
Exploring Life's Small Moments in a Vast World
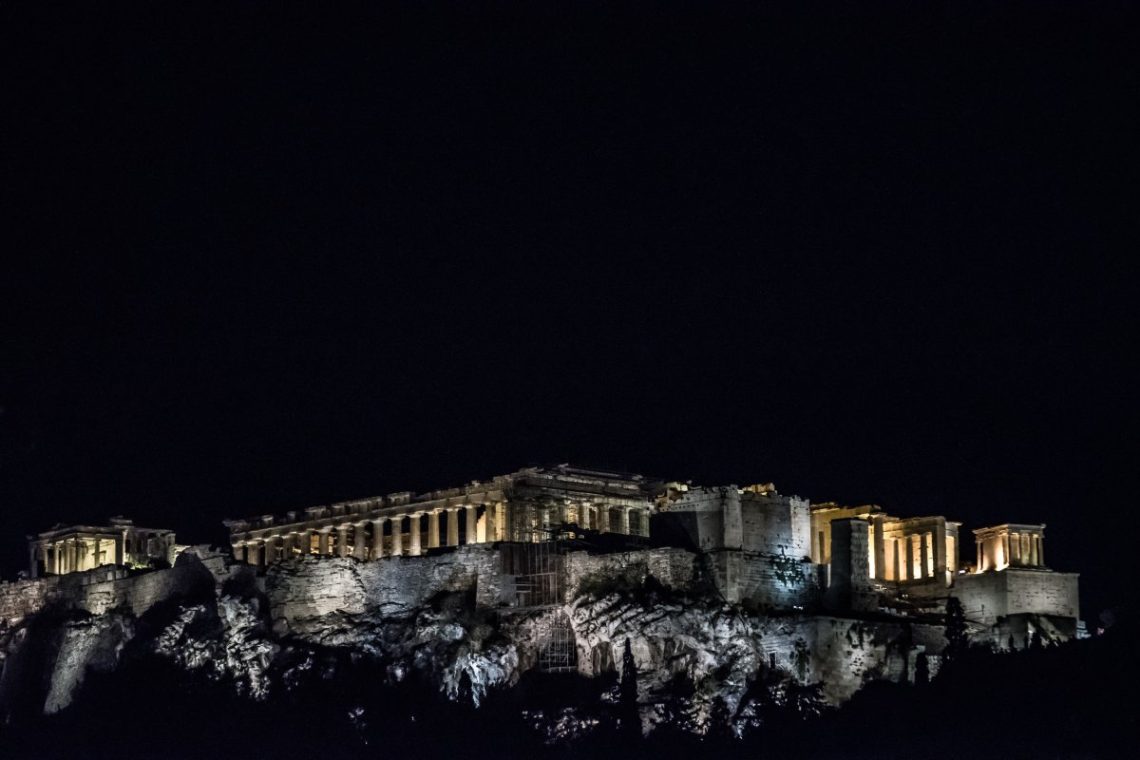


The Ultimate Athens Dark Tourism Guide (Updated 2024)
When we think of Athens, our minds race to images of ancient ruins, golden beaches, and traditional tavernas. But there’s a darker, more enigmatic side to this ancient city – a side that even I, as a local, was unaware of for most of my life. This is the world of dark tourism and, in Athens, it has a deep story to tell.
This guide is a local’s effort to gather all the most important dark tourism spots in Athens, Greece. It is updated for 2023 and, as new spots are discovered, it will be updated.
What is Dark Tourism?
Before diving in the best Athens dark tourism spots, let’s get clear on one thing. Dark tourism , also known as grief tourism or black tourism, involves traveling to places historically associated with death and tragedy . For some, it’s about confronting fear or understanding different aspects of human nature. For others, it might be an act of remembrance or an exploration of grey periods in history. It’s an oportunity for a new understanding and appreciation of those who came before us, the struggles they faced, and the legacies they left behind.
Travel Insurance for Greece
One of the first things that has to come to your mind when planning a trip is insurance.
Safetywing’s Nomad Insurance is one of the best options available out there. With a maximum coverage of 365 days, they are a great option whether you are a Nomad or not! They offer very low rates, but excellent coverage and immediate support (in a few minutes!). The best part? Nomad Insurance can be purchased even if you have left your home country already.
Lastly, they also cover extreme sports , something that can come in very handy if you are an adventurous soul.

The BEST Athens Dark Tourism Spots in 2024
The athens war museum.
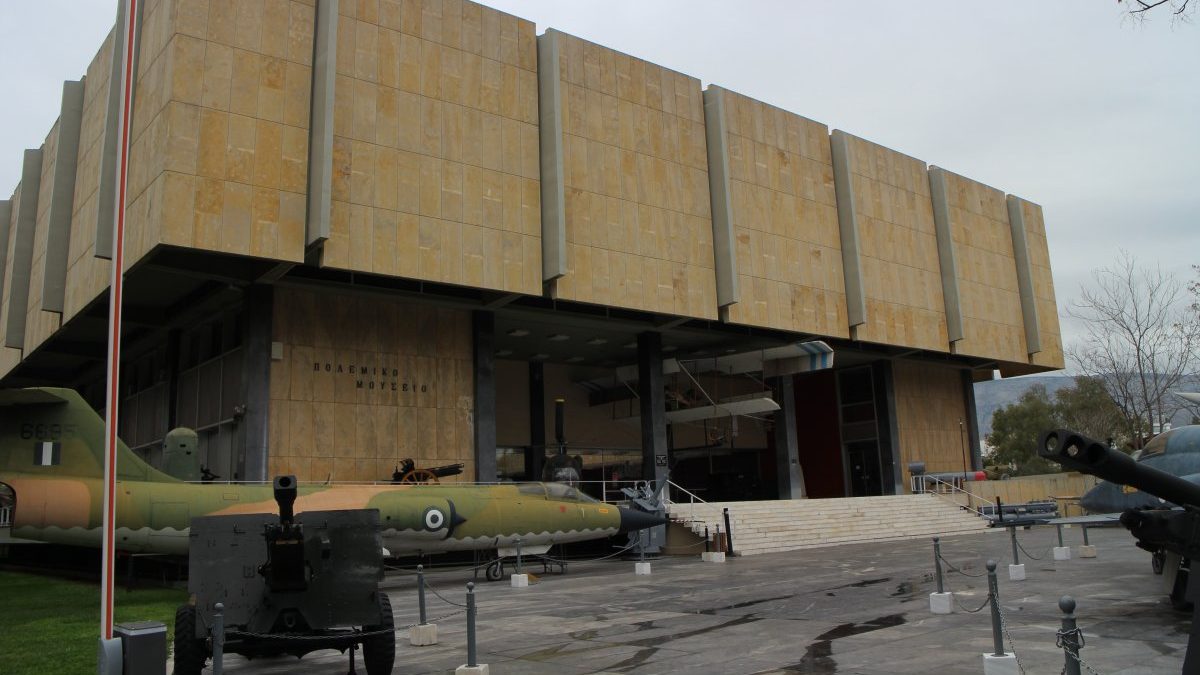

One might argue that the real charm of Athens lies not only in its ancient monuments but in the many, many museums that uncover different parts of its history.
The War Museum is a significant Athens dark tourism spot that offers a unique opportunity to explore the city’s military history. Located in the center Athens, the museum houses a massive collection of artifacts, documents, and exhibits related to Greece’s involvement in various wars and conflicts.
From ancient battles to modern warfare, the museum provides an extensive overview of the country’s military past. The exhibits cover topics such as the Greek War of Independence, World War I, World War II, and the Greek Civil War. Additionally, the museum offers displays of the strategic importance of Athens during various conflicts, shedding light on the city’s role as a military stronghold.
However, for me, the most impressive part of the museum is its extensive collection of military vehicles . There, you can see tanks, armored vehicles, artillery pieces, and aircrafts that were used in different periods of Greek military history.
The Athens War Museum is open Monday-Sunday 09:00-17:00. As for the cost, entrance is 6 euros for adults , while there is a 3 euro, reduced ticket available too.
The Rifle Range (Skopeftirio) of Kaisariani

This historical site , once used as a shooting range, has evolved into a symbol of Greek contributions to the resistance against Axis forces during World War II. It was here where 200 Greek partisans were executed by the Nazi Occupation Forces on May 1, 1944.
Today, local authorities have transformed the place in a modern memorial site, a proper tribute to those who proudly stood against the Nazis. The area is part of a massive park, very popular among local families. It is the perfect place for a walk, and even better for a picnic.
In skopeftireio also operates a museum dedicated to EAM , the biggest Greek resistance force during WWII. Original wartime artifacts, documents, and photographs are among the many exhibits you will find there.
The “1941-1944 Memorial Site”
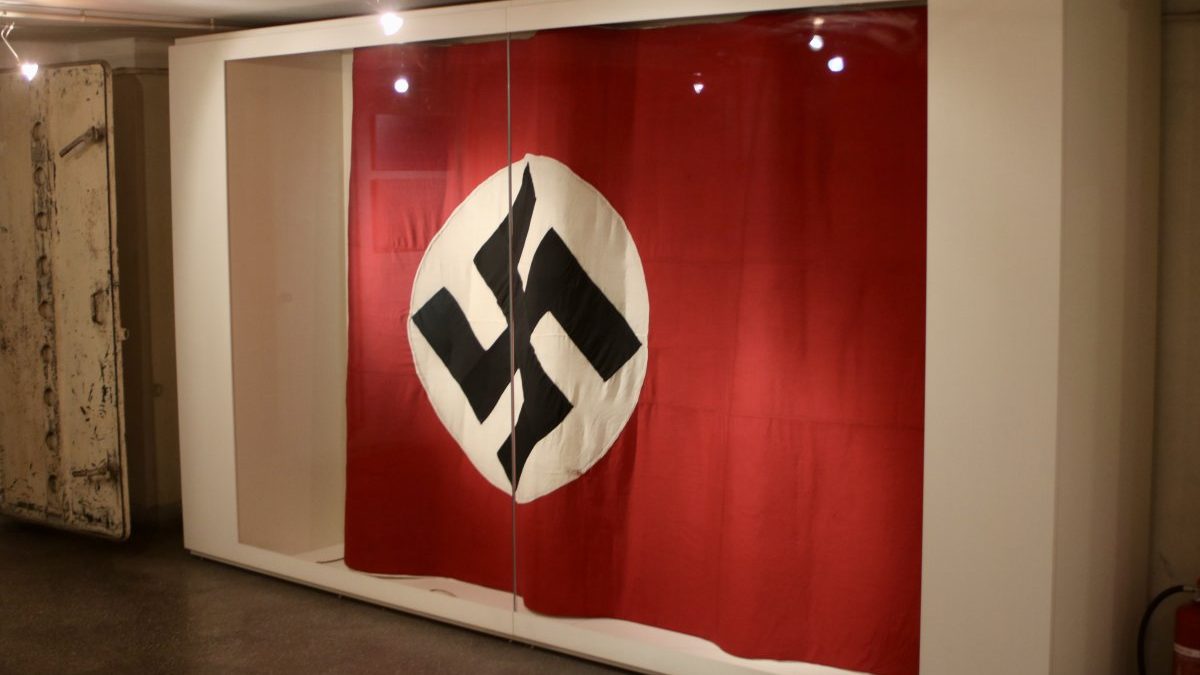

In the beginning, this place was never meant to become among the Athens dark tourism spots. In August 1894, the “I ETHNIKI” General Insurance Company purchased the 4 Korai Street mansion to house its head offices there.
During World War II, Greece was occupied by Axis powers. As part of their military administration, the occupying forces established Kommandanturen, the headquarters for the military administration and the local branch of the occupying power.
In Athens, the central Komandatur was housed in the basement of the 4 Korai Street building and was responsible for maintaining control, enforcing orders, and overseeing various aspects of governance in the occupied territories.
The building basements were used as detention centers. Men and women were kept inside before being transferred to other prisons. They were often being held for days without food or water. Because of the thick walls and the metal doors, the basements were soundproof. That’s why even though the building was right in the city center, nothing could be heard outside.
Prisoners would carve stories on the walls, like their names, why they were detained, or how they were treated inside the building basements. German soldiers occasionally painted the walls to erase the cravings, but again the prisoners would write their stories so people would know the truth when they found them.
In the following years, Ethniki Insurance commenced works to preserve the Mansion and repair the damages caused by the consecutive requisitions. The detention centers underwent restoration and conservation work to better show off the detainees’ graffiti and messages on the metal doors, walls, and windows. Texts, names, dates, drawings, etc., were preserved, and the two basements were opened to the public.
You can find more information on my seperate piece on the sight .
The Athens Polytechnic

One of the most haunting and powerful Athens dark tourism spots is the Athens Polytechnic University . It was here, in 1973, during a time under the military junta, that students and intellectuals protested against oppression.
Their peaceful resistance was met with brutal force, a tragedy that included a tank crashing through the university gates . The short-lived, yet potent uprising was named the ‘Athens Polytechnic Uprising’, and it’s a key symbol for democracy in Greece. Every year at 17th November students gather there, play music and pay their respects. Afterwards, a march through Athens follows.
The original gate, the one crashed by the tank, is still there to see . I would recommend getting there to leave a flower – a small tribute to the brave students that risked their own lifes against the oppressor.
The Haidari Concentration Camp (Block 15)
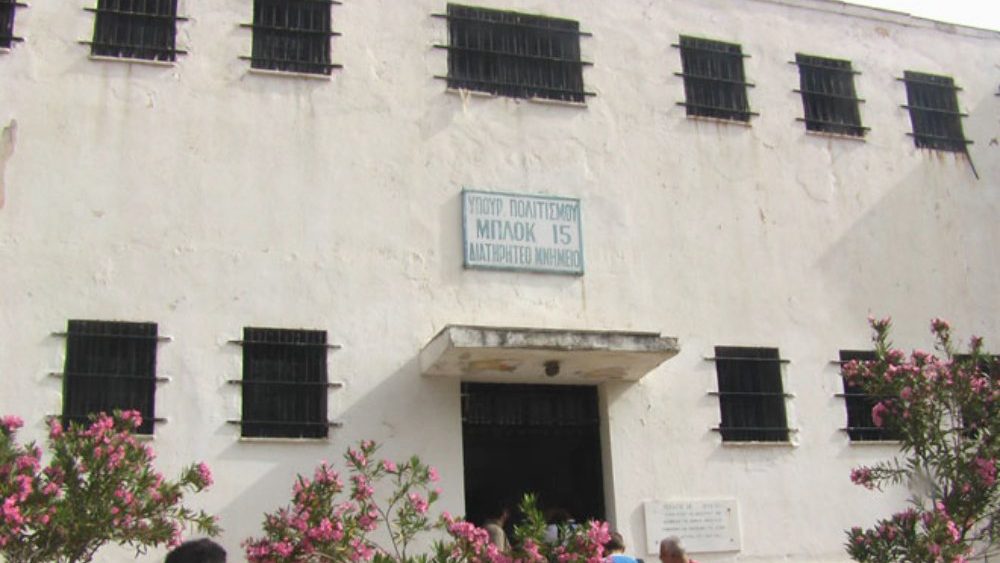

The Haidari concentration camp , also known as Block 15, was the largest Nazi concentration camp in Greece during World War II, where thousands of people were imprisoned.
The camp served as a place of imprisonment for political dissidents, resistance fighters, and Jews. It was notorious for its harsh living conditions, forced labor, and executions.
Hopefully, block 15 will become a museum and one of the best dark tourism spots in Athens in the next few years, after many years of popular demanding. Visiting this site will soon be opportunity to learn more about the atrocities committed during the war and pay tribute to the victims who suffered and lost their lives in this camp.
The EAT-ESA Museum
Now, let’s talk about the EAT-ESA museum , a lesser-known, but crucial part of the Athens dark tourism scene. Not usually on the typical tourist maps, this museum chronicles the brutal days of the military junta that ruled Greece from 1967 to 1974.
The museum’s exhibits are dedicated to the lives lost and the hardships during this δαρκ period. A collection of photographs, personal items, and disturbing artifacts provide a brutally honest portrayal of the realities under this oppressive regime.
Among its exhibits is the correspondence between imprisoned individuals and their loved ones, revealing the diabolical human rights violations that took place. You can contact them directly to book a tour to the museum.
The Parnitha Sanatorium
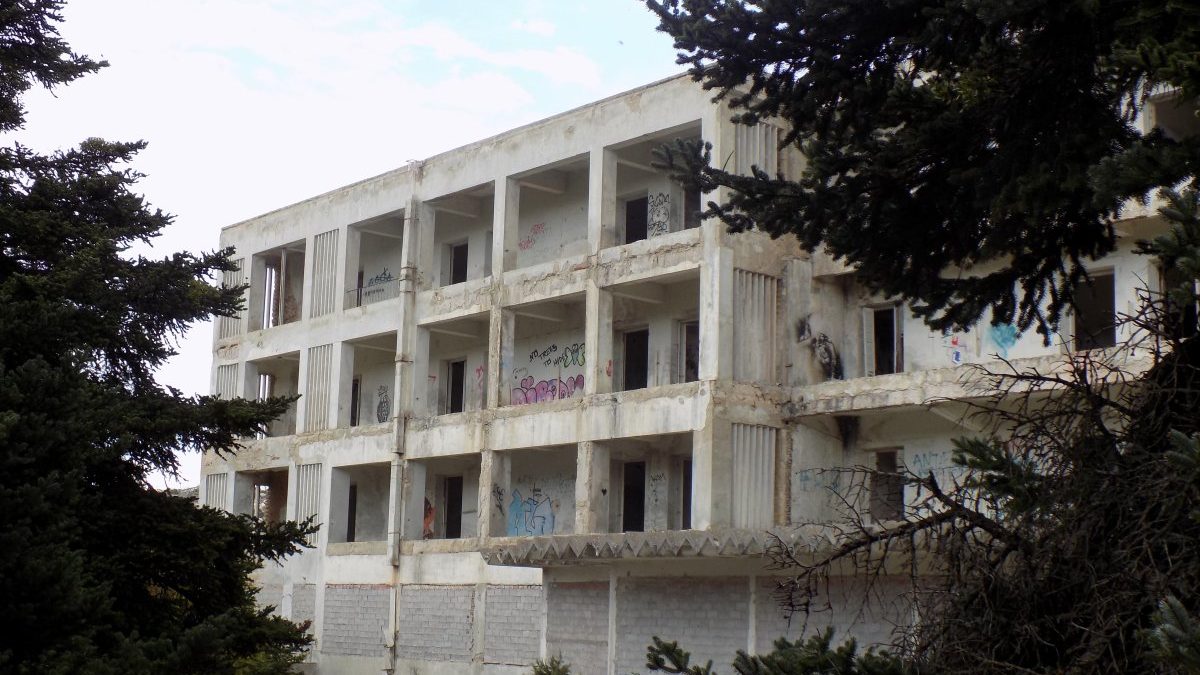

High on the Mount Parnitha and hidden by pine forests stands the Parnitha Sanatorium . It was built in the late 1910’s to house the tuberculosis patients (Around 100.000 greeks had lost their life from TB (!).
However, during World War II, the building took a turn for the darker. It was converted into a camp for political prisoners and later served as a treatment center for soldiers. More hauntingly, in its later years, the sanatorium became home to many children orphaned during the Greek Civil War.
After the discovery of penicillin, the Sanatorium gradually fell into decline. By 1965, the building housed the Xenia Hotel and later the School of Tourism Professions, which operated until 1985. Ever since, the facilities have remained completely abandoned.
There have been many urban legends about the Sanatorium , with many people claiming that have seen or heard ghosts inside! After the massive earthquake that hit Athens in 1999, the Sanatorium was deemed unstable and people were banned from entering. However, many people enchanted by its abandoned aura, still take the risk and enter.
The main way to get to the Sanatorium is driving, so that’s sommething important to know. Keep in mind that the sanatorium itself is still officially closed to the public , so you enter at your own risk. Better safe than sorry! However, for me is one of the best Athens dark tourism spots!
The Marathon Tumulus
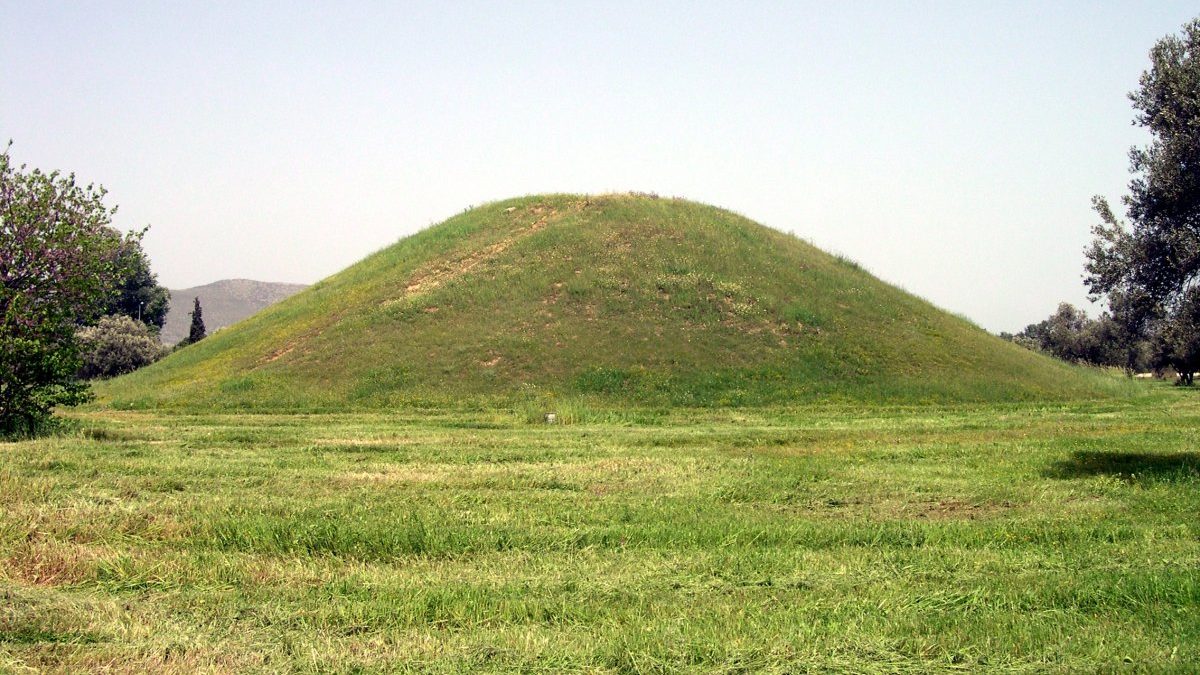

Located about 40 kilometers northeast of Athens, is the historic Marathon Tumulus . An artificial hill, erected in memory of the Athenian soldiers who perished in the Battle of Marathon in 490 BC, this site embodies both the triumph and tragedy of war. Did you expect to learn about ancient Athens dark tourism spots today?
The Battle of Marathon was one of the most crucial moments in world history – where the Athenians beat the advancing Persians against all odds. However, it was at a cost that cannot be overlooked – the lives of 192 Athenians. The bodies of the Athenians lost in the fight were buried inside this very tomb .
Around the tomb, artifacts and grave goods recovered from the site are displayed in the Archaeological Museum of Marathon . These relics offer a taste of the world-famous ancient Athenian civilization and the lives that were lost on the battlefield. Entry tickets include both the tomb and the archaeological museum and they cost 6 euros . There is a discounted, 3 euro ticket available too.
In terms of logistical tips, getting to the Marathon Tomb from Athens involves a bus (around 1.5 hours) or a car ride, so it’s a perfect day trip opportunity for history enthusiasts. You can take the bus (KTEL) to Marathon from the Nomismatokopeio metro station. Tickets can only be purchased by cash directly into the bus. They cost 3,7 euros each way.
Here you can find the up-to-date timetables to get to Marathon from Athens:
The Penteli cave (Davelis cave)
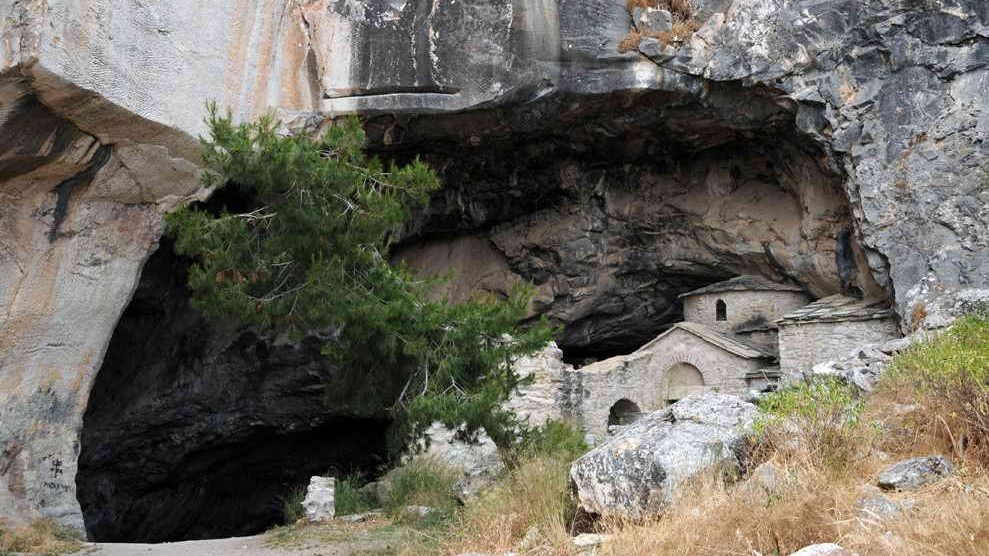

The Davelis Cave on the outskirts of Athens is a different stop on the Athens dark tourism trail. Caves are often associated with tales of the underworld, but this one in particular has its fair share of supernatural stories.
The cave was once thought to be the hideout of an infamous eighteenth-century outlaw, Davelis. It’s said that a network of tunnels extends far into the mountain. Before that, it was an ancient greek temple dedicated to panas and an orthodox church. It is said that some of the monks spent their entire lifes there.
Locals and past visitors often share stories of strange apparitions, unusual “cold spots”, audio disturbances, and the feeling of being watched. While personally not a fan of the supernatural, I found those stories quite interesting.
The First Cemetery of Athens
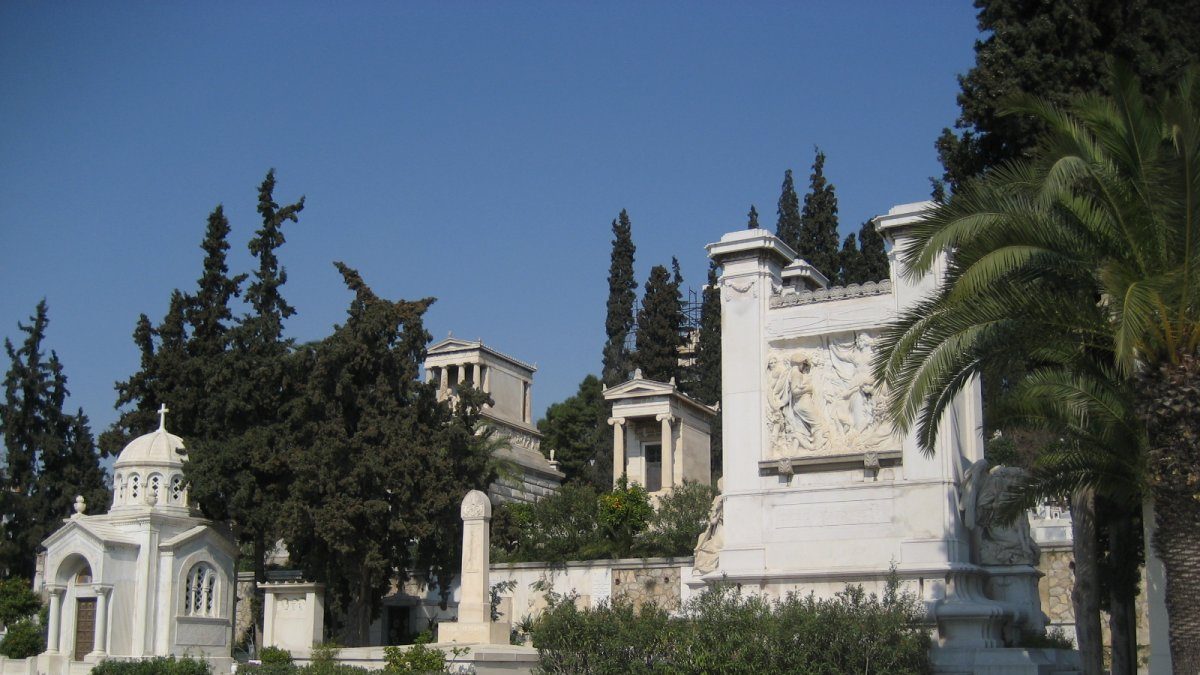

The first cemetery in Athens was established in 1837 as the city’s first organized burial ground and became the final resting place for many important figures in Greek history.
The cemetery is located in the neighborhood of Mets and covers an area of approximately 170,000 square meters. It is not only a place for burial but also a fascinating open-air museum that shows the evolution of Greek funerary art and architecture over the years.
Within the First Cemetery of Athens, you’ll find the graves of significant individuals such as politicians, artists, writers, and scholars. Some of the most notable figures buried here include Eleftherios Venizelos, a prominent Greek leader, and Melina Mercouri, a famous Greek actress and politician.
Walking through the cemetery is a chance to explore the different architectural styles of the tombs, from neoclassical to modernist designs. It is a different and unique opportunity to learn more about into the history and culture of Athens while paying respects to those who rest there.
Final Thoughts
Athens has always been a city that invites exploration. But off the beaten track of the Parthenon and Plaka, and you’ll experience a whole different side to the city – the darker side of Athens tourism. It is a side that triggers the curious part of you, that draws you into the shadows of history, and one that is worth discovering.
You May Also Like

The Complete Guide to Hiking Drakolimni (Greek Dragon lake)

Why you should Plan a Trip to Wadi Rum in 2024

The 25+ Best Reasons to Visit Syria in 2024
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Athens Dark Tourism Guide 2023 (updated for 2024)
- Athens Blog

Travel insurance in 2024: Being safe while travelling to Athens (updated)

Η.Μ.S TRIUMPH Submarine found deep into the Aegean after 80 years

Table of contents
Introducing athens’ dark tourism scene, exploring the ruins and monuments of ancient greece.
- Taking in the Urban Legends of Athens' Streets
Penetrating the Mysterious Crypts of Athens
Seeking out the haunted houses in athens, notable dark tourism sites in athens, the athens war museum, overview and historical significance, notable exhibits and collections, visiting information, the kaisariani rifle range (skopeftirio), historical context, transformation into a memorial site, the 1941-1944 memorial site, the fascinating history of 4 korai street mansion, how to visit and what to expect, the athens polytechnic university, significance of the polytechnic uprising.
- Commemorative Events and the Gate's Symbolism
The Haidari Concentration Camp (Block 15)
Its history during world war ii, current status and the future as a museum, the parnitha sanatorium, origins and various uses throughout history, status as an abandoned site and visitor advice, the davelis cave, legends and history surrounding the cave, the cave as a natural and mythological point of interest, the first cemetery of athens, cemetery as a historic site and open-air museum, notable graves and examples of funerary art, sample itinerary for a dark tourist visit to athens.
Welcome to the ultimate dark tourism guide for Athens in 2023! Whether you’re a seasoned traveler looking for something a bit out of the ordinary, or an outsider curious about an ancient culture and its hidden secrets, this guide will provide all the information you need. From exploring long-forgotten mine shafts on world-renowned archaeological sites, to uncovering historically significant events in haunted cathedrals, get ready to explore some unforgettable experiences around Athens with our user-friendly google maps feature. Travelers can use this interactive map as they navigate their way through history while discovering exciting national monuments and iconic cultural hubs around town. Be warned though: there are arrows along the route that point towards places best left undiscovered due to their potentially spooky vibes so be sure not to click past them too quickly!

Welcome to Athens, a city rich in history and culture. While most visitors come to explore the ancient temples and marvel at the stunning architecture, there is another side to Athens that has been gaining popularity among tourists – its dark tourism scene. From the time of the Ottoman Empire to Greece's more recent economic crisis, Athens has experienced its fair share of dark and tragic events. And for those interested in exploring the city's haunting past, there are plenty of options to choose from. Take a tour of the infamous prison, where political dissidents were tortured during the military dictatorship or visit the site of a devastating terrorist attack that shook the city in 2003. While Athens' dark tourism scene may not be for everyone, it does offer a unique opportunity to explore the city's troubled, yet fascinating history.
Embark on a journey back in time to the ancient Greek civilization and explore the ruins and monuments that still stand tall today. From the iconic Parthenon in Athens to the impressive Temple of Zeus in Olympia, the architecture alone is awe-inspiring. But these structures are not just aesthetically pleasing - they are windows to the past, offering insight into the daily lives, myths, and beliefs of the ancient Greeks. Imagine walking along ancient roads, marveling at the intricate details of sculptures that have stood for millennia, and soaking in the rich history of this remarkable civilization. A visit to these ancient ruins and monuments is a must for any history buff or travel enthusiast.
Taking in the Urban Legends of Athens' Streets
As you wander the streets of Athens, you may begin to hear whispers of the city's urban legends. From the infamous "Melo-Katsourbos," a mischievous jester who reportedly haunts the streets of Monastiraki, to the eerie tales of the abandoned Psychiko Children's Hospital, there's no shortage of chilling stories to send shivers down your spine. But these legends aren't all frights and horrors. Some, like the story of the Beggar's Opera, offer a glimpse into the city's rich cultural history. So next time you're strolling through Athens, keep your ears open and see what stories you can uncover. Who knows what secrets and mysteries lurk just around the corner?
Welcome to Athens, a city steeped in mystery and history. As you wander through the bustling streets, it's hard not to feel in awe of the ancient wonders surrounding you. But if you're a true adventurer at heart, then you must venture underground to the mysterious crypts of Athens. Once used to house the remains of the dead, these crypts now hold centuries of secrets waiting to be discovered. Imagine walking through narrow passageways, surrounded by cold stone walls and dimly lit torches, feeling the weight of history bearing down on you. With every step, you'll uncover new clues to the past, from ancient hieroglyphics to hidden treasures. So grab your flashlight, and let's journey into the heart of Athens' intriguing past!
Athens, the historic capital of Greece, is a city rich in ancient myths and legends. If you're seeking an adrenaline rush and spine-tingling adventure, Athens is home to a plethora of haunted houses that are sure to give you goosebumps. From the eerie and abandoned mansion on Kifissia Avenue to the notorious Tower of the Winds, said to be home to the powerful wind daemon Boreas, there is an abundance of spooky spots to explore. Brave souls seeking something truly out of the ordinary can even visit the abandoned underground catacombs beneath the city, where ghosts of ancient Greeks are said to roam. So, book your tickets, pack your bags, and get ready to embark on an unforgettable ghost-hunting adventure in Athens.
Nestled in the heart of the city, the Athens War Museum stands as a sentinel to Greece's storied past. Established in 1975, its architectural grandeur hints at the treasures within, encapsulating the valor and sacrifice of Greek soldiers. The museum holds paramount significance in illustrating the city's role as a battleground in various conflicts.
The museum boasts a staggering collection of over 20,000 artifacts, each telling its own tale of heroism and hardship. Visitors encounter everything from antiquated weaponry from the Greco-Persian Wars to contemporary military technology. Notable exhibits include an Avro Anson plane, used during the Nazi occupation, and a fascinating array of uniforms worn by Greek soldiers throughout history.
Opening its gates from Monday to Sunday, the museum invites you to traverse through time from 09:00 to 17:00. Reaching the site is convenient, with several public transport links available. Admission costs start from 6 euros for adults, making it a must-see destination for any history enthusiast visiting Athens.
A mere whisper among locals not long ago, the Kaisariani Rifle Range has emerged as a monument to courage and resistance. It was here, in the grim days of May 1944, that the Nazi Occupation Forces executed 200 Greek partisans, etching a somber chapter in Athens' history.
Today, the rifle range is a testimony to the indomitable spirit of Greek resistance. Local authorities have meticulously transformed the once-forbidding grounds into a tranquil memorial site. Visitors can pay their respects at this hallowed ground and reflect upon the sacrifices made for freedom.
The story of the 4 Korai Street Mansion is one of resilience and remembrance. A mundane building took on a cloak of darkness during the WWII occupation, sheltering the Kommandantur—infamous for its role in detention and governance under Axis control. In the subterranean cells, countless tales of defiance and survival were etched into the walls by the imprisoned, a solemn yet powerful record.
Immersive and memorable, a visit here is a reverent experience. The remnants of wartime detention facilities offer a chilling reminder of those tumultuous times. Given the restored nature of the space, visitors walk in the shoes of the prisoners, experiencing the stark reality that no history book can fully convey.
The Athens Polytechnic Uprising of 1973 epitomizes the struggle for democracy and truth. When an autocratic junta stifled civil liberties, the resounding call for freedom echoed through the university's halls, a call that was met with fatal force.
Commemorative Events and the Gate's Symbolism
Today, the Polytechnic still hosts events to commemorate the uprising, keeping its memory alive. The charred remains of the university gate, breached by a tank in a fateful clash between the youth and the junta, remain untouched. It stands as a permanent testament to the power of protest and the perils that come with it.
A hushed visitation amidst the tranquil suburb of Haidari reveals the stark contrast of war's horrors. Block 15, a part of the Haidari Concentration Camp, saw the detention and torture of Greek citizens by the Nazi regime. Today, it serves as a vital archival and research center dedicated to preserving the memory of those who endured the camps' injustices.
Efforts are underway to transform this site into a museum, ensuring that the lessons from history remain relevant in contemporary discourse. By shedding light on the excesses of totalitarian regimes, visitors will gain a profound understanding of the perils of prejudice and aggression.
Nestled upon Mount Parnitha's verdant slopes, the Parnitha Sanatorium once offered a sanctuary for tuberculosis patients. Converted into an emergency hospital during World War II, it witnessed the struggles of the wounded, serving as a canvas for tales of perseverance and hope.
The site now lies abandoned, a haunting reminder of the past. As such, it provides a unique opportunity for contemplation. Visitors are advised to approach the sanatorium with respect for its history. The dilapidated structures and eerie silence serve as a poignant backdrop for reflections on the passage of time and the endurance of the human spirit.
The Davelis Cave, steeped in myth and historical intrigue, is a natural formation that has been the subject of many a tale. Home to a variety of fascinatingly eerie formations, the cave's depths conceal secrets that invite intrepid explorers to unravel the mysteries within.
It serves as a natural and mythological point of interest in the region. The cave's geological features, including spectacular stalactites and stalagmites, offer a sensory adventure through time. As you venture deeper, the cave's resonance with history and myth becomes palpable, making for an enthralling experience.
The First Cemetery of Athens exists not only as a resting place for the departed but also as an open-air museum. The grandeur of its ornate tombs and the illustrious figures interred within its hallowed grounds provide a unique reflection on the city's cultural and political history.
Notable figures from the annals of Greek history find their final repose here. The cemetery's diverse array of sculptures and funerary art styles is a tapestry of artistic expression. A stroll through these avenues is akin to a guided tour through the milestones of Greek society, revealing narratives often untold.
Athens is a city steeped in history, and for dark tourists, there are many compelling destinations that explore the darker side of this ancient city. Start your day by visiting the eerie Kokkinia execution site, where over 200 prisoners were executed during the Greek Civil War. Next, head to the controversial Museum of Anti-Dictatorial and Revolutionary Art, which houses a collection of artifacts from Greece's turbulent history. In the afternoon, explore the Athens War Museum, which boasts a vast collection of military memorabilia, including tanks and fighter jets. End the day with a trip to the ancient Kerameikos Cemetery, the final resting place for notable Athenians of the past. As a dark tourist, Athens offers a unique perspective to those seeking an unconventional travel experience.
Athens is the perfect destination for any dark tourist looking to experience an abundance of mystery, creepy vibes and a mystery deep-rooted in history. Visitors can explore ancient ruins, uncover old legends, enter crypts and buildings with secrets locked deep inside. Even the local cuisine has added flavor derived from centuries-old folk recipes. If you are looking to embark on a journey through time, then be sure to make Athens your next stop where you can reconnect with the city's darkness of the past. So make sure to check out our sample itinerary if you're brave enough to take on a daring dark tour in Athens!
Last updated on February 25th, 2024 at 08:38 am
Related posts

The religion of the city and the importance of the acropolis in Ancient Greece

Ancient Greek Diet, the Guide

The Cultural Debate Around Marina Satti’s “Zari” and Modern Greek Society

- dark tourism
- Search & Find

EXPERIENCES
A chilling journey of ‘dark tourism’ around greece.
Unearthing sites suffused with history's melancholy tones, certain to ignite intrigue among visitors
BY GIANNIS KOUTROUDIS
Translated by sophia velopoulos, published 02 june 2023, the sanctuary of the great gods on samothrace/photo: shutterstock.
We will navigate the labyrinth of “dark tourism.” A curious phenomenon has taken root in recent years – travellers are increasingly drawn towards narratives etched in shadow rather than the typical sun-soaked experiences. Thus, the rise of “dark tourism”, a global movement transforming travel into an exploration of humanity’s grim past. Morose? Possibly. Controversial? Certainly. But undeniably, dark tourism plays a pivotal role in preserving our historical memory, breathing life into narratives long obscured by time’s relentless march.
In this spirit, we present a selection of Greece’s most notorious dark tourism destinations, offering a distinct travel experience for those desiring a taste of the unconventional.
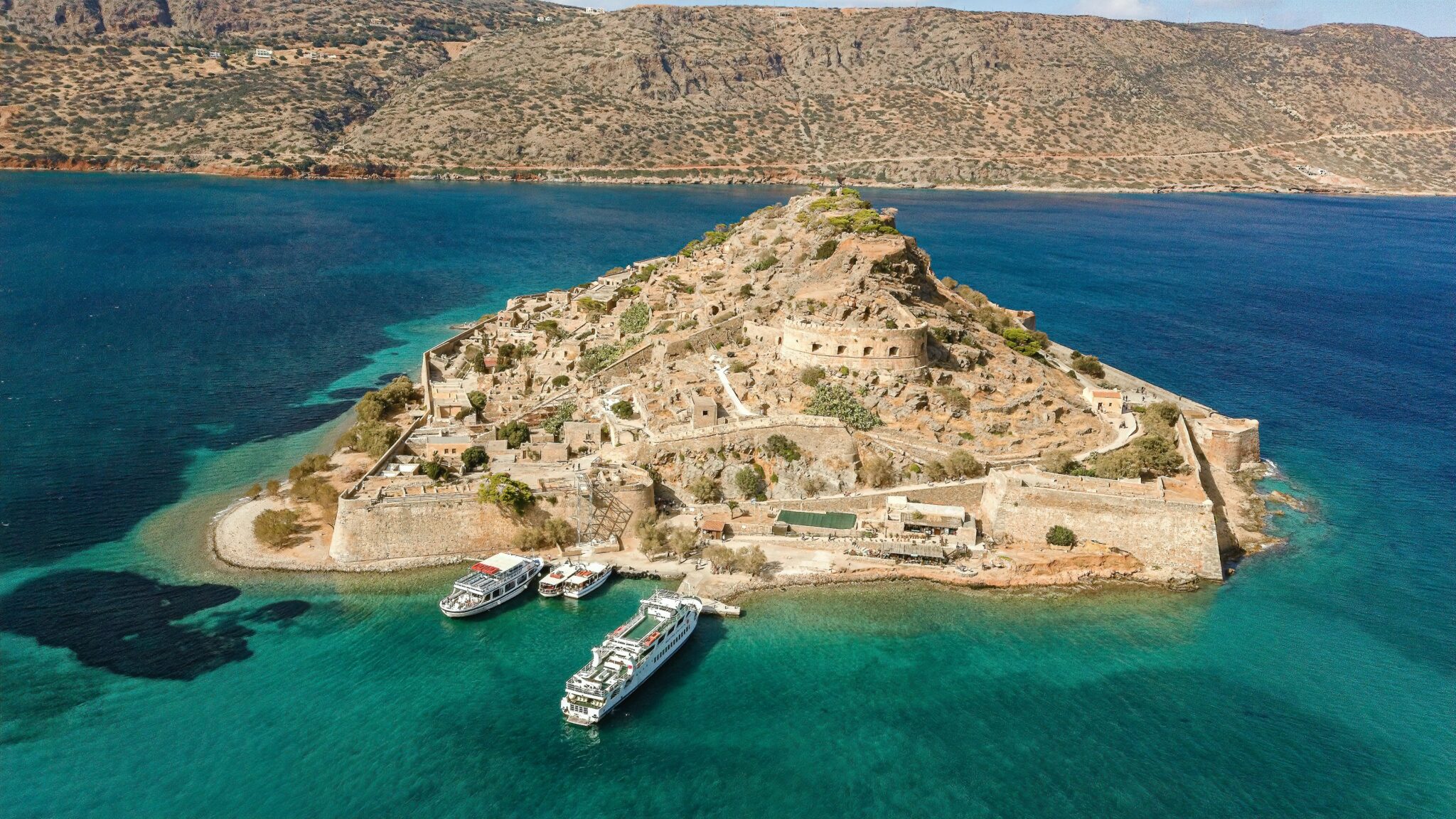
Spinalonga, Crete
Consider Spinalonga, Crete, an island of barely 100 square metres . Yet its history looms large, a colossal monument to human suffering. In 1903 , this abandoned Venetian fortress morphed into a leper colony , a place of exile for those afflicted with this incurable disease.
Dark, isn’t it? But there’s more. The notoriety of Spinalonga grew so profound that patients across Europe found themselves bound for this tiny enclave. With no cure for leprosy available, Spinalonga became a one-way journey, a farewell to freedom, to life itself.

Spinalonga/Photo: Unsplash
Despite these grim realities, Spinalonga didn’t surrender to despair. It blossomed into a vibrant community, connected to Plaka by the ceaseless rhythm of the sea. Its residents, during the German Occupation , launched a unique rebellion, leveraging the occupiers’ inherent fear to secure free ally radios . A daring defiance of authority in a place where normalcy had long ceased to exist.
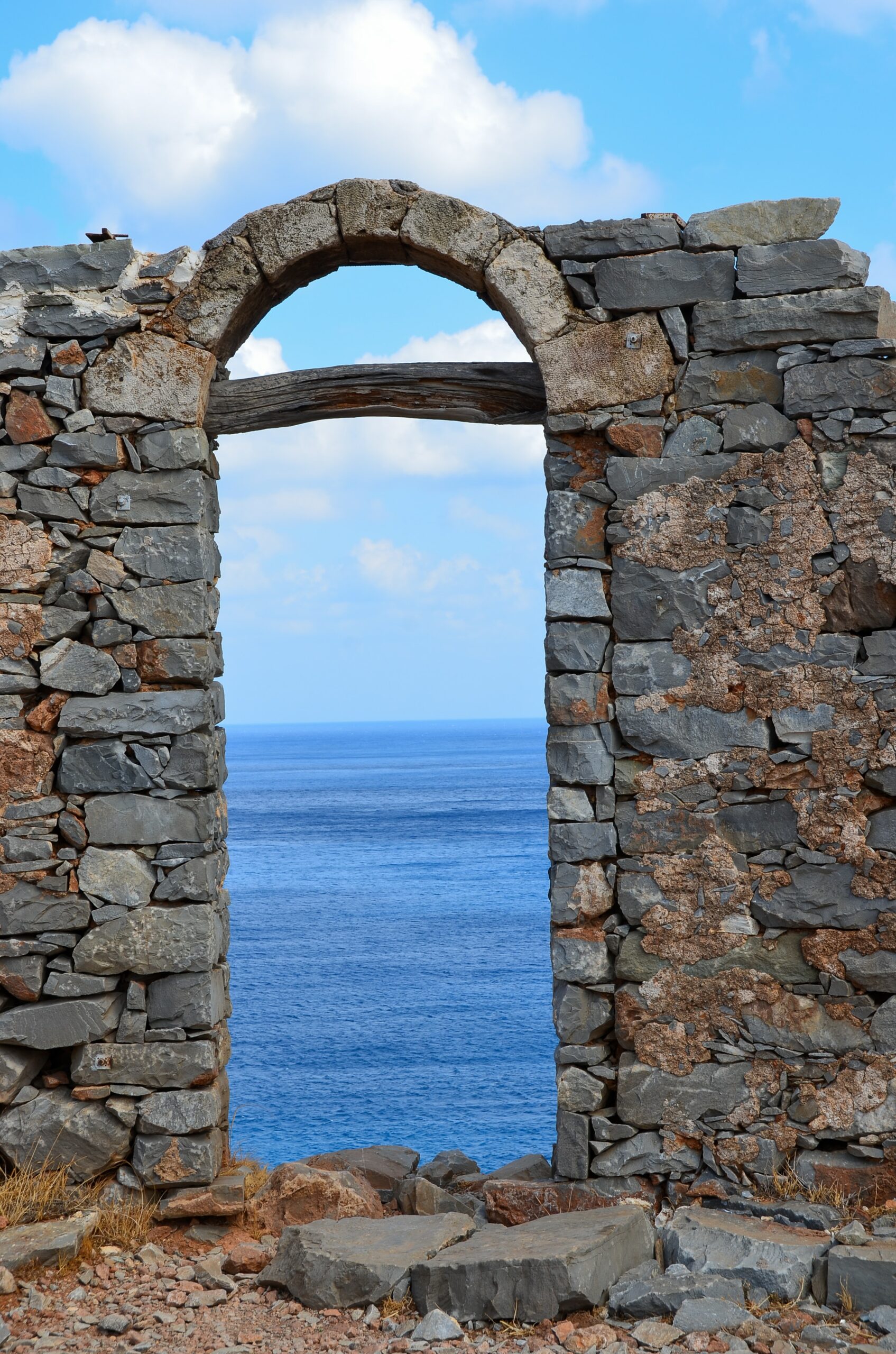

Photo: Unsplash

Spinalonga/Photo: Kanella Klimatsida/Eurokinissi
With the advent of effective antibiotics , Spinalonga’s story started drawing to a close. This once bustling island slowly deflated, only to be reclaimed by silence. Yet, in a twist of fate, this once-doomed rock has become one of Crete’s most frequented dark tourism hotspots. Its tragic history now casting a hauntingly beautiful glow.
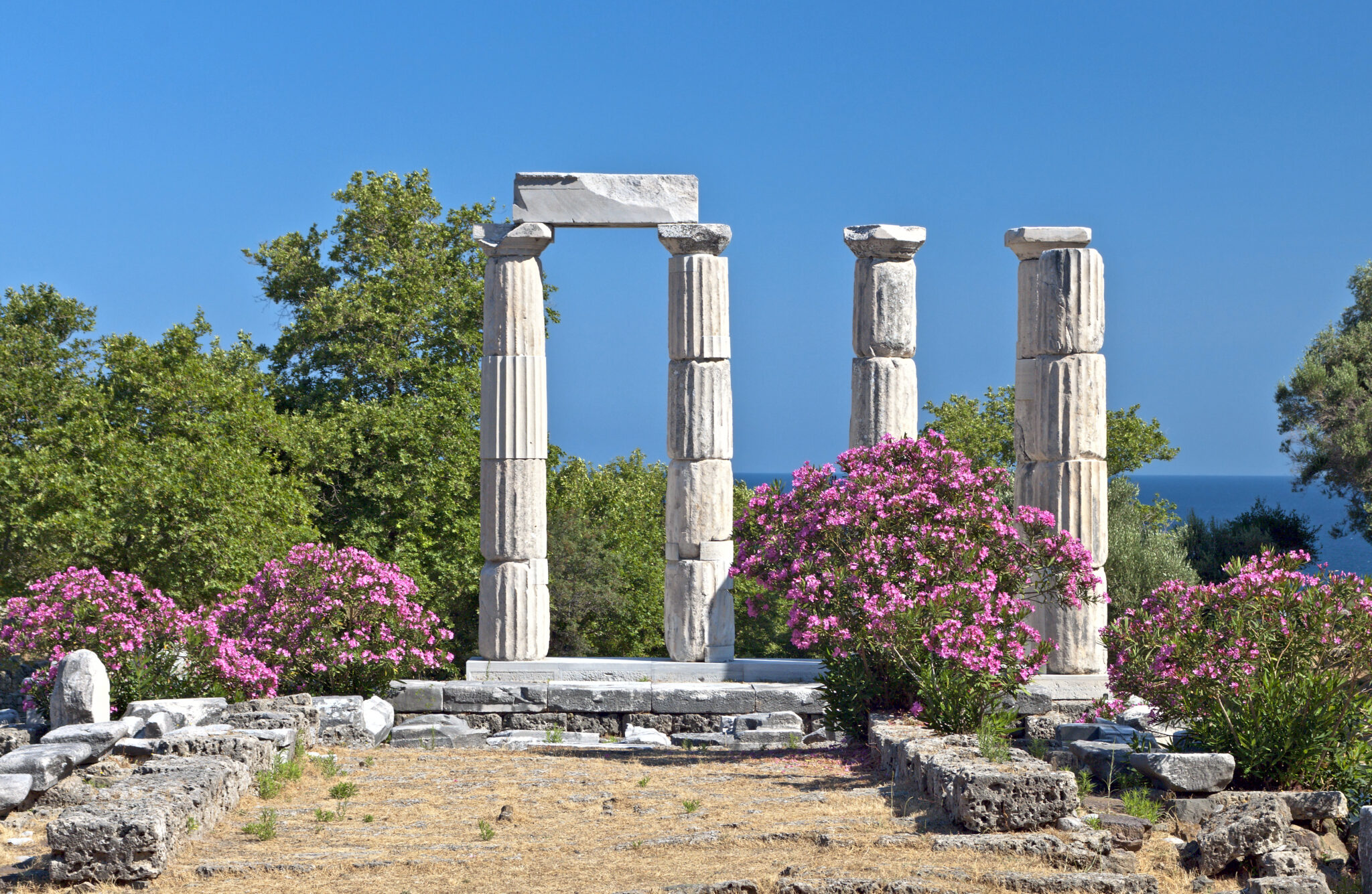

Photo: Shutterstock

Sanctuary of the Great Gods/Photo: Panagiotis Savvidis
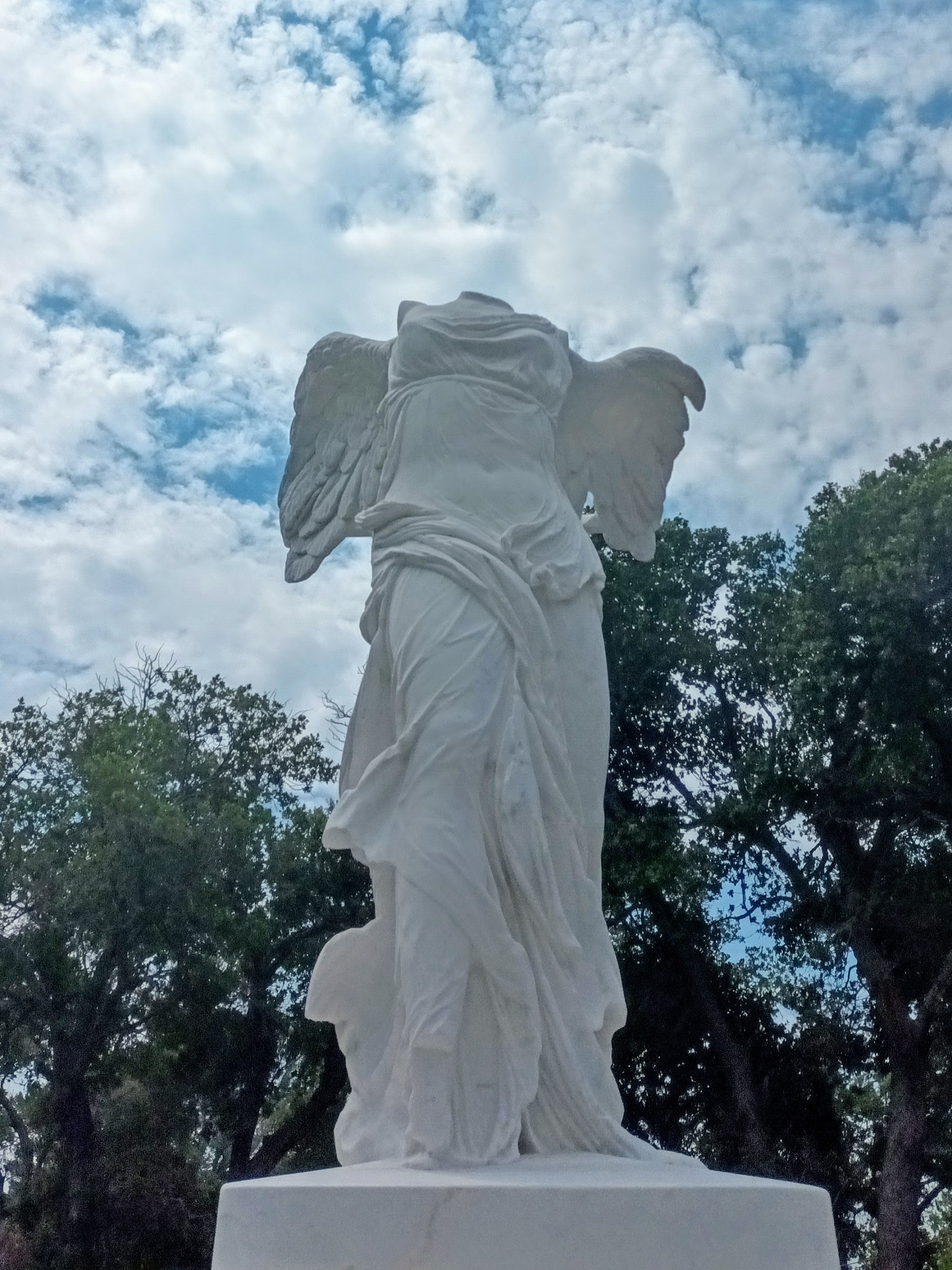

Replica of the Winged Victory of Samothrace/Photo: Panagiotis Savvidis
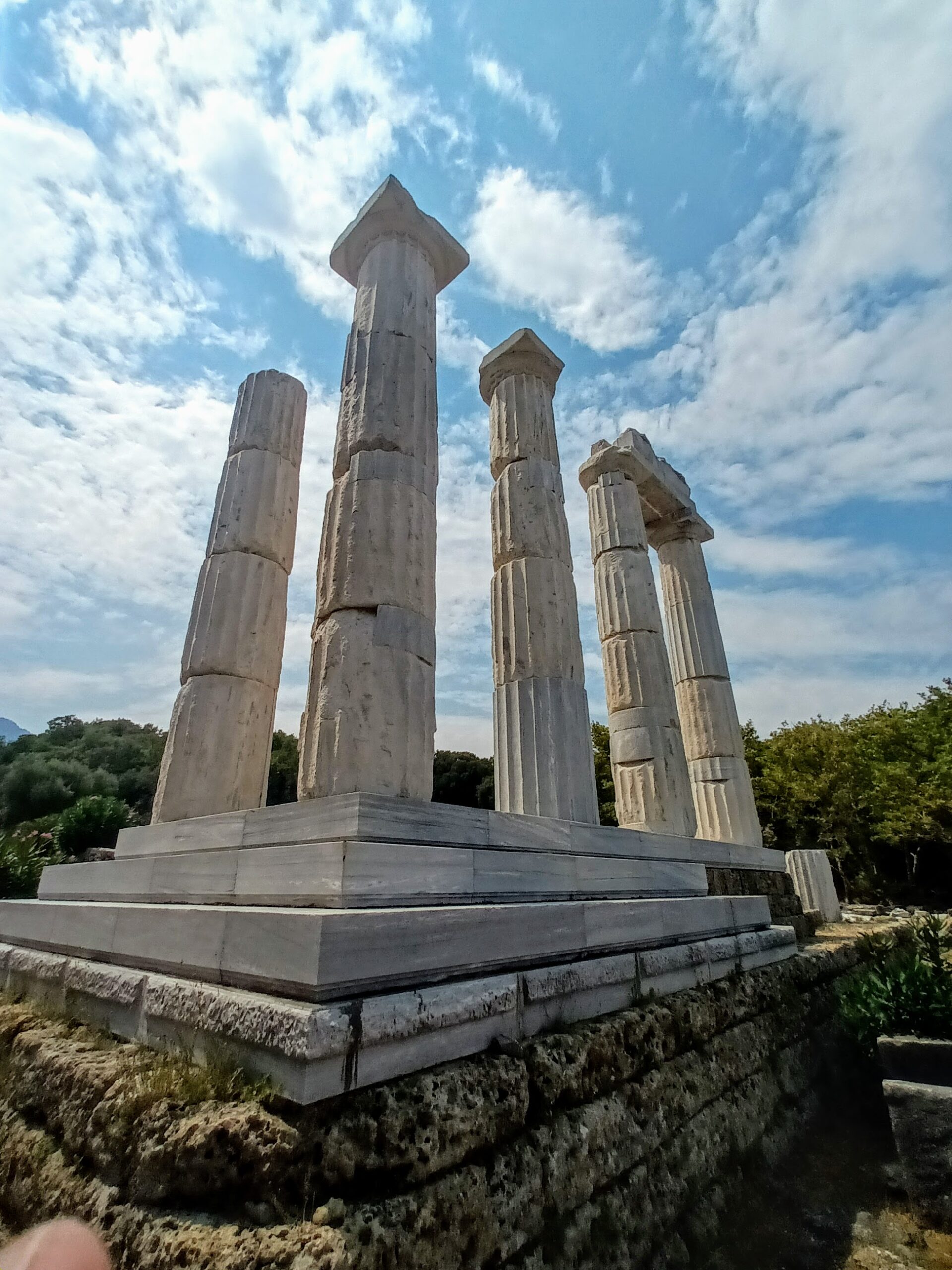
Sanctuary of the great gods, samothrace.
Venture into the Sanctuary of the Great Gods on Samothrace. Though now a serene archaeological site, it’s among the most enigmatic monuments in Greece. The site is entangled with the Kabeirian Mysteries, ancient rites venerating chthonic deities unfamiliar in mainland Greece.
At this sanctuary, Zeus , Hera , and Aphrodite were overlooked. Instead, aristocrats and slaves alike participated in secretive ceremonies, offering cryptic sacrifices to honour deities that remain, to this day, elusive to researchers.
Current findings suggest the Kabeirian Mysteries originated from ancient Anatolian religions, which found their way to Samothrace for reasons obscured by time. Legend has it, the site’s aura was so powerful that any uninitiated individual who dared to enter would invite grave misfortune, some said they would be cursed for life. Pay a visit to Samothrace and attempt to untangle this ancient enigma. Perhaps you’ll be the one to decode its mysteries.
Δείτε αυτή τη δημοσίευση στο Instagram. Η δημοσίευση κοινοποιήθηκε από το χρήστη John Xenos (@giannhs_xenos)
War Museum of Leros
Among the murkier recesses of the Leros tunnel, one can glimpse relics of a bleaker past: Fascist Italy’s symbology, Nazi Germany’s anti-asphyxiation suits, helmets peppered with bullet holes, and even submarine torpedoes, all displayed with a certain morose pride.
Δείτε αυτή τη δημοσίευση στο Instagram. Η δημοσίευση κοινοποιήθηκε από το χρήστη Іван Олександрович Каберне (@ivankaberne)
This tunnel bore witness to the Battle of Leros, where Fascist Italy’s forces bit, scratched, and clawed to retain one of their last territories in the Eastern Mediterranean. A visit, is guaranteed to send shivers down your spine. You’ll be handed a shot-sized, yet potent taste of the horrors from humanity’s darkest war in recent history.
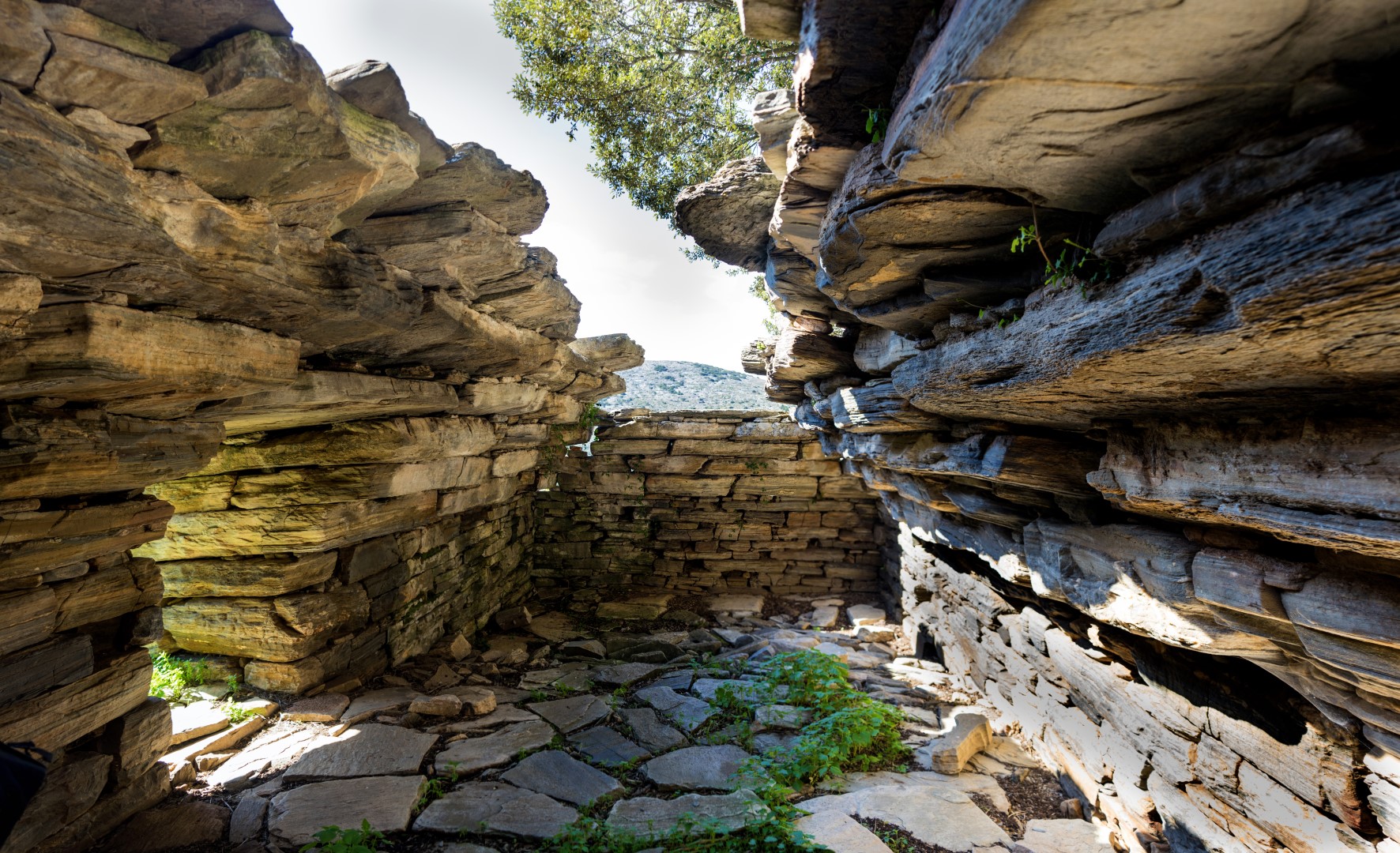

Dragon Houses of Southern Euboea/Photo: Shutterstock
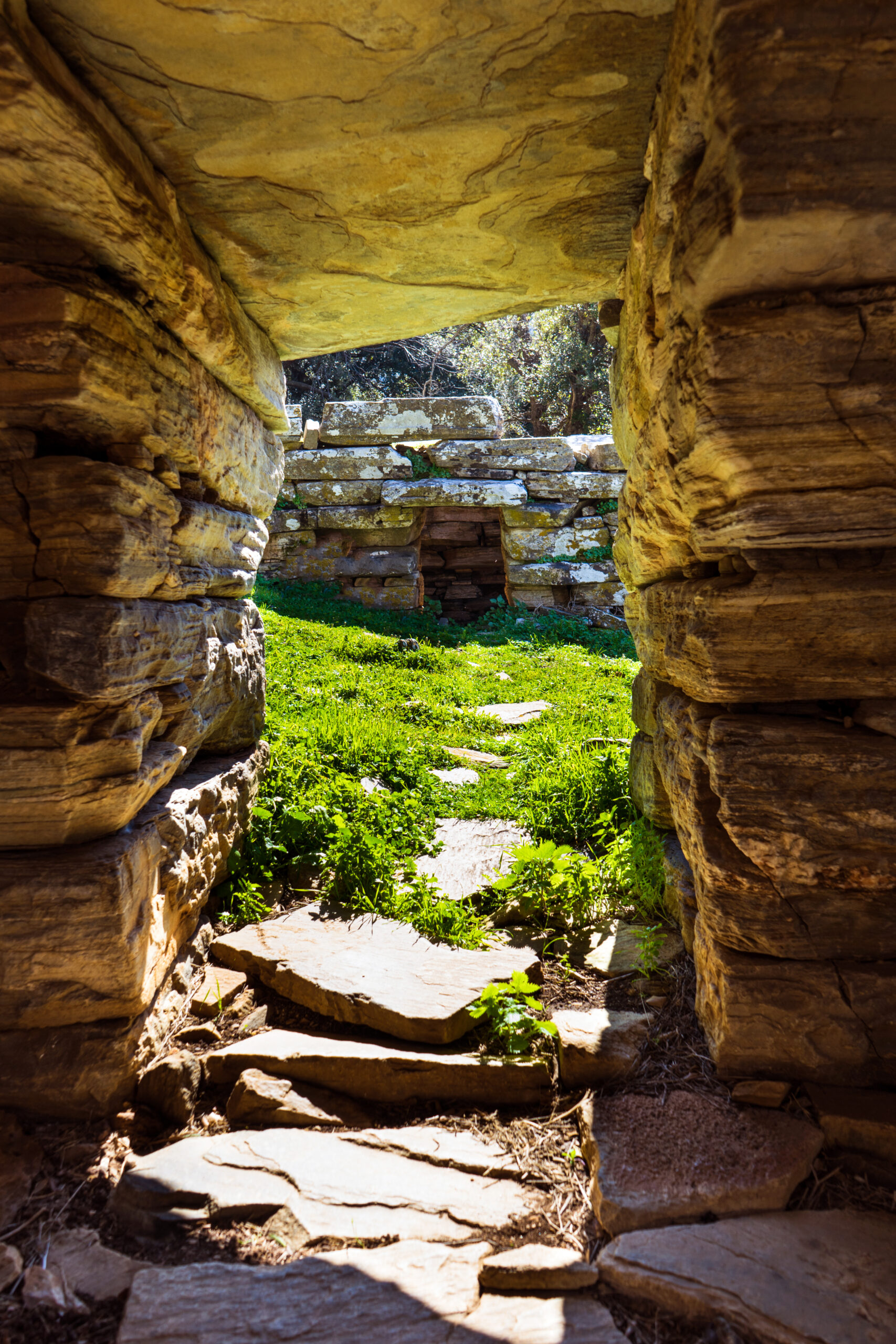

Dragon Houses of Southern Euboea/Evia
Next, let’s explore the enigmatic Dragon Houses of Southern Euboea. Only 25 of these enigmatic structures exist, and their purpose remains a riddle. Were they homes, places for exiles, or temples? We’re not certain. Constructed in the early Hellenistic period, these Dragon Houses are monolithic stone structures set at dominating locations.
These edifices, made of enormous grey stones, were presumably built by individuals with Herculean strength. With no definitive findings in the area, it’s almost as if these houses sprang from the earth. Surely, a tale that’d set your ‘dark intrigue’ alarm ringing.
So, if you’re eager to uncover the secrets of the Dragon Houses, all you need is a comfortable pair of shoes and an appetite for mystery. And remember, if you manage to solve this enigma, do share your revelation. We’d all love to delve deeper into the true purpose of these mysterious structures.
Medieval castles and peculiar Dragon houses in a charming destination in Greece
Eastern Crete’s Charm: History, Luxury and Authenticity
Mystic Samothrace – Extreme activities for adventure seekers
RELATED ARTICLES

UNKNOWN GREECE
Prassa, kimolos’ postcard-perfect beach.

FOOD & DRINK
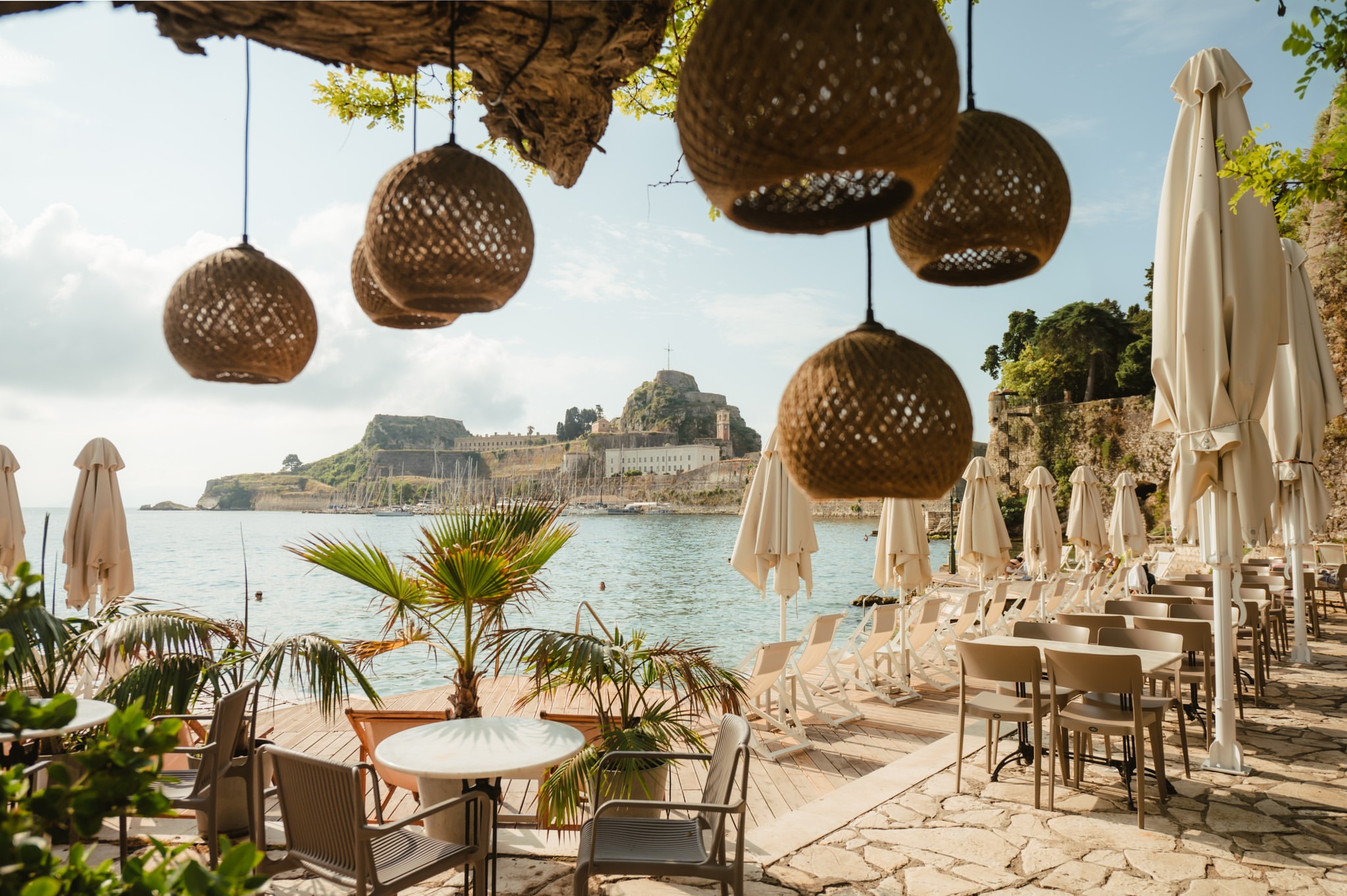
Hanging loose at corfu’s best beach clubs in 2024.
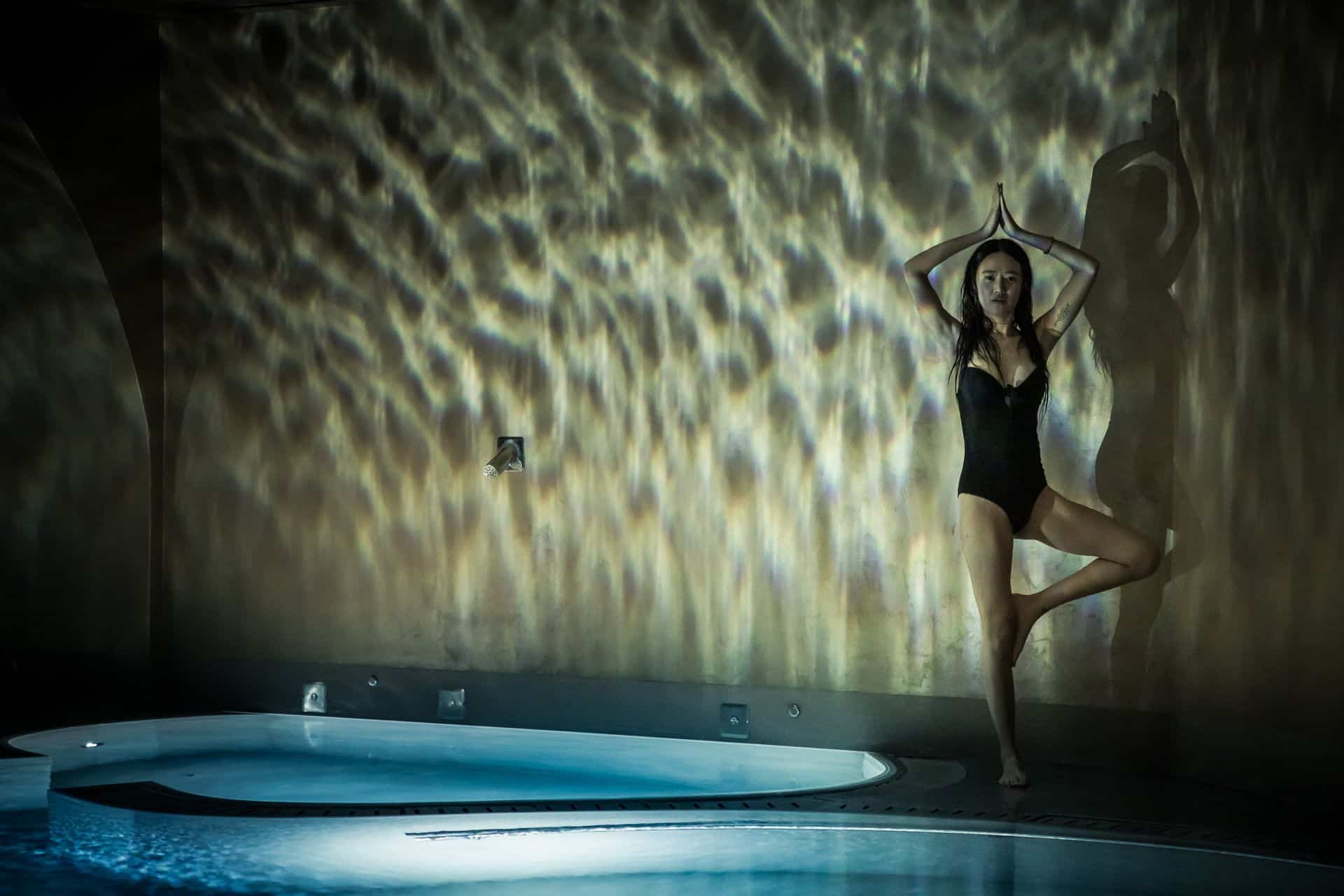

Greece’s Best Yoga Destinations in 2024
Ano Taxiarches: Ilia’s Unique Traditional Settlement
Dark Tourism and Cultural Resources: Investigating the Local Stakeholders’ Perceptions in Thessaloniki, Greece
- Conference paper
- First Online: 29 May 2024
- Cite this conference paper

- Anna Kyriakaki 3 ,
- Petros Papastefanou nAff3 &
- Eirini Arvanitaki nAff4
Part of the book series: Springer Proceedings in Business and Economics ((SPBE))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Conference of the International Association of Cultural and Digital Tourism
Many researchers view dark tourism as the dark side of cultural tourism or an authentic glance at cultural and heritage resources. Noteworthy is the fact that there is an essential connection between cultural tourism and dark tourism. But what is the difference between them? Is Dark tourism a worthwhile development choice for destinations and historical cities? To answer these questions, this paper investigates the perceptions of local stakeholders in the historical city of Thessaloniki, Greece. The qualitative method was used through personal interviews with local stakeholders. The results of the research indicate that cultural resources, such as historical buildings or sites, local myths, urban legends, monuments, religious sites, cemeteries, historical narratives, etc., could attract not only cultural tourists but also dark tourists. Additionally, stakeholders recognize the importance of dark tourism as niche tourism based on seeking authentic experiences, especially by tourists with an emotional involvement or connection with the destination. Also, their responses indicate that dark tourism can provide many chances for historical cities to succeed in sustainable tourism development through the utilization and prominence of cultural resources (tangible and intangible).
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Allman, H. (2017). Motivations and intentions of tourists to visit dark tourism locations . Iowa State University.
Book Google Scholar
Ashworth, G. J., & Tunbridge, J. E. (1990). The tourist-historic city . Belhaven.
Google Scholar
Auschwitz-Birkenau State Museum. (2020). 2 million 320 thousand visitors at the Auschwitz Memorial in 2019. Scribbr http://www.auschwitz.org/en/museum/news/2-million-320-thousand-visitors-at-the-auschwitz-memorial-in-2019,1400.html
Babbie, E. (2011). Introduction in social research . Kritiki. (in Greek).
Battilani, P., Bernini, C., & Mariotti, A. (2018). How to cope with dissonant heritage: A way towards sustainable tourism development. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 26 (8), 1417–1436. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2018.1458856
Article Google Scholar
Best, M. (2007). Norfolk Island: Thanatourism, history and visitor emotions. Shima: The International Journal of Research into Island Cultures , 1 (2), 30–48.
Biran, A., Poria, Y., & Oren, G. (2011). Sought experiences at (dark) heritage sites. Annals of Tourism Research, 38 (3), 820–841.
Bittner, M. (2011). Dark tourism: evaluation of visitors experience after visiting thanatological tourist attractions. Turizam, 15 (4) 148–158. https://doi.org/10.5937/Turizam1104148B
Bowman, M. S., & Pezzullo, P. C. (2009). What’s so ‘Dark’ about ‘Dark Tourism’? Death, tours, and performance. Tourist Studies, 9 (3), 187–202. https://doi.org/10.1177/1468797610382699
Brown, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research Psychology, 3 , 77–101.
Causevic, S., & Lynch, P. A. (2011). Phoenix tourism: Post-conflict tourism role. Annals of Tourism Research, 38 (3), 780–800.
Christou, E. (2019). Dark tourism, Philoxenia Thessaloniki. Scribbr https://philoxenia.helexpo.gr/sites/default/files/gfx/2019/dark_tourism/20191112pre/dark-tourism-christou.pdf
Cohen, E. (2018). Thanatourism: A comparative approach. In P. R. Stone, R. Hartmann, T. Seaton, R. Sharpley, & L. White (Eds.), Handbook of dark tourism (pp. 157–171). Palgrave Macmillan.
Cohen, E. (2011). Educational dark tourism at an in popular site: The Holocaust Museum in Jerusalem. Annals of Tourism Research, 38 (1), 193–209.
Dale, C., & Robinson, N. (2011). Research themes for tourism (pp. 205–217). CABI.
Dann, G. (1998). The dark side of tourism . University of Luton.
Deerwester, J. (2019). Chernobyl snags 19 Emmy nominations, inspiring tourism wave. But is disaster site safe? USA TODAY . Scribbr https://eu.usatoday.com/story/travel/destinations/2019/07/15/chernobyl-becomeofficial-tourist-attraction-but-safe/1712623001/ , 02.09.2019.
Foley, M., & Lennon, J. J. (1996). JFK and dark tourism: A fascination with assassination. International Journal of Heritage Studies, 2 (4), 198–211. https://doi.org/10.1080/13527259608722175
Galanis, P. (2018). Data analysis in qualitative research. Thematic analysis. Archives of Greek Medicine, 35 (3), 416–421.
Garcia, B. R. (2012). Management issues in dark tourism attractions: The case of ghost tours in Edinburgh and Toledo. Journal of Unconventional Parks, Tourism and Recreational Research, 4 (1), 14–19.
Hanks, M. (2016). Haunted heritage: The cultural politics of ghost tourism, populism, and the past . Routledge.
Henderson, J. (2001). War as a tourist attraction: The case of Vietnam. International Journal of Tourism, 2 (4), 269–280.
Heřmanová, Ε, & Abrhám, J. (2015). Holocaust tourism as a part of the dark tourism. Czech Journal of Social Sciences, Business and Economics, 4 , 16–33.
Holmes, M., & Inglis, D. (2004). Selling the Specter: Ghost stories and tourism in modern Scotland. Studies in Travel Writing, 8 (2), 107–123.
Jureniene, V., & Radzevicius, M. (2022). Peculiarities of sustainable cultural development: A case of dark tourism in Lithuania. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 15 (6), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15060264
Kazalarska, S. (1998). ‘Dark Tourism’: Reducing dissonance in the interpretation of atrocity at selected museums in Washington, D.C.
Kunwar, R. R., & Karki, N. (2019). Dark tourism: Understanding the concept and recognizing the values. Journal of APF Command and Staff College, 2 (1), 42–59. https://doi.org/10.3126/japfcsc.v2i1.26731
Larson, J., & Urry, G. (1990). Gazing and performing. In The tourist Gaze .
Lennon, J. J., & Seaton, A. V. (2004). Thanatourism in the early 21st century: Moral panics, ulterior motives and alterior desires. In T. V. Singh (Ed.), New horizons in tourism: Strange experiences and stranger practices (pp. 63–82). CABI. https://doi.org/10.1079/9780851998633.0063
Lennon, J. J., & Foley, M. (1999). Interpretation of the unimaginable: The U.S. Holocaust memorial museum, Washington, D. C., and “dark tourism”. Journal of Travel Research , 38 (1), 46–50.
Lennon, J. J., & Foley, M. (2000). Dark tourism: The attraction of death and disaster . Continuum.
Lewis, H., Schrier, T., & Xu, S. (2022). Dark tourism: Motivations and visit intentions of tourists. International Hospitality Review, 36 (1), 107–123. https://doi.org/10.1108/IHR-01-2021-0004
Liberato, D., Liberato, P., & Gonçalves, A. (2019). Dark tourism, the dark side of cultural tourism. Application to the city of Porto. In V. Katsoni, & M. Segarra-Oña (Eds.), Smart Tourism as a Driver for Culture and Sustainability. Springer Proceedings in Business and Economics . Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03910-3_12
Light, D. (2017). Progress in dark tourism and thanatourism research: An uneasy relationship with heritage tourism. Tourism Management, 61 , 275–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2017.01.011
McCain, G., & Ray, N. M. (2003). Legacy tourism: The search for personal meaning in heritage travel. Tourism Management, 24 (6), 713–717.
Minic, N. (2012). Development of “dark” tourism in the contemporary society. Journal of the Geographical Institute Jovan Cvijic, SASA, 62 , 81–103.
Pelton, R. (2003). The world’s most dangerous places (5th ed.). Harper Resource.
Podoshen, J. S., Venkatesh, V., & Jin, Z. (2014). Theoretical reflections on dystopian consumer culture: Black metal. Marketing Theory, 14 (2), 207–227.
Raine, R. (2013). A dark tourism spectrum. International Journal of Culture, Tourism and Hospitality Research, 7 (3), 242–256.
Robb, E. (2009). Violence and recreation: Vacationing in the realm of dark tourism. Anthropology and Humanism, 34 (1), 51–60.
Ryan, C. (2007). Battlefield tourism: History, place and interpretation . Elsevier.
Sharpley, R. (2014). Host perceptions of tourism: A review of the research. Tourism Management, 42 , 37–49.
Sharpley, R., & Stone, P. R. (Eds.) (2009). The darker side of travel: The theory and practice of dark tourism. Aspects of tourism series . Channel View Publications.
Stone, P. R. (2011). Dark tourism: Towards a new post-disciplinary research agenda. International Journal of Tourism Anthropology, 1 (3/4), 318–332.
Stone, P. R. (2006). A dark tourism spectrum: Towards a typology of death and macabre related tourist sites, attractions and exhibitions. Tourism: An Interdisciplinary International Journal , 54 (2), 145–160.
Strange, C., & Kempa, M. (2003). Shades of dark tourism: Alcatraz and Robben Island. Annals of Tourism Research, 30 (2), 386–405.
Tercia, C., Teichert, T., Sirad, D. A., & Murniadi, K. (2022). Storytelling in the communication of dark tourism. Consumer Behavior in Tourism and Hospitality, 17 (1), 107–126. https://doi.org/10.1108/CBTH-06-2021-0152
Trihas, N., Zouganeli, S., & Antonaki, M. (2012). TV-induced tourism in “The Island” of Spinalonga. In International Conference on Tourism (ICOT2012) Setting the Agenda for Special Interest Tourism: Past, Present and Future , 23–26 May, Archanes, Crete, Greece.
Tsartas, P., Zagkotsi, S., & Kyriakaki, A. (2020). Tourists, travels, places. Sociology tourism approaches . Kritiki (in Greek).
Tsironis, C. (2019). Dark tourism, Philoxenia Thessaloniki. Scribbr https://philoxenia.helexpo.gr/sites/default/files/gfx/2019/dark_tourism/20191112pre/dark-tourism-tsironis.pdf
Walter, T. (2009). Dark tourism: Mediating between the dead and the living. In R. Sharpley, & P. R. Stone (Ed.), The darker side of travel: The theory and practice of dark tourism (pp. 39–55). Channel View Publications. https://doi.org/10.21832/9781845411169-004
Yan, B. J., Zhang, J., Zhang, H. L., Lu, S. J., & Guo, Y. R. (2016). Investigating the motivation experience relationship in a dark tourism space: A case study of the Beichuan earthquake relics, China. Tourism Management, 53 , 108–112.
Yankholmes, A., & McKercher, B. (2015). Understanding visitors to slavery heritage sites in Ghana. Tourism Management, 51 , 22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2015.04.003
Yuill, S. M. (2003). Dark tourism: Understanding visitor motivation at sites of death and disaster [MB thesis]. Texas A&M University. Scribbr https://hdl.handle.net/1969.1/89
Zheng, C., Zhang, J., Qian, L., Jurowski, C., Zhang, H., & Yan, B. (2018). The inner struggle of visiting ‘dark tourism’ sites: Examining the relationship between perceived constraints and motivations. Current Issues in Tourism, 21 (15), 1710–1727. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2016.1220512
Download references
Author information
Petros Papastefanou
Present address: University of the Aegean, Chios, Greece
Eirini Arvanitaki
Present address: Hellenic Open University, Heraklion, Greece
Authors and Affiliations
University of the Aegean, Chios, Greece
Anna Kyriakaki
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Anna Kyriakaki .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
University of West Attica, Athens, Greece
Vicky Katsoni
University of Malta, Msida, Malta
George Cassar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Kyriakaki, A., Papastefanou, P., Arvanitaki, E. (2024). Dark Tourism and Cultural Resources: Investigating the Local Stakeholders’ Perceptions in Thessaloniki, Greece. In: Katsoni, V., Cassar, G. (eds) Recent Advancements in Tourism Business, Technology and Social Sciences. IACuDiT 2023. Springer Proceedings in Business and Economics. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-54338-8_51
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-54338-8_51
Published : 29 May 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-54337-1
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-54338-8
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
National Geographic content straight to your inbox—sign up for our popular newsletters here

Dark tourism: when tragedy meets tourism
The likes of Auschwitz, Ground Zero and Chernobyl are seeing increasing numbers of visitors, sparking the term 'dark tourism'. But is it voyeuristic or educational?
Days after 71 people died in a London tower block fire last June, something strange started to happen in the streets around it. Posters, hastily drawn by members of the grieving community of Grenfell Tower, appeared on fences and lamp posts in view of the building's blackened husk.
'Grenfell: A Tragedy Not A Tourist Attraction,' one read, adding — sarcastically — a hashtag and the word 'selfies'. As families still searched for missing inhabitants of the 24-storey block, and the political shock waves were being felt through the capital, people had started to arrive in North Kensington to take photos. Some were posing in selfie mode.
"It's not the Eiffel Tower," one resident told the BBC after the posters attracted the attention of the press. "You don't take a picture." Weeks later, local people were dismayed when a coachload of Chinese tourists pulled up nearby so that its occupants could get out and take photos.
Grenfell Tower, which still dominates the surrounding skyline (it's due to be demolished in late 2018), had become a site for 'dark tourism', a loose label for any sort of tourism that involves visiting places that owe their notoriety to death, disaster, an atrocity or what can also loosely be termed 'difficult heritage'.
It's a phenomenon that's on the rise as established sites such as Auschwitz and the September 11 museum in Manhattan enjoy record visitor numbers. Meanwhile, demand is rising among those more intrepid dark tourists who want to venture to the fallout zones of Chernobyl and Fukushima, as well as North Korea and Rwanda. In Sulawesi, Indonesia, Western tourists wielding GoPros pay to watch elaborate funeral ceremonies in the Toraja region, swapping notes afterwards on TripAdvisor.
Along the increasingly crowded dark-tourist trail, academics, tour operators and the residents of many destinations are asking searching questions about the ethics of modern tourism in an age of the selfie and the Instagram hashtag. When Pompeii, a dark tourist site long before the phrase existed, found itself on the Grand Tour of young European nobility in the 18th century, dozens of visitors scratched their names into its excavated walls. Now we leave our mark in different ways, but where should we draw the boundaries?
Questions like these have become the life's work of Dr Philip Stone , perhaps the world's leading academic expert on dark tourism. He has a background in business and marketing, and once managed a holiday camp in Scotland. But a fascination with societal attitudes to mortality led to a PhD in thanatology, the study of death, and a focus on tourism.
"I'm not even a person who enjoys going to these places," Stone says from the University of Central Lancashire, where he runs the Institute for Dark Tourism Research. "But what I am interested in is the way people face their own mortality by looking at other deaths of significance. Because we've become quite divorced from death yet we have this kind of packaging up of mortality in the visit economy which combines business, sociology, psychology under the banner of dark tourism. It's really fascinating to shine a light on that."
Historical roots
The term 'dark tourism' is far newer than the practice, which long predates Pompeii's emergence as a morbid attraction. Stone considers the Roman Colosseum to be one of the first dark tourist sites, where people travelled long distances to watch death as sport. Later, until the late 18th century, the appeal was starker still in central London, where people paid money to sit in grandstands to watch mass executions. Hawkers would sell pies at the site, which was roughly where Marble Arch stands today.
It was only in 1996 that 'dark tourism' entered the scholarly lexicon when two academics in Glasgow applied it while looking at sites associated with the assassination of JFK. Those who study dark tourism identify plenty of reasons for the growing phenomenon, including raised awareness of it as an identifiable thing. Access to sites has also improved with the advent of cheap air travel. It's hard to imagine that the Auschwitz-Birkenau memorial and museum would now welcome more than two million visitors a year (an average of almost 5,500 a day, more than two-thirds of whom travel to the Polish site from other countries in Europe) were it not for its proximity to Krakow's international airport.
Peter Hohenhaus, a widely travelled dark tourist based in Vienna, also points to the broader rise in off-the-beaten track tourism, beyond the territory of popular guidebooks and TripAdvisor rankings. "A lot of people don't want mainstream tourism and that often means engaging with places that have a more recent history than, say, a Roman ruin," he says. "You go to Sarajevo and most people remember the war being in the news so it feels closer to one's own biography."
Hohenhaus is also a fan of 'beauty in decay', the contemporary cultural movement in which urban ruins have become subject matter for expensive coffee-table books and a thousand Instagram accounts. The crossover with death is clear. "I've always been drawn to derelict things," the 54-year-old says. As a child in Hamburg, he would wonder at the destruction of war still visible around the city's harbour.
That childhood interest has developed into an obsession; Hohenhaus has visited 650 dark tourist sites in 90 countries, logging them all and more besides on his website . He has plans to put together the first dark tourism guidebook. His favourite holiday destination today is Chernobyl and its 'photogenic' ghost town. "You get to time travel back into the Soviet era but also into an apocalyptic future," he says. He also enjoys being emotionally challenged by these places. "I went to Treblinka in 2008 and heard the story of a teacher at an orphanage in Warsaw who was offered a chance to escape but refused and went with his children to the gas chambers. Stories like that are not everyday, you mull over them. Would you have done that?"
But while, like any tourism, dark tourism at its best is thought-provoking and educational, the example of Grenfell Tower hints at the unease felt at some sites about what can look like macabre voyeurism. "I remember the Lonely Planet Bluelist book had a chapter about dark tourism a while ago and one of the rules was 'don't go back too early'," Hohenhaus says. "But that's easier said than calculated. You have to be very aware of reactions and be discreet when you're not in a place with an entrance fee and a booklet." Hohenhaus said he had already thought about Grenfell Tower and admits he would be interested to see it up close. "It's big, it's dramatic, it's black and it's a story you've followed in the news," he says. "I can see the attraction. But I would not stand in the street taking a selfie."
A mirror to mortality
An urge to see and feel a place that has been reduced to disaster shorthand by months of media coverage is perhaps understandable, but Stone is most interested in the draw — conscious or otherwise — of destinations that hold up a mirror to our own mortality. "When we touch the memory of people who've gone what we're looking at is ourselves," he says. "That could have been us in that bombing or atrocity. We make relevant our own mortality." That process looks different across cultures — and generations — and Stone says we should take this into account before despairing of selfie takers at Grenfell Tower or Auschwitz.
"I've heard residents at Grenfell welcoming visitors because it keeps the disaster in the public realm, but they didn't like people taking photos because it's a visual reminder that you're a tourist and therefore somehow defunct of morality," he explains. "We're starting to look at selfies now. Are they selfish?" Stone argues that the language of social media means we no longer say "I was here", but "I am here — see me". He adds: "We live in a secular society where morality guidelines are increasingly blurred. It's easy for us to say that's right or wrong, but for many people it's not as simple as that."
"Travel itself is innately voyeuristic," argues Simon Cockerel, the general manager of Koryo Tours , a North Korea specialist based in Beijing. Cockerel, who has lived in China for 17 years and joined Koryo in 2002, says demand has grown dramatically for trips to Pyongyang and beyond, from 200 people a year in the mid 1990s, when the company started, to more than 5,000 more recently. He has visited the country more than 165 times and says some clients join his tours simply to bag another country, and some for bragging rights. But the majority have a genuine interest in discovering a country — and a people — beyond the headlines.
"I've found everyone who goes there to be sensitive and aware of the issues," he says. "The restrictions do create a framework for it to be a bit like a theme park visit but we work hard to blur those boundaries. More than 25 million people live in North Korea, and 24.99 million of them have nothing to do with what we read in the news and deserve to be seen as people not as zoo animals or lazy caricatures."
More challenging recently has been the US ban on its citizens going to North Korea, imposed last summer after the mysterious death of Otto Warmbier. The American student had been arrested in Pyongyang after being accused of trying to steal a propaganda poster. Americans made up about 20% of Koryo's business, but Cockerel argues the greater loss is to mutual perception in the countries. "The North Korean government represent Americans as literal wolves with sharpened nails," he says. "At least a few hundred Americans going there was a kind of bridgehead against that. Now that's gone."
At Grenfell Tower, responsible tourism may yet serve to keep alive the memory of the disaster, just as it does, after a dignified moratorium, at Auschwitz and the former Ground Zero. Hohenhaus says he will resist the urge to go until some sort of memorial is placed at the site of the tower. At around the time of a commemorative service at St Paul's Cathedral six months after the fire, there were calls for the site eventually to be turned into a memorial garden. The extent to which Hohenhaus and other dark tourists are welcomed will be decided by the people still living there.
Five of the world's dark tourism sites
1. North Korea Opened to visitors in the late 1980s, North Korea now attracts thousands of tourists each year for a peek behind the headlines.
2. Auschwitz-Birkenau The former Nazi death camp became a memorial in 1947 and a museum in 1955. It's grown since and in 2016 attracted a record two million visitors.
3. 9/11 Memorial and Museum Built in the crater left by the twin towers of the World Trade Center, the museum, opened in 2014, has won plaudits for its portrayal of a disaster and its impact.
4. Rwanda Visitor numbers to genocide memorials have grown in Cambodia and Bosnia as well as in Rwanda, where there are several sites dedicated to the 1994 massacre of up to a million people. The skulls of victims are displayed.
5. Chernobyl & Pripyat, Ukraine Several tour companies exist to send visitors to the exclusion zone and ghost town left otherwise empty after the nuclear accident in 1986. All are scanned for radiation as they leave.
Published in the March 2018 issue of National Geographic Traveller (UK)
Find us on social media
Facebook | Instagram | Twitter
Related Topics
- EDUCATIONAL TRAVEL
- CULTURAL TOURISM
- HISTORY AND CIVILIZATION
You May Also Like

They inspire us and teach us about the world: Meet our 2024 Travelers of the Year

An insider's guide to Denver, Colorado's wildly creative capital
For hungry minds.

10 reasons to visit the East Coast in 2024

An architectural tour of the Georgian capital, Tbilisi

7 of the UK's best gallery cafes

A long weekend in Orkney

How to plan a walking tour of Glasgow in the footsteps of Charles Rennie Mackintosh
- Environment
- Paid Content
- Photography
- Perpetual Planet
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
Dialogue in the Dark

Top ways to experience nearby attractions

Most Recent: Reviews ordered by most recent publish date in descending order.
Detailed Reviews: Reviews ordered by recency and descriptiveness of user-identified themes such as wait time, length of visit, general tips, and location information.
Also popular with travelers

Dialogue in the Dark - All You Need to Know BEFORE You Go (2024)
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Beaches? Cruises? ‘Dark’ Tourists Prefer the Gloomy and Macabre
Travelers who use their off time to visit places like the Chernobyl nuclear plant or current conflict zones say they no longer want a sanitized version of a troubled world.

By Maria Cramer
North Korea. East Timor. Nagorno-Karabakh, a mountainous enclave that for decades has been a tinderbox for ethnic conflict between Armenians and Azerbaijanis.
They’re not your typical top tourist destinations.
But don’t tell that to Erik Faarlund, the editor of a photography website from Norway, who has visited all three. His next “dream” trip is to tour San Fernando in the Philippines around Easter , when people volunteer to be nailed to a cross to commemorate the suffering of Jesus Christ, a practice discouraged by the Catholic Church.
Mr. Faarlund, whose wife prefers sunning on Mediterranean beaches, said he often travels alone.
“She wonders why on earth I want to go to these places, and I wonder why on earth she goes to the places she goes to,” he said.
Mr. Faarlund, 52, has visited places that fall under a category of travel known as dark tourism , an all-encompassing term that boils down to visiting places associated with death, tragedy and the macabre.
As travel opens up, most people are using their vacation time for the typical goals: to escape reality, relax and recharge. Not so dark tourists, who use their vacation time to plunge deeper into the bleak, even violent corners of the world.
They say going to abandoned nuclear plants or countries where genocides took place is a way to understand the harsh realities of current political turmoil, climate calamities, war and the growing threat of authoritarianism.
“When the whole world is on fire and flooded and no one can afford their energy bills, lying on a beach at a five-star resort feels embarrassing,” said Jodie Joyce, who handles contracts for a genome sequencing company in England and has visited Chernobyl and North Korea .
Mr. Faarlund, who does not see his travels as dark tourism, said he wants to visit places “that function totally differently from the way things are run at home.”
Whatever their motivations, Mr. Faarlund and Ms. Joyce are hardly alone.
Eighty-two percent of American travelers said they have visited at least one dark tourism destination in their lifetime, according to a study published in September by Passport-photo.online, which surveyed more than 900 people. More than half of those surveyed said they preferred visiting “active” or former war zones. About 30 percent said that once the war in Ukraine ends, they wanted to visit the Azovstal steel plant, where Ukrainian soldiers resisted Russian forces for months .
The growing popularity of dark tourism suggests more and more people are resisting vacations that promise escapism, choosing instead to witness firsthand the sites of suffering they have only read about, said Gareth Johnson, a founder of Young Pioneer Tours , which organized trips for Ms. Joyce and Mr. Faarlund.
Tourists, he said, are tired of “getting a sanitized version of the world.”
A pastime that goes back to Gladiator Days
The term “dark tourism” was coined in 1996, by two academics from Scotland, J. John Lennon and Malcolm Foley, who wrote “Dark Tourism: The Attraction to Death and Disaster.”
But people have used their leisure time to witness horror for hundreds of years, said Craig Wight, associate professor of tourism management at Edinburgh Napier University.
“It goes back to the gladiator battles” of ancient Rome, he said. “People coming to watch public hangings. You had tourists sitting comfortably in carriages watching the Battle of Waterloo.”
Professor Wight said the modern dark tourist usually goes to a site defined by tragedy to make a connection to the place, a feeling that is difficult to achieve by just reading about it.
By that definition, anyone can be a dark tourist. A tourist who takes a weekend trip to New York City may visit Ground Zero. Visitors to Boston may drive north to Salem to learn more about the persecution of people accused of witchcraft in the 17th century. Travelers to Germany or Poland might visit a concentration camp. They might have any number of motivations, from honoring victims of genocide to getting a better understanding of history. But in general, a dark tourist is someone who makes a habit of seeking out places that are either tragic, morbid or even dangerous, whether the destinations are local or as far away as Chernobyl.
In recent years, as tour operators have sprung up worldwide promising deep dives into places known for recent tragedy, media attention has followed and so have questions about the intentions of visitors, said Dorina-Maria Buda, a professor of tourism studies at Nottingham Trent University .
Stories of people gawking at neighborhoods in New Orleans destroyed by Hurricane Katrina or posing for selfies at Dachau led to disgust and outrage .
Were people driven to visit these sites out of a “sense of voyeurism or is it a sense of sharing in the pain and showing support?” Professor Buda said.
Most dark tourists are not voyeurs who pose for photos at Auschwitz, said Sian Staudinger, who runs the Austria-based Dark Tourist Trips , which organizes itineraries in the United Kingdom and other parts of Europe and instructs travelers to follow rules like “NO SELFIES!”
“Dark tourists in general ask meaningful questions,” Ms. Staudinger said. “They don’t talk too loud. They don’t laugh. They’re not taking photos at a concentration camp.”
‘Ethically murky territory’
David Farrier , a journalist from New Zealand, spent a year documenting travels to places like Aokigahara , the so-called suicide forest in Japan, the luxury prison Pablo Escobar built for himself in Colombia and McKamey Manor in Tennessee, a notorious haunted house tour where people sign up to be buried alive, submerged in cold water until they feel like they will drown and beaten.
The journey was turned into a show, “Dark Tourist,” that streamed on Netflix in 2018 and was derided by some critics as ghoulish and “sordid.”
Mr. Farrier, 39, said he often questioned the moral implications of his trips.
“It’s very ethically murky territory,” Mr. Farrier said.
But it felt worthwhile to “roll the cameras” on places and rituals that most people want to know about but will never experience, he said.
Visiting places where terrible events unfolded was humbling and helped him confront his fear of death.
He said he felt privileged to have visited most of the places he saw, except McKamey Manor.
“That was deranged,” Mr. Farrier said.
Professor Buda said dark tourists she has interviewed have described feelings of shock and fear at seeing armed soldiers on streets of countries where there is ongoing conflict or that are run by dictatorships.
“When you’re part of a society that is by and large stable and you’ve gotten into an established routine, travel to these places leads you to sort of feel alive,” she said.
But that travel can present real danger.
In 2015, Otto Warmbier , a 21-year-old student from Ohio who traveled with Young Pioneer Tours, was arrested in North Korea after he was accused of stealing a poster off a hotel wall. He was detained for 17 months and was comatose when he was released. He died in 2017, six days after he was brought back to the United States.
The North Korean government said Mr. Warmbier died of botulism but his family said his brain was damaged after he was tortured.
Americans can no longer travel to North Korea unless their passports are validated by the State Department.
A chance to reflect
Even ghost tours — the lighter side of dark tourism — can present dilemmas for tour operators, said Andrea Janes, the owner and founder of Boroughs of the Dead: Macabre New York City Walking Tours.
In 2021, she and her staff questioned whether to restart tours so soon after the pandemic in a city where refrigerated trucks serving as makeshift morgues sat in a marine terminal for months.
They reopened and were surprised when tours booked up fast. People were particularly eager to hear the ghost stories of Roosevelt Island, the site of a shuttered 19th-century hospital where smallpox patients were treated .
“We should have seen as historians that people would want to talk about death in a time of plague,” Ms. Janes said.
Kathy Biehl, who lives in Jefferson Township, N.J., and has gone on a dozen ghost tours with Ms. Janes’s company, recalled taking the tour “Ghosts of the Titanic” along the Hudson River. It was around 2017, when headlines were dominated by President Trump’s tough stance on refugees and immigrants coming into the United States.
Those stories seemed to dovetail with the 100-year-old tales of immigrants trying to make it to New York on a doomed ship, Ms. Biehl said.
It led to “a catharsis” for many on the tour, she said. “People were on the verge of tears over immigration.”
Part of the appeal of dark tourism is its ability to help people process what is happening “as the world gets darker and gloomier,” said Jeffrey S. Podoshen , a professor of marketing at Franklin and Marshall College, who specializes in dark tourism.
“People are trying to understand dark things, trying to understand things like the realities of death, dying and violence,” he said. “They look at this type of tourism as a way to prepare themselves.”
Mr. Faarlund, the photo editor, recalled one trip with his wife and twin sons: a private tour of Cambodia that included a visit to the Killing Fields , where between 1975 and 1979 more than 2 million Cambodians were killed or died of starvation and disease under the Khmer Rouge regime.
His boys, then 14, listened intently to unsparing and brutal stories of the torture center run by the Khmer Rouge. At one point, the boys had to go outside, where they sat quietly for a long time.
“They needed a break,” Mr. Faarlund said. “It was quite mature of them.”
Afterward, they met two of the survivors of the Khmer Rouge, fragile men in their 80s and 90s. The teenagers asked if they could hug them and the men obliged, Mr. Faarlund said.
It was a moving trip that also included visits to temples, among them Angkor Wat in Siem Reap, and meals of frog, oysters and squid at a roadside restaurant.
“They loved it,” Mr. Faarlund said of his family.
Still, he can’t see them coming with him to see people re-enact the crucifixion in the Philippines.
“I don’t think they want to go with me on that one,” Mr. Faarlund said.

52 Places for a Changed World
The 2022 list highlights places around the globe where travelers can be part of the solution.
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram , Twitter and Facebook . And sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to receive expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation. Dreaming up a future getaway or just armchair traveling? Check out our 52 Places for a Changed World for 2022.
Maria Cramer is a reporter on the Travel desk. Please send her tips, questions and complaints about traveling, especially on cruises. More about Maria Cramer
Open Up Your World
Considering a trip, or just some armchair traveling here are some ideas..
52 Places: Why do we travel? For food, culture, adventure, natural beauty? Our 2024 list has all those elements, and more .
The Alaska Highway: On an epic road trip, a family plots a course from Alaska to the Lower 48, passing through some of Canada’s most spectacular scenery .
Minorca: Spend 36 hours on this slow-paced Spanish island , which offers a quieter and wilder retreat than its more touristy neighbors.
Japan: A new high-speed train stop unlocks Kaga, a destination for hot springs, nourishing food and traditional crafts , as an easy-to-reach getaway from Tokyo.
London: The Victoria and Albert Museum is a treasure trove of art and design. Here’s one besotted visitor’s plan for taking it all in .
Tourism’s dark side: Are those who love Greece killing it?
Average Greek property prices increased by 12 percent last year and are set to increase by another 14 percent this year, according to Bank of Greece data.

Athens, Greece – Shortly after the conservative New Democracy party came to power in Greece in 2019, computer scientist Nikos Larisis left his job in the Netherlands and repatriated to the Mediterranean country for a salary worth a third of the 9,000 euros ($9,500) he was making per month.
He appeared to vindicate New Democracy’s pledge to bring back about half a million educated young workers who had fled the country’s economic depression from 2010 to 2018.
Keep reading
‘without rules we cannot live’: greece seeks ways to tackle ‘overtourism’ ‘without rules we cannot live’: greece ..., after slew of disasters, greeks wonder what is happening to their democracy after slew of disasters, greeks wonder ..., an ex-goldman sachs banker vies to preside over the troubled greek left an ex-goldman sachs banker vies to ....
The conservatives returned to power for a second term in June with little evidence that many Greeks had followed in Larisis’s footsteps.
Even he and his fiancee, Eleftheria Tsiartsiani, a public elementary schoolteacher, had been feeling stuck and were considering going abroad.
They were paying a quarter of their joint income in rent and could not borrow enough money to buy the two-bedroom home in which they dreamed of starting their family.
Then the government announced a 1.8-billion-euro ($1.9bn) programme to help young couples buy their first home.
“Eleftheria told me, ‘Niko, we can buy a home. We can reconsider. We needn’t pick up stakes and leave,'” Larisis told Al Jazeera.
But after looking into the government’s offer, called My Home, the couple became disillusioned.
“It wasn’t designed well at all. It led people on and destroyed their dreams,” Larisis said.

Larisis and Tsiartsiani could borrow 90,000 euros ($96,000) under the programme, but that did not secure an attractive family home in a market geared towards foreign buyers spending 250,000 euros ($270,000) for a Golden Visa, which at the time offered them five years of legal residence and a path to citizenship. The spending requirement for the Golden Visa has since changed to double that amount.
“I’m going to let the state keep its 90,000 euros,” Tsiartsiani said. “There’s no point in buying a small, old apartment, dark and dank, that doesn’t fit our needs, smelling of mould in an unkempt building and being in debt up to my neck for the rest of my life.”
Moreover, Tsiartsiani said: “We saw a lot of sales ads that stipulated, ‘The property isn’t for sale through the My Home programme.'”
Sellers told the couple they did not believe they would get their money from the government and wanted cash only.
The experience convinced the couple that Greek law was tilted in favour of non-Greeks.
My Home did not allow beneficiaries to rent out their property and restricted them to buying a property close to work. The Golden Visa programme has no such limitations.
“There’s a big party going on. Foreign capital is trying to take advantage of the situation here, and the laws are helping them. Golden Visas allow people to come and buy homes here … while others are struggling with loans they can’t repay,” Larisis said.
The sting in tourism’s tail
Greece’s big economic success under New Democracy has been tourism, which has boomed since the COVID-19 pandemic, attracting three times Greece’s population each year. It brought in a near-record 18 billion euros ($19bn) in revenue last year.
Tourism helps bring in the foreign currency with which Greece services its loans, and it has helped existing homeowners. About 105,000 properties are now offered on short-term rentals through Airbnb.
But it has also worsened a demographic problem. By restoring real estate value lost during the depression, it has put first homes out of the reach of young people.
“We emerged from the pandemic with a bit of extra cash, … which was mainly concentrated on housing,” said real estate consultant Stelios Bouras, who runs the Greek Guru real estate news website. “Working at home, people wanted larger houses. … This coincided also with a massive increase in Greek homes going to foreign buyers.”
Average Greek property prices increased by 12 percent last year, and are set to increase by another 14 percent this year, according to Bank of Greece data.
That has spurred investment in real estate, but almost all of it is geared towards the top end of the market.
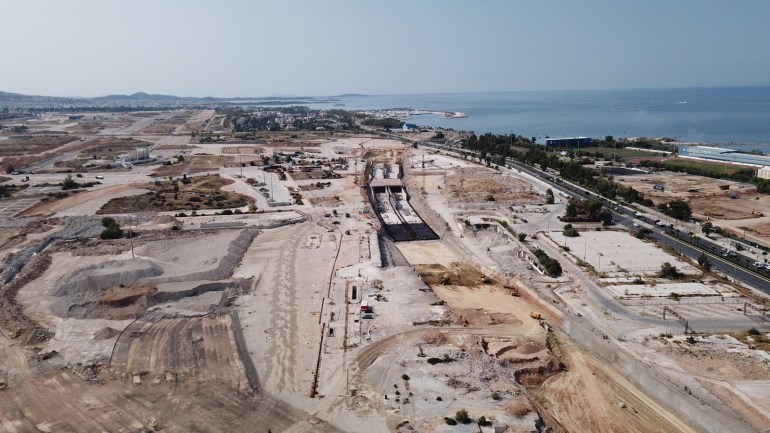

The Ellinikon is a prime example – a 600-hectare (1,500-acre) urban redevelopment of what used to be the Athens airport, nestled among the city’s southern suburbs.
Its first project, Marina Tower, now rising along the Attica shore, will be Greece’s tallest building when it is finished.
It will also be one of the most expensive. Every floor has been sold at a reputed 16,000 euros ($17,000) per square metre (nearly 11sq ft).
The Ellinikon’s owners said real estate will average 10,000 euros ($10,600) per square metre, but that is still well above the capabilities of most Greeks.
“The growth in the market which everyone is citing right now in terms of investment is for your high net worth individual from abroad and your top income level in Greece,” Bouras told Al Jazeera.
“For the vast majority, there is zero development. And if you look at government policy to increase supply levels, there is almost no movement,” he added.
The Ellinikon’s CEO makes no apology for the fact that 30 percent of the 1.2 billion euros ($1.27bn) of real estate he has already sold has gone to Syrians, Egyptians, Emiratis, other Europeans and Americans.
Odysseas Athanasiou argued that by attracting foreign buyers, The Ellinikon opens up Greece’s stagnant economy.
“For many, many decades, Greece was redistributing the pie of wealth, or poverty, if you will, and now with the new income that is coming from all places in the world, we are bringing in new money. The new money will be distributed more or less to everybody,” Athanasiou told Al Jazeera.
Among other benefits, Athanasiou says, The Ellinikon will create 80,000 permanent jobs.
Shrinking, ageing population
Greek society faces a potentially existential problem, and property prices are making it worse.
Its population has been shrinking since the turn of the century. That shrinkage accelerated after its eurozone partners imposed austerity policies on it in return for emergency loans in 2010.
Greece’s birth rate fell by 30 percent from 2011 to 2021 to under 84,000 per year, slipping ever-further below the death rate, according to the Hellenic Statistical Service.
The cumulative population loss during that decade was 329,451, which roughly tallies with the 2021 census recording a 3.1 percent population drop.
Given that each Greek paid on average 5,758 euros ($6,125) in taxes and social security contributions last year, this drop represents a loss of nearly 2 billion euros ($2.13bn) a year in state revenue – about 3.2 percent – over the long term.
Analysts said that by mid-century, Greece could find it difficult to generate the current level of state revenue – 60 billion euros last year ($64bn) – or man its armed forces.
The population drop is especially damaging in combination with ageing. Only 4.2 million Greeks work, supporting a total population of 10.5 million, including three million pensioners.
New Democracy has begun Greece’s first capitalised social security scheme for the under 25s, but for now, the majority of pensioners relies on current contributions.
New Democracy has also launched a series of measures to tackle the population decline and may have had a measure of success.
It delivered on promises to reduce the income tax, sales tax and social security contributions and offered paternity leave and extended daycare.
It offered a 2,000-euro ($2,200) cash handout per child, raised the tax rebate for families by 1,000 euros ($1,065) and now promises to drive up average salaries from 1,170 to 1,500 euros ($1,245 to $1,600).
Signs of improvement
Greece may have begun to see a faint heartbeat of improvement. Live births increased by 1.2 percent in 2020 and by 0.7 percent in 2021.
But My Home, its biggest direct measure to help young couples move ahead with their lives, has met with mixed results.
The programme was meant to accommodate 137,000 young people, but only 4,500 applications have received state approval and not all of them have gone on to receive bank approval.
“All programmes undergo evaluation and correction,” Maria Syrregela, deputy labour minister under the previous government told Al Jazeera. “My Home was the start of an ongoing state programme to provide housing.”
Syrregela was in charge of demographic policy, and perhaps her biggest achievement was that she got the opposition to sign onto a multiyear plan of action.
“Demographic policy isn’t about doing something today and having tangible results tomorrow,” she said.
“If you start a programme now, you might see results in 10 years. That’s why governments tended not to bother.”

30 Dark Tourism Destinations and How to Visit
By: Author Zachary Friedman
Posted on Last updated: March 1, 2024
Categories Travel Destinations
Home » Travel » Travel Destinations » 30 Dark Tourism Destinations and How to Visit
Many of us have a natural morbid curiosity. Death, disasters, atrocities, and destruction fascinate us. Every year, millions of people travel to some of the darkest and most tragic sites on earth to satisfy that curiosity as well as to gain a deeper understanding of the events that took place there. This is called dark tourism. In this guide, we’ll outline some of the most popular dark tourism destinations and explain how to visit them. We’ll also explain exactly what dark tourism is and talk a bit about the ethics, controversies, and motivations of dark tourism.
Personally, I’m a big fan of dark tourism. Over the years, I’ve visited many of the dark tourism sites on this list. In this guide, I’ll share my experience.

Table of Contents
- Auschwitz-Birkenau Memorial, Poland
- Chernobyl Nuclear Disaster Site, Ukraine
- Choeung Ek Killing Fields and S-21, Cambodia
- September 11 Memorial and Museum, New York
- Hiroshima Peace Memorial Park and Museum, Japan
- Kigali Genocide Memorial, Rwanda
- Pompeii, Italy
- Slave Castles, Ghana
- Sedlec Ossuary, Czech Republic
- Alcatraz Island, San Francisco
- Suicide Forest (Aokigahar), Japan
- Fukushima, Japan
- Robben Island, South Africa
- Pearl Harbor, Hawaii
- The Colosseum, Rome
- Mount St. Helens, Washington
- Anne Frank House and Museum, Amsterdam
- Various Nuclear Test Sites
- The Catacombs of Paris
- Warsaw Ghetto, Poland
- Perm-36 Gulag, Russia
- Cremations on the Ganges River in Varanasi, India
- WWII memorials and museums in Berlin, Germany
- Communist Leader Mausoleums
- Somme Battlefield, France
- Verdun Battlefield, France
- D-Day Beaches and Memorials in Normandy
- Antietam National Battlefield, Sharpsburg, Maryland
- Cu Chi Tunnels, Vietnam
What is Dark Tourism?
Dark tourism is a relatively new term for a form of tourism that involves travel to a site where death, tragedy, disaster, violence, atrocity, or suffering took place. This could include sites of genocide, assassination, natural disaster, war, terrorism, man-made disaster, etc. Usually, dark tourism sites have some kind of historical significance. They could also be the site of a recent or ongoing tragic event. Dark tourism is also called black tourism, morbid tourism, and grief tourism.
A few of the most well-known and popular dark tourism sites in the world include the ruins of Pompeii, Auschwitz concentration camp, the site of the Chornobyl nuclear disaster, the Paris Catacombs, Gettysburg, Ground Zero, and the 9/11 memorial in New York. In each of these sites, death, suffering, tragedy, or disaster took place.
Most people visit dark tourism sites for educational purposes. These sites usually have interesting histories. Some people visit because these sites pique a morbid curiosity. Others just want to witness large scale destruction and damage. Everyone has their own motivation.
There are different types of dark tourism as well. For example, dark tourism and heritage tourism are sometimes closely related. For example, someone may choose to visit Holocaust sites to learn about the events that their ancestors experienced. Descendants of slaves may choose to visit slavery heritage sites. Some consider this a form of dark tourism as well.
To consider someone a dark tourist, they must visit the site for dark tourism purposes. Some sites have a dark element but aren’t exclusively visited for dark tourism purposes. For example, if you visit Mount St. Helens to go for a hike, you’re not a dark tourist. If you visit to learn about the volcanic eruption and the damage it caused, you are a dark tourist.
Dark Tourism Destinations
1. auschwitz-birkenau memorial and museum, poland.

Located outside of Krakow, Poland, Auschwitz was the largest and most deadly of the Nazi concentration camps. Between 1.1 and 1.6 million men, women, and children were murdered here during the Holocaust. Auschwitz is one of the largest mass murder sites in the world.
Today, the site symbolizes genocide and the evil acts that humans inflict upon one another. It also acts as a valuable education tool to help prevent atrocities such as the Holocaust from happening again.
Auschwitz is actually a series of 40 concentration camps rather than one large camp. Auschwitz I is the older and smaller camp where political prisoners were held. Here, you’ll see a terrifying exhibition of some of the inmates’ possessions including piles of suitcases, shoes, and human hair.
Auschwitz-Birkenau, which is located a couple of miles down the road, is a much larger concentration camp and extermination camp. Here, you’ll find the ruins of the infamous gas chambers, barracks with wooden shelves where prisoners slept, and the train track which was used to haul thousands of people into the camp.
Auschwitz has become a mass tourist site seeing over 2 million visitors per year and over 60 million visitors since the site opened in 1947. This is probably the world’s biggest and most well known dark tourism site. The Auschwitz Memorial is free to enter but you should book in advance. Only a limited number of tickets are available per day because the site is so popular.
2. Chernobyl Nuclear Disaster Site, Ukraine

On April 26, 1986, the world’s worst nuclear meltdown took place at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant near Pripyat, Ukraine. This disaster caused the death of around 4,000 individuals from radiation-related illness as well as the displacement of over 300,000.
The area is still not safe for people to inhabit, even though some have moved back into their villages anyway. In fact, scientists believe it could take 20,000 years before the exclusion zone is completely safe. The radiation has dissipated enough for tourists to make short visits on guided tours.
Several tour companies offer day trips and multi-day trips to Chernobyl from the nearby city of Kyiv. During the tour, you’ll see the radiation-contaminated Red Forrest and eerie abandoned buildings including the famous Pripyat Amusement Park and a Kindergarten. You’ll also learn about the impact the disaster had on the region.
Keep in mind that there is still a risk of radiation poisoning when visiting the Chernobyl exclusion zone. Radiation levels are still hazardous in much of the zone. Your guide will explain the safety precautions you must take and guide you through the areas that are safe enough to visit.
Chernobyl is one of the world’s most famous and popular dark tourism sites. The recent HBO miniseries, Chernobyl, greatly increased the popularity of the area. Following the release of the show, tourism increased by 30%.
Note: Currently, it’s not possible to visit this site. Hopefully, it will be possible to visit again in the near future.
3. Choeung Ek Killing Fields and Tuol Sleng Genocide Museum (S-21), Cambodia
The Khmer Rouge regime came into power after the Cambodian civil war ended in 1975. The new government was called the Communist Party of Kampuchea. Their leader was prime minister Pol Pot.
Immediately following the end of the war, the Cambodian genocide began. From 1975 to 1979, between 1.7 and 2.5 million people were killed at 300 sites throughout the country. These sites are known as killing fields.
The most famous of these killing fields is Choeung Ek, which is located about 11 miles outside of Phnom Penh, the capital of Cambodia. It is estimated that around 17,000 men, women, and children were killed at this site. Many were killed violently with knives, scythes, bats, and bayonets. This is the main memorial for the Cambodian genocide.
At this site, you’ll see a memorial Buddhist stupa made of glass. Inside the stupa, there are 5,000 human skulls. Many of the displayed skulls are catastrophically damaged, showing the brutal manner in which the victims were killed. The site also includes a mass grave that contains the remains of almost 9,000 people that were exhumed from the surrounding area. Human bones still litter the entire site. Occasionally fragments wash up after heavy rain.
Another famous Cambodian Genocide site is the Tuol Sleng Genocide Museum or S-21. This museum is located in Phnom Penh. Originally, this site was built as a secondary school but was converted into a prison by the Khmer Rouge. Around 20,000 people were imprisoned here during Pol Pot’s reign. Many were tortured and killed. Here, you’ll see prison cells, photos of victims, as well as an exhibit that documents the events of the Cambodian genocide.
4. National September 11 Memorial and Museum, New York

This New York City memorial and museum was built to commemorate and honor the 2,977 people who died in the September 11, 2001 terror attacks as well as the six people who died in the 1993 World Trade Center bombings. The memorial sits on the site where the twin towers once stood.
The main memorial, called Reflecting Absence, consists of two 1-acre pools that occupy the exact footprints where the Twin Towers stood. Each pool features a large waterfall. Bronze parapets with the name of each victim etched in surround the pools. The September 11 Museum, located underground, contains thousands of images, artifacts, recordings, and videos. The exhibit tells the complete story of the events of 9/11.
This site is fairly controversial. Partly for the high price of entry ($24) but mostly for the fact that the remains of over 1000 victims were placed in a tomb in the bedrock under the museum. Many people find this disrespectful. Even so, the 9/11 Memorial is one of the world’s most popular dark tourism sites. Over 6 million people visit this memorial per year.
5. Hiroshima Peace Memorial Park and Museum
This memorial and museum commemorate and honor the city of Hiroshima and the 140,000 people who died when the United States dropped an atomic bomb on the city on August 6, 1945. It also memorializes the world’s first nuclear attack. The aim is to educate people about the danger of nuclear weapons as well as to promote peace.
The atom bomb, codenamed “Little Boy,” detonated 600 meters above the busiest part of downtown Hiroshima. The explosion essentially leveled the area except for a few ruins. This event marked the beginning of the end of WWII. Japan surrendered on August 15, 1945. The park was built on the site of the bombing. Today, the Hiroshima Peace Memorial Park contains a number of monuments as well as a museum and a lecture hall.
Hiroshima Peace Memorial Museum is the main feature of the park. The museum educates visitors about the events leading up to the bombing as well as the catastrophic effect the bomb had on the city. You’ll see photos and artifacts from the bombing. A major section of the museum is dedicated to the stories of the victims and survivors.
The A-Bomb Dome is the second most important site in the park. This is the ruins of the Hiroshima Prefectural Industrial Promotion Hall. Today, it’s just a shell of a building. This building is significant because it is one of the only buildings that survived the blast. Most structures in Hiroshima were built from wood and burned up in fires that the bomb started. This building was also just 150 meters from the hypocenter of the blast. It has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
A few more significant points of interest in Hiroshima Peace Memorial Park include Children’s Peace Monument, Peace Flame, Peace Bells, Peace Pagoda, Gates of Peace, and Atomic Bomb Memorial Mount. You could easily spend half a day wandering around the park viewing the various monuments and memorials.
3 days after the bombing of Hiroshima on August 9, 1945, The United States bombed the city of Nagasaki in a second nuclear attack. Today, you’ll find a number of memorials and museums including the Atomic Bomb Museum, Peace Park, Oka Masaharu Memorial Peace Museum, and more.
6. Rwanda Genocide Sites (Kigali Genocide Memorial and Murambi Genocide Memorial)
In 1990, a rebel group of Tutsi refugees called the Rwanda Patriotic Front (RPF) invaded Rwanda from Uganda. This started the Rwandan Civil War. President Juvénal Habyarimana signed peace accords in 1993. The following day, the president was assassinated. Genocidal killings of Tutsi people began soon after and the civil war resumed.
The Rwandan genocide lasted from April 7 to July 15, 1994. During that time 500,000-1,000,000 people were killed. This includes about 70% of Rwanda’s Tutsi population. The genocide ended when the RPF captured Kigali and gained control of the country. The government and genocidaires were forced into Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo).
Today, there are a number of genocide memorials located throughout the country. The largest and most visited is the Kigali Genocide Memorial Centre. The remains of an astonishing 250,000 people are interred at this site. The attached museum includes three exhibits. The first documents the events of genocide from start to finish. The second exhibit is a memorial to the children who died. It includes photos and details about their lives, things they liked, and the way they died. The third exhibit covers genocide around the world.
The Murambi Genocide Memorial (Murambi Technical School), located in southern Rwanda is one of the darkest dark tourism destinations on the planet. Here, around 50,000 Tutsi men, women, and children were murdered by Hutu Interahamwe militiamen in April of 1994.
The Tutsis were told that they could safely shelter at the school and that the French military would protect them. This turned out to be a trap. After being starved for several days to weaken them, they were attacked and killed. Only 34 people survived the attack and escaped. At Murambi, the remains of 800 people are displayed partially decomposed and preserved by lime.
7. Pompeii, Italy

This ancient Roman city was wiped out when nearby Mount Vesuvius erupted in 79 AD. Historians estimate that about 2,000 people died in the disaster. The thick layer of ash and pumice that covered the city preserved this little slice of ancient Rome.
At the ruins, you can see beautifully preserved artwork, pottery, casts of people who died, houses, an amphitheater, and more. Pompeii is a UNESCO World Heritage site and is one of Italy’s most popular tourist destinations with over 2.5 million visitors per year.
Some people question whether or not Pompeii is actually a dark tourism site due to the age of the site. After all, the eruption occurred nearly 2000 years ago. In my opinion, Pompeii is absolutely a dark tourism site due to the large scale death and destruction that happened here. The age of the site is irrelevant.
8. Slave Castles, Ghana (Cape Coast Castle and Elmina Castle)
During the colonial period of West Africa, the British, Dutch, and Portuguese built around 40 castles or forts along the Gold Coast. The Europeans originally used these castles as trading posts for timber or gold.
During that time, African slaves were in high demand in the Americas. The European traders quickly found that the slave trade was more profitable.
They modified their forts to hold as many slaves as possible. Usually in an underground dungeon. African slavers would capture slaves inland then sell them to the Europeans who lived in the castles on the coast. The slaves stayed in the castles until they were shipped across the Atlantic to the Americas.
Living conditions for the slaves were horrible. Slavers shackled and packed the slaves into the castle’s dungeons. There was very little light or ventilation. There was no water or sanitation so the floors were covered in waste. Many became ill. The slaves lived in these conditions for up to three months before being shipped across the Atlantic.
Today, dark tourists visit these castles to learn about the horrors of the slave trade. Two of the most significant castles to visit include Elmina Castle and Cape Coast Castle. Both are located in Ghana. Guided tours are available.
Elmina Castle was the first European trading post and is the oldest European building in Sub Saharan Africa. The Portuguese built the castle in 1482. Today, it is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Here, you can see the famous ‘Door of No Return’ where slaves exited the castle before boarding ships to Brazil and other Portuguese colonies. You’ll also see the dungeon where the slaves were held as well as the living quarters for the European slavers, who lived on the upper floors of the castle.
Cape Coast Castle was built by Swedish traders in 1653. Over the years, the castle changed hands multiple times until it came into British possession. Here, you can see the dungeons where slaves were held and cannons that were used to defend the fort. In 2009, President Obama visited Cape Coast Castle during his visit to Ghana.
9. Sedlec Ossuary, Czech Republic
This small Roman Catholic chapel is located in a cemetery in a suburb of the city of Kutná Hora in the Czech Republic. Here, you’ll find the remains of 40,000-70,000 people. Initially, the remains were moved from the cemetery into the basement of the chapel to solve an overcrowding problem that was caused by the plague in the 14th century.
In 1870, a local artist named František Rint rearranged the piles of bones into artwork. The most impressive piece is a massive chandelier in the center of the chapel that is made entirely from human bones. Supposedly it contains at least one of every bone in the human body.
Another interesting piece is a large coat of arms made from bones. In the corners of the chapel, you’ll find large stacks of bones. There are cabinets filled with damaged skulls of those who were killed violently in war. The artist also signed his name in bones.
You can visit Selded Ossuary as a day trip from Prague. It’s easy to visit independently by train. Organized tours are available as well. The chapel is pretty small. It only takes 20 minutes or so to see the whole thing. The place gets pretty crowded as it receives over 200,000 visitors per year.
10. Alcatraz Federal Penitentiary, San Francisco

Also known as The Rock, Alcatraz Federal Penitentiary was a maximum-security prison from 1934-1963. It is located on an island in the San Francisco Bay, 1.25 miles offshore. During the 29 years that the prison operated, some of the hardest criminals of the day served time here including the infamous Al Capone, Machine Gun Kelly, Henri Young, and ‘the Birdman of Alcatraz’, Robert Stroud.
For punishment, prisoners were sent to solitary confinement, known as ‘the hole’ at Alcatraz. These inmates got one shower and one hour of exercise per week. Almost equally punishing for some, the prison sits close enough to the mainland that prisoners could see people going about their lives on the outside.
Today, Alcatraz is San Francisco’s most popular tourist attraction with up to 1.5 million visitors per year. The National Park Service manages the island. After arriving at the island by boat, you can take a tour of the prison. You’ll see the prison cells, learn about the dark history of the island, and hear stories of former inmates. Much of the prison remains the way it was while the prison was in operation.
11. Suicide Forest (Aokigahar), Japan
This forest, located to the Northwest of Mount Fuji, is famous for being one of the most popular suicide site in Japan. In 2003, a record was made when 105 bodies were found in the forest. In 2010, over 200 people attempted suicide here with 54 of those being successful.
The most common methods of suicide used are hanging and drug overdose. Because the suicide rate is so high here, Japanese officials installed a sign at the entry to the park which urges suicidal people to seek help.
Part of the reason for the popularity of this forest as a suicide site is that the area has long been associated with death in Japanese culture. The forest is said to be haunted by the yūrei, which are spirits that can’t leave our world.
Here, visitors can roam about the many trails that wind throughout the 30 square kilometer forest. This is an excellent place to enjoy the solitude of the dense forest. Tours are available as well.
Some visitors come here to see if they can spot a body. As you can imagine, this is a very controversial form of dark tourism. For example, YouTuber Logan Paul was criticized for filming a video of a man who had recently committed suicide here in 2018.
12. Fukushima, Japan
On March 11, 2011, an earthquake off the east coast of Japan triggered a tsunami that flooded the reactors at Fukushima nuclear power plant and caused an electrical grid failure. The reactors lost their cooling which led to three nuclear meltdowns at the plant. 154,000 people had to be evacuated. Many were never able to return to their homes.
Today, there is a 20 km exclusion zone surrounding the nuclear plant to protect people from radiation exposure. In 2018 tours to visit the exclusion area began. In 2020, The Great East Japan Earthquake and Nuclear Disaster Memorial Museum opened. On the tour, you’ll see abandoned structures and witness the effects that the disaster had on the region.
13. Robben Island, South Africa
Robben Island, located in Table Bay, north of Cape Town, was used as a prison from the colonial times of the late 1600s until 1996. The prison gained notoriety during the apartheid era of South Africa. It held political prisoners between 1961 and 1991.
The most famous prisoner was political revolutionary, Nobel Peace Prize recipient, and president of South Africa, Nelson Mandela. He served 18 of his 27-year imprisonment on Robben Island before his release in 1990. in 1994, South Africa elected Mandela as the first president. A total of three former inmates went on to become South African presidents including Kgalema Motlanthe and Jacob Zuma.
Conditions in the prison were incredibly harsh. Prisoners were held isolated from one another in small cells. The prison was segregated by race. Food rations were small and communication with the outside world was limited. Prisoners were also forced to do hard labor in a lime quarry located on the island.
Today, Robben Island is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a South African National Heritage Site. The only way to visit Robben Island is on a guided tour. The tour leaves from Cape Town and lasts for about 3.5 hours. The guides are all former prisoners. They take you around the prison and share their first-hand stories about their time there. You’ll see the lime quarry where the prisoners were forced to work as well as Nelson Mandela’s prison cell.
14. Pearl Harbor, Hawaii
On December 7, 1941, the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service surprise attacked the United States naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The goal of the attack was to prevent the United States Navy fleet from interfering with the Japanese military plans to expand throughout Southeast Asia. If Japan crippled the United States fleet was crippled, they could invade and conquer US and British held territories such as the Philippines, Guam, Singapore, Malaysia, and Hong Kong, as well as other small islands of the Pacific.
The Japanese launched a massive attack with 353 aircraft which took off from six aircraft carriers. They sank 4 of the 8 battleships stationed at Pearl Harbor. They seriously damaged the other four. 188 aircraft were also destroyed in the attack 159 were damaged. The attack killed 2,403 Americans and injured 1,178. The attack also damaged or destroyed a considerable amount of the base’s infrastructure including a power station, piers, various buildings, and more.
The most significant loss was the battleship USS Arizona. It suffered a direct hit to an ammunition magazine which exploded and caused the ship to sink almost instantly. 1,000 sailors sank with the ship.
The attack on Pearl Harbor dragged the United States into World War II. The day after the attack, Japan declared war on the United States. The next day, the United States declared war on Japan. Three days later, Germany and Italy both declared war on the United States.
Today, there are a number of museums and memorials at Pearl Harbor that commemorate the attack. The main site is the USS Arizona memorial. This memorial straddles the sunken ship and is accessible only by boat. Inside, you’ll see a number of exhibits including one of the ship’s anchors, a shrine with the names of all of those who died as well as some plaques with information about the attack. There is also an opening in the floor where you can view the deck of the ship underwater. Onshore, there is also a museum that outlines the events leading up to the attack and the attack itself.
Nearby, you can also view the USS Missouri Memorial, USS Utah Memorial, USS Oklahoma Memorial, Pacific Aviation Museum, and USS Bowfin Museum.
15. The Colosseum, Rome

Built in Ancient Rome between 72-80 AD, the Colosseum is one of the oldest and most recognizable dark tourism sites. At the time, it was the largest amphitheater ever built with a capacity of 50,000-80,000 spectators. The Colosseum, also known as the Flavian Amphitheatre, hosted a number of dark and violent events including gladiatorial events, executions, animal hunts, and battle re-enactments.
The most famous of these events were the gladiatorial contests. People and animals brutally battled to the death for the entertainment of thousands of spectators. Most gladiators were slaves, criminals, or prisoners of war but some volunteered to seek fame and fortune.
Exotic wild animals including lions, hippos, rhinos, elephants, bears, tigers, crocodiles, etc. were brought in from Africa and the Middle East. These animals were used for hunts or battles. In some cases, people were fed to lions.
Over the course of the 400 years that these gladiatorial events took place, historians estimate that around 400,000 people died in the Colosseum. Some people consider these events the earliest form of dark tourism.
Today, the Colosseum is one of the top tourist destinations in Rome and the world. Around 7 million people visit this site per year. There are a number of guided tours available. You’ll see the underground level where the gladiators prepared to fight, the arena floor where the gladiatorial fights took place, areas where the animals were kept, and artwork.

16. Mount St. Helens, Washington
The 1980 volcanic eruption of Mount St. Helens killed 57 people and caused a great deal of destruction to the mountain and surrounding area including the largest landslide in recorded history. The eruption was so violent that the mountain’s elevation decreased by 1300 feet. The top completely blew off.
Many tourists come to visit the area each year. Today, you can see tree stumps and dead trees that still stand around the blast site. There is a visitor center with an exhibition about the eruption. In the visitor center, they also have a small movie theater that shows a short documentary about the event. The surrounding state park offers plenty of hiking, camping, climbing, and other recreational activities.
17. Montserrat
This volcanic island in the Caribbean is sometimes called a modern-day Pompeii. The Soufriere Hills Volcano became active in the mid-1990s and slowly covered the former capital of Plymouth in ash. The town was evacuated in 1997 just before a major eruption covered much of it.
The volcano is still very active today, periodically spewing ash, smoke, and gasses across 1/3 of the island. Occasionally pyroclastic flows cover more of the island’s land. Travelers can hike to a lookout point to view smoke spewing from the volcano and maybe get a glimpse of Plymouth. It is also possible to view the volcano and town by boat. It is unsafe to visit the town of Plymouth at this time.
16. Anne Frank House and Museum, Amsterdam
In this famous canal house Anne Frank, her family, and four others hid from Nazi persecution for 761 days. They quietly lived in a hidden part of the house called the Secret Annex. Anne Frank is famous for keeping a diary of her daily thoughts and experiences during her days in hiding during World War II.
Sadly, Anne Frank and the others hiding in the Secret Annex were betrayed by an unknown informant and discovered by the Nazis on August 4, 1944. The Nazis split them up and moved them to various concentration camps. Anne Frank died in Bergen-Belsen concentration camp in February of 1945 when she was just 15 years old. Anne’s father Otto, who survived the Holocaust, discovered his daughter’s diary after the war and published it in 1947.
The canal house where the two families hid is a now museum that attracts up to 1.2 million visitors per year. Here, you can walk through the Secret Annex where Anne Frank and her family hid. The original diary is on display in the attached museum. The museum also includes a permanent exhibit about the life of Anne Frank and her experience during the war.
19. Nuclear Test Sites
Since nuclear testing began in 1945, 8 countries have detonated around 2056 nuclear bombs at dozens of test sites around the world. A few nuclear test sites that you can visit include:
- Semipalatinsk Test Site (The Polygon)- Semipalatinsk was the Soviet Union’s primary nuclear test site from 1949-1991. It is located on the steppe of northeastern Kazakhstan. More nuclear weapons detonated here than anywhere else on the planet. Beginning in 2014 parts of the area have opened up for tourism. There isn’t all that much to see here outside of some massive craters and some concrete towers and bunkers that housed instruments to measure the blasts.
- Nevada Test Site- This site was the United States’ main nuclear testing site from the time it was established in 1951 until nuclear testing ended in 1992. The site is located about 65 miles to the northeast of Las Vegas. Here, you can see a number of large craters in the desert where nuclear weapons were detonated for testing purposes. Monthly public tours are offered but are often fully booked months in advance. This is a difficult place to visit.
- Bikini Atoll, Martial Islands- This was one of the United States’ main nuclear test sites. Between 1946 and 1958, 23 atomic bomb tests were performed here. The blasts turned out to be more destructive than anticipated and resulted in significant contamination to the surrounding area. Probably the biggest attraction for tourists here is Scuba diving the 10 ships that were sunk during nuclear tests. This is a risky area to visit due to the significant levels of radiation that still exist.
20. Catacombs of Paris, France

This network of underground ossuaries underneath the city of Pairs holds the remains of around 6 million people. The tunnels were originally mine tunnels. The Paris Catacombs were built to solve the problem of the city’s overflowing cemeteries. The dead were crowding the living. Starting in 1786, the city began transporting human remains from the city’s cemeteries into the underground tunnels by covered wagon during the night. The catacombs open to tourism in 1867.
Today, the Catacombs are one of the more popular tourist destinations in Paris. You can book a guided tour and wander through the labyrinth of bone filled tunnels and view the millions of bones stacked neatly throughout. Around 300,000 people visit this site per year. It is only accessible by tour.
21. Warsaw Ghetto, Poland
Ghettos were segregated neighborhoods where Jewish people were forced to live while under Nazi occupation during WWII. The largest of these was the Warsaw Ghetto. The area actually consists of two smaller ghettos with a footbridge between them. At its peak, approximately 460,000 people lived in Warsaw Ghetto.
During the Uprising the ghetto was almost completely destroyed. Today, you can visit the area and view a small number of streets and buildings that survived. The monument called ‘The Footbridge of Memory’ stands at the site of the original footbridge.
22. Perm-36 Gulag, Russia
Following the Bolshevik Revolution, the Soviet Union built a large system of forced labor camps to imprison ‘enemies of the state.’ These included government officials, military members, and regular citizens. Anyone who was anti-communist or anti-Stalin was imprisoned. These camps were known as gulags. Millions of people were held in these camps and forced to perform backbreaking work in extremely brutal conditions.
Perm-36 is the only remaining Soviet gulag. It is located about 60 miles from the Russian city of Perm in the Western Ural Mountains. The camp operated from 1946-1987. Perm-36 is unique because it was not closed after Stalin’s death in 1953. This is one of the only gulags that was not demolished after the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991.
When Perm-36 opened, it was used as a forced labor camp for regular criminals. In later years, the camp housed political prisoners. The prisoners were forced to do logging work. Some political prisoners lived in 24 hour closed cells. Perm 36 was considered the harshest political camp in the Soviet Union.
Today’s site operates as a museum and memorial called The Museum of the History of Political Repression Perm-36. It opened to the public in 1995. Here, you’ll see the wooden barracks that the prisoners built, various prison buildings, and an exhibit about the gulag system and the prisoners. You’ll also learn about the economic benefit that the gulag system created for the Soviet Union.
23. Cremations on the Ganges River in Varanasi, India

Varanasi is a holy city located on the Ganges river in Uttar Pradesh, India. The city has become a popular dark tourism destination for its famous Hindu cremation ceremonies that take place on the banks of the river. In the Hindu religion, people believe that cremation on the banks of the Ganges river breaks the cycle of reincarnation so they can achieve salvation. Along the river, dozens of cremations take place out in the open every day.
The bodies are placed atop piles of wood and set on fire until they turn to ash. The ashes are then scattered in the Ganges River, which is considered a holy site in the Hindu religion. Poor families who cannot afford a cremation sometimes release the entire body of their loved one in the river to decompose naturally. Some terminally ill people travel to Varanasi so they can die and be cremated in the holy city.
Tourists are welcome to view and experience these cremation ceremonies. When you arrive at the famous ghats on the bank of the river in Varanasi, you’ll clearly see the cremation sites. Just look for the smoke. You’ll see open areas with large fires and piles of wood sitting around. The cremations take place here.
For a few dollars, you can hire a guide to walk you through the cremation site and explain how the process works. There are multiple cremations taking place simultaneously at all hours of the day. You can walk right up and see the cremation and feel the heat from the fire and smell the smoke.
As you can imagine, this is a fairly controversial form of dark tourism. After all, you are essentially attending a cremation for touristic purposes as the family grieves of the loss of their loved one. Some view this as voyeuristic. It’s up to you to decide whether or not this form of dark tourism is ethical.
24. Berlin, Germany

Berlin is one of the darkest cities on earth. It was the capital of Nazi Germany, one of the world’s most evil regimes. Next, it became the most significant city in the cold war. It was also the capital of the socialist single-party regime of the former GDR. As a result, Berlin is packed with dozens of dark tourism sites. A few of the most popular ones include:
- Memorial to the Murdered Jews of Europe (the Holocaust Memorial)- This memorial is to the Jewish people murdered during the Holocaust. It contains 2,711 concrete slabs ranging in height from .2-4.7 meters. The slabs are arranged in a grid pattern over a 19,000 square meter site. Below the memorial is an information center that contains the names of 3 million Holocaust victims as well as photographs and letters. This memorial is quite controversial. Partly because it is so vague. There is no mention of Nazi Germany or the Holocaust on the memorial itself or in the official name of the memorial. People also use the site as a recreational area, sitting or standing on the pillars. Many consider this to be disrespectful. Due to its size and design, the memorial is difficult to defend from vandals.
- Berlin Wall- Between 1961 and 1989, this concrete barrier divided West Berlin from surrounding East Germany. The German Democratic Republic (East Germany) constructed the wall to prevent East Germans from defecting to the west. The four-meter tall wall extended 155km (96 miles) and cut through 55 streets. Today, you can see several small sections of the wall still standing in the city. The largest is is a 1.4 km section that is part of the Berlin Wall Memorial. Here, you can see the graffiti on the west side and learn about the historical significance of the wall.
- Checkpoint Charlie Museum- Checkpoint Charlie is the most well-known crossing between East and West Berlin. The original guardhouse was preserved and today is part of the Checkpoint Charlie museum. Here, you can see exhibits about the Berlin Wall, the Cold War, and some famous escape attempts.
- Jewish Museum- Designed by architect Daniel Libeskind, the Jewish Museum is one of Germany’s best and most popular museums as well as one of Berlin’s most striking landmarks. Here, you’ll find thousands of artifacts, photos, religious objects, and archives that document the struggle of the German Jewish people from the Middle Ages to the present time. The museum also houses a massive library and hosts various events throughout the year.
- Topography of Terror Museum- This museum is located on the site of the Gestapo secret police and SS headquarters. Allied bombings destroyed the original building in 1945. After many years of delay, the museum opened in 2010. The main exhibit focuses on policing under Nazi rule. You’ll see photos, documents, short films, and artifacts that show the crimes that the SS and Gestapo committed throughout Europe. The grounds of the museum also contain some historic artifacts including a large section of the Berlin Wall. You’ll also see an excavated trench that exposes the cellar wall, where political prisoners were kept, tortured, and ofttimes executed.
- DDR Museum- This newer museum outlines life in East Berlin under communist rule with a hands-on approach. Here, you’ll see a recreation of an interrogation room, prison cell, and an apartment. You can try on clothing and watch television from the era. The exhibit covers food, music, daily life, education, architecture, and more. You’ll also learn about the mass surveillance conducted during the time. This is a private museum and is one of Berlin’s most popular.
25. Communist Leader Mausoleums
For whatever reason, communists love to embalm their leaders after they die and put the bodies on public display. A few famous mausoleums you can visit include:
- Lenin Mausoleum- This mausoleum is located in the Red Square in the center of Moscow. Inside, you can view the embalmed corpse of the Soviet leader Vladimir Lenin. The body has been on public display since shortly after his death in 1924. The mausoleum is open to the public and free to enter. Stalin’s body was put on display here from 1953-1961 but was removed and buried near the mausoleum.
- Ho Chi Minh Mausoleum- This mausoleum is located in Ba Dinh Square in Hanoi, Vietnam. Inside, you can view the embalmed body of Vietnamese revolutionary and president Ho Chi Minh, who died in 1969. The body is kept in a dimly lit glass case which is heavily guarded by military honor guards. The mausoleum is open to the public.
- Mausoleum of Mao Zedong- This large mausoleum, also known as Chairman Mao Memorial Hall, is located in the center of Tienanmen Square in central Beijing. Here, you can view the embalmed remains of Mao Zedong, who served as the Chairman of the Communist Party of China from 1945-1976. Interestingly, Chairman Mao wanted to be cremated. The mausoleum is open to the public.
- Kumsusan Palace of the Sun (Kim Il Sung Mausoleum)- This absolutely massive palace is located in the North Korean capital of Pyongyang. The building was intended to be the official residence of Kim Il Sung but was converted into a mausoleum when he died in 1994. Inside, you can view the embalmed remains of North Korean founder Kim Il Sung as well as his son and former leader of North Korea, Kim Jong Il. Both bodies lie inside of glass sarcophaguses. The mausoleum is open to the public. Foreigners can only enter the palace when they are on an official government tour.
26. Somme Battlefield, France
The Battle of the Somme was a WWI battle fought between the French Third Republic and British Empire against the German Empire. The battle took place between July 1 and November 18, 1916. Over three million men fought in the Battle of the Somme. One million were killed, injured, or went missing, making this the most bloody battle of WWI and possibly the most deadly battle in world history.
Several factors contributed to the massive amount of death in the battle. First, the battlefield was small. The Germans were also well prepared and trained for trench warfare. An incredible amount of heavy artillery was also used in this battle.
The Battle of the Somme ended when British Commander in Chief Sir Douglas Haig decided to stop the offensive near the Somme River. When the battle ended, the British and French armies had gained just six miles of land. Modern historians are not in agreement as to whether or not the battle was a success.
Today, there are a number of monuments, museums, cemeteries, and battle sites that you can visit in Somme. The Remembered Trail leads visitors through some of the most significant locations. It’s is a great place to start in the region. Guided tours of the area are also available.
27. Verdun Battlefield, France
The battle of Verdun lasted from February 21-December 18, 1916, making it the longest battles in World War One at 302 days. This battle was also one of the most costly with up to 1 million casualties between the French and German armies.
Today, you can view the battlefield complete with shell craters that are still visible over 100 years later. You’ll also find several memorials including an ossuary. The battlefield itself contains the remains of 100,000 soldiers. You can also visit the Verdun Memorial Museum which features artifacts from the battle as well as information about the time.
28. D-Day Beaches and Memorials in Normandy
On June 6, 1944, the Allied Forces invaded Nazi occupied France on the beaches of Normandy. This operation, known as Operation Overlord, was the largest amphibious invasion in world history. This event marked the beginning of the liberation of France and Western Europe and eventually led to the Allied victory over the Third Reich on the Western Front. The D-Day invasion of Normandy resulted in 4,000-9,000 German casualties and around 10,000 Allied casualties including 4,414 deaths.
Today, there are dozens of memorials, museums, and war cemeteries along the beaches of Normandy as well as further inland. A few of the most significant D-Day sites to visit include:
- Beach landing sites- The 50 miles stretch of Normandy beach was divided into 5 sections where the invasion took place. The beach landing sites include Utah, Omaha, Gold, Juno, and Sword. Today, you can visit each of the 5 beaches. Probably the most popular beach to visit is Omaha. Here, you’ll see German bunkers and the sculpture Les Braves which commemorates the American soldiers who died on D-Day.
- Utah Beach Museum- This museum outlines the entire D-Day invasion from the planning phase until the end of the battle. Here, you’ll see vehicles, artifacts, and photographs from the massive invasion. The museum overlooks Utah Beach.
- Normandy American Cemetery and Memorial- This cemetery, overlooking Omaha Beach, contains 9,388 graves of American soldiers who died in WWII. Mostly on D-Day.
- Overlord Museum- This museum, located near Omaha Beach and the American cemetery, documents the time period between the Allied landing and the liberation of Paris. Here, you’ll see thousands of artifacts from the invasion including tanks and cannons as well as photos and reconstructed battle scenes.
- Pegasus Bridge- 6000 British paratroopers landed here with supplies and weapons just past midnight on June 6, 1944. Their job was to secure the bridge so German reinforcements couldn’t cross. The current bridge is a reconstruction of the original, which was destroyed.
- Memorial Museum of the Battle of Normandy- This museum, which is located in Bayeux, outlines the military operation in detail. Here, you’ll see military equipment, artifacts, photos, and a fantastic short film about the D-Day landings.
- Caen Memorial Center- This museum outlines the battle of Normandy from the end of WWI all the way to the beginning of the Cold War. This gives you a great overview of the historical events leading up to the war and their effects on Europe and the world. Here, you’ll see letters and personal belongings from soldiers, airplanes, and a short documentary film with footage of the D-Day invasion.
- Airborne Museum- This museum, located in Sainte-Mère-Église, focuses on the paratroopers who landed in Normandy the night before the attack. Here, you’ll see photos, artifacts, tanks, and airplanes including a WACO glider and C-47 that you can enter.
29. Antietam National Battlefield, Sharpsburg, Maryland
On September 17, 1862, Confederate General Robert E. Lee and his Army of Northern Virginia battled Union General George B. McClellan and his Army of the Potomac in the Battle of Anteteitum near Sharpsburg, Maryland. This was the bloodiest battle of the American Civil War with 22,717 dead, injured, or missing. This massive loss of life took place over the course of just 12 hours.
The battle ended when Lee decided to withdraw back to Virginia. McClellan decided not to follow him. The Union claimed victory. After the battle, President Lincoln announced his Emancipation Proclamation which freed 3.5 million slaves.
Antietam is considered to be one of the most well-preserved American Civil War Battlefields. Probably because it was one of the first battlefields preserved in 1890. Today, visitors can take a self-guided tour of the battlefield or hire a tour guide. You’ll see landmarks of the battle such as the Cornfield, Dunker Church, and Burnside’s Bridge.
30. Cu Chi Tunnels, Vietnam
The Cu Chi Tunnels are a massive network of underground tunnels located outside of Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. They were used by Viet Cong soldiers for a number of purposes including hiding spots, supply routes, living quarters, hospitals, and food and weapons caches. They were famously used as a base of operation for the North Vietnamese during the Tết Offensive in 1968.
Life in the Cu Chi Tunnels was difficult. Air quality was poor. The tunnels were cramped and claustrophobic. Food and water were limited. Rodents, ants, snakes, scorpions, and spiders infested the tunnels. Diseases including Malaria and intestinal parasites were common. During heavy bombing campaigns, soldiers had to stay in the tunnels for days at a time.
Today, the Cu Chi Tunnels are a war memorial operated by the Vietnamese government. They are also a popular tourist dark tourist attraction. You can visit the tunnels on a day trip from Ho Chi Minh City. Here, you can crawl through a safe section of the tunnels, watch a short film about the war, and view some different booby traps and trap doors as well as an entrance into the tunnels. There is also a firing range where you can shoot Vietnam War era weapons including an M60 machine gun.
My Experience: Why I Enjoy Dark Tourism
My main motivation to visit dark tourism sites is education. For whatever reason, I wasn’t interested in history when I was in school. I just found it boring. Now, I love history. By visiting dark tourist sites, I have gained a deeper understanding of some of the most significant events in world history. It’s so much more real and engaging when you are standing where an event took place and exploring the landscape and looking at actual artifacts.
It’s also amazing to see how human civilization evolves over the years. For example, 2000 years ago, gladiator games were an acceptable form of entertainment. Most people would not be okay with that today. It is also interesting to see how technology, weapons, clothing, politics, and more have changed throughout the years. The world was a completely different place just 20 years ago. Times change quickly.
I also have a pretty strong morbid curiosity. Dark things simply interest me. I find it fascinating to imagine the horrors that humans have endured and overcome.
Final Thoughts About Dark Tourism
Dark tourism often gets a bad rap in the media. People get the idea that it is disrespectful, voyeuristic, sick, or even unethical. Some country’s tourism departments also try to hide their dark tourism sites because they fear a bad reputation. They may not want people to associate the country with its dark past.
The truth is that most dark tourism is simply educational. People like to visit these sites to learn about their history. They also satisfy our natural morbid fascination. There is nothing wrong with visiting dark tourist places, as long as you do so respectfully.
One important thing to remember is that dark tourism is not a new form of tourism. People have been visiting dark sites for as long as tourism has existed. For example, tourists began visiting Pompeii in the 1800s. The gladiatorial games could be considered one of the earliest forms of dark tourism. Those began when the Colosseum opened in 80 AD. People are naturally interested in these types of destinations and will continue to be.
Dark tourism is also a very broad term. Many of the world’s most visited tourism sites can be considered dark tourism sites. There is also a lot of overlap with mass tourism. Most people don’t travel exclusively to visit dark sites. Instead, they pair dark tourism with regular tourist attractions. For example, if someone is in Hawaii, they may spend a day visiting Pearl Harbor and the various memorials then go to the beach the next day. If someone visits Kyiv, they’ll probably take a day trip to Chornobyl because it’s one of the biggest tourist attractions in the region. It’s common to pair dark tourist sites with other types of sites.
Hopefully, this guide helps you in planning your visit to some of the world’s best dark tourism sites.
If you’re on the fence about dark tourism, check out my guide to the ethics and criticisms of dark tourism.
Are you a dark tourist? Share your favorite dark tourism destination in the comments below!
Pin it for later!

More from Where The Road Forks
- 35 Types of Tourism
- How to Plan a Round the World Trip
- 30 Free Things to do While Traveling
- The Best Solo Travel Destinations
- Whale Watching in South Africa: Where to Go
- 21 Free Airline Stopover Options
Zachary Friedman is an accomplished travel writer and professional blogger. Since 2011, he has traveled to 66 countries and 6 continents. He founded ‘Where The Road Forks’ in 2017 to provide readers with information and insights based on his travel and outdoor recreation experience and expertise. Zachary is also an avid cyclist and hiker. Living as a digital nomad, Zachary balances his professional life with his passions for hiking, camping, cycling, and worldwide exploration. For a deeper dive into his journey and background, visit the About page. For inquiries and collaborations, please reach out through the Contact page. You can also follow him on Facebook.
Sharing is caring!
Sign me up for the newsletter!
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Politics of Development
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >
Dark Tourism as History: Dark Tourism in History
Tony Seaton is Emeritus Professor of Travel and Tourism Behaviour and History at The University of Bedfordshire, UK.
- Published: 19 December 2022
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Dark tourism or, thanatourism, a term used as an encyclopaedic alternative (Jafari 1996, 578) 1 , only emerged as a collective area of named study in the last decade of the twentieth century. Both terms had their origins in the recognition of the long history and widespread occurrence of traveling encounters with different kinds of engineered and orchestrated remembrance of the dead. Many may have originally been an accidental or incidental by-product of travel, but increasingly they became deliberate goals of different kinds of pilgrimage, the most important being religious, but others being more secular (e.g. visiting the graves of writers, historic battlefields). In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries these occasional, sepulchral encounters were increasingly transformed into purposeful, mass tourism practices, induced by new ideologies of an evolving, European modernity, among them: antiquarianism, Romanticism, the gothic and patriotic displays of national pageantry and imperial display. Dark tourism’s identifying activity, visitation to commemorative sites, inherently makes it a travel form likely to feature more frequently in debates around “the politics of remembrance,” an expanding multi-cultural domain about the continuing status of historical events and figures. The chapter finishes with an illustrative, case history exemplifying some of the main issues in remembrance and remembrancing, in the context of a recent addition to dark tourism repertoires—the visitation of flooded villages as industrial disaster sites.
Dark Tourism is a concept relatively new to the world of tourism studied by social scientists, and even more so in the “real world” of travel and tourism experienced by many millions of global travelers. Yet “dark” encounters are among the oldest of travel encounters, and ones that can be widely recognized in contemporary life once the ideas behind what may seem an odd linguistic conjunction (“dark” plus “tourism”) are recognized.
This chapter is in two parts and addresses two main, historical questions, one of which is academic; the other one of praxis . The first is about the origins of dark tourism as a named entity in the academic study of recreational choice. The second is about its main experiential features in historical travel patterns. The two parts are inextricably linked since academic discussion about what dark tourism is affects what past practices are recognized as its history, and even the extent to which it has a history. The inquiry appraises dark tourism’s defining forms, the similarities and dissimilarities within them, and their significance in social and societal terms.
The chapter ends with a case study of an environmental and community disaster, the flooding and submersion of a village, induced 150 years ago as collateral damage in industrial development that was to be widely repeated around the world later. It has emerged as a new kind of dark tourism attraction. Its trajectory from disaster site to visitor attraction marks a central theme in this chapter about the nature of dark tourism, as remembrance of fatality and mortality that is inherently susceptible to revision, as ways of remembering people, and to remember as events change in society. The case also demonstrates the impact of visual images, particularly photography and film, in effecting and affecting remembrance.
The Academic Discovery of Dark Tourism
Dark tourism first entered academic inquiry in 1996 in a collection of articles in a special issue of the International Journal of Heritage ( IJHS ), edited by John Lennon, and later in a book cowritten with Malcolm Foley. 2 The name suggested a striking paradox: that tourism, the recreational form often satirized as the “have-a-nice-day” industry, might not always be the pursuit of light, life, and happiness, but a taste for commercial encounters with death exemplified, for example, in visiting celebrity memorials, genocide sites, and war cemeteries. The notion was one that was to provoke modest, moral panic in the media about commercialization of death, 3 reminiscent of public anxieties about “resurrection men” who sold corpses—murdered or snatched from city graveyards—to medical institutions in the 1830s. 4 In fact, “resurrection men” would not fit Lennon and Foley’s vision of what dark tourism was. They argued that it was a postmodern eruption, “an interest in recent death, disaster and atrocity … in the late twentieth and early twenty-first centuries … a product of circumstances of the late modern world and a significant influence upon these circumstances.” 5 Though recognizing that earlier kinds of travel encounters with death might resemble dark tourism, they were excluded because there was no evidence of intentional visitation, and they had not happened “within living memory.” The view bore similarities to the hypothesis of postmodern “black spots” by the sociologist Chris Rojek for sites where traumatic events had taken place that were visited as touristic “escape attempts” from the world of everyday life. 6 There was the suggestion that the new tourism was suspect in consumer terms (“a fascination with assassination” was the title of one article on the Kennedy assassination), a commodification of death as spectacle for paying visitors. 7 Since all three hailed dark tourism as postmodern, it logically had no significant history. It was the unprecedented shape of things coming and to come. Research case studies in Lennon and Foley’s book Dark Tourism exemplified this neophiliac premise with the inclusion of four chapters on the Jewish Holocaust, and individual ones on the John F. Kennedy assassination, the war sites of the two world wars, and tourism developments in partitioned North Cyprus. An alternative approach to dark tourism appeared in the same issue of IJHS and a later one. 8 It treated the subject under a different name, thanatourism, defined as: “travel to a location wholly, or partially, motivated by the desire for actual or symbolic encounters with death, particularly, but not exclusively, violent death.” 9 This perspective extended the history of dark tourism and the travel experiences within it from a few major atrocity sites in the present to many more going back into the distant past. Thanatourism, it was argued, was not just travel to view atrocities and disasters that had “happened in living memory.” It derived from older, Judeo-Christian traditions of pilgrimage and thanatopsis, prescribing reflection on mortality to their followers. Such thoughts were induced and aided by devotional texts and artifacts which carried memento mori –messages to the living that one day they must die, and ars moriendi counseling on how to do it well. 10 Thanatourism could thus be seen as travel that brought death to the mind, and pilgrimage a way of paying homage to others who had gone before. “Thanatourism” was a more neutral term than “dark tourism” because it lessened the transgressive associations of the word “dark” in recognition that not all traveling encounters with death held sinister undertones. Though Holocaust and genocide memorials evoked unspeakable crimes, paying homage to fallen soldiers and visiting graves of poets and other revered groups and individuals did not. Moreover, the name thanatourism located it more explicitly as a subset of thanatology. 11 The paper offered a constitutive typology of five thanatouristic and dark tourism travel categories:
travel to witness public enactments of death, a form largely proscribed in modern Western societies, though once common in gladiatorial contests in ancient Rome, and in public executions in Britain until 1868;
travel to see the sites of multiple fatality (e.g. Holocaust sites, the battlefield of Waterloo, the town of Lockerbie, Scotland, where a Pan-Am jet was brought down by a terrorist bomb in 1988), and sites of individual deaths ranging from roadside memorials for accident victims, to “blue plaque” domestic sites where cultural celebrities had died;
travel to internment sites and memorials to the dead in graveyards, catacombs, and war cemeteries;
travel to view material evidence or symbolic representations of death, in locations unconnected with their occurrence including, police and military museums, and many kinds of exhibition, including the “Chamber of Horrors” in Madame Tussaud’s which displayed artifacts of murder (weapons, victims’ clothing) alongside wax effigies of the serial killers responsible; and
travel for reenactments of historic carnage, particularly battlefield simulations, staged by members of societies dedicated to particular wars, e.g., Civil War Societies in Britain and America, and Napoleonic battle societies in Europe.
A Historiography of Dark Tourism
Whatever the differences in periodizing and characterizing it, the notion of tourism as “dark” acted as a “refresh” button for researchers who had previously never made a link between the two. For students it was, and has remained, a popular option for undergraduate and postgraduate studies in leisure and tourism. Whether called “dark tourism” or “thanatourism,” the effect was to detonate a developing literature of journal articles, book chapters and conference papers over the next two decades, as well as journalistic attention. 12
The first decade (1996 to 2005) was dominated by ad hoc case studies of individual sites and events that fell into three of the five, dark tourism categories: travel to death sites; travel to internment sites; and travel to view exhibited evidence and symbolic representations. Research subjects included Holocaust sites, 13 historic battlefields, 14 slavery sites in the United Kingdom and the United States, 15 criminal museums and prisons, 16 cemeteries as visitor attractions, 17 and celebrity death sites. 18
The first phase of dark tourism research also included alternative conceptual typologies to the five-attribute category initially proposed. The late Graham Dann produced a site typology of four alliterative thanatourism categories: “houses of horror, “fields of fatality,” “tours of torment,” and “themed thanatos.” Within each were subsumed eleven constitutive subcategories, also alliteratively named (“Morbid museums,” “the Hell of Holocaust,” “Cemeteries for Celebrities,” etc.), followed by a discussion of eight motivations that included “fear of phantoms,” “chasing change,” and “yearning for yesteryear.” 19 Other typologies included those of Richard Sharpley and Philip R. Stone, 20 who adapted a spectrum model of dark tourism, as originally suggested by Tony Seaton, 21 but using different and more numerous criteria for grading sites and experiences that scored them on a darkest/lightest scale, a line of development later pursued by Rachael Raine. 22
Case study work also included investigations into key questions of motivation for dark travel, and that of whether dark tourists were an identifiable segment whose behavior varied sui generis from that of other kinds of tourist (e.g. cultural tourists, golf tourists etc.), or whether the notion of dark tourism was a concept that concealed several kinds of distinctive behavior, each with its own clients and motivations (e.g., Holocaust visitors, battlefield walkers, churchyard, and graveyard visitors). One attempt to identify an overarching motivation behind all dark tourism was the sequestration thesis, first put by Geoffrey Gorer in 1964, 23 revisited briefly by Seaton, 24 and more extensively by Stone. 25 The thesis proposed that death was a taboo subject, suppressed or, in Stone’s terms, made “absent” in modern living, thus depriving people of opportunities for thanatopsis which had been normal in the past. Dark tourism, it was claimed, restored mediated links between the living and the dead, by allowing tourists an existential space to reflect, through gazing on the death sites of “significant others,” on their own mortality. Problems with the thesis later focused on the meaning of “sequestration” and “death … made absent,” since the notion was capable of three different meanings and interpretations: the silencing of thanatopsis (i.e., social suppression of reflection and discussion of death); the exclusion of cultural representations of death (e.g., in art, literature, and the mass media); and the ways in which modern funerary practices removed custody of the body from home and family, and consigned its storage, treatment, and disposal to industry professionals. Gorer had most in mind the latter effect, one which dark tourism could hardly address since, unlike bodysnatching, 26 it was never an intervention in the physical treatment and disposal of bodies by the funeral industry or anyone else. There were also problems with accepting assertions that modern society sequesters or makes “absent” representations of death, given the volume of coverage of war, violence, and murder which routinely colonize media news and entertainment, in print, broadcasting, and increasingly in the privately supplied and leaked photo exposures of social media. It is only if “absence” is treated as the normative silencing of reflection and discussion of death in society, that dark tourism could appear as a restorative experience, precipitating discussions of mortality which would not otherwise take place. Stone, in his work on responses to a body parts exhibition mounted internationally by Gunter Von Hagen, found it did provoke some ontological discussions of life and death among visitors. 27 Similarly, an exhibition of skeletons from different periods, recovered during building excavations in London, generated involvement and reflections on death among secondary school children, when exhibited at the Welcome Library in the capital in 2008. They were, however, primarily in response to questions asked in a self-completion survey administered as part of the visit. 28
No common, general motivation emerged from any of the many, separate surveys of specific “dark” activities. Indeed, some research respondents, when asked, denied interest in, “encounters with death” as a reason for visits, and named different ones, including, interests in history, heritage, education, and, for Australian and New Zealand tourists traveling to Gallipoli, national pride in viewing the site of Anzac, military coming-of-age during World War I. 29 Except in the case of Holocaust visits and battlefield tours, dark encounters were not always discrete, premeditated choices, but made as part of a multistop, package tour schedules. Thus, after a decade or more, research was no nearer to isolating generic motivations for dark travel, or producing a plausible profile of those who could be definitively hailed as, “the real Dark Tourists revealed.” 30 Dark tourism, it seemed, could not be segmentally profiled like other kinds of niche tourism. Moreover, some suppliers of dark tourism, including battlefield tour operators and cemetery managers, did not accept that the business they were in should be characterized as “dark.” Dark tourism thus appeared to be a transaction involving two groups of missing persons: the consumers and the suppliers. This was a problem that had never existed historically when dark encounters were incidental, and had yet to be viewed and named as a transactional market between consumers and suppliers.
Another problem in dark tourism’s discursive evolution was one from within its own academic ranks. This was about its “theoretical fragility,” a phrase that briefly became something of a mantra. 31 Was it anything but a magpie, a hybrid of ideas derived from other disciplinary areas and applied to an endless case of samples? Questions of disciplinary coherence and overlap were most directed at dark tourism’s relations to heritage studies, and its subaltern forms, “dissonant heritage” and “contested heritage,” first explored by John E. Tunbridge and Gregory J. Ashworth. 32 Tazim Jamal and Linda Lelo commented on its crossover features; “a dark tourist,” they noted, might equally be called a “heritage tourist” or a “secular pilgrim.” 33 Duncan Light appraised dark tourism’s relationship with heritage, calling it a “troubled” field. 34 A year later, a reference text, the Handbook of Dark Tourism Studies made explicit the links between the two in an edited section called, “Tourism and Heritage Landscapes” with coverage of atrocity sites, memorial sites, battlefields, and museums as common areas of interest. 35 In the same year, Glenn Hooper explored the dark tourism/heritage interface in an edited collection of international cases with an introductory chapter by heritage veterans Tunbridge and Ashworth. 36
There was no resolution to these internal debates. In retrospect they look like “turf wars” among academics arguing over disciplinary ownership and proprietary rights to comment on issues raised in dark tourism debate. The most pertinent observation, perhaps, about its existence as a distinct and legitimate field of inquiry was that within a decade work in the new field problematized issues and generated inquiries about the relationship between tourism, travel, and death that had never previously been recognized or addressed in any discipline.
And it went on doing so. Work in dark tourism expanded in the second decade of the twenty-first century in conferences, journals, and books which included four edited collections. 37 The subject also expanded in undergraduate and postgraduate programs internationally. Holocaust studies, the best funded in research terms, dominated the field in number of outputs in disciplinary publications. Other disasters and atrocities appeared in research agendas: the Chernobyl nuclear accident, 38 Rwanda genocide, 39 and Dallen Timothy produced a wide-ranging overview of dark tourism in the USA. 40 The novelty of its name and the focus on modern, mega-instances implicitly made dark tourism seem an ultracontemporary phenomenon; it is difficult to open any guidebook or travel memoir of the last two centuries that does not include the “dark” practices of grave visiting, memorial trips, battlefield tourism, and so forth.
Dark Tourism and the Politics of Remembrance
In the new millennium a number of geopolitical events and trends began to affect the status of dark tourism. The events included continuing conflicts following the break-up of Eastern Europe, particularly in the Crimea and the Ukraine; conflicts and instability in the Middle East; a second, Western invasion of Iraq; the aftermath of the “9/11 attacks” in America and the growth of world terrorism; and unprecedented movements of people as political refugees and economic migrants. The decade also coincided with several historical anniversaries: the start and finish of World War I and II and specific phases within them (the Battle of Britain, Stalingrad, Pearl Harbor, D-Day landings, etc.); the Russian Revolutions of 1905 and 1917 ; and the 1916 uprising in Ireland. All of them were issues that came with historical baggage that stirred up feelings about the past, and triggered public debate, among groups inside and outside the countries involved, on what past events had been and how they should be commemorated, if at all. Conflicting versions of historical blame and praise multiplied and, owing to the growth of social media, minority views gained currency that might have gone unheard in predigital times.
The results were rising protests against narratives that were once unchallenged, and direct action at sites where they were commemorated. Monuments, statues, and memorials were vandalized or removed. In Iraq the pulling down of Saddam Hussein’s statue was orchestrated and filmed for international TV news to valorize the triumphant closure of a Western invasion that later created anarchy. Statues of former communist leaders were removed from public spaces in ex-Soviet bloc countries, but provoked protests in Lithuania, when bought by an entrepreneur to exhibit as theme park attractions. At Corpus Christi College, Oxford, students demanded the removal of a statue commemorating Cecil Rhodes, which for nearly a century had celebrated a British imperialist whose legacies funded scholarships at Oxford. In 2019 a Sino-Western war of words broke out at the removal and standardization of Muslim graves in Uyghur cemeteries in Xinjiang Province of China, criticized by Western observers as cultural erasure, and even genocide of a religious minority, which had inhabited the area for centuries.
In academia historians and social scientists had, for a decade, become increasingly interested in forms of ethnic, national, and sectional narratives of the past. The 1990s saw a spate of book-length studies on remembrance and the writing of history, 41 including a Companion to Historiography of almost 1,000 pages. 42 In the social sciences there was exponential growth, following Edward Said’s work on “Orientalism,” of postcolonial studies into the ways Western cultures had historically represented non-Western cultures as inferior, and not infrequently as transgressive kinds of “other.” 43 These developments, which have since become known issues in “the politics of identity and remembrance,” had direct implications for those working in heritage and dark tourism. Heritage discourse and management had previously been a rather genteel world where specialist curators in museums or galleries made aesthetic choices and professional judgments about what was installed and remembered. It increasingly became one fraught with political perils, which were increasingly discussed. 44 Remembrance had traditionally been a semisacred concept, meaning a state of private reflection on loss and bereavement; or, as metonymy for memorials and rituals commemorating national tragedies, as in, “Ceremonies of Remembrance” and “Gardens of Remembrance.” In the 2000s remembrance became a more contentious notion, weaponized by critics for interrogating the legitimacy of some commemorative displays, and the power structures authorizing them.
For dark tourism the questions provoked were fundamental. The protests and direct action at sites of remembrance called into question what dark tourism was or, to borrow Wittgenstein’s interrogative phrase, what “state of affairs” it represented; 45 and particularly whether it was about encounters with death. None of the protests at commemorative sites were encounters with death—which has and always will be an unknown abstraction—but physical tilts directed at physical installations: headstones, statues, monuments, memorial tablets, and ritual ceremonies. Was this not also true of dark tourism encounters? The praxis in dark tourism had, it transpired, never been encounters with death but with visits to sites created or marked as remembrance. Bringing it more in line with what was the real “state of affairs” surely meant abandoning “death” as the focal encounter, and accommodating material remembrance as the experiential goal. A revised definition, aimed to reflect these realities, was proposed that frames dark tourism as “encounters with the engineering and orchestration of remembrance of mortality or fatality” (where mortality was death from natural causes, while fatality was premature decease, in violent, nefarious, or spectacular circumstances). 46 The revised focus revealed a number of “states of affairs” that had not previously been obvious. There were four principal ones: First, that it is the living , not the dead , who have both the first and the last word in remembrance in the control they exert over the engineered choice, siting and orchestration of commemorative measures; and second, they also retain the power to change the nature of remembrance in the future. This power may be limited for family memorials with restricted audiences which are typically extant for only a few generations. Where commemoration is targeted at mass audiences for longer, indefinite periods by national bodies and great public or private corporations, it becomes significant social engineering. In democracies this is likely to involve the active or passive consent of several, or many, stakeholders likely to be exposed to, or affected by, what commemoration is being engineered, and how the orchestration is accomplished. Engineers of public remembrance may thus be called to account before, during, and after commemorative measures are put in place. Third, that the remembrance perspective affects the way the history of dark tourism is viewed. It makes it difficult to imagine it as a latter-day innovation concerned only with atrocity and disasters in modern times. It makes it coeval with the history of human communities on earth, since most known societies have engineered and orchestrated remembrance of the dead in big and small ways. The Assyrians, Egyptians, Persians, Greeks, and Romans all erected public monuments and left inscriptions for remembering and honoring religious figures, and inculcating homage to emperors, kings, and other potentates. They were installed in public places for exposure to local and regional populations as they went about their business and, to a lesser extent, to impress foreign visitors. Many people would have had encounters with them, but they would have mainly been incidental and unplanned, except in special circumstances where the memorial itself became the message, rather than the subject it celebrated, and attracted curious visitors in its own right. This was the case, according to enduring myth, with the Seven Wonders of the World. 47 Fourth, crucially, in academic terms, conceptualizing dark tourism as travel encounters with engineered remembrance, makes it a quintessential study area in the wider study of the “politics of remembrance.”
Dark Tourism as Praxis in History
Dark tourism, as travel tastes for visiting sites and spaces commemorating different kinds and intensities of mortality and fatality, only grew to be a generic tourism preoccupation in Britain and Europe in the late-eighteenth century and early nineteenth centuries. Before that for around 200 years, the dominant tourism form had been the Grand Tour, which accorded no particular importance to representations of death sui generis (see Verhoeven , this volume). 48 It was a European ritual tour, routed mainly through France, Switzerland, Germany, and Holland for young aristocrats and the gentry. Lasting up to three years, its manifest purpose was as a crash course in classical antiquity, Christian history, and art viewed in galleries, churches, cathedrals and other public buildings. It was also often a form of social bonding and hedonistic indulgence among European elites ( Seaton 2019 ) 49
Representations of mortality and fatality were, in fact, abundant among Christian paintings, sculptures, and buildings viewed by Grand Tourists, but were viewed primarily as religious and artistic exhibits, rather than with any of the cultural relativism that underpins inspection through the prism of the “politics of remembrance.” The default stance of grand tourists was to regard their own cultural assumptions, religious and nationalistic, as normative and universalistic ones. The only sepulchral encounters they had with sites that were coded with less prescriptive cultural meanings were campo santo sites in Rome, Naples, and Pisa, which were mass burial sites for the poor, and ossuaries where the bones of the dead were displayed in catacomb as curiosities rather than homilies. 50 In Rome even catacombs could be viewed as religious shrines rather than macabre spectacles, since they had been early Christian meeting places, and some of their walls bore graffiti that could pass as sacred art. By contrast, dark tourism, as a widespread travel preoccupation with representations of death, was a product of changing material and ideological factors at work in the late-eighteenth and early-nineteenth centuries. Some involved reinvention and repurposing. Some were new.
Pilgrimage Renewed and Reinvented
Pilgrimage had been a long-standing tradition in Christendom of visiting sites at home and abroad associated with sacred figures (see Craig , this volume). Abroad meant Palestine, Jerusalem and the Holy Land, and for Catholics, it included Rome. There was also a network of British shrines to lesser Christian saints and martyrs, the most important being that of Thomas Becket (1120–1170) at Canterbury. During the Reformation, Protestant countries abolished pilgrimage as a Catholic superstition that was denounced by religious leaders and humanists, the most notable being Erasmus. It made a “dark” comeback in several ways. The first was during and after the Napoleonic Wars, when English visitors to France began to make excursions to Catholic churches and monasteries—previously seen as the devil’s abodes—to witness the mob destruction or vandalism of ecclesiastical property during the French Revolution. The prime site was Saint Denis, the Cathedral where French kings and queens had been buried. There artifacts and monuments, torn from churches and monasteries were put on display for visitors as a makeshift “museum.” The result appalled English tourists so that after nearly 300 years of demonization, Catholic clergy came to be seen as Christian comrades-in-arms, and victims of an anti-Christ who was no longer the Pope, but Napoleon. My enemy’s enemy had become my friend. Thomas Cook and Son revived pilgrimage to pre-Reformation destinations with tours to Rome, the Vatican, Palestine, and the Holy Land (see Barton , this volume). 51
In addition to these revivals, a new kind of secular pilgrimage grew up during the nineteenth century to places commemorating celebrities of nation and empire. In Britain the graves, memorial monuments and death sites of literary and artistic figures, particularly poets, 52 became shrines that coexisted alongside those for more official figures. In Westminster Abbey and St Paul’s, poets and novelists shared monuments and memorials with royal and ecclesiastical notables. Elsewhere in Britain, the last whereabouts and resting places of celebrities formed a growing dark tourism circuit which were widely publicized in travel memoirs, illustrated guidebooks, and magazine features by writers, some of whom specialized as paparazzi of the posthumous. One was William Howitt whose “Homes and Haunts of the British Poets” comprised essays on the geographical origins and deaths of thirty-six writers. 53 A dozen editions were sold over the next sixty years. He had previously published another much-reprinted book of dark tours in the North that included: celebrity memorials and burial places (St. Bede and Thomas Bewick, the celebrated wood engraver), battlefields (Culloden and Flodden), mining disasters, murders, executions, and apparitions. 54 A work that drew more explicit analogies between “pilgrimage” and dark tourism was by Mrs. Samuel Carter Hall, wife of the editor of the Art Journal who in 1850 published “Pilgrimages to English Shrines.” It was successful enough for her to bring out a sequel two years later which included an authorial aside, hinting at the pleasurable schadenfreude that lurks in certain kinds of dark tourism encounter: “Pilgrimages! what is life but a pilgrimage over graves! The older we grow, the better we comprehend the force of this sad truth; life is indeed a ‘pilgrimage over graves;’ but how different are the ideas and emotions they suggest or excite.” 55 The two volumes included chapters on tombs, death sites and memorials to writers and artists, among them: Christopher Wren, Thomas Flaxman, Thomas Gray, and William Hogarth, with additional chapters on the execution of Lady Jane Grey, and the plague village of Eyam whose residents quarantined themselves to likely death in order not to spread the disease.
A related influence on dark tourism was antiquarianism. Like pilgrimage, this was nothing new. It was a legacy of the Renaissance revival of interest in classical antiquity among educated European elites in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, in part politically and patriotically generated by the growth of new nation-states and dynasties such as the Tudors, when rulers and ruled joined forces in discovering evidence of ancient, cultural traditions. This involved enthusiastic searches for written texts, artifacts, and sites of architectural and archaeological significance involving quests to libraries, burial grounds, ruins, and ancient ecclesiastical foundations where they pored over old documents, memorial tablets, tomb inscriptions, and other sepulchral survivals.
Antiquarians increased throughout the seventeenth century, leading to the foundation of the Society of Antiquaries in 1717–1718. 56 Its members were periodically satirized as eccentric old men, shut off from real life by their fixation with musty books, moldering remains, and fragments of broken artifacts. Nonetheless, the antiquarian mindset increased among educated travelers across Europe, particularly after the discovery of Pompeii and Herculaneum in the 1740s, where excavations captivated generations of tourists in Italy. 57 In Britain, antiquarianism became a gentlemanly hobby, often among clerics discovering local history in their parish travels. It resulted in the publication of substantial town and county histories, as well as briefer guidebook information for visitors to individual churches. Antiquarianism, in conjunction with archaeology, led to a desire for take-home mementos, which tempted visitors to chip off fragments from sites at home and abroad. 58
The Dark Appeals of Romanticism
More powerful than pilgrimage or antiquarianism in its impact on dark tourism was that of romanticism, a complex cultural phenomenon characterized as, “a heterogeneous mixture of philosophic, aesthetic, religious and emotional concepts.” 59 It colonized middle-class aesthetic tastes throughout the nineteenth century, providing escapes from the prosaic or oppressive realities of industrialization and urbanization at home, to the imagined worlds of other places and other times in literature, music, and art. Tourism gave physical reality to some of these longed-for romantic contrasts: in landscape tastes (picturesque scenery in Italy, the Lake District, and Wales); among traditional, rural populations (peasant communities in regional dress in Brittany and Scotland); through exposure to traditional myths and folklore in books with titles such as Legends of the Rhine and Border Ballads of Scotland; 60 in attending regional festivals of song and dance; and in brief retreats from the modernity of railway conveyance to retro-travel forms (jaunting-carts in Ireland, camel rides during Holy Land tours, and pony trekking through Iceland, a land with few roads and no railways). 61
Dark tourism offered two of the most powerful forms of escape into romantic otherness. The first was the world of the past and the second was vicarious experience of death, the most feared and mysterious of all “others.” The past was where the dead had lived and died, and there were special places where their presence lingered. Reflections on death, once devotional practices at home, became recreational trips further afield: in visiting celebrity memorials, battle fields, and in enjoying the more frivolous pleasures of ghost trains, haunted houses, and other fairground attractions.
These dark tastes and recreations were critically affected by sociological factors arising from population change and revolutionary developments in the production and consumption of printed words and images from the late-eighteenth century onwards. Printing moved from being a hand-powered craft that had hardly changed in the 300 years since Caxton, to a modern, machine production technology, capable of producing thousands, rather than hundreds, of copies per day of newspapers, magazines, and cheap books. Costs fell, allowing more people to buy them, and literacy grew. The result was an expanding audience for reading of all kinds. It was most potent among the middle classes, but it was also observable among sections of laboring populations where the growing take-up of cheap reading was satirized in the 1830s as the “March of Intellect.” 62 The net effect was that new ideas circulated more quickly than ever before. Without the printed word the concepts and activities, later recognized as romantic, including those that primed dark tourism, would never have taken hold.
Two key ideas that permeated the landscapes and dreamscapes of romanticism were the Gothic and sublime. The Gothic was an aesthetic categorization, variously applied in judgments of architecture, ecclesiastical decoration, and literature from c. 1740 and throughout the nineteenth century, that implicitly drew a binary contrast between the rule-governed styles of classical cultures and the more unruly, plenitude of vernacular ones. In architecture and art the Gothic Revival meant a crusading preference for indigenous Anglo-Saxon styles found, it was claimed, in medieval, Christian church buildings of England, France, and Germany, with their soaring heights, pointed arches, and abundant decorative effects, in opposition to the geometric restraint and laws of classical and Palladian styles from Greece and Italy. Its proponents included Augustus Pugin, John Ruskin, Walter Scott, and less well-known, but important opinion-formers in publishing and graphic reproduction. One was the prolific engraver, John Britton, who published many, finely illustrated viewbooks depicting Gothic buildings at home and abroad; and John Parker, the Oxford religious publisher who specialized in gothic ecclesiastical design. 63 All extended the province of dark tourism.
Of equal impact to dark tourism was Gothic literature, which first emerged in the mid-eighteenth century in the sepulchral travelogues of a literary group who became known as “graveyard” writers. Three of the most successful were Edward Young, with his poem “Night Thoughts” (1749); Robert Blair with his poem, “The Grave” (1743); and in 1746, James Hervey, with a prose work called “Meditations among the Tombs.” The themes they explored—the brevity of life, the inevitability of death, the need to reflect and prepare for eternity—were conventional, thanatoptic ones, common in memento mori and ars moriendi texts going back to the Middle Ages. The difference was that previously “the grave” had been symbolic shorthand for death; in the work of Young, Blair, and Hervey it was also physical location, described at length or imagined in visceral detail as a visitor attraction. Hervey’s book had been inspired by a tour of Cornwall when he had stopped off at a village church in Kilkhampton, Devon, to read epitaphs in the churchyard and memorial tablets within the church. None of these works, however, came close to the crowning achievement of graveyard travelogues by Thomas Gray with his Elegy Written in a Country Church Yard. 64 Published in the 1750, it remains the best-known poem of the eighteenth century and one which has given country churchyards an iconic place in English culture and dark tourism. 65 The precincts of Stoke Poges Church in Buckinghamshire, which is believed to have inspired it, has a large, stone memorial to Gray and his work, and his grave is close to the church entrance. All four works were forerunners of what has been described as, “the therapeutically melancholic side of Romanticism.” 66 William Blake, the most Gothic of all English artists, later illustrated editions of all three works, and William Wordsworth took time off from poetry for writing prose essays on epitaphs and memorials. 67
An even more influential form than graveyard travelogues in dark tourism creation was the Gothic novel. It was a genre of horror and sensation that has been called “literary terrorism,” which was first introduced in Horace Walpole’s The Castle of Otranto (1764) and followed by Anna Radcliffe’s The Mysteries of Udolpho (1794) , and then by a torrent of works that were to fill a bibliography by Montague Summers that was over five hundred pages long. 68 Their plots were characteristically set abroad in Catholic countries, especially Italy, where superstition and transgression reigned in castles, monasteries, and haunted houses, freely equipped with locked rooms, secret cabinets, dungeons, and supernatural apparitions. The villains were evil monks, depraved noblemen and wicked guardians, who preyed on innocent orphans and helpless women relatives. Gothic novels enjoyed a runaway success between 1760 and the 1830s, particularly among women readers, a trend satirized in Jane Austen’s novel, Northanger Abbey published in 1818. It then declined, but morphed into mystery novels with more domestic, contemporary settings by Sheridan Le Fanu, Edgar Alan Poe, and Wilkie Collins. The Gothic played an important part in influencing the perceptions of place that tourists took with them on their travels at home and abroad. It can be found in the attraction of visiting ancient castles, ruined monasteries, haunted houses, and locations with pronounced—which means “promoted”—atmospherics of gloom, decay, and the uncanny. 69 Historians too affected Gothic travel perceptions in offering a Lapsarian view of the world which emphasized the destructive effects of time and change on places and people. In England Edward Gibbon’s work, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire (1776–1787), became a bestselling sensation. Inspiration for it came when he wandered as a tourist among the ruins of ancient Rome, and then spent more than ten years writing a six-volume work trying to account for how they were all that was left of an empire that had ruled Europe for 600 years. In France, almost coincidentally, Constantin Volney published The Ruins of Empire , 70 a philosophical work which also made the ravages of time, change, and death an underlying leitmotif. Both works were translated and inculcated a mindset among educated, European tourists who made it de rigeur to view landscapes that evoked melancholic reflections on death and oblivion, while enjoying the pleasant, recreational Schadenfreude of knowing that they had not yet become victims, and would soon be returning safe from their excursions to hotel or pensione for a well-earned meal. The poet Percy Bysshe Shelley encapsulated this dark tourism mindset in his sonnet, “Ozymandias,” which describes the metaphorical tears he shed in stumbling upon the bust and remains of a once-great monarch of all that he surveyed, abandoned and half-hidden in the sand. 71
Romanticism and the Gothic incorporated a related ideology that became inscribed in dark tourism praxis. It was that of the sublime, a classical concept given new life by Edmund Burke in a slim volume first printed in 1757. 72 It was a treatise on aesthetics that proposed a simple idea—that aesthetic pleasure was not necessarily tranquil contemplation of beauty in art or life; it could also be found in disturbing natural or man-made phenomena that provoked fear, particularly if they were indistinct or partly obscured (e.g., in mist, semidarkness, or storm clouds). Sublime thrills became desiderata of the dark tourist gaze, in which delight competed with shock and awe in exposure to violence in nature (volcanoes, great waterfalls, storms at sea, etc.); displays of massed human power (scenes of destruction, and orchestrated, military parades); and supernatural narratives. All these ideas account for a long-standing paradox: that what is apparently “seen” with the eye is actually the preconditioned mind encountering and recognizing the cultural coding invested in sights and sites. It is antecedent conditioning which turns spaces into places, and “stuff happening” into significant form and occasion.
Cemeteries and the Transformations of Internment
Dark tourism tastes were not just down to new ideas processed by imagination. There were more visceral factors which affected the repertoires of dark tourism which resonated physically in Britain and Europe. A macabre one in rapidly growing cities was how and where to bury the dead—and keep them buried. Until the mid-eighteenth-century graveyards were plain affairs with burial sites marked, if at all, with a simple, wooden memorial board, featuring a name and, occasionally, an emblematic sign: a cross or a death’s head carving. Only the gentry had more durable memorials, on brass or marble tablets inside churches on walls or floors, and in full body effigies and head-and-shoulder busts arranged around the sides. Church yards and public burial grounds were less sacrosanct and more plebeian and were sometimes used for mundane, or even profane, activities. Booksellers and market stalls flourished round St Paul’s Cathedral in London. Hogarth depicted gambling taking place in a London church yard; and the artist, Thomas Rowlandson, drew burlesque cartoons of sexual activity on “table-top” tombs.
As populations in towns and cities increased, the situation changed. Spaces for burying the dead began to run out. To cope public authorities stacked bodies closer and higher together, in multiplying tiers, under thinner and thinner coverings of soil, so that burials per acre increased exponentially. The result was that in populous areas graveyards became a health hazard for those living near, as the earth gave up its dead and bodies decomposed near the surface of graves, or actually floated free of them in wet weather. The dangers were revealed in a sensational book by a London surgeon in 1839, 73 and a government report which detailed the “dangerous and fatal results produced by the unwise and revolting custom of inhuming the dead in the midst of the living.” 74 It showed that in some parts of London, the density of corpse distribution was over a thousand per acre. It was followed by a supplementary Parliamentary Report, written by Edwin Chadwick, which statistically analyzed the scale of the health hazards between 1830 and 1840, and looked at practices in Europe for dealing with them. 75
The solution was the garden cemetery, located out-of-town, away from populations and, ideally, in elevated settings swept by fresh, clean air. First adopted in Sweden, they spread through other European countries, including Père Lachaise in Paris in 1804, and in Liverpool and Glasgow in the late 1820s and 1830s. 76 By the time Chadwick’s survey was published the cemetery movement was underway in London with cemeteries opening in Highgate, Nunhead, Brompton, West Norwood, Tower Hamlets, Kensal Green, and Abney Park. They followed functional and aesthetic features proposed by George Alfred Walker and Chadwick. They were also influenced J. C. Loudon’s pioneering work “On the Laying Out, Planting, and Managing of Cemeteries and on the Improvement of Churchyards,” which became a classic work on sepulchral design. 77
James Curl has written extensively on the architecture and aesthetics of cemeteries and internment nationally 78 and regionally in the United Kingdom (Curl 1977, 1980 , 1981 , 2001 ). 79 The look and character of cemeteries was also improved by the coming of the railways which made easier and cheaper the transportation of monumental stone, thus putting memorials and headstones within the reach and budgets of people previously restricted to local materials or none at all. Rail also shaped the most macabre of all cemeteries: Brookwood in Surrey, which was built to take the overflow of corpses from London and had its own station for receiving them on a single ticket running direct from Waterloo to their final destination. The aesthetics of internment brought about by the garden cemetery revolution was one of the unanticipated consequences of history. Conceived for health reasons as secure resting places for the dead, they evolved as recreational spaces for the living, designed to be within easy reach of visitors, offering picturesque layout and planting and, as time went on, by the architectural variety of their monuments. Guidebooks to all the main London cemeteries were produced that promoted their funerary functionality, but also their picturesque and elegiac effects for dark tourists. Today more than 400 cemeteries belong to the Association of Significant Cemeteries in Europe, founded two decades ago, to promote them as visitor attractions (Felicori and Zanotti 2004; Seaton 2015 ). 80
Another unintended consequence of the cemetery movement was to add a new pastime to the repertoire of middle-class touring, epitaph collecting. Monumental inscriptions had always been prized by antiquarians studying Greek and Roman culture during the Renaissance and later as primary sources of national and local history. On James Harvey’s grave was inscribed a commendation on the value of epitaphs as history and religious lessons in stone:
What biography is to history, an epitaph is to biography. It is a sketch which marks the great outlines of character and excites curiosity to view the portraits as painted on the pages of history. It is likewise an epitome which teaches us … that time is on the wing,—that every rank and age must fall prey to his depredations … (and) that religion is the only defence against the horrors of death, and the only guide to the joys of eternity. 81
This high-minded view was not always apparent in the epitaph literature that flourished in the nineteenth century. By the 1880s, a bibliography listed more than a hundred separate works with titles suggesting that entertainment as much as improvement was the main attraction. Viewing them promised lively titillation as they were named as: ludicrous, merry, queer, panegyrical, satirical, humorous, whimsical, curious, quaint, monkish, and not to be found in any other collection . 82 Epitaphs were also organized by geographic categories: by continents and subcontinents (America, India, Bengal, and Madras); by country (West Indies, France, and Scotland); by towns and cities (London, Westminster, Rome, Glasgow, Edinburgh, Canterbury, and Winchester); and there were compilations of those in single, country churchyards (Cockermouth, Charlton King, and Framlingham). Magazines and journals also featured epitaphs, suggesting their broad and diverse appeals. They appeared in specialist antiquarian and archaeological publications, in the transactions of local history societies, and in general interest magazines with a popular readership including Chambers’s Journal , Tait’s Edinburgh Magazine , Temple Bar, and Household Words (Charles Dickens’s monthly). There were also entries in encyclopedias, including the Encyclopaedia Britannica , and a society dedicated to sepulchral remembrance, The Society for Preserving Memorials of the Dead, published its own magazine between 1883 and 1885. 83
In the USA sepulchral travel and garden cemetery development more than kept pace with European fashions. Internment space was initially abundant and burials were not confined, as in Europe, to demarcated, walled-off, graveyards. This changed as the density of burials per acre increased in settler towns, along with the problems of maintaining graves that became neglected over time. Mount Auburn, the first garden cemetery, was consecrated in 1831 in Cambridge, Massachusetts and Green-Wood in Brooklyn, New York was opened in 1842. Both published illustrated, coffee table guidebooks, 84 and American cemeteries evolved as picturesque developments, competing for public attention by position, plantations, monumental variety, and history. In the 1880s two hundred copies of the first book-length, sepulchral bibliography in the world was published. 85
The cumulative impact of these developments was to foster a sepulchral mindset that particularly affected educated, middle-class touring behavior and generated guidebook recommendations for excursions that included: trips by candlelight round ruined monasteries and monk’s graveyards at Tintern Abbey and other locations in England; midnight descents into catacombs and ossuaries in Europe, accompanied by servants with burning torches; trips round royal and ecclesiastical memorials in Westminster Abbey, St Paul’s, and great religious sites in Europe; exploration of Campo Santos in Italy; visits to the Paris Morgue to gaze at corpses, found dead in the streets or fished up from the Seine; 86 and reverential reflection at the graveside of dead poets and writers wherever they could be found. 87 It also included taking in the fields of Waterloo, the first European battlefield to become a mass tourism site. This involved an all-day drive out from Brussels to view the immense “lion” monument, buy a guidebook written by Edward Cotton, an old soldier turned on-site gift shop and museum entrepreneur, and returning home with battle souvenirs (buttons, badges, and bullets from the battlefield, some of them manufactured, it was said, in Birmingham to meet demand); and folios of Gerard’s lithographs of the principal skirmishing points, memorials and mausolea, none of which featured the French. 88
Governance and Remembrance: The Urban Wallpaper of Mortality and Fatality
A new and less obvious influence on dark tourism generation in Britain during the later nineteenth century was the Victorian state, and the forms of engineered and orchestrated remembrance of mortality and fatality it promoted. These had been inscribed in Britain’s judicial system since medieval times, in the practice of publicly executing and punishing criminals in front of sightseeing crowds, and then distributing their body parts at crossroads, along highways, and on bridges as a warning of the long reach of the law for enemies of the state. 89 In Queen Victoria’s reign these brutal, outdoor displays were terminated by Parliament, but streets and public spaces were retained and progressively reconfigured as different aides memoires about the might and majesty of the Victorian empire. Three initiatives were to affect dark tourism exposure: the state funeral, the progressive expansion of memorial statuary, and blue plaque signage.
Royal funerals had always been ceremonial occasions of “pageants and power,” 90 but until the early nineteenth century they were conducted semi-privately with less overt street-level orchestration. The two earliest to approach the status of national occasions were Nelson’s funeral in 1805 and fifteen years later, that of George III, which drew large crowds on to the streets, with the tolling of church bells, and memorial sermons in London churches and across the provinces. 91
The number and scale of state funerals in Victorian England increased and were extended to nonroyal, national, and imperial celebrities. Their impact was first seen at the funeral of the Duke of Wellington in 1852. He had died on September 14, but agreement between the Crown, the Government, and Parliament on the details of the ceremony took two months, and the funeral did not take place until November 15. It was an unprecedented PR success and tourism bonanza, filling lodging houses and hotels in the metropolis before, during, and after the event. It started with a week during which Wellington’s body lay in state for visitors to pay their respects. A quarter of a million people filed past his coffin. The day itself brought more than a million sightseers on to the streets to watch a processional cortege that took two hours to pass by. They came from all over London. There were also invited VIPs from the provinces: mayors, provosts, and chairs of municipalities and county councils, representatives from religious groups, and from the universities. Also lining the route were thousands of day trippers from across England, who had bought cheap excursion tickets that the railways had refused to allow until the 1850s. It has been estimated that the funeral was watched by half of London and 5 percent of all the people of Great Britain. 92 In towns and cities across the country shops and businesses closed for the day, and people joined the party by proxy, as spectators or participants of memorial services held in provincial churches and cathedrals. The week after another 100,000 visited St Paul’s to see where the great event had taken place. State funerals for non-royal figures later included William Gladstone, David Livingstone, and Major General Charles Gordon of Khartoum. 93 The climactic one of the era was Queen Victoria’s own funeral in 1901, the epic scale of which, as imperial theater and civil religion, can still be witnessed in its processional, gun-carriaged, street-thronged splendor, as the first royal funeral to be filmed and widely photographed. Great royal funerals were necessarily in short supply, and even when royal marriages and jubilees were added to the roll call of national rejoicing, great open-air occasions were still infrequent. However, during the latter half of the century and into the next, two more ubiquitous kinds of street commemoration advanced in London and cities throughout the Empire. The first was the spread of public statues to political, cultural, and military heroes. In 1844 there were only 22 statues; by 1867 there were 41; by 1920, 215; by 1928, 350. In 1981 there were 370 on the outside of Parliament alone, and other government buildings had many more. 94
The second was the development of “blue plaque” signage on London houses and buildings of historic interest, recording, among other things, where national celebrities had lived and died. Until 1900 there were only thirty-four, but in 1901 the new Greater London Council took over responsibility for them, and by 1935 had published five volumes of additions to the stock. 95 Each building was inventoried: by original owner, private, or institutional; by address; and by sponsoring agency when not the Council. Blue plaque signage was official exploitation of the already established tourism fashion for visiting places where the famous had worked and died. The result was that in London, statues, blue plaque sites and memorials, all sited for maximum impact and exposure, surrounded native Londoners and still do so for the 20 million visitors who arrive annually in the metropolis, to wander the streets, or sit out in London’s parks and public gardens.
In addition to these Victorian initiatives, two world wars in the twentieth century have produced an international array of British war memorials, the most numerous being the 1,400 or more in France and Belgium as part of the Imperial, later the Commonwealth, War Graves Commission. 96 Others exist in churchyards, village greens, and on buildings and city walls, throughout Britain.
These official investments in historical remembrance, and other more tourist-oriented animations of Britain’s past, have provoked criticism. Robert Hewison viewed the British “heritage industry” as nostalgic excess, 97 and Patrick Wight saw the presented culture of Britain as fixation with, “living in an old country.” 98 But they miss the point. Irrespective of tourism generation, remembrance of national mortality and fatality have evolved as essential features of governance and state craft across the developed world. They mold historical identity of a country and its people by providing exemplary, or cautionary, role models, to follow or reject, as personification of national values. But no version of remembrance is ever final closure. Historical memory of individuals and events changes according to when they were written and, crucially, by those who control remembrance policies and the resources to implement them. The VE Day celebrations in Western Europe in 2020 provided a suggestive instance of the moving politics of commemoration. Russia was an ally of Britain and America in the victory over Germany, and the Red Army were mythologized at the time as iconic comrades, with a government-backed campaign in the United States and United Kingdom. Russia’s losses to the Nazis amounted to 27 million fatalities. Yet seventy-five years later Russia was written out of official VE celebration agendas in Europe, a “state of affairs” that supports the observations made earlier, that it is the living who engineer and orchestrate remembrance, or silence it.
Although governments and large corporate interests may shape the form and location of commemorative sites of mortality and fatality, their impact as dark tourism may be limited. In London few visitors come specially to view statues or houses, except in rare cases such as the Albert Memorial or Nelson’s Column. More commonly they may register with visitors, if at all, as fleeting, pass-by encounters, that some may stop briefly to read, and, in the case of a blue plaque house, visit when open to the public. This question of impact is crucial. Dark tourism involves a spectrum of different events and locations, ranging from individual street memorials to a few mega-events that dominate media and academic agendas (e.g., Holocaust and other disaster sites). All share a generic identity as engineered and orchestrated remembrance of fatality and mortality, but the volume and quality of the encounters they represent may vary profoundly. Is, for example, being briefly exposed to a blue plaque sign a dark tourism encounter? How long must site contact last “to count” as a significant encounter? How intentional must an encounter be to be authentic? These are difficult questions yet to be answered.
The case history that follows exemplifies some of these issues raised and the ways in which remembrance of fatality and mortality may evolve and change over time. Its subject is one that has received little attention in dark tourism research, that of occupational fatality and community displacement in industrial development. This has not just been about technological change in the production of goods, it also involved new transport networks accompanied by disruptive physical transformation. Canal and railway building required land appropriation, demolition of residential areas, mainly among the urban poor, and often human fatalities in the construction and operation of new transit forms. The case focuses on dam building and urban water supply, and the spectacular obliteration of communities accompanying them, seen on an epic scale in Wales in the 1880s and later internationally. It is the story of the flooding of community spaces and the creation of, perhaps, the most bizarre of all remembered dark tourism sites, the sunken village under the water.
Case Study: Dark Tourism and Remembrance: Vyrnwy, Llanwddyn, and Whalley Bridge 1888–2020
In the summer of 2019 a disaster threatened Whalley Bridge, a small town in Derbyshire, UK. After weeks of unprecedented rainfall, a nearby dam wall threatened to collapse and flood the town below. Residents were evacuated and the nation looked on as engineers fought to prevent the disaster. After six weeks they were successful and evacuees began to return to their homes, only to encounter a new inundation, not of water, but tourists, including “busloads of Chinese” arriving to view the disaster scene that never was. The press, hearing of the tourism revenues among local shopkeepers, hailed a unique situation with the headline: “Disaster tourism arrives in Whaley Bridge after dam incident.” 99 In fact, it was not such a tourism novelty. While Whalley’s fate hung in the balance a rarely seen photographic record had come to light of a dam flooding in rural Wales, more than 130 years before. Llanwddyn was a village of 450 inhabitants in the River Vyrnwy valley, sixty miles from Liverpool, an English industrial city with a population that had more than quadrupled in 50 years. The city’s growth had created recurrent crises in water supply and, after running out of suitable, local options, the Municipal Council identified Llanwddyn as the site for a new reservoir, and sought Parliamentary permission to build a dam, flood the village, and create a lake there. In 1881 an Act was passed allowing development.
Despite local opposition work began on the dam foundations in October 1882. For the next five years a work force of one thousand stone masons and laborers worked on the construction. Forty of them lost their lives in the process. Once the dam was completed the flooding began submerging a church, two chapels, four pubs and around 100 houses. In mitigation of the community catastrophe, the Liverpool Council re-housed residents in a new settlement near the created lake, built a new church on a hillside above it and, nearby a sloping burial ground to which they transferred the bodies and gravestones from the old churchyard. 100
A Council concern throughout the project was the management of public relations in engineering and orchestrating remembrance of the dam development for posterity. Official details of the choice of location, geographical features, costs and engineering features were recorded and publicized. The development was promoted as the first, all-masonry dam in Britain, and the artificial reservoir as the largest in Europe. These details made news in specialist publications and attracted technical sightseers to the Vyrnwy site, during and after the construction. 101
As the development progressed engineered remembrance of the construction was cast more durably in iron, memorial tablets, struck successively to mark three phases of the project: the laying of the foundation stone in 1881; the official Parliamentary conclusion, unveiled by the Prince of Wales in 1910; and changes made between 1933 and 1938. The tablets were sited and mounted at the entrance to the bridge across the dam top, so all visitors had to pass them in crossing on to, or off, the bridge. However, the most powerful form of engineered remembrance, and one that was to establish Vyrnwy’s tourism identity for a century or more, was not textual, but architectural. It was the building of a sporting lodge-cum-hotel above the dam with spectacular views down the lake, and a twelve-mile path around it planted with tree cover. For a century the area became a noted sporting resort for hunting, shooting, and fishing. In 1992 an illustrated hotel history was published. The first chapter described the creation of Vyrnwy as “one of the greatest feats of engineering in the Victorian era,” but the main content was of shooting and fishing records, grand social occasions, and fine dining. 102 The flooding and fatalities in construction received brief mention but the numbers of the dead, it was said, were about the norm for workers killed in comparable industrial projects at the time. There was no mention of resident feelings or opposition to displacement at the unprecedented sinking of a whole village which survive in the disparate evidence of oral tradition and regional news accounts to this day. 103 These can also be sensed in the unexpected reappearance after a century of a large, leather-bound, photographic album, produced by the Liverpool Council for their records, but never widely exhibited. It is in two parts and comprises 21 full-page, before-and-after photographs of the dam construction which lends weight to Lennon’s recent notes on the resonance of photographic imaging in dark tourism generation. 104 Part one depicts the titanic scale of the project: the cavernous excavations, the earth moving-machines (Figure 1 ) and the rise of the dam towering seventy-five feet above the disappeared village, and the pygmy figures of workers among it all (Figure 2 ).

Dam Construction 1.

Dam Construction 2.
Part two offers an elegiac, slower movement to this percussive spectacle. It shows two images of Llanwddyn on a summer afternoon before the flood: a tiny village street, an ancient church, an old-fashioned general store, brothers and sisters holding the hand of little ones (Figure 3 ); and women gossiping at a garden gate, a hen pecking its way through dust, and villagers in working clothes staring, unsmiling, at the camera (Figure 4 ).

Llanwddyn before.

Llanwddyn to be submerged.
For the modern viewer the juxtaposed photographs act as allegorical emblems of a dark effacement, that of a traditional way-of-life buried under the juggernaut of industrial advance. It is remembrance that resonates with walkers who leave the path around Lake Vyrnwy and climb to the church and the memorials in the graveyard on the hill where a hundred exhumed bodies from the flooded churchyard were carried in carts, and reburied, by local people who had lived in the houses that were lost. Similar images exist of demolition during early Victorian railway building but, as lithographic prints, they cast a softer, more picturesque halo over devastation compared with the starker realism of photography that came later. 105
Vyrnwy and Whalley Bridge represent chapters in dark tourism created by flooding in dam and reservoir building that was to be repeated in Britain at: Mardale in Cumbria (1935), 106 Ashopton in Derbyshire (1943), 107 and in the 1960s at Capel Celyn in Wales, less than two hours away from Llanwddyn. 108 All became causes célèbres in which local communities clashed with governmental authorities invoking the primacy of the public good over claims of minority rights. Internationally sunken villages multiplied throughout the twentieth century, becoming collateral damage as mega-water projects proliferated across continents. In the new millennium they have begun to attract website coverage from bloggers, planners, and regional tourism promoters. In 2014 an urban heritage posting hailed the gothic appeal of, “Underwater Ghost Cities & Buildings.” 109 A year later they were identified as a network of generic tourism attractions under the headline, “10 Drowned Towns You Can Visit.” 110 The ten included Villa Epecuén in Argentina which had been an elite resort for the rich and famous since the 1920s, but was submerged when a dam broke in 1985; 111 Shi Cheng, flooded in 1959 to become “China’s ‘Atlantis in the East’” with monuments below the waves going back to 1777; 112 as well as Potosi in Venezuela; 113 and Port Royal in Jamaica. 114 In the United States there were more than sixty locations “flooded by the creation of dams, destroyed by the advancing sea, or washed away in floods and never rebuilt.” They stretched from California to Maryland and New York. 115 Canada became part of this network of nemesis by water with a posting of ten communities submerged in the construction of the Saint Lawrence Seaway. 116 The global spread is so great it has been suggested as an air tour opportunity. 117
The fascination of sunken villages as dark tourism sites—what Bess Lovejoy terms their “mental floss”—rests in their appeals to the mind and imagination. 118 At the outset this lies in their prospective power to obliterate and transform place and community by flood. Once constructed it is the nightmare possibility of technological failure causing dams to break, bridges to collapse, and in modern times, nuclear catastrophe to inundate power stations; all of them, visions of mega-death by water.
Death by water on a grand scale also holds unique, mythic terrors evoking memories of biblical and classical catastrophe of Noah’s Ark, Atlantis, Santorini, 119 and other flood myths in world religions, explored in the anthropology of Sir James Frazer. 120 Sunken villages also represent a variation of the aesthetic Rose Macaulay: once called “the pleasure of ruins,” 121 a gothic disposition that is turbo-charged under water as townscapes mutate into submerged wastelands of “mildewed crosses, lonely spires, barely-visible stone foundations, and rusting bed frames.” 122 More than any kind of dark tourism, sunken villages come closest to delivering encounters with the uncanny in its most quintessential guise, as haunted landscapes of spectral reappearance and the returning undead. This revenant fantasy seems close to reality during hot summers when the waters of lakes and reservoirs shrink and what once was, reappears as what is. Such special effects happen intermittently at a number of sunken villages. At Vilarinho Da Furnas, flooded by the Portuguese Electricity Company, part of the village reappears in autumn and winter, and there is a nearby museum to tell the story. 123 At Kalyazin, in Russia, church steeples rise above the waves and bells, lost below the water, are rumored to ring out again. 124 In St. Thomas, Nevada, certain buildings remained visible which now include houses, a square, and a cemetery. 125 In Flagstaff, Arizona, a historical society archives and exhibits memorials to the sinking in 1949. 126
Llandwddyn’s first reappearance was in 1933, the year the Loch Ness Monster made news. Today visitors to Lake Vyrnwy do not have to wait for hot summers for the revenant experience. It can be imagined in viewing the engine house at the edge of the lake, which was built to look like a medieval, Bavarian tower. It is there all the year round and on a grey day, seen through enveloping mist, it resembles the spectral castle in Grimm’s Norse Mythology that sank under the waters. A photograph of the view is on sale at the hotel.
Dark Tourism History: Making the Dead Work for the Living
Encounters with forms of “engineered and orchestrated remembrance”—seen here as the defining features of dark tourism—have existed throughout history, and are ones that everyone has incidentally engaged in from time to time. The sepulchral features they comprise only became a prime consideration set in traveling and recreational tastes and practices in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. This was because of social and ideological factors which included: the aftermath of pilgrimage, the growth of antiquarian tastes, and the many, revolutionary effects of Romanticism—particularly the discursive coding of landscape as travel spectacle with sublime and gothic, as well as picturesque, features. Romanticism and cemetery development also valorized the celebration and acting out of elegiac displays of sentiment at memorials and grave sides, encouraged in guidebooks, which became part of an aestheticized cult of “beautiful death” for which the Victorians became famous. 127 The recency of dark tourism as a named recreational form is why there have been, and continue to be, academic debates over its meaning, temporal origins (traditional, modern, or postmodern?), and its position in relation to other disciplines and travel concepts (heritage studies, human geography, the history of pilgrimage, etc.). A less-parochial issue is where its history is leading. In the past dark tourism has been mainly situated and studied as an agenda in the private sphere: the world of lifestyle, personal taste, and recreational choice. This may be changing. In the new millennium there are winds of ideological change, drawing it into a more public and controversial arena, that of “the politics of commemoration,” 128 a movement that began in academia in the 1990s as critical, postcolonial history, and has since gone viral in news agendas internationally. It has stimulated organized protests involving direct action at sites commemorating colonial figures and events through demonstrations, vandalism of memorials, and attempts to remove statues. Dark tourism has been, and will be, unavoidably affected, since its central activity is travel to view engineered and orchestrated remembrance that includes many such sites.” 129
The consequences may be two-fold. One is mounting threats to specific sites that may require protection, a contingency the English Parliament recognized in February 2021 in preparing a law making the taking down of monuments illegal without planning permission. The second may be the growth of a more informed, dark tourist, whose gaze is turned on those commemorated, but equally directed to the pragmatics of commemorative choices: who is commemorated and who might have been, but is not, and the features of their memorials (forms, events, number, siting, scale, etc.).
The sunken village material represents continuing research that dramatizes issues about the evolution of “engineered and orchestrated remembrance” as dark tourism’s “trademark” feature. Unlike death and the dead, previously assumed to be the visitor encounters in dark tourism, remembrance has no closure. It is always susceptible to change by the living. Over time remembrance of Llanwddyn went from being a traditional, rural village with a history published by the local vicar a decade before to obliteration and metamorphosis as a dam development. 130 It was then commemorated at different times as a necessity in regional water supply; a monument to British engineering; an elite sporting lodge and luxury hotel; and an intermittent, dark tourism phenomenon. The rediscovery of the photographic album offers a striking discursive text to add to those in circulation as supporting this emerging interest in sunken locations.
The case illustrates how what people and events are remembered at commemorative sites over time, reflect the interests, power, and resources of the living. It is they who metaphorically ventriloquize the form and content of memorial messages, through which the dead seem to speak. Sunken villages are new as collective, dark tourism locations. They may, however, be seen as a subset of a larger and neglected domain of spaces in the “politics of commemoration,” that of industrial devastation and fatality which for two centuries has included mining disasters, losses at sea, toxic factory conditions, transport accidents, and catastrophes of industrial pollution affecting human communities and natural habitats. These and associated effects of climate change, may in the future become more explicit agendas in dark tourism visits, not just as sights to see, but as lessons that stimulate reflection and engagement.
Further Reading
Curl, James Stevens. The Victorian Celebration of Death . Stroud: Sutton Publishing, 1980 .
Google Scholar
Google Preview
Curl, James Stevens. A Celebration of Death . London: Batsford, 1981 .
Dann, Graham. M. S. , and Seaton, A. V. ( 2001 ): Slavery, Contested Heritage and Thanatourism . New York: Haworth Hospitality Press.
Hooper, G. , and J. J. Lennon . Dark Tourism: Practice and Interpretation . Aldershot: Ashgate, 2018 .
Lennon, J. J. , and M. Foley . Dark Tourism: The Attraction of Death and Disaster . London: Continuum, 2000 .
Lloyd, D. Battlefield Tourism: Pilgrimage and the Commemoration of the Great War in Britain, Australia, 1919–1939 . Oxford: Berg, 1998 .
Macaulay, Rose. The Pleasure of Ruins , 2nd ed. Thames and Hudson, 1964 .
Seaton, A. V. “ Guided by the Dark: From Thanatopsis to Thanatourism. ” International Journal of Heritage Studies 2, no. 4 ( 1996 ): 234–244.
Seaton A. V. “ Thanatourism at Waterloo. ” Annals of Tourism Research 26, no. 1 ( 1997 ): 130–158.
Seaton, Tony. “Cultivated Pursuits: Cultural tourism as Metempsychosis and Metensomatosis,” in Routledge Handbook of Cultural Tourism , ed. Melanie Smith and Greg Richards . London: Routledge, 2013 , 19–27.
Sharpley, R. and P. R. Stone (eds.), The Darker Side of Travel: The Theory and Practice of Dark Tourism . Bristol: Channel View, 2009 , 23–38.
Stone, P. P. , Hartmann, R. , Seaton, A.V. , Sharpley, R. and L. White (eds.), The Palgrave Handbook of Dark Tourism Studies . London: MacMillan, 2018 , 377–507
Wolffe, John. Great Deaths Grieving, Religion, and Nationhood in Victorian and Edwardian Britain . London: The British Academy, 2000 .
1 Jafar Jafari Encyclopaedia of Tourism : 578. (London and New York: Routledge, 2000)
2 International Journal of Heritage Studies 2, no. 4 (1996): 578. This is the issue that introduced dark tourism and proposed the two the main approaches; J. J. Lennon , and M. Foley , Dark Tourism: The Attraction of Death and Disaster (London: Continuum, 2000).
3 A. V. Seaton , and J. Lennon , “Thanatourism in the Early 21st Century: Moral Panics, Ulterior Motives and Alterior Desires,” in New Horizons in Tourism: Strange Experiences and Stranger Practices , ed. T. V. Singh (Oxford: CABI Publishing, 2004), 64–68.
4 James Moores Ball , The Sack-Em’Up Men: An Account of the Rise and Fall of the Modern Resurrectionists (Edinburgh: Oliver and Boyd, 1928).
Lennon, Foley, Dark Tourism , 3.
6 Chris Rojek , Ways of Escape (Basingstoke: Macmillan, 1993).
7 M. Foley , and J.J. Lennon “JFK and Dark Tourism: A Fascination with Assassination,” International Journal of Heritage Studies 2, no. 4 (1996): 198–211.
8 A. V. Seaton , “Guided by the Dark: From Thanatopsis to Thanatourism,” International Journal of Heritage Studies 2, no. 4 (1996): 234–244 ; A. V. Seaton , “Thanatourism and Its discontents: An Appraisal of a Decade’s Work with Some Future Directions,” in The Sage Handbook of Tourism Studies , eds. Tazim Jamal , and Mike Robinson (London: Sage, 2009), 521–542.
Seaton, “Guided by the Dark,” 234–244.
10 M emento mori aids comprised a variety of literary and artistic texts, and artifacts that were read, worn, kept at hand, and studied including death’s head rings, desk-top skulls and other emblems of death. A major literary and artistic convention promoting memento mori reflections was the “Dance of Death,” a parade of people from all walks of life being led away to their doom by Death, a skeletal figure dancing ahead of them which was featured in books, drama, and dances. Ars Moriendi were Catholic texts on how to face and endure dying. The classic study of the genre is by Mary Catharine O’Connor , The Art of Dying Well: The Development of the Ars Moriendi (New York: Columbia University Press, 1942). An account of the Ars Moriendi in England is by Nancy Lee Beaty , The Craft of Dying The Tradition of the Ars Moriendi in England (New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 1970).
11 Tony Seaton , “Thanatourism and Its Discontents,” in The Sage Handbook of Tourism Studies , eds. Tazim Jamal and Mike Robinson (Los Angeles and London: Sage, 2009), 534–536.
12 D. Joly , The Dark Tourist: Sightseeing in the World’s Most Unlikely Destinations (London: Simon and Schuster, 2010).
13 G. Ashworth “Holocaust Tourism and Jewish Culture: The Lessons of Krakow-Kazimierz,” in Tourism and Cultural Change , eds. M. Robinson , M., Evans , and N. Callaghan (Newcastle: University of Northumbria, 2002), 363–367 ; W. Miles , “Auschwitz: Interpretation and Darker Tourism,” Annals of Tourism Research 29, no. 4 (2002): 1175–1178 ; Lennon and Foley, Dark Tourism ; G. Ashworth , and R. Hartmann . Horror and Human Tragedy Revisited: The Management of Sites of Atrocity for Tourism (New York: Cognizant, 2005).
14 J. Henderson , “War as a Tourist Attraction: The Case of Vietnam,” International Journal of Tourism Research 6, no. 2 (2000): 97–117 ; D. Lloyd , Battlefield Tourism: Pilgrimage and the Commemoration of the Great War in Britain, Australia, 1919–1939 (Oxford: Berg, 1998) ; A. V. Seaton , “Thanatourism at Waterloo,” Annals of Tourism Research 26, no. 1 (1997): 130–158 ; A. V. Seaton , “Another Weekend Away Looking for Dead Bodies’: Battlefield Tourism on the Somme and in Flanders,” Journal of Tourism and Recreational Research 25, no. 3 (2000): 63–78 ; J. H. Iles , “Recalling the Ghosts of War: Performing Tourism on the Battlefields of the Western Front,” Text and Performance Quarterly 26 (2006): 162–180 ; J. H. Iles , “Consuming the Contested Heritage of War: Tourism, Territoriality and the Memorial Landscapes of the Western Front,” in Heritage at the Interface , ed. G. Hopper (Gainesville, FL: University Press of Florida, 2018).
15 G. M. S. Dann , and A. V. Seaton , Slavery, Contested Heritage and Thanatourism (New York: The Haworth Hospitality Press, 2001).
16 C. Strange , and M. Kempa ,“Shades of Dark Tourism: Alcatraz and Robben Island,” Annals of Tourism Research 30, no. 2 (2003): 386–403 ; S. Hodgkinson , and D. Urquhart , “Prison Tourism: Exploring the Spectacle of Punishment in the UK,” in Dark Tourism: Practice and Interpretation , eds. G. Hooper and J. J. Lennon (Abingdon: Routledge, 2017), 40–54.
17 A. V. Seaton , “Thanatourism’s Final frontiers? Internment Sites and Memorials as Sacred and Secular Pilgrimage,” Journal of Tourism Recreation Research 27, no. 2 (2002):73–82 ; Tony Seaton , M. North , and G. Gajda , “Last Resting Places? Recreational Spaces or Thanatourism Attractions—the Future of Historic Cemeteries and Churchyards in Europe,” in Landscapes of Leisure: Space, Place and Identities , eds. Sean Gammon , and Sam Elkington (Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan, 2015), 79.
18 Derek H. Alderman , “Writing on the Graceland Wall: On the Importance of Authorship in Pilgrimage Landscape,” Tourism Recreation Research 27, no. 2 (2002): 27–35 ; T. Blom , “Morbid Tourism: A Postmodern Market Niche with an Example from Althorpe,” Norwegian Journal of Geography 54 (2000): 29–36 ; Robert Ryan , “Standing Where Hitler fell,” Sunday Times , December 15, 2002, T3.
19 Graham M. S. Dann , “The Dark Side of Tourism,” in Studies and Reports, Serie L. Sociologie/Psychologies/Philosophie/Anthropology 14 (1998), Aix-en-Provence, France: Centre International de Recherches et d’Etudes Touristiques.
20 R. Sharpley , “Travels to the Edge of Darkness: Towards a Typology of ‘Dark Tourism’’, in Taking Tourism to the Limits: Issues, Concepts and Managerial Perspectives , eds. C. Ryan , S. J. Page , and M. Aicken (London: Elsevier Ltd., 2005), 215–226 ; P. R. Stone , “A Dark Tourism Spectrum: Towards a Typology of Death and Macabre Related Tourist Sites, Attractions and Exhibitions,” Tourism: An Interdisciplinary Journal 54, no. 2 (2006): 145–160 ; Rachel Raine , “A Dark Tourism Spectrum,” International Journal of Culture, Tourism and Hospitality Research 7, no. 3 (2006): 242–256.
Seaton, ”Guided by the Dark,” 240, 243.
Raine, “A Dark Tourism Spectrum.”
23 Geoffrey Gorer , Death, Grief and Mourning (New York: Doubleday, 1965).
Seaton, ”Guided by the Dark,” 243.
25 P. Stone , “Making Absent Death Present: Consuming Dark Tourism in Contemporary Society,” in The Darker Side of Travel: The Theory and Practice of Dark Tourism , eds. R. Sharpley and P. R. Stone (Bristol: Channel View, 2009), 23–38.
26 James Moore Ball , The Sack-‘Em-Up Men: An Account of the Rise and Fall of the Modern Resurrectionists (Edinburgh: Oliver and Boyd, 1928).
27 P. Stone , ‘Dark Tourism and Significant Other Death: Towards a Model of Mortality Mediation’, Annals of Tourism Research , 39(3): 1565–1587.
28 Tony Seaton , “Purposeful Otherness: Approaches to the Management of Thanatourism”, in The Darker Side of Travel , R. Sharpley and P. R. Stone , (Bristol: Channel, 2009), 75–108.
29 P. Slade , “Gallipoli Thanatourism: The Meaning of ANZAC,” Annals of Tourism Research 30, no. 4 (2003): 779–794.
Seaton and Lennon. “Thanatourism in the Early 21st Century.”
Stone, ”Making Absent Death.”
32 J.E. Tunbridge , J. E. and G.J. Ashworth , “Dissonant Heritage: The Management of the Past as a Resource in Conflict” (Chichester: Wiley, 1996).
33 Tazim Jamal , and Linda Lelo , “Exploring the Conceptual and Analytical Framing of Dark Tourism: From Darkness to Intentionality,” in Tourist Experience Contemporary Perspectives , R. Sharpley and B. Stone (Bristol: Channel View, 2011), 29–42.
34 D. Light , “Progress in Dark Tourism and Thanatourism Research: An Uneasy Relationship with Heritage Tourism,” Tourism Management 61 (2016): 275–301.
35 Philip. Stone , Rudi. Hartmann , Tony. Seaton , Richard. Sharpley , and Leanne. White , eds., The Palgrave Handbook of Dark Tourism Studies : 377–507 (London: MacMillan Publishers Ltd, 2018).
36 G. E. Tunbridge and G. J. Ashworth , “Is All Tourism Dark?” in Dark Tourism: Practice and Interpretation , eds. G. Hooper , and J.J. Lennon (Abingdon: Routledge, 2017), 12–25.
37 Sharpley and Stone , The Darker Side of Travel Dark Tourism and Place Identity: Managing and Interpreting Dark Places , eds. L. White , and E. Frew (Routledge, Oxford, 2013) ; G. Hooper, G. , and J.J. Lennon , eds., Dark Tourism: Practice and Interpretation (Abingdon: Routledge, 2017) ; Philip R. Stone , Rudi Hartmann , Tony Seaton , Richard Sharpley and Leanne White , The Palgrave Handbook of Dark Tourism Studies (London: Palgrave Macmillan, 2018).
38 G. Bird , M.Westcott , and N. Thiessen , “Marketing Dark Heritage: Building Brands, Myth-Making and Social Marketing,” in The Palgrave Handbook , P. Stone et al., 645–665 ; K. Hannam , and Ganna Yakovska , “Tourism, Mobilities, Spectralities, and the Hauntings of Chernobyl” in, P. Stone et al. The Palgrave Handbook , op. cit. 318–333.
39 R. Sharpley , and Mona Friederich , “Genocide Tourism in Rwanda: Contesting the Concept of “The Dark Tourist,” in Dark Tourism: Practice and Interpretation , eds. G. Hooper . and J. J. Lennon (Abingdon: Routledge, 2017), 134–136.
40 D. Timothy , “Sites of Suffering, Tourism, and the Heritage of Darkness: Illustrations from the United States,” in The Palgrave Handbook , ed. P. Stone et al. (2018) op. cit., 381–398.
41 M. T. Clanchy , From Memory to Written record. England 1066-1307 (Blackwell: Oxford and Cambridge, 1993) ; Mary Carruthers , The Book of Memory. A Study of Memory in |Medieval Culture (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1990) ; Janet Coleman , Ancient and Medieval Memoirs: Studies in the Reconstruction of the Past (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1992) ; Donald R. Kelley , ed, Versions of History from Antiquity to the Enlightenment (New Haven, CT: Yale University Press,, 1991) ; Gabrielle M. Spiegel , The Past as Text: The Theory and Practice of Medieval Historiography (Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1997).
42 Michael Bentley , Companion to Historiography (London: Routledge, 1997).
43 Edward Said , Orientalism (London: Penguin Books, 1978, 1995) ; Edward Said , Culture and Imperialism (London: Chatto and Windus, 1993) ; Homi Bhabha (ed.), Nation and Narration (London: Routledge, 1992) ; Homi Bhabba , The Location of Culture (London: Routledge, 1994).
44 Nataliya Danilova , The Politics of War Commemoration in the UK and Russia (London: Palgrave Macmillan Memory Studies, 2015) ; A. Erll, A. and A. Nunning (eds.), Cultural Memory Studies: An International and Interdisciplinary Handbook (Berlin: de Gruyter, 2008) ; B. Graham and P. Howard (eds.), The Ashgate Research Companion to Heritage and Identity (Aldergate: Ashgate, 2007) ; A. King , Memorials of the Great War in Britain: The Symbolism and Politics of Remembrance (London: Bloomsbury, 2014) ; D. Viejo-Rose , “Memorial Functions: Intent, Impact and the Right to Remember,” Memory Studies 4, no. 4 (2011): 465–480 ; Craig Wight “Contested National Tragedies: An Ethical Dimension,” in The Darker Side of Travel , eds. Sharpley and Stone , 129–144 ; C. A. Wight , and J. Lennon , “Selective Interpretation and Eclectic Human Heritage in Lithuania,” Tourism Management 28, no. 2 (2007): 234–254 ; Paul Williams , Memorial Museums: The Global Rush to Commemorate Atrocities (Oxford: Berg, 2007).
45 Ludwig Wittgenstein , Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus (London: Routledge, 1922). In this famous and formidable treatise on language, logic, and meaning, Wittgenstein started with disarmingly, simple phrases to engage the reader in pursuing a revolutionary track of complex, theoretical dissidence that was argued in several hundred axioms and assertions. The aim of the “Tractatus” was to demonstrate how the meaning of language was anchored in basic and underlying social contexts, not just a matter of formal, linguistic logic. “State of affairs” and, “that which is the case” were two of the phrases he used to contrast what he saw as the reality of language in actual use , compared to its status as grammatical and syntactical logic. The real “state of affairs” in dark tourism, it is here argued, is “remembrance” as the focal issue, not “death” as previously supposed. “Engineered remembrance” is the actual “state of affairs” confronting both dark tourism consumers and suppliers. “Remembrance” in material form, not “death,” is “that which is the case”—the de facto object of “the tourist gaze.”
46 Tony Seaton , “Patrimony, Engineered Remembrance and Ancestral Vampires: Appraising Thanatouristic Resources in Ireland and Italy,” in Hooper Lennon , Dark Tourism , 55–68 ; A. V. Seaton , “Encountering Engineered and Orchestrated Remembrance: A Situational Model of Dark Tourism and Its History,” in P. Stone et al., The Palgrave Handbook , 9–33.
47 John and Elizabeth Romer . The Seven Wonders of the World (London: Michael O’Mara Books Limited, 1995).
48 Jeremy Black , The British and the Grand Tour (London: Routledge, 1985) ; Edward Chaney , The Evolution of the Grand Tour: Anglo-Italian Cultural Relations since the Renaissance (London: Frank Cass, 1998) ; John Towner , An Historical Geography of Recreation and Tourism in the Western World 1540–1940 (Chichester: John Wiley and Sons, 1996) ; A. V. Seaton , in Keywords for Travel Writing Studies , eds. C. Fosdick , C. , Z. Kinsley , Z and K. Walchester (2019), 108–110.
49 A. V. Seaton , in Keywords for Travel Writing Studies , eds. C. Fosdick , C. , Z. Kinsley , Z and K. Walchester (2019), 108–110.
50 Paul Koudounaris , The Empire of Death. A Cultural History of Ossuaries and Charnel Houses (London: Thames and Hudson, 2011).
51 R. Fraser Rae , The Business of Travel: A Fifty Year’s Record of Progress (London: Thomas Cook and Son, 1891) ; John Pudney , The Thomas Cook Story (London: Michael Joseph, 1953) ; Piers Brendon , Thomas Cook’s 150 years of Popular Tourism (London: Martin Secker and Warburg, 1992).
52 Paul Westover , Necroromanticism: Travelling to Meet the Dead, 1750–1860 (London: Palgrave Macmillan, 2012).
53 William Howittt , Homes and Haunts of English Poets , 2 vols. (London: Richard Bentley, 1847).
54 William Howitt , Visits to Remarkable Places: Old Halls, Battlefields etc. , 2 vols. (London: Longman, Orme, Green Brown and Longmans, 1840).
55 S. Carter Hall , Pilgrimages to English Shrines , vol 2 (London: Arthur Hall, Virtue and Co., 1853), 154.
56 Joan Evans , A History of the Society of Antiquaries (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1956), 1–60.
Jonathan Skinner “The Smoke of an Eruption and the Dust of an Earthquake: Dark Tourism, the Sublime, and the Reanimation of the Disaster Location,” in Stone et al., 125–150.
Two of the sites that suffered most from take-away memento seekers were Shakespeare’s Stratford, and the Catacombs at Rome.
59 John Howes Gleason , The Genesis of Russophobia in Great Britain 22 (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1950), 22.
For Scottish lore and legend see, Walter Scott’s works which were intended to sell Caledonia to the world. His “Minstrelsy of the Scottish Border Consisting of Historical and Romantic Ballads,” first published in 1802 in 2 vols. in Kelso by James Ballantyne, was reprinted throughout the century. It abounds in battles, blood, and thunder.
Jaunting-cart in Ireland, camel rides during Holy Land tours, and pony trekking through Iceland, a land with few roads and no railways.
62 “The March of Intellect” was an ironical, journalistic name for the growth in popular reading in the 1830s brought about by technological advances in the speed and volume of printing, and reduced cost of publishing, Entrepreneurs like Charles Knight exploited these to democratize reading by publishing cheap editions of classic works, including Shakespeare’s works, and a “Penny Encyclopaedia” issued in weekly parts. The name was seized upon by graphic satirists like Robert Seymour and George Cruikshank who depicted dustmen reading books, cockneys discussing philosophy and politics. In London their caricatures were hung in shop windows, for the middle classes they were bought as single items or sets, but also hired in scrap books of caricatures lent out for dinner parties and chic weekend entertainment. Graphic satire offers the major artistic record of tourism taste in the 19th century; Tony Seaton , “The Tourist Experience in Graphic Satire 1796-1914”in Tijana Rakic , and Jo-Anne Lester , Travel, Tourism and Art: 13–34 .
63 There is abundant contemporary and modern literature on the Gothic. A classic, often revised, is Kenneth Clark , The Gothic Revival: Essays in the History of Taste (London: John Murray, 1928, rev. 1950 and 1962). Michael Charlesworth has edited a substantial compilation of extracts from Gothic texts: The Gothic revival 1720–1870 , 3 vols. (Robertsbridge, East SussexHelm Information, 2002). Britton’s life and career are described in his neglected, two-volume autobiography which includes a catalogue of his topographical works, as well as interesting contextual material relevant to dark tourism’s expansion on landscape, ecclesiastical illustration, and commercial engraving. John Britton , The Auto-Biography of John Britton , 2 vols. (London: Printed for the Author, 1850).
64 For Gray’s life, see Robert L. Mack , Thomas Gray: A Life (New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 2000).
65 Ronald Fletcher , In a Country Churchyard (Batsford, London, 1976).
66 Ian Ousby , The Englishman’s England. Taste, Travel and the Rise of Tourism (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1993), 387–388.
67 William Wordsworth , “Upon Epitaphs,” in The Prose Works of William Wordsworth , ed. Alexander Grosart , vol. 3 (London: Edward Moxon, 1876), 25–75.
68 Montague Summers , A Gothic Bibliography (London: Fortune Press, n.d. [1940]).
69 The gothic has attracted exhibitions and an enormous and continuing literature since its appearance in the late eighteenth century. It was one of the first cultural developments to be named as an influence in Dark Tourism/Thanatourism ( Seaton. op. cit. 1996 : 237–238). Its history may be pleasurably sampled in many, modern illustrated studies including: Richard Davenport-Hines , Gothic Four hundred years of excess, horror, evil and ruin (London: Fourth Estate 1998) ; and, Terror and Wonder. The Gothic Imagination which accompanied a major exhibition at the British Library in 2015 London: British Library 2014).
70 Constantin Volney , Les Ruines ou Meditations sur les Revolutions des Empires (Paris. Translated into English 1802. [publisher?]
Percy Bysshe Shelley wrote the sonnet “Ozymandias” in 1817. It was first included in volume 3 of his collected, poetical works, chosen and edited in four volumes in 1839 by his wife Mary, the author of Frankenstein .
72 Edmund Burke’s Philosophical Enquiry into the Origin of our Ideas of the Sublime and Beautiful was first published in an edition of 500 in 1757. It was quickly translated into other languages, achieving European influence. The best critical edition is by J. T. Boulton (London: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1958). Earlier in the century the Sublime had attracted a book length study published anonymously in London with no publisher “A Treatise on the Sublime … Translated from the Greek of Longinus with Critical Reflections, Remarks and Observations, by M. Boileau, M. Dacier, and M. Boivin” (1712). Samuel H. Monk , The Sublime: A Study of Critical Theories in XVIII-Century England (Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan, 1935) ; Richard John Hipple , The Beautiful, the Sublime, and the Picturesque in Eighteenth-Century British Aesthetic Theory (Carbondale, IL: Southern Illinois University Press, 1957) ; Marjorie Hope Nicolson , Mountain Gloom and Mountain Glory. The Development of the Aesthetics of the Infinite (Ithaca, NY: Cornell University, 1959). A recent selection of short readings on aspects of the Sublime is by Cian Duffy and Peter Howell , Cultures of the Sublime: Selected Readings 1750–1830 (Basingstoke: Palgrave MacMillan, 2015).
73 G. A. Walker , Gatherings from Graveyards (London: Longman and Company, 1830).
74 Report from the Select Committee of Improvement of the Health of Towns … Effect of Internment of Bodies in Town (London: The House of Commons, 1842).
75 Edwin Chadwick , Report on the Sanitary Condition of the Labouring Population of Great Britain Supplementary Report on the Results of a Special Inquiry into the Practice of Internment in Towns (London: C. Clowes and Sons, 1843).
76 Pere La Chaise; Michel Dansel , Au Pere-Lachaise. Son histoires, ses secrets, ses promenades . (Nancy: Fayard, 1972) ; George Blair , Biographic and Descriptive Sketches of Glasgow Necropoli s (Glasgow: Ogle and Son,1857). For Sweden and Liverpool, see James Stevens Curl A Celebration of Death : 151–154 and 206–210 (London: Batsford, 1981).
77 J.C. Loudon ,. On the Laying Out, Planting and Managing of Cemeteries and on the Improvements of Churchyards (London: Printed for the author, and sold by Longmans, Brown, Green and Longmans, 1843, 1981).
78 Since the 1970s James Stevens Curl has been a notable and continuing campaigner on behalf of historic cemeteries. His two most important book-length, general studies have been A Celebration of Death (New York: Scribners, 1980). The Victorian Celebration of Death (Stroud: Sutton Publishing, 2000)
79 Curl’s works on specific cemeteries have included: “Nunhead Cemetery, London,” Transactions of the Ancient Monuments Society 1980: 14–22 , 1980; “Northern Cemetery under Threat: Jesmond, Newcastle on Tyne,” Country Life , June 12, 1981: 68–69 [pages]; Kensal Green Cemetery: The Origins and Development of the General Cemetery of All Souls, Kensal Green, London, 1824 – 2001 (London: Phillimore, 2001). An extensive bibliography of Curl’s pioneering studies on cemeteries and funerary culture can be found at, http://www.jamesstevenscurl.com/james-stevens-curl-complete-works , accessed 18.6.22
80 The Association of Significant Cemeteries in Europe was inaugurated in Bologna in 2001. It quickly attracted 59 members, which grew to 130 in 99 countries by 2015, and numbered over 200 in 2020. See Mauro Felicori and Annalisa Zanotti, “Cemeteries of Europe: A Historical Heritage to Appreciate and Restore”; Tony Seaton , “Last Resting Places? Recreational Spaces? or Thanatourism Attractions? The Future of Historic Cemeteries and Churchyards in Europe” in Landscapes of Leisure: Space, Place and Identities , eds. Sean Gammon and Sam Elkington (Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan, 2015), 71–95.
81 Anonymous, Herveiana (Scarborough: John Cole, 1823), 114–115.
82 William Andrews , Curious Epitaphs (London: Hamilton, Adams and Company, 1883).
The Society for Preserving Memorials of the Dead, published from 1883 to 1885.
84 James Smillie , Green-wood Illustrated … with Descriptive Notices by Nehemiah Cleaveland (New York: Robert Martin, 1847) ; Mount Auburn Illustrated …with Descriptive Notices by Cornelia W. Walter ” (New York: Martin and Johnson, (n.d. [c. 1850]).
85 John Townshend , Sepulchral Literature: A Catalogue of Some Books Relating to the Disposal of the Bodies and Perpetuating the Memories of the Dead (New York, 1887)
86 John Edmondson , Death and Tourist : Dark Encounters in Mid-Nineteenth Century London via the Paris Morgue , in,, Stone et al., 2018, op. cit., 77–102.
87 Paul Westover , Necromanticism Travelling to Meet the Dead, 1750–1860 (Basingstoke: Palgrave-Macmillan).
88 A.V. Seaton , “War and Thanatourism: Waterloo 1815–1914,” Annals of Tourism Research , 26, No 1 (1999): 130–158.
89 Stony Seaton and Graham M. S. “Dann, “Crime and Dark Tourism: The Carnivalesque Spectacles of the English Judicial System,” in, Stone 2018, op. cit. 33–76
90 John Wolffe , Great Deaths Grieving, Religion, and Nationhood in Victorian and Edwardian Britain (London: British Academy, 2000).
91 E. Pierce , A Concise Biographical Memoir of George III … also an Account of his Lying in State at Windsor; the Procession and other Solemnities observed at the Royal Funeral (London: Sherwood, Neely and Jones, 1820).
Wolffe, Great Deaths , 44–45.
Wolffe, Great Deaths .
94 Lord Edward Gleichan , London’s Open-Air Statuary (London: Longmans, Green and Co., 1928), xv ; Arthur Byron , London Statues: A Guide to London’s Outdoor Statues and Sculpture (London: Constable, 1928)
95 London County Council, Indications of Houses of Historical Interest in London , 6 vols. (London: London County Council, 1901–1930).
96 Memorials of the two World Wars have been well documented. They include Sydney Hurst, The Silent Cities: An Illustrated Guide to the War Cemeteries and memorials to the “Missing” in France and Flanders: 1914–1918 (London: Methuen, 1929, 1933) ; Philip Longworth , The Unending Vigil: A History of the Commonwealth War Graves Commission 1917–1967 (London: Constable, 1967) ; Trefor Jones , On Fame’s Eternal Camping Ground: A study of First World War Epitaphs in the British Cemeteries of the Western Front (Pinner: T. G. Jones, 2007) ; Gaynor Kavanagh , Museums and the First World War: A Social History (London: Leicester University Press, 1994) ; David Saunders , Britain’s Maritime Memorials and Mementoes (Sparkford: Haynes Publishing, 1996) ; David and Betty Beaty Light Perpetual: Aviators’ Memorial Windows (Shrewsbury: Airlife, 1995).
97 Robert Hewison , The Heritage Industry: Britain in a Climate of Decline (London: Methuen, 1987).
98 Patrick Wright , On Living in an Old Country: National Past in Contemporary Britain (London: Verso Books, 1986).
99 The Guardian (2019): “Disaster tourism arrives in Whaley Bridge after dam incident,” https://www.theguardian.com/uk-news/2019/sep/09/disaster-tourism-arrives-in-whaley-bridge-after-dam , accessed July 28, 2020.
100 Rowlands, D. W. L. , History and Description of Llanwyddn and Lake Vyrnwy (Llanwyddn Parochial Church Council: Llanwddyn Parochial Church Council: Welshpool Printing Company, 1974), 12–15.
101 The Council kept a record of the development in a large album of photographs from which the four illustrations here are taken. One of the technical site visitors was G.F. Deacon a leading authority on water supply engineering who later praised it, See, G. F. Deacon , “Vyrnwy,” Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers , Vol cx1: 111–113, July; 1892. The dam was also described in a standard reference work on water supply which featured Vyrnwy as the photographic frontispiece, see W.K. Burton , (1898): “The Water Supply of Towns and the Construction of Waterworks” (London: Crosby Lockwood and Son, 1898): 76–78.
102 John Baynes , George Westropp George , and Simon Baynes , Lake Vyrnwy The Story of a Sporting Hotel (Shrewsbury: Quiller, 2019), 3–13.
Newspaper accounts and stories passed down to current residents have been identified, but the COVID crisis of 2020 and 2021 has delayed recording and analysis, planned for late 2021.
104 J. J. Lennon , “Dark Tourism Visualisation: Some Reflections on the Role of Photography,” in Stone et al, The Palgrave Handbook , 585–603.
105 The best-known graphic records of railway constructions are the lithographs of John Bourne , Drawings of the London and Birmingham Railway (London: Ackermann and Co. and C. Tilt, 1839) ; John Bourne , The History and description of the Great Western Railway (London: David Bogue, 1846).
108 Capel Celyn , “The Drowning of Capel Celyn,” Medium.com (1963), https://medium.com/datadriveninvestor/the-drowning-of-capel-celyn-109496dc611e ; and https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5ui2rFSP6AM , both accessed March 11, 2020.
109 WebUrbanist, “Drowned Towns,” WebUrbanist (2014) https://weburbanist.com/2014/03/10/drowned-towns-10-underwater-ghost-cities-buildings/2/ , accessed May 12, 2022.
110 Bess Lovejoy , “Ten Drowned Cities You Can Visit,” Mental Floss , 2015, https://www.mentalfloss.com/article/66680/10-drowned-towns-you-can-visit , accessed December 30, 2020.
111 “The Ruins of Villa Epecuan,” The Atlantic , 2011, https://www.theatlantic.com/photo/2011/07/the-ruins-of-villa-epecuen/100110/ .
Si Cheng (2014): “China’s Atlantis of the East.” Si Cheng was flooded in 1959 to make way for Qiandao lake (also known as Thousand Island lake) for the Xin’an River Dam project. Nearly 300,000 people had to relocate, some of whom had families that had lived in the area for centuries; http://www.bbc.com/travel/story/20140711-chinas-atlantis-of-the-east , accessed June 8, 2022.
Potosi in Venezuela was flooded in 1985 but over the next thirty years the church spire has gradually emerged from beneath the waters; https://www.atlasobscura.com/places/drowned-church-potosi , accessed June 6, 2022.
Port Royal in Jamaica was a “sunken pirate city” that disappeared in the 1690s due to a natural disaster. Today most of the remains of the 17th century city lie under up to 40 feet of water. In 1969, Edwin Link discovered the most famous artifact: a pocket watch dated 1686, stopped at exactly 11:43; https://www.atlasobscura.com/places/sunken-pirate-stronghold-at-port-royal , accessed June 4, 2022.
115 “ “Flooded Towns of America,” Wikipedia, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_flooded_towns_in_the_United_States ; Pinterest https://www.pinterest.co.uk/pin/347621664966005596/ , accessed January 21, 2021.
116 “Lost Villages of the St. Lawrence River, Canada’s Atlantis,” Global News , 2018, https://globalnews.ca/news/4369620/lost-villages-of-the-st-lawrence-river-canadas-atlantis/ , accessed January 1, 2021.
117 “Airtours,” Ar-Tour.com , http://ar-tour.com/guides/stories-of-submerged-towns-1/the-lost-villages.aspx .
Santorini was an earthquake disaster site in the past that has produced floods and sunamis. See, Jonathan Skinner, “The Smoke of an Eruption and the Dust of an Earthquake. Dark Tourism, the Sublime, and the Reanimation of the Disaster Location” in, Stone et al., op. cit. 2018 : 125–150. In the present Santorini offers tourists the double appeal of earthquakes and inundations as day tours. https://www.viator.com/tours/Santorini/Volcano-and-Hot-Springs-Tour/d959-156401P1 , accessed June 3, 2022.
120 Floods received brief mentions in James Frazer’s twelve-volume study of myths and superstitions, The Golden Bough (1890–1915), and extended treatment later in, James Frazer , Folk-lore in the Old Testament. Studies in Comparative Religion Legend and Law, vol. 3 (London: Macmillan, 1919).
121 Rose Macaulay , The Pleasure of Ruins (London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson, 1953).
http://www.weburbanist.com/2014/03/10/ , accessed January 30, 2021.
Vilarinho Da Furnas Portugal had origins going back 2,000 years. It was flooded by the Portuguese Electricity Company in 1972. Parts reappear in Autumn and Winter. The Museum was opened in 1981; www.atlasobscura.com/places/vilarinho-da-fuma/ , accessed January 30, 2021.
Stalin ordered the flooding of Kalyazin in 1939 to build Uglich Reservoir. Submerged buildings have reappeared and Christian Services still take place inside the Tower; https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uglich_Reservoir , accessed January 17, 2021.
St Thomas, Monument City, Nevada, was flooded in 1985 in creation of the Hoover Dam, leaving only the church steeple visible. In 2008 many houses, a square, and a cemetery reappeared; https://www.onlyinyourstate.com/indiana/underwater-ghost-town-in/ , accessed January 16, 2021.
Flagstaff was flooded in 1949 in the construction of the Long Falls Dam; https://www.onlyinyourstate.com/maine/underwater-city-me/ , accessed January 16, 2021. The Dead River Historical Society Museum includes a memorial exhibit to the “lost” towns of Flagstaff Village and Dead River Plantation; https://sites.google.com/site/deadriverareahistory/home/the-flooding-of-flagstaff/ , accessed January 16, 2021.
127 The sentimentalized aesthetics surrounding dying and funerary practices have been the subject of many studies, including those by James Curll, The Victorian Celebration of Death (Stroud: Sutton Publishing, 1980) and A Celebration of Death (London: Batsford, 1981) ; John Morley , Death, Heaven and the Victorians (London: Studio Vista, 1971) ; and in David Robinson , and Dean Koontz , Beautiful Death. Art of the Cemetery (London: Studio Vista, 1996).
128 “Politics of commemoration,” and the related areas of “Politics of History” and “Politics of Remembrance,” have been widely debated by historians and social scientists since the Millennium. See six national examples at “Politics of Memory,” Wikipedia , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Politics_of_memory ; and Maria Bucur and Nancy M. Wingfield , Staging the Past: The Politics of Commemoration in Habsburg Central Europe, 1848 to the Present (West Lafayette, IN: Purdue University Press, 2001).
129 For discussion of modern dark tourism and the politics of remembrance see, Tony Seaton , “Remembrancing, Remembrance Gangs, and Co-opted Encounters: Loading and Reloading Dark Tourism Experiences,” in The Routledge Handbook of the Tourist Experience , ed. Richard Sharpley (Abingdon: Routledge, 2022).
130 Thomas Henry , “History of the Parish of Llanwddyn,” Montgomeryshire: Collections Historical and Archaeological (Vol 4, 1873): 391–406.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Last Minute
- TERMS OF USE
- PRIVACY POLICY

How to spend an unforgettable weekend in Edinburgh

What are recursive islands?

The best islands to visit in the Stockholm archipelago

30 reasons why traveling is good for you

Norwegian islands that everyone should visit

Explore the best fishing spots in Britain
© Shutterstock
0 / 30 Fotos
1 / 30 Fotos
This is the largest mass murder site in human history. An estimated 1.1 million people died here (the majority Jewish), more than at any other Nazi concentration camp. Visiting Auschwitz is an especially moving and deeply emotional experience.
© Getty Images
2 / 30 Fotos
Located just outside the town of Kutna Hora is a small medieval chapel. Venture inside and you're greeted by more than 40,000 human bones decorating the interior.
3 / 30 Fotos
Tuol Sleng Genocide Museum, Cambodia - A high school building in Phnom Penh was appropriated by Pol Pot's Khmer Rouge security forces and turned into a prison known as Security Prison 21. An estimated 20,000 people were imprisoned here. Only 12 are known to have survived.
4 / 30 Fotos
Once the thriving capital of the Caribbean island of Montserrat, Plymouth was buried by debris and volcanic ash after the explosive eruption of the Soufrière Hills volcano in 1997. A modern-day Pompeii, what's left of the city has become a destination for the morbidly curious.
5 / 30 Fotos
Undulating earth marking the outline of trenches serves as a permanent reminder of how real World War I was for the many millions caught up in the conflict.
6 / 30 Fotos
The final resting place for 250,000 victims of the genocide against the Tutsi, the center also honors the more than one million estimated to have died in the 1994 conflict.
7 / 30 Fotos
Eloquently described as the "Sea of Trees" due to its verdant canopy, Aokigahara forest, resting in the foothills of Mount Fuji, is known more darkly as the world's second-most popular destination for those wanting to end their lives. Warning! If you visit here you're very likely to come across someone who has taken their own life, such is the destination's grim reputation.
8 / 30 Fotos
National September 11 Memorial & Museum, USA - New York City has honored the 2,977 victims of the September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks with a remarkable installation consisting of a pair of granite pools marking the footprints of the two towers. An adjacent museum houses a collection of artifacts, images, oral recordings, and videos from that fateful day.
© Public Domain
9 / 30 Fotos
Even in summer, a mildly disturbing air permeates around this Scottish Highlands landmark. The fact is that on February 13, 1692, around 38 men from the Clan McDonald were cut down by government forces in what was later dubbed the Glencoe Massacre. In winter, this is a dark and brooding destination.
10 / 30 Fotos
Yingxiu Township Memorial Sculpture, China - On May 12, 2008, a deadly earthquake shook Yingxiu Township to pieces. In all, around 90,000 people in Sichuan Province lost their lives. A large granite clock erected in front of a collapsed school reads 2:28 pm, the time the first tremors struck.
11 / 30 Fotos
Located in Liepaja on the Baltic Sea coast, Karosta was used as a Nazi and Soviet military prison, where torture and execution were commonplace. Decommissioned in 1994, the prison is now a museum, and visitors can spend a night in the guardhouse as an "inmate."
12 / 30 Fotos
One of the most poignant reminders of the numerous atrocities carried out by the Nazis during World War II, this ruined village has been left as a memorial to the 642 inhabitants who were murdered on June 10, 1944, in a reprisal attack carried out by an SS Panzer Division.
13 / 30 Fotos
The ancient Roman city was buried under 4 to 6 m (13 to 20 ft) of volcanic ash and pumice in the catastrophic eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 BCE. Plaster casts of victims lie on site among the extensive ruins.
© Getty Images
14 / 30 Fotos
Dozens of creepy toy dolls adorn the trees on this island in the Xochimico canal system, south of Mexico City. It's said that the dolls, placed by locals, are possessed by the benign spirits of a number of girls who drowned in the canal waters.
15 / 30 Fotos
Nearly two million combatants were killed, wounded, or captured during the apocalyptic Battle of Stalingrad. Renamed Volgograd, the city honors the largest confrontation in World War II with this museum, which stands next to the eerie ruins of an old mill, one of the few buildings that survived the onslaught.
16 / 30 Fotos
Vlad the Impaler, the barbaric 15th-century warlord who inspired Bram Stoker's Dracula, ordered the repair and strengthening of this remote citadel, perched high up on the plateau of Mount Cetatea.
17 / 30 Fotos
This macabre former place of worship in the city of Évora is lined with the broken skeletons of around 5,000 monks. The warning above the entrance reads in translation: "We bones that are here, await yours."
18 / 30 Fotos
Dachau, set on the outskirts of Munich, was the first of the Nazi concentration camps to open in Germany, this in 1933. By the time it was liberated on April 29, 1945, the majority of the camp's prisoners were classified as political prisoners (and most of them were Catholic).
19 / 30 Fotos
The Battle of Belchite, in Aragon, took place in August and September 1937 during the Spanish Civil War. The town was completely destroyed, but Francisco Franco ordered that the ruins be left untouched. The empty shells of once handsome buildings stand as testimony to the savagery of the fighting.
20 / 30 Fotos
Hiroshima Peace Memorial, Japan - Linger here after dark when the crowds have dispersed and the full horror of that horrific August 6 day in 1945 slowly but inexorably sinks in.
21 / 30 Fotos
Glance upwards when you hit the trails in the mountain province of Sagada. Suspended from cliff faces in Echo Valley are dozens of suspended coffins. Some are centuries old while others date back just a few years. They are all occupied.
22 / 30 Fotos
Hidden away in the forest of Western Siberia is this former Soviet forced labor camp. This is the only proper memorial site and museum at an authentic gulag prison.
23 / 30 Fotos
During the 1993 war in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh, the town of Agdam was captured by Armenian forces and the residents were forced to flee. It's been abandoned ever since. It's illegal to enter, but intrepid travelers have found ways to bypass the authorities and catch a glimpse of this near ruined destination.
24 / 30 Fotos
Babi Yar, Ukraine - A name synonymous with the unspeakable horrors perpetrated by the Nazis during World War II, Babi Yar, a ravine near the capital Kiev, was the scene of massacres carried out by German forces at the end of September 1941 and in January and February, 1942.
25 / 30 Fotos
Memorial Hall of the Victims in Nanjing Massacre by Japanese Invaders, China - Nanjing, the then-capital of China, fell to Japanese forces on December 13, 1937. In six weeks, an estimated 300,000 inhabitants were massacred. The museum memorializes those who were killed.
26 / 30 Fotos
Dating back to the late 19th century, this cemetery in Athens, Ohio, is the final resting place of deceased patients from the Athens Lunatic Asylum. The mental hospital was notorious for carrying out questionable lobotomy procedures, and for several alleged paranormal sightings said to have taken place in and around the premises.
27 / 30 Fotos
One of the Vietnam War's darkest episodes took place on March 16, 1968, when US troops killed up to 500 South Vietnamese civilians in what became known as the My Lai Massacre. A memorial stands in the nearby hamlet of Tịnh Khe.
28 / 30 Fotos
Deep under the French capital is a network of tunnels lined to the ceiling with skulls and bones. These catacomb ossuaries mark the final resting place of around six million Parisians, originally moved from overcrowded cemeteries in the 18th century.
See also: Creepy abandoned malls around the world
29 / 30 Fotos
Shutterstock
Getty Images
Getty Images
Dark tourism: following a gruesome travel itinerary
Visitor attractions historically associated with death, destruction, and tragedy.

21/05/24 | StarsInsider
TRAVEL Dark tourism
A re you a "dark tourist," someone who deliberately seeks out places blighted by death, destruction, and tragedy?
While traveling the world visiting cemeteries, war memorials, natural disaster sites, and former prisons can, perhaps, satisfy a morbid curiosity, it's also about paying respects to the dead, and remembering what happened and why.
Browse the gallery for a gruesome travel itinerary.
RECOMMENDED FOR YOU

What are the most densely populated islands in the world?

Google’s top travel destinations in 2024 for Americans

National Geographic’s top 30 travel destinations in 2024

Bark Air's first luxury flight for dogs takes off!

Sustainable travel: tips and tricks for the eco-conscious explorer

The wettest and driest countries in the world

The only country located in all four hemispheres

Matsuri: The traditional festivals of Japan

30 unforgettable weekend getaways in the USA

Europe's most amazing beaches

Go away! Countries that want to reduce the number of tourists
Places in Europe where three countries meet

Mountains that cross international borders

Cities with the most bars per capita in the world

A beginner's guide to backpacking in the wilderness

Discover the 30 most exhilarating Munros

Incredible places from Greek mythology you can visit today

The best barge canal holiday destinations in Europe

The ultimate guide to creating a weekend getaway travel itinerary

How many countries can you visit in one day?

Europe's most underrated cities, according to travel experts

The biggest mistakes tourists make at national parks

Countries with the easiest citizenship options

These Norwegian churches are the last of their kind in the world

The best (and worst) airports in the world in 2024

Be a tourist in your own city and fall in love all over again

The world's most dangerous beaches

Europe bound: an American's handbook for living the dream abroad

30 islands ranked by their highest point

The best bike trails in each US state
CELEBRITY Relationships
These celebrities have dated regular people
CELEBRITY Feuds
From slaps to knockouts: celebs who fought each other
LIFESTYLE Taxes
Where in the world are people paying the highest taxes?
LIFESTYLE Usa
Proposed US states and territories that never were
LIFESTYLE Crime
Where are the survivors of these infamous kidnappings now?
CELEBRITY Curiosities
The richest fictional characters of all time
FOOD Nutrition
Foods that help fight acid reflux and heartburn
LIFESTYLE Safety
The 30 most dangerous countries in the world in 2024
CELEBRITY Pope francis
Pope Francis' natural enemy
LIFESTYLE Sports
30 fascinating facts you didn't know about the Summer Olympics
© 2024 Stars Insider. All rights reserved..

Don’t miss out...
on the latest TV shows, movies, music, and exclusive content from the entertainment industry!
Τι είναι το dark tourism και πώς η Ελλάδα θα καταστεί “σκοτεινός” τουριστικός προορισμός

- 18/01/2023, 14:50

Στον σκοτεινό τουρισμό , ο οποίος βασίζεται στην επίσκεψη σημείων που έχουν συνδεθεί με αρνητικά γεγονότα και θάνατο , στρέφονται ολοένα και περισσότεροι τουρίστες διεθνώς προκειμένου να βιώσουν εμπειρίες που τους βγάζουν έξω από τη ζώνη ασφαλείας που έχουν συνηθίσει στην καθημερινότητά τους.
Με δεδομένο ότι αυτή τη στιγμή η παγκόσμια τουριστική βιομηχανία ανέρχεται σε 30 δισεκατομμύρια δολάρια , ποσό το οποίο αναμένεται να αυξηθεί κατά 8 δις το διάστημα 2030 – 2032, και οι λάτρεις του “σκοτεινού” τουρισμού αποτελούν το 2%, αντιλαμβάνεται κανείς τις προοπτικές ανάπτυξης που υπάρχουν. Αν νομίζετε ότι είναι κάτι φρέσκο που μόλις πρόσφατα έκανε την εμφάνισή του στην αγορά, καλύτερα να αναθεωρήσετε τις αρχικές σας σκέψεις μιας και δεν συνιστά νέα τάση, αλλά αποτελεί μία σύγχρονη μορφή αναδυόμενης τουριστικής δραστηριότητας.
Όπως αναφέρει στο Fortune η Ιωάννα Μυταφτσή , Υποψήφια Διδάκτωρ Ειδικών Μορφών Τουρισμού στο Αριστοτέλειο Πανεπιστήμιο Θεσσαλονίκης και Συντονίστρια Θεματικής Ενότητας, Ειδικών Μορφών Τουρισμού στην Γραμματεία Παραγωγικού Τομέα της Νέας Δημοκρατίας, κάνοντας μια ιστορική αναδρομή θα δούμε ότι πάντα υπήρχε η τάση του ταξιδιού που σε φέρνει αντιμέτωπο με τον θάνατο του άλλου. Τρανό παράδειγμα είναι, όπως επισημαίνει, το Κολοσσαίο ή η επίσκεψη τόπων που στο παρελθόν έχουν πραγματοποιηθεί δημόσιες εκτελέσεις.

Προσθέτει πως ο σκοτεινός τουρισμός τα τελευταία 25 – 30 χρόνια έχει αποκτήσει οργανωμένη μορφή , κυρίως λόγω της έρευνας που εκπονεί η ακαδημαϊκή κοινότητα και των εκτενών αφιερωμάτων που φιλοξενούνται σε επιστημονικά περιοδικά.
«Η ζήτηση για τον dark tourism αυξάνεται αλλά ακόμα δεν είναι ευρέως γνωστός στην Ελλάδα . Θα έλεγα, ωστόσο, ότι υπάρχουν τεράστιες προοπτικές ανάπτυξης του στην Ελλάδα, η οποία ως χώρα διαθέτει την πλούσια ιστορική πολιτιστική κληρονομιά από δύο Παγκόσμιους Πολέμους. Με το σωστό branding και marketing , την ανάπτυξη τουριστικών σκοτεινών εμπειριών, καθώς επίσης και τη δημιουργία των κατάλληλων υποδομών, η Ελλάδα θα μπορέσει να καταστεί σκοτεινός τουριστικός προορισμός» λέει χαρακτηριστικά η κα Μυταυτσή.
Ως επισκέψιμοι τόποι που θα μπορούσαν να συμπεριληφθούν στη λίστα για σκοτεινό τουρισμό είναι το σημείο δολοφονίας του Καποδίστρια , η Σπιναλόγκα , τα νησιά εξορίας Μακρόνησος – Γυάρος ακόμη και το Πολυτεχνείο , θα μπορούσε μελλοντικά να καταστεί σκοτεινός τουριστικός προορισμός. Όσο για την πόλη που έχει βαθιά σκοτεινή ιστορία αυτή είναι, σύμφωνα με την κα Μυταυτσή, η Θεσσαλονίκη.
«Η μεγαλύτερη φοβία για τους τουρίστες δεν είναι ο πόλεμος, αλλά το κόστος διαβίωσης»
« Το απόκοσμο και ο θάνατος προσελκύουν το ενδιαφέρον και προσδίδουν εμπειρία διότι η συναισθηματική φόρτιση, η θλίψη, ο πόνος, ακόμη και ο κίνδυνος είναι στοιχεία που ελκύουν τον άνθρωπο . Άλλωστε ο σύγχρονος τουρίστας δεν αρκείται στα συνηθισμένα καταναλωτικά τουριστικά προϊόντα. Αναζητά την εμπειρία εκείνη που θα του αλλάξει τη ζωή ή θα αποτελέσει μία πολύτιμη προσθήκη σε αυτή».
Καταλήγει λέγοντας πως τα κίνητρα που ωθούν τον ταξιδιώτη να προσφύγει σε αυτή την εναλλακτική μορφή τουρισμού είναι πολλά, ποικίλα και πολυδιάστατα το βασικότερο ωστόσο είναι η μνήμη . Ακολουθούν η περιέργεια, το ενδιαφέρον για την ιστορία, εκπαιδευτικοί λόγοι, η συμφιλίωση με την θνησιμότητα, αλλά και το προσκύνημα δικών μας ανθρώπων που χάθηκαν σε συγκεκριμένα σημεία.
ΔΙΑΒΑΣΤΕ ΠΕΡΙΣΣΟΤΕΡΕΣ ΕΙΔΗΣΕΙΣ:
- Η Ελλάδα στην κορυφή της προτίμησης των Αυστριακών τουριστών
- Ποιο ελληνικό νησί βρίσκεται στους 10 κορυφαίους προορισμούς του 2023

Are You In?
Join our mailing list and receive the latest news and travel offers from our team. don’t worry, we hate spam as much as you do.
Visiting Athens in the Winter: Weather – What to Pack – Things to Do
- Last Updated on: Jan 16, 2024
- Read Time 12 mins
- Published: Nov 18, 2019
We Need Your Support!
We want to remind you that Athens by Locals is reader-supported. By booking tours, hotels, tickets, and other travel services through the links on our website, you can help us continue providing valuable content and information. Note that we receive a small commission only if you make a booking using our links at the time of your visit. So, if you're not quite ready to book yet, you can save this post and the links and return to make your booking when the time is right. We genuinely appreciate your support and are thrilled to have you in our travel community. Please don't hesitate to reach out if you have any questions or need assistance. Happy travels!
Visiting Athens in the winter is not an idea that comes up very often among travelers. Mostly known as a summer destination, Athens lures hordes of travelers from May until the end of August. However, few know that the Greek capital is equally charming in the wintertime, offering plenty of choices for things to do. In fact, if you want to see the city without the tourist crowds, the perfect time of the year to visit Athens is from November until the end of March.
Here are what you should know about visiting Athens in the winter and a few ideas to add to your to-do list.
Athens Weather in the Winter
Even though temperatures are significantly lower in winter than in summer, the weather in Athens is still quite pleasant.
January and February are the coldest months of the year, with temperatures between 13 and 5 degrees Celsius.
However, the days have started getting chilly since November. Rainfalls aren’t uncommon during these months, but usually, they don’t last long.

You’ll probably get your vitamin D dose even if you’re visiting the Greek capital in the heart of winter.
If you want to know more about the best season to visit Athens, please read our detailed guide here .
Athens Temperatures in the Winter
What clothes to pack for your trip to athens in the winter.
Now that you know what the weather is like in Athens in the winter, you know that you have to leave your flip-flops and shorts back home.
Don’t worry, though; you don’t need to master the art of layering to survive the cold in Athens. A sweater and a jacket will be more than enough to keep warm while visiting the Greek capital .
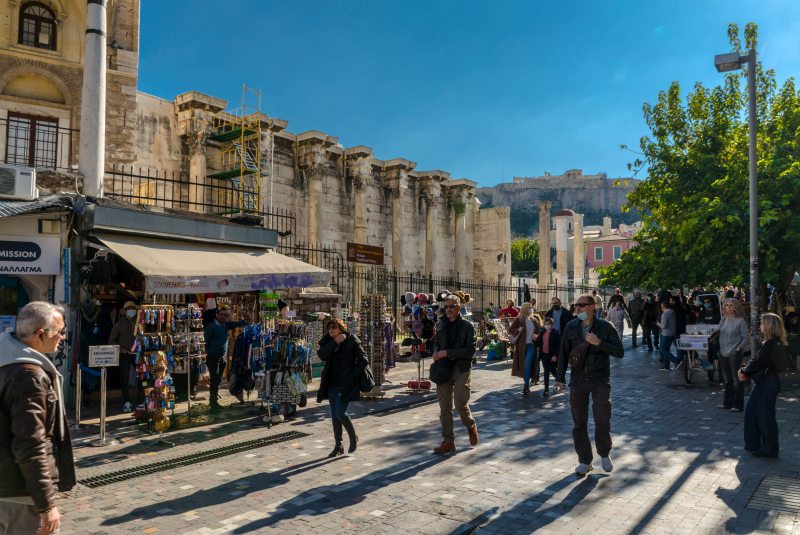

If you’re coming from a northern European country, you’ll probably cope with the weather quite easily.
Having said that here are a few suggestions for your winter in Athens packing list:
- Warm clothes (Jackets, gloves, scarves, winter hats, etc)
- A raincoat for the rainy days
- Comfortable footwear for getting around and sightseeing
- Extra pairs of socks. Rain in Athens is rare and usually brief but very sudden
- Sunglasses and sunscreen. Even in winter, Athens is very sunny
- Mosquito repellent. Especially if you’re planning to take a seaside trip
- A body wallet to avoid pickpockets
- An international power adapter
- A power bank and extra chargers
Do you still need help? You’re in luck. We have put together the ultimate travel checklist for Athens. Check it out right below.

Planning a Trip to Athens: The Ultimate Travel Checklist
Why visit athens during wintertime, book a flight and a hotel room at a lower price.
As winter is the off-peak travel season in Athens, prices drop. From November until the beginning of March you can find low-cost flights from several European cities . Moreover, accommodation in Athens is much cheaper compared to summer. Hotel rooms and Airbnbs can be found at lower prices even in the center of Athens. Plus, in many landmarks, prices are reduced during the winter months. For example, the Acropolis entrance fee is €20 from the 1st of April to the 31st of October and €10 from the 1st of November to the 31st of March.
Pleasant weather for outdoor activities
In the summer, temperatures often hit 40 degrees Celsius in the daytime. Walking around the city or doing one of Athens’s numerous outdoor activities can become very difficult under the sun’s heat. In winter, though, especially in December, the weather allows you to explore the great outdoors . On a sunny winter day, you can, for example, easily walk on top of Mt Lycabettus, or go hiking at Philopappos Hill .

Escape the tourist crowds
One of the best things about visiting Athens in the winter is that there are significantly fewer tourists.
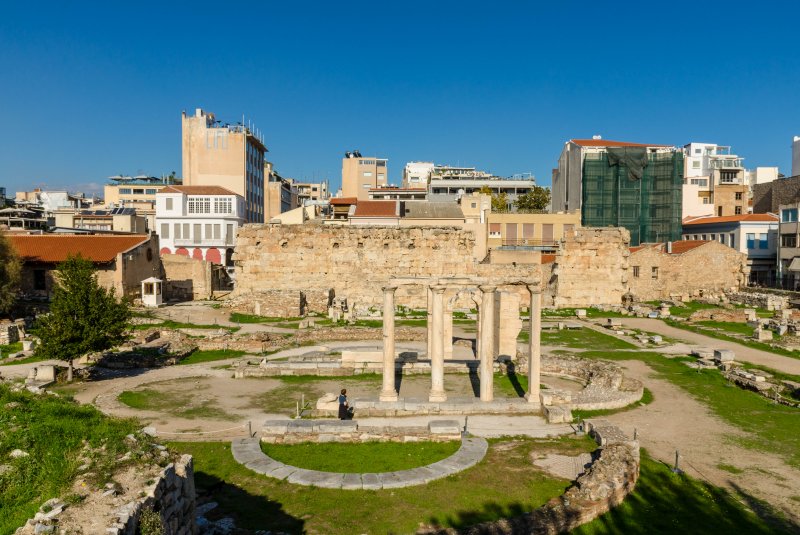

Not only will you see the city’s authentic side but you’ll also avoid the long queues at the city’s archeological sites and museums.
Imagine visiting the most famous attractions like the Parthenon or the Acropolis Museum at your own pace without squeezing through hundreds of people to get a nice photo.

Athens Uncovered: Must-Visit Places for Every Traveler
Taste authentic greek winter food.
Greek food and the gastronomy of Athens are two of the main reasons why travelers love visiting the city repeatedly. But did you know that visiting Athens in the winter will make for a completely new culinary experience? Greek cuisine is very seasonal, meaning many dishes can only be enjoyed in wintertime. Make sure to try fresh wild greens, lahanodolmades (the famous cabbage rolls), and rakomelo (boiled raki with honey and carnation). Also, if you’re visiting during Christmas, dig deep into a plate of melomakarona (honey biscuits) or diples (deep-fried dough with honey).

Experience Christmas and New Year’s Eve in Athens
Like most religious holidays, Christmas in Greece is traditionally a family affair.
Most of the shopping streets, museums, and archaeological sites close down on Christmas Eve and the city starts looking as real as possible.
Grab this opportunity to explore crowded places like Anafiotika and Dionysiou Aeorpagitou Street, and you’ll immediately feel like a local.
On the other hand, New Year’s Eve in Athens is probably the year’s busiest day. There’s a lot of shopping, numerous events, fine dining, and a lot of drinking all day.

After sundown, the city becomes a great party and locals hang around until the morning.
Planning to visit during the Christmas holidays? Then, you need to take a look at this guide right below.

Christmas in Athens: Weather – Tips – Where to Go and What to Do
Things to do in athens in the winter, explore plaka and anafiotika.
Now is your chance. You’ll never be able to see either Plaka or Anafiotika more comfortably without the hordes of tourists passing by.

Get lost in the narrow pedestrian streets of Plaka and discover the oldest street in Athens , enjoy a cup of Greek coffee and do some souvenir shopping while admiring the picturesque alleys and neoclassical buildings that will make you believe you are strolling through a postcard.

The Picturesque Plaka Neighborhood in Athens
Visit a museum on a rainy day.
Don’t worry if it happens to rain while you’re in Athens. You were bound to visit a few museums at some point anyway.
Apart from all the obvious choices like the Acropolis Museum , the National Archaeological Museum , and the National Art Gallery , you could also try something more peculiar like the Museum of Greek Popular Musical Instruments or The Museum of Cycladic Art.

Exploring the Cultural Treasures of Athens: A Comprehensive Guide to the Museums of Athens
And if you get tired of browsing through the exhibits, you can always have a break to enjoy some coffee and the sounds of rain.
After all, there’s only one thing better than a museum on a rainy day: museum restaurants and cafes .
Explore the Stavros Niarchos Foundation Cultural Center
Just a few minutes away from downtown Athens, the Stavros Niarchos Foundation Cultural Center is a must-visit attraction and a great option for a winter walk.

Within the beautiful complex, you’ll find the National Library of Greece, the Greek National Opera, and huge green open spaces with an artificial canal.
You can even get a bus from the city center to SNFCC completely free of charge.

Stavros Niarchos Foundation Cultural Centre (SNFCC)
Take a seaside trip to the athenian riviera.
The Athenian Riviera is among the most beloved places in the city among locals.
Granted, a stroll down the beach is not quite the same in wintertime, but you’ll still be able to enjoy breathtaking views, exquisite food, and shopping at the most famous southern suburbs of Athens like Voula and Glyfada.

The Athens Riviera: A World-Class Destination for Sea, Sun, and Sights
Climb up lycabettus hill.
Lycabettus is the tallest and most popular hill in Athens. It overlooks the Attica basin and offers immaculate views of the city.
You can either walk up the hill or ride the cable car that goes all the way to the top starting from the foothill of Lycabettus in the upscale neighborhood of Kolonaki.
It runs every half an hour, and the ride is quite enjoyable. Tickets cost 10 euros for a round trip.

Explore the National Garden of Athens
The National Gardens of Athens in Syntagma are also an exceptional choice for a winter walk.
You can easily get there just by walking a few minutes from the Parliament on Syntagma Square .
Just grab a cup of coffee and walk through the gardens, do a bit of birdwatching, and discover peculiar monuments and old buildings hidden among the labyrinthine pathways.

Nature’s Oasis in the Heart of Athens: A Guide to National Garden and Zappeion Hall
See the parthenon on acropolis hill.
We’ve mentioned it a few times in this article already but we can’t stress this enough: visiting Athens in the winter is the best time to see all the famous ancient sites that are swarmed with people any other time of the year.
And so the Parthenon couldn’t be missing from this list. The walk up the hill to admire the magnificent temple will be the highlight of your trip.

Exploring the Heart of Ancient Greece: A Visit to the Acropolis of Athens
Visit the city’s markets.
Even though markets take place all year round, in the winter, there are more options, as during the summertime, many vendors go on holiday.
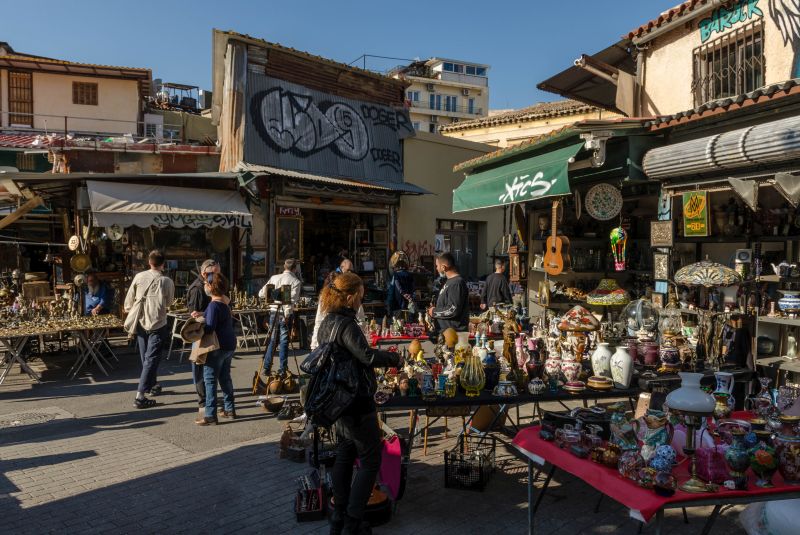

Food markets like the Athens Central Market, antique markets, and fashionable markets all over the city center.
Most of them are held on the weekends or Sundays attracting locals and tourists.

A Hidden Foodie Oasis: Visit the Athens Central Market
Hammam experience.
There isn’t a better way to warm up on a winter day than a traditional hammam experience. Hammam Baths in the Thissio neighborhood feature traditional hammam rooms that are ideal for some moments of pure relaxation. Moreover, the luxurious and cozy space offers massage services as well as manicure, pedicure and body hair removal, and facial cleansing services.
Go Ice Skating
Even though it rarely snows in Athens, some ice rinks around the city will set you in a wintery mood. Ice n Skate, close to Eleonas Metro station, the 1,000-square-meter ice rink close to the department store Athens Heart Mall, and the Ice Arena at Athens Concert Hall (Megaron) are the best places for honing your ice-skating skills.

Take a day trip from Athens
Even though Athens has a lot to offer, we would highly recommend taking a day trip to delve deeper into local culture and get a taste of rural Greece.
Still, we would suggest you stay clear of any seaside destinations like the Saronic Gulf islands , as life in these islands tends to be very slow in the winter.
Instead, you can admire the astonishing monasteries with a trip to Meteora or learn more about the history of Greece with a day trip to Ancient Olympia .
If you want to check for more great options for a day trip destination from Athens, read the article below.

Best Day Trips From Athens To: Ancient Sites – Islands – Towns
Where to stay in athens in the winter.
Choosing a hotel in Athens if you’re visiting in the winter will be much easier than looking for one during peak season.
Still, you should be looking for the best location if you want to have all the famous attractions within walking distance from your hotel.
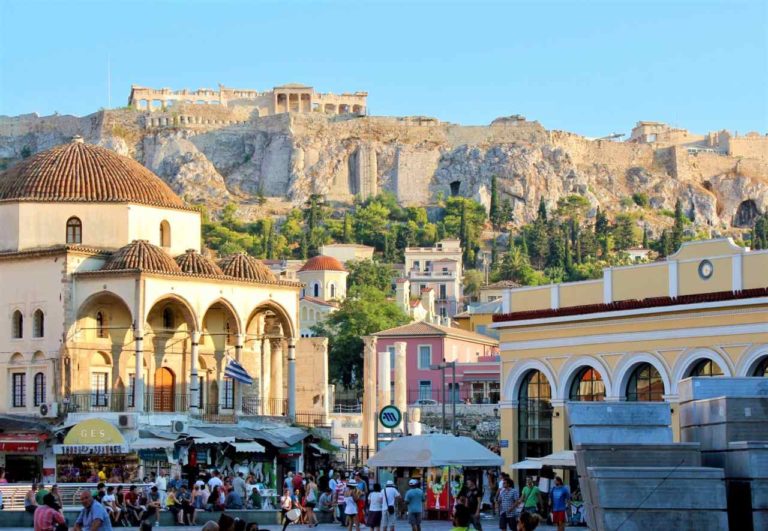

Stay In the Heart of Athens in These Top Hotels Near Acropolis
We would recommend choosing a hotel in the city center and specifically in the areas around the Acropolis: Koukaki, Thission, Monastiraki, Petralona, and Syntagma.
In short, all the sought-after areas where it’s almost impossible to find availability in the summer.
You can search and compare hotels, and find all the rates on Booking.com , the largest booking platform worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions about Visiting Athens in the Winter
Should i visit greece in winter.
Definitely yes. Visiting Greece in the winter is a different experience than visiting any other time of the year.
Is Athens worth visiting in December?
December is actually the warmest winter month in Athens. We highly recommend visiting in December, especially if you plan to spend Christmas in Athens.
Is Athens worth visiting in January?
January is one of the slower months for tourism, but that’s why it’s a great idea to visit then.
Is Athens warm in winter?
Athens is quite warm in the winter with an average temperature of 9 °C (48.3 °F) and a minimum temperature of around 6 °C (42.8 °F).
Does it snow in Athens in December?
Snow is very uncommon in Athens, especially in the city center. It normally snows only a few days a year. Still, you may see snow in Athens if you are lucky enough.
What’s the coldest month in Athens?
The coldest month in Athens is January.
Which area of Athens is best to stay in during winter?
Any area in the city center and close to the Acropolis like Syntagma, Monastiraki, Koukaki or Thission would be an excellent choice.
What do you wear in Athens in the winter?
Athens is rarely extremely cold. A normal winter jacket and jeans would be enough most of the time. However, make sure to pack some warm winter clothes just in case temperatures drop below normal levels during your trip.
To sum it up, Athens is a great city for a short getaway in the heart of the winter.
This guide aims to introduce you to the wintery side of the Greek capital and present you with the most important things to keep in mind before you start looking for hotels and booking your tickets .
A Quick Reminder:
Remember that Athens By Locals is here to guide you with planning the perfect trip to Athens and help you every step along the way. If you didn’t found what you’re looking for, or need any recommendations about your trip to Athens, feel free to contact us and we will do our best to help you. Please be as more detailed as possible regarding your subject so as to help you better.
If you like what you read please scroll down at the end of this page and subscribe to Athens By Locals so next time to receive more articles like this straight forward to your email. Join us on Facebook for comments, photos, and other fun stuff. If you enjoy this article please share it with your friends on Facebook.
Athens By Locals
THIS ARTICLE WAS WRITTEN/EDITED BY A TEAM MEMBER OF ATHENS BY LOCALS
Related Posts

A Sea Adventure in Athens: The Best Experiences You Can Live by Chartering a Yacht

Local Tips for the Best Things to Do on a Sunday in Athens

Athens on a Budget: 26 Free Things to Do in Athens
Copyright © 2024 Athens By Locals © All rights reserved. No part of this site may be reproduced without our written permission. Images owned by Athens By Locals. Image Banks or Companies promoted.

20 Unique Dark Tourism Sites Around The World
Disclosure: Advertising and affiliate services, including Amazon Associates, help the cost of running my blog. Clicking ads or making purchases through affiliate links may, at no additional cost to you, earn me a small commission. I appreciate your support .

One of the most unique tourism trends in recent years might have to be the fascination with so-called dark tourism sites. There’s always been a curiosity when it comes to places that might have a historic connection with tragic events. But while there are many reasons for people wanting to visit such sites, dark tourism is not a bad thing.
You might argue that visiting these dark tourism sites is a way of preserving the past. Or making sure the same horrific things don’t happen again . And while you might get some mixed reactions from people about your travel plans, they are fascinating places. And I believe they are places that the world should know about.
Disclaimer: The following article has travel suggestions in both Russia and Ukraine, however was written before the current events unfolded. I have chosen to leave them in this article in the spirit of the original topic covered here, however I am in no way recommending visiting either Russia or Ukraine at this time . Please check current travel conditions for any country you plan on visiting and travel safely.
What is Dark Tourism?
Dark tourism sites are places which we can associate with death, destruction or some kind of disaster. While some might see them as morbid, you’d be surprised at how many places you’ve visited with such connotations. For example, have you ever been to the Tower of London? Full of torture chambers and stories of gruesome events. What about the Colosseum in Rome? The deadly gladiator events here were some of the most bloody spectator sports in history.
We think of them as historical sites in a way we don’t think of some of the following places in the same way. Is it because that was so long ago? Does the length of time before we start exploring these sites really make a difference in how our visiting them should be perceived?
How should I behave at dark tourism sites?

Societal rules about museums are ingrained in us from an early age. But a lot of people worry about what to do while visiting somewhere with such a dark past. How do you behave? What if you do the wrong thing?
Respect is key . Remember that these sites, while open for you to enjoy, learn and experience, are the sites of some pretty bad and horrific things . Be aware of those around you as you never know if they might have a connection to where you are.
While it’s unfair to say you shouldn’t talk or show enthusiasm, use common sense and read the room . A concentration camp is nowhere to be giggling with your friends, a memorial park is not somewhere to be shouting…you get the idea.
Unique Dark Tourism Sites To Visit
Whether you’re a big history buff or just curious in anything a little macabre, these are some dark tourism sites around the world you likely don’t want to miss. From recent tragic events to centuries-old historical happenings, you can’t deny how incredibly interesting these places are.
Alcatraz Prison – San Francisco, USA

Possibly one of the most eerie and fascinating dark tourism sites you will ever visit is Alcatraz . A prison so notorious that it still receives millions of visitors a year. Located on an island in San Francisco ‘s bay area, you now get to experience seeing it from the inside like a prisoner. So close to land but so far away.
The only way to reach Alcatraz island is by a pre-booked boat tour . The tour is popular and often sells out months in advance. There are no food or drinks allowed except at the boat dock area, so plan your day accordingly. You also have a steep walk to the prison at the top of the hill, but there are motorized vehicle transfers for those with mobility issues.
Explore the prison and the grounds with an impeccably narrated audio tour by former guards and inmates. You’ll be led through cells, the recreation areas, the kitchen and more. Learn about the riots, the escapes and the deaths that happened here, and the most famous prisoners to ever call Alcatraz home.
Gravensteen Castle – Ghent, Belgium
Contributed by Cecilie from Worldwide Walkers

Gravensteen Castle in Ghent is a classic example of dark tourism sites in Europe. The castle was built back in 1180 and housed the Count of Flanders for many centuries until it became a court, a prison, and even a cotton factory.
It’s the dark horror stories of torture that really attract visitors to Gravensteen castle. While visiting, you’ll walk through torture rooms and see all the different tools used to punish criminals back in the Middle Ages.
Many people have died within the castle walls in the most horrific ways, which creates a dark haunted feeling to the place. It’s this uncomfortable feeling that leaves you both intrigued and distressed after your visit.
While it might sound very disturbing, the free audio guide does a wonderful job carrying out all the stories in an interesting way with respect to history. It’s a great place to learn about the history of Belgium’s city Ghent . You can even get one of the greatest city views from the castle roof.
Silver Mines – Potosi, Bolivia
Contributed by Deb from The Visa Project

While there are many landmarks to see in Potosi , a unique attraction is to visit one of these working mines. A guided tour let’s you witness the working conditions of the miners.
If you live in Bolivia , you would come across many extreme tourist offerings but this one would probably be one of the darkest. The Cerro Rico mountains silver mines made Potosi a major economic center of the Spanish empire back in the colonial times.
Mining is more or less still done in 18th century style – using old tools, hand and dynamite. No modern safety equipment or protocols. Although you would be introduced to El Diablo, the mountain’s devil-god to who the miners offer cigarettes, liquor as well as blood of an animal slaughtered on the spot for their protection. Child labor is pretty common and you can buy dynamite in the local market!
You will be advised to chew on coca leaves to help with breathlessness if taking a tour through the mines . The miners work in really harsh and dangerous conditions and many get lung diseases afterwards. If you visit, definitely leave a generous tip for the miners.
Port Arthur Penal Colony – Tasmania, Australia
Contributed by Mark from Wyld Family Travel

Port Arthur lies at the bottom of the world in southern Tasmania Australia . Port Arthur was a British penal colony set up in Australia, designed to break prisoners both mentally and physically. To be sent here from England was being sent as far away from your home as possible.
The youngest prisoner was 11 years old and around 70,000 prisoners called Port Arthur home. Prisoners at Port Arthur endured harsh working gangs that built much of Tasmania. The Asylum at the site pays testament to the mental torture these convicts were put through with many slowly losing their minds. Prisoners were regularly flogged to break them into submission.
Port Arthur prison was opened 20 years from 1833-1853 and 7,000 convicts died there. In modern times Port Arthur is also the location for the largest mass shooting in Australian history. This was the catalyst for the strict gun rules Australia lives by now.
Port Arthur is today one of the most interesting places to visit when in Tasmania. The prison site has been preserved with original building and tours explaining the history of the location.
Museum of the Occupation of Latvia – Riga, Latvia

As a former Soviet occupied country, Latvia still has many historic sites linked to the KGB. One of the most interesting activities you can do in Riga is visit the Corner House. This was the old headquarters of the Soviet KGB in Latvia.
True KGB style, if you didn’t know this museum existed you might not be able to find it. A inconspicuous doorway leads into a building straight out of the 50s. Here you can find out about the KGB in the city at that time.
The museum is free or you can pay 10 EUR for a guided tour. The tour might be worth it to see parts of the museum you wouldn’t otherwise get to. Walk through the rooms where the KGB worked and to areas of the building where the prisoners would have been taken.
The storyboards depict historical stories of the KGB in Riga, Latvia , and the “criminals” they arrested, tortured and killed here. This is really one of the most unique dark tourism sites in the Baltic states.
Jallianwala Bagh Memorial Park – India
Contributed by Neha from Travelmelodies

Etched in the history of India as a dark moment, is the incident of Jallianwala Bagh. Located in the holy city of Amritsar in Punjab, it remains one of the most popular places to visit in Amritsar . Jallianwala Bagh is a memorial park in the honor the people that were wounded and lost lives on the fateful day of 13 April, 1919.
Back in 1919, India was under the rule of British and the people of India were protesting for Independence. Over a thousand people had gathered in the Jallianwala park on the festive day of Baisakhi to silently protest the arrest of few national leaders. But General Dyer opened fire unannounced on these people killing and injuring many.
The Jallianwala Bagh now houses a museum with pictures and documents related to the event and some memorial structures in honor of the martyrs. There is a ‘Martyrs Well’ in which some people jumped to save themselves from the bullets. There’s even a wall with bullet markings on it.
Every evening there is a light and sound show that throws light on the unfolding of the event. It is a must visit place and is located next to the Golden temple.
Gori, Georgia
Contributed by Emily from Wander-Lush

The small city of Gori,Georgia has a rather dark claim to fame. It’s the birthplace of Ioseb Jughashvili, better known as former Soviet dictator Joseph Stalin.
An easy day trip from Tbilisi , Gori has become one of the most-visited places in Georgia because of its Stalin connection. The main attraction is the Stalin State Museum, a grandiose sandstone building in the center of the city.
In the yard is one of few remaining Stalin statues still standing in Georgia today. Also the small wooden house where Stalin was born in 1878, and the armored railway carriage he used to travel around the USSR.
The museum opened in 1957 and exhibits remain much the same – that is to say, very Soviet-style. It has a very selective curatorial approach with most artefacts relating to Stalin’s early years and some pretty glaring gaps. With limited information in English it’s recommended to take the guided tour for a few extra dollars.
Visiting the museum is a totally bizarre experience, but it gives an interesting insight into how Stalin’s memory is treated in Georgia today. Some people in Gori (and elsewhere in Georgia) still venerate the dictator, but the younger generations less so.
There are plenty of things to do in Gori that have nothing to do with Stalin. The magnificent Gori Castle, the old town, and the hilltop Gori Jvari church. It’s these attractions that most residents would prefer you remember Gori for.
Tham Piew Cave – Laos
Contributed by Marie from A Life Without Borders

Laos holds the unfortunate title of the most heavily bombed country on Earth. It bore the brunt of clandestine bombing campaigns waged by the USA on Laos during the 1960s and 1970s. Phonsavan in the province of Xieng Khouang, was particularly decimated. In fact, unexploded ordnance still affects local communities to this day.
Many visitors to the region enjoy Phonsavan’s major tourist sights such as the UNESCO site Plain of Jars. But few venture off the beaten track to discover the site of one of the worst days in Lao history.
On 24 November 1968, just one single missile fired from a US fighter plane killing 374 innocent villagers taking refuge in Tham Piew Cave. Just 60 kilometers from Phonsavan city, the cave is a somber and emotional place to visit. But it is important in the turbulent history of Laos, even if little known throughout the rest of the world.
The site’s information center holds extremely confronting photographs of the immediate aftermath of that fateful day, together with the history of the Secret War in Laos. A moving statue of a man carrying a lifeless child marks the entrance to the memorial park. Walk through a peaceful forest to the mouth of the charred cave. Here visitors can leave offerings of incense at the small shrine for those who perished within.
Chernobyl Exclusion Zone, Ukraine
Contributed by Kami from My Wanderlust

The Chernobyl Exclusion Zone is a well-known place all over the world. On April 26th, 1986 the biggest nuclear disaster in the world took place here, changing people’s lives forever. As a result of the catastrophe, the whole area around the power plant became a closed zone. Inhabitants of numerous towns and villages had to move away.
Today you can visit the Exclusion Zone but you need to do it with an official Chernobyl tour . There are plenty of them departing from Kyiv daily and you can choose between day trips and multiday tours. Now, all these years after the disaster the area is safe to visit and the radiation is low.

During your trip, you will see numerous places in the zone, including the power plant itself. But the biggest highlight is the abandoned town of Pripyat. When the disaster happened it was one of the most modern cities in the former USSR, but now nature has taken over the place.
Keep in mind that even if the Chernobyl zone is a very touristy and popular place, it is also a place of great tragedy. Make sure to visit the place with respect and follow your guide’s instructions. Still, this is a fascinating place to visit and everyone visiting Ukraine should include a Chernobyl tour in their itinerary .
Catacombs – Paris, France
Contributed by Debbie from World Adventurists

Even the City of Light and Love has a dark history. One of the most fascinating places to visit is the Catacombs of Paris . The Catacombs have a sad history, full of bones of the unknown. In the 17th century, Paris cemeteries were overflowing so badly that there was no longer space to properly bury their dead. Overflowing graves led to the solution of using the underground tunnels to house the bones.
Approximately six million people have been laid to rest underground. Today the bones are neatly stacked, including some designs made from the bones. At some points there are femurs arranged from the floor almost to the ceiling, with rows of skulls in between, or formed into shapes like a cross.
Visiting the Catacombs, it will make you really wonder what their lives were like back then, who they were, and the cause of each death. It is very humbling.
The Catacombs of Paris are extremely popular. It is more expensive, but to skip the line, you will want to buy your ticket in advance . It can also get chilly down there, so bring a light sweater with you. Allow for at least an hour and a half to wander the Catacombs once you are inside.
Lenin Mausoleum – Moscow, Russia
Contributed by De Wet & Jin, Museum of Wander

In the center of the Red Square in Moscow is a somewhat inconspicuous structure which reminds somewhat of a pyramid. But the long line of Russians and tourists is a giveaway that it is one of the most popular things to do in Moscow .
Inside this step pyramid is where the embalmed body of Vladimir Lenin is on display. Everyone is welcome to visit and pay their respects, or simply come and look at the former Soviet leader for bragging rights.
Visitors to Lenin’s Mausoleum visitors are first searched by military personnel, and bags (and cameras) have to be deposited. There are also a few strictly enforced rules while inside the mausoleum: no talking, hands out of your pockets, no hats and the line must keep moving at all times. Disobey, and a Russian soldier will reprimand you.

The atmosphere as well as the temperature inside the mausoleum is chilling. The line moves quite slowly, so you’ll get a good look at Lenin’s body, which has been on display here for almost a hundred years.
The mausoleum is free to enter and open on Tuesdays, Wednesdays, Thursdays, and Saturdays from 10:00–13:00. Behind the mausoleum is the gravesite of former Soviet ruler, Joseph Stalin, another interesting place to see.
Tianenmen Square – Beijing, China

Dark tourism sites don’t come more secretive than that of one of the world’s biggest massacres in recent history. Tianenmen Square, the public square in China’s capital, Beijing . While most visitors to China will have heard of the Tianenmen Square Massacre, the event is so censored within China that many people don’t know the full extent of it.
In 1989 students led a 6 week long protest after the death of a pro-reform official from the Communist Party of China. The fear was that the country would fall into economic decline and that the corruption in place would become worse. As the protests continued the military were brought in and things quickly got out of hand.
There are varying reports of anywhere from 300-3000 deaths of the tens of thousands of people who protested. While the square is peaceful now, there is always a high security presence as well as airport-style check points.
The square is used for many important national celebrations and Chairman Mao Zedong announced the founding of the People’s Republic of China here in 1949. His embalmed body is now on display in a mausoleum there.
Other than that there’s not a lot happening in the square now. However, the Imperial Palace (also known as the Forbidden City) is across from Tianenmen and is an impressive place to visit.
Bodie ghost town, California USA
Contributed by Olivia from Girl With Blue Sails

Bodie State Historic Park, once a booming California gold town, is now a notorious ghost town. It sits in a memorialized state of “arrested decay” with dilapidated buildings preserved in their state of abandonment from the late 1800’s. Walking down the dusty, dirt roads of Bodie invokes a bit of a dark appreciation and wonder about what happened to the people that lived here.
Visitors can walk through the main streets of the town, seeing the various houses, stores, and saloons. Canned goods still on store shelves, original newspapers in the buildings, and old wooden pews still in the church. There are old forgotten cars in the grass, rusting and being overgrown by nature.
Bodie is most popular with history buffs, photographers, and those who love to visit dark tourism sites. Plan your trip to Bodie in the morning to avoid the peak desert heat. While walking through Bodie can be a grim experience, it also provides a unique and realistic glimpse of 1800s California mining life.
Choeung Ek Killing Fields – Phnom Penh, Cambodia
Contributed by Tasha Amy from Backpackers Wanderlust

The Killing Fields, also known as Choeung Ek Geocidal Centre, is located just a short 17 kilometer journey from Phnom Penh city center . This closeness is important considering the horrible events which occurred here between 1975 and 1979.
During this period, Cambodia was run by the Khmer Rouge Regime communist party who arrested and executed anyone they saw as a threat. This included people with education, opposing beliefs, or anyone who stood up for what was right.
Quite a few foreigners even got executed after accidentally stumbling upon Cambodia during this period. Children were trained as soldiers and those who were disobedient were killed. For a greater understanding of life under the direction of the Khmer Rouge and Pol Pot watch the film First They Killed My Father .
The Killing Fields outside of Phnom Penh is just one of many locations across the country. Though this one is the most known due to the fact of the horrible acts performed here.
You can book a tour or visit by tuk tuk. The tuk tuk ride for the day should cost you around $12.00. Once at the Killing Fields make sure you hire the audio guide for the stories of those who lived through these events.
Nazi Rally Grounds – Nuremberg, Germany
Contributed by LeAnna from Wander In Germany

It’s no secret that Germany is riddled with a dark, difficult, and oppressing past. However, decades after WWII, the country does a phenomenal job of walking the fine line between erasing the atrocities and showing respect as well as raising awareness of exactly just what happened.
One such place is the unfinished Nazi Rally Grounds in Nuremberg . These huge grounds were Hitler’s vision for an enormous epi-center and headquarters for the Third Reich.
Walking around the lake at the site, it’s almost easy to not realize exactly what you are standing on. However, on the grounds is the Nazi Dokumentation Zentrum. Here you can see all the blueprints and plans for the grand scheme Hitler envisioned. It makes walking the grounds that much more realistic.
The museum does an exceptional job of showing exactly how a man with such polarizing, disgusting, racist views could enchant not only an entire nation, but take over much of Europe.
While in Germany, doing any sort of Nazi salute or tribute in public is illegal. Therefore, this site is not flocked to by Neo Nazis, but instead is seen as a place of learning from the past.
Guanajuato Mummy Museum – Mexico
Contributed by Shelley from Travel Mexico Solo

The Museo de las Momias (Museum of the Mummies) is one of the most popular places to visit, and best things to do in Guanajuato City, Mexico .
One of the most famous of Mexico’s dark tourism sites has about 100 mummified human bodies on display, in both glass cases and in the open. Most of the bodies are from older adults, but the museum also claims to have the “world’s smallest mummy” of an approximately nine-month-old child.
While not for everyone, it is the most visited place in Guanajuato City . When visiting, you’ll notice Mexican families with children of all ages. In Mexico, death is a much less taboo subject than in other countries — evidenced by annual festivals like Día de Muretos (Day of the Dead).
The story of the mummies is as fascinating (and bizarre) as seeing them in person. Between 1865-1958, Guanajuato’s government decided to start collecting a “grave tax” on buried bodies. If left unpaid by the living relatives for three years, the body was exhumed.
Located in arid Central Mexico, Guanajuato has extremely dry soil and the bodies came out of the ground incredibly well preserved. When the government ended the grave tax in 1958, they had so many mummified bodies that they created this museum.
House of Terror – Budapest, Hungary
Contributed by Marco from Nomadic Fire

Budapest is popular with both tourists and expats for stunning architecture, gorgeous scenery along the Danube river, and affordable cost of living . The city is also home to the infamous museum: the House of Terror.
This museum juxtaposes two of the cruelest regimes of the 20th century: Nazi Germany and Soviet Russia. Fittingly located in a building that was once the headquarters of both the Nazi and Communist secret police, the museum is an important reminder of both the crimes perpetrated by those regimes and their victims’ courage and resistance.
Stepping into the House of Terror transports visitors back to a terrifying time in Europe’s history. The museum’s artifacts include personal items confiscated by the secret police. It also tells stories such as a family’s desperate attempt to hide a young boy and baby girl from the Nazis during the Holocaust. Although now a museum, many rooms remain exactly as they were when the headquarters were operational. This includes prison cells, rooms filled with torture devices, and a guillotine scale model.
You can spend anywhere from 45 minutes to a few hours wandering around this well-curated museum. Through exhibits of movie posters, photos, and re-created scenes.
9/11 Memorial and Museum – New York City, USA

One of the most emotional activities on a trip to New York is visiting the 9/11 museum. Built below the original location of the Twin Towers, the World Trade Center site of the 2001 disaster. Entering the museum from the street level, you descend past the twisted metal remains of the massive steel beams that once held the tower up.
The museum is a somber place which stirs up a lot of raw feelings from anyone who visits. It guides you on a journey from the history of the WTC towers to a timeline of the events of that morning.
With witness testimonials, photographs and messages left by those who didn’t make it, the museum is very hard to experience. But the exhibits also talk about what has happened since, what they have learned and why this site is so important. Outdoors, the footprints of the original towers have now been turned into two giant pools. The name of every single victim is engraved around them.
Did you know that white roses are placed at the name of any victim whose birthday it would have been that day? As dark tourism sites go, this one is especially somber given how recently the event took place. But it’s well worth a visit if you’re in New York .
Imperial Crypt – Vienna, Austria
Contributed by Martina & Jürgen from PlacesofJuma

A really cool spot and interesting dark tourism site not to be missed on any visit to Vienna is the Imperial Crypt. It is a real insider tip among Vienna’s best attractions and a visit is an eerie experience.
The Imperial Crypt is the final resting place of many of the most famous Habsburgs from Europe. Hidden under the Capuchin Church, it can be visited on a guided tour daily from 10:00 to 18:00.
The crypt is the final resting place of 150 members of the Habsburgs. Among the most famous are Emperor Franz Joseph I, Empress Sisi and Crown Prince Rudolf and Maria Theresa. Walking through the ten dark rooms of the imperial crypt, you travel through a 400-year-long stylistic epoch. You’ll see richly decorated coffins are sometimes even adorned with skulls.
The Habsburgs were preoccupied with their death and therefore had the sarcophagus made according to their wishes. Why not take a tour where you will get lots of information about the funeral rituals?
Auschwitz Concentration Camp – Poland
Contributed by Sean from LivingOutLau

Auschwitz is arguably one of the most tragic sites in the entire world. It was the largest of many German Nazi concentration camp and extermination center in World War II. Over 1.1 million men, women, and children, mostly Jews, lost their lives here. The collective genocide of WWII, known as the Holocaust, is one of the most horrific events in human history.
The Auschwitz-Birkenau Memorial and Museum is now a site where visitors can learn more about how the events unfolded, living conditions, defenses that were set up to prevent the captives from escaping and more.

Auschwitz is more than just a popular attraction in Poland; it is a place where visitors can understand human nature. Auschwitz is the standing testimony of the terror that humans can do to each other. It warns out what happens when an ethnic group is dehumanized. A visit to Auschwitz is solemn and eye-opening.
The best way to visit Auschwitz is to take a tour from Krakow , the nearest touristy city from Auschwitz. As part of your Krakow itinerary , don’t forget to book your tour as early as possible. There are multiple languages you can choose to have the tour in and the English-speaking tours are always the first ones to run out!
Visiting popular dark tourism sites
There’s no denying that visiting many of these dark tourism sites around the world is uncomfortable. The atrocities that happened there or the stories they tell are often unfathomable. But dark tourism sites are just as important as any museum or regular attraction.
Whether or not you want to visit any (or all) of the sites on this post, you have to agree that they are truly fascinating. As long as you have good reasons for wanting to visit, and a respectful attitude towards them you will be welcomed.
If you’ve enjoyed reading this post leave a comment or share using the social media buttons below. Which of these dark tourism sites are you most interested in visiting to learn more about?

Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

37 thoughts on “20 Unique Dark Tourism Sites Around The World”
I really appreciate this post and how you emphasized that respect is key. I so agree! I think visiting these places can be very powerful and very educational. I’ve visited four on this list, as well as a few others not mentioned, and am so grateful for those experiences to learn more and witness humanity’s dark history.
Absolutely love the unique concept of this post. I especially appreciated how you included the section on mindfulness and respect. Hope to pay many of these places a visit.
this was a great post… and while these sites aren’t for everyone, i think it’s important to connect with ‘dark’ parts of the past, so we don’t repeat those same mistakes.
It is very rare to come across such posts. I absolutely loved the concept. Keep up the awesome work.
This is such an interesting guide! I have been to a few of these places and I’ve also visited some older prisons around the world that have a dark past to them. I definitely have to visit some of these in the future. Especially the ones in Europe!
This is one of the most unique posts I’ve seen in a while! I honestly haven’t been to most of the places on this list, but I’m bookmarking it for later.
I have visited a number if these sites but never heard of the them, ‘dark tourism’ before. I can understand how the term has come about. I always leave these sites very reflective. There’s no denying they have an enormous impact on me. I have pinned the post because, in my opinion, ‘dark tourisn’ is an important aspect of world travel.
I have been to a few of them and wrote about the profound realizations I went through. Thanks for sharing a thought-provoking post.
I love how you mentioned the importance of respect when visiting these places. These places really make you think! It’s important to not forget the ‘dark’ parts of history so it doesn’t happen again.
I definitely find places that would class as ‘dark tourism’ interesting. Although to be fair, we very rarely remember the ‘good’ and ‘peaceful parts of history so I think most places could be considered ‘dark’ in one way or another! I’ve only visited Alcatraz from the places on this list but it was definitely a fascinating place and I’d love to go back. I’d like to visit the catacombs in Paris too. There’s also a lot on this list that I haven’t heard of before but I’d definitely love to check them out. Thanks for the great guide!
This list is very important given the history of these places! It’s also interesting to note the different feelings at each of them. I haven’t been to every single one, but Auschwitz, Alcatraz, 9/11, the House of Terror, Catacombs, and Gravensteen Castle (wow, I didn’t realize how many I had been to) but all of them were so uniquely dark. I think Auschwitz was my most striking and moving, though.
This is such an interesting post. It’s so heartbreaking to read through some of the dark things that have happened around the world. I believe it’s important that we visit these places to pay our respects and remember the people whose lives were drastically impacted by these places. I appreciated how you emphasized the importance of showing respect at these places. Thank you for sharing this post!
You can learn so much at these dark tourism sites. The 911 memorial has moved me to tears. I’m not sure I could visit the mummy museum.
I’ve been to Alcatraz and the Catacombs, but it was interesting to discover some new ideas from this list. And yes, mindfulness and respect are so important, particularly for several entries on the list.
As a historian I’m interested in visiting these sites, although we’ve skipped them the last years, since we found our son to young for them. I’ve been to 2 of the sites mentioned.
What a great list of dark tourism places to visit! I’ve been to many of these such as Alcatraz, Bodie, Ghent and 9/11 memorial. I’d love to visit Chernobyl and the catacombs in Paris.
What an interesting article and list of places to visit. I’ve visited a few on this list and I agree with you, visiting these places can be very educational, but we need to be respectful.
What a great post. Yes, I have been to a few of these dark tourist sites and am now adding a few more to my bucket list.
What an utterly informative and sobering post. I visited the Killing Fields in Cambodia back in 2013 but today still hold it so close to my heart.
Lenin’s Mausoleum was a surreal experience to say the least. No stopping, no taking photos, only getting a quick glance at Lenin before being ushered out. Auschwitz was another one that was really eye opening for me and a unique although sad experience.
What a fascinating post! I have never visited any of those sites other than the World Trade Center site in NYC. I would be interested in seeing several of them. sites like that are so educational and bring history to the forefront.
Thank you for this important post. I think sites of dark tourism are important for exposing atrocities of the past for many reasons. They allow us to pay tribute to those who have suffered, but more importantly, hopefully they instil in visitors the importance of playing a role in ensuring that history isn’t repeated.
I’m not sure that ‘penal tourism’ (sites such as Alcatraz and Eastern State Penitentiary) need to be included in the category of ‘dark tourism.’ My visits to S-21 and Cheoung Ek in Cambodia can’t be equated to the failings of a penal system. My visits to the Anne Frank House in Amsterdam, Dachau in Germany, or Auschwitz in Poland can’t be compared to Alcatraz.
‘Dark tourism’ and ‘penal tourism’ are important, but… separate.
Thank you for bringing attention to this issue.
that’s a fair point, and I’m in no way comparing one of these places to another, but understand that many people also have different levels of comfort in where they might want to visit so wanted to include a wide range of places. There are certain sites (like the ones you mentioned) that are always going to be the worst of the worst with regards to history. Thanks for reading
Very cool article! Haven’t seen many like this one. I’m actually in Tasmania right now!!
I have not done a lot of tourist type things alone, but one was Alcatraz. Fascinating experience walking that prison by myself and the audio tour.
I love this! I really want to try dark tourism after I saw “Dark Tourist” on Netflix! I totally agree with you, visiting these sites is very educational and an eye opener. And yes, respect is the key. It applies to everywhere we go! I will definitely save this for my future travels! 🙂
This is an interesting list. We’ve visited some already – like the catacombs in Paris. And some – like Tschernobyl are on our bucketlist!
Great compilation! There are so many places to go for dark tourism. And I know I can’t brave to most of them. I guess I can do it with museums. Opss how I missed the Crypt museum in Vienna!
What an interesting and informative article. I’ve been to a few of these sites, as well as a few more that didn’t make your list. I think that travelling is learning- and it’s important to visit places such as these to honour, respect and learn from our past.
In a way, I am really into some aspects of dark tourism, I love things that are creepy or have a ghost story behind it. I did find a few spots on this list that interest me such as the castle in Belgium. Looks beautiful and with an interesting story!
Dark tourism is no doubt not everyone’s cuppa tea. Travel ushers understanding and these sites may serve as monuments that will remind humanity about life itself and not taking the same dark path twice.
Great post Emma, I love visiting places like these (or, in some cases, “love” would definitely not be the appropriate word, but I think they’re important to visit). The hardest place I’ve ever visited is the Killing Fields in Cambodia. Horrendous. The genocide museum in Sarajevo in Bosnia was hard-hitting too. I’d be really interested to visit that KGB museum in Latvia!
Very good topic and original. i agree in most of the places listed, indeed most of them are scenario of some of the darkest moments of humanitty. I have only one thing that I don’t understand by you choose to put Lenin Mausoleum? Independently of the personal believes of rach one, Lenin led the biggest and most sucessul revolution in history . Poeple can like it more or less but I don’t how his resting place is part of dark tourist places….If would be Stalin inside ok, but this one i don’t get it. Great work overall, I am argentinian and I really appreciate that you brought-up the story of Potosi…. Well done! Looking forward for your next post!
Thanks for reading. For this one it’s also more about the fact that you can visit the body of Lenin and that it is on display as dark tourism is focused around often morbid places. There are a few countries that have former leaders on display – Ho Chi Minh in Vietnam, Chairman Mao in China – and I think the idea of visiting one of these places to see an embalmed body on display is a little dark in itself
Got your point! You know that is the same guy who embalmed Lenin and Ho Chi Minh? 😁
Great post! Especially seeing these are all easily accessible, no trespassing required. I have only been to a few, but I really recommend the Nuremberg Ralley Ground and the adjacent museum. Few people visit, and it is quite eerie. Also, the 1936 Olympic Village in Berlin which is similar architecture to Nuremberg rallye grounds, it was really abandoned a few years ago, I think more touristic now.
Have definitely been to a few dark tourist sites but Chernobyl has been on my list for ages now!
One of the most eye opening museums was the Anne Frank in Amsterdam but definitely want to keep visiting some new ones.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
Become an FT subscriber
Try unlimited access only $1 for 4 weeks.
Then $75 per month. Complete digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Cancel anytime during your trial.
- Global news & analysis
- Expert opinion
- Special features
- FirstFT newsletter
- Videos & Podcasts
- Android & iOS app
- FT Edit app
- 10 gift articles per month
Explore more offers.
Standard digital.
- FT Digital Edition
Premium Digital
Print + premium digital, ft professional, weekend print + standard digital, weekend print + premium digital.
Essential digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- Global news & analysis
- Exclusive FT analysis
- FT App on Android & iOS
- FirstFT: the day's biggest stories
- 20+ curated newsletters
- Follow topics & set alerts with myFT
- FT Videos & Podcasts
- 20 monthly gift articles to share
- Lex: FT's flagship investment column
- 15+ Premium newsletters by leading experts
- FT Digital Edition: our digitised print edition
- Weekday Print Edition
- Videos & Podcasts
- Premium newsletters
- 10 additional gift articles per month
- FT Weekend Print delivery
- Everything in Standard Digital
- Everything in Premium Digital
Complete digital access to quality FT journalism with expert analysis from industry leaders. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- 10 monthly gift articles to share
- Everything in Print
- Make and share highlights
- FT Workspace
- Markets data widget
- Subscription Manager
- Workflow integrations
- Occasional readers go free
- Volume discount
Terms & Conditions apply
Explore our full range of subscriptions.
Why the ft.
See why over a million readers pay to read the Financial Times.
International Edition

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The BEST Athens Dark Tourism Spots in 2024. The Athens War Museum. The Rifle Range (Skopeftirio) of Kaisariani. The "1941-1944 Memorial Site". The Athens Polytechnic. The Haidari Concentration Camp (Block 15) The EAT-ESA Museum. The Parnitha Sanatorium. The Marathon Tumulus.
As a dark tourist, Athens offers a unique perspective to those seeking an unconventional travel experience. Athens is the perfect destination for any dark tourist looking to experience an abundance of mystery, creepy vibes and a mystery deep-rooted in history. Visitors can explore ancient ruins, uncover old legends, enter crypts and buildings ...
Dark Tourism - the online travel guide to dark, unusual & weird places around the world. Dark Tourism - the guide to dark travel destinations around the world ... There is a War Museum in Athens that presumably covers all this. Since the end of the military dictatorship of the 1960s and 70s, Greece has become a more or less stable democracy and ...
Dark tourism in Greece. Since the beginning of the civilised world, people engage in macabre, mournful and "dark" interactions and, paradoxically, pursue traumatic experiences in the context of social interaction and fun. Public executions, death rituals, battles sites, disasters and atrocities, are some of the examples that attracted, and ...
In this spirit, we present a selection of Greece's most notorious dark tourism destinations, offering a distinct travel experience for those desiring a taste of the unconventional.. Spinalonga, Crete. Consider Spinalonga, Crete, an island of barely 100 square metres.Yet its history looms large, a colossal monument to human suffering.
Many researchers view dark tourism as the dark side of cultural tourism or an authentic glance at cultural and heritage resources. Noteworthy is the fact that there is an essential connection between cultural tourism and dark tourism. ... Athens, Greece. Vicky Katsoni . University of Malta, Msida, Malta. George Cassar . Rights and permissions ...
A guide to the most notable dark tourism destinations around the world, where to find them, and whether or not you should visit. ... I came to Athens on vacation in 2017, fell in love with the city, and never left! I created this site to help you explore Athens and wider Greece like a local and experience all of the things that most tourists miss.
Peter Hohenhaus, a widely travelled dark tourist based in Vienna, also points to the broader rise in off-the-beaten track tourism, beyond the territory of popular guidebooks and TripAdvisor rankings.
Dialogue in the Dark. Leave the world of sight for an experience of a lifetime.Dialogue in the Dark is a guided tour through your familiar surroundings in the city of Athens without leaving the sense of security of the theater installation. By eliminating the use of sight, everyday situations become completely new experiences.
170. The Aokigahara forest in Japan, known as the suicide forest, is a dark tourism destination. Ko Sasaki for The New York Times. By Maria Cramer. Oct. 28, 2022. North Korea. East Timor. Nagorno ...
Greece's birth rate fell by 30 percent from 2011 to 2021 to under 84,000 per year, slipping ever-further below the death rate, according to the Hellenic Statistical Service. The cumulative ...
15. The Colosseum, Rome. Built in Ancient Rome between 72-80 AD, the Colosseum is one of the oldest and most recognizable dark tourism sites. At the time, it was the largest amphitheater ever built with a capacity of 50,000-80,000 spectators.
Abstract. Dark tourism or, thanatourism, a term used as an encyclopaedic alternative (Jafari 1996, 578) 1, only emerged as a collective area of named study in the last decade of the twentieth century.Both terms had their origins in the recognition of the long history and widespread occurrence of traveling encounters with different kinds of engineered and orchestrated remembrance of the dead.
While traveling the world visiting cemeteries, war memorials, natural disaster sites, and former prisons can, perhaps, satisfy a morbid curiosity, it's also about paying respects to the dead, and remembering what happened and why. Browse the gallery for a gruesome travel itinerary. SHARE THIS ARTICLE. Visitor attractions historically associated ...
8. Don't eat in Plaka. Plaka is a gorgeous neighbourhood so although it's a very touristy area it's a must-visit when you're in Athens. But that doesn't mean that you should eat here. While the cafés around the Anafiotika area are extremely popular with locals, the restaurants are very much tourist traps.
Τι είναι το dark tourism και πώς η Ελλάδα θα καταστεί "σκοτεινός" τουριστικός προορισμός ΜΑΡΙΑ ΑΚΡΙΒΟΥ 18/01/2023, 14:50
The 'darkness' in dark tourism. The locution 'dark tourism' has undergone critical scrutiny, as detractors claim that it entails negative cultural connotations (Dunnett, Citation 2014; Edensor, Citation 2013), and prefer definitions perceived as more neutral, such as thanatourism.Regardless of the word used to describe visits to places related to death, negativity may be implied ...
2 Dark Tourist, season 1, episode 1, 'Latin America', presented by David Ferrier, released July 20, 2018, on Netflix, online streaming. 3 In the early nineteenth century, the Oxford English Dictionary first defined tourism, stressing the still novel concept of 'travelling for pleasure'.
Athens Weather in the Winter. Even though temperatures are significantly lower in winter than in summer, the weather in Athens is still quite pleasant. January and February are the coldest months of the year, with temperatures between 13 and 5 degrees Celsius. However, the days have started getting chilly since November.
Gravensteen Castle - Ghent, Belgium. Contributed by Cecilie from Worldwide Walkers. Photo Credit: Cecilie, Worldwide Walkers Gravensteen Castle in Ghent is a classic example of dark tourism sites in Europe.The castle was built back in 1180 and housed the Count of Flanders for many centuries until it became a court, a prison, and even a cotton factory.
In 2019, Athens welcomed 17.8mn international arrivals. But since then, with a break during the pandemic, the shift towards tourism has accelerated, without a plan to protect residents. Five new ...