- svg]:stroke-accent-900"> 826K
- svg]:stroke-accent-900"> 622K
- svg]:stroke-accent-900"> 246K
- svg]:stroke-accent-900"> 45K

Why Is My Circuit Breaker Tripping? 4 Potential Problems and Solutions
By Glenda Taylor , Bob Vila , Evelyn Auer
Updated on Jun 17, 2024 2:08 PM EDT
6 minute read
We may earn revenue from the products available on this page and participate in affiliate programs. Learn More ›
What You Need to Know
- A tripping circuit breaker could be a sign of an overloaded circuit, a short circuit, a ground fault, or a worn-out breaker.
- Homeowners will want to hire an electrician to determine the cause of the frequently tripping circuit breaker.
- Electricians may recommend replacing the circuit breaker, installing GFCI outlets, or rewiring part or all of the home.
Q: Every few hours—sometimes minutes!—my living room and one side of my kitchen lose electrical power. I’ll check the breaker panel and, sure enough, a circuit breaker has tripped…again. Should I call an electrician, or is there a simple DIY fix I can try first?
A: While it’s frustrating when a circuit breaker keeps tripping, they are important safety mechanisms. Designed to shut off the electrical current when something goes wrong, circuit breakers are one of the best ways of protecting a home from an electrical fire. “When a circuit breaker trips, typically it is because we use too much electricity, which causes it to overload and turn off,” says Christopher Haas, expert electrician and owner of Haas & Sons Electric in Millersville, Maryland. For those who need an electrical panels 101 refresher course or aren’t sure how to reset circuit breakers, each breaker has an on/off switch and controls a separate electrical circuit in the home. When a breaker trips, its switch automatically flips “off,” and it must be manually turned back on to restore electricity to the circuit. For those wondering, “Is it dangerous if a circuit breaker keeps tripping?” the answer is that it can be, depending on the source of the problem. An electrician can ultimately deal with the root issue, but a little sleuthing will reveal whether it’s something that’s easily remedied.
In many cases, the cause of a circuit breaking tripping is an overloaded circuit.
A circuit overloads when more electrical current is being drawn through the wires than they can handle, tripping the circuit breaker. If this happens, there may be a few additional signs:
- Buzzing noises coming from outlets
- Devices charging slowly
- Electrical outlets not working
- Flickering lights
- Scorch marks on outlets and light switches
If a circuit breaker keeps tripping in one room, homeowners can test for circuit overload by turning off all the switches in the affected area and unplugging all appliances and devices. After the breaker is flipped back on, the devices can be turned back on one at a time, with homeowners waiting a few minutes in between to see if the circuit remains on. If the breaker trips before all the appliances are turned on, the experiment can be repeated, this time turning them on in a different order. It may be necessary to do this several times to find out how many appliances can be operated at once before the circuit overloads.
“As a short-term solution, you can unplug unnecessary appliances to prevent tripping circuit breakers. You may still get some trips, but you can limit them by unplugging devices that you don’t need to use,” advises Dan Mock, vice president of operations at Mister Sparky , an electrical company with 90 locations in the U.S. The best long-term solution, however, is to pay an electrician for the cost to rewire the house and add additional circuits. The cost to replace an electrical panel is about $1,274 on average.
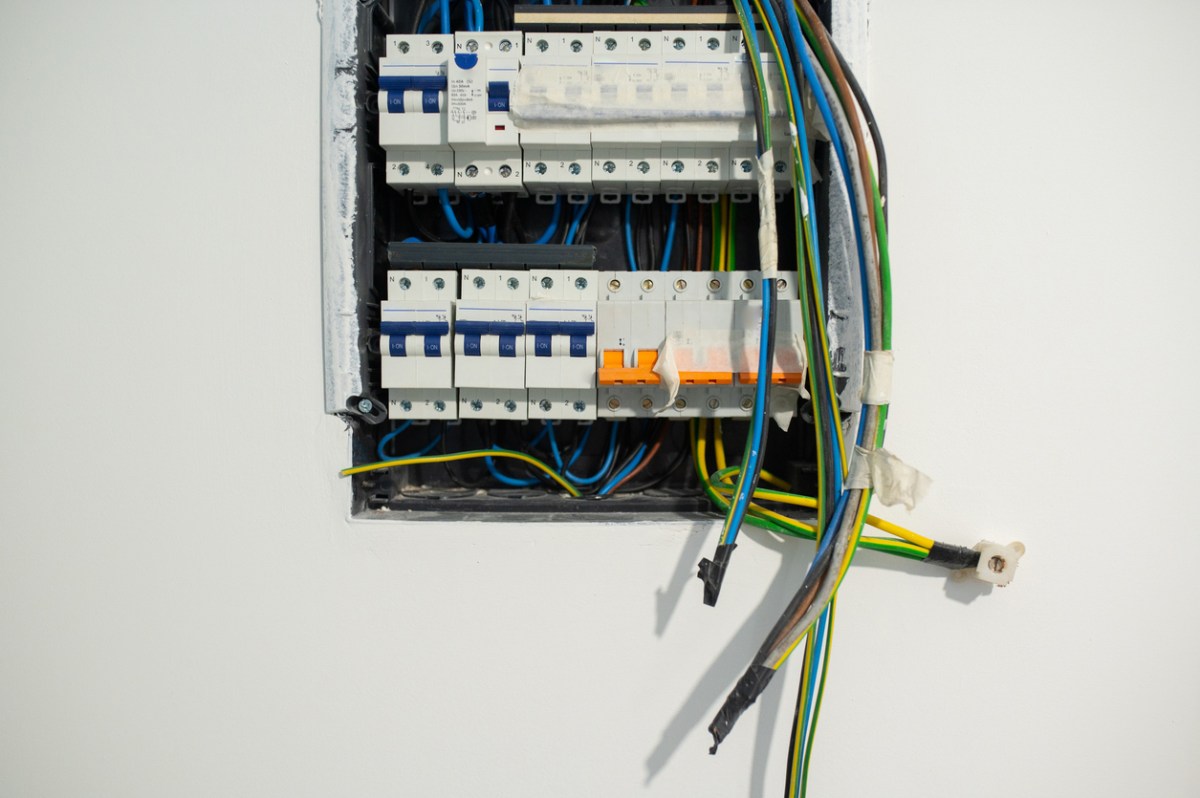
Other times, the issue may be caused by a short circuit.
A “short” circuit means that two wires that should not be coming into contact are inadvertently touching, triggering a sudden surge of electricity through the wires. A short can occur in an outlet, a switch, or within an appliance if wires are loose or have been chewed through by mice or pets. Some signs of a short circuit include:
- Popping sounds
- Discolored outlets or switches
- Burning smells
Testing to see if an appliance has a short is similar to testing for an overloaded circuit. When an appliance that has a short in its wiring is turned on, it will immediately trip the circuit. Homeowners can also try plugging it into an outlet in a different room. If the breaker for that room trips, there’s a short in the appliance (if it’s unclear what breaker goes to what room, the breaker can be identified with one of the best circuit breaker finders ). Electrical shorts can be a major fire hazard, so it’s a good idea to call a licensed electrician for this circuit breaker repair. It’s wise to stop using the outlet or appliance until a pro takes care of the problem.
Another potential cause of a circuit breaker tripping is a ground fault.
A ground fault occurs when the electricity running through a home’s wiring diverts from the wiring loop and travels to the ground, usually due to faulty wiring or water infiltration in an outlet or switch box. Water is a conductor, which is why walking through puddles is often listed as something not to do in a power outage in case of downed power lines. Once water makes contact with wires, electricity can jump from the wiring loop and follow the water trail. This creates a surge in electricity leading to a tripped circuit breaker. If a person comes in contact with the electricity that is on its way to the ground, this can result in electrocution. Homeowners may notice a few signs of a ground fault, including:
- Tripped GFCI (ground fault circuit interrupter) outlets;
- A burning smell coming from an outlet; and
- Lights flickering.
Newer electrical breakers have features designed to protect against the danger of ground faults. According to Haas, “Ground fault breakers sense electricity going to earth as opposed to going through the wires of the circuit. You’ll find [these] for bathrooms, kitchens, garages, exteriors, and basements.” GFCI outlets are another safety feature that shut off the electric current within a fraction of a second of sensing a ground fault.
If a ground fault is the problem, the cause of the errant water must be discovered and repaired, and any damaged wiring must also be replaced. It’s also a good idea to install GFCI outlets in rooms where water is commonly used. A GFCI outlet costs $210 on average.
Sometimes a bad or worn-out circuit breaker can be the culprit.
In some cases, the circuit breaker itself may be faulty. Breakers that are old, damaged, or were installed incorrectly may trip frequently for no apparent reason. Alternatively, faulty breakers may not trip when they are supposed to, leaving the home at risk of electrical fire. Some signs of a bad circuit breaker include:
- The circuit breaker getting hot and tripping frequently;
- The circuit breaker won’t reset;
- It has been over 10 years since the breaker was last serviced; and
- The breaker has scorch marks.
An important electrical safety tip to keep in mind is that resetting a breaker over and over again can cause what is called an arc flash, which is a small electrical explosion that can be deadly. If resetting the breaker once does not remedy the issue, it’s a good idea for the homeowner to hire an electrician near them who knows how to replace a circuit breaker safely. Mock warns, “Don’t take any chances with circuit breakers. Instead, call a licensed electrician who knows the safe ways to replace breaker boxes, upgrade circuits, and diagnose potential electrical problems in your home.” Wiring a breaker box is a job to leave to an experienced electrician.
A professional electrician can help determine the specific cause of a frequently tripping circuit breaker.
Most circuit breaker problems—aside from those explained in the sections above—will need to be inspected and addressed by a licensed electrician. According to the Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI) , each year “thousands of people in the United States are critically injured and electrocuted as a result of electrical fires, accidents, [or] electrocution in their own homes.” While homeowners may be tempted to save on electrician costs by attempting circuit breaker replacement or repair themselves, electrical work is not suitable for casual DIYers. “Yes, you have to pay, but you can save many hours of head-scratching by hiring an electrician. Electricians will also have all the right tools for diagnosing and repairing the circuit,” Haas adds. “Lastly, they will come with a warranty/guarantee should something arise, and they will typically return at no additional cost.”
Your Biggest Questions About Heat Pumps, Answered Your Biggest Questions About Heat Pumps, Answered
By Tony Carrick
Anker’s New Home Battery Tower Is a Sleek, Modular Step Toward Complete Energy Independence Anker’s New Home Battery Tower Is a Sleek, Modular Step Toward Complete Energy Independence
By Chase Brush
855-695-1195
Schedule Service

Top 5 Reasons Your Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping: Effective Solutions to Common Electrical Issues
A circuit breaker that repeatedly trips is more than just an annoying inconvenience; it’s a sign of an issue within your electrical system that requires attention. The circuit breaker’s primary role is to safeguard your home from electrical hazards, so when it trips, it’s doing its job to prevent potential electrical fires or other dangers. Several factors can cause your breaker to trip, including circuit overload, short circuits, ground faults, or a malfunctioning breaker itself. Understanding why your circuit breaker trips and how to address the problem not only can save you from persistent trouble but also help ensure the safety of your home.
Troubleshooting the reasons behind a tripping circuit breaker is a critical skill for homeowners. It involves interpreting the signs your electrical system presents and knowing how to reset the breaker correctly. While some issues, like resetting a tripped breaker or reducing an overloaded circuit, are within the realm of DIY fixes, others, such as dealing with short circuits or faulty wiring, require the expertise of a licensed electrician. It’s essential to know when to tackle the problem yourself and when to call professionals for help, ensuring that you maintain a safe and functional electrical system.
Key Takeaways
- Identifying the cause of a tripping circuit breaker is crucial for safety and system integrity.
- Resetting a tripped breaker involves following proper steps to ensure electrical safety.
- Knowing when to consult a professional electrician is important for troubleshooting complex circuit breaker issues.
Understanding Circuit Breakers and Their Function
In this section, you’ll learn precisely what a circuit breaker is and how it functions as a safety mechanism to prevent electrical fires.
What is a Circuit Breaker?
A circuit breaker is an automatic electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by excess current resulting from an overload or short circuit. It works by interrupting the flow of electricity upon detecting a fault condition. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset to resume normal operation.
How Circuit Breakers Prevent Electrical Fires
Circuit breakers play a crucial role in maintaining your safety by mitigating fire hazards. If an electrical overload or short occurs, a breaker will “trip”, effectively cutting off power to the affected circuit. This interruption in electrical flow stops excessive current that can cause overheating, which if left unchecked, could result in electrical fires. By acting as a safeguard, circuit breakers help to preserve both your electrical system and your physical safety
Reasons for Circuit Breaker Tripping
When your circuit breaker trips, it’s often due to preventable electrical issues within your home. Understanding why this happens is the first step in addressing the problem.
1. Overloaded Circuits
Overload occurs when you demand more electrical power from a circuit than it can handle. Common signs of an overloaded circuit include appliances that seem underpowered or lights that dim when you use other appliances. To rectify this, try:
- Unplugging unnecessary devices to reduce the electrical load.
- Spreading high-energy appliances across different circuits.
2. Short Circuits
A short circuit is a more serious issue marked by two wires touching that should not—an occurrence potentially hazardous and a common reason for tripping . This can result from a variety of issues including damaged wires or faulty appliances. If you notice a burning smell or scorched outlets, the next steps include:
- Powering off the circuit.
- Inspecting your appliances and wiring for damage.
- Seeking professional help if you’re not experienced with electrical work.
3. Ground Faults
Ground faults are similar to short circuits but involve a hot wire touching a ground wire or metal box. They often occur in areas at risk for moisture intrusion, such as kitchens or bathrooms. Manage ground faults by:
- Testing GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlets regularly.
- Keeping appliances away from water sources.
- Consult with an electrician to ensure proper grounding of all outlets.
4. Power Surges
External power surges due to lightning or changes in the power grid and internal surges, when high-power appliances turn on and off, can trip breakers.
5. High-Power Appliances
High-power appliances like microwaves, hair dryers, and air conditioners can trip breakers, particularly if other devices are used on the same circuit simultaneously.

How to Properly Reset a Tripped Breaker
If you’re faced with a tripped breaker, it’s crucial to approach the reset process with a focus on electrical safety to avoid hazards. Ensuring you follow the proper steps can safeguard both your well-being and your home’s electrical system.
Assessing the Safety Before Resetting
Firstly , verify that there is no apparent danger in your surroundings. If you notice any unusual signs, such as scorch marks on outlets or a burning smell, do not attempt to reset the breaker; instead, consult a professional electrician. Additionally, ensure that the area around your electrical panel is dry to prevent the risk of electric shock.
Step-by-Step Reset Process
follow these steps to reset your tripped breaker:
- Identify the Tripped Breaker : Look for the breaker that is positioned in the middle, indicating that it has tripped.
- Unplug Devices : Before resetting, unplug all devices connected to the tripped circuit to prevent further overload when the power is restored.
- Reset the Breaker : Flip the tripped breaker firmly to the ‘Off’ position and then to the ‘On’ position.
By taking these measures, you can reset your breaker safely and effectively. Remember to always prioritize safety when dealing with electrical issues. If the breaker trips again after you have reset it, or if you are unsure at any stage, it is essential to contact a qualified electrician.
Preventive Measures and When to Call a Professional
To ensure the safety and reliability of your home’s electrical system, adopt a proactive approach. Regular maintenance can prevent circuit breaker issues while recognizing when professional intervention is necessary can save you from more extensive problems.
Regular Maintenance and Inspections
Conducting regular maintenance on your electrical system is pivotal to preventing unexpected circuit disruptions. At least once a year, inspect your electrical wiring, looking for signs of wear and tear. Test safety devices like GFCI outlets periodically to confirm they’re functioning properly.
Upgrading Your Electrical System
If your home is older, it may be time to consider upgrading your electrical system. This could include replacing old wiring that can’t handle modern electrical loads or adding additional circuits. Upgrades provide not only enhanced safety but also improved functionality for your everyday power needs.
Hiring a Licensed Electrician
In certain scenarios, it’s crucial to entrust the job to a professional electrician like Kaminskiy Care and Repair. Tasks like diagnosing frequent breaker trips, repairing faulty wiring, or upgrading your electrical panel should be handled by a qualified electrician to ensure the work adheres to code and maintains your safety.
Understanding why your circuit breaker keeps tripping is essential for maintaining a safe and functional electrical system in your home. From overloaded circuits to faulty appliances, each cause has a specific solution. Regular checks and maintenance can help you avoid these issues and the inconveniences they bring.
For expert advice and professional service, contact Kaminsky Care and Repair. Our skilled electricians can help you diagnose and fix any electrical issues, ensuring your home remains safe and your power is uninterrupted. Trust us to provide reliable solutions tailored to your needs. Remember, dealing with electrical systems can be hazardous. Always consider professional help for complex issues to ensure safety and efficacy.
Frequently Asked Questions
When addressing issues with your circuit breaker, understanding the potential causes of tripping can be crucial in finding the right solution.
Even with no appliances connected, your circuit breaker may trip due to wiring issues such as a ground fault or damage to the insulation of the wires within the affected circuit.
A circuit breaker that frequently trips could signify a serious electrical problem, such as a potential fire hazard due to overloaded circuits or faulty wiring.
If your breaker trips immediately after resetting, this could indicate a direct short circuit or a ground fault in one of the connected appliances or within the circuit wiring itself.
Check for overload by unplugging all devices and then reconnecting them one at a time. Also, inspect outlets and switches for signs of damage, scorch marks, or loose connections.
Yes, a circuit breaker can trip after a period due to a slow-building overload or a thermal trip caused by a heating issue within the breaker itself.
Begin by documenting when the trips occur to identify any patterns. Then, systematically test the devices and outlets on the circuit, looking for worn cords or plugs, and inspect the breaker itself for signs of damage or wear.
10 Steps to Take When Your Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping

What is a Circuit Breaker?
Take these 10 steps if your circuit breaker keeps tripping..
- Step 1: Identify the cause
- Step 2: Unplug appliances and devices
- Step 3: Reset the circuit breaker
- Step 4: Observe for immediate re-tripping
- Step 5: Determine the load
- Step 6: Assess the electrical load
- Step 7: Divide the load
- Step 8: Address wiring issues
- Step 9: Consider professional assistance
- Step 10: Maintain regular electrical inspections
Who should I call for an electrical repair service?

Are you tired of sweltering summers and costly AC repairs? If so, you're not alone. Many homeowners grapple with the decision of whether to invest in an ac main...

Bringing color into your home interior is a great way to add personality, warmth, and visual interest to your living space. Whether you're starting with a blank...

Without electricity, the modern world would cease to exist. However, we must take proper precautions and maintain our electrical systems for safe consumption - ...

1335 Martin Luther King Jr Ave
Dunedin, fl 34698, (727) 648-6101.

1335 Martin Luther King Jr Ave, Dunedin, FL 34698
CALL US: (727) 648-6101

5 Reasons Your Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping and What You Can Do About It
Keep losing power, and aren't sure why here are five of the most common reasons why a circuit breaker keeps tripping, and what you can do to fix the problem..

1. Ground Fault
2. short circuit, 3. circuit overload, 4. arc fault, 5. damaged breakers, circuit breaker keeps tripping.
Newer Post >
Buell Electric's Blog

Shedding Light on Your Home: Finding the Right Electrician in Tampa

How Electricians Keep Up with Changing Technology in the Industry

The Importance of Regular Electrical Maintenance For Your Business

Marine Electrical Standards and Regulations You Need to Know

The Benefits of Installing a Smart Home System

Understanding the Different Types of Electrical Wiring in Your Home
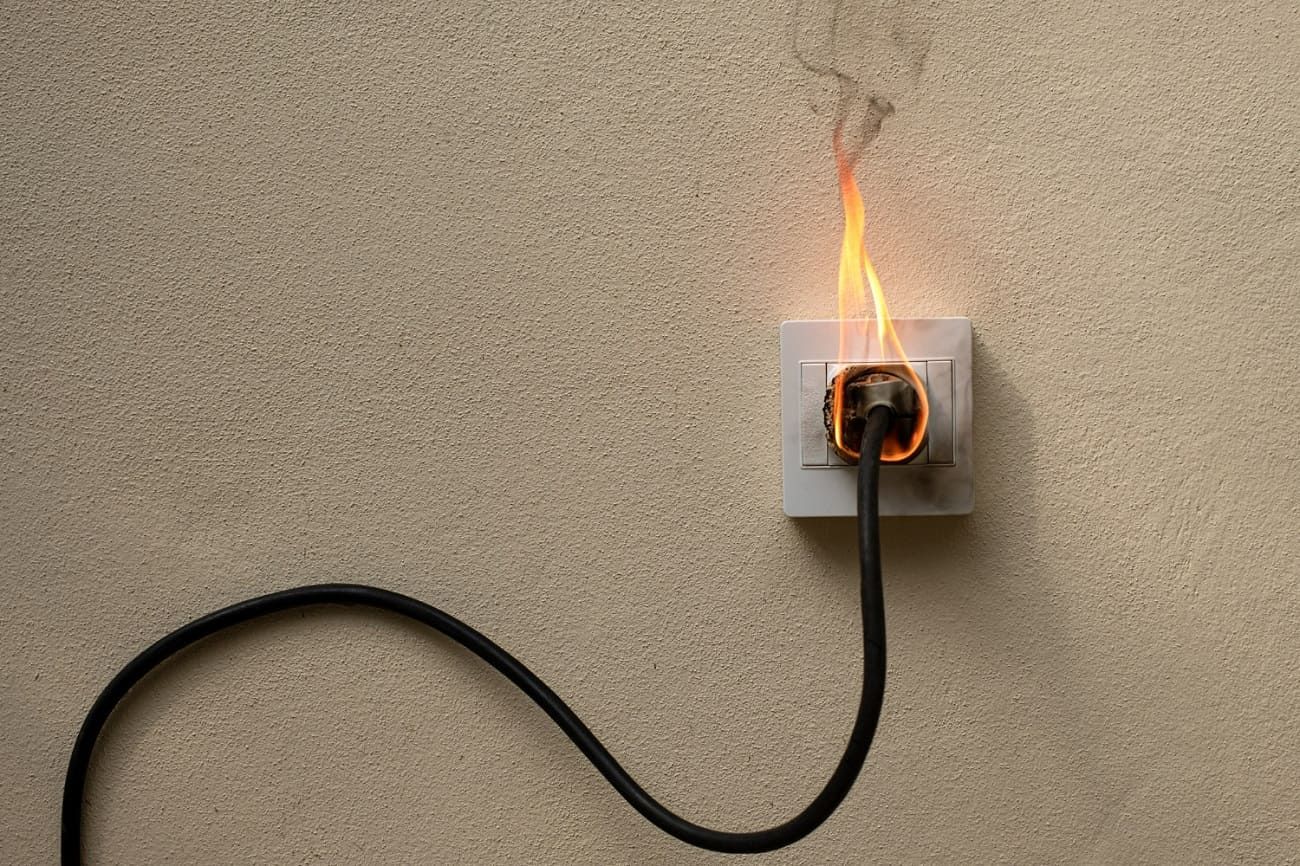

How to Prepare Your Home for an Electrical Emergency

5 Reasons Your Ceiling Fan Installation Should be Left to the Pros

5 Tips for Hiring Residential Electrical Services

8 Common Outdoor Lighting Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
[email protected]
Mon-fri 9:00 am - 5:00 pm sat-sun 10:00 am - 5:00 pm privacy page, connect with us:.

Mon-Fri 9:00 AM - 5:00 PM Sat-Sun 10:00 AM - 5:00 PM
All Rights Reserved | Buell Electric, Inc.

WhatsApp Our Local Electrician To Get a Fast Response & Quote For Your Electrical Needs.

What Causes Circuit Breakers To Trip?
- June 1, 2024
If your circuit breakers are often tripping, there’s no need to worry. This is a typical issue. Below, you’ll find reasons why this occurs and tips for avoiding it going forward. Get a handle on your circuit breaker issues!
Table of Contents
Understanding Circuit Breaker Tripping
Circuit breakers are protection devices for electrical circuits. When too much current passes, the breaker trips, stopping the flow of electricity and preventing damage. This can be caused by faulty wiring, too many appliances on one circuit, or a ground fault.
Overloading can cause tripping. This happens when too many devices are connected to a single circuit. Heat builds up in the wires, which can start fires or cause damage. To prevent this, distribute loads across multiple circuits and don’t connect too many appliances to one outlet.
Short circuits also lead to tripping. This happens when two wires with opposite charges come in contact or when a wire touches something grounded. This causes an immediate surge in current that triggers the breaker. Check for exposed wires or insulation damage, and call an electrician if you spot any signs of trouble.
Ground faults can also cause tripping. This happens when there’s an unintentional connection between a live wire and a conductive surface. Install GFCIs to avoid this.
In short, know what causes circuit breakers to trip. Identify potential hazards like overloading, short circuits, and ground faults. Take steps to prevent accidents and ensure your electrical equipment is safe. If you’re unsure how to handle electrical problems, call a licensed electrician.
Overloading Causes
Circuit breakers trip to stop overheating, electrical fires, and damage to electrical parts. Plugging in too many devices can cause the circuit to become overloaded, so the breaker trips to cut off the power.
Short circuits are like a blind date gone wrong. They can be explosive, and often end in disaster. This happens when a hot wire comes into contact with a neutral or insulation/water. This throws off the electric balance, causing danger and tripping.
Short Circuit Causes
A short circuit happens when a low-resistance path appears between two points in the circuit that aren’t usually connected. This can cause too much current to flow, making a circuit breaker trip. Insulation or wiring damage, faulty appliances, and circuit overload are the most common reasons for a short circuit. It’s critical to identify and fix the root cause quickly to avoid electrical fires and other dangers .
When too much power passes through a circuit, the circuit breaker will automatically turn off. It’s designed to protect wiring and guard against electrical accidents . But if the breaker trips regularly, there may be underlying issues that need investigation and repair. Often times, this means upgrading or replacing components.
Sometimes short circuits are caused by human error or wear and tear. But they may also come from design or installation problems. Planning and upkeep from local electricians can keep electrical systems running safely and appropriately for a long time. If your circuit breaker is tripping a lot, get an experienced technician to review your system and suggest solutions that match your needs and budget .
Overheating Causes
Circuit breakers are essential safety features. They stop electrical fires and protect your appliances. When overloaded, too much current flows, producing heat. This causes the breaker to trip!
Other factors can cause overheating. Damaged insulation on wires increases resistance. Loose connections add resistance and heat. High temperatures and poor ventilation worsen the situation.
It’s important to maintain and service the electrical system. Checks of all components will make sure they work efficiently. To avoid tripping, prevent overheating. This will reduce energy consumption and safeguard equipment. So, let’s learn about circuit breakers and how they deal with overloads!
Circuit Breaker Types
Circuit breakers are essential for any electrical system. They prevent overloaded and faulted circuits . There are different types of circuit breakers suitable for specific electrical loads.
See the table below for the different types of circuit breakers and their functions:
It is crucial to select the right type of breaker. Each one has its own advantages in specific situations. For instance, thermal circuit breakers are perfect for small appliances like hair dryers or irons . Meanwhile, magnetic circuit breakers are great for bigger loads such as air conditioners or refrigerators .
Remember, circuit breakers are like Beyoncé – they can handle a lot, but have their limits.
Circuit Breaker Ratings and Specifications
Circuit breakers are designed to protect electrical circuits from overloads. To ensure that circuits and appliances are safe, the ratings and specifications of circuit breakers need to be understood.
If a circuit breaker trips often, it may mean there’s an issue. It’s best to get professional help in these cases. Time to go on a hunt for your electrical wiring!
Troubleshooting Circuit Breaker Tripping
Circuit breakers can flip out for multiple reasons, like overloads , short circuits , and ground faults .
Overloads happen when too much electricity passes through the circuit, creating too much heat and tripping the breaker. Short circuits are when two or more wires touch, resulting in extra current. Ground faults occur when the power takes an unexpected route, like through a person’s body.
To figure out why your circuit breaker is tripping, it’s important to figure out what is going on and act accordingly. Inspections and maintenance can also help avoid future tripping.
Stop your circuit breaker from misbehaving with these prevention tips!
Preventing Circuit Breaker Tripping
A circuit breaker tripping can be prevented with understanding. When circuits are overloaded, breakers trip to avoid overheating and potential fires. Here are 3 steps that can help you prevent circuit breakers tripping:
- Know the electrical load – work out how many appliances & devices are connected to one circuit. Don’t overload them by spreading high-energy equipment across multiple circuits .
- Look after your appliances – ensure all your appliances & devices are in good condition, with no damaged cords or frayed wires.
- Upgrade your system – if you’re tripping breakers often you may need to upgrade the electrical system with higher capacity breakers or more circuits.
Plus, investing in surge protectors can also assist in preventing circuit overload and subsequent tripping of breakers. By following these steps you can make sure your home’s electricity runs safely and without interruption due to circuit breakers tripping.
Remember: these precautions will keep you from tripping more than just your circuit breakers!
Safety Precautions
Safety must be taken seriously when dealing with circuit breakers . Always switch off the main power supply before beginning work. Wear protective gear such as insulated gloves and boots to stay safe from electrocution. Never touch wires or components inside the box without proper training. Keep the area around the breaker box free from any flammable substances. Inspect breakers for damage or wear regularly .
Label each circuit breaker correctly . Test them frequently for functionality. This will help identify circuits quickly in case of an emergency. These precautions and practices ensure safety while dealing with circuit breakers. When in doubt, blame it on the circuit breaker – it’s always a good scapegoat for electrical woes!
Circuit breakers are essential components of any electrical system. They stop too much current flowing and thus, protect against potential fires . The most common cause for tripping is overload. But, other causes like short circuits and ground faults can also cause the breaker to trip. When it trips, there is something wrong that needs to be fixed right away.
Short circuits occur when two wires touch each other. This creates a low resistance path which allows a lot of current to flow with no load. Ground faults occur when the hot wire touches something incorrectly wired or with a damaged cord.
To prevent tripping, regular maintenance of the electrical system is needed. Keeping appliances in good condition, replacing worn-out cords and fixtures, and periodically checking for loose wires all help reduce the chances of tripping. In summary, understanding why the breaker trips and taking precautionary measures will keep you safe and save you repair costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what causes a circuit breaker to trip.
There are several possible causes, including overheating due to circuit overload, short circuits, ground faults, and age-related wear and tear.
2. How can I prevent my circuit breaker from tripping?
You can avoid overloading your circuit by keeping the number of electrical appliances used on one circuit to a minimum, regularly checking wires for signs of wear and tear, and not using too many extension cords.
3. What should I do if my circuit breaker keeps tripping?
If your circuit breaker is constantly tripping, it is important to identify and fix the underlying issue. Contact an electrician to inspect and repair any faulty wiring or electrical devices.
4. Can a circuit breaker trip without an overload?
Yes, a circuit breaker can trip due to a short circuit or a ground fault, which may occur without an overload.
5. How do I reset a tripped circuit breaker?
To reset a tripped circuit breaker, turn it off and then back on again. Make sure to identify and correct the underlying issue that caused the trip before restoring power.
6. What is the lifespan of a circuit breaker?
The lifespan of a circuit breaker can vary depending on usage and other factors. However, most circuit breakers last between 10 and 30 years.
Related posts:
- What Causes Power Outages?
- How Do I Know If A Sparking Outlet Is Dangerous?
- Electrical Safety Check When Buying A House in Puchong
- Does Your DB Board Need Repair Or Replacement?
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

- Make A Payment
By clicking submit, you authorize Alure Home Improvements to reach out to you with questions about your project, via phone, email, or text. Message/data rates apply. Consent is not a condition of purchase. You may unsubscribe at any time. Terms & Conditions | Privacy Policy
Why Does My Circuit Breaker Keep Tripping and How to Fix It?

When you notice that the circuit breaker is tripping the first time, it is easy to not worry about this at all. But the more times that this happens, the easier it is to see it as a big problem. Outside of being annoying, it could be a sign that something is wrong with your system.
Working out the exact reason why your circuit continues to trip is a challenge. However, if you know where to look and what may be causing the problem can really make a difference. Some of the reasons why your circuit breaker is tripping and some of the steps you can take to fix this problem include:
Why is My Circuit Breaker Tripping?
There are different reasons why your circuit breaker may be struggling and tripping. This can happen on occasion, but if it does it often, it is a sign that something is wrong. Some of the most common reasons a circuit breaker is tripping includes:
1. The Circuits are Overloaded
The reason this is called a circuit breaker is that it is designed to break up the circuit when too much current tries to run through. For example, if your circuit is designed to be 20 amps and you are running 30 amps to it, the breaker is going to stop this and trip in an effort to keep the home safe .
Often we try to plug too many things into the same circuit. This causes it to overload and will make it hard to protect your home. The circuit breakers will do their best and can trip to do this.
2. You Need to Do a Heavy-Up
Sometimes it is hard to know how much the circuit is able to take or how much your appliances are sending over to the circuit. You may find that the appliance is running way higher than you expected and this can cause the circuit to trip. If this is the cause, it may be time to do a heavy-up.
To keep it simple, a heavy-up is a way to increase the amperage that comes into the home at your service panel. This allows you to upgrade your circuit breakers and electrical system to receive and handle more energy at the same time. If you do this, be prepared for the whole service panel to get replaced with this.
3. The Circuits are Shorting
This could be a serious problem because it relates back to the wiring in the home. There are several wires that are attached to the outlet. When the wires get close enough for two hot wires to touch each other, or a hot wire is able to touch a neutral wire, this causes the circuits to trip.
If this is the main problem with your circuit breaker, then it is important to get someone over to take a look. It will not fix itself and could lead to a lot of damage from a fire inside the home.
4. You Have a Ground Fault
A ground fault will sometimes happen when a hot wire is touching something it shouldn’t, but this time it is touching the metal outlet box. This can be dangerous too and you need to get a professional over to see what is going on and see what your options are to fix it.
5. Faulty Appliances or Bad Wiring
If something is wrong with your appliances or the wiring is not doing well in your home, then this can be enough to make your circuits stop working well. A faulty appliance can cause a circuit over and over again. When this is the case, you should consider replacing the appliance to keep things safe.
If one of your outlets has not been wired well, then it may be enough to make the breaker trip. If you get the same results out of one particular outlet, even when you try to fix it, then a qualified electrician needs to take a look at it for you.
How to Fix Circuit Breakers That Trip
When a circuit breaker trips once or twice, then it is usually not a big deal. This is a sign that there was a surge to the system and it was able to keep your appliances safe. This is what the system is meant to do. When the circuit breaker seems to trip over and over again, then this is a sign that you need to make some changes.
If you have a circuit breaker that seems to trip many times, then there are a few things you are able to do. Often the problem is that too many things are plugged into the same circuit. By unplugging a few of them, you may be able to fix it all.
If you are researching some of the potential issues and notice that only one appliance is making this happen, then unplug that one and add something else there. If you can do this without the circuit tripping, this means that you need to replace that appliance.
In some cases, the issue is going to be from old wiring in your home. Even if it was installed right, there is the potential that it has just gotten old. When this is the case, it is time to call in an electrician to check the wiring and see what is causing the issue. They can help get the wiring up to code to keep you safe.
Taking Care of Your Circuit Breaker
The circuit breaker in your home is an important component. You want to make sure that it is taken care of to ensure all your electricity and appliances always work, without causing damage to the home. When the circuits start to trip, it is a sign that something is wrong.
There are many reasons why your circuit breakers are struggling with tripping and running into problems. When you notice some of the issues above, it is time to take care of the circuits and make sure they get fixed early on.
Gabe Nelson is a content specialist of over 7 years of experience, currently working with baypower.com . Just out of high school he set off crab fishing on the Bering sea in Alaska. From there he went back home to finish his college degree at the University of Montana. He has written hundreds of content pieces in numerous niches. Currently, he lives in Missouri with his wife and kids.
Image by Michal Jarmoluk from Pixabay
- Additions and New Construction
- All Exteriors
- Alterations
- Customer Service
- Customer Stories
- Design & Planning Show
- Educational Resources
- Extreme Makeover Home Edition
- Fashion Show
- General Remodeling
- Green Living
- Handyman Home Services
- Home Entertainment
- Home Improvement
- Home Improvements
- How to Tips
- In The Community
- Off-the-Wall Remodeling Stories
- Social Media
- Tips & Tricks
Time and again, Alure Home Solutions has been recognized as a leader in the remodeling industry for delivering superior work at a great value, along with remarkable customer service. Trust, credibility, peace of mind – these are the bedrocks that our reputation was built on.

Simply fill out the form below and we’ll send the guide to you right away. We are happy to be your friend in the business, so please don’t hesitate to contact us with any questions you may have!

- Custom Kitchens
- 10 Day Kitchens
- Kitchen Cabinets
- Kitchen Countertops Long Island | Alure Home Solutions
- Kitchen Island and Tables | Alure Home Solutions
- Kitchen Galleries
- Custom Bathrooms
- 5 Day Bathrooms
- Walk-In Tubs
- Tub to Shower Conversion
- Aging In Place
- Bathroom Galleries
- Windows Gallery
- Entry Doors | Front Doors | Alure Home Solutions
- Sliding Doors
- Doors Gallery
- Owens Corning Roofing
- Storm Damage Repair
- Roofing Gallery
- About Alure
- Awards & Recognition
- Whitepapers
- Manufacturers
- Community Service
Electrical Repair
Ceiling Fan Repair
Electrical Panel Repair
Emergency Electrician
Lighting Repair Service
Installations
Carbon Monoxide and Smoke Detector Installation
Exhaust Fan Installation Service
Home Backup Generator Services
EV Charger Installation and Service
Outlet Installation
Ballast and Bulb Replacement
Commercial Specialty Lighting
Lighting Controls
Retrofit Lighting
Bathroom and Kitchen Lighting
Chandelier Installation
Motion Sensors
Track and Accent Lighting
Landscape Lighting
Recessed Lighting Installation
Electrical Safety
Electrical Code Updates
GFCI Outlet Installation & Replacement
Circuit Breaker Replacement
Home Wiring Updates
Dedicated Computer Circuits

Beginner’s Guide to Identifying a Tripped Circuit Breaker
Key highlights.
- Understanding the different types of circuit breakers and their functions
- Common reasons for circuit breaker trips: overloaded circuits, short circuits, and ground faults
- Steps to troubleshoot and reset a tripped circuit breaker
- When to call in professional help for persistent tripping or serious electrical issues
- Tips for maintaining your circuit breaker panel to prevent future trips
- FAQs: Why does a circuit breaker keep tripping? Can I replace a circuit breaker myself? How to know if a circuit breaker is faulty? What’s the difference between a circuit breaker and a fuse? Why did my circuit breaker trip? What to do when a tripped breaker is found? What causes a circuit breaker to trip? How to prevent frequent tripping? Can frequent tripping indicate a larger electrical issue in the home? When to call a professional to fix a tripped circuit breaker
Introduction
Hey there! Ever had that moment when all the lights suddenly go out in your home? Yeah, this can be a bit annoying, especially when the big Basketball game is about to start or when you are rushing to get the kids ready for school in the morning! Well, chances are, your circuit breaker decided to take a little break. But don’t worry, it’s actually a safety feature designed to prevent any electrical disasters.
Think of it like your circuit breaker playing superhero, swooping in to save the day when there’s too much electrical action going on. It’s there to protect you from overloads, short circuits, and ground faults, kind of like your own personal electric guardian angel.
Now, I get it, dealing with a tripped circuit breaker can be a bit of a hassle. But fear you’re your Tripp your personal electrical guide from the Doctor Electric Team is here to guide you through the process with some friendly tips and tricks. Consider this your beginner’s guide to tackling those annoying tripped circuit breakers like a pro. So, let’s dive in and get your power back on in no time!
Understanding Circuit Breakers: The Basics
Before we get into finding a tripped circuit breaker, let’s talk about what they are. A circuit breaker is like a traffic cop for electricity in your home’s electrical panel, also called a service panel or breaker box. It controls the electricity flow, keeping your electrical system safe from overloads and problems. If a circuit breaker trips, it’s like it puts up a “stop” sign for electricity to prevent damage or dangerous situations.
What is a Circuit Breaker?
Think of a circuit breaker as your electrical system’s guardian. It’s like a super cool switch that can be turned on or off manually or even flips itself off automatically when it senses weird stuff happening with the electricity.
If the electricity flow gets too intense for the circuit breaker to handle, it does its magic and disconnects the circuit. This way, it prevents the electrical wires and your fancy appliances from getting all hot and bothered or worse, damaged.
Circuit breakers are like the superheroes of your home’s electrical system, making sure everything stays safe and sound, and avoiding those nasty electrical fires and accidents.
Types of Circuit Breakers and Their Functions
Let’s talk about the different types of circuit breakers. Knowing what they do can help you pick the right one for your electrical needs Here are some common types of circuit breakers:
- Magnetic Circuit Breakers: Picture this: a superhero with electromagnetism as their superpower! These circuit breakers use electromagnetic force to trip when the electrical current goes above the limit they’re designed for. They’re like the Flash, super-fast in detecting and reacting to electrical surges.
- Thermal Circuit Breakers: These circuit breakers have metal strips that act as their sensors. When there’s an overload or a fault, the strips heat up, bend, and cut off the power. It’s like a safety valve that keeps the temperature from getting too hot in your electrical system.
- Thermal-Magnetic Circuit Breakers: Think of these circuit breakers as the ultimate protectors. They combine the powers of both magnetic and thermal circuit breakers, providing double the defense against overloads and short circuits. They’re like the Avengers of the circuit breaker world, ready to tackle any electrical challenge.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI): GFCIs are the safety experts when it comes to preventing shocks. They’re designed to detect imbalances in electrical current and quickly interrupt the flow of electricity if it’s taking an unintended path, like through water or a person. They’re like invisible shields protecting us from electrical hazards, especially in areas like bathrooms and kitchens.

Common Reasons for Circuit Breaker Trips
Circuit breakers can sometimes get a little jumpy and trip for various reasons. Let’s explore some of the most common causes and how to prevent them:
Overloaded Circuit: When you cram too many appliances or devices into one outlet, it can cause the circuit to get overloaded and trip the breaker. It’s like a traffic jam in your electrical system. The solution? Spread out your power-hungry friends by using different outlets or try to limit the number of appliances on one circuit.
Short Circuit: Ever seen sparks fly when you plug in a faulty appliance? That’s a short circuit. It happens when the “hot” wire (the one that carries electricity) touches the “neutral” wire (the one that returns electricity). It’s like a shortcut that electricity takes, causing a surge and tripping the breaker. Unplug the faulty appliance and call an electrician if it keeps happening.
Ground Fault: If electricity takes a detour through an unintended path, like a person or water, it’s called a ground fault. It’s like a sneaky escape route for electricity. This can trip the breaker to prevent electrical shocks or fires. If you suspect a ground fault, consult with a qualified electrician for help.
Overloaded Circuits: Recognizing the Signs
An overloaded circuit occurs when you have too many electrical devices or appliances drawing power from a single circuit. This can lead to a tripped circuit breaker and potential hazards. Here are some signs that you may have an overloaded circuit:
- Frequently tripping circuit breaker: If your circuit breaker trips frequently, especially when using certain appliances or devices, it could be a sign of an overloaded circuit.
- Flickering or dimming lights: When you turn on multiple appliances or devices, you may notice your lights flickering or dimming. This indicates that the circuit is struggling to handle the power load.
- Warm electrical outlets: If your electrical outlets feel warm to the touch or emit a burning smell, it could be a sign of an overloaded circuit. This can be dangerous and should be addressed promptly.
To avoid overloading your circuits, distribute the electrical load evenly among different circuits in your home. Consider using power strips with built-in circuit breakers to protect against overloads and ensure that you’re not exceeding the capacity of the circuit. If you frequently experience circuit breaker trips due to an overloaded circuit, it may be necessary to consult a licensed electrician to assess and upgrade your electrical system.
Short Circuits: Identifying and Preventing Risks
A short circuit occurs when a hot wire comes into contact with another hot wire or a neutral wire, causing a surge of electricity. This can be caused by wiring issues, damaged appliances, or faulty electrical connections. Here’s how to identify and prevent short circuits:
- Signs of a short circuit: If you notice sparks, a burning smell, or a sudden loss of power without tripping the circuit breaker, it could be a sign of a short circuit.
- Inspect the wiring: Check for any visible signs of damage, such as frayed wires, loose connections, or exposed conductors. Damaged or deteriorating wiring can increase the risk of short circuits.
- Avoid overloading outlets: Do not plug too many devices into a single outlet, as this can increase the risk of a short circuit. Use power strips with built-in surge protectors to distribute the load evenly.
- Use proper electrical insulation: Ensure that all wires are properly insulated and protected to prevent contact with other wires or surfaces.
- Seek professional help: If you suspect a short circuit or are unsure about the safety of the wiring in your home, it is recommended to consult a licensed electrician who can identify and resolve the issue safely.
Preventing short circuits is essential for the safety of your home and family. Regularly inspect your electrical system, address any wiring issues promptly, and avoid overloading outlets to minimize the risk of short circuits.
Ground Faults: Safety Measures and Solutions
Ground faults occur when electricity flows through an unintended path, such as water or a person. This can result in electrical shocks and fires. Here are some safety measures and solutions to prevent ground faults:
- Install Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs): GFCIs are designed to detect ground faults and quickly interrupt the flow of electricity, protecting against electrical shocks. Install GFCI outlets in areas where water is present, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor outlets.
- Test GFCIs regularly: GFCIs have a built-in test button to ensure they are working correctly. Test them monthly by pressing the test button and verifying that the power is cut off. Reset them afterward to restore power.
- Avoid using electrical devices near water: Keep electrical devices away from water sources to reduce the risk of ground faults. This includes using extension cords and appliances in wet areas.
- Inspect and maintain electrical wiring: Regularly inspect the wiring in your home for signs of wear, damage, or aging. Replace any damaged or worn-out wiring to minimize the risk of ground faults.
- Consult a licensed electrician: If you experience frequent ground faults or are unsure about the safety of your electrical system, it is recommended to consult a licensed electrician for professional inspection and repairs.
By implementing these safety measures and solutions, you can protect yourself and your home from ground faults and ensure the electrical system operates safely.
Beginner’s Guide: Preparing to Troubleshoot Your Circuit Breaker
Before attempting to troubleshoot a tripped circuit breaker, it’s important to prioritize safety. Dealing with electricity can be hazardous, so it’s crucial to take the necessary precautions. Here are some important safety measures to keep in mind when preparing to troubleshoot your circuit breaker:
- Turn off all appliances and devices connected to the circuit that tripped to prevent power surges or electrical shocks.
- Identify the location of your electrical panel or breaker box, usually found in the basement, garage, or utility closet.
- Familiarize yourself with the different circuit breakers in your panel and their corresponding circuits.
- If you’re unsure or uncomfortable working with electrical systems, it’s always best to contact a licensed electrician for assistance.
By prioritizing safety and taking the necessary precautions, you can troubleshoot your tripped circuit breaker effectively and minimize the risk of accidents or further electrical issues.
Safety First: What You’ll Need
To ensure a safe and successful troubleshooting process, it’s important to gather the necessary tools and equipment. Here’s what you’ll need:
- Flashlight: A flashlight will help you see clearly in the electrical panel, especially if it’s located in a dimly lit area.
- Non-contact voltage tester: This tool allows you to check if a circuit is live or if there’s still electricity flowing through it without making direct contact.
- Screwdriver: You may need a screwdriver to remove the cover of the electrical panel and access the circuit breakers.
- Safety gloves and goggles: It’s essential to protect yourself from electrical shocks and debris. Wear safety gloves and goggles to minimize the risk of injury.
- Knowledge of your electrical system: Understand which circuit breakers correspond to specific areas of your home before troubleshooting. If you’re unsure, consult a licensed electrician for guidance.
Keep in mind that electrical work can be dangerous, and if you’re not confident in your abilities or uncomfortable working with your electrical system, it’s always best to consult a licensed electrician to ensure your safety and avoid potential hazards.
Identifying Your Circuit Breaker Panel
Your circuit breaker panel, also known as the breaker box, is the central hub for controlling the electrical circuits in your home. It’s important to locate and identify your circuit breaker panel before troubleshooting a tripped breaker. Here’s how to find it:
- Look for a metal box: Circuit breaker panels are typically housed in a metal box mounted on a wall. Common locations include basements, garages, utility closets, or other designated electrical rooms.
- Check for labels or markings: The circuit breaker panel may have labels or markings indicating which breakers correspond to specific areas of your home, such as kitchen, living room, or bedroom.
- Open the panel cover: Once you’ve located the circuit breaker panel, use a screwdriver to remove the cover and access the circuit breakers.
It’s important to exercise caution when working with your circuit breaker panel. If you’re unsure or uncomfortable, it’s recommended to contact a licensed electrician for assistance in identifying your circuit breaker panel.
Step-by-Step Guide to Resetting a Tripped Circuit Breaker
Resetting a tripped circuit breaker is a simple process that can be done by following a few easy steps. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you reset a tripped circuit breaker safely and effectively:
Step 1: Locating the Tripped Breaker
Step 2: ensuring safety before proceeding, step 3: resetting the circuit breaker, step 4: identifying the cause of the trip.
By following these steps, you can reset a tripped circuit breaker and restore power to the affected circuit. However, it’s important to identify the cause of the trip to prevent further issues and ensure the safety of your electrical system.
The first step in resetting a tripped circuit breaker is to locate the specific breaker that has tripped. Here’s how to do it:
- Locate your electrical panel or circuit breaker box, usually found in a basement, garage, or utility closet.
- Open the panel cover using a screwdriver, exposing the circuit breakers.
- Visually inspect the circuit breakers and look for one that is in the middle position or slightly shifted from the “on” position. This indicates a tripped breaker.
Once you have identified the tripped breaker, make a note of its location and proceed to the next step to ensure safety before resetting it.
Before resetting a tripped circuit breaker, it’s crucial to take safety measures to avoid electrical hazards. Follow these steps to ensure safety before proceeding:
- Turn off all appliances and devices connected to the tripped circuit to prevent power surges.
- If there is a power outage in your home, make sure to determine the cause. If it’s only a specific circuit that has lost power, it’s likely due to a tripped breaker.
- If you’re unsure or uncomfortable working with your electrical system, it’s recommended to contact a licensed electrician for assistance.
By following these safety measures, you can minimize the risk of electrical shocks or accidents while troubleshooting a tripped circuit breaker.
Once you have taken the necessary safety precautions, you can proceed to reset the tripped circuit breaker. Follow these steps to reset the circuit breaker:
- Locate the tripped breaker, which will be in the middle position or slightly shifted from the “on” position.
- Firmly push the tripped breaker to the “off” position and then back to the “on” position.
- If the breaker stays in the “on” position without tripping or feeling loose, it has been successfully reset.
If the breaker does not reset or continues to trip, there may be a more serious issue that requires professional attention. In such cases, it’s recommended to contact a licensed electrician to diagnose and resolve the problem.
After resetting the tripped circuit breaker, it’s important to identify the cause of the trip to prevent future occurrences. Here are some common causes of circuit breaker trips and how to determine the cause:
By identifying the cause of the trip, you can take appropriate measures to address the issue and prevent future circuit breaker trips. However, if you’re unsure or unable to determine the cause, it’s best to consult a licensed electrician for professional assistance.
When to Call in the Professionals
While resetting a tripped circuit breaker can often be done by homeowners, there are certain situations where it’s best to call in a professional electrician. Here are some instances when you should consider contacting a licensed electrician:
- Persistent Tripping: If your circuit breaker trips frequently, even after resetting it, there may be an underlying electrical problem that requires professional attention.
- Serious Electrical Issues: If you notice signs of serious electrical issues, such as burning smells, charred outlets, or flickering lights, it’s important to have a professional electrician assess and address the problem.
- Lack of Electrical Expertise: If you’re unsure about your electrical knowledge or uncomfortable working with your electrical system, it’s always safer to rely on the expertise of a licensed electrician.
Calling in a professional electrician ensures that the issue is properly diagnosed, resolved, and that your electrical system is safe and up to code.
Persistent Tripping: Knowing When It’s Beyond DIY
If your circuit breaker trips frequently, even after resetting it, it may indicate an underlying electrical problem that requires the expertise of a licensed electrician. Here are some signs that the issue may be beyond DIY troubleshooting:
- Tripping on Multiple Circuits: If the circuit breaker trips on different circuits throughout your home, it could indicate a more widespread problem in the electrical system.
- Tripping Without Overloaded Circuits: If the circuit breaker trips even when the electrical load is within the rated capacity, it suggests a fault in the system.
- Intermittent Tripping: If the circuit breaker trips intermittently or randomly, it can be a sign of a loose connection, damaged wiring, or other electrical faults.
In these situations, it’s best to contact a licensed electrician who has the expertise to diagnose and resolve complex electrical issues. They can ensure the safety of your electrical system and provide appropriate solutions.
Signs of Serious Electrical Issues
Certain signs indicate serious electrical issues that should not be ignored. If you notice any of these signs, it’s crucial to contact a licensed electrician for immediate assistance:
- Burning Smell: A persistent burning smell, especially around outlets or electrical panels, could indicate overheating or electrical arcing, which can lead to fires.
- Charred Outlets or Switches: If you find discolored or charred outlets, switches, or wiring, it suggests excessive heat buildup and potential fire hazards.
- Flickering or Dimming Lights: If your lights flicker or dim without an apparent cause, it may indicate loose connections or faulty wiring, which can lead to electrical failures or fires.
- Electrical Work: If you’ve recently had electrical work done and experience unusual electrical issues afterward, it’s essential to have a professional electrician inspect the work for potential problems.
Ignoring these signs of serious electrical issues can pose significant safety risks. It’s important to contact a licensed electrician promptly to evaluate and address the underlying problems.
Maintaining Your Circuit Breaker Panel
Proper maintenance of your circuit breaker panel is essential to ensure its optimal performance and prevent unnecessary trips. Here are some maintenance tips to keep in mind:
- Regular Checks: Periodically inspect your circuit breaker panel for signs of damage, such as loose connections, corrosion, or overheating. Address any issues promptly.
- Balancing Loads: Distribute the electrical load evenly across different circuits to avoid overloading and tripping.
- Updating Old Circuit Breakers: If you have an older home with outdated circuit breakers, consider upgrading them to newer models with higher capacities and enhanced safety features.
By following these maintenance tips, you can prolong the lifespan of your circuit breaker panel, reduce the risk of trips, and ensure the safety of your electrical system.
Regular Checks and Balancing Loads
Regular checks and balancing the electrical load in your home are essential for maintaining the performance and safety of your circuit breaker panel. Here’s what you can do:
- Regular Checks: Periodically inspect your circuit breaker panel for any signs of damage or wear, such as loose connections, corrosion, or charred components. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage or hazards.
- Balancing Loads: Distribute the electrical load evenly across different circuits in your home. Avoid overloading a single circuit by plugging in too many appliances or devices. Consider using power strips with surge protectors to distribute the load.
- Amperage Rating: Understand the amperage rating of your circuit breakers and the maximum load they can handle. Avoid exceeding the amperage rating to prevent tripping and potential damage to the circuit breaker or electrical system.
By performing regular checks and balancing the electrical load, you can ensure that your circuit breaker panel operates efficiently and minimize the risk of trips and electrical hazards.
Updating Old Circuit Breakers
If you live in an older home with outdated circuit breakers, it may be necessary to update them to ensure the safety and efficiency of your electrical system. Here’s why you should consider updating old circuit breakers:
- Enhanced Safety: Newer circuit breakers come with improved safety features, such as arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs) and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), which provide enhanced protection against electrical hazards.
- Higher Capacities: Older circuit breakers may have lower amperage ratings and may not be able to handle the electrical demands of modern appliances and devices. Upgrading to higher-capacity circuit breakers can prevent overloading and tripping.
- Code Compliance: Electrical codes and standards evolve over time. Updating your circuit breakers ensures that your electrical system complies with current codes and regulations, providing peace of mind and safety.
When updating circuit breakers, it’s important to consult a licensed electrician who can assess your electrical system and recommend the appropriate upgrades for your specific needs.
Remember, safety first when dealing with circuit breakers. Understanding the basics and common reasons for trips can help you troubleshoot effectively. Always prioritize safety and know when to seek professional help. Regular maintenance and updates are key to preventing future issues. If you’re unsure or face persistent tripping, don’t hesitate to get in touch with a professional for assistance. Your home’s electrical system is essential for your safety, so ensure it’s always well-maintained. Stay safe and informed!
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does my circuit breaker keep tripping.
Circuit breakers can trip due to various reasons, including an overloaded circuit, a short circuit, or a ground fault. These trips are safety measures to protect your electrical system from damage or hazards. Identifying and addressing the cause of the trips can help prevent recurring issues.
Can I replace a circuit breaker myself?
While some homeowners may have the knowledge and skills to replace a circuit breaker, it’s recommended to consult a licensed electrician for safety reasons. Working with electricity can be dangerous, and a professional electrician can ensure that the replacement is done correctly and safely.
How do I know if my circuit breaker is faulty?
If you’re experiencing frequent circuit breaker trips, flickering lights, or other electrical issues, it could indicate a faulty circuit breaker. A licensed electrician can inspect and test the breaker to determine if it needs to be replaced.
What’s the difference between a circuit breaker and a fuse?
Circuit breakers and fuses both protect electrical circuits from overloads and faults. However, while circuit breakers can be reset and reused, fuses need to be replaced after they trip. Circuit breakers are more commonly used in modern electrical panels.
Why Did My Circuit Breaker Trip?
Circuit breakers can trip due to electrical overloads, short circuits, or ground faults. These trips occur to protect your electrical system from damage or hazards. Identifying the cause of the trip can help prevent future occurrences.
What should be done when a tripped breaker is found?
When you find a tripped breaker, it’s important to follow the proper procedure for resetting it. Turn off all appliances connected to the circuit, locate the tripped breaker, reset it by moving the switch to the “off” and then “on” position, and ensure that the cause of the trip is identified and resolved.
What causes a circuit breaker to trip?
Circuit breakers can trip due to various reasons, including an overloaded circuit, loose electrical connections, or electrical faults. These trips occur to protect your electrical system from damage or hazards.
How can you prevent circuit breakers from frequently tripping in the future?
To prevent circuit breakers from frequently tripping, distribute the electrical load evenly across different circuits, avoid overloading circuits, and implement proper circuit management. Consider upgrading your electrical system if necessary.
Can frequent tripping of a circuit breaker indicate a larger electrical issue in the home?
Frequent tripping of a circuit breaker can indicate a larger electrical issue, such as overloaded circuits or faulty wiring. It is advisable to have a licensed electrician conduct an electrical inspection to identify and address any underlying problems.
When should you call a professional to fix a tripped circuit breaker?
You should call a professional electrician if you’re uncomfortable working with your electrical system, if you experience persistent circuit breaker trips, or if you notice signs of serious electrical issues. A professional electrician has the expertise to diagnose and resolve complex electrical problems safely.

Recent Posts
- Beginner’s Guide to Identifying a Tripped Circuit Breaker March 14, 2024
Service Areas Sidebar
- Electrician in Berea, KY
- Electrician in Richmond, KY
- Electrician in Lexington, KY
- Electrician in Frankfort, KY
- Electrician in Georgetown, KY
- Electrician in Jessamine County, KY
- Electrician in Versailles, KY
- Electrician in Winchester, KY
- Electrician in Nicholasville, KY
Latest Projects
No results found.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
5+ Reasons Why Your Breaker Keeps Tripping – And How to Fix It
Your breaker may trip due to circuit overload, short circuits, ground faults, outdated wiring, or a faulty breaker. Follow tips to fix each issue and ensure safety.

Your circuit breaker will trip once in a while if it detects an electrical fault. After all, that’s what it’s designed to do. Without the breaker, you could be putting yourself, loved ones, and property at risk of electrocutions and fires. But what if the breaker keeps tripping and leaves you in pitch darkness?
Before you call an electrician, consider implementing the tips below. You’ll discover the root causes and what to do if your breaker keeps tripping.
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases. Thanks!
Why Does My Breaker Keep Tripping?
If your breaker frequently trips, examine your electric power system to determine if the issue results from one of the following causes.
Hey hey! Don’t forget to subscribe to get our best content 🙂
Type your email…
Circuit Overload
Have you checked whether you’re dealing with an overloaded circuit? A circuit overload occurs when the wires receive more electrical current than they can handle.
Each circuit has a maximum current it can handle. The breaker will trip if it detects that the current exceeds the circuit’s capacity.
Often, a circuit overload happens if you’ve plugged multiple appliances, including high-power devices, into the circuit. You might notice that power goes out in your kitchen or living room when the breaker trips. That’s a telltale that a single circuit in either of the rooms is powering multiple appliances.
- Disconnect all the devices and reset the breaker.
- Before connecting an appliance, allow your electric power system to rest for a few minutes. Plug in your devices one at a time.
- If it trips again as you plug in the devices, relocate the appliances to other outlets.
- If the breaker continues to trip, call an electrician to troubleshoot the problem.
Short Circuit
A short circuit might be another reason why your breaker keeps tripping. Unlike circuit overloads, short circuits have more potential to cause fires.
A short circuit happens when a live or “hot” wire touches a neutral wire. When the two wires touch, they cause a sudden surge of current through the wires. This surge leads to a circuit overload, which causes the breaker to trip. If your circuit breaker fails to trip, it can put your property at risk of fire.
To know whether the culprit is a short circuit, you can look for sparks, smoke, burning smells, or popping sounds. A short circuit will occur in a switch, outlet, or within the circuit breaker due to the following reasons:
- Slipped wires
- Damaged wires
- Loose connections
Do you know what to do if your breaker keeps tripping? Unless you have professional experience, avoid trying to fix a short circuit in your electric power system. The affected cables can instigate fire and further damage. You may also get electrocuted. Call your electrician to fix the problem.
Ground Faults
When it comes to ground faults, a live or “hot” wire touches a ground wire or the breaker’s outer casing. This contact causes a sudden surge of current passing through the breaker. The breaker will trip if it detects more electricity than it can handle.
Ground faults occur when water enters the appliance or an outlet. If it touches the hot wire, the current changes its route and follows the water path. This might cause electrocution if you touch the water with bare hands or feet.
Thankfully, the National Electrical Code (NEC) requires buildings to install Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlets . These outlets can detect ground faults and cut off the current.

- Find where the water is coming from and fix it. If it’s damaged roofing directing rainwater into the box, call a roofer to fix it.
- Replace damaged wiring. Call your electrician to replace the damaged wiring to avoid causing further damage.
- If you’ve not installed GFCI outlets, call a licensed electrician to install them for you.
Outdated Wiring
Outdated wiring is prevalent in older homes. If you live in an old house, you’re likely to have a breaker that keeps tripping. The electric power system in that home can only handle low-power devices. If you plug in modern appliances, you might experience frequent breaker trips due to circuit overload.
Old aluminum wires might melt when the circuit overloads. The melting cables might burn the plastic casing, causing a fire.
If you check the insulation in one of your outdated wires, you might find it deteriorating. When this insulation touches a conductor, it can cause a ground fault.
According to the National Fire Prevention Association (NFPA), faulty wiring leading to electrical failure is one of the main causes of fires in residential areas. The wiring can be outdated if you live in a house over 40 years old. Outdated and faulty wiring will likely cause a fire during overloads or short circuits.
The only way to fix outdated wiring is to have it replaced. Find a professional who’ll inspect the wiring and upgrade it.
A Bad Circuit Breaker
If your breaker doesn’t stop tripping even after fixing some or all of the above causes, then your breaker might be faulty. Sometimes, a breaker will trip even when it’s newly installed. This might be due to an undersized breaker, manufacturer’s defect, or loss of efficiency. If one of these is the case, your breaker will trip even if there are no overloading, short circuits, or ground faults.
When inspecting your old wiring, check whether you’re working with an old breaker. It may no longer produce electricity for your modern appliances if it’s old. You should also check whether the breaker is tripping due to a lack of maintenance.
Avoid tampering with your faulty breaker, especially if you don’t have the necessary skills. Call a certified electrician to diagnose the problem and fix it. If your breaker is old or beyond repair, they can replace it.
How To Reset a Tripped Breaker
If your breaker won’t stop tripping, resetting it is the first thing you might consider. Resetting the circuit breaker is a great way to determine what causes the tripping.
To reset your breaker:
- Locate the appliance’s handle or switch and move it to the “OFF” position.
- Before this, ensure you’ve unplugged all the devices.
- Move the switch to the “ON” position.
When turning the switch on, the breaker might produce sparks that might cause a fire or electrocution. To be safe, avoid standing near and directly facing the panel. You can stand at the side or a few steps back. After resetting, allow the breaker to rest for a few minutes before plugging in your devices. Now you know what to do if your breaker keeps tripping.
The following are some of the most common questions people have asked about circuit breakers.
How can you tell if your circuit breaker has gone bad?
The following symptoms should help you know that your circuit breaker has gone bad:
- Frequent tripping
- Unable to reset
- Burnt smell
- Scorch marks on its box
- Visibly damaged breaker
- Worn-out breaker
- Hot circuit breaker
What causes the breaker not to reset?
A breaker might fail to reset if it has gone bad. The breaker won’t reset if you’ve plugged in too many devices that consume a lot of power.
What is the average life of a circuit breaker?
The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) states that the lifespan of breakers is between 30-40 years . Factors such as fluctuating voltages and poor power ratings can affect the life of your breaker.

Jeff (pen name for privacy) is our primary contributor. Previously, he has worked at 84 Lumber as a manager trainee and contractor sales rep. Before that, he worked for a local plumbing firm doing everything from rough-ins to septic repair and more.
Similar Posts

What Is a 24V Power Supply & What Is It Used For?

5 Key Factors Affecting Your Extension Cord’s Lifespan

5 Reasons Canless Recessed Lighting Is Ideal for Your Home

5 Expert Tips to Shield Extension Cords from Rain

5 Steps to Plug Generator Into House Safely & Effectively

What Is a Platform Ladder & What Is It Used For?
Discover more from journeyman hq.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
Why Does My Breaker Keep Tripping?
January 31, 2024
If you're like most homeowners, you and your loved ones consume a significant amount of electricity daily. From storing food in your refrigerator to simply flipping on a light switch , you utilize numerous sources of electricity in your daily routine. Your home's electrical circuit regulates electricity usage while keeping your home safe. If an overcurrent or short circuit threatens to overload the system, the circuit breaker will trip to keep damage at bay.
However, if your circuit breaker seems to be tripping more frequently than usual, this could indicate an underlying problem. It's important to recognize the warning signs that your breaker needs repair and be prepared to call a professional as soon as possible.
Here are some common issues that may give you an answer to the question, "Why does my breaker keep tripping?"
- Overloaded circuits
- Short circuits
- Ground faults
- Aging electrical components
- Appliance issues
- Inadequate wiring
Contact Patrick Riley | Isley’s Trusted Experts to Restore Your Electrical Circuit
Don't hesitate to get in touch with our seasoned pros. Our dedicated team is proud to offer upfront, honest pricing and 100% satisfaction guarantees on all work. Thanks to our polite Phoenix pros and dedication to customer service, we've become the preferred choice of countless homeowners in the area.
Overloaded Circuits
If you're wondering, "Why does my breaker keep tripping with nothing plugged in?" there are various possible causes. Two of the most common reasons include the overuse of extension cords and multiple plug adapters used on the same circuit. For example, running multiple blow dryers and hair styling tools at once will quickly overwhelm the circuit. As a result, the breaker will shut off the connection to keep severe damage at bay. If you regularly use multiple plug adapters on the same circuit, your breaker will trip often as a protection mechanism to prevent the circuit from overloading.
Short Circuits
Some people use these terms interchangeably, but a short circuit isn't the same as an overloaded circuit. An overload occurs when an outlet or circuit takes on more power than it can manage. Alternatively, a short circuit occurs when the electricity changes course from the longer, intended route to the shorter route, also known as the path of least resistance. This results in electricity creating a shorter circuit than the prescribed circuit — hence the term "short circuit."
Short circuits are caused by many factors, including old or damaged outlets, water coming into contact with wiring, damaged electrical cable sheathing, and pests chewing through wires. A seasoned pro will quickly identify the root cause of the problem.
Ground Faults
A ground fault is an unintended source of contact between an energized conductor and a grounded equipment frame. When this happens, the fault current's path of return travels through the grounding system. This means that any equipment automatically becomes a part of the system. Because ground faults typically occur due to insulation breakdown, it's crucial to reach out to a professional as soon as possible to prevent further damage from taking place.
Aging Electrical Components
Just like any other appliance or device in your home, your electrical circuit's components need to be properly cared for and maintained on a regular basis. Neglecting to do so can result in faulty electrical connections, which increases the risk of device malfunction. If your electrical components are nearing the end of their lifespan, they will struggle to meet your home's electrical demands. This may result in your circuit breaker tripping more often.
Appliance Issues
In some cases, your electrical appliances can trip your circuit breaker. This is especially true if any of your appliances have faulty wiring. Be sure to repair or replace the electrical wiring as soon as possible to prevent more severe and costly damage. If you're unsure whether your wiring needs a routine repair or a full-scale replacement, don't hesitate to contact a professional electrician. They will provide a clear answer to the question "What causes a breaker to trip?" and implement the best solution for your needs.
Inadequate Wiring
If your circuit breaker frequently trips, it could indicate dangerous inadequate wiring . This happens when the wires in your home cannot cope with the electrical current passing through them, leading to an overload and causing the breaker to trip. It's important to address this problem promptly. Ignoring inadequate wiring can lead to more serious consequences, including total electrical failure or, in extreme cases, a fire.
Contact Patrick Riley | Isley’s Highly Trained Electricians
Don't delay calling our highly trained team of electricians for help. Our flexible scheduling and financing options have earned us the trust of countless homeowners like you.
Get 10% off (Up to $150)

Ty Lindsay is the Director of Field Operations at Patrick Riley | Isley’s and a 15-year veteran of the plumbing and HVAC trades. In 2010, Ty earned his Journeyman’s plumbing license. He became a Master Plumber five years later and earned his Journeyman HVAC technician’s license that same year. Ty’s breadth of knowledge in plumbing and HVAC includes both residential and commercial work. He’s been a loyal member of the Patrick Riley | Isley’s team since 2016.
- Central AC Repair
- Central AC Install
- Mini Split Install
- Duct Sealing
- Duct Cleaning
- Emergency AC Repair
- Worry-Free Home Comfort
- VIP Maintenance Plan
- All Cooling Services
- Furnace Repair
- Furnace Install
- Heat Pump Repair
- Heat Pump Install
- All Heating Services
- Tank Water Heater Repair
- Tank Water Heater Install
- Tankless Water Heater Repair
- Tankless Water Heater Install
- Sewer Line Repair
- Slab Leak Detections & Repairs
- All Plumbing Services
- Drain Cleaning
- Panel Repair
- Panel Replacement
- Circuit Breaker Replacements
- Whole-Home Rewiring
- Indoor Lighting
- Ceiling Fans
- Backup Generators
- Smart Home Automation
- Electrical Inspection
- All Electrical Services
- Service Area
- Testimonials
- Referral Program
- Buyer's Guides
- Troubleshooting
- All Articles
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Home and Garden
- Home Maintenance
- Electrical Maintenance
- Electrical and Electronic Circuits
Does Your Circuit Breaker Keep Tripping? Here’s How to Find the Cause
Last Updated: May 6, 2023 Fact Checked
Common Causes of Tripped Circuits
Finding overloaded circuits, finding short circuits, finding ground faults.
This article was co-authored by Jesse Kuhlman and by wikiHow staff writer, Johnathan Fuentes . Jesse Kuhlman is a Master Electrician and the Owner of Kuhlman Electric based in Massachusetts. Jesse specializes in all aspects of home and residential wiring, troubleshooting, generator installation, and WiFi thermostats. Jesse is also the author of four eBooks on home wiring including "Residential Electrical Troubleshooting" which covers basic electrical troubleshooting in residential homes. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 22,554 times.
Picture this: you’re watching TV or browsing on your phone when, suddenly, half the lights in your home turn off. You check your circuit breaker and flip one of the switches back to “ON,” but an hour later it trips again…and again. Sound familiar? Having your circuit breaker trip over and over can be frustrating, but don’t sweat. In this article, we’ll explain the most common causes of a tripped circuit breaker. Keep reading to learn which causes might apply to your situation, when to try do-it-yourself fixes, and when it’s best to call an electrician.
Things You Should Know
- The most common causes of tripped circuit breakers are overloaded circuits, short circuits, and ground faults.
- Test for overloaded circuits by resetting your breaker and plugging in devices until it trips again. The device that caused the trip is overloading the circuit.
- Test for short circuits by resetting your breaker and plugging in items into different sockets. The device or socket that always trips the breaker likely has a short circuit.
- Have an electrician test for ground faults if you’ve already ruled out overloaded and short circuits. Ground faults are too dangerous to test for on your own.

- For example, if your bathroom and kitchen are part of the same circuit—that is, the plugs in your kitchen and bathroom are all connected to the same switch on your circuit breaker—then the breaker might trip if you run your microwave and hair dryer at the same time.

- Short circuits often happen when wires come loose or get damaged by corrosion or wear and tear, or even from an animal chewing through them. [3] X Research source
- Short circuits can occur in the wiring in your home or in individual devices. For instance, a refrigerator can have a short circuit due to a loose wire.

- Ground faults often happen due to water leaking into outlets or devices. They also occur when loose or corroded wires come into contact with ground wires, or when defective devices cause electricity to flow to a ground wire.

- If you have multiple devices sharing a single outlet in the area affected by the tripped breaker, it’s likely that that group of devices is causing the overload. [6] X Research source

- Wear safety goggles or stand to the side of a breaker when flipping a switch to “ON” in case of sparks.
- If the switches aren’t labeled, narrow down the affected area by flipping the switch to “ON” and checking which devices and lights turn on again.
- If multiple switches tripped at the same time, there might be an overloaded circuit in more than one area of your home, or you may have another issue such as a short circuit or ground fault.

- If none of the devices immediately trip the circuit breaker, it’s possible that your circuit isn’t getting overloaded right away. Leave the devices plugged in and turned on for a few minutes to see if the breaker trips again.
- If the breaker trips after several minutes, try the process again, but leave 1-2 less important devices unplugged. Eventually, you’ll find a combination of devices that doesn’t trip the circuit breaker.

- Leave your devices plugged in and on for a few hours. If the circuits are not overloaded, the circuit breaker shouldn’t trip.
- If the circuit breaker trips for the same part of your home again, plug additional devices into other outlets. You may need to try different combinations of plugs and outlets to see which combination doesn’t overload your circuits.
- If you try several combinations and the breaker continues to trip, it’s possible that you have a short circuit or ground fault somewhere in your home.

- If devices are plugged into surge protectors, unplug each device from the surge protector before unplugging the surge protector itself.

- If the circuit breaker trips whenever you plug something into a particular outlet, you probably have a short circuit in that outlet.
- If one particular device always trips the breaker, but other devices don’t, you probably have a short circuit in that particular device.

- If the device you want to test is too large to move—such as a kitchen refrigerator or washing machine—use a long extension cord to reach other outlets.

- If you find a short circuit in an individual device, check if your product is covered by a warranty. If it is covered, you might be able to get it fixed or replaced for free. [14] X Trustworthy Source Federal Trade Commission Website with up-to-date information for consumers from the Federal Trade Commisson Go to source

- Tell your electrician which outlet or area of your home is affected by the tripped circuit breaker. This will help them narrow down the exact problem.
- Avoid using sockets that appear water-logged or that show signs of water damage.
Expert Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://nps.edu/documents/111291366/111353794/SafetyGram_Circuit_Breaker_Panels.pdf/eab72177-f7b7-4f6f-b7bc-f7efde96df4f?t=1423776819000
- ↑ https://engineering.mit.edu/engage/ask-an-engineer/what-is-a-short-circuit/
- ↑ https://www.coynecollege.edu/how-to-deal-unsafe-electrical-wiring/
- ↑ https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/2018-12/fy07_sh-16586-07_4_electrical_safety_participant_guide.pdf
- ↑ https://ask-the-electrician.com/how-to-fix-a-overloaded-circuit-breaker-problem/electrical-wiring-2/
- ↑ http://thecircuitdetective.com/treeshort.php
- ↑ https://consumer.ftc.gov/articles/warranties
- ↑ https://tools.niehs.nih.gov/wetp/public/Course_download2.cfm?tranid=2495
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life

Breaker Keeps Tripping: Understanding the Common Causes and Solutions
When a circuit breaker trips, it protects your device and circuit; it’s just doing its job unless it is damaged.
Do you notice that sometimes the lights of a residential place go off due to circuit breaker tripping, or sometimes the fuse blows up? It is due to some faults in the electrical network. I see these faults too much because I work as an electrical maintenance engineer.
I will discuss different reasons that cause circuit breaker tripping. I won’t rely only on my long work experience as an engineer, which is now about 15 years, but also I will provide you with the results of deep searching about circuit breaker tripping.
Table of Contents
How To Find The Reason Behind Tripping My Circuit Breaker?
Tripping of a circuit breaker can occur due to various reasons, such as overloading, short circuits, ground faults, or issues with the electrical appliances or wiring. Here are some steps to help you identify the reason behind the tripping:
Identify the Circuit: Determine which circuit breaker has tripped and which area of the house or building is affected. This can help narrow down the potential causes.
Unplug Appliances: If the tripping occurs when a specific appliance is used, unplug that appliance and try resetting the circuit breaker. If the breaker does not trip, the appliance might be faulty and cause an overload.
Check for Overloading: Assess whether the circuit is overloaded by connecting too many high-powered devices to the same circuit. Try redistributing the load by connecting devices to different circuits.
Inspect for Short Circuits: Examine the electrical outlets, switches, and wiring for signs of damage or exposed wires that could be causing a short circuit. If you notice any issues, consult a qualified electrician to repair or replace the affected components.
Look for Ground Faults: Ground faults occur when a hot wire comes into contact with a ground wire or a metal wall box. Use a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) tester to identify any potential ground fault issues and address them accordingly.
Check for Wet Conditions: If the circuit is in a damp or wet area, it could lead to a ground fault. Ensure that all electrical components in such areas are moisture-resistant and properly grounded.
Inspect the Breaker Itself: Examine the circuit breaker for any signs of damage, corrosion, or overheating. If you notice any issues, consider replacing the circuit breaker with a new one.
Consult a Professional Electrician: If you are unable to identify the cause of the tripping or if you suspect a more complex electrical issue, it is advisable to consult a licensed electrician. They can conduct a comprehensive inspection of the electrical system and troubleshoot any underlying problems.
It is crucial to prioritize safety when dealing with electrical issues. If you are unsure about how to proceed or are not comfortable handling electrical components, it is best to seek professional assistance to ensure a safe and effective resolution to the problem.
What would cause a circuit breaker to keep tripping?
Now, after this quick discussion for non-technical persons. let’s move to the electrical engineering discussion.
Overloaded Circuit:
One of the main reasons for circuit breaker tripping is the overloaded circuit in the electrical system. When many loads are connected to the circuit, the circuit attempts to draw a greater electrical load than its rated value. Due to this, the circuit breaker heats up, and the breaker tripping occurs.

Electrical Short Circuit:
Another reason for the breaker tripping is the electrical short circuit. A short circuit occurs due to low insulation resistance .
When the positive and negative (live and neutral) terminal connects with each other in the absence of any resistance. This causes an unimpeded flow of electricity. A large amount of current flows through a breaker that causes tripping.
It is worth mentioning here how to decide whether the tripping occurs due to a short circuit . The answer is clear and simple. If a circuit breaker trips instantly again and again after you reset it, the tripping occurs due to a short circuit.
How Do I Know That I Have a Short Circuit at the House? If you find fuses being blown regularly or a circuit breaker tripping frequently, it might be a symptom of a short circuit.
A fuse will usually explode, or a circuit breaker will trip instantly. If a new fuse with the proper rating also blows, you’ve got a short circuit.
If a circuit breaker is reset and it trips again instantly, as you connect it, you have a short circuit or a broken circuit breaker. Read my detailed article about Electrical short circuits, why is it dangerous?
Ground Fault:
Another reason that causes the circuit breaker tripping is the ground fault. A ground fault is a type of short circuit when a hot wire comes in contact with the ground or any other type of metal.
The ground fault causes an increase in the flow of current. It causes the circuit breaker to heat up and as a result, circuit breaker tripping occurs.
Some ground faults are not detectable by normal MCB. So it’s recommended to use GFCI (ground fault circuit interrupter) This is better for human safety as this breaker can detect small milli-amperes and trips before a shock happens. Read my article on my other site: Surge Protectors and GFCI Outlets: Can They Safely Coexist?
When fluctuation or sparking occurs between two-wire connections at a point. Arc faults occur.
Sometimes the screws at a point become loose, In this case, AFCI (arc fault circuit interrupter) is recommended.
While the circuit breaker is an Arc fault interpreter (AFCI ). It detects the early wiring problem and trips in advance to stop the flow of a large amount of current.
Bad Circuit Breaker:
Sometimes the circuit and loads are all OK and in good condition. But the breaker keeps tripping randomly.
This is a sign that the circuit breaker is bad. Like any device, breakers have a lifetime, and then breakers go bad . And it’s time to replace it.
The circuit breaker keeps tripping immediately
If your circuit breaker keeps tripping immediately after resetting it, this indicates a severe electrical issue that requires prompt attention. Here are some steps to follow to address the problem:
Identify the Problem Circuit: Determine which specific circuit is causing the repeated tripping. This can help pinpoint the area of concern and focus your troubleshooting efforts.
Disconnect All Appliances: Unplug or disconnect all devices and appliances from the circuit that keeps tripping the breaker. If the breaker doesn’t trip after disconnection, the issue may be related to one of the appliances or devices.
Check for Short Circuits or Ground Faults: Inspect the wiring, outlets, and switches for signs of damage, exposed wires, or any moisture intrusion. Focus on the affected circuit and look for any visible signs that might indicate a short circuit or ground fault.
Examine the Breaker Itself: Check the circuit breaker for any signs of damage, overheating, or wear. A faulty breaker could be the root cause of the repeated tripping. Consider replacing the circuit breaker with a new one if it appears damaged.
Consult a Professional Electrician: If you are unable to identify the cause of the immediate tripping, or if the issue persists despite your troubleshooting efforts, it is essential to seek assistance from a qualified electrician. They can perform a comprehensive inspection of the electrical system and troubleshoot the problem effectively.
It is crucial to prioritize safety when dealing with electrical issues. If you are uncertain about how to proceed or are uncomfortable handling electrical components, it is best to seek professional help.
Electrical problems can be complex and potentially dangerous, so it is important to have them addressed by a licensed electrician to ensure the safety of your property and its occupants.
Can a circuit breaker trip for no reason?
A breaker will trip for no reason if it malfunctions . A breaker will trip when a short circuit occurs on an electrical circuit, causing sparks, popping sounds, or smoke to be produced.
A loose connection, slipping wire, or even damage from animals chewing on cables could cause this.
If you didn’t find any faults like a short circuit , overload, or lost connection, your circuit breaker might be old and unable to carry current anymore.
In other words, it has become bad. It would be best if you replaced it for the circuit to continue operating.
Why is the circuit breaker tripping without load?
If your circuit breaker trips without loads, a wire with damaged insulation somewhere in the electrical panel or in power outlets can be the cause of breaker tripping and will continue to do so until you fix it .
A general wiring issue can potentially be the reason why a circuit breaker trips. You can have obsolete wiring if your home is older.
The issue with older electrical systems is that new technology and appliances frequently demand more power than previous systems can safely handle.
The older wiring can’t keep up with the increasing demands as our daily energy needs increase. This may be the problem if several breakers are often tripping without a load. Otherwise, there can be a problem with the breaker panel itself.
When your breaker trips without any load being present, you should take into consideration the following three wiring problems:
Current Leakage: One possibility is that one or more of the input wires have current leakage, which causes the circuit breaker to trip even when there isn’t a load attached to it. If so, your annoying issue is taking place for your own benefit. tripping is a precaution for the safety of your all-electrical devices.
Damaged Wires : Not simply the input cables might be damaged; it could happen everywhere. They could have been accessed by pests or insects that, only by gnawing, caused significant harm. This kind of issue may be sufficient to trigger a breaker trip even with no loads.
A Loose Wire in an Outlet : This loose wiring issue may be pretty frustrating. In other words, a loose wire in one of your outlets will keep your breaker continuously tripping. If you have a GFCI outlet, this is a very typical issue (Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupter).
Why shouldn’t you reset a tripped circuit breaker immediately?
The straightforward answer is that you shouldn’t reset a circuit breaker unless you are sure of the reason for the fault and that it poses no danger.
Note that if you reset it immediately it may trip again in case it is still hot, even if the fault is cleared.
Circuit breakers are there to safeguard your family, your house, and yourself. When a circuit breaker trips, it indicates that a current greater than the trip current is passing through it.
In case of a faulty circuit or wires, or a short circuit, the circuit breaker will trip again immediately if you reset it.
The short circuit current makes the circuit breaker get hot and trip, it should be cooled before you reset it.
Can a tripped breaker stop a fire?
Yes, if tripping happen before the fire catch wires or panel. But it won’t if tripping happens after the fire catch wires or panel .
There can be two scenarios, 1 st one is before the wiring or breaker panel catches fire.
And 2 nd is the role of the circuit breaker after catching fire let’s explore both scenarios in detail below:
Role of circuit breaker before Catch Fire :
Tripped circuit breakers can prevent fire and protect electrical systems against overloads and short circuits, circuit breakers assure electrical safety in homes, offices, and other buildings as well as for industrial uses.
The circuit breaker instantly shuts off the electrical circuit when a problem is found, protecting the wires and reducing the chance of catching fire.
Role of circuit breaker after catching fire:
Tripped circuit breakers didn’t play any role and could not provide safety to the system after catching fire.
If the circuit breaker is not tripped due to any reason or sometimes the fault current is too much bigger than the rating of the cable, then the circuit breaker wiring or panel box catches fire.
Can tripping circuit breaker damage your devices?
Tripping circuit breakers themselves do not typically cause direct damage to your electrical devices.
In fact, the primary purpose of a circuit breaker is to protect your devices and electrical system from potential damage due to electrical overloads or short circuits.
When a circuit is overloaded or a short circuit occurs, the circuit breaker is designed to trip and cut off the flow of electricity, preventing excessive current from damaging your devices and wiring.
However, frequent or repetitive tripping of circuit breakers may indicate underlying issues within the electrical system that could potentially affect connected devices. Repeated tripping may point to problems such as overloading, short circuits, ground faults, or other electrical faults that could impact the functionality and safety of your devices.
Indirectly, sudden loss of power due to a tripped circuit breaker can cause data loss or corruption in electronic devices like computers, especially if they are not connected to an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). Additionally, frequent power fluctuations resulting from faulty electrical systems can gradually wear down sensitive electronic components, reducing the lifespan of your devices over time.
To prevent potential damage to your devices, it’s important to address any electrical issues promptly. If you notice persistent circuit breaker trips, it’s advisable to consult a qualified electrician to identify the underlying cause and ensure that your electrical system is functioning safely and efficiently. Taking proactive steps to maintain your electrical system can help prevent potential damage to your devices and ensure the safety of your property.
Why is the Main circuit breaker tripping?
The main breaker can trip for a variety of reasons. Whether it be a lightning strike, a power surge from the utility company, or an overload to the electrical panel, the main breaker can be tripped due to any of these factors.
Furthermore, the main circuit breakers can trip simply because they’re worn out . There might be a situation when a branch circuit breaker fails and is no longer capable of tripping as designed, which may result in the main breaker tripping to provide secondary safety shutoffs in the event that the individual circuit breaker fails.
Furthermore, If the total load demand becomes too much or if there is any significant issue with the electrical system, the main breaker cuts off electricity to the entire house.
These issues often entail brief power spikes, although it may be necessary to detect system issues occasionally.
The main circuit breaker “tripping” is somewhat uncommon since often, individual circuit breakers trip long before the main breaker has to shut down.
Does weather affect the circuit breaker?
Yes, weather affects the circuit breakers . In response to the heat generated by the circuit breaker, the bimetallic strip inside the breaker flexes and trips the breaker.
The hot weather also can cause a breaker to trip, it all depends on the thermal effect of heat that causes the bimetallic strip inside the breaker to flex and trip it.
On the other hand, as compared to hot weather, cold weather didn’t affect the circuit breaker as much as lead to tripping, but if there is a foggy season and too much moisture in the environment, that can cause tripping the breaker.
A breaker’s components can also be adversely affected by the ambient heat in the air surrounding the breaker. A circuit breaker should typically not be heated over 140°F. If it happens, it indicates a potential trip of the circuit breaker.
If you can’t keep your finger on the plastic portion of the circuit breaker without being burnt, it’s too hot, according to a reliable “rule of thumb.”
Why do my breakers trip when it rains?
The main cause of a breaker’s trip after the storm is a short circuit brought on by water .
Due to heavy rain, the electrical wire isolation may deteriorate after water exposure, causing a short circuit. Improper panel box installation might be another reason your circuit breaker tripped during the storm.
Rainwater may get into your circuit in a number of ways if the main line is not installed properly.
Water may enter your wiring conduits through the wire leading to the meter and electrical circuit. It’s also conceivable that the conduit or hose you used to install your main line will let water through.
Because of this, if the breaker box is in the basement, water may wet your circuit. The worst possible scenario for your house is a wet circuit breaker.
A wet circuit is dangerous because you might get electrocuted in addition to the electrical problems it can create.
Can you reset a breaker in the rain?
It is generally not recommended to reset a circuit breaker while it is raining or in wet conditions . Water can significantly increase the risk of electrical hazards, potentially leading to electric shocks or other safety risks.
Resetting a circuit breaker in the rain could expose you to electrical currents and pose a danger to your safety.
To ensure your safety when dealing with electrical components, including circuit breakers, it’s crucial to follow these guidelines:
- Safety First: Prioritize your safety at all times. Do not attempt to handle electrical components in wet conditions or when you are standing on a wet surface.
- Turn Off the Main Power: If you need to access the circuit breaker panel during wet conditions, make sure to turn off the main power to the house or the affected circuit before attempting any reset.
- Wait for Dry Conditions: If the circuit breaker trips during the rain, it is advisable to wait until the weather improves and the area is dry before attempting to reset it.
- Take Precautionary Measures: If you must work on electrical components in damp conditions, wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as rubber gloves, rubber-soled shoes, and other safety gear to minimize the risk of electrical shock.
If you are unsure about how to safely handle a circuit breaker or if you are uncomfortable with electrical work, it is best to seek assistance from a qualified electrician.
Professional electricians have the necessary expertise and equipment to handle electrical components safely, even in adverse weather conditions.
Prioritizing safety is essential to prevent accidents and ensure the protection of both you and your property.
Can a storm and lightning cause a CB to trip?
Yes, storms and lightning can potentially cause a circuit breaker to trip. Lightning strikes can induce power surges in electrical systems, leading to a sudden increase in electrical current that exceeds the circuit breaker’s capacity.
In response to the excessive current, the circuit breaker will trip, cutting off the power supply to the affected circuit or the entire house to prevent electrical damage or fire hazards.
Additionally, storms can cause power fluctuations and electrical disturbances, which might impact the stability of the electrical supply. These fluctuations can result in overloading or short circuits within the electrical system, leading to the tripping of the circuit breakers.
To protect your electrical system during storms and lightning, consider taking the following precautions:
- Install Surge Protectors: Use surge protectors to safeguard sensitive electronic devices from power surges caused by lightning strikes or other electrical disturbances.
- Unplug Electronic Devices: Unplug sensitive electronic devices during thunderstorms to prevent potential damage from power surges or lightning strikes.
- Invest in Lightning Protection Systems: Consider installing lightning protection systems, such as lightning rods and surge arresters, to divert lightning strikes away from your property and protect your electrical system.
- Maintain the Electrical System: Regularly inspect and maintain your electrical system to ensure that it is in good condition and capable of withstanding electrical disturbances caused by storms and lightning.
If you experience frequent circuit breaker trips during storms or if you suspect damage to your electrical system as a result of a lightning strike, it is advisable to seek the assistance of a licensed electrician.
A professional electrician can assess the condition of your electrical system, identify any potential issues, and implement necessary measures to safeguard your property from electrical hazards.
Will a breaker trip if wires touch each other?
Yes, a circuit breaker can trip if wires touch each other, especially if the wires create a short circuit.
When wires make direct contact or create a path with low resistance between the hot and neutral wires or between the hot wire and the ground, a short circuit occurs.
This causes a sudden increase in electrical current, exceeding the circuit breaker’s capacity and triggering it to trip.
The purpose of a circuit breaker is to protect the electrical system and connected devices from potential damage caused by overcurrent situations like short circuits. When the circuit breaker trips due to a short circuit, it interrupts the flow of electricity and prevents further damage to the wiring, appliances, and other electrical components.
To prevent wires from touching and causing a short circuit, it’s essential to follow proper wiring practices, including:
- Using appropriate wire connectors and junction boxes to secure and protect wire connections.
- Insulating exposed wires to prevent contact with other wires or conductive materials.
- Maintaining proper wire spacing and organization to minimize the risk of accidental contact.
If you suspect that wires are touching or if you experience frequent circuit breaker trips, it’s essential to consult a licensed electrician to inspect your electrical system.
A professional electrician can identify any potential wiring issues, troubleshoot the cause of the tripping, and ensure the safety and functionality of your electrical system.
Can the circuit breaker trip if you hold it?
The circuit breaker standard UL489 requires circuit breakers to be “trip free”. A trip-free circuit breaker will still trip if you hold it in the ON position.
Yes, you can hold the toggle up, but that does not stop the breaker from tripping under an over-current condition.
A circuit breaker cannot be forced if it trips repeatedly; it will keep opening and burn out.
It is usually not harmful to have a momentary connection, as it will only last for a short time.
You will need to resolve the problem causing the trip and then you will need to replace the circuit breaker if it went bad.
Why is the circuit breaker not tripping?
The circuit breaker may not trip if it malfunctions due to (an entirely mechanical problem, or sustains partial or total damage ) Occasionally, a circuit breaker will not trip in circumstances of fault like a short circuit, or overload, indicating it is bad and must be replaced.
It is also possible for the cause of the problem to be entirely mechanical, which means there may be a physical switch that is stuck in the “on” position.
The circuit breaker may also malfunction without tripping if it sustains partial or total damage. On occasion, a power failure occurs as internal components melt. To ensure appropriate operation, examine the circuit breaker and replace the broken one.
Signs of damaged/ faulty circuit
- Inspect the circuit breakers for any burning odors.
- If the panel feels hot to the touch, the circuit is either broken or overloaded.
- If the circuit is beyond its prime or is too old, replace it with a new one.
- Parts become melted or scorched due to heat.
- The item is defective if it trips off more frequently while gadgets draw more power.
What happens if a breaker doesn’t trip in faults condition?
If a circuit breaker fails to trip during a fault condition, it can lead to various hazardous situations, including:
- Overheating and Fire Risk: When a circuit experiences an overload or short circuit, excessive current flows through the wires, leading to overheating. If the circuit breaker does not trip to interrupt the flow of current, the wires, insulation, or other electrical components can overheat and potentially ignite a fire.
- Equipment Damage: The excessive current in the circuit can damage connected electrical devices, appliances, and other equipment. Without the protection of the circuit breaker, the electrical components can sustain irreparable damage, leading to costly repairs or replacements.
- Electrocution and Safety Hazards: In the absence of circuit protection, the risk of electric shock or electrocution increases, especially if someone comes into contact with live wires or faulty electrical equipment.
- Damage to the Electrical System: Continual overloading or short circuits without interruption from the circuit breaker can cause significant damage to the overall electrical system, including the wiring, panels, and other connected components. This can lead to extensive repairs and pose a safety risk to the property.
To mitigate the risks associated with a circuit breaker failing to trip during a fault condition, it is crucial to regularly inspect and maintain the electrical system. Consider the following measures:
- Schedule Regular Inspections: Arrange for periodic inspections of the electrical system by a qualified electrician to ensure that the circuit breakers are functioning correctly.
- Test the Circuit Breakers: Conduct routine tests on the circuit breakers to verify that they trip appropriately during overload or short circuit situations.
- Upgrade to Advanced Protection: Consider installing advanced protection devices, such as ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) and arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs), to enhance the safety and reliability of the electrical system.
Prioritizing regular maintenance and promptly addressing any issues with the circuit breakers or the electrical system can help prevent hazardous situations and ensure the safety and functionality of your property.
Is the circuit breaker tripping a good or bad thing?
Yes, circuit breaker tripping is good from the perspective of the safety of your home and home appliances .
It also provides protection against dangerous electrical fire hazards due to short circuits and overloading as long as it is not a bad CB .
But sometimes, apparently, you didn’t see any issue, but your circuit breaker keeps tripping and can get you in trouble.
It can be due to wiring issues like too much old wiring, damaged cables, or loose cable connection, which is difficult to troubleshoot because you have to check all the outlet’s wiring connected to the breaker.
That can be time-consuming, but it’s necessary to troubleshoot the fault and rectify it as soon as possible to avoid any bigger damage or loss.
Install my Free Android App on Google Play :
Electrical Cables Most Common Tables
And, my Electrical Calculations App “”
Discover more great content by subscribing to My channel
Looking to stay ahead of the game in the world of electrical engineering? Subscribe to my YouTube channel and gain access to exclusive content you won’t find anywhere else!
The staff I recommend
(Amazon Affiliate Links to products I believe are high quality):
- Economy 120 Volt/60Hz AC Power Source – Step-Down Voltage & Frequency Converters 1800W
- UNI-T Digital Multimeter Tester UT139C
- 50-Amp Extension Cord for RV “100ft”
- Voltage Stabilizer 110/220v
- Hair Dryer “best selling “
- TOSHIBA EM131A5C-BS Countertop Microwave Ovens
Disclaimer : This contains affiliate links to Amazon products. I may earn a commission for purchases made through these links.
You Might Also Like

Fuses (for Beginners), AC fuse in DC circuits
Motor overcurrent causes, effect and protection.

Grounding Systems In Electricity (21 Answers For Beginners)
What Is Overcurrent? (Causes, Effects, and Protection)
Stay safe and connected: why grounding your panel is critical.


How To Tell If A Circuit Breaker Is Bad – 3 Different Ways
The symptoms of a bad circuit breaker can easily be confused with other issues. Constant or periodic tripping is the most notable trait of a faulty breaker, but that can also happen for other reasons. We’re going to show you exactly how to tell if a circuit breaker is bad and needs replacing.
If you want to know about the nature of breakers and how they are supposed to operate, skip down to the What A Circuit Breaker Is And Why We Have Them section.
Now let’s dig in…
Warning: Do not work on electrical equipment unless you are confident in your own capabilities. There is a real risk of electric shock.
Also, before you do any testing, be sure you don’t have any sensitive equipment plugged into the circuit under investigation. It’s unhealthy for electronic devices to be cycled on and off repeatedly.
How To Tell If A circuit breaker Is Bad
Table of Contents
Before starting the troubleshooting process, it’s good to ask yourself a few key questions so that you are effective and efficient in solving the issue. You don’t want to end up chasing your own tail!
Important Troubleshooting Questions To ask Yourself
These questions will help narrow down the possible offender:
- For example, if a breaker only trips in the winter, or after a rainfall, it could be caused by water intrusion into an outside light or outlet. If it only trips at night, it could be a certain light (perhaps exterior) that is the culprit.
- Will the breaker reset? Once the breaker has tripped, can you reset it by flipping the handle all the way off, and then back on? If it won’t hold, you have a dead short or a bad breaker.
- How long will the breaker stay reset? If the breaker will reset, how long before it trips again? Is it a few seconds? An hour? Or is it very inconsistent? If there’s a delay of a second or two before it trips, it is likely a water intrusion issue.
For much more detailed information on identifying why a breaker is tripping, see this article: Why Does My Circuit Breaker Keep Tripping?

Electrical Terms
Now, it’s critical to define a few terms so that we all understand each other. Like any profession, we electricians use terminology that is not always obvious to someone else.
So I want to be sure that you know exactly what I mean – especially if you’re just starting to learn about electrical. Here are a few terms that are pertinent to this article:
- Load: Any device, appliance, or equipment that uses electricity to operate (toaster, light, fan, etc.)
- Outlet/Plug/Receptacle: Receptacle outlet used for plugging a load into. Though these three words have specific unique definitions in the electrical code, the common usage is as though they are synonyms. Therefore, I will use them interchangeably unless otherwise noted.
- Breaker Panel: The enclosure that contains the breakers which feed and protect the circuits in your house. Also called a panel , breaker box , fuse box , and fuse panel (even though there are no fuses in a beaker panel; it’s a legacy term).
- AFCI: Arc-fault circuit interrupter. This can refer to a breaker or outlet.
- GFCI : Ground-fault circuit interrupter. Breaker or outlet.
- DF : Dual Function (AFCI/GFCI combo device). Breaker or outlet.
With those terms defined, now we can get into the troubleshooting.
Connect with an Appliance Repair Tech
Click here to use the chatbox to speak with one of our technicians. No in-home service calls. No appointments.
There are three ways to test a breaker: with a multimeter , without a multimeter , and by swapping . I’ll walk you through each approach, starting with the easiest (least technical) first.
Testing for a bad breaker without a multimeter
I’m going to take you through a step-by-step process to test your breaker. And you will not need a multimeter to do this. For multimeter testing, skip to that section below.
This approach isn’t necessarily going to give you 100% certainty, but I recommend it as the first step to any troubleshooting task. It will weed out many of the potential culprits and get you pointed in the right direction fairly quickly.

This is a simple process of elimination:
- Disable all loads on the circuit.
- Turn off all lights, fans, etc. Unplug all appliances and devices on the circuit. Don’t forget about outside, attic, and crawlspace loads.
- Reset the breaker. If it won’t reset, go to the next section ( Swapping ).
- If it resets, turn on ALL LOADS one-by-one, waiting a minute or so in-between.
- Turn on all lights, and plug in all normal loads (and turn them on), one at a time. Leave them on throughout the test.
- Look for an offending device or appliance on the circuit
- Do not ignore power strips, surge protectors, phone chargers, etc.
- If the breaker trips when you plug in a certain load, you’ve likely found the culprit – either the appliance or the outlet. Unplug the device and turn the breaker back on to repeat the test. Don’t assume the first trip wasn’t a coincidence.
- If it trips again, leave the original circuit off and plug the device into a live circuit, preferably one of the same amperage rating.
- If the breaker trips, the device is to blame. You’ve found your culprit.
- If the device works fine, it is probably a circuit breaker issue. To be certain, move on to the Testing For A Bad Breaker With A Multimeter section below.
If you have all the loads operating on the circuit, and the breaker doesn’t trip, then it’s probably not a breaker issue. Most likely, there is a device or appliance that is intermittently acting up.
To narrow it down, see this article on why a breaker keeps tripping randomly.
Testing for a bad Breaker by Swapping
Swapping breakers is the fastest way to quickly narrow down the possibilities. However, it means doing some work inside the electrical panel. So, as long as you’re confident in your abilities to do so safely, by all means, read on.
First, we’re going to isolate the breaker from the circuit. But the way you do this will depend on your particular situation. Here are the three options:
If the breaker won’t reset :
- Turn off the MAIN breaker to deenergize the panel.
- Try to reset the tripped circuit breaker. If it still won’t reset, it’s bad. If it resets, move on to the next step.
- Remove the breaker panel cover.
- Loosen the screw terminal where the wire is attached to the breaker.
- Remove the wire and bend it out of the way, making sure it doesn’t touch anything.
- Turn the MAIN back on and try to reset the tripped breaker.
- If it still won’t reset, the breaker is likely bad. But to be sure, proceed to Testing For A Bad Breaker With A Multimeter below.
- If it resets, it could still be a weak breaker, but is more likely a circuit or load issue. Proceed to the next step to find out which.

If the breaker trips intermittently :
- Turn off MAIN breaker to deenergize panel.
- Remove panel cover.
- With a bit of masking tape, label the tripped breaker ‘B’ for BAD.
- Locate another breaker that matches the tripped breaker and label it ‘T’ for TEST.
- Swap the two breakers in the panel.
- Turn the MAIN on and flip on the two swapped circuit breakers.
- If ‘T’ holds, and ‘B’ trips, then ‘B’ is likely faulty.
- If ‘T’ trips, and ‘B’ holds, then it is a circuit or load issue.
- ‘B’ could be worn out and can no longer handle normal loads
- ‘T’ is probably fine and there is still a load or circuit issue.
- ‘B’ might be weak and the original circuit is nearly maxed out. ‘T’ is healthy and can handle it. ‘B’ can handle the smaller load of the other circuit… for now. Replace ‘B’ with a new beaker.
- It’s possible that the circuit is maxed-out just enough to trip ‘B’ but not ‘T’ due to milliamp differences in tolerance. This is highly unlikely.
If it is an AFCI, GFCI, or DF breaker :
To test an AFCI, GFCI, or DF breaker, follow steps from the previous section, swapping like-for-like breakers. However, there are a few extra things to check when troubleshooting these breaker types.
For instance, one way to see if the problem is a short-circuit or overload (as opposed to a neutral-to-ground fault) is to swap out the tripping breaker (‘B’) with a regular breaker (‘T’) of the same amperage.
If the regular breaker trips, it’s a short or overload situation. This rules out ground-faults, arc-faults, and nuisance tripping (which is not uncommon with AFCI and DF breakers).
If ‘T’ holds, five things are possible:
- An arc-fault in the circuit
- A ground-fault in the circuit (perhaps water intrusion)
- An appliance issue (check cords for damage)
- An over-sensitive breaker
- The neutral is grounded out
Note: If the breaker was only tripping every now and then, you may have to wait long periods of time in-between some of the above steps. Since most circuits serve a variety of loads, the total load on the breaker will tend to fluctuate often over the course of a day, week, and month.
See the following articles for explanations of arc and ground fault breakers:
What Is An Arc Fault Breaker? What Is A GFCI Breaker? What Is A Dual Function Breaker?
Testing for a bad Breaker with a multimeter
There are three ways you can test for a bad circuit breaker using a multimeter : voltage, amperage, and continuity. Knowing each way is helpful for those who may not own a multimeter , but rather only possess a voltmeter, ammeter, or ohmmeter.
Here is a very basic but top quality multimeter that I own myself, and highly recommend. Yes, you can find cheaper ones, but Fluke has a stellar reputation for a reason.
Note: We may earn a small commission on some purchases, at no additional cost to you. Thanks for your support!

A voltage or continuity test will verify the mechanical open/close function of the breaker. An amperage test will determine whether the breaker is weak and perhaps tripping prematurely.
Let’s take a look at each approach. First, remove the panel cover.
Testing Voltage:
- With the breaker on, test the voltage between the breaker terminal and the ground or neutral bar. You should read approximately 120 volts. If it’s a 2-pole breaker, you should read 120 volts between each breaker terminal and the ground or neutral bar.
- If your voltage readings are more than 10% above or below 120 volts, check other breakers and the MAIN breaker. You might have a utility voltage issue.
- If your breaker won’t reset, and so you can’t take a voltage measurement, refer to the Test A Circuit Breaker By Swapping section above. Remove the wire, turn the breaker on, and test the terminal voltage to ground.
- Flip the breaker on and off while measuring voltage to make sure the beaker is working properly.
Testing Amperage:
If the breaker will reset and hold, do a load test by measuring amps.
- Identify the single wire (usually black) that is attached to the breaker terminal.
- Set your multimeter to AMPS and clamp it around the single wire, positioning it in such a way that you can read the display.
- Turn the breaker on.
- Make sure all loads on the circuit are on (lights, heaters, fans, appliances, etc.).
- Plug in and run all devices that normally operate on the circuit. Sometimes this isn’t completely practical, but do your best.
- With everything running simultaneously, read the display on the meter.
- You should not have a reading above the breaker rating (typically 15 or 20 amps).
- If your reading is at or higher than the breaker rating, your circuit is overloaded. Don’t panic, as there might be simple solutions available .
- If your reading shows at least several amps below the breaker rating, you’re in good shape.
- If your breaker trips before it hits its amp rating, it may be weak. Try plugging in different loads (toaster, portable heater, etc.) to the circuit to confirm.
Testing Continuity:
If you don’t have a multimeter handy, but do have an ohmmeter, there is another way to test a breaker. It’s not quite as convenient, but it’ll get the job done in a pinch.

- Turn off the MAIN breaker so that the panel is deenergized.
- For best results, loosen the screw attaching the wire to the breaker and remove the wire. But this step is not necessary.
- Remove the breaker from the busbar. Most breakers rock outward from the center of the panel, pivoting on the foot behind the terminal screw. Others can be slightly different.
- Once the breaker is out, measure the continuity between the jaws (that attach to the busbar) and the screw terminal.
- Set your multimeter or ohmmeter to CONTINUITY or OHMS. If you have multiple ohm settings, the lowest is best.
- With the breaker in the OFF position, you should get either no reading at all, infinite, open, or OL (open loop). The precise reading will depend on your meter.
- If you get any ohm reading when the breaker is off, that means it is allowing voltage through and is therefore faulty. Replace it.
- Now, with the breaker in the ON position, you should read zero ohms, or nearly zero. You should also hear a continuous beep if your meter is equipped with audible notification.
- If you don’t get an ohm reading of zero (or nearly zero because some meters are imprecise), that means the internal breaker contacts are not fully closed and are inhibiting current flow. Replace it.

Replacing a Bad Breaker
Now let’s go over the process of changing out a breaker. It’s a fairly simple process and poses minimal danger as long as all precautions are followed closely.
Here is a quick run-down of the steps.
- Turn off the MAIN breaker and remove the panel cover.
- Loosen the terminal screw on the breaker and remove the wire.
- Remove the breaker by rocking it out from the center (in most panels), pivoting on the foot, just behind the terminal screw.
- Once pivoted, slide the foot out of the holding bracket.
- With a new breaker that matches exactly , reverse the procedure. Be sure that the new breaker is firmly seated on the bus and the screw terminal is tight on the wire.
What a Circuit Breaker is and Why We Have Them
Here is a rundown of what a breaker is and why we need them in a circuit.
How A Breaker Works
A circuit breaker acts as a sort of gateway between the electrical power at your breaker panel and the circuit that brings that power to your lights and outlets. Think of it as a simple switch that turns on and off the power to the circuit.
However, unlike a normal switch, it also ‘senses’ current flow and will automatically shut off (trip) when the current exceeds its amperage rating. It then must be reset manually.
The reason for this automatic tripping feature, is to protect the wire. If too much amperage (volume of electricity) flows through a wire, it will overheat and melt, thereby causing a fire.
There are two ways a breaker protects the wire:
- Overcurrent protection: In the case that there is too big of a load on the circuit, the breaker will trip when the amperage draw on the circuit is above its rating.
- Short-circuit protection: In the case of either a line-to-line or line-to-ground fault, the breaker will trip instantly.
Both of these functions are extremely crucial to prevent fires from occurring.
Note: As mentioned in a previous section, there are also a couple of special types of breakers ( AFCI & GFCI ) that protect the circuit from other kinds of faults.
How Does A Circuit Breaker Stop Working?
There are a few different ways a breaker might fail:

- Worn-out internal parts: Over time, a breaker’s internal parts can wear down and begin to weaken and malfunction. Usually, this is only if the breaker has seen high amounts of tripping and resetting.
- Melted internal connection: If a breaker has a severe trauma event (e.g. a big short-circuit or voltage surge) it is possible, though unusual, for the internal mechanism to get welded together. The breaker will not trip. In some cases, it will not even shut off manually.
- Worn-out switch mechanism : If a breaker is used as a switch daily, this can eventually wear out the switching mechanism and cause premature breaker failure.
- Manufacturing defect: Sometimes it’s just a simple case of poor quality. This is rare, but every now and then, a faulty product slips past the quality control process at the factory.
Related: Circuit Breaker Is On, But No Power To Outlet
Here are some of the more common questions about breakers. I’ve given concise answers here for convenience. For more detail, see the above article and associated links.
What happens when a circuit breaker goes bad?
When a circuit breaker fails, it can happen in four basic ways:
- It doesn’t trip when it’s supposed to
- It trips more often than it should
- It won’t reset at all
- It won’t turn off
I’ve seen all four situations over the course of my career.
Can a circuit breaker go bad without tripping?
Yes. Though very uncommon, a breaker can fail to trip when it is supposed to, causing an overheated circuit. There is usually no way to know until it is too late.
Certain brands of breakers have been banned over the years due to this danger. Higher standards are in place nowadays, so only specific older brands are known to be a concern. FPE & Zinsco panels are the biggest red flags.
What are the symptoms of a bad circuit breaker?
As noted above, there are a few tell-tale things that are typical signs of a bad circuit breaker.
- If it trips often and you have thoroughly checked the circuit for shorts and overload, it’s likely bad.
- If you can’t reset it, that could indicate failure. Though, it could be a circuit issue.
- If you can’t turn it off manually, it is bad.
How to tell if a GFCI circuit breaker is bad
GFCI breakers are a little more difficult to evaluate because they have extra sensors incorporated into them.
However, many indicators are similar to a regular breaker.
- If the breaker is on, but you have no power on the circuit, the breaker could be bad. Test for voltage with a multimeter right at the breaker terminal to be sure.
- If pressing the small TEST button on the breaker does not trip it, it is bad.
- If it is tripped or off, and won’t reset without a wire connected to it, it is bad.
- If it trips frequently, it could be bad. However, it may be detecting a ground fault on the circuit somewhere. That means it’s doing its job. Find and fix the ground fault.

What causes a circuit breaker to go bad?
Frequent tripping and resetting of the breaker can wear it out and cause premature failure. This can be a result of chronic overloading of the circuit, or a recurring short circuit.
Also, using the breaker as a switch (flipping it several times a day) can eventually wear it out. Some breakers are rated as switches; others are not.
A power surge could fry the innards of some breakers, depending on their sensitivity and type. Lightning can be responsible for this.
Can a bad circuit breaker cause the lights to flicker?
If the breaker is right on the verge of failure, it is possible that it can cause lights to flicker. This, however, is not very common.
Usually, flickering lights is caused by a bad connection somewhere in the circuit – or at the light itself.
On the other hand, lights that fluctuate slightly in brightness, are typically caused by overload on the circuit.
For example, if you plug a vacuum into a nearly full circuit, you may see the lights dim briefly when you hit the ON switch. The vacuum motor draws an extra amount of amperage at startup, briefly overtaxing the circuit.
Final Thoughts
Testing for a bad circuit breaker is fairly easy to do. If you follow the steps above that apply to your situation, you should be able to determine with confidence whether your breaker is still good or not.
Remember to always match a replacement breaker exactly to the old breaker. Never upsize the breaker.
When working in the panel, when possible, always turn off the MAIN breaker. It’s not worth the risk.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Header Sidebar Menu Address Widget
Electrical Safety
5 reasons your circuit breaker trips frequently.
- Jeff LeSuer
- 22 February 2018
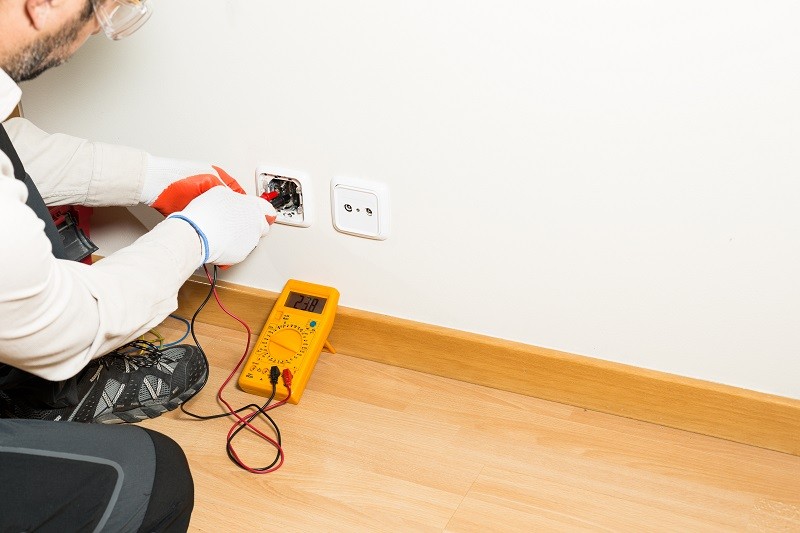

Table of Contents
Do your circuit breakers continue to trip? Are you tired of having to deal with the issue? If so, this can be quite frustrating. However, there are a few things you can do to handle these issues and get the electrical components in your home working properly and consistently.
What Happens when a Breaker Trips?
When a breaker in your home trips, it means that the current flowing into it has exceeded its capacity. If this happens, then the breaker will “trip” or turn everything off, stopping the flow of electrical current to that portion of your home. This is a safety feature , but if it happens more than it should, it can become quite annoying.
Common Causes of Breaker Tripping
There are more than a few things that can result in your breakers to trip; however, here are the five common reasons this may be happening.
- Excessive use of appliances. Every breaker in your home is designed to provide a set amount of electric current. This is measured in amps. If the amps are exceeded, then the breaker is going to trip. This often happens if you buy a new TV and attempt to power it by a circuit that is already at capacity.
- Appliances that require a large amount of electricity. There are some appliances, such as hair dryers, microwaves, portable heaters and vacuums that require a large amount of power. You should always operate these on a dedicated circuit to avoid issues.
- Damaged or worn out breakers. Some situations of frequently tripped breakers have to do with the breakers in question being worn out. Just like any other tool or appliance, your breakers have a set shelf life and will eventually stop working. If and when this happens, you may notice they begin to trip at random times, or that they may stop operating completely. You can call an electrician to replace the circuit breaker in question, which will fix the issue completely.
- Lightning strikes or storms. While this isn’t the most common cause of a tripped circuit breaker, storms can cause some issues. It is a good idea to consider whole-house surge protection to help prevent this. With this in place, you can also protect your high-cost, vital home appliances.
- Bad or improper wiring. If a wire starts to become worn, or if it is damaged, it will open up the home and the circuits to short circuiting. This will result in circuit tripping, and it is quite dangerous. As a result, you need to have your home’s wiring inspected regularly to ensure no issues are present.
You can’t be too careful when it comes to the electrical components in your home. If you think there is a problem and are unsure of how to handle it, you should call the professionals for assistance.

- February 22, 2018
HUGE SAVINGS WHEN YOU USE THESE FUSION ELECTRIC COUPONS
Home safety inspection.
*Applies to labor only. Must mention coupon at time of service. All repairs and installations require a trip charge of $89. Not valid with other offers.
off any residential service or repair
Off panel upgrades, get fast, affordable electrical repair with the service you deserve, same-day service available, call: (913) 563-7975.
- 616-987-0978

Flat River Electric LLC
218 S. Washington St Lowell, MI 49331
Office Number
- [email protected]
- Service Upgrade
- Panel Upgrades
- Electric Vehicle Charger Installation
- Whole Home Automatic Generator
- Portable Generator
- Belding, MI
- Byron Center, MI
- Caledonia, MI
- East Grand Rapids, MI
- Grand Rapids, MI
- Grandville, MI
- Kentwood, MI
- Rockford, MI Electrician
- Wyoming, MI
- Warning Signs of an Overloaded Electrical Circuit
- 7 Electrical Tips to Keep Your Family Safe
- What Causes Lights to Flicker and Dim?
- What Would Cause an Electrical Outlet to Melt?
Is it Dangerous if a Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping?
- Are Ungrounded Outlets Safe?
- Tips for Childproofing Electrical Outlets & Power Strips
- Signs Your Electrical Wiring is Outdated
- How to Protect Electronics from Power Surges
- Should I Switch to LED Light Bulbs?
- 5 Reasons You Need a Standby Generator
- How to Read a Carbon Monoxide Detector
- 5 Electrical Problems Most Common in Summer
- Why is My Electrical Outlet Sparking?
- 7 Reasons to Switch to LED Light Bulbs
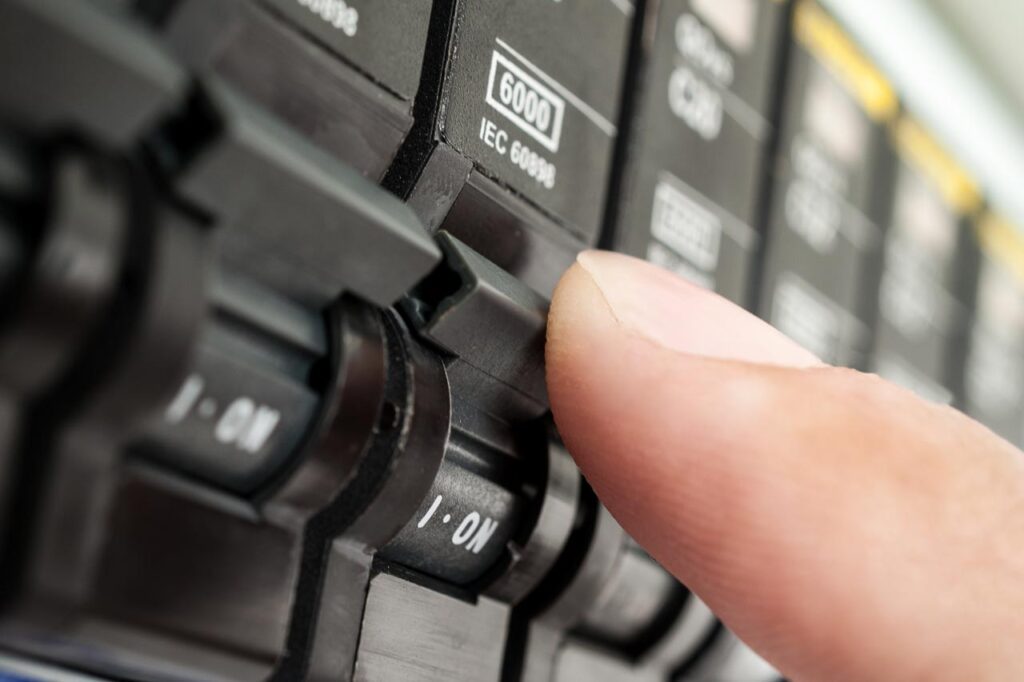

A circuit breaker trips if the demand for electricity exceeds the circuit’s capacity. For example, plugging in too many Christmas lights can trip the circuit breaker. If your circuit breaker keeps tripping, you’ll need to call one of our electricians in Lowell, MI . That way, our electrical contractors will be able to find out why your circuit breaker tripped and offer solutions.
Don’t Ignore a Tripping Circuit Breaker
Don’t ignore a circuit breaker that keeps tripping. This is a sign that one of your circuits is getting overloaded on a regular basis. Your circuits are only able to handle up to a certain level of voltage. Beyond this voltage, you run the risk of starting an electrical fire. This is why the circuit breaker trips, shutting off the flow of electricity in your home.
A power outage from a tripped circuit breaker can be annoying. Yet, it’s important to remember that your circuit breaker serves an important purpose . A circuit breaker prevents high amounts of electricity from overheating wires. If the wires get too hot, they can start an electrical fire. If your circuit breaker keeps tripping, don’t wait to call one of our electricians. Call today!
Common Reasons for a Circuit Breaker to Trip
Your circuit breaker will trip if you exceed the circuit’s capacity for electricity. This often happens when you plug in seasonal items, such as space heaters or Christmas lights.
You don’t have to plug in a large appliance to trip the circuit breaker if you’re close to maximum capacity. At this point, even something as small as plugging in a hairdryer could trip the circuit breaker . If you’re unsure what’s tripping your circuit breaker, call our electricians. We’ll be able to find a solution that works for you.
Your circuit breaker could also be tripping due to a short circuit or ground fault. These issues are more serious and need attention from our electricians. You should especially call us if you notice your wall outlet plate has melted or smells like smoke.
How We Fix Circuit Breakers
We may recommend that you upgrade your electrical panel if your home is over 40 years old. Today’s homeowners demand much more electricity than previous generations for microwaves, refrigerators, and other technology.
Depending on your home, we may recommend a complete home rewire or an update to your electrical panel. For example, you may only need another circuit and respective circuit breaker. That way, your electrical system will be able to handle your energy needs.
You may need a new electrical panel if:
- Your circuit breaker trips often
- There are interruptions in power
- Appliances can’t run on full power
We always put your safety first when installing or updating an electrical panel. For example, you’ll need ground fault circuit interrupters for outlets in wet areas like bathrooms. That way, you reduce your risk of electric shock injury.
Call Us Today
Our electrical contractors in Lowell, MI work hard to make sure your home is safe. To request a service call for a circuit breaker, call Flat River Electric at (616) 987-0596 .
Related Blog Posts
5 Reasons Your Circuit Breaker May Be Tripping
What Causes Overloaded Circuits?
Dangers of Nonworking Electrical Devices or Circuits
This blog post has been updated.
- Flat River Electric LLC, 218 S. Washington St Lowell, MI 49331
Helpful Links
Service area.
Copyright © 2024 – Flat River Electrical, LLC . All Rights Reserved.
Request Service
What can we do for you, service needed.

Information About Your Request
Drag and Drop (or) Choose Files
Customer Status
Have we served you in the past?

What Time Of Day Is Best For You?
What to Do when a Circuit Breaker Trips Intermittently

A circuit breaker that trips open intermittently may be indicative of a circuit overload or an intermittent short circuits. Two reasons a circuit breaker trips open are circuit overloads and short circuits. Circuit breakers, like the older, Edison-based fuses, are designed to protect electrical writing against circuit overloads and short circuits.
Short circuits occur when a hot wire comes into contact with the circuit's neutral conductors or when it comes into contact with some grounded surface. Short circuits are relatively easy to diagnose because the circuit breaker will not hold after resetting until the short circuit is located and repaired. Circuit overloads, on the other hand, are not so easy to diagnose because, depending on the amount of the overload current, the circuit may hold after being reset until the heat building up from the overload current causes the thermally operated circuit breaker to trip open once again.
A third possible cause for a circuit breaker to trip open is that the circuit breaker itself has become defective. Circuit breakers becoming defective is not a common problem with residential wiring systems, but it can happen. There might have been a manufacturing defect with the circuit breaker that the QC inspections did not catch. This kind of problem usually makes itself known relatively soon after the CB is newly installed. Another cause for a CB to become defective is a power surge that causes so much heat in such a short period of time that the bi-metal strip in the CB is weakened or damaged in some other way.
How much circuit current constitutes a circuit overload?
Residential 120-volt branch circuits are either protected by circuit breakers rated at 15-amperes or 20-amperes but that does not mean that these circuits can be loaded down at constant 15 or 20-amperes current. The reason for that is that most circuit breakers are designed to only carry a continuous current of up to 80 percent of their rated current. In other words, a circuit protected by a 15-ampere CB has a load rating of 1,440-Watts or 12-Amperes.
A circuit protected by a 20-Ampere CB should be loaded to 1,920-Watts or 16-Amperes. These maximum safe loads are not only required by the CB's design, they are requirements of the National Electric Code (NEC). There is one exception to this rule, some circuit breakers are designed to carry 100-percent of their rated current and those CB's are so marked on their cases.
Troubleshooting and Isolating circuit overloads
If you do not already own a clamping ammeter, now is the time to procure. There are many quality clamping meters on the market today at very reasonable prices but one of the best sources of tools for the do-it-yourself person is Harbor Freight. You could spend hundreds of dollars for a clamping meter but the Cen-Tech 7—Function, clamp—on multimeter sold by Harbor Freight for less than $30 will be all the meter the average do-it-yourself person will ever need for residential electrical work. This meter tests resistance and AC and DC voltage without splicing wires or puncturing insulation. The meters 17-test ranges include
- DC Voltage—4 ranges 200mV/20V/200V/1000V
- AC CurrentAC Voltage—2 ranges 200V/750V—3 ranges 20A/200A/1000A
- Resistance—5 Ranges 200Ω/2kΩ/20kΩ/200kΩ/2MΩ
- And a Continuity Test.
The actual product/operating manual is available in pdf format here .
Safety First
One of the very first rules that every do-it-yourself person is taught when doing an electrical project is to always turn the electricity off first by switching the circuit breaker to the off position. But, as James Thurber (1894-1961), the writer and cartoonist once said, “There is no exception to the rule that every rule has an exception.” This is one of those exceptions for electrical safety rules. When performing an electrical circuit load test, just as when performing circuit voltage tests, the power must be left on.
Performing the load test
Ido not believe in reinventing the wheel. I have already published a step by step guide called “ How to Tell If You Have a Faulty Breaker in Your Breaker Box ” on e-How.
Circuit overloaded
If the circuit is actually overloaded, the meter indicates a load of more than 12-Amperes on a 15-Ampere circuit or a 16-Ampere load on a 20-Ampere circuit, you will need to reduce the load by moving some of the plugged in loadsto a different branch circuit.
Replacing a defective circuit breaker
If the load current is 80 percent or less of the circuit breaker rated amperes and the breaker continues to trip open, you will need to replace the circuit breaker. For a good step-by-step guide for removing and replacing a defective branch circuit CB, go to Replacing a Breaker in Your Panel .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Find out the cost to replace an electrical panel. On every breaker, there will be an "On" and "Off" position. On a tripped breaker, the handle will be in the middle, neither On nor Off. To reset, flip the handle to Off first, then to On. Stand to the side of the panel and turn your face away when flipping breakers.
Devices charging slowly. Electrical outlets not working. Flickering lights. Scorch marks on outlets and light switches. If a circuit breaker keeps tripping in one room, homeowners can test for ...
When your circuit breaker trips, it's often due to preventable electrical issues within your home. Understanding why this happens is the first step in addressing the problem. 1. Overloaded Circuits. Overload occurs when you demand more electrical power from a circuit than it can handle. Common signs of an overloaded circuit include appliances ...
If you suspect a short circuit, unplug your appliances and check the wires for melted coverings. You might also notice a burning smell coming from the outlet. Call in a professional electrician to find the source of the problem. 3. Circuit Overload. Circuit overloads are the most common reason that a breaker trips.
To reset it, switch the breaker all the way to the "off" position first, and then firmly switch it back to the "on" position. This reset process restores power to the circuit and allows you to test if the breaker continues to trip or if the issue has been resolved. Step 4: Observe for immediate re-tripping.
Here are five reasons your circuit breaker keeps tripping, as well as some ways you can diagnose the cause. 1. Ground Fault. Environmental factors may sometimes create an unintended path to the ground. If a hot circuit brushes up against a conductive surface, the electricity will follow this path rather than the wire.
If a circuit breaker trips often, it may mean there's an issue. It's best to get professional help in these cases. Time to go on a hunt for your electrical wiring! Troubleshooting Circuit Breaker Tripping. Circuit breakers can flip out for multiple reasons, like overloads, short circuits, and ground faults.
The reason this is called a circuit breaker is that it is designed to break up the circuit when too much current tries to run through. For example, if your circuit is designed to be 20 amps and you are running 30 amps to it, the breaker is going to stop this and trip in an effort to keep the home safe. Often we try to plug too many things into ...
Resetting a tripped circuit breaker is a simple process that can be done by following a few easy steps. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you reset a tripped circuit breaker safely and effectively: Step 1: Locating the Tripped Breaker. Step 2: Ensuring Safety Before Proceeding. Step 3: Resetting the Circuit Breaker.
A circuit breaker is a switch inside your breaker box that monitors the flow of electricity on a circuit and turns off or trips if the circuit becomes damaged or overloaded. ... running too many high-amp electrical appliances at a time is often the cause of a tripped breaker. If an electrical overload is the problem, unplugging any unnecessary ...
Short Circuit. A short circuit might be another reason why your breaker keeps tripping. Unlike circuit overloads, short circuits have more potential to cause fires. A short circuit happens when a live or "hot" wire touches a neutral wire. When the two wires touch, they cause a sudden surge of current through the wires.
Flip Back to ON Position. When you find the circuit breaker That's switched off, flip it back into the ON position. You should feel a slight resistance when flipping the lever and hear a clicking sound signaling that it's been flipped back on. This should restore power but if it doesn't, you may need to flip your breaker one more time.
This may result in your circuit breaker tripping more often. Appliance Issues. In some cases, your electrical appliances can trip your circuit breaker. This is especially true if any of your appliances have faulty wiring. Be sure to repair or replace the electrical wiring as soon as possible to prevent more severe and costly damage.
Check the panel every time you plug a new appliance in. If the breaker trips, do this experiment again but plug things on in a different order. If your breaker keeps tripping, you know you have an overloaded circuit. Off the bat, let us mention a few solutions here. Dedicated circuits may resolve this issue.
Leave the devices plugged in and turned on for a few minutes to see if the breaker trips again. If the breaker trips after several minutes, try the process again, but leave 1-2 less important devices unplugged. Eventually, you'll find a combination of devices that doesn't trip the circuit breaker. 4.
The main circuit breaker "tripping" is somewhat uncommon since often, individual circuit breakers trip long before the main breaker has to shut down. Does weather affect the circuit breaker? Yes, weather affects the circuit breakers. In response to the heat generated by the circuit breaker, the bimetallic strip inside the breaker flexes and ...
Swap the two breakers in the panel. Turn the MAIN on and flip on the two swapped circuit breakers. If 'T' holds, and 'B' trips, then 'B' is likely faulty. If 'T' trips, and 'B' holds, then it is a circuit or load issue. If both breakers trip…. 'B' could be worn out and can no longer handle normal loads.
A ground fault can happen when a hot or active wire contacts the ground wire. The ground wire is a grounded portion of the junction box or a grounded area of an appliance. When a hot wire and a ground wire make contact, large amounts of current go through the circuit breaker, which will often cause the circuit breaker to trip.
Find your circuit box and search for the breaker (s) in the OFF position. Some circuit breakers have a red or orange color if they are switched OFF. Flip the breaker from OFF to ON. Then, simply turn back on the appliances and devices you turned off in step 1, and you should be fine. If your circuit breaker keeps tripping, it's time to call ...
Lightning strikes or storms. While this isn't the most common cause of a tripped circuit breaker, storms can cause some issues. It is a good idea to consider whole-house surge protection to help prevent this. With this in place, you can also protect your high-cost, vital home appliances. Bad or improper wiring.
Common Reasons for a Circuit Breaker to Trip. Your circuit breaker will trip if you exceed the circuit's capacity for electricity. This often happens when you plug in seasonal items, such as space heaters or Christmas lights. You don't have to plug in a large appliance to trip the circuit breaker if you're close to maximum capacity. At ...
If the load current is 80 percent or less of the circuit breaker rated amperes and the breaker continues to trip open, you will need to replace the circuit breaker. For a good step-by-step guide for removing and replacing a defective branch circuit CB, go to Replacing a Breaker in Your Panel. If you have a circuit breaker that continues to trip ...
When a GFCI outlet keeps tripping, there must be a reason. Instead of just resetting the GFCI, you should also investigate the cause of the trip. Ground Faults: Ground faults occur when electrical current finds an unintended path to ground. These are often caused by worn insulation, conductive dust, water, or other soft grounds.