Online Language Dictionaries
Perfect tenses, continuous (progressive) and emphatic tenses, compound continuous (progressive) tenses, conditional, subjunctive.
*Blue letters in conjugations are irregular forms. ( example ) *Red letters in conjugations are exceptions to the model. ( example )
Report a problem.


Travel Past Tense
Commonwealth travelled, US traveled past tense of travel is Commonwealth travelled, US traveled.
Travel verb forms
Conjugation of travel.
- What is the past tense of tup in English?
- What is the second form of verb TUPE?
- What is the third form of verb turbanize in English?
- What is the conjugation of turbinate in English?
- Conjugate turbocharge in English?
- turkey-trot
PastTenses is a database of English verbs. One can check verbs forms in different tenses. Use our search box to check present tense, present participle tense, past tense and past participle tense of desired verb.
Conjugation verb travel
Model : cancel
Auxiliary : have , be
Other forms: travel oneself / not travel
Contractions
in the U.K. spelling we double up the 'l' in preterite and participle endings
The verb has several variants of conjugation, which may correspond to different meanings. Please use the menu to select one or all variants.
- he/she/it travels
- they travel
- I travelled/traveled
- you travelled/traveled
- he/she/it travelled/traveled
- we travelled/traveled
- they travelled/traveled
Present continuous
- I am travelling/traveling
- you are travelling/traveling
- he/she/it is travelling/traveling
- we are travelling/traveling
- they are travelling/traveling
Present perfect
- I have travelled/traveled
- you have travelled/traveled
- he/she/it has travelled/traveled
- we have travelled/traveled
- they have travelled/traveled
- I will travel
- you will travel
- he/she/it will travel
- we will travel
- they will travel
Future perfect
- I will have travelled/traveled
- you will have travelled/traveled
- he/she/it will have travelled/traveled
- we will have travelled/traveled
- they will have travelled/traveled
Past continous
- I was travelling/traveling
- you were travelling/traveling
- he/she/it was travelling/traveling
- we were travelling/traveling
- they were travelling/traveling
Past perfect
- I had travelled/traveled
- you had travelled/traveled
- he/she/it had travelled/traveled
- we had travelled/traveled
- they had travelled/traveled
Future continuous
- I will be travelling/traveling
- you will be travelling/traveling
- he/she/it will be travelling/traveling
- we will be travelling/traveling
- they will be travelling/traveling
Present perfect continuous
- I have been travelling/traveling
- you have been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it has been travelling/traveling
- we have been travelling/traveling
- they have been travelling/traveling
Past perfect continuous
- I had been travelling/traveling
- you had been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it had been travelling/traveling
- we had been travelling/traveling
- they had been travelling/traveling
Future perfect continuous
- I will have been travelling/traveling
- you will have been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it will have been travelling/traveling
- we will have been travelling/traveling
- they will have been travelling/traveling
- let's travel
- travelling/traveling
- travelled/traveled
Perfect participle
- having travelled/traveled
Helping millions of people and large organizations communicate more efficiently and precisely in all languages.
To support our work, we invite you to accept cookies or to subscribe.
You have chosen not to accept cookies when visiting our site.
The content available on our site is the result of the daily efforts of our editors. They all work towards a single goal: to provide you with rich, high-quality content. All this is possible thanks to the income generated by advertising and subscriptions.
By giving your consent or subscribing, you are supporting the work of our editorial team and ensuring the long-term future of our site.
If you already have purchased a subscription, please log in
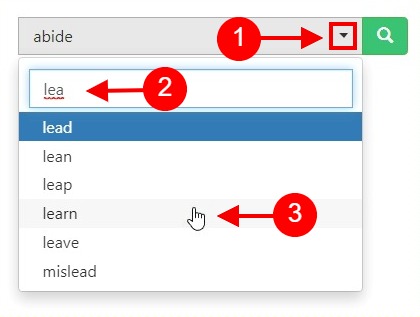
How to conjugate "to travel" in English?
English "to travel" conjugation.
- traveled; travelled
Full conjugation of "to travel"
Translations for "to travel", present continuous, simple past, past continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, conditional, conditional present, conditional present progressive, conditional perfect, conditional perfect progressive, subjunctive, present subjunctive, past subjunctive, past perfect subjunctive, present participle, past participle.
Translations for "to travel" in our English dictionaries
Popular English verbs
Find out the most frequently used verbs in English.
CULTURE & TRAVEL
Social login.
'travel' conjugation table in English
Past participle, present participle, present continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous.
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

All ENGLISH words that begin with 'T'
Here are the past tense forms of the verb travel
👉 Forms of verb travel in future and past simple and past participle. ❓ What is the past tense of travel.
Travel: Past, Present, and Participle Forms
What are the 2nd and 3rd forms of the verb travel.
🎓 What are the past simple, future simple, present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect forms of the base form (infinitive) ' travel '? 👉 It's quite simple -->
Learn the three forms of the English verb 'travel'
- the first form (V1) is 'travel' used in present simple and future simple tenses.
- the second form (V2) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in past simple tense.
- the third form (V3) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in present perfect and past perfect tenses.
What are the past tense and past participle of travel?
What is the past tense of travel.
The past tense of the verb "travel" is "travelled (BrE)", or "traveled (AmE)", and the past participle is "travelled (BrE)" or "traveled (AmE)".
Verb Tenses
Past simple — travel in past simple travelled (BrE), traveled (AmE) (V2) . Future simple — travel in future simple is travel (will + V1) . Present Perfect — travel in present perfect tense is travelled (BrE), traveled (AmE) (have/has + V3) . Past Perfect — travel in past perfect tense is travelled (BrE), traveled (AmE) (had + V3) .
travel regular or irregular verb?
👉 Is 'travel' a regular or irregular verb? The verb 'travel' is regular verb .
Examples of Verb travel in Sentences
- These days we travelled 1400 km (Past Simple)
- We didn't travel that long (Past Simple)
- She has travelled extensively in the Philippines (Present Perfect)
- I can't travel without you (Present Simple)
- We usually travel to work by bus (Present Simple)
- A plane travels faster than a train (Present Simple)
- They are travelling together since 2018 (Present Continuous)
- You can travel by foot, why not? (Present Simple)
- Unfortunately you can't travel without a ticket, so please proceed to the ticket office (Present Simple)
- How many countries have you travelled to? (Present Perfect)
Along with travel, words are popular see and tell .
Verbs by letter: r , d , u , c , m , p , b , w , h , a , e , g , s , q , j , l , t , f , o , n , k , i , v , y , z .
English verbs
- 318 Irregular verbs
- 904 Regular verbs
- 5 Modal verbs
- 407 Phrasal verb
Online verb dictionary
We are currently working to add new verbs and examples to our website, along with detailed descriptions. Please send us a message if you have any requests or suggestions, and we will add them as quickly as we can. Thank you for your interest in our website!
our editor - Peter (Certified TEFL Tutor with over 8 years experience)
Have a question or find mistake?
- Slovenščina
- FAQ Technical Questions
- Text Translation
- Vocabulary Trainer
- Online Dictionary
- Login
- Online dictionary
- Products & Shop
- Conjugation
- Vocabulary trainer
- Dictionary API
- Add to home screen
- Browse the dictionaries
- Terms and conditions of use
- Supply chain
- Data Protection Declaration
- Legal notice
- Privacy Settings
- EN');"> English
- FR');"> French
- DE');"> German
- LA');"> Latin
- ES');"> Spanish
Verb Table for travel
- Simple tenses
- Continuous tenses
Conditional
Simple tenses • continuous tenses • conditional • imperative • impersonal, present perfect, past perfect, will -future, going to -future, future perfect, conditional past, past participle, browse the conjugations (verb tables), look up "travel" in other languages, links to further information.
You can suggest improvements to this PONS entry here:
We are using the following form field to detect spammers. Please do leave them untouched. Otherwise your message will be regarded as spam. We are sorry for the inconvenience.
My search history
- Most popular
- English ⇄ German
- English ⇄ Slovenian
- German ⇄ Spanish
- German ⇄ French
- German ⇄ Greek
- German ⇄ Polish
- Arabic ⇄ English
- Arabic ⇄ German
- Bulgarian ⇄ English
- Bulgarian ⇄ German
- Chinese ⇄ English
- Chinese ⇄ French
- Chinese ⇄ German
- Chinese ⇄ Spanish
- Croatian ⇄ German
- Czech ⇄ German
- Danish ⇄ German
- Dutch ⇄ German
- Elvish ⇄ German
- English ⇄ Arabic
- English ⇄ Bulgarian
- English ⇄ Chinese
- English ⇄ French
- English ⇄ Italian
- English ⇄ Polish
- English ⇄ Portuguese
- English ⇄ Russian
- English → Serbian
- English ⇄ Spanish
- Finnish ⇄ German
- French ⇄ Chinese
- French ⇄ English
- French ⇄ German
- French ⇄ Italian
- French ⇄ Polish
- French ⇄ Slovenian
- French ⇄ Spanish
- German ⇄ Arabic
- German ⇄ Bulgarian
- German ⇄ Chinese
- German ⇄ Croatian
- German ⇄ Czech
- German ⇄ Danish
- German ⇄ Dutch
- German ⇄ Elvish
- German ⇄ English
- German ⇄ Finnish
- German ⇄ Hungarian
- German → Icelandic
- German ⇄ Italian
- German ⇄ Japanese
- German ⇄ Latin
- German ⇄ Norwegian
- German ⇄ Persian
- German ⇄ Portuguese
- German ⇄ Romanian
- German ⇄ Russian
- German → Serbian
- German ⇄ Slovakian
- German ⇄ Slovenian
- German ⇄ Swedish
- German ⇄ Turkish
- Dictionary of German Spelling
- Greek ⇄ German
- Hungarian ⇄ German
- Italian ⇄ English
- Italian ⇄ French
- Italian ⇄ German
- Italian ⇄ Polish
- Italian ⇄ Slovenian
- Italian ⇄ Spanish
- Japanese ⇄ German
- Latin ⇄ German
- Norwegian ⇄ German
- Persian ⇄ German
- Polish ⇄ English
- Polish ⇄ French
- Polish ⇄ German
- Polish ⇄ Italian
- Polish ⇄ Russian
- Polish ⇄ Spanish
- Portuguese ⇄ English
- Portuguese ⇄ German
- Portuguese ⇄ Spanish
- Romanian ⇄ German
- Russian ⇄ English
- Russian ⇄ German
- Russian ⇄ Polish
- Slovakian ⇄ German
- Slovenian ⇄ English
- Slovenian ⇄ French
- Slovenian ⇄ German
- Slovenian ⇄ Italian
- Slovenian ⇄ Spanish
- Spanish ⇄ Chinese
- Spanish ⇄ English
- Spanish ⇄ French
- Spanish ⇄ German
- Spanish ⇄ Italian
- Spanish ⇄ Polish
- Spanish ⇄ Portuguese
- Spanish ⇄ Slovenian
- Swedish ⇄ German
- Turkish ⇄ German
Identified ad region: ALL Identified country code: RU -->

Select your English level
To personalize your experience.
- To Travel Conjugation
In the US the spelling 'traveling' and 'traveled' are preferred.
Continuous Perfect
Conditional.
We notice you're using an ad blocker.
Linguasorb is free and ad supported, without ad revenue we can't exist. Certain features such as audio, directly cost us money and so are disabled for ad block users.
Please disable your ad blocker for this site if you wish to use the premium features.
Alternatively you can become a supporter and remove the ads completely .
Onlymyenglish.com
Learn English
Travel Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Table of Contents
Travel past tense
Travel past participle, travel verb forms v1 v2 v3 v4, conjugation of travel, more verb past tense, you might also like.

Tear Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Animate Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Detach Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Engrave Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Blur Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Deserve Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3
Travel Past Tense: Verb Forms, Conjugate TRAVEL
- commonwealth travelled, us traveled
The past tense of travel is commonwealth travelled, us traveled
The Forms of Travel
Conjugate travel, travel in present simple (indefinite) tense, travel in present continuous (progressive) tense, travel in present perfect tense, travel in present perfect continuous tense, travel in past simple (indefinite) tense, travel in past continuous (progressive) tense, travel in past perfect tense, travel in past perfect continuous tense, travel in future simple (indefinite) tense, travel in future continuous (progressive) tense, travel in future perfect tense, travel in future perfect continuous tense, leave a comment cancel reply.

Past Tense of Travel: Traveling Back in Time
By: Author Oliver
Posted on Last updated: August 12, 2023
Sharing is caring!
Welcome to our article on the past tense of travel! If you’re learning English grammar, you know that understanding verb tenses is an essential part of the language. The past tense is particularly important, as it allows us to talk about events and experiences that have already happened. In this article, we’ll explore the basics of English tenses, give an overview of the past tense, and focus specifically on how to use the past tense when talking about travel.
Travel is one of the most common topics of conversation, and being able to talk about past trips is a great way to connect with others and share experiences. However, using the past tense correctly can be tricky, especially when it comes to irregular verbs and complex sentence structures. In this article, we’ll provide plenty of examples and exercises to help you master the past tense of travel. We’ll also cover some common mistakes to avoid and provide additional resources for further learning.
So whether you’re planning your next trip or just want to improve your English skills, read on to learn everything you need to know about the past tense of travel!
Key Takeaways
- The past tense is essential for talking about past events and experiences, past tense of ‘travel’ is ‘traveled’
- By practicing with examples and exercises, you can improve your use of the past tense of travel and avoid common mistakes.

Past Tense of Travel
Travel is a verb that is commonly used in the past tense. In this section, we will cover the formation and usage examples of the past tense of travel.
To form the past tense of travel, we add “-ed” to the base form of the verb. For example:
- I traveled to Europe last summer.
- She traveled to Asia for business.
- We traveled to South America for vacation.
Simple Past
The simple past is used to describe a completed action in the past. Regular verbs like travel are formed by adding -ed to the base form. For example:
- I traveled to Paris last year.
Past Continuous
The past continuous is used to describe an action that was in progress at a specific point in the past. It is formed by using the past tense of “to be” (was/were) and the present participle (-ing) of the main verb. Here are some examples:
- I was traveling to Paris when I got a call from my boss.
Usage Examples
The past tense of travel is used to talk about a completed action in the past. Here are some examples:
- I traveled to Japan last year and had an amazing time.
- She traveled to Italy for her honeymoon and fell in love with the country.
- We traveled to Mexico for our anniversary and enjoyed the beautiful beaches.
We can also use the past tense of travel to talk about a past habit or routine. For example:
- When I was younger, I traveled to different countries every summer.
- She traveled for work every week and got used to living out of a suitcase.
- We traveled to visit our family every holiday season.
In conclusion, the past tense of travel is formed by adding “-ed” to the base form of the verb and is used to talk about completed actions or past habits. Practice using the past tense of travel in your own sentences to improve your English grammar skills.
Common Mistakes with Past Tense of Travel
If you are learning English, you might be struggling with the past tense of the verb “travel.” Here are some common mistakes people make and how to avoid them.
Mixing Past and Present Tenses
One of the most common mistakes is mixing past and present tenses. For example, saying “I travel to Paris last year” instead of “I traveled to Paris last year.” To avoid this mistake, remember to use the past tense of “travel” when referring to something that happened in the past.
Using the Present Participle
Another mistake is using the present participle instead of the past tense. For example, saying “I am traveling to London last week” instead of “I traveled to London last week.” To avoid this mistake, remember to use the past tense of “travel” when referring to something that happened in the past.
Using the Wrong Auxiliary Verb
Using the wrong auxiliary verb is also a common mistake. For example, saying “I was travel to Rome” instead of “I traveled to Rome.” To avoid this mistake, remember to use the correct auxiliary verb (in this case, “did”) when forming the past tense.
Example Sentences
Here are some example sentences to help you practice using the past tense of “travel” correctly:
- I traveled to Japan last summer.
- She visited her grandparents in Florida last month.
- They took a road trip across the United States.
- We flew to Paris for our honeymoon.
- He backpacked through Europe after college.
Remember, practice makes perfect! Keep practicing using the past tense of “travel” correctly, and soon it will become second nature.
Exercises to Practice Past Tense of Travel
Learning English grammar can be challenging, especially when it comes to mastering the past tense of travel. To help you improve your skills, we have compiled a list of exercises that you can use to practice and perfect your past tense of travel.
Interactive Exercises
Interactive exercises are a great way to practice the past tense of travel. They allow you to engage with the material and receive immediate feedback on your progress. Here are a few interactive exercises you can try:
- Fill in the Blank: In this exercise, you will be given a sentence with a blank space where the past tense verb should go. Your task is to fill in the blank with the correct past tense verb. For example, “I ___ to Paris last year.” The correct answer would be “went.”
- Matching: In this exercise, you will be given a list of past tense verbs and a list of travel-related words. Your task is to match the past tense verb with the correct travel-related word. For example, “flew” would match with “airplane.”
Written Exercises
Written exercises are another great way to practice the past tense of travel. They allow you to focus on the material and practice at your own pace. Here are a few written exercises you can try:
- Sentence Writing: In this exercise, you will be given a travel-related word, and your task is to write a sentence using the correct past tense verb. For example, “train” could be used in the sentence, “I ___ to New York on a train.”
- Paragraph Writing: In this exercise, you will be given a prompt related to travel, and your task is to write a paragraph using the correct past tense verbs. For example, “Write a paragraph about your last vacation.” You could write, “Last summer, I ___ to Hawaii with my family. We ___ on the beach, ___ in the ocean, and ___ at some amazing restaurants.”
By practicing these exercises, you will improve your understanding and mastery of the past tense of travel. Keep practicing, and before you know it, you’ll be a pro at English grammar!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the past tense of travel?
The past tense of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English. Both spellings are correct, but American English tends to drop the second “l” in the past tense and past participle forms of the verb.
Is it spelled Travelled or traveled?
As mentioned above, both spellings are correct. The difference in spelling is due to the variation in American and British English.
Which is correct travel or travelling?
Both “travel” and “travelling” are correct, but “traveling” is the preferred spelling in American English, while “travelling” is the preferred spelling in British English.
What’s the difference between travel and Travelled?
“Travel” is the present tense of the verb, while “travelled” is the past tense. The difference between the two is the time frame in which the action occurs.
What is the V2 form of travel?
The V2 form of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English.
What is the V3 form of travel?
The V3 form of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English.
In summary, the past tense of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English. Both spellings are correct, and the difference in spelling is due to the variation in American and British English. Additionally, “traveling” is the preferred spelling in American English, while “travelling” is the preferred spelling in British English.
The past tense of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English. Both spellings are correct, but American English tends to drop the second \"l\" in the past tense and past participle forms of the verb.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"Is it spelled Travelled or traveled?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"Which is correct travel or travelling?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
Both \"travel\" and \"travelling\" are correct, but \"traveling\" is the preferred spelling in American English, while \"travelling\" is the preferred spelling in British English.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What's the difference between travel and Travelled?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
\"Travel\" is the present tense of the verb, while \"traveled\" is the past tense. The difference between the two is the time frame in which the action occurs.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the V2 form of travel?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The V2 form of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the V3 form of travel?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The V3 form of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English.
In summary, the past tense of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English. Both spellings are correct, and the difference in spelling is due to the variation in American and British English. Additionally, \"traveling\" is the preferred spelling in American English, while \"travelling\" is the preferred spelling in British English.
- Recent Posts
- Plural of Safe: What It Is and How to Use It Correctly - October 3, 2023
- Purple Color Names: Different Hues of Purple - October 2, 2023
- Addition Transition Words for Clear and Cohesive Writing - September 30, 2023
Related posts:
- Past Tense of Buy: How to Use them Correctly in English Grammar
- Mastering English Grammar: The Definitive Guide to Understanding the Past Tense of Cost
- Past Tense of Drag: Dragged Through Time
- Hoped or Hoped For? Mastering the Past Tense of Hope with Ease
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Table of irregular verbs
Note that be has several irregular forms:
Present: ( I ) am , ( she, he, it ) is , ( you , we , they ) are
Past: ( I, she, he, it ) was , ( you , we , they ) were
-ed form: been

Word of the Day
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
a long period when there is little or no rain

Fakes and forgeries (Things that are not what they seem to be)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Travel past tense
Learn past tenses to communicate in English accurately
Meaning of travel
to go from one place to another, typically over a distance of some length.

- 1. Every summer, she travels to a new country to explore different cultures.
- 2. He often travels by train because he enjoys watching the scenery.
- 3. They travel to work together in a carpool to save on gas and reduce emissions.

Past Simple
- 1. Last summer, I traveled to Italy with my family.
- 2. She traveled across the country by train for her research project.
- 3. They traveled through several small towns to experience the local culture.

Past Participle
- 1. By the end of their gap year, they had traveled through five continents.
- 2. She had traveled to over twenty countries before turning thirty.
- 3. We had traveled all night to reach the mountains by sunrise.
Learn more words on the go
Master verb forms with Promova!

Bare infinitive
- Regular actions or routines. Example. I travel to work by train every day. Example. The Earth travels around the sun. Example. He travels to Italy every summer. Example. She travels with her job. Example. My flight travels at 10 PM tonight.
- Facts or general truths. Example. I travel to work by train every day. Example. The Earth travels around the sun. Example. He travels to Italy every summer. Example. She travels with her job. Example. My flight travels at 10 PM tonight.
- Habitual actions. Example. I travel to work by train every day. Example. The Earth travels around the sun. Example. He travels to Italy every summer. Example. She travels with her job. Example. My flight travels at 10 PM tonight.
- Permanent situations. Example. I travel to work by train every day. Example. The Earth travels around the sun. Example. He travels to Italy every summer. Example. She travels with her job. Example. My flight travels at 10 PM tonight.
- Timetabled or scheduled events (in the near future). Example. I travel to work by train every day. Example. The Earth travels around the sun. Example. He travels to Italy every summer. Example. She travels with her job. Example. My flight travels at 10 PM tonight.
- Completed actions in the past at a specific time. Example. I traveled to France last year. Example. Last weekend, I traveled to the countryside, visited my grandparents, and came back late Sunday. Example. When I was a child, I traveled with my family every summer. Example. She traveled alone before she got married.
- A series of completed actions in the past. Example. I traveled to France last year. Example. Last weekend, I traveled to the countryside, visited my grandparents, and came back late Sunday. Example. When I was a child, I traveled with my family every summer. Example. She traveled alone before she got married.
- Habits in the past. Example. I traveled to France last year. Example. Last weekend, I traveled to the countryside, visited my grandparents, and came back late Sunday. Example. When I was a child, I traveled with my family every summer. Example. She traveled alone before she got married.
- Past facts or generalizations which are no longer true. Example. I traveled to France last year. Example. Last weekend, I traveled to the countryside, visited my grandparents, and came back late Sunday. Example. When I was a child, I traveled with my family every summer. Example. She traveled alone before she got married.
- Perfect tenses. Example. I have traveled to ten different countries so far. Example. Before she moved to Italy, she had traveled all around Europe. Example. By next year, I will have traveled to every continent. Example. The package has been traveled through various countries before it arrived. Example. The traveled paths of this jungle are safe for tourists. Example. They are a welltraveled couple who have visited over fifty countries.
- Present Perfect. Expresses an action that occurred at an unspecified time before now or an action that started in the past and continues in the present. Example. I have traveled to ten different countries so far. Example. Before she moved to Italy, she had traveled all around Europe. Example. By next year, I will have traveled to every continent. Example. The package has been traveled through various countries before it arrived. Example. The traveled paths of this jungle are safe for tourists. Example. They are a welltraveled couple who have visited over fifty countries.
- Past Perfect. Describes an action that was completed before another action or time in the past. Example. I have traveled to ten different countries so far. Example. Before she moved to Italy, she had traveled all around Europe. Example. By next year, I will have traveled to every continent. Example. The package has been traveled through various countries before it arrived. Example. The traveled paths of this jungle are safe for tourists. Example. They are a welltraveled couple who have visited over fifty countries.
- Future Perfect. Indicates an action that will have been completed before a specific time in the future. Example. I have traveled to ten different countries so far. Example. Before she moved to Italy, she had traveled all around Europe. Example. By next year, I will have traveled to every continent. Example. The package has been traveled through various countries before it arrived. Example. The traveled paths of this jungle are safe for tourists. Example. They are a welltraveled couple who have visited over fifty countries.
- Passive Voice. The book was written by an author who has traveled the world. Example. I have traveled to ten different countries so far. Example. Before she moved to Italy, she had traveled all around Europe. Example. By next year, I will have traveled to every continent. Example. The package has been traveled through various countries before it arrived. Example. The traveled paths of this jungle are safe for tourists. Example. They are a welltraveled couple who have visited over fifty countries.
- Adjectives/Participial adjectives. Example. I have traveled to ten different countries so far. Example. Before she moved to Italy, she had traveled all around Europe. Example. By next year, I will have traveled to every continent. Example. The package has been traveled through various countries before it arrived. Example. The traveled paths of this jungle are safe for tourists. Example. They are a welltraveled couple who have visited over fifty countries.
- In constructing sentences and choosing the appropriate tense to use, it's crucial to consider the timing of the action (past, present, future), the completeness of the action, and whether the action is habitual, a general fact, or part of a sequence of actions. Understanding these use cases can help you effectively communicate timing, duration, and the nature of actions or states in your writing and speaking. Example. I have traveled to ten different countries so far. Example. Before she moved to Italy, she had traveled all around Europe. Example. By next year, I will have traveled to every continent. Example. The package has been traveled through various countries before it arrived. Example. The traveled paths of this jungle are safe for tourists. Example. They are a welltraveled couple who have visited over fifty countries.
Common mistakes
Confusion between forms.
One common mistake involves the use of the past simple and past participle forms of 'travel' in American and British English. In American English, 'traveled' and 'traveled' are used for both the past simple and past participle forms. However, in British English, 'travelled' and 'travelled' are preferred. Mistakes occur when learners mix these conventions, using American spelling in a British context or vice versa. For example, a British English speaker might incorrectly write 'I traveled to France last year,' instead of the British-preferred 'I travelled to France last year.'

Incorrectly using the present form
Another mistake is using the present tense 'travel' when the past simple 'traveled/travelled' or the past participle 'traveled/travelled' is required. This error often happens in complex tenses or when learners are unsure about tense consistency. For instance, saying 'Yesterday, I travel to New York' instead of the correct 'Yesterday, I traveled to New York.'

Misuse in perfect tenses
Learners frequently err by omitting the auxiliary verb 'have' in perfect tenses, leading to incorrect sentences. For the past participle form 'traveled/travelled' to be used correctly, it must be preceded by 'have' or 'has.' A common mistake is saying 'I traveled to Italy last summer' when referring to an experience at an unspecified time, which should be 'I have traveled to Italy.'

Past tense quiz
Check your skills and find areas for improvement
Frequently asked questions
What is the past simple form of 'travel', what is the past participle form of 'travel', how do i use the past participle of 'travel' in a sentence, can you explain the difference between the use of past simple and past participle of 'travel' with an example.
Conjugation of verb (past tense) travel
Past simple, traveled; travelled, past participle.
- ⭐Conjugation
- Podmínkové věty
- Frázová slovesa
- ⭐Conditional
- ⭐Subjunktiv
- ⭐Participle
Conjugation of the regular verb [travel]
Conjugation is the creation of derived forms of a verb from its principal parts by inflection (alteration of form according to rules of grammar). For instance, the verb "break" can be conjugated to form the words break, breaks, broke, broken and breaking.
The term conjugation is applied only to the inflection of verbs, and not of other parts of speech (inflection of nouns and adjectives is known as declension). Also it is often restricted to denoting the formation of finite forms of a verb – these may be referred to as conjugated forms, as opposed to non-finite forms, such as the infinitive or gerund, which tend not to be marked for most of the grammatical categories.
Conjugation is also the traditional name for a group of verbs that share a similar conjugation pattern in a particular language (a verb class). A verb that does not follow all of the standard conjugation patterns of the language is said to be an irregular verb .
Present Continuous
Past continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, conditional of the regular verb [travel].
Causality (also referred to as causation or cause and effect ) is influence by which one event, process, state or object (a cause) contributes to the production of another event, process, state or object (an effect) where the cause is partly responsible for the effect, and the effect is partly dependent on the cause. In general, a process has many causes, which are also said to be causal factors for it, and all lie in its past. An effect can in turn be a cause of, or causal factor for, many other effects, which all lie in its future.
The conditional mood (abbreviated cond) is a grammatical mood used in conditional sentences to express a proposition whose validity is dependent on some condition, possibly counterfactual.
English does not have an inflective (morphological) conditional mood, except in as much as the modal verbs could, might, should and would may in some contexts be regarded as conditional forms of can, may, shall and will respectively. What is called the English conditional mood (or just the conditional) is formed periphrastically using the modal verb would in combination with the bare infinitive of the following verb. (Occasionally should is used in place of would with a first person subject – see shall and will. Also the aforementioned modal verbs could, might and should may replace would in order to express appropriate modality in addition to conditionality.)
Conditional present -->
Conditional present progressive -->, conditional perfect -->, conditional perfect progressive -->, subjunktiv of the regular verb [travel].
The subjunctive is a grammatical mood, a feature of the utterance that indicates the speaker's attitude toward it. Subjunctive forms of verbs are typically used to express various states of unreality such as: wish, emotion, possibility, judgement, opinion, obligation, or action that has not yet occurred; the precise situations in which they are used vary from language to language. The subjunctive is one of the irrealis moods, which refer to what is not necessarily real. It is often contrasted with the indicative, a realis mood which is used principally to indicate that something is a statement of fact.
Subjunctives occur most often, although not exclusively, in subordinate clauses, particularly that-clauses. Examples of the subjunctive in English are found in the sentences "I suggest that you be careful" and "It is important that she stay by your side."
The subjunctive mood in English is a clause type used in some contexts which describe non-actual possibilities, e.g. "It's crucial that you be here" and "It's crucial that he arrive early." In English, the subjunctive is syntactic rather than inflectional, since there is no specifically subjunctive verb form. Rather, subjunctive clauses recruit the bare form of the verb which is also used in a variety of other constructions.
Present subjunctive -->
Past subjunctive -->, past perfect subjunctive -->, imperativ of the regular verb [travel].
The imperative mood is a grammatical mood that forms a command or request.
An example of a verb used in the imperative mood is the English phrase "Go." Such imperatives imply a second-person subject (you), but some other languages also have first- and third-person imperatives, with the meaning of "let's (do something)" or "let them (do something)" (the forms may alternatively be called cohortative and jussive).
Imperativ -->
Participle of the regular verb [travel].
The past participle is one of the most important parts of English grammar. It’s used to express perfect tenses and to form the passive voice. It’s also a useful tool for writing sentences that describe actions that started in the past and are still happening today. The past participles of irregular verbs don’t follow a specific pattern and can have numerous endings.
Present participle -->
Past participle -->, recent articles.
- Past perfect and past perfect progressive – understanding the differences
- Past perfect progressive tense
- Present perfect and past perfect - understanding the differences
- Past simple and past perfect tenses - understanding the differences
- Past perfect tense affirmative sentences
Start with any verb and browse through irregular verbs in alphabetical order
Use the button "Random choice"
Looking for a specific irregular verb?
regular verbs & Irregular verbs
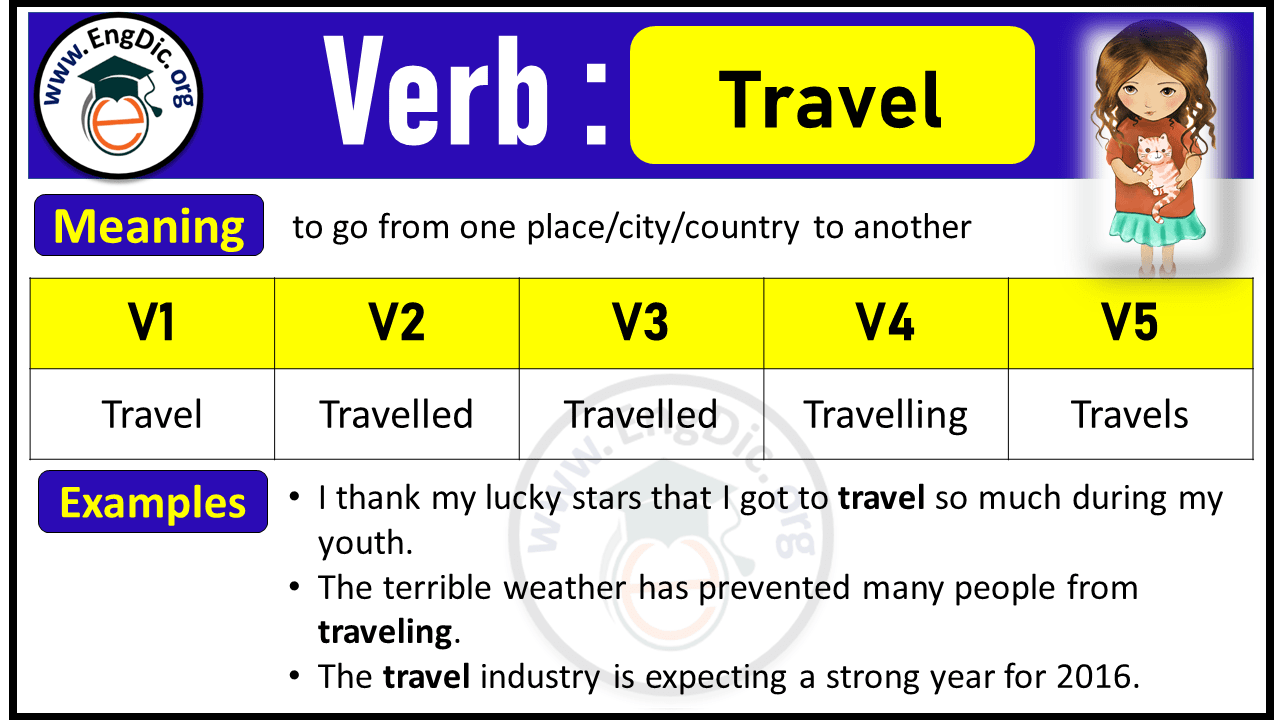
Travel Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
Meaning: to go from one place/city/country to another
Travel Verb Forms V1 V2 V3 V4 V5
Travel past tense:.
Past Tense of Travel is Traveled .
Example: Sarah Traveled by Train.
Travel Past Participle:
Past Participle Form of Travel is Traveled .
Example: Sarah has Traveled by Train.
Travel Present Participle:
Present Participle Form of Travel is Travelling .
Example: Sarah is Travelling by Train.
Travel 3rd Person Singular:
3rd Person Singular of Travel is Travels .
Example: Sarah Travels by Train.
Travel Conjugation
Indefinite / simple present tense.
- I Travel by Train.
- We/You/They Travel by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam Travels by Train.
Present Continuous Tense
- I am Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They are Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam is Travelling by Train.
Present Perfect Tense
- I have Traveled by Train.
- We/You/They have Traveled by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam has Traveled by Train.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- I have been Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They have been Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam has been Travelling by Train.
Indefinite / Simple Past Tense
- I Traveled by Train.
- We/You/They Traveled by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam Traveled by Train.
Past Continuous Tense
- I was Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They were Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam was Travelling by Train.
Past Perfect Tense
- I had Traveled by Train.
- We/You/They had Traveled by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam had Traveled by Train.

Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- I had been Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They had been Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam had been Travelling by Train.
Indefinite / Simple Future Tense
- I will Travel by Train.
- We/You/They will Travel by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam will Travel by Train.
Future Continuous Tense
- I will be Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They will be Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam will be Travelling by Train.
Future Perfect Tense
- I will have Traveled by Train.
- We/You/They will have Traveled by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam will have Traveled by Train.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
- I will have been Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They will have been Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam will have been Travelling by Train.
Past Tense of Travel Phrasal Verbs
Explore Other Verb Forms:
What is the Future Tense of Travel?
Future Tense of Travel is “ will Travel” .
What is the Present Tense of Travel?
Present Tense of Travel is “ Travel + s/es or ing” .
What is the Past Perfect Tense of Travel?
Past perfect tense of take is “ had Traveled ”.
Related Posts

Polish Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)

Open Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
Hinder Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
Fit Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
Satiate Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
Waste Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
About the author.
Hi, I'm USMI, engdic.org's Author & Lifestyle Linguist. My decade-long journey in language and lifestyle curation fuels my passion for weaving words into everyday life. Join me in exploring the dynamic interplay between English and our diverse lifestyles. Dive into my latest insights, where language enriches every aspect of living.
English Grammar Here
Travel V1 V2 V3 V4 V5, Past Simple and Past Participle Form of Travel

Verb; Travel
Meaning; trip, journey, voyage, peregrination, eyre
V1, V2, V3, V4, V5 Form of Travel
Synonym for Travel
- peregrination
- sightseeing
- cultivation
When learning English you need to know the meaning of certain words first, and then sort the words appropriately according to grammatical rules. Verbs in a regular structure can be transformed with a simple rule, whereas in irregular verbs, this situation is slightly different. It may be a good start to make some memorization and learn how to use the verbs in the right places.
Here are Verb Forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 pdf
Related Posts

Rise Past Simple, Simple Past Tense of Rise, Past Participle, V1 V2 V3 Form Of Rise

Dry Past Simple, Simple Past Tense of Dry Past Participle, V1 V2 V3 Form Of Dry

Turn V1 V2 V3 V4 V5, Past Simple and Past Participle Form of Turn
About the author.
Participles – Present, Past and Perfect
How to form the present participle, how to form the past participle, when to use participles in english, additional uses, the perfect participle.
- Lingolia Plus English
What is a participle?
A participle is an impersonal form of a verb that can be used as an adjective or to form compound tenses .
There are two types of participles in English; present participles (boring, doing, eating …) and past participles (bored, done, eaten …) .
These can be combined to form perfect participles (having done, having said …) , which are used in participial phrases .
Learn how to form English participles and when to use them, then practise in the interactive exercises.
Today, Ella is running her first ever marathon.
She’s been training for months and has done many practise races in preparation for the real thing.
Feeling nervous, Ella approaches the start line with the other excited runners.
The atmosphere is amazing : loud music is playing and it’s inspiring to see so many runners focusing on the same goal.
Ella’s predicted time is around 5 hours, but she thinks she can do better.
The starting pistol is fired and the race begins!
Form the present participle by adding -ing to the infinitive of the verb.
Spelling rules
- remove the final -e before adding -ing (note: -ee stays the same)
- double the final consonant when it follows a short, stressed vowel (exceptions: -w, -x and -y )
- an -ie at the end of the infinitive becomes -y
- British English doubles the final -l of verbs like cancel, travel, etc.
Present participle vs. gerund
When the -ing form is used as a noun, it is actually a gerund and not a present participle.
Learn more about which verbs take the gerund in English .
The past participle is also known as the third form of the verb (e.g. do–did– done ).
For regular verbs, we add -ed to the infinitive . This means that for regular verbs, the past participle is identical to the simple past form.
Irregular verbs have their own form, which must be learned by heart. Sometimes the past participle is the same as the simple past form, sometimes it is different.
Learn more about irregular verbs in English grammar .
English participles have two main uses:
1. Forming compound tenses
- use the present participle ( -ing form) in progressive tenses
- use the past participle (3rd form of the verb) in perfect tenses
- use the past participle of be (= been) and the present participle of the main verb in perfect progressive tenses
As you can see from the examples above, despite what their names may suggest, the present and past participles are not just restricted to the present and past tenses!
2. Adjectives
The second use for the participles is as adjectives .
They can come before the noun they modify or after linking verbs like be .
Often, we have to choose between participle adjective pairs (e.g. bored vs. boring; confused vs. confusing …).
The difference is as follows:
- use the past participle to describe a feeling or effect
- use the present participle to describe the person/thing that causes said feeling or effect
Head over to our section on adjectives to learn more about adjectives ending in -ing and -ed .
Read on to look at each of the participles individually.
While the participles are mainly used in compound tenses and as adjectives, there are some additional uses:
The passive voice
The past participle is used with the verb be to form the passive .
Learn more about the passive voice in English grammar .
The present participle as an adverb
In some cases, the present participle appears as an adverb . These modify verbs, adjectives and other adverbs.
Participial phrases (clauses)
Participles are used to create participial phrases (also known as participial clauses or participle phrases ). These are adjective phrases that begin with a present, past or perfect participle.
Participial phrases are used in in written language. They allow us to give more information about a noun without having to use a full clause.
The participial phrase must refer to the same noun as the main clause.
Participial phrases are often used to shorten relative clauses .
Check out our page about participial phrases in English for more information and exercises.
The perfect participle is formed with the present participle of have and the past participle of the main verb (e.g. having said, having done, having left … ).
Unlike the standard present and past participles, the perfect participle is only used in participial phrases and is mostly limited to written English.
The perfect participle emphasises that an action was already completed when another action took place.
How good is your English?
Find out with Lingolia’s free grammar test
Take the test!
Maybe later
Past Participles in English Grammar
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
In English grammar, the past participle refers to an action that was started and completed entirely in the past. It is the third principal part of a verb, created by adding -ed, -d , or -t to the base form of a regular verb (the first two principal parts are the base form and past tense).
The past participle is generally used with an auxiliary (or helping) verb— has, have , or had— to express the perfect aspect, a verb construction that describes events occurring in the past that are linked to a later time, usually the present. In addition to the perfect aspect (or perfect tense), the past participle can be used in a passive voice or as an adjective.
Past Participles of Regular Verbs
To understand past participles, you first need to know how to make a verb past tense . To do so, add ed , d , or t , as in these examples that show the verb on the left and the simple past tense on the right:
- Jump > jumped
- Sleep > slept
- Touch > touched
Turning these verbs into past participles is also simple: Make the verb past tense and precede it with an auxiliary verb , as in these examples that list the simple past on the left and the past participle on the right:
- Jump > have jumped
- Sleep > have slept
- Touch > have touched
Though they may seem similar, there is a difference between the regular past tense and past participle. The regular past has only one part while the past participle always has two or more parts and generally requires an auxiliary verb. An example of a sentence with a regular verb would be: "I helped my friend." You helped your friend at some time in the past, but you might continue to help her at some point in the future.
The same sentence with a past participle verb would be: "I have helped my friend." You began helping your friend in the past and completed the action of helping her in the past.
Past Participle of Irregular Verbs
The past participle forms of irregular verbs have various endings, including -d ( said ), -t ( slept ), and -n ( broken ). Irregular verbs are trickier to form in the simple past than regular verbs, as these examples illustrate:
- Blow > blew
- Freeze > froze
- Go > went
To form the past participle of these irregular verbs, precede them with an auxiliary verb:
- Blow > has blown, have blown
- Freeze > has frozen, have frozen
- Went > has gone, have gone
Common Irregular Past Participles
Viewing some of the most common irregular verbs, together with the simple past as well as their past participle forms, can help understand how they are formed.
Additionally, the verb wear is a classic example of an irregular verb that can be complicated to use as a past participle. You might wear underwear today if you are expressing action in the present. You wore underwear yesterday if you are expressing the simple past. To use the same irregular verb as a past participle, however, you might say, "I have worn my Superman underwear." This implies that you donned your Superman underwear in the past but you are no longer doing so.
Meanings and Forms of Past Participles
The past participle can indicate past, present, and future meanings, according to "Essentials of English: A Practical Handbook Covering All the Rules of English Grammar and Writing Style," which notes that the past participle has both perfect and progressive forms, as in these examples:
"Thus deceived , he will be outraged. [Both actions are in the future.]
"Baffled by your attitude, I cannot help you. [Both actions are in the present.]
"Baffled by your attitude, I could not help you. [Both actions in the past.]"
In the first sentence, the participle acts like an appositive , renaming the subject he . The two actions occur completely in the future: He will be outraged and he ( will be ) deceived . Note how the past participle includes an implied form of a "to be" verb: will be .
In the second sentence, baffled is still a past participle but the action will have been started and completed entirely in the present. The past participle includes an implied auxiliary verb— having been— so the full sentence would read: " Having been baffled by your attitude, I cannot help you." The action of being baffled starts and is completed entirely in the present, as is the (non)action of not helping.
In the same way, the third sentence starts with a past participle describing an action that started and was completed entirely in the past. The past participle also serves as an appositive adjective , describing the pronoun (and subject of the sentence) . The full sentence would read: " Having been baffled by your attitude, I could not help you." The subjunctive mood in the second half of the sentence describes an action— could not help— that happened (or in this case did not happen) entirely in the past.
Key Takeaways
- The past participle is the third principal part of a verb, created by adding -ed , -d , or -t to the base form of a regular verb.
- Past participles indicate actions completed in the past and are often used with auxiliary verbs like "has," "have," or "had."
- Past participles can convey past, present, and future meanings. Their usage depends on the context and auxiliary verbs used alongside them.
- The Principal Parts of Verbs
- An Introduction to Irregular Verbs in English
- Difference Between a Weak and Strong Verb
- How to Conjugate Verbs
- Simple Past Tense Definition and Examples
- How to Use the Irregular Verb 'Ride'
- German Regular Verbs: Past Tenses
- 10 Types of Verbs
- Using Spanish Past Participles: They’re Both Verbs and Adjectives
- 100 Key Terms Used in the Study of Grammar
- Understanding Verb Tenses
- Irregular Verbs: From H to S
- Practice in Using the Present Perfect in English Grammar
- A Step-By-Step Conjugation of Simple Past-Tense Verbs in Spanish
- Understanding Present and Past Participles
- Understanding the Types of Verbs in English Grammar

paper-free learning
- conjunctions
- determiners
- interjections
- prepositions
- affect vs effect
- its vs it's
- your vs you're
- which vs that
- who vs whom
- who's vs whose
- averse vs adverse
- 250+ more...
- apostrophes
- quotation marks
- lots more...
- common writing errors
- FAQs by writers
- awkward plurals
- ESL vocabulary lists
- all our grammar videos
- idioms and proverbs
- Latin terms
- collective nouns for animals
- tattoo fails
- vocabulary categories
- most common verbs
- top 10 irregular verbs
- top 10 regular verbs
- top 10 spelling rules
- improve spelling
- common misspellings
- role-play scenarios
- favo(u)rite word lists
- multiple-choice test
- Tetris game
- grammar-themed memory game
- 100s more...
Past Participle
What is a past participle.
- It is formed from a verb.
- It is used as an adjective or to form verb tense.
- It probably ends "-ed," "-d," "-t," "-en," or "-n."
Table of Contents
A Closer Look at a Past Participle
Find the past participle test, video lesson, examples of past participles used as adjectives, past participles in participle phrases, past participles used in verb tenses, examples of past participles used in verb tenses, forming the past participle (regular verbs), forming the past participle (irregular verbs), why past participles are important.

- Here's the past participle: whispered
- Here it is used as an adjective : The whispered word
- Here it is used to form a verb tense : She had whispered him the answer.
Are you a visual learner? Do you prefer video to text? Here is a list of all our grammar videos .
Examples of Past Participles Being Used As Adjectives
- Here is a laminated copy to replace your torn one.
- Stuffed deer heads on walls are bad enough, but it's worse when they have streamers in their antlers because then you know they were enjoying themselves when they were shot. (TV host Ellen DeGeneres)
- A torn jacket is soon mended, but hard words bruise the heart of a child. (Poet Henry Longfellow)
- Scandal is gossip made tedious by morality. (Poet Oscar Wilde)
- The enemy is anybody who's going to get you killed , no matter which side he's on. (Author Joseph Heller)
- The boy taken to hospital has recovered.
- I have a heart wracked with sorrow .
- Battered by the wind , John fell to his knees.
- Finally broken , Lee lowered his gloves.
- I had crossed the line. I was free, but there was no one to welcome me to the land of freedom. I was a stranger in a strange land. (Political activist Harriet Tubman)
- I had seen birth and death but had thought they were different. (Poet T S Eliot)
- I phoned my dad to tell him I had stopped smoking. He called me a quitter.
- Don't take the wrong side of an argument just because your opponent has taken the right side.
- Poets have been mysteriously silent on the subject of cheese.
- Like all great travellers, I have seen more than I remember, and remember more than I have seen . (British Prime Minister Benjamin Disraeli)
- I have taken more out of alcohol than alcohol has taken out of me.
- By September, Jenny will have taken over that role.
- I hope that, when I leave this planet, I will have touched a few people in a positive way. (Actor Will Rothhaar)
- jump > jumped
- paint > painted
- chat > chatted
- stop > stopped
- sew > sewed
- play > played
- fix > fixed
- incur > incurred
- prefer > preferred
- open > opened
- enter > entered
- swallow > swallowed
- thrive > thrived
- guzzle > guzzled
- cry > cried
- fry > fried
- arise > arisen
- catch > caught
- choose > chosen
- know > known
More about Participles
- The Past Participle
- The Present Participle
(Benefit 1) Use a fronted participle phrase to say two things about your subject efficiently.
- Imbued with both common sense and enthusiasm , Patrick is always quick to find a cost-effective solution.
(Trap 1) Beware misplaced modifiers and dangling modifiers!
- Past and present participles are key building blocks in any language.
- Using an upfront participle phrase lets you shoehorn more information into a sentence.
- If you use an upfront participle phrase, put the word being modified next.

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
Learning Resources
more actions:
This test is printable and sendable
Help Us Improve Grammar Monster
- Do you disagree with something on this page?
- Did you spot a typo?
Find Us Quicker!
- When using a search engine (e.g., Google, Bing), you will find Grammar Monster quicker if you add #gm to your search term.
You might also like...
Share This Page

If you like Grammar Monster (or this page in particular), please link to it or share it with others. If you do, please tell us . It helps us a lot!
Create a QR Code

Use our handy widget to create a QR code for this page...or any page.
< previous lesson
next lesson >
Past Tense of travel: Conjugations in Past and Present Participles

What is the past tense of “travel?” Most commonly, the past tense of the word “travel” is “travelled.” Although the word form will change based on its participle. And the sentence where it’s used. For example, referencing “travel” in the present participle form will change it to “travelling,” but in the infinitive form, will be “travel.”
What is the past tense of the word "travel"
The past tense (past participle) form of “travel” is “travelled.” The infinitive of the word form is “travel.” The present participle form is “travelling.” The past tense form is “travelled” and past participle form is “travelled.”
Understanding verb tenses
The general grammar rules that govern past tenses are as follows. The simple past tense form is created by adding a -ed or -d affix to the root word of the verb. Some verbs use a -t variation where they end in a -t. For example, when "dream" turns into "dreamt."
The past perfect tense is formed for regular verbs (ending in -ed, -d, or -t) by adding "had" followed by the verb. For example, "I had finished ."
The past continuous tense is formed by the verb "be" followed by the affix or ending of -ing. For example, " we were having dinner."
Lastly, the past perfect continuous tense is formed by adding "had been" followed by the affix or ending of -ing. For example, "I had been building a castle with my sister."
For more information on forming all past tenses, visit our " understanding verb tenses " resource.
Sentence examples for the past tense of the word "travel"
- Infinitive: I travel.
- Present participle: She is travelling.
- Past tense: I travelled.
- Past particle: I have travelled.
Verb forms of the word "travel"
Example sentences in all verb forms:
Indefinite present tense
Present continuous tense.
She/he/it is travelling.
Present perfect continuous tense
She/he/it has/had travelled.
Present perfect tense
She/he/it has/had been travelling.
Simple past tense
She/he/it travelled.
Past continuous tense
She/he/it were travelling.
Past perfect tense
Perfect continuous tense.
She/he/it will/shall travel.
Simple future tense
She/he/it will/shall be travelling.
Future perfect tense
She/he/it will/shall have travelled.
Future perfect continuous tense
She/he/it will/shall have been travelling.
Sentence examples in all forms
Sentence examples in all participles and parts of speech :
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy
Conjugación verbo travel - inglés
Modelo : cancel
Auxiliar : have , be
Otras formas: travel oneself / not travel
Contracciones
in the U.K. spelling we double up the 'l' in preterite and participle endings
La declinación de este verbo presenta algunas variantes ortográficas que podrían conllevar significados distintos. Seleccione una variante o todas en el menù.
- he/she/it travels
- they travel
- I travelled/traveled
- you travelled/traveled
- he/she/it travelled/traveled
- we travelled/traveled
- they travelled/traveled
Present continuous
- I am travelling/traveling
- you are travelling/traveling
- he/she/it is travelling/traveling
- we are travelling/traveling
- they are travelling/traveling
Present perfect
- I have travelled/traveled
- you have travelled/traveled
- he/she/it has travelled/traveled
- we have travelled/traveled
- they have travelled/traveled
- I will travel
- you will travel
- he/she/it will travel
- we will travel
- they will travel
Future perfect
- I will have travelled/traveled
- you will have travelled/traveled
- he/she/it will have travelled/traveled
- we will have travelled/traveled
- they will have travelled/traveled
Past continous
- I was travelling/traveling
- you were travelling/traveling
- he/she/it was travelling/traveling
- we were travelling/traveling
- they were travelling/traveling
Past perfect
- I had travelled/traveled
- you had travelled/traveled
- he/she/it had travelled/traveled
- we had travelled/traveled
- they had travelled/traveled
Future continuous
- I will be travelling/traveling
- you will be travelling/traveling
- he/she/it will be travelling/traveling
- we will be travelling/traveling
- they will be travelling/traveling
Present perfect continuous
- I have been travelling/traveling
- you have been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it has been travelling/traveling
- we have been travelling/traveling
- they have been travelling/traveling
Past perfect continuous
- I had been travelling/traveling
- you had been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it had been travelling/traveling
- we had been travelling/traveling
- they had been travelling/traveling
Future perfect continuous
- I will have been travelling/traveling
- you will have been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it will have been travelling/traveling
- we will have been travelling/traveling
- they will have been travelling/traveling
- let's travel
- travelling/traveling
- travelled/traveled
Perfect participle
- having travelled/traveled
Ayudando a millones de personas y grandes organizaciones a comunicar con más eficacia y precisión en todos los idiomas.
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of wake
(Entry 1 of 3)
intransitive verb
transitive verb
Definition of wake (Entry 2 of 3)
Definition of wake (Entry 3 of 3)
- knock up [ British ]
Examples of wake in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'wake.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
partly from Middle English waken (past wook , past participle waken ), from Old English wacan to awake (past wōc , past participle wacen ); partly from Middle English wakien, waken (past & past participle waked ), from Old English wacian to be awake (past wacode , past participle wacod ); akin to Old English wæccan to watch, Latin vegēre to enliven
akin to Middle Low German wake wake, Norwegian dialect vok , Old Norse vǫk hole in ice
before the 12th century, in the meaning defined at intransitive sense 1a
13th century, in the meaning defined at sense 1
1627, in the meaning defined at sense 1
Phrases Containing wake
- in someone's or something's wake
- in the wake of
wake and bake
- wake - robin
- wake up and smell the coffee / roses
- wake - up call
Articles Related to wake

The Grammatical History of 'Awaken' /...
The Grammatical History of 'Awaken' / 'Awoken' / 'Awakened'
Wake up, people.

The new sense of 'woke' is gaining popularity
Dictionary Entries Near wake
Cite this entry.
“Wake.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/wake. Accessed 18 Jun. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of wake.
Kids Definition of wake (Entry 2 of 3)
Kids Definition of wake (Entry 3 of 3)
from Old English wacan "to awake" and Old English wacian "to be awake"
of Germanic origin
More from Merriam-Webster on wake
Nglish: Translation of wake for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of wake for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about wake
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, birds say the darndest things, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), games & quizzes.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What is the past tense of "travel?". Most commonly, the past tense of the word "travel" is "traveled.". Although the word form will change based on its participle. And the sentence where it's used. For example, referencing "travel" in the present participle form will change it to "traveling," but in the infinitive form ...
travel. 'travel' is the model of its conjugation. In American English, the preferred spelling does not include a doubled final consonant before -ing or -ed. infinitive: present participle: past participle: (to) travel. traveling.
Conjugation of Travel. Simple / Indefinite Present Tense. He/She/It travels . I travel. You/We/They travel. Present Continuous Tense. He/She/It is Commonwealth travelling, US traveling. I am Commonwealth travelling, US traveling. You/We/They are Commonwealth travelling, US traveling.
Conjugate the English verb travel: indicative, past tense, participle, present perfect, gerund, conjugation models and irregular verbs. Translate travel in context, with examples of use and definition.
'to travel' conjugation - English verbs conjugated in all tenses with the bab.la verb conjugator. To support our work, we invite you to accept cookies or to subscribe. ... Past participle. english. traveled; travelled; More information. Full conjugation of "to travel" Translations for "to travel" Full conjugation of "to travel" Indicative ...
Present Continuous. I am travelling or traveling you are travelling or traveling he/she/it is travelling or traveling we are travelling or traveling you are travelling or traveling they are travelling or traveling.
The English verb 'travel' is pronounced as [ˈtrævl]. Related to: regular verbs. 3 forms of verb travel: Infinitive (travel), Past Simple - (travelled (BrE)), Past Participle - (travelled (BrE)).. Here are the past tense forms of the verb travel. 👉 Forms of verb travel in future and past simple and past participle. What is the past tense of travel.
Conjugate the verb travel in all tenses: present, past, participle, present perfect, gerund, etc.
To Travel Conjugation; To Travel Infinitive: to travel Gerund: travelling Past participle: travelled Simple past: travelled. Note. In the US the spelling 'traveling' and 'traveled' are preferred. Irregular forms Auxilliary verb Spelling change Use contractions. Positive Negative. Indicative.
Visit. Travelled is the past tense of the word travel. Travelled is the past participle of the word travel. travel past form, verb forms, v1v2v3, Inf.
Travel in Past Continuous (Progressive) Tense. Singular. Plural. I was commonwealth travelling, us traveling. We were commonwealth travelling, us traveling. You were commonwealth travelling, us traveling. You were commonwealth travelling, us traveling. He/She/It was commonwealth travelling, us traveling. They were commonwealth travelling, us ...
The correct answer would be "went.". Matching: In this exercise, you will be given a list of past tense verbs and a list of travel-related words. Your task is to match the past tense verb with the correct travel-related word. For example, "flew" would match with "airplane.". Written Exercises.
Table of irregular verbs - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Similar to the past simple form, the past participle form of 'travel' is 'traveled' in American English and 'travelled' in British English. It is used in perfect tenses to talk about actions that have a connection to the present or were completed at an unspecified time in the past. For example, 'I have traveled/travelled to over 10 countries.'.
Conjugation is the creation of derived forms of a verb from its principal parts by inflection (alteration of form according to rules of grammar). For instance, the verb "break" can be conjugated to form the words break, breaks, broke, broken and breaking. The term conjugation is applied only to the inflection of verbs, and not of other parts of speech (inflection of nouns and adjectives is ...
Meaning: to go from one place/city/country to another Travel Verb Forms V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 Base Form/Infinitive (V1): Travel Past Tense (V2): Traveled Past Participle Form (V3): Traveled Present Participle/Gerund (V4): Travelling 3rd Person Singular (V5): Travels Travel Past Tense: Past Tense of Travel is Traveled. Example: Sarah Traveled by Train. Travel Past Participle: Past Participle Form of ...
Verb; Travel. Meaning; trip, journey, voyage, peregrination, eyre. V1, V2, V3, V4, V5 Form of Travel. Synonym for Travel. When learning English you need to know the meaning of certain words first, and then sort the words appropriately according to grammatical rules. Verbs in a regular structure can be transformed with a simple rule, whereas in ...
A tale of two variants. What to Know. When it comes to spelling the forms of the verb travel, traveled and traveling are more common in the U.S., and travelled and travelling are dominant everywhere else. Spelling is typically clear-cut in modern English: forty unfailingly betrays four; the sweet treat after dinner is spelled dessert, not desert.
A past participle is a word derived from a verb that can be used as an adjective, to form perfect verb tenses, and to form the passive voice. It is one of two types of participles, along with present participles. The past participles of regular verbs are usually formed by adding the suffix "-ed" (e.g., "learn" becomes " learned ").
A participle is an impersonal form of a verb that can be used as an adjective or to form compound tenses. There are two types of participles in English; present participles (boring, doing, eating …) and past participles (bored, done, eaten …). These can be combined to form perfect participles (having done, having said …), which are used ...
In English grammar, the past participle refers to an action that was started and completed entirely in the past. It is the third principal part of a verb, created by adding -ed, -d, or -t to the base form of a regular verb (the first two principal parts are the base form and past tense). The past participle is generally used with an auxiliary ...
A Closer Look at a Past Participle Let's look at the past participle of the verb to whisper: Here's the past participle: whispered; Here it is used as an adjective: The whispered word; Here it is used to form a verb tense: She had whispered him the answer. Find the Past Participle Test It's your go! Select the past participle in the following ...
What is the past tense of "travel?". Most commonly, the past tense of the word "travel" is "travelled.". Although the word form will change based on its participle. And the sentence where it's used. For example, referencing "travel" in the present participle form will change it to "travelling," but in the infinitive form ...
Conjugación verbo travel en inglés, ver modelos de conjugación inglés, verbos irregulares. ... in the U.K. spelling we double up the 'l' in preterite and participle endings. ... Conjugación verbo travel inglés: present, past tense, past perfect, present perfect, future. Ver la traducción en contexto para travel y su definición.
The meaning of WAKE is to be or remain awake. How to use wake in a sentence.