
100+ Tourism Research Topics: Trends and Future Directions

Tourism research stands at the crossroads of exploration and understanding, dissecting the intricacies of an industry that transcends geographical boundaries. In this blog, we delve into the realm of tourism research topics, examining their importance, trends, popular areas of study, challenges faced by researchers, and the future directions that the field is poised to take.
Key Trends in Tourism Research
Table of Contents
- Sustainable Tourism
Sustainable tourism has become a cornerstone of research in recent years, reflecting the global shift towards eco-conscious travel. Researchers are delving into the intricate balance between satisfying the wanderlust of tourists and preserving the environment.
Initiatives such as wildlife conservation, eco-friendly accommodations, and community engagement are key focus areas.
Technology in Tourism
The pervasive influence of technology on tourism cannot be overstated. From online booking platforms to virtual reality experiences, researchers are exploring the impact of technology on travel behavior.
Emerging areas of study include the use of artificial intelligence in personalized travel recommendations and the implications of augmented reality for enhancing tourist attractions.
What is the Importance of Tourism Research for Students?
Tourism research holds significant importance for students pursuing studies in various disciplines, including tourism management, hospitality, business, sociology, and environmental studies. Here are some key reasons why tourism research is valuable for students:
Academic Enrichment
- Increases Understanding: By conducting study on the tourist business, students may increase their comprehension of the intricate relationships between the economic, social, cultural, and environmental facets of the sector.
- Application of Theoretical information: This increases the practical relevance of their education by giving them the chance to apply the theoretical information they have learned in the classroom to real-world situations.
Skill Development
- Research Skills: Gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data are just a few of the vital research skills that come from conducting tourist research. These abilities are adaptable and useful in a range of work environments.
- Communication abilities: Through research papers, presentations, and conversations, students learn how to effectively express their results, which improves both their writing and spoken communication abilities.
Industry Insights
- Current Trends and Issues: Research allows students to stay abreast of current trends, challenges, and emerging issues in the tourism industry. This awareness is crucial for adapting to the dynamic nature of the field.
- In-Depth Knowledge: By delving into specific tourism research topics, students gain in-depth knowledge of particular sectors within the industry, positioning themselves as experts in specialized areas.
Career Opportunities
- Competitive Advantage: Having experience in tourism research can provide students with a competitive advantage in the job market. Employers value candidates who can bring a research-driven perspective to decision-making.
- Diverse Career Paths: Whether in academia, policy-making, destination management, or market analysis, a background in tourism research opens doors to a variety of career paths within the broader field of tourism and hospitality.
Contributions to Sustainable Practices
- Environmental and Social Responsibility: Tourism research often focuses on sustainable practices. Students, through their research, can contribute ideas and solutions for promoting responsible tourism, minimizing negative impacts on the environment and local communities.
Global Perspective
- Cultural Awareness: Researching diverse tourism topics exposes students to various cultures, traditions, and perspectives. This global perspective is crucial in an industry where interactions with people from different backgrounds are common.
Problem-Solving Skills
- Analytical Thinking: Research involves analyzing complex issues and developing solutions. This cultivates students’ analytical thinking and problem-solving skills, valuable attributes in any professional setting.
Personal Growth
- Confidence Building: Successfully conducting research and presenting findings builds students’ confidence in their abilities. It empowers them to tackle challenges and approach tasks with a systematic mindset.
In summary, tourism research is a multifaceted learning experience that goes beyond textbooks, providing students with the skills, knowledge, and perspectives needed for a successful and impactful career in the tourism industry or related fields.
100+ Tourism Research Topics: Category Wise
- Impact of Technology on Travel
- Cultural Tourism and Heritage Preservation
- Dark Tourism: Ethics and Motivations
- Community-Based Tourism for Socioeconomic Development
- Wildlife Tourism and Conservation
- Gastronomic Tourism: Culinary Experiences
- Adventure Tourism: Risk and Reward
- Medical Tourism: Trends and Implications
- Religious Tourism and Pilgrimages
- LGBTQ+ Tourism: Diversity in Travel
- Film Tourism: Influence on Destination Choice
- Cruise Tourism: Environmental Impact
- Rural Tourism: Exploring Off-the-Beaten-Path
- Urban Tourism and City Planning
- Educational Tourism: Learning Journeys
- Wellness Tourism: Mind and Body Retreats
- Space Tourism: Future Frontiers
- Luxury Tourism and Experiential Travel
- Sports Tourism: Events and Impact
- Volunteer Tourism: Traveling for a Cause
- Accessible Tourism: Inclusive Travel
- Niche Tourism: Unusual Destinations
- The Psychology of Tourist Behavior
- Destination Marketing and Branding
- Over-tourism: Challenges and Solutions
- Impacts of Climate Change on Tourism
- Cruise Tourism: Cultural Interactions
- Heritage Tourism Management
- Tourism and Globalization
- Impact of Political Instability on Tourism
- COVID-19 and Tourism: Recovery Strategies
- Solo Travel: Trends and Safety Concerns
- E-Tourism: Online Booking Trends
- Responsible Tourism Practices
- Agritourism: Farm and Rural Experiences
- Wildlife Sanctuaries: Balancing Conservation and Tourism
- Backpacking Culture: Trends and Challenges
- Tourism Entrepreneurship and Innovation
- Social Media Influencers in Tourism
- Geotourism: Exploring Geological Wonders
- Virtual Reality in Tourism Experiences
- Tourism Policy and Regulation
- Sustainable Transportation in Tourism
- Wellness Retreats: Trends and Impacts
- Coastal and Marine Tourism
- Historical Tourism and Interpretation
- Space-Archaeology and Cultural Heritage Tourism
- Cross-Cultural Communication in Tourism
- Slow Tourism: Embracing the Journey
- Geopolitics and Tourism
- Adventure Sports Tourism: Risk Management
- Wellness Tourism: The Spa Industry
- Religious Festivals and Tourism
- Volunteer Tourism: Cultural Exchange
- Impacts of Terrorism on Tourism
- Tourism and Gender Equality
- Dark Sky Tourism: Stargazing Adventures
- Social Justice in Tourism
- Music Tourism: Festivals and Events
- Cruise Tourism: Port Infrastructure
- Urban Regeneration through Tourism
- Wellness Tourism: Mindful Travel
- Cultural Appropriation in Tourism
- Sports Mega-Events and Tourism
- Virtual Tourism: Exploring from Home
- Tourism Education and Training
- Destination Resilience to Crises
- Adventure Tourism: Environmental Stewardship
- Slow Food Movement and Culinary Tourism
- Accessible Tourism: Technology Solutions
- Adventure Tourism: Cultural Immersion
- Experiential Learning in Tourism
- Tourism and Biodiversity Conservation
- Indigenous Tourism: Empowerment and Challenges
- Film-Induced Tourism: Pop Culture Impact
- Ephemeral Tourism Events
- Adventure Tourism: Cultural Sensitivity
- Slum Tourism: Ethical Considerations
- Tourism and Water Conservation
- Space Tourism: Ethical Considerations
- Rural Tourism: Community Engagement
- Wellness Tourism: Mind-Body Connection
- Tourism and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Adventure Tourism: Extreme Sports
- The Role of Festivals in Tourism
- Cultural Tourism and Social Inclusion
- Wellness Tourism: Alternative Therapies
- Tourism and Human Rights
- Heritage Conservation and Tourism
- Adventure Tourism: Risk Perception
- Virtual Reality Museums and Tourism
- Responsible Wildlife Tourism
- Tourism and Disaster Management
- Festivals as Cultural Tourism Attractions
- Adventure Tourism: Psychological Benefits
- Wellness Tourism: Eco-Friendly Retreats
- Tourism and Aging Population
- Culinary Tourism: Fusion Cuisine
- Adventure Tourism: Cross-Cultural Interactions
Challenges and Opportunities in Tourism Research
Data collection and analysis.
While technology has streamlined data collection, challenges persist in ensuring data accuracy and relevance. Researchers are exploring advanced methodologies, such as big data analytics and machine learning, to overcome these hurdles and derive meaningful insights.
Globalization and Tourism
The globalization of the tourism industry poses both challenges and opportunities. Researchers are scrutinizing the impact of global trends on local economies, cultural identities, and the environment. Striking a balance between global and local interests is a complex task that requires careful consideration.
Future Directions in Tourism Research
Emerging tourism destinations.
The landscape of tourist destinations is ever-evolving. Researchers are turning their attention to emerging destinations, investigating the factors that contribute to their rise and the implications for the broader tourism industry.
This includes understanding the appeal of off-the-beaten-path locations and the potential challenges associated with their sudden popularity.
Post-Pandemic Tourism
The COVID-19 pandemic has reshaped the tourism industry in unprecedented ways. Researchers are exploring the long-term effects of the pandemic on travel behavior, destination preferences, and the overall structure of the tourism sector.
Strategies for recovery and resilience are also under the microscope as the industry adapts to the new normal.
Resources for Tourism Research Topics
- Academic Journals and Publications: Leading academic journals in tourism research, such as the “Journal of Sustainable Tourism” and the “Annals of Tourism Research,” provide a wealth of knowledge for researchers. These publications cover a wide array of topics, from sustainable practices to cultural tourism.
- Conferences and Events: Attending conferences and events, such as the “International Conference on Tourism Research” and the “World Tourism Forum,” offers researchers the opportunity to engage with peers, present their work, and stay abreast of the latest developments in the field.
- Online Databases and Research Platforms: Online databases, including Google Scholar, ResearchGate, and Tourism Management Database , provide access to a vast repository of research articles, theses, and reports. These platforms facilitate collaboration and information exchange among researchers.
In conclusion, the landscape of tourism research topics is vast and dynamic, reflecting the multifaceted nature of the tourism industry. As researchers continue to explore sustainable practices, emerging trends, and the post-pandemic landscape, the importance of their work cannot be overstated.
By navigating the challenges and embracing the opportunities presented, tourism researchers contribute to a more informed and resilient industry, ensuring that the joy of travel remains accessible for generations to come.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Elsevier - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Reviving tourism industry post-COVID-19: A resilience-based framework
Gagan deep sharma.
a University School of Management Studies, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, Sector 16C, Dwarka, New Delhi, India
Asha Thomas
b Jagan Institute of Management Studies, Sector 5, Rohini, New Delhi, India
Justin Paul
c University of Puerto Rico, San Juan, PR, USA
The COVID-19 pandemic struck the tourism industry severely. Based on the review of 35 papers that studied the tourism industry in the wake of the pandemic, we propose a resilience-based framework for reviving the global tourism industry post-COVID-19. Our framework outlines four prominent factors for building resilience in the industry: government response, technology innovation, local belongingness, and consumer and employee confidence. We argue that using such inclusive resilience; the tourism industry may transform into a new global economic order characterized by sustainable tourism, society's well-being, climate action, and the involvement of local communities. We also offer directions for future research in the area.
1. Introduction
The outbreak of COVID-19 has posed critical health challenges worldwide. The pandemic is one of the most highly contagious outbreaks in recent human history, with more than 46 million cases and 1.2 million deaths (as on 31st October 2020) ( https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ ). Given the high speed of transmission of the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), governments worldwide have had no other option but to impose lockdowns. The spread of the virus has severely threatened lives, and measures such as lockdowns have posed a critical risk to the masses' livelihoods ( Sharma & Mahendru, 2020 ). The economic shocks of the pandemic are being observed across all industries and sectors worldwide. While some industries can adapt to digital platforms and continue their struggle for survival ( Mehrolia, Alagarsamy, & Solaikutty, 2020 ), a few industries have encountered unprecedented failures due to travel restrictions and social distancing, thereby finding it extremely difficult to survive the pandemic. Tourism is one industry that cannot hold its ground without the mobility of tourists. The fall of 22% in tourist numbers in the first quarter of 2020 (compared to the same quarter of 2019), and the threat of 60% to 80% fall throughout 2020 (compared to 2019), are some indications of the havoc that the COVID-19 pandemic can cause for the global tourism industry ( World Tourism Organization, 2020 ). Tourism is one of the most labour-intensive sectors. Such a slowdown for the industry may put millions of jobs at risk, thereby threatening to roll back the progress made on the front of sustainable development goals ( World Tourism Organization, 2020 ).
As indicated by Rivera (2020) , examining the hospitality and tourism industries in the pandemic context is of paramount importance. Researchers have started to focus on this area, yet there is only limited work available so far. A search query on the Web of Science database yielded no more than 45 results that studied the impact of COVID-19 on the tourism industry. These studies are also observed to be all over the place, which poses a directional challenge for scholarship in the area. Such variance in studies fails to significantly enrich the body of knowledge, thereby proving to be of limited use to policymakers and practitioners.
The WHO (2017) recommends rapid reviews to provide timely evidence for policymakers to respond to the emergency. Since the COVID-19 pandemic threatens to be particularly fatal for the tourism industry, a rapid review of the available literature is highly recommended. Such a review will not merely consolidate the findings of the existing studies but also provide insights and directions for future researchers to focus on the appropriate problems plaguing the sector.
The above discussion drives our motivation to perform a review of the challenges being faced by the global tourism industry in the wake of COVID-19. The research questions for our study are set as follows:
To observe the impact of COVID-19 on the tourism industry by studying the emerging body of knowledge in the field;
To suggest a policy framework that enables market players and governments worldwide to cope with the challenges emerging for the global tourism industry from the outbreak of the pandemic.
Out of the 47 papers found on the Web of Science database, we discovered that 10 do not meet the inclusion criteria (detailed in the methodology section). We rigorously reviewed 37 papers to synthesize their findings and propose a framework for further advancement of the scholarship in this area. Our results reveal that the pandemic has created severe roadblocks for the tourism industry, and the way ahead seems to be rocky. We learn that this challenge may open the doors for local tourism, eco-tourism, and sustainable tourism, which have long been part of the discussion but have failed to take any tangible shape so far. Four significant themes emerge from our work, namely, sustainable tourism, climate action, transformation to the new global economic order, and resilience. We make a significant theoretical and practical contribution to the field by suggesting a coping-up mechanism, which revolves around resilience. Our framework includes resilience from market players, governments, non-government agencies, and all other stakeholders.
The remainder of our paper is organized as follows: The next section discusses the methodology of our work, the third section presents the thematic discussion, the fourth section highlights the future research agenda, and the last section concludes by outlining the policy framework to deal with the challenges emerging from COVID-19 for the tourism industry.
2. Methodology
The systematic reviewing methodology is followed in this paper. The advent of this methodology in the field of management is recent ( Paul & Criado, 2020 ; Tranfield, Denyer, & Smart, 2003 ). This methodology is driven by its merits in the form of systematic, transparent, and replicable review ( Cook, Greengold, Ellrodt, & Weingarten, 1997 ; Cook, Mulrow, & Haynes, 1997 ; Hao & al, 2019 ; Wolf, Shea, & Albanese, 2001 ). It is also inspired by prior review articles ( Bansal, Garg, & Sharma, 2019 ; Dhaliwal, Singh, & Paul, 2020 ; Gilal, Zhang, Paul, & Gilal, 2019 ; Jain, Sharma, & Mahendru, 2019 ; Paul & Feliciano-Cestero, 2020 ; Paul & Mas, 2020 ; Rosado-Serrano, Paul, & Dikova, 2018 ; Talan & Sharma, 2019 ; Thomas & Paul, 2019 ).
Records were searched employing the Web of Science database. The usage of this database ensures a consistent standard for the articles. Using keywords like “COVID-19,” “tourism,” “hospitality,” and “coronavirus,” we found 47 records. Since the problem of COVID-19 pertains to 2020, the records are fewer in number. Nevertheless, given the mandate of the WHO for rapid reviews, we consider it worthwhile to conduct a review in this pivotal field. These records were then screened through titles and abstracts. It was discovered that 37 papers fell within our theme, while the remaining 10 did not. These 37 papers were selected for further analysis. These papers are shown in Table 1 .
Reviewed papers.
To arrive at the appropriate themes studied in the selected papers, we ran a cluster analysis on these papers' keywords through the VOS viewer project developed by Leiden University, the Netherlands. Through this approach, we came up with four clusters, namely, sustainable tourism, climate action, transformation to the new global economic order, and resilience. We use these clusters as the themes for our work, and group the keywords of the 35 records within these themes, which drive the thematic discussion of our study.
This analysis leads to the development of three clusters as detailed in Table 2 .
Keywords and clusters.
3. Thematic discussion
Fig. 1 exhibits the prominent keywords clustered into three groups. First, the focus of research has been around the future of tourism, wherein the body of knowledge is concerned about the future of tourism sector, specifically in the context of communities and the cause of sustainability. Second, the scholarship is engaged in deliberating on the issues of resilience, mobility, degrowth, and sustainable tourism. Finally, there is an ongoing discussion around geopolitics, climate change, and transformation to the new situation through a reset of the sector. We use these keywords to draw two major themes, comprising four sub-themes, as exhibited in Fig. 2 . This thematic discussion is presented below.

Clusters of keywords used by the reviewed literature.

Thematic framework.
3.1. Resilience
The business world recognizes resilience as a crisis management tool/strategy for business stability and adaptability to all types of risks, during natural disasters and emergencies. Furthermore, business resilience is linked to the organization's ability to adapt to the environment and new circumstances to mitigate the effects of the incident ( Supardi, Kudus, Hadi, & Indonesia, 2020 ). Resilience strategies require coordination, various crisis management techniques, good relationships (among all stakeholders), a comprehensive network, recognition of risks and opportunities, and timely and scalable intervention ( Alves, Lok, Luo, & Hao, 2020 ; Fitriasari, 2020 ). The literature on resilience identifies proactive, absorptive/adaptive, reactive, or dynamic attributes of resilience ( Supardi et al., 2020 ).
Historically, the tourism industry has quickly bounced back after disasters, pandemics, and epidemics like Ebola, Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) and severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Local, regional, or national governments are aiding in the industry's recovery by luring investors through tax breaks, lenient land-use rules, etc. ( Brouder, 2020 ; Ioannides & Gyimóthy, 2020 ). Before international travel can resume, domestic tourism will boost the resumption of the tourism industry in the wake of the pandemic. Other factors, including technological resilience, local belongingness, and customer and employee confidence, may help build industry resilience, which is the need of the hour.
3.1.1. Governments' response to COVID-19: A new outlook
Businesses across industries are looking forward to “business as usual”, and the tourism industry is no exception. All the industries are banking largely upon “government stimulus packages and interventions” to improve their productivity. For instance, TUI, the world's most prominent multinational tourism organization, is taking the UK and German governments' aid and has announced cost reduction in its operations across the world ( Higgins-Desbiolles, 2020 ). The government has become a significant role player in the economy of tourism ( Table 3 ). This has resulted in the re-nationalization of airlines, tourism firms, and networks like airports. This is something different in comparison to earlier crises, which created curiosity in research and institutions and had no “policy impact,” particularly in the tourism industry ( Hall et al., 2020 ). Tsionas (2020) discusses post-COVID-19 problems and mentions that “opening at limited capacity” of almost 33% is a good option. He proposes that government subsidies would be needed to support such lower capacities. There has been massive government intervention in the working and operation of the tourism industry during the COVID-19 crisis ( Higgins-Desbiolles, 2020 ). Discussing Macao's reaction to the pandemic in a “3-wave analogy,” McCartney (2020) observes that the wave of recovery will push toward “public-private partnership and cooperation.” In future, the effect of such governmental response on tourism will create a novel outlook.
Government response to COVID-19. (Source : OEDC, 2020)
3.1.2. Technology innovation
Technology is a major force in creating flexibility in the tourism industry ( Hall et al., 2020 ). Disasters help in speeding up changes in technology. During COVID-19, people have taken massive aid from technology experts. There are instances of robots replacing people, applications on mobiles being employed to track people's contacts, or Big Data analytics forecasting COVID-19 spread among the masses. Robot, automation technologies, and artificial intelligence can reduce cost, improve liquidity, and enhance flexibility. This will also help maintain social distancing ( Assaf & Scuderi, 2020 ; Thomas & Chopra, 2020 ), as technology can connect people without any physical contact. Thus, technology can handle pandemic-specific problems such as screening travellers, discovering COVID-19 cases and tracking contacts, ensuring online education for students, etc. ( Hall et al., 2020 ). Many reports show a surge in the public's trust in technology, their readiness to connect, and their willingness to change their attitudes toward technology. People have now started ignoring privacy issues to get a more significant technology benefit ( Stankov et al., 2020 ). Gretzel et al. (2020) has presented the “six transformative e-tourism research pillars” for bringing in changes in e-tourism by proactively using IT resources for short-term and long-term purposes.
3.1.3. Local belongingness
The global aspect seems broken that calls for local belongingness to come to the rescue ( Brouder et al., 2020 ; Chang et al., 2020 ). During the pandemic and post-COVID-19, domestic tourism is poised to dominate the scene with most travellers coming from nearby areas ( Haywood, 2020 ). In many places, domestic travel is limited to visiting friends and relatives, but this will expand to leisure tourism soon. International travel will gradually revive when the borders open and international flights are permitted to operate without any hindrances ( Baum & Hai, 2020 ). Many countries and regions have restricted movements by imposing bans and other stringent requirements on entry and exit, which has subtly impacted the global tourism industry. According to Higgins-Desbiolles (2020) and Baum and Hai (2020) , the right to travel or enjoy gainful employment in the hospitality and tourism industry will not be allowed in the near-immediate future. “Tourism bubbles,” or local links built during the disaster, will act as a flexible plan. Future travel will depend on combined self-care, such as the suggestion to open the Trans-Tasman bubble between Australia and New Zealand ( Carr, 2020 ), or the potential fast-tracking of immigration clearance between the Republic of Korea and China ( Mostafanezhad et al., 2020 ). The feeling of belongingness among locals will dictate terms for the revival of the tourism industry.
3.1.4. Consumer and employee confidence
It is essential to gain consumer confidence to restart the halted industry of tourism. Learning from disaster planning and fighting the drive to turn away from failures experienced in the future are the critical pathways to be followed ( Rivera, 2020 ). The revival of the tourism industry will depend on boosting confidence in travelling and lessening the perception of risk involved ( Assaf & Scuderi, 2020 ). The impact of COVID-19 influences consumers' perception of tourism product and services ( Yu et al., 2020 ). Mao et al. (2020) focuses on human capital and gaining employee confidence.
3.2. Transformation to the new global economic order
Transformations like restarting, reorganizing, and assimilating the tourism industry according to the latest standards and rules are required to revive the industry ( Lew et al., 2020 ). The renewal will be impacted by the government's response to climate change and the need for a carbon-free economy. After the pandemic, the global economic and political systems will encompass changing patterns concerning climate change mitigation, sustainable tourism, local communities, and society's well-being.
3.2.1. Sustainable tourism
The present times are the most appropriate to promote a sustainable and equitable tourism industry ( Benjamin et al., 2020 ). As per Carr (2020) , original cultural sites suggest happiness, physical condition, environmental responsibility, and conventional ecological information. Such sites form the future of “cultural sustainability” and it is essential to manage these prudently for the development of the economy. In the aftermath of COVID-19, the tourism industry is bound to be reorganized based on actual planning and not just paperwork. The industry needs to be oriented toward education, environmental and social justice, and racial healing. There is a need for wary people (For instance, tourists, local communities, SMEs, Government) to take advantage of the present grave situation as it will allow more tourist experiences. The industry's service providers need to be encouraged to push a new demand by changing their unsustainable product offers. Such measures can connect, support, and take care of the whole tourism industry to everyone's advantage ( Stankov et al., 2020 ). The market players should also confront the means and systems that will prevent and transform harmful and weak tourism ( Higgins-Desbiolles, 2020 ). There is an essential requirement for a charter for setting up a stable and sustainable tourism industry. There is a disconnect between what UNWTO (World Tourism Organization) is preaching (sustainability) and what is exercising (growth expansion). These disconnects need to be understood and repaired before considering tourism's future ( Brouder et al., 2020 ; Nepal, 2020 ). The ongoing impermanent process of deglobalization has presented the tourism industry with a unique opportunity to recreate sustainability by leaving aside the “dark sides” of recent years, such as environmental deprivation, economic abuse, or congestion ( Niewiadomski, 2020 ). Sustainability is a continuous procedure to attain positive outcomes and is defined by changing beliefs, wishes, information, skills, and public awareness ( Galvani et al., 2020 ). Expert knowledge and experience ( Chang et al., 2020 ; Prideaux et al., 2020 ) need to be put into practice for shifting toward sustainable tourism.
3.2.2. Well-being of society
The South American concept Buen Vivir was examined by Everingham and Chassagne (2020) . This is a non-Western alternative to neoliberal capitalism for moving tourism priorities from economic growth to the welfare of, and meaningful connections in, the society at large and covering the ecological balance. The impact of COVID-19 is such that how people live and travel has changed completely. Preferences are now shifting toward connecting and shopping locally. The virus has offered an opportunity to the tourism industry to recreate and contribute to society's welfare ( Benjamin et al., 2020 ; Rowen, 2020 ). Life, health, environment, etc., are the focused areas during disasters. According to Benjamin et al. (2020) , it is essential to select a program that encourages sustainable and equitable development where people can acknowledge the planet and shift their current unsustainable views on tourism. In addition, Benjamin et al. (2020) point out that the change should concentrate on equity. This will necessitate positive and slow changes relating to systems' interconnectedness, where economic growth is not considered a default parameter of social and ecological well-being ( Cheer, 2020 ). The scholarship in the field of tourism needs to acknowledge tourism as an industry with a focus on societal well-being ( Benjamin et al., 2020 ).
3.2.3. Climate action
The pandemic's effect is worsening due to global climate changes ( Sharma et al., 2020 ; Sharma & Mahendru, 2020 ; Sharma, Talan, Srivastava, Yadav, & Chopra, 2020 ). Crossley (2020) studies the connection between pandemic and climate change and explores how the damage done to the environment can be repaired and can be attached to ecological grief. Emotional dynamics can further help understand tourists' behavior, covering the constant “attitude-behavior” gap concerning sustainable tourism. COVID-19 offers an opportunity to tackle the impact of climate change by shifting from the present model of “high resource consumption” to one that is “environmentally friendly” ( Gössling et al., 2020 ; Prideaux et al., 2020 ).
3.2.4. Local communities – the centres of transformation.
Local communities are the centres of transformation for the tourism industry during this pandemic. There may be future disagreements in local areas as tourists take the help of these local communities and governments for their business. Changes being considered by tourist destinations relating to modifications in a carbon-free economy are significant (Rideau et al., 2020). Changes at the local level may help restore neocolonial and neoliberal biases ( Everingham & Chassagne, 2020 ; Renaud, 2020 ; Tremblay-Huet, 2020 ).
Since the tourism industry has come to a halt and social distancing acts are relevant, even small-scale local-level activity is considered harmful. People have to think about the local community at large ( Lapointe, 2020 ). According to Renaud (2020) , the industry of cruise tourism should approve a “local mobility” model, which means that large cruise ships will be forbidden, but a fleet of smaller ships will be allowed. During the pandemic, social unity, self-sacrifice, and a sympathetic attitude are as significant as wearing a face mask to protect oneself and others. Post-COVID-19 times will allow service providers to rethink and reset the tourism industry for the future. There is a need for a “community-centered tourism framework” with responsible approaches to reset, redescribe, and refamiliarize the tourism industry in the interest of local communities. A deeper understanding of remote communities' challenges and acts may help transform the sector ( Tremblay-Huet, 2020 ). Some research studies consider these times as a defining moment for resetting the industry of tourism ( Higgins-Desbiolles, 2020 ). Developed countries are considering domestic or “proximity tourism” based on local thought and local acting theory.
4. A resilience-based framework for the new global economic order
Based on literature review, we propose a resilience-based framework for the new global economic order ( Fig. 3 ). This framework stems from the challenges posed by COVID-19 and the containment measures (such as lockdown) to the global tourism industry. The advisories issued to the tourists by various governments have further added fuel to the fire, resulting in the decline of revenues ( World Tourism Organization, 2020 ). The tourism industry seems to have moved from “over-tourism” to “non-tourism” at once ( Gössling et al., 2020 ). The increasing unemployment in other sectors of the global economy will also reflect in the number of tourist visits in the coming years. Segments of the tourism industry, including airlines, hospitality, sports events, restaurants, and cruises, are bound to be hammered by the pandemic. The proposed resilience-based framework can help transform the industry both during and after COVID-19.

Resilience-based framework for the new global economic order.
Organizational studies are focusing on sustainable change deal with resilience and deployment of adaptive capabilities by providing insights into recovery responses. Crises and emergencies such as COVID-19 also extend global visibility and understanding. This pandemic will contribute to creating new business models, which will essentially determine the industry's chances of survival by transforming it into a much more sustainable form. The tourism industry needs to demonstrate resilience from several sides. We broadly propose that three segments, namely, governments, market players, and local communities, need to get their act together to lend resilience to the industry. Technological innovations need to rise to a higher level for speeding up creations in tourism and hospitality. Artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of things (IoT), and technologies relating to location, navigation, drones, and robotics, are a few areas that need enhancements. This can promote flexible thinking within the tourism industry. This pandemic has compelled industry leaders to explore and analyze other better-suited technologies to reboot the industry and regain consumer confidence. Existing literature notes that the tourism industry has previously been quick to bounce back from the shocks of epidemics, pandemics, and global crises. However, governments realize that the shock of COVID-19 is unique since it is not possible to market the unsold capacity in coming years, causing a permanent setback for the industry. Governments should strive to build an atmosphere in which they attract investors through a variety of opportunities in the prevalent spirit of neoliberalism, such as offering tax breaks, relaxing strict land-use laws, etc. ( Brouder, 2020 ). Governments may promote the local embeddedness of tourism businesses to improve the element of belongingness. Supporting these arguments, Di Domenico, Haugh, and Tracey (2010) observe that local economies react to crises by working together and through social work, and Johannisson and Olaison (2007) note that rural firms have better prospects of recovery than their urban counterparts. Henceforth, the support from the government, coupled with local belongingness, may pave the way for the transformation of the tourism industry. The challenge is different for large-scale multinational players in the industry, focusing on local supply chains to minimize the costs. They may need to review their activities and rely on narrower and sub-national supply chains. This may include sourcing more resources locally, be it food, raw materials, service providers, or the composition of the workforce. Post-pandemic times may entail a long-term decrease in the appeal of certain growth spots now deemed too risky. Such a situation may augur well for less popular, less populated regions by providing them the opportunity to improve their appeal as potential tourism destinations.
Resilience from all sides of the value-chain may transform the tourism industry into the new global economic order characterized by sustainable tourism, climate action, societal well-being, and involvement of local communities. Studies have observed that the tourism industry indirectly contributes to pandemics in multiple ways, including food wastages leading to industrialized food production ( Hall & Gössling, 2013 ), human interference with wildlife and deforestation ( Barlow et al., 2016 ; Lade et al., 2020 ), and climate change conditions ( Scott, Hall, & Gössling, 2019 ). The lockdown in many countries and the adoption of significant restrictions on borders has also drastically affected the tourism economy worldwide. The movement from “over-tourism” to “under-tourism” is bound to reverse the scene of climate change to a large extent ( Hall & Gössling, 2013 ). COVID-19 is leading to some positive outcomes for the tourism industry. Declined demand in the aviation industry is already causing airlines to phase out outdated aircraft. Restrictions on overseas travel for international students, business travellers, political leaders, etc., are leading to increased leverage from video-conferencing ( Banister & Stead, 2004 ; Cohen, Hanna, & Gössling, 2018 ). These changes are bound to reorient the global tourism industry in a “sustainable” way, which focuses more on inclusive development, rather than the abstract notion of “growth.” Carbon footprint reductions may gain more traction worldwide, as is already seen across main tourist destinations. Similarly, the mobility of visitors could transform significantly, not only in the immediate future but over a long period. The relentless neophilia and the disturbing desire for (often irresponsible) exploration in distant places may be replaced by recreation and travel much closer to home.
5. Future research agenda
COVID-19 has triggered unprecedented casualties for mankind in life-changing circumstances. The shock and effect of this pandemic are so strong that research work across all fields is subject to pre-COVID-19 and post-COVID-19 classifications. The post-COVID-19 research is bound to be characterized by economic, environmental, and social setbacks, and the policy suggestions to counter those. Given the tourism industry's sensitivity to this pandemic situation, the body of knowledge in the field of tourism needs some quick and sound work to prepare for the future. Following most downloaded review articles ( Dhaliwal et al., 2020 ; Paul & Benito, 2018 ), we provide directions for future research in this section to set up an interesting future research agenda for the research in the tourism industry in the post-COVID-19 period. It is important to examine how businesses can translate this crisis chaos into transformative innovation. Never before has tourism research felt the need to hold its purpose as much as today.
Post-crisis tourism research must align academic and corporate interests. We present the future research agenda in two segments. One, based on the gaps in the existing literature, we present the research questions for tourism research to explore different sub-topics in the context of COVID-19. Two, we present a research agenda to test our resilience-based framework ( Table 4 ) and derive propositions which can be used as testable hypotheses in future studies by others.
Themes and research questions for future scholarship in tourism and COVID-19.
Future researchers may test the resilience-based framework in line with Fig. 3 . Using the tenets included in the resilience framework, we derive propositions in this study which can be used as either research questions or hypotheses in future studies.
Tourism industry has to resort to internal measures, including technology innovation and building consumer and employee confidence, to build resilience to fight COVID-19;
External factors, including government measures and local belongingness, significantly contribute to the tourism industry's quest for resilience to revive from the COVID-19 shock;
Resilience strategies based on internal and external factors mediate the revival of the tourism industry from the shock of COVID-19 by transforming it to the new global economic order, which comprises sustainable tourism, the well-being of society, mitigating climate change, and strengthening of local communities.
These topical ideations can be actualized by applying versatile methodologies. The case-study method is by far the most prominently used method in tourism research in the context of a crisis. However, as suggested by most of the related works ( Haywood, 2020 ; Nepal, 2020 ; Rivera, 2020 ; Tsionas, 2020 ), it would be advisable to employ conceptual, quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods to inform the questions about the contemporary tourism industry.
6. Conclusion
The tourism industry was seen as a major cause and carrier of the novel coronavirus that triggered the outbreak of COVID-19. The unsustainable practices of the industry didn't help the cause of sustainable living worldwide. The pandemic has nearly brought the global tourism industry to a halt. All stakeholders in the industry must work together to make the industry sufficiently resilient to deal with the crisis. Based on the studies conducted to understand the tourism industry in the context of COVID-19, we propose a resilience-based framework for the industry. Through our framework, we argue that with the help of the resilient approach from governments, market players, technology innovators, and the workforce employed in the industry, the tourism sector may end up evolving in a much more sustainable way post-pandemic. The involvement of local communities is going to be immensely critical in this journey, as the restrictions on international travel may stay longer than anticipated. Such developments would widen not only the base of the tourism industry but also present opportunities for less-developed tourism spots to grow further. Large-scale tourism players would need a reboot to survive in post-pandemic times. Still, acting in line with our resilience-based framework, small-scale players certainly can emerge victorious and ensure the well-being of the society at large while also facilitating sustainable tourism.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no funding were received for this research.
Biographies

Gagan Deep Sharma is an Associate Professor at the University School of Management Studies, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, New Delhi, India. His fields of research interest includes Systematic reviewing, Sustainable development, Resliience-based strategy, Neuroeconomics, and Behavioural economics.

Asha Thomas is Assistant Professor at Jagan Institute of Management Studies (JIMS), New Delhi. Her areas of research interest include knowledge management, Organizational behavior, Marketing. She has about 12 years of experience in teaching, as well as over 3 years of experience in IT and Telecom Industry. She is currently pursuing Doctorate program as a Part-time Research Scholar from the prestigious Delhi Technological University. She has several national and international research papers to her credit. She has also presented papers in National and International Conferences. She also serves as reviewer for several top international journals.

Justin Paul , serves as Editor-in-chief of International Journal of Consumer studies and as an Associate Editor of Journal of Business Research. He is a full professor of PHD & MBA programs, University of Puerto Rico, USA. He holds three honorary titles as ‘Distinguished Professor’ with three reputed universities- Indian Institute of Management (IIM—K) and SIBM, Pune and MS university in TN state of India. He has published over 100 articles in SSCI listed journals. He is an author of 8 books. He has served as a faculty member with University of Washington and Rollins college, Florida, USA. His website is drjustinpaul.com.
- Alves J.C., Lok T.C., Luo Y., Hao W. Research Square; 2020. Crisis Management for Small Business during the COVID-19 outbreak: Survival, resilience and renewal strategies of firms in Macau; pp. 1–29. PREPRINT (June) [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Assaf A., Scuderi R. COVID-19 and the recovery of the tourism industry. Tourism Economics. 2020 doi: 10.1177/1354816620933712. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Banister D., Stead D. Impact of information and communications technology on transport. Transport Reviews. 2004 doi: 10.1080/0144164042000206060. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bansal S., Garg I., Sharma G.D. Social entrepreneurship as a path for social change and driver of sustainable development: A systematic review and research agenda. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2019; 11 (4):1091. doi: 10.3390/su11041091. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barlow J., Lennox G.D., Ferreira J., Berenguer E., Lees A.C., Nally R.M.…Gardner T.A. Anthropogenic disturbance in tropical forests can double biodiversity loss from deforestation. Nature. 2016; 535 (7610):144–147. doi: 10.1038/nature18326. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Baum T., Hai N.T.T. Hospitality, tourism, human rights and the impact of COVID-19. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management. 2020; 32 (7):2397–2407. doi: 10.1108/IJCHM-03-2020-0242. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Benjamin S., Dillette A., Alderman D.H. “We can’t return to normal”: Committing to tourism equity in the post-pandemic age. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1759130. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brouder P. Reset redux: Possible evolutionary pathways towards the transformation of tourism in a COVID-19 world. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1760928. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brouder P., Teoh S., Salazar N.B., Mostafanezhad M., Pung J.M., Lapointe D.…Clausen H.B. Reflections and discussions: Tourism matters in the new normal post COVID-19. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1770325. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Buckley R. Conservation implications of COVID19: Effects via tourism and extractive industries. Biological Conservation. 2020; 247 doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2020.108640. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carr A. COVID-19, indigenous peoples and tourism: A view from New Zealand. Tourism Geographies. 2020; 0 (0):1–12. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1768433. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chang C.L., McAleer M., Ramos V. A charter for sustainable tourism after COVID-19. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2020; 12 (9) doi: 10.3390/su12093671. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cheer J.M. Human flourishing, tourism transformation and COVID-19: A conceptual touchstone. Tourism Geographies. 2020:1–11. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1765016. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen H., Huang X., Li Z. A content analysis of Chinese news coverage on COVID-19 and tourism. Current Issues in Tourism. 2020:1–8. doi: 10.1080/13683500.2020.1763269. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cohen S.A., Hanna P., Gössling S. The dark side of business travel: A media comments analysis. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment. 2018 doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2017.01.004. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook D.J., Greengold N.L., Ellrodt A.G., Weingarten S.R. The relation between systematic reviews and practice guidelines. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1997; 127 :210–216. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-127-3-199708010-00006. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook D.J., Mulrow C.D., Haynes R.B. Systematic reviews: Synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1997; 126 :376–380. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-126-5-199703010-00006. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Crossley É. Ecological grief generates desire for environmental healing in tourism after COVID-19. Tourism Geographies. 2020; 0 (0):1–10. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1759133. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dhaliwal A., Singh D.P., Paul J. The consumer behavior of luxury goods: A review and research agenda. Journal of Strategic Marketing. 2020:1–27. [ Google Scholar ]
- Di Domenico M.L., Haugh H., Tracey P. Social bricolage: Theorizing social value creation in social enterprises. Entrepreneurship: Theory and Practice. 2010 doi: 10.1111/j.1540-6520.2010.00370.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Everingham P., Chassagne N. Post COVID-19 ecological and social reset: Moving away from capitalist growth models towards tourism as Buen Vivir. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1762119. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fitriasari F. How do small and medium-sized enterprises (SME) survive the COVID-19 outbreak? Jurnal Inovasi Ekonomi. 2020; 5 (3):53–62. doi: 10.22219/jiko.v5i3.11838. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gallego I., Font X. Changes in air passenger demand as a result of the COVID-19 crisis: Using Big Data to inform tourism policy. Journal of Sustainable Tourism. 2020 doi: 10.1080/09669582.2020.1773476. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Galvani A., Lew A.A., Perez M.S. COVID-19 is expanding global consciousness and the sustainability of travel and tourism. Tourism Geographies. 2020:1–10. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1760924. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gilal F.G., Zhang J., Paul J., Gilal N.G. The role of self-determination theory in marketing science: An integrative review and agenda for research. European Management Journal. 2019 doi: 10.1016/j.emj.2018.10.004. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gössling S., Scott D., Hall C.M. Pandemics, tourism and global change: A rapid assessment of COVID-19. Journal of Sustainable Tourism. 2020:1–20. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2020.1758708. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gretzel U., Fuchs M., Baggio R., Hoepken W., Law R., Neidhardt J.…Xiang Z. e-Tourism beyond COVID-19: A call for transformative research. Information Technology and Tourism. 2020; 22 (2):187–203. doi: 10.1007/s40558-020-00181-3. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hall C.M., Gössling S. Sustainable culinary systems: Local foods, innovation, tourism and hospitality. 2013. Sustainable Culinary Systems: Local foods, innovation, tourism and hospitality; pp. 1–314. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hall C.M., Scott D., Gössling S. Pandemics, transformations and tourism: Be careful what you wish for. Tourism Geographies. 2020:1–22. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1759131. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hao A., al e. Two decades of research on nation branding: A review and future research agenda. International Marketing Review. 2019 doi: 10.1108/IMR-01-2019-0028. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Haywood K.M. A post-COVID future: Tourism community re-imagined and enabled. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1762120. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Higgins-Desbiolles F. Socialising tourism for social and ecological justice after COVID-19. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1757748. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Iaquinto B.L. Tourist as vector: Viral mobilities of COVID-19. Dialogues in Human Geography. 2020; 10 (2):174–177. doi: 10.1177/2043820620934250. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ioannides D., Gyimóthy S. The COVID-19 crisis as an opportunity for escaping the unsustainable global tourism path. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1763445. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jain M., Sharma G.D., Mahendru M. Can i sustain my happiness? A review, critique and research agenda for economics of happiness. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2019; 11 (22):6375. doi: 10.3390/su11226375. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Johannisson B., Olaison L. The moment of truth - reconstructing entrepreneurship and social capital in the eye of the storm. Review of Social Economy. 2007 doi: 10.1080/00346760601132188. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lade S.J., Steffen W., de Vries W., Carpenter S.R., Donges J.F., Gerten D.…Rockström J. Human impacts on planetary boundaries amplified by Earth system interactions. Nature Sustainability. 2020; 3 (2):119–128. doi: 10.1038/s41893-019-0454-4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lapointe D. Reconnecting tourism after COVID-19: The paradox of alterity in tourism areas. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1762115. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lew A.A., Cheer J.M., Haywood M., Brouder P., Salazar N.B. Visions of travel and tourism after the global COVID-19 transformation of 2020. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1770326. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mao Y., He J., Morrison A.M., Andres Coca-Stefaniak J. Effects of tourism CSR on employee psychological capital in the COVID-19 crisis: From the perspective of conservation of resources theory. Current Issues in Tourism. 2020 doi: 10.1080/13683500.2020.1770706. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McCartney G. The impact of the coronavirus outbreak on Macao. From tourism lockdown to tourism recovery. Current Issues in Tourism. 2020 doi: 10.1080/13683500.2020.1762549. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mehrolia S., Alagarsamy S., Solaikutty V.M. Customers response to online food delivery services during COVID-19 outbreak using binary logistic regression. International Journal of Consumer Studies. 2020 doi: 10.1111/ijcs.12630. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mostafanezhad M., Cheer J.M., Sin H.L. Geopolitical anxieties of tourism: (Im)mobilities of the COVID-19 pandemic. Dialogues in Human Geography. 2020; 10 (2):182–186. doi: 10.1177/2043820620934206. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nepal S.K. Travel and tourism after COVID-19 – Business as usual or opportunity to reset? Tourism Geographies. 2020:1–5. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1760926. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Niewiadomski P. COVID-19: From temporary de-globalisation to a re-discovery of tourism? Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1757749. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paul J., Benito G.R. A review of research on outward foreign direct investment from emerging countries, including China: What do we know, how do we know and where should we be heading? Asia Pacific Business Review. 2018; 24 (1):90–115. [ Google Scholar ]
- Paul J., Criado A.R. The art of writing literature review: What do we know and what do we need to know? International Business Review. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.ibusrev.2020.101717. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paul J., Feliciano-Cestero M.M. Five decades of research on foreign direct investment by MNEs: An overview and research agenda. Journal of Business Research. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.04.017. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paul J., Mas E. Toward a 7-P framework for international marketing. Journal of Strategic Marketing. 2020; 28 (8):681–701. doi: 10.1080/0965254X.2019.1569111. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Prideaux B., Thompson M., Pabel A. Lessons from COVID-19 can prepare global tourism for the economic transformation needed to combat climate change. Tourism Geographies. 2020:1–12. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1762117. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Renaud L. Reconsidering global mobility–distancing from mass cruise tourism in the aftermath of COVID-19. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1762116. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rivera M.A. Hitting the reset button for hospitality research in times of crisis: Covid19 and beyond. International Journal of Hospitality Management. 2020; 87 doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102528. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Romagosa F. The COVID-19 crisis: Opportunities for sustainable and proximity tourism. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1763447. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosado-Serrano A., Paul J., Dikova D. International franchising: A literature review and research agenda. Journal of Business Research. 2018 doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2017.12.049. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rowen I. The transformational festival as a subversive toolbox for a transformed tourism: Lessons from Burning Man for a COVID-19 world. Tourism Geographies. 2020:1–8. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1759132. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Scott D., Hall C.M., Gössling S. Global tourism vulnerability to climate change. Annals of Tourism Research. 2019; 77 :49–61. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2019.05.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sharma G.D., Ghura A.S., Mahendru M., Erkut B., Kaur T., Bedi D. Panic during COVID-19 pandemic! A qualitative investigation into the psychosocial experiences of a sample of Indian people. Frontiers in Psychology. 2020; 11 (October):1–7. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.575491. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sharma G.D., Mahendru M. Lives or livelihood: Insights from locked-down India due to COVID19. Social Sciences & Humanities Open. 2020; 2 (1) doi: 10.1016/j.ssaho.2020.100036. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sharma G.D., Talan G., Srivastava M., Yadav A., Chopra R. A qualitative enquiry into strategic and operational responses to Covid-19 challenges in South Asia. Journal of Public Affairs. 2020 doi: 10.1002/pa.2195. May. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stankov U., Filimonau V., Vujičić M.D. A mindful shift: An opportunity for mindfulness-driven tourism in a post-pandemic world. Tourism Geographies. 2020:1–10. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1768432. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Supardi S., Kudus U.M., Hadi S., Indonesia U.I. New perspective on the resilience of SMEs proactive, adaptive, reactive from business turbulence: A systematic review. Journal of Xi’an University of Architecture & Technology. 2020; XII (V) doi: 10.37896/jxat12.05/1524. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Talan G., Sharma G.D. Doing well by doing good: A systematic review and research agenda for sustainable investment. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2019; 11 (2):353. doi: 10.3390/su11020353. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thomas A., Chopra M. Digital transformation in business and society. Palgrave Macmillan; Cham: 2020. On how big data revolutionizes knowledge management; pp. 39–60. [ Google Scholar ]
- Thomas A., Paul J. Knowledge transfer and innovation through university- industry partnership: An integrated theoretical view. Knowledge Management Research & Practice. 2019; 17 (4):436–448. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tranfield D., Denyer D., Smart P. Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. British Journal of Management. 2003; 14 :207–222. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tremblay-Huet S. COVID-19 leads to a new context for the “right to tourism”: A reset of tourists’ perspectives on space appropriation is needed. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1759136. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trupp A., Dolezal C. Tourism and the sustainable development goals in Southeast Asia. Austrial Journal of South-East Asian Studies. 2020; 13 (1):1–16. doi: 10.18111/9789284417254. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tsionas M.G. COVID-19 and gradual adjustment in the tourism, hospitality, and related industries. Tourism Economics. 2020 doi: 10.1177/1354816620933039. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wolf F.M., Shea J.A., Albanese M.A. Toward setting a research agenda for systematic reviews of evidence of the effects of medical education. Teaching and Learning in Medicine. 2001; 13 :53–60. doi: 10.1207/s15328015tlm1301_11. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- World Health Organization . World Health Organization; 2017. Rapid reviews to strengthen health policy and systems: A practical guide. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- World Tourism Organization International tourism numbers could fall 60–80% in 2020. 2020. https://www.unwto.org/news/covid-19-international-tourist-numbers-could-fall-60-80-in-2020 [Press Release −7 May 2020]. Retrieved July 22, 2020, from.
- Yu F., Du L., Ojcius D.M., Pan C., Jiang S. Measures for diagnosing and treating infections by a novel coronavirus responsible for a pneumonia outbreak originating in Wuhan, China. Microbes Infect. 2020; 22 (2):74–79. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2020.01.003. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, sustainability in hospitality and tourism: a review of key research topics from 1994 to 2020.
International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management
ISSN : 0959-6119
Article publication date: 23 March 2022
Issue publication date: 26 July 2022
The purpose of this study is to examine the scientific research related to sustainability in hospitality and tourism from 1994 to 2020 by conducting bibliometric and science mapping analyses and to discuss the implications for prospective research opportunities.
Design/methodology/approach
Keyword co-occurrences with 2,980 published papers collected from the Web of Science (Social Science Citation Index and Emerging Sources Citation Index) were used for the bibliometric-based analysis. The authors use SciMAT software which offers relevant outputs, such as research themes and graphical outputs (strategic diagrams, cluster networks and science mapping representing the temporal evolution of the themes).
The findings show that biodiversity conservation, sustainable attitudes, climate change, protected areas, satisfaction and environmental management were the focal motor-themes in the studied periods. Additionally, four areas for future investigation are identified and discussed: sustainable behavior and environmental sustainability; consumption, demand and economic growth; tourism development and strategies; and rural tourism, poverty, ethics and education.
Research limitations/implications
This analysis shows insightful results processing a high number of published documents. However, the authors recommend further research focused on qualitative literature review for each critical topic.
Originality/value
The authors are unaware of analogous, completed and recent work about sustainability in hospitality and tourism. The authors believe this article is of great value to academics and practitioners because it synthesizes and disseminates the research topic while providing an outstanding basis for identifying research opportunities.
- Bibliometric analysis
- Science mapping analysis
- Sustainability
- Hospitality
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the University of Castilla-La Mancha for the financial support provided for this research under the Call for Research Groups (Reference: 2021-GRIN-31010), and to the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness under the 2019 Call for R&D Projects (Project reference number: PID2019-105726RB-I00).
Molina-Collado, A. , Santos-Vijande, M.L. , Gómez-Rico, M. and Madera, J.M. (2022), "Sustainability in hospitality and tourism: a review of key research topics from 1994 to 2020", International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management , Vol. 34 No. 8, pp. 3029-3064. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-10-2021-1305
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2020, Emerald Publishing Limited
Related articles
All feedback is valuable.
Please share your general feedback
Report an issue or find answers to frequently asked questions
Contact Customer Support
The future of tourism: Bridging the labor gap, enhancing customer experience
As travel resumes and builds momentum, it’s becoming clear that tourism is resilient—there is an enduring desire to travel. Against all odds, international tourism rebounded in 2022: visitor numbers to Europe and the Middle East climbed to around 80 percent of 2019 levels, and the Americas recovered about 65 percent of prepandemic visitors 1 “Tourism set to return to pre-pandemic levels in some regions in 2023,” United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), January 17, 2023. —a number made more significant because it was reached without travelers from China, which had the world’s largest outbound travel market before the pandemic. 2 “ Outlook for China tourism 2023: Light at the end of the tunnel ,” McKinsey, May 9, 2023.
Recovery and growth are likely to continue. According to estimates from the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) for 2023, international tourist arrivals could reach 80 to 95 percent of prepandemic levels depending on the extent of the economic slowdown, travel recovery in Asia–Pacific, and geopolitical tensions, among other factors. 3 “Tourism set to return to pre-pandemic levels in some regions in 2023,” United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), January 17, 2023. Similarly, the World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC) forecasts that by the end of 2023, nearly half of the 185 countries in which the organization conducts research will have either recovered to prepandemic levels or be within 95 percent of full recovery. 4 “Global travel and tourism catapults into 2023 says WTTC,” World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC), April 26, 2023.
Longer-term forecasts also point to optimism for the decade ahead. Travel and tourism GDP is predicted to grow, on average, at 5.8 percent a year between 2022 and 2032, outpacing the growth of the overall economy at an expected 2.7 percent a year. 5 Travel & Tourism economic impact 2022 , WTTC, August 2022.
So, is it all systems go for travel and tourism? Not really. The industry continues to face a prolonged and widespread labor shortage. After losing 62 million travel and tourism jobs in 2020, labor supply and demand remain out of balance. 6 “WTTC research reveals Travel & Tourism’s slow recovery is hitting jobs and growth worldwide,” World Travel & Tourism Council, October 6, 2021. Today, in the European Union, 11 percent of tourism jobs are likely to go unfilled; in the United States, that figure is 7 percent. 7 Travel & Tourism economic impact 2022 : Staff shortages, WTTC, August 2022.
There has been an exodus of tourism staff, particularly from customer-facing roles, to other sectors, and there is no sign that the industry will be able to bring all these people back. 8 Travel & Tourism economic impact 2022 : Staff shortages, WTTC, August 2022. Hotels, restaurants, cruises, airports, and airlines face staff shortages that can translate into operational, reputational, and financial difficulties. If unaddressed, these shortages may constrain the industry’s growth trajectory.
The current labor shortage may have its roots in factors related to the nature of work in the industry. Chronic workplace challenges, coupled with the effects of COVID-19, have culminated in an industry struggling to rebuild its workforce. Generally, tourism-related jobs are largely informal, partly due to high seasonality and weak regulation. And conditions such as excessively long working hours, low wages, a high turnover rate, and a lack of social protection tend to be most pronounced in an informal economy. Additionally, shift work, night work, and temporary or part-time employment are common in tourism.
The industry may need to revisit some fundamentals to build a far more sustainable future: either make the industry more attractive to talent (and put conditions in place to retain staff for longer periods) or improve products, services, and processes so that they complement existing staffing needs or solve existing pain points.
One solution could be to build a workforce with the mix of digital and interpersonal skills needed to keep up with travelers’ fast-changing requirements. The industry could make the most of available technology to provide customers with a digitally enhanced experience, resolve staff shortages, and improve working conditions.
Would you like to learn more about our Travel, Logistics & Infrastructure Practice ?
Complementing concierges with chatbots.
The pace of technological change has redefined customer expectations. Technology-driven services are often at customers’ fingertips, with no queues or waiting times. By contrast, the airport and airline disruption widely reported in the press over the summer of 2022 points to customers not receiving this same level of digital innovation when traveling.
Imagine the following travel experience: it’s 2035 and you start your long-awaited honeymoon to a tropical island. A virtual tour operator and a destination travel specialist booked your trip for you; you connected via videoconference to make your plans. Your itinerary was chosen with the support of generative AI , which analyzed your preferences, recommended personalized travel packages, and made real-time adjustments based on your feedback.
Before leaving home, you check in online and QR code your luggage. You travel to the airport by self-driving cab. After dropping off your luggage at the self-service counter, you pass through security and the biometric check. You access the premier lounge with the QR code on the airline’s loyalty card and help yourself to a glass of wine and a sandwich. After your flight, a prebooked, self-driving cab takes you to the resort. No need to check in—that was completed online ahead of time (including picking your room and making sure that the hotel’s virtual concierge arranged for red roses and a bottle of champagne to be delivered).
While your luggage is brought to the room by a baggage robot, your personal digital concierge presents the honeymoon itinerary with all the requested bookings. For the romantic dinner on the first night, you order your food via the restaurant app on the table and settle the bill likewise. So far, you’ve had very little human interaction. But at dinner, the sommelier chats with you in person about the wine. The next day, your sightseeing is made easier by the hotel app and digital guide—and you don’t get lost! With the aid of holographic technology, the virtual tour guide brings historical figures to life and takes your sightseeing experience to a whole new level. Then, as arranged, a local citizen meets you and takes you to their home to enjoy a local family dinner. The trip is seamless, there are no holdups or snags.
This scenario features less human interaction than a traditional trip—but it flows smoothly due to the underlying technology. The human interactions that do take place are authentic, meaningful, and add a special touch to the experience. This may be a far-fetched example, but the essence of the scenario is clear: use technology to ease typical travel pain points such as queues, misunderstandings, or misinformation, and elevate the quality of human interaction.
Travel with less human interaction may be considered a disruptive idea, as many travelers rely on and enjoy the human connection, the “service with a smile.” This will always be the case, but perhaps the time is right to think about bringing a digital experience into the mix. The industry may not need to depend exclusively on human beings to serve its customers. Perhaps the future of travel is physical, but digitally enhanced (and with a smile!).
Digital solutions are on the rise and can help bridge the labor gap
Digital innovation is improving customer experience across multiple industries. Car-sharing apps have overcome service-counter waiting times and endless paperwork that travelers traditionally had to cope with when renting a car. The same applies to time-consuming hotel check-in, check-out, and payment processes that can annoy weary customers. These pain points can be removed. For instance, in China, the Huazhu Hotels Group installed self-check-in kiosks that enable guests to check in or out in under 30 seconds. 9 “Huazhu Group targets lifestyle market opportunities,” ChinaTravelNews, May 27, 2021.
Technology meets hospitality
In 2019, Alibaba opened its FlyZoo Hotel in Huangzhou, described as a “290-room ultra-modern boutique, where technology meets hospitality.” 1 “Chinese e-commerce giant Alibaba has a hotel run almost entirely by robots that can serve food and fetch toiletries—take a look inside,” Business Insider, October 21, 2019; “FlyZoo Hotel: The hotel of the future or just more technology hype?,” Hotel Technology News, March 2019. The hotel was the first of its kind that instead of relying on traditional check-in and key card processes, allowed guests to manage reservations and make payments entirely from a mobile app, to check-in using self-service kiosks, and enter their rooms using facial-recognition technology.
The hotel is run almost entirely by robots that serve food and fetch toiletries and other sundries as needed. Each guest room has a voice-activated smart assistant to help guests with a variety of tasks, from adjusting the temperature, lights, curtains, and the TV to playing music and answering simple questions about the hotel and surroundings.
The hotel was developed by the company’s online travel platform, Fliggy, in tandem with Alibaba’s AI Labs and Alibaba Cloud technology with the goal of “leveraging cutting-edge tech to help transform the hospitality industry, one that keeps the sector current with the digital era we’re living in,” according to the company.
Adoption of some digitally enhanced services was accelerated during the pandemic in the quest for safer, contactless solutions. During the Winter Olympics in Beijing, a restaurant designed to keep physical contact to a minimum used a track system on the ceiling to deliver meals directly from the kitchen to the table. 10 “This Beijing Winter Games restaurant uses ceiling-based tracks,” Trendhunter, January 26, 2022. Customers around the world have become familiar with restaurants using apps to display menus, take orders, and accept payment, as well as hotels using robots to deliver luggage and room service (see sidebar “Technology meets hospitality”). Similarly, theme parks, cinemas, stadiums, and concert halls are deploying digital solutions such as facial recognition to optimize entrance control. Shanghai Disneyland, for example, offers annual pass holders the option to choose facial recognition to facilitate park entry. 11 “Facial recognition park entry,” Shanghai Disney Resort website.
Automation and digitization can also free up staff from attending to repetitive functions that could be handled more efficiently via an app and instead reserve the human touch for roles where staff can add the most value. For instance, technology can help customer-facing staff to provide a more personalized service. By accessing data analytics, frontline staff can have guests’ details and preferences at their fingertips. A trainee can become an experienced concierge in a short time, with the help of technology.
Apps and in-room tech: Unused market potential
According to Skift Research calculations, total revenue generated by guest apps and in-room technology in 2019 was approximately $293 million, including proprietary apps by hotel brands as well as third-party vendors. 1 “Hotel tech benchmark: Guest-facing technology 2022,” Skift Research, November 2022. The relatively low market penetration rate of this kind of tech points to around $2.4 billion in untapped revenue potential (exhibit).
Even though guest-facing technology is available—the kind that can facilitate contactless interactions and offer travelers convenience and personalized service—the industry is only beginning to explore its potential. A report by Skift Research shows that the hotel industry, in particular, has not tapped into tech’s potential. Only 11 percent of hotels and 25 percent of hotel rooms worldwide are supported by a hotel app or use in-room technology, and only 3 percent of hotels offer keyless entry. 12 “Hotel tech benchmark: Guest-facing technology 2022,” Skift Research, November 2022. Of the five types of technology examined (guest apps and in-room tech; virtual concierge; guest messaging and chatbots; digital check-in and kiosks; and keyless entry), all have relatively low market-penetration rates (see sidebar “Apps and in-room tech: Unused market potential”).
While apps, digitization, and new technology may be the answer to offering better customer experience, there is also the possibility that tourism may face competition from technological advances, particularly virtual experiences. Museums, attractions, and historical sites can be made interactive and, in some cases, more lifelike, through AR/VR technology that can enhance the physical travel experience by reconstructing historical places or events.
Up until now, tourism, arguably, was one of a few sectors that could not easily be replaced by tech. It was not possible to replicate the physical experience of traveling to another place. With the emerging metaverse , this might change. Travelers could potentially enjoy an event or experience from their sofa without any logistical snags, and without the commitment to traveling to another country for any length of time. For example, Google offers virtual tours of the Pyramids of Meroë in Sudan via an immersive online experience available in a range of languages. 13 Mariam Khaled Dabboussi, “Step into the Meroë pyramids with Google,” Google, May 17, 2022. And a crypto banking group, The BCB Group, has created a metaverse city that includes representations of some of the most visited destinations in the world, such as the Great Wall of China and the Statue of Liberty. According to BCB, the total cost of flights, transfers, and entry for all these landmarks would come to $7,600—while a virtual trip would cost just over $2. 14 “What impact can the Metaverse have on the travel industry?,” Middle East Economy, July 29, 2022.
The metaverse holds potential for business travel, too—the meeting, incentives, conferences, and exhibitions (MICE) sector in particular. Participants could take part in activities in the same immersive space while connecting from anywhere, dramatically reducing travel, venue, catering, and other costs. 15 “ Tourism in the metaverse: Can travel go virtual? ,” McKinsey, May 4, 2023.
The allure and convenience of such digital experiences make offering seamless, customer-centric travel and tourism in the real world all the more pressing.

Three innovations to solve hotel staffing shortages
Is the future contactless.
Given the advances in technology, and the many digital innovations and applications that already exist, there is potential for businesses across the travel and tourism spectrum to cope with labor shortages while improving customer experience. Process automation and digitization can also add to process efficiency. Taken together, a combination of outsourcing, remote work, and digital solutions can help to retain existing staff and reduce dependency on roles that employers are struggling to fill (exhibit).
Depending on the customer service approach and direct contact need, we estimate that the travel and tourism industry would be able to cope with a structural labor shortage of around 10 to 15 percent in the long run by operating more flexibly and increasing digital and automated efficiency—while offering the remaining staff an improved total work package.
Outsourcing and remote work could also help resolve the labor shortage
While COVID-19 pushed organizations in a wide variety of sectors to embrace remote work, there are many hospitality roles that rely on direct physical services that cannot be performed remotely, such as laundry, cleaning, maintenance, and facility management. If faced with staff shortages, these roles could be outsourced to third-party professional service providers, and existing staff could be reskilled to take up new positions.
In McKinsey’s experience, the total service cost of this type of work in a typical hotel can make up 10 percent of total operating costs. Most often, these roles are not guest facing. A professional and digital-based solution might become an integrated part of a third-party service for hotels looking to outsource this type of work.
One of the lessons learned in the aftermath of COVID-19 is that many tourism employees moved to similar positions in other sectors because they were disillusioned by working conditions in the industry . Specialist multisector companies have been able to shuffle their staff away from tourism to other sectors that offer steady employment or more regular working hours compared with the long hours and seasonal nature of work in tourism.
The remaining travel and tourism staff may be looking for more flexibility or the option to work from home. This can be an effective solution for retaining employees. For example, a travel agent with specific destination expertise could work from home or be consulted on an needs basis.
In instances where remote work or outsourcing is not viable, there are other solutions that the hospitality industry can explore to improve operational effectiveness as well as employee satisfaction. A more agile staffing model can better match available labor with peaks and troughs in daily, or even hourly, demand. This could involve combining similar roles or cross-training staff so that they can switch roles. Redesigned roles could potentially improve employee satisfaction by empowering staff to explore new career paths within the hotel’s operations. Combined roles build skills across disciplines—for example, supporting a housekeeper to train and become proficient in other maintenance areas, or a front-desk associate to build managerial skills.
Where management or ownership is shared across properties, roles could be staffed to cover a network of sites, rather than individual hotels. By applying a combination of these approaches, hotels could reduce the number of staff hours needed to keep operations running at the same standard. 16 “ Three innovations to solve hotel staffing shortages ,” McKinsey, April 3, 2023.
Taken together, operational adjustments combined with greater use of technology could provide the tourism industry with a way of overcoming staffing challenges and giving customers the seamless digitally enhanced experiences they expect in other aspects of daily life.
In an industry facing a labor shortage, there are opportunities for tech innovations that can help travel and tourism businesses do more with less, while ensuring that remaining staff are engaged and motivated to stay in the industry. For travelers, this could mean fewer friendly faces, but more meaningful experiences and interactions.
Urs Binggeli is a senior expert in McKinsey’s Zurich office, Zi Chen is a capabilities and insights specialist in the Shanghai office, Steffen Köpke is a capabilities and insights expert in the Düsseldorf office, and Jackey Yu is a partner in the Hong Kong office.
Explore a career with us
- How it works

Useful Links
How much will your dissertation cost?
Have an expert academic write your dissertation paper!
Dissertation Services

Get unlimited topic ideas and a dissertation plan for just £45.00
Order topics and plan

Get 1 free topic in your area of study with aim and justification
Yes I want the free topic

Tourism and Hospitality Dissertation Topics
Published by Grace Graffin at January 10th, 2023 , Revised On May 17, 2024
Introduction
As a tourism student, you will be required to study the basics of tourism, hospitality, and event management. Some important issues surrounding tourism include but are not limited to medicine, finance, culture, geography, and more.
We understand that choosing the right dissertation topic can be a bit overwhelming for you. Therefore, our writers have provided a comprehensive list of topics for the tourism dissertation. These topics are recent, relevant, and exploratory enough for you to conduct a comprehensive research study.
We can even customise topics according to your needs. So, go through our list of dissertation topics, choose the one that interests you, and let us know if you would like any help from our writers.
Check our dissertation example to get an idea of how to structure your dissertation .
You can review step by step guide on how to write your dissertation here.
Latest Tourism Research Topics
Investigating how the tourism industry has taken green and sustainable measures- a case study of uk.
Research Aim: This study will investigate the various aspects of the UK tourism industry geared towards making green and sustainable measures for environmental benefits. It will also look into the consumer’s perspective towards green tourism and its positive and negative impacts on the tourism industry and the tourists. It also helps you better understand the concept of a green environment and its influence on the tourism industry.
Environmental Management Systems and their Implementation in the UK- A Systematic Review.
Research Aim: This study will explore the quality of environmental management systems, environmental performance, improvements, and implementation in the UK. We will focus on different companies with high environmental impacts and how they have improved the environment and the use of environmental management systems (EMS). This study will also look into how it has changed or influenced the hospitality industry.
Investigating the impact of Social Media Recommendations on Hotel Booking in the UK.
Research Aim: Social media is a part of every aspect of our daily life. This research will investigate the influence of social media on tourism and specifically on choosing a hotel; it will also help you evaluate if consumers perceive social media-based recommendations differently than more traditional sources of internet-based marketing. Qualitative research will be used in this, followed by thematic analysis to find the role of social media in recommendations and influencing consumers’ searches. This will help us better understand how VR makes decisions and hotel bookings.
Assessing the Impact of Virtual Reality on Tourism.
Research Aim: Virtual reality (VR) is an emerging technology in tourism. This study will find the impact of virtual reality on the tourism industry. It will also investigate consumer behaviour towards it. We will better understand how VR has affected the tourism industry and significantly influenced the results. TAM research model will be developed to describe the nature of the 3D virtual world. It will also cover some psychological aspects to understand the consumer perspective.
Role of Social Media Marketing in deciding a Travel Destination- A Systematic Review.
Research Aim: This study investigates the role of social media marketing in deciding a travel destination. This study aims to find and understand how social media can achieve marketing objectives. Taking a quantitative approach, we will find the role of social media marketing and its effect on making travel choices through interviews and surveys. It will further explore the tourist’s perception, expectations, and experiences.
Investigating the Negative Impact of Travel Bans
Research Aim: This study explores the negative effects of travel bans on social, economic, cultural, and public health aspects. The study aims to analyse the repercussions of travel restrictions to inform policymaking. It will further investigate ways to avoid adverse consequences while promoting global mobility and cooperation.
An Exploration of the Hospitality Industry Wages
Research Aim: To investigate the wage structures in the hospitality industry. This study explores factors influencing disparities and evaluates their implications. Insights will be provided on wage fairness, workplace satisfaction, gender discrimination, and industry competitiveness. It will also cover policies and practices to improve employee well-being and organisational performance.
Effects of Covid-19 on Tourism and Hospitality Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: tourism after coronavirus pandemic - way forward for tourism and hospitality industry in the uk or any other country of your choice.
Research Aim: Tourism is a reason for most of the human mobility in the modern world. According to the World Tourism Organisation (2020), international tourism has indicated continuous growth for the tenth consecutive year, reporting 1.5 billion international tourist arrivals in 2019 and an estimated 1.8 billion international tourist arrivals by 2030 )people are forecasted to be. This particular research will focus on the effects of the Covid-19 outbreak on the tourism and hospitality industry in the United Kingdom or any other country of your choice.
Topic 2: Investigating the Long Term Effects of Prolonged and New Travel Restrictions on the UK Tourism Industry
Research Aim: Britain will require anyone entering the country to self-quarantine for two weeks, and other European countries are pondering similar measures, but the prospects of prolonged and even new travel restrictions are destroying what hopes the continent’s airlines and tourist industry have been harbouring of at least a partial coronavirus rebound. Can the tourism sector of the UK overcome these challenges?
Topic 3: Coronavirus: Dubai Tourism Insists Emirate's Hotel Sector is Healthy, Rejects Bloomberg Report but Is It Really the Case?
Research Aim: Dubai’s Department of Tourism and Commerce Marketing (Dubai Tourism) has denied a Bloomberg report about the emirate’s hospitality businesses adversely affected by the coronavirus pandemic. This research will employ primary research methodology to gather data from the key stakeholders of the Emirates hotel industry to assess whether or not the ongoing COVID-19 crisis is causing panic and financial damage to the hotel industry.
Topic 4: Will Easing the Travel Restrictions Benefit the UK Tourism Sector in the Short Term?
Research Aim: Many European countries, including the UK, are easing lockdown measures, including tourist destinations preparing for the summer. Cafes and restaurants in London and other cities hardest hit by the virus in the UK have opened two weeks behind the rest of the country. However, with most travellers preferring to stay home in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic, how effective are these measures going to be?
Topic 5: Coronavirus outbreak: Caribbean Tourism Struggles as Visitors Stay Home
Research Aim: In the Caribbean, the government plans to require all visitors to undergo rapid Covid-19 testing upon entry. They hope provisions such as virus tests for all industry workers and socially distanced resort dining will make people feel comfortable travelling. This research study will explore whether the measures taken by the Caribbean government will actually encourage the visitors to leave the comfort of their home and travel in the midst of the Covid-19 Crisis.
Ecotourism and Community Participation Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: online tourism agents and websites.
Research Aim: This research aims to study online tourism websites and travelling agents
Topic 2: Advances in Tourism and Hospitality Post-pandemic
Research Aim: This research aims to assess the advances in Tourism and Hospitality post-pandemic
Topic 3: Impacts of Social Distancing on Tourism Managements
Research Aim: This research aims to study the impacts of social distancing on tourism managements
Topic 4: Advances in Hotel Management Post-pandemic
Research Aim: This research aims to assess advances in Hotel management post-pandemic
Topic 5: The Linguistic Roots of the Word “Hospitality” across Different Languages
Research Aim: This research investigates the linguistic roots of the word hospitality across different languages and the semantic shifts over time.
Topic 6: The Relationship Between the Host and the Guest
Research Aim: This research explores the relationship between the host and the guest and how both need to act under laws and regulations.
Economic Conditions and Local Tourism Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: factors impacting destination selection for medical tourism.
Research Aim: Medical tourism is a growing trend. An increasing number of people travel to another country, seeking medical treatment which is expensive or unavailable on their own. Various factors impact the destination selection process for medical treatment purposes. The destination can be local or international. With limited evidence on the factors that impact destination selection for medical tourism, there is a need for a comprehensive study exploring these factors in detail.
Topic 2: Impact of Low budget Airline Services on Boosting International Tourism in Europe: A Case Study of Ryanair.
Research Aim: With increasing costs of air travelling, the demand for low-budget airline services is on the rise. Ryanair is one of the leading low-budget airline services based in the UK. Its cheap air tickets attract many regular travellers. Given this, the main aim of this research will be to explore whether or not low-budget airlines are actually helping to increase international tourism in Europe or not. This research will be conducted based on quantitative data which will be collected from a sample of Ryanair international tourism travellers.
Topic 3: Eco-friendly Practices and Their Effect on Hotel Selection Decision: A Case Study of UK Hospitality Industry.
Research Aim: Various technologies can be implemented to achieve eco-friendliness, such as; internet of things, automation technology, bamboo industrialisation, and sustainable building construction. On the other hand, eco-friendly practices include; water and energy conservation, renewable energy use, waste recycling and management, alternative plastic products, and more. Many hotels in the UK install solar panels and automated systems, which generate renewable energy and ensure complete automation for lights and water. It is worth evaluating how eco-friendly technologies and practices affect the hotel selection decision of guests in the UK hospitality industry.
Topic 4: How Economic Conditions of a Country Impact its Local Tourism: Identifying the Economic Factors Influencing the Tourism Sector.
Research Aim: Economic factors have a great impact on tourism. When a country is economically strong, it spends a great deal on tourism development. On the other hand, tourism could be adversely affected if a country is struggling with its finances. This research aims to investigate and critically analyse the economic factors which tend to affect the tourism sector of a country. The study will also weigh the economic upsides and downsides of these factors concerning local tourism.
Topic 5: Assessing the Impact of Social Media Platforms on Tourism Destination Selection.
Research Aim: These days, social media websites play a tremendous role for tourists in destination selection. The experiences and reviews that people share on online social platforms have a huge impact on making or breaking the future of any tourist destination. This research will analyze the role of different social media platforms in choosing tourism destinations among tourists. This research will also shed light on the rationale and factors people rely on social media to select their tourism destination.
Topic 6: Assessing the Impact of Government Rules, Regulations, and Policies on Tourism Development: A Case Study of Developing Countries.
Research Aim: The tourism sector of any country is greatly looked after by governmental and regulatory bodies. This research will analyze the role played by such bodies from the perspective of policymaking and regulation implementation. The study will also explore how the impact of policymaking and government regulations in developed countries might be different from that of developing countries.
Topic 7: Analysing the Impact of Natural Hazaresearch will measure the customer satisfaction of British lesbians after they have undergone gender reassignment at the Yanhee International Hospital in Bangkok.
Research Aim: Natural hazards can have a disastrous effect on the tourism industry of any country. The UK is one of the countries where the tourism industry has experienced huge success. Thus, this research will be carried out to analyze the impact of such hazards on the UK’s tourism sector.
Topic 8: Assessing the Factors and Preferences Impacting Tourist's Decisions to Travel to a Dark Tourism Site.
Research Aim: As a result of a shift in preferences of tourists and an urge to explore and learn, dark tourism has gained immense popularity and success in recent times. This research will explore the factors and reasons why tourists choose dark places as their tourism destination.
Topic 9: The Impact of Travel Bloggers and vloggers on the Tourism Industry.
Research Aim: Travel bloggers and vloggers are an important part of the tourism industry now. These people travel the world, document their experiences through their writing or videos, and influence people. Tourists throughout the world now depend on their reviews and choose their travel destinations accordingly. This research will aim to explore how these influencers have completely changed the tourism industry.

Educational Tourism Dissertation Topics
Tourism has gained tremendous popularity among academicians and researchers in recent times. Educational tourism primarily takes into consideration technical competencies and new knowledge gained outside the classroom environment.
Educational tourism brings to light the idea of travelling to learn about the cultures of other nations. Exchange student programmes are perhaps the most commonly employed educational tourism strategy, allowing students to learn about the culture of the host nation through research work and travel. Possible areas of research in this field of tourism for your dissertation are provided below;
Topic 1: Educational Tourism Programmes and the Popularity of Host Nations
Research Aim: This research will discuss the educational exchange programmes in detail and will also assess how educational tourism can add to the appeal of the host nations for prospective tourists.
Topic 2: Factors Affecting the Decision of British Students to Join International Student Exchange Programmes.
Research Aim: Even though student exchange programmes are popular throughout the world, there are certain countries where they are practised the most. This research will study one such country, the UK, concerning the factors that encourage British students to join international exchange programmes.
Topic 3: Factors Contributing Towards the Success of Work & Study Programmes in the UK
Research Aim: This research will analyse the factors that contribute towards the success of study programmes in the UK, i.e. benefits of studying in the UK and the attractiveness of the UK as a place to live and study.
Topic 4: To Analyse the Satisfaction of International Students Enrolled in Student Exchange Programmes in the UK
Research Aim: This research will cover an important topic, i.e., measure the satisfaction of international students enrolled in exchange programs in the UK – the same topic can be used for any other country such as the USA or Canada.
Topic 5: To Investigate Potential Marketing and Communication Tools to Promote “any country” as the Best Place to Pursue Higher Education.
Research Aim: This research will investigate and conclude the most successful marketing and communication tools that are used to promote exchange programmes in a particular country. The topic can be customised according to the country of your choice.
Topic 6: What are the factors Influencing British Students’ Decision to Join Academic Year Exchange Programme in Japan?
Research Aim: Japan is one of the most popular destinations when it comes to student exchange programmes. This research will assess the factors that influence a British student’s decision to go to Japan to pursue education.
Topic 7: To Examine the Popularity of Student Exchange Programmes Offered by Chinese-speaking Countries.
Research Aim: This research will explore the reasons for the popularity of student exchange programmes in countries where Chinese is the official language such as Hong Kong, Taiwan, China, etc.
Topic 8: To Investigate the Attitude and Perception of British Students toward Summer Camps.
Research Aim: Summer camps are extremely popular in the west. This research will explore the perceptions of British students towards summer camps and what motivates them to attend them.
Topic 9: Factors Affecting the Decision of University Students to Pursue a Placement Programme in the US?
Research Aim: This research will aim to understand the rationale of university students’ decisions to pursue placement programmes in the US,
Topic 10: To Examine the Satisfaction of University Students Returning from Cultural Exchange Programmes in the US.
Research Aim: This research will aim to understand the satisfaction of university students who are on their way back from exchange programmes in the US.
Medical Tourism Dissertation Topics
Medical tourism is a new area of study in the tourism industry. The gap in the prices of medical facilities available in developing and developed countries is significant, propelling many patients to travel to far destinations to benefit from economic, medical services.
Similarly, many financially well-off patients decide to have medical treatment in foreign countries with advanced and established medical systems that provide state-of-the-art medical facilities unavailable in their home countries.
Although there may be insufficient secondary data to analyse this tourism sub-topic, researching this area will prove to be interesting. You can choose your medical tourism dissertation topics from this list.
Topic 1: Investigating the Reasons Why British Citizens Travel to Different Countries for their Dental Procedures
Research Aim: This research will identify and discuss in detail the reasons why British citizens travel to different countries for dental treatment.
Topic 2: The efficacy of marketing and communication tools employed by Thai plastic surgery and extreme makeover service providers – An investigation into the attitude and perception of British travellers.
Research Aim: A large number of British citizens travel to Thailand for cosmetic and plastic surgeries. This research will aim to understand the attitudes and perceptions of British travellers who opt for these surgeries in a foreign country. The research will also assess the marketing and communication tools employed by Thai medical service providers.
Topic 3: To Identify and Discuss Critical Marketing Strategies to Promote a Weight Loss Centre in the UK.
Research Aim: This research will talk about the marketing strategies that are undertaken in the UK to promote weight loss centres.
Topic 4: Measuring Customer satisfaction of British Lesbians After Having Sex Reassignment at Yanhee International Hospital, Bangkok
Research Aim: This research will measure the customer satisfaction of British lesbians after they have undergone gender reassignment at the Yanhee International Hospital in Bangkok.
Topic 5: To Examine the Factors Influencing the Decisions of British Women to Buy Body Contour Tour Packages in East Asia.
Research Aim: This study will analyze the factors that influence the decision-making of British women when burying body contour tour packages in East Asia.
Topic 6: To Investigate the Extent to Which Swiss Weight Control Tour Packages Have Influenced Women in the UK.
Research Aim: This research will focus on the decision-making detriments of British Women who opt to purchase weight control tour packages in Switzerland.
Topic 7: How Young British Females Perceive Facial Lifting package Tours in East Asia?
Research Aim: This study will analyze how young British females perceive facial lifting package tours in East Asia.
Topic 8: To Understand and Discuss the Factors Affecting Buying Decisions to Benefit from Extreme Makeover Tour Packages in Eastern Europe.
Research Aim: This research will critically explore the factors that influence the buying decision of customers who purchase extreme makeover packages from Eastern Europe.
Topic 9: How Attractive are the Plastic Surgery Makeover Services to Female British Customers – A Qualitative Study
Research Aim: This research will understand and analyze the attractiveness of plastic surgery makeover services that influence British females to purchase them. The research will be descriptive in nature.
Topic 10: How Homosexual Men Choose Medical Tour Packages for Sex Reassignment.
Research Aim: This study will investigate gender reassignment tour packages that interest homosexual men and the factors influencing their decision-making process.
Tourism Management Dissertation Topics
Tourism management is perhaps the most interesting area of the tourism industry. It mainly involves travelling for the purpose of leisure and recreation. People travelling to other countries and outside their usual environment with the intent of leisure can be classified as tourists.
It should be noted that the phenomenon of tourism has grown tremendously in recent years, thanks to the impact of globalisation. There are many countries such as Malaysia, Thailand, Singapore, Maldives, and Fiji, whose largest source of income is tourism. In these countries, tourism generates huge revenue for the government and also provides employment opportunities for the working class as well as businesses.
The suggestions below can help you to narrow your research for your tourism dissertation.
Topic 1: How British Tourists Perceive Chinese World Heritage Tour – A Qualitative Study
Research Aim: This research will focus on how British tourists perceive Chinese heritage and what compels them to visit China.
Topic 2: Exploring the Factors that Make London the Most Popular Destination for Christmas Shopping
Research Aim: This research will analyse and explore the various factors that promote London as one of the most attractive destinations for Christmas shopping.
Topic 3: Investigating the Underlying Factors that British Citizens Consider when Choosing a Destination for Their Winter Holidays.
Research Aim: This research will analyse the various factors that British citizens consider and evaluate when choosing a destination for their winter vacations.
Topic 4: An Analysis of Factors Affecting Employees’ Motivation in Luxury Hotels of Dubai.
Research Aim: This research will study the factors influencing employee motivation in luxury and five-star hotels in Dubai. The study will make use of secondary data and primary research to establish the exact factors that motivate employees to work for luxury hotels in Dubai.
Topic 5: How the Tourism Industry of Thailand Responded to the Tsunami.
Research Aim: This study will dive into the past to establish how the Thai tourism industry responded to Tsunami.
Visit our topics database to view 100s of dissertation topics in your research area.
Topic 6: Factors Influencing British Customers’ Decisions of Purchasing Egypt Tour Packages.
Research Aim: This research will explore the factors that British citizens consider when planning their holiday to Egypt.
Topic 7: Attitude and Perception of British Tourists Toward Thailand as a Winter Holiday Destination
Research Aim: This study will research why the British choose Thailand as their winter holiday destination.
Topic 8: The Increasing Popularity of Cruise Travel in South Africa Among British Tourists
Research Aim: This research will consider the reasons why South African cruise is extremely popular amongst British tourists.
Topic 9: To Investigate the Efficacy of Integrated Marketing Communication Tools to Restore the Image of Amsterdam as the Best Tourist Destination in Europe
Research Aim: This research will explore the marketing and communication tools utilized to market Amsterdam as the best tourism destination in Europe.
Topic 10: Factors Influencing British Customers’ Decision to Choose a Particular Destination During the Summer/winter Holiday
Research Aim: This research will discuss all the factors that influence British citizens to choose a destination for their summer or winter holidays. This topic can be customized according to a country of your choosing.
Hospitality Dissertation Topics
Hospitality industry consists of casinos, resorts, restaurants, hotels, catering as well as other businesses that serve the tourists. At its core hospitality can be defined as the relationship between a guest and the hotel.
Other aspects of hospitality include but are not limited to liberality, friendliness, warm welcome, entertainment, goodwill, and reception. Modern-day businesses pride themselves on their acts of hospitality. Thus, it is an extremely interesting sub-topic to base your dissertation on. Some topics in this area of tourism are suggested below.
Topic 1: Examining How Popular Travel Agents Such as eBrooker and Opodo are Perceived by British Tourists
Research Aim: This research will evaluate some of the best and most popular travel agents such as Opodo and eBookers and how they assist British tourists with their destination planning.
Topic 2: Identifying the Factors that Influence Leisure Hotel Buying Decisions of British Customers
Research Aim: This research will identify the factors that influence British customers’ decision to opt for luxury hotels.
Topic 3: Identifying Features of a leisure hotel that attract British honeymoon couples
Research Aim: This research will identify features of a luxury hotel that attract British couples looking for a honeymoon location.
Topic 4: Investigating Hospitality Practices of Popular Leisure Hotels in Dubai
Research Aim: This study will investigate hospitality purchases of attractive luxury hotels in Dubai.
Topic 5: What are the Prime Factors Influencing Restaurant Selection Decisions of Young British Couples?
Research Aim: This research will explore the factors that influence British couples to select restaurants for their time out.
Topic 6: Investigating and Reviewing Strategies Employed by Hotel Restaurants and Pubs in London to Keep Their Employees Motivated
Research Aim: This research will study an important aspect of the tourism industry, i.e., how hotel restaurants and pubs in London keep their employees motivated.
Topic 7: Exploring the Relationship Between Culture and Leisure Hotel Buying Decisions in London.
Research Aim: This research will investigate the relationship between how customers in London choose a luxury hotel based on their culture.
Topic 8: Creating Brand Sales and Recognition Using Integrated Marketing Communication Tools.
Research Aim: This research will explore how brand sales and recognition are built using various marketing and communication tools.
Topic 9: Understanding the Relationship Between Customers’ Buying Decisions and Leisure Hotel Hospitality Features within the Context of Overseas Holidays
Research Aim: This research will explore the relationship between customers’ decision to choose a luxury hotel while visiting different countries.
Topic 10: The Impact of Hospitality Companies’ Brand Image on Tourists’ Buying Decisions.
Research Aim: This research will first talk about different hospitality companies and how their brand image impacts tourists’ buying decisions.
Black Tourism Dissertation Topics
Black tourism, also known as dark tourism and grief tourism, involves travelling to historical sites/places associated with death, casualties, and suffering.
Dark or black tourist sites such as battlefields, monuments, castles, Tsunami sites, and Ground Zero are man-made or natural. They are found commonly in Scotland, South Asia, China, and Eastern Europe.
Dark tourism may not be the ideal choice for many students. However, it is an exciting topic to explore. Possible research topics under this field of tourism are listed below:
Topic 1: How Local Communities Can Benefit Commercially and Socially from Tours to Death/Casualty Sites – A Qualitative Study
Research Aim: This research will explore the various benefits that local communities can experience from touring death or casualty sites.
Topic 2: Attitude and Perception of Tourists Towards Taj Mahal in India
Research Aim: Taj Mahal can be categorised as a dark tourism site because many people consider it a mausoleum. This research will discuss the attitude and perceptions of tourists when visiting the Taj Mahal.
Topic 3: To Investigate and Identify the Factors Influencing Tourists’ Decisions to Visit gGrief Sites in the UK
Research Aim: This research will explore the factors that influence the decisions of tourists to visit grief sites in the UK.
Topic 4: Is Mercat Tour in Scotland a Grief Tourism Site for Potential Tourists?
Research Aim: Mercat Tour in Scotland is considered a ghost site. This study will explore what makes this site a dark tourism destination.
Topic 5: Developing a Highly Effective Marketing Strategy to Promote London Dungeon Among the Tourists
Research Aim: This research will understand the various marketing strategies undertaken to promote the London Dungeon amongst tourists.
Topic 6: What are the Primary Factors Influencing British Tourists’ Decision to Choose Grief Sites?
Research Aim: This research will understand the various factors that influence British tourists’ decision to select a dark tourism site.
Topic 7: Developing a Marketing Strategy to Promote Beaumaris Prison in Wales as Another Black Tourism Site in Britain
Research Aim: This research will focus on developing a successful marketing strategy that will help promote Beaumaris Prison in Wales as a black tourism site in Britain.
Topic 8: How are Man-made Grief tourism Sites are Perceived by British Tourists?
Research Aim: This research will discover how British tourists perceive man-made dark tourism destinations.
Comparing the Man-made Black Tourism Sites with the Natural Disaster Grief Sites from the Perspective of Tourists
Research Aim: This research will compare manmade and natural dark tourism destinations with a focus on tourists’ perceptions.
Topic 10: Do the Local Communities Economically Benefit from Tourists Visiting Dark Tourism Sites?
Research Aim: This research will explore whether or not local communities are impacted in any way when dark tourist sites in their locality are visited.
Sustainability and Tourism Dissertation Topics
At its core, this field of tourism primarily focuses on the way tourists can live harmoniously with the planet earth. Ecotourist sites or sustainable tourist sites are those that promote fauna and flora and cultural heritage. Another objective of eco-tourism is to provide social and economic opportunities to local communities. Some interesting topics worth exploring, in this area, are suggested below:
Topic 1: Investigating the Impact of the Internet on the Growth of Eco-tourism in the UK
Research Aim: This research will study the impact of the internet on the rising eco-tourism trend in the UK.
Topic 2: Factors Affecting British Customers’ Decision of Choosing an Eco-tourism
Research Aim: This research will study the reason why British tourists opt for an eco-tourism site as compared to traditional destinations.
Topic 3: Establishing and Discussing Strategies to Promote Swansea as the Best Eco-tourist Spot in the UK
Research Aim: This research will discuss the various ways through which Swansea can be promoted as the best eco-tourist spot in the UK.
Topic 4: Analysing the Role of Price in the Selection of Eco-tourism Destinations
Research Aim: This research will understand the various factors that influence the tourists’ decision to choose an eco-friendly site for their next holiday destination.
Topic 5: Examining the Use of Integrated Marketing Communication Tools to Promote Eco-tourism in Great Britain
Research Aim: This research will study and analyze the different ways through which integrated marketing communication tools should be used to promote eco-tourism in the UK.
Topic 6: Comparing Developing World Eco-tourism Sites Against Western Eco-tourism Sites
Research Aim: This study will compare developing eco-tourism sites and developed or Western eco-tourism sites. The study will conclude which sites tourists prefer and what factors lead them to their decision.
Topic 7: Does Eco-tourism Develop Social and Economic Opportunities for Local Communities?
Research Aim: This research will explore whether or not eco-tourism helps develop social and economic opportunities in the local communities. If it does, the study will explore those factors as well.
Topic 8: Exploring the Factors Affecting the Buying Decisions of Customers Interested in Eco-tourism Sites
Research Aim: This research will identify and discuss the various factors that affect the buying decision of customers who are interested in eco-tourism sites. These factors will then be explored in detail in this study.
Topic 9: Analysis of the Potential of Edinburgh as an Eco-tourism Site in the UK
Research Aim: This research will compare manmade and natural dark tourism destinations and will also include tourists’ perceptions.
Topic 10: Assessing the Impact of Grass Root level Education in Promoting Sustainable Tourism in Europe – A Review of the Literature
Research Aim: This research will discuss the impact of grass root level education to promote sustainable tourism in Europe. The study will be based on the qualitative research method.
Important Notes:
As a tourism and hospitality student looking to get good grades, it is essential to develop new ideas and experiment with existing tourism and hospitality theories – i.e., to add value and interest to your research topic.
The field of tourism and hospitality is vast and interrelated with many other academic disciplines like civil engineering, construction, law, engineering management, healthcare, mental health, artificial intelligence, physiotherapy, sociology, management, marketing, and nursing . That is why it is imperative to create a project management dissertation topic that is particular and sound and actually solves a practical problem that may be rampant in the field.
We can’t stress how important it is to develop a logical research topic; it is the basis of your entire research. There are several significant downfalls to getting your topic wrong: your supervisor may not be interested in working on it, the topic has no academic creditability, the research may not make logical sense, and there is a possibility that the study is not viable.
This impacts your time and efforts in writing your dissertation as you may end up in a cycle of rejection at the very initial stage of the dissertation. That is why we recommend reviewing existing research to develop a topic, taking advice from your supervisor, and even asking for help in this particular stage of your dissertation.
While developing a research topic, keeping our advice in mind will allow you to pick one of the best tourism and hospitality dissertation topics that fulfil your requirement of writing a research paper and add to the body of knowledge.
Therefore, it is recommended that when finalizing your dissertation topic, you read recently published literature to identify gaps in the research that you may help fill.
Remember- dissertation topics need to be unique, solve an identified problem, be logical, and be practically implemented. Please take a look at some of our sample tourism and hospitality dissertation topics to get an idea for your dissertation.
How to Structure Your Tourism and Hospitality Dissertation
A well-structured dissertation can help students to achieve a high overall academic grade.
- A Title Page
- Acknowledgements
- Declaration
- Abstract: A summary of the research completed
- Table of Contents
- Introduction : This chapter includes the project rationale, research background, key research aims and objectives, and the research problems to be addressed. An outline of the structure of a dissertation can also be added to this chapter.
- Literature Review: This chapter presents relevant theories and frameworks by analyzing published and unpublished literature available on the chosen research topic in light of the research questions to be addressed. The purpose is to highlight and discuss the relative weaknesses and strengths of the selected research area while identifying any research gaps. A breakdown of the topic and key terms can have a positive impact on your dissertation and your tutor.
- Methodology: The data collection and analysis methods and techniques employed by the researcher are presented in the Methodology chapter, which usually includes research design, research philosophy, research limitations, code of conduct, ethical consideration, data collection methods, and data analysis strategy .
- Findings and Analysis: The findings of the research are analysed in detail under the Findings and Analysis chapter. All key findings/results are outlined in this chapter without interpreting the data or drawing any conclusions. It can be useful to include graphs , charts, and tables in this chapter to identify meaningful trends and relationships.
- Discussion and Conclusion: The researcher presents his interpretation of results in this chapter and states whether the research hypothesis has been verified or not. An essential aspect of this section is to establish the link between the results and evidence from the literature. Recommendations with regard to the implications of the findings and directions for the future may also be provided. Finally, a summary of the overall research, along with final judgments, opinions, and comments, must be included in the form of suggestions for improvement.
- References: Make sure to complete this in accordance with your University’s requirements
- Bibliography
- Appendices: Any additional information, diagrams, graphs that were used to complete the dissertation but not part of the dissertation should be included in the Appendices chapter. Essentially, the purpose is to expand the information/data.
About ResearchProspect Ltd
ResearchProspect is a UK-based academic writing service that provides help with Dissertation Proposal Writing, PhD Proposal Writing, Dissertation Writing, Dissertation Editing, and Improvement.
For further assistance with your dissertation, take a look at our full dissertation writing service .
Our team of writers is highly qualified and is an expert in their respective fields. They have been working for us for a long time. Thus, they are well aware of the issues as well as the trends of the subject they specialise in.
Need more Topics.?
Free Dissertation Topic
Phone Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Graduate PHD
Academic Subject
Area of Research
Frequently Asked Questions
How to find dissertation topics about tourism and hospitality.
To find tourism and hospitality dissertation topics:
- Examine industry trends and challenges.
- Explore cultural, environmental, or tech impacts.
- Research niche areas like ecotourism or event management.
- Analyse customer behaviour and satisfaction.
- Consider sustainable practices.
- Select a topic aligning with your passion and career aspirations.
What is the best research topic for tourism?
There is no one best topic, but here is a trending topic. “The Impact of Virtual Reality Technology on Tourist Experience and Destination Promotion: A Comparative Analysis.” This research topic explores how VR technology affects tourist perceptions, engagement, and decision-making and its implications for destination marketing strategies, comparing traditional methods with VR-based approaches in tourism promotion.
You May Also Like
Need interesting and manageable science dissertation topics or thesis? Here are the trending science dissertation titles so you can choose the most suitable one.
Need interesting and manageable Cryptocurrency – Bitcoin, Etherum & Ripple on dissertation topics or thesis? Here are the trending Cryptocurrency – Bitcoin, Etherum & Ripple dissertation titles so you can choose the most suitable one.
Are you looking for a dissertation topic on dementia? We have a list of the top 55 dementia dissertation topics by experts for you to ace your dissertation.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Portland Tourism Chief to Retire After 19-Year Tenure

Dawit Habtemariam , Skift
June 24th, 2024 at 4:00 PM EDT
Portland is going to need another tourism champion, one who will be an outspoken advocate.
Dawit Habtemariam
Portland is losing a tourism champion. Jeff Miller , who has served for 19 years as CEO and president of Travel Portland , the city’s destination marketing organization, will retire in December, reported Northstar Meetings Group .
Miller oversaw the city’s tourism recovery and led a staff of about 70 full- and part-time employees and an annual budget of about $30 million. He defended Portland’s image against negative media associations with crime and violence. News outlets had repeatedly shown images of the city in a doom loop years after the civil unrest surrounding the murder of George Floyd subsided.
“What the press has reported on Portland has changed dramatically,” Miller told Skift last June . “Now, if we can just get them to stop using pictures from three years ago, we will be fine.”
Portland had to fill the gap left by conventions pulling out amid the unrest. “During the pandemic, with a hundred days of protest and all of the violence and all the reporting, most cities rebooked [conventions] into future years. And we did too, but not to the degree that other cities did,” Miller told Skift in September.
“Our team has done an amazing job of filling those holes, but there are more to be filled,” he said.
Reversing Negative Suburban Traveler Sentiment
A major objective of Miller was to reignite suburbanite interest in visiting Portland’s downtown.
The share of Portlanders who would recommend the city to out-of-town friends and family fell from 88 percent in 2017 to 61 percent in 2023 , with most of the negative sentiment concentrating in the suburbs, according to Travel Portland.
Miller pointed to the spread of remote work and negative media coverage as the reasons why suburbanite sentiment dropped.
“The reputational damage that Portland suffered certainly extended locally and Portlanders have always been very, very proud of their city,” said Miller. “I think it’s taken a bit of time to get people back into the core to see what’s going on.”
Against Public Drug Abuse
Miller publicly spoke out in support of a ban on public drug use. In November 2020, Oregon approved ballot Measure 110, decriminalizing possession of small amounts of controlled substances.
Miller spoke up on the impact of public drug use on the city’s tourism industry. “Portland’s hospitality crisis is in crisis, and it can be linked to the conditions on our streets with open drug dealing and usage,” he told the city council at a hearing in September .
In that same month, Portland’s city council passed an ordinance that banned the use of controlled substances on public property.
“We need to make major and significant changes, compassionate changes, but we need to find places for these people to get off the street,” Miller told Skift in September.
Miller spoke on-stage at the Skift Global Forum in New York last September.
The Daily Newsletter
Our daily coverage of the global travel industry. Written by editors and analysts from across Skift’s brands.
Have a confidential tip for Skift? Get in touch
Tags: ceos , destination marketing organizations , dmos , executives , portland , tourism

New ATRI Research: Industry Costs Increased More than 6 Percent During Freight Recession

FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Tuesday, June 25, 2024
Contact: Alex Leslie (651) 641-6162
Washington, D.C. – The American Transportation Research Institute (ATRI) released today the findings of its 2024 Analysis of the Operational Costs of Trucking . This annual report analyzes line-item costs, operating efficiencies, and revenue benchmarks by fleet sector and size, providing crucial benchmarking for motor carriers and a comprehensive overview of the financial state of trucking for decisionmakers in both industry and government.
The overall marginal costs of operating a truck hit $2.270 per mile in 2023. While the increase was only 0.8 percent over the previous year, when surcharge-protected fuel costs are excluded, marginal costs rose 6.6 percent to $1.716 per mile.
Overall, 2023 expenses rose moderately across most categories, with average costs across line-items increasing at less than half the rates experienced during 2021 and 2022. Truck and trailer payments grew by 8.8 percent to $0.360 per mile, driver wages grew by 7.6 percent to $0.779 per mile, and repair and maintenance costs grew by 3.1 percent to $0.202 per mile. The exception to this trend was truck insurance premiums, which grew by 12.5 percent to $0.099 per mile after two years of negligible change.
The soft 2023 freight market posed many challenges for operational efficiency, as tracked in the report. Deadhead mileage, a critical financial drain, rose to an average of 16.3 percent for all non-tank operations, and driver turnover rose by five percentage points in the truckload sector.
These pressures combined with low freight rates strained profitability across the industry. Average operating margins were 6 percent or lower in all fleet sizes and sectors other than LTL. The truckload and specialized sectors experienced drops in per-mile or per-truck revenue, and most saw “other costs” – expenses outside of the core marginal line-items – increase as a share of total revenue.
The report also includes analyses of cost trends in 2024 and beyond, including, for the first time, carrier-reported changes in Q1 2024 costs.
“The current economic environment makes cost management essential to successful operations,” said Gregg Troian, PGT Trucking President . “ATRI’s Operational Costs report provides the targeted costs and operational benchmarks necessary to identify opportunities for reducing expenses and how to best act on those opportunities in our fleet.”
The full report is available on ATRI’s website here . Participating carriers receive a customized report directly comparing their operations to an anonymized peer group of the same sector and size.
ATRI is the trucking industry’s 501c3 not-for-profit research organization. It is engaged in critical research relating to freight transportation’s essential role in maintaining a safe and efficient transportation system.

The American Transportation Research Institute (ATRI) has been engaged in critical transportation studies and operational tests since 1954. ATRI is a 501(c)(3) not-for-profit research organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with offices in Atlanta, Minneapolis, and Sacramento.
ATRI’s primary mission is to conduct transportation research, with an emphasis on the trucking industry’s essential role in a safe, efficient and viable transportation system. ATRI’s research focus areas include: Congestion and Mobility; Economic Analysis; Safety and Security; Technology and Operations; Environment; and Transportation Infrastructure.
ATRI’s extensive experience covers a broad range of commercial vehicle operations including leadership and/or participation in numerous national freight analyses, technology research initiatives and field operational tests.
ATRI presently manages the U.S. DOT’s Freight Mobility Program, and has provided freight mobility and performance measures technical assistance to 31 state DOTs and 11 of the 15 largest MPOs in the U.S. ATRI has received top research awards from ITS America, TIDA, University of Minnesota and the Institute of Transportation Engineers.
Follow ATRI
Research hot topics, popular downloads.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- Americans’ Views of Government’s Role: Persistent Divisions and Areas of Agreement
2. Americans’ views of government aid to poor, role in health care and Social Security
Table of contents.
- Views on the efficiency of government
- Views on the government’s regulation of business
- Confidence in the nation’s ability to solve problems
- Views on the effect of government aid to the poor
- Views on government’s role in health care
- Views on the future of Social Security
- Trust in government
- Feelings toward the federal government
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology
Majorities of Americans see a role for government on several safety net issues.
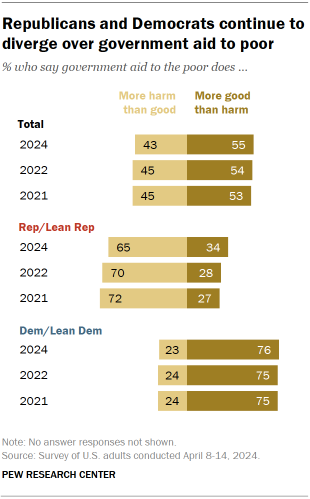
- 65% say the government has a responsibility to ensure all Americans have health care coverage.
- 55% say government aid to the poor does more good than harm.
- 79% say Social Security benefits should not be reduced in any way.
A majority of Americans (55%) say that, overall, government aid to the poor does more good than harm, while about four-in-ten (43%) say it does more harm than good.
Republicans and Republican-leaning independents continue to be critical of government aid to the poor:
- 65% say government aid does more harm than good, while 34% say it does more good than harm.
- However, the share of Republicans saying government aid has a positive effect is up 6 percentage points since 2022.
As in past years, about three-quarters of Democrats (76%) say government aid to the poor has an overall positive effect (23% say it does more harm).
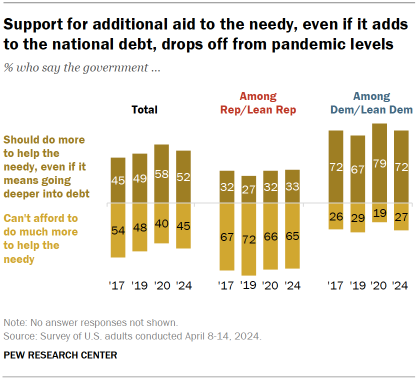
About half of Americans (52%) now say the government should do more to help the needy, even if it means going deeper into debt. By comparison, 45% say the government can’t afford to do much more to help the needy.
Support for doing more to help those in need, even if the debt increases, is 6 percentage points lower than it was in June 2020, in the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- About seven-in-ten Democrats (72%) say the government should do more to help the needy, down from 79% who said the same in 2020.
- A far smaller share of Republicans – 33% – say the government should do more even if it leads to additional debt. Views among Republicans are largely unchanged since 2020.
Government assistance to people in need
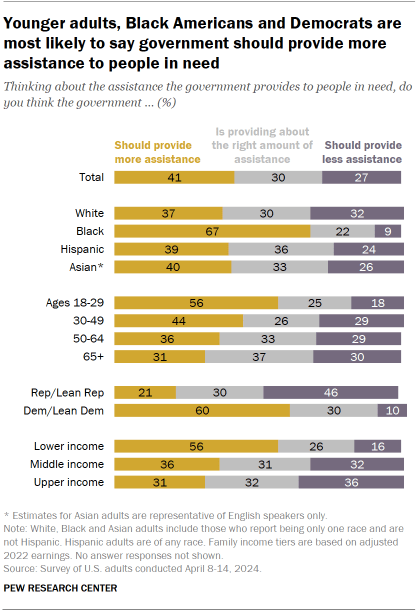
About four-in-ten Americans (41%) say the government should provide more assistance to people in need, while about a quarter say it should provide less (27%). Three-in-ten say the government is providing about the right amount of assistance.
Like other attitudes about social safety net policies, there are wide partisan differences.
Six-in-ten Democrats say the government should provide more assistance to people in need. Just one-in-ten say it should provide less, while three-in-ten say the current level is about right.
By comparison, 46% of Republicans say the government should provide less assistance, while 21% say it should provide more.Three-in-ten say the government is providing the right amount of assistance.
There are other demographic differences:
- Two-thirds of Black adults say the government should provide more assistance to people in need, while smaller shares of Asian (40%), Hispanic (39%) and White (37%) adults say the same.
- Younger adults are more likely than older adults to say the government should provide more assistance.
- A majority of lower-income adults (56%) say the government should provide more assistance. Smaller shares of middle- (36%) and upper-income (31%) adults say the same.
About two-thirds of Americans (65%) say it is the federal government’s responsibility to make sure all Americans have health care coverage, while roughly a third (34%) say it does not.
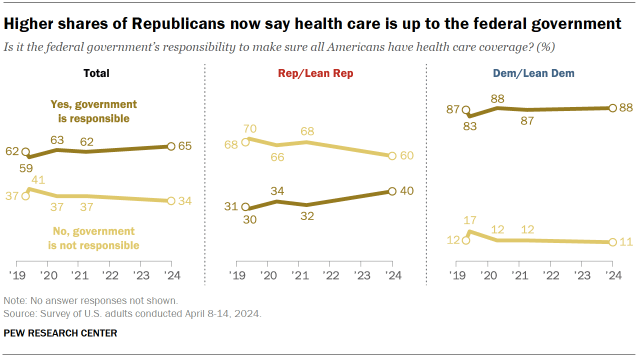
Americans are slightly more likely to say it is the government’s responsibility to ensure health care coverage for all than they were a few years ago (62% in 2021). While Democratic opinion has not changed over this period, the share of Republicans who say government has this responsibility has grown.
- Four-in-ten Republicans and Republican-leaning independents now say it is the government’s responsibility to ensure health care coverage for all, up from 32% who said this in 2022. Six-in-ten say it is not the government’s responsibility, down from 68% who said the same three years ago.
- Democrats and Democratic leaners overwhelmingly hold the view that the government has a responsibility to ensure health care coverage: 88% say this. Democrats’ views on this question are largely unchanged in recent years.
Views by party and income
Majorities of adults at all income levels say the government is responsible for ensuring health care coverage. However, lower-income adults (73%) are more likely than upper- (63%) or middle-income (62%) adults to say this.
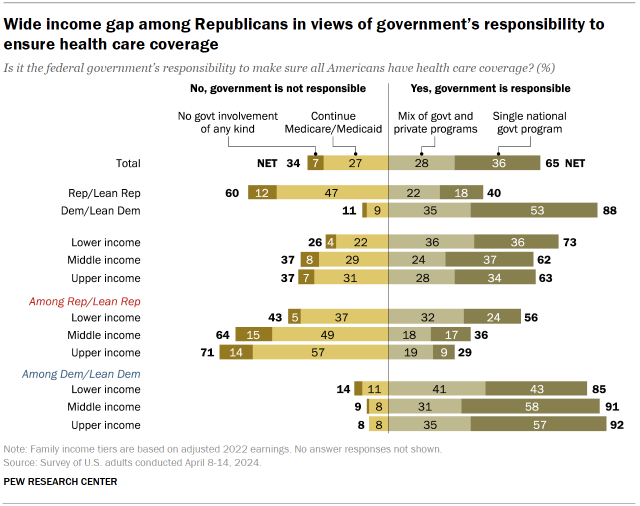
Among Republicans, there are differences within income groups on whether government is responsible for ensuring all Americans have health care coverage:
- 56% of lower-income Republicans say it is the government’s responsibility to make sure all Americans have health care coverage, including about a quarter (24%) who say this should be done through a single national government program.
- Middle-income (36%) and upper-income Republicans (29%) are far less likely to say the government has a responsibility to ensure people have health care coverage. Majorities in both of these groups say it is not the government’s responsibility.
By comparison, more than eight-in-ten Democrats across all income levels say the government is responsible for ensuring all Americans have health care coverage.
- Overall, about half of Democrats (53%) say this should be done through a single national government program. About six-in-ten upper-income (57%) and middle-income (58%) Democrats say this, compared with about four-in-ten lower-income Democrats (43%).
Americans overwhelmingly (79%) say Social Security benefits should not be reduced in any way, including four-in-ten who say it should cover more people with greater benefits. Roughly two-in-ten (19%) say some future reductions need to be considered.
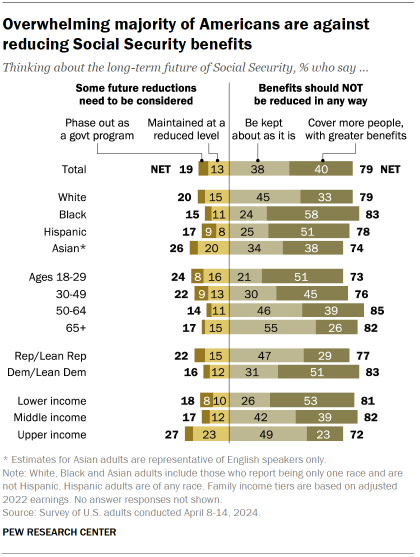
Wide majorities of both Republicans and Democrats do not support Social Security benefit reductions: 77% of Republicans and 83% of Democrats say Social Security benefits should not be reduced in any way.
However, Democrats (51%) are more likely than Republicans (29%) to say Social Security should be expanded.
Across demographic groups there is broad opposition to Social Security benefit cuts. But there are more sizable differences in support for expanding benefits:
- Black (58%) and Hispanic (51%) adults are more likely than White (33%) and Asian (38%) adults to say benefits should be expanded.
- Older adults are less likely than those in other age groups to say benefits should be expanded to cover more people with greater benefits: 26% of those 65 and older say this. By comparison, adults under 30 (51%) are most likely to favor expansion.
- Lower-income adults are the most supportive of expanding Social Security benefits: 53% say this, compared with 39% of those in middle-income families and 23% of upper-income adults.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Election 2024
- Federal Government
- Government Spending & the Deficit
- Health Care
- Partisanship & Issues
- Social Security & Medicare
- Trust in Government
6 facts about presidential and vice presidential debates
Biden, trump are least-liked pair of major party presidential candidates in at least 3 decades, cultural issues and the 2024 election, more than half of americans are following election news closely, and many are already worn out, americans have mixed views about how the news media cover biden’s, trump’s ages, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In summary, tourism research is a multifaceted learning experience that goes beyond textbooks, providing students with the skills, knowledge, and perspectives needed for a successful and impactful career in the tourism industry or related fields. 100+ Tourism Research Topics: Category Wise. Sustainable Tourism; Impact of Technology on Travel
A few topics, for example, eco-tourism, rural tourism, tourist management and planning, and marketing strategies for sustainable tourism (Topics 2, 3, 14, 16, and 23) have followed a declining trend, which suggests that academic research in these areas may have reached a maturity level and researchers' attention has shifted toward more novel ideas.
Relevant answer. Mohd Hafiz Hanafiah. May 7, 2023. Answer. Hello Maksim. This is a challenging task because there is no definitive method to establish the exact count of researchers working in the ...
3. Lack of empathy. Lack of empathy limits AI's ability to interact and understand people's emotional needs. In situations that require greater understanding, such as mental health care or ...
1. Introduction. The tourism industry is one of the world's fastest-growing industries. The industry is renowned for its potential to create employment opportunities, aiding in the fight against unemployment and poverty [[1], [2], [3]].In 2019, before the COVID-19 pandemic weakened global economies, the tourism industry was responsible for 10.6% of global employment and 10.4% of the global GDP ...
to identify the topics and trends that will shape future tourism research and practice. This note sets out to develop an agenda for tourism research post COVID-19. We surveyed several industry and academic experts seeking their opinion on three important questions: What potential future topics are needed to address the impact of COVID-19?
Tourism and Hospitality Research (THR) is firmly established as an influential and authoritative, peer-reviewed journal for tourism and hospitality researchers and professionals. THR covers applied research in the context of Tourism and Hospitality in areas such as policy, planning, performance, development, management, strategy, operations, marketing and consumer behavior…
Post-crisis tourism research must align academic and corporate interests. We present the future research agenda in two segments. One, based on the gaps in the existing literature, we present the research questions for tourism research to explore different sub-topics in the context of COVID-19.
Tourism forecasting has been a focal point of tourism research over the past few decades as a result of the corresponding rapid development and expansion of the tourism industry. A bibliometric analysis, based on 543 articles retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection database, was carried out to provide insights into hot topics as well ...
In this knowledge framework, this research described specific leading research aspects and discussed the guidance that COVID-19 research has brought to the tourism industry. A literature review of current research on COVID-19 and tourism is vital to piece together a complete answer, highlighting neglected areas of research and pointing out ...
Research on the effects of COVID-19 on citizen health and its economic impact on the tourism industry and cities are intersectional and highly developed topics, although of little relevance. Furthermore, we identified the challenges of future city development, tourism research and practice, and we proposed future directions for research on city ...
Nov 26, 2023. Answer. In principle, sustainable tourism development is not just about marketing. It focuses on balancing environmental, social and economic aspects to ensure long-term benefits for ...
The purpose of this study is to examine the scientific research related to sustainability in hospitality and tourism from 1994 to 2020 by conducting bibliometric and science mapping analyses and to discuss the implications for prospective research opportunities.,Keyword co-occurrences with 2,980 published papers collected from the Web of ...
In the era of digital transformation, Big Data have assumed a crucial role in changing the global travel and providing significant challenges and opportunities for established companies, as well as new entrants into the tourism industry. All these companies can get valuable information on Big Data for predicting tourist demand, enabling better ...
The tourism industry is changing rapidly and has become increasingly competitive: more tourism destinations are emerging worldwide, ... Tourism research helps address basic questions about your activities and services. Common issues and questions might include: TOURISM TRENDS
Not really. The industry continues to face a prolonged and widespread labor shortage. After losing 62 million travel and tourism jobs in 2020, labor supply and demand remain out of balance. 6 "WTTC research reveals Travel & Tourism's slow recovery is hitting jobs and growth worldwide," World Travel & Tourism Council, October 6, 2021.
6,926 views. 4 articles. Follow us. Provides evidence-based research for academics and researchers, industry leaders, policymakers, and consumers to achieve sustainable forms of tourism.
Effects of Covid-19 on Tourism and Hospitality Dissertation Topics. Topic 1: Tourism after Coronavirus Pandemic - Way Forward for Tourism and Hospitality Industry in the UK or Any Other Country of Your Choice. Topic 2: Investigating the Long Term Effects of Prolonged and New Travel Restrictions on the UK Tourism Industry.
This quality makes them especially useful in the travel and tourism industry. 2. They're timely. With the ability to collect data even in an offline environment, intercept surveys are great for getting feedback from people as their visit/interaction is still fresh in their minds.
The Handbook of Research on Smart Technology Applications in the Tourism Industry is an essential reference source that discusses the use of intelligent systems in tourism as well as their influence on consumer relationships. Featuring research on topics such as digital advertising, wearable technology, and consumer behavior, this book is ...
The global travel industry made significant progress in its recovery from the pandemic last year. But the tourism boom has brought challenges to certain destinations, including helping make some ...
Answer. For finding correlation, you may be able to use the historical/past data about tourism activities and income inequality. In order to establish causality, you need to control all the other ...
Abstract. This chapter covers some of the basic skills associated with designing a questionnaire for tourism research. It considers different types of questions and when to use each. It considers question format in some detail, as well as overall questionnaire structure. It also looks at tactics associated with coding the results from ...
The digital economy, the tourism industry, and ecological protection are closely related, which holds paramount significance for regional sustainable development. Based on panel data from 2011 to 2021 in the Yellow River Basin, the study scrutinizes the spatial and temporal variances and driving factors of the three-system coupling coordination degree. The results indicate that: (1) The ...
Portland is losing a tourism champion. Jeff Miller , who has served for 19 years as CEO and president of Travel Portland , the city's destination marketing organization, will retire in December ...
American s are evenly divided in their preferences for the size of government. Yet a somewhat greater share wants the government to do more to solve problems than say it is doing too much better left to others. There is a persistent belief that government is wasteful: 56% say it is "almost always wasteful and inefficient."
The American Transportation Research Institute (ATRI) has been engaged in critical transportation studies and operational tests since 1954. ATRI is a 501(c)(3) not-for-profit research organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with offices in Atlanta, Minneapolis, and Sacramento. ATRI's primary mission is to conduct transportation research, with an emphasis on the trucking industry's ...
His goal was to provide applicable information that would benefit the U.S. rice industry. The Terry Siebenmorgen Memorial Scholarship will be awarded to undergraduate students majoring in food science, with a preference given to students pursuing rice-related research or work. Please support this award by donating online. Industry Alliance Meeting
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions.
Tourism. ChapterPDF Available. The Tourism Industry: An Overview. September 2017. September 2017. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-49849-2_1. In book: Travel Marketing, Tourism Economics and the Airline ...