Make Your Vocabulary Skyrocket With These Space Words
- Space Words
- Take The Quiz
Our universe is unfathomably huge and getting bigger all of the time, according to the Big Bang model and the theory of universe expansion . That’s a pretty cool concept and term, right? As the theory goes, dark energy (more on this later) is causing the universe to continually stretch itself.
Studying the universe introduces us to some fascinating concepts in general: black holes , rogue planets , Oort clouds— and white holes , too? If you are a casual space explorer, you probably already know stellar objects like comets , asteroids , meteors , and galaxies . But there is so much more out there for you to discover! Jump in our (word) rocket ship as we boldly discover some awesome intergalactic words.
From Earth, a pulsar resembles a flickering star. In reality, a pulsar is a neutron star —a really dense object left over when a big star dies—that radiates beams of light in two directions. The pulsar rotates as it shines light beams, which makes it appear to blink or pulse as it spins away from Earth and points its lights in other directions.
Asterism is a fancy word that means “a group of stars.” So, what makes an asterism different from a constellation ? The 88 constellations in the sky have officially recognized names and shapes. Asterisms are those other groups of stars that aren’t officially recognized but still have popular names. The Big Dipper (part of Ursa Major ) and Orion’s Belt (part of Orion ) are two examples of commonly known asterisms.
Just like the Earth, the Sun has an atmosphere surrounding it. The outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere is called the corona . Because the Sun is so bright, you can only see the corona during a total solar eclipse . The Sun’s corona is very dense and, mysteriously, has a much higher temperature than the Sun itself.
A facula (plural faculae ) is an unusually bright spot on the surface of the sun. A facula is smaller and harder to see than the more well known sunspots . Both faculae and sunspots are caused by bubbles of hot gas and both are used to keep track of the solar cycle. As one last bit of trivia, the word facula is Latin for “little torch.”
A nebula is a cloud of dust and gas in outer space. While that may not sound terribly exciting, nebulae act as star nurseries as they have the perfect conditions that new stars need to form. The word nebula comes from Latin and means “mist,” “vapor,” or “cloud.”

planetesimal
A planetesimal is a small celestial object formed from dust, rocks, and other materials. According to one theory, planetesimals may be the building blocks that combined together to form the early planets of the universe. Planetesimals may have also played a part in the formation of the Earth’s moon and some of the other moons in our solar system as well.
Do you know the difference between a meteor, comet, and asteroid?
rogue planet
A rogue planet is a planet that doesn’t orbit a star. Many planets, like Earth, are part of a solar system and orbit around a central star. Rogue planets, on the other hand, are not confined to drift around a star and roam wherever they want across space. Because they aren’t next to a star and don’t emit light themselves, rogue planets are very hard for astronomers to find. Despite their lack of starry friends, evidence suggests that it may be possible for life to exist on rogue planets.
As you likely know, a black hole is a region of space where the gravity is so intense that not even light can escape. We often imagine black holes as terrifying objects that suck in all the matter around them.
A white hole is the theoretical opposite of a black hole, a celestial object that would endlessly expel matter out of it. According to Albert Einstein’s theories, black holes and white holes serve as the entrance and exits of wormholes that would allow travel through time and space. Other modern theories propose that a white hole could theoretically exist as the final stage of a black hole, where all of the mass sucked into a black hole is released back out again.
A quasar is a celestial object located very far away from us in distant galaxies. Quasars are a result of gas and stars accumulating into a disk around a gigantic black hole. This disk emits a huge amount of heat, making quasars some of the brightest objects in all of the known universe. Quasars also emit radiation (and in some cases, radio waves ) into space, which is how we have been able to find them. In fact, the name quasar is short for “quasi-stellar radio source,” which refers to the radio telescopes that were first used to detect them.
A blazar is basically identical to a quasar except for one quality: its angle toward Earth. Typically, a quasar is angled slightly toward Earth; that means we can detect its light and radio wave emissions. A blazar is angled directly toward the Earth so that the light and radiation shoots directly toward us. This difference in angle makes a blazar appear even brighter than an already absurdly luminous quasar.
Go Behind The Words!
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
The Oort Cloud is the furthest outer region of our solar system, being more than a thousand times away from the Sun than Pluto is. The Oort Cloud is often imagined as a bubble of icy objects that exists around our solar system. The Oort Cloud could possibly contain trillions of celestial objects and is the source of many comets that pass through our solar system. The Oort Cloud is named for astronomer Jan Oort, who originally theorized its existence.
dark matter
Dark matter is a theoretical, invisible form of matter that exists in space. The word matter is used to refer to all of the stuff that takes up space as we know it. In outer space, everything is positioned where it is because of gravity. We can see what is going on in outer space because of light. However, there are areas of outer space where astronomers can detect mass (due to gravity) but nothing in that area is emitting or absorbing light. Because something must be there, this invisible “missing mass” is known as dark matter .
According to scientific estimates, dark matter makes up about 27 percent of space. This may not sound like much, but the “regular matter” that makes up our Earth and all the suns and planets accounts for less than 5 percent of the universe! But wait, we are only at about 32 percent of the universe. What is the rest of it made of?
dark energy
The answer, according to modern science, is dark energy. Dark energy is a theoretical form of energy that exerts negative, repulsive pressure. In the simplest sense, dark energy is basically “reverse gravity” that causes things to repel away from each other rather than attract each other as is the case with gravity. Dark energy is thought to be responsible for the expansion of our universe and is what the “empty space” of outer space is believed to be made out of.
No, a cat didn’t just walk across the keyboard. In astronomy, a syzygy is an alignment of three celestial objects. For example, when the Earth, sun, and moon are all positioned in a line to cause an eclipse, they are aligned in syzygy . This incredibly cruel word to use in a game of Hangman comes from the Greek word syzygía , meaning “union” or “pair.” In addition to syzygy , other cool words that astronomers use to refer to space observations include azimuth , parsec , ephemeris , and albedo .
Hyperjump over to take the quiz!
Did this list of cosmic words launch you into the stratosphere? You can jump into the void and review this expansive list of terms and their meanings with our word list here . Or, demonstrate your new grasp of space by heading to our short quiz on these words.
Take another outer space word trip right from your home with these words.
Current Events
Science & Technology

Trending Words
[ koh- uh d- ven -cher ]
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.

Space Words to Explore the Incredible Faraway Galaxies
By: Author ESLBUZZ
Posted on Last updated: September 6, 2023
Sharing is caring!
Are you interested in learning more about space words? If so, you’ve come to the right place! In this article, we’ll explore the vocabulary related to outer space, the solar system, and beyond. Whether you’re a student, an English learner, or just someone who loves to explore the cosmos, this article is for you.
Space Words

Understanding Space Words
Learning space vocabulary can be challenging, but it is essential for understanding the universe and communicating about it. In this section, we’ll cover some of the most common space words and their meanings.
Planets are celestial bodies that orbit a star, such as our sun. There are eight planets in our solar system: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Here are some more space words related to planets:
Example sentence: Jupiter is a gas giant planet.
A moon is a natural satellite that orbits a planet. Our moon is the fifth largest moon in the solar system. Here are some more space words related to the moon:
Example sentence: The moon’s surface has many craters.
A spacecraft is a vehicle designed for travel or operation in space. Here are some more space words related to spacecraft:
Example sentence: The space shuttle was used for many missions to the International Space Station.
A star is a luminous sphere of plasma held together by its own gravity. There are billions of stars in our galaxy alone. Here are some more space words related to stars:
Example sentence: The constellation Orion is easily visible in the winter sky.
The universe is everything that exists, including all matter and energy. It is estimated to be around 13.8 billion years old. Here are some more space words related to the universe:
Example sentence: The cosmic microwave background radiation is one of the strongest pieces of evidence for the Big Bang theory.
Space Words: The Solar System
The Solar System is a fascinating and vast collection of celestial bodies that includes the Sun, planets, dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, and comets.
Inner Planets
The inner planets, also known as the terrestrial planets, are the four planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. These planets are characterized by their relatively small size, rocky surfaces, and proximity to the Sun.
Outer Planets
The outer planets, also known as the gas giants, are the four largest planets in the Solar System: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. These planets are characterized by their massive size, gaseous atmospheres, and distance from the Sun.
The Sun is the center of the Solar System and all the planets orbit around it. Each planet has its own unique orbit and rotates on its own axis. The inner planets have shorter orbits and rotate faster than the outer planets.
The surfaces of the inner planets are primarily made up of rock and metal, while the outer planets are mostly composed of gas and ice. Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune also have rings made up of ice and rock particles that orbit around them.
Space Words: The Universe and Beyond
Galaxies are huge systems of stars, planets, gas, and dust that are held together by gravity. They are the building blocks of the universe. There are three main types of galaxies: spiral, elliptical, and irregular. Here are some words associated with galaxies:
Example sentence: The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy that contains our solar system.
Black Holes
A black hole is a region of space where the gravitational pull is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. They are formed when a massive star dies and its core collapses. Here are some words associated with black holes:
Example sentence: The event horizon is the point of no return around a black hole.
Stars are giant balls of hot gas that produce light and heat through nuclear reactions. They are the most important objects in the universe because they provide the energy that makes life possible. Here are some words associated with stars:
Example sentence: A supernova is an explosion that occurs when a star runs out of fuel.
Constellations
A constellation is a group of stars that form a recognizable pattern in the sky. They were used by ancient civilizations for navigation and storytelling. Here are some words associated with constellations:
Example sentence: Orion is a prominent winter constellation that is easy to spot in the night sky.
Space Words: Space Exploration
Space exploration is the study and discovery of outer space, including the exploration of planets, stars, and galaxies beyond Earth’s atmosphere. It involves the use of various technologies and equipment, including spacecraft, satellites, telescopes, and more.
Astronauts and Spacecrafts
Astronauts are individuals who are trained to travel and work in space. They are responsible for operating and maintaining spacecraft, conducting scientific experiments, and performing spacewalks. Spacecraft, on the other hand, are vehicles designed to travel in space, including rockets, shuttles, and probes.
Here are some words related to astronauts and spacecraft:
Example sentence: Astronauts use spacecraft to explore outer space and conduct scientific experiments.
Satellites and Telescopes
Satellites and telescopes are essential tools for space exploration. Satellites are objects that orbit around a planet or moon, while telescopes are instruments used to observe distant objects in space.
Here are some words related to satellites and telescopes:
Example sentence: Satellites are used to collect data and images of Earth and other planets in our solar system.
Space Missions
Space missions are expeditions carried out to explore outer space. These missions are often conducted by national space agencies, such as NASA in the United States, or privately funded companies, such as SpaceX.
Here are some words related to space missions:
Example sentence: NASA’s recent space mission to Mars involved sending a rover to explore the planet’s surface and collect data.
Teaching Space Words
As a teacher, it is important to engage students in the learning process. One way to do this is by incorporating fun and interactive activities that help students learn space vocabulary. In this section, we will explore some engaging activities and interactive games that can be used to teach space vocabulary to students.
Engaging Activities
- Word Wall: Create a word wall with space-related vocabulary words. This is a great way to introduce new words and reinforce previously learned words. Students can refer to the word wall throughout the unit to help with their understanding of the concepts.
- Space Scavenger Hunt: Create a scavenger hunt where students have to find and identify space-related objects in the classroom or around the school. This is a fun and interactive way to get students moving while learning new words.
- Space Vocabulary Bingo: Create a bingo game using space-related vocabulary words. This is a fun way to reinforce vocabulary and keep students engaged.
- Space Vocabulary Charades: Create a list of space-related vocabulary words and have students act them out while their classmates try to guess the word. This is a fun way to reinforce vocabulary and get students up and moving.
Interactive Games
- Space Vocabulary Memory Game: Create a memory game using space-related vocabulary words. This is a fun and interactive way to reinforce vocabulary and help students with their memory skills.
- Space Vocabulary Hangman: Create a hangman game using space-related vocabulary words. This is a fun way to reinforce vocabulary and help students with their spelling skills.
- Space Vocabulary Quiz: Create a quiz using space-related vocabulary words. This is a great way to assess students’ understanding of the concepts and reinforce vocabulary at the same time.
- Space Vocabulary Matching Game: Create a matching game using space-related vocabulary words and their definitions. This is a fun and interactive way to reinforce vocabulary and help students with their understanding of the concepts.
Some space words that can be used in these activities and games include:
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some words related to space and the universe?
- Solar system
What are some space words that start with ‘I’?
- Interstellar
- Intergalactic
What are some Earth and space words?
What are some 6-letter space words?
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the vocabulary for space exploration?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
- Extravehicular activity (EVA)
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are some ancient words for space?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
- Aether (Greek)
- Caelum (Latin)
- Nuit (Egyptian)
- Nut (Egyptian)
- Tiamat (Babylonian)
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are some space words that start with 'I'?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are some Earth and space vocabulary words?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are some 6-letter space-themed words?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
That's all for now. Happy learning!
- Recent Posts
- Ed Words: Expand Your Vocabulary and Improve Your Writing! - April 15, 2024
- List of Ethnicities and Their Cultures from Around the World - April 2, 2024
- Mastering English Writing: Essential Transitional Words for Body Paragraphs - March 25, 2024
Related posts:
- Words that Start with F: Expand Your Vocabulary with These F Words
- 50 Words that Start with N for Your Writing Arsenal
- 50+ Wonderful Words that Start with W: Expand Your Vocabulary Today!
- 100 Words Ending in D to Expand Your English Vocabulary

50 space terms for understanding the universe
The National Aeronautics and Space Agency, or NASA, was founded on July 29, 1958, when President Dwight D. Eisenhower signed the National Aeronautics and Space Act, one year after the Soviets launched Sputnik 1, the world's first artificial satellite. NASA was designed from the start to push the bounds of space exploration with research into aerospace and aeronautics as well as with a civilian space program.
In honor of World Space Week , which takes place Oct. 4-10, Stacker compiled a list of key astronomy and astrophysics terms from a variety of authoritative science communication sources, including Crash Course: Astronomy , How Stuff Works , and International Comet Quarterly.
As the agency unrelentingly forged a path toward astronomical discovery, NASA also invented a number of technologies that we use in our everyday lives. These include artificial limbs, LASIK surgery, improved water filtration, camera phones, freeze-dried foods, memory foam, LED lights, and even the Dust Buster. In fact, it was a NASA scientist who invented the Super Soaker squirt gun .
Keep reading to learn the terms that are commonly used in this fascinating field.
You may also like: Can you answer these real 'Jeopardy!' questions about space?
#1. Aberration of light
Similar to how raindrops hit a moving car window as if from an angle, an aberration of light is the phenomenon where stars or other celestial bodies appear from Earth to be slightly off from their true position. This happens because of motion—specifically, the interaction of the Earth's movement with the speed of light causes this confusing phenomenon.
#2. Alpha Centauri
Alpha Centauri is the name of the closest star system to earth. It comprises two main stars, Alpha Centauri A and Alpha Centauri B, as well as the closest of the three stars, Proxima Centauri. In 2016, astronomers found an Earth-sized planet orbiting Proxima Centauri, later named Proxima b. While this planet shows signs that life could exist, astronomers are still unsure how habitable it is.
#3. Andromeda Galaxy
Also known as M31, this galaxy is the closest to the Milky Way, where the Earth exists. Andromeda Galaxy has a similar structure to the Milky Way; it is spiral in shape and has a large density of stars, dust, and gas. Because of its proximity, it is the only galaxy that can be seen from Earth with the unaided eye, particularly on fall and winter nights.
#4. Asteroid
Asteroids are chunks of rock or metal that used to be parts of other small planets that have broken off due to a collision in space and now orbit the sun. The word asteroid means "star-like," referring to their emission of light. Asteroids can be lumped into orbital groupings called families and form into an asteroid belt.
#5. Barycenter
A barycenter is the common center mass around which a solar system orbits. While it has become common knowledge that planets orbit stars, it is, in fact, the barycenter that both stars and planets orbit around. Our solar system's barycenter is constantly changing position based on where each of the planets is in its orbit, ranging from being near the center of the sun to being just outside its surface.
#6. Big Bang
The Big Bang Theory is a model describing the origin of the universe. It explains how the universe expanded from a high-density, high-temperature state into the cosmos we see today. Although there are alternative theories, this is the most widely recognized theory of how the universe began.
#7. Binary star
Binary stars are systems that only contain two stars that orbit together. Together, they orbit a common center of mass. There are two types of binary stars: wide binaries and close binaries. Wide binaries orbit with a significant distance apart from each other, causing them to have little effect on each other. Close binaries orbit closely and actually can acquire material from one another.
#8. Black hole
Made famous by Einstein's theory of general relativity, a black hole is the small dense core remnant of a dead star. Since the density of this core is more than about three times more than the density of the sun, the strong force of gravity produces a black hole.
#9. Brown dwarf
A brown dwarf is born from a collapse of gas and dust, similar to stars. This collapse creates a large amount of energy that gets trapped in a ball of material. The energy emits light from within for tens of millions of years, becoming dimmer as time passes.
#10. Celestial sphere
A celestial sphere is a tool used in spherical astronomy. It is a sphere with a large radius that is concentric with Earth. The sky surrounding the Earth is projected on the sphere, which is helpful for astronomers when they are attempting to plot positions in situations where distances aren't important.
Besides being a beautiful phenomenon rarely visible from Earth, comets are icy, frozen balls of gas, rock, and dust. Comets gain their trademark bright glow by emitting gas as their orbit passes close to the sun, sometimes even resulting in a glowing tail.
#12. Constellation
One of the first things we learn about space is its many constellations. From Orion and his belt to the mythical Seven Sisters and the Big and Little Dipper, constellations map out a group of stars that form shapes in the sky. Explorers first used constellations to map directions as well as a tool for storytelling.
#13. Dark energy
Like the cosmic mystery its name evokes, dark energy is hard to define. The easiest way to think of it is a property of space that accounts for an expanding universe. The universe's "empty space" may still have its own, dark energy. However, scientists are still trying to pin down the properties of this dark energy that makes up most of the universe.
#14. Dark matter
Somewhat similar to dark energy, dark matter also covers a large chunk of the universe and remains quite mysterious to scientists. The main difference is that dark matter explains more about how groups of objects in the universe function together. Though scientists have a greater understanding of what dark matter isn't than what it is, a leading theory posits dark matter is made from exotic particles like axions or Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPS).
#15. Doppler shift
Also known to most as the Doppler effect, the Doppler shift explains the phenomenon of the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer. This can be observed when an ambulance drives past you and the volume of the siren doesn't quite match with the proximity of the ambulance to you.
#16. Eclipse
An eclipse refers to one body in space moving into the shadow of another body. Eclipses can exist in two forms—solar and lunar—depending on the orbit of the Earth and moon. With a lunar eclipse, the moon moves behind the Earth. During a solar eclipse, the moon orbits between the Earth and the sun.
#17. Equinox
During an equinox, Earth experiences an even 12 hours of daytime and 12 hours of nighttime. This occurs twice a year: The March equinox marks spring's arrival in the Northern Hemisphere and Fall in the Southern Hemisphere. The September equinox ushers in the fall's arrival in the north and spring in the south.
#18. Escape velocity
Escape velocity is the speed that an object needs in order to escape a planet or moon's gravitational pull. For example, the escape velocity for a spaceship to leave the surface of Earth is about 25,000 miles per hour.
#19. Exoplanet
When planets exist beyond our solar system and orbit a star other than the sun, they are called an exoplanet. Exoplanets are extremely hard to see, as they are often hidden by the glare of the star they orbit. Because of that, the first exoplanet was not recognized until 1992.
#20. Fermi paradox
Named after Italian-American physicist Enrico Fermi, the Fermi paradox is a theory using statistical analysis to postulate why we have yet to see signs of life on other planets within our galaxy. The paradox assesses the likeliness that there are similar planets to Earth within the Milky Way, and likely have the ability to support life, yet no signs of life have been found which means it's a paradox.
#21. Galaxy
We all know that we live in the Milky Way galaxy, but what exactly is a galaxy ? A galaxy is a wide-ranging mix of dust, gas, stars, and various solar systems brought together by a singular gravitational pull.
#22. Gamma-ray burst
A gamma-ray burst is the most violent type of explosion in the universe. The explosion itself emits more energy in 10 seconds than the sun will emit in its lifetime. When it happens, it's the brightest source of light in the observable universe. Satellite evidence suggests gamma-ray bursts are the result of matter collapsing into black holes.
#23. Gravity
Based on the Latin word for "weight," gravity is a natural phenomenon where things with mass or energy are drawn toward its center. The force of gravity is what keeps us planted on Earth's surface and also keeps the Earth orbiting the sun.
#24. Hypergalaxy
A hypergalaxy consists of one large dominant galaxy surrounded by various smaller tertiary galaxies. The Milky Way and our neighboring Andromeda galaxies are both hypergalaxies.
#25. Light-year
A light-year is as simple a concept as its name suggests. It is an astronomical distance that measures the distance that light travels in a year. One light-year roughly equates to 6 trillion miles.
#26. Magellanic clouds
Understanding Magellanic clouds has become a propelling source of understanding distant galaxies. They consist of two irregular galaxies that orbit the Milky Way. Orbiting about 200,000 light-years away, the Magellanic clouds are formed by the Large Magellanic Cloud and the Small Magellanic Cloud.
#27. Magnitude
Magnitude refers to a mathematical measurement for something's size or extent in comparison to other similar objects. In astronomy, magnitude is a unitless system used to measure the varying degrees of brightness of objects in the sky. Greek astronomer Hipparchus introduced the concept of magnitude for classifying stars in 129 B.C., referring to the brightest stars in the sky as "first magnitude."
#28. Meteor
A meteor is a rocky object or asteroid that vaporizes when entering the Earth's atmosphere. They're often called "shooting stars" and provide a beautiful glowing tail as they enter the atmosphere. Next time you see one, be sure to make a wish upon a meteor!
#29. Milky Way
The Earth's galactic home, the Milky Way is a spiral galaxy that is constantly rotating. The Milky Way contains a high amount of dust and gas wrapped around the central galactic bulge. The galactic bulge contains a dense amount of dust, gas and stars. And within that bulge, exists a large black hole (see slide #8). Our solar system lies about 30,000 light-years from the galaxy's center.
The moon is a heavenly body that orbits the Earth and happens to be the easiest object to spot in the night sky. As the moon orbits our planet, we see it go through "phases," where at different times different proportions of the moon's surface are visible. These phases have guided time since the beginning of humanity. The calendar month roughly replicates the moon's orbit of the Earth.
#31. Nebula
A nebula is a large cloud of dust and gas in space that is produced when a star dies. The gas and dust eventually clump together into a mass large enough to form its own gravity. Nebulae can also be places for new stars to form and are sometimes referred to as "star nurseries."
#32. Nebular hypothesis
The Nebular hypothesis is the most widely accepted theory of how our solar system was born. The theory itself was born during the Scientific Revolution from the 16th to 18th centuries. The theory's essence states that our solar system was birthed from a nebula billions of years ago. The theory has also been applied to how all stars came to be.
#33. Neutron star
Neutron stars are small, but very dense objects that are birthed by the explosive death of a giant star. Neutron stars can exist in two states. The first is a pulsar, which emits a narrow radiation beam. The second is a magnetar, which has a powerful magnetic field that has the force to distort atoms.
#34. Oort Cloud
Named after astronomer Jan Oort whose theory about a cloud comprising a shell of icy objects existing beyond the Kuiper Belt, or the region that exists in our solar system beyond Neptune, could be responsible for the long-term comets visible from Earth (like Halley's). The cloud is theorized to comprise the remains of disc materials of planets and the sun.
In short, an orbit is the gravitationally curved trajectory of an object in space. In other words, an orbit is the circular motion in which objects in space travel due to gravity's pull. For example, the moon orbits around the Earth and the Earth orbits around the sun in a circular motion. An object that orbits another is called its satellite.
#36. Parallax
Measuring using parallax involves estimating the distance of nearby celestial objects by measuring movement against more distant celestial objects. This method is often used when measuring distances of neighboring stars, called stellar parallax.
#37. Quasar
Quasars are large distant objects in space that are powered by large, powerful black holes. They tend to shine so brightly that their light eclipses the old galaxies that they exist within. They are capable of emitting thousands of times more energy than the Milky Way emits.
#38. Red giant
A red giant is a star that is reaching its final days and approaching death. If a star has turned into a red giant, the star is in the last states of its stellar evolution and expands. Our own sun will eventually expand and turn into a red giant—but not for a few billion years.
#39. Red shift
Red shift and blue shift explain how light changes wavelength as objects in space move closer or farther from each other. As an object moves away from us, the light is shifted towards the red end of the color spectrum. In turn, as it moves closer, the light shifts towards the blue end of the spectrum. Along with blue shift, red shift is hugely valuable in understanding the universe's expansion.
#40. Solar system
A solar system is a gravitationally bound system of a sun and the objects that orbit it. That includes the bodies that orbit the objects orbiting the sun. For example, our solar system contains the sun, the planets that orbit it, as well as moons and other objects that orbit them.
#41. Solar wind
Solar wind is a wind streaming solar particles and plasma from the sun. As a solar wind carries charged particles from the sun towards the Earth could have catastrophic effects for Earth's habitants. But don't worry, Earth's magnetic field provides a pretty sturdy shield against any of these negative effects.
#42. Spaghettification
Sometimes referred to as the "noodle effect," spaghettification is when the extreme tidal forces stretch out objects to be long and thin like a noodle. This effect can also be caused by the immense gravitational pull of a black hole.
Other than serving as beautiful guiding lights in our sky, stars are astronomical objects that are composed of gas that pulls itself together with its own gravitational pull. Nuclear fusion at the star's core creates the light that stars emit.
#44. Star cluster
In the same way that planets can be gravitationally bound to the sun, causing them to orbit it, stars can also cluster together due to gravity. Two types of star clusters can be determined: globular clusters and open clusters. Globular clusters are tight clusters of thousands of older stars, whereas open clusters are made up of a few hundred very young stars.
#45. Supernova
A supernova is the largest explosion that can be seen with the human eye. A supernova occurs as the last step of a dying massive star that emits an extremely bright light. This occurs in the death of a star at least five times the mass of our solar system's sun.
#46. Telescope
A telescope is the signature tool of astronomers to see far objects out in space in further detail. Today, telescopes are designed with curved mirrors that gather light from the sky and concentrate it so that far away objects are visible.

#47. Theory of relativity
The theory of relativity was developed by Albert Einstein in 1905 and includes both theories of special relativity and general relativity. The theory determines that the laws of physics are the same for all non-accelerating observers and was monumental in introducing a framework for space and time.
Tides are the rise and fall of sea level that is caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun. They are one of the most reliable phenomena in the world. The difference between high and low tide is called the tidal range.
#49. White dwarf
A white dwarf is a relatively small star that is about the size of a planet that is very dense. It is essentially a star that has exhausted all of its nuclear fuel from within. It expels most of its outer material, leaving a white-hot core that cools over the next billion years.
#50. Universe
And lastly, we have landed at the universe. A loaded definition that has flummoxed scientists for generations, a universe contains billions of galaxies and even more stars along with their planets, moons, asteroids, comets, dust, and gas, all of which exists swirling around in the massive thing we call space.
You may also like: Can you answer these real 'Jeopardy!' questions about space?
Trending Now
Top 100 country songs of all time.

50 most meaningful jobs in America

50 best colleges on the East Coast

100 best 'SNL' episodes

bottom_desktop desktop:[300x250]
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Space travel
Smart vocabulary: related words and phrases.
The SMART Vocabulary cloud shows the related words and phrases you can find in the Cambridge Dictionary that make up this topic. Click on a word to go to the definition.

Word of the Day
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
a high, round collar that does not fold over on itself, or a piece of clothing with this type of collar

Fakes and forgeries (Things that are not what they seem to be)
Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
Global site navigation
- Celebrity biographies
- Messages - Wishes - Quotes
- TV-shows and movies
- Fashion and style
- Capital Market
- Celebrities
- Family and Relationships
Local editions
- Legit Nigeria News
- Legit Hausa News
- Legit Spanish News
- Legit French News
100+ space words and their meanings that would be fun to learn
Space is a vast expanse with lots of marvellous and unimaginable things; some are discovered while others remain unknown. Space exploration has revealed a lot to help understand the components of space. Learning some space words will enrich your astronomy vocabulary and enhance your understanding of space composition.
PAY ATTENTION: Click “See First” under the “Following” tab to see Legit.ng News on your Facebook News Feed!

You might have come across various space-related words and wondered what they mean. While some words might seem complex to understand, some are simple and have easy meanings. Have a look at some amazing space words and their meanings to improve your knowledge of space.
Aesthetic words associated with space and the universe
Even though outer space is a mysterious place, it is full of extreme beauty. With components ranging from dust particles to huge rocks, the space has many things to explore. Here are some aesthetic words to enhance your space vocabulary.

25 best anime openings fans can recognise from the first note
- Accretion - A process by which dust and gas accumulate into larger bodies such as stars and planets.
- Antipodal point - A point on the direct opposite side of a planet.
- Binary - A system of two stars that revolve around a common centre of gravity.
- Bolide - A term used to describe an exceptionally bright meteor.
- Disk - The surface of the sun or other celestial body projected against the sky.
- Equinox - The two points at which the sun crosses the celestial equator in its yearly path in the sky.
- Galactic nucleus - A tight concentration of stars and gas found in the innermost regions of a galaxy .
- Giant planet - Planets much larger than the earth.
- Luminosity - The amount of light emitted by a star.
- Meteor - A tiny particle of rock or dust that burns away in the earth's atmosphere.
- Nebula - A cloud of dust and gas in space illuminated by one or more stars.
- Obliquity - The angle between a body's equatorial plane and orbital plane.
- Photosphere - The bright visible surface of the sun.
- Retrograde - When an object moves in the reverse sense of normal motion.
- Satellite - A natural or artificial body in orbit around a planet.
- Solar eclipse - A phenomenon that occurs when the earth passes into the moon's shadow.
- Sunspot - Cooler areas of the sun's surface than surrounding areas.
- Trojan - An object orbiting in the Lagrange points of another (larger) object.
- Variable star - A star whose brightness changes over days, weeks, months, or years.
- Yellow dwarf - An ordinary star such as the sun at a stable point in its evolution.

Top 10 ugly fish: the weirdest-looking sea creatures in the world
PAY ATTENTION: Join Legit.ng Telegram channel! Never miss important updates!
Interesting words associated with space
Undoubtedly, some space words are exciting, and you will want to know their meanings when you find such words . Here is a list of some interesting space words you should know.

- Achondrite - A stone meteorite that contains no chondrules.
- Andromeda galaxy - a spiral galaxy in the constellation of Andromeda that is visible to the naked eye.
- Cepheid variable - This is a variable star whose light pulsates in a regular cycle.
- Constellation - A group of stars that make an imaginary picture in the sky.
- Double star - A group of two stars.
- Exocomet - A comet outside the solar system.
- Fireball - An extremely bright meteor.
- Galilean moons - The name given to Jupiter's four largest moons, Io, Europa, Callisto, and Ganymede.
- Iron meteorite - A meteorite composed mainly of iron mixed with smaller amounts of nickel.
- Kirkwood gaps - Regions in the main belt of asteroids where few or no asteroids are found.
- Meteoroid - A small, rocky object in orbit around the sun, smaller than an asteroid.
- Oort cloud - a spherical shell surrounding everything in the solar system .
- Planetary nebula - A shell of gas surrounding a small, white star.
- Ring galaxy - A galaxy that has a ring-like appearance.
- Seeing - A measure of the atmosphere’s stability.
- Spacewear - Clothes to be worn in space
- Star cluster - A collection of stars orbiting a common centre of mass.
- Stone meteorite - A meteorite that resembles a terrestrial rock and is composed of similar materials.
- Tektite -A small, glassy material formed by the impact of a large body, usually a meteor or asteroid.
- Umbra - The area of total darkness in the shadow caused by an eclipse.
- Zenith - The point in the sky that is directly overhead.

100+ celestial names for boys and girls that are out of this world
Cool Space Words
What are some cool space words you have ever heard? Even though there are many complicated astrology terminologies, cool and simple space terms also exist. Have a look at the list below.

- Aphelion - The point in the orbit of a planet or other celestial body where it is farthest from the sun.
- Astrophobia - a severe and irrational fear of stars and space.
- Celestial poles - The North and South poles of the celestial sphere.
- Comet - A gigantic ball of ice and rock that orbit the sun in a highly eccentric orbit.
- Eclipse - The total or partial blocking of one celestial body by another.
- Extragalactic - A term that means outside of or beyond the galaxy.
- Galaxy - A large grouping of stars.
- Half-moon - First or last quarter of lunar eclipse.
- Jet - A narrow stream of gas or particles ejected from an accretion disk surrounding a star or black hole.
- Limb - The outer edge or border of a planet or other celestial body.
- Magnetosphere - The area around a planet most affected by its magnetic field.
- Occultation - An event that occurs when one celestial body conceals or obscures another.
- Parallax - The apparent change in position of two objects viewed from different locations.
- Quasar - A supermassive black hole gorging on gas at the centre of a distant galaxy.
- Rotation - The spin of a body about its axis.
- Solar wind - A flow of charged particles that travel from the sun out into the solar system.
- Stony iron - A meteorite that contains regions resembling both a stone meteorite and an iron meteorite.
- Superior planet - A planet that exists outside the orbit of the earth.
- Supernova remnant - An expanding shell of gas ejected at high speeds by a supernova explosion.
- Variable star - A star that fluctuates in brightness.
- Waning - The changing illumination of the moon (or other body) over time.

Top 50 moon quotes that will inspire you
Pretty words related to space
Here is a compilation of some pretty space words you might come across.
- Apogee - The point in the moon's orbit or other satellite where it is farthest from the earth.
- Coma - An area of dust or gas surrounding the nucleus of a comet.
- Faculae - Bright patches visible on the sun's surface or photosphere.
- Inclination - A measure of the tilt of a planet's orbital plane in relation to that of the earth.
- Lunar eclipse - A phenomenon that occurs when the moon passes into the earth's shadow.
- Neutrino - A fundamental particle produced by the nuclear reactions in stars.
- Orbit - The path of a celestial body as it moves through space.
- Ejecta - A material from beneath the surface of a body such as a moon or a planet ejected by an impact such as a meteor and distributed around the surface.
- Protostar - Dense regions of molecular clouds where stars are forming.
- Radio galaxy - A galaxy that gives off large amounts of energy in radio waves.
- Stellar wind - The ejection of gas from the surface of a star.
- Supernova - A star ending its life in a huge explosion.
- Terrestrial planet - A name given to a planet composed mainly of rock and iron, similar to that of earth.
- Big bang - The theory that suggests that the universe was formed from a single point in space during a cataclysmic explosion many years ago.
- Celestial equator - An imaginary line that divides the celestial sphere into a northern and southern hemisphere.
- Inferior planet - A planet that orbits between the earth and the sun.
- Space shuttle - a reusable spacecraft with wings for a controlled descent through the earth's atmosphere.
- Star - A massive ball of gas that generates prodigious amounts of energy from nuclear fusion in its hot, dense core.
- Dwarf planet - A celestial body orbiting the sun that is massive enough to be rounded by its gravity but has not cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals and is not a satellite.
- Virgo cluster - A gigantic cluster of over 2000 galaxies located mainly within the constellation of Virgo.
- White dwarf - A tiny, white star formed when an average-sized star uses up its fuel supply and collapses.

A fascinating Star Wars quiz: How well do you know the saga?
Fancy space-themed words
Looking for fancy space words? Here is a list of fancy space-themed words and their meanings to help you understand what there are.

- Ablation - A process whereby the atmosphere melts away and removes the surface material of an incoming meteorite.
- Aurora - A glow in a planet's ionosphere caused by the interaction between the planet's magnetic field and charged particles from the sun.
- Blue moon - A term used to describe an extra full that occurs in a season. It usually refers to the third full moon in a season with four full moons.
- Double asteroid - Two asteroids that revolve around each other and are held together by gravity.
- Escape velocity - The speed required for an object to escape the gravitational pull of a planet or other body.
- Flare star - A faint red star that appears to change brightness due to explosions on its surface.
- Hypernova - a very energetic supernova thought to result from an extreme core-collapse scenario.
- Libration - An effect caused by the apparent wobble of the moon as it orbits the earth.
- Main belt - The area between Mars and Jupiter where most of the asteroids in our solar system are found.
- Meteor shower - An event where many meteors enter the earth's atmosphere from the same direction in space at nearly the same time.
- Nova - A star that flares up to several times its original brightness for some time before returning to its original state.
- Perigee - The point in the moon's orbit or other satellite at which it is closest to the earth.
- Red giant - A stage in the evolution of a star when the fuel begins to exhaust and the star expands to about fifty times its normal size.
- Saturn - A giant planet that is surrounded by three planar concentric rings of ice particles; the 6th planet from the sun
- Shell star - A type of star which is believed to be surrounded by a thin envelope of gas, which is often indicated by bright emission lines in its spectrum.
- Star - A giant ball of hot gas that creates and emits its own radiation through nuclear fusion .
- Sunspot - A temporary dark blemish on the sun's surface that is a planet-size region of gas cooler than its surroundings.
- Supermoon - A term used to describe a full moon that occurs during the moon's closest approach to the earth.
- Terminator - The line on the moon or a planet that divides the bright, sunlit part from the part in shadow.
- Tidal force - The differential gravitational pull exerted on any extended body within the gravitational field of another body.
- Zodiac - Greek for circle of animals. It’s the set of constellations situated along the ecliptic in the sky, through which the Sun, Moon, and planets move.

Discover impressive details about a habitable planet in a new solar system
What are heavenly bodies?
They are also known as celestial bodies. They are objects found in space and include planets, stars, moons and comets.
How long is 1 hour in space?
An hour in space is equal to an hour on earth.
Why is the moon not a planet?
The moon is not a planet because it revolves around the earth, unlike other planets, which revolve around the sun. It also does not have a gravitational pull, a common characteristic of planets.
There are many space words, and as space exploration continues, new things are discovered, generating more space terminologies. From the above lists, you can master some space terms and explain them.
READ ALSO : 50+ quotes about lockdown life everyone in the world can relate to
Legit.ng recently published an article about lockdown quotes everyone can relate to. The COVID-19 pandemic brought unprecedented times, and many people learned valuable lessons during the lockdown.

Get fascinated with these sunflower tattoo designs
Numerous quotes emerged as people tried to cope with the new lifestyle of staying most of the time indoors. While it seemed a tough moment for many, others found the fun side of it and came up with hilarious, memorable quotes.
Source: Legit.ng
Muhunya Muhonji (Lifestyle writer) Muhunya has been a writer for more than three years. He graduated from Egerton University in 2014 with a degree in Agricultural Economics. He is also a certified public accountant and tax expert. Muhunya joined Legit.ng in July 2021 and writes about various topics such as entertainment, technology, business, and biographies. In 2023, Muhunya finished the AFP course on Digital Investigation Techniques. In March 2024, he completed the Google News Initiative course. Email: [email protected]
Outer Space Vocabulary
one of thousands of rocky objects that move in orbits mostly between those of Mars and Jupiter and have diameters from a fraction of a mile to nearly 500 miles (800 kilometers)
a heavenly body with such strong gravity that light cannot escape it and that is thought to be caused by the collapse of a massive star
a small bright heavenly body that develops a cloudy tail as it moves in an orbit around the sun
a heavenly body similar to a planet but too small to clear other objects from its orbit
Dwarf Planets in our solar system:
Ceres : a dwarf planet that orbits within the asteroid belt with a mean distance from the sun of 2.7 astronomical units (260 million miles) and a diameter of 590 miles (950 kilometers)
Eris : a dwarf planet with a mean distance from the sun of 67 astronomical units (6.2 billion miles) and a diameter of 1500 miles (2400 kilometers)
Haumea : a dwarf planet that orbits within the Kuiper belt with a mean distance from the sun of 43 astronomical units (6.45 billion kilometers) and a diameter of approximately 890 miles (1,430 kilometers)
Makemake : a dwarf planet that orbits within the Kuiper belt with a mean distance from the sun of 46 astronomical units (6.85 billion kilometers) and a diameter of approximately 930 miles (1,500 kilometers)
Pluto : a celestial object that orbits the sun at an average distance of 3.7 million miles (5.9 million kilometers) and has a diameter of about 1500 miles (2300 kilometers) and is often considered one of the planets
any one of the very large groups of stars that make up the universe
a unit of length in astronomy equal to the distance that light travels in one year or about 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers)
one of the small pieces of matter in the solar system that enter the earth's atmosphere where friction may cause them to glow and form a streak of light
a broad band of light that stretches across the sky and is caused by the light of a very great number of faint stars
a smaller body that revolves around a planet
any large heavenly body that orbits a star (as the sun)
Planets in our solar system:
Mercury : the planet that is nearest the sun and has a diameter of about 3000 miles (4700 kilometers)
Venus : the planet that is second in order of distance from the sun and has a diameter of about 7,500 miles (12,100 kilometers)
Earth : the planet that is thirds in distance from the sun. The planet that we live on.
Mars : the planet that is fourth in order of distance from the sun, is known for its redness, and has a diameter of about 4200 miles (6800 kilometers)
Jupiter : the planet that is fifth in order of distance from the sun and is the largest of the planets with a diameter of about 89,000 miles (140,000 kilometers)
Saturn : the planet that is sixth in distance from the sun and has a diameter of about 75,000 miles (120,000 kilometers)
Uranus : the planet that is seventh in order of distance from the sun and has a diameter of about 32,000 miles (51,000 kilometers)
Neptune : the planet that is eighth in order of distance from the sun and has a diameter of about 31,000 miles (50,000 kilometers)
the sun and the planets, asteroids, comets, and meteors that revolve around it
any of the heavenly bodies except planets which are visible at night and look like fixed points of light
the heavenly body in our solar system whose light makes our day and around which the planets revolve
Word of the Day
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!
Games & Quizzes

Space Travel Words
Words related to space travel.
Below is a massive list of space travel words - that is, words related to space travel. The top 4 are: spacefaring , voyage , cruise and journey . You can get the definition(s) of a word in the list below by tapping the question-mark icon next to it. The words at the top of the list are the ones most associated with space travel, and as you go down the relatedness becomes more slight. By default, the words are sorted by relevance/relatedness, but you can also get the most common space travel terms by using the menu below, and there's also the option to sort the words alphabetically so you can get space travel words starting with a particular letter. You can also filter the word list so it only shows words that are also related to another word of your choosing. So for example, you could enter "spacefaring" and click "filter", and it'd give you words that are related to space travel and spacefaring.
You can highlight the terms by the frequency with which they occur in the written English language using the menu below. The frequency data is extracted from the English Wikipedia corpus, and updated regularly. If you just care about the words' direct semantic similarity to space travel, then there's probably no need for this.
There are already a bunch of websites on the net that help you find synonyms for various words, but only a handful that help you find related , or even loosely associated words. So although you might see some synonyms of space travel in the list below, many of the words below will have other relationships with space travel - you could see a word with the exact opposite meaning in the word list, for example. So it's the sort of list that would be useful for helping you build a space travel vocabulary list, or just a general space travel word list for whatever purpose, but it's not necessarily going to be useful if you're looking for words that mean the same thing as space travel (though it still might be handy for that).
If you're looking for names related to space travel (e.g. business names, or pet names), this page might help you come up with ideas. The results below obviously aren't all going to be applicable for the actual name of your pet/blog/startup/etc., but hopefully they get your mind working and help you see the links between various concepts. If your pet/blog/etc. has something to do with space travel, then it's obviously a good idea to use concepts or words to do with space travel.
If you don't find what you're looking for in the list below, or if there's some sort of bug and it's not displaying space travel related words, please send me feedback using this page. Thanks for using the site - I hope it is useful to you! 🐨
- spacefaring
- spaceflight
- hypertravel
- peregrinate
- peregrination
- cybertravel
- circumnavigation
- round trip ticket
- buy souvenir
- cosmopolitan
- between deck
- go back home
- motion sickness
- experience different culture
- visit other country
- book holiday
- hand luggage
- see new place
- choose destination
- plane ticket
- mode of transport
- go to airport
- fly in airplane
- passenger ticket
- arrive at destination
- return ticket
- mode of transportation
- board plane
- drive your car
- business trip
- save your money
- gravity-assist
- visit relative
- fellow traveller
- destination
- accommodate
- aeronautics
- rollercoaster
- pseudospace
- kilometrage
- spaceworthy
- hammerspace
- thanatourism
- astronautics
- biomedicine
- adventurous
- astronavigation
- dangerousness
- intercontinental
- rollercoasters
- transportation
- get on plane
- bioastronautics
- retrorocket
- go someplace
- subarachnoid space
- space simulator
- accommodation
- space guidance
- change of location
- difficultly
- horseriding
- space reconnaissance
- family activity
- horseback ride
- dead air space
- fast than light
- interstellar space
- space alien
- toll highway
- train ticket
- space opera
- phase space
- get somewhere
- bedroom community
- kuiper belt
- spring break
- space satellite
- mathematical space
- outer space
- learn foreign language
- interplanetary space
- metric space
- dead reckon
- head for hill
- many planet
- travel long distance
- bragg's law
- aeromedicine
- rubber duck
- satchel bag
- move walkway
- radio control helicopter
- time travel
- rough and tumble
- talk on phone
- water travel
- roller coaster
- yuri gagarin
- yuri alekseyevich gagarin
- dinner party
- space rocket
- nintendo wii
- time space convergence
- wet blanket
- science fiction
- climb mountain
- action potential
- computer game
- sleigh ride
- go for drive
- equestrian sport
- helium balloon
- play marble
- go on vacation
- paper airplane
- cruise ship
- visit friend
- make fun of
- epicyclic train
- bladder be empty
- lose something
- go somewhere
- move sidewalk
- road warrior
That's about all the space travel related words we've got! I hope this list of space travel terms was useful to you in some way or another. The words down here at the bottom of the list will be in some way associated with space travel, but perhaps tenuously (if you've currenly got it sorted by relevance, that is). If you have any feedback for the site, please share it here , but please note this is only a hobby project, so I may not be able to make regular updates to the site. Have a nice day! 🐊
Which Language Do You Want to Learn?
- Inside Babbel
- Babbel Bytes
ARTICLES ABOUT
Jargon watch: astronauts and the language of space travel.

“5-4-3-2-1-0 booster ignition and liftoff!” You’ve probably heard the familiar sounds of a spaceship launch countdown at some point, but there are plenty of other space-related words and phrases that may be totally unintelligible to you. Astronaut lingo has been around as long as NASA itself. In fact, some of the earliest space slang was pretty hilarious, like referring to Cape Canaveral as “Malfunction Junction” or an astronaut’s adjustable seat as a “barber chair.”
Astronaut lingo has toned down quite a bit since the 1960s, and now it largely comprises jargon words and acronyms to describe technical aspects of spaceships and interstellar travel. While most of it’s only really useful if you plan to join NASA or visit the International Space Station , there are a few pieces of slang that have made it into our general lexicon. What may have started in outer space eventually became popular among civilians down on Earth.
This list, which is by no means comprehensive, will introduce you to some of the most common or interesting astronaut lingo. And if you can’t get enough of outer space linguistics, check out this explanation of where some common space exploration terms originated.
A Brief Guide To Astronaut Lingo
abort — to cut short or cancel a mission, first used in reference to space-flight in 1946
airlock — a room with two doors that allows astronauts to enter and exit a spacecraft without letting air out
command module — the compartment of a spacecraft that carries the crew, communications equipment and controls
downlink — radio signal sent to Earth from a spacecraft
glitch — a hitch, snag or malfunction; now used universally
keyhole — a part of the sky where an antenna cannot track a spacecraft due to technical limitations
liftoff — when a rocket leaves the launch pad and begins its flight into space
L minus (L-) — refers to the days, hours and minutes left until launch (L-0). T minus (T-) refers to the time remaining until launch on the official countdown clock. L- time and T- time are usually synced .
LOX — stands for liquid oxygen , which, when combined with fuel, creates a propellant that can be used to launch a rocket
nadir — the downward direction from a spacecraft to the center of a planet below (opposite the zenith )
puffy head bird legs — the feeling of a congested head and wobbly legs astronauts get upon the loss of gravity, which allows the fluid in their bodies to move around
screw the pooch — to make an embarrassing mistake (and yes, this phrase did originally come from NASA)
some words — instructions or advice given between astronauts and ground control, as in “We have some words for you about the signal light issue”
Spacecraft Event Time (SCET) — local time for events that happen aboard the spacecraft (the time on Earth minus the elapsed time between Earth and the spacecraft)
uplink — radio signal sent to a spacecraft from Earth
zenith — the point on a planet directly above the spacecraft (opposite the nadir )
zero gravity — the weightlessness astronauts experience in space due to an apparent absence of gravity (though gravity is still technically in effect)
Header Photo by The New York Public Library on Unsplash

Basics of Spaceflight: Glossary
Use your browser's " FIND " capability to locate a word right away on this page. You should also have a good English dictionary at hand. Additional resources are the "SEARCH BSF" function at the bottom of each page, and the Units of Measure section. You might also wish to consult the SEDS Basic Astronomical Terms page, or the NASA Thesaurus . Some additional glossaries that may be useful are linked here .
a, A -- Acceleration. a = Δ velocity / Δ time. Acceleration = Force / Mass
A -- Ampere, the SI base unit of electric current.
Å -- Angstrom (0.0001 micrometer, 0.1 nm).
A Ring -- The outermost of the three rings of Saturn that are easily seen in a small telescope.
AAAS -- American Association for the Advancement of Science.
AACS -- Attitude and Articulation Control Subsystem onboard a spacecraft.
AAS -- American Astronomical Society.
AC -- Alternating current.
Acceleration -- Change in velocity . Note that since velocity comprises both direction and magnitude (speed), a change in either direction or speed constitutes acceleration.
ALT -- Altitude.
ALT -- Altimetry data.
AM -- Ante meridiem (Latin: before midday), morning.
am -- Attometer (10 -18 m).
AMMOS -- Advanced Multimission Operations System.
Amor -- A class of Earth-crossing asteroid .
AO -- Announcement of Opportunity.
AOS -- Acquisition Of Signal, used in DSN operations.
Aphelion -- Apoapsis in solar orbit.
Apoapsis -- The farthest point in an orbit from the body being orbited.
Apogee -- Apoapsis in Earth orbit.
Apochron -- Apoapsis in Saturn orbit.
Apojove -- Apoapsis in Jupiter orbit.
Apollo -- A class of Earth-crossing asteroid .
Apolune -- Apoapsis in lunar orbit.
Apselene -- Apoapsis in lunar orbit.
Argument -- Angular distance.
Argument of periapsis -- The argument (angular distance) of periapsis from the ascending node.
Ascending node -- The point at which an orbit crosses a reference plane (such as a planet's equatorial plane or the ecliptic plane) going north.
Asteroids -- Small bodies composed of rock and metal in orbit about the Sun.
Aten -- A class of Earth-crossing asteroid .
Attometer -- 10 -18 meter.
Astronomical Twilight -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
au -- Astronomical Unit, based on the mean Earth-to-Sun distance, 149,597,870 km. Refer to "Units of Measure" section for complete information.
AZ -- Azimuth.
B -- Bel, a unit of ratio equal to ten decibels . Named in honor of telecommunications pioneer Alexander Graham Bell.
B Ring -- The middle of the three rings of Saturn that are easily seen in a small telescope.
Barycenter -- The common center of mass about which two or more bodies revolve.
Beacon -- Downlink from a spacecraft that immediately indicates the state of the spacecraft as being one of several possible states by virtue of the presence and/or frequency of the subcarrier. See Chapter 10.
Bel -- Unit of ratio equal to ten decibels. Named in honor of telecommunications pioneer Alexander Graham Bell.
Billion -- In the U.S., 10 9 . In other countries using SI, 10 12 .
Bi-phase -- A modulation scheme in which data symbols are represented by a shift from one phase to another. See Chapter 10.
BOT -- Beginning Of Track, used in DSN operations.
BPS -- Bits Per Second, same as Baud rate.
BSF -- Basics of Space Flight (this document).
BVR -- DSN Block Five (V) Receiver.
BWG -- Beam waveguide 34-m DSS, the DSN's newest DSS design.
c -- The speed of light, 299,792 km per second.
C-band -- A range of microwave radio frequencies in the neighborhood of 4 to 8 GHz.
C Ring -- The innermost of the three rings of Saturn that are easily seen in a small telescope.
Caltech -- The California Institute of Technology.
Carrier -- The main frequency of a radio signal generated by a transmitter prior to application of any modulation.
Cassegrain -- Reflecting scheme in antennas and telescopes having a primary and a secondary reflecting surface to "fold" the EMF back to a focus near the primary reflector.
CCD -- Charge Coupled Device, a solid-state imaging detector.
C&DH -- Command and Data Handling subsystem on board a spacecraft, similar to CDS.
CCS -- Computer Command subsystem on board a spacecraft, similar to CDS.
CCSDS -- Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems, developer of standards for spacecraft uplink and downlink, including packets.
CDR -- GCF central data recorder.
CDS -- Command and Data Subsystem onboard a spacecraft.
CDSCC -- DSN's Canberra Deep Space Communications Complex in Australia.
CDU -- Command Detector Unit onboard a spacecraft.
Centrifugal force -- The outward-tending apparent force of a body revolving around another body.
Centimeter -- 10 -2 meter.
Centripetal acceleration -- The inward acceleration of a body revolving around another body.
CGPM -- General Conference of Weights and Measures, Sevres France. The abbreviation is from the French. CGPM is the source for the multiplier names (kilo, mega, giga, etc.) listed in this document.
Chandler wobble -- A small motion in the Earth's rotation axis relative to the surface, discovered by American astronomer Seth Carlo Chandler in 1891. Its amplitude is about 0.7 arcseconds (about 15 meters on the surface) with a period of 433 days. It combines with another wobble with a period of one year, so the total polar motion varies with a period of about 7 years. The Chandler wobble is an example of free nutation for a spinning non-spherical object.
Channel -- In telemetry, one particular measurement to which changing values may be assigned. See Chapter 10.
CIT -- California Institute of Technology, Caltech.
Civil Twilight -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
Clarke orbit -- Geostationary orbit.
CMC -- Complex Monitor and Control, a subsystem at DSCCs.
CMD -- DSN Command System. Also, Command data.
CNES -- Centre National d'Études Spatiales, France.
Conjunction -- A configuration in which two celestial bodies have their least apparent separation.
Coherent -- Two-way communications mode wherein the spacecraft generates its downlink frequency based upon the frequency of the uplink it receives.
Coma -- The cloud of diffuse material surrounding the nucleus of a comet.
Comets -- Small bodies composed of ice and rock in various orbits about the Sun.
CRAF -- Comet Rendezvous / Asteroid Flyby mission, cancelled.
CRS -- Cosmic Ray Subsystem, high-energy particle instrument on Voyager.
CRT -- Cathode ray tube video display device.
DC -- Direct current.
DC -- The DSN Downlink Channel, several of which are in each DSN Downlink Tracking & Telemetry subsystem, DTT.
DCC -- The DSN Downlink Channel Controller, one of which is in each DSN Downlink Channel, DC.
DCPC -- The DSN Downlink Channel Processor Cabinet, one of which contains a DSN Downlink Channel, DC.
DEC -- Declination.
Decibel -- dB , an expression of ratio (see dB, above). One tenth of a Bel. See NIST website for further definition.
Declination -- The measure of a celestial body's apparent height above or below the celestial equator.
Density -- Mass per unit volume. For example , the density of water can be stated as 1 gram/cm 3 .
Descending node -- The point at which an orbit crosses a reference plane (such as a planet's equatorial plane or the ecliptic plane) going south.
DKF -- DSN keyword file, also known as KWF.
Doppler effect -- The effect on frequency imposed by relative motion between transmitter and receiver. See Chapter 6 .
Downlink -- Signal received from a spacecraft.
DSOT -- Data System Operations Team, part of the DSMS staff.
DSCC -- Deep Space Communications Complex, one of three DSN tracking sites at Goldstone, California; Madrid, Spain; and Canberra, Australia; spaced about equally around the Earth for continuous tracking of deep-space vehicles.
DSMS -- Deep Space Mission System, the system of computers, software, networks, and procedures that processes data from the DSN at JPL.
DSN -- Deep Space Network, NASA's worldwide spacecraft tracking facility managed and operated by JPL.
DSS -- Deep Space Station, the antenna and front-end equipment at DSCCs.
DT -- Dynamical Time. Replaces Ephemeris Time, ET, as the independent argument in dynamical theories and ephemerides. Its unit of duration is based on the orbital motions of the Earth, Moon, and planets. DT has two expressions, Terrestrial Time, TT, (or Terrestrial Dynamical Time, TDT), and Barycentric Dynamical Time, TDB. More information on these, and still more timekeeping expressions, may be found at the U.S. Naval Observatory website .
DTT -- The DSN Downlink Tracking & Telemetry subsystem.
Dyne -- A unit of force equal to the force required to accelerate a 1-g mass 1 cm per second per second. Compare with Newton.
E -- Exa, a multiplier, x10 18 from the Greek "hex" (six, the "h" is dropped). The reference to six is because this is the sixth multiplier in the series k, M, G, T, P, E. See the entry for CGPM.
Earth -- Third planet from the Sun, a terrestrial planet.
Eccentricity -- The distance between the foci of an ellipse divided by the major axis.
Ecliptic -- The plane in which Earth orbits the Sun and in which solar and lunar eclipses occur.
EDL -- (Atmospheric) Entry, Descent, and Landing.
EDR -- Experiment Data Record.
EHz -- ExaHertz (10 18 Hz)
EL -- Elevation.
Ellipse -- A closed plane curve generated in such a way that the sums of its distances from the two fixed points (the foci) is constant.
ELV -- Expendable launch vehicle.
EM -- Electromagnetic.
EMF -- Electromagnetic force (radiation).
EMR -- Electromagnetic radiation.
EOT -- End Of Track, used in DSN operations.
Equator -- An imaginary circle around a body which is everywhere equidistant from the poles, defining the boundary between the northern and southern hemispheres.
Equinox -- The equinoxes are times at which the center of the Sun is directly above the Earth's equator. The day and night would be of equal length at that time, if the Sun were a point and not a disc, and if there were no atmospheric refraction. Given the apparent disc of the Sun, and the Earth's atmospheric refraction, day and night actually become equal at a point within a few days of each equinox. The vernal equinox marks the beginning of spring in the northern hemisphere, and the autumnal equinox marks the beginning of autumn in the northern hemisphere.
ERC -- NASA's Educator Resource Centers.
ERT -- Earth-received time, UTC of an event at DSN receive-time, equal to SCET plus OWLT.
ESA -- European Space Agency.
ESP -- Extra-Solar Planet, a planet orbiting a star other than the Sun. See also Exoplanet.
ET -- Ephemeris time, a measurement of time defined by orbital motions. Equates to Mean Solar Time corrected for irregularities in Earth's motions. Obsolete, replaced by TT, Terrestrial Time.
eV -- Electron volt, a measure of the energy of subatomic particles.
Exoplanet -- Extrasolar planet. A planet orbiting a star other than the Sun.
Extrasolar planet -- A planet orbiting a star other than our Sun. Exoplanet.
FDS -- Flight Data Subsystem.
FE -- Far Encounter phase of mission operations.
Femtometer -- 10 -15 meter.
Fluorescence -- The phenomenon of emitting light upon absorbing radiation of an invisible wavelength.
fm -- Femtometer (10 -15 m)
FM -- Frequency modulation.
FTS -- DSN Frequency and Timing System. Also, frequency and timing data.
FY -- Fiscal year.
G -- Universal Constant of Gravitation . Its tiny value (G = 6.6726 x 10 -11 Nm 2 /kg 2 ) is unchanging throughout the universe.
G -- Giga, a multiplier, x10 9 , from the Latin "gigas" (giant). See the entry for CGPM.
g -- Acceleration due to a body's gravity. Constant at any given place, the value of g varies from object to object (e.g. planets), and also with the distance from the center of the object. The relationship between the two constants is: g = GM/r 2 where r is the radius of separation between the masses' centers, and M is the mass of the primary body (e.g. a planet). At Earth's surface, the value of g = 9.8 meters per second per second (9.8m/s 2 ). See also weight .
g -- Gram, a thousandth of the metric standard unit of mass (see kg ). The gram was originally based upon the weight of a cubic centimeter of water, which still approximates the current value.
Gal -- Unit of gravity field measurement corresponding to a gravitational acceleration of 1 cm/sec 2 .
Galaxy -- One of billions of systems, each composed of numerous stars, nebulae, and dust.
Galilean satellites -- The four large satellites of Jupiter so named because Galileo discovered them when he turned his telescope toward Jupiter: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto.
Gamma rays -- Electromagnetic radiation in the neighborhood of 100 femtometers wavelength.
GCF -- Ground Communications Facilities, provides data and voice communications between JPL and the three DSCCs.
GDS -- Ground Data System, encompasses DSN, GCF, DSMS, and project data processing systems.
GDSCC -- DSN's Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex in California.
GEO -- Geosynchronous Earth Orbit.
Geostationary -- A geosynchronous equatorial circular orbit. Also called Clarke orbit.
Geosynchronous -- A direct, circular, low inclination orbit about the Earth having a period of 23 hours 56 minutes 4 seconds.
GHz -- Gigahertz (10 9 Hz).
GLL -- The Galileo spacecraft.
GMT -- Greenwich Mean Time. Obsolete. UT, Universal Time is preferred.
Gravitational waves -- Einsteinian distortions of the space-time medium predicted by general relativity theory (not yet directly detected as of March 2010). (Not to be confused with gravity waves, see below.)
Gravity assist -- Technique whereby a spacecraft takes angular momentum from a planet's solar orbit (or a satellite's orbit) to accelerate the spacecraft, or the reverse. See Chapter 4.
Gravity waves -- Certain dynamical features in a planet's atmosphere (not to be confused with gravitational waves, see above).
Great circle -- An imaginary circle on the surface of a sphere whose center is at the center of the sphere.
GSSR -- Goldstone Solar System Radar, a technique which uses very high-power X and S-band transmitters at DSS 14 to illuminate solar system objects for imaging.
GTL -- Geotail spacecraft.
GTO -- Geostationary (or geosynchronous) Transfer Orbit.
HA -- Hour Angle.
Halo orbit -- A spacecraft's pattern of controlled drift about an unstable Lagrange point (L1 or L2 for example) while in orbit about the primary body (e.g. the Sun).
HEF -- DSN's high-efficiency 34-m DSS, replaces STD DSSs.
Heliocentric -- Sun-centered.
Heliopause -- The boundary theorized to be roughly circular or teardrop-shaped, marking the edge of the Sun's influence, perhaps 100 AU from the Sun.
Heliosphere -- The space within the boundary of the heliopause, containing the Sun and solar system.
HEMT -- High-electron-mobility transistor, a low-noise amplifier used in DSN.
HGA -- High-Gain Antenna onboard a spacecraft.
Hohmann Transfer Orbit -- Interplanetary trajectory using the least amount of propulsive energy. See Chapter 4.
Horizon -- The line marking the apparent junction of Earth and sky. For the technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory's Astronomical Applications .
h -- Hour, 60 minutes of time.
Hour Angle -- The angular distance of a celestial object measured westward along the celestial equator from the zenith crossing. In effect, HA represents the RA for a particular location and time of day.
ICRF -- International Celestial Reference Frame. The realization of the ICRS provided by the adopted positions of extragalactic objects. Link .
ICRS -- International Celestial Reference System. Conceptual basis for celestial positions, aligned with respect to extremely distant objects and utilizing the theory of general relativity. Link .
IERS -- International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service. Link .
IF -- Intermediate Frequency. In a radio system, a selected processing frequency between RF (Radio Frequency) and the end product (e.g. audio frequency).
Inclination -- The angular distance of the orbital plane from the plane of the planet's equator, stated in degrees.
IND -- JPL's Interplanetary Network Directorate, formerly IPN-ISD.
Inferior planet -- Planet which orbits closer to the Sun than the Earth's orbit.
Inferior conjunction -- Alignment of Earth, Sun, and an inferior planet on the same side of the Sun.
Ion -- A charged particle consisting of an atom stripped of one or more of its electrons.
IPAC -- Infrared Processing and Analysis Center at Caltech campus on Wilson Avenue in Pasadena.
IPC -- Information Processing Center, JPL's computing center on Woodbury Avenue in Pasadena.
IPN-ISD -- (Obsolete. See IND) JPL's Interplanetary Network and Information Systems Directorate, formerly TMOD.
IR -- Infrared, meaning "below red" radiation. Electromagnetic radiation in the neighborhood of 100 micrometers wavelength.
IRAS -- Infrared Astronomical Satellite.
ISM -- Interstellas medium.
ISO -- International Standards Organization.
ISOE -- Integrated Sequence of Events.
Isotropic -- Having uniform properties in all directions.
IUS -- Inertial Upper Stage.
JGR -- Journal Of Geophysical Research.
Jovian -- Jupiter-like planets, the gas giants Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
JPL -- Jet Propulsion Laboratory, operating division of the California Institute of Technology.
Jupiter -- Fifth planet from the Sun, a gas giant or Jovian planet.
K -- Kelvin, the SI base unit of thermodynamic temperature.
K-band -- A range of microwave radio frequencies in the neighborhood of 12 to 40 GHz.
kg -- Kilogram. See below.
Keyhole -- An area in the sky where an antenna cannot track a spacecraft because the required angular rates would be too high. Mechanical limitations may also contribute to keyhole size. Discussed in depth under Chapter 2 .
kHz -- kilohertz.
Kilogram (kg) -- the SI base unit of mass, based on the mass of a metal cylinder kept in France. See also g (gram).
Kilometer -- 10 3 meter.
Klystron -- A microwave travelling wave tube power amplifier used in transmitters.
km -- Kilometers.
KSC -- Kennedy Space Center, Cape Canaveral, Florida.
KWF -- Keyword file of events listing DSN station activity. Also known as DKF, DSN keyword file.
Kuiper belt -- A disk-shaped region about 30 to 100 AU from the Sun considered to be the source of the short-period comets.
LAN -- Local area network for inter-computer communications.
Large Magellanic Cloud -- LMC, the larger of two small galaxies orbiting nearby our Milky Way galaxy, which are visible from the southern hemisphere.
Laser -- Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Compare with Maser.
Latitude -- Circles in parallel planes to that of the equator defining north-south measurements, also called parallels.
L-band -- A range of microwave radio frequencies in the neighborhood of 1 to 2 GHz.
LCP -- Left-hand circular polarization.
Leap Second -- A second which may be added or subtracted to adjust UTC at either, both, or neither, of two specific opportunities each year.
Leap Year -- Every fourth year, in which a 366th day is added since the Earth's revolution takes 365 days 5 hr 49 min.
LECP -- Low-Energy Charged-Particular Detector onboard a spacecraft.
LEO -- Low Equatorial Orbit.
LGA -- Low-Gain Antenna onboard a spacecraft.
Light -- Electromagnetic radiation in the neighborhood of 1 nanometer wavelength.
Light speed -- 299,792 km per second, the constant c.
Light time -- The amount of time it takes light or radio signals to travel a certain distance at light speed.
Light year -- A measure of distance, the distance light travels in one year, about 63,197 au.
LMC -- Large Magellanic Cloud, the larger of two small galaxies orbiting nearby our Milky Way galaxy, which are visible from the southern hemisphere.
LMC -- Link Monitor and Control subsystem at the SPCs within the DSN DSCCs.
LNA -- Low-noise amplifier in DSN, either a maser or a HEMT.
Local time -- Time adjusted for location around the Earth or other planets in time zones.
Longitude -- Great circles that pass through both the north and south poles, also called meridians.
LOS -- Loss Of Signal, used in DSN operations.
LOX -- Liquid oxygen.
m -- Meter (U.S. spelling; elsewhere metre), the international standard of linear measurement.
m -- milli- multiplier of one one-thousandth, e.g. 1 mW = 1/1000 of a Watt, mm = 1/1000 meter.
m, M -- Mass. The kilogram is the standard unit of mass. Mass = Acceleration / Force .
M -- Mega, a multiplier, x10 6 (million) from the Greek "megas" (great). See the entry for CGPM.
M100 -- Messier Catalog entry number 100 is a spiral galaxy in the Virgo cluster seen face-on from our solar system.
Major axis -- The maximum diameter of an ellipse.
Mars -- Fourth planet from the Sun, a terrestrial planet.
Maser -- A microwave travelling wave tube amplifier named for its process of Microwave Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Compare with Laser. In the Deep Space Network, masers are used as low-noise amplifiers of downlink signals, and also as frequency standards.
Mass -- A fundamental property of an object comprising a numerical measure of its inertia; the amount of matter in the object. While an object's mass is constant (ignoring Relativity for this purpose), its weight will vary depending on its location. Mass can only be measured in conjunction with force and acceleration .
MC-cubed -- Mission Control and Computing Center at JPL (outdated).
MCCC -- Mission Control and Computing Center at JPL (outdated).
MCD -- DSN's maximum-likelihood convolutional decoder, the Viterbi decoder.
MCT -- Mission Control Team, JPL Section 368 mission execution real-time operations.
MDSCC -- DSN's Madrid Deep Space Communications Complex in Spain.
Mean solar time -- Time based on an average of the variations caused by Earth's non-circular orbit. The 24-hour day is based on mean solar time.
Mercury -- First planet from the Sun, a terrestrial planet.
Meridians -- Great circles that pass through both the north and south poles, also called lines of longitude.
MESUR -- The Mars Environmental Survey project at JPL, the engineering prototype of which was originally called MESUR Pathfinder, later Mars Pathfinder.
Meteor -- A meteoroid which is in the process of entering Earth's atmosphere. It is called a meteorite after landing.
Meteorite -- Rocky or metallic material which has fallen to Earth or to another planet.
Meteoroid -- Small bodies in orbit about the Sun which are candidates for falling to Earth or to another planet.
MGA -- Medium-Gain Antenna onboard a spacecraft.
MGN -- The Magellan spacecraft.
MGSO -- (Obsolete. See TMOD) JPL's Multi-mission Ground Systems Office.
MHz -- Megahertz (10 6 Hz).
Micrometer -- µm, 10 -6 meter.
Micron -- Obsolete terms for micrometer, µm (10 -6 m).
Milky Way -- The galaxy which includes the Sun and Earth.
Millimeter -- 10 -3 meter.
MIT -- Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
MLI -- Multi-layer insulation (spacecraft blanketing). See Chapter 11 .
mm -- millimeter (10 -3 m).
MO -- The Mars Observer spacecraft.
Modulation -- The process of modifying a radio frequency by shifting its phase, frequency, or amplitude to carry information.
MON -- DSN Monitor System. Also, monitor data.
Moon -- A small natural body which orbits a larger one. A natural satellite. Capitalized, the Earth's natural satellite.
Moonrise -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
Moonset -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
MOSO -- Multimission Operations Systems Office at JPL.
MR -- Mars relay.
µm -- Micrometer (10 -6 m).
Multiplexing -- A scheme for delivering many different measurements in one data stream. See Chapter 10.
N -- Newton, the SI unit of force equal to that required to accelerate a 1-kg mass 1 m per second per second (1m/sec 2 ). Compare with dyne.
N -- North.
Nadir -- The direction from a spacecraft directly down toward the center of a planet. Opposite the zenith.
NASA -- National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
Nautical Twilight -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
NE -- Near Encounter phase in flyby mission operations.
Neptune -- Eighth planet from the Sun, a gas giant or Jovian planet.
NiCad -- Nickel-cadmium rechargable battery.
NIMS -- Near-Infrared Mapping Spectrometer onboard the Galileo spacecraft.
NIST -- National Institute of Standards .
nm -- Nanometer (10 -9 m).
nm -- Nautical Mile, equal to the distance spanned by one minute of arc in latitude, 1.852 km.
NMC -- Network Monitor and Control subsystem in DSN.
NOCC -- DSN Network Operations Control Center at JPL.
Nodes -- Points where an orbit crosses a reference plane.
Non-coherent -- Communications mode wherein a spacecraft generates its downlink frequency independent of any uplink frequency.
Nucleus -- The central body of a comet.
Nutation -- A small nodding motion in a rotating body. Earth's nutation has a period of 18.6 years and an amplitude of 9.2 arc seconds.
NRZ -- Non-return to zero. Modulation scheme in which a phase deviation is held for a period of time in order to represent a data symbol. See Chapter 10.
NSP -- DSN Network Simplification Project. A project that re-engineered the DSN to consolidate seven data systems into two data systems that handle the same data types.
OB -- Observatory phase in flyby mission operations encounter period.
One-way -- Communications mode consisting only of downlink received from a spacecraft.
Oort cloud -- A large number of comets theorized to orbit the Sun in the neighborhood of 50,000 au.
OPCT -- Operations Planning and Control Team at JPL, "OPSCON." Obsolete, replaced by DSOT, Data Systems Operations Team.
Opposition -- Configuration in which one celestial body is opposite another in the sky. A planet is in opposition when it is 180 degrees away from the Sun as viewed from another planet (such as Earth). For example, Saturn is at opposition when it is directly overhead at midnight on Earth.
OPNAV -- Optical Navigation (images).
OSI -- ISO's Open Systems Interconnection protocol suite.
OSR -- Optical Solar Reflector, thermal control component onboard a spacecraft.
OSS -- Office Of Space Science, NASA. Obsolete, replaced by Science Mission Directorate (SMD).
OSSA -- Office Of Space Science and Applications, NASA (Obsolete, see OSS).
OTM -- Orbit Trim Maneuver, spacecraft propulsive maneuver.
OWLT -- One-Way Light Time, elapsed time between Earth and spacecraft or solar system body.
Packet -- A quantity of data used as the basis for multiplexing, for example in accordance with CCSDS.
PAM -- Payload Assist Module upper stage.
Parallels -- Circles in parallel planes to that of the equator defining north-south measurements, also called lines of latitude.
Pathfinder -- The Mars Environmental Survey (MESUR) engineering prototype later named Mars Pathfinder.
PDS -- Planetary Data System.
PDT -- Pacific Daylight Time.
PE -- Post Encounter phase in flyby mission operations.
Periapsis -- The point in an orbit closest to the body being orbited.
Perigee -- Periapsis in Earth orbit.
Perichron -- Periapsis in Saturn orbit.
Perihelion -- Periapsis in solar orbit.
Perijove -- Periapsis in Jupiter orbit.
Perilune -- Periapsis in lunar orbit.
Periselene -- Periapsis in lunar orbit.
Phase -- The angular distance between peaks or troughs of two waveforms of similar frequency.
Phase -- The particular appearance of a body's state of illumination, such as the full or crescent phases of the Moon.
Phase -- Any one of several predefined periods in a mission or other activity.
Photovoltaic -- Materials that convert light into electric current.
PHz -- Petahertz (10 15 Hz).
PI -- Principal Investigator, scientist in charge of an experiment.
Picometer -- 10 -12 meter.
PIO -- JPL's Public Information Office.
Plasma -- Electrically conductive fourth state of matter (other than solid, liquid, or gas), consisting of ions and electrons.
PLL -- Phase-lock-loop circuitry in telecommunications technology.
Plunge -- In describing the tracking motion of an AZ-EL or ALT-AZ mounted radio telescope, to "plunge" means to exceed 90° in elevation and then to continue tracking as elevation decreases on the other side without swiveling around in azimuth. This is not a capability of DSN antennas.
Pluto -- Ninth planet from the Sun, sometimes classified as a small terrestrial planet.
pm -- Picometer (10 -12 m).
PM -- Post meridiem (Latin: after midday), afternoon.
PN10 -- Pioneer 10 spacecraft.
PN11 -- Pioneer 11 spacecraft.
Prograde -- Orbit in which the spacecraft moves in the same direction as the planet rotates. See retrograde.
PST -- Pacific Standard Time.
PSU -- Pyrotechnic Switching Unit onboard a spacecraft.
Quasar -- Quasi-stellar object observed mainly in radio waves. Quasars are extragalactic objects believed to be the very distant centers of active galaxies.
Radian -- Unit of angular measurement equal to the angle at the center of a circle subtended by an arc equal in length to the radius. Equals about 57.296 degrees.
RAM -- Random Access Memory.
RCP -- Right-hand circular polarization.
Red dwarf -- A small star, on the order of 100 times the mass of Jupiter.
Reflection -- The deflection or bouncing of electromagnetic waves when they encounter a surface.
Refraction -- The deflection or bending of electromagnetic waves when they pass from one kind of transparent medium into another.
REM -- Receiver Equipment Monitor within the Downlink Channel (DC) of the Downlink Tracking & Telemetry subsystem (DTT).
Retrograde -- Orbit in which the spacecraft moves in the opposite direction from the planet's rotation. See prograde.
RF -- Radio Frequency.
RFI -- Radio Frequency Interference.
Right Ascension -- The angular distance of a celestial object measured in hours, minutes, and seconds along the celestial equator eastward from the vernal equinox.
Rise -- As in ascending above the horizon, for the technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory's Astronomical Applications .
RNS -- GCF reliable network service.
ROM -- Read Only Memory.
RPIF -- Regional Planetary Imaging Data Facilities.
RRP -- DSN Receiver & Ranging Processor within the Downlink Channel (DC) of the Downlink Tracking & Telemetry subsystem (DTT).
RS -- DSN Radio Science System. Also, radio science data.
RTG -- Radioisotope Thermo-Electric Generator onboard a spacecraft.
RTLT -- Round-Trip Light Time, elapsed time roughly equal to 2 x OWLT.
S -- South.
s -- Second, the SI base unit of time (see this extensive definition).
SA -- Solar Array, photovoltaic panels onboard a spacecraft.
SAF -- Spacecraft Assembly Facility, JPL Building 179.
SAR -- Synthetic Aperture Radar
Satellite -- A small body which orbits a larger one. A natural or an artificial moon. Earth-orbiting spacecraft are called satellites. While deep-space vehicles are technically satellites of the Sun or of another planet, or of the galactic center, they are generally called spacecraft instead of satellites.
Saturn -- Sixth planet from the Sun, a gas giant or Jovian planet.
S-band -- A range of microwave radio frequencies in the neighborhood of 2 to 4 GHz.
SC -- Steering Committee.
SCET -- Spacecraft Event Time, equal to ERT minus OWLT.
SCLK -- Spacecraft Clock Time, a counter onboard a spacecraft.
Sec -- Abbreviation for Second.
Second -- the SI base unit of time. See this extensive definition.
SEDR -- Supplementary Experiment Data Record.
SEF -- Spacecraft event file.
SEGS -- Sequence of Events Generation Subsystem.
Semi-major axis -- Half the distance of an ellipse's maximum diameter, the distance from the center of the ellipse to one end.
Set -- As in going below the horizon, for the technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory's Astronomical Applications .
SFOF -- Space Flight Operations Facility, Buildings 230 and 264 at JPL.
SFOS -- Space Flight Operations Schedule, product of SEGS.
Shepherd moons -- Moons which gravitationally confine ring particles.
SI -- The International System of Units (metric system). See also Units of Measure .
SI base unit -- One of seven SI units of measure from which all the other SI units are derived. See SI derived unit. See also Units of Measure .
SI derived unit -- One of many SI units of measure expressed as relationships of the SI base units. For example, the watt, W, is the SI derived unit of power. It is equal to joules per second. W = m 2 ⋅ kg ⋅ s –3 (Note: the joule, J, is the SI derived unit for energy, work, or quantity of heat.) See also Units of Measure .
Sidereal time -- Time relative to the stars other than the Sun.
SIRTF -- Space Infrared Telescope Facility.
SMC -- Small Magellanic Cloud, the smaller of two small galaxies orbiting nearby our Milky Way galaxy, which are visible from the southern hemisphere.
SMD -- Science Mission Directorate, NASA (previously Office Of Space Science, OSS).
SOE -- Sequence of Events.
Solar wind -- Flow of lightweight ions and electrons (which together comprise plasma) thrown from the Sun.
SNR -- Signal-to-Noise Ratio.
SPC -- Signal Processing Center at each DSCC.
Specific Impulse -- A measurement of a rocket's relative performance. Expressed in seconds, the number of which a rocket can produce one pound of thrust from one pound of fuel. The higher the specific impulse, the less fuel required to produce a given amount of thrust.
Spectrum -- A range of frequencies or wavelengths.
SSA -- Solid State Amplifier in a spacecraft telecommunications subsystem, the final stage of amplification for downlink.
SSI -- Solid State Imaging Subsystem, the CCD-based cameras on Galileo.
SSI -- Space Services, Inc., Houston, manufacturers of the Conestoga launch vehicle.
STD -- Standard 34-m DSS, retired from DSN service.
STS -- Space Transportation System (Space Shuttle).
Subcarrier -- Modulation applied to a carrier which is itself modulated with information-carrying variations.
Sunrise -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
Sunset -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
Sun synchronous orbit -- A spacecraft orbit that precesses, wherein the location of periapsis changes with respect to the planet's surface so as to keep the periapsis location near the same local time on the planet each orbit. See walking orbit.
Superior planet -- Planet which orbits farther from the Sun than Earth's orbit.
Superior conjunction -- Alignment between Earth and a planet on the far side of the Sun.
SWG -- Science Working Group.
TAU -- Thousand AU Mission.
TCM -- Trajectory Correction Maneuver, spacecraft propulsive maneuver.
TDM -- Time-division multiplexing.
Termination shock -- Shock at which the solar wind is thought to slow to subsonic speed, well inside the heleopause.
T -- Tera, a multiplier x10 12 , from the Greek teras (monster). See the entry for CGPM.
Terrestrial planet -- One of the four inner Earth-like planets.
Three-way -- Coherent communications mode wherein a DSS receives a downlink whose frequency is based upon the frequency of an uplink provided by another DSS.
TMOD -- (Obsolete. See IPN-ISD) JPL's Telecommunications and Mission Operations Directorate. Formerly MGSO.
THz -- Terahertz (10 12 Hz).
TLM -- DSN Telemetry data.
TLP -- DSN Telemetry Processor within the DTT Downlink Channel.
TOS -- Transfer Orbit Stage, upper stage.
Transducer -- Device for changing one kind of energy into another, typically from heat, position, or pressure into a varying electrical voltage or vice-versa, such as a microphone or speaker.
Transit -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
Transponder -- Electronic device which combines a transmitter and a receiver.
TRC -- NASA's Teacher Resource Centers. Obsolete, now called Educator Resource Centers, ERC.
TRK -- DSN Tracking System. Also, Tracking data.
TRM -- Transmission Time, UTC Earth time of uplink.
True anomaly -- The angular distance of a point in an orbit past the point of periapsis, measured in degrees.
Twilight -- For technical definition, please follow this link to the U.S. Naval Observatory Astronomical Applications website.
TWNC -- Two-Way Non-Coherent mode, in which a spacecraft's downlink is not based upon a received uplink from DSN.
Two-way -- Communications mode consisting of downlink received from a spacecraft while uplink is being received at the spacecraft. See also coherent .
TWT -- Traveling Wave Tube, downlink power amplifier in a spacecraft telecommunications subsystem, the final stage of amplification for downlink (same unit as TWTA).
TWTA -- Traveling Wave Tube Amplifier, downlink power amplifier in a spacecraft telecommunications subsystem, the final stage of amplification for downlink (same unit as TWT).
TXR -- DSN's DSCC Transmitter assembly.
ULS -- Ulysses spacecraft.
Uplink -- Signal sent to a spacecraft.
UPL -- The DSN Uplink Tracking & Command subsystem.
Uranus -- Seventh planet from the Sun, a gas giant or Jovian planet.
USO -- Ultra Stable Oscillator, in a spacecraft telecommunications subsystem.
UT -- Universal Time, also called Zulu (Z) time, previously Greenwich Mean Time. UT is based on the imaginary "mean Sun," which averages out the effects on the length of the solar day caused by Earth's slightly non-circular orbit about the Sun. UT is not updated with leap seconds as is UTC.
UTC -- Coordinated Universal Time , the world-wide scientific standard of timekeeping. It is based upon carefully maintained atomic clocks and is highly stable. Its rate does not change by more than about 100 picoseconds per day. The addition or subtraction of leap seconds, as necessary, at two opportunities every year adjusts UTC for irregularities in Earth's rotation. The U.S. Naval Observatory website provides information in depth on the derivation of UTC.
UV -- Ultraviolet (meaning "above violet") radiation. Electromagnetic radiation in the neighborhood of 100 nanometers wavelength.
UWV -- DSN Microwave subsystem in DSSs which includes waveguides, waveguide switches, LNAs, polarization filters, etc.
Velocity -- A vector quantity whose magnitude is a body's speed and whose direction is the body's direction of motion.
Venus -- Second planet from the Sun, a terrestrial planet.
VGR1 -- Voyager 1 spacecraft.
VGR2 -- Voyager 2 spacecraft.
VLBI -- DSN Very Long Baseline Interferometry System. Also, VLBI data. Link .
W -- Watt, a measure of electrical power equal to potential in volts times current in amps.
Walking orbit -- A spacecraft orbit that precesses, wherein the location of periapsis changes with respect to the planet's surface in a useful way. See Sun-synchronous.
Wavelength -- The distance that a wave from a single oscillation of electromagnetic radiation will propagate during the time required for one oscillation.
Weight -- The gravitational force exerted on an object of a certain mass. The weight of mass m is mg Newtons, where g is the local acceleration due to a body's gravity.
WWW -- World-Wide Web.
X-band -- A range of microwave radio frequencies in the neighborhood of 8 to 12 GHz.
X-ray -- Electromagnetic radiation in the neighborhood of 100 picometer wavelength.
Z -- Zulu in phonetic alphabet, stands for UT, Universal Time.
Zenith -- The point on the celestial sphere directly above the observer. Opposite the nadir.
Discover More Topics From NASA
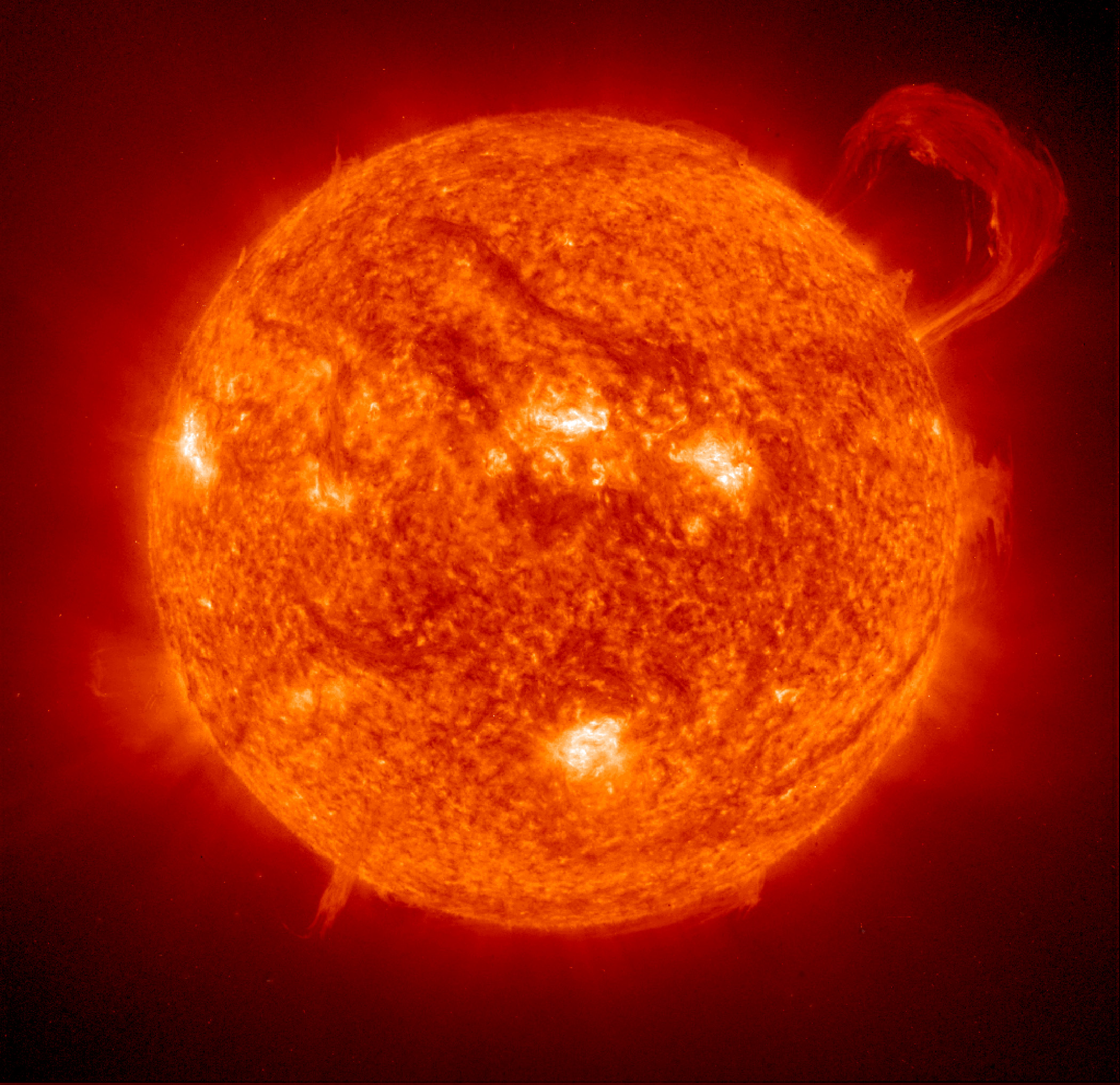

Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
Kuiper Belt

MyVocabulary.com

- Word Roots #1 Beginner
- Word Roots #1 Intermediate
- Word Roots #1 Advanced
- Word Roots #2 Beginner
- Word Roots #2 Intermediate
- Word Roots #2 Advanced
- Word Roots #3 Beginner
- Word Roots #3 Intermediate
- Word Roots #3 Advanced
- Word Roots #4 Beginner
- Word Roots #4 Intermediate
- Word Roots #4 Advanced
- Word Roots #5 Beginner
- Word Roots #5 Intermediate
- Word Roots #5 Advanced
- Word Roots #7 Beginner
- Word Roots #7 Intermediate
- Word Roots #7 Advanced
- Word Roots #8 Beginner
- Word Roots #8 Intermediate
- Word Roots #8 Advanced
- Word Roots #9 Beginner
- Word Roots #9 Intermediate
- Word Roots #9 Advanced
- Word Roots #10 Beginner
- Word Roots #10 Intermediate
- Word Roots #10 Advanced
- Word Roots #11 Beginner
- Word Roots #11 Intermediate
- Word Roots #11 Advanced
- Word Roots #12 Beginner
- Word Roots #12 Intermediate
- Word Roots #12 Advanced
- 112 Prefix Words by Alpha
- 112 Prefix Words by Grade
- 32 Suffix Words by Grade
- 32 Suffix Words by Alpha
- SEQU SECU #1
- SPECT SPIC #1
- MISS MITT #1
- CEPT CIP CAP #1
- VERT VERS #1
- STA SIST STIT #1
- REG RECT RIG #1
- PEND PENS POUND #1
- Alphabetical-All Subject & Themed Puzzles
- English Language Arts
- English Literature
- General Interest
- Health, Nutrition & PE
- Holidays & Celebrations
- Performing Arts & Fine Arts
- Science & Math
- Social Studies & History
- All themed Crosswords
- All themed Fill-in-the-Blanks
- All themed Definition Match
- All themed Word Search
- All themed WordPuzzles
- Alphabetical: all word lists A to E
- Alphabetical: all word lists F to O
- Alphabetical: all word lists P to Z
- Animals, Birds, Insects
- Business, Economics
- English, Language Arts
- Foreign Language, ESL, ELL, LEP
- Health and Physical Education
- History, Social Studies
- Holidays, Celebrations
- People, Groups
- Vocational Education
- GRE Test Prep
- Word List by Title
- Word List by Author
- 17 Novel Puzzles
Space and Solar System Vocabulary Word List (356)
share this!
April 16, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
written by researcher(s)
Space exploration: A luxury or a necessity?
by Daniel Fillion, The Conversation

"Oh, come on Daniel, space travel is so expensive, and pointless!" These were the words of my friend Max, during a Christmas party where I was discussing my thesis project: studying places on Earth where the living conditions are so extreme, they could hold lessons for future space missions.
This disdainful attitude toward space research is actually quite common.
Space exploration is currently booming. Just think of the Artemis missions, SpaceX's ambitious plans for Mars, the deployment of the James Webb telescope or the recent "race to the moon."
A number of large-scale projects are getting the green light now, mainly from NASA, including the Artemis II mission that will carry four astronauts to the moon, which will have Canadian astronaut Jeremy Hansen aboard . This will be a first since 1972. Incredibly, it's been 50 years since the last human mission to Earth's natural satellite.
Although many people find space exploration inspiring, others are skeptical and even angered by what they see as an unjustifiable waste of resources and money on an activity that only spreads pollution to another place. This sums up the feelings of my friend Max.
In this article, I will try to prove him wrong.
Humans are explorers first
My great curiosity has led me to travel to extreme places so I can study them . But I am not the only one with this desire to explore.
In my Grade 9 history class, my teacher stood on top of her desk and, with a grave and serious tone, went on to act out Jacques Cartier's arrival in North America in her own, colorful style. A few years earlier, I had learned about how the first humans left their caves to climb mountains. One hundred and thirty years ago, humans sailed further and further south until they saw the glacial landscapes of Antarctica for the first time . At the same time, humans were attempting to dominate the skies and aiming for the beyond with planes and rockets—which is how we got to the moon.
What is the common denominator in our history? Exploration, of course.
Human nature is characterized by a propensity to travel, to look further and to discover. We are all curious by nature. If we stop wanting to explore, we stop being human.
The Earth has rings
So, my friend Max, let me invite you outside. It's a beautiful, starry night with no moon. It's a bit cold, but at least the atmosphere isn't too humid, which makes the sky more transparent. We can see stars flickering. Some are blue, others are red. And the more our eyes adapt, the more the sky reveals its secrets.
Suddenly, something else stands out. It's another light, but it's not flashing, and it's moving quite quickly. A shooting star? No, the atmosphere would have burned it up in a few seconds .
It's a satellite, one of thousands that orbit the Earth like rings. These satellites are a direct consequence of space exploration. We would be living in a completely different world without them.

Indeed, not an hour goes by in our lives when we don't use a satellite .
On the one hand, you would likely have gotten lost on your way here, Max, because there would have been no GPS to show you which exit to take. And secondly, I wouldn't have been able to help you find your way because there would be no wifi. We can push our thinking even further; agriculture, environmental monitoring, communications, the weather, even banks, all of these depend on satellites.
But how does this work? You have to understand that these satellites move so quickly they actually circle the Earth several times a day. Combined with a very large workforce, they provide a complete view of the globe. From the middle of the oceans to the highest mountains and the almost inaccessible poles, we have eyes everywhere. By drawing on this vast quantity of observations, we obtain data on changes to the earth's surface, the spread of forest fires, the movement of winds, the melting of ice and many other things, while enabling global communication and credit card transactions .
Space exploration was the trigger that enabled us to develop and operate these technologies. And it doesn't stop there.
Two birds, one stone
The practice of medicine in remote areas also benefits from space exploration. It's not easy for communities in remote areas to access health care, especially since hospitals don't always have the sophisticated equipment they need.
If you think about it, when astronauts explore space, they become a small population in a very, very remote region. It's true. What happens if someone has a really bad stomach ache? Or breaks an arm? They don't have time to come back home for treatment, so we have to react, and quickly.
Scientific research in telemedicine has developed to address this important issue, producing a number of innovative technologies. And if these are useful for astronauts, why not use them for rural populations, too?
A few years ago, three Québec researchers from different universities were working on a tiny probe that could rapidly analyze and diagnose a blood sample .
Although some prototypes are not yet on the market, others are already in widespread use, such as the ultrasound scanner designed by NASA . This scanner takes precise photos of organs and bones that can be transmitted to a doctor, who will then have crucial information on hand to recommend treatments.
In a way, space exploration provides us with opportunities to respond to urgent needs on Earth. So, Max, are you beginning to see the need for it?
Another perspective
Finally, I have to admit that I find it rather encouraging to see Russians, Americans, Japanese, Canadians and Europeans living together on the Space Station. Not so long ago, some of these countries were attacking each other with nuclear bombs. In space, no such borders exist.
Exploration brings people together. It opens our eyes to new perspectives. It shows us that we're all in the same boat together. That's pretty important, don't you think, Max?
Our planet is magnificent and unique, an oasis of impossible life. But it is fragile. We need to protect it. That's why exploring beyond the Earth should not be considered a luxury; it's an investment in our shared humanity.
So, Max, when Jeremy Hansen and his crew take off in 2025, will you be there to watch them?
Provided by The Conversation
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Saturday Citations: Bacterial warfare, a self-programming language model, passive cooling in the big city
Jun 15, 2024
Some CRISPR screens may be missing cancer drug targets
Novel photocatalyst enables efficient ester reduction with blue light

Physicists confirm quantum entanglement persists between top quarks, the heaviest known fundamental particles
Jun 14, 2024

25 years of massive fusion energy experiment data open on the 'cloud' and available to everyone
Quantum entangled photons react to Earth's spin

Q&A: Barrier islands and dunes protect coastlines, but how are environmental changes affecting them and adjacent land?
A new weapon in the battle against antibiotic resistance: Temperature

Sharks have depleted functional diversity compared to the last 66 million years, study finds

Quebec lake meteorite impact yields rare rocks and evidence of extreme heat
Relevant physicsforums posts, question about the silicon-burning process beyond iron.
6 hours ago
How 'Messy' are Fusion Reaction Chains in Stars?
Jun 13, 2024
Some photos of the Moon
A question regarding heliocentric latitude.
Jun 12, 2024
Very last pulse from a neutron star
Should luminosity distance be 0 at z=0.
Jun 11, 2024
More from Astronomy and Astrophysics
Related Stories

Through astronaut eyes, virtual reality propels gateway forward
Apr 10, 2024

What delays to the Artemis II and III missions mean for Canada
Jan 15, 2024

To the moon and back: NASA's Artemis II crew rehearses splashdown
Feb 29, 2024

NASA astronauts test SpaceX elevator concept for Artemis lunar lander
Dec 21, 2023

Artemis launch brings us closer to space exploration goals
Aug 26, 2022

NASA is looking for commercial Mars missions. Do people still want to go to Mars?
Feb 5, 2024
Recommended for you

Would astronauts' kidneys survive a roundtrip to Mars?

Human bodies mostly recover from space, tourist mission shows

Researchers explore how the immune system goes awry during space travel and the implications for human aging on Earth

Short commercial space flights may not have big impact on health

New method could allow multi-robot teams to autonomously and reliably explore other planets
Jun 9, 2024

Virgin Galactic completes final spaceflight before two-year pause
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

COMMENTS
idioms. nouns. flight. suggest new. Another way to say Space Travel? Synonyms for Space Travel (other words and phrases for Space Travel).
dark matter. Dark matter is a theoretical, invisible form of matter that exists in space. The word matter is used to refer to all of the stuff that takes up space as we know it. In outer space, everything is positioned where it is because of gravity. We can see what is going on in outer space because of light.
Space Words. Below is a massive list of space words - that is, words related to space. The top 4 are: galaxy, stardust, universe and cosmos. You can get the definition (s) of a word in the list below by tapping the question-mark icon next to it. The words at the top of the list are the ones most associated with space, and as you go down the ...
So without further ado, let's embark on a cosmic journey as we delve into a carefully curated list of words related to space. From astronomical terms to astronautics, constellations to cosmic events, this compilation will equip you with the celestial lexicon you need to navigate the fascinating world of space. Astronaut.
go abroad. go camping. go into orbit. go riding. hop. v. incentive travel. Space Travel related words and phrases. Related words and phrases for Space Travel.
Words related to space travel can be a fascinating aspect of human language, as they encapsulate the vastness, complexity, and wonder of outer space. From technical jargon to visionary concepts, having a collection of these related words can be immensely helpful in understanding and discussing the various aspects of space exploration, astronomy ...
Definitions For Our List Of Words Related To Space Travel Astronaut. A person trained to travel and work in outer space. Rocket. A vehicle or device propelled by rocket engines, typically used for space exploration or launching satellites. Spaceship. A vehicle designed for travel or operation in outer space.
Here are some more space words related to the universe: Word. Definition. Black hole. A region of space with a gravitational pull so strong that nothing, including light, can escape. Galaxy. A system of millions or billions of stars, along with gas and dust, held together by gravity.
Eclipse. An eclipse refers to one body in space moving into the shadow of another body. Eclipses can exist in two forms—solar and lunar—depending on the orbit of the Earth and moon. With a lunar eclipse, the moon moves behind the Earth. During a solar eclipse, the moon orbits between the Earth and the sun. #17.
List of Space Words. Space exploration has been a source of fascination for centuries, with mankind continually striving to reach the stars. To help with this ongoing quest, scientists and engineers have developed a specialized vocabulary filled with words that are unique to space exploration. Whether you're looking to understand a news article about the latest space mission or want to learn ...
Another word for Space Travel? Words for Space Travel (other words for Space Travel).
A rocket flight or journey beyond Earth's atmosphere, often involving orbital movement. Noun. . Exploration of outer space. space exploration. cosmic exploration. interstellar exploration. space research. galactic exploration.
Space travel - related words and phrases | Cambridge SMART Vocabulary
Astrophobia - a severe and irrational fear of stars and space. Celestial poles - The North and South poles of the celestial sphere. Comet - A gigantic ball of ice and rock that orbit the sun in a highly eccentric orbit. Eclipse - The total or partial blocking of one celestial body by another.
a unit of length in astronomy equal to the distance that light travels in one year or about 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers) meteor | see definition ». one of the small pieces of matter in the solar system that enter the earth's atmosphere where friction may cause them to glow and form a streak of light.
space travel: 1 n a voyage outside the Earth's atmosphere Synonyms: spacefaring , spaceflight Type of: voyage a journey to some distant place
Space Travel Words. Below is a massive list of space travel words - that is, words related to space travel. The top 4 are: spacefaring, voyage, cruise and journey. You can get the definition (s) of a word in the list below by tapping the question-mark icon next to it. The words at the top of the list are the ones most associated with space ...
Space words can be exciting and confusing! Start your own discovery of astronomy and outer space with some basic vocabulary words. ... intergalactic - travel between galaxies; interstellar - between stars; Oort cloud - shell around our solar system in the shape of a sphere;
Astronaut lingo has been around as long as NASA itself. In fact, some of the earliest space slang was pretty hilarious, like referring to Cape Canaveral as "Malfunction Junction" or an astronaut's adjustable seat as a "barber chair.". Astronaut lingo has toned down quite a bit since the 1960s, and now it largely comprises jargon words ...
Chandler wobble -- A small motion in the Earth's rotation axis relative to the surface, discovered by American astronomer Seth Carlo Chandler in 1891. Its amplitude is about 0.7 arcseconds (about 15 meters on the surface) with a period of 433 days. It combines with another wobble with a period of one year, so the total polar motion varies with ...
travel to or penetrate into. planet. a celestial body that revolves around the sun. orbit. the path of a celestial body in its revolution about another. astronaut. a person trained to travel in a spacecraft. Earth. the 3rd planet from the sun; the planet we live on.
What are space words? Increase your cosmic vocabulary using the list below and enrich your child's exploration of the universe. Space Words. Asteroid - Small, rocky objects that orbit the Sun. Asteroid belt - The region between Mars and Jupiter that contains the largest population of asteroids in our solar system.; Astronaut - A person trained to travel in a spacecraft.
www.myvocabulary.com offers more than 650 word lists. To see The Solar System, Eclipse and Science vocabulary vocabulary word lists, please go to the home page for word games, interactive worksheets, word puzzles and themed content that align with Common Core Standards. 2500 pages of free content are available only online. There are no fees.
"Oh, come on Daniel, space travel is so expensive, and pointless!" These were the words of my friend Max, during a Christmas party where I was discussing my thesis project: studying places on ...