
Galvin Power is reader-supported. When you buy via our links, we may earn a commission at no cost to you. Learn more

What is a Shunt Trip Breaker and How Does It Work?
Written by Edwin Jones / Fact checked by Andrew Wright
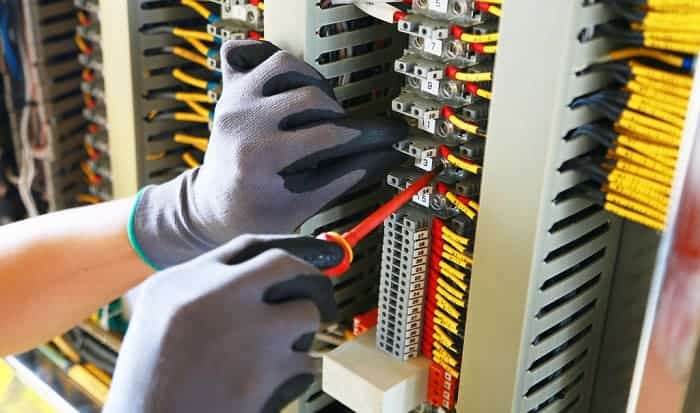

What is a shunt trip breaker? Does it add protection to your electrical system?
The shunt trip breaker is a combination of the shunt trip accessory and the main circuit breaker. This installs on the main breaker to add protection to your electrical system. This adds security to your electrical system as it manually or automatically cuts the electric supply in your circuit.
This accessory can help prevent short circuits and avoid electrical damage should a disaster occur in your home.
Let me tell you more about the shunt trip breaker to help you decide if you need additional protection for your electrical system.
Table of Contents
What is Shunt Trip Breaker and How Does It Work
Where are shunt trip breakers most used, how to install a shunt trip accessory to the breaker.
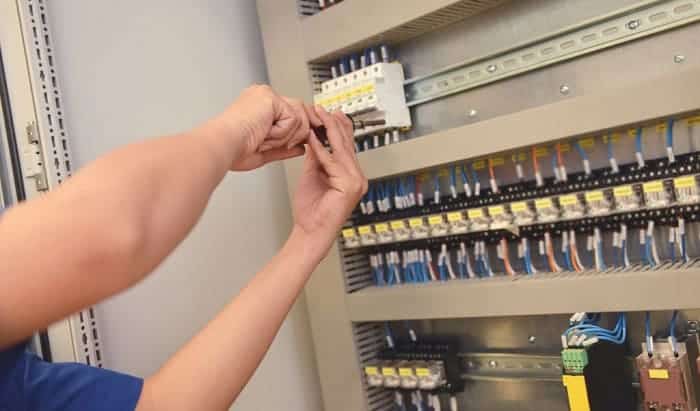

You should know that shunt trip breakers are different from GFCI circuit breakers.
The GFCI circuit breaker contains one big white tail wire for neutral connections only. It cannot be connected to any control package because the GFCI circuit breaker is solely designed to detect a sudden electrical surge. It has no other purpose but to cut power in case of a short.
Meanwhile, the shunt trip breaker wiring comprises two wires. One connected to the ground, and another to a control system. The control system can be connected to a sensor or to a manual switch. When activated, the shunt trip accessory will cause the main breaker to trip.
For example, if you install a shunt trip with a smoke detector, it will activate and cut off the power should the smoke sensor trigger. It can also be installed with a remote switch , allowing you to trip your breaker manually.
It is crucial to know the difference between a regular circuit breaker and a circuit breaker installed with shunt trip accessories.
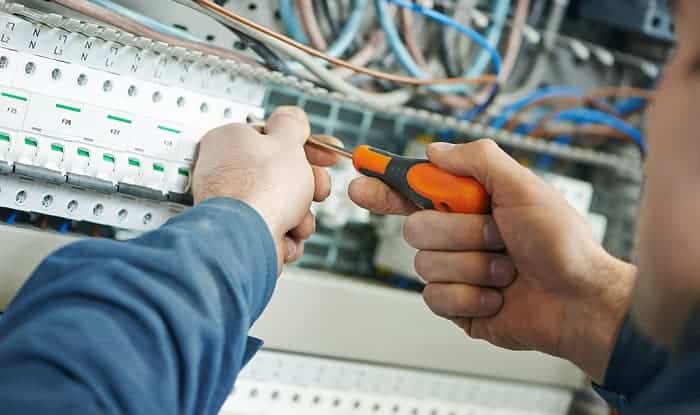

The shunt trip definition means that it is a way to cut off electrical power through other sensors, not just via thermal activation. Since this is an optional accessory for a circuit breaker, it is not required for a home electrical system.
However, it is recommended for added safety. This is especially true if you’re working with industrial machinery. Furthermore, you can use it as a manual emergency switch to shut down your main breaker.
Before installing a shunt trip, consider its cost and your existing system. You may need to change the breaker panel and circuit breakers, especially if it is not compatible with shunt trips. You may also need a new line to connect the remote emergency switch to your breaker box.
Generally, most commercial kitchens, elevators, and offices have this shunt trip breaker because it is required. Commercial kitchens use this device in compliance with ANSI/ASME CSD-1, while elevators and escalators comply with ASME A17.1. These codes refer to the controls and safety standards provided by ASME’s.
This question is a topic of discussion among Reddit members as well. Join the conversation here:
Found at a dominos by u/Guilty_Sympathy_496 in electricians
Mostly, installing a shunt trip relay requires that the breaker and the shunt be from the same maker. Also, not all breaker models are compatible with this accessory.
Once you’re sure that your system can take a shunt trip accessory, installation is pretty much straightforward. You can watch this video by Aaron CBIONE for some tutorials.
Note: Every circuit breaker comes with different instructions. It would depend on the brand and model of the breaker .
However, the critical part of every installation is that you need to connect the shunt to your sensor. You may need a shunt trip breaker diagram as a reference to ensure correct installation.
Also, check the brand and model of your breaker before proceeding with the installation. Some makers only allow a factory install of the shunt trip and other accessories. DIY installation may void the warranty of your breakers. It’s best to read up on the manual or consult an electrical professional before making any changes.
What is a shunt trip breaker? The shunt trip is an optional accessory for a circuit breaker for added protection to your system. It is designed to connect to a secondary sensor. It will trip the breaker automatically if the sensor is triggered. It can also be activated via a remote switch that you can install.
Do you think that a circuit breaker is enough to protect your investment? Or do you want an additional layer of protection for your electrical circuit? If you’re not decided yet, reach out to me in the comments section below, and I will be happy to help you.

I am Andrew Wright. With 8 years of experience designing, installing, and maintaining electrical power systems. I love my job, and I have always wanted to offer others the necessary help so they can take care of their houses.

- Horizontal terminal
- Vertical terminal
- Front terminal
- Vertical terimnal adapter
- Front terminal adapter
- Integrated trip unit (DP3)
- Modular trip unit
- General use (WS)
- Generator use (WM)
- Special protection (WB)
- Protective coordination (WF)
- Ground fault (G1)
- Earth leakage (E1)
- 2nd Pre-alarm (AP)
- Neutral 50% (N5)
100-240V AC/DC without alarm contact (P1)
24-60V DC without alarm contact (P2)
- 100-240V AC/ 100-125V DC with alarm contact (P3)
24-60V DC with alarm contact (P4)
100-240V DC with alarm contact by Solid State Relay (P5)
- Trip unit display (DP1)
- Panel board display (DP2)
- Extension module (EX1)
- Making current release switch
- Temperature alarm
- Field test device (Y-2005)
- Test jumper
- CC-link interface unit
- Modbus-RTU interface unit
- Profibus-DP interface unit
- Motor charging device
- Closing coil
- Shunt trip device
- Under voltage trip device
- Auxiliary switch
- Cell switch
- Shorting NC (b) contact
- Interphase barrier
- Safety shutters
- Terminal cover
- Mis-insertion preventer
- Drawout interlock
- Position lock
- Push button cover
- Cylinder lock
- Castel lock
- Door interlock
- Mechanical interlock
- Condenser trip device
- Lifting hook
- Load circuit conductors type
- Transformer grounding wire type

Product featurers

- Vertical terminal adapter

100-240V AC/100-125V DC with alarm contact (P3)

ZCT (Load circuit conductors type)

ZCT (Transformer grounding wire type)

- "AE-SW" is the single series of Mitsubishi Electric's ACB for easy choice of quality products.
- Rating from 630A to 6300A with three compact frames.
- Frame1: AE630-SW to AE2000-SWA, Frame2: AE2000-SW to AE4000-SWA, Frame3: AE4000-SW to AE6300-SW
- Fixed or Drawout mounted with 3 or 4 pole versions are available.
- Compliance with IEC 60947-2, JIS C 8201-2-1. CCC certification for GB 14048.2.
- With Third party IEC 60947-2 certification from KEMA for all range of ACB.
- Various Marine standards Lloyd's Register of Shipping, Bureau Veritas, American Bureau of Shipping and etc.
- Uniform accessories for every frame size of ACB.
- Stable switching operation thanks to Double spring switching mechanism. movie
- Modular trip unit with Protection and Metering based modules for easy upgradability. movie
- Color changing LCD backlight on trip unit for easy notification in the event of Pre-alarm and Fault. movie
- Double multiplication setting on Rated current and Pre-alarm for more precise value setting.
- Icu = Ics = Icw = Min. 65kA (1sec) / Icw = Min. 50 kA (3sec) for better discrimination with branch circuit breakers.
- Communication through CC-link, Modbus-RTU and Profibus-DP available for remote control and energy monitoring.
- Lower watt loss ACB contribute to reducing temperature rise inside panel and waste of energy flow.
- Zero arc space provides more reliable and safety operation for AE630-SW to AE4000-SWA at 600V AC or less.
- Reverse connection is available without any limitation.
Connections

- Various terminal connections are available based on panel board specifications.
- The different types of terminal connections between line side and load side are also available. (For AE2000-SWA, AE4000-SWA, AE4000-SW, AE5000-SW and AE6300-SW models, only vertical terminal is available.)
- Reverse connection is available without any limitation. movie
- Various terminal connections are available based on panel specifications.
Electronic trip unit

- Integrated trip unit with monitoring display for current and harmonics along with Fault memory function.
- Color changing LCD backlight on trip unit for easy notification in the event of Pre-alarm and Fault.
- Current level (60/80/100% of rating), Pre-alarm, Overload and Trip cause are indicated with different color of LED.
- Adjustable Pre-alarm (68%-100% of rated current) and Overload alarm (115% of rated current) as standard.
- Self-diagnose and Error indication LED for Trip Unit as standard (Self-diagnose on Malfunction of Microprocessor and Hardware, Miswiring related to Trip unit and etc) movie

- Modular trip unit with Protection and Metering based modules for easy upgradability as well as communication.
- Color changing LCD and optional protection units such as Ground fault, Earth leakage, 2nd Pre-alarm are modular.
- Self-diagnose and Error indication LED for Trip Unit as standard. (Self-diagnose on Malfunction of Microprocessor and Hardware, Miswiring related to Trip unit and etc) movie
Main protection module

- Main protection modules are available for most common applications like transformers, cables, motors and generators protection. movie
Optional protection module

- Optional protection module for Ground fault, Earth leakage, 2nd Pre-alarm and Neutral pole 50% protection.
- With these protection based modules, no need to change the whole Trip unit to change the specification. movie
Power supply module

- Power supply module is required for the LED indication on Trip unit, Metering and Communication function.
- Power supply without alarm contact or with 6 alarm contacts are available based on rated voltage.
- 6 alarm contacts include LTD, STD/INST, Ground fault/Earth leakage/Additional Pre-alarm, Pre-alarm, Temperature alarm, Error on Trip unit. movie

- Color changing LCD backlight for Modular trip unit is available.
- Record 10 trip history inclusive the types of protection cause (LSIGE, Under voltage, Temperature alarm).
- At the time of trip and alarming, the backlight color automatically change for easy notification. movie

- Color changing LCD backlight for Panel board mounted type is also available.

- Expansion module is required for metering and display function. movie

- VT unit is required to measure voltages, powers, energy, harmonics current. movie

- This switch makes Instantaneous operation (INST) ineffective once after the breaker is closed.
- This is used for expanding the selective combination with branch circuit breakers. movie

- Temperature alarm is available to identify the abnormal heat with main contacts of the breaker.
- The alarm is indicated by LED on Trip unit and it can also output signal in case Power supply module with alarm contacts (P3/P4/P5) is used.
- It makes it easy to notify the time of maintenance or replacement of the breaker. movie
Test equipment

- The operation of Electronic trip unit can be tested with this Field test device (Y-2005). movie

- While the breaker taken out of its cradle, the Test jumper enables the breaker to be electrically open and closed.
- The operating sequence of the breaker also can be checked. movie
Communication

- For intelligent energy management, the communication modules connect the breaker to higher level of remote control and energy monitoring in the combination with Mitsubishi Electric products.
- The communication available with CC-Link, Modbus-RTU or Profibus-DP. movie

- For remote control of the breaker via communication system, this Input and output unit is required. With this, it become possible to control the breaker remotely, like open and close operation or Spring charging.
- This makes it easy to enhance communication for local applications. movie
Remote control

- The breaker is remotely charged by the Motor charging device.
- When the breaker is closed, the double springs inside the breaker are charged automatically. movie

- The breaker is remotely closed by the Closing coil.
- It is one-pulse driven to prevent pumping and burnout of coil as standard. movie

- The Shunt trip device turns the breaker opened immediately when the operational voltage is applied.
- A cut off switch is equipped as standard to prevent burnout of coil as standard. movie

- This device automatically open the breaker if the operational voltage is not applied or drops below specific value.
- This protect electrical equipments against voltage fluctuation and also can be used for remote control of the breaker.
- There are three types of operating time. Instantaneous (0.2 sec), 0.5 sec and 3.0 sec. movie
Indication contact

- OCR alarm is provided with Electrical trip unit as standard.
- Automatic reset type and Manual reset type are available.
- For Automatic reset type, alarm is 1 NO contact of short-time operation (30ms), being output when the breaker trip. movie

- Auxiliary switches make a signal for the switching (open/closed) status of the breaker. movie

- This switches (NO/NC contact) indicate the drawout position (CONNECTED, TEST, and DISCONNECTED) of the breaker.
- The arbitrary combination up to 4 pieces is available. movie

- When drawout ACB from "CONNECT" to "TEST" position, this contact is used to short the auxiliary switch (NC contact). Thus, maintaining the correct sequence of operation of the external control circuit. movie
Safety device

- This barrier enhance the interphase insulation between the terminal portions of the breaker, and prevents short-circuit due to conductive inclusion or dust. movie

- The Safety shutters cover the cradle side of conductors and prevent contact with them when ACB is drawn out.
- The shutter lock is also available as an option. movie

- The Terminal cover prevents from careless touching to the live part of control terminals.
- Protection degree is IP20. movie

- Mis-insertion preventer allow only specified circuit breakers can be inserted into the cradle.
- Five patterns of Mis-insertion preventers are available. (Not available for AE4000-SW~AE6300-SW.) movie
Locking device

- When the breaker is ON, the drawout handle cannot be inserted into the breaker.
- The insertion and drawout operation of the breaker cannot be done unless the OFF button is pressed. movie

- During insertion and drawout operation, the drawout mechanism of the breaker is automatically locked at "TEST" and "Connect" position as standard.
- Once the lock plate is pushed in, the lock is released and the operation can be continued. movie

- The Push button cover prevents unintentional manual switching operation by the push button.
- The Push button cover can be locked by the padlock. movie

- The breaker can be locked in the open position with the Cylinder lock.
- It provide reliable protection for personal during maintenance activities. Also, it can be used for interlocking two or more breakers which only allows the key to be removed when the breaker is in the open position. movie

- The breaker can be locked in the open position with the Castel lock.
- In this lock, only the key lock set-up for Castel lock is available and the key must be supplied by the customers. movie

- With Door interlock, the panel door cannot be opened unless the breaker is in open position.
- A wire type mechanical interlock allows flexibility of the circuit breakers' position inside the panel. movie

- Mechanical interlock is the device to prevent parallel closing operation of 2 or 3 units of breakers.
- It assure the interlock mechanically between the breakers. movie
Other accessories

- The Door frame improves the appearance. It is installed after cutting out the panel door. movie

- Dust cover prevents the dust or water entering into the panel board when ACB is used with the front cut panel.
- Protection degree is IP54. movie

- The open/close operations of the breaker can be recorded by a 5 digit counter. movie

- Even if the power supply fails, the breaker can be electrically opened in the combination with the Condenser trip device and the Shunt trip device within a definite time. movie

- Lifting hook is the metal fitting to suspend the breaker main body when it is removed from the cradle. movie

- For 3 pole circuit breakers used in 3 phase 4 wire systems, the Neutral CT is used for ground fault protection and over current protection of Neutral phase. movie

- ZCT is used to detect earth leakage current in the combination with earth leakage protection module (E1).
- ZCT of ACB's load circuit conductors type or Transformer grounding wire type are available. movie
- Hazard Categories and Special Symbols
- Please Note
- Validity Scope
- Document Scope
- Related Documents
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Range Description
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Range Convention
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Circuit Breakers
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Switches
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Neutral Position on Four Pole (4P) Devices
- Fixed Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Description
- Fixed Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Accessories Description
- Fixed Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Terminal Block Description
- Drawout Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Definition
- Standard Masterpact MTZ Circuit Breaker or Switch Description
- Masterpact MTZ Circuit Breaker with ArcBlok™ Technology Description
- Drawout Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Accessories Description
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Cradle Description
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Cradle Accessories Description
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Cradle Terminal Block Description
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Product Identification Label
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Product Checked Label
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Accessory Side Label
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Faceplate Label
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 QR Code
- Control Unit Layout
- Micrologic X Status LEDs
- Local HMI Display Screen with Contextual and Dedicated Buttons
- NFC Communication Zone
- Bluetooth Activation Button and LED
- Micrologic X Control Unit Test Button
- Micrologic X Control Unit Test/Reset Button
- Micrologic X Control Unit Mini USB Port
- Micrologic X Control Unit Overload and Trip Cause LEDs
- Micrologic X Internal Battery
- Micrologic X VPS Voltage Power Supply Module
- Micrologic Control Unit QR Code
- Micrologic X Control Unit Identification Number
- Micrologic X Control Unit Type
- Micrologic X Sensor Plug
- Go2SE Presentation
- Go2SE Landing Page Description
- Go2SE Characteristics
- Go2SE Download Documents
- Go2SE Download Customer Care App
- Go2SE Download EcoStruxure Facility Expert App
- Go2SE Safe Repository
- Go2SE Download Masterpact MTZ Mobile App
- Go2SE Purchase Additional Features
- Masterpact MTZ—Ambient Temperature
- Masterpact MTZ—Extreme Atmospheric Condition
- Masterpact MTZ—Industrial Environments
- Masterpact MTZ—Vibration
- Masterpact MTZ—Altitude
- Masterpact MTZ—Electromagnetic Disturbances
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Device Status Indication
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Device Status Description
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Device Auxiliary Switches (OF)
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Anti-Pumping Function
- Charging the Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Closing Spring
- Masterpact MTZ Manual Operation with the Spring Charging Handle (MCH)
- Masterpact MTZ Electrical Operation with a Spring Charging Motor (MCH)
- Masterpact MTZ Operation According to Control Mode Configuration
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Operation in Manual Mode
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Operation in Auto: Local Mode
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Operation in Auto: Remote Mode
- Setting the Micrologic X Control Mode
- Displaying the Micrologic X Control Mode
- Micrologic X Control Mode Predefined Events
- Conditions Required to Open
- Opening the Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Mechanism in All Control Modes
- Opening the Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Mechanism in Auto Control Mode
- Conditions Required to Close
- Closing the Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Mechanism
- Inhibiting the Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Closing Function
- Conditions Required to Reset
- Resetting the Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Mechanism
- Conditions for Engaging the ERMS Function
- Energy Reducing Maintenance Setting (ERMS) Function Operating Principles
- Engaging the ERMS Function
- Disengaging the Energy Reducing Maintenance Setting (ERMS) Function
Masterpact Shunt Close (XF), Shunt Trip (MX) and Undervoltage Release (MN) Accessories
Masterpact shunt close (xf), masterpact shunt trip (mx), masterpact undervoltage release (mn), masterpact communicating internal isolation module, masterpact electrical closing pushbutton (bpfe), masterpact ready-to-close contact (pf), masterpact spring charging motor (mch), masterpact electrical remote reset (res), masterpact erms switch module (esm), masterpact grounding kit (kmt), masterpact mechanical operation counter (cdm), masterpact ulp port module, masterpact embedded ethernet interface (eife), masterpact ethernet interface (ife) for one circuit breaker, masterpact ethernet switchboard server (ife), masterpact ifm modbus-sl (rtu) interface for one circuit breaker, masterpact io input/output application module.
- Use a Platform Lift for Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Device
- Lifting a Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Device
- Lifting a Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Cradle
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Drawout Handling Conditions
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Drawout Positions
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Drawout Position Contacts
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Drawout Position Contact Without EIFE Ethernet Interface
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Drawout Position Contacts with EIFE Ethernet Interface
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Cradle Management Function
- Racking Out from Connected to Test Position
- Racking Out from Test to Disconnected Position
- Racking-In from Disconnected to Test Position
- Racking In from Test to Connected Position
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Device Removal
- Lifting the Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Device
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Circuit Breaker Weights
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Optional Cradle Rejection Feature
- Installing Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Devices in the Cradle
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 VBP Pushbutton Locking Accessory
- Locking the Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Pushbuttons
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 VCPO OFF-Position Locking Accessory
- Locking the Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Device Open with VCPO
- Unlocking the Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Device Locked with VCPO
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 VSPO OFF-Position Locking Accessory
- Locking the Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Device Open with VSPO
- Unlocking the Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Locked Open with VSPO
- Locking a Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Cradle in with VSPO
- Locking a Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Cradle with Padlocks
- Unlocking a Padlocked Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Cradle
- Locking a Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Cradle with Keylocks
- Unlocking a Keylocked Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Cradle
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Cradle Locking with VSPD Keylock Accessory
- Converting the Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Cradle for Keylocking
- Locking the Mastepact MTZ Shutters with Shutter Position Indication and Locking Accessory
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Cradle Rejection
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Cradle Rejection Pin Locations
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Cradle Rejection Recommended Pin Combinations
- VPEC Door Interlock Accessory
- Using VPEC Accessory to Lock the Equipment Door
- Unlocking Equipment Door Locked with VPEC Accessory
- VPOC Open-Door Racking Interlock
- Activating the VPOC Racking Interlock
- Deactivating the VPOC Racking Interlock
- Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 IPA Cable-Type Door Interlock
- Mechanical Interlocking Between Two Masterpact MTZ Devices
- Mechanical Interlocking Between Three Main Masterpact MTZ Device
- Mechanical Interlocking Between Two Main and One Tie Masterpact MTZ Devices
- Mechanical Interlocking Between Two Main and One Replacement Masterpact MTZ Devices
- Masterpact MTZ DAE Automatic Spring-Discharge Interlock
- Inserting the Racking Handle with IBPO Racking Interlock Installed
- Notification of a Masterpact MTZ Trip or Alarm
- Identifying the Cause of a Masterpact MTZ Trip or Alarm Using the Micrologic X Control Unit
- Diagnostic Data after a Masterpact MTZ Circuit Breaker Trip
- Using the Display Screen and LEDs to Find the Cause of a Trip
- Using the Display Screen and LEDs to Find the Cause of an Alarm
- Masterpact MTZ Reset Sequence
- Identifying the Masterpact MTZ Trip Cause
- Acknowledging a Trip Message on Micrologic X Control Units
- Clearing the Electrical Fault Before Reclosing the Masterpact MTZ Circuit Breaker
- Inspecting the Masterpact MTZ Circuit Breaker and Switchboard after a Trip on a Short Circuit
- Masterpact MTZ Circuit Breaker Reset Sequence
- Masterpact MTZ Circuit Breaker Trip Cause Identification
- Micrologic X Display Screen Trip Message Acknowledgement
- Recommended Actions After a Trip Due to Invalid Micrologic X Control Unit Self Test
- Micrologic X Control Unit Diagnosis Sequence
- Identifying the Micrologic X Control Unit Alarm
- Acknowledging the Alarm on the Micrologic X Display Screen
- Recommended Action after Detection of a High Severity Micrologic X Control Unit Alarm
- Recommended Action after Detection of a Medium Severity Micrologic X Alarm
- Identify the Problem
- Acknowledging the Error Message
- Action after Receiving Error Message
- Masterpact MTZ Devices Overview
- Masterpact MTZ Devices Scope
- Masterpact MTZ Devices Equipment
- Masterpact MTZ Devices Test Form
- Masterpact MTZ Devices Visual Inspection
- Masterpact MTZ Devices Condition of Connections and Auxiliaries
- Masterpact MTZ Devices Firmware Compatibility Check
- Micrologic X Control Unit Settings
- Masterpact MTZ Devices Functional Checks
- Masterpact MTZ Devices Check of Spring Charging Motor (MCH) (If Installed)
- Check Masterpact MTZ Devices M2C Programmable Contact and IO Module (If Installed)
- Check ESM ERMS Switch Module (If Installed)
- Check Masterpact MTZ Devices Electrical Continuity
- Check Masterpact MTZ Devices High-Voltage Insulation
- Check Micrologic X Control Unit Ready LED Status
- Test the Tripping Function with EcoReach Software
- Test the Tripping Mechanism with the Test Button (Micrologic 6.0X Control Units)
- Communication Network Test with Ecoreach Software
- Masterpact MTZ Devices Remote Control Tests
- Masterpact MTZ Devices Final Checks
- Project Report Generated by Ecoreach Software
- Communication Test Report Generated by Ecoreach Software
- How to Use the Masterpact MTZ Test Form
- Masterpact MTZ Device Identification
- Masterpact MTZ Devices Preliminary Checks
- Masterpact MTZ Devices Functional and Interlock Checks
- Masterpact MTZ Devices Electrical Continuity Checks
- Masterpact MTZ Device Insulation Test
- Micrologic X Control Unit Ready LED Check
- Micrologic X Control Unit Tripping Mechanism Test
- Micrologic 6.0X Test Button Tripping Mechanism Test
- Masterpact MTZ Communication Tests
- Masterpact MTZ Device Final Checks
- Troubleshooting the Masterpact MTZ Device
- Layer Model for Troubleshooting Masterpact MTZ Devices
- Troubleshooting the Masterpact MTZ Device with Assistance
- Maintenance of the Masterpact MTZ Device
- Troubleshooting the Cradle
- Troubleshooting Unexpected Tripping
- Device Cannot be Closed by Using the Mechanical Closing Pushbutton
- Device Cannot be Opened by Using the Mechanical Opening Pushbutton
- Device Cannot be Closed by External Pushbutton/Electrical Order
- Device Cannot be Opened by External Pushbutton/Electrical Order
- Device Cannot be Reset Using RES Electrical Remote Reset
- Additional Troubleshooting—Check Mechanical Operations
- Device Cannot be Controlled from the Masterpact MTZ Mobile App
- Inhibit Closing by IO Module is Not Operational
- Device Cannot be Controlled from the Masterpact MTZ Mobile App Connected Through Bluetooth
- Additional Troubleshooting—Check Mechanical and Electrical Operations
- Device Cannot be Controlled from the IO Module
- Device Cannot be Controlled from Ecoreach Software Connected to a Mini USB Port
- Device Cannot be Controlled from Ecoreach Software Connected by IFE, EIFE, or IFM Interface
- Device Cannot be Controlled from IFE or EIFE Webpages
- Device Cannot be Controlled with a Remote Controller Connected from IFE, EIFE, or IFM Interface
- Device Cannot be Controlled from the FDM128 Display
- Additional Troubleshooting—Check Communication Network
- Description of the Green Premium Label
- Accessing the Green Premium Ecolabel
- Check Product Environmental Criteria
- Environmental Critera of the Green Premium Ecolabel
- RoHs Requirements Compliance
- REACh Regulation Compliance
- PEP Ecopassport Compliance
- EoLI Compliance
For the best experience of this site, please enable Javascript for the www.productinfo.schneider-electric.com domain.
Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3 Operating Accessories
The shunt close (XF), shunt trip (MX), and undervoltage release (MN) are optional accessories mounted inside the device. They can be of standard type or diagnostic and communicating type (standard or with diagnostic function for the undervoltage release [MN]).
The standard XF, MX, and MN accessories can have either impulse-type or maintained actions, depending on the incoming commands.
The Masterpact shunt close (XF) is available as standard or with the diagnostic and communicating function.
The shunt close closes the circuit breaker instantaneously when powered if the spring mechanism is charged. The minimum duration of the pulse operating order must be 200 ms.
For information on installation, consult the instruction sheet on the Schneider Electric website:
Standard shunt close (XF): NVE40749
Diagnostic and communicating shunt close (XF diag&com): NVE40766
The Masterpact shunt trip (MX) is available as standard or with the diagnostic and communicating function.
The shunt trip opens the circuit breaker instantaneously when powered. The minimum duration of the pulse operating order must be 200 ms. The MX standard trip locks the circuit breaker in OFF position if the command is maintained.
Standard shunt trip (MX): NVE40749
Diagnostic and communicating shunt trip (MX diag&com): NVE40766
The Masterpact undervoltage release (MN) is available as standard or with the diagnostic and communicating function.
The undervoltage release instantaneously opens the circuit breaker when its supply voltage drops to a value between 35% and 70% of its rated voltage. If there is no supply to the release, it is impossible to close the circuit breaker, either manually or electrically. Any attempt to close the circuit breaker has no effect on the main contacts. Circuit breaker closing is enabled again when the supply voltage of the release returns to 85% of its rated value.
Standard undervoltage release (MN): NVE40749
Diagnostic undervoltage release (MN diag): NVE40766
The internal isolation module for Micrologic X control units provides double isolation in compliance with IEC 60664-1 (up to 12 kV). It also provides isolation between the diagnostic and communicating shunt close (XF diag&com), diagnostic and communicating shunt trip (MX diag&com), diagnostic undervoltage release (MN diag), and the electrical closing pushbutton (BPFE).
For information on accessory installation, consult instruction sheet NVE40748 on the Schneider Electric website.
The electrical closing pushbutton (BPFE) carries out electrical closing of the circuit breaker. It takes into account the internal closing conditions of the device and the external conditions that are part of the control and monitoring system of the installation. It connects to the standard shunt closes (XF) or the communicating shunt close (XF diag&com).
If the BPFE is being used, it is recommended to lock access to the closing pushbutton using the VBP accessory because the closing pushbutton does not take into account internal and external conditions.
This optional accessory is mounted on the front cover of the device.
For information on accessory installation, consult instruction sheet NVE40773 on the Schneider Electric website.
The ready-to-close contact (PF) indicates remotely that the circuit breaker is ready to close..
It indicates that the circuit breaker is ready to close when:
The circuit breaker is in the open position.
The spring mechanism is charged.
There is no maintained opening order.
This optional accessory is mounted inside the device.
For information on accessory installation, consult instruction sheet NVE35466 on the Schneider Electric website.
The spring charging motor (MCH) automatically charges the spring mechanism when the circuit breaker is closed, allowing instantaneous closing of the circuit breaker following opening.
For information on accessory installation, consult instruction sheet NVE35483 on the Schneider Electric website.
Following tripping, this function resets the overcurrent trip switch (SDE) and the mechanical indicator to enable circuit breaker closing.
The use of a shunt close (XF) is required with this option.
The additional overcurrent trip switch (SDE2) is not compatible with RES.
For information on accessory installation, consult instruction sheet NVE35503 on the Schneider Electric website.
The ERMS switch module (ESM) is an optional accessory mounted inside of the device.
It is used to engage ERMS protection settings with an external selector switch. The ESM module works in conjunction with the ERMS Digital Module, which must also be installed.
The ERMS switch module (ESM) is not compatible with M2C programmable contacts because they are installed in the same physical place.
The grounding kit (KMT) allows the circuit breaker mechanism to be grounded when the front cover is removed. The grounding is made through the cradle for the drawout version and through the mounting side plate for the fixed version.
For information on accessory installation, consult instruction sheet NVE35480 on the Schneider Electric website.
The mechanical operation counter (CDM) counts the number of operating cycles and is visible on the front panel. It is compatible with manual and electrical control functions.
This accessory is required for all source-changeover systems.
For information on accessory installation, consult instruction sheet NVE35485 on the Schneider Electric website.
The ULP port module:
Supplies 24 Vdc power to the Micrologic X control unit.
Integrates the ULP termination with the Micrologic X control unit.
Allows the connection of the Micrologic X control unit to external ULP modules, such as the embedded Ethernet interface (EIFE)) or the Ethernet interface (IFE).
The ULP port module is optional on the fixed device and standard on the drawout device. It is mounted with the terminal blocks of the device.
For information on accessory installation, consult the instruction sheet on the Schneider Electric website:
ULP port module for fixed Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3: NVE40791 .
ULP port module for drawout Masterpact MTZ2/MTZ3: NVE40797
The embedded Ethernet interface (EIFE) enables drawout Masterpact MTZ circuit breakers to be connected to an Ethernet network. It provides digital access to all the data delivered by the Micrologic X control unit.
In addition, it monitors the position of the device in the cradle: connected, test, and disconnected.
This optional accessory is mounted on the cradle of the drawout device.
For information on accessory installation, consult instruction sheet NVE23550 on the Schneider Electric website.
For information on accessory usage, refer to user Enerlin’X EIFE Embedded Ethernet Interface for One Masterpact MTZ Drawout Circuit Breaker - User Guide (DOCA0106EN) , available on the Schneider Electric website.
The Ethernet interface (IFE) provides an Ethernet access to a single device. The device is connected to the IFE interface through the ULP port module and a prefabricated ULP cord.
For information on accessory installation, consult instruction sheet HRB49218 on the Schneider Electric website.
For information on accessory usage, refer to Enerlin’X IFE Ethernet Interface for One Circuit Breaker - User Guide (DOCA0084EN) , available on the Schneider Electric website.
The Ethernet switchboard server (IFE) provides Ethernet access to one or several circuit breakers. It allows the following communication architectures:
One single circuit breaker connected to the IFE server through the ULP port module.
Up to 20 circuit breakers, including up to 12 Compact NSX devices, through the IFM Modbus-SL (RTU) interface for one circuit breaker stacked to the IFE server.
For information on accessory installation, consult instruction sheet HRB49218 , available at the Schneider Electric website.
For information on accessory usage, refer to Enerlin’X IFE Ethernet Interface for One Circuit Breaker - User Guide (DOCA0084EN) on the Schneider Electric website.
The IFM Modbus-SL (RTU) interface provides access from a single device to a Modbus serial line communication network. The device is connected to the IFM interface through the ULP port module and a prefabricated ULP cord.
For information on installation, consult the instruction sheet on the Schneider Electric website: https://www.schneider-electric.us/en/download/document/NVE85393/.
The IO input/output application module for one circuit breaker is one component of the ULP architecture.
The IO input/output application module uses built-in applications to enhance control and monitoring functions. Its resources are:
Six self-powered digital inputs for either NO and NC dry contact or pulse counters.
Three digital outputs that are bistable relay (5 A maximum).
One analog input for a Pt100 temperature sensor.
For information on accessory installation, consult instruction sheet HRB49217 on the Schneider Electric website.
For information on accessory usage, refer to Enerlin’X IO Input/Output Application Module for One Circuit Breaker - User Guide (0613IB1317) on the Schneider Electric website.
Show QR code for this page
Was this helpful?
The Unique Burial of a Child of Early Scythian Time at the Cemetery of Saryg-Bulun (Tuva)
<< Previous page
Pages: 379-406
In 1988, the Tuvan Archaeological Expedition (led by M. E. Kilunovskaya and V. A. Semenov) discovered a unique burial of the early Iron Age at Saryg-Bulun in Central Tuva. There are two burial mounds of the Aldy-Bel culture dated by 7th century BC. Within the barrows, which adjoined one another, forming a figure-of-eight, there were discovered 7 burials, from which a representative collection of artifacts was recovered. Burial 5 was the most unique, it was found in a coffin made of a larch trunk, with a tightly closed lid. Due to the preservative properties of larch and lack of air access, the coffin contained a well-preserved mummy of a child with an accompanying set of grave goods. The interred individual retained the skin on his face and had a leather headdress painted with red pigment and a coat, sewn from jerboa fur. The coat was belted with a leather belt with bronze ornaments and buckles. Besides that, a leather quiver with arrows with the shafts decorated with painted ornaments, fully preserved battle pick and a bow were buried in the coffin. Unexpectedly, the full-genomic analysis, showed that the individual was female. This fact opens a new aspect in the study of the social history of the Scythian society and perhaps brings us back to the myth of the Amazons, discussed by Herodotus. Of course, this discovery is unique in its preservation for the Scythian culture of Tuva and requires careful study and conservation.
Keywords: Tuva, Early Iron Age, early Scythian period, Aldy-Bel culture, barrow, burial in the coffin, mummy, full genome sequencing, aDNA
Information about authors: Marina Kilunovskaya (Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation). Candidate of Historical Sciences. Institute for the History of Material Culture of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Dvortsovaya Emb., 18, Saint Petersburg, 191186, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Vladimir Semenov (Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation). Candidate of Historical Sciences. Institute for the History of Material Culture of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Dvortsovaya Emb., 18, Saint Petersburg, 191186, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Varvara Busova (Moscow, Russian Federation). (Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation). Institute for the History of Material Culture of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Dvortsovaya Emb., 18, Saint Petersburg, 191186, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Kharis Mustafin (Moscow, Russian Federation). Candidate of Technical Sciences. Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Institutsky Lane, 9, Dolgoprudny, 141701, Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Irina Alborova (Moscow, Russian Federation). Candidate of Biological Sciences. Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Institutsky Lane, 9, Dolgoprudny, 141701, Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Alina Matzvai (Moscow, Russian Federation). Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Institutsky Lane, 9, Dolgoprudny, 141701, Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected]
Shopping Cart Items: 0 Cart Total: 0,00 € place your order
Price pdf version
student - 2,75 € individual - 3,00 € institutional - 7,00 €

Copyright В© 1999-2022. Stratum Publishing House
635th Anti-Aircraft Missile Regiment
635-й зенитно-ракетный полк
Military Unit: 86646
Activated 1953 in Stepanshchino, Moscow Oblast - initially as the 1945th Anti-Aircraft Artillery Regiment for Special Use and from 1955 as the 635th Anti-Aircraft Missile Regiment for Special Use.
1953 to 1984 equipped with 60 S-25 (SA-1) launchers:
- Launch area: 55 15 43N, 38 32 13E (US designation: Moscow SAM site E14-1)
- Support area: 55 16 50N, 38 32 28E
- Guidance area: 55 16 31N, 38 30 38E
1984 converted to the S-300PT (SA-10) with three independent battalions:
- 1st independent Anti-Aircraft Missile Battalion (Bessonovo, Moscow Oblast) - 55 09 34N, 38 22 26E
- 2nd independent Anti-Aircraft Missile Battalion and HQ (Stepanshchino, Moscow Oblast) - 55 15 31N, 38 32 23E
- 3rd independent Anti-Aircraft Missile Battalion (Shcherbovo, Moscow Oblast) - 55 22 32N, 38 43 33E
Disbanded 1.5.98.
Subordination:
- 1st Special Air Defence Corps , 1953 - 1.6.88
- 86th Air Defence Division , 1.6.88 - 1.10.94
- 86th Air Defence Brigade , 1.10.94 - 1.10.95
- 86th Air Defence Division , 1.10.95 - 1.5.98
Follow Puck Worlds online:
- Follow Puck Worlds on Twitter
Site search
Filed under:
- Kontinental Hockey League
Gagarin Cup Preview: Atlant vs. Salavat Yulaev
Share this story.
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Twitter
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options

Share All sharing options for: Gagarin Cup Preview: Atlant vs. Salavat Yulaev
Gagarin cup (khl) finals: atlant moscow oblast vs. salavat yulaev ufa.
Much like the Elitserien Finals, we have a bit of an offense vs. defense match-up in this league Final. While Ufa let their star top line of Alexander Radulov, Patrick Thoresen and Igor Grigorenko loose on the KHL's Western Conference, Mytischi played a more conservative style, relying on veterans such as former NHLers Jan Bulis, Oleg Petrov, and Jaroslav Obsut. Just reaching the Finals is a testament to Atlant's disciplined style of play, as they had to knock off much more high profile teams from Yaroslavl and St. Petersburg to do so. But while they did finish 8th in the league in points, they haven't seen the likes of Ufa, who finished 2nd.
This series will be a challenge for the underdog, because unlike some of the other KHL teams, Ufa's top players are generally younger and in their prime. Only Proshkin amongst regular blueliners is over 30, with the work being shared by Kirill Koltsov (28), Andrei Kuteikin (26), Miroslav Blatak (28), Maxim Kondratiev (28) and Dmitri Kalinin (30). Oleg Tverdovsky hasn't played a lot in the playoffs to date. Up front, while led by a fairly young top line (24-27), Ufa does have a lot of veterans in support roles: Vyacheslav Kozlov , Viktor Kozlov , Vladimir Antipov, Sergei Zinovyev and Petr Schastlivy are all over 30. In fact, the names of all their forwards are familiar to international and NHL fans: Robert Nilsson , Alexander Svitov, Oleg Saprykin and Jakub Klepis round out the group, all former NHL players.
For Atlant, their veteran roster, with only one of their top six D under the age of 30 (and no top forwards under 30, either), this might be their one shot at a championship. The team has never won either a Russian Superleague title or the Gagarin Cup, and for players like former NHLer Oleg Petrov, this is probably the last shot at the KHL's top prize. The team got three extra days rest by winning their Conference Final in six games, and they probably needed to use it. Atlant does have younger regulars on their roster, but they generally only play a few shifts per game, if that.
The low event style of game for Atlant probably suits them well, but I don't know how they can manage to keep up against Ufa's speed, skill, and depth. There is no advantage to be seen in goal, with Erik Ersberg and Konstantin Barulin posting almost identical numbers, and even in terms of recent playoff experience Ufa has them beat. Luckily for Atlant, Ufa isn't that far away from the Moscow region, so travel shouldn't play a major role.
I'm predicting that Ufa, winners of the last Superleague title back in 2008, will become the second team to win the Gagarin Cup, and will prevail in five games. They have a seriously well built team that would honestly compete in the NHL. They represent the potential of the league, while Atlant represents closer to the reality, as a team full of players who played themselves out of the NHL.
- Atlant @ Ufa, Friday Apr 8 (3:00 PM CET/10:00 PM EST)
- Atlant @ Ufa, Sunday Apr 10 (1:00 PM CET/8:00 AM EST)
- Ufa @ Atlant, Tuesday Apr 12 (5:30 PM CET/12:30 PM EST)
- Ufa @ Atlant, Thursday Apr 14 (5:30 PM CET/12:30 PM EST)
Games 5-7 are as yet unscheduled, but every second day is the KHL standard, so expect Game 5 to be on Saturday, like an early start.
Loading comments...
- Yekaterinburg
- Novosibirsk
- Vladivostok
- Tours to Russia
- Practicalities
- Russia in Lists
Rusmania • Deep into Russia
Out of the Centre
Savvino-storozhevsky monastery and museum.

Zvenigorod's most famous sight is the Savvino-Storozhevsky Monastery, which was founded in 1398 by the monk Savva from the Troitse-Sergieva Lavra, at the invitation and with the support of Prince Yury Dmitrievich of Zvenigorod. Savva was later canonised as St Sabbas (Savva) of Storozhev. The monastery late flourished under the reign of Tsar Alexis, who chose the monastery as his family church and often went on pilgrimage there and made lots of donations to it. Most of the monastery’s buildings date from this time. The monastery is heavily fortified with thick walls and six towers, the most impressive of which is the Krasny Tower which also serves as the eastern entrance. The monastery was closed in 1918 and only reopened in 1995. In 1998 Patriarch Alexius II took part in a service to return the relics of St Sabbas to the monastery. Today the monastery has the status of a stauropegic monastery, which is second in status to a lavra. In addition to being a working monastery, it also holds the Zvenigorod Historical, Architectural and Art Museum.
Belfry and Neighbouring Churches
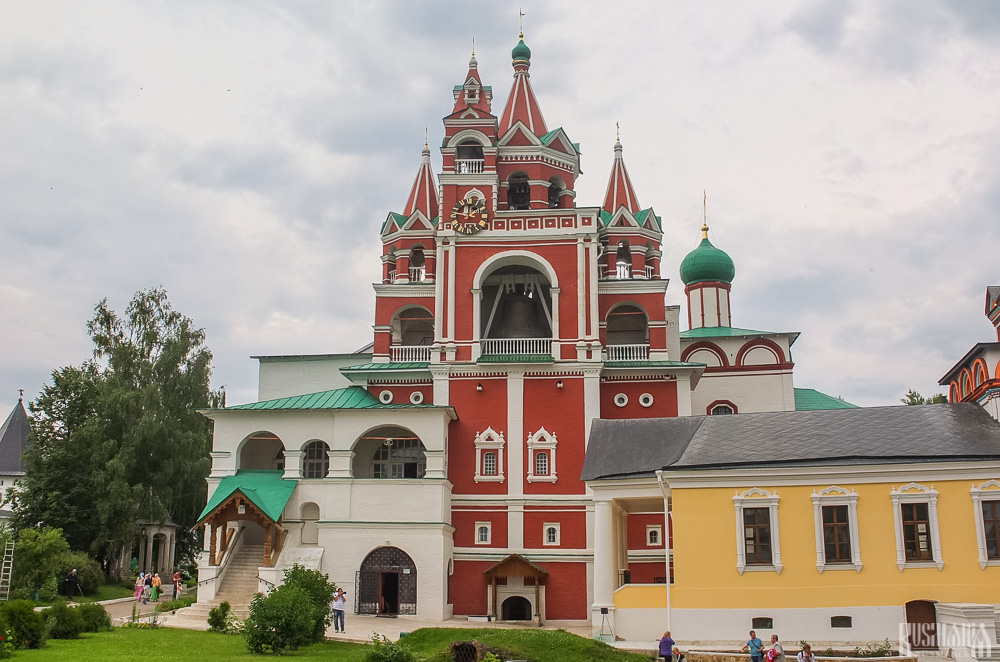

Located near the main entrance is the monastery's belfry which is perhaps the calling card of the monastery due to its uniqueness. It was built in the 1650s and the St Sergius of Radonezh’s Church was opened on the middle tier in the mid-17th century, although it was originally dedicated to the Trinity. The belfry's 35-tonne Great Bladgovestny Bell fell in 1941 and was only restored and returned in 2003. Attached to the belfry is a large refectory and the Transfiguration Church, both of which were built on the orders of Tsar Alexis in the 1650s.
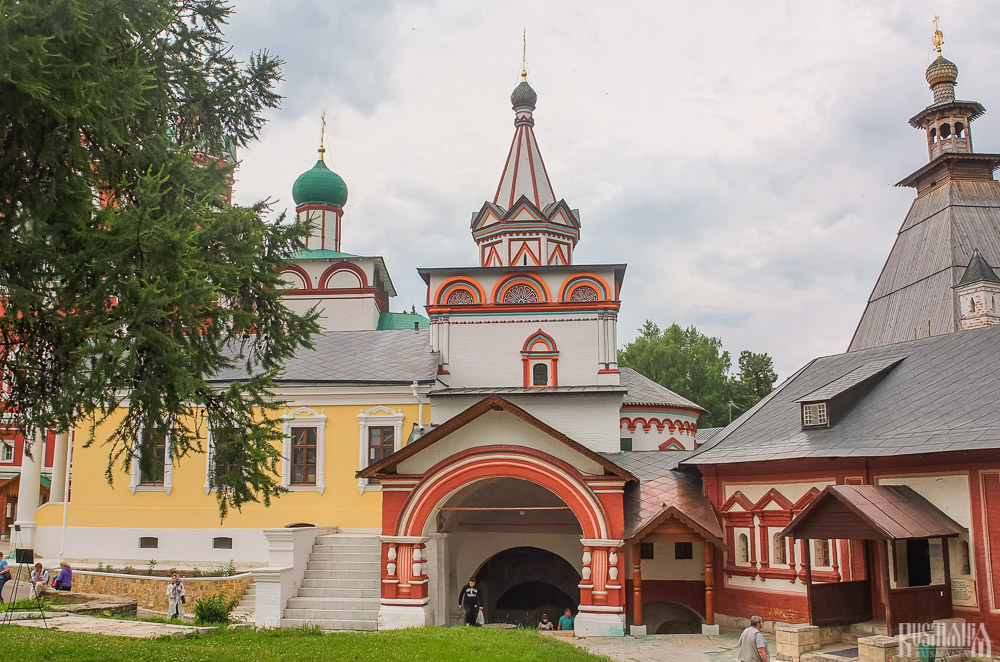

To the left of the belfry is another, smaller, refectory which is attached to the Trinity Gate-Church, which was also constructed in the 1650s on the orders of Tsar Alexis who made it his own family church. The church is elaborately decorated with colourful trims and underneath the archway is a beautiful 19th century fresco.
Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral
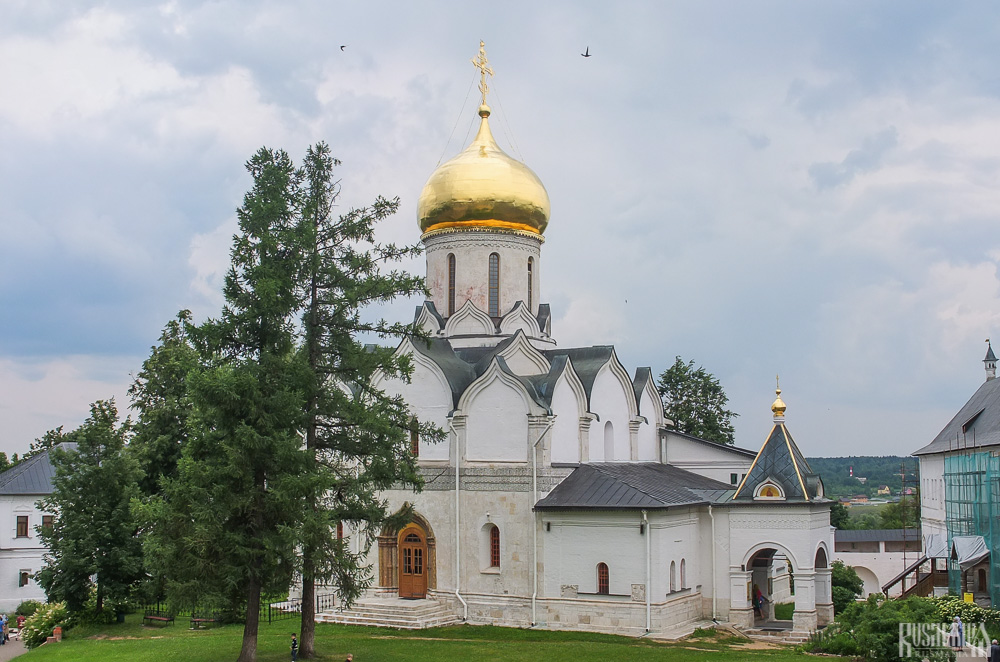

The Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral is the oldest building in the monastery and among the oldest buildings in the Moscow Region. It was built between 1404 and 1405 during the lifetime of St Sabbas and using the funds of Prince Yury of Zvenigorod. The white-stone cathedral is a standard four-pillar design with a single golden dome. After the death of St Sabbas he was interred in the cathedral and a new altar dedicated to him was added.
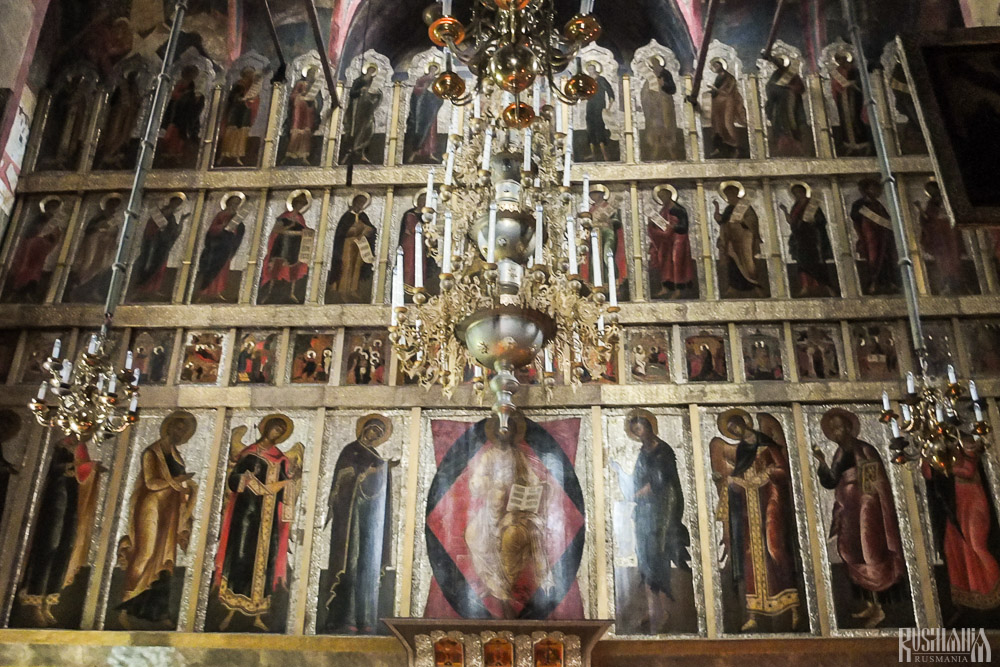

Under the reign of Tsar Alexis the cathedral was decorated with frescoes by Stepan Ryazanets, some of which remain today. Tsar Alexis also presented the cathedral with a five-tier iconostasis, the top row of icons have been preserved.
Tsaritsa's Chambers

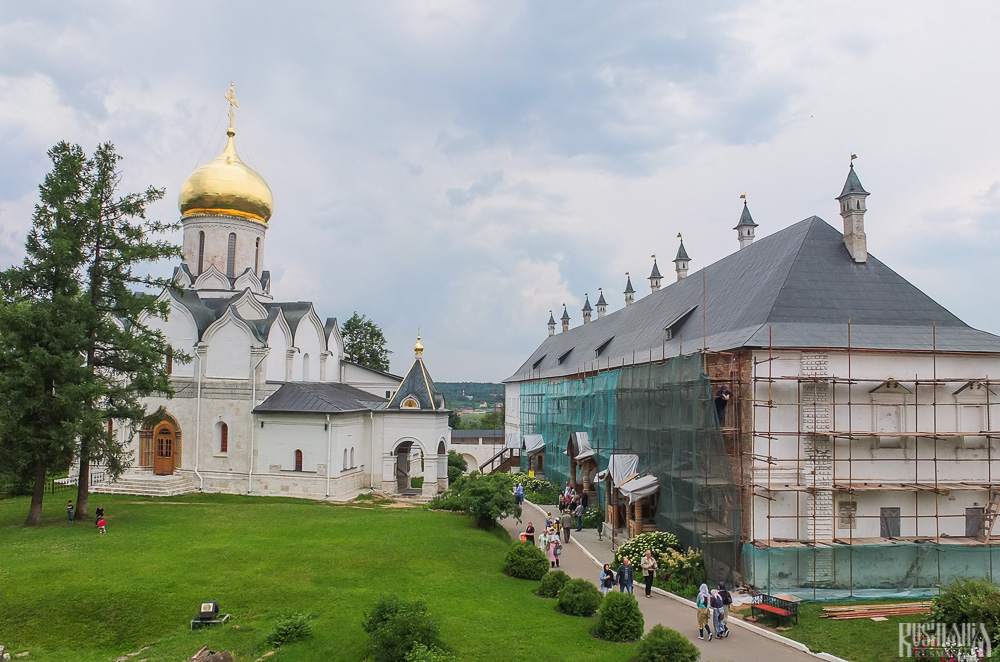
The Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral is located between the Tsaritsa's Chambers of the left and the Palace of Tsar Alexis on the right. The Tsaritsa's Chambers were built in the mid-17th century for the wife of Tsar Alexey - Tsaritsa Maria Ilinichna Miloskavskaya. The design of the building is influenced by the ancient Russian architectural style. Is prettier than the Tsar's chambers opposite, being red in colour with elaborately decorated window frames and entrance.
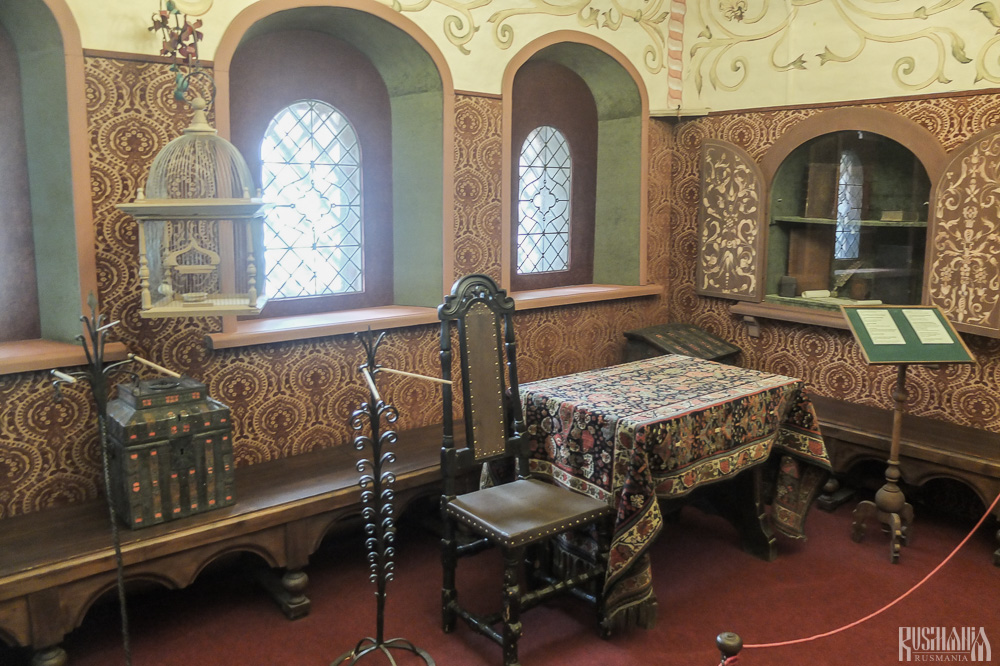

At present the Tsaritsa's Chambers houses the Zvenigorod Historical, Architectural and Art Museum. Among its displays is an accurate recreation of the interior of a noble lady's chambers including furniture, decorations and a decorated tiled oven, and an exhibition on the history of Zvenigorod and the monastery.
Palace of Tsar Alexis

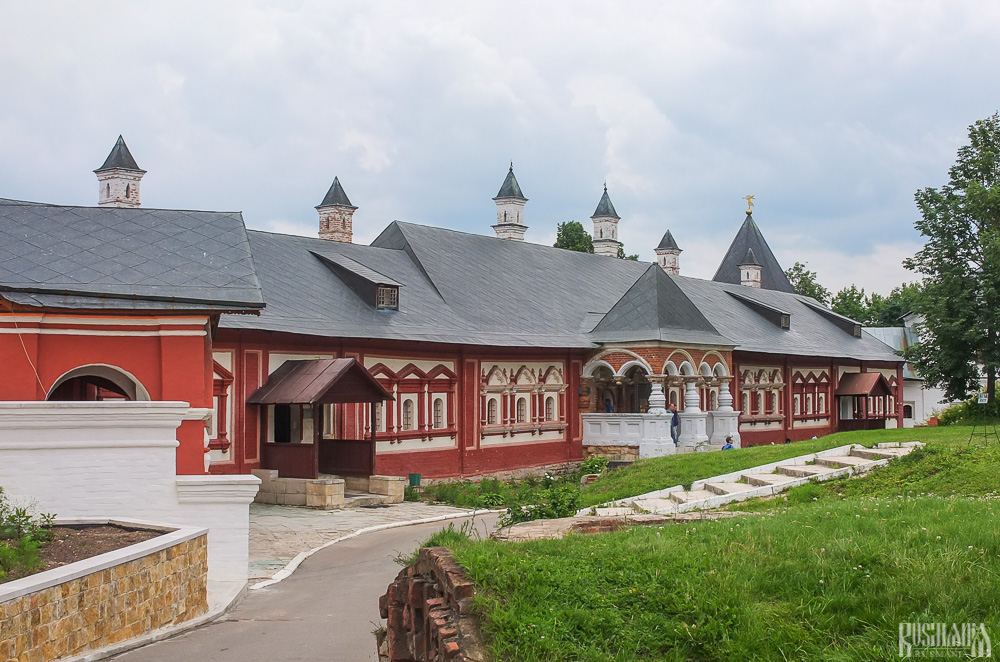
The Palace of Tsar Alexis was built in the 1650s and is now one of the best surviving examples of non-religious architecture of that era. It was built especially for Tsar Alexis who often visited the monastery on religious pilgrimages. Its most striking feature is its pretty row of nine chimney spouts which resemble towers.

Plan your next trip to Russia
Ready-to-book tours.
Your holiday in Russia starts here. Choose and book your tour to Russia.
REQUEST A CUSTOMISED TRIP
Looking for something unique? Create the trip of your dreams with the help of our experts.

COMMENTS
A shunt-trip breaker is merely a breaker that can be tripped "remotely" by applying a voltage to a built-in electromagnetic coil. Note that most are not designed for the coil to be continuously energized; supplying the tripping circuitry from the breaker itself is a common way to provide this. An interlock is a mechanical method of preventing ...
Product description. The shunt trip technology enhances safety by providing a means to open a safety switch electronically. When using an emergency stop, safety interlock or similar means, the remote operation capability of the shunt trip switch no longer requires personnel to manually open the switch with the handle, enhancing safety and ...
This is accomplished with a set of mechanical interlock auxiliary contacts which comes standard as 1-N/O and 1-N/C contact. The auxiliary contacts prevent the elevator from descending down and injuring any workers that could be working in the elevator shaft. ... DC Shunt Trip Switch Version Available - Consult Factory . Multi-Unit Fusible ...
Control pole interlock Field-installed kit, 400-600 A sizes Field- or factory-installed for K-Series switches Fuse pullers Not available Standard in Type 4X and 12 enclosed switches through 200 A field- or factory-installed for all other 30-200 A switches General-Duty Heavy-Duty Double-Throw Shunt Tipr Enclosed Rotary Safety Switch
The shunt trip opens the circuit breaker when its coil is energized by a voltage input (see Table 1). It is supplied with yellow and white ... the trip unit interlock plate in the RF Frame breaker. Step 11: The installed left accessory tray should look as shown with secondary leads extending out behind the trip unit. Secondary
2.1 Shunt Tripping Scheme. This is the most commonly used tripping scheme. The protective relay (PR) contact is arranged directly to trip the circuit breaker and it simultaneously energises an auxiliary unit X which then reinforces the contact that is energising the trip coil. The scheme is shown in Figure 1.
The shunt trip is an essential safety feature that allows for remote shut off of the power to the elevator in case of an emergency or malfunction. The wiring diagram provides a visual representation of the electrical connections and components involved in the shunt trip system. It includes various elements such as circuit breakers, relays ...
Mersen's fusible shunt trip switch is a UL Listed industrial control panel offering remote load-break disconnection capability to emergency circuits. An array of available options allows for maximum functionality to be built into a single compact panel. Panels built for elevator applications feature control transformers (fusing both
The shunt trip technology enhances safety by providing a means to open a safety switch electronically. When using an emergency stop, safety interlock or similar means, the remote operation capability of the shunt trip switch no longer requires personnel t o manually open the switch with the handle, enhancing safety and improving productivity.
The shunt trip breaker is a combination of the shunt trip accessory and the main circuit breaker. This installs on the main breaker to add protection to your electrical system. This adds security to your electrical system as it manually or automatically cuts the electric supply in your circuit. This accessory can help prevent short circuits and ...
The shunt trip technology enhances safety by providing a means to open a safety switch electronically. When using an emergency stop, safety interlock or similar means, the remote operation capability of the shunt trip switch no longer requires personnel to manually open the switch with the handle, enhancing safety and improving productivity.
Shunt trip device. Under voltage trip device. OCR alarm. Auxiliary switch. Cell switch. Shorting NC (b) contact. Drawout interlock. Position lock. Push button cover. Cylinder lock. Castel lock. Door interlock. Mechanical interlock. Door frame. Dust cover. Counter. Condenser trip device. Neutral CT. Lifting hook. ZCT (Load circuit conductors ...
A shunt trip (MX1); see Shunt Trip (MX1) and Shunt Close (XF) for more information. Optionally, the function may be completed with: ... The door interlock prevents the compartment door from being opened when the circuit breaker is in the connected or test position. If the circuit breaker is put into the connected position with the door open ...
shunt trip disconnect switch LPS1 T20 R2 K G N1 B F1 - 100A, 208V, w/24VDC FIRE SAFETY INTERFACE RELAY (3 PDT, 10 A, 120 V) Item #: 0218582
Product. Article Number (Market Facing Number) 3VA9988-0BM10. Product Description. SHUNT TRIP LEFT FOR ELECTRICAL INTERLOCKING 24 V DC ACCESSORY FOR 3VA1 and 3VA20 up to 3VA25. Product family. Accessories and Spare Parts 3VA9, for IEC Circuit Breakers up to 1250A. Product Lifecycle (PLM) PM300:Active Product.
Installation Instructions for Shunt Trip for R-Frame Series C Circuit Breakers and Molded Case Switches. 2 Instruction LeafletIL29C150G Effective December 2011 ... depressthecover interlock lever andreset circuit breaker. b. Using a small flat-bladescrewdriver,depressshunt trip plunger (Fig.2-3).Circuitbreaker should moveto
The Masterpact shunt trip (MX) is available as standard or with the diagnostic and communicating function. The shunt trip opens the circuit breaker instantaneously when powered. The minimum duration of the pulse operating order must be 200 ms. The MX standard trip locks the circuit breaker in OFF position if the command is maintained.
Burial 5 was the most unique, it was found in a coffin made of a larch trunk, with a tightly closed lid. Due to the preservative properties of larch and lack of air access, the coffin contained a well-preserved mummy of a child with an accompanying set of grave goods. The interred individual retained the skin on his face and had a leather ...
635th Anti-Aircraft Missile Regiment. 635-й зенитно-ракетный полк. Military Unit: 86646. Activated 1953 in Stepanshchino, Moscow Oblast - initially as the 1945th Anti-Aircraft Artillery Regiment for Special Use and from 1955 as the 635th Anti-Aircraft Missile Regiment for Special Use. 1953 to 1984 equipped with 60 S-25 (SA-1 ...
The shunt trip (Fig. 1-1) provides remote controlled elec-trical tripping for the circuit breaker. It consists of an inter-mittent rated solenoid with a tripping plunger and a cutoff switch attached to a plug-in module. The plug-in module is mounted in slots in the top of the trip unit and occupies the accessory cavity in the circuit breaker frame.
Much like the Elitserien Finals, we have a bit of an offense vs. defense match-up in this league Final. While Ufa let their star top line of Alexander Radulov, Patrick Thoresen and Igor Grigorenko loose on the KHL's Western Conference, Mytischi played a more conservative style, relying on veterans such as former NHLers Jan Bulis, Oleg Petrov, and Jaroslav Obsut.
Zvenigorod's most famous sight is the Savvino-Storozhevsky Monastery, which was founded in 1398 by the monk Savva from the Troitse-Sergieva Lavra, at the invitation and with the support of Prince Yury Dmitrievich of Zvenigorod. Savva was later canonised as St Sabbas (Savva) of Storozhev. The monastery late flourished under the reign of Tsar ...
Mersen's fusible shunt trip switch is a UL Listed industrial control panel offering remote load-break disconnection capability to emergency circuits. An array of available options allows for maximum functionality to be built into a single compact panel. Panels built for elevator applications feature control transformers (fusing both