Conjugation verb trip
Model : stop
Auxiliary : have , be
Other forms: trip oneself / not trip
Contractions
- he/she/it trips
- you tripped
- he/she/it tripped
- they tripped
Present continuous
- I am tripping
- you are tripping
- he/she/it is tripping
- we are tripping
- they are tripping
Present perfect
- I have tripped
- you have tripped
- he/she/it has tripped
- we have tripped
- they have tripped
- I will trip
- you will trip
- he/she/it will trip
- we will trip
- they will trip
Future perfect
- I will have tripped
- you will have tripped
- he/she/it will have tripped
- we will have tripped
- they will have tripped
Past continous
- I was tripping
- you were tripping
- he/she/it was tripping
- we were tripping
- they were tripping
Past perfect
- I had tripped
- you had tripped
- he/she/it had tripped
- we had tripped
- they had tripped
Future continuous
- I will be tripping
- you will be tripping
- he/she/it will be tripping
- we will be tripping
- they will be tripping
Present perfect continuous
- I have been tripping
- you have been tripping
- he/she/it has been tripping
- we have been tripping
- they have been tripping
Past perfect continuous
- I had been tripping
- you had been tripping
- he/she/it had been tripping
- we had been tripping
- they had been tripping
Future perfect continuous
- I will have been tripping
- you will have been tripping
- he/she/it will have been tripping
- we will have been tripping
- they will have been tripping

Perfect participle
- having tripped
Helping millions of people and large organizations communicate more efficiently and precisely in all languages.
Online Language Dictionaries
Perfect tenses, continuous (progressive) and emphatic tenses, compound continuous (progressive) tenses, conditional, subjunctive.
*Blue letters in conjugations are irregular forms. ( example ) *Red letters in conjugations are exceptions to the model. ( example )
Report a problem.

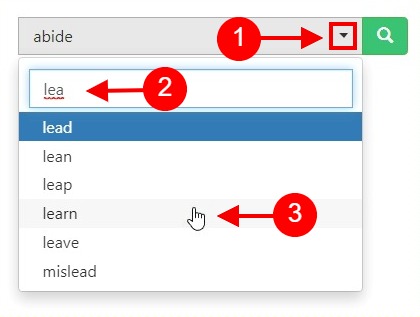
Trip Past Tense
tripped past tense of trip is tripped.
Trip verb forms
Conjugation of trip.
- What is the past tense of tyne in English?
- What is the second form of verb type?
- What is the third form of verb typecast in English?
- What is the conjugation of typeset in English?
- Conjugate typewrite in English?
- ubiquitinate
PastTenses is a database of English verbs. One can check verbs forms in different tenses. Use our search box to check present tense, present participle tense, past tense and past participle tense of desired verb.

Select your English level
To personalize your experience.
- To Trip Conjugation
Continuous Perfect
Conditional.
We notice you're using an ad blocker.
Linguasorb is free and ad supported, without ad revenue we can't exist. Certain features such as audio, directly cost us money and so are disabled for ad block users.
Please disable your ad blocker for this site if you wish to use the premium features.
Alternatively you can become a supporter and remove the ads completely .
Trip Past Tense: Verb Forms, Conjugate TRIP
The past tense of trip is tripped
The Forms of Trip
Conjugate trip, trip in present simple (indefinite) tense, trip in present continuous (progressive) tense, trip in present perfect tense, trip in present perfect continuous tense, trip in past simple (indefinite) tense, trip in past continuous (progressive) tense, trip in past perfect tense, trip in past perfect continuous tense, trip in future simple (indefinite) tense, trip in future continuous (progressive) tense, trip in future perfect tense, trip in future perfect continuous tense, leave a comment cancel reply.
Conjugation of verb (past tense) trip

Past simple
Past participle.
- ⭐Conjugation
- Podmínkové věty
- Frázová slovesa
- ⭐Conditional
- ⭐Subjunktiv
- ⭐Participle
- ⭐Phrasal verbs
Conjugation of the regular verb [trip]
Conjugation is the creation of derived forms of a verb from its principal parts by inflection (alteration of form according to rules of grammar). For instance, the verb "break" can be conjugated to form the words break, breaks, broke, broken and breaking.
The term conjugation is applied only to the inflection of verbs, and not of other parts of speech (inflection of nouns and adjectives is known as declension). Also it is often restricted to denoting the formation of finite forms of a verb – these may be referred to as conjugated forms, as opposed to non-finite forms, such as the infinitive or gerund, which tend not to be marked for most of the grammatical categories.
Conjugation is also the traditional name for a group of verbs that share a similar conjugation pattern in a particular language (a verb class). A verb that does not follow all of the standard conjugation patterns of the language is said to be an irregular verb .
Present Continuous
Past continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, conditional of the regular verb [trip].
Causality (also referred to as causation or cause and effect ) is influence by which one event, process, state or object (a cause) contributes to the production of another event, process, state or object (an effect) where the cause is partly responsible for the effect, and the effect is partly dependent on the cause. In general, a process has many causes, which are also said to be causal factors for it, and all lie in its past. An effect can in turn be a cause of, or causal factor for, many other effects, which all lie in its future.
The conditional mood (abbreviated cond) is a grammatical mood used in conditional sentences to express a proposition whose validity is dependent on some condition, possibly counterfactual.
English does not have an inflective (morphological) conditional mood, except in as much as the modal verbs could, might, should and would may in some contexts be regarded as conditional forms of can, may, shall and will respectively. What is called the English conditional mood (or just the conditional) is formed periphrastically using the modal verb would in combination with the bare infinitive of the following verb. (Occasionally should is used in place of would with a first person subject – see shall and will. Also the aforementioned modal verbs could, might and should may replace would in order to express appropriate modality in addition to conditionality.)
Conditional present -->
Conditional present progressive -->, conditional perfect -->, conditional perfect progressive -->, subjunktiv of the regular verb [trip].
The subjunctive is a grammatical mood, a feature of the utterance that indicates the speaker's attitude toward it. Subjunctive forms of verbs are typically used to express various states of unreality such as: wish, emotion, possibility, judgement, opinion, obligation, or action that has not yet occurred; the precise situations in which they are used vary from language to language. The subjunctive is one of the irrealis moods, which refer to what is not necessarily real. It is often contrasted with the indicative, a realis mood which is used principally to indicate that something is a statement of fact.
Subjunctives occur most often, although not exclusively, in subordinate clauses, particularly that-clauses. Examples of the subjunctive in English are found in the sentences "I suggest that you be careful" and "It is important that she stay by your side."
The subjunctive mood in English is a clause type used in some contexts which describe non-actual possibilities, e.g. "It's crucial that you be here" and "It's crucial that he arrive early." In English, the subjunctive is syntactic rather than inflectional, since there is no specifically subjunctive verb form. Rather, subjunctive clauses recruit the bare form of the verb which is also used in a variety of other constructions.
Present subjunctive -->
Past subjunctive -->, past perfect subjunctive -->, imperativ of the regular verb [trip].
The imperative mood is a grammatical mood that forms a command or request.
An example of a verb used in the imperative mood is the English phrase "Go." Such imperatives imply a second-person subject (you), but some other languages also have first- and third-person imperatives, with the meaning of "let's (do something)" or "let them (do something)" (the forms may alternatively be called cohortative and jussive).
Imperativ -->
Participle of the regular verb [trip].
The past participle is one of the most important parts of English grammar. It’s used to express perfect tenses and to form the passive voice. It’s also a useful tool for writing sentences that describe actions that started in the past and are still happening today. The past participles of irregular verbs don’t follow a specific pattern and can have numerous endings.
Present participle -->
Past participle -->, phrasal verbs of the regular verb [trip], recent articles.
- Past perfect and past perfect progressive – understanding the differences
- Past perfect progressive tense
- Present perfect and past perfect - understanding the differences
- Past simple and past perfect tenses - understanding the differences
- Past perfect tense affirmative sentences
Start with any verb and browse through irregular verbs in alphabetical order
Use the button "Random choice"
Looking for a specific irregular verb?
regular verbs & Irregular verbs
- Slovenščina
- FAQ Technical Questions
- Text Translation
- Vocabulary Trainer
- Online Dictionary
- Login
- Online dictionary
- Products & Shop
- Conjugation
- Vocabulary trainer
- Dictionary API
- Add to home screen
- Browse the dictionaries
- Terms and conditions of use
- Supply chain
- Data Protection Declaration
- Legal notice
- Privacy Settings
- EN');"> English
- FR');"> French
- DE');"> German
- LA');"> Latin
- ES');"> Spanish
Verb Table for trip
- Simple tenses
- Continuous tenses
Conditional
Simple tenses • continuous tenses • conditional • imperative • impersonal, present perfect, past perfect, will -future, going to -future, future perfect, conditional past, past participle, browse the conjugations (verb tables).
- triple-tongue
Look up "trip" in other languages
Links to further information.
You can suggest improvements to this PONS entry here:
We are using the following form field to detect spammers. Please do leave them untouched. Otherwise your message will be regarded as spam. We are sorry for the inconvenience.
My search history
- Most popular
- English ⇄ German
- English ⇄ Slovenian
- German ⇄ Spanish
- German ⇄ French
- German ⇄ Greek
- German ⇄ Polish
- Arabic ⇄ English
- Arabic ⇄ German
- Bulgarian ⇄ English
- Bulgarian ⇄ German
- Chinese ⇄ English
- Chinese ⇄ French
- Chinese ⇄ German
- Chinese ⇄ Spanish
- Croatian ⇄ German
- Czech ⇄ German
- Danish ⇄ German
- Dutch ⇄ German
- Elvish ⇄ German
- English ⇄ Arabic
- English ⇄ Bulgarian
- English ⇄ Chinese
- English ⇄ French
- English ⇄ Italian
- English ⇄ Polish
- English ⇄ Portuguese
- English ⇄ Russian
- English → Serbian
- English ⇄ Spanish
- Finnish ⇄ German
- French ⇄ Chinese
- French ⇄ English
- French ⇄ German
- French ⇄ Italian
- French ⇄ Polish
- French ⇄ Slovenian
- French ⇄ Spanish
- German ⇄ Arabic
- German ⇄ Bulgarian
- German ⇄ Chinese
- German ⇄ Croatian
- German ⇄ Czech
- German ⇄ Danish
- German ⇄ Dutch
- German ⇄ Elvish
- German ⇄ English
- German ⇄ Finnish
- German ⇄ Hungarian
- German → Icelandic
- German ⇄ Italian
- German ⇄ Japanese
- German ⇄ Latin
- German ⇄ Norwegian
- German ⇄ Persian
- German ⇄ Portuguese
- German ⇄ Romanian
- German ⇄ Russian
- German → Serbian
- German ⇄ Slovakian
- German ⇄ Slovenian
- German ⇄ Swedish
- German ⇄ Turkish
- Dictionary of German Spelling
- Greek ⇄ German
- Hungarian ⇄ German
- Italian ⇄ English
- Italian ⇄ French
- Italian ⇄ German
- Italian ⇄ Polish
- Italian ⇄ Slovenian
- Italian ⇄ Spanish
- Japanese ⇄ German
- Latin ⇄ German
- Norwegian ⇄ German
- Persian ⇄ German
- Polish ⇄ English
- Polish ⇄ French
- Polish ⇄ German
- Polish ⇄ Italian
- Polish ⇄ Russian
- Polish ⇄ Spanish
- Portuguese ⇄ English
- Portuguese ⇄ German
- Portuguese ⇄ Spanish
- Romanian ⇄ German
- Russian ⇄ English
- Russian ⇄ German
- Russian ⇄ Polish
- Slovakian ⇄ German
- Slovenian ⇄ English
- Slovenian ⇄ French
- Slovenian ⇄ German
- Slovenian ⇄ Italian
- Slovenian ⇄ Spanish
- Spanish ⇄ Chinese
- Spanish ⇄ English
- Spanish ⇄ French
- Spanish ⇄ German
- Spanish ⇄ Italian
- Spanish ⇄ Polish
- Spanish ⇄ Portuguese
- Spanish ⇄ Slovenian
- Swedish ⇄ German
- Turkish ⇄ German
Identified ad region: ALL Identified country code: RU -->
Verb "trip"

For the settings to take effect, you must restart the trainer Restart
Conjugation
Simple tense.
Present Simple
- he, she trips
Past Simple
- you tripped
- he, she tripped
- they tripped
Future Simple
- I will trip
- you will trip
- he, she will trip
- we will trip
- they will trip
Continuous Tense
Present Simple Continuous
- I am tripping
- you are tripping
- he, she is tripping
- we are tripping
- they are tripping
Past Simple Continuous
- I was tripping
- you were tripping
- he, she was tripping
- we were tripping
- they were tripping
Future Simple Continuous
- I will be tripping
- you will be tripping
- he, she will be tripping
- we will be tripping
- they will be tripping
Perfect Tense
Present Perfect
- I have tripped
- you have tripped
- he, she has tripped
- we have tripped
- they have tripped
Past Perfect
- I had tripped
- you had tripped
- he, she had tripped
- we had tripped
- they had tripped
Future Perfect
- I will have tripped
- you will have tripped
- he, she will have tripped
- we will have tripped
- they will have tripped
Perfect Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Continuous
- I have been tripping
- you have been tripping
- he, she has been tripping
- we have been tripping
- they have been tripping
Past Perfect Continuous
- I had been tripping
- you had been tripping
- he, she had been tripping
- we had been tripping
- they had been tripping
Future Perfect Continuous
- I will have been tripping
- you will have been tripping
- he, she will have been tripping
- we will have been tripping
- they will have been tripping
Conditional
- I would trip
- you would trip
- he, she would trip
- we would trip
- they would trip
- I would have tripped
- you would have tripped
- he, she would have tripped
- we would have tripped
- they would have tripped
Present Continuous
- I would be tripping
- you would be tripping
- he, she would be tripping
- we would be tripping
- they would be tripping
Perfect Continuous
- I would have been tripping
- you would have been tripping
- he, she would have been tripping
- we would have been tripping
- they would have been tripping
- we Let's trip
Other verbs
Be the first to comment.
Add comment
Past tense of trip
Simple past, past participle, all forms of the verb trip, share this page.
bottom_desktop desktop:[300x250]

Describing a Trip | Past Simple

A fun lesson for beginner ESL students to learn the past simple regular verbs, past simple irregular verbs, vocabulary, and expressions about describing a trip. Watch the ESL video about describing a trip using Past Simple and use the ESL Printable and Digital storytelling flashcards to practice the past simple using new vocabulary and expressions to talk about a past trip.
Warm Up Questions
- Do you like to travel?
- What kinds of things do you like to do when you travel?
- What are 3 things that you have to take with you when you travel?
- What countries have you been to?
- What’s your dream vacation?
ESL Listening Talking about a Trip using the Past Simple
Watch the following YouTube video:
Listening Questions – Talking About A Trip In The Past
- How was Tony’s trip?
- How was the weather?
- How were the people?
- How was the hotel?
- Was it expensive?
- What did Tony do on his trip?
- How was the food?
- Did Tony have a good trip?
ESL Printable and Digital Flashcards to Talk about a Trip in the Past
Use the following ESL printable flashcards to talk about a trip using the past simple.

Matching – Vocabulary to Talk about a Past Trip
Match the words on the left with the meanings on the right.
ESL Listening Transcripts Talking about a Trip in the Past
Samantha: How was your trip?
Tony: It was really fun.
Samantha: How was the weather?
Tony: The weather was beautiful. It was warm and sunny every day.
Samantha: How were the people?
Tony: The people were very friendly and helpful.
Samantha: What did you do?
Tony: I had some meetings; I ate at some delicious restaurants and I did some sightseeing.
Samantha: How was the hotel?
Tony: The hotel was very nice. The service was great.
Samantha: I see! How was the food?
Tony: The food was amazing. I ate many different kinds of food.
Samantha: Was it expensive?
Tony: I think it was reasonable. I didn’t spend too much money.
Samantha: Sounds like you had a wonderful vacation!
Tony: Yes, just one bad thing happened.
Samantha: Really? What happened?
Tony: I got sick. I got food poisoning.
Samantha: Wow, that’s awful. I thought you said that the food was delicious.
ESL Gamification: Gamify your Lessons with Digital Badges & Stamps
Choose from hundreds of ESL digital badges and stamps to gamify lessons and motivate students.

www.pocketpassport.com Questions? [email protected]
Reference: B2L19
Are You a Teacher?
Get access to over 500 lessons.
- Audio Files
- Downloadable PDF’s
- Digital Quizzes & Flashcards
- Grammar Tools
- Gamification Tools
- Add Student Accounts
- Create & Sell Courses
Are You a Student?
Improve your….
- Vocabulary & Idioms

- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Customer Care is here to help!
Copyright 2022 Procketpassport.com.
All Right reserved.
- Full Access to Select Lessons
- New Lessons Added Every Week
- Free Lessons Include:
- PowerPoints
- Everything in Free +
- Full Access to ALL Lessons
- Lesson & Course Builder
- Easily Create Sales Pages
- Sell Courses Online
- Upload Your Own Content
- Student Accounts
- Premium Teacher & Student Tools
- Online Reservation System
- Feedback & Evaluation Tools
- Full Admin Tools
- Full Customization
- & Lots More!
Enter your email address below where you would like us to send the free sample!
Your privacy is protected..
Your Free Sample will arrive shortly. Have a great day!
English Grammar Here
Travel V1 V2 V3 V4 V5, Past Simple and Past Participle Form of Travel

Verb; Travel
Meaning; trip, journey, voyage, peregrination, eyre
V1, V2, V3, V4, V5 Form of Travel
Synonym for Travel
- peregrination
- sightseeing
- cultivation
When learning English you need to know the meaning of certain words first, and then sort the words appropriately according to grammatical rules. Verbs in a regular structure can be transformed with a simple rule, whereas in irregular verbs, this situation is slightly different. It may be a good start to make some memorization and learn how to use the verbs in the right places.
Here are Verb Forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 pdf
Related Posts

Rise Past Simple, Simple Past Tense of Rise, Past Participle, V1 V2 V3 Form Of Rise

Dry Past Simple, Simple Past Tense of Dry Past Participle, V1 V2 V3 Form Of Dry

Turn V1 V2 V3 V4 V5, Past Simple and Past Participle Form of Turn
About the author.
Here are the past tense forms of the verb travel
👉 Forms of verb travel in future and past simple and past participle. ❓ What is the past tense of travel.

Travel: Past, Present, and Participle Forms
What are the 2nd and 3rd forms of the verb travel.
🎓 What are the past simple, future simple, present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect forms of the base form (infinitive) ' travel '? 👉 It's quite simple -->
Learn the three forms of the English verb 'travel'
- the first form (V1) is 'travel' used in present simple and future simple tenses.
- the second form (V2) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in past simple tense.
- the third form (V3) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in present perfect and past perfect tenses.
What are the past tense and past participle of travel?
What is the past tense of travel.
The past tense of the verb "travel" is "travelled (BrE)", or "traveled (AmE)", and the past participle is "travelled (BrE)" or "traveled (AmE)".
Verb Tenses
Past simple — travel in past simple travelled (BrE), traveled (AmE) (V2) . Future simple — travel in future simple is travel (will + V1) . Present Perfect — travel in present perfect tense is travelled (BrE), traveled (AmE) (have/has + V3) . Past Perfect — travel in past perfect tense is travelled (BrE), traveled (AmE) (had + V3) .
travel regular or irregular verb?
👉 Is 'travel' a regular or irregular verb? The verb 'travel' is regular verb .
Examples of Verb travel in Sentences
- These days we travelled 1400 km (Past Simple)
- We didn't travel that long (Past Simple)
- She has travelled extensively in the Philippines (Present Perfect)
- I can't travel without you (Present Simple)
- We usually travel to work by bus (Present Simple)
- A plane travels faster than a train (Present Simple)
- They are travelling together since 2018 (Present Continuous)
- You can travel by foot, why not? (Present Simple)
- Unfortunately you can't travel without a ticket, so please proceed to the ticket office (Present Simple)
- How many countries have you travelled to? (Present Perfect)
Along with travel, words are popular see and tell .
Verbs by letter: r , d , u , c , m , p , b , w , h , a , e , g , s , q , j , l , t , f , o , n , k , i , v , y , z .
English verbs
- 318 Irregular verbs
- 904 Regular verbs
- 5 Modal verbs
- 407 Phrasal verb
Online verb dictionary
We are currently working to add new verbs and examples to our website, along with detailed descriptions. Please send us a message if you have any requests or suggestions, and we will add them as quickly as we can. Thank you for your interest in our website!
our editor - Peter (Certified TEFL Tutor with over 8 years experience)
Have a question or find mistake?

Past Tense of Travel: Traveling Back in Time
By: Author Oliver
Posted on Last updated: August 12, 2023
Sharing is caring!
Welcome to our article on the past tense of travel! If you’re learning English grammar, you know that understanding verb tenses is an essential part of the language. The past tense is particularly important, as it allows us to talk about events and experiences that have already happened. In this article, we’ll explore the basics of English tenses, give an overview of the past tense, and focus specifically on how to use the past tense when talking about travel.
Travel is one of the most common topics of conversation, and being able to talk about past trips is a great way to connect with others and share experiences. However, using the past tense correctly can be tricky, especially when it comes to irregular verbs and complex sentence structures. In this article, we’ll provide plenty of examples and exercises to help you master the past tense of travel. We’ll also cover some common mistakes to avoid and provide additional resources for further learning.
So whether you’re planning your next trip or just want to improve your English skills, read on to learn everything you need to know about the past tense of travel!
Key Takeaways
- The past tense is essential for talking about past events and experiences, past tense of ‘travel’ is ‘traveled’
- By practicing with examples and exercises, you can improve your use of the past tense of travel and avoid common mistakes.

Past Tense of Travel
Travel is a verb that is commonly used in the past tense. In this section, we will cover the formation and usage examples of the past tense of travel.
To form the past tense of travel, we add “-ed” to the base form of the verb. For example:
- I traveled to Europe last summer.
- She traveled to Asia for business.
- We traveled to South America for vacation.
Simple Past
The simple past is used to describe a completed action in the past. Regular verbs like travel are formed by adding -ed to the base form. For example:
- I traveled to Paris last year.
Past Continuous
The past continuous is used to describe an action that was in progress at a specific point in the past. It is formed by using the past tense of “to be” (was/were) and the present participle (-ing) of the main verb. Here are some examples:
- I was traveling to Paris when I got a call from my boss.
Usage Examples
The past tense of travel is used to talk about a completed action in the past. Here are some examples:
- I traveled to Japan last year and had an amazing time.
- She traveled to Italy for her honeymoon and fell in love with the country.
- We traveled to Mexico for our anniversary and enjoyed the beautiful beaches.
We can also use the past tense of travel to talk about a past habit or routine. For example:
- When I was younger, I traveled to different countries every summer.
- She traveled for work every week and got used to living out of a suitcase.
- We traveled to visit our family every holiday season.
In conclusion, the past tense of travel is formed by adding “-ed” to the base form of the verb and is used to talk about completed actions or past habits. Practice using the past tense of travel in your own sentences to improve your English grammar skills.
Common Mistakes with Past Tense of Travel
If you are learning English, you might be struggling with the past tense of the verb “travel.” Here are some common mistakes people make and how to avoid them.
Mixing Past and Present Tenses
One of the most common mistakes is mixing past and present tenses. For example, saying “I travel to Paris last year” instead of “I traveled to Paris last year.” To avoid this mistake, remember to use the past tense of “travel” when referring to something that happened in the past.
Using the Present Participle
Another mistake is using the present participle instead of the past tense. For example, saying “I am traveling to London last week” instead of “I traveled to London last week.” To avoid this mistake, remember to use the past tense of “travel” when referring to something that happened in the past.
Using the Wrong Auxiliary Verb
Using the wrong auxiliary verb is also a common mistake. For example, saying “I was travel to Rome” instead of “I traveled to Rome.” To avoid this mistake, remember to use the correct auxiliary verb (in this case, “did”) when forming the past tense.
Example Sentences
Here are some example sentences to help you practice using the past tense of “travel” correctly:
- I traveled to Japan last summer.
- She visited her grandparents in Florida last month.
- They took a road trip across the United States.
- We flew to Paris for our honeymoon.
- He backpacked through Europe after college.
Remember, practice makes perfect! Keep practicing using the past tense of “travel” correctly, and soon it will become second nature.
Exercises to Practice Past Tense of Travel
Learning English grammar can be challenging, especially when it comes to mastering the past tense of travel. To help you improve your skills, we have compiled a list of exercises that you can use to practice and perfect your past tense of travel.
Interactive Exercises
Interactive exercises are a great way to practice the past tense of travel. They allow you to engage with the material and receive immediate feedback on your progress. Here are a few interactive exercises you can try:
- Fill in the Blank: In this exercise, you will be given a sentence with a blank space where the past tense verb should go. Your task is to fill in the blank with the correct past tense verb. For example, “I ___ to Paris last year.” The correct answer would be “went.”
- Matching: In this exercise, you will be given a list of past tense verbs and a list of travel-related words. Your task is to match the past tense verb with the correct travel-related word. For example, “flew” would match with “airplane.”
Written Exercises
Written exercises are another great way to practice the past tense of travel. They allow you to focus on the material and practice at your own pace. Here are a few written exercises you can try:
- Sentence Writing: In this exercise, you will be given a travel-related word, and your task is to write a sentence using the correct past tense verb. For example, “train” could be used in the sentence, “I ___ to New York on a train.”
- Paragraph Writing: In this exercise, you will be given a prompt related to travel, and your task is to write a paragraph using the correct past tense verbs. For example, “Write a paragraph about your last vacation.” You could write, “Last summer, I ___ to Hawaii with my family. We ___ on the beach, ___ in the ocean, and ___ at some amazing restaurants.”
By practicing these exercises, you will improve your understanding and mastery of the past tense of travel. Keep practicing, and before you know it, you’ll be a pro at English grammar!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the past tense of travel?
The past tense of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English. Both spellings are correct, but American English tends to drop the second “l” in the past tense and past participle forms of the verb.
Is it spelled Travelled or traveled?
As mentioned above, both spellings are correct. The difference in spelling is due to the variation in American and British English.
Which is correct travel or travelling?
Both “travel” and “travelling” are correct, but “traveling” is the preferred spelling in American English, while “travelling” is the preferred spelling in British English.
What’s the difference between travel and Travelled?
“Travel” is the present tense of the verb, while “travelled” is the past tense. The difference between the two is the time frame in which the action occurs.
What is the V2 form of travel?
The V2 form of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English.
What is the V3 form of travel?
The V3 form of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English.
In summary, the past tense of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English. Both spellings are correct, and the difference in spelling is due to the variation in American and British English. Additionally, “traveling” is the preferred spelling in American English, while “travelling” is the preferred spelling in British English.
The past tense of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English. Both spellings are correct, but American English tends to drop the second \"l\" in the past tense and past participle forms of the verb.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"Is it spelled Travelled or traveled?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"Which is correct travel or travelling?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
Both \"travel\" and \"travelling\" are correct, but \"traveling\" is the preferred spelling in American English, while \"travelling\" is the preferred spelling in British English.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What's the difference between travel and Travelled?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
\"Travel\" is the present tense of the verb, while \"traveled\" is the past tense. The difference between the two is the time frame in which the action occurs.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the V2 form of travel?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The V2 form of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the V3 form of travel?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The V3 form of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English.
In summary, the past tense of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English. Both spellings are correct, and the difference in spelling is due to the variation in American and British English. Additionally, \"traveling\" is the preferred spelling in American English, while \"travelling\" is the preferred spelling in British English.
- Recent Posts
- Plural of Safe: What It Is and How to Use It Correctly - October 3, 2023
- Purple Color Names: Different Hues of Purple - October 2, 2023
- Addition Transition Words for Clear and Cohesive Writing - September 30, 2023
Related posts:
- Past Tense of Buy: How to Use them Correctly in English Grammar
- Mastering English Grammar: The Definitive Guide to Understanding the Past Tense of Cost
- Past Tense of Drag: Dragged Through Time
- Hoped or Hoped For? Mastering the Past Tense of Hope with Ease

Past Simple Tense: How to Use It, With Examples
Published by
Olivia Drake
On this page:
Simple past tense definition
The simple past tense is a verb tense that is used to describe completed actions or events that occurred in the past. The simple past tense is commonly used in storytelling and narration, as well as in conversations about past experiences. In this article, we will explain how to use the simple past and provide examples to help you understand it better.
When to use the simple past tense?
1. Actions That Occurred in the Past The simple past tense is commonly used to describe actions that happened in the past. For example:
- I walked to the store.
- They studied English last night.
- She ate pizza for dinner.
2. Completed Actions Completed ActionsThe simple past tense is used to describe actions that were completed in the past. For example:
- I finished my homework before dinner.
- They left for the airport at 5am.
- She visited her grandparents last weekend.
3. Sequences of Events in the Past The simple past tense can also be used to describe a sequence of events that occurred in the past. For example:
- I woke up, brushed my teeth, and ate breakfast.
- They arrived at the party, greeted their friends, and danced all night.
- She got dressed, packed her bags, and left for the airport.
4. Past Habits or States The simple past tense can be used to describe habits or states in the past. For example:
- I always drank coffee in the morning.
- They lived in New York City for ten years.
- She had curly hair when she was a child.
5. Specific point in the past To talk about a specific point in the past. For example:
- He finished his project last night at 10 pm.
How to form the simple past tense?
The simple past tense is formed using the past form of the main verb. The structure of a simple past form is as follows:
Subject + past form of the verb
The formation of the simple past tense depends on whether the verb is regular or irregular:
1. For regular verbs, simply add “-ed” to the base form of the verb to form the past simple tense. For example:
- walk (base form) -> walked (past simple)
- play (base form) -> played (past simple)
- watch (base form) -> watched (past simple)
2. For irregular verbs, the simple past form is different from the base form of the verb and must be learned individually. Some common irregular verbs and their past simple forms include:
- go (base form) -> went (past simple)
- eat (base form) -> ate (past simple)
- see (base form) -> saw (past simple)
- do (base form) -> did (past simple)
Note that there are some verbs that are both regular and irregular, depending on their meaning. For example:
- “learned” (regular) and “learnt” (irregular) are both used in different regions and contexts.
Also, it’s important to remember that the verb “be” has two different past simple forms: “was” (for the singular pronouns: I, he, she, it) and “were” (for the plural pronouns: we, you, they).
Here are some examples of the past simple tense in use:
- Regular verb: “She played tennis yesterday.”
- Irregular verb: “He went to the store last night.”
- Irregular verb: “I saw a movie last weekend.”
- Regular verb: “We walked to the park.”
- Irregular verb: “They did their homework before dinner.”
How to make a negative form?
To make a negative sentence in the past simple tense, you need to use the auxiliary verb “did” and the negative particle “not” (or “n’t”). The formula forming the simple past is:
Subject + did not (didn’t) + base form of the verb + object
For example:
- I did not (didn’t) go to the party last night.
- He did not (didn’t) finish his homework on time.
- They did not (didn’t) visit their grandparents over the weekend.
Note that the contracted form “didn’t” is more commonly used in spoken English.
Also, for regular verbs, the negative form is formed by adding “-not” (or “-n’t”) to the auxiliary verb “did” and using the base form of the verb. For example:
- I did not (didn’t) walk to the store.
- She did not (didn’t) play soccer last weekend.
- They did not (didn’t) watch a movie yesterday.
How to make a question form?
You can read more here about the question form
Can I use the simple past tense to talk about ongoing actions in the past?
No, the past simple tense is not used to talk about ongoing actions in the past. It is used to describe a completed action or event that happened at a specific time in the past. If you want to talk about an action that was in progress in the past, you should use the past continuous tense.
For example, if you want to describe an action that was ongoing in the past, you could say “I was reading a book,” using the past continuous tense. If you were to use the past simple tense, it would imply that you had already finished reading the book, and would say “I read a book” use the simple past instead.
Can I use the simple past tense to talk about future events from a past perspective?
No, the simple past tense is not typically used to talk about future events, even from a past perspective. It is primarily used to describe completed actions or events that occurred at a specific point in the past.
If you want to talk about a future event from a past perspective, you would typically use the past perfect tense. For instance, “By the time I arrived at the party, the cake had already been cut,” suggests that the cake was cut before the speaker arrived at the party.
Alternatively, you could use the present perfect tense to describe a future event that has already been planned or arranged. For instance, “I have reserved a table at the restaurant for tomorrow night,” suggests that the reservation has already been made for a future event.
What are some common irregular verbs in the simple past tense?
In English, there are many irregular verbs, which means their past tense and past participle forms do not follow the rules of the regular -ed ending pattern. Here are some common irregular verbs in the simple past tense:
- have -> had
- say -> said
- make -> made
- come -> came
- take -> took
It is important to remember that irregular verbs do not follow a specific rule, so they need to be memorized.
Are there any exceptions or special cases when using the simple past tense?
Yes, there are a few exceptions and special cases when using the simple past tense in English:
- Modal verbs (can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would) do not have a past tense form. Instead, their past meaning is expressed through the use of the perfect infinitive (e.g. could have, should have, would have).
- The verb “to be” has two past tense forms: “was” for the singular subjects (I, he, she, it) and “were” for the plural subjects (we, you, they).
- Some verbs have the same past simple form as their base form. For instance, “cut” is the past simple form of “cut,” and “put” is the past simple form of “put.”
- The simple past tense is sometimes used in conditional sentences to express a hypothetical situation that is unlikely or impossible. For example, “If I had known you were coming, I would have baked a cake.”
- In reported speech , the simple past tense is often used to report a past action or event. For example, “She said she saw the movie yesterday.” Here, the original statement might have been “I saw the movie yesterday,” but in the reported speech, the simple past tense “saw” is changed to “said she saw.”
If you've read this far, you likely found value in our content. We measure the quality of our articles in various ways, and one significant metric is the number of shares. If you appreciated this piece, please spread the word.
Leave a reply cancel reply, i’m olivia.

Welcome to my virtual classroom! Join me on a journey of language and learning, where we explore the wonders of English together. Let’s discover the joy of words and education!
Let’s connect
Join the fun!
Stay updated with our latest tutorials and ideas by joining our newsletter.
Type your email…
Recent posts
Modal verbs in conditional sentences with examples, questions in future perfect continuous tense with examples, questions in future perfect tense with examples, questions in future continuous tense with examples, questions in future indefinite (simple) tense with examples, questions in past perfect continuous tense with examples, discover more from fluent english grammar.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
Search form
- A1-A2 grammar
Past simple – regular verbs
Alfie took his driving test for the second time this morning. Did he pass?
Instructions
As you watch the video, look at the examples of regular past simple verbs. They are in red in the subtitles. Then read the conversation below to learn more. Finally, do the grammar exercises to check you understand, and can use, regular past simple verbs correctly.
Oliver: So, how did it go? Did you pass? Alfie: No, I failed ... again! Oliver: I don’t believe it! How did you fail again? What happened this time? Alfie: You won’t believe it! Oliver: No? No way, Alfie, not the same as last time? Alfie: Yep. Oliver: No way! Not another cat? Alfie: I know! I’m in shock! I love cats! Oliver: So, what happened? Alfie: Well, I stopped at a zebra crossing to let an old man cross the road. No problem there. He walked across the road so I started to drive. Just then a cat appeared from nowhere! Oliver: Did you hit it? Alfie: I did. It was impossible to stop. Oliver: I don’t believe you, Alfie. You’re joking, aren’t you? You didn’t fail, did you? Nobody can kill two cats on two driving tests! Alfie: What can I say? I know - it’s totally crazy. The owner of the cat arrived ... Oliver: Oh no ... and? Alfie: Well, he said it wasn’t my fault, the cat escaped from the garden ... the driving instructor agreed too. So, we carried on with the test, but I was too nervous and I crossed a red traffic light. Oliver: Poor you, mate! Do you want to come over? Alfie: Yeah, OK. See you in five minutes.
The past simple is the most common way of talking about past events or states which have finished. It is often used with past time references (e.g. yesterday, two years ago).
Please explain past events or states!
A past event could be one thing that happened in the past, or a repeated thing.
I stopped at a zebra crossing. We carried on with the test. We played tennis every day in August.
A state is a situation without an action happening.
We stayed at my grandparents' house last summer.
How do you form the past simple?
Regular past simple forms are formed by adding - ed to the infinitive of the verb.
start → start ed kill → kill ed jump → jump ed
That seems easy!
Yes, but there are some spelling rules. If a verb ends in - e , you add - d .
agree → agree d like → like d escape → escape d
If a verb ends in a vowel and a consonant, the consonant is usually doubled before - ed .
stop → sto pp ed plan → pla nn ed
If a verb ends in consonant and - y , you take off the y and add - ied .
try → tr ied carry → carr ied
But if the word ends in a vowel and - y , you add - ed .
play → play ed enjoy → enjoy ed
OK, not quite so easy! But the past simple form doesn't change at all for I, you, he, she, we and they , does it?
No, the form doesn't change. See, it is easy!
What about the pronunciation of the - ed ending?
There are three kinds of pronunciation: /d/, /t/ and /ɪd/. Look at the table below.
Aaagh! How do I know how to pronounce each one?
Good question. Well, really all you need to know is that /d/ is easier to say after arrive , and /t/ is easier to say after ask . For /ɪd/, the infinitive ends in a /d/ or a /t/ sound already so you must add an extra syllable for these verbs.
All right, that makes sense, but how do you form questions and negatives?
With the verb did (do in the past ) + the infinitive.
Did y ou pass? You didn't fail , did you? Yes, I did. / No, I didn't.
Right, thanks, I've got it now!
Good. But you also need to learn the irregular past simple forms.
You mean there are verbs that don't end in - ed in the past?
Yes, they don't all end in - ed . Have a look at the past simple irregular verbs too.
Check your grammar: true or false - past simple regular verbs
Check your grammar: gap fill - past simple regular verbs, check your grammar: multiple choice - past simple regular verbs, worksheets and downloads.
Did you like this grammar snack? What did you do yesterday? Tell us about your day.

Sign up to our newsletter for LearnEnglish Teens
We will process your data to send you our newsletter and updates based on your consent. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the "unsubscribe" link at the bottom of every email. Read our privacy policy for more information.
Press Herald
Account Subscription: ACTIVE
Questions about your account? Our customer service team can be reached at [email protected] during business hours at (207) 791-6000 .
- Local & State
Cirque du Soleil, Greek Festival, Pete Davidson and more happening this weekend
See a Maine State Ballet performance and get your fill of lobster rolls.

You are able to gift 5 more articles this month.
Anyone can access the link you share with no account required. Learn more .
With a Press Herald subscription, you can gift 5 articles each month.
It looks like you do not have any active subscriptions. To get one, go to the subscriptions page .
Loading....
We know that this weekend’s forecast for the next several days is a bit on the sketchy side, with some rain forecasted.
But will that stop us from getting out there and doing a whole bunch of stuff?
Absolutely not, because it’s still summer in Maine. Plus, we all know that if you want the weather to change here, you just need to give it a minute.

Portland Jazz Orchestra performing with Katie Oberholtzer at Congress Square Park. Photo by Christopher Andrew
Fingers crossed for tonight’s free performance in Congress Square Park from the Portland Jazz Orchestra. The music starts at 6 p.m.
See Portland Jazz Orchestra for free on Thursday
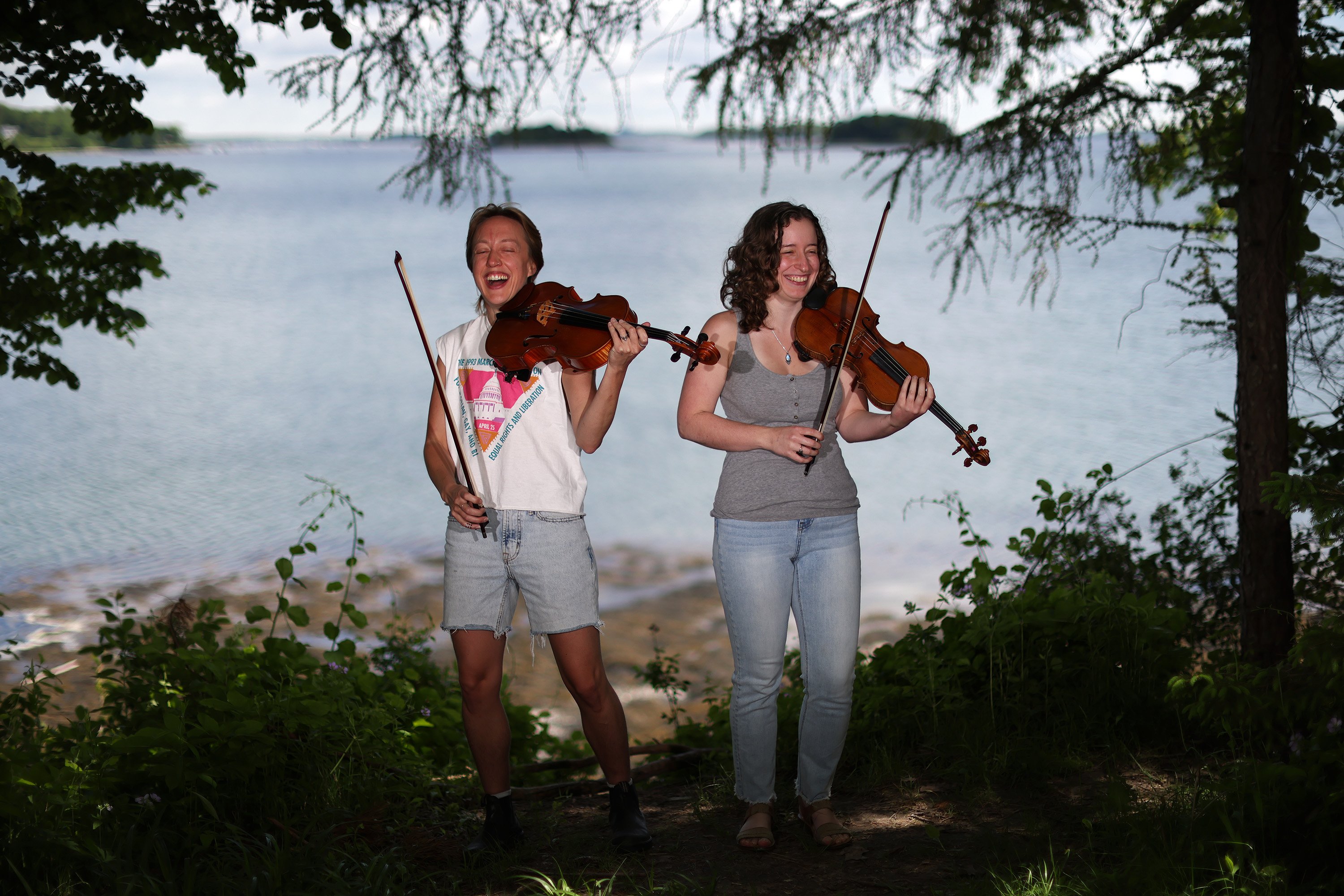

Kal Sugatski, left, and Katherine Liccardo laugh while pausing to remember the next segment of a song while playing their instruments on a forested shoreside trail on Mackworth Island for a portrait. Ben McCanna/Staff Photographer
Vigorous Tenderness immersive performance on Mackworth Island is Friday from 6-7:30 p.m. (Original date was today, change due to weather forecast). Advertisement
Concert series Vigorous Tenderness celebrates the change in seasons and classical music
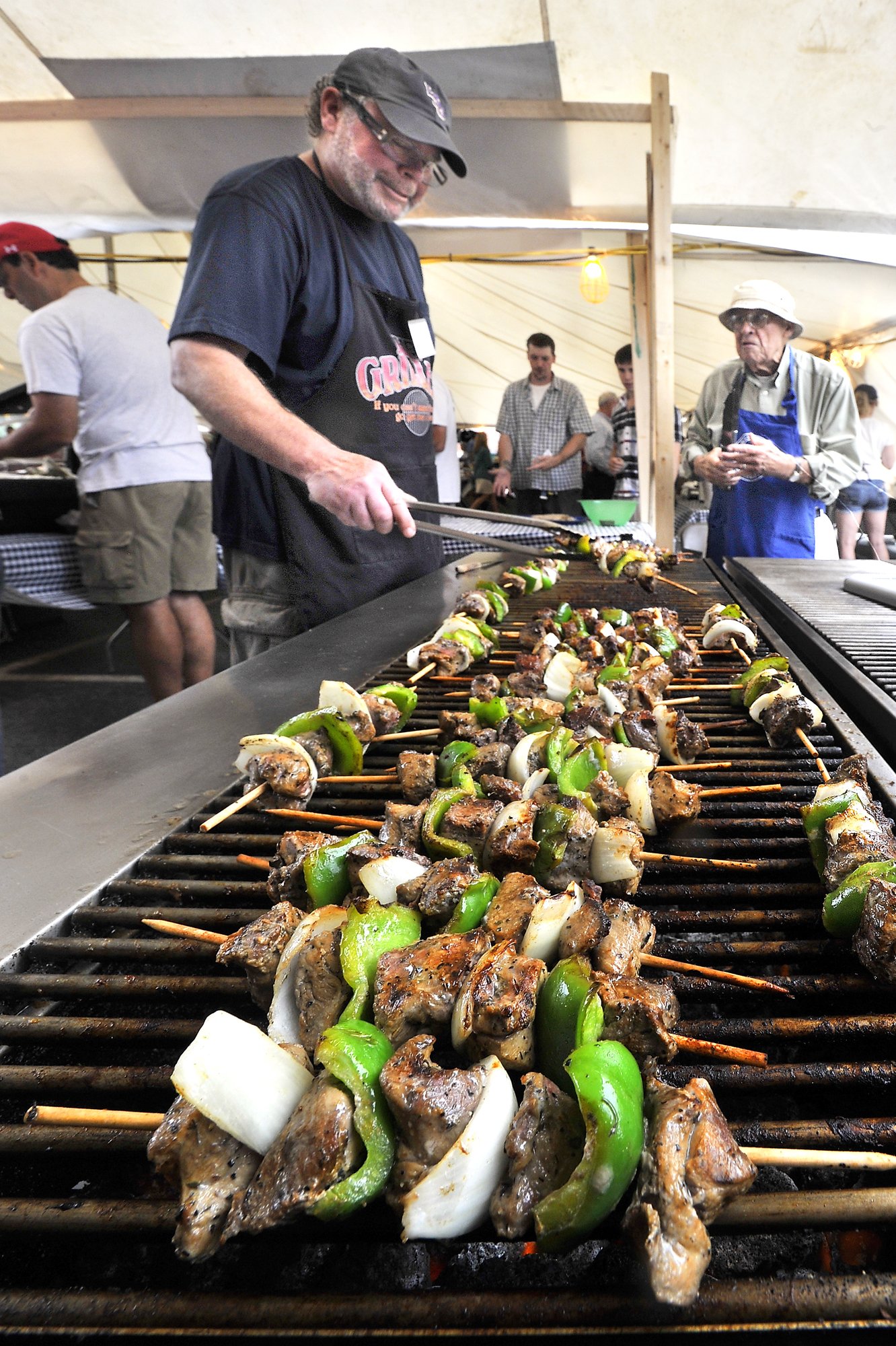

There’s plenty to eat at the Greek Festival in Portland. Gordon Chibroski/Staff Photographer
Thankfully, the Greek Festival in Portland is beneath a gigantic tent. The festival started today and runs through Saturday. It’s also the first entry on our annual list of can’t-miss summer events . The La Kermesse Franco-Americaine Festival also starts today and runs through Sunday.
Make it your best summer yet with these 17 events
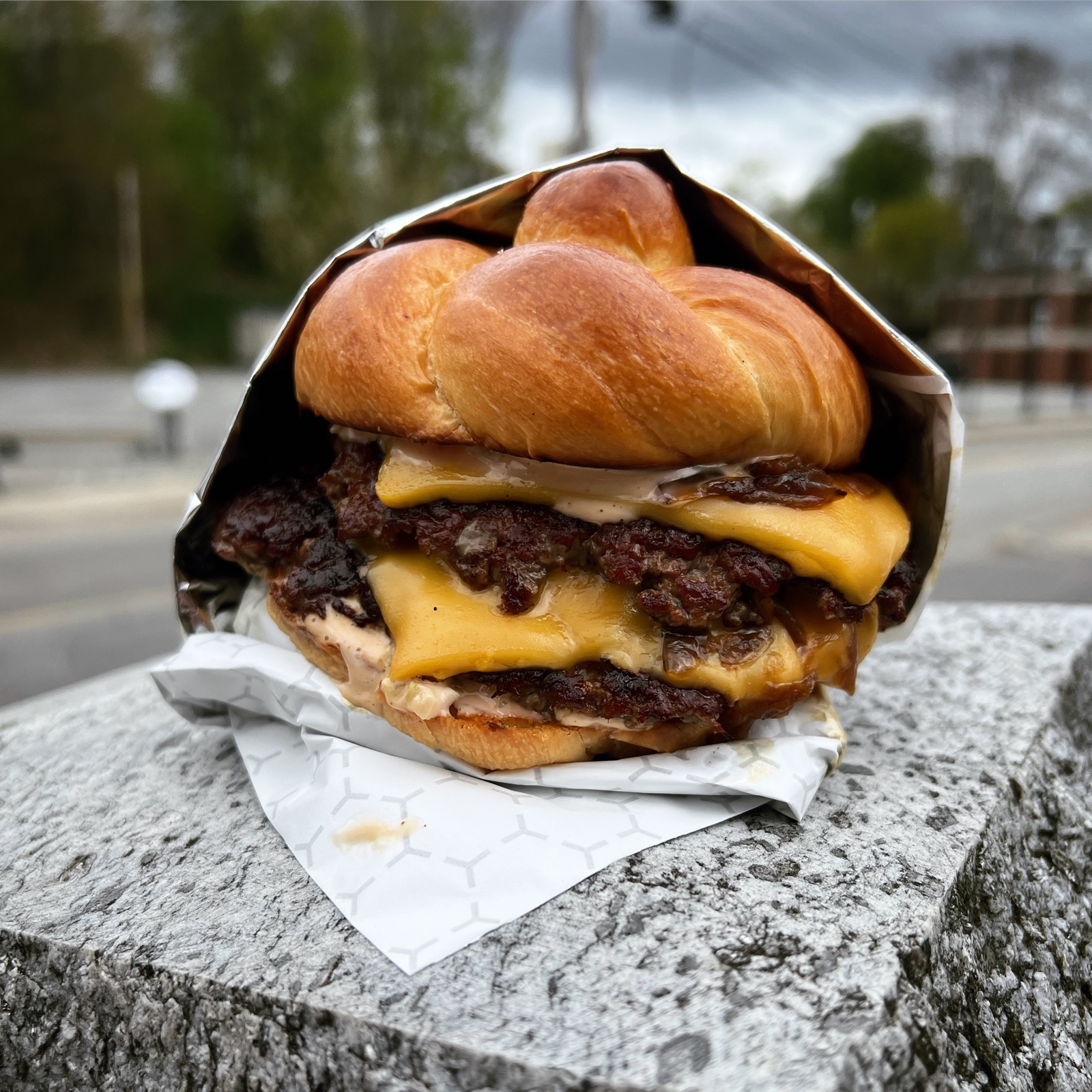

Sole Pane’s brioche knot on the double burger from Kennebec Meat Co. Courtesy of Kennebec Meat Co.
If Greek food isn’t your thing, maybe a burger is. But not just any burger. The Kennebec Meat Co. in Bath makes a legendary one, and it’s only available on Saturdays.
This Bath butcher shop’s burger is worth planning your Saturday around
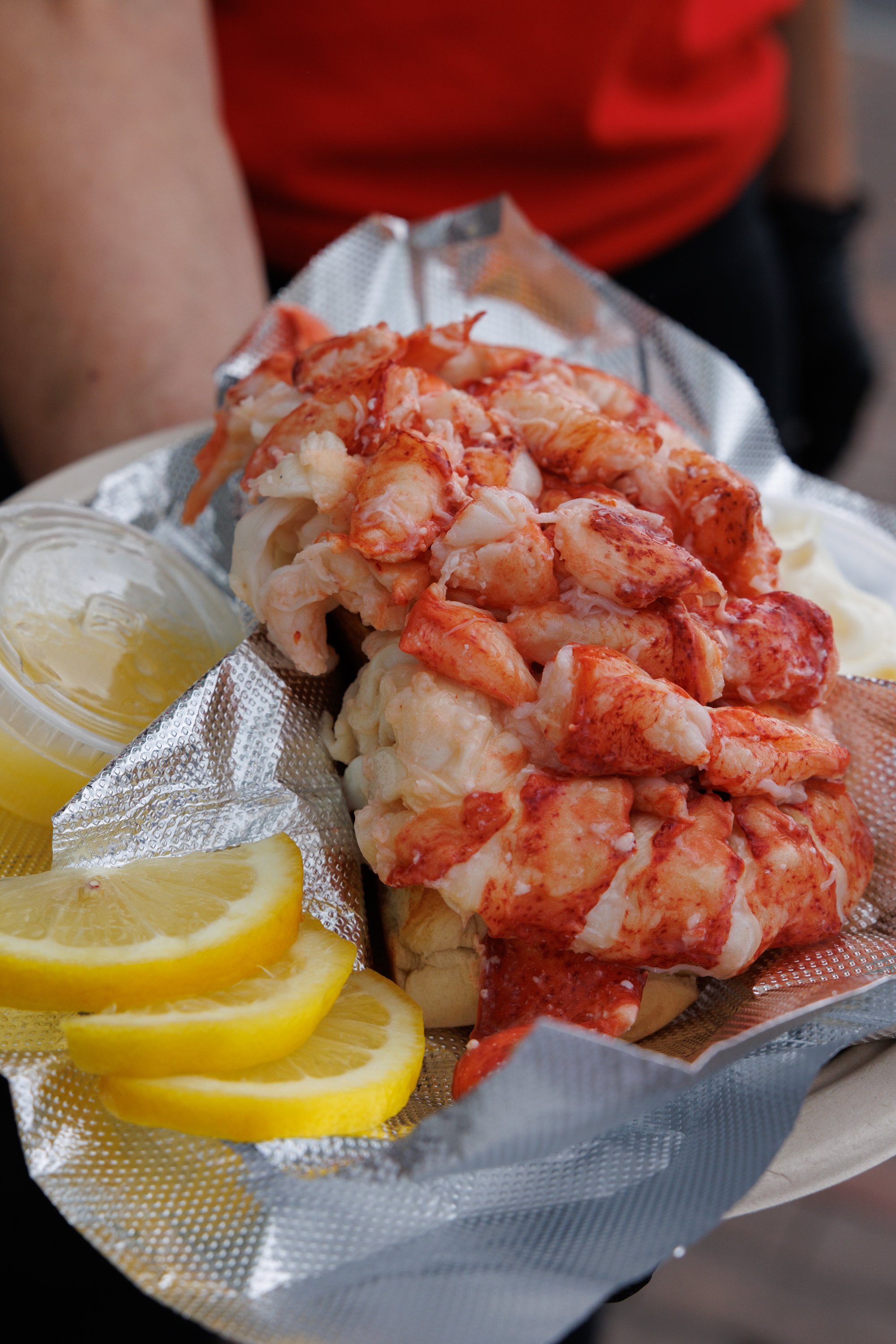

The lobster roll at Red’s Eats in Wiscasset. Brianna Soukup/Staff Photographer
Still not satisfied? We’ve got two words for you: Lobster rolls! Here are seven places to get a great one, including Red’s Eats in Wiscasset and the White Barn Inn in Kennebunk.
What do you look for in a lobster roll? Here are 7 of Maine’s best, for all different reasons
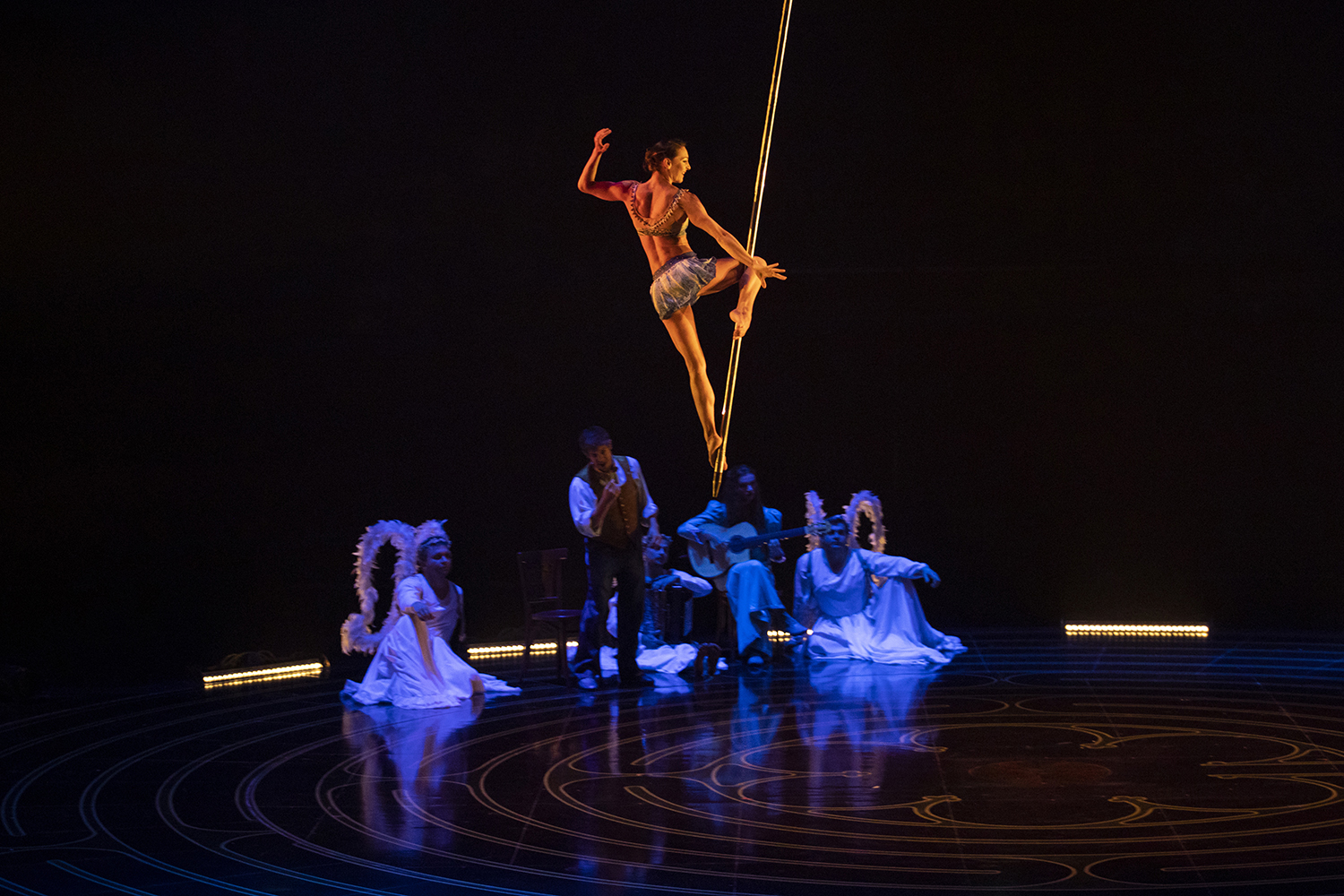

A scene from Cirque du Soleil’s Corteo show. Photo by Maja Prgomet
Let’s shift from food to Cirque du Soleil’s Corteo show at the Cross Insurance Arena in Portland. Performances start tonight and run through Sunday. Other weekend options include Pete Davidson Friday at Merrill Auditorium and “Dancer’s Choice” tonight and tomorrow at Maine State Ballet.
See Cirque du Soleil, Maine State Ballet and Pete Davidson, all this weekend
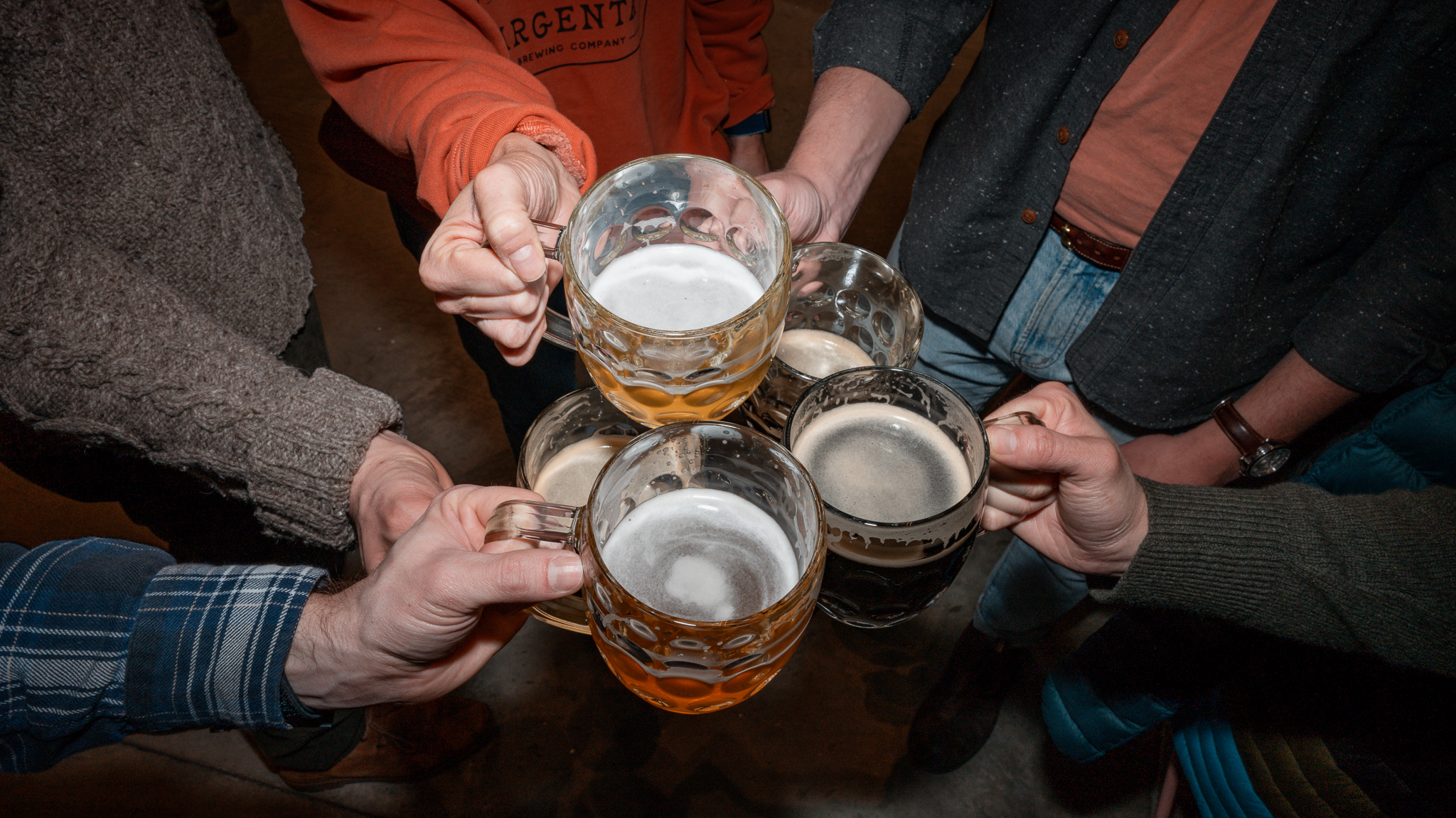

Lagers clink at Argenta Brewing. Photo by Amanda Bizzaro
Quench your thirst this weekend (or anytime) with a cold lager. We’ve got several ideas of where to enjoy one including Bissell Brothers, Argenta Brewery and Batson River. Cheers!
Lagers gain in popularity at Maine’s craft breweries. Here’s where to find them.
Modify your screen name
Join the Conversation
Please sign into your Press Herald account to participate in conversations below. If you do not have an account, you can register or subscribe . Questions? Please see our FAQs .
Your commenting screen name has been updated.
Send questions/comments to the editors.
Member Log In
Please enter your username and password below. Already a subscriber but don't have one? Click here .
Not a subscriber? Click here to see your options
Struggling Yankees look to regain past form at Toronto
- Medium Text
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Sports Chevron
Starters for angels, tigers look to prove their worth.
It would not be wrong to say starting pitcher Griffin Canning has had a disappointing season, but the Los Angeles Angels' right-hander is moving in the right direction if his most recent start is any indication.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Conjugate the English verb trip: indicative, past tense, participle, present perfect, gerund, conjugation models and irregular verbs. Translate trip in context, with examples of use and definition.
Learn the three forms of the English verb 'trip'. the first form (V1) is 'trip' used in present simple and future simple tenses. the second form (V2) is 'tripped' used in past simple tense. the third form (V3) is 'tripped' used in present perfect and past perfect tenses.
past participle: (to) trip tripping tripped definition: in Spanish in French in Italian: Open All Desktop View. ... he, she, it: trips: we: trip: you: trip: they: trip: simple past ... *Blue letters in conjugations are irregular forms. *Red ...
This is a reference page for trip verb forms in present, past and participle tenses. Find conjugation of trip. Check past tense of trip here. ... Simple Future Tense; He/She/It will/shall trip. I will/shall trip. You/We/They will/shall trip. Future Continuous Tense;
To Trip Conjugation; To Trip Infinitive: to trip Gerund: tripping Past participle: tripped Simple past: tripped Irregular forms Auxilliary verb Spelling change Use contractions. Positive Negative. Indicative. Positive Negative. Present. I trip I trip: you trip you trip: he/she/it trips he/she/it trips:
The past simple form of 'trip' is 'tripped.' The past participle form is also 'tripped.' How do I use the past simple form 'tripped' in a sentence? The past simple form 'tripped' is used to describe an action that happened at a specific time in the past. For example. 'I tripped over the rug yesterday.'
Trip in Present Perfect Continuous Tense. Singular. Plural. I have been tripping. We have been tripping. You have been tripping. You have been tripping. He/She/It has been tripping. They have been tripping.
Conjugation of verb (past tense) trip. trot. Infinitive trip /tɹɪp/ Past simple tripped /tɹɪpt/ Past participle tripped /tɹɪpt/ trick. trot. TOP 12 be ... Conjugation is the creation of derived forms of a verb from its principal parts by inflection (alteration of form according to rules of grammar). For instance, the verb "break" can be ...
Conjugate the verb trip in all tenses: present, past, participle, present perfect, gerund, etc. ... Verb Table for trip. Simple tenses; Continuous tenses; Conditional; ... We are using the following form field to detect spammers. Please do leave them untouched. Otherwise your message will be regarded as spam.
Conjugation of the verb Trip in all tenses: future, present and past. 🎮 Conjugation trainer for memorizing forms. ... Base Form Past Simple Past Participle Gerund trip: tripped: tripped: tripping [trɪp] [ˈtrɪpt] ... Present Simple Continuous Past Simple Continuous Future Simple Continuous.
Find the simple past tense and past particle of the verb trip. Also see how to use the verb trip in the past tense with some examples.
Answer. The past tense of trip is tripped . The third-person singular simple present indicative form of trip is trips . The present participle of trip is tripping . The past participle of trip is tripped . Find more words!
Use the following ESL printable flashcards to talk about a trip using the past simple. Matching - Vocabulary to Talk about a Past Trip. Match the words on the left with the meanings on the right. 1. reasonable: 2. friendly: 3. helpful: 4. awful: 5. expensive: 6. sick: a. high price: b. very bad:
The past forms don't change. I took a taxi to the airport. (take → took) That was when we spoke. (speak → spoke) One person gave me his last bar of chocolate. (give → gave) I see what you mean. I made, you made, he made, she made, it made, we made, they made! Exactly!
We use the past simple to describe the main events of a story in chronological order. When I arrived home, I took off my shoes and then I relaxed on the sofa. Master the Past Simple with our A2 pre-intermediate grammar lesson, featuring intuitive charts, interactive exercises, and vivid examples!
Simple past. The simple past tense is used when discussing completed past events or actions.. For regular verbs, the simple past tense is formed by adding the suffix "-ed" to the infinitive form of the verb (e.g., "wait" becomes "waited"). For irregular verbs, the formation of the past tense does not follow a single pattern (e.g., "run" becomes "ran," and "bring ...
Verb; Travel. Meaning; trip, journey, voyage, peregrination, eyre. V1, V2, V3, V4, V5 Form of Travel. Synonym for Travel. When learning English you need to know the meaning of certain words first, and then sort the words appropriately according to grammatical rules. Verbs in a regular structure can be transformed with a simple rule, whereas in ...
Learn the three forms of the English verb 'travel'. the first form (V1) is 'travel' used in present simple and future simple tenses. the second form (V2) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in past simple tense. the third form (V3) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in present perfect and past perfect tenses.
To form the past tense of travel, we add "-ed" to the base form of the verb. For example: I traveled to Europe last summer. She traveled to Asia for business. We traveled to South America for vacation. Simple Past. The simple past is used to describe a completed action in the past. Regular verbs like travel are formed by adding -ed to the ...
To make a negative sentence in the past simple tense, you need to use the auxiliary verb "did" and the negative particle "not" (or "n't"). The formula forming the simple past is: Subject + did not (didn't) + base form of the verb + object. For example: I did not (didn't) go to the party last night. He did not (didn't) finish ...
What Is Simple Past Tense? | Examples & Exercises. Published on June 28, 2024 by Sophie Shores, MA. We use the simple past tense form of a verb to talk about actions and events that were completed in the past (e.g., "I walked to work yesterday").. For regular verbs, we usually form the simple past tense by adding "-ed" to the base form of the verb (e.g., "jump" becomes "jumped").
Regular past simple forms are formed by adding - ed to the infinitive of the verb. That seems easy! Yes, but there are some spelling rules. If a verb ends in - e, you add - d. If a verb ends in a vowel and a consonant, the consonant is usually doubled before - ed. If a verb ends in consonant and - y, you take off the y and add - ied.
Exercise 3. Fill in the gaps with the correct past simple forms of the verbs in brackets. Two summers ago we 1 (have) a holiday in Scotland. We 2 (drive) there from London, but our car 3 (break) down on the motorway and we 4 (spend) the first night in Birmingham. When we 5 (get) to Edinburgh we 6 (not can) find a good hotel - there 7 (not be ...
Exercise 3. Complete the text with these verbs in past simple. arrive - ask - fly - go - pay - say - stop - take - tell - think - want. Two summers ago, we 1 on a trip to New York. We 2 from Manchester to John F. Kennedy International Airport. The journey was long, but we were very excited; we are from a little village and ...
See a Maine State Ballet performance and get your fill of lobster rolls.
The Toronto Blue Jays return from a 1-4 rain-shortened road trip for an eight-game homestand that begins Thursday night with the opener of a four-game series against the struggling New York Yankees.