
- [ May 9, 2024 ] Moon Phases: What They Are & How They Work Solar System
- [ April 3, 2024 ] Giordano Bruno Quotes About Astronomy Astronomy Lists
- [ March 28, 2024 ] Shakespeare Quotes: Comets, Meteors and Shooting Stars Astronomy Lists
- [ March 28, 2024 ] Shakespearean Quotes About The Moon Astronomy Lists
- [ November 30, 2022 ] The Night Sky This Month: December 2022 Night Sky

5 Bizarre Paradoxes Of Time Travel Explained
December 20, 2014 James Miller Astronomy Lists , Time Travel 58

There is nothing in Einstein’s theories of relativity to rule out time travel , although the very notion of traveling to the past violates one of the most fundamental premises of physics, that of causality. With the laws of cause and effect out the window, there naturally arises a number of inconsistencies associated with time travel, and listed here are some of those paradoxes which have given both scientists and time travel movie buffs alike more than a few sleepless nights over the years.
Types of Temporal Paradoxes
The time travel paradoxes that follow fall into two broad categories:
1) Closed Causal Loops , such as the Predestination Paradox and the Bootstrap Paradox, which involve a self-existing time loop in which cause and effect run in a repeating circle, but is also internally consistent with the timeline’s history.
2) Consistency Paradoxes , such as the Grandfather Paradox and other similar variants such as The Hitler paradox, and Polchinski’s Paradox, which generate a number of timeline inconsistencies related to the possibility of altering the past.
1: Predestination Paradox
A Predestination Paradox occurs when the actions of a person traveling back in time become part of past events, and may ultimately cause the event he is trying to prevent to take place. The result is a ‘temporal causality loop’ in which Event 1 in the past influences Event 2 in the future (time travel to the past) which then causes Event 1 to occur.
This circular loop of events ensures that history is not altered by the time traveler, and that any attempts to stop something from happening in the past will simply lead to the cause itself, instead of stopping it. Predestination paradoxes suggest that things are always destined to turn out the same way and that whatever has happened must happen.
Sound complicated? Imagine that your lover dies in a hit-and-run car accident, and you travel back in time to save her from her fate, only to find that on your way to the accident you are the one who accidentally runs her over. Your attempt to change the past has therefore resulted in a predestination paradox. One way of dealing with this type of paradox is to assume that the version of events you have experienced are already built into a self-consistent version of reality, and that by trying to alter the past you will only end up fulfilling your role in creating an event in history, not altering it.
– Cinema Treatment
In The Time Machine (2002) movie, for instance, Dr. Alexander Hartdegen witnesses his fiancee being killed by a mugger, leading him to build a time machine to travel back in time to save her from her fate. His subsequent attempts to save her fail, though, leading him to conclude that “I could come back a thousand times… and see her die a thousand ways.” After then traveling centuries into the future to see if a solution has been found to the temporal problem, Hartdegen is told by the Über-Morlock:
“You built your time machine because of Emma’s death. If she had lived, it would never have existed, so how could you use your machine to go back and save her? You are the inescapable result of your tragedy, just as I am the inescapable result of you .”
- Movies : Examples of predestination paradoxes in the movies include 12 Monkeys (1995), TimeCrimes (2007), The Time Traveler’s Wife (2009), and Predestination (2014).
- Books : An example of a predestination paradox in a book is Phoebe Fortune and the Pre-destination Paradox by M.S. Crook.
2: Bootstrap Paradox
A Bootstrap Paradox is a type of paradox in which an object, person, or piece of information sent back in time results in an infinite loop where the object has no discernible origin, and exists without ever being created. It is also known as an Ontological Paradox, as ontology is a branch of philosophy concerned with the nature of being or existence.
– Information : George Lucas traveling back in time and giving himself the scripts for the Star War movies which he then goes on to direct and gain great fame for would create a bootstrap paradox involving information, as the scripts have no true point of creation or origin.
– Person : A bootstrap paradox involving a person could be, say, a 20-year-old male time traveler who goes back 21 years, meets a woman, has an affair, and returns home three months later without knowing the woman was pregnant. Her child grows up to be the 20-year-old time traveler, who travels back 21 years through time, meets a woman, and so on. American science fiction writer Robert Heinlein wrote a strange short story involving a sexual paradox in his 1959 classic “All You Zombies.”
These ontological paradoxes imply that the future, present, and past are not defined, thus giving scientists an obvious problem on how to then pinpoint the “origin” of anything, a word customarily referring to the past, but now rendered meaningless. Further questions arise as to how the object/data was created, and by whom. Nevertheless, Einstein’s field equations allow for the possibility of closed time loops, with Kip Thorne the first theoretical physicist to recognize traversable wormholes and backward time travel as being theoretically possible under certain conditions.
- Movies : Examples of bootstrap paradoxes in the movies include Somewhere in Time (1980), Bill and Ted’s Excellent Adventure (1989), the Terminator movies, and Time Lapse (2014). The Netflix series Dark (2017-19) also features a book called ‘A Journey Through Time’ which presents another classic example of a bootstrap paradox.
- Books : Examples of bootstrap paradoxes in books include Michael Moorcock’s ‘Behold The Man’, Tim Powers’ The Anubis Gates, and Heinlein’s “By His Bootstraps”
3: Grandfather Paradox
The Grandfather Paradox concerns ‘self-inconsistent solutions’ to a timeline’s history caused by traveling back in time. For example, if you traveled to the past and killed your grandfather, you would never have been born and would not have been able to travel to the past – a paradox.
Let’s say you did decide to kill your grandfather because he created a dynasty that ruined the world. You figure if you knock him off before he meets your grandmother then the whole family line (including you) will vanish and the world will be a better place. According to theoretical physicists, the situation could play out as follows:
– Timeline protection hypothesis: You pop back in time, walk up to him, and point a revolver at his head. You pull the trigger but the gun fails to fire. Click! Click! Click! The bullets in the chamber have dents in the firing caps. You point the gun elsewhere and pull the trigger. Bang! Point it at your grandfather.. Click! Click! Click! So you try another method to kill him, but that only leads to scars that in later life he attributed to the world’s worst mugger. You can do many things as long as they’re not fatal until you are chased off by a policeman.
– Multiple universes hypothesis: You pop back in time, walk up to him, and point a revolver at his head. You pull the trigger and Boom! The deed is done. You return to the “present,” but you never existed here. Everything about you has been erased, including your family, friends, home, possessions, bank account, and history. You’ve entered a timeline where you never existed. Scientists entertain the possibility that you have now created an alternate timeline or entered a parallel universe.
- Movies : Example of the Grandfather Paradox in movies include Back to the Future (1985), Back to the Future Part II (1989), and Back to the Future Part III (1990).
- Books : Example of the Grandfather Paradox in books include Dr. Quantum in the Grandfather Paradox by Fred Alan Wolf , The Grandfather Paradox by Steven Burgauer, and Future Times Three (1944) by René Barjavel, the very first treatment of a grandfather paradox in a novel.
4: Let’s Kill Hitler Paradox
Similar to the Grandfather Paradox which paradoxically prevents your own birth, the Killing Hitler paradox erases your own reason for going back in time to kill him. Furthermore, while killing Grandpa might have a limited “butterfly effect,” killing Hitler would have far-reaching consequences for everyone in the world, even if only for the fact you studied him in school.
The paradox itself arises from the idea that if you were successful, then there would be no reason to time travel in the first place. If you killed Hitler then none of his actions would trickle down through history and cause you to want to make the attempt.
- Movies/Shows : By far the best treatment for this notion occurred in a Twilight Zone episode called Cradle of Darkness which sums up the difficulties involved in trying to change history, with another being an episode of Dr Who called ‘Let’s Kill Hitler’.
- Books : Examples of the Let’s Kill Hitler Paradox in books include How to Kill Hitler: A Guide For Time Travelers by Andrew Stanek, and the graphic novel I Killed Adolf Hitler by Jason.
5: Polchinski’s Paradox
American theoretical physicist Joseph Polchinski proposed a time paradox scenario in which a billiard ball enters a wormhole, and emerges out the other end in the past just in time to collide with its younger version and stop it from going into the wormhole in the first place.
Polchinski’s paradox is taken seriously by physicists, as there is nothing in Einstein’s General Relativity to rule out the possibility of time travel, closed time-like curves (CTCs), or tunnels through space-time. Furthermore, it has the advantage of being based upon the laws of motion, without having to refer to the indeterministic concept of free will, and so presents a better research method for scientists to think about the paradox. When Joseph Polchinski proposed the paradox, he had Novikov’s Self-Consistency Principle in mind, which basically states that while time travel is possible, time paradoxes are forbidden.
However, a number of solutions have been formulated to avoid the inconsistencies Polchinski suggested, which essentially involves the billiard ball delivering a blow that changes its younger version’s course, but not enough to stop it from entering the wormhole. This solution is related to the ‘timeline-protection hypothesis’ which states that a probability distortion would occur in order to prevent a paradox from happening. This also helps explain why if you tried to time travel and murder your grandfather, something will always happen to make that impossible, thus preserving a consistent version of history.
- Books: Paradoxes of Time Travel by Ryan Wasserman is a wide-ranging exploration of time and time travel, including Polchinski’s Paradox.
Are Self-Fulfilling Prophecies Paradoxes?
A self-fulfilling prophecy is only a causality loop when the prophecy is truly known to happen and events in the future cause effects in the past, otherwise the phenomenon is not so much a paradox as a case of cause and effect. Say, for instance, an authority figure states that something is inevitable, proper, and true, convincing everyone through persuasive style. People, completely convinced through rhetoric, begin to behave as if the prediction were already true, and consequently bring it about through their actions. This might be seen best by an example where someone convincingly states:
“High-speed Magnetic Levitation Trains will dominate as the best form of transportation from the 21st Century onward.”
Jet travel, relying on diminishing fuel supplies, will be reserved for ocean crossing, and local flights will be a thing of the past. People now start planning on building networks of high-speed trains that run on electricity. Infrastructure gears up to supply the needed parts and the prediction becomes true not because it was truly inevitable (though it is a smart idea), but because people behaved as if it were true.
It even works on a smaller scale – the scale of individuals. The basic methodology for all those “self-help” books out in the world is that if you modify your thinking that you are successful (money, career, dating, etc.), then with the strengthening of that belief you start to behave like a successful person. People begin to notice and start to treat you like a successful person; it is a reinforcement/feedback loop and you actually become successful by behaving as if you were.
Are Time Paradoxes Inevitable?
The Butterfly Effect is a reference to Chaos Theory where seemingly trivial changes can have huge cascade reactions over long periods of time. Consequently, the Timeline corruption hypothesis states that time paradoxes are an unavoidable consequence of time travel, and even insignificant changes may be enough to alter history completely.
In one story, a paleontologist, with the help of a time travel device, travels back to the Jurassic Period to get photographs of Stegosaurus, Brachiosaurus, Ceratosaurus, and Allosaurus amongst other dinosaurs. He knows he can’t take samples so he just takes magnificent pictures from the fixed platform that is positioned precisely to not change anything about the environment. His assistant is about to pick a long blade of grass, but he stops him and explains how nothing must change because of their presence. They finish what they are doing and return to the present, but everything is gone. They reappear in a wild world with no humans and no signs that they ever existed. They fall to the floor of their platform, the only man-made thing in the whole world, and lament “Why? We didn’t change anything!” And there on the heel of the scientist’s shoe is a crushed butterfly.
The Butterfly Effect is also a movie, starring Ashton Kutcher as Evan Treborn and Amy Smart as Kayleigh Miller, where a troubled man has had blackouts during his youth, later explained by him traveling back into his own past and taking charge of his younger body briefly. The movie explores the issue of changing the timeline and how unintended consequences can propagate.
Scientists eager to avoid the paradoxes presented by time travel have come up with a number of ingenious ways in which to present a more consistent version of reality, some of which have been touched upon here, including:
- The Solution: time travel is impossible because of the very paradox it creates.
- Self-healing hypothesis: successfully altering events in the past will set off another set of events which will cause the present to remain the same.
- The Multiverse or “many-worlds” hypothesis: an alternate parallel universe or timeline is created each time an event is altered in the past.
- Erased timeline hypothesis : a person traveling to the past would exist in the new timeline, but have their own timeline erased.
Related Posts
© Copyright 2023 Astronomy Trek
Matador Original Series
10 key destinations for the historical time traveler.
Two hundred years ago a traveler had to wait months to traverse oceans. We now have the means to wake up in New York and fall asleep in Sydney, all in the same day.
The trend: travel is becoming exponentially more accessible to the common man.
But the tradeoff is that culture and history are being lost. Remote islanders maintain their outdated tribal customs merely to get a buck from the nearest walking wallet with a camera. Cities that in ancient times were considered quaint and romantic have become nothing more than identical concrete jungles.
We’re losing the remnants of human history with each passing day – why not find a means to time travel for leisure? Where would you go if you had a weekend in any city in any century?
1. Rome, Height of the Empire
No one in living memory has ever really seen the Colosseum. Whatever your religious beliefs, there used to be gods in that city; watching over the empire from their marbled countenance, and ensuring trade on one of the first greatest centers of business in the western world: the Roman Forum.
Imagine being able to walk down the epitome of civilization; they didn’t call the period after Christianity spread and the empire fell The Dark Ages for no good reason. ..
2. Kyoto, 16th Century
In the 1500’s, Kyoto served as the national capital and home to the imperial family. Tokyo (then Edo) was little more than a fishing village at this time, not yet placed on the map by the empowering of the Tokugawa Shogunate.
In modern times, many travelers journey to Kyoto to discover only remnants of what was once one of the most beautiful and mystical places on the planet. Back in its heyday, this Japanese city would have been the richest and most populated next to Osaka.
The predecessors to geisha gently walking in their kimonos, made from imported Chinese silk; visions of the mountains to the north and east not yet lost in a sea of grey; everything under ten meters high.
The only downside? Not much fresh fish or sushi: transporting the latest catch from Osaka to Kyoto took a while to perfect, and sushi was still in its infancy.
3. United States, The Old West
Back to the Future had the right idea – many people at one point imagine themselves as a cowboy or cowgirl.
What would you give to be riding on horseback on a cool summer morning in the undeveloped expanse of the western territories? Nothing for hundreds of miles in any direction, except perhaps the whistle of a steam locomotive and wandering tribes of Native Americans.
Of course, if you go back far enough in history, any land can be considered unexplored or undiscovered, but there’s a certain romantic connotation that stirs up when thinking about the American movement to the west.
It’s the promise of the unknown – traveling towards the Pacific, having uprooted everything stable, everything civilized in the east, and seeing where the Oregon Trail took you.
4. Ancient Egypt, c. 2500 BC
Watch the building of the pyramids and learn more about archaeoastronomy – skylights in the pyramids were carved so that certain constellations could be viewed at a set time of year.
Even the great structures themselves were arranged on the sand corresponding to the placement of three stars overhead. Discover the meaning of the Great Sphinx – who knows why it was built? Maybe some pharaoh just had a mutant pet.
Cairo will surely be hot and dry during this period in history, so remember to pack light loose-fitting clothing and plenty of sunscreen. If you wait around for another five hundred years, you might catch the finishing touches on Deir el Bahri .
5. London, 14th Century
“…the truth was that the modern world was invented in the Middle Ages. Everything from the legal system, to nation-states, to reliance on technology, to the concept of romantic love had first been established in medieval times.” – Timeline, Michael Crichton
Everyone wants to be a knight in shining armor or a princess fair and true. Chivalry isn’t dead. In fact, if you choose to travel to London roughly seven hundred years ago, you’ll find it quite alive and well.
A walking tour of this city will let you face the first real London Bridge, providing the only access across the Thames. Canterbury Tales by Chaucer paints a rather vivid picture of this era. Many of the buildings in London we associate with medieval times were already in place: The Tower of London, Westminster Hall, Westminster Abbey.
Remember to apply insect repellant liberally, as the Black Death was known to pass through Britain and France in this century.
6. Chang’an, Han Dynasty
The origin of The Silk Road and a golden age in Chinese history, when Confucian principles laid down the foundation for society and Buddhism was just beginning to spread. Travel west along this trade route and in a matter of months, you’ll reach the Roman Empire.
7. Chichen Itza, 5th century
Although you may not be in a temple of doom, it’s wise to heed the words of Indiana Jones and “protect your heart!” As one of the largest Mayan cities on the Yucatan Peninsula, Chichen Itza was the site of human sacrifices.
It’s true that quite a few of the largest temples are very well preserved in modern Mexico, but I challenge you to find another time or place in which ancient games that could rival basketball were played. Best to arrive before the Toltec siege.
8. India, c. 600 BC
The Buddha had about forty-five good years of teaching from the time of his reaching enlightenment under the Bodhi Tree to his death. Don’t waste them. Meeting the Awakened One and learning the dhamma firsthand would be an experience for which almost anyone in Asia would trade his or her life. Try and eliminate the suffering in your heart before your departure…
9. New York City, Roaring 20’s
By the time the 1920’s dawned in New York City, the modern version of a cityscape was already formed: Macy’s department stores, the public library, Grand Central Terminal, and the then world’s tallest Woolworth Building.
Unfortunately construction on the Empire State Building won’t commence until after the crash of ’29, but take advantage of this period in history with your choice of taxicabs or horse drawn carriages. Watch Lindbergh start his journey across the Atlantic. Gaze at the audience of women in hoop skirts and men in all too stiff and uncomfortable suits.
10. Babylon, c. 600 BC
One of the seven wonders of the ancient world: the hanging gardens of Babylon. As one of the first empires in human history, Babylon was built in the shadow of ancient Sumeria near the Euphrates River, and may have even been the source of the legendary Tower of Babel with its own Temple of Marduk.
I’m sure there are many asking “Why not see some dinosaurs?” Think a little practically in this impractical form of travel and question if you’d prefer camping in the late Cretaceous (and being trampled to death), or blending with the masses and observing the election of a Roman consul firsthand.
Besides, if a Tyrannosaur doesn’t get you, the meteor will later on.
Community Connection
You’ve been to the past, now meet travelers that we still remember tale. Read 10 Travelers and Why Their Tales Made History . Also, what other trends might we see in the future of travel? Check out 6 Predictions For the Future Of Travel .
Where and when would you go if you had a ticket guaranteeing a weekend of fun in any place at any time?
Trending Now
New tallest waterslide in north america: wisconsin waterpark debuts 145-foot-tall slide this memorial day weekend, grammy winner macy gray opens up on living in la, fame, and her favorite country to visit, discover matador, adventure travel, train travel, national parks, beaches and islands, ski and snow.
We use cookies for analytics tracking and advertising from our partners.
For more information read our privacy policy .
Matador's Newsletter
Subscribe for exclusive city guides, travel videos, trip giveaways and more!
You've been signed up!
Follow us on social media.
Time travel is theoretically possible, calculations show. But that doesn't mean you could change the past.
- Time travel is possible based on the laws of physics, according to researchers.
- But time-travelers wouldn't be able to alter the past in a measurable way, they say.
- And the future would essentially stay the same, according to the reseachers.

Imagine you could hop into a time machine, press a button, and journey back to 2019, before the novel coronavirus made the leap from animals to humans.
What if you could find and isolate patient zero? Theoretically, the COVID-19 pandemic wouldn't happen, right?
Not quite, because then future-you wouldn't have decided to time travel in the first place.
For decades, physicists have been studying and debating versions of this paradox: If we could travel back in time and change the past, what would happen to the future?
A 2020 study offered a potential answer: Nothing.
"Events readjust around anything that could cause a paradox, so the paradox does not happen," Germain Tobar, the study's author previously told IFLScience .
Tobar's work, published in the peer-reviewed journal Classical and Quantum Gravity in September 2020, suggests that according to the rules of theoretical physics, anything you tried to change in the past would be corrected by subsequent events.
Related stories
Put simply: It's theoretically possible to go back in time, but you couldn't change history.
The grandfather paradox
Physicists have considered time travel to be theoretically possible since Albert Einstein came up with his theory of relativity. Einstein's calculations suggest it's possible for an object in our universe to travel through space and time in a circular direction, eventually ending up at a point on its journey where it's been before – a path called a closed time-like curve.
Still, physicists continue to struggle with scenarios like the coronavirus example above, in which time-travelers alter events that already happened. The most famous example is known as the grandfather paradox: Say a time-traveler goes back to the past and kills a younger version of his or her grandfather. The grandfather then wouldn't have any children, erasing the time-traveler's parents and, of course, the time-traveler, too. But then who would kill Grandpa?
A take on this paradox appears in the movie "Back to the Future," when Marty McFly almost stops his parents from meeting in the past – potentially causing himself to disappear.
To address the paradox, Tobar and his supervisor, Dr. Fabio Costa, used the "billiard-ball model," which imagines cause and effect as a series of colliding billiard balls, and a circular pool table as a closed time-like curve.
Imagine a bunch of billiard balls laid out across that circular table. If you push one ball from position X, it bangs around the table, hitting others in a particular pattern.
The researchers calculated that even if you mess with the ball's pattern at some point in its journey, future interactions with other balls can correct its path, leading it to come back to the same position and speed that it would have had you not interfered.
"Regardless of the choice, the ball will fall into the same place," Dr Yasunori Nomura, a theoretical physicist at UC Berkeley, previously told Insider.
Tobar's model, in other words, says you could travel back in time, but you couldn't change how events unfolded significantly enough to alter the future, Nomura said. Applied to the grandfather paradox, then, this would mean that something would always get in the way of your attempt to kill your grandfather. Or at least by the time he did die, your grandmother would already be pregnant with your mother.
Back to the coronavirus example. Let's say you were to travel back to 2019 and intervene in patient zero's life. According to Tobar's line of thinking, the pandemic would still happen somehow.
"You might try and stop patient zero from becoming infected, but in doing so you would catch the virus and become patient zero, or someone else would," Tobar said, according to Australia's University of Queensland , where Tobar graduated from.
Nomura said that although the model is too simple to represent the full range of cause and effect in our universe, it's a good starting point for future physicists.
Watch: There are 2 types of time travel and physicists agree that one of them is possible
- Main content
- The Magazine
- Stay Curious
- The Sciences
- Environment
- Planet Earth
What Are Wormholes, and Could They Be the Answer to Time Travel?
Wormholes, cosmic tunnels also known as einstein-rosen bridges, are a staple of science fiction. could they allow real-world humans to travel back in time.

The sci-fi landscape is littered with wormholes. From Douglas Adam's Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy and Rick and Morty to the Marvel Cinematic Universe, these theoretical constructs allow characters to zip between distant points in the universe as easy as stepping through a doorway.
An Einstein-Rosen bridge is the simplest kind of wormhole. And while it can, in theory, allow you to meet a new friend from a distant part of the universe, there are some important reasons why it won’t let you travel back in time.
Black Holes, White Holes and Wormholes
Let’s start with everybody’s favorite astronomical mystery: a black hole . Despite their fearsome reputation, they’re actually rather simple creature. They have a point of infinite density, known as the singularity, in their centers. They are surrounded by a boundary called the event horizon.
The event horizon doesn’t exist in the same way that the surface of a planet exists. Instead it’s just a mathematical line in the sand that tells you one thing: if you cross within that special distance, you’re trapped forever, because you’ll have to travel faster than the speed of light to escape.
Read More: 'Fuzzballs' Might Be the Answer to a Decades-Old Paradox About Black Holes
And that’s it. That’s a black hole. A singularity and an event horizon. All things that cross the event horizon will never escape back into the universe – things go in and never come out.
Mathematically we can also define the polar opposite of a black hole, which is conveniently called a white hole. White holes also have a singularity, but their event horizons act differently. Anything already on the outside of a white hole (like, the entire universe) can never, ever cross within it, no matter how hard it tries. And anything already inside the white hole will find itself ejected from it faster than the speed of light.
Now when we take a black hole and a white hole and connect their singularities together, we get an entirely new kind of object: an Einstein-Rosen bridge , better known as a wormhole.
Read More: Astronomers Found a Baffling Black Hole That Existed 13 Billion Years Ago
What Is a Wormhole?
Wormholes are essentially hollow tubes through space and time that can connect very distant regions of the universe. A star may be thousands of light-years away, but a wormhole can connect that star to us with a tunnel only a few steps long.
Wormholes also have the somewhat mystical ability to allow backwards time travel. If you take one end of the wormhole and accelerate it to a speed close to that of light, it will experience time dilation — its internal “clock” will run slower than the rest of the universe.
That will cause the two ends of the wormhole to no longer be synchronized in time. Then you could walk in one end and end up in your own past. Voilà: time travel.
Read More: Is There a Particle That Can Travel Back in Time?
Can Humans Travel Through Wormholes?
There's just one, tiny, teensy problem with this setup: Einstein-Rosen bridges are indeed wormholes, but the entrance to the wormhole sits behind the black hole event horizon. And the number one rule of black hole event horizons is that once you cross them, you’re never allowed to escape. Ever.
Once you pass through a black hole event horizon, you are forced towards the singularity, where you are guaranteed to meet your gruesome end. In other words, once you enter an Einstein-Rosen bridge, you will never escape.
So, the unfortunate truth with Einstein-Rosen bridges is that while they appear to be magical doorways to distant reaches of the universe, they are just as deadly as black holes. When you enter you can meet other travelers who have fallen in from the other side, and you could even carry on a conversation…briefly, before you both struck the singularity.
There have been attempts to stabilize Einstein-Rosen bridges and make them traversable by somehow getting their entrances to sit outside the event horizon. So far the only way we know how to do this is with exotic matter. If you threaded the wormhole tunnel with matter that had negative mass, then in principle you could have a not-deadly-at-all wormhole.
Alas, negative matter does not appear to exist in the universe, and so our wormhole — and time travel — dreams will have to remain as mere mathematical fantasies.
Read More: What Did Einstein's Theories Say About the Illusion of Time?
- space exploration
Already a subscriber?
Register or Log In

Keep reading for as low as $1.99!
Sign up for our weekly science updates.
Save up to 40% off the cover price when you subscribe to Discover magazine.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

- LISTEN & FOLLOW
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
- Amazon Music
- Amazon Alexa
Your support helps make our show possible and unlocks access to our sponsor-free feed.
Paradox-Free Time Travel Is Theoretically Possible, Researchers Say

Matthew S. Schwartz

A dog dressed as Marty McFly from Back to the Future attends the Tompkins Square Halloween Dog Parade in 2015. New research says time travel might be possible without the problems McFly encountered. Timothy A. Clary/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
A dog dressed as Marty McFly from Back to the Future attends the Tompkins Square Halloween Dog Parade in 2015. New research says time travel might be possible without the problems McFly encountered.
"The past is obdurate," Stephen King wrote in his book about a man who goes back in time to prevent the Kennedy assassination. "It doesn't want to be changed."
Turns out, King might have been on to something.
Countless science fiction tales have explored the paradox of what would happen if you went back in time and did something in the past that endangered the future. Perhaps one of the most famous pop culture examples is in Back to the Future , when Marty McFly goes back in time and accidentally stops his parents from meeting, putting his own existence in jeopardy.
But maybe McFly wasn't in much danger after all. According a new paper from researchers at the University of Queensland, even if time travel were possible, the paradox couldn't actually exist.
Researchers ran the numbers and determined that even if you made a change in the past, the timeline would essentially self-correct, ensuring that whatever happened to send you back in time would still happen.
"Say you traveled in time in an attempt to stop COVID-19's patient zero from being exposed to the virus," University of Queensland scientist Fabio Costa told the university's news service .
"However, if you stopped that individual from becoming infected, that would eliminate the motivation for you to go back and stop the pandemic in the first place," said Costa, who co-authored the paper with honors undergraduate student Germain Tobar.
"This is a paradox — an inconsistency that often leads people to think that time travel cannot occur in our universe."
A variation is known as the "grandfather paradox" — in which a time traveler kills their own grandfather, in the process preventing the time traveler's birth.
The logical paradox has given researchers a headache, in part because according to Einstein's theory of general relativity, "closed timelike curves" are possible, theoretically allowing an observer to travel back in time and interact with their past self — potentially endangering their own existence.
But these researchers say that such a paradox wouldn't necessarily exist, because events would adjust themselves.
Take the coronavirus patient zero example. "You might try and stop patient zero from becoming infected, but in doing so, you would catch the virus and become patient zero, or someone else would," Tobar told the university's news service.
In other words, a time traveler could make changes, but the original outcome would still find a way to happen — maybe not the same way it happened in the first timeline but close enough so that the time traveler would still exist and would still be motivated to go back in time.
"No matter what you did, the salient events would just recalibrate around you," Tobar said.
The paper, "Reversible dynamics with closed time-like curves and freedom of choice," was published last week in the peer-reviewed journal Classical and Quantum Gravity . The findings seem consistent with another time travel study published this summer in the peer-reviewed journal Physical Review Letters. That study found that changes made in the past won't drastically alter the future.
Bestselling science fiction author Blake Crouch, who has written extensively about time travel, said the new study seems to support what certain time travel tropes have posited all along.
"The universe is deterministic and attempts to alter Past Event X are destined to be the forces which bring Past Event X into being," Crouch told NPR via email. "So the future can affect the past. Or maybe time is just an illusion. But I guess it's cool that the math checks out."
- time travel
- grandfather paradox
Is time travel even possible? An astrophysicist explains the science behind the science fiction
Published: Nov 13, 2023
By: Magazine Editor

Written by Adi Foord , assistant professor of physics , UMBC
Curious Kids is a series for children of all ages. If you have a question you’d like an expert to answer, send it to [email protected] .
Will it ever be possible for time travel to occur? – Alana C., age 12, Queens, New York
Have you ever dreamed of traveling through time, like characters do in science fiction movies? For centuries, the concept of time travel has captivated people’s imaginations. Time travel is the concept of moving between different points in time, just like you move between different places. In movies, you might have seen characters using special machines, magical devices or even hopping into a futuristic car to travel backward or forward in time.
But is this just a fun idea for movies, or could it really happen?
The question of whether time is reversible remains one of the biggest unresolved questions in science. If the universe follows the laws of thermodynamics , it may not be possible. The second law of thermodynamics states that things in the universe can either remain the same or become more disordered over time.
It’s a bit like saying you can’t unscramble eggs once they’ve been cooked. According to this law, the universe can never go back exactly to how it was before. Time can only go forward, like a one-way street.
Time is relative
However, physicist Albert Einstein’s theory of special relativity suggests that time passes at different rates for different people. Someone speeding along on a spaceship moving close to the speed of light – 671 million miles per hour! – will experience time slower than a person on Earth.
People have yet to build spaceships that can move at speeds anywhere near as fast as light, but astronauts who visit the International Space Station orbit around the Earth at speeds close to 17,500 mph. Astronaut Scott Kelly has spent 520 days at the International Space Station, and as a result has aged a little more slowly than his twin brother – and fellow astronaut – Mark Kelly. Scott used to be 6 minutes younger than his twin brother. Now, because Scott was traveling so much faster than Mark and for so many days, he is 6 minutes and 5 milliseconds younger .
Some scientists are exploring other ideas that could theoretically allow time travel. One concept involves wormholes , or hypothetical tunnels in space that could create shortcuts for journeys across the universe. If someone could build a wormhole and then figure out a way to move one end at close to the speed of light – like the hypothetical spaceship mentioned above – the moving end would age more slowly than the stationary end. Someone who entered the moving end and exited the wormhole through the stationary end would come out in their past.
However, wormholes remain theoretical: Scientists have yet to spot one. It also looks like it would be incredibly challenging to send humans through a wormhole space tunnel.
Paradoxes and failed dinner parties
There are also paradoxes associated with time travel. The famous “ grandfather paradox ” is a hypothetical problem that could arise if someone traveled back in time and accidentally prevented their grandparents from meeting. This would create a paradox where you were never born, which raises the question: How could you have traveled back in time in the first place? It’s a mind-boggling puzzle that adds to the mystery of time travel.
Famously, physicist Stephen Hawking tested the possibility of time travel by throwing a dinner party where invitations noting the date, time and coordinates were not sent out until after it had happened. His hope was that his invitation would be read by someone living in the future, who had capabilities to travel back in time. But no one showed up.
As he pointed out : “The best evidence we have that time travel is not possible, and never will be, is that we have not been invaded by hordes of tourists from the future.”
Telescopes are time machines
Interestingly, astrophysicists armed with powerful telescopes possess a unique form of time travel. As they peer into the vast expanse of the cosmos, they gaze into the past universe. Light from all galaxies and stars takes time to travel, and these beams of light carry information from the distant past. When astrophysicists observe a star or a galaxy through a telescope, they are not seeing it as it is in the present, but as it existed when the light began its journey to Earth millions to billions of years ago. https://www.youtube.com/embed/QeRtcJi3V38?wmode=transparent&start=0 Telescopes are a kind of time machine – they let you peer into the past.
NASA’s newest space telescope, the James Webb Space Telescope , is peering at galaxies that were formed at the very beginning of the Big Bang, about 13.7 billion years ago.
While we aren’t likely to have time machines like the ones in movies anytime soon, scientists are actively researching and exploring new ideas. But for now, we’ll have to enjoy the idea of time travel in our favorite books, movies and dreams.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article and see more than 250 UMBC articles available in The Conversation.
Tags: CNMS , Physics , The Conversation
Related Posts
- Science & Tech

Partnership with biotech giant Genentech benefits UMBC graduate students

“Hidden” sex differences in neurological reward pathways suggest opportunity for improved psychiatric therapeutics

Ph.D. candidate Emily Faber improving climate modeling with NOAA fellowship
Search UMBC Search
- Accreditation
- Consumer Information
- Equal Opportunity
- Privacy PDF Download
- Web Accessibility
Search UMBC.edu

Is Time Travel Possible?
We all travel in time! We travel one year in time between birthdays, for example. And we are all traveling in time at approximately the same speed: 1 second per second.
We typically experience time at one second per second. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
NASA's space telescopes also give us a way to look back in time. Telescopes help us see stars and galaxies that are very far away . It takes a long time for the light from faraway galaxies to reach us. So, when we look into the sky with a telescope, we are seeing what those stars and galaxies looked like a very long time ago.
However, when we think of the phrase "time travel," we are usually thinking of traveling faster than 1 second per second. That kind of time travel sounds like something you'd only see in movies or science fiction books. Could it be real? Science says yes!
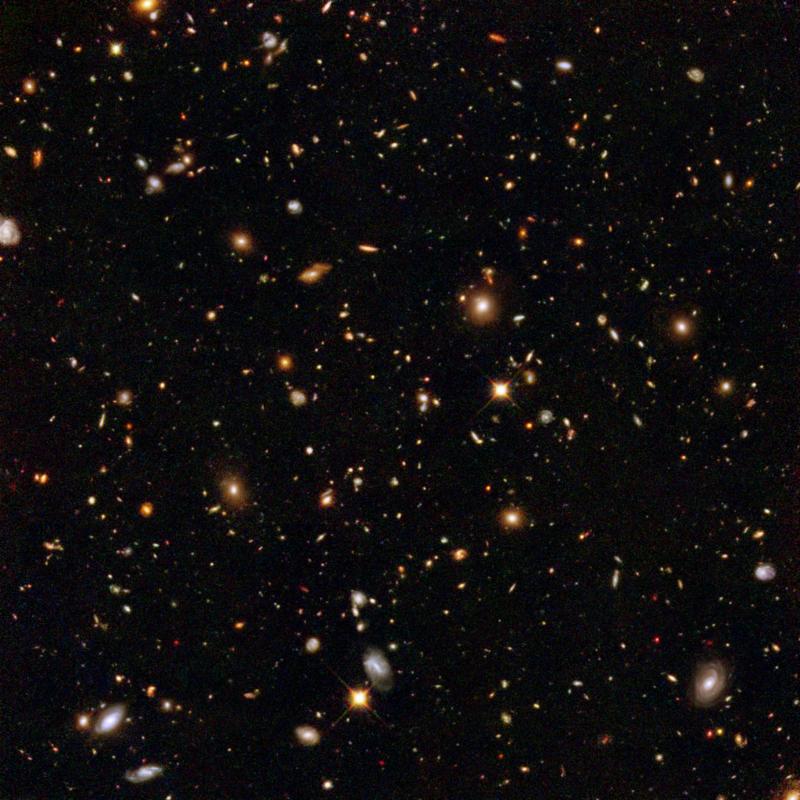

This image from the Hubble Space Telescope shows galaxies that are very far away as they existed a very long time ago. Credit: NASA, ESA and R. Thompson (Univ. Arizona)
How do we know that time travel is possible?
More than 100 years ago, a famous scientist named Albert Einstein came up with an idea about how time works. He called it relativity. This theory says that time and space are linked together. Einstein also said our universe has a speed limit: nothing can travel faster than the speed of light (186,000 miles per second).
Einstein's theory of relativity says that space and time are linked together. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
What does this mean for time travel? Well, according to this theory, the faster you travel, the slower you experience time. Scientists have done some experiments to show that this is true.
For example, there was an experiment that used two clocks set to the exact same time. One clock stayed on Earth, while the other flew in an airplane (going in the same direction Earth rotates).
After the airplane flew around the world, scientists compared the two clocks. The clock on the fast-moving airplane was slightly behind the clock on the ground. So, the clock on the airplane was traveling slightly slower in time than 1 second per second.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Can we use time travel in everyday life?
We can't use a time machine to travel hundreds of years into the past or future. That kind of time travel only happens in books and movies. But the math of time travel does affect the things we use every day.
For example, we use GPS satellites to help us figure out how to get to new places. (Check out our video about how GPS satellites work .) NASA scientists also use a high-accuracy version of GPS to keep track of where satellites are in space. But did you know that GPS relies on time-travel calculations to help you get around town?
GPS satellites orbit around Earth very quickly at about 8,700 miles (14,000 kilometers) per hour. This slows down GPS satellite clocks by a small fraction of a second (similar to the airplane example above).
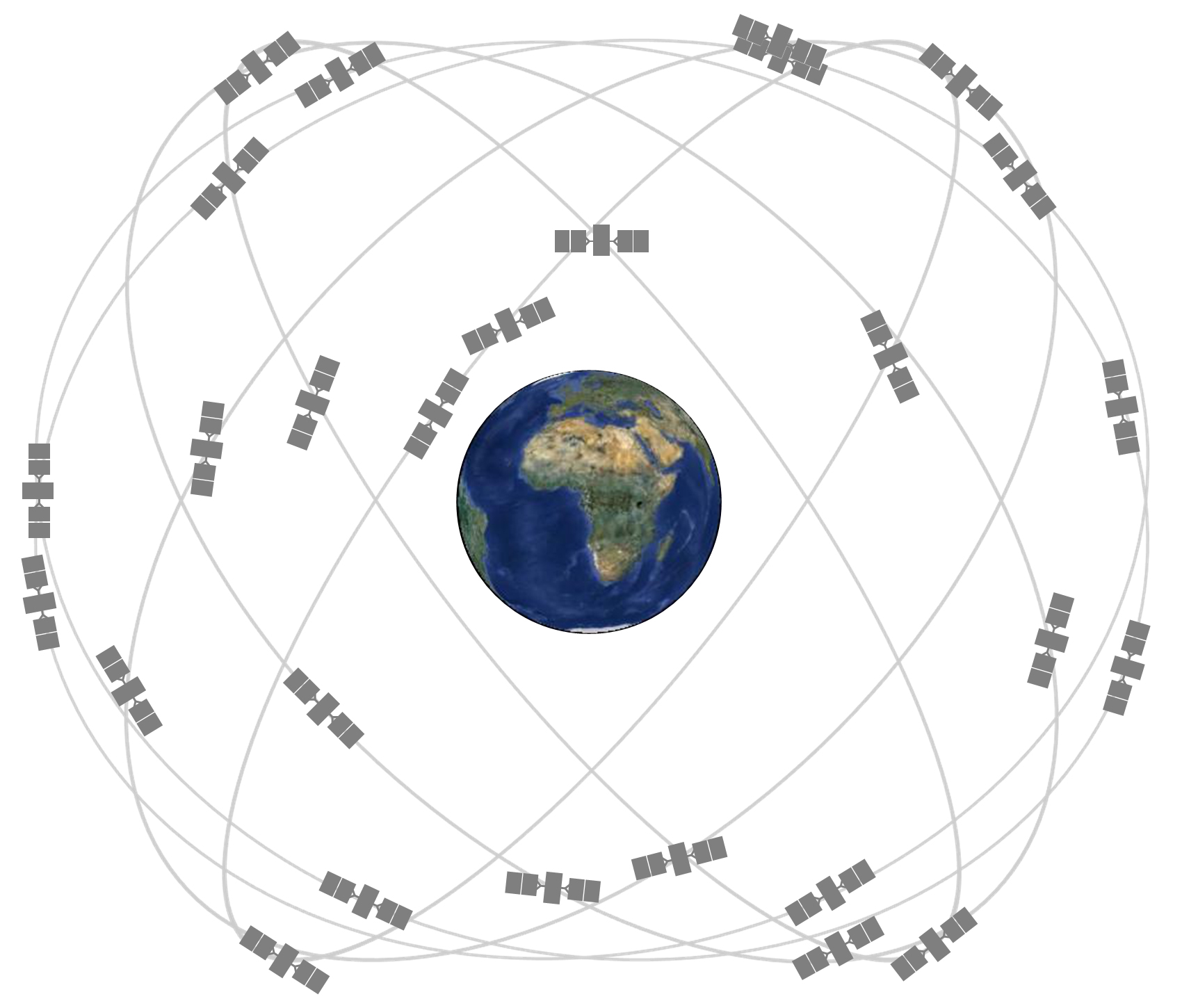
GPS satellites orbit around Earth at about 8,700 miles (14,000 kilometers) per hour. Credit: GPS.gov
However, the satellites are also orbiting Earth about 12,550 miles (20,200 km) above the surface. This actually speeds up GPS satellite clocks by a slighter larger fraction of a second.
Here's how: Einstein's theory also says that gravity curves space and time, causing the passage of time to slow down. High up where the satellites orbit, Earth's gravity is much weaker. This causes the clocks on GPS satellites to run faster than clocks on the ground.
The combined result is that the clocks on GPS satellites experience time at a rate slightly faster than 1 second per second. Luckily, scientists can use math to correct these differences in time.
If scientists didn't correct the GPS clocks, there would be big problems. GPS satellites wouldn't be able to correctly calculate their position or yours. The errors would add up to a few miles each day, which is a big deal. GPS maps might think your home is nowhere near where it actually is!
In Summary:
Yes, time travel is indeed a real thing. But it's not quite what you've probably seen in the movies. Under certain conditions, it is possible to experience time passing at a different rate than 1 second per second. And there are important reasons why we need to understand this real-world form of time travel.
If you liked this, you may like:
Welcome to Time Travel Events
Upcoming shows.

June 1, 2024
Join us for a night out feeling without the late night finish.

Cryptid High Tea
June 8, 2024.
Tea, biscuits, entertainment, and most of all.... cryptid stories.

Atlanta Cosplay Yard Sale
August 24, 2024.
Need cosplay ideas, accessories, or total outfits right before DragonCon?? We got the spot for you!
Tickets and Extras

Cryptid High Tea Collection
$ 15.00.

$ 35.00
We go into details of events we've done or events we will do, information, winter underland.
Enjoy the darker side of the holiday season this November. Welcome to Winter Underland! A brand new show featuring all the shadows the holidays can offer: Tickets are $5 each – 12 and under are Read more…

ACYS and CCS Cosplay Yard Sale
Atlanta Cosplay Yard Sale and Charlie’s Collectible Show have teamed up to host a Cosplay Yard Sale to get you ready for MomoCon! Our vendors have new and used cosplay pieces to complete costumes. Some Read more…

The Goblin Market FAQ
We get a lot of questions about The Goblin Market each year. We do understand that it is a unique event, so we’re going to do our best to help answer some common questions you Read more…
Need to contact us?

Time Travel: Observing Cosmic History
By observing light from faraway cosmic objects, the Hubble Space Telescope is like a time machine. Light takes time to reach Hubble, because it travels great distances. That means images captured by Hubble today, show what the objects looked like years ago!

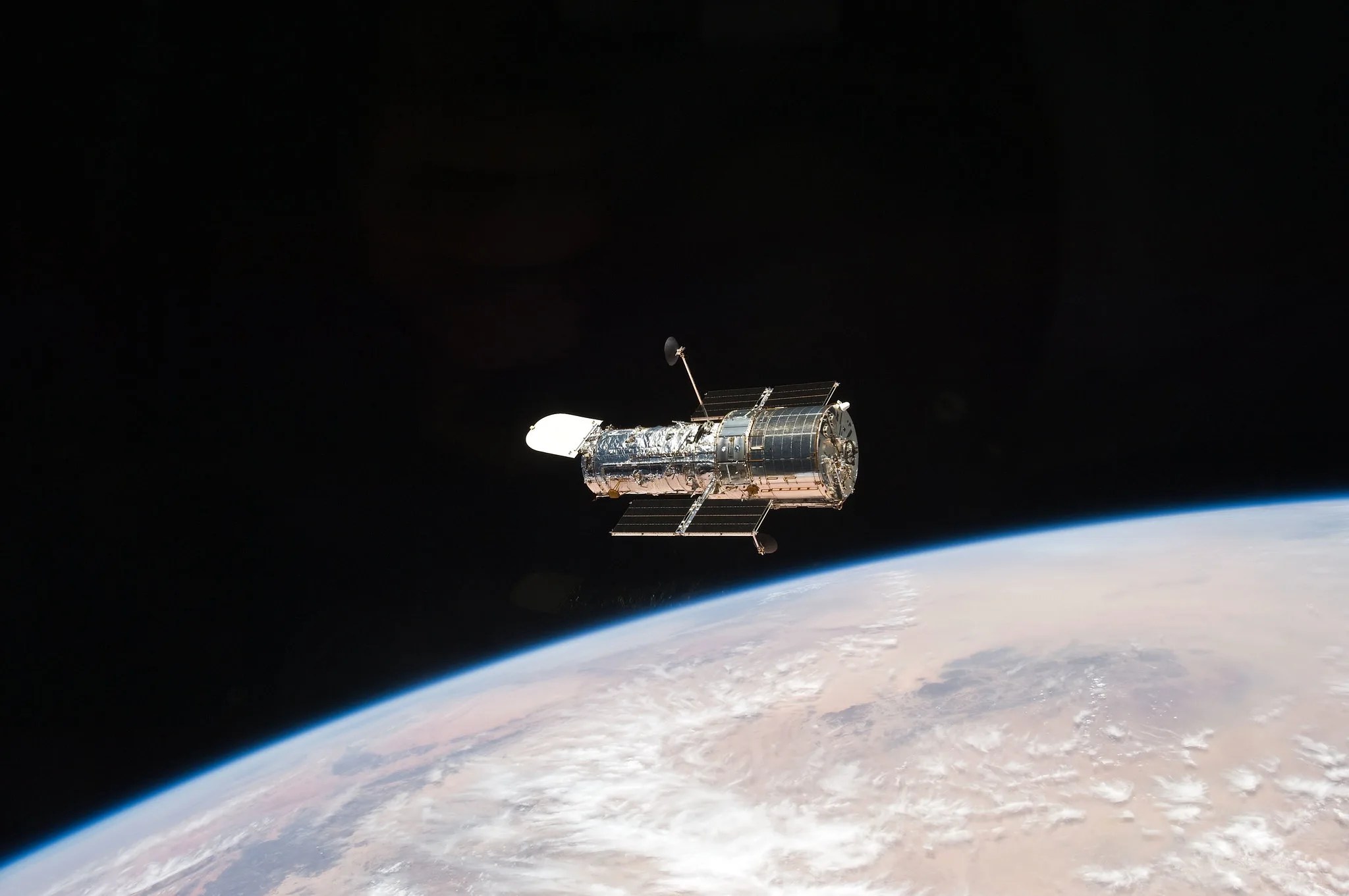
The Hubble Space Telescope is many things. It’s an observatory, a satellite, and an icon of cultural and scientific significance – but perhaps most interestingly, Hubble is also a time machine.
Hubble isn’t that far away, locked in a low-Earth orbit just a few hundred miles up that takes about 90 minutes to complete. But with its position just above Earth’s murky atmosphere, Hubble’s transformative view of our universe literally lets us witness our universe’s past. It allows us to effectively travel back in time.
How does that work? After all, Hubble doesn’t travel beyond our solar system, or even our home planet’s gravity. It certainly doesn’t have any sci-fi elements you might find in Doctor Who or Back to the Future.

Light Travel
The answer is simply light.
The term “light-year” shows up a lot in astronomy. This is a measure of distance that means exactly what it says – the distance that light travels in one year. Given that the speed of light is 186,000 miles (299,000 kilometers) per second, light can cover some serious ground over the course of 365 days. To be precise, almost 6 trillion miles (9.5 trillion kilometers)!
Traveling Back in Time: 8 minutes
Hubble works by gathering light from objects in our universe – some as close as our Moon, and some as distant as galaxy clusters that are billions of light-years away. All that light takes time to reach the telescope, just as it takes time for light to travel from its source to our eyes. For example, our Sun is located about 93 million miles (150 million kilometers) from Earth. That means that it takes roughly eight minutes for its light to reach us here on our planet, so when we look at the Sun (though directly is never recommended!) we see it exactly as it was eight minutes in the past.
Cosmically speaking, the 93 million miles between us and the Sun are nothing. We orbit around just one of billions of stars in the Milky Way Galaxy, which is one of countless trillions of galaxies in the universe.
With that in mind, time travel gets more intense when Hubble observes objects beyond our star system.
Traveling Back in Time: 4 years
Aside from our Sun, the next closest star to us is named Proxima Centauri. It’s about four light-years away, which makes it a close neighbor on a universal scale. But even with Hubble’s sharp, powerful vision, Proxima Centauri remains a point-like object – demonstrating our universe’s unfathomably large size.

Traveling Back in Time: 700 years
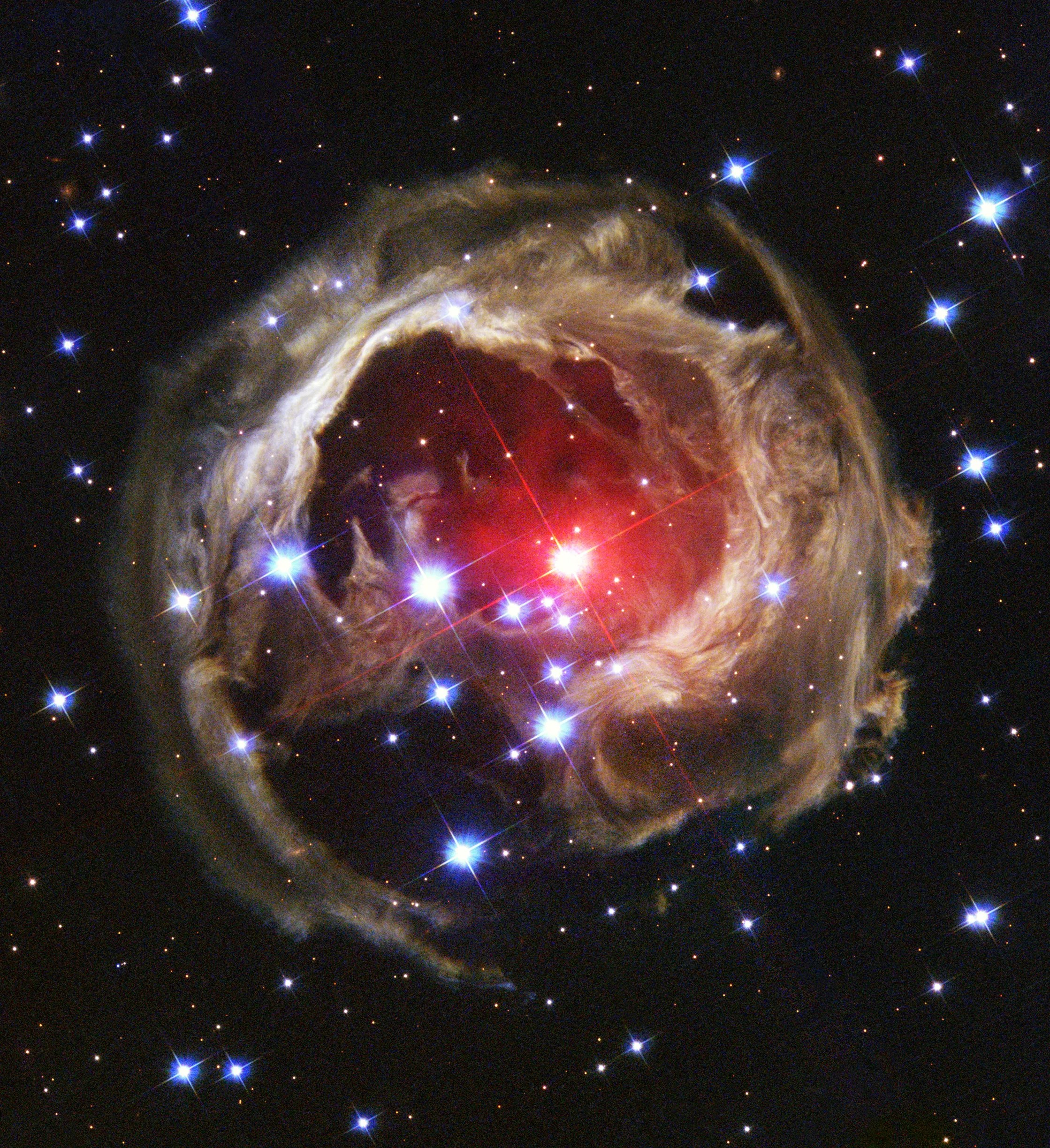
Another stellar target of Hubble’s is named Betelgeuse, which is about 700 light-years from Earth. Again, this means that when Hubble looks at Betelgeuse, the star appears exactly as it was 700 years ago. As one of the brightest stars in our sky, astronomers believe it’s likely that even the earliest humans knew of it, as this star appears in stories from several cultures.
This red supergiant star began to dim significantly in the fall of 2019, losing about 60% of its brightness within months. But by April 2020, its regular brightness returned. Hubble studied Betelgeuse and found out that the star “blew its top” – it went through a surface mass ejection, in which the star spewed out a large amount of its surface material into space. When that material in space cooled down, it became a dust cloud that temporarily blocked some of the star’s light.
Hubble’s unique ability to observe in ultraviolet light helped reveal the details of this dimming event and its aftermath. In this range of light, Hubble can better observe the hot layers of atmosphere above a star’s surface.
The telescope continues to be the go-to observatory for scientists who study Betelgeuse. Because it’s taken this long for the light from Betelgeuse to reach us, only in very recent history have we witnessed a cosmic event unfolding that really occurred about 700 years ago!
Scientists also believe that Betelgeuse is on the verge of going supernova – dying in an explosive event. In fact, it may have already done so, but the light from the explosion still hasn’t reached us. There’s a good chance that Betelgeuse no longer exists, though we can still see it today from Earth.
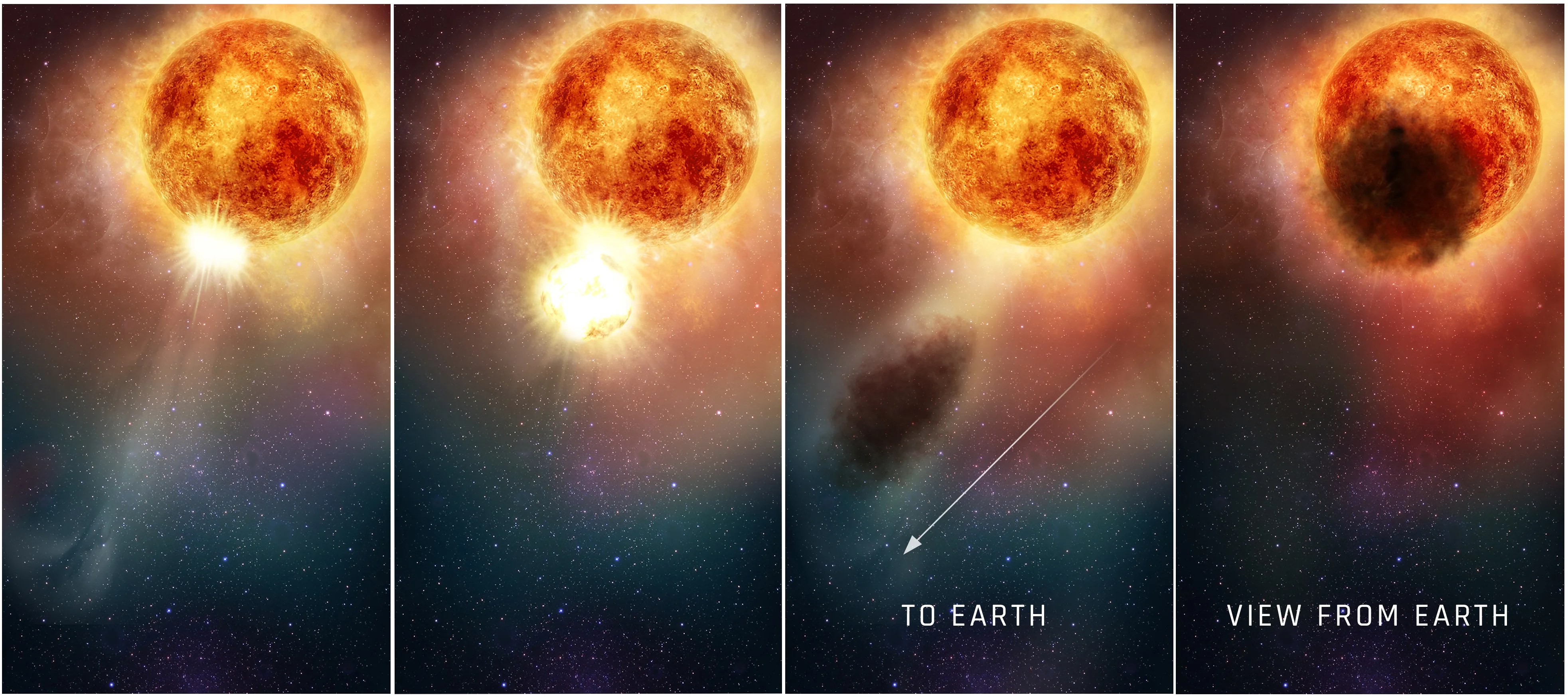
Traveling Back in Time: 6,500 years
Nebulae are clouds of gas and dust where stars are birthed, or the remnants of a dead or dying star itself. These beautiful, ethereal cosmic objects are the subject of some of Hubble’s most iconic images, but they can also teach us more about how our universe behaves and evolves.
For example, a favorite target for Hubble is the Crab Nebula, located about 6,500 light-years away. There are records from 1054 CE written by Chinese astronomers noting the new presence of a shockingly bright “guest” star in the sky, visible even during the daytime. Turns out, they actually saw a supernova – a star’s explosive death – which became the Crab Nebula, made up by the remnants of this violent event. Of course, those Chinese astronomers witnessed a supernova explosion that occurred about 5446 BCE, but it took the light from the explosion 6,500 years to reach Earth in the year 1054.

Traveling Back in Time: 2.5 million years
When Hubble looks beyond our own galaxy, we can watch cosmic history unfold over eons.
The Andromeda Galaxy is a whopping 2.5 million light-years away, but that’s just the closest major galaxy to us here in the Milky Way. Observing Andromeda is like staring into a vision from 2.5 million years ago – back during the Paleolithic period on Earth, when very early humans existed.
And if Andromeda is the closest major galaxy to us, it’s difficult to comprehend just how far the light from the most distant observed galaxies has traveled.
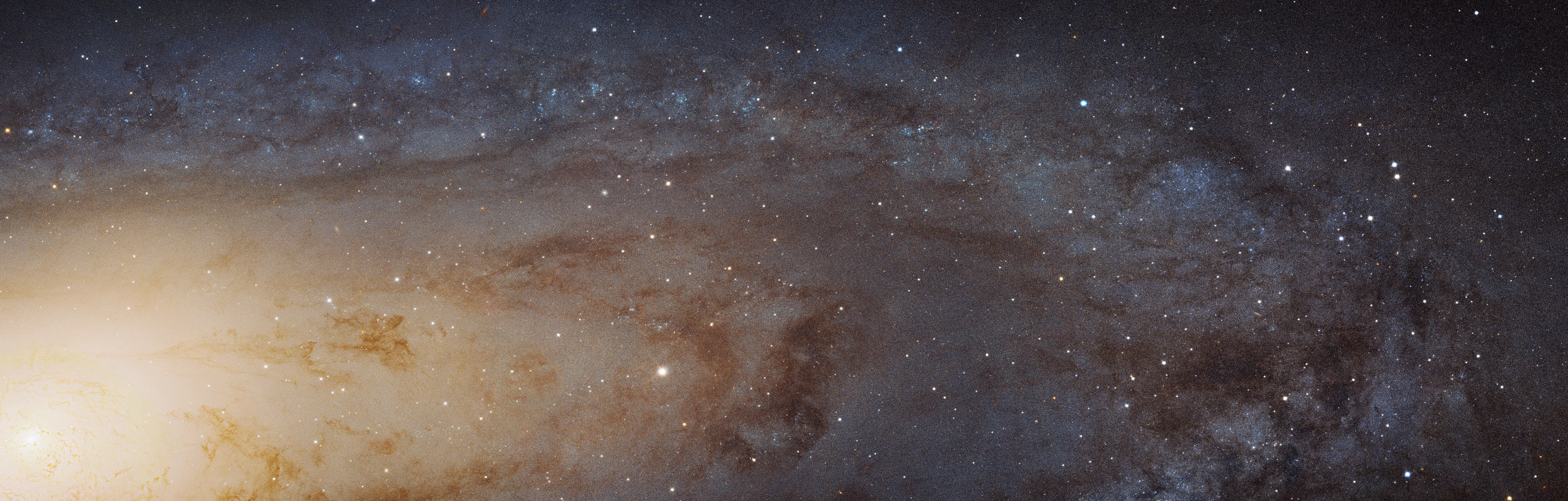

Traveling Back in Time: 12.9 billion years
Another Hubble record is for observing the most distant individual star ever detected, named Earendel. This faraway star emitted its light within the first billion years of the universe, which is about 13.8 billion years old, so it took quite a while to reach Hubble! In fact, that observation was only made possible by nature’s magnifying glass – an astronomical phenomenon known as gravitational lensing. When a massive cosmic object has enough gravity, its gravitational field can magnify and bend light coming from objects located behind it. The gravity of a galaxy cluster located between Hubble and Earendel magnified the star’s light, making it detectable. The type of star that Earendel seems to be typically have brief lives, only surviving about half a billion years. That means Earendel has ceased to exist for over 12 billion years, yet we are able to look back in time and watch Earendel during its short life.

Traveling Back in Time: 13.4 billion years
Perhaps some of Hubble’s most legendary observations are its deep field images, which collect light from thousands of galaxies that are billions of light-years away.
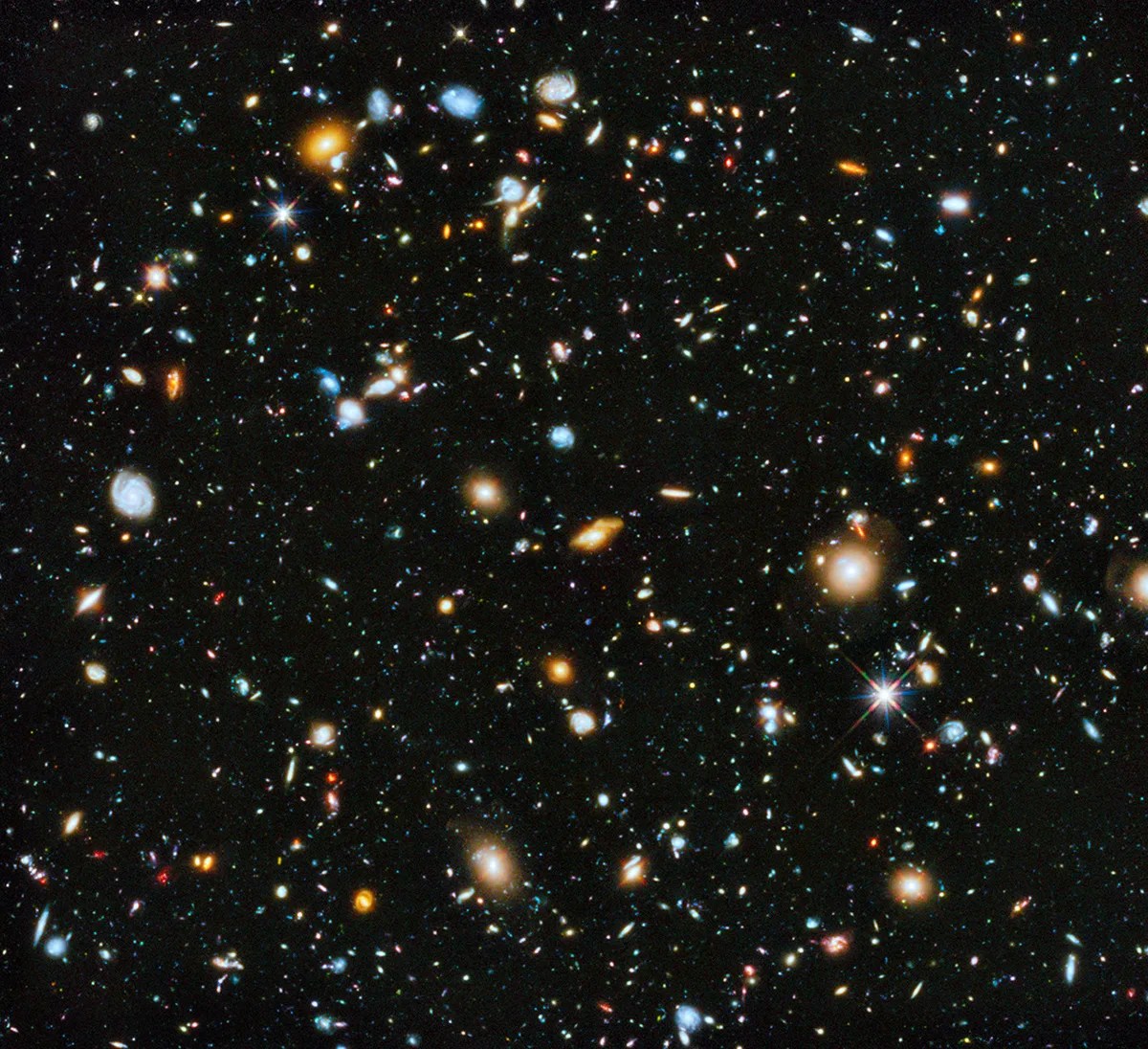

With this type of imagery, we can better understand how our universe changes over time by puzzling out how galaxies evolve. The farther back we look with Hubble, the closer we get to the the big bang, when the universe began – so the most distant galaxies observed by Hubble often appear to us as the “youngest” ones – giving us a sneak peek at the universe in its infancy. Because these galaxies emitted their light when they were young, we get to witness them in their early stages. These early galaxies often appear simpler and smaller than the grandiose spiral galaxies and merged galaxies we see closer to us in distance, and therefore in time. These young galaxies are actually old galaxies now as they have evolved over the time this light has taken to reach us.
Hubble’s farthest observation is of a galaxy named GN-z11, observed as it was 13.4 billion years in the past! This places it within just 400 million years of the big bang itself.
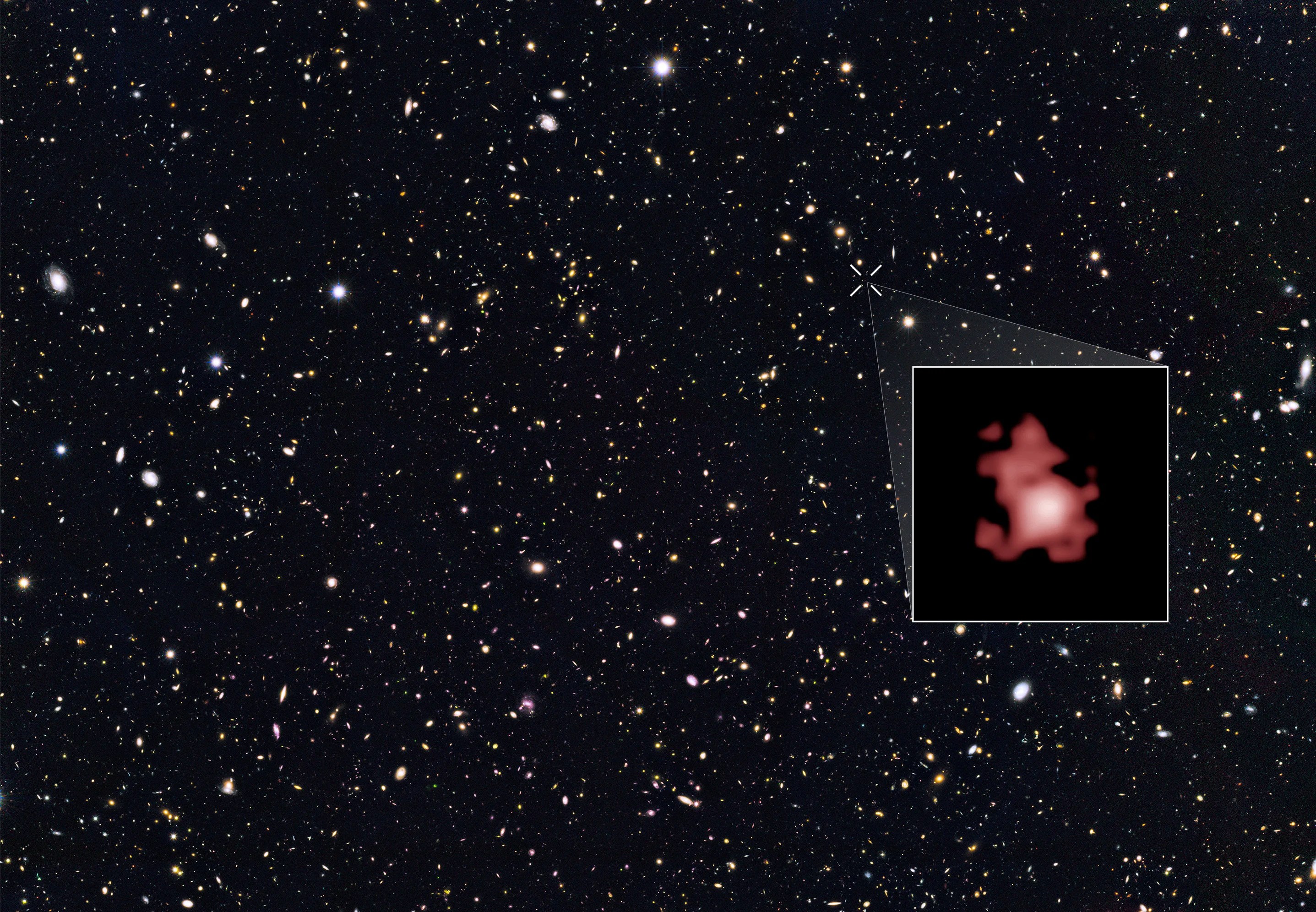

Watching Our Universe Over Time
Observations of the most distant objects, like GN-z11 and Earendel, give astronomers exciting insight into the environment of our early universe. The light we see literally traveled from all the way back then!
Our universe remains mysterious, mind-bendingly large, and ever-expanding, but by gathering light from near and far – from the recent past to the dawn of the universe itself – Hubble helps answer questions about where we are and how the universe works.
At its core, astronomy is really just archaeology. Cosmic objects give off light, letting us learn more about their lives. It can take a long, long time for light to reach Hubble – just one telescope orbiting just one planet in just one solar system in just one galaxy. Scientists use Hubble like the time machine that it is to piece together the history and mystery of the cosmos, giving us all a glimpse right up to the edge of the universe – and time itself.
Explore More Hubble

The Lost Universe
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has vanished from Earth’s timeline. Only an ambitious crew of adventurers can uncover what was lost. Are you up to the challenge?

Hubble Science Highlights
Hubble has affected every area of astronomy. Its most notable scientific discoveries reflect the broad range of research and the breakthroughs it has achieved.

Hubble's Cultural Impact
Even if you don't know anything about the Hubble Space Telescope, its pictures have been a part of your life.
What is Hubble Observing?
See the area of sky Hubble is currently investigating or explore its upcoming and past targets.
Hubble E-books
Investigate the mysteries of the universe with Hubble. Learn Hubble's history and dive deeper into its discoveries by downloading our e-books.

Time travel could be possible, but only with parallel timelines
Assistant Professor, Physics, Brock University
Disclosure statement
Barak Shoshany does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Brock University provides funding as a member of The Conversation CA-FR.
Brock University provides funding as a member of The Conversation CA.
View all partners
Have you ever made a mistake that you wish you could undo? Correcting past mistakes is one of the reasons we find the concept of time travel so fascinating. As often portrayed in science fiction, with a time machine, nothing is permanent anymore — you can always go back and change it. But is time travel really possible in our universe , or is it just science fiction?
Read more: Curious Kids: is time travel possible for humans?
Our modern understanding of time and causality comes from general relativity . Theoretical physicist Albert Einstein’s theory combines space and time into a single entity — “spacetime” — and provides a remarkably intricate explanation of how they both work, at a level unmatched by any other established theory. This theory has existed for more than 100 years, and has been experimentally verified to extremely high precision, so physicists are fairly certain it provides an accurate description of the causal structure of our universe.
For decades, physicists have been trying to use general relativity to figure out if time travel is possible . It turns out that you can write down equations that describe time travel and are fully compatible and consistent with relativity. But physics is not mathematics, and equations are meaningless if they do not correspond to anything in reality.
Arguments against time travel
There are two main issues which make us think these equations may be unrealistic. The first issue is a practical one: building a time machine seems to require exotic matter , which is matter with negative energy. All the matter we see in our daily lives has positive energy — matter with negative energy is not something you can just find lying around. From quantum mechanics, we know that such matter can theoretically be created, but in too small quantities and for too short times .
However, there is no proof that it is impossible to create exotic matter in sufficient quantities. Furthermore, other equations may be discovered that allow time travel without requiring exotic matter. Therefore, this issue may just be a limitation of our current technology or understanding of quantum mechanics.

The other main issue is less practical, but more significant: it is the observation that time travel seems to contradict logic, in the form of time travel paradoxes . There are several types of such paradoxes, but the most problematic are consistency paradoxes .
A popular trope in science fiction, consistency paradoxes happen whenever there is a certain event that leads to changing the past, but the change itself prevents this event from happening in the first place.
For example, consider a scenario where I enter my time machine, use it to go back in time five minutes, and destroy the machine as soon as I get to the past. Now that I destroyed the time machine, it would be impossible for me to use it five minutes later.
But if I cannot use the time machine, then I cannot go back in time and destroy it. Therefore, it is not destroyed, so I can go back in time and destroy it. In other words, the time machine is destroyed if and only if it is not destroyed. Since it cannot be both destroyed and not destroyed simultaneously, this scenario is inconsistent and paradoxical.
Eliminating the paradoxes
There’s a common misconception in science fiction that paradoxes can be “created.” Time travellers are usually warned not to make significant changes to the past and to avoid meeting their past selves for this exact reason. Examples of this may be found in many time travel movies, such as the Back to the Future trilogy.
But in physics, a paradox is not an event that can actually happen — it is a purely theoretical concept that points towards an inconsistency in the theory itself. In other words, consistency paradoxes don’t merely imply time travel is a dangerous endeavour, they imply it simply cannot be possible.
This was one of the motivations for theoretical physicist Stephen Hawking to formulate his chronology protection conjecture , which states that time travel should be impossible. However, this conjecture so far remains unproven. Furthermore, the universe would be a much more interesting place if instead of eliminating time travel due to paradoxes, we could just eliminate the paradoxes themselves.
One attempt at resolving time travel paradoxes is theoretical physicist Igor Dmitriyevich Novikov’s self-consistency conjecture , which essentially states that you can travel to the past, but you cannot change it.
According to Novikov, if I tried to destroy my time machine five minutes in the past, I would find that it is impossible to do so. The laws of physics would somehow conspire to preserve consistency.
Introducing multiple histories
But what’s the point of going back in time if you cannot change the past? My recent work, together with my students Jacob Hauser and Jared Wogan, shows that there are time travel paradoxes that Novikov’s conjecture cannot resolve. This takes us back to square one, since if even just one paradox cannot be eliminated, time travel remains logically impossible.
So, is this the final nail in the coffin of time travel? Not quite. We showed that allowing for multiple histories (or in more familiar terms, parallel timelines) can resolve the paradoxes that Novikov’s conjecture cannot. In fact, it can resolve any paradox you throw at it.
The idea is very simple. When I exit the time machine, I exit into a different timeline. In that timeline, I can do whatever I want, including destroying the time machine, without changing anything in the original timeline I came from. Since I cannot destroy the time machine in the original timeline, which is the one I actually used to travel back in time, there is no paradox.
After working on time travel paradoxes for the last three years , I have become increasingly convinced that time travel could be possible, but only if our universe can allow multiple histories to coexist. So, can it?
Quantum mechanics certainly seems to imply so, at least if you subscribe to Everett’s “many-worlds” interpretation , where one history can “split” into multiple histories, one for each possible measurement outcome – for example, whether Schrödinger’s cat is alive or dead, or whether or not I arrived in the past.
But these are just speculations. My students and I are currently working on finding a concrete theory of time travel with multiple histories that is fully compatible with general relativity. Of course, even if we manage to find such a theory, this would not be sufficient to prove that time travel is possible, but it would at least mean that time travel is not ruled out by consistency paradoxes.
Time travel and parallel timelines almost always go hand-in-hand in science fiction, but now we have proof that they must go hand-in-hand in real science as well. General relativity and quantum mechanics tell us that time travel might be possible, but if it is, then multiple histories must also be possible.
- Time travel
- Theoretical physics
- Time machine
- Albert Einstein
- Listen to this article
- Time travel paradox

Centre Director, Transformative Media Technologies

Stephen Knight Lecturer in Medieval Literature

Postdoctoral Research Fellowship

Social Media Producer

Dean (Head of School), Indigenous Knowledges
World Clock Meeting Planner
Find the best time to call people in other time zones.
- Pick date and locations
- Find a time
- Show details
Please note: if some of the participants are in the United Kingdom, you should select a city there (e.g., London), instead of UTC/GMT.
The United Kingdom is one hour ahead of GMT during Daylight Saving Time (DST), and this service will adjust for DST automatically.
Need some help?
Elsewhere on timeanddate.com

Event Time Announcer – Create New Event
The Event Time Announcer shows the local time in cities all over the world at a given time in the past or future. Can be shared with users worldwide.

Time Zone Converter – Time Difference Calculator
Find the exact time difference with the Time Zone Converter – Time Difference Calculator which converts the time difference between places and time zones all over the world.

Create Your Own Countdown
Make your own countdown to any date.

Get the time at any given coordinate on Earth, calculate time zone conversions.

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Time Travel
There is an extensive literature on time travel in both philosophy and physics. Part of the great interest of the topic stems from the fact that reasons have been given both for thinking that time travel is physically possible—and for thinking that it is logically impossible! This entry deals primarily with philosophical issues; issues related to the physics of time travel are covered in the separate entries on time travel and modern physics and time machines . We begin with the definitional question: what is time travel? We then turn to the major objection to the possibility of backwards time travel: the Grandfather paradox. Next, issues concerning causation are discussed—and then, issues in the metaphysics of time and change. We end with a discussion of the question why, if backwards time travel will ever occur, we have not been visited by time travellers from the future.
1.1 Time Discrepancy
1.2 changing the past, 2.1 can and cannot, 2.2 improbable coincidences, 2.3 inexplicable occurrences, 3.1 backwards causation, 3.2 causal loops, 4.1 time travel and time, 4.2 time travel and change, 5. where are the time travellers, other internet resources, related entries, 1. what is time travel.
There is a number of rather different scenarios which would seem, intuitively, to count as ‘time travel’—and a number of scenarios which, while sharing certain features with some of the time travel cases, seem nevertheless not to count as genuine time travel: [ 1 ]
Time travel Doctor . Doctor Who steps into a machine in 2024. Observers outside the machine see it disappear. Inside the machine, time seems to Doctor Who to pass for ten minutes. Observers in 1984 (or 3072) see the machine appear out of nowhere. Doctor Who steps out. [ 2 ] Leap . The time traveller takes hold of a special device (or steps into a machine) and suddenly disappears; she appears at an earlier (or later) time. Unlike in Doctor , the time traveller experiences no lapse of time between her departure and arrival: from her point of view, she instantaneously appears at the destination time. [ 3 ] Putnam . Oscar Smith steps into a machine in 2024. From his point of view, things proceed much as in Doctor : time seems to Oscar Smith to pass for a while; then he steps out in 1984. For observers outside the machine, things proceed differently. Observers of Oscar’s arrival in the past see a time machine suddenly appear out of nowhere and immediately divide into two copies of itself: Oscar Smith steps out of one; and (through the window) they see inside the other something that looks just like what they would see if a film of Oscar Smith were played backwards (his hair gets shorter; food comes out of his mouth and goes back into his lunch box in a pristine, uneaten state; etc.). Observers of Oscar’s departure from the future do not simply see his time machine disappear after he gets into it: they see it collide with the apparently backwards-running machine just described, in such a way that both are simultaneously annihilated. [ 4 ] Gödel . The time traveller steps into an ordinary rocket ship (not a special time machine) and flies off on a certain course. At no point does she disappear (as in Leap ) or ‘turn back in time’ (as in Putnam )—yet thanks to the overall structure of spacetime (as conceived in the General Theory of Relativity), the traveller arrives at a point in the past (or future) of her departure. (Compare the way in which someone can travel continuously westwards, and arrive to the east of her departure point, thanks to the overall curved structure of the surface of the earth.) [ 5 ] Einstein . The time traveller steps into an ordinary rocket ship and flies off at high speed on a round trip. When he returns to Earth, thanks to certain effects predicted by the Special Theory of Relativity, only a very small amount of time has elapsed for him—he has aged only a few months—while a great deal of time has passed on Earth: it is now hundreds of years in the future of his time of departure. [ 6 ] Not time travel Sleep . One is very tired, and falls into a deep sleep. When one awakes twelve hours later, it seems from one’s own point of view that hardly any time has passed. Coma . One is in a coma for a number of years and then awakes, at which point it seems from one’s own point of view that hardly any time has passed. Cryogenics . One is cryogenically frozen for hundreds of years. Upon being woken, it seems from one’s own point of view that hardly any time has passed. Virtual . One enters a highly realistic, interactive virtual reality simulator in which some past era has been recreated down to the finest detail. Crystal . One looks into a crystal ball and sees what happened at some past time, or will happen at some future time. (Imagine that the crystal ball really works—like a closed-circuit security monitor, except that the vision genuinely comes from some past or future time. Even so, the person looking at the crystal ball is not thereby a time traveller.) Waiting . One enters one’s closet and stays there for seven hours. When one emerges, one has ‘arrived’ seven hours in the future of one’s ‘departure’. Dateline . One departs at 8pm on Monday, flies for fourteen hours, and arrives at 10pm on Monday.
A satisfactory definition of time travel would, at least, need to classify the cases in the right way. There might be some surprises—perhaps, on the best definition of ‘time travel’, Cryogenics turns out to be time travel after all—but it should certainly be the case, for example, that Gödel counts as time travel and that Sleep and Waiting do not. [ 7 ]
In fact there is no entirely satisfactory definition of ‘time travel’ in the literature. The most popular definition is the one given by Lewis (1976, 145–6):
What is time travel? Inevitably, it involves a discrepancy between time and time. Any traveller departs and then arrives at his destination; the time elapsed from departure to arrival…is the duration of the journey. But if he is a time traveller, the separation in time between departure and arrival does not equal the duration of his journey.…How can it be that the same two events, his departure and his arrival, are separated by two unequal amounts of time?…I reply by distinguishing time itself, external time as I shall also call it, from the personal time of a particular time traveller: roughly, that which is measured by his wristwatch. His journey takes an hour of his personal time, let us say…But the arrival is more than an hour after the departure in external time, if he travels toward the future; or the arrival is before the departure in external time…if he travels toward the past.
This correctly excludes Waiting —where the length of the ‘journey’ precisely matches the separation between ‘arrival’ and ‘departure’—and Crystal , where there is no journey at all—and it includes Doctor . It has trouble with Gödel , however—because when the overall structure of spacetime is as twisted as it is in the sort of case Gödel imagined, the notion of external time (“time itself”) loses its grip.
Another definition of time travel that one sometimes encounters in the literature (Arntzenius, 2006, 602) (Smeenk and Wüthrich, 2011, 5, 26) equates time travel with the existence of CTC’s: closed timelike curves. A curve in this context is a line in spacetime; it is timelike if it could represent the career of a material object; and it is closed if it returns to its starting point (i.e. in spacetime—not merely in space). This now includes Gödel —but it excludes Einstein .
The lack of an adequate definition of ‘time travel’ does not matter for our purposes here. [ 8 ] It suffices that we have clear cases of (what would count as) time travel—and that these cases give rise to all the problems that we shall wish to discuss.
Some authors (in philosophy, physics and science fiction) consider ‘time travel’ scenarios in which there are two temporal dimensions (e.g. Meiland (1974)), and others consider scenarios in which there are multiple ‘parallel’ universes—each one with its own four-dimensional spacetime (e.g. Deutsch and Lockwood (1994)). There is a question whether travelling to another version of 2001 (i.e. not the very same version one experienced in the past)—a version at a different point on the second time dimension, or in a different parallel universe—is really time travel, or whether it is more akin to Virtual . In any case, this kind of scenario does not give rise to many of the problems thrown up by the idea of travelling to the very same past one experienced in one’s younger days. It is these problems that form the primary focus of the present entry, and so we shall not have much to say about other kinds of ‘time travel’ scenario in what follows.
One objection to the possibility of time travel flows directly from attempts to define it in anything like Lewis’s way. The worry is that because time travel involves “a discrepancy between time and time”, time travel scenarios are simply incoherent. The time traveller traverses thirty years in one year; she is 51 years old 21 years after her birth; she dies at the age of 100, 200 years before her birth; and so on. The objection is that these are straightforward contradictions: the basic description of what time travel involves is inconsistent; therefore time travel is logically impossible. [ 9 ]
There must be something wrong with this objection, because it would show Einstein to be logically impossible—whereas this sort of future-directed time travel has actually been observed (albeit on a much smaller scale—but that does not affect the present point) (Hafele and Keating, 1972b,a). The most common response to the objection is that there is no contradiction because the interval of time traversed by the time traveller and the duration of her journey are measured with respect to different frames of reference: there is thus no reason why they should coincide. A similar point applies to the discrepancy between the time elapsed since the time traveller’s birth and her age upon arrival. There is no more of a contradiction here than in the fact that Melbourne is both 800 kilometres away from Sydney—along the main highway—and 1200 kilometres away—along the coast road. [ 10 ]
Before leaving the question ‘What is time travel?’ we should note the crucial distinction between changing the past and participating in (aka affecting or influencing) the past. [ 11 ] In the popular imagination, backwards time travel would allow one to change the past: to right the wrongs of history, to prevent one’s younger self doing things one later regretted, and so on. In a model with a single past, however, this idea is incoherent: the very description of the case involves a contradiction (e.g. the time traveller burns all her diaries at midnight on her fortieth birthday in 1976, and does not burn all her diaries at midnight on her fortieth birthday in 1976). It is not as if there are two versions of the past: the original one, without the time traveller present, and then a second version, with the time traveller playing a role. There is just one past—and two perspectives on it: the perspective of the younger self, and the perspective of the older time travelling self. If these perspectives are inconsistent (e.g. an event occurs in one but not the other) then the time travel scenario is incoherent.
This means that time travellers can do less than we might have hoped: they cannot right the wrongs of history; they cannot even stir a speck of dust on a certain day in the past if, on that day, the speck was in fact unmoved. But this does not mean that time travellers must be entirely powerless in the past: while they cannot do anything that did not actually happen, they can (in principle) do anything that did happen. Time travellers cannot change the past: they cannot make it different from the way it was—but they can participate in it: they can be amongst the people who did make the past the way it was. [ 12 ]
What about models involving two temporal dimensions, or parallel universes—do they allow for coherent scenarios in which the past is changed? [ 13 ] There is certainly no contradiction in saying that the time traveller burns all her diaries at midnight on her fortieth birthday in 1976 in universe 1 (or at hypertime A ), and does not burn all her diaries at midnight on her fortieth birthday in 1976 in universe 2 (or at hypertime B ). The question is whether this kind of story involves changing the past in the sense originally envisaged: righting the wrongs of history, preventing subsequently regretted actions, and so on. Goddu (2003) and van Inwagen (2010) argue that it does (in the context of particular hypertime models), while Smith (1997, 365–6; 2015) argues that it does not: that it involves avoiding the past—leaving it untouched while travelling to a different version of the past in which things proceed differently.
2. The Grandfather Paradox
The most important objection to the logical possibility of backwards time travel is the so-called Grandfather paradox. This paradox has actually convinced many people that backwards time travel is impossible:
The dead giveaway that true time-travel is flatly impossible arises from the well-known “paradoxes” it entails. The classic example is “What if you go back into the past and kill your grandfather when he was still a little boy?”…So complex and hopeless are the paradoxes…that the easiest way out of the irrational chaos that results is to suppose that true time-travel is, and forever will be, impossible. (Asimov 1995 [2003, 276–7]) travel into one’s past…would seem to give rise to all sorts of logical problems, if you were able to change history. For example, what would happen if you killed your parents before you were born. It might be that one could avoid such paradoxes by some modification of the concept of free will. But this will not be necessary if what I call the chronology protection conjecture is correct: The laws of physics prevent closed timelike curves from appearing . (Hawking, 1992, 604) [ 14 ]
The paradox comes in different forms. Here’s one version:
If time travel was logically possible then the time traveller could return to the past and in a suicidal rage destroy his time machine before it was completed and murder his younger self. But if this was so a necessary condition for the time trip to have occurred at all is removed, and we should then conclude that the time trip did not occur. Hence if the time trip did occur, then it did not occur. Hence it did not occur, and it is necessary that it did not occur. To reply, as it is standardly done, that our time traveller cannot change the past in this way, is a petitio principii . Why is it that the time traveller is constrained in this way? What mysterious force stills his sudden suicidal rage? (Smith, 1985, 58)
The idea is that backwards time travel is impossible because if it occurred, time travellers would attempt to do things such as kill their younger selves (or their grandfathers etc.). We know that doing these things—indeed, changing the past in any way—is impossible. But were there time travel, there would then be nothing left to stop these things happening. If we let things get to the stage where the time traveller is facing Grandfather with a loaded weapon, then there is nothing left to prevent the impossible from occurring. So we must draw the line earlier: it must be impossible for someone to get into this situation at all; that is, backwards time travel must be impossible.
In order to defend the possibility of time travel in the face of this argument we need to show that time travel is not a sure route to doing the impossible. So, given that a time traveller has gone to the past and is facing Grandfather, what could stop her killing Grandfather? Some science fiction authors resort to the idea of chaperones or time guardians who prevent time travellers from changing the past—or to mysterious forces of logic. But it is hard to take these ideas seriously—and more importantly, it is hard to make them work in detail when we remember that changing the past is impossible. (The chaperone is acting to ensure that the past remains as it was—but the only reason it ever was that way is because of his very actions.) [ 15 ] Fortunately there is a better response—also to be found in the science fiction literature, and brought to the attention of philosophers by Lewis (1976). What would stop the time traveller doing the impossible? She would fail “for some commonplace reason”, as Lewis (1976, 150) puts it. Her gun might jam, a noise might distract her, she might slip on a banana peel, etc. Nothing more than such ordinary occurrences is required to stop the time traveller killing Grandfather. Hence backwards time travel does not entail the occurrence of impossible events—and so the above objection is defused.
A problem remains. Suppose Tim, a time-traveller, is facing his grandfather with a loaded gun. Can Tim kill Grandfather? On the one hand, yes he can. He is an excellent shot; there is no chaperone to stop him; the laws of logic will not magically stay his hand; he hates Grandfather and will not hesitate to pull the trigger; etc. On the other hand, no he can’t. To kill Grandfather would be to change the past, and no-one can do that (not to mention the fact that if Grandfather died, then Tim would not have been born). So we have a contradiction: Tim can kill Grandfather and Tim cannot kill Grandfather. Time travel thus leads to a contradiction: so it is impossible.
Note the difference between this version of the Grandfather paradox and the version considered above. In the earlier version, the contradiction happens if Tim kills Grandfather. The solution was to say that Tim can go into the past without killing Grandfather—hence time travel does not entail a contradiction. In the new version, the contradiction happens as soon as Tim gets to the past. Of course Tim does not kill Grandfather—but we still have a contradiction anyway: for he both can do it, and cannot do it. As Lewis puts it:
Could a time traveler change the past? It seems not: the events of a past moment could no more change than numbers could. Yet it seems that he would be as able as anyone to do things that would change the past if he did them. If a time traveler visiting the past both could and couldn’t do something that would change it, then there cannot possibly be such a time traveler. (Lewis, 1976, 149)
Lewis’s own solution to this problem has been widely accepted. [ 16 ] It turns on the idea that to say that something can happen is to say that its occurrence is compossible with certain facts, where context determines (more or less) which facts are the relevant ones. Tim’s killing Grandfather in 1921 is compossible with the facts about his weapon, training, state of mind, and so on. It is not compossible with further facts, such as the fact that Grandfather did not die in 1921. Thus ‘Tim can kill Grandfather’ is true in one sense (relative to one set of facts) and false in another sense (relative to another set of facts)—but there is no single sense in which it is both true and false. So there is no contradiction here—merely an equivocation.
Another response is that of Vihvelin (1996), who argues that there is no contradiction here because ‘Tim can kill Grandfather’ is simply false (i.e. contra Lewis, there is no legitimate sense in which it is true). According to Vihvelin, for ‘Tim can kill Grandfather’ to be true, there must be at least some occasions on which ‘If Tim had tried to kill Grandfather, he would or at least might have succeeded’ is true—but, Vihvelin argues, at any world remotely like ours, the latter counterfactual is always false. [ 17 ]
Return to the original version of the Grandfather paradox and Lewis’s ‘commonplace reasons’ response to it. This response engenders a new objection—due to Horwich (1987)—not to the possibility but to the probability of backwards time travel.
Think about correlated events in general. Whenever we see two things frequently occurring together, this is because one of them causes the other, or some third thing causes both. Horwich calls this the Principle of V-Correlation:
if events of type A and B are associated with one another, then either there is always a chain of events between them…or else we find an earlier event of type C that links up with A and B by two such chains of events. What we do not see is…an inverse fork—in which A and B are connected only with a characteristic subsequent event, but no preceding one. (Horwich, 1987, 97–8)
For example, suppose that two students turn up to class wearing the same outfits. That could just be a coincidence (i.e. there is no common cause, and no direct causal link between the two events). If it happens every week for the whole semester, it is possible that it is a coincidence, but this is extremely unlikely . Normally, we see this sort of extensive correlation only if either there is a common cause (e.g. both students have product endorsement deals with the same clothing company, or both slavishly copy the same influencer) or a direct causal link (e.g. one student is copying the other).
Now consider the time traveller setting off to kill her younger self. As discussed, no contradiction need ensue—this is prevented not by chaperones or mysterious forces, but by a run of ordinary occurrences in which the trigger falls off the time traveller’s gun, a gust of wind pushes her bullet off course, she slips on a banana peel, and so on. But now consider this run of ordinary occurrences. Whenever the time traveller contemplates auto-infanticide, someone nearby will drop a banana peel ready for her to slip on, or a bird will begin to fly so that it will be in the path of the time traveller’s bullet by the time she fires, and so on. In general, there will be a correlation between auto-infanticide attempts and foiling occurrences such as the presence of banana peels—and this correlation will be of the type that does not involve a direct causal connection between the correlated events or a common cause of both. But extensive correlations of this sort are, as we saw, extremely rare—so backwards time travel will happen about as often as you will see two people wear the same outfits to class every day of semester, without there being any causal connection between what one wears and what the other wears.
We can set out Horwich’s argument this way:
- If time travel were ever to occur, we should see extensive uncaused correlations.
- It is extremely unlikely that we should ever see extensive uncaused correlations.
- Therefore time travel is extremely unlikely to occur.
The conclusion is not that time travel is impossible, but that we should treat it the way we treat the possibility of, say, tossing a fair coin and getting heads one thousand times in a row. As Price (1996, 278 n.7) puts it—in the context of endorsing Horwich’s conclusion: “the hypothesis of time travel can be made to imply propositions of arbitrarily low probability. This is not a classical reductio, but it is as close as science ever gets.”
Smith (1997) attacks both premisses of Horwich’s argument. Against the first premise, he argues that backwards time travel, in itself, does not entail extensive uncaused correlations. Rather, when we look more closely, we see that time travel scenarios involving extensive uncaused correlations always build in prior coincidences which are themselves highly unlikely. Against the second premise, he argues that, from the fact that we have never seen extensive uncaused correlations, it does not follow that we never shall. This is not inductive scepticism: let us assume (contra the inductive sceptic) that in the absence of any specific reason for thinking things should be different in the future, we are entitled to assume they will continue being the same; still we cannot dismiss a specific reason for thinking the future will be a certain way simply on the basis that things have never been that way in the past. You might reassure an anxious friend that the sun will certainly rise tomorrow because it always has in the past—but you cannot similarly refute an astronomer who claims to have discovered a specific reason for thinking that the earth will stop rotating overnight.
Sider (2002, 119–20) endorses Smith’s second objection. Dowe (2003) criticises Smith’s first objection, but agrees with the second, concluding overall that time travel has not been shown to be improbable. Ismael (2003) reaches a similar conclusion. Goddu (2007) criticises Smith’s first objection to Horwich. Further contributions to the debate include Arntzenius (2006), Smeenk and Wüthrich (2011, §2.2) and Elliott (2018). For other arguments to the same conclusion as Horwich’s—that time travel is improbable—see Ney (2000) and Effingham (2020).
Return again to the original version of the Grandfather paradox and Lewis’s ‘commonplace reasons’ response to it. This response engenders a further objection. The autoinfanticidal time traveller is attempting to do something impossible (render herself permanently dead from an age younger than her age at the time of the attempts). Suppose we accept that she will not succeed and that what will stop her is a succession of commonplace occurrences. The previous objection was that such a succession is improbable . The new objection is that the exclusion of the time traveler from successfully committing auto-infanticide is mysteriously inexplicable . The worry is as follows. Each particular event that foils the time traveller is explicable in a perfectly ordinary way; but the inevitable combination of these events amounts to a ring-fencing of the forbidden zone of autoinfanticide—and this ring-fencing is mystifying. It’s like a grand conspiracy to stop the time traveler from doing what she wants to do—and yet there are no conspirators: no time lords, no magical forces of logic. This is profoundly perplexing. Riggs (1997, 52) writes: “Lewis’s account may do for a once only attempt, but is untenable as a general explanation of Tim’s continual lack of success if he keeps on trying.” Ismael (2003, 308) writes: “Considered individually, there will be nothing anomalous in the explanations…It is almost irresistible to suppose, however, that there is something anomalous in the cases considered collectively, i.e., in our unfailing lack of success.” See also Gorovitz (1964, 366–7), Horwich (1987, 119–21) and Carroll (2010, 86).
There have been two different kinds of defense of time travel against the objection that it involves mysteriously inexplicable occurrences. Baron and Colyvan (2016, 70) agree with the objectors that a purely causal explanation of failure—e.g. Tim fails to kill Grandfather because first he slips on a banana peel, then his gun jams, and so on—is insufficient. However they argue that, in addition, Lewis offers a non-causal—a logical —explanation of failure: “What explains Tim’s failure to kill his grandfather, then, is something about logic; specifically: Tim fails to kill his grandfather because the law of non-contradiction holds.” Smith (2017) argues that the appearance of inexplicability is illusory. There are no scenarios satisfying the description ‘a time traveller commits autoinfanticide’ (or changes the past in any other way) because the description is self-contradictory (e.g. it involves the time traveller permanently dying at 20 and also being alive at 40). So whatever happens it will not be ‘that’. There is literally no way for the time traveller not to fail. Hence there is no need for—or even possibility of—a substantive explanation of why failure invariably occurs, and such failure is not perplexing.
3. Causation
Backwards time travel scenarios give rise to interesting issues concerning causation. In this section we examine two such issues.
Earlier we distinguished changing the past and affecting the past, and argued that while the former is impossible, backwards time travel need involve only the latter. Affecting the past would be an example of backwards causation (i.e. causation where the effect precedes its cause)—and it has been argued that this too is impossible, or at least problematic. [ 18 ] The classic argument against backwards causation is the bilking argument . [ 19 ] Faced with the claim that some event A causes an earlier event B , the proponent of the bilking objection recommends an attempt to decorrelate A and B —that is, to bring about A in cases in which B has not occurred, and to prevent A in cases in which B has occurred. If the attempt is successful, then B often occurs despite the subsequent nonoccurrence of A , and A often occurs without B occurring, and so A cannot be the cause of B . If, on the other hand, the attempt is unsuccessful—if, that is, A cannot be prevented when B has occurred, nor brought about when B has not occurred—then, it is argued, it must be B that is the cause of A , rather than vice versa.
The bilking procedure requires repeated manipulation of event A . Thus, it cannot get under way in cases in which A is either unrepeatable or unmanipulable. Furthermore, the procedure requires us to know whether or not B has occurred, prior to manipulating A —and thus, it cannot get under way in cases in which it cannot be known whether or not B has occurred until after the occurrence or nonoccurrence of A (Dummett, 1964). These three loopholes allow room for many claims of backwards causation that cannot be touched by the bilking argument, because the bilking procedure cannot be performed at all. But what about those cases in which it can be performed? If the procedure succeeds—that is, A and B are decorrelated—then the claim that A causes B is refuted, or at least weakened (depending upon the details of the case). But if the bilking attempt fails, it does not follow that it must be B that is the cause of A , rather than vice versa. Depending upon the situation, that B causes A might become a viable alternative to the hypothesis that A causes B —but there is no reason to think that this alternative must always be the superior one. For example, suppose that I see a photo of you in a paper dated well before your birth, accompanied by a report of your arrival from the future. I now try to bilk your upcoming time trip—but I slip on a banana peel while rushing to push you away from your time machine, my time travel horror stories only inspire you further, and so on. Or again, suppose that I know that you were not in Sydney yesterday. I now try to get you to go there in your time machine—but first I am struck by lightning, then I fall down a manhole, and so on. What does all this prove? Surely not that your arrival in the past causes your departure from the future. Depending upon the details of the case, it seems that we might well be entitled to describe it as involving backwards time travel and backwards causation. At least, if we are not so entitled, this must be because of other facts about the case: it would not follow simply from the repeated coincidental failures of my bilking attempts.
Backwards time travel would apparently allow for the possibility of causal loops, in which things come from nowhere. The things in question might be objects—imagine a time traveller who steals a time machine from the local museum in order to make his time trip and then donates the time machine to the same museum at the end of the trip (i.e. in the past). In this case the machine itself is never built by anyone—it simply exists. The things in question might be information—imagine a time traveller who explains the theory behind time travel to her younger self: theory that she herself knows only because it was explained to her in her youth by her time travelling older self. The things in question might be actions. Imagine a time traveller who visits his younger self. When he encounters his younger self, he suddenly has a vivid memory of being punched on the nose by a strange visitor. He realises that this is that very encounter—and resignedly proceeds to punch his younger self. Why did he do it? Because he knew that it would happen and so felt that he had to do it—but he only knew it would happen because he in fact did it. [ 20 ]
One might think that causal loops are impossible—and hence that insofar as backwards time travel entails such loops, it too is impossible. [ 21 ] There are two issues to consider here. First, does backwards time travel entail causal loops? Lewis (1976, 148) raises the question whether there must be causal loops whenever there is backwards causation; in response to the question, he says simply “I am not sure.” Mellor (1998, 131) appears to claim a positive answer to the question. [ 22 ] Hanley (2004, 130) defends a negative answer by telling a time travel story in which there is backwards time travel and backwards causation, but no causal loops. [ 23 ] Monton (2009) criticises Hanley’s counterexample, but also defends a negative answer via different counterexamples. Effingham (2020) too argues for a negative answer.
Second, are causal loops impossible, or in some other way objectionable? One objection is that causal loops are inexplicable . There have been two main kinds of response to this objection. One is to agree but deny that this is a problem. Lewis (1976, 149) accepts that a loop (as a whole) would be inexplicable—but thinks that this inexplicability (like that of the Big Bang or the decay of a tritium atom) is merely strange, not impossible. In a similar vein, Meyer (2012, 263) argues that if someone asked for an explanation of a loop (as a whole), “the blame would fall on the person asking the question, not on our inability to answer it.” The second kind of response (Hanley, 2004, §5) is to deny that (all) causal loops are inexplicable. A second objection to causal loops, due to Mellor (1998, ch.12), is that in such loops the chances of events would fail to be related to their frequencies in accordance with the law of large numbers. Berkovitz (2001) and Dowe (2001) both argue that Mellor’s objection fails to establish the impossibility of causal loops. [ 24 ] Effingham (2020) considers—and rebuts—some additional objections to the possibility of causal loops.
4. Time and Change
Gödel (1949a [1990a])—in which Gödel presents models of Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity in which there exist CTC’s—can well be regarded as initiating the modern academic literature on time travel, in both philosophy and physics. In a companion paper, Gödel discusses the significance of his results for more general issues in the philosophy of time (Gödel 1949b [1990b]). For the succeeding half century, the time travel literature focussed predominantly on objections to the possibility (or probability) of time travel. More recently, however, there has been renewed interest in the connections between time travel and more general issues in the metaphysics of time and change. We examine some of these in the present section. [ 25 ]
The first thing that we need to do is set up the various metaphysical positions whose relationships with time travel will then be discussed. Consider two metaphysical questions:
- Are the past, present and future equally real?
- Is there an objective flow or passage of time, and an objective now?
We can label some views on the first question as follows. Eternalism is the view that past and future times, objects and events are just as real as the present time and present events and objects. Nowism is the view that only the present time and present events and objects exist. Now-and-then-ism is the view that the past and present exist but the future does not. We can also label some views on the second question. The A-theory answers in the affirmative: the flow of time and division of events into past (before now), present (now) and future (after now) are objective features of reality (as opposed to mere features of our experience). Furthermore, they are linked: the objective flow of time arises from the movement, through time, of the objective now (from the past towards the future). The B-theory answers in the negative: while we certainly experience now as special, and time as flowing, the B-theory denies that what is going on here is that we are detecting objective features of reality in a way that corresponds transparently to how those features are in themselves. The flow of time and the now are not objective features of reality; they are merely features of our experience. By combining answers to our first and second questions we arrive at positions on the metaphysics of time such as: [ 26 ]
- the block universe view: eternalism + B-theory
- the moving spotlight view: eternalism + A-theory
- the presentist view: nowism + A-theory
- the growing block view: now-and-then-ism + A-theory.
So much for positions on time itself. Now for some views on temporal objects: objects that exist in (and, in general, change over) time. Three-dimensionalism is the view that persons, tables and other temporal objects are three-dimensional entities. On this view, what you see in the mirror is a whole person. [ 27 ] Tomorrow, when you look again, you will see the whole person again. On this view, persons and other temporal objects are wholly present at every time at which they exist. Four-dimensionalism is the view that persons, tables and other temporal objects are four-dimensional entities, extending through three dimensions of space and one dimension of time. On this view, what you see in the mirror is not a whole person: it is just a three-dimensional temporal part of a person. Tomorrow, when you look again, you will see a different such temporal part. Say that an object persists through time if it is around at some time and still around at a later time. Three- and four-dimensionalists agree that (some) objects persist, but they differ over how objects persist. According to three-dimensionalists, objects persist by enduring : an object persists from t 1 to t 2 by being wholly present at t 1 and t 2 and every instant in between. According to four-dimensionalists, objects persist by perduring : an object persists from t 1 to t 2 by having temporal parts at t 1 and t 2 and every instant in between. Perduring can be usefully compared with being extended in space: a road extends from Melbourne to Sydney not by being wholly located at every point in between, but by having a spatial part at every point in between.
It is natural to combine three-dimensionalism with presentism and four-dimensionalism with the block universe view—but other combinations of views are certainly possible.
Gödel (1949b [1990b]) argues from the possibility of time travel (more precisely, from the existence of solutions to the field equations of General Relativity in which there exist CTC’s) to the B-theory: that is, to the conclusion that there is no objective flow or passage of time and no objective now. Gödel begins by reviewing an argument from Special Relativity to the B-theory: because the notion of simultaneity becomes a relative one in Special Relativity, there is no room for the idea of an objective succession of “nows”. He then notes that this argument is disrupted in the context of General Relativity, because in models of the latter theory to date, the presence of matter does allow recovery of an objectively distinguished series of “nows”. Gödel then proposes a new model (Gödel 1949a [1990a]) in which no such recovery is possible. (This is the model that contains CTC’s.) Finally, he addresses the issue of how one can infer anything about the nonexistence of an objective flow of time in our universe from the existence of a merely possible universe in which there is no objectively distinguished series of “nows”. His main response is that while it would not be straightforwardly contradictory to suppose that the existence of an objective flow of time depends on the particular, contingent arrangement and motion of matter in the world, this would nevertheless be unsatisfactory. Responses to Gödel have been of two main kinds. Some have objected to the claim that there is no objective flow of time in his model universe (e.g. Savitt (2005); see also Savitt (1994)). Others have objected to the attempt to transfer conclusions about that model universe to our own universe (e.g. Earman (1995, 197–200); for a partial response to Earman see Belot (2005, §3.4)). [ 28 ]
Earlier we posed two questions:
Gödel’s argument is related to the second question. Let’s turn now to the first question. Godfrey-Smith (1980, 72) writes “The metaphysical picture which underlies time travel talk is that of the block universe [i.e. eternalism, in the terminology of the present entry], in which the world is conceived as extended in time as it is in space.” In his report on the Analysis problem to which Godfrey-Smith’s paper is a response, Harrison (1980, 67) replies that he would like an argument in support of this assertion. Here is an argument: [ 29 ]
A fundamental requirement for the possibility of time travel is the existence of the destination of the journey. That is, a journey into the past or the future would have to presuppose that the past or future were somehow real. (Grey, 1999, 56)
Dowe (2000, 442–5) responds that the destination does not have to exist at the time of departure: it only has to exist at the time of arrival—and this is quite compatible with non-eternalist views. And Keller and Nelson (2001, 338) argue that time travel is compatible with presentism:
There is four-dimensional [i.e. eternalist, in the terminology of the present entry] time-travel if the appropriate sorts of events occur at the appropriate sorts of times; events like people hopping into time-machines and disappearing, people reappearing with the right sorts of memories, and so on. But the presentist can have just the same patterns of events happening at just the same times. Or at least, it can be the case on the presentist model that the right sorts of events will happen, or did happen, or are happening, at the rights sorts of times. If it suffices for four-dimensionalist time-travel that Jennifer disappears in 2054 and appears in 1985 with the right sorts of memories, then why shouldn’t it suffice for presentist time-travel that Jennifer will disappear in 2054, and that she did appear in 1985 with the right sorts of memories?
Sider (2005) responds that there is still a problem reconciling presentism with time travel conceived in Lewis’s way: that conception of time travel requires that personal time is similar to external time—but presentists have trouble allowing this. Further contributions to the debate whether presentism—and other versions of the A-theory—are compatible with time travel include Monton (2003), Daniels (2012), Hall (2014) and Wasserman (2018) on the side of compatibility, and Miller (2005), Slater (2005), Miller (2008), Hales (2010) and Markosian (2020) on the side of incompatibility.
Leibniz’s Law says that if x = y (i.e. x and y are identical—one and the same entity) then x and y have exactly the same properties. There is a superficial conflict between this principle of logic and the fact that things change. If Bill is at one time thin and at another time not so—and yet it is the very same person both times—it looks as though the very same entity (Bill) both possesses and fails to possess the property of being thin. Three-dimensionalists and four-dimensionalists respond to this problem in different ways. According to the four-dimensionalist, what is thin is not Bill (who is a four-dimensional entity) but certain temporal parts of Bill; and what is not thin are other temporal parts of Bill. So there is no single entity that both possesses and fails to possess the property of being thin. Three-dimensionalists have several options. One is to deny that there are such properties as ‘thin’ (simpliciter): there are only temporally relativised properties such as ‘thin at time t ’. In that case, while Bill at t 1 and Bill at t 2 are the very same entity—Bill is wholly present at each time—there is no single property that this one entity both possesses and fails to possess: Bill possesses the property ‘thin at t 1 ’ and lacks the property ‘thin at t 2 ’. [ 30 ]
Now consider the case of a time traveller Ben who encounters his younger self at time t . Suppose that the younger self is thin and the older self not so. The four-dimensionalist can accommodate this scenario easily. Just as before, what we have are two different three-dimensional parts of the same four-dimensional entity, one of which possesses the property ‘thin’ and the other of which does not. The three-dimensionalist, however, faces a problem. Even if we relativise properties to times, we still get the contradiction that Ben possesses the property ‘thin at t ’ and also lacks that very same property. [ 31 ] There are several possible options for the three-dimensionalist here. One is to relativise properties not to external times but to personal times (Horwich, 1975, 434–5); another is to relativise properties to spatial locations as well as to times (or simply to spacetime points). Sider (2001, 101–6) criticises both options (and others besides), concluding that time travel is incompatible with three-dimensionalism. Markosian (2004) responds to Sider’s argument; [ 32 ] Miller (2006) also responds to Sider and argues for the compatibility of time travel and endurantism; Gilmore (2007) seeks to weaken the case against endurantism by constructing analogous arguments against perdurantism. Simon (2005) finds problems with Sider’s arguments, but presents different arguments for the same conclusion; Effingham and Robson (2007) and Benovsky (2011) also offer new arguments for this conclusion. For further discussion see Wasserman (2018) and Effingham (2020). [ 33 ]
We have seen arguments to the conclusions that time travel is impossible, improbable and inexplicable. Here’s an argument to the conclusion that backwards time travel simply will not occur. If backwards time travel is ever going to occur, we would already have seen the time travellers—but we have seen none such. [ 34 ] The argument is a weak one. [ 35 ] For a start, it is perhaps conceivable that time travellers have already visited the Earth [ 36 ] —but even granting that they have not, this is still compatible with the future actuality of backwards time travel. First, it may be that time travel is very expensive, difficult or dangerous—or for some other reason quite rare—and that by the time it is available, our present period of history is insufficiently high on the list of interesting destinations. Second, it may be—and indeed existing proposals in the physics literature have this feature—that backwards time travel works by creating a CTC that lies entirely in the future: in this case, backwards time travel becomes possible after the creation of the CTC, but travel to a time earlier than the time at which the CTC is created is not possible. [ 37 ]
- Adams, Robert Merrihew, 1997, “Thisness and time travel”, Philosophia , 25: 407–15.
- Arntzenius, Frank, 2006, “Time travel: Double your fun”, Philosophy Compass , 1: 599–616. doi:10.1111/j.1747-9991.2006.00045.x
- Asimov, Isaac, 1995 [2003], Gold: The Final Science Fiction Collection , New York: Harper Collins.
- Baron, Sam and Colyvan, Mark, 2016, “Time enough for explanation”, Journal of Philosophy , 113: 61–88.
- Belot, Gordon, 2005, “Dust, time and symmetry”, British Journal for the Philosophy of Science , 56: 255–91.
- Benovsky, Jiri, 2011, “Endurance and time travel”, Kriterion , 24: 65–72.
- Berkovitz, Joseph, 2001, “On chance in causal loops”, Mind , 110: 1–23.
- Black, Max, 1956, “Why cannot an effect precede its cause?”, Analysis , 16: 49–58.
- Brier, Bob, 1973, “Magicians, alarm clocks, and backward causation”, Southern Journal of Philosophy , 11: 359–64.
- Carlson, Erik, 2005, “A new time travel paradox resolved”, Philosophia , 33: 263–73.
- Carroll, John W., 2010, “Context, conditionals, fatalism, time travel, and freedom”, in Time and Identity , Joseph Keim Campbell, Michael O’Rourke, and Harry S. Silverstein, eds., Cambridge MA: MIT Press, 79–93.
- Craig, William L., 1997, “Adams on actualism and presentism”, Philosophia , 25: 401–5.
- Daniels, Paul R., 2012, “Back to the present: Defending presentist time travel”, Disputatio , 4: 469–84.
- Deutsch, David and Lockwood, Michael, 1994, “The quantum physics of time travel”, Scientific American , 270(3): 50–6.
- Dowe, Phil, 2000, “The case for time travel”, Philosophy , 75: 441–51.
- –––, 2001, “Causal loops and the independence of causal facts”, Philosophy of Science , 68: S89–S97.
- –––, 2003, “The coincidences of time travel”, Philosophy of Science , 70: 574–89.
- Dummett, Michael, 1964, “Bringing about the past”, Philosophical Review , 73: 338–59.
- Dwyer, Larry, 1977, “How to affect, but not change, the past”, Southern Journal of Philosophy , 15: 383–5.
- Earman, John, 1995, Bangs, Crunches, Whimpers, and Shrieks: Singularities and Acausalities in Relativistic Spacetimes , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Effingham, Nikk, 2020, Time Travel: Probability and Impossibility , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Effingham, Nikk and Robson, Jon, 2007, “A mereological challenge to endurantism”, Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 85: 633–40.
- Ehring, Douglas, 1997, “Personal identity and time travel”, Philosophical Studies , 52: 427–33.
- Elliott, Katrina, 2019, “How to Know That Time Travel Is Unlikely Without Knowing Why”, Pacific Philosophical Quarterly , 100: 90–113.
- Fulmer, Gilbert, 1980, “Understanding time travel”, Southwestern Journal of Philosophy , 11: 151–6.
- Gilmore, Cody, 2007, “Time travel, coinciding objects, and persistence”, in Oxford Studies in Metaphysics , Dean W. Zimmerman, ed., Oxford: Clarendon Press, vol. 3, 177–98.
- Goddu, G.C., 2003, “Time travel and changing the past (or how to kill yourself and live to tell the tale)”, Ratio , 16: 16–32.
- –––, 2007, “Banana peels and time travel”, Dialectica , 61: 559–72.
- Gödel, Kurt, 1949a [1990a], “An example of a new type of cosmological solutions of Einstein’s field equations of gravitation”, in Kurt Gödel: Collected Works (Volume II), Solomon Feferman, et al. (eds.), New York: Oxford University Press, 190–8; originally published in Reviews of Modern Physics , 21 (1949): 447–450.
- –––, 1949b [1990b], “A remark about the relationship between relativity theory and idealistic philosophy”, in Kurt Gödel: Collected Works (Volume II), Solomon Feferman, et al. (eds.), New York: Oxford University Press, 202–7; originally published in P. Schilpp (ed.), Albert Einstein: Philosopher-Scientist , La Salle: Open Court, 1949, 555–562.
- Godfrey-Smith, William, 1980, “Travelling in time”, Analysis , 40: 72–3.
- Gorovitz, Samuel, 1964, “Leaving the past alone”, Philosophical Review , 73: 360–71.
- Grey, William, 1999, “Troubles with time travel”, Philosophy , 74: 55–70.
- Hafele, J. C. and Keating, Richard E., 1972a, “Around-the-world atomic clocks: Observed relativistic time gains”, Science , 177: 168–70.
- –––, 1972b, “Around-the-world atomic clocks: Predicted relativistic time gains”, Science , 177: 166–8.
- Hales, Steven D., 2010, “No time travel for presentists”, Logos & Episteme , 1: 353–60.
- Hall, Thomas, 2014, “In Defense of the Compossibility of Presentism and Time Travel”, Logos & Episteme , 2: 141–59.
- Hanley, Richard, 2004, “No end in sight: Causal loops in philosophy, physics and fiction”, Synthese , 141: 123–52.
- Harrison, Jonathan, 1980, “Report on analysis ‘problem’ no. 18”, Analysis , 40: 65–9.
- Hawking, S.W., 1992, “Chronology protection conjecture”, Physical Review D , 46: 603–11.
- Holt, Dennis Charles, 1981, “Time travel: The time discrepancy paradox”, Philosophical Investigations , 4: 1–16.
- Horacek, David, 2005, “Time travel in indeterministic worlds”, Monist (Special Issue on Time Travel), 88: 423–36.
- Horwich, Paul, 1975, “On some alleged paradoxes of time travel”, Journal of Philosophy , 72: 432–44.
- –––, 1987, Asymmetries in Time: Problems in the Philosophy of Science , Cambridge MA: MIT Press.
- Ismael, J., 2003, “Closed causal loops and the bilking argument”, Synthese , 136: 305–20.
- Keller, Simon and Nelson, Michael, 2001, “Presentists should believe in time-travel”, Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 79: 333–45.
- Kiourti, Ira, 2008, “Killing baby Suzy”, Philosophical Studies , 139: 343–52.
- Le Poidevin, Robin, 2003, Travels in Four Dimensions: The Enigmas of Space and Time , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2005, “The Cheshire Cat problem and other spatial obstacles to backwards time travel”, Monist (Special Issue on Time Travel), 88: 336–52.
- Lewis, David, 1976, “The paradoxes of time travel”, American Philosophical Quarterly , 13: 145–52.
- Loss, Roberto, 2015, “How to Change the Past in One-Dimensional Time”, Pacific Philosophical Quarterly , 96: 1–11.
- Luminet, Jean-Pierre, 2011, “Time, topology, and the twin paradox”, in The Oxford Handbook of Philosophy of Time , Craig Callender (ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199298204.003.0018
- Markosian, Ned, 2004, “Two arguments from Sider’s Four-Dimensionalism ”, Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 68: 665–73.
- Markosian, Ned, 2020, “The Dynamic Theory of Time and Time Travel to the Past”, Disputatio , 12: 137–65.
- Maudlin, Tim, 2012, Philosophy of Physics: Space and Time , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Meiland, Jack W., 1974, “A two-dimensional passage model of time for time travel”, Philosophical Studies , 26: 153–73.
- Mellor, D.H., 1998, Real Time II , London: Routledge.
- Meyer, Ulrich, 2012, “Explaining causal loops”, Analysis , 72: 259–64.
- Miller, Kristie, 2005, “Time travel and the open future”, Disputatio , 1: 223–32.
- –––, 2006, “Travelling in time: How to wholly exist in two places at the same time”, Canadian Journal of Philosophy , 36: 309–34.
- –––, 2008, “Backwards causation, time, and the open future”, Metaphysica , 9: 173–91.
- Monton, Bradley, 2003, “Presentists can believe in closed timelike curves”, Analysis , 63: 199–202.
- –––, 2009, “Time travel without causal loops”, Philosophical Quarterly , 59: 54–67.
- Nerlich, Graham, 1981, “Can time be finite?”, Pacific Philosophical Quarterly , 62: 227–39.
- Ney, S.E., 2000, “Are grandfathers an endangered species?”, Journal of Philosophical Research , 25: 311–21.
- Price, Huw, 1996, Time’s Arrow & Archimedes’ Point: New Directions for the Physics of Time , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Putnam, Hilary, 1975, “It ain’t necessarily so”, in Mathematics, Matter and Method , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, vol. 1 of Philosophical Papers , 237–49.
- Reinganum, Marc R., 1986, “Is time travel impossible? A financial proof”, Journal of Portfolio Management , 13: 10–2.
- Riggs, Peter J., 1991, “A critique of Mellor’s argument against ‘backwards’ causation”, British Journal for the Philosophy of Science , 42: 75–86.
- –––, 1997, “The principal paradox of time travel”, Ratio , 10: 48–64.
- Savitt, Steven, 1994, “The replacement of time”, Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 74: 463–73.
- –––, 2005, “Time travel and becoming”, Monist (Special Issue on Time Travel), 88: 413–22.
- Sider, Theodore, 2001, Four-Dimensionalism: An Ontology of Persistence and Time , Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- –––, 2002, “Time travel, coincidences and counterfactuals”, Philosophical Studies , 110: 115–38.
- –––, 2004, “Replies to Gallois, Hirsch and Markosian”, Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 68: 674–87.
- –––, 2005, “Traveling in A- and B- time”, Monist (Special Issue on Time Travel), 88: 329–35.
- Simon, Jonathan, 2005, “Is time travel a problem for the three-dimensionalist?”, Monist (Special Issue on Time Travel), 88: 353–61.
- Slater, Matthew H., 2005, “The necessity of time travel (on pain of indeterminacy)”, Monist (Special Issue on Time Travel), 88: 362–9.
- Smart, J.J.C., 1963, “Is time travel possible?”, Journal of Philosophy , 60: 237–41.
- Smeenk, Chris and Wüthrich, Christian, 2011, “Time travel and time machines”, in The Oxford Handbook of Philosophy of Time , Craig Callender (ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, online ed. doi:10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199298204.003.0021
- Smith, Joseph Wayne, 1985, “Time travel and backward causation”, Cogito , 3: 57–67.
- Smith, Nicholas J.J., 1997, “Bananas enough for time travel?”, British Journal for the Philosophy of Science , 48: 363–89.
- –––, 1998, “The problems of backward time travel”, Endeavour , 22(4): 156–8.
- –––, 2004, “Review of Robin Le Poidevin Travels in Four Dimensions: The Enigmas of Space and Time ”, Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 82: 527–30.
- –––, 2005, “Why would time travellers try to kill their younger selves?”, Monist (Special Issue on Time Travel), 88: 388–95.
- –––, 2011, “Inconsistency in the A-theory”, Philosophical Studies , 156: 231–47.
- –––, 2015, “Why time travellers (still) cannot change the past”, Revista Portuguesa de Filosofia , 71: 677–94.
- –––, 2017, “I’d do anything to change the past (but I can’t do ‘that’)”, American Philosophical Quarterly , 54: 153–68.
- van Inwagen, Peter, 2010, “Changing the past”, in Oxford Studies in Metaphysics (Volume 5), Dean W. Zimmerman (ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, 3–28.
- Vihvelin, Kadri, 1996, “What time travelers cannot do”, Philosophical Studies , 81: 315–30.
- Vranas, Peter B.M., 2005, “Do cry over spilt milk: Possibly you can change the past”, Monist (Special Issue on Time Travel), 88: 370–87.
- –––, 2009, “Can I kill my younger self? Time travel and the retrosuicide paradox”, Pacific Philosophical Quarterly , 90: 520–34.
- –––, 2010, “What time travelers may be able to do”, Philosophical Studies , 150: 115–21.
- Wasserman, Ryan, 2018, Paradoxes of Time Travel , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Williams, Donald C., 1951, “The myth of passage”, Journal of Philosophy , 48: 457–72.
- Wright, John, 2006, “Personal identity, fission and time travel”, Philosophia , 34: 129–42.
- Yourgrau, Palle, 1999, Gödel Meets Einstein: Time Travel in the Gödel Universe , Chicago: Open Court.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- Time Travel , entry by Joel Hunter (Truckee Meadows Community College) in the Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy .
causation: backward | free will: divine foreknowledge and | identity: over time | location and mereology | temporal parts | time | time machines | time travel: and modern physics
Copyright © 2024 by Nicholas J.J. Smith < nicholas . smith @ sydney . edu . au >
- Accessibility

Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2024 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
- Newsletters
Time travel: five ways that we could do it
Cathal O’Connell
Cathal O'Connell is a science writer based in Melbourne.
In 2009 the British physicist Stephen Hawking held a party for time travellers – the twist was he sent out the invites a year later (No guests showed up). Time travel is probably impossible. Even if it were possible, Hawking and others have argued that you could never travel back before the moment your time machine was built.
But travel to the future? That’s a different story.
Of course, we are all time travellers as we are swept along in the current of time, from past to future, at a rate of one hour per hour.
But, as with a river, the current flows at different speeds in different places. Science as we know it allows for several methods to take the fast-track into the future. Here’s a rundown.
1. Time travel via speed
This is the easiest and most practical way to time travel into the far future – go really fast.
According to Einstein’s theory of special relativity, when you travel at speeds approaching the speed of light, time slows down for you relative to the outside world.
This is not a just a conjecture or thought experiment – it’s been measured. Using twin atomic clocks (one flown in a jet aircraft, the other stationary on Earth) physicists have shown that a flying clock ticks slower, because of its speed.
In the case of the aircraft, the effect is minuscule. But If you were in a spaceship travelling at 90% of the speed of light, you’d experience time passing about 2.6 times slower than it was back on Earth.
And the closer you get to the speed of light, the more extreme the time-travel.
Computer solves a major time travel problem
The highest speeds achieved through any human technology are probably the protons whizzing around the Large Hadron Collider at 99.9999991% of the speed of light. Using special relativity we can calculate one second for the proton is equivalent to 27,777,778 seconds, or about 11 months , for us.
Amazingly, particle physicists have to take this time dilation into account when they are dealing with particles that decay. In the lab, muon particles typically decay in 2.2 microseconds. But fast moving muons, such as those created when cosmic rays strike the upper atmosphere, take 10 times longer to disintegrate.
2. Time travel via gravity
The next method of time travel is also inspired by Einstein. According to his theory of general relativity, the stronger the gravity you feel, the slower time moves.
As you get closer to the centre of the Earth, for example, the strength of gravity increases. Time runs slower for your feet than your head.
Again, this effect has been measured. In 2010, physicists at the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) placed two atomic clocks on shelves, one 33 centimetres above the other, and measured the difference in their rate of ticking. The lower one ticked slower because it feels a slightly stronger gravity.
To travel to the far future, all we need is a region of extremely strong gravity, such as a black hole. The closer you get to the event horizon, the slower time moves – but it’s risky business, cross the boundary and you can never escape.
And anyway, the effect is not that strong so it’s probably not worth the trip.
Assuming you had the technology to travel the vast distances to reach a black hole (the nearest is about 3,000 light years away), the time dilation through travelling would be far greater than any time dilation through orbiting the black hole itself.
(The situation described in the movie Interstellar , where one hour on a planet near a black hole is the equivalent of seven years back on Earth, is so extreme as to be impossible in our Universe, according to Kip Thorne, the movie’s scientific advisor.)
The most mindblowing thing, perhaps, is that GPS systems have to account for time dilation effects (due to both the speed of the satellites and gravity they feel) in order to work. Without these corrections, your phones GPS capability wouldn’t be able to pinpoint your location on Earth to within even a few kilometres.
3. Time travel via suspended animation
Another way to time travel to the future may be to slow your perception of time by slowing down, or stopping, your bodily processes and then restarting them later.
Bacterial spores can live for millions of years in a state of suspended animation, until the right conditions of temperature, moisture, food kick start their metabolisms again. Some mammals, such as bears and squirrels, can slow down their metabolism during hibernation, dramatically reducing their cells’ requirement for food and oxygen.
Could humans ever do the same?
Though completely stopping your metabolism is probably far beyond our current technology, some scientists are working towards achieving inducing a short-term hibernation state lasting at least a few hours. This might be just enough time to get a person through a medical emergency, such as a cardiac arrest, before they can reach the hospital.
In 2005, American scientists demonstrated a way to slow the metabolism of mice (which do not hibernate) by exposing them to minute doses of hydrogen sulphide, which binds to the same cell receptors as oxygen. The core body temperature of the mice dropped to 13 °C and metabolism decreased 10-fold. After six hours the mice could be reanimated without ill effects.
Unfortunately, similar experiments on sheep and pigs were not successful, suggesting the method might not work for larger animals.
Another method, which induces a hypothermic hibernation by replacing the blood with a cold saline solution, has worked on pigs and is currently undergoing human clinical trials in Pittsburgh.
4. Time travel via wormholes
General relativity also allows for the possibility for shortcuts through spacetime, known as wormholes, which might be able to bridge distances of a billion light years or more, or different points in time.
Many physicists, including Stephen Hawking, believe wormholes are constantly popping in and out of existence at the quantum scale, far smaller than atoms. The trick would be to capture one, and inflate it to human scales – a feat that would require a huge amount of energy, but which might just be possible, in theory.
Attempts to prove this either way have failed, ultimately because of the incompatibility between general relativity and quantum mechanics.
5. Time travel using light
Another time travel idea, put forward by the American physicist Ron Mallet, is to use a rotating cylinder of light to twist spacetime. Anything dropped inside the swirling cylinder could theoretically be dragged around in space and in time, in a similar way to how a bubble runs around on top your coffee after you swirl it with a spoon.
According to Mallet, the right geometry could lead to time travel into either the past and the future.
Since publishing his theory in 2000, Mallet has been trying to raise the funds to pay for a proof of concept experiment, which involves dropping neutrons through a circular arrangement of spinning lasers.
His ideas have not grabbed the rest of the physics community however, with others arguing that one of the assumptions of his basic model is plagued by a singularity, which is physics-speak for “it’s impossible”.
The Royal Institution of Australia has an Education resource based on this article. You can access it here .
Related Reading: Computer solves a major time travel problem
Originally published by Cosmos as Time travel: five ways that we could do it
Please login to favourite this article.
- Realizations to Blow Your Mind
- Pop Culture Mysteries We're...
- Technically True Is Still True
- Thoughts You Can Never Unthink
- The Truth About Getting Older
- Historical Shower Thoughts ...
- Great Thoughts That Pop Up ...
- Superstitions You Secretly ...
- Things Makings Us All Dumber
- Things Worth a Little Extra...
- Social Issues to Care About
- Things Your Mom Was Right A...
- Signs Someone Is a Good Person
- Greatest Duos of All Time
- 16 Historical Shower Thoughts That Make A Weird...
- The Decades Of A Person's Life, Ranked By Peopl...
- 20 Supposedly Fun Things That Actually Kind Of ...
- Whose Side Are You On? Viewers Decide Who's Rig...
Historical Events You Most Want To Go Back And See
Every history buff has considered the historical events they would want to witness—from the construction of the pyramids to the moon landing, the historical milestones on this list would have been amazing to see firsthand. And don't forget, woolly mammoths were still alive when the pyramids were built, though you probably wouldn't spot one in Egypt.
And then there are all the historical mysteries you could solve with a little time travel. Who really shot JFK? Do the Illuminati control the world ? And what were the completely naked Ancient Greek Olympic games like?
So if you could go back to a moment in history, which would you choose, and why? Wars and battles might not be the best historical events to witness, but what about Hannibal crossing the Alps or the Gettysburg Address? Or would you choose to party with Marie Antoinette or watch Leonardo paint the Mona Lisa? These are some of the most significant historical events we'd want to go back in time to see in person.
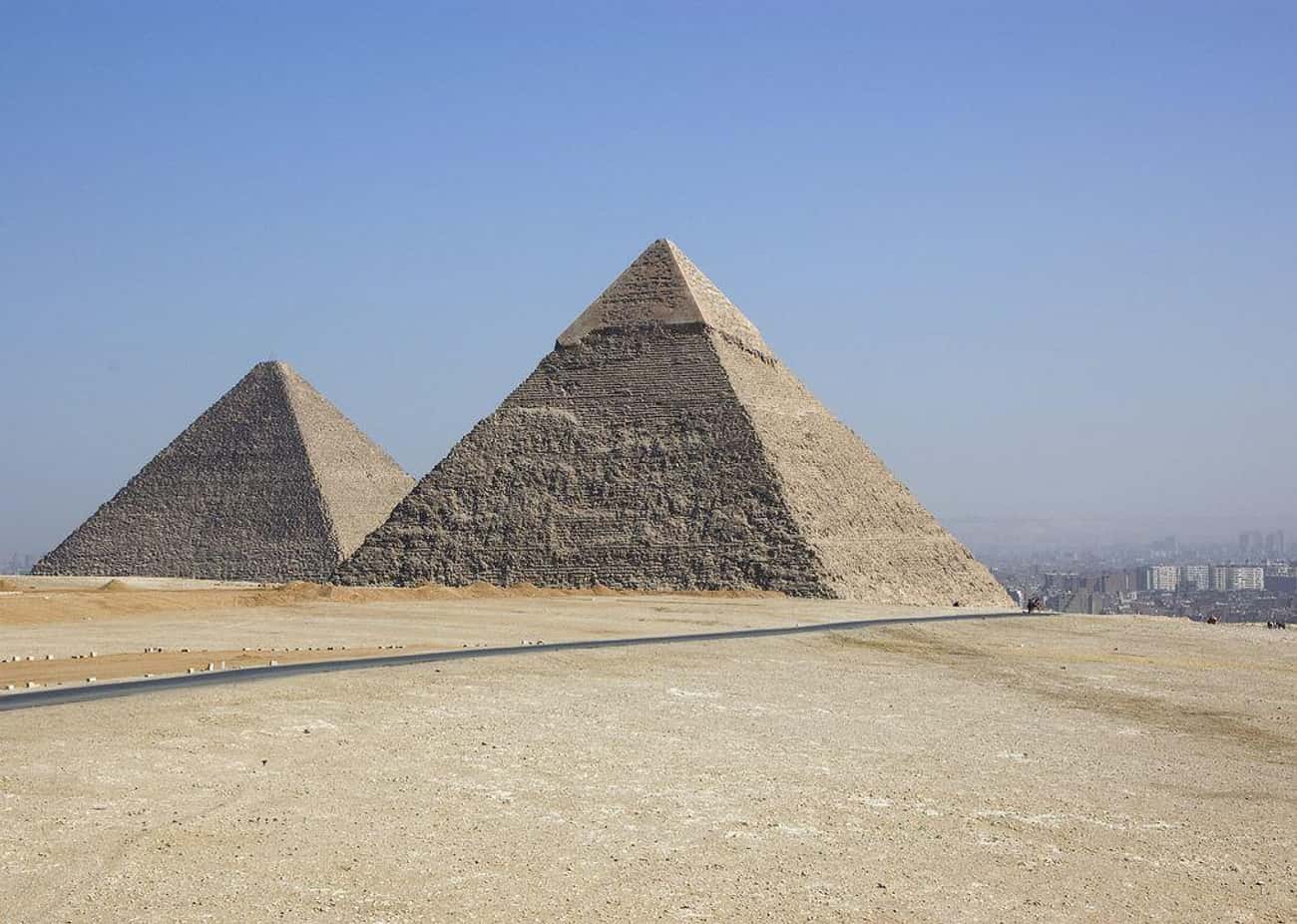

The Building of the Great Pyramids At Giza
What Was It?
Of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World , only the pyramids of Giza still stand. But they looked quite different when they were built around 2400 BCE. Then, the pyramids were encased in white limestone and may have been topped with a gold capstone . The tallest pyramid contains 2.3 million blocks of stone, and each averages about 2.5 tons, or 5,000 pounds.
Why It Would've Been Awesome To Experience:
How were the pyramids built? Were they constructed by slaves or farmers? And what did they look like when they were brand new? The pyramids are more than just marvels of engineering––they are also shrouded in mystery. A first-hand account would finally settle the age-old debate: was it aliens who actually built the pyramids ?

- laszlo-photo
The Construction of Stonehenge
The 100 upright stones that make up Stonehenge stand in a circle. For centuries, historians and visitors have wondered about the massive monument. In the twelfth century, Geoffrey of Monmouth even speculated that the wizard Merlin built Stonehenge. Today, we know that it likely took 1,500 years to build Stonehenge, but the purpose of the monument is still a mystery.
Was the massive stone monument just a burial ground, or did it serve other purposes? How did people move the enormous stones as far as 200 miles? And how was Stonehenge constructed, without even using the wheel? Stonehenge is one of the great mysteries in history, and by witnessing it first hand, you'd know all the answers.
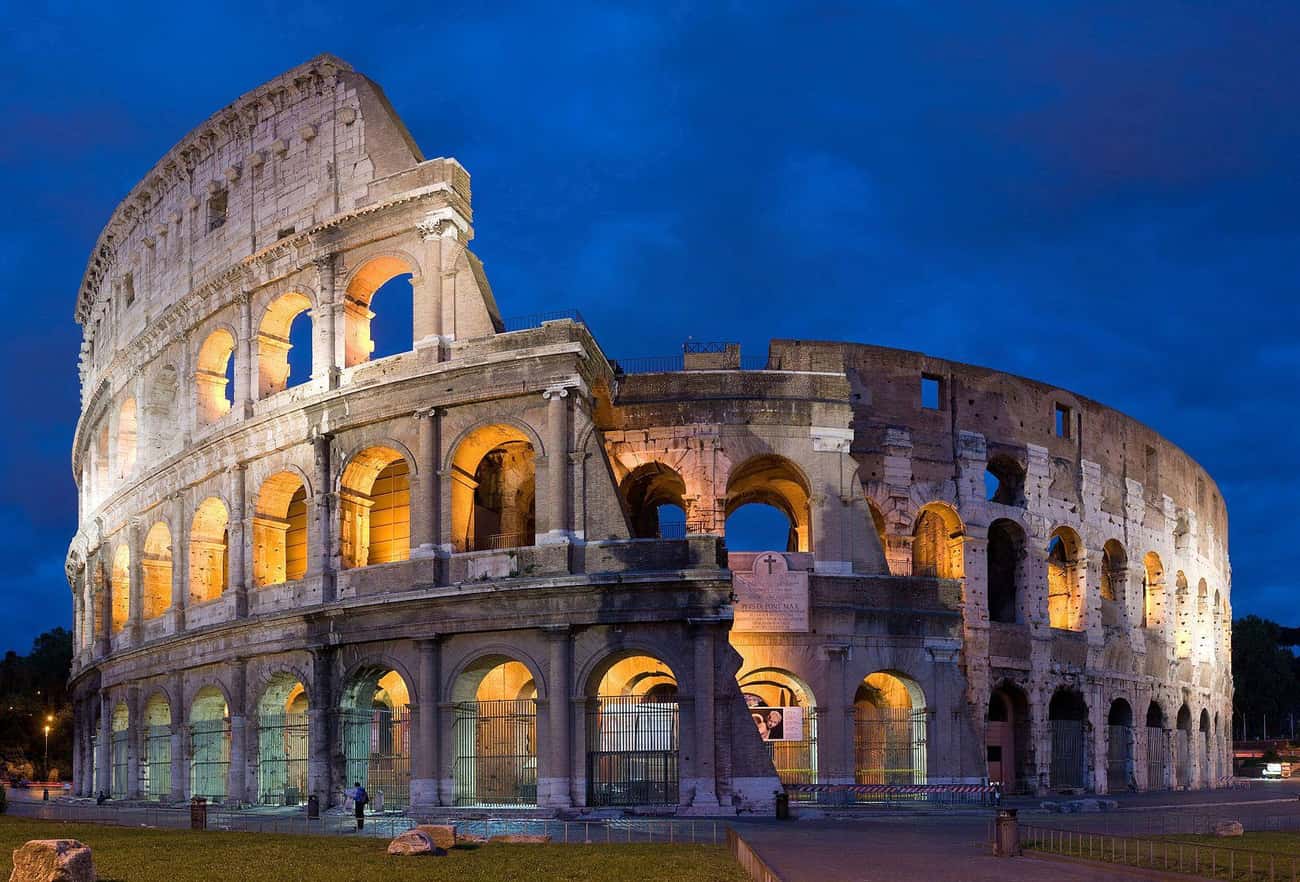

- Wikimedia Commons
- CC BY SA-2.5
The Ancient Greek Olympics
Fans of the winter and summer Olympics know that the modern games date back to 1896, but the Olympic Games are much older than that––their roots go back 3,000 years to athletic competitions held in the Ancient Greek city of Olympia. Originally, the only event was a 192-meter footrace called the stade, which gives us the modern word "stadium."
Fun fact: Roman Emperor Nero competed in an Olympic chariot race in 67 CE, and declared himself the winner even though he fell off his chariot during the event. And yes, the male Olympians during the ancient games competed in the buff . Apparently clothing just slowed them down.

- David R. Scott
- Wikimedia Commons/Public Domain
The Moon Landing
On July 20, 1969, the first human set foot on the moon. The moon landing was, according to Neil Armstrong, "one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind." NASA's amazing technological feat fulfilled President Kennedy's challenge to put a man on the moon and showed humans' ability to reach beyond our planet.
Half a billion people watched the moon landing live, but none of them saw Armstrong step onto the moon's surface in person. That would be a historical event worth witnessing, and would clear up all the conspiracy theories about whether or not the moon landing was faked.

- biblevector
The Birth of Jesus
Around the year zero in a manger in Bethlehem, a child was born. Jesus founded one of the most important religions in history , but it started with humble beginnings. As Christians believe, the adult Jesus practiced miracles, died on the cross, and was resurrected. And it all began with the nativity.
Admittedly, childbirth isn't typically a spectator event, but all the paintings make the Nativity seem pretty amazing. And many would love to go back in time to meet Jesus, so why not check out his birth?

- Anonymous/Library of Congress
The Wright Brothers Flying
On December 17, 1903, Orville Wright took flight, coasting at 6.8 miles per hour for about 120 feet. The Wright Brothers made history with their flying machine. It almost happened three days earlier, but Wilbur stalled out and crashed the plane.
Fun fact: Wilber and Orville decided who would take the first flight with a coin toss. They managed four flights on that historic day, until a gust of wind tossed their flyer and damaged it. The take off was a major technological achievement in the history of mankind and a historical event worth witnessing first hand.

- dharder9475
- CC-BY-NC 2.0
The Signing Of The Declaration of Independence
On July 4, 1776, the Continental Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence , an aspirational document asserting America's right to choose its own government. The founding document of the United States influenced revolutions around the world, including the French Revolution, and boldly made a case for inalienable rights.
“We hold these truths to be self-evident; that all men are created equal"—the United States might not always live up to Jefferson's lofty goals, but witnessing the moment that the country declared its independence would be pretty amazing.

- David Bachrach
Lincoln's Gettysburg Address
Abraham Lincoln's most famous speech was only 272 words long, but it encapsulated America's ideals. The Gettysburg Address was delivered on November 19, 1863 at the site of one of the bloodiest battles of the Civil War. Lincoln's powerful address, beginning with "Four score and seven years ago," also introduced generations of schoolchildren to the archaic "score" as a measure of time.
The Gettysburg Address is one of the most important speeches in American history, and witnessing it live on a historically significant battlefield would be powerful. Plus, it would settle debates surrounding Lincoln's speaking voice. Was it, in fact, shrill and squeaky , as some have claimed?

- George Cruikshank
An Original Shakespeare Play
William Shakespeare , the greatest playwright in the English language, wrote for the masses in Elizabethan England. But what were his plays like when they were first performed? The raucous crowds were almost another character in the show, and Shakespeare's stunning works were always crowd pleasers.
The costumes, the stage, and the crowds of Romeo and Juliet , Hamlet , or maybe Macbeth would be incredible to see. Watching one of Shakespeare's plays performed live would be amazing, and maybe you'd get to see the Bard himself––he reportedly played the ghost of Hamlet's father. Just don't expect to see any women on stage.

- Martin van Meytens
Party With Marie Antoinette
The French aristocracy knew how to throw a good party, and few raged as hard as Marie Antoinette . The queen's royal lifestyle, gilt with gold and dazzling luxuries, was so extreme it helped to provoke a revolution against the entire monarchy. But before the French Revolution brought it all crashing down, Marie Antoinette knew how to celebrate.
Marie Antoinette's wild masquerade parties featured extravagant gowns, jewels, champagne fountains, and towers of candies and cakes. Who wouldn't want to don a mask and join the soirée?

- Leonardo da Vinci
Watch Leonardo Paint The 'Mona Lisa'
It's the world's most famous painting. Leonardo da Vinci's Mona Lisa might be in the Louvre today, but the artist completed the masterpiece between 1503 and 1519 when he lived in Florence. The Mona Lisa changed art for the next 500 years, making it one of the most influential works in history.
First, just watching Leonardo paint would be amazing. But witnessing the painting of the Mona Lisa would also solve a few historical mysteries. Who, exactly, was the woman who sat for Leonardo's portrait? And what's the story behind her mysterious smile?

- World Telegram/Library of Congress
The Harlem Renaissance
The music of Louis Armstrong, the words of Zora Neal Hurston and Langston Hughes, the jazz clubs of Harlem—the Harlem Renaissance turned a New York City neighborhood into a Black cultural mecca, stretching from the 1910s through the mid-1930s.
Why It Would've Been Awesome To Experience:
Speakeasies sold illegal liquor and boomed with the sound of jazz—Duke Ellington, Bessie Smith, Fats Waller, and Cab Calloway performed in Harlem, putting a sound to W.E.B Du Bois's Black Pride movement. The sights and sounds of Harlem in the 1920s just call out to time travelers.

John F. Kennedy's Assassination
On November 22, 1963, President John F. Kennedy was assassinated. Millions of Americans watched the horrific events on television and remember where they were that fateful day. But even decades later, conspiracy theorists still wonder who really shot JFK.
The bloody shooting would be terrible to witness in person, but it would provide important answers to the still-raging mystery behind who shot JFK. Was Lee Harvey Oswald really acting alone? What was happening on the grassy knoll? And was there a conspiracy to assassinate the president?

- Ward, Lock, & Co.
Hannibal Crossing The Alps
In 218 BCE, one of the greatest generals in history led one of the greatest sneak attacks in history. Hannibal kicked off the Second Punic War between Carthage and Rome when he led a massive force of 100,000 troops and 40 war elephants across the Alps to invade Rome. His plan may have ultimately failed, but over 2,000 years later it is still remembered as one of the most astonishing military campaigns of all time.
Let's be honest: there are a lot of reasons to avoid going back to see wars. Napoleon's defeat at Waterloo , the downing of the Spanish Armada , or the attack on Pearl Harbor were all momentous historical events—and they were all incredibly destructive. But if you're a fan of military history, seeing Hannibal lead a massive army, including elephants, across the snowy Alps would be amazing, and a lot safer than other war-related historical experiences.

- L. C. McClure
California's Gold Rush
In 1849, thousands of people descended on California, hoping to strike gold and become rich overnight. The Gold Rush of 1849 transformed America and the West Coast after James Wilson Marshall, who was building a water-powered sawmill, found flakes of gold at the base of the Sierra Nevada Mountains. “It made my heart thump, for I was certain it was gold," Marshall said. Within weeks, three quarters of the men in San Francisco were off to hunt for treasure.
The Gold Rush probably didn't smell great, but it was a crazy moment in history. The 49ers extracted $2 billion worth of gold during the Gold Rush—and time travelers might just manage to snatch a nugget or two to bring back.
- Historical Events
- Historical Figures
Whatcha thinkin' about? Instead of pennies for your thoughts, here are lists of interesting things to ponder while you gaze at your navel and explore the depths of your true self.

20 Best Time-Travel Shows Ranked

If you could travel back and forth through time, where would you go? What would you do? Who would you talk to? Even better, if you were writing a book, making a movie, or working on a television show about time travel, what would you include? The best TV shows about time travel all feature characters who visit other eras for various compelling (or even life-threatening) reasons. Maybe it's to prevent a coming apocalypse, maybe it's just to save one person's life — but as many of these shows teach, small changes can have big effects, and many of these characters learn that their time-traveling can change the world.
Now, there are some great time travel-adjacent shows that don't quite fit this list. A fun romp like "Early Edition," for example, utilizes a time-traveling newspaper and potentially a time-traveling cat, but doesn't in and of itself feature a lot of time travel. Likewise, something like "Terminator: The Sarah Connor Chronicles" is rooted in a time travel premise, but stays mostly in one time. With all that said, here's a look at our choices for the 20 best time travel shows on TV.
Save the cheerleader, save the world. That's what future Hiro Nakamura (Masi Oka) tells present-day Hiro when he appears to him from the future, and that's what establishes "Heroes" as way more than just a superhero show.
The NBC series follows a group of regular people who develop special powers, not unlike mutants in the "X-Men" series, after a mysterious worldwide eclipse. Each character gains their own individual abilities. Claire Bennet (Hayden Panettiere) develops the ability to heal from any injury. Senator Nathan Petrelli (Adrian Pasdar) gains the ability to fly, while his brother Peter (Milo Ventimiglia) can temporarily absorb others' powers. Still, few of these characters have cooler abilities than Hiro, who can influence the space-time continuum. This means he can teleport, slow down time — and, of course, time travel.
Understandably, Hiro's power set becomes a serious asset throughout the series, and his path to perfect his abilities is one of "Heroes'" strongest story arcs. The first few times he travels through time don't go as planned, and throughout the series, things can get in the way of him ending up where he wants to go or when he wants to be. While Hiro's time-traveling is just one part of the larger story, it's definitely one of the show's highlights – especially since Oka is so darn charming as the character.
19. 11.22.63
One of the best Stephen King TV series out there, the eight-episode "11.22.63" follows a man named Jake Epping (James Franco). He's a relatively normal guy who receives a chance to change history when his friend Al (Chris Cooper) tells him he's found a way to travel back in time. Al tells Jake that the portal he's discovered goes back to the year 1960 and that he's been working on a plan to stop the assassination of President John F. Kennedy.
Al's age and advancing cancer diagnosis prevent him from following through on the plan, however, and he asks Jake to take over for him. Jake agrees, but soon his quest is met with pushback from a mysterious source. As it turns out, the past doesn't want to be changed, and every step Jake takes toward preventing JFK's assassination leads to more cracks in the timeline.
A charming and exciting time travel drama, "11.22.63" is a well-executed, twisty tale that only ranks so low on this list because it's in such great company. If you're looking for a quick, self-contained time travel miniseries that revolves around one of modern America's most notable events, this show is well worth a watch.
When Oceanic Airlines Flight 815 crash lands on a deserted island, wacky and scary things start happening to the survivors. ABC's "Lost" deals with flashbacks, flash-forwards, mysterious groups that already have a presence on the island, a black smoke monster — and, as it turns out, an ancient battle between good and evil. One of the great appointment television shows before streaming broke through, "Lost" had fans talking about it and theorizing about its mysteries on a weekly basis.
The sci-fi drama captivated viewers for six seasons, and though time travel is referenced throughout the entire series run, it plays the biggest role in Season 4. As the island itself leaps from place to place and from time to time, the main group of characters jumps with it, encountering previous versions of themselves and island events that occurred in the past, and suffering from the effects of temporal displacement. The most beloved episode dealing with time travel is undoubtedly "The Constant," in which fan-favorite Desmond Hume (Henry Ian Cusick) figures out a way to stop his consciousness from jumping through time by finding his constant — his true love, Penny (Sonya Walger).
Of course, "Lost" is not just a time travel show, and famously covers such a wide variety of mysteries and sci-fi concepts that viewers might find it hard to keep up. As such, it ends up with this relatively low ranking.
Like "Lost", "Fringe" is considered one of the most binge-worthy sci-fi shows of all time but the fact that it isn't exclusively about time travel means it lands near the tail end of this particular list. The ABC show revolves around a science-fiction conglomerate that dabbles with interdimensional travel, wormholes, and alternate realities. Anna Torv stars as FBI Agent Olivia Dunham, who heads up the bureau's Fringe Division. With the help of "mad scientist" Dr. Walter Bishop (John Noble), his estranged son Peter (Joshua Jackson), and their lab assistant Astrid Farnsworth (Jakisa Nicole), Dunham explores cases involving fringe science — be they about time travel, mind control, experiments gone wrong or any other strange and obscure criminal activity.
Time travel is more of a looming presence early in "Fringe," particularly present in the character of the Observer (Michael Cerveris), a bald, pale, genetically advanced human from the future. While Season 1 and Season 2 deal with the battle between two dimensions and realities, time travel really becomes an element in Season 3. Seasons 4 and 5 then deal with alternate timelines and the Observers that infiltrate the world from the future, intent on wiping out humanity. As you might expect, things can get a bit confusing, but the show sure is fun.
16. The Umbrella Academy
You have to respect a show that's so high-concept that time travel doesn't even get top billing. "The Umbrella Academy" boasts mysterious events, family drama, dance numbers, a talking chimpanzee, some of the cleverest superpowers in superhero shows, and a robot mom — and that's just scratching the surface. Based on "The Umbrella Academy" comics created by Gerard Way of My Chemical Romance fame, the Netflix show is a saga that exploits everything from the butterfly effect to the grandfather paradox for emotional and comedic impact.
The central Hargreeves family consists of a group of kids all born on the same day, adopted by the same eccentric billionaire (Colm Feore). He has trained them to protect the world with their various superpowers, but they aren't particularly great at it, and their strict upbringing has left them with a wide array of issues and deep rifts between them. The dysfunctional bunch starts out fairly estranged, but slowly bonds to save humanity from an apocalyptic event ... only to cause another potential apocalyptic event by sprinkling themselves across time.
In between the tears in the space-time continuum, "The Umbrella Academy" is ultimately an ensemble story about found (and re-found) family, as well as a truly unique superhero show where personal failure and the side-effects of costumed crimefighter life play a huge role. However, since Season 1 largely approaches time travel through Number Five (Aidan Gallagher) and the Temps Aeternalis agency, and much of Season 3 focuses on a present-day alternate reality, only the 1960s-themed Season 2 goes truly all in on the concept of sending all main characters to a different era.
15. Sliders
"Sliders" is a 1990s sci-fi adventure series that features Jerry O'Connell and friends getting lost across the multiverse. O'Connell ("Stand By Me") plays boy genius Quinn Mallory, inventor of the Timer — a device that lets him and his friends "slide" through a wormhole vortex into different versions of Earth. The thing about wormhole vortexes, though, is that they like to misbehave, meaning Quinn and his buds never know where they're headed next on their adventures. This makes their quest to get back home to their own Earth a tricky one.
"Sliders" starts off fun and strong, and is at its best when having bonkers fun — like when Rembrandt (Cleavant Derricks) discovers a world where he could have been Elvis-level famous — and when it's exploring real-world issues in a high-concept dimension, like when the crew visits an Earth that treats men worse than women. Even if you've seen it before, it's definitely worth a re-watch, because "Sliders" is one TV show that's better than you remember.
14. Continuum
On "Continuum," Kiera Cameron (Rachel Nichols) is a Protector – think futuristic government agent from even more futuristic equipment — from the year 2077. She gets transported to the year 2012 along with a group of murderous terrorists, forcing Kiera to remain in the past as she chases them down. Fortunately, her gadgets and knowledge of the past soon come in handy and she finds loyal allies. Unfortunately, her enemies also know their history and plan on altering it for their own gain.
"Continuum" milks the premise for all it's worth, while avoiding the pitfall of becoming a run-in-the-mill procedural with an unchanging status quo. While Kiera does handle her share of case-of-the-week story arcs, they're often connected to the group she pursues, and she never lets go of her primary target of stopping the terrorists. In order to avoid disrupting the timeline, she also has to go to great lengths to avoid revealing that either she or her targets are time travelers — and when their actions inevitably end up changing the future, she has to deal with the consequences.
13. Timeless
If ever there was a time travel show that was canceled too soon, it's Eric Kripke and Shawn Ryan's "Timeless." The NBC sci-fi series stars Abigail Spencer as the historian Lucy, Matt Lanter as the soldier Wyatt, and Malcolm Barrett as Rufus, a scientist who makes up a team trying to prevent a mysterious organization from altering the courses of history through time travel. They're up againsts Garcia Flynn (Goran Višnjić), who travels throughout history intending to influence major events like the Hindenburg disaster. However, the team soon realizes that the villain they thought they were fighting is much larger and infiltrates the historical timeline in ways they never imagined.
Instead of focusing on the usual historical suspects, "Timeless" often highlights forgotten people of color, women, and lesser-known historical figures, giving them their due and celebrating their contributions to society. This element of the show can be seen in the way Rufus, for instance, is reluctant to join the team because he knows how Black people are treated in the eras they visit.
Despite its intriguing concept, the show was canceled after Season 1, but fans caused such an uproar that NBC reversed the decision of canceling "Timeless" and renewed it for another season. After Season 2, NBC pulled the plug once more, and again, the fans cried foul. In a kind of compromise, NBC greenlit a special two-hour series finale that ties up loose ends and gives much-needed closure to the story.
12. 12 Monkeys
The "12 Monkeys" SyFy series is based on the 1995 film of the same name that stars Bruce Willis and Brad Pitt — though the series makes a fair few changes to stretch the plot into a four-season sci-fi drama. The series stars Aaron Sanford as James Cole, a scavenger from the year 2024 who's tasked with traveling to 2015 in order to stop the release of a biological weapon. In the movie, James is helped by a psychologist named Kathryn Railly played by Madeleine Stowe, but here, he befriends a virologist named Dr. Cassandra "Cassie" Railly (Amanda Schull). Pitt's character, Jeffrey Goines, is also gender-swapped here, with Emily Hampshire playing Jennifer Goines.
Like the movie, the series deals with the Cassandra Complex, the idea that we have a hard time believing concerns about the future, no matter how likely and provable they are. It also deals with circular time and the idea that past events can be affected by future ones. If those aspects of the film lift your time travel antennae, the four-season show dives even deeper.
11. Paper Girls
"Paper Girls" is a brilliant time travel show that was canceled way ahead of its time. Based on the comics by Brian K. Vaughan and Cliff Chiang, this Amazon series tells the story of a group of 1990s tween girls who get attacked by futuristic invaders. They manage to escape into the future, where one of the girls, Erin (Riley Lai Nelet ), meets her adult self (Ali Wong).
The show dispenses with grandfather paradox hand-wringing and instead uses the concept of the girls confronting their past and future selves, to brutally honest and hilarious effect. Young Erin is horrified to find out how much of herself she's abandoned by the time she turns into Old Erin, and refuses to let life work out that way. It motivates Erin to want to return to her home time even more — this kid has a clock to beat. However, there are two sides to the coin, and Old Erin is also able to care for her young self in ways she never felt able to when she was younger. It's a beautiful and potent visual metaphor that other characters also make good on.
All in all, "Paper Girls" is a feast for the eyes as much as its ensemble cast is a feast for the soul. Plus, Jason Mantzoukas playfully chewing scenery as the ominous Grand Father? This show could have lasted until the end of time — or at least until Season 2.
10. Timewasters
"Timewasters" is a time travel comedy about a Black British jazz band that accidentally time-slips back to 1920s London, among other timelines. The quartet stumbles into an earlier time perod via a disgusting elevator that, yes, doubles as a time machine. Once the crew shows up in the past, they're treated like freaks, but they gain some measure of success as musicians. While the crew eventually tries to return to the present, they also have a "Back to the Future" moment when they seemingly get stuck in the 1950s.
"Timewasters" is full of funny jokes and great music, and it's a groundbreaking show in a number of ways. "People like us never get to time travel — it's what white people do, like skiing or brunch," creator Daniel Lawrence Taylor told the Royal Television Society . "For me, race is so important." Taylor also stars in "Timewasters," along with Kadiff Kirwan ("Slow Horses"), Adelayo Adedayo ("Some Girls"), and Samson Kayo ("Our Flag Means Death"). The show is also an excellent destination if you're into spotting a variety of British actors and comedians ... including Joseph Quinn, who went on to rise to fame as Eddie Munson on "Stranger Things."
9. Outlander
Based on the series of novels by Diana Gabaldon, Starz's "Outlander" follows the story of a World War II nurse named Claire (Caitriona Balfe) who finds herself thrown back in time after visiting a circle of mysterious Druid stones. She arrives in 18th Century Scotland and, after being taken in by a band of gruff Scots, she marries the dashing young Jamie Fraser (Sam Heughan) in order to avoid being taken prisoner by her real husband's (Tobias Menzies) apparent evil ancestor, Black Jack Randall (Menzies). Claire lives through a time of great upheaval in Scotland when tensions with British control are rising and history-making battles loom in the near future. Despite being initially reluctant to stay, she and Jamie fall deeply in love, and their romance remains the backbone of the series.
The entire "Outlander" timeline takes some time to explain, what with several 20th-century characters taking the trip to the 18th century and the show covering versions of notable real-world historical events. Without further spoilers, all there is to say is that if you enjoy time travel shows that lean heavily toward historical drama, "Outlander" is where it's at. Also, if you view Tobias Menzies as an incorrigible dweeb due to his performance as Edmure Tully on "Game of Thrones," his monstrous "Outlander" villain is guaranteed to erase that image.
8. Quantum Leap
"Quantum Leap" stars Scott Bakula as Dr. Sam Beckett, a physicist who invents a way to travel through time. When the corporation funding his project threatens to shut it down, Sam uses himself as a guinea pig to test out the method. He finds himself thrown back in time, but in another person's body. The only other entity aware of his 'leap" is a hologram of his colleague and best friend, Admiral Al Calavicci (Dean Stockwell). Al tells Sam that he must correct things that went wrong in the past before being allowed to leap back to his own time and body, and can only use the resources of the project's supercomputer, Ziggy.
With Sam leaping back and forth into different bodies at different times, the show uses a variant of the traditional procedural set up. New characters turn up to guest star and Sam gets to save the day, have a fling, and learn something new before leaping to the next destination, which just might be home one of these days.
The series ran on NBC from 1989 to 1993, but its combination of time travel and case-of-the-week antics has proved enduring enough that "Quantum Leap" even gets a shout-out in "Avengers: Endgame." Despite being over three decades old, it remains a cool time travel series worth checking out.
7. The 4400
In the opening scenes of "The 4400," an enormous ball of light drops 4,400 people at the foot of Mount Rainier in Washington. They soon realize that they were all taken from some other point in time and deposited into the year 2004, unaged and without any memories of where they'd been. At first, everyone assumes that these people have been abducted by aliens. However, it soon turns out that the truth is far more time travel-related.
The returned people soon start developing "Heroes"-style powers that range from telekinesis to telepathy and super-strength, which people from the future have entrusted with to prevent various catastrophic events that they want to avoid in their timeline. Unfortunately, the 2004 government considers the powered folks a threat, and inhibits their powers with a neurological drug.
The stories that unfold from this setup are exactly as complex and entertaining as you'd imagine, with various members of the titular group treating their powers in different ways and society having a hard time dealing with them. Unfortunately, "The 4400" ended abruptly after four seasons on a somewhat ambiguous note, but even so, it's a fun show to revisit.
6. Travelers
In Netflix's "Travelers," time-traveling operatives from a post-apocalyptic future are tasked with preventing certain events that have led to the downfall of society in their own present day of 2018. The travelers' consciousness takes over a person in the desired time who's just about to die, and the operative then lives out the rest of that person's days though with the mission in mind ... and a strict set of rules they must follow. Apart from a list of ways they're not allowed to interact with the past, they're also strictly forbidden from communicating with other known travelers outside their team, save for special circumstances dictated by the Director, who communicates by temporarily taking over children.
It's a unique and complex premise, and the way the travelers scope out potential targets for takeover and learn to live as them is as timely as it comes — they use social media, GPS locations, and other readily available online information for their time-travel tricks. This adds a layer of present-day dread to the show's fascinating take on time travel.
Loki Laufeyson (Tom Hiddleston) meets his match when he comes up against the Time Variance Authority in one of the Marvel Cinematic Universe's most ambitious Disney+ shows, "Loki." The TVA is so dedicated to maintaining a particular sacred timeline that they purge all alternate realities where someone made a choice they deem wrong, which might not always make sense, but precision isn't the point here. It's the idea of playfulness versus control.
The Loki we see here is an alternate-timeline variant of the one the audiences are familiar with, and thus starts the show in full "The Avengers" villain mode before life — and time — starts grinding him down. Working with TVA agent Mobius M. Mobius (Owen Wilson), he starts redeeming himself by tracking down an apparently evil version of himself, Sylvie (Sophia Di Martino) ... and ultimately tackling the biggest challenges time can offer.
The God of Mischief's surprisingly human path of reckoning is the heart of a show that's deliciously stylish, silly, and sometimes scary. "Loki" takes a cops-and-robbers crime caper into time travel territory and explores hefty themes with a light touch, from mindless compliance to self-serving overseers to criminalizing anyone deemed different. "Loki" isn't just a time travel show — it's a show about everything time can offer and more, with characters dancing between eras as you might step from room to room. Also, it has Alligator Loki, who's objectively the best Loki of all.
If "Loki" is too light-hearted for you, Netflix's "Dark" might be your jam ... provided you can make sense of its incredibly convoluted time travel storyline. Four families weave a tangled web of time travel in this German-language psychological thriller about missing kids, a rotten town, and how almost all of our secrets come out in time. In other words, it's a good time travel show, but it's definitely not a feel-good time travel show.
"Dark" follows its many characters over the course of their lifetimes and, at one point, has three timelines going at once. Part of the intrigue and challenge of watching the show is trying to understand how (and when) each timeline threads into the other. If you decide to watch it, it's best to have an evidence board and plenty of red yarn ready to chart the relationships and betrayals the town of Winden sees over the years.
While "Dark" is as much a show about human connection and how frayed it can become as it is about time travel, it's also the MVP of using as many time travel paradoxes as possible during its three-season run. "Dark" is also an innovator in the field of wormhole placement. Wormholes are already not to be trusted, but a wormhole underneath a nuclear power plant? No, thank you.
3. Beforeigners
What happens when a bunch of Viking-era warriors, 19th-century figures, and Stone Age people pop up in modern-day Oslo? "Beforeigners" attempts to answer that question while navigating twisty murder mysteries with such efficiency that the Norwegian series may be best described as "crime travel." Adding to the intrigue is the way it focuses more on the present-day relationship between the time refugees and their modern counterparts than on how they showed up in the first place.
"Beforeigners" centers around the odd-couple partnership between hardened police detective Lars Haaland (Nicolai Cleve Broch) and eager new Viking police recruit Alfhildr Enginnsdóttir (Krista Kosonen), who investigate things like the murder of a Stone Age victim and even look into crimes with possible ties to Jack the Ripper.
The metaphor of time migration is an apt one for immigration, and this sci-fi show explores tricky real-life issues with plenty of scope. Creators Anne Bjørnstad and Eilif Skodvin got their start in comedy writing, and their commitment to the bit is evident in the show, including the language used. "Early on, I contacted researchers, professors who helped us. We also constructed the language that Stone Age people spoke, and even with the language from the 19th century: We worked on it to make it sound right," Bjørnstad told Variety . "Why not invest in language, which is such a big part of a person's identity?"
2. Russian Doll
"Russian Doll" could be pitched as "Natasha Lyonne's 'Groundhog Day,'" but that still wouldn't hint at half of the show's charm and emotion. This Netflix offering is a mind-bending time loop dramedy that's a stylish and surreal exploration of life, death, and all the trauma in between. Season 1 of "Russian Doll" features Nadia (Lyonne) stuck reliving her 36th birthday until she inevitably dies and resets back to her friend's bathroom. Later in the season, she discovers a fellow time traveler (Charlie Barnett). They quickly realize that the way out of their dead ends and into a new life is through helping each other.
Season 2 takes some departures from the recursive reality set up in the first season, bending viewers' minds even more thoroughly. "Russian Doll" goes deep, but keeps a sense of humor even as it twists the knife in its characters' hearts — and their timelines. The show keeps audiences just oriented enough by linking its time loops to recognizable spaces and sound cues. You will never look at the subway the same way again, and you will probably never get Harry Nilsson's "Gotta Get Up" out of your head.
1. Doctor Who
Really, could any other show top a list like this? The untold history of "Doctor Who" goes all the way back to 1963, when the show premiered on the BBC. The series follows the adventures of a Time Lord who calls themselves the Doctor — an alien being from the planet Gallifrey who travels through space and time on a craft called the TARDIS, which is charmingly disguised as an old-fashioned British police call box and is famously bigger on the inside. Every Doctor has their own companions – humans who follow the Doctor throughout space and time, helping people, battling new and recurring villains, and dealing with the assorted wibbly-wobbly stuff on the Doctor's timeline .
The original series ran from 1963 through 1989 and established the neat trick of recasting the Doctor every few years or so, thanks to the premise that the character has multiple lives and can reincarnate himself into different physical bodies. The modern series was revived in 2005 with Christopher Eccleston as the Doctor, and talented actors like David Tennant (twice), Matt Smith, Peter Capaldi, Jodie Whitaker, and Ncuti Gatwa have followed in his footsteps. Even without the fact that no other show has time travel quite as integrated into its very premise as "Doctor Who," the show's sheer longevity and cultural impact are more than enough to make it the king of the time travel hill.

- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Sign In Sign Up
- 20 Historical Events We’d Go Back and Witness If Time Travel Was Real
- Player View
1. 30 January 1969, the Beatles playing on the roof of the Apple building in London. -galvinonthewing
2. i’d watch reactor 4 explode from very far away. and maybe in a special suit. -c_cooke1, 3. death/resurrection of jesus. let's see if the there is any basis behind christianity. i don't know of any other religion based on such a singular event. -imreverse_giraffe, 4. strasbourg 1518, to witness the event where the whole town succumbed to mass hysteria and danced themselves to death over 2 months. -tomr84, 5. the premier of beethoven’s 9th symphony in vienna. -ghost-lumos, 6. would love to see and hear dinosaurs roaming around our land. -rci_ancilla, 7. the collapse of the berlin wall. -thebk_1er, 8. for a long time, the mediterranean sea was cut off from the atlantic ocean and the rivers flowing into it were not enough to prevent it drying up completely. at some point in time, the ocean was able to cut an opening at gibraltar and millions of cubic meters of water poured into the basin. that, i would like to have seen. -comicsnerd, 9. when the golden gate bridge was finished, my father was one of the first to walk across it. he died when i was 8. would love to see him again. -gml0206, 10. a tour of library of alexandria before it was destroyed. -suvenpan, 11. as a geologist, the lake agassiz flood. during the last glacial period, over 12,000 years ago, there was a massive lake in the middle of the north american continent fed by glacial meltwater. this lake is now known as lake agassiz. at its peak, the lake was larger than all of the current great lakes combined . estimates put it at 440,000 square kilometers in area. most of that water was held in place by glacial and topographic dams. at the end of the last ice age, the largest ice body containing the lake to the east in hudson bay retreated / melted, causing the lake to drain almost completely - in less than nine months . a freshwater lake with tens of thousands of years of history and input, and more fresh water than all other freshwater bodies on the planet at that time combined, drained in less than a year. the flooding was likely unprecedented, carrying erratics (boulders) the size of small houses hundreds of miles away. as the water drained into hudson bay and other outlets, the global sea level rose by 1-3 meters. lake winnipeg, lake manitoba, red lake, and lake of the woods are the largest remnants of lake agassiz. -allfunandgaymes, 12. 1980 olympics at lake placid, ice hockey medal round, usa vs ussr. -ixprometheusix, 13. jfk assassination with a bunch of hi res cameras. -spazmanaut, 14. the mlk “i have a dream” speech. that speech always gave me chills. i’m a 3rd grade teacher and always show it to my students to end our lessons on mlk. i show it the friday before the mlk weekend. -deleted, 15. i would love to see the debut of a molière play at versailles. -leomarius, 16. assuming i have a safe vantage point on some kind of space ship, i choose the planetary impact that's believed to have given us the moon. -ancientsumeriangod, 17. i'd go back in time to watch neil armstrong step on the moon on tv. it's mankind's greatest achievement, and something i wish i could've been born 4 or 5 decades earlier to see. -mythicforgeftw, 18. the winged hussars charge it was so impressive that a battle nearby stopped just to watch them charge. -nighthawk0954, 19. the building of the pyramids. -essexenglishman, 20. queen at live aid in 1985, from the footage you can tell it was an amazing event but to be there and experience it must have been something else. -duldain92.

Share This Image
- REPLAY GALLERY

- NEXT GALLERY

- Funny Memes and Pics to Noscope Your Opponents With (34 Images)

- Log in for Comments
- New! You can now add images to your comments! Click here for details!
Related Galleries

eBaum's Picks


Official websites use .boston.gov
A .boston.gov website belongs to an official government organization in the City of Boston.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Boston Celtics Victory Parade and Traffic Advisory
The City of Boston will host a duck boat parade on Friday, June 21, 2024, to celebrate the Celtics winning their 18th NBA Championship.
- Last updated: June 21, 2024
Parade Route and Map
The parade will begin at 11 a.m. on Causeway Street and then follow Staniford Street to Cambridge Street to Tremont Street to Boylston Street, before ending near the Hynes Convention Center.
Download the map (pdf)
Public Transportation
Those attending the parade are strongly encouraged to use public transportation. Riders can find more information on MBTA service, parking, paying fares, and more during Friday’s Celtics Championship Parade on the MBTA's website .
The MBTA will have increased subway service and modified Commuter Rail schedules with additional train times before and after the parade. Riders are strongly encouraged to purchase roundtrip fares in advance.
Accessibility
The parade route will include two designated accessible viewing areas - on City Hall Plaza on the Cambridge Street side and outside of the Boston Public Library on Boylston Street. There is no reserved seating at these viewing areas.
Bluebikes, the regional bike share service, is another great way to get around the City. Information on passes and station locations may be found on the Bluebikes website .
Parking Restrictions (No Parking)
- Causeway Street , Both sides from North Washington Street to Merrimac Street
- Staniford Street , Both sides from Causeway Street to Cambridge Street
- Cambridge Street , Both sides from Staniford Street to Tremont Street
- Tremont Street , Both sides from Cambridge Street to Boylston Street
- Boylston Street , Both sides from Washington Street to Massachusetts Avenue
- Charles Street South , Both sides from Park Plaza to Boylston Street
- Charles Street , Both sides from Beacon Street to Boylston Street
- Arlington Street , Both sides from Newbury street to Saint James Avenue
- Berkeley Street , Both sides from Saint James Avenue to Newbury Street
- Clarendon Street , Both sides from Saint James Avenue to Newbury Street
- Dartmouth Street , Both sides from Newbury Street to Saint James Avenue
- Exeter Street , Both sides from Newbury Street to Blagden Street
- Fairfield Street , Both sides from Boylston Street to Newbury Street
- Gloucester Street , Both sides from Boylston Street to Newbury Street
- Hereford Street , Both sides from Boylston Street to Newbury Street
- Cambria Street , Both sides, from Boylston Street to end at Hynes Center garage
- Scotia Street , Both sides, from Saint Cecilia Street to Dalton Street
- Saint Cecilia Street , Both sides, from Belvidere Street to Boylston Street
- Dalton Street , Both sides, from Belvidere Street to Boylston Street
- Providence Street , Both sides, from Arlington Street to Berkeley Street
- West Street , Both sides, from Washington Street to Tremont Street
- Temple Place , Both sides, from Washington Street to Tremont Street
- Bromfield Street , Both sides, from Washington Street to Tremont Street
- Park Street , Both sides, from Tremont Street to Beacon Street
- Beacon Street , Both sides, from Somerset Street to Tremont Street
- School Street , Both sides, from Tremont Street to Province Street
- Somerset Street , Both sides, from Ashburton Place to Cambridge Street
- New Chardon Street , Both sides, from Cambridge Street to Merrimac Street (Congress Street)
- Bowdoin Street , Both sides, from Dern Street to Cambridge Street
- New Sudbury Street , Both sides, from Cambridge Street to Hawkins Street
- Congress Street , Both sides, from New Sudbury Street to State Street
- State Street , Both sides, from Congress Street to Court Street
- Court Street , Both sides, from Washington Street to Cambridge Street
- New Chardon Street , Both sides, from Cambridge Street to Merrimac Street (Congress Street)
- Staniford Street , Both sides, from Cambridge Street to Merrimac Street
- Lomasney Way , Both sides, from Causeway Street to Nashua Street
- Lancaster Street , Both sides, from Causeway Street to Merrimac Street
- Portland Street , Both sides, from Causeway Street to Valenti Way
- Friend Street , Both sides, from Causeway Street to Valenti Way
- Canal Street , Both sides, from Causeway Street to Valenti Way
- Haverhill Street , Both sides, from Causeway Street to Valenti Way
- Beverly Street , Both sides, from Causeway Street to Valenti Way
- Medford Street , Both sides, from Causeway Street to North Washington Street
- Plympton Street , Both sides, from Albany Street to Harrison Avenue
- East Dedham Street , Both sides, from Harrison Avenue to Albany Street
Public Safety
Please note:.
- Underage and public drinking of alcohol will not be tolerated.
- Boston Police and Boston EMS will have a large presence along the parade route.
- The Office of Emergency Management will also have misting tents out to provide cooling relief at City Hall Plaza and the Boston Common, along with cooling towels.
- Residents are encouraged to sign up for AlertBoston emergency notifications for the latest updates.
Be aware of the heat
While the previously declared heat emergency will have ended by Friday, first responders will be ready to help those feeling adverse effects from the heat. Please remember to stay hydrated and use sunscreen.
Read the public safety update

Time Travel Tuesday: local architecture

PANAMA CITY, Fla. (WJHG/WECP) -A look at some local architecture with historian Bill Hudson in this weeks’ Time Travel Tuesday.
If you are looking to chat about local history, you can contact Bill Hudson at (850) 785-3364.
Copyright 2024 WJHG. All rights reserved.

Young man pronounced dead in ER after drowning in Panama City Beach

Woman found unresponsive in gulf, pronounced dead

Investigation into PCB Police Chief Talamantez finds allegations are unfounded

Authorities release information on woman who died after swimming in gulf

Motorcycle accident leaves one person dead
Latest news.

Contract awarded for construction of Martin Theatre

The Panama City Beach Police Department is set to beef up presence on the beach

Panama City social district could expand

BDS officials release ESE evaluation results

Latitude Margaritaville Amenity Expansion
- Summer Racing ExternalLink
- Champions League
- Motor Sports
- High School
- Shop ExternalLink
- PBR ExternalLink
- 3ICE ExternalLink
- Stubhub ExternalLink
- Play Golf ExternalLink
2024 Travelers Championship live stream, TV schedule, channel, where to watch, tee times, radio, golf coverage
A busy three-week stretch in professional golf comes to an end this week in connecticut.
The 2024 Travelers Championship appears to be heading to an exciting finish. Taking to TPC River Highlands once again, Sunday's final round has moved into a playoff as world No. 1 Scottie Scheffler and Tom Kim battle for the trophy and a massive prize money payout .
Failing to card a single under-par round in a tournament for the first time in his professional career, Scheffler looks to get back on the wagon and capture his sixth victory of the season. A win at TPC River Highlands would be his first at a course which saw Xander Schauffele reign supreme in 2022.
The world No. 2 continues to display his consistency on a weekly basis and has now notched four straight top 10s dating back to the Wells Fargo Championship. With plenty of form in tow, Schaffuele seeks his second win of the season and second trophy at the Travelers Championship.
All times Eastern; streaming start times approximated
Round 4 - Sunday
Round starts: 6:50 a.m.
PGA Tour Live: 6:50 a.m. - 1 p.m. -- PGA Tour Live
Live TV coverage: 12-2 p.m. on Golf Channel, fubo (Try for free) Live streaming: 12-2 p.m. on Peacock
Live TV coverage: 2-6 p.m. on CBS Live simulcast: 2-6 p.m. on CBSSports.com and the CBS Sports App
Radio: 1-6 p.m. -- PGA Tour Radio
Our Latest Golf Stories
2024 Rocket Mortgage Classic picks, predictions, odds
Cbs sports staff • 4 min read.
2024 Rocket Mortgage Classic odds, expert picks
2024 Rocket Mortgage Classic One and Done expert picks
2024 Rocket Mortgage Classic PGA DFS picks, lineups
Cbs sports staff • 3 min read.
2024 Rocket Mortgage Classic preview, expert picks
Patrick mcdonald • 5 min read, 2024 open championship odds, picks, predictions, share video.

How to watch the 2024 Travelers Championship

Rocket Mortgage Classic preview, expert picks

Is Scottie in 2024 actually rivaling Tiger in 2000?

Protestors with smoke bombs tackled at Travelers

Travelers purse: Scheffler up to $28M in winnings

Cameron Young shoots 59 in Round 3 at the Travelers

Tiger receives exemption into signature events

Charlie Woods qualifies for first U.S. Junior Amateur

Davis Love III enthused about golf's young stars

Johnny Damon: How I started loving golf

Crucial Details To Know About 2024's Best Disney Fan Event: D23 Expo
D isney's biggest event, D23: The Ultimate Disney Fan Event (formerly known as the D23 Expo, or what we'll be calling the D23 Fan Event for short) is officially coming to Anaheim, California, this August — and it's bringing a mega dose of magic, excitement, and surprises for dedicated Disney fans to enjoy! Held every two years, the D23 Fan Event is hailed as the ultimate celebration for lovers of all things Disney (as well as Pixar, Marvel, and Star Wars, of course).
A fully immersive experience that takes attendees behind the scenes on the new and unique attractions at Disney theme parks , upcoming launches, and film & TV announcements, the event promises to deliver some pretty unforgettable moments.
From themed exhibitions to cosplay events, never-before-seen movie previews, and panels and discussions, the three-day extravaganza is designed to celebrate only the best of the Disney brand, along with all of its real-life magic. Put simply, if you think you love Disney, the D23 Fan Event is the place for you.
Read more: The 100 Most Popular American Tourist Destinations
Can You Still Get Tickets To The D23 Fan Event?
Per the event's official website, tickets are only available for official members of the D23 Disney Fan Club who are enrolled as either a General Member or D23 Gold Member. This basically means that, unless you're a member or know someone who currently holds an active membership, you won't be able to purchase tickets for the event.
In addition to this slight setback, it's also worth highlighting that tickets to the D23 Fan Event typically sell out months in advance — and this year's expo is no different. Nonetheless, it's still possible to purchase resale tickets and simply have the passes transferred to you, although keep in mind that a valid D23 Fan Club membership is still required for this.
However, this doesn't mean that non-attendees or new fans have to miss out on any (okay, on some ) of the fun! Per the company's Chief Brand Officer, Asad Ayaz, portions of this year's event will actually be streamed on the Disney+ platform for the very first time (via Deadline ). Not only will this help the brand bring a little more magic into their fans' homes, but it'll also expand the experience to international Disney-heads who have missed out on the celebration in the past.
When And Where Is The D23 Fan Event Happening
This year, the D23 Fan Event will take place between August 9 and 11 at the Anaheim Convention Center and Honda Center. As a central hub, most of the event's main activities will take place at the Convention Center, including hands-on experiences and interactive exhibits, as well as themed pavilions dedicated to Pixar, Disney+, Marvel Studios, Lucasfilm, and a special Disney archival display.
As for the Honda Center, the venue will host three main events throughout the long weekend: the Disney Entertainment Showcase, happening Friday (August 9) at 7:00 p.m.; the Disney Experiences Showcase, which takes place on Saturday (August 10) at 7:00 p.m.; and the Disney Legends Ceremony, which helps close-off the weekend on Sunday (August 11) at 5:00 p.m.
In terms of moving between the two venues, attendees will also be happy to know that official D23 shuttles to and from the Anaheim Convention Center and Honda Center will be available for ticketed guests to enjoy. These come at no extra charge on a first-come, first-served basis and run continuously throughout the three days.
What To Expect From This Year's D23 Fan Event
Although most of the event's specific details are kept under wraps, attendees should be ready for some pretty big surprises and exciting reveals. For starters, rumor has it that the weekend is expected to feature a whopping 50+ panels and discussions. Along with this, guests should also expect the main floor to be filled with interactive booths and exhibits from Disney brands and partners — including the chance to personally meet with imagineers, animators, and filmmakers.
Additionally, ticketed guests will also have the opportunity to participate in some pretty exciting moments that could include exclusive ride and attraction announcements of everything coming to Disney Parks , future plans for Disney TV & film projects, potential updates on popular overseas parks like Disneyland Paris , live performances and demonstrations, and a bunch of other unveilings and updates related to the Disney brand.
Lastly, attendees can find even more ways to remember the experience with a dedicated shopping area that's filled with limited-edition and collectible merchandise, including D23-branded goodies courtesy of the Walt Disney Company Store. Other shopping highlights include the fan-favorite Mickey's of Glendale store, as well as the Hollywood Studio Store and the Emporium Shop.
Top Tips For First-Time Attendees
With so much to see, do, and enjoy, first-time attendees to the D23 Fan Event might be feeling a little overwhelmed with planning their days to ensure maximum enjoyment. Luckily, there are a few things you can do to prepare for the experience — and keep your cool in the process.
First things first, the most important thing when hitting up the D23 Fan Event is to have a plan in place. A great way to make this work is to download the official D23 app (available on both the App Store and Google Play Store). The app will include a full schedule of events (as well as a map) that you can quickly save and keep track of — that way, you'll always know where to go next. Word of warning for first-time visitors, though: Make sure you're prepared to deal with the seemingly never-ending lines and wait times. Have some flexibility in your plans and decide ahead of time what experiences you're willing to wait for and which ones you're willing to skip if it's too crowded.
Beyond that, days at the D23 Fan Event run very long, which means you'll also want to be ready for that. This includes bringing a reusable water bottle, carrying some light snacks in your bag, having an external charger in case your phone starts to run out of juice, and even packing a sweater to deal with the cold once you're inside the venue. Oh, and of course: Don't forget your mouse ears!
More Ways To Enjoy The 2024 D23 Fan Event
If you're craving even more Disney magic, you'll be happy to know that there will be additional activities to enjoy alongside other D23 members in the days leading up to the main weekend. Keep in mind, however, that these events require additional ticket purchases, all of which are available through the official D23 Fan Event website.
Kicking things off is the first-ever D23 Day at Angel Stadium. Happening on Sunday, August 4, attendees can watch the LA Angels take on the NY Mets, and even get their hands on a one-of-a-kind D23 Mickey Mouse bobblehead — decked out in an Angels uniform. On Tuesday, August 6, D23 members are also welcome to join an official "fan meet-up" at the Anaheim Packing District, which includes an evening of entertainment, food, and drink that are all perfectly Disney-themed. The following night, fans can kick back with a special outdoor screening of "The Incredibles" to celebrate the film's 20th anniversary at the Pearson Park Amphitheatre.
Last, but definitely not least, on Thursday, August 8, California's Disneyland Resort will also get in on the fun with their own D23 Day. What does that look like? From rope drop 'til close, both Disneyland and Disney California Adventure will welcome D23 ticket holders to participate in plenty of unique experiences — including a custom cavalcade, dance party, special photo opportunities, and more.
Read the original article on Explore .

Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
FACT SHEET: President Biden Announces New Actions to Keep Families Together
Since his first day in office, President Biden has called on Congress to secure our border and address our broken immigration system. As Congressional Republicans have continued to put partisan politics ahead of national security – twice voting against the toughest and fairest set of reforms in decades – the President and his Administration have taken actions to secure the border, including:
- Implementing executive actions to bar migrants who cross our Southern border unlawfully from receiving asylum when encounters are high;
- Deploying record numbers of law enforcement personnel, infrastructure, and technology to the Southern border;
- Seizing record amounts of fentanyl at our ports of entry;
- Revoking the visas of CEOs and government officials outside the U.S. who profit from migrants coming to the U.S. unlawfully; and
- Expanding efforts to dismantle human smuggling networks and prosecuting individuals who violate immigration laws.
President Biden believes that securing the border is essential. He also believes in expanding lawful pathways and keeping families together, and that immigrants who have been in the United States for decades, paying taxes and contributing to their communities, are part of the social fabric of our country. The Day One immigration reform plan that the President sent to Congress reflects both the need for a secure border and protections for the long-term undocumented. While Congress has failed to act on these reforms, the Biden-Harris Administration has worked to strengthen our lawful immigration system. In addition to vigorously defending the DACA (Deferred Action for Childhood arrivals) policy, the Administration has extended Affordable Care Act coverage to DACA recipients and streamlined, expanded, and instituted new reunification programs so that families can stay together while they complete the immigration process. Still, there is more that we can do to bring peace of mind and stability to Americans living in mixed-status families as well as young people educated in this country, including Dreamers. That is why today, President Biden announced new actions for people who have been here many years to keep American families together and allow more young people to contribute to our economy. Keeping American Families Together
- Today, President Biden is announcing that the Department of Homeland Security will take action to ensure that U.S. citizens with noncitizen spouses and children can keep their families together.
- This new process will help certain noncitizen spouses and children apply for lawful permanent residence – status that they are already eligible for – without leaving the country.
- These actions will promote family unity and strengthen our economy, providing a significant benefit to the country and helping U.S. citizens and their noncitizen family members stay together.
- In order to be eligible, noncitizens must – as of June 17, 2024 – have resided in the United States for 10 or more years and be legally married to a U.S. citizen, while satisfying all applicable legal requirements. On average, those who are eligible for this process have resided in the U.S. for 23 years.
- Those who are approved after DHS’s case-by-case assessment of their application will be afforded a three-year period to apply for permanent residency. They will be allowed to remain with their families in the United States and be eligible for work authorization for up to three years. This will apply to all married couples who are eligible.
- This action will protect approximately half a million spouses of U.S. citizens, and approximately 50,000 noncitizen children under the age of 21 whose parent is married to a U.S. citizen.
Easing the Visa Process for U.S. College Graduates, Including Dreamers
- President Obama and then-Vice President Biden established the DACA policy to allow young people who were brought here as children to come out of the shadows and contribute to our country in significant ways. Twelve years later, DACA recipients who started as high school and college students are now building successful careers and establishing families of their own.
- Today’s announcement will allow individuals, including DACA recipients and other Dreamers, who have earned a degree at an accredited U.S. institution of higher education in the United States, and who have received an offer of employment from a U.S. employer in a field related to their degree, to more quickly receive work visas.
- Recognizing that it is in our national interest to ensure that individuals who are educated in the U.S. are able to use their skills and education to benefit our country, the Administration is taking action to facilitate the employment visa process for those who have graduated from college and have a high-skilled job offer, including DACA recipients and other Dreamers.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Today Is the Longest Day of the Year in the Northern Hemisphere
We have Earth’s off-kilter tilt to thank for the summer solstice, as well as the different seasons.

By Katrina Miller
On Thursday, everyone in the northern half of our planet will experience the summer solstice. It’ll be the longest day of the year north of the Equator, and it is the scientific start of summer.
Earth has a solstice every six months, in June and in December. Leading up to the summer solstice, the sun appears in a higher spot in the sky at the same time each day until it reaches its maximum point.
After the summer solstice, the days will get shorter. The sun will appear lower in the sky each day until the winter solstice, on Dec. 21.
What time is the summer solstice this year?
According to the National Weather Service , the summer solstice will occur on Thursday at 4:51 p.m. Eastern time. This is the moment during the day when the sun reaches its most northern point in the sky during the year.
Why do we have solstices?
The sun’s height in the sky each day changes because Earth spins on an axis that is tilted 23.5 degrees away from vertical. This means that depending on the time of year the hemispheres lean either toward or away from the sun.
This is what gives Earth its seasons: When the northern half of the planet leans toward the sun, it experiences summer; at the same time, the southern half of the planet leans away from the sun, and is in winter. It is a mystery why Earth is angled this way, though some astronomers believe that its tilt paved the way for life to exist .
In the Northern Hemisphere, the summer solstice happens when Earth’s tilt toward the sun is greatest. Despite this, the hottest temperatures of the year usually occur a few weeks later , in July or August, because it takes time for the sun’s rays to warm our planet.
Do other planets in our solar system have solstices?
Any planet that is tilted will have solstices. According to NASA , every planet in our solar system has an axial tilt, but some are more pronounced than others.
Venus and Jupiter have only slight leans, around 3 degrees, while Mercury, at 0.03 degrees, is barely slanted at all. On the other hand, Uranus is oriented a whopping 97.8 degrees from vertical, causing one of its poles to point directly at the sun at times. That extreme tilt causes it to have some of the most dramatic seasons in our solar system.
Saturn and Neptune both have tilts close to Earth’s. So does Mars, at 25.2 degrees, although the red planet’s tilt has shifted dramatically over millions of years .
How do people celebrate the summer solstice?
Every year, people around the world ring in the June solstice with midsummer bonfires, festivals and — for those living above the Arctic Circle — midnight sun celebrations . At the other end of the world, scientists living in Antarctica throw their annual midwinter feast to commemorate the longest, darkest night on the continent.
Others travel to ancient ruins, like Stonehenge in England or the Temple of the Sun in Peru, to greet the solstice sun the way ancient peoples once did.
Katrina Miller is a science reporter for The Times based in Chicago. She earned a Ph.D. in physics from the University of Chicago. More about Katrina Miller
What’s Up in Space and Astronomy
Keep track of things going on in our solar system and all around the universe..
Never miss an eclipse, a meteor shower, a rocket launch or any other 2024 event that’s out of this world with our space and astronomy calendar .
The company SpaceX achieved a key set of ambitious goals on the fourth test flight of a vehicle that is central to Elon Musk’s vision of sending people to Mars.
Euclid, a European Space Agency telescope launched into space last summer, finally showed off what it’s capable of with a batch of breathtaking images and early science results.
A dramatic blast from the sun set off the highest-level geomagnetic storm in Earth’s atmosphere, making the northern lights visible around the world .
With the help of Google Cloud, scientists who hunt killer asteroids churned through hundreds of thousands of images of the night sky to reveal 27,500 overlooked space rocks in the solar system .
Is Pluto a planet? And what is a planet, anyway? Test your knowledge here .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1: Predestination Paradox. A Predestination Paradox occurs when the actions of a person traveling back in time become part of past events, and may ultimately cause the event he is trying to prevent to take place. The result is a 'temporal causality loop' in which Event 1 in the past influences Event 2 in the future (time travel to the past ...
Chang'an, Han Dynasty. The origin of The Silk Road and a golden age in Chinese history, when Confucian principles laid down the foundation for society and Buddhism was just beginning to spread. Travel west along this trade route and in a matter of months, you'll reach the Roman Empire. 7. Chichen Itza, 5th century.
One attempt at resolving time travel paradoxes is theoretical physicist Igor Dmitriyevich Novikov's self-consistency conjecture, which essentially states that you can travel to the past, but you cannot change it. According to Novikov, if I tried to destroy my time machine five minutes in the past, I would find that it is impossible to do so.
Doc Brown and Marty McFly in "Back to the Future." Universal Pictures. Time travel is possible based on the laws of physics, according to researchers. But time-travelers wouldn't be able to alter ...
Wormholes also have the somewhat mystical ability to allow backwards time travel. If you take one end of the wormhole and accelerate it to a speed close to that of light, it will experience time dilation — its internal "clock" will run slower than the rest of the universe. That will cause the two ends of the wormhole to no longer be ...
According a new paper from researchers at the University of Queensland, even if time travel were possible, the paradox couldn't actually exist. Researchers ran the numbers and determined that even ...
Time isn't the same everywhere. Some scientists are exploring other ideas that could theoretically allow time travel. One concept involves wormholes, or hypothetical tunnels in space that could create shortcuts for journeys across the universe.If someone could build a wormhole and then figure out a way to move one end at close to the speed of light - like the hypothetical spaceship ...
In Summary: Yes, time travel is indeed a real thing. But it's not quite what you've probably seen in the movies. Under certain conditions, it is possible to experience time passing at a different rate than 1 second per second. And there are important reasons why we need to understand this real-world form of time travel.
Welcome to Time Travel Events UPCOMING SHOWS. Day-Glo June 1, 2024. Join us for a night out feeling without the late night finish. Cryptid High Tea June 8, 2024. Tea, biscuits, entertainment, and most of all.... cryptid stories. Atlanta Cosplay Yard Sale August 24, 2024.
"The maths checks out - and the results are the stuff of science fiction," said physicist Fabio Costa from the University of Queensland, who supervised the research. Fabio Costa (left) and Germain Tobar (right). (Ho Vu) The research smoothed out the problem with another hypothesis, that time travel is possible but that time travelers would be restricted in what they did, to stop them ...
Time Travel. Time travel is commonly defined with David Lewis' definition: An object time travels if and only if the difference between its departure and arrival times as measured in the surrounding world does not equal the duration of the journey undergone by the object. For example, Jane is a time traveler if she travels away from home in ...
The answer is simply light. The term "light-year" shows up a lot in astronomy. This is a measure of distance that means exactly what it says - the distance that light travels in one year. Given that the speed of light is 186,000 miles (299,000 kilometers) per second, light can cover some serious ground over the course of 365 days.
Time travel has long fascinated us, and while the flux capacitor might still be a work in progress, the allure of witnessing historic events firsthand remains strong. Many users on a social media ...
Time travel and parallel timelines almost always go hand-in-hand in science fiction, but now we have proof that they must go hand-in-hand in real science as well. General relativity and quantum ...
World Clock Meeting Planner. Find the best time to call people in other time zones. Please note: if some of the participants are in the United Kingdom, you should select a city there (e.g., London), instead of UTC/GMT. The United Kingdom is one hour ahead of GMT during Daylight Saving Time (DST), and this service will adjust for DST automatically.
Time Travel. First published Thu Nov 14, 2013; substantive revision Fri Mar 22, 2024. There is an extensive literature on time travel in both philosophy and physics. Part of the great interest of the topic stems from the fact that reasons have been given both for thinking that time travel is physically possible—and for thinking that it is ...
In the lab, muon particles typically decay in 2.2 microseconds. But fast moving muons, such as those created when cosmic rays strike the upper atmosphere, take 10 times longer to disintegrate. 2 ...
On July 20, 1969, the first human set foot on the moon. The moon landing was, according to Neil Armstrong, "one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind." NASA's amazing technological feat fulfilled President Kennedy's challenge to put a man on the moon and showed humans' ability to reach beyond our planet.
17. Fringe. Fox. Like "Lost", "Fringe" is considered one of the most binge-worthy sci-fi shows of all time but the fact that it isn't exclusively about time travel means it lands near the tail end ...
Time travel is the hypothetical activity of traveling into the past or future. ... The non-scientific term timeline is often used to refer to all physical events in history, so that where events are changed, the time traveler is described as creating a new timeline. Early science fiction stories feature characters who sleep for years and awaken ...
20. Queen at live aid in 1985, from the footage you can tell it was an amazing event but to be there and experience it must have been something else. -Duldain92. 30 January 1969, the Beatles playing on the roof of the Apple building in London. -galvinonthewing. 20/20.
Public Transportation. Those attending the parade are strongly encouraged to use public transportation. Riders can find more information on MBTA service, parking, paying fares, and more during Friday's Celtics Championship Parade on the MBTA's website.. The MBTA will have increased subway service and modified Commuter Rail schedules with additional train times before and after the parade.
A person who claims to be a time traveler from the future warns that five major events, from WW3 to a supervolcano, are still yet to come in 2024. Naturally, the time traveler shared his frightening revelations about the future on TikTok where he goes by the user name "Radianttimetraveler.". "Attention!
The following description was submitted by the event organizer. Join Adventure Chef Adam Glick at Powell's Beaverton for a meet-and-greet and book signing of his debut cookbook Live Free, Eat Well: Elevated Cuisine for Outdoorsy Travelers and Modern Nomads. Just in time for the season's outdoor adventures, camping trips, and holidays like 4th of July comes a beautifully imagined cookbook ...
PANAMA CITY, Fla. (WJHG/WECP) -A look at some local architecture with historian Bill Hudson in this weeks' Time Travel Tuesday. If you are looking to chat about local history, you can contact ...
Failing to card a single under-par round in a tournament for the first time in his professional career, Scheffler looks to get back on the wagon and capture his sixth victory of the season.
Frodo on Mount Doom deciding he wanted to keep the RING :D. Alexander The Great the day he died. The Sinking Of The Titanic. The trail of a suspect in the murder of Carrie Brown. 17 votes, 74 comments. 47M subscribers in the AskReddit community. r/AskReddit is the place to ask and answer thought-provoking questions.
This year, the D23 Fan Event will take place between August 9 and 11 at the Anaheim Convention Center and Honda Center. As a central hub, most of the event's main activities will take place at the ...
Since his first day in office, President Biden has called on Congress to secure our border and address our broken immigration system. As Congressional Republicans have continued to put partisan ...
What time is the summer solstice this year? According to the National Weather Service, the summer solstice will occur on Thursday at 4:51 p.m. Eastern time. This is the moment during the day when ...