and you keep update all of us. Electrical Contractor
Pretty good post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wanted to say that I have really enjoyed reading your blog posts. Any way I'll be subscribing to your feed and I hope you post again soon. Big thanks for the useful info. appliance installation and configuration
You have worked nicely with your insights that makes our work easy. The information you have provided is really factual and significant for us. Keep sharing these types of article, Thank you. Commercial Electrical Contractors Oregon
Follow Us On Facebook
Latest Post
Green electronics: sustainable pcb manufacturing practices.
.webp)
Popular Topics
Voltage drop calculation based on national electrical code.
How To Prepare Schedule of Loads

How to Calculate Voltage Drop of Distributed Loads

What is SELV and PELV Circuits?

How to Perform Coordination Study of OCPD and Cable in Electrical Design

How to Calculate Transformer Voltage Drop

Types and Classes of Current Transformers According to IEC 60441

What is the Importance of X/R Ratio?
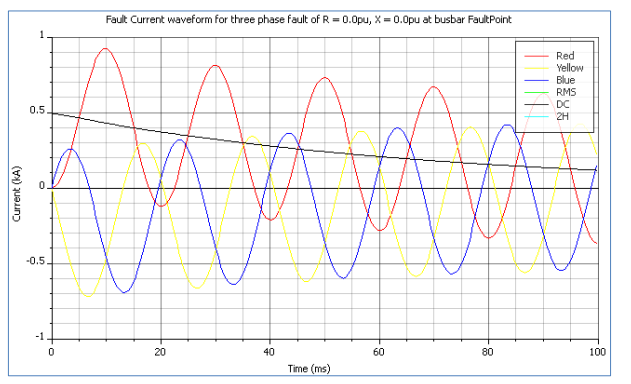
What is Multiple Earthed Neutral?

Learning Is Not Necessarily An Outcome of Teaching


Diferencia entre breaker o disyuntores MCB, MCCB, ELCB y RCCB

El breaker o disyuntor eléctrico es un tipo de dispositivo de conmutación que se puede activar automáticamente así como manualmente para controlar y proteger un sistema eléctrico.
Como un sistema de alimentación maneja grandes corrientes, el correcto diseño y puesta en operación de la protección debe hacerse para asegurar el control del arco producido durante el proceso de interrupción del interruptor automático. Esta es la definición fundamental de los disyuntores o breakers. Estos mismos se han dividido en varios tipos basados en categorías especiales en las que se han subdividido y que relaciono a continuacion:
MCB-Disyuntor en miniatura o minibreaker:
MCB es un dispositivo electromecánico que protege un circuito eléctrico de una sobrecorriente, que puede producirse por cortocircuito, sobrecarga o problemas en el equipo. Este disyuntor es una mejor opción que un fusible ya que no requiere cambio una vez que se identifica la sobrecarga. Un MCB puede ser simplemente repuesto y, por lo tanto, ofrece una mejor protección operacional y una mayor manejabilidad sin incurrir en un enorme costo de operación. El principio de funcionamiento de MCB es simple.
La función de MCB es interrumpir el flujo eléctrico a través del circuito una vez que se detecta un problema. En condiciones normales esta protección es un interruptor que se apaga cuando la corriente que fluye a través de él pasa el límite máximo aceptable. Generalmente, estos están diseñados para protegerse contra sobrecorriente y cortocircuito.
Los disyuntores MCB están sustituyendo las unidades de fusible para aplicaciones domésticas e industriales de baja potencia de una manera muy rápida. En el sistema de cableado, el MCB es una mezcla de las tres funciones, tales como protección de cortocircuito , sobrecarga y conmutación. Protección de la sobrecarga mediante el uso de una tira bimetálica y protección contra cortocircuito mediante solenoides.
Estos se pueden obtener en diferentes números de polos como uno, doble, triple y cuatro polos con polos neutros si es necesario. La corriente nominal oscila entre 0,5-120A con una capacidad simétrica de cortocircuito de 3-25KA, a un nivel de voltaje de 100 o 440V, dependiendo el fabricantes esto puede variar.
Características del MCB:
Las características de un MCB incluyen principalmente las siguientes
- La corriente nominal no es superior a 120 amperios
- Normalmente, las características de disparo no son ajustables
- Funcionamiento magnético / térmico
Disyuntor o breaker de caja moldeada MCCB:
El MCCB se utiliza para proteger el sistema eléctrico en distribución y comúnmente cuenta con soporte al cortocircuito y protección de sobrecarga. Este disyuntor es un dispositivo electromecánico que protege un circuito de cortocircuito y sobrecorriente. Ofrecen protección contra cortocircuitos y sobrecorrientes para circuitos de 63 Amps-2000 Amps. Las funciones primarias de MCCB es dar un medio para abrir manualmente un circuito y abrir automáticamente un circuito bajo condiciones de cortocircuito o sobrecarga. En un circuito eléctrico, la sobrecorriente puede resultar de un diseño defectuoso.
El MCCB (Disyuntor o breaker de caja moldeada) es una opción a un fusible ya que no necesita cambiarse una vez que se activa por sobrecarga. A diferencia de un fusible, este interruptor de circuito se puede reiniciar simplemente después de un problema y ofrece mayor seguridad y facilidad del operador sin necesidad de coste operacional. Generalmente, estos breakers o disyuntores tienen protección para corriente térmica en cuanto a sobrecorriente y el elemento magnético para la operación ante cortocircuito con un funcionamiento más rápido.
Características del MCCB:
Las características de un MCCB (interruptor industrial) incluyen principalmente las siguientes
- La gama de corriente nominal hasta 2000 amperios
- La corriente de disparo puede ajustarse.
- Funcionamiento magnético / térmico.
ELCB – Disyuntor de fuga a tierra:
El ELCB se utiliza para proteger el circuito de fugas eléctrica. Cuando alguien recibe una descarga eléctrica, este cortacircuitos corta la potencia en un tiempo de 0,1 segundos o menos para proteger la seguridad personal y evitar que funcione el circuito contra cortocircuito y sobrecarga.
Un ELCB se utiliza para detectar una corriente que fluye a través de la tierra (cable de tierra). Si la corriente de tierra que excede unos pocos miliamperios se detecta, el ELCB dispara (desconecta) el circuito de la alimentación. ELCB también se conoce como Interruptor de Circuito de Falla a Tierra (GFCI)
ELCB es un dispositivo de seguridad utilizado en un sistema eléctrico con alta impedancia de tierra para evitar choques. Este «revisa» pequeñas tensiones extraviadas en las partes metálicos del equipo eléctrico e interrumpe el circuito si se detecta un voltaje inseguro. El principio principal de los protectores de fugas de Tierra es detener las lesiones a los seres humanos y la naturaleza debido a una descarga eléctrica.
Este disyuntor breaker es un tipo especializado de relé enclavado que tiene una estructura de alimentación de red conectada a través de sus contactos de conmutación para que el circuito se desconecte de la fuente de alimentación en condiciones inseguras.
El ELCB detecta las corrientes de falla entre el cable de fase y el cable de tierra dentro de la instalación que protege. Si existe suficiente tensión a través de la bobina de detección en el disyuntor, éste apagará la alimentación y se mantendrá apagado hasta que se restablezca manualmente.
Propiedades de ELCB
Las características de un ELCB incluyen principalmente lo siguiente:
- Este interruptor de circuito sensa la fase, el cable de tierra y el neutro.
- El funcionamiento de este disyuntor depende de la fuga de corriente.
RCCB (disyuntor de corriente residual):
El disyuntor RCCB dispara el circuito cuando se detecta cualquier desajuste entre corriente de fase y corriente de neutro. Esto significa que el RCCB funciona para fallos a tierra (cuando los cables de fase entran en contacto con el suelo).
Los RCCB más ampliamente utilizados son dispositivos de 30 mA y 100 mA, lo que significa que dispararán el circuito si la diferencia entre la corriente de fase y la corriente de neutro es superior a 30 mA y 100 mA, respectivamente.
La mayoría de los RCCB están diseñados para disparar el circuito dentro de 30 milisegundos cuando se detecta un desajuste. Los RCCB son extremadamente eficaces para prevenir los riesgos de descargas eléctricas.
Por ejemplo, si alguien toca accidentalmente el cable de fase, una parte de la corriente fluirá a través del cuerpo humano y, por lo tanto, causará desajuste entre la corriente de fase y la corriente de neutro. En este caso, el RCCB disparará el circuito casi instantáneamente y así evitará el riesgo de descarga eléctrica.
Un RCCB es un equipo esencial de detección de corriente utilizado para proteger un circuito de baja tensión de una falla. Se compone de un dispositivo de conmutación utilizado para apagar el circuito cuando se produce un fallo en este. RCCB tiene como objetivo proteger a una persona de los choques eléctricos.
Los incendios y la electrocución se deben a un cableado incorrecto o a fallas a tierra. Este tipo de disyuntor se utiliza en situaciones en las que se produce un choque repentino o un fallo en el circuito.
Los disyuntores de corriente residual RCCB son el dispositivo más seguro para detectar y disparar contra las corrientes de fuga eléctrica, garantizando así la protección contra descargas eléctricas causadas por contactos indirectos. Estos dispositivos deben utilizarse en serie con un MCB o fusible que los proteja de las tensiones térmicas y dinámicas potencialmente perjudiciales de cualquier sobrecorriente.
Por ejemplo, una persona entra repentinamente en contacto con un alambre vivo abierto en un circuito eléctrico. En esta situación, en ausencia de este interruptor automático, puede producirse un fallo a tierra y no ser detectado por una protección común por lo cual esta persona se encontraría en una situación peligrosa de recibir un choque. Pero, si el circuito tiene una proteccion RCCB el disyuntor protegerá el circuito en menos de 30ms lo que evitaría que una persona tenga una descarga eléctrica.
Características de RCCB:
Las características de un RCCB incluyen principalmente las siguientes

- Ambos cables de fase y neutro están conectados a través de RCCB
- Siempre que se produce algún fallo a tierra, entonces dispara el circuito.
- La cantidad de suministros de corriente a través de la línea debe volver a través de neutro.
Se que tienes una pregunta, cual es la diferencia entre un disyuntor o breakers ELCB y RCCB?
- ELCB es el nombre antiguo y se refiere a menudo a los dispositivos de voltaje que ya no están disponibles y se recomienda reemplazarlos si se encuentra uno.
- RCCB o RCD es el nuevo nombre que especifica la operación actual (de ahí el nuevo nombre para distinguir de la tensión operada).
- El nuevo RCCB es mejor porque detectará cualquier falla a tierra. El tipo ELCB sólo detecta fallas a tierra que fluyen de nuevo a través del cable de tierra principal, por lo que dejaron de utilizarse.
- La manera fácil de ver un viejo ELCB operado por voltaje es buscar el cable de tierra principal conectado a través de él.
- RCCB sólo tendrá las conexiones de línea y neutro.
- ELCB está trabajando basado en la corriente de fuga de tierra. Pero RCCB no tiene sensibilidad o conectividad de la Tierra, porque fundamentalmente la corriente de fase es igual a la corriente neutra en fase única. Es por eso que RCCB puede disparar cuando las dos corrientes son deferentes y soportar hasta que ambas corrientes sean iguales. Tanto el neutro como las corrientes de fase son diferentes, lo que significa que la corriente fluye a través de la Tierra.
- Por último ambos están trabajando para lo mismo, pero la diferencia varia en la conectividad.
- RCD no necesariamente requiere una conexión a tierra en sí (sólo supervisa el vivo y neutral). Además, detecta los flujos de corriente a tierra, incluso en equipos sin tierra propia. Esto significa que un RCD seguirá dando protección contra fallas en equipos que tienen una tierra defectuosa. Son estas propiedades las que han hecho que el RCD sea más popular que sus rivales. Por ejemplo, los disyuntores de fuga a tierra (ELCB) fueron ampliamente utilizados hace unos diez años. Estos dispositivos midieron la tensión en el conductor de tierra; si esta tensión no era cero, esto indicaba una fuga de corriente a tierra. El problema es que los ELCB necesitan una conexión de tierra externa, al igual que el equipo que protege. Como resultado, el uso de ELCBs ya no se recomienda.
6 comentarios en «Diferencia entre breaker o disyuntores MCB, MCCB, ELCB y RCCB»
consulta estimado en relación a los transformadores tengo una duda por ejemplo un transformación de distribución presenta diferentes cantidad de potencia que puede entregar no obstante, por ejemplo en el tendido publico las fases que salen de este son de 220 V como se aplica la ley de ohm ahí. Ya que el voltaje es constante, pero si la la intensidad de corriente que aporta es mayor como su voltaje no aumenta ya que son directamente proporcional? ya que por ejemplo teorico si le toma la corriente en un enchufe no es lo mismo que si le toma la corriente de las 2 fases de un disyuntor MCCB ya que lo mas probable que quedaria quemado, ya que se supone que la intensidad de la correinte es mayor (ademas de presentar las fases un mayor diametro los cables) quedo atento
Nacho, hola!
Cual es la pregunta exactamente?
dentro de la distribucion de la energia los transformadores de distribucion en las calles de nuestras ciudades aportan energia mediantes 3 fases R,S,T y el neutro, mi pregunta es que hace que cuando una persona se electrocuta en el tendido de baja tension sea tan dañino o mortal, tengo un caso que llego en el hospital con la mano completamente quemada por realizar contacto en las 2 fases de un breaker mccb La energia en la distribucion va a baja tension pero circula mucha corriente? existe mayor amperaje?
saludos ojala me puedas ayudar
El problema es la diferencia de potencial (Diferencia de «voltaje»), porque?, porque la corriente tiende a fluir desde un «voltaje» a otro, cuando se toca una fase y tierra la corriente fluye atravez del cuerpo hacia la tierra de un mayor «voltaje» (Puede ser 220V a un menor «voltaje» 0V) comúnmente quemando tejidos , nuestro cuerpo en este caso seria una resistencia, y como somos en gran porcentaje agua, la conducción de corriente es mas fácil. Tener presente que corriente es Voltaje sobre resistencia (V/R), por lo tanto a menor resistencia mayor corriente, la resistencia del cuerpo humano no es mucha por lo tanto la corriente puede ser alta para lo que teoricamente resiste el cuerpo, pero mas que esto, el daño por quemaduras puede ser peor que el daño por electrocusion.
Por eso las personas que hacen mantenimiento a lineas de alta tensión no se electrocutan porque están al mismo potencial al mismo «voltaje» que la linea, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gu3KN2sQNH4 https://www.hsa.org.uk/electricidad/corriente-voltaje-y-resistencia
un cordial saluddo,m gusto tu explicaciones de comando a seguir,felicitaciones,ing cesar paez,carabobo venezuela..
Gracias CEsar
Deja un comentario Cancelar la respuesta
Lo siento, debes estar conectado para publicar un comentario.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Resetting a tripped circuit breaker is a simple process that can be done by following a few easy steps. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you reset a tripped circuit breaker safely and effectively: Step 1: Locating the Tripped Breaker. Step 2: Ensuring Safety Before Proceeding. Step 3: Resetting the Circuit Breaker.
If you suspect a short circuit, unplug your appliances and check the wires for melted coverings. You might also notice a burning smell coming from the outlet. Call in a professional electrician to find the source of the problem. 3. Circuit Overload. Circuit overloads are the most common reason that a breaker trips.
In most cases, fixing tripped circuit breakers is as simple as flipping a switch. Only proceed with this solution if you know the cause of the tripped breaker is something simple, like too many appliances running or a damaged power cord. To fix a tripped breaker, flip the switch to the "off" position, and then to the "on" position to ...
Circuit breakers are protection devices for electrical circuits. When too much current passes, the breaker trips, stopping the flow of electricity and preventing damage. This can be caused by faulty wiring, too many appliances on one circuit, or a ground fault. Overloading can cause tripping.
Follow these steps to reset a tripped breaker: First, slide the breaker handle all the way towards the outside edge of the panel. Next, slide the breaker panel towards the center of the electrical panel. The handle should stay on. If you hear it the breaker trip again or if it returns to the center, call for service.
Find out the cost to replace an electrical panel. On every breaker, there will be an "On" and "Off" position. On a tripped breaker, the handle will be in the middle, neither On nor Off. To reset, flip the handle to Off first, then to On. Stand to the side of the panel and turn your face away when flipping breakers.
The breaker, working in tandem with a fuse, serves as an electrical unit's internal sensing mechanism. At the slightest sense of excess current, the circuit breaker will "trip," triggering a cease in all electrical activity within the circuit. Not only can such a smart mechanism help with preventing damage to wires and other electrical ...
Devices charging slowly. Electrical outlets not working. Flickering lights. Scorch marks on outlets and light switches. If a circuit breaker keeps tripping in one room, homeowners can test for ...
There are two main sizes of breakers in a house: 15 amp and 20 amp. The amp rating explains how much current the breaker can handle before it will trip, and each requires a certain size of wire. Fifteen-amp breakers require a 14-gauge wire, while 20-amp breakers require a 12-gauge wire. How They Work. A 15-amp breaker won't necessarily trip ...
However, dealing with constantly tripping breakers can be frustrating. It is crucial to understand why circuit breakers trip and the possible causes behind these issues. In this comprehensive guide, we will breakdown how circuit breakers work, common causes of tripped breakers, and the importance of electrical safety in your home.
El funcionamiento del breaker principal de circuito eléctrico se basa en el principio de interrupción del flujo de corriente eléctrica cuando se detecta una sobrecarga o un cortocircuito en el sistema eléctrico. Este dispositivo consta de varios componentes clave que trabajan en conjunto para lograr esta función de protección.
One of the most common reasons for a tripped breaker is loose electrical connections. Aluminum wires tend to expand and contract, thereby loosening over time. Another common cause for your breaker to trip is a direct electrical short in the wiring or equipment. You can tell if this is the problem if the breaker trips instantly once the unit ...
Flip Back to ON Position. When you find the circuit breaker That's switched off, flip it back into the ON position. You should feel a slight resistance when flipping the lever and hear a clicking sound signaling that it's been flipped back on. This should restore power but if it doesn't, you may need to flip your breaker one more time.
Disconnect all the devices and reset the breaker. Before connecting an appliance, allow your electric power system to rest for a few minutes. Plug in your devices one at a time. If it trips again as you plug in the devices, relocate the appliances to other outlets. If the breaker continues to trip, call an electrician to troubleshoot the problem.
Ignoring the underlying problem and resetting the breakers could result in fire, hazard conditions, or electrocution risk. Be Safe. Call a professional electrician for help. E. 1. An Overloaded Circuit is Causing the Breaker to Trip. The most common reason for a breaker to trip is an overloaded circuit.
But if you want to trip a breaker intentionally, here are some very easy steps to follow. Plug an appliance into an outlet fed by the circuit that the breaker you want to trip is serving. If there are existing lights, you can just turn one of those on as another option. Open the electrical panel (breaker box) and search for the breaker ...
The breakers trip to turn off the power and cut off the flow of electricity to avoid problems that might exacerbate and cause more damage. There are a few reasons that this can happen, but it usually boils down to three situations: 1. Ground Fault Surges. The first cause of a breaker trip is a ground fault, which happens when it detects that ...
A shunt trip is a device designed to switch-off the circuit breaker remotely. When energized, a shunt release instantaneously activates the circuit breaker mechanism ensuring a rapid disconnection from the power source. This device is an optional accessory in a circuit breaker that will be powered externally and can be activated thru PLC and ...
Así en esta gráfica de un magnetotérmico: El punto frame indica el punto en que la caída del tiempo alcanza el rectángulo (no señalado en el gráfico), y el trip el punto señalado en el gráfico cómo Curva D-MA. La A indica Amperios. De acuerdo con ello, hablando de Amperios (eje horizontal) el punto AF es siempre menor que el punto AT ...
ABB code Protection Function Threshold Trip Time Trip Curve I Short-circuit I3 = Off - 1 - 1.5 - 2 - 2.5 - 3 - 3.5 - 4.5 - 5.5 - 6.5 - 7 - 7.5 - 8 - 8.5 - 9 - 10 x In t3 ≤ 15ms for XT2-XT4 t3 ≤ 20ms for XT5-XT6 t3 ≤ 30ms for XT7 t=k Ekip M DIP LIU ABB code Protection Function Threshold Trip Time Trip Curve
ment and optimization of Siemens circuit breakers. This makes Siemens circuit breakers able to meet all the demands placed on high-voltage switchgear. Due to the consistent application of our modular design, the 3AP1 FG 145 kV circuit breaker is made using the same range of components as all Siemens circuit breakers, whether air- or gas-
TH(H)QB-RC breakers also feature quick-make/ quick-break mechanisms, common trip bars, and easy-to-spot trip indication to help ensure safety and reliability. TH(H)QB-RC breakers are available in 1, 2, and 3 pole versions and can be ordered with auxiliary contact and shunt trip accessories. TH(H)QB-RC is a member of the Q Line Miniature
El MCCB (Disyuntor o breaker de caja moldeada) es una opción a un fusible ya que no necesita cambiarse una vez que se activa por sobrecarga. A diferencia de un fusible, este interruptor de circuito se puede reiniciar simplemente después de un problema y ofrece mayor seguridad y facilidad del operador sin necesidad de coste operacional.