Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution, update may 10, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |

Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Travel Advisory July 24, 2023
Indonesia - level 2: exercise increased caution.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed.
Exercise increased caution in Indonesia due to terrorism and natural disasters. Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Do Not travel to:
- The provinces of Central Papua (Papua Tengah) and Highland Papua (Papua Pegunungan) due to civil unrest.
Terrorists continue plotting possible attacks in Indonesia. Terrorists may attack with little or no warning, targeting police stations, places of worship, hotels, bars, nightclubs, markets/shopping malls, and restaurants.
Natural disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis or volcanic eruptions may result in disruptions to transportation, infrastructure, sanitation, and the availability of health services.
Demonstrations occur frequently and have the potential to become violent. Avoid demonstrations and crowds.
Indonesia’s revised criminal code, which takes effect January 2026, includes penalties for defamation, blasphemy, cohabitation, and sex outside of marriage. It is unclear how Indonesian authorities will implement the revised criminal code.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Indonesia.
If you decide to travel to Indonesia:
- Monitor local media for breaking events and be prepared to adjust your plans.
- Visit the websites for Badan Geologi (Indonesian Geological Agency, Indonesian language only) for the latest information from the Government of Indonesia on current natural disasters.
- Review the CDC’s suggestions on how to prepare for natural disasters.
- Be aware of your personal safety and security at all times.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program ( STEP ) to receive alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Ensure your passport is valid for at least six months beyond your intended stay.
- Follow the Department of State Facebook and Twitter . Follow the U.S. Embassy Jakarta on Facebook , Instagram , and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Indonesia.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Central Papua and Highland Papua– Level 4: Do Not Travel
In Central Papua and Highland Papua, violent demonstrations and conflict could result in injury or death to U.S. citizens. Avoid demonstrations and crowds. Armed separatists may kidnap foreign nationals.
The U.S. government has limited ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in Central Papua and Highland Papua as U.S. government employees must obtain special authorization before traveling to those areas.
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
Six months beyond arrival date. Indonesia does not accept the 12-page U.S. emergency passport for entry into Indonesia.
Two blank visa pages required for entry stamp
Yes, Visa or Visa on Arrival
100,000,000 Indonesian rupia (approx. $7,000 USD)
Embassies and Consulates
U.s. embassy jakarta.
Jl. Medan Merdeka Selatan No. 3 - 5 Jakarta 10110, Indonesia Telephone: +(62)(21) 5083-1000 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(62)(21) 5083-1000 ext. 0 (operator) Email: [email protected]
U.S. Consulate General Surabaya Jl. Citra Raya Niaga No. 2 Surabaya 60217 Indonesia Telephone: +(62)(31) 297-5300 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(62)(811) 334-183 Email: [email protected]
U.S. Consular Agency Bali Jalan Hayam Wuruk 310, Denpasar, Bali Telephone: +(62)(361) 233-605 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: Please contact the U.S. Consulate in Surabaya:+(62)(811) 334-183 Email: [email protected]
American Consulate Medan, Sumatra Uni Plaza Building 4th Floor (West Tower) Jl. Let. Jend. MT Haryono A-1 Medan 20231, Indonesia Telephone: +(62)(61) 451-9000 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(62)(61) 451-9000 Email: [email protected]
The U.S. Consulate in Medan provides only emergency assistance to U.S. citizens and does not offer routine consular services.
Destination Description
See the Department of State’s Fact Sheet on Indonesia for information on U.S.- Indonesia relations.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
Entry Requirements: To enter Indonesia, your passport must have at least two blank pages and be valid for at least six months beyond the date of your arrival in Indonesia. If your passport does not meet these requirements, you will be denied entry into Indonesia. The Government of Indonesia will not admit travelers holding the 12-page U.S. emergency passport, issued by U.S. embassies and consulates overseas.
Visa-on-Arrival: If you meet the requirements, you can apply for a visa on arrival at some international airports, seaports, or land crossings. To apply for the visa on arrival, you must have an ordinary (non-emergency) passport with at least 6 months of validity from the date you plan to enter and the date you plan to leave Indonesia and a return or onward flight booking to another country. There is a 500,000 Indonesian Rupiah fee (about $35). The visa on arrival is valid for up to 30 days. You may extend a Visa-on-Arrival once at the immigration office one week before it expires for an additional 30 days for a maximum of 30 additional days, for another 500,000 Rupiah.
- Official visit or government duties;
- Business meeting;
- Procurement of goods;
- Official meeting; or
Electronic Visa-On-Arrival: You may also apply for an electronic Visa on Arrival (e-VOA) in advance if you are entering Indonesia at Soekarno-Hatta International Airport in Jakarta or Ngurah Rai International Airport in Bali. Check the e-VOA requirements from Indonesian Immigration before applying. To apply for an e-VOA see https://molina.imigrasi.go.id/ .
Visa: Travel for more than 30 days and travel for non-VOA purposes, including employment and journalism, requires that the appropriate visa be obtained from an Indonesian embassy or consulate before arrival. If you are traveling on an emergency passport, you must obtain a visa before arrival in Indonesia.
If you overstay your visa, you are subject to a fine of 1 million Indonesian rupiah (about $70 USD at current exchange rates; fees may change at any time) per day and may be detained and deported. U.S. citizens have been jailed for visa overstays or entering the country on the wrong visa class for their purpose of travel . Travelers coming to Indonesia for non-tourism purposes are strongly encouraged to consult Indonesian Immigration’s website. Travelers should generally carry a copy of their passport with them whenever possible to establish their identity and proof of Indonesian visa.
You must exit Indonesia using the same passport that you used to enter. If this passport is replaced for any reason before you depart Indonesia, you must apply with Immigration to obtain a “special pass” (exit permit) in your new passport prior to departing.
Dual-Nationality: Indonesia has laws that prohibit Indonesian citizens from holding additional nationalities. If you are an Indonesian with dual nationality, you could be compelled to renounce your Indonesian nationality through a formal act of renunciation. Please research Indonesian nationality laws and consult with a local attorney regarding any specific circumstance.
The U.S. Department of State is unaware of any HIV/AIDS entry restrictions for visitors to or foreign residents of Indonesia. The Government of Indonesia screens incoming passengers in response to reported outbreaks of pandemic illnesses.
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction , and customs regulations on our websites.
Safety and Security
Terrorism: Terrorist groups and those inspired by such organizations are intent on attacking U.S. citizens abroad. Terrorists are increasingly using less sophisticated methods of attack – including knives, firearms, and vehicles – to target crowds. Frequently, their aim is unprotected or vulnerable targets, such as:
- High-profile public events (sporting contests, political rallies, demonstrations, holiday events, celebratory gatherings, etc.)
- Hotels, clubs, and restaurants frequented by tourists
- Places of worship
- Shopping malls and markets
- Public transportation systems (including subways, buses, trains, and scheduled commercial flights)
Extremists in Indonesia aspire to carry out violent attacks against Indonesian and foreign targets, and police have arrested more than 1,200 individuals on terrorism-related charges since 2018. Extremists may target both official and private establishments, including government offices, hotels, bars, nightclubs, shopping areas, restaurants, and places of worship. Be aware of your personal safety and security at all times.
Recent incidents of extremist violence include a December 2022 suicide bombing at a police station in Bandung, West Java that killed one police officer, a March 2021 bomb attack against a church in Makassar, South Sulawesi which injured 20 civilians, and May 2018 bomb attacks against three churches in Surabaya, East Java which killed 15 civilians and injured 50.
Demonstrations are very common in Jakarta, Surabaya, and other large cities, but less common in Bali. You should avoid demonstrations and other mass gatherings, since even those intended to be peaceful can become violent. U.S. citizens have been detained for participating in protests. Demonstrations may become more frequent ahead of the Indonesian general elections scheduled for February 2024.
Currently, travel by U.S. government personnel to the provinces of Central Papua (Papua Tengah) and Highland Papua (Papua Pegunungan) is restricted to mission-essential travel that is approved in advance by the Embassy. Papuan separatists have kidnapped foreigners in the past and a New Zealand national was kidnapped by a separatist group in Nduga Regency in February 2023.
For more information, see our Terrorism page.
Crime: In the last year several American citizens were victims of violent and serious crimes in Indonesia, particularly in Bali. As with any major tourist destination, U.S. citizens traveling in Indonesia are especially encouraged to always remain vigilant of their surroundings and read the following advisories carefully. Take sensible measures to protect yourself and your belongings. Closely monitor bags and luggage and carry only essential items. Take particular care of your passport and bank cards and avoid traveling alone.
Police presence and responsiveness is less than it is in the United States, making it more difficult to report crimes quickly and receive police attention. U.S. citizens often cite language barriers as a major hindrance when reporting crimes.
Pickpocketing, sexual assault, vehicle theft, armed car-jacking, snatch and grab robberies of cell phones and purses, and residential break-ins are common. Avoid traveling to isolated areas late at night. Be aware of your surroundings, particularly vehicles or individuals that might be following you.
Use a reputable taxi company or hire a taxi either at a major hotel or shopping center and ensure the driver’s identity card is visible. If you are booking a car via a mobile app, always ensure that the driver is the same as the person on the app, share your journey with a friend via the in-app option, and know the contact information for the app’s security center. Be aware of drivers falsely claiming to be registered with online ride hailing apps.
Credit card fraud is a common problem in Indonesia. Criminals have “skimmed” credit/debit cards to access and drain bank accounts. Use an ATM in a secure location, such as a major bank branch, and check the machine for evidence of tampering. Monitor your account statements regularly.
Tourists and Indonesians have suffered from serious illness and have even died from "drink-spiking” and drink poisoning incidents, particularly in clubs and nightspots in urban and tourist areas. There have been reports of sexual assaults and drink spiking in Bali, Lombok, and the Gili Islands. Make sure drinks are prepared in your sight and be careful about accepting drinks from strangers at clubs and parties or leaving drinks unattended. Tourists have also been robbed after taking visitors to their hotel rooms, and in some cases have found that their drinks were spiked. There have also been deaths and serious illnesses caused by drinking alcoholic drinks contaminated with methanol. These cases have occurred in bars, shops, and hotels in popular tourist areas like Bali, Lombok, the Gili Islands, and Sumatra.
Sexual Assault: Women travelling alone may be subject to harassment and verbal abuse. Sexual assault, harassment, and rape occur. To minimize the risk, avoid travelling alone, especially at night; remain particularly vigilant in less populous areas; and be careful when dealing with strangers or recent acquaintances. Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers. Be wary of accepting snacks, beverages, gum, or cigarettes from new acquaintances. These items may contain drugs that could put you at risk of sexual assault and robbery. Local authorities may not respond adequately to reports of sexual violence and harassment. If you are the victim of a sexual assault, you should report it immediately to local authorities and to the U.S. Embassy or U.S. Consulate General.
Demonstrations occur frequently. They may take place in response to political or economic issues, on politically significant holidays, and during international events.
- Demonstrations can be unpredictable. Avoid areas around protests and demonstrations.
- Past demonstrations have turned violent.
- Check local media for updates and traffic advisories.
- Participating in demonstrations on a tourist visa can lead to deportation.
International Financial Scams: See the Department of State and the FBI pages for information.
Internet romance and financial scams occur in Indonesia. Scams are often initiated through Internet postings/profiles or by unsolicited emails and letters. Scammers almost always pose as U.S. citizens who have no one else to turn to for help. Common scams include:
- Romance/Online dating
- Money transfers
- Lucrative sales
- Gold purchase
- Contracts with promises of large commissions
- Grandparent/Relative targeting
- Free Trip/Luggage
- Inheritance notices
- Work permits/job offers
- Bank overpayments
Victims of Crime:
Sexual assault: U.S. citizen victims of sexual assault should seek prompt medical assistance, contact the Embassy or nearest Consulate, and call the local police at 112. For a criminal investigation to be initiated by the police, the victim must make a full statement to the local police, in person. Remember that local authorities are responsible for investigating and prosecuting crime. U.S. citizen victims of sexual assault may choose to be accompanied by a translator.
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
- Help you find appropriate medical care
- Assist you in reporting a crime to the police
- Contact relatives or friends with your written consent
- Explain the local criminal justice process in general terms
- Provide a list of local attorneys
- Provide our information on victim’s compensation programs in the U.S.
- Provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical support in cases of destitution. Follow this link for more information
- Help you find accommodation and arrange flights home
- Replace a stolen or lost passport
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence are encouraged to contact the Embassy for assistance.
Tourism: The tourism and recreational activity industries are unevenly regulated, and safety inspections for equipment and facilities do not commonly occur. Hazardous areas/activities are not always identified with appropriate signage, and staff may not be trained or certified either by the host government or by recognized authorities in the field. Water sports, especially diving, can be hazardous in Indonesia with operators lightly regulated and hyperbaric chambers available only in Bali and Ambon. Traffic is hazardous in Indonesia and U.S. citizens are frequently injured while riding rented motorbikes. Wearing a helmet is required by law. In the event of an injury, appropriate medical treatment is typically available only in/near major cities, and only basic stabilization may be available. Serious injuries require medical evacuation to another country. First responders are generally unable to provide urgent medical treatment or to access areas outside of major cities. Boat and ferry incidents are frequent; vessels rarely carry appropriate sizes and numbers of safety vests; passengers are encouraged to bring their own. U.S. citizens are strongly encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage ( http://travel.state.gov/content/passports/en/go/health/insurance-providers.html ).
Please note: The U.S. Embassy and Consulates do not pay the medical expenses of private U.S. citizens in Indonesia. It is the traveler’s responsibility to ensure adequate medical insurance coverage or funds for medical expenses.
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to Indonesian laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Criminal cases can take months or even years to resolve, and suspects can be held without charges for up to 60 days, and in many cases longer. Indonesia‘s revised criminal code, which takes effect January 2026, includes penalties for defamation, blasphemy, cohabitation, and sex outside of marriage. Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to stay up-to-date.
If you are convicted of possession, use, or trafficking of illegal drugs in Indonesia, you may be subject to heavy fines, long jail sentences, and even the death penalty. Some prescription medications that are available in the United States are illegal in Indonesia. Some drugs used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are illegal in Indonesia. Marijuana, Cannabis, hash, “edibles,” and products containing CBD or THC remain illegal in Indonesia, including for medicinal purposes. A medical prescription does not make it legal. If you take such products to Indonesia or purchase or use them in Indonesia, you can be arrested and face imprisonment, fines, deportation, or the death penalty. Illegal drug convictions often result in lengthy prison sentences, even at the simple possession level. Indonesian prison conditions are harsh and do not meet U.S. standards. Many prisons are overcrowded and provide minimal services. The costs of basic services, including healthcare, often must be borne by the prisoner.
Individuals establishing a business or practicing a profession that requires additional permits or licensing should seek information from the competent local authorities prior to practicing or operating a business.
Furthermore, some laws are also prosecutable in the United States regardless of local law. For examples, see our website on crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website.
Arrest Notification: If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy immediately. See our webpage for further information.
Counterfeit and Pirated Goods: Although counterfeit and pirated goods are prevalent in many countries, they may still be illegal according to local laws. You may also pay fines or have to give them up if you bring them back to the United States. See the U.S. Department of Justice website for more information.
Faith-Based Travelers: See the following webpages for details:
- Faith-Based Travel Information
- nternational Religious Freedom Report – see country reports
- Human Rights Report – see country reports
- Hajj Fact Sheet for Travelers
- Best Practices for Volunteering Abroad
LGBTQI+ Travelers: LGBTQI+ status or conduct is not illegal, but local authorities sometimes take legal action against, or tolerate harassment of people engaging in LGBTQI+ relationships or openly expressing LGBTQI+ identity. Some local governments have passed laws criminalizing LGBTQI+ relationships. Same-sex marriages or civil unions recognized as valid in other countries are not legally recognized in Indonesia. The Indonesian Parliament revised the criminal code to include penalties for cohabitation and sex outside of marriage. These revisions, however, will not come into force until January 2026, and how they will be implemented is unclear.
See our LGBTQI+ Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details .
Sharia Law: Sharia law is enforced in Aceh province and may exist unofficially or through local legislation in other areas. The law is intended for Muslims and should not apply to non-Muslims or foreign visitors. You should be respectful of local traditions, mindful of social norms, and seek guidance from local police if confronted by Sharia authorities.
Earthquakes and Tsunamis: There are approximately 4,000 earthquakes per year in Indonesia, or more than 10 per day on average. While most earthquakes are mild, some cause significant destruction and can trigger tsunamis. Tsunami warning systems may not be operable, or reports of tremors and tsunamis may be delayed. Local construction standards are lower than in the United States, and many structures including hotels and malls are prone to damage or collapse in an earthquake. Access to disaster-affected areas is often difficult and assistance from the U.S. Embassy may be limited.
If a major earthquake or landslide occurs close to shore, you should follow the instructions of local authorities, bearing in mind that a tsunami could arrive within minutes. The Indonesia Tsunami Early Warning Centre issues tsunami warnings when a potential tsunami with significant impact is imminent or expected.
Volcanoes: There are 127 active volcanoes in Indonesia. Eruptions frequently cause travel delays, displace local populations, and disrupt economic activities.
Environmental Quality: Air quality in Indonesia’s major cities can range from "unhealthy for sensitive groups" to "unhealthy." Current air quality data for Jakarta can be found on the Embassy’s Air Quality page. Tap water is not potable throughout Indonesia and should not be consumed.
Mountain Hiking: When hiking in mountainous areas, obtain current information on local conditions, travel with a reputable guide, have overseas medical insurance, and carry a local mobile phone. Never go hiking or climbing alone. Particularly dangerous trails may not be clearly labeled as such. Hikers on Puncak Jaya in Papua should have realistic primary and backup plans for climbing down the mountain. Tour operators have abandoned climbers. Taking shortcuts through private property is considered trespassing and is not a safe or legal alternative to a proper plan. If possible, ensure your hiking plans are registered and known to local authorities and/or tourism operators, as this helps identify your presence in these areas in the event of an emergency.
Dual Nationality: Indonesian law does not recognize dual nationality for adults over 18 years of age. U.S. citizens who are also Indonesian nationals may be required to renounce their Indonesian citizenship and may also be deported. Please visit our Dual Nationality page .
Travelers with Disabilities: Persons with disabilities will face severe difficulties in Indonesia as most public places and transportation facilities do not accommodate disabled people. The law in Indonesia prohibits discrimination against persons with mental and physical disabilities, but the law is seldom enforced. Social acceptance of persons with disabilities in public is not as prevalent as in the United States. Expect accessibility to be extremely limited in public transportation, lodging, communication/information, and general infrastructure.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: Women traveling alone may be subject to harassment and verbal abuse. Sexual assault, harassment, and rape occur. To minimize the risk, avoid travelling alone, especially at night; remain particularly vigilant in less populous areas; and be careful when dealing with strangers or recent acquaintances. Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers. Be wary of accepting snacks, beverages, gum, or cigarettes from new acquaintances. These items may contain drugs that could put you at risk of sexual assault and robbery. While domestic violence is illegal in Indonesia, these laws are rarely enforced. Local authorities may not respond adequately to reports of sexual violence and harassment. If you are the victim of a sexual assault, you should report it immediately to local authorities and to the U.S. Embassy or U.S. Consulate General and seek medical attention. See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
The Government of Indonesia requires all non-Indonesian citizens entering the country to be fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
Medical Care: For emergency services in Indonesia dial 112.
Sanitation and health care conditions in Indonesia are far below U.S. standards. Routine medical care is available in all major cities, although most expatriates leave the country for all but the most basic medical procedures. Physicians and hospitals often expect payment or sizable deposits before providing medical care, even in emergency and/or life-threatening situations. See our Embassy's website for a list of English-speaking doctors and hospitals, but keep in mind that even in large cities the quality of English-speaking medical personnel will vary and there are often communication difficulties. In remote areas there may be no English-speaking medical personnel. Psychological and psychiatric services are limited, even in the larger cities, with hospital-based care only available through government institutions.
Ambulance services are not widely available, and training and availability of emergency responders may be below U.S. standards. Ambulances are not staffed with trained paramedics and often have little or no medical equipment. Injured or seriously ill travelers may prefer to take a taxi or private vehicle to the nearest major hospital rather than wait for an ambulance.
We do not pay medical bills. Be aware that U.S. Medicare/Medicaid does not apply overseas. Most hospitals and doctors overseas do not accept U.S. health insurance.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept cash payments. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage. Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information on type of insurance you should consider before you travel overseas.
We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation, which can exceed over $100,000 per person.
Always carry your prescription medication in original packaging, along with your doctor’s prescription. Be aware that Indonesian authorities may consider some prescription drugs as illegal narcotics. The Indonesian government does not publish a list of which pharmaceuticals are considered contraband, and these decisions may be arbitrary.
U.S. citizens are advised against mailing or shipping by courier any medications to Indonesia. Indonesian authorities pay close attention to packages containing pharmaceuticals and may detain or arrest recipients of both prescription and over the counter medications. Even if a medication is legal or has been prescribed in the United States, it may be considered an illegal narcotic in Indonesia. U.S. citizens are advised to only hand carry prescription medications into the country, in the original packaging with a copy of any prescription. The U.S. Embassy and Consulates cannot assist you with the importation and/or release of medications.
Marijuana, Cannabis, hash, “edibles,” and products containing CBD or THC remain illegal in Indonesia, including for medicinal purposes. A medical prescription does not make it legal.
Local pharmacies carry a range of products of variable quality, availability, and cost. Counterfeit pharmaceuticals are a significant risk; patronize only reputable pharmacies. Malaria, dengue, Japanese encephalitis, and Zika virus are mosquito borne diseases in Indonesia. Prevention of mosquito bites is strongly encouraged; malaria preventive medication is needed in some areas. Pregnant women should be aware that Indonesia is a CDC Zika risk area and that Zika can be spread by mosquitos as well as sexual contact . Diarrheal diseases are very common throughout Indonesia and food and water precautions are recommended. Rabies is prevalent in animals and animal contact should be avoided.
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Further health information:
- World Health Organization
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Air Quality: Visit AirNow Department of State for information on air quality at U.S. Embassies and Consulates. See the OPTIONAL stock language below for additional suggestions.
The U.S. Embassy maintains a list of doctors and hospitals. We do not endorse or recommend any specific medical provider or clinic.
Medical Tourism and Elective Surgery
- Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for information on Medical Tourism, the risks of medical tourism, and what you can do to prepare before traveling to Indonesia.
- We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation in the event of unforeseen medical complications.
- Your legal options in case of malpractice are very limited in Indonesia.
Pharmaceuticals
- Exercise caution when purchasing medication overseas. Pharmaceuticals, both over the counter and requiring prescription in the United States, are often readily available for purchase with little controls. Counterfeit medication is common and may prove to be ineffective, the wrong strength, or contain dangerous ingredients. Medication should be purchased in consultation with a medical professional and from reputable establishments.
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Food and Drug Administration are responsible for rules governing the transport of medication back to the United States. Medication purchased abroad must meet their requirements to be legally brought back into the United States. Medication should be for personal use and must be approved for usage in the United States. Please visit the U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Food and Drug Administration websites for more information.
Water Quality
- Tap water is not potable. Bottled water and beverages are generally safe, although you should be aware that many restaurants and hotels serve tap water unless bottled water is specifically requested. Be aware that ice for drinks may be made using tap water.
Adventure Travel
- Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information about Adventure Travel .
General Health Language
The following diseases are prevalent:
- Tuberculosis
- Chikungunya
- Use the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended mosquito repellents and sleep under insecticide-impregnated mosquito nets. Chemoprophylaxis is recommended for all travelers even for short stays.
- Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information about Resources for Travelers regarding specific issues in Indonesia.
Air Quality
- Air pollution is a significant problem in several major cities in Indonesia. Consider the impact smog and heavy particulate pollution may have on you and consult your doctor before traveling if necessary. People at the greatest risk from particle pollution exposure include:
- Infants, children, and teens
- People over 65 years of age
- People with lung disease such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema
- People with heart disease or diabetes
- People who work or are active outdoors
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety: Traffic in Indonesia is hazardous, congested, and undisciplined. Traffic signals are frequently ignored and often in disrepair. Motor vehicles share the roads with other forms of transportation such as pedicabs and pushcarts. Buses and trucks are often dangerously overloaded and travel at high speeds. Accidents between a car and a motorcycle are viewed as the fault of the driver of the car. Consider these risks before driving your own vehicle, especially if you are unaccustomed to Indonesian road conditions. When an accident results in personal injury, Indonesian law requires both drivers to await the arrival of a police officer to report the accident.
Public Transportation: Air, ferry, and road accidents that result in fatalities, injuries, and significant damage are common. While all forms of transportation are regulated in Indonesia, oversight is spotty, maintenance may not be properly performed, and rescue and emergency capacity are limited. Indonesia has experienced several fatal plane crashes and non-fatal runway overruns in recent years. Also in recent years, several ferry accidents and a train collision resulted in dozens of fatalities and even more injuries because of over-crowding and unsafe conditions.
See our Road Safety page for more information. Also, visit Indonesia's national tourist office online for road safety information.
Aviation Safety Oversight: The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed the government of Indonesia’s Civil Aviation Authority as being in compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of Indonesia’s air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA’s safety assessment page .
Since 2014, several private pilots have inadvertently crossed into Indonesian airspace and have been detained and paid heavy fines. If you intend to fly on private aircraft through Indonesian airspace, get clearances from Indonesian aviation authorities before you depart.
Maritime Safety and Security: Inter-island travel by boat or ferry can be dangerous: storms can appear quickly, vessels may be over-crowded and lack basic safety equipment, and safety standards vary. Ferries have sunk, resulting in loss of life. The Indonesian Search and Rescue Agency records boat and ferry accidents resulting in injuries and deaths yearly. Boats and ferries used in tourism or general transportation frequently break down, stranding passengers or capsizing; not all boats are equipped with adequate life vests. Make sure you are satisfied with safety equipment and life jackets before travelling.
Piracy: Maritime piracy and other related crimes in and around Indonesian waters continue. Recent reports include thefts of valuables or cargo from boats that are in port and out at sea. Before traveling by sea, especially in the Strait of Malacca between Riau Province and Singapore, and in the waters north of Sulawesi and Kalimantan, review the current security situation with local authorities. Be vigilant, reduce opportunities for theft, establish secure areas on board, and report all incidents to the coastal and flag state authorities.
Maritime Travel: Mariners planning travel to Indonesia should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts on the Maritime Administration website . Information may also be posted to the websites of the U.S. Coast Guard and the National Geospace Intelligence Agency (select “broadcast warnings”).
In recent years, private vessels have inadvertently anchored in Indonesian waters, especially near Singapore, and have been detained and paid heavy fines.
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Indonesia . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
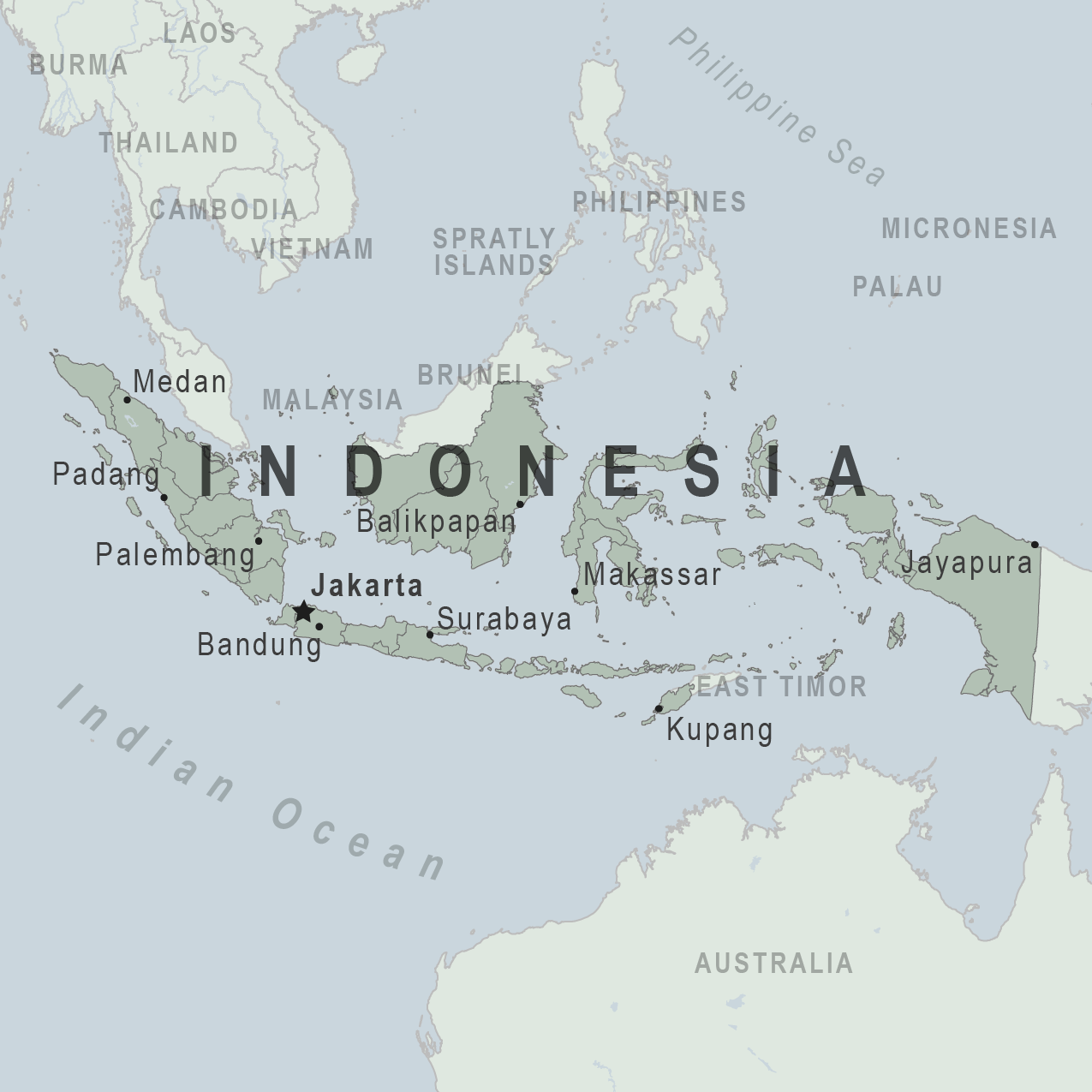
Assistance for u.s. citizens, indonesia map, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Make two copies of all of your travel documents in case of emergency, and leave one with a trusted friend or relative.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Learn more

Information on how to stay safe and healthy abroad. About us.
- Destinations
- Asia (East)
- Asia (Central)
- Australasia & Pacific
- Central America
- Europe & Russia
- Middle East
- North America
- South America & Antarctica
Indonesia (Asia)
Advice for all destinations, vaccinations and malaria risk.
Review both the Vaccination and Malaria sections on this page to find out if you may need vaccines and/or a malaria risk assessment before you travel to this country.
If you think you require vaccines and/or malaria risk assessment, you should make an appointment with a travel health professional:
- How to make an appointment with a travel health professional
A travel health risk assessment is also advisable for some people, even when vaccines or malaria tablets are not required.
- Do I need a travel health risk assessment?
Risk prevention advice
Many of the health risks experienced by travellers cannot be prevented by vaccines and other measures need to be taken.
Always make sure you understand the wider risks at your destination and take precautions, including:
- food and water safety
- accident prevention
- avoiding insect bites
- preventing and treating animal bites
- respiratory hygiene
- hand hygiene
Our advice section gives detailed information on minimising specific health risks abroad:
- Travel Health Advice A-Z
Other health considerations
Make sure you have travel insurance before travel to cover healthcare abroad.
Find out if there are any restrictions you need to consider if you are travelling with medicines .
Know how to access healthcare at your destination: see the GOV.UK English speaking doctors and medical facilities: worldwide list
If you feel unwell on your return home from travelling abroad, always seek advice from a healthcare professional and let them know your travel history.
Vaccinations
- Confirm primary courses and boosters are up to date as recommended for life in Britain - including for example, seasonal flu vaccine (if indicated), MMR , vaccines required for occupational risk of exposure, lifestyle risks and underlying medical conditions.
- Courses or boosters usually advised: Diphtheria; Poliomyelitis; Tetanus.
- Other vaccines to consider: Hepatitis A; Rabies; Typhoid.
- Selectively advised vaccines - only for those individuals at highest risk: Cholera; Hepatitis B; Japanese Encephalitis.
Yellow fever vaccination certificate required for travellers aged 9 months or over arriving from countries with risk of yellow fever transmission .
Notes on the diseases mentioned above
Risk is higher during floods and after natural disasters, in areas with very poor sanitation and lack of clean drinking water.
- Diphtheria : spread person to person through respiratory droplets. Risk is higher if mixing with locals in poor, overcrowded living conditions.
Risk is higher where personal hygiene and sanitation is poor.
Risk is higher for long stays, frequent travel and for children (exposed through cuts and scratches), those who may require medical treatment during travel.
- Japanese Encephalitis : spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. This mosquito breeds in rice paddies and mainly bites between dusk and dawn. Risk is highest for long stay travellers to rural areas, particularly if unable to avoid mosquito bites.
- Tetanus : spread through contamination of cuts, burns and wounds with tetanus spores. Spores are found in soil worldwide. A total of 5 doses of tetanus vaccine are recommended for life in the UK. Boosters are usually recommended in a country or situation where the correct treatment of an injury may not be readily available.
- Typhoid : spread mainly through consumption of contaminated food and drink. Risk is higher where access to adequate sanitation and safe water is limited.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease transmitted by mosquitoes.You cannot be vaccinated against malaria.
Malaria precautions
- Malaria risk is present throughout the year in most areas. Risk is high on the island of Sumba and on all islands and in all areas of the provinces of Papua and West Papua.
- In the following areas the risk is not high enough to warrant antimalarial tablets for most travellers, however, it may be considered for certain groups who may be at higher risk (see below under Low risk with additional advice ): Mentawai islands, Lahat and Pesawaran regencies on the island of Sumatra, the whole of Kalimantan, West Lombok regency of the island of Lombok, all islands in East Nusa Tenggara province including Komodo (but not the island of Sumba, see above), West Sulawesi province on the island of Sulawesi and all islands in Maluku and North Maluku provinces.
- There is low to no risk in Jakarta municipality, the islands of Java, Bali and the provinces of Sulawesi and surrounding islands (except West Sulawesi province, see above).
- Malaria precautions : avoid mosquito bites by covering up with clothing such as long sleeves and long trousers especially after sunset, using insect repellents on exposed skin and, when necessary, sleeping under a mosquito net.
- Check with your doctor or nurse about suitable antimalarial tablets.
- See malaria map – additional information can be found by clicking on the Regional Information icon below the map.
- High risk areas: atovaquone/proguanil OR doxycycline OR mefloquine is usually advised.
- Low risk with additional advice: antimalarial tablets are not usually recommended, however, they can be considered for certain travellers who may be at higher risk e.g. longer stay in rural areas, visiting friends or relatives, those with medical conditions, immunosuppression or those without a spleen. Atovaquone/proguanil OR doxycycline OR mefloquine is advised for those at risk.
- Low to no risk: antimalarial tablets are not usually advised.
- If you have been travelling in a malarious area and develop a fever seek medical attention promptly. Remember malaria can develop even up to one year after exposure.
- If travelling to an area remote from medical facilities, carrying standby emergency treatment for malaria may be considered.
Other Health Risks
Altitude and travel, dengue fever, schistosomiasis.
There is a risk of exposure to coronavirus (COVID-19) in this country.
Please be aware that the risk of COVID-19 in this country may change at short notice and also consider your risk of exposure in any transit countries and from travelling itself.
- The 'News' section on this page will advise if significant case increases or outbreaks have occurred in this country.
Prior to travel, you should:
- Check the latest government guidance on the FCDO Foreign travel advice and country specific pages for travel to this country and the rules for entering the UK on return.
- Ensure you are up to date with UK recommendations on COVID-19 vaccination.
- You can check this in the FAQ's.
- If you are at increased risk of severe COVID-19 you should carefully consider your travel plans and consider seeking medical advice prior to making any decisions.
For further information, see Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and COVID-19: Health Considerations for Travel pages.
Polio Vaccination Exit Recommendations
If you are visiting this country for longer than 4 weeks, you may be advised to have a booster dose of a polio-containing vaccine if you have not had one in the past 12 months. You should carry proof of having had this vaccination. Please speak to a travel health professional to discuss.
Zika Virus Infection
This country has been categorised as having a risk of Zika (ZIKV) virus transmission.
ZIKV is mainly spread through mosquito bites. The mosquito responsible most commonly bites during daylight hours and is common in towns and cities.
The illness is usually mild but infection during pregnancy may lead to babies being born with birth defects. There is no vaccine currently available against ZIKV.
Advice for All Travellers
You should practice strict mosquito bite avoidance at all times. Do not travel without adequate travel insurance . Seek pre-travel health advice from a travel health professional 6 to 8 weeks in advance of travel.
Additional recommendations for pregnant travellers or those planning pregnancy
If you are planning pregnancy in the very near future you should consider whether you should avoid travel to this country.
- contact your GP, obstetrician or midwife for further advice, even if you have not been unwell or had any symptoms of ZIKV infection
- use barrier methods of contraception during and after travel and for the duration of your pregnancy, even in you have not been unwell or had any symptoms of ZIKV infection
- If you develop symptoms of ZIKV infection, it is recommended that you avoid becoming pregnant for a further 2 months following your recovery
- 2 months afterwards if you are female
- 3 months afterwards if you are male or if both partners travelled
These measures reduce the chance of sexual transmission of ZIKV and/or the risk of ZIKV infection in pregnancy.
For further information, see Zika virus infection page.
- 23 May 2024 - Advice on Dengue Fever if Travelling Abroad
- 70 additional items in the news archive for this country
back to top
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Indonesia Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
Be aware of current health issues in Indonesia. Learn how to protect yourself.
Level 2 Practice Enhanced Precautions
- Global Polio May 23, 2024 Some international destinations have circulating poliovirus. Before any international travel, make sure you are up to date on your polio vaccines. Destination List: Afghanistan, Algeria, Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Guinea, Indonesia, Kenya, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Pakistan, Republic of the Congo, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, Sudan, Tanzania, including Zanzibar, Yemen, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Level 1 Practice Usual Precautions
- Updated Global Dengue June 25, 2024 Dengue is a year-round risk in many parts of the world, with outbreaks commonly occurring every 2–5 years. Travelers to risk areas should prevent mosquito bites. Destination List: Afghanistan, Argentina, Brazil, Burkina Faso, Cambodia, Colombia, Costa Rica, Curaçao, Ecuador, including the Galápagos Islands, Ethiopia, Fiji, French Guiana (France), Guadeloupe, Guatemala, Guyana, Honduras, Indonesia, Laos, Mali, Martinique (France), Mauritius, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Samoa, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Uruguay
- Global Measles May 28, 2024 Many international destinations are reporting increased numbers of cases of measles. Destination List: Afghanistan, Angola, Armenia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, India, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Lebanon, Liberia, Libya, Malaysia, Mauritania, Nepal, Niger, Nigeria, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Republic of South Sudan, Republic of the Congo, Romania, Russia, Senegal, Somalia, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Syria, Tajikistan, Togo, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Yemen, Zambia
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
Chikungunya
There has been evidence of chikungunya virus transmission in Indonesia within the last 5 years. Chikungunya vaccination may be considered for the following travelers:
- People aged 65 years or older, especially those with underlying medical conditions, who may spend at least 2 weeks (cumulative time) in indoor or outdoor areas where mosquitoes are present in Indonesia, OR
- People planning to stay in Indonesia for a cumulative period of 6 months or more
Chikungunya - CDC Yellow Book
Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Indonesia.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers of all ages traveling to Indonesia.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
Japanese Encephalitis
Recommended for travelers who
- Are moving to an area with Japanese encephalitis to live
- Spend long periods of time, such as a month or more, in areas with Japanese encephalitis
- Frequently travel to areas with Japanese encephalitis
Consider vaccination for travelers
- Spending less than a month in areas with Japanese encephalitis but will be doing activities that increase risk of infection, such as visiting rural areas, hiking or camping, or staying in places without air conditioning, screens, or bed nets
- Going to areas with Japanese encephalitis who are uncertain of their activities or how long they will be there
Not recommended for travelers planning short-term travel to urban areas or travel to areas with no clear Japanese encephalitis season.
Japanese encephalitis - CDC Yellow Book
Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine for US Children
CDC recommends that travelers going to certain areas of Indonesia take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for Indonesia.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
In Indonesia poliovirus has been identified in the past year.
Travelers to Indonesia are at increased risk of exposure to poliovirus.
Vaccine recommendations : Adults traveling to Indonesia who received a complete polio vaccination series as children may receive a single lifetime booster dose of inactivated polio vaccine; travelers who are unvaccinated or not fully vaccinated should receive a complete polio vaccination series before travel. Children who are not fully vaccinated will be considered for an accelerated vaccination schedule .
Polio - CDC Yellow Book
Polio: For Travelers
Dogs infected with rabies are commonly found in Indonesia.
If rabies exposures occur while in Indonesia, rabies vaccines are typically available throughout most of the country.
Rabies pre-exposure vaccination considerations include whether travelers 1) will be performing occupational or recreational activities that increase risk for exposure to potentially rabid animals and 2) might have difficulty getting prompt access to safe post-exposure prophylaxis.
Please consult with a healthcare provider to determine whether you should receive pre-exposure vaccination before travel.
For more information, see country rabies status assessments .
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
Yellow Fever
Required for travelers ≥9 months old arriving from countries with risk for YF virus transmission. 1
Yellow Fever - CDC Yellow Book
- Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
- Avoid floodwater
Clinical Guidance
Schistosomiasis
- Wading, swimming, bathing, or washing in contaminated freshwater streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, or untreated pools.
Avoid bug bites
- Mosquito bite
- Avoid Bug Bites
- Mosquito bite
- An infected pregnant woman can spread it to her unborn baby
Airborne & droplet
Avian/bird flu.
- Being around, touching, or working with infected poultry, such as visiting poultry farms or live-animal markets
- Avoid domestic and wild poultry
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Indonesia, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH)
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Indonesia. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Indonesia include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Schistosomiasis, a parasitic infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Indonesia. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Indonesia’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in some parts of Indonesia. If you are going to a risk area, fill your malaria prescription before you leave, and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Indonesia may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Indonesia, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
For information traffic safety and road conditions in Indonesia, see Travel and Transportation on US Department of State's country-specific information for Indonesia .
Traffic flows on the left side of the road in Indonesia.
- Always pay close attention to the flow of traffic, especially when crossing the street.
- LOOK RIGHT for approaching traffic.
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Indonesia for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Update Traveling to Indonesia - Indonesia
Update traveling to indonesia.
Foreign tourists are allowed to travel to Indonesia with a Visa on Arrival (VOA) and a visa applied at the Indonesian representatives (KBRI).
Updated: 15 June 2023
Travel advice : Reisadvies Indonesië | Ministerie van Buitenlandse Zaken (nederlandwereldwijd.nl)
Travel Update: Indonesia lifts COVID-19 Restrictions
Since June 9 2023, it is not required anymore to show proof of Covid-19 vaccination to enter or to travel in Indonesia. For more information: here
Consular Services
The consular section is fully open.
Schedule your consular appointment
We are open for Civic Integration Exams. Schedule your Civic Integration Exams appointment
For any questions and advice, please send an email
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Pinpoint Travel Health

Foreign Travel Advice Indonesia
Table of Contents
Warning: FCDO advises against all travel to certain areas of Indonesia.

- Warnings and Insurance
- Entry Requirements
- Safety and Security
- Regional Risks
- Getting Help
Warnings and Insurance:
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) offers advice on travel risks to assist British nationals in making informed decisions. Learn more about FCDO travel advice.
ENTER YOUR DESTINATION FOR YOUR CUSTOM TRAVEL BRIEF
Areas Where FCDO Advises Against Travel:
Mount Marapi, Western Sumatra FCDO advises against all travel to within 3 km of the crater of Mount Marapi in West Sumatra.
Mount Sinabung Area, Karo Regency FCDO advises against all travel within 5 km of the Mount Sinabung crater in Karo Regency, North Sumatra.
Mount Semeru Area, Lumajang Regency FCDO advises against all travel within 5 km of the crater of Mount Semeru in Lumajang Regency, East Java. FCDO also advises against all travel to the southeast area of Mount Semeru along the Besuk Kobokan river (approximately 13 km from the crater). Maintain a distance of at least 500 m from the Besuk Kobokan riverbank.
Find out more about why FCDO advises against travel.
Before You Travel: No travel can be guaranteed safe. Read all the advice in this guide, as well as support for British nationals abroad , which includes:
- Advice on preparing for travel abroad and reducing risks
- Information for women, LGBT, and disabled travelers
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram. You can also sign up to receive email notifications when this advice is updated.
Travel Insurance: If you choose to travel, research your destinations and get appropriate travel insurance. Insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities, and potential expenses in an emergency.
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office ( FCDO ) provides advice about risks of travel to help British nationals make informed decisions. Find out more about FCDO travel advice .
Areas where FCDO advises against travel
Your travel insurance could be invalidated if you travel against FCDO advice. Consular support is also severely limited where FCDO advises against travel.
- Pattani province
FCDO advises against all but essential travel to Pattani province.
- Yala province
FCDO advises against all but essential travel to Yala province.
- Narathiwat province
FCDO advises against all but essential travel to Narathiwat province.
Southern Songkhla province
FCDO advises against all but essential travel to Southern Songkhla province, except for:
- the areas north of and including the A43 road between Hat Yai and Sakom
- the areas north-west of the train line which runs between Hat Yai and Padang Besar
Hat Yai to Padang Besar train line
FCDO advises against all but essential travel on the Hat Yai to Padang Besar train line.
Find out more about why FCDO advises against travel .
Before you travel
No travel can be guaranteed safe. Read all the advice in this guide as well as support for British nationals abroad which includes:
- advice on preparing for travel abroad and reducing risks
- information for women, LGBT+ and disabled travellers
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this advice is updated.
Travel insurance
If you choose to travel, research your destinations and get appropriate travel insurance . Insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities and expenses in an emergency.
This advice reflects the UK government’s understanding of current rules for people travelling on a full ‘British citizen’ passport from the UK, for the most common types of travel.
The authorities in Thailand set and enforce entry rules. If you’re not sure how these requirements apply to you, contact the Royal Thai Embassy in the UK.
COVID-19 rules
Countries may restrict travel or bring in rules at short notice. Check with your travel company or airline for changes.
If you test positive for COVID-19, you may need to stay where you are until you test negative. You may also need to seek treatment there.
You should also read TravelHealthPro’s general COVID-19 advice for travellers .
Travel to Thailand
If you are visiting Thailand and then travelling to a country that requires an RT-PCR test for entry, you will need to buy medical insurance that covers COVID-19 treatment before you arrive in Thailand.
Passport validity requirements
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months from when you enter Thailand.
You could be refused entry to Thailand if your passport is damaged or has pages missing.
If you’re a dual national, to avoid problems at immigration, you must leave Thailand on the same passport you used to enter.
If you need to renew or apply for a new British passport, see overseas British passport applications .
Visa requirements
British passport holders arriving by air or land can enter Thailand without a visa (visa exemption) for the purpose of tourism for a period not exceeding 30 days.
If you intend to stay longer (for work, study or other reasons) you need a visa before you travel.
For more information on visas or entry requirements, contact the Royal Thai Embassy or local Immigration Office.
Overstaying your visa
If you stay beyond the period of your visa, you will be fined 500 Thai baht a day up to a maximum of 20,000 baht. You risk being:
- held in detention
- deported at your own expense
- banned from re-entering Thailand for up to 10 years
Conditions in detention centres can be harsh.
Vaccination requirements (other than COVID-19)
At least 8 weeks before your trip, check the vaccinations and certificates you need on TravelHealthPro .
Depending on your circumstances, this may include a yellow fever vaccination certificate.
Customs rules
There are strict rules about goods that can be brought into and taken out of Thailand . You must declare anything that may be prohibited or subject to tax or duty.
Importing cigarettes
It is illegal to import more than 200 cigarettes per person into Thailand. This is enforced at customs on arrival. If you go over the limit, you could be fined 10 times the value. Your cigarettes will likely be confiscated.
You should also read FCDO’s overall travel advice and regional risks advice .
There is a high threat of terrorist attack globally affecting UK interests and British nationals, including from groups and individuals who view the UK and British nationals as targets. Stay aware of your surroundings at all times.
UK Counter Terrorism Policing has information and advice on staying safe abroad and what to do in the event of a terrorist attack. Find out how to reduce your risk from terrorism while abroad .
Terrorism in Thailand
Terrorists are very likely to try to carry out attacks in Thailand.
FCDO advises against all but essential travel to the following due to regular terrorist attacks:
- Southern Songkhla province, except for the areas north of and including the A43 road between Hat Yai and Sakom; and the areas north-west of the train line which runs between Hat Yai and Padang Besar
- Hat Yai to Padang Besar train line, which was attacked in 2022
Martial law is in place in most areas in these provinces, which means security forces have greater security enforcement and investigative powers.
However, terrorist attacks could take place anywhere in Thailand. Attacks could be indiscriminate, including in places visited by foreigners. Stay aware of your surroundings, keep up to date with local media reports and follow the advice of local authorities.
Targets might include:
- security forces
- government offices
- shops and supermarkets
- transport infrastructure
Recent attacks include:
- in 2019, there were a number of small explosions in Bangkok Satun City, and Phatthalung province in the south of Thailand
- in 2018, there was a series of small explosions on Samila beach in Songkhla City
Political situation
The political situation can be unpredictable and has led to periods of civil and political unrest. Avoid protests, political gatherings, demonstrations and marches.
Personal ID
Police may ask to check your passport. If you do not have it with you, you could be arrested.
Reporting a crime
Report any crime to the Thai police before you leave Thailand. Your case may not be investigated if you try to report it later.
Local authorities, including the police, may pass details of a crime, including photos, to the media without a person’s consent.

Protecting your belongings
You should:
- be aware of pickpockets and bag snatchers, especially thieves on motorbikes
- take care when travelling in open transport like tut-tuts
- keep valuables secure and out of sight
- avoid sleeping on buses and trains – people have had items taken from bags while asleep
Keep hold of your passport. Don’t hand it over as a guarantee, for example to motorcycle or jet ski rental businesses. Companies may hold on to passports against claimed damage.
Violent crime
Violent crime, including gun crime, rarely involves tourists. However several foreign nationals were victims of gun violence in Bangkok in 2018. Take care when travelling in unfamiliar areas and avoid walking through isolated areas alone, especially at night.
Sexual assault
Violent sexual assaults and unprovoked attacks can happen in tourist areas across Thailand. Attacks are most common during full moon parties or similar events, and near bars late at night.
Drink spiking
Drink spiking and drug-assisted sexual assault does happen in tourist areas around Thailand, with male and female victims. Do not leave your drinks unattended or accept drinks from strangers.
Be drink aware
Drinks served in bars overseas are often stronger than those in the UK. Alcohol and drugs can make you less alert and less aware of your environment. This can make you more vulnerable to accidents, injuries, robbery and assaults.
Be aware of credit card fraud. Do not lose sight of your card during transactions. There have been incidents of ATM skimming. Use an ATM in a bank and always protect your PIN.
Be wary of job offers that appear too good to be true. People have arrived in Thailand and been illegally transported to neighbouring countries on the promise of high-paying jobs, which turn out to be scams. When you re-enter Thailand you may then be detained while your immigration status is validated.
There have been incidents of:
- passports confiscated by scammers
- victims being held in poor living conditions
- coercion into undertaking wider online scamming activity
- pressure to make large payments to be released from sham jobs
Detention facilities
Conditions in prisons and other detention facilities in Thailand are harsh, with limited access to healthcare. Detainees have died in custody.
Laws and cultural differences
You should be aware of differences between UK and Thai law and local customs.
The British Embassy in Bangkok has a video on what to be aware of when living or travelling in Thailand:
- Facebook – visiting Thailand video
- Twitter – visiting Thailand video
Criticising the Thai monarchy
Criticising the Thai monarchy (lèse-majesté) is illegal. The law can be interpreted broadly and carries a long jail sentence. British and Thai journalists, human rights defenders, and members of the public have faced charges for raising concerns, making political comments, sharing articles online that could been seen as negative towards Thailand, or making accusations about individuals.
Posting images on social media
Posting images on social media of people drinking alcohol or wearing clothing considered inappropriate can be illegal. Both the person who uploaded the images and the people in them could be fined or imprisoned.
Smoking and e-cigarette bans
While cigarettes are common, you could be fined up to 5,000 Thai baht for smoking them in public. E-cigarettes are illegal. You could be fined or imprisoned for using them.
Illegal drugs and prison sentences
Thailand has strict laws against drug use, possession and trafficking. Possessing small quantities of illegal substances can lead to heavy fines or imprisonment. Possessing Class A drugs can lead to the death penalty.
Private recreational use of cannabis is legal if the Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) content is below 0.2% by weight. Cannabis use in public places is illegal. The Ministry of Public Health has made it legal to grow, use, distribute and sell cannabis products, but this has not been enshrined in law so some restrictions may remain. Check with the local authorities if you are unsure.
See more information on usage, and registration for distributing or selling cannabis, on PR Thai Government (Thai Ministry of Public Health) .
Some British nationals have suffered severe psychiatric problems because of drug use, sometimes leading to suicide.
While cannabis is legal in Thailand in certain circumstances, be aware of the next place you are travelling to, where it may be illegal. This includes residual amounts, for example in bags, clothing or blood.
Under UK law, cannabis remains a Class B drug, and it is illegal to take cannabis into the UK.
LGBT+ travellers
Thailand is generally a safe place for LGBT+ travellers.
Thailand has no legislation on same-sex marriage. Same-sex marriages are not legally recognised. Read more advice for LGBT+ travellers .
Wildlife, animal products and souvenirs
It’s illegal to buy, sell, kill or capture any protected wild animal or trade its parts without a license . Ivory trade is banned.
Buying property in Thailand
Buying property in Thailand is not straightforward. Make sure you understand local laws and consult a lawyer before making financial commitments. British people have been victims of property scams.
Outdoor activities
Elephant treks.
Elephant treks can be dangerous, especially if elephants are mistreated or not handled properly. Use a reliable, licensed tour guide. British nationals have been seriously injured and killed because handlers have lost control of the elephant.
Swimming safely
Take care when swimming off coastal areas, especially during monsoon season. People have drowned in strong riptides. You should:
- follow warning signs, especially red flags
- only swim from approved beaches, with flags
Jellyfish can swim close to the shore, particularly during the rainy season. Jellyfish stings can be fatal. Take local advice from hotel management and dive centres.
Take care when swimming, diving, kayaking or white water rafting in rivers or close to waterfalls, particularly in the rainy season. Currents can be extremely strong.
Diving schools and rescue service standards are not always as high as in the UK. Check the dive operator’s credentials and make sure you’re covered by your insurance.
If you’ve had no previous diving experience:
- ask your dive operator to explain what cover they offer before signing up
- check safety equipment is available on the boat
Check that they have appropriate plans in place for emergencies, including their ability to get assistance to evacuate divers to the nearest hyperbaric chamber.
Transport risks
Road traffic accidents.
Thailand has a high number of road traffic accidents, particularly with motorcycles. The World Health Organisation (WHO) ranks Thailand as one of the world’s deadliest countries for fatalities on motorcycles .
Licenses and permits
Apply for a Thai driving licence or, if you already hold a UK licence, an International Driving Permit .
If you drive a car or ride a motorcycle in Thailand without a valid licence, it could invalidate your travel insurance if you have an accident or injury.
Car and motorcycle hire
Motorcycles and scooters for hire in beach resorts are often unregistered and cannot be used legally on a public road. Before you hire a vehicle, make sure you’re covered by your travel insurance and check the small print of the lease agreement.
Do not hand over your passport as a guarantee against returning a motorcycle or scooter.
By law, you must wear a helmet when riding a motorcycle.
Lots of passenger boat services operate between the mainland and islands. Boats can sink or collide, which has led to fatalities, including of British nationals. Accidents are usually due to:
- overloading
- poor maintenance
- rough seas, particularly during monsoon season
Travellers with limited mobility
Wheelchair access is often limited across Thailand due to uneven paving, obstacles and a lack of facilities such as lifts and ramps. This includes public transport systems. Many taxis have limited storage space for wheelchairs.
See FCDO advice on disability and travelling abroad .
Extreme weather and natural disasters
Rainy season.
The rainy season is generally from May to October. In Koh Samui and the south east of Thailand it is from November to March. However, the rainy season has been more unpredictable recently.
Heavy storms cause disruption including flooding and landslides. Lakes, caves and waterfalls are particularly at risk of dangerous flash flooding.
Follow the Thai Meteorological Department for weather warnings.
Earthquakes
Earthquakes and tremors can happen in Northern Thailand.
Earthquake Track lists recent activity.
See the US Federal Emergency Management Agency for what to do in an earthquake.
You should also read FCDO’s overall travel advice and safety and security advice .
Cambodian border
Take extra care in border areas and follow the instructions of local authorities. The line of the international border near the Preah Vihear temple is disputed by Cambodia and Thailand. There are unexploded landmines in the border area. Stay on marked paths especially around Ta Krabey.
Stay alert to the local situation when travelling anywhere near to the border with Cambodia , and at land crossings between the 2 countries.
Laos border
Not all land border crossings into Laos are open to foreigners. You may need to get a Laos visa before you arrive to cross the border. Follow the instructions of local authorities and be vigilant in the border areas.
Myanmar border
The security situation in Myanmar is unpredictable and liable to change without notice. See travel advice for Myanmar .
Before you travel check that:
- your destination can provide the healthcare you may need
- you have appropriate travel insurance for local treatment or unexpected medical evacuation
This is particularly important if you have a health condition or are pregnant.
Emergency medical number
Dial 1669 and ask for an ambulance.
Contact your insurance or medical assistance company promptly if you’re referred to a medical facility for treatment.
Vaccinations and health risks
At least 8 weeks before your trip check:
- the latest information on vaccinations and health risks in TravelHealthPro’s Thailand guide
- where to get vaccines and whether you have to pay on the NHS travel vaccinations page
Health risks in Thailand include:
- dengue fever
See the ‘Other risks’ section of the TravelHealthPro Thailand guide for more on health risks .
To avoid mosquito-borne viruses, such as dengue fever and Zika virus, take steps to avoid being bitten by mosquitoes.
Air quality
There can be high levels of air pollution in large cities. This includes Bangkok and Chiang Mai, which are also affected by seasonal regional smoke haze from the burning of trees. The high pollution and particulate count sometimes reach dangerous levels. This may worsen bronchial, sinus or asthma conditions.
Check air quality levels for many cities on the World Air Quality Index website .
The legal status and regulation of some medicines prescribed or bought in the UK can be different in other countries.
Hospitals and pharmacies across Thailand will usually accept UK prescriptions. Brand name medication can often be more expensive than locally produced medication.
Medication sold on the street may not be genuine or may have been stolen. Taking medication without medical advice or a prescription can have serious health consequences.
Read best practice when travelling with medicines on TravelHealthPro . The NHS has information on whether you can take your medicine abroad .
Healthcare facilities in Thailand
FCDO has a list of English-speaking doctors in Thailand . All hospitals require guarantee of payment before treating patients. Make sure you have adequate health insurance.
Private hospitals in Thailand are of a high standard but can be expensive. Public hospitals and clinics do not always meet UK standards, particularly outside Bangkok.
COVID-19 healthcare in Thailand
Check the latest information on risk from COVID-19 risk for Thailand on TravelHealthPro .If you have severe symptoms, or any questions related to COVID-19, while in Thailand, call the Thai COVID-19 Hotline on 1422. There is more information on the PR Thai Government Facebook page .
Travel and mental health
Read FCDO guidance on travel and mental health . There is also mental health guidance on TravelHealthPro .
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office ( FCDO ) cannot provide tailored advice for individual trips. Read this travel advice and carry out your own research before deciding whether to travel.
Emergency services in Thailand
Telephone: 1669 (ambulance, fire, police)
Ambulance: hotline 1669
Fire: hotline 199
Police: hotline 191
Contact your travel provider and insurer
Contact your travel provider and your insurer if you are involved in a serious incident or emergency abroad. They will tell you if they can help and what you need to do.
Refunds and changes to travel
For refunds or changes to travel, contact your travel provider. You may also be able to make a claim through insurance. However, insurers usually require you to talk to your travel provider first.
Find out more about changing or cancelling travel plans , including:
- where to get advice if you are in a dispute with a provider
- how to access previous versions of travel advice to support a claim
Support from FCDO
FCDO has guidance on staying safe and what to do if you need help or support abroad, including:
- finding English-speaking lawyers , funeral directors and translators and interpreters in Thailand
- dealing with a death in Thailand
- being arrested in Thailand
- getting help if you’re a victim of crime
- what to do if you’re in hospital
- if you are affected by a crisis , such as a terrorist attack
Contacting FCDO
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this travel advice is updated.
Help abroad in an emergency
If you are abroad and you need emergency help from the UK government, contact the British Embassy Bangkok .
You can also contact FCDO online
FCDO in London
You can call FCDO in London if you need urgent help because something has happened to a friend or relative abroad.
Telephone: 020 7008 5000 (24 hours)
Find out about call charges
Risk information for British companies
The Overseas Business Risk service offers information and advice for British companies operating overseas on how to manage political, economic, and business security-related risks.
Destination Highlight

Labuan Bajo

Tanjung Kelayang

Subscribe and Get Free Travel E-Book
Thank you for subscribing to our travel guide newsletter. we know you will enjoy it, travel inspiration.

Wonderful.Indonesia
See the Destination
Travel Guide

InDOnesia CARE
The Ministry of Tourism and Creative Economy introduced InDOnesia CARE, a symbol of support for Indonesia’s strong effort in implementing the cleanliness, health, safety, and environment protocols across the tourism industry as mandatory precautions. All to assure travelers that InDOnesia CARE for your safety, health, hygiene and comfort.

Make sure to learn about all the immigration requirements that should be fulfilled before visiting Indonesia, including e-passport and e-visa.

General Information
Find everything you need to know about how to get here, what regulations that should be noted, and many other things vital in arranging your travel plan to Indonesia.

Visit our other website
This is the official website of the Ministry of Tourism, Republic of Indonesia. The contents listed on this website are intended for informational purposes rather than commercial. Any displayed sale is meant as a token of partnership and will always redirect you to our partners' sites.

Is it safe to travel to France? The latest advice
T he French government has raised its terror alert to the highest possible level, “emergency”, following the terror attack in Moscow that left more than 135 people dead.
French prime minister Gabriel Attal said the decision was taken “in light of the Islamic State’s claiming responsibility for the [Moscow] attack and the threats weighing on our country”.
France’s terror threat system has three levels. The highest level is announced if there is a terrorist attack in France or overseas, or if an attack on French soil is considered to be imminent.
France was already on high alert for potential terrorist attacks, with the Paris Olympics and Paralympics due to take place in the capital this summer.
The updated terror alert comes just days before the UK Easter school holidays, when thousands of British holidaymakers will travel across the Channel for a getaway.
What is the Foreign Office advice for France?
The UK Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office (FCDO) France advice, which was last updated on February 20, reads: “There is a high threat of terrorist attack globally affecting UK interests and British nationals, including from groups and individuals who view the UK and British nationals as targets. You should remain vigilant at all times.”
“Methods of attack have included knife attacks, shootings, bombings and vehicle attacks. Be vigilant in public places and follow the advice of local French authorities,” the FCDO adds.
The FCDO lists shopping centres, entertainment establishments, cultural events, public transport and places of worship as settings where “indiscriminate” terrorism attacks could take place.
Check the France FCDO page for the latest advice.
What happened in the Moscow terror attack?
On Friday, terrorists carried out an attack at the Crocus City Hall on the outskirts of Moscow, killing at least 137 and injuring 140.
Four men, all of whom are citizens of Tajikistan, have been formally charged with committing a group terrorist attack. The attack has been claimed by the Afghanistan-based Islamic State Khorasan Province (IS-K) group.
On March 7, the United States warned its citizens in Russia that extremists had “imminent plans to target large gatherings in Moscow” and specifically mentioned concert venues. It advised Americans to avoid large gatherings.
What should I do if I get caught up in a terrorist attack?
Britain’s counter-terrorism police gives advice on what to do in the event of an emergency . This includes to run to a place of safety: “This is better than trying to surrender or negotiate.” To hide: “It is better to hide than confront. Barricade yourself in, turn your phone to silent and use only when it is safe to do so.” And to tell: “Make sure you know the local emergency numbers in the country you are travelling to. For all EU countries call 112.”
Have there been recent terrorist attacks in France?
There have been a number of terrorist attacks in France over the past decade. In January 2015, eight cartoonists, two guests and two police officers were murdered at the offices of the satirical magazine Charlie Hebdo . The gunmen identified as belonging to al-Qaeda.
In November that year, in the deadliest terrorist attack in French history, 131 people were killed and 413 were injured in a series of shooting and grenade attacks at the Bataclan music venue, near the Stade de France and at several restaurants and bars across Paris. Islamic State claimed responsibility for the attacks.
In July 2016, 86 people were killed and 434 injured in Nice after a 19-tonne cargo truck was driven into crowds during Bastille Day celebrations on the Promenade des Anglais in Nice. Again Islamic State claimed responsibility.
What if I want to cancel my trip to France?
If you have booked a package holiday to France and want to cancel your trip for any reason, contact your tour operator and they might offer flexibility with alternative dates.
But bear in mind that, because the Foreign Office has not issued any advice against travel to France, there is no guarantee that you will receive a refund, nor will you be able to claim money back with your travel insurance company.
If you have booked flights and accommodation independently, and wish to cancel your holiday, contact your travel providers as soon as possible to see if you can rearrange your plans. Note, however, that given the circumstances, it is unlikely you will receive a full refund.
Sign up to the Front Page newsletter for free: Your essential guide to the day's agenda from The Telegraph - direct to your inbox seven days a week.

🙌 Awesome, you're subscribed!
Thanks for subscribing! Look out for your first newsletter in your inbox soon!
Get us in your inbox
Sign up to our newsletter for the latest and greatest from your city and beyond
By entering your email address you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy and consent to receive emails from Time Out about news, events, offers and partner promotions.
Awesome, you're subscribed!
The best things in life are free.
Sign up for our email to enjoy your city without spending a thing (as well as some options when you’re feeling flush).
Déjà vu! We already have this email. Try another?
- Things to Do
- Food & Drink
- Arts & Culture
- Time Out Market
- Coca-Cola Foodmarks
- Los Angeles
Greece heatwave 2024: is it safe to travel and should you cancel your holiday
As the country continues to be scorched by its earliest heatwave on record, here is everything you need to know if you have a trip booked

Greece is one of the sunniest countries in Europe , and the bright weather paired with lovely beaches and striking scenery have made it a well-established summer getaway spot for years.
However, Greece’s warm temperatures make it highly prone to heatwaves and wildfires, which are only becoming more common because of the climate emergency. After extreme temperatures scorched the country in a Europe-wide heatwave last summer , it looks like Greece is just at the beginning of a long and searingly hot summer.
Wildfires have spread around Paphos in Cyprus , and the Acropolis, Greece’s most popular tourist attraction, was forced to close during the hottest parts of the day last week, but areas across the country have felt the heat. Here is everything you need to know about the Greece heatwave if you have a trip booked.
Which areas have been affected by the heatwave in Greece?
Areas across Greece have been affected by the heatwave – it’s thought to be caused by winds bringing in hot air and dust from north Africa. Temperatures in the capital of Athens reached 43C last week, the islands of Rhodes and Samos have both experienced at least 40C, and in Chania, on Crete ’s northwestern coast, it soared to 44.5C.
In Greece, temperatures above 38C which last at least three days constitute a heatwave.
So, is it safe to travel to Greece right now?
Travelling to Greece hasn’t been advised against, but if you have a trip booked, you’ll need to take precautions to stay safe. In some areas, people have been told to remain indoors between 11am and 3pm, and last week it was reported that schools were suspended and attractions, including the Acropolis, were closed due to wildfire fears .
Greece’s extreme temperatures have so far led to the deaths of five tourists, the first of which was British author and TV presenter Michael Mosely on the island of Symi, and three more are currently missing. Some of these were out hiking during the hottest parts of the day.
What islands were affected by the wildfires?
Back in April, there was a wildfire on the island of Crete which injured three people. More recently, Paphos, a city in southwest Cyprus, has experienced wildfires. Five villages in the area were evacuated, and many homes and farms have been destroyed by the fire. Thankfully, no casualties have been reported as a result of wildfires.
What is the UK Foreign Office saying?
The Foreign Office hasn’t advised against travelling to Greece, but on the safety and security section of the website, it reads: ‘There are active wildfires across Greece, including in populated areas on the mainland and a number of islands. Wildfires are highly dangerous and unpredictable. The situation can change quickly. Follow ‘112 Greece’ on X (formerly known as Twitter) for official updates.
You should:
- take care when visiting or driving through woodland areas
- make sure cigarette ends are properly extinguished
- not light barbecues
Causing a forest fire is treated as a criminal offence in Greece even if unintentional. If you see a forest fire, call the emergency services on 112. Forest fires can also cause travel disruption in wider areas.’
There’s more advice in this section about what to do if you find yourself in an area affected by wildfires – you can read that here .
What are your rights if you’ve booked a trip to Greece?
You won’t be entitled to a refund on your trip, as the Foreign Office hasn’t advised against travel to Greece. However, if you are concerned, it’s worth contacting your travel provider to see what can be done – you may be able to move the dates you travel.
What’s the hottest Greece has ever been?
Greece actually holds the record for the hottest temperature ever recorded in Europe. On July 10 1977, Elefsina (which is in the Athens metropolitan area) reached a scorching 48C. The longest heatwave ever recorded in Greece was in July 2023, lasting for 16 days.
ICYMI: Is it safe to travel to Rhodes right now? The latest advice after the earthquake in Greece .
Stay in the loop: sign up to our free Time Out Travel newsletter for all the latest travel news.
Been there, done that? Think again, my friend.
Discover Time Out original video
- Press office
- Investor relations
- Work for Time Out
- Editorial guidelines
- Privacy notice
- Do not sell my information
- Cookie policy
- Accessibility statement
- Terms of use
- Modern slavery statement
- Manage cookies
- Advertising
Time Out Worldwide
- All Time Out Locations
- North America
- South America
- South Pacific
Election latest: Rishi Sunak accused of 'behaving badly' in final debate - as he and Keir Starmer get brutal audience question
Follow reaction and fallout from the final head-to-head between the prime minister and Labour leader ahead of polling day on 4 July.
Wednesday 26 June 2024 23:00, UK
- General Election 2024
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
Sunak and Starmer's final debate
- Voters can't pick a winner in snap poll
- Labour frontbencher says PM 'behaved badly'
- Audience member asks brutally blunt question
- Starmer says Sunak 'bullied into action' over betting
- 'A deal with the Taliban?' - PM mocks Labour's migration plan
- Jon Craig: No love lost between Sunak and Starmer - and it showed
- Sam Coates: Sunak put his opponent on the spot - but poll shows strategy didn't win over public
- Live reporting by Faith Ridler , Ollie Cooper and Katie Williams
- Police to investigate betting scandal cases
- Protester climbs on top of Tory campaign bus
- Man arrested in honeytrap scandal | Labour suspends suspect
Election essentials
- Manifesto pledges: Conservatives | Greens | Labour | Lib Dems | Plaid | Reform | SNP
- Trackers: Who's leading polls? | Is PM keeping promises?
- Campaign Heritage: Memorable moments from elections gone by
- Follow Sky's politics podcasts: Electoral Dysfunction | Politics At Jack And Sam's
- Read more: Who is standing down? | Key seats to watch | What counts as voter ID? | Check if your constituency is changing | Guide to election lingo | How to watch election on Sky News
Thanks for joining us for an extremely busy night here in the Politics Hub, including for the final debate between Rishi Sunak and Sir Keir Starmer before the general election next Thursday.
You can scroll through the page to catch up with the highlights.
And we'll be back from 6am with all the very latest.
Until then - read all the latest from Sky News below:
By Tim Baker , political reporter, in Nottingham
One of the more amusing moments of the debate tonight was Robert, who told Rishi Sunak he was a "mediocre" prime minister and said Sir Keir's strings were being pulled by senior members of the Labour Party.
He is brought into the spin room by BBC production staff for journalists to talk to.
He tells us that he is a life-long Conservative voter - but at the moment is undecided.
Robert says he has recorded the debate and will be watching it again when he gets home.
However, he reckons he is leaning towards the Conservatives - believe Sir Keir has an "undeclared agenda".
Daisy Cooper, the deputy leader of the Liberal Democrats, has said the UK "deserves so much better" than the leaders' debate held tonight.
Reacting to the clash between Rishi Sunak and Sir Keir Starmer, she said: "Tonight the audience spoke for the nation when they asked: is this really the best we've got?
"Our country deserves so much better than what we watched this evening.
"Liberal Democrats are listening to you and fighting hard for the issues that matter to people.
"From the NHS to tackling the cost of living, we want a fair deal for our country.”
A Conservative win would mean "five more years of chaos" and Rishi Sunak has shown tonight "just how out of touch he is", Labour's campaign coordinator has said.
Reacting to the leader's debate, Pat McFadden said Sir Keir Starmer "exposed the Tory manifesto as unfunded".
"Keir Starmer and Labour will return politics to public service, putting country before party in stark contrast to partygate and dodgy COVID contracts," he said.
"On 4 July, we have a chance to turn the page and start to rebuild with Labour."
Tonight was an "important moment" for Rishi Sunak as he put his opponent "on the spot", says our deputy political editor Sam Coates .
Coates says he thinks the prime minister would have been "very happy" with his performance - and adds that some of his aides were even "punching the air" after the debate.
It was a performance Mr Sunak "desperately needed earlier in the campaign", he adds.
He says Mr Sunak had a "clear strategy... to demand answers from Keir Starmer on tax and whether it will go up, on welfare and how you get people off benefits, on 'smashing the gangs' and whether the Rwanda policy is needed..."
Coates says Sir Keir provided a "range" of answers as the prime minister sparred with him.
"Sometimes he had specifics, sometimes he did not," he says.
"That strategy, although executed in a way I think that the Conservative Party tonight is very happy with, has nevertheless been judged not decisively in Keir Starmer or Rishi Sunak's favour," says Coates, referring to the YouGov poll showing there was no winner in the final debate of the election (see 21.38 post).
The final TV clash of the election campaign was an ill-tempered shouting match, at least from Rishi Sunak.
Sir Keir was more measured. More prime ministerial, perhaps?
As he had to as the underdog, Mr Sunak went on the attack from the start until the very end and unveiled a new campaign slogan: "Don't surrender…"
He said it no fewer than 15 times during the 75-minute debate. That’s once every five minutes.
But just like the England-Slovenia Euros match 24 hours earlier, the result was a draw: 50%-50% exactly, according to pollsters YouGov.
At the outset, the PM served notice that he wanted to talk about tax, while Sir Keir wanted to talk about politicians gambling.
As Mr Sunak read out prepared lines, it was a smart ad lib from Sir Keir that won the first round of applause.
"If you listened to people in the audience a bit more you might not be so out of touch," he said, in a familiar Labour attack line.
But the PM was strong and came out on top in exchanges on illegal migrants crossing the Channel.
One of the best moments came when a member of the audience, Robert, asked a devastating question: "Are you two really the best we’ve got to the next prime minister of our great country?"
By the end, the debate closed out as it began - with Mr Sunak shouting over the Labour leader. It wasn't a good look.
And as the debate ended, there was no handshake between the pair, which is unusual for these TV clashes.
At least party leaders pretend to be civilised towards each other usually.
There's clearly no love lost between these two - and it showed.
Darren Jones, shadow chief secretary to the Treasury, is among the Labour representatives in the spin room this evening.
He's asked first about his leaked comments that Labour's target for decarbonising the economy will cost "hundreds of billions" of pounds.
Sir David Davis, who sticks around for this encounter, asks why Mr Jones's party "downgraded" their net zero plans.
"Because you guys crashed the economy," the shadow chief secretary responds.
Sunak 'behaved badly' in debate
On the leader's debate, Mr Jones says Sir Keir Starmer came across as "clearly more prime ministerial" - and adds that he thinks Rishi Sunak behaved "quite badly".
"He didn't answer questions that were put to him and was constantly speaking over Keir and Mishal [Husain, the BBC host]."
He denies Sir Keir's remarks that Mr Sunak is out of touch were "below the belt".
"Rishi Sunak is going around the country telling everyone that they've never had it so good... they crashed the economy, people at home know that because they paid the price for it."
Up to spin for the Conservatives is ex-minister David Davis.
"This debate was very important," he says, noting it's the final one before the public decides who to back.
He was a fan of Rishi Sunak's new attack line - the repeated pleas to voters not to "surrender" their borders or finances to Labour.
"[Sunak has] faced a once-in-a-generation issue in terms of a war in Europe, he's faced a once-in-a-century issue in terms of a pandemic, and he did it with an economy from which we'd inherited massive debts in the past," he adds.
After all that, "he managed to get inflation down from 11% to 2% in six months".
"The public will look at this and say: 'We've got a difficult world, all sorts of disruptions at home and abroad, who will deal with it the best of these two'?" he says.
"I know who I'll be voting for."
With minutes to go, a group of smiling Labour spinners arrived to watch the final summations.
Darren Jones - under fire for his comments about the cost of going for net zero, revealed in The Telegraph - tells Sky News it's clear who was more prime ministerial during the debate.
He and the other Starmer backers then burst away to the various cameras and microphones to talk up their leader.
Meanwhile, serious faced Conservatives enter from the other end of the room to give their verdicts.
Tory candidate - and former minister - David Davis says he thinks Rishi Sunak's repetition of the "surrender" phrase will have gone down well.
This just in from YouGov - which has found there was no winner in tonight's BBC leaders' debate, the last of the general election campaign.
Asked who performed best - the results came in exactly 50/50.
Our deputy political editor Sam Coates says there will likely be disappointment in the Conservative ranks over this result.
"Neck-and-neck polling doesn't seem to me like it's going to change the race," he says.
"I think there's a really interesting question about Rishi Sunak's tactics, in my view, watching that, he was effective in highlighting the choice - the policy difference between the two men.
"I wonder looking at that poll whether that's what the public are really looking for."
However, there were distinctions when viewers were asked who performed better on certain topics.
Rishi Sunak came out on top on immigration and tax, while Sir Keir Starmer performed better on welfare and the UK's relationship with the EU.
Labour also just edged ahead on the economy - with 47% saying they performed better, and 43% backing the Tories.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free

We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
Bring photo ID to vote Check what photo ID you'll need to vote in person in the General Election on 4 July.
Foreign travel advice
Get advice about travelling abroad, including the latest information on coronavirus, safety and security, entry requirements and travel warnings.
Countries or territories
226 Countries or territories
Countries starting with A
- Afghanistan
- Antarctica/British Antarctic Territory
- Antigua and Barbuda
Countries starting with B
- Bonaire/St Eustatius/Saba
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- British Indian Ocean Territory
- British Virgin Islands
- Burkina Faso
Countries starting with C
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Cook Islands, Tokelau and Niue
- Côte d'Ivoire
- Czech Republic
Countries starting with D
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Dominican Republic
Countries starting with E
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
Countries starting with F
- Falkland Islands
- Federated States of Micronesia
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia
Countries starting with G
- Guinea-Bissau
Countries starting with H
Countries starting with i, countries starting with j, countries starting with k, countries starting with l.
- Liechtenstein
Countries starting with M
- Marshall Islands
- Myanmar (Burma)
Countries starting with N
- Netherlands
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- North Korea
- North Macedonia
Countries starting with O
Countries starting with p.
- The Occupied Palestinian Territories
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Pitcairn Island
Countries starting with Q
Countries starting with r, countries starting with s.
- São Tomé and Principe
- Saudi Arabia
- Sierra Leone
- Solomon Islands
- South Africa
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- South Korea
- South Sudan
- St Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
- St Kitts and Nevis
- St Martin and St Barthélemy
- St Pierre & Miquelon
- St Vincent and the Grenadines
- Switzerland
Countries starting with T
- Timor-Leste
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turkmenistan
- Turks and Caicos Islands
Countries starting with U
- United Arab Emirates
Countries starting with V
Countries starting with w.
- Wallis and Futuna
- Western Sahara
Countries starting with Y
Countries starting with z, get updates for all countries, is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
FCDO advises against all travel within 5 km of the crater of Mount Semeru in Lumajang Regency, East Java. FCDO also advises against all travel to the southeast area of Mount Semeru along the Besuk ...
To enter Indonesia, your passport must have an 'expiry date' at least 6 months after the date you arrive and have at least 2 blank pages. Check with your travel provider or the nearest ...
Indonesia's revised criminal code, which takes effect January 2026, includes penalties for defamation, blasphemy, cohabitation, and sex outside of marriage. It is unclear how Indonesian authorities will implement the revised criminal code. Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Indonesia.
Quick Facts. Six months beyond arrival date. Indonesia does not accept the 12-page U.S. emergency passport for entry into Indonesia. Two blank visa pages required for entry stamp. Yes, Visa or Visa on Arrival. None. 100,000,000 Indonesian rupia (approx. $7,000 USD)
At least 8 weeks before your trip check: the latest information on health risks and find out what vaccinations you need for Indonesia on TravelHealthPro. where to get vaccines and whether you have ...
30 November 2023. New International Travel Regulations to Enter Indonesia as of 1 February 2022. As an immediate follow-up to prevent the spread of SARS-COV-2 B.1.1.529 from South Africa and some other countries in the world, COVID-19 Task Force issued the Circular of the Head of the COVID-19 Handling Task Force Number 4 of 2022 regarding International Travel Health Protocol during the Corona ...
Hotline Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia (Kemenkes): +62215210411, +62812 12123119. Hotline Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Indonesia (Kemlu): +6281290070027. It is our hope to spread the news that activities and businesses run as usual in Indonesia while we also pray that this outbreak can soon be contained globally.
Event: Alert: COVID-19 Update 2021 Indonesian Travel Restrictions, U.S. Embassy Jakarta, Indonesia (29 November 2021) The Government of Indonesia has announced new travel restrictions in response to the discovery of the new "Omicron" variant of COVID-19: Foreign nationals will not be allowed entry to Indonesia if they have had any transit ...
Due to the increase in the spread of the new SARS-CoV-2 virus variants (Alpha, Beta, Delta, and Gamma) in various countries in the world, including Indonesia, Head of the COVID-19 Task Force, Ganip Warsito, issued an Addendum to the Circular of the COVID-19 Handling Task Force Number 8 of 2021 regarding International Travel Health Protocols During the Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19 ...
Location: Indonesia Event: Government Announces New Travel Restrictions Effective September 19, 2021, the Government of Indonesia (GOI) introduced new Effective September 19, 2021, the Government of Indonesia (GOI) introduced new travel requirements and COVID-19 testing procedures which will affect all travelers arriving to or traveling within Indonesia.
Check the latest government guidance on the FCDO Foreign travel advice and country specific pages for travel to this country and the rules for entering the UK on return. Ensure you are up to date with UK recommendations on COVID-19 vaccination. Check if you are at increased risk of severe COVID-19. You can check this in the FAQ's.
U.S. Consular Agency in Bali, Indonesia. +62-361-233-605 or +62-21-5083-1000 after hours. [email protected]. For regular updates, follow the U.S. Consulate General in Surabaya on Twitter and Facebook and the U.S. Embassy in Jakarta at Twitter and Facebook. State Department - Consular Affairs.
The government has issued updated provisions regarding the terms and documents required for overseas travellers who come to Indonesia. This latest set of rules was issued through circular letter 25/2022 regarding health protocols for overseas travel during the COVID-19 pandemic and has been signed by Lt. Gen. Suharyanto.. In these new regulations, there are a number of entry points for foreign ...
Read this travel advice and carry out your own research before deciding whether to travel. Emergency services in Indonesia. Ambulance: 118. Fire: 112. Police: 110. Contact your travel provider and ...
Australian Government travel advice for Indonesia. Exercise a high degree of caution. Travel advice level YELLOW. Understand the risks, safety, laws and contacts. ... Latest update: The Bali Provincial Government has introduced a new tourist levy of IDR 150,000 per person to foreign tourists entering Bali. The tourist levy is separate from the ...
Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas. If you choose to drive a vehicle in Indonesia, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork. Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
General Travel Advice. Irish citizens require a visa to enter Indonesia. Travellers can apply for an Indonesian visa on arrival (valid for 30 days) at a cost of IDR 500,000. The visa on arrival can be extended once (by an additional 30 days maximum) by applying to a local Indonesian immigration office. Travellers should extend their visa within ...
Foreign tourists are allowed to travel to Indonesia with a Visa on Arrival (VOA) and a visa applied at the Indonesian representatives (KBRI). Travel Update: Indonesia lifts COVID-19 Restrictions. Since June 9 2023, it is not required anymore to show proof of Covid-19 vaccination to enter or to travel in Indonesia. For more information: here
/foreign-travel-advice/indonesia e2c44bf1-0b96-4034-9ac8-96f6e0181a80 Updated assessment that terrorists are likely to try to carry out attacks in Indonesia ('Safety and security' page).
General Information. Find everything you need to know about how to get here, what regulations that should be noted, and many other things vital in arranging your travel plan to Indonesia. Explore Indonesia's diverse beauty, culture, and adventure on Indonesia Travel. Plan your journey to this tropical paradise.
Take particular care in Palu, Poso and Tentena. Be alert to the risk of politically motivated violence. There is conflict between the Indonesian security forces and terrorists, including attacks ...
The UK Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office (FCDO) France advice, which was last updated on February 20, reads: "There is a high threat of terrorist attack globally affecting UK ...
The Foreign Office hasn't advised against travelling to Greece, but on the safety and security section of the website, it reads: 'There are active wildfires across Greece, including in ...
Latest FCDO travel advice for Indonesia including on entry requirements, safety and security and local laws and customs. Reduce your risk from terrorism while abroad How to minimise your risk, and ...
Thanks for joining us for an extremely busy night here in the Politics Hub, including for the final debate between Rishi Sunak and Sir Keir Starmer before the general election next Thursday.
In 2024, 127 Indonesians received prestigious U.S. Department of State Fulbright Program scholarships to study and conduct research in the United States, an increase of 22 over last year. Recipients include 54 Fulbright Master's Degree awardees, 37 Fulbright Doctoral Degree awardees, and 36 Fulbright Visiting Scholars who will conduct postdoctoral research in the United States.
Get advice about travelling abroad, including the latest information on coronavirus, safety and security, entry requirements and travel warnings.