Wander-Lush

World’s Best Cultural Tourism Destinations: 30 Cultural Trips to Take This Year
Discover the best cultural trips and immersive travel experiences our world has to offer. From Southern India to the High Arctic, here are the top 30 countries and regions for cultural tourism this year .
With many of us now on the lookout for deeper and more meaningful travel experiences , cultural tourism – travel that prioritises learning about and appreciating different ways of life – has never been more appealing.
Immersive cultural experiences give travellers an opportunity to see the world from a different perspective, form meaningful relationships, and develop new skills. They can also open the door to a slower, more sustainable type of travel that has benefits for local communities and a lighter impact on the planet.
Whether you’re a seasoned cultural traveller researching for your next trip or you’re interested in getting off-the-beaten-track but aren’t sure where to start, I hope this guide to culture and travel offers you some food for thought!
I also suggest reading these tips for socially responsible travel for advice about engaging with different cultures in a sensitive and mindful way.
Please note: This post contains affiliate links, meaning I may earn a commission if you make a purchase by clicking a link (at no extra cost to you). Learn more.
This post may contain sponsored links for which I received compensation.
What is cultural tourism?
Cultural travel is as broad and multifaceted as culture itself – it’s difficult to pin down, and highly subjective. For me, cultural tourism is a kind of travel that prioritises activities and experiences designed to immerse you in a way of life that differs from your own.
It might involve consuming tangible cultural products (museums, archaeological sites, food , tea ) or encountering intangible cultural elements (rituals, performances, processes). As well as art, literature, religious monuments and the like, it also encompasses ways of living, values and beliefs – both historical and contemporary.
It’s almost impossible to avoid local culture when you travel. No matter your motivation, it’s inevitable that you’ll end up experiencing some aspect of local culture, even if it’s something as simple as eating local cuisine or learning a few words of the language.
Apart from these incidental encounters, cultural tourism represents a more concerted effort to engage with local culture through specialised activities. In the same way an adventure traveller might seek out a particular hiking route, for example, a cultural traveller might plan their trip around a festival.
Cultural vacations might involve:
- Learning a new skill, for example through a cooking class or craft workshop
- Attending a local festival or event
- Participating in a ritual or ceremony
- Eating local food
- Staying with a family at a homestay
- Immersing yourself in the local community by teaching English as a foreign language
- Visiting a community-based tourism project
- Visiting World Heritage Sites and immersive museums
- Taking a locally guided tour
There’s lots more to cultural trips (as you’ll soon see), but these are some of the common elements we tend to associate with this genre of travel.
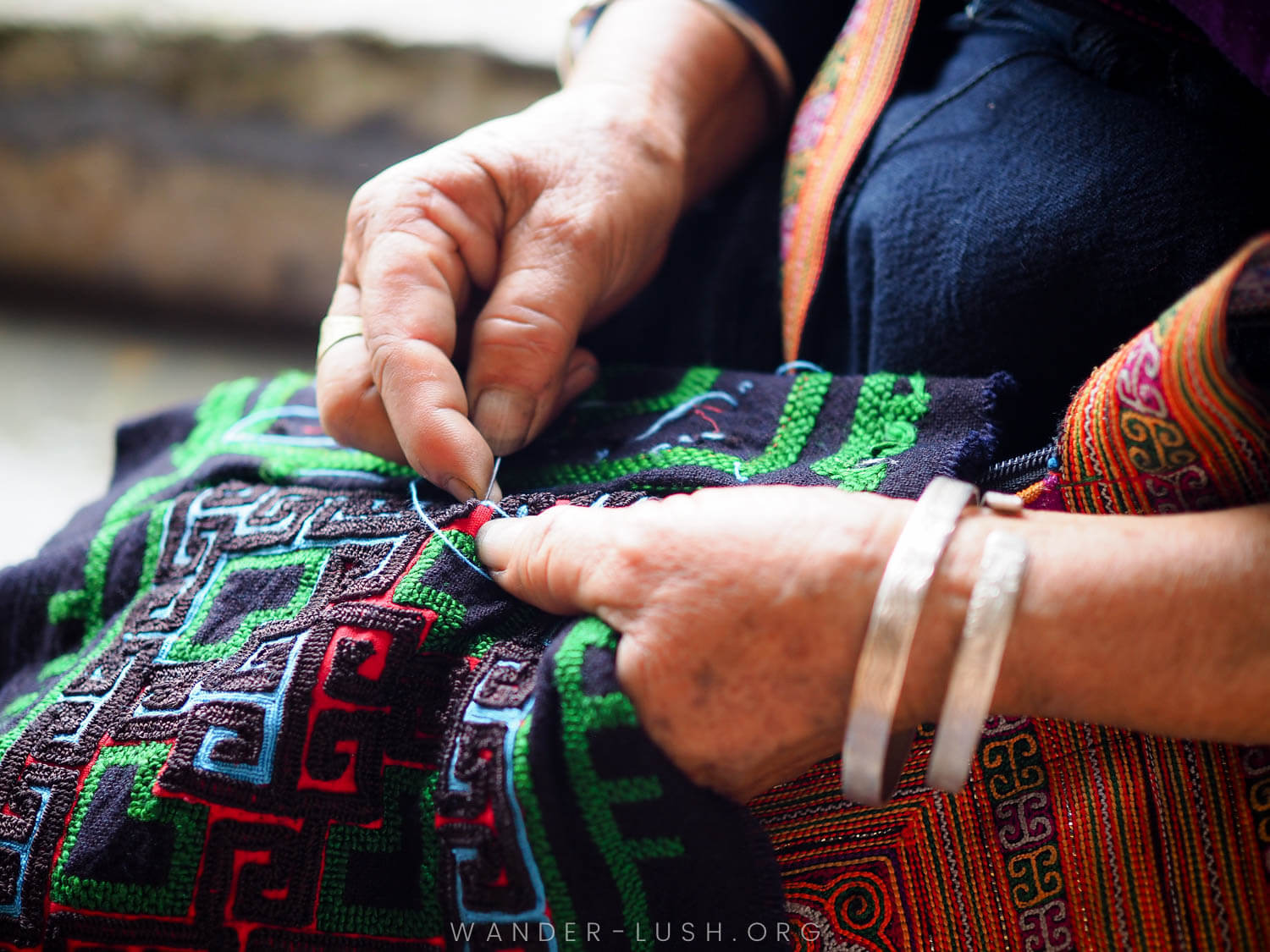

Pros and cons of cultural travel
Cultural travel is almost a guaranteed way to enrich your experience as a tourist. But it’s worth noting that this type of travel has both benefits and downsides for host communities.
Cultural tourism helps to encourage the preservation of culture and heritage by keeping endangered traditions alive. There might be little demand for heritage handicraft skills, for example, but outside interest (and an opportunity to earn an income) could be enough to safeguard a tradition that might otherwise have been lost.
By the same token, cultural tourism can incentivise better protections for physical heritage sites, ensuring that monuments and the like remain accessible for future generations. Cultural tourism can have far-reaching social impacts and environmental benefits when it gives rise to new social enterprises, local businesses and women-led ventures geared towards giving tourists an immersive experience.
On the other hand, there’s always a question mark around authenticity when it comes to cultural travel. If a ritual is performed for the benefit of outsiders, does it lose its meaning? Commodification of culture for tourism is a serious issue that impacts many communities and can be damaging to social and economic development more broadly.
Cultural tourism often involves travelling to more remote areas, which introduces a whole host of other pros and cons. A road constructed for the benefit of tourists is also new infrastructure for the community – but it might speed up globalisation and cultural erosion, while the very presence of tourists can worsen environmental pollution or cause rifts between different social groups.
These are complicated issues. Personally, I think cultural exchange is one of the most important aspects of travel and when managed properly and in a way that actively involves communities, the benefits can outweigh the drawbacks.
Top 30 countries & regions for cultural trips
There’s not a town, city, county or region in the world that doesn’t have something amazing to offer in terms of local culture. This makes it very hard to pick the ‘best’ places for cultural tourism.
However, each of these 30 hand-picked destinations stands out for its extravagant festivals and celebrations, rich cuisine and heritage handicrafts that give travellers a window on culture, heritage and the local way of life.
At the end of the list, you’ll find my top tips for having a more culturally immersive travel experience no matter where in the world you go.
Cultural destinations in the Americas
Antioquia Department, Colombia • Cuba • Ecuador • Big Island of Hawaii, USA • Orleans Parish, USA • Oaxaca, Mexico
Colombia’s Antioquia Department – for pueblos, bandeja paisa & Botero
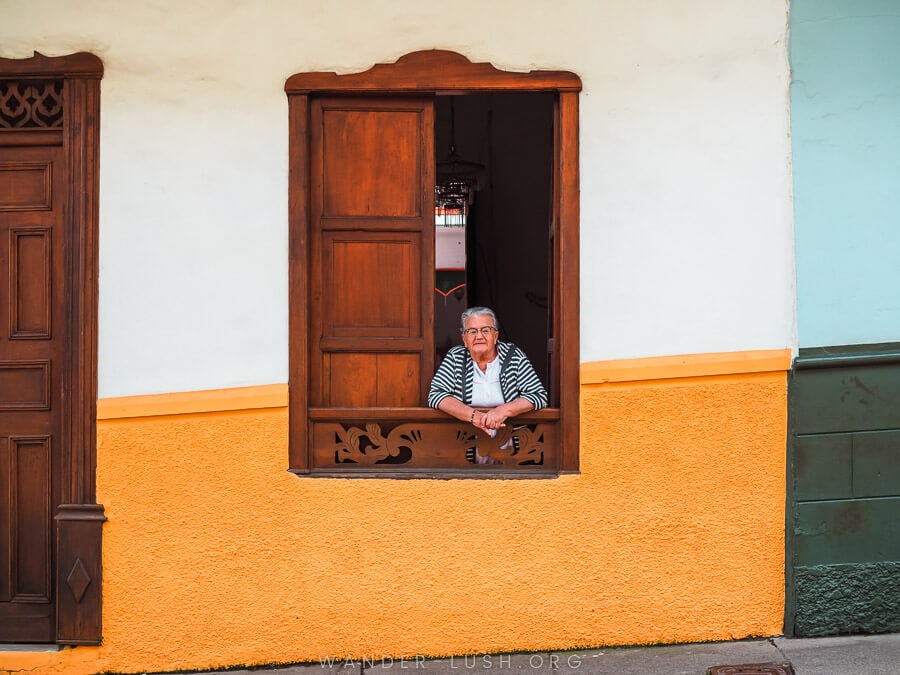

A melange of Indigenous traditions and colonial influences, there are few destinations in the world more culturally vibrant or intriguing than Colombia.
Antioquia Department in the north-west – with the city of Medellin as its capital – has become one of the most popular destinations in the country for tourists, beloved for its exquisite landscapes, colourful small towns and coffee farming heritage.
Along with several other departments, this part of Colombia is home to the Paisas , a self-defined cultural group whose name is derived from a Spanish word meaning ‘countryman’. They speak their own dialect, eat their own cuisine, and pass down their culture through a rich tradition of music and folklore.
Modern-day Antioquian culture is defined by the region’s artists, writers and poets. And then there’s the city of Medellin itself, which has undergone a huge transformation in recent years and is now considered one of the country’s main cultural hubs.
Top cultural experiences in Antioquia
Eat Paisa cuisine: One of the biggest joys of visiting Antioquia is experiencing the food scene. Paisa cuisine is heavily influenced by the topography and way of life in the Colombian Andes – carb-heavy dishes that feature beans, rice and maize are designed to fuel bodies for back-breaking work on the land. Bandeja Paisa is by far the most popular traditional dish and a must-eat in Medellin. The Antioquian version of a ploughman’s lunch, it consists of carne asada (grilled steak), chicharrón (crispy pork rind), rice and red beans served with a slice of avocado, fried plantains, a fried egg and a corn arepa on the side. It’s not for the faint hearted!
Visit a pueblo : Colombia is renowned for its small towns with colourful painted facades and pretty flower boxes. Antioquia is home to some of the loveliest pueblos in the country, including Jardin , Jericó and Santa fe de Antioquia, to name but a few. Developed during Spanish times, most follow the same basic town plan: A public square, a market, a church, and rows and rows of houses built in the region’s vernacular style. If you’re short on time, Pueblo Paisa in Medellin is a model village in the heart of the capital.
Shop at the San Alejo Handicraft Market: If you happen to be visiting Medellin on the first Saturday of the month, don’t miss this unique opportunity to see Colombia’s handicraft traditions on display. Vendors from across the region descend on the city to sell traditional products, including woven Wayuu bags, and artisanal foods. You can chat to the vendors and watch live demonstrations to see how these Indigenous handicrafts are produced.
Visit Comuna 13: A locally guided tour of Medellin’s Comuna 13 will allow you to delve into the city’s tumultuous recent past in a respectful and mindful way. This collection of once-notorious city neighbourhoods has become a symbol for the nation’s transformation and cultural revitalisation. Street art, music and other expressions of local creativity are all on display for visitors to enjoy.
Cuba – for Mambo, classic cars & casas particulares
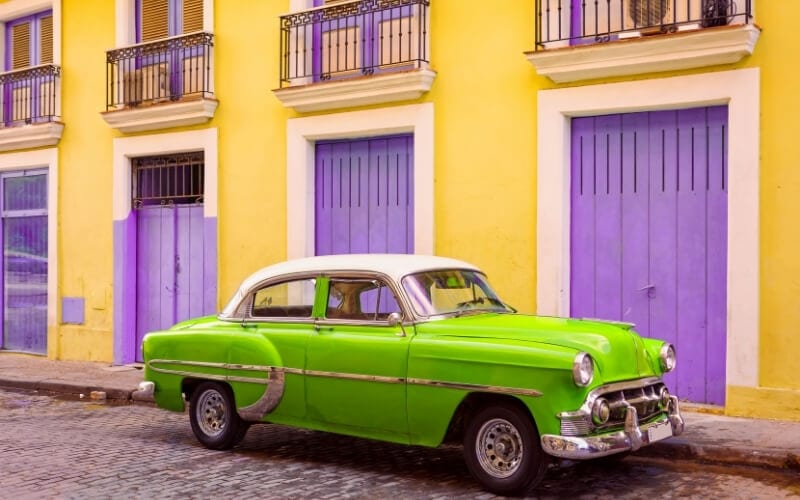

The native Taino Indians called their beautiful island Cubanacán. When the Spaniards arrived in 1511, they shortened it to ‘Cuba’ and claimed it for Spain, labelling it “the most beautiful land human eyes have ever beheld.”
Ethnically, the country is a vibrant mix of Europeans, Africans brought over as enslaved workers throughout the 1700s, and a large group of Chinese imported as indentured servants. Sadly, the original inhabitants have largely disappeared.
On December 31, 1959 the Cuban Revolution succeeded in converting the country into a communist nation. Since then – and due to the mutually adversarial relationship with the United States – the island nation has existed in semi-isolation, frozen in time.
The cars that roam the streets are the same classic American models from the 1950s, and the frequently crumbling buildings have enjoyed little renovation.
Despite Cuba’s trying history, the spirit of the people lives on and in its rich and celebrated culture. Before you go, learn the dos and don’t of visiting Cuba .
Top cultural experiences in Cuba
Dance the night away at a musical venue: Cuba is the birthplace of dozens of musical genres including Mambo, Cha-Cha-Cha and Afro-Cuban Jazz. These Afro-European genres have contributed and enriched music categories around the world. Be sure to experience one of Cuba’s world-famous carnivals and Jazz Festivals.
Overdose on art and architecture: With nine UNESCO World Heritage sites and an amazing collection of museums, Cuba is a culture vulture’s paradise. Most are found in the capital city of Havana, but you also find little gems in the second city, Santiago de Cuba, and the perfectly preserved colonial city of Trinidad. Cuba’s architecture ranges from Spanish colonial and French Baroque to 1920s Art Deco. Visit the Museum of Fine Arts in Havana and the Bacardi Museum in Santiago to start; but don’t miss the quirky Rum Museum or the delectable Museum of Chocolate either.
Stay at a Cuban homestay: These Airbnb-type experiences are called ‘ casas particulares ‘. This is your opportunity to live with a Cuban family and delve into the culture.
Go hiking: Cuba’s national parks, biosphere reserves and 1,500 miles (2,400km) of coastline provide an opportunity to experience the outdoor culture.
By Talek from Travels With Talek
Ecuador – for jungle homestays, festivals & colada morada

A country with just over 17 million people, Ecuador is an extremely culturally diverse nation and a cultural tourism destination that should not to be overlooked.
Retaining a strong influence from Spanish colonisation, with widely-celebrated Catholic festivals and traditions, there is also a diverse mix of Andean Indigenous groups and traditions that dominate the mountainous centre of the country. In the east, the influence of various Amazonian Indigenous groups and their traditions is strong.
The coast of Ecuador, meanwhile, is marked by African influence from the cultures of enslaved peoples brought during colonisation.
With such a diversity of cultures – each with their own festivals, traditional foods and more – there are plenty of immersive experiences to partake in across the country that make a trip to Ecuador a must for any cultural traveller.
Top cultural experiences in Ecuador
Visit a remote community in the Amazon rainforest: One of the most popular and fascinating cultural experiences for travellers to Ecuador is to visit an Indigenous community to learn about and experience the rich traditions. Even a jungle tour of the Amazon on a budget can be tailored to include a visit to an Indigenous community, where you’ll learn to make traditional dishes and beverages such as chicha . Tribes deeper in the Amazon that welcome visitors often offer more in-depth cultural experiences including homestays, ritual cleansings, or even ayahuasa retreats.
Celebrate Easter in Ecuador: In addition to the Indigenous traditions in Ecuador, there are many popular celebrations from the Catholic tradition that travellers can partake in. Easter celebrations during Holy Week include Quito’s parade, known as the Procesión Jesús del Gran Poder, which features thousands of purple-hooded devotes carrying crosses and statues. Make sure you enjoy a bowl of traditional Fanesca , a rich and creamy soup made with 12 grains representing the 12 Disciples.
Dress up for Día de los Difuntos : Another cultural celebration with Indigenous roots is the Día de los Difuntos or ‘Day of the Deceased’, marked on November 2nd. Ecuador celebrates by honouring the dead and visiting cemeteries. Celebrations also include preparing and eating guaguas de pan , bread in the shape of a baby filled with fruit jam, and drinking colada morada , a thick, sweet drink made with berries and fruit and thickened with blue corn flour before being served warm. These delicious treats are sold in bakeries across the country for at least a month prior to the festivities. The largest celebrations are held in Indigenous communities such as Otavalo in Northern Ecuador.
By Carley from Home to Havana
The Big Island of Hawaii – for palm weaving, stargazing & petroglyphs
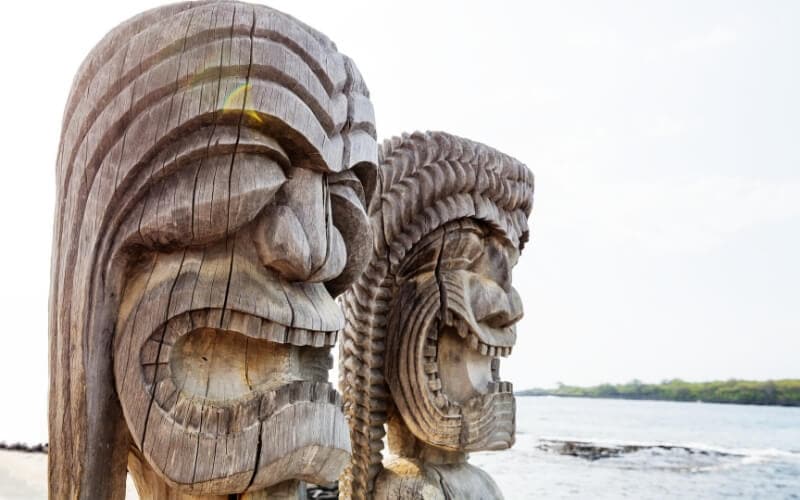

The natural abundance of the Big Island of Hawaii, the largest island in the Hawaiian archipelago, is nothing short of spectacular. With eight different climate zones, three active volcanoes, and the most mesmerising waterfalls and beaches in different shades, there’s a wealth of diversity to explore on the Big Island .
This unique natural setting is also home to several important cultural sites. After all, this is the Hawaiian island where the first Polynesian settlers arrived, where the first ruler of the Kingdom of Hawaii, King Kamehameha the Great, was born, and where the European explorers first arrived.
With such a rich heritage, it comes as no surprise that Hawaiian culture is still very much alive on the Big Island. Here are some experiences that allow you to explore the island’s heritage.
Top cultural experiences on the Big Island of Hawaii
Take a self-guided tour of the Pu’uhonua o Hōnaunau National Historical Park: Just south of Kailua-Kona, there’s a site where the royal family and their warriors once lived. It’s very well preserved and you can still see the thatched huts, an ancient temple, wooden carvings and fishponds. But this site was more than just a royal retreat: When Hawaiians broke the law or kapu , they were condemned to death. The only option to escape their fate was reaching this sanctuary, known as the Place of Refuge. You can visit this intriguing site on a self-guided tour.
Learn the traditional Hawaiian art of weaving palm fronds: In the Hawaiian craft known as lau niu , the leaves of the coconut palm were used to thatch roofs, create baskets and even hats. There’s a handful of workshops where you can learn this traditional craft from a professional weaver. Not only does it make for a unique experience, it also allows you to craft your own handmade Hawaiian souvenir.
Go stargazing at Maunakea: In Hawaiian culture, the dormant Maunakea volcano, with its unique alpine Lake Waiau, is considered sacred. They believed the summit to be the realm of the gods and the meeting place of earth and sky. To this day, cultural rituals are performed on the slopes of Maunakea. This intriguing volcano is home to the world’s largest astronomical observatory, the Onizuka Center for International Astronomy, which hosts a regular stargazing program.
Check out the Hawaiian petroglyphs: Hawaiian petroglyphs tell the stories of ancient times and give a unique inside into the different cultural beliefs on the islands. You can find carvings of canoes, turtles, babies and more at one of the petroglyph sites that dot the Big Island, such as the Puuloa Petroglyph site in Hawaii Volcanoes National Park or the Puako Petroglyph Archaeological Preserve near the Mauna Lani Resort.
Conquer the ocean in an outrigger canoe: Step aboard a double-hull outrigger canoe and explore the shore in the same way the Polynesian settlers did centuries ago. This type of canoe features lateral support floats or outriggers fastened to one or to both sides of the hull. Learn how to paddle and work as a team as you glide along the Kona reefs teeming with fish. If you’re lucky, you might even spot a pod of dolphins.
By Sarah from CosmopoliClan
Orleans Parish – for jazz, Madi Gras & creole cooking
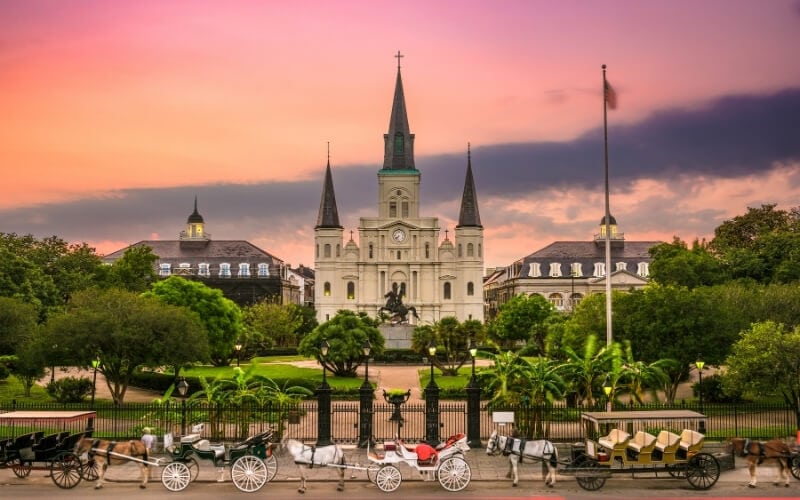

When it comes to cultural destinations, few cities have as much to offer as New Orleans and the surrounding parishes. Located in Southeastern USA, New Orleans is all about tradition and culture. The city’s unique heritage comes from a blend of French, Spanish, Cajun, and Creole cultures.
Combined, these groups have given birth to something truly iconic. The beautiful Mardi Gras celebrations are a remnant of the French colonial era, while the beautiful Spanish colonial architecture in Jackson Square is worthy of a walking tour .
You will also find unique Cajun cuisine served in the city’s most popular restaurants. Add in the many historical museums, southern plantation homes, and distinct architectural styles and Orleans Parish makes for the ultimate cultural destination in the US.
Top cultural experiences in New Orleans
Join a Mardi Gras parade: New Orleans is well-known for its lavish and grand Mardi Gras parades and balls. Visitors can enjoy the festivities for an entire month in the lead up to the big day. Outside of Mardi Gras, there are plenty of other festivals in New Orleans to check out as well.
Listen to jazz: New Orleans is the birthplace of jazz. The city’s Creole population gathered and celebrated in the city’s Congo Square on Sundays and thus jazz was born!
Tour a plantation home: Many southern plantation homes are located along the banks of the Mississippi. These can be seen on a road trip along the Great River Road. On a tour, you will learn about pre-Civil war life in the South and the history of slavery. Learn more about the ethics of visiting plantation homes here .
By Ketki from Dotted Globe
Oaxaca – for Indigenous cuisine, Zapotec rugs & mezcal
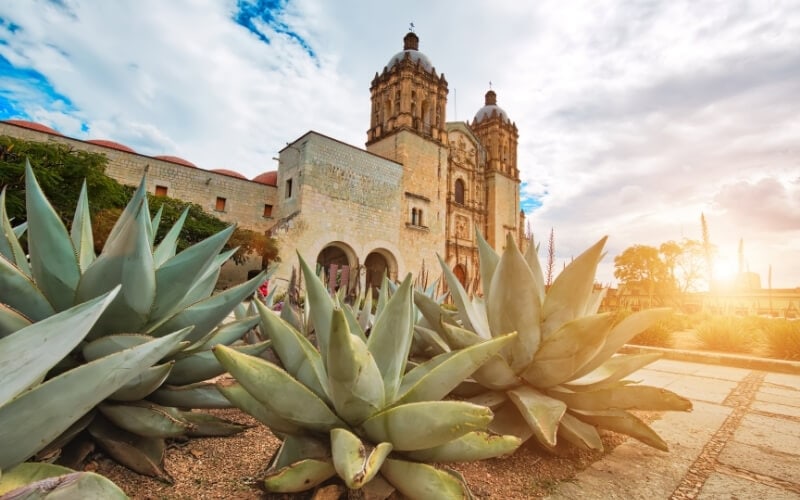

The state of Oaxaca is a cultural hub in Mexico. Void of resorts or even big-name hotel chains, Oaxaca is rich in flavourful cuisine, celebrations, and Indigenous revitalisation.
Located in southern Mexico, Oaxaca features a variety of different landscapes, from lush hills and forests, to dry arid deserts and blissful beaches. However, the community atmosphere of Oaxaca is what keeps people coming back, both international visitors and Mexican residents alike.
Oaxaca is known as the food capital of Mexico, with dozens of celebrity chefs. Notably, Indigenous culture is very visible in Oaxaca, with 16 recognised Indigenous groups in the state. Zapotec weaving is one of the most sought-after souvenirs in the area – and Mexico in general – and it comes from Oaxaca.
Top cultural experiences in Oaxaca
Celebrate Dia de los Muertos : Oaxaca City is a top destination for Dia de los Muertos (Day of the Dead), with its dazzling parades, intricate family altars and abundant festivities. Dia de los Muertos is a pre-Columbian tradition that honours deceased loved ones with food, drink, and merriment. So, if you happen to visit Oaxaca during a festival like Dia de los Muertos, bring comfortable shoes for fun activities throughout the day. Oaxaca City is an extremely walkable city, and you will want to explore every inch of its mural lined walls.
Eat Oaxacan cuisine: Since Oaxacan cuisine is also central to the region’s identity, sign up for a food tour with a local to learn the origins of some of the most popular dishes and what makes Oaxacan food and flavour so unique and different from other states in Mexico. Or, if you want to take a more hands-on approach, take a cooking class with a world-class chef at Casa de los Sabores and learn how to make mole and other Oaxacan staples.
Visit a Zapotec village: If you’d prefer to focus on Indigenous cuisine, take a day trip out to the Zapotec village of Teotitlán del Valle for a cooking class at El Sabor Zapoteco . After you finish, there are many things to do in Teotitlán del Valle , but you will probably want to get your fill of shopping at the many boutique shops for best quality Zapotec rugs.
Drink mezcal: If you’re a fan of hard drinks, Oaxaca is a great destination for mezcal tasting! Hop on any tour and view the vast agave fields as you taste mezcal throughout the day. Depending on the season, you may even get to try your hand at using the harvesting machete!
By Kay from The Awkward Traveller
Learn more: A local’s guide to the best of Mexican culture and an in-depth guide to Mayan culture in the Yucatan .
Cultural travel destinations in Europe
French Basque Country • Armenia • Sicily • Greece • Bosnia & Herzegovina • Russia • Northern Europe’s Arctic Regions • The Greater Caucasus • Andalusia, Spain
French Basque Country – for frontons , fêtes & espadrilles

The Basque country at the southwestern-most tip of France is one of those regions you might not guess is French – at least not at first.
The half-timbered houses are painted oxblood or green, and the Euskara (Basque) language, Europe’s oldest, is related to no other tongue. The Basques are also among the oldest ethnic groups of Europe.
Basque culture is unique and is spread among seven provinces, of which three are in France (the other four are in Spain). The Basques have their own festivals, music and dances, their own foods, games and folklore, as well as an acute sense of history and heritage.
Top cultural experiences in French Basque Country
Here are just a few cultural experiences to whet your appetite for all things Basque!
Gastronomy: The food is different from your regular French fare. For example, the Espelette pimento is spicier than seasonings you’ll find elsewhere in France, and food itself is taken to new heights here – the region has the highest number of Michelin stars per capita in the world. And let’s not forget the pintxo , the Basque equivalent of the Spanish tapas.
Fronton s: You’ll find one of these walls in every Basque village – it’s what Basques use to play their national sport, Basque pelota (known in some countries as jai alai). It’s played with a racquet-like bat which scoops up the ball. Then, a bit like squash, the players fling it back and forth against the wall, or fronton.
Family-owned businesses: Basque artisanal traditions run deep, whether it’s leatherwork, espadrilles, Basque linen or beret making. This is a region in which hand-made goods thrive and where mass-production takes a back seat. The local government makes sure family businesses are promoted and Basque know-how exported, however stiff the competition – there are special labels for family businesses, and even labels for those businesses that have been around for more than a century (and there are plenty). As a result, hand-made goods from this small region find their way around the world, symbolising not only Basque savvy but Basque determination to hang on to its heritage.
Bayonne Festival: With its one million annual participants, the Fêtes de Bayonne is France’s largest festival. It was ‘borrowed’ in 1932 from not-too-distant Pamplona in Spain, but has grown immeasurably since. Each July, visitors dress up in white clothes and red scarves (and a red beret, of course) and spend five days eating, drinking, singing Basque songs and watching Basque sports. The Festival includes bullfighting, which has a long tradition in the region, although this particular sport might be short-lived given the growing opposition to it.
By Leyla from Offbeat France
Bosnia & Herzegovina – for old bazaars, woodcarving & kahva
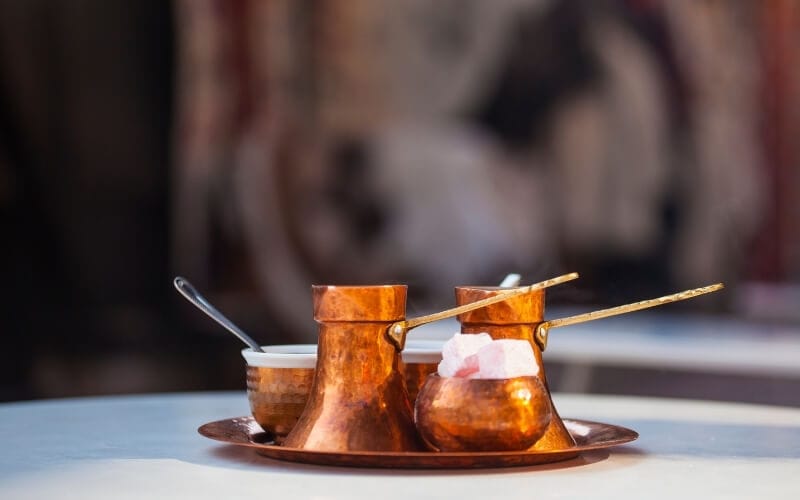

Bosnia and Herzegovina is one of the most culturally and ethnically diverse countries in the Balkans . If you have your sights set on this lesser-visited part of Europe for your next cultural trip, it’s the perfect setting to learn about the region’s different – often competing – influences and how they’ve shaped modern life.
Bosnia is the original cultural melting pot, and Sarajevo is where it all comes to a head. The city is divided into two parts – Ottoman and European – with the sprawling Old Bazaar on one side, and the Austro-Hungarian planned portion of the capital on the other. A plaque on the pavement marks the spot where East Meets West.
But the boundaries aren’t always that clear. Bosnia and Herzegovina’s character is a combination of Bosnian, Serb and Croat, layered with Jewish, Romanian, Albanian and Turkish traditions. The vignette of a mosque’s minaret and a church bell tower rising up side by side is a perfect motif for the country’s diversity.
Top cultural experiences in Bosnia & Herzegovina
Explore Sarajevo’s Old Bazaar: One of the most beautiful Ottoman bazaars in the region (and there are a lot), just wandering the rows of picturesque wooden shops connected by cobbled streets – the sound of coppersmiths beating intricate designs onto plates ringing in your ears – is a completely immersive experience. At the kafane coffeehouses, where kahva and rakia are served with much pageantry, you get a feel for famous Bosnian hospitality.
Take a food tour of Sarajevo: Bosnians are fiercely proud of their national cuisine. Dishes such as burek (filled savoury pastry) and cevapi are a common ground and bring the country together. A food tour of Sarajevo takes you behind the scenes on some of the city’s liveliest markets and busiest restaurants while giving you an insight into the history behind some of the country’s most iconic dishes.
Visit a woodcarving master in Konjic: Sarajevo in particular has an incredibly rich art and literature scene, as evidenced in the many festivals that take place in the city throughout the year. Bosnia’s heritage handicrafts shine a light on the culture of craftsmanship that has bestowed the country with so many beautiful landmarks over the years. Woodcarving has been practiced for generations in the city of Konjic and today, visitors can tour the masters’ workshops for an up-close encounter.
See the Stećci Medieval Tombstone Graveyards: Stećci medieval tombstones were laid during the time of the Bosnian Kingdom. Recognised as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, they’re found throughout the territory including in forests close to the border with Serbia . Carved from limestone, the Stećci contain motifs and inscriptions and provide a rare window onto this epoch of the country’s history that’s still shrouded in much mystery.
Greece – for markets, mythology & Orthodox Easter
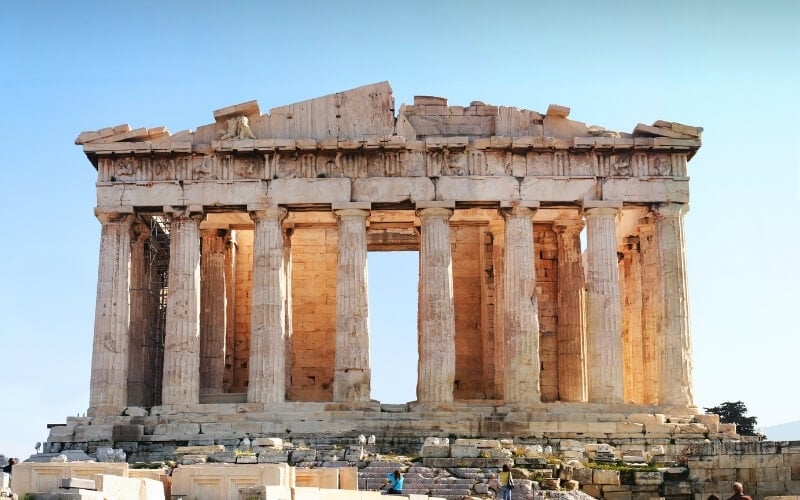

Greece is a country rich in culture, from the legacy of ancient history and mythology to traditional cuisine and celebratory festivals that still bring people together to this day. Greek nationals tend to be very proud of their history and culture , which can be seen in the well-executed museums, galleries and archaeological sites throughout the country.
Believed to be the ‘birthplace of Western civilisation’, Greece is known for its scholars, medics, architects, philosophers and politicians that shaped the way the world works today. This makes the country an excellent choice for cultural tourism as there are simply so many things to see and do that will both satiate your wanderlust while also teaching you new things.
Whether you’re interested in archaeological excavations, gastronomic tours, local festivals or ancient architecture, Greece certainly has you covered.
Top cultural experiences in Greece
Take a Mythology Tour of Ancient Athens: Athens has a whole host of archaeological sites to explore , from the Ancient Agora and Hadrian’s Library to the world-famous Acropolis and Parthenon perched on a hillside overlooking the city. One of the best ways to discover these sites is via a Mythology Tour that takes you around the best historic monuments and ruins while also giving you interesting information about the city and country’s history and mythology. This tour , suitable for all ages, gives you skip-the-line access to some of Athens’ most important landmarks along with an experienced guide to give you detailed history about how Greece became the centre of the world.
Visit the Athens Central Market: If your idea of cultural tourism involves food, you might be interested in a trip to the Athens Central Market and a local cookery class. A gastronomic experience allows you to soak up the sights and smells of the city’s biggest market, picking up local produce and souvenirs while also trying some tasty titbits along the way . You’ll then take your purchases back to the kitchen where you’ll cook up a storm using local recipes and techniques. Try classics like Dolmades (stuffed vine leaves), Tzatziki and Spanakopita (spinach and feta pies) to give you a real taste of traditional Greek cuisine.
Attend the Epidaurus Festival: The Ancient Theatre of Epidaurus, a grand amphitheatre located on the bank of the Acropolis Complex, runs an annual summer festival of art. The festival combines modern and traditional music, theatre and dance with the picturesque Ancient Greek setting, making it a real highlight for any traveller. Over the years, the Epidaurus festival has played host to names like Frank Sinatra, Maria Callas and Luciano Pavarotti.
Celebrate Orthodox Easter in Greece: Easter is one of the biggest traditional festivals on the Orthodox calendar, so no matter where you are in Greece during this time, you’re sure to come across some pretty exciting celebrations! One destination that always enjoys epic Easter festivities is the island of Corfu. Local Easter traditions begin on Palm Sunday (a week before Easter) and there are different festivities each day leading up to the main event.
Palm Sunday sees a large procession of the Holy Shrine; Monday, Tuesday and Wednesday see locals preparing their Easter meals and sweet specialities, going to evening ceremonies and lighting up the town with lanterns; Maundy Thursday is egg-painting day; Good Friday features the mournful marches of the philharmonic orchestra and the procession of epitaphs; Good Saturday features an artificial earthquake(!), bell ringing, the throwing of clay pots and tossing coins into a barrel; and the whole week culminates on Easter Sunday with a celebration of the Resurrection of Christ – fireworks, marches, music and traditional family meals galore!
By Chrysoula from Athens and Beyond
Learn more: 7 awesome cultural activities in Athens .
Russia – for ballet, banyas & borscht
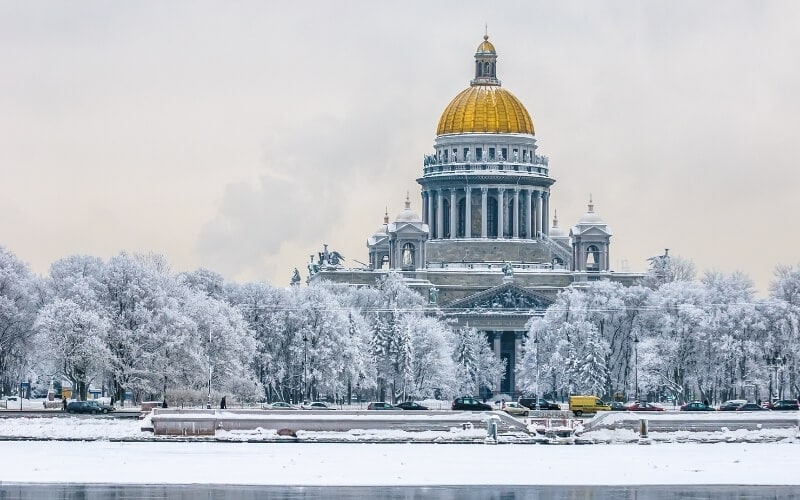

While many may think of Russia as cold and grey, this could not be further from the truth. From the famous colourful onion domes of St. Basil’s Cathedral to the gilded fountains of the Peterhof Palace, Russia’s beauty is undeniable.
Russia is also a country rich in culture and filled with literature, ballet, painting and classical music.
Top cultural experiences in Russia
To really delve into Russian culture, there are a few experiences you should have whilst here.
Experience a Russian banya : One of the best cultural experiences you can have in Russia is to visit a banya . A banya is similar to a sauna. The biggest difference, though, is that a banya has high levels of humidity, while a sauna usually has dry air. They’ve been a part of Russian life for over a thousand years! You wear funny felt hats to protect your hair and ears from the heat. This also helps to regulate your body temperature, so you are able to sit in the banya for a longer period of time.
Another interesting aspect of the Russian banya is ‘flogging’ using birch twigs ( venik ). This is supposed to benefit your health and improve your immune system, and honestly, if you have someone who knows what they are doing, it does feel really good!
After you’ve gone in and out of the banya a couple times, you then cool yourself off by taking a quick, cold shower, jumping into a cold pool or tub (banyas do have these), jumping into a snowbank (seriously). Or… You can just jump in a frozen lake!
See a ballet at the Bolshoi: Seeing a ballet at the Bolshoi Theatre is one of the best things to do in Moscow and all of Russia in general. Even though ballet did not originate in Russia, Russian ballet is world-renowned, and the locals are incredibly proud of the tradition. If you can, try to see a performance of The Nutcracker or Swan Lake on the historic stage. Tickets sell out very quickly, so don’t delay in purchasing them once they go on sale!
Experience NYE: New Year’s Eve is the biggest holiday in Russia. This is because Christmas was forbidden during the Soviet years. Many traditions were moved from Christmas to the New Year, including keeping presents under the Christmas tree and visits from the Russian equivalent of Santa. Celebrations and fireworks take place across the country on December 31 – the biggest and most famous displays are in Moscow’s Red Square and Gorky Park.
Sample Russian cuisine: No trip to Russia would be complete without experiencing the local cuisine. The best Russian food and drinks to sample on your visit are: Pelmeni (a Russian dumpling filled with meat and usually topped with sour cream); borscht (a traditional Russian soup whose main ingredient is beetroot); beef stroganoff (a Russian dish made with sautéed beef in a sauce with smetana ); syrniki (essentially a cottage cheese pancake topped with jam or sour cream – SO good!); kvass (a fermented beverage made from rye bread); and caviar and vodka (alas, you can’t come to Russia and not try caviar and vodka!)
By Lindsey from Have Clothes, Will Travel
Northern Europe’s Arctic Regions – for reindeer & Sami traditions
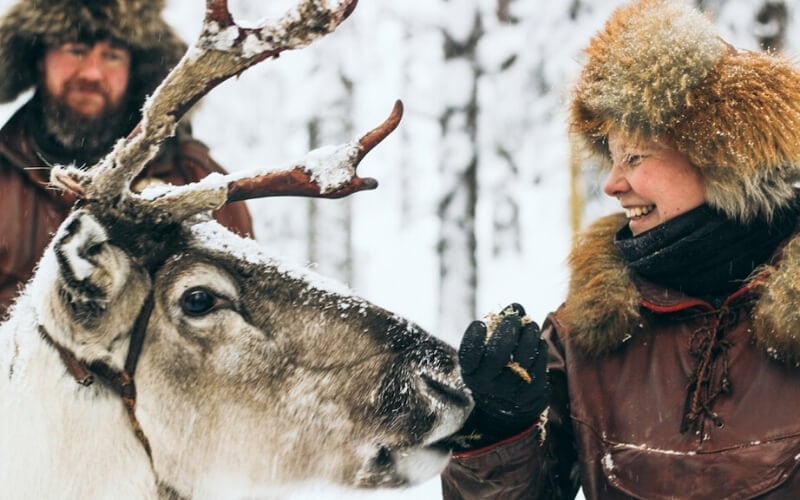

In Europe’s high northern reaches, you will find one of the continent’s oldest and most distinct cultures, the Sami. Spread across the Arctic regions of Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Russia, the Sami are Indigenous people who have traditionally led a nomadic lifestyle, known for herding their reindeer between their summer and winter feeding grounds.
The origins of the Sami are largely unknown, and it is believed that they once inhabited grounds much further south. But years of persecution drove them north and forced them to decrease livestock numbers in order to maintain their way of life.
Against all odds, they have managed to hold onto large parts of their culture, including languages, traditions and ceremonies. As the modern world has encroached further north, there have been clashes over natural resources and land, which has put the plight of the Sami at the forefront of people’s minds in recent years and led to movements to protect the people and the culture.
Top cultural experiences in the Arctic regions
Head to Tromso for an immersive Sami experience: Today, there are plenty of ways you can learn about and experience Sami culture. During the winter months, there are many Sami experiences in Tromsø, Norway and beyond where you can educate yourself about the Sami way of life, hear stories that have been passed down through the generations, and eat traditional foods.
Shop at a Sami market: Keep an eye out for Sami markets where you can purchase handmade traditional items.
Participate in a Sami festival: Norway is known to have the largest festivals and in various Arctic cities, you will find Sami festivals on National Sami Day (February 6th). In the summer, there are also Sami music festivals, such as the one found near Murmansk in Russia.
A visit to Northern Europe’s Arctic region is one of the most meaningful cultural trips in Europe as it helps bring attention to a group of people who have spent many years marginalised in their respective modern-day societies.
By Megan from Megan Starr
Andalusia – for Moorish architecture, tapas & Flamenco

Andalusia is an autonomous region in Southern Spain, geographically bounded by Spain’s southern coast. It’s culturally vibrant and very distinctive when compared to other parts of Spain such as Catalunya.
This part of the country was ruled by the Moors for centuries, and Moorish influence is evident in the cuisine, architecture and culture. Seville, Cordoba and Granada are all among the best Spain city breaks and each serve as a good base for exploring more of the region.
Top cultural experiences in Andalusia
Marvel at the Moorish architecture: The Andalusian architecture will capture your attention as soon as you land there, and this is probably the easiest way to start digging into the region’s past and cultural evolution. Cities like Seville and Granada have major UNESCO sites that will blow your mind – the style is in no way similar to buildings in France or even northern Spain for that matter. Islamic calligraphy and intricate details are most evident at the Real Alcazar Palace in Seville, the Alhambra in Granada , and the Mezquita in Cordoba.
Go tapas hopping: People in Andalusia are known for being a more little laid back, and generally enjoy food, family and companionship. Popular ‘tapas hopping’ is best experienced in Andalusia. Tapas bars in the south cultivate a cosy atmosphere with rounds of $1 dollar beers, spinach and chickpeas, cheese, and churros. Moorish/Muslim influence can be seen in the preparation of some foods, especially marzipan, and in the use of herbs and spices such as cumin and cilantro.
Watch a Flamenco performance: After food, flamenco is what defines Andalusia. Flamenco is a dance that is synonymous with Southern Spain and is one of the most energetic and passionate forms of dance/storytelling. Flamenco shows in Seville and other cities in Andalusia are a great way to understand and enjoy this side of Southern Spanish culture.
By Mayuri from To Some Place New
Cultural tourism destinations in the Asia Pacific
Central Australia • Timor-Leste • Sarawak, Malaysia • Cambodia • Japan • Bhutan • Kerala, India • Rajasthan, India • Uzbekistan • The Tibetan Plateau • Taiwan
Central Australia – for ancient landscapes, ochre & bush tucker

The Arrernte and Anangu people have lived in Central Australia for over 20,000 years. From Uluru and Kata Tjuta (the Olgas) to the MacDonnell Ranges and Alice Springs, they have made their home in one of Australia’s driest and hottest regions.
The landscape, its plants and animals permeate every aspect of their culture. The natural environment is the basis for the Creation (or Dreamtime) stories at the core of their beliefs, ceremonies and traditions.
Their relationship with the land also has a practical aspect as a source of food, shelter and medicine. The Arrernte and Anangu’s land management techniques, native foods and art have all found their ways into broader Australian life.
Today, members of the communities have roles as guides, ranges and managers of major tourism businesses. For travellers, there are many opportunities to appreciate the on-going connection the Arrernte and Anangu people have with the Central Australian landscape.
Top cultural experiences in Central Australia
Visit Uluru (Ayres Rock): You can’t go to Central Australia and not visit Uluru. It is an iconic Australian landmark and when you visit this enormous rock, you’ll find many ways to immerse yourself in Indigenous culture. At Yulara Resort you can join a free session to learn about Indigenous food, crafts and didgeridoo playing.
On your way to Uluru, stop at the Cultural Centre. There are ranger talks about the area’s wildlife, how the Anagu have lived in the area for thousands of years, and how that knowledge is used to manage the park today. There are also galleries featuring local art and craft. For something a bit different, try a Segway tour of the rock . As you cruise around the 10 km base, you get a wonderful explanation of the Creation Stories tied to many of the rock’s features, caves and waterholes.
Ochre Pits: Ochre is a natural clay that comes in a range of colours and has been used for ceremonial and medicinal purposes for thousands of years. The Ochre Pits are at a site in the West MacDonnell Ranges where ochre has been collected by Arrernte men for generations. The Ochre Pits are an easy and accessible stop as you tour the gorges of the West MacDonnell Ranges. The colourful ochre cliff face is spectacular and it is quite an experience to be in the presence of a site that has been used for so long and continues to play a role in Arrernte life.
Alice Springs Desert Park: With the lives and lore of the Arrernte tied so closely to the environment, this combination of a wildlife park and botanic garden gives you a great insight into their relationship with the land. Besides the fantastic desert animal exhibits, there is a full program of keeper and cultural talks over the day. Learn about surviving in the desert, bush food and the meaning many of the animals have in the daily life of the Arrernte. The park is in Alice Springs with the West MacDonnell Ranges providing a spectacular backdrop.
By Natalie & Steve from Curious Campers
Timor-Leste – for sacred houses, tais weaving & Cristo Rei

Asia’s youngest nation, tiny Timor-Leste fought hard for its independence, first from Portugal and later from Indonesia. Holding strong to customs and beliefs is part of the resistance and against all odds, the Timorese have managed to pass down many traditions through music, dance and storytelling.
Fiestas held year-round throughout the country showcases these oral traditions, while in recent years, contemporary collectives have began building on the nation’s heritage of performance arts to process the events of the past and express their visions for the future.
There aren’t many physical reminders of Timor’s time as a Portuguese colony left – most architecture was subsequently destroyed – but the invisible influence is still there, along with the influence of the Catholic Church.
In the more remote regions, ethnic groups such as the Fataluku speak their own language and observe a fascinating array of cultural practices you won’t find anywhere else on Earth.
Top cultural experiences in Timor-Leste
Tais weaving: Timor’s ornate national textiles are storytelling objects, filled with symbols inspired by folktales and animist traditions. At the Tais market in Dili you can shop for handwoven tais scarves and tablecloths, while visiting a weaving centre such as Koperativa Lo’ud gives you a chance to see the natural dyeing and weaving process in person.
See the uma lulik in Lospalos: Part of the Fataluku tradition, these sacred houses perched high on stilts symbolise the link between the dead and the living. They are sacred objects that cut an impressive profile as you pass them on the coast around far-eastern Timor.
Make the pilgrimage to Cristo Rei: Standing 27 metres tall on a hill overlooking the capital, Dili, Cristo Rei is the ultimate symbol of Timor-Leste’s piety. More than 99% of Timorese are Christian, and the church has played a huge role in shaping the island’s character post-independence. Walking the 590-step path lined with Stations of the Cross is a right of passage. At the top, views of Dili, Atauro Island and the sparkling coastline.
Sarawak, Malaysia – for ikat textiles, longhouses & forest trekking

The largest of Malaysia’s 13 states , Sarawak envelops much of Borneo. Local culture and way of life is intimately intertwined with the island’s flora and fauna and offers visitors experiences quite distinct from anything you find in Peninsular Malaysia.
Life, history, culture and spirituality is all heavily influenced by the area’s Indigenous peoples, most notably the Iban. Malaysia’s mix of Malay, Indian, Muslim, Chinese and British culture can also be felt in Kuching , the autonomous state’s biggest city and a hub for culture and the arts.
Top cultural experiences in Sarawak
Visit a museum in Kuching: The Tun Jugah Textile Museum, the Sarawak Cultural Village and the Sarawak State Museum – all in or near Kuching – offer immersive exhibits that explore Iban culture. The former is dedicated almost completely to the art of ikat weaving, a time-honoured craft tradition that’s kept alive by artisans and students who learn to dye and weave at the museum workshop.
Stay in an Iban longhouse: Travelling up river into the forest to spend the night at an Iban longhouse is an unforgettable experience. As well as sleeping in traditional quarters, you’ll get to taste home-cooked food and experience various oral traditions, including Renong singing and Ensera storytelling.
Eat Sarawak cuisine: Malaysia is a foodie’s paradise and Sarawak is no exception. In addition to the usual mix of cuisines served up at hawker markets, the state boasts many regional breakfast specialties including Sarawak laksa, kolo mee (Sarawakian noodles) and ayam pansuh (chicken cooked in bamboo).
Cambodia – for Theravada Buddhism, apsara & golden silk

It’s easy to think of Cambodian culture as a relic of the past – a crumbling stupa or a cobwebbed museum display. But nothing could be further from the truth.
Khmer culture is a living, breathing thing, and it permeates everything – from underrated Cambodian cuisine to the country’s handicraft industry and the young collectives in Battambang and Kampot who are reviving the arts scene.
Many traditions and art forms almost lost during the 1970s have been brought back from the brink by artists and entrepreneurs determined to keep Cambodian culture alive.
Whether you’re interested in the legacy of the most powerful Golden Age state, the Khmer Empire, or discovering reminders of the Kingdom’s time as part of French Indochina in the beautiful colonial architecture and peppercorn plantations, it’s never been easier for visitors to get a feel for Cambodian culture.
Top cultural experiences in Cambodia
Take a Buddhism tour of Siem Reap: Spirituality plays a huge role in contemporary Cambodian life and there’s no better lens for exploring the country through. After you’ve taken in the Temples of Angkor that blend Hinduism and Buddhism, learn the ins and outs of Theravada Buddhism with an immersive Buddhism tour of Siem Reap . It’s a life-changing experience that teaches you how ancient beliefs coexist with modern society.
Watch an Apsara performance: It wasn’t so long ago that Cambodia’s national dance, Apsara, was considered an endangered art form. Artist and genocide surviver Arn Chorn-Pond has almost single-handedly revived Apsara traditions through his organisation Cambodian Living Arts. Nothing captures the Cambodian spirit like the understated but immensely beautiful performance. Nightly shows are held in Phnom Penh along with hands-on Apsara workshops that teach visitors the basic moves.
Go forest trekking in Mondulkiri: Mondulkiri and Ratanakiri in Cambodia’s far north-east are two of the country’s most remote provinces , known for their thick forests and biodiversity, including wild elephants. Ethnic minority groups including the Tampuan and the Bunong have developed sustainable tourism offerings, hosting guests at homestays and organising guided forest treks. During the tours, you get a glimpse of how people have coexisted with the forest for generations, and learn about the struggles they face today.
Seek out Khmer handicrafts: From Siem Reap’s Golden silk to Takeo cotton and clay pottery in Kampong Chhnang, every Cambodian province has its specialty crafts, many of which are still made by hand according to traditional techniques. In addition to making the perfect Cambodia souvenir , many co-ops offer tours and workshops so you can see the processes up close.
Japan – for ryokans , geisha culture & tea ceremonies

For those seeking an immersive cultural travel experience, Japan offers visitors a unique look at some of the oldest and most beautiful traditions in the world.
From the historic temples and shrines found throughout the country to the many spiritual and cultural celebrations, there are plenty of opportunities for visitors to Japan to learn about the various philosophies and spiritual traditions that underpin Japanese culture.
Top cultural experiences in Japan
Observe a temple ritual: Consider participating in some of the various rituals at Japan’s temples and shrines. This is especially beneficial if you’re visiting Japan with kids , as it helps to gain a better understanding and appreciation for Japanese customs. Many people in Japan have deep-seated beliefs in symbolism. At the temples and shrines, you can observe and participate in practices that will bring you good fortune, luck, prosperity or health.
Spend the night in a ryokan : To truly embrace Japanese culture, book a stay at a ryokan rather than a hotel. These traditional Japanese inns typically feature rooms with tatami-matted floors and communal onsens or bathhouses. Guests tend to walk around the ryokan in a yukata or lounging kimono and slippers. It is also common for guests to walk around barefoot, as it is considered unclean to wear shoes inside.
Drink matcha : A tea ceremony is another immersive experience that is unique to Japan. Although popular throughout Japan, tea ceremonies are especially prominent in Kyoto, the home of geisha culture. Geishas are treated somewhat like celebrities in Japan, and booking a geisha performance and tea ceremony can be expensive and fairly difficult to arrange. However, you can book a tea ceremony with a maiko , or geisha apprentice, for a more modest price. This one-of-a-kind ritual ceremony is sure to be one of the most memorable travel experiences you’ll have in Japan!
By Melissa from Parenthood and Passports
Bhutan – for handicrafts, thangka & fertility symbols

Most people think of the Tiger’s Nest when they think of Bhutan. But this small, mountainous nation has a wealth of cultural history to offer in addition to its ornate monasteries.
Bhutan is a nation of crafters. In every town and city you will find streetwise vendors selling all manner of clothing, kitchenware, homeware and decorations that have been made using techniques that have been taught and passed down for hundreds of years.
Likewise, if you turn your attention to the buildings, you’ll see that many of them are adorned with colourful decals and patterns, especially designs that depict the eight auspicious signs which, among other things, represent wealth, good fortune, purity and harmony.
Bhutan is the only country in the world to measure their country’s wellbeing based on Gross National Happiness as opposed to Gross Domestic Production, which makes it (un)officially the happiest country on Earth.
Best cultural experiences in Bhutan
Attend a Tshechu ceremony: The annual Tshechu ceremonies show off Bhutan’s handicraft history perfectly. Throughout the year, locals gather across the country in regional Tshechus to celebrate Bhutan’s culture by singing traditional songs and performing dances in elaborate, brightly coloured costumes. At the Tsechu celebrations, an enormous religious banner or thangka depicting the country’s founder, Guru Rinpoche, is unveiled. The thangka is the size of a three storey building, hundreds of years old, and has not faded through the centuries due to the tradition of making sure that the light of the sun never touches it, so it’s still incredibly colourful and detailed.
Visit the Choki Traditional Art School: In order to see the historical handicrafts of Bhutan in production for yourself, make sure to visit the Choki Traditional Art School. Located just to the north of the capital city of Thimpu, here you can witness the students being taught how to weave, paint and sculpt masks, clothes, models, tapestries and dioramas from Bhutan’s history. Students’ ages range from elementary through to late teens, with all levels of skill on display. The students’ creations can then be bought from the school craft shop, with the proceeds helping fund the continuation of the institute’s classes.
Spot the phallus in Punakham: Punakham is the former capital of Bhutan, and was the seat of government until 1955. Located in the north of the country, the town is notable to western tourists for one particular reason. In the 15th century, a controversial master named Lama Drukpa Kunley (also known as the ‘Divine Madman’) popularised the phallus as a means to ward off slander and provide protection for those who lived in houses that displayed it prominently. Yes, it may be taboo for most of the world, but not here – these graphic symbols of fertility and good luck are artistically painted on walls everywhere!
By Jeremy from Cultura Obscura
Kerala, India – for houseboats, tea estates & contemporary art

Dubbed ‘God’s Own Country’, Kerala is a noodle-shaped state in the Southwest of India on the Malabar Coast. It’s known for its beautiful nature – especially a series of canals known as the backwaters and the hilly terrain of the Western Ghats Mountains.
Kerala people are officially the most literate in India and have the longest life expectancy. It is often said the Keralites have the best quality of life in this part of India, and that things are a lot more advanced. This is conveyed in the increasingly popular field of ecotourism and other initiatives.
The region is a beautiful mix of influences and religions. The spice trade has flourished in the area, which brought about European colonisation. You can feel Portuguese influence to this day, especially in the town of Kochi.
Top cultural experiences in Kerala
Cruise Kerala’s backwaters on a houseboat: With the decline of goods being transported on water, Kerala’s trade boats were repurposed into houseboats, and now provide a unique immersive experience on the famous backwaters. The most popular route is between Alleppey and Kumarakom or Kolam. Spending at least one night on the backwaters is necessary for the ultimate houseboat experience.
Soak up the tea heritage in Munnar: Munnar in the Western Ghats is famous for its tea production. You can visit several tea estates in the area and enjoy a tasting. In the village of Munnar, you can also experience the peaceful coexistence of three religions. There’s a Hindu temple, a Catholic church and a mosque all within a few meters from each other.
Attend the Muziris Biennale in Kochi: A bi-annual international exhibition of contemporary art takes place in Kochi. This is the largest festival of its kind in Asia. When the biennale is on, the whole city lives it. The main space for the festival is a large complex of empty buildings near the port. Here, art installations covering all possible mediums bring the space to life. It’s a wonderful sight and quite a modern undertaking in Kerala.
Watch the artists at work at Kerala Kalamandalam: This is one of India’s most traditional universities of art and culture. Students learn Indian performing arts, especially those typical for Kerala. When visiting, you can observe students practicing unique dances with distinct facial expressions such as the Kathakali or Ottan Thullal, learning martial arts, and playing on unique musical instruments. The school is located in Cheruthuruthy.
By Veronika from Travel Geekery
Learn more: 9 amazing cultural encounters in Kerala .
Rajasthan, India – for folk dance, thaali & camel fairs

Rajasthan, the ‘Land of Kings’, is one of the most historically and culturally significant states of India. Over the centuries, Rajasthan has witnessed many rulers and many epic battles. Each built their own magnanimous fort and helped develop the region’s rich culture of art, dance and literature.
Over the past few decades, the Ghoomar dance from Jodhpur region and Kalbeliya dance of the deserts of Jaisalmer and Bikaner have become famous all over the world. Along with dance, folk music and songs relating the heroic tales of epic battles, these form an essential part of Rajasthan culture.
Against a backdrop of the vast Thar Desert, this has all shaped the culture of Rajasthan as we see it today.
Top cultural experiences in Rajasthan
Rajasthan offers travellers a plethora of unique cultural experiences .
Be a bystander at the Pushkar Camel Fair: The Pushkar Camel Fair, held every year in November, is one of the largest animal trading fairs in the world. This colourful carnival is a great opportunity for travellers to experience the charm-in-chaos of traditional melas (Indian fairs) along with a huge tribal gathering. In 2018, nearly half-a-million people visited this multi-day festival. Pushkar is only 150km from Rajasthan’s capital, Jaipur, and is easily accessible by road.
Visit Choki Dhani: A resort village merely 20km from Jaipur, Choki Dhani is the go-to place to experience a collection of Rajasthan cultural experiences. Spread across 10 acres, this uniquely designed resort-village reflects the grandeur of the Rajasthani tradition. Visitors can experience Rajasthani traditional folk dance, watch a puppet show, see skits and sketches depicting important battles, and relish a traditional Rajasthani thaali (set meal), eaten while seated on the floor.
Watch a Dharohar dance performance: The Dharohar dance show at Bagore Ki Haveli in Udaipur is a mesmerising experience in itself. This hour-long show is a combination of many traditional, tribal and folk dances local to the region along with a puppet show. One of the highlights of the show is when an 80-year-old folk dancer performs with more than 10 earthen pots stacked on her head.
By Mainak from Places in Pixel
Uzbekistan – for ceramics, Silk Road heritage & plov

Uzbekistan is an upcoming cultural destinations in Central Asia. With a new visa policy, it is now easier than ever to visit the country – and there are many good reasons to do so.
Uzbekistan was once an important part of the famous Silk Road and has a rich cultural heritage that is still visible in the beautiful Islamic architecture and historic sites throughout the country.
Uzbekistan’s major cities including Samarkand, Khiva and Bukhara were multicultural melting pots where people from all over the world exchanged goods, ideas and philosophies. The Turks, Greeks, Persians, Russians and Mongols all ruled parts of what is now Uzbekistan. Each of them left behind their own influence.
With so much history around, it’s sometimes easy to forget modern Uzbek culture, but this is just as interesting. The Uzbek people are very friendly and will give you a warm welcome to their world of delicious Uzbek food, traditional dance and music, and beautiful handicrafts.
Top cultural experiences in Uzbekistan
Taste Uzbek cuisine: One of the highlights of Uzbek culture is without doubt its food. The best way to learn more about Uzbek food is by taking an Uzbek cooking class. Tashkent is a great place to do so and also has some great restaurants where you can try the country’s national dishes. The Plov Center serves plates of the national dish to thousands of people every day – the huge steaming pots and pans outside are impressive enough to warrant a visit.
Explore ikat and ceramic traditions: Another great cultural experience in Uzbekistan is to explore the country’s beautiful handicrafts. The Fergana valley is home to several centres of handicraft production where they still use traditional techniques. Margilon is famous for its ikat silk textiles and there are several silk factories that offer free tours to see how it’s done. The Usmanov Ceramic Workshop in Rishton also welcomes visitors for a short visit to see its pottery production and design process.
Watch a dance performance: Traditional dance and music is an important part of Uzbek culture. Uzbek dance is an ancient art that has been perfected over hundreds of years. In Bukhara, there are almost daily performances in the Nadir Divan Begi madrasah showing the traditional dances from the different regions in the country.
By Ellis from Backpack Adventures
Learn more: Things to do in Uzbekistan for cultural travellers .
The Tibetan Plateau – for horse trekking & nomadic culture
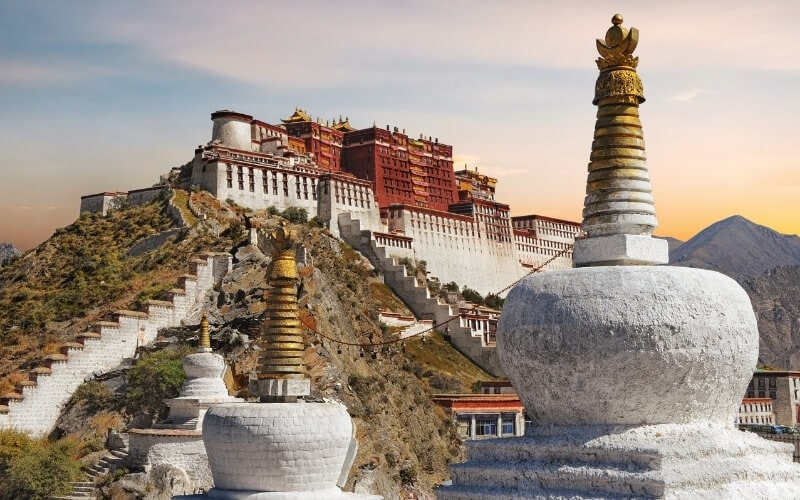

Sprawled across the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau, in the remote northern tip of China’s Sichuan province, Ruoergai town and county do not appear on Google maps. To Google, this locality is known by its Tibetan name, Zoige.
After 12 hours of following your car GPS from Chengdu to Zoige, climbing onto the Tibetan Plateau , Chinese road signs welcome you to Ruoergai, 3,500 meters above sea level.
Top cultural experiences on the Tibetan Plateau
Witness nomadic culture: Remote and isolated, Zoige/Ruoergai is the best place in the world to witness the disappearing Tibetan nomadic culture. All you have to do is drive around this vast, open grassland to catch a glimpse. You’ll see white nomads’ tents with smoky chimneys scattered on the sides of the road, surrounded by herds of domestic yak and protected by the menacing Tibetan mastiffs. The nomads are mistrustful of outsiders, which is not surprising given political tensions in the region.
Go horse trekking: Yet there is a way to experience the nomadic culture first-hand here – by taking a horse-trekking adventure with the local Tibetan Horse Trekking Agency in the nearby town of Langmusi. Tours range from a day hike to the hills – the domain of the nomads – to a multi-day horseback adventure with overnight stays in nomad tents. Guides are local Tibetans, so while you may not be having extensive discussions in English, you’ll be welcome in nomadic households.
Visit the monasteries and mosques in Langmusi: Encircled by forest-covered mountains, the small sleepy town of Langmusi is inhabited by three ethnic groups: Amdo Tibetans, Han Chinese and Hui Muslims. So, even just a visit to the town is a unique cultural experience. There are two large Tibetan monasteries on the hills above the town and a Hui mosque at its centre.
The nearest airport to Langmusi is Gannan Xiahe Airport, 130 km away. From Xiahe, you can take a bus to Langmusi, or arrange a car with a driver via Tibetan Horse Trekking.
By Margarita from The Wildlife Diaries
Taiwan – for night markets, Confucianism & forbidden relics

An island nestled off the coast of Mainland China, Taiwan is fast becoming one of the best cultural tourism destinations in Asia.
Its long history and combination of cultural influences – including Indigenous culture, Mainland China, Korea and even Japan – make Taiwan as intriguing as it is complex. Bustling with life, amazing food and beautiful scenery, this island has it all.
Top cultural experiences in Taipei
Eat your way through the Night Markets in Taipei: The capital city of Taiwan, Taipei, offers a world of things for people to see and do . One of the most popular culturally immersive activities for visitors is to head down to the local night market, the biggest one being the Shiling Night Market. Along with delicious local foods, you can also find clothes, accessories, games, cosmetics and more. Night Markets are significant because they play a huge role in Taiwanese culture . Locals and tourists alike flock to these areas each and every day to shop and socialise.
Observe the rituals at a Taiwanese temple: Taiwan is a very religious country with most people following either Buddhism or Confucianism. Many temples are built around these religions in a very extravagant manner. Visitors can take part in the prayer ceremony, burn some incense, or just sit back and observe. If you’re interested in visiting these temples, one of the best places to start is the Songshan Ciyou Temple, which is conveniently located right next to the Raohe Night Market.
Visit the National Palace Museum: This museum houses thousands of cultural relics, art and artefacts, including many items that were carried out of the Forbidden City in China and moved to Taiwan to protect them from destruction during the Chinese Civil War. It’s one of the largest collections of its kind in the world. Here, you can learn how the Chinese language was formed, see what kinds of ancient tools and weapons were used throughout history, and witness what life was like many hundreds of years ago.
By Wayne from Daily Tourist
Learn more: The best cultural experiences in Taiwan .
Cultural trips in Africa & the Middle East
Ethiopia • Oman • Mauritius • Morocco
Ethiopia – for coal-fired coffee, churches & injera

Ethiopia is a country like no other. Here in North East Africa, the steaming tribal lowlands of the Rift Valley collide with the cool thin air of the Northern highlands. The fertile lands towards the West produces some of the world’s best coffee, while the wind from the East carries whispers from Arabia. It’s truly a spectacular place to visit.
Ethiopia is even more unique in terms of its cultural treasures. As the only country in Africa never to be colonised, Ethiopia is a truly African country with African culture. If you want to see lions chase and eat zebras, go somewhere else. If you want to see and experience African culture at its purest, then book your ticket to Ethiopia already!
Top cultural experiences in Ethiopia
Visit the city of Lalibela: Situated in the northern highlands, Lalibela is the most important pilgrimage site in the country for the predominantly Orthodox Christian population of Ethiopia. It is here that you’ll find eleven incredible churches completely hewn from the rock. If you see only one place in Ethiopia, make it Lalibela.
Attend Sunday Mass: The UNESCO recognised Lalibela churches still function as churches, and attending a Sunday morning service before sunrise with hundreds of pilgrims is an experience that you won’t forget. Afterwards you can join the crowds eating injera while basking in the morning sun. Be prepared for the fact that everyone will want to come and talk to you.
Hike to a remote mountain community: Hiking into the mountains surrounding Lalibela will take you to small farming communities where time has seemingly stood still. It’s also possible to visit one of these communities for a day and learn how to cook traditional Ethiopian dishes such as injera , tibs or shiro . You’ll also find a few cave churches and monasteries in these mountains. The priests will be eager to show off their ancient treasures for a small tip.
Participate in a traditional coffee ceremony: Ethiopia is considered the birthplace of coffee, and man are you in for treat! The best way to drink a cup of buna (Ethiopian coffee) is to attend a coffee ceremony. It starts off with the hostess washing green coffee beans and then roasting them in a pan over an open fire. The coals are infused with natural incense made from tree resin. You’ll see bags of these tree resin for sale in markets all over Ethiopia. Finally the coffee beans are ground and brewed in a special coffee pot called a jebena . It’s expected that guests will have at least three cups of buna, but why stop there?
By De Wet & Jin from Museum of Wander
Oman – for dhow boats, frankincense & Bedouin culture

Unlike some of its more glitzy neighbours who’ve traded their souqs for skyscrapers, Oman has approached cultural preservation from a different angle. It’s often called out as the most culturally ‘authentic’ country in the region .
This part of the Middle East has long been a melting pot of Arabian and East African cultures, with a strong South Asian influence. Semi-nomadic Bedouin tribes that paint the desert with their costumes and brightly coloured carpets are less accessible, but a range of tourist-friendly desert experiences allow you to brush with this part of Omani culture.
Contemporary Omani traditions are deeply tied to Ibadism and revolve around an annual calendar of Islamic festivities.
Top cultural experiences in Oman
Get lost in a souq: Perfumed by rose petals and frankincense, Oman’s souqs are a treat for the senses. Roam displays of henna and spices while getting a feel for commerce and culture. Muttrah Souq in the capital, Muscat, and the delightful Nizwa Souq are both must-visits.
Visit a dhow workshop in Sur: Not only are Oman’s wooden boats an impressive feat of engineering, they’re steeped in legend and tradition. In Sur, the home of Sinbad the Sailor, you can watch expert craftsmen fitting the vessels together without glue or nails.
Spend the night at a desert camp. The Sharqiya Sands, Oman’s slice of The Empty Quarter, is the territory of nomads. Bedouin-inspired desert camps recreate the experience of staying with a Bedouin tribe – albeit with a luxury edge! Spending the night in a desert camp involves listening to folk music, eating Omani food, while the very lodgings – the tent lined with carpets you’re sleeping in – is part of the Bedouin tradition.
Mauritius – for street food, Sega & sugarcane
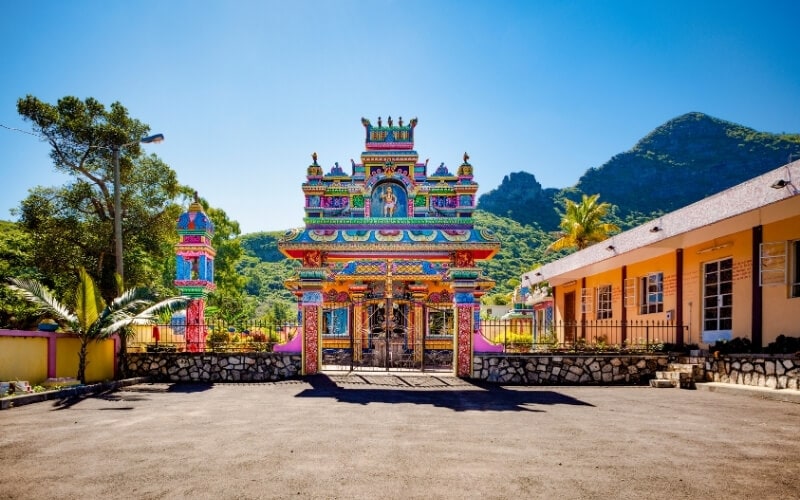

The island nation of Mauritius is normally associated with splendid white-sand beaches and luxury resorts – thus its inclusion on this list of cultural trips might come as a bit of a surprise.
Yes, this is an island paradise incarnate, but it also happens to be one of the most ethnically and religiously diverse countries in the region, with African, Indian, Chinese and South Asian cultures – along with layers of Dutch, French and British influence – all accounted for.
Many elements of Mauritian culture can be traced back to the island’s plantation roots and the legacy of slavery. Mauritians honour this period of history while proudly showing off their culture in everything from the cuisine to the music.
Top cultural experiences in Mauritius
Take a street food tour of Port Louis: Mauritian food, much like Mauritian society itself, combines Chinese, Indian, Creole, East African and European flavours. Must-try dishes include vindaye , an adaptation of West Indian vindaloo, Chatini (chutney) is a popular condiment and traces its roots back to British-Indian origins, briani (biryani) and creations gifted from the island’s Chinese community, such as bol renversé (a layered dish of rice, chicken, shrimp and vegetables). The best way to get a grasp of these edible delights is by joining a guided street food tour of the capital, Port Louis .
Watch a Sega performance: Recognised by UNESCO for its value to Intangible Cultural Heritage, Mauritian Sega is a performance art characterised by music, song, dance and costume. It started out as an expression of pain and loss practiced by slave communities but has morphed over time into a colourful, optimistic expression of local culture. Elaborate Sega costumes moving to the tune of Creole lyrics is a . Many hotels offer Sega performances.
Visit an old sugarcane farm: Mauritius’ history of slavery and plantation farming has left an indelible mark on the island. Visiting preserved plantation homes and crumbling sugar mills is a step back in time to the colonial period, while regenerated cane fields such as those on Frederica Reserve now serve as a sanctuary for the island’s wildlife.
Learn more: 8 ways to experience Mauritian culture .
Morocco – for riads , tajines & mint tea

By all accounts, Morocco is a beguiling destination . The most popular country to visit in North Africa, it stands out for its diversity of landscapes and cultural experiences.
Morocco is an important gateway to the rest of Africa, and has been since Roman times. Its position at the northernmost tip of the continent – with a coast shared between the Atlantic and the Mediterranean – means it’s been at the centre of conquests and various cultural overlap throughout the ages.
Today, Morocco lives with the legacies of various civilisations, including Roman, Phoenician, Jewish, Berber, Arabic, Spanish and French. Morocco has a very hospitable culture, steeped in a refined art of living. When you visit the imperial cities of Marrakech and Fes, or the coastal towns of Essaouira and El Jadida, you will notice a multitude of little details typical of Moroccan life.
This art of living and careful hospitality is very important in Morocco and, as a visitor, you can experience it in many different ways.
Top cultural experiences in Morocco
Try your hand at Moroccan cuisine: Moroccan cuisine is world-famous for its use of spices and mix of sweet and savoury flavours. Every restaurant offers a selection of delicious tajines , a stew of meat and vegetables. Couscous is on the menu every Friday and if you like sweets, you will be in heaven. Sweet biscuits mixing flower, almond and spice flavours make a delicious afternoon treat. If you’re interested in learning new skills, cooking classes are often available in traditional riads in Marrakech. Moroccan cuisine takes time and care, but the results are delicious and quite easy to recreate at home.
Shop for authentic handicrafts at a souq : Another great way to experience the heart of Morocco is to spend time in the souks. Shopping in Morocco is a fun experience and haggling for a good price is the norm. You have to engage with merchants, ask questions, make small talk and, most importantly, have fun with it! Never lose your smile and sense of humour, and it will great fun! The most spectacular shopping experience is in Marrakech due to the volume and intensity of the medina. It’s easy to get lost but that’s part of the experience too!
Sip mint tea, a Moroccan tradition: When you travel throughout Morocco, you will notice that mint tea is served everywhere. This is a pivotal element of Moroccan hospitality. Green tea is mixed with fresh mint leaves and served in little decorated glasses. There is a little bit of theatre in serving mint tea, with the brass or silver teapot held high above the glass… Traditionally, mint tea is served with a lot of sugar, but these days it is common for sugar to be served on the side, so you can dose it yourself. And you can even buy a set of decorated tea glasses in the souk as a souvenir!
By Delphine from Lester Lost
How to have a more culturally immersive travel experience anywhere in the world
It doesn’t matter if it’s a remote community or a popular city – there are things you can do to have a more enriching cultural travel experience no matter where you’re going.
Here are 10 practical tips to help you on your way.
1. Do your research before you go: Familiarise yourself with local customs and learn a bit of the history so you know what types of experiences to look out for. This guide is a great start!
2. Seek out festivals and special events: Many tourism boards feature a calendar on their website, or you can try using Facebook to find local events. Check out my four-part series about the world’s best festivals, starting here .
3. Eat local. Food is one of the easiest routes to culture. Here are my tips for eating local when you travel.
4. Stay at a homestay. Spending time with a local family will give you an invaluable insight into daily life. Here are my tips for using homestays in Vietnam.
5. Participate in a class or workshop . Trying a cooking class, handicraft workshop or any other hands-on experience is one of the easiest ways to immerse yourself in local culture. I recommend using Get Your Guide , Airbnb Experiences, Cookly or Backstreet Academy to find opportunities.
6. Learn a bit of the language. Even knowing a few basic words will show you’re interested and can go a long way to forming relationships.
7. Shop local. Support artisans and heritage skills. Here are my tips for finding authentic and meaningful souvenirs .
8. Slow down. The best cultural experiences are often spare-of-the-moment and can’t be planned in advance. Keep some flexibility in your travel itinerary for spontaneous detours.
9. Go your own way. You don’t always have to follow the pack. Venturing away from the crowds will often give you access to unique and meaningful experiences.
10. Don’t be afraid to ask questions. If in doubt, ask a local. Remember that cultural tourism is all about exchange – don’t just take, make sure you give something back in return.
Are you a cultural tourist? Which of these destinations is your favourite? What other places would you add to the list? I’d love to hear your suggestions in the comments below!

World’s best cultural trips: Save it & share it on Pinterest
More cultural travel inspiration.
- 30+ amazing cultural experiences around the world
- Best cultural festivals around the world
- Best destinations for tea culture
- Best destinations for wine culture
- Unique food cultures around the globe
- My collection of cultural travel guides for 30+ cities and regions
- World’s best unique & underrated travel destinations
This is a very wonderful article about cultural destinations! Thank you so much for sharing!
One can easily visit India and experience the different kinds of cultures in a particular place. Tourism in India has been much more managed and safe with passage of time. Rajasthan tourism has been the most reliable and safe in India. One can enjoy all the traditional dishes and enjoy living in the palaces as a hotel room in different cities. But, whenever you are visiting to Rajasthan, India travel guide is a must because one can easily lose track of pathways in the puzzle like roads of the cities in Rajasthan. One can easily plan for a Kerala tour packages because of the minimal expenses in the state.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Subscribe to future posts
Advisory Council on Historic Preservation
Each year, millions of travelers visit America’s historic places. The National Trust for Historic Preservation defines heritage tourism as “traveling to experience the places, artifacts, and activities that authentically represent the stories and people of the past and present.” A high percentage of domestic and international travelers participate in cultural and/or heritage activities while traveling, and those that do stay longer, spend more, and travel more often. Heritage tourism creates jobs and business opportunities, helps protect resources, and often improves the quality of life for local residents.
The ACHP has encouraged national travel and tourism policies that promote the international marketing of America’s historic sites as tourism destinations. The ACHP also engages in ongoing efforts to build a more inclusive preservation program, reaching out to diverse communities and groups and engaging them in dialogue about what parts of our national legacy should be more fully recognized, preserved, and shared.
The ACHP developed Preserve America , a national initiative to encourage and support community efforts for the preservation and enjoyment of America’s cultural and natural heritage. In partnership with other federal agencies, the initiative has encouraged the use of historic assets for economic development and community revitalization, as well as enabling people to experience and appreciate local historic resources through heritage tourism and education programs. These goals have been advanced by an Executive Order directing federal agencies to support such efforts, a community designation program, and a recognition program for outstanding stewardship of historic resources by volunteers.
From 2004-2016, over 900 Preserve America Communities were designated in all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and two territories, as well as nearly 60 Preserve America Stewards . Many Preserve America Communities are featured in “Discover Our Shared Heritage” National Register on-line travel itineraries . From 2006 through 2010, the National Park Service (in partnership with the ACHP) awarded more than $21 million in Preserve America Grants to support sustainable historic resource management strategies, with a focus on heritage tourism.
These links are being provided as a convenience and for informational purposes only; if they are not ACHP links, they do not constitute an endorsement or an approval by the ACHP of any of the products, services or opinions of the corporation or organization or individual. The ACHP bears no responsibility for the accuracy, legality, or content of the external site or for that of subsequent links. Please contact the external site for answers to questions regarding its content, including its privacy policies.
Related resources.
Take advantage of the search to browse through the World Heritage Centre information.
Sustainable Tourism
UNESCO World Heritage and Sustainable Tourism Programme

The UNESCO World Heritage and Sustainable Tourism Programme represents a new approach based on dialogue and stakeholder cooperation where planning for tourism and heritage management is integrated at a destination level, the natural and cultural assets are valued and protected, and appropriate tourism developed.
World Heritage and tourism stakeholders share responsibility for conservation of our common cultural and natural heritage of Outstanding Universal Value and for sustainable development through appropriate tourism management.
Facilitate the management and development of sustainable tourism at World Heritage properties through fostering increased awareness, capacity and balanced participation of all stakeholders in order to protect the properties and their Outstanding Universal Value.
Focus Areas

Policy & Strategy
Sustainable tourism policy and strategy development.

Tools & Guidance
Sustainable tourism tools

Capacity Building
Capacity building activities.

Heritage Journeys
Creation of thematic routes to foster heritage based sustainable tourism development

A key goal of the UNESCO WH+ST Programme is to strengthen the enabling environment by advocating policies and frameworks that support sustainable tourism as an important vehicle for managing cultural and natural heritage. Developing strategies through broad stakeholder engagement for the planning, development and management of sustainable tourism that follows a destination approach and focuses on empowering local communities is central to UNESCO’s approach.
Supporting Sustainable Tourism Recovery
Enhancing capacity and resilience in 10 World Heritage communities
Supported by BMZ, and implemented by UNESCO in collaboration with GIZ, this 2 million euro tourism recovery project worked to enhance capacity building in local communities, improve resilience and safeguard heritage.
Policy orientations
Defining the relationship between world heritage and sustainable tourism
Based on the report of the international workshop on Advancing Sustainable Tourism at Natural and Cultural Heritage Sites (Mogao, China, September 2009), the World Heritage Committee at its 34th session adopted the policy orientations which define the relationship between World Heritage and sustainable tourism ( Decision 34 COM 5F.2 ).
World Heritage and Tourism in a Changing Climate

Providing an overview of the increasing vulnerability of World Heritage sites to climate change impacts and the potential implications for and of global tourism.

Sustainable Tourism Tools
Manage tourism efficiently, responsibly and sustainably based on the local context and needs

People Protecting Places is the public exchange platform for the World Heritage and Sustainable Tourism Programme, providing education and information, encouraging support, engaging in social and community dialogue

The ' How-To ' guides offer direction and guidance to managers of World Heritage tourism destinations and other stakeholders to help identify the most suitable solutions for circumstances in their local environments and aid in developing general know-how.
English French Russian

Helping site managers and other tourism stakeholders to manage tourism more sustainably
Capacity Building in 4 Africa Nature Sites
A series of practical training and workshops were organized in four priority natural World Heritage sites in Africa (Lesotho, Malawi, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia and Zimbabwe) with the aim of providing capacity building tools and strategies for site managers to help them manage tourism at their sites more sustainably.
Learn more →
15 Pilot Sites in Nordic-Baltic Region
The project Towards a Nordic-Baltic pilot region for World Heritage and Sustainable Tourism (2012-2014) was initiated by the Nordic World Heritage Foundation (NWHF). With a practical approach, the project has contributed to tools for assessing and developing sustainable World Heritage tourism strategies with stakeholder involvement and cooperation.
Supporting Community-Based Management and Sustainable Tourism at World Heritage sites in South-East Asia
Entitled “The Power of Culture: Supporting Community-Based Management and Sustainable Tourism at World Heritage sites in South-East Asia", the UNESCO Office in Jakarta with the technical assistance of the UNESCO World Heritage and Sustainable Tourism Programme and the support from the Government of Malaysia is spearheading the first regional effort in Southeast Asia to introduce a new approach to sustainable tourism management at World Heritage sites in Malaysia, the Philippines and Indonesia.

Cultural tourism is one of the largest and fastest-growing global tourism markets. Culture and creative industries are increasingly being used to promote destinations and enhance their competitiveness and attractiveness.
Many locations are now actively developing their cultural assets as a means of developing comparative advantages in an increasingly competitive tourism marketplace, and to create local distinctiveness in the face of globalization.
UNESCO will endeavour to create networks of key stakeholders to coordinate the destination management and marketing associated with the different heritage routes to promote and coordinate high-quality, unique experiences based on UNESCO recognized heritage. The goal is to promote sustainable development based on heritage values and create added tourist value for the sites.
UNESCO World Heritage Journeys of the EU
Creating heritage-based tourism that spurs investment in culture and the creative industries that are community-centered and offer sustainable and high-quality products that play on Europe's comparative advantages and diversity of its cultural assets.
World Heritage Journeys of Buddhist Heritage Sites
UNESCO is currently implementing a project to develop a unique Buddhist Heritage Route for Sustainable Tourism Development in South Asia with the support from the Korea International Cooperation Agency (KOICA). South Asia is host to rich Buddhist heritage that is exemplified in the World Heritage properties across the region.

Programme Background
In 2011 UNESCO embarked on developing a new World Heritage and Sustainable Tourism Programme.
The aim was to create an international framework for the cooperative and coordinated achievement of shared and sustainable outcomes related to tourism at World Heritage properties.
The preparatory work undertaken in developing the Programme responded to the decision 34 COM 5F.2 of the World Heritage Committee at its 34th session in Brasilia in 2010, which requested
“the World Heritage Centre to convene a new and inclusive programme on World Heritage and Sustainable Tourism, with a steering group comprising interested States Parties and other relevant stakeholders, and also requests the World Heritage Centre to outline the objectives and approach to the implementation of this programme".
The Steering Group was comprised of States Parties representatives from the six UNESCO Electoral Groups (Germany (I), Slovenia (II), Argentina (III), China (IV), Tanzania (Va), and Lebanon (Vb)), the Director of the World Heritage Centre, the Advisory Bodies (IUCN, ICOMOS and ICCROM), the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) and the Swiss Government as the donor agency.
The Government of Switzerland has provided financial support for specific actions to be undertaken by the Steering Group. To coordinate and support the process, the World Heritage Centre has formed a small Working Group with the support of the Nordic World Heritage Foundation, the Government of Switzerland and the mandated external consulting firm MartinJenkins.
The World Heritage Committee directed that the Programme take into account:
- the recommendations of the evaluation of the concluded tourism programme ( WHC-10/34.COM/INF.5F.3 )
- the policy orientation which defines the relationship between World Heritage and sustainable tourism that emerged from the workshop Advancing Sustainable Tourism at Natural and Cultural Heritage Sites (Mogao, China, September 2009) ( WHC-10/34.COM/INF.5F.1 )
Overarching and strategic processes that the new World Heritage and Sustainable Tourism Programme will be aligned with include the Strategic Objectives of the World Heritage Convention (the five C's) ( Budapest Declaration 2002 ), the ongoing Reflections on the Future of the World Heritage Convention ( WHC-11/35.COM/12A ) and the Strategic Action Plan for the Implementation of the World Heritage Convention 2012-2022 ( WHC-11/18.GA/11 ), the Relationship between the World Heritage Convention and Sustainable Development (WHC-10/34.COM/5D), the World Heritage Capacity Building Strategy ( WHC-10/34.COM/5D ), the Global Strategy for a Representative, Balanced and Credible World Heritage List (1994), and the Evaluation of the Global Strategy and PACT initiative ( WHC-11/18.GA/8 - 2011 ).
In addition, the programme development process has been enriched by an outreach to representatives from the main stakeholder groups including the tourism sector, national and local governments, site practitioners and local communities. The programme design was further developed at an Expert Meeting in Sils/Engadine, Switzerland October 2011. In this meeting over 40 experts from 23 countries, representing the relevant stakeholder groups, worked together to identify the overall strategic approach and a prioritised set of key objectives and activities. The proposed Programme was adopted by the World Heritage Committee in 2012 at its 36th session in St Petersburg, Russian Federation .
International Instruments
International Instruments Relating to Sustainable Development and Tourism.
Resolutions adopted by the United Nations, charters adopted by ICOMOS, decisions adopted by the World Heritage Committee, legal instruments adopted by UNESCO on heritage preservation.
Resolutions adopted by the United Nations
- Report by the Department of Economics and Social Affairs: Tourism and Sustainable Development: The Global Importance of Tourism at the United Nations’ Commission on Sustainable Development 7th Session (1999)
- Resolution A/RES/56/212 and the Global Code of Ethics for Tourism adopted by the United Nations World Tourism Organization (1999)
Charters adopted by ICOMOS
- The ICOMOS International Cultural Tourism Charter (1999)
- The ICOMOS Charter for the Interpretation and Presentation of Cultural Heritage Sites (2008)
Decisions adopted by the World Heritage Committee
- Decision (XVII.4-XVII.12) adopted by the World Heritage Committee at its 25th Session in Helsinki (2001)
- Decision 33 COM 5A adopted by the World Heritage Committee at its 30th Session in Seville (2009)
- Decision 34 COM 5F.2 adopted by the World Heritage Committee at its 34th Session in Brasilia (2010)
- Decision 36 COM 5E adopted by the World Heritage Committee at its 36th Session in Saint Petersburg (2012)
Legal instruments adopted by UNESCO on heritage preservation in chronological order
- Convention on the Means of Prohibiting and Preventing the Illicit Import, Export and Transfer of Ownership of Cultural Property (1970)
- The Recommendation for the Protection of Movable Cultural Property (1978)
- The Recommendation on the Safeguarding of Traditional Culture and Folklore (1989)
- The Convention on the Protection of the Underwater Cultural heritage (2001)
- The Convention on the Protection and Promotion of the Diversity of Cultural Expressions (2005)
Other instruments
- Other instruments OECD Tourism Trends and Policies 2012 (French forthcoming)
- Programme on Sustainable Consumption and Production (In English)
- Siem Reap Declaration on Tourism and Culture 2015 – Building a New Partnership Model

Decisions / Resolutions (5)
The World Heritage Committee,
- Having examined Document WHC/18/42.COM/5A,
- Recalling Decision 41 COM 5A adopted at its 41st session (Krakow, 2017) and Decision 40 COM 5D adopted at its 40th session (Istanbul/UNESCO, 2016), General:
- Takes note with appreciation of the activities undertaken by the World Heritage Centre over the past year in pursuit of the Expected Result to ensure that “tangible heritage is identified, protected, monitored and sustainably managed by Member States, in particular through the effective implementation of the 1972 Convention ”, and the five strategic objectives as presented in Document WHC/18/42.COM/5A;
- Welcomes the proactive role of the Secretariat for enhancing synergies between the World Heritage Convention and the other Culture and Biodiversity-related Conventions, particularly the integration of relevant synergies aspects in the revised Periodic Reporting Format and the launch of a synergy-related web page on the Centre’s website;
- Also welcomes the increased collaboration among the Biodiversity-related Conventions through the Biodiversity Liaison Group and focused activities, including workshops, joint statements and awareness-raising;
- Takes note of the Thematic studies on the recognition of associative values using World Heritage criterion (vi) and on interpretation of sites of memory, funded respectively by Germany and the Republic of Korea and encourages all States Parties to take on board their findings and recommendations, in the framework of the identification of sites, as well as management and interpretation of World Heritage properties;
- Noting the discussion paper by ICOMOS on Evaluations of World Heritage Nominations related to Sites Associated with Memories of Recent Conflicts, decides to convene an Expert Meeting on sites associated with memories of recent conflicts to allow for both philosophical and practical reflections on the nature of memorialization, the value of evolving memories, the inter-relationship between material and immaterial attributes in relation to memory, and the issue of stakeholder consultation; and to develop guidance on whether and how these sites might relate to the purpose and scope of the World Heritage Convention , provided that extra-budgetary funding is available and invites the States Parties to contribute financially to this end;
- Also invites the States Parties to support the activities carried out by the World Heritage Centre for the implementation of the Convention ;
- Requests the World Heritage Centre to present, at its 43rd session, a report on its activities. Thematic Programmes:
- Welcomes the progress report on the implementation of the World Heritage Thematic Programmes and Initiatives, notes their important contribution towards implementation of the Global Strategy for representative World Heritage List, and thanks all States Parties, donors and other organizations for having contributed to achieving their objectives;
- Acknowledges the results achieved by the World Heritage Cities Programme and calls States Parties and other stakeholders to provide human and financial resources ensuring the continuation of this Programme in view of its crucial importance for the conservation of the urban heritage inscribed on the World Heritage List, for the implementation of the Recommendation on the Historic Urban Landscape and its contribution to achieving the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals related to cities as well as for its contribution to the preparation of the New Urban Agenda, and further thanks to China and Croatia for their support for the implementation of the Programme;
- Also acknowledges the results achieved of the World Heritage Marine Programme, also thanks Flanders, France and the Annenberg Foundation for their support, notes the increased focus of the Programme on a global managers network, climate change adaptation strategies and sustainable fisheries, and invites States Parties, the World Heritage Centre and other stakeholders to continue to provide human and financial resources to support for the implementation of the Programme;
- Further acknowledges the results achieved in the implementation of the World Heritage Sustainable Tourism Programme, in particular the development of the Sustainable Tourism and Visitor Management Assessment tool and encourages States Parties to participate in the pilot testing of the tool, expresses appreciation for the funding provided by the European Commission and further thanks the Republic of Korea, Norway, and Seabourn Cruise Line for their support in the implementation of the Programme’’s activities;
- Further notes the progress in the implementation of the Small Island Developing States Programme, its importance for a representative, credible and balanced World Heritage List and building capacity of site managers and stakeholders to implement the World Heritage Convention , thanks furthermore Japan and the Netherlands for their support as well as the International Centre on Space Technology for Natural and Cultural Heritage (HIST) and the World Heritage Institute of Training & Research for the Asia & the Pacific Region (WHITRAP) as Category 2 Centres for their technical and financial supports and also requests the States Parties and other stakeholders to continue to provide human, financial and technical resources for the implementation of the Programme;
- Takes note of the activities implemented jointly by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) and ICOMOS under the institutional guidance of the World Heritage Centre, in line with its Decision 40 COM 5D, further requests the World Heritage Centre to disseminate among the States Parties the second volume of the IAU/ICOMOS Thematic Study on Astronomical Heritage and renames this initiative as Initiative on Heritage of Astronomy, Science and Technology;
- Also takes note of the progress report on the Initiative on Heritage of Religious Interest, endorses the recommendations of the Thematic Expert Consultation meetings focused on Mediterranean and South-Eastern Europe (UNESCO, 2016), Asia-Pacific (Thailand, 2017) and Eastern Europe (Armenia, 2018), thanks the States Parties for their generous contribution and reiterates its invitation to States Parties and other stakeholders to continue to support this Initiative, as well as its associated Marketplace projects developed by the World Heritage Centre;
- Takes note of the activities implemented by CRATerre in the framework of the World Heritage Earthen Architecture Programme, under the overall institutional guidance of the World Heritage Centre, and of the lines of action proposed for the future, if funding is available;
- Invites States Parties, international organizations and donors to contribute financially to the Thematic Programmes and Initiatives as the implementation of thematic priorities is no longer feasible without extra-budgetary funding;
- Requests furthermore the World Heritage Centre to submit an updated result-based report on Thematic Programmes and Initiatives, under Item 5A: Report of the World Heritage Centre on its activities, for examination by the World Heritage Committee at its 44th session in 2020.
1. Having examined document WHC-12/36.COM/5E,
2. Recalling Decision 34 COM 5F.2 adopted at its 34th session (Brasilia, 2010),
3. Welcomes the finalization of the new and inclusive Programme on World Heritage and Sustainable Tourism and notes with appreciation the participatory process for its development, objectives and approach towards implementation;
4. Also welcomes the contribution of the Steering Group comprised of States Parties representatives from the UNESCO Electoral Groups, the World Heritage Centre, the Advisory Bodies (IUCN, ICOMOS, ICCROM), Switzerland and the United Nations World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) in the elaboration of the Programme;
5. Thanks the Government of Switzerland, the United Nations Foundation and the Nordic World Heritage Foundation for their technical and financial support to the elaboration of the Programme;
6. Notes with appreciation the contribution provided by the States Parties and other consulted stakeholders during the consultation phase of the Programme;
7. Takes note of the results of the Expert Meeting in Sils/Engadin (Switzerland), from 18 to 22 October 2011 contributing to the Programme, and further thanks the Government of Switzerland for hosting the Expert Meeting;
8. Adopts the World Heritage and Sustainable Tourism Programme;
9. Requests the World Heritage Centre to refine the Draft Action Plan 2013-2015 in an Annex to the present document and to implement the Programme with a Steering Group comprised of representatives of the UNESCO Electoral Groups, donor agencies, the Advisory Bodies, UNWTO and in collaboration with interested stakeholders;
10. Notes that financial resources for the coordination and implementation of the Programme do not exist and also requests States Parties to support the implementation of the World Heritage and Sustainable Tourism Programme;
11. Further requests the World Heritage Centre to report biennially on the progress of the implementation of the Programme;
12. Notes with appreciation the launch of the Programme foreseen at the 40th Anniversary of the World Heritage Convention event in Kyoto, Japan, in November 2012
1. Having examined Document WHC-10/34.COM/INF.5F.1 and WHC-10/34.COM/INF.5F.3,
2. Highlighting that the global tourism sector is large and rapidly growing, is diverse and dynamic in its business models and structures, and the relationship between World Heritage and tourism is two way: tourism, if managed well, offers benefits to World Heritage properties and can contribute to cross-cultural exchange but, if not managed well, poses challenges to these properties and recognizing the increasing challenges and opportunities relating to tourism;
3. Expresses its appreciation to the States Parties of Australia, China, France, India, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom, and to the United Nations Foundation and the Nordic World Heritage Foundation for the financial and technical support to the World Heritage Tourism Programme since its establishment in 2001;
4. Welcomes the report of the international workshop on Advancing Sustainable Tourism at Natural and Cultural Heritage Sites (Mogao, China, September 2009) and adopts the policy orientation which defines the relationship between World Heritage and sustainable tourism ( Attachment A );
5. Takes note of the evaluation of the World Heritage Tourism Programme by the UN Foundation, and encourages the World Heritage Centre to take fully into account the eight programme elements recommended in the draft final report in any future work on tourism ( Attachment B );
6. Decides to conclude the World Heritage Tourism Programme and requests the World Heritage Centre to convene a new and inclusive programme on World Heritage and Sustainable Tourism, with a steering group comprising interested States Parties and other relevant stakeholders, and also requests the World Heritage Centre to outline the objectives and approach to implementation of this programme, drawing on the directions established in the reports identified in Paragraphs 4 and 5 above, for consideration at the 35th session of the World Heritage Committee (2011);
7. Also welcomes the offer of the Government of Switzerland to provide financial and technical support to specific activities supporting the steering group; further welcomes the offer of the Governments of Sweden, Norway and Denmark to organize a Nordic-Baltic regional workshop in Visby, Gotland, Sweden in October 2010 on World Heritage and sustainable tourism; and also encourages States Parties to support the new programme on World Heritage and Sustainable Tourism including through regional events and the publication of materials identifying good practices;
8. Based upon the experience gained under the World Heritage Convention of issues related to tourism, invites the Director General of UNESCO to consider the feasibility of a Recommendation on the relationship between heritage conservation and sustainable tourism.
Attachment A
Recommendations of the international workshop
on Advancing Sustainable Tourism at Natural and Cultural Heritage Sites
Policy orientations: defining the relationship between World Heritage and tourism
1. The tourism sector
The global tourism sector is large and rapidly growing, is diverse and dynamic in its business models and structures.
Tourists/visitors are diverse in terms of cultural background, interests, behaviour, economy, impact, awareness and expectations of World Heritage.
There is no one single way for the World Heritage Convention , or World Heritage properties, to engage with the tourism sector or with tourists/visitors.
2. The relationship between World Heritage and tourism
The relationship between World Heritage and tourism is two-way:
a. World Heritage offers tourists/visitors and the tourism sector destinations
b. Tourism offers World Heritage the ability to meet the requirement in the Convention to 'present' World Heritage properties, and also a means to realise community and economic benefits through sustainable use.
Tourism is critical for World Heritage:
a. For States Parties and their individual properties,
i. to meet the requirement in the Convention to 'present' World Heritage
ii. to realise community and economic benefits
b. For the World Heritage Convention as a whole, as the means by which World Heritage properties are experienced by visitors travelling nationally and internationally
c. As a major means by which the performance of World Heritage properties, and therefore the standing of the Convention , is judged,
i. many World Heritage properties do not identify themselves as such, or do not adequately present their Outstanding Universal Value
ii. it would be beneficial to develop indicators of the quality of presentation, and the representation of the World Heritage brand
d. As a credibility issue in relation to: i. the potential for tourism infrastructure to damage Outstanding Universal Value
i. the threat that World Heritage properties may be unsustainably managed in relation to their adjoining communities
ii. sustaining the conservation objectives of the Convention whilst engaging with economic development
iii. realistic aspirations that World Heritage can attract tourism.
World Heritage is a major resource for the tourism sector:
a. Almost all individual World Heritage properties are significant tourism destinations
b. The World Heritage brand can attract tourists/visitors,
i. the World Heritage brand has more impact upon tourism to lesser known properties than to iconic properties.
Tourism, if managed well, offers benefits to World Heritage properties:
a. to meet the requirement in Article 4 of the Convention to present World Heritage to current and future generations
b. to realise economic benefits.
Tourism, if not managed well, poses threats to World Heritage properties.
3. The responses of World Heritage to tourism
The impact of tourism, and the management response, is different for each World Heritage property: World Heritage properties have many options to manage the impacts of tourism.
The management responses of World Heritage properties need to:
a. work closely with the tourism sector
b. be informed by the experiences of tourists/visitors to the visitation of the property
c. include local communities in the planning and management of all aspects of properties, including tourism.
While there are many excellent examples of World Heritage properties successfully managing their relationship to tourism, it is also clear that many properties could improve:
a. the prevention and management of tourism threats and impacts
b. their relationship to the tourism sector inside and outside the property
c. their interaction with local communities inside and outside the property
d. their presentation of Outstanding Universal Value and focus upon the experience of tourists/visitors.
a. be based on the protection and conservation of the Outstanding Universal Value of the property, and its effective and authentic presentation
b. work closely with the tourism sector
c. be informed by the experiences of tourists/visitors to the visitation of the property
d. to include local communities in the planning and management of all aspects of properties, including tourism.
4. Responsibilities of different actors in relation to World Heritage and tourism
The World Heritage Convention (World Heritage Committee, World Heritage Centre, Advisory Bodies):
a. set frameworks and policy approaches
b. confirm that properties have adequate mechanisms to address tourism before they are inscribed on the World Heritage List
i. develop guidance on the expectations to be include in management plans
c. monitor the impact upon OUV of tourism activities at inscribed sites, including through indicators for state of conservation reporting
d. cooperate with other international organisations to enable:
i. other international organisations to integrate World Heritage considerations in their programs
ii. all parties involved in World Heritage to learn from the activities of other international organisations
e. assist State Parties and sites to access support and advice on good practices
f. reward best practice examples of World Heritage properties and businesses within the tourist/visitor sector
g. develop guidance on the use of the World Heritage emblem as part of site branding.
Individual States Parties:
a. develop national policies for protection
b. develop national policies for promotion
c. engage with their sites to provide and enable support, and to ensure that the promotion and the tourism objectives respect Outstanding Universal Value and are appropriate and sustainable
d. ensure that individual World Heritage properties within their territory do not have their OUV negatively affected by tourism.
Individual property managers:
a. manage the impact of tourism upon the OUV of properties
i. common tools at properties include fees, charges, schedules of opening and restrictions on access
b. lead onsite presentation and provide meaningful visitor experiences
c. work with the tourist/visitor sector, and be aware of the needs and experiences of tourists/visitors, to best protect the property
i. the best point of engagement between the World Heritage Convention and the tourism sector as a whole is at the direct site level, or within countries
d. engage with communities and business on conservation and development.
Tourism sector:
a. work with World Heritage property managers to help protect Outstanding Universal Value
b. recognize and engage in shared responsibility to sustain World Heritage properties as tourism resources
c. work on authentic presentation and quality experiences.
Individual tourists/visitors with the assistance of World Heritage property managers and the tourism sector, can be helped to appreciate and protect the OUV of World Heritage properties.
Attachment B
Programme elements recommended by the Draft Final Report of the Evaluation of the World Heritage Tourism Programme by the UN Foundation:
1. Adopt and disseminate standards and principles relating to sustainable tourism at World Heritage sites;
2. Support the incorporation of appropriate tourism management into the workings of the Convention ;
3. Collation of evidence to support sustainable tourism programme design, and to support targeting;
4. Contribution of a World Heritage perspective to cross agency sustainable tourism policy initiatives;
5. Strategic support for the dissemination of lessons learned;
6. Strategic support for the development of training and guidance materials for national policy agencies and site managers;
7. Provision of advice on the cost benefit impact of World Heritage inscription;
8. Provision of advice on UNESCO World Heritage branding.
1. Having examined Documents WHC-09/33.COM/5A, WHC- 09/33.COM/INF.5A.1, WHC-09/33.COM/INF.5A.2, and WHC-09/33.COM/INF.5A.3 ,
2. Recalling Decision 32 COM 5 adopted at its 32nd session (Quebec City, 2008),
3. Takes note with appreciation of the activities undertaken by the World Heritage Centre over the past year in pursuit of the Committee's five Strategic Objectives;
4. Takes also note of the findings of the study undertaken by UNESCO's Internal Oversight Service on the mapping of the workload of the World Heritage Centre presented in Document WHC-09/33.COM/INF.5A.3;
5. Notes with satisfaction that the World Heritage Centre is working with the secretariats of intergovernmental committees of related conventions such as the Convention for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage , and the Convention for the Protection of the Underwater Cultural Heritage-2001 and recommends that such cooperation be encouraged as this would further strengthen the work of the Centre;
6. Requests the World Heritage Centre to prepare a document on the World Heritage Convention and its cooperation and exchange with other conventions and programmes in the field of cultural heritage for discussion at the 34th session of the World Heritage Committee (2010);
7. Also requests the World Heritage Centre, in future reports on activities undertaken, to further strengthen the information and analysis available to States Parties by:
a) Retaining the current format to report activities and including an update on progress with implementing the Committee's decisions,
b) Describing the criteria by which the World Heritage Centre makes decisions as to which activities under the Convention it undertakes,
c) And including, on a discretionary basis, analysis of strategic issues and new directions;
8. Further requests the World Heritage Centre to produce, on an experimental basis, an indexed audio verbatim recording of the proceedings of the 33rd Session in addition to the standard summary records (as produced since the 26th session of the World Heritage Committee);
9. Notes the outline provided by the World Heritage Centre of its roles and the roles of the Advisory Bodies and agrees that this topic be further discussed at the 34th session of the Committee in 2010 under a separate agenda item;
10. Requests furthermore the World Heritage Centre to outline the forward direction of the World Heritage thematic programmes and initiatives, to enable an understanding of how these themes connect with and integrate into general programmes, and how they might be resourced;
11. Notes that the Centre already proactively engages women in its Heritage Programmes in Asia, Africa and the Caribbean as part of its gender balance policy and the provision of equal opportunity to all, and recommends that gender balance and community involvement be prioritized in the Centre's programmes;
12. Adopts the World Heritage Thematic Programme on Prehistory presented in Annex 1 of document WHC-09/33.COM/5A ;
13. Requests the World Heritage Centre to reconsider the term "prehistory", to better recognize the continuing cultures of indigenous communities, to ensure global representation in the identification and conservation of related properties, and to present a report on progress in developing an Action Plan on Prehistory and World Heritage at its 34th session in 2010;
14. Notes with concern the ongoing destruction of some of these fragile sites, including the recent destruction of the Rock Art sites of Tardrat Acacus in Libya, and requests the State Party to take immediate action and other measures as necessary to address the problem in consultation with the World Heritage Centre and to invite a joint World Heritage Centre / ICOMOS mission;
15. Expresses its gratitude to the Governments of Bahrain, South Africa and Spain for the financial and technical support for the various international scientific encounters, and recognizes the proposal of the Government of Spain in establishing a centre for the research of Prehistory;
16. Recalling the Decision of the World Heritage Committee 31 COM.21C to carry out a programme of sustainable development concerning the conservation of earthen architecture, thanks the Governments of Italy and France for their support of the programme on earthen architecture in Africa and the Arab States in particular, and requests the potential financial donors and the States Parties to support the implementation of activities and further requests the World Heritage Centre to submit a progress report at its 35th session in 2011;
17. Takes note of the progress report on the World Heritage Tourism Programme;
18. Thanks the Governments of Australia, China, France, India, Switzerland and United Kingdom, who have worked in close collaboration with the World Heritage Centre and the Advisory Bodies, the World Tourism Organization and other partners, for contributing to the Initiative of Sustainable Tourism;
19. Expresses its gratitude to the Governments of Australia and China for the organization of a workshop on sustainable tourism at the World Heritage site, Mogao Caves, China, in September-October 2009 and requests that the following elements be submitted to the Committee for examination at its 34th session in 2010:
a) A report on the workshop,
b) The subsequent recommendations of the workshop regarding the adoption of best practices policy guidance, and concerning the changes proposed for the Operational Guidelines for the implementation of the World Heritage Convention ,
c) A document concerning the progress of the World Heritage Programme on Tourism;
20. Finally requests the Director of the World Heritage Centre to identify supplementary sources of funding to put into place a sufficient number of staff and resources at the World Heritage Centre and the Advisory Bodies in order to continue to efficiently contribute to the resolution of problems related to World Heritage conservation.
XVII.8 The Secretariat provided the following justifications for the selection:
- Tourism - growing threats on World Heritage sites from tourism which, if sustainably managed could offer socio-economic development opportunities;
- Forests - since close to 60 of the natural sites on the World Heritage List are forests and that the lessons being learned from the large-scale UNESCO-UN Foundation projects in the tropical forest sites in the Democratic Republic of the Congo can serve as case studies to enrich the programme;
- Cities - since close to 200 of the cultural sites on the List are historic centres or entire cities, and because 20% of the Fund's international assistance have served to address the challenge of urban heritage conservation;
- Earthen structures - since some 30 of the cultural sites on the List are included in this category, and due to the particularity of conservation of earthen heritage, and threats.
XVII.10 The Committee expressed its appreciation for the clarity of the presentation and the justifications provided. Indicating strong support for the overall programming approach, the Committee however indicated the need for the programme to respond to the priorities established by the Committee and to create strong links with the results of the Global Strategy actions and Periodic Reporting. The Committee approved the four proposed themes of the programmes in this first series of initiatives and authorized the Centre to proceed in their development.
Cutting Edge | Bringing cultural tourism back in the game
The growth of cultural tourism
People have long traveled to discover and visit places of historical significance or spiritual meaning, to experience different cultures, as well as to learn about, exchange and consume a range of cultural goods and services. Cultural tourism as a concept gained traction during the 1990s when certain sub-sectors emerged, including heritage tourism, arts tourism, gastronomic tourism, film tourism and creative tourism. This took place amidst the rising tide of globalization and technological advances that spurred greater mobility through cheaper air travel, increased accessibility to diverse locations and cultural assets, media proliferation, and the rise of independent travel. Around this time, tourism policy was also undergoing a shift that was marked by several trends. These included a sharper focus on regional development, environmental issues, public-private partnerships, industry self-regulation and a reduction in direct government involvement in the supply of tourism infrastructure. As more cultural tourists have sought to explore the cultures of the destinations, greater emphasis has been placed on the importance of intercultural dialogue to promote understanding and tolerance. Likewise, in the face of globalization, countries have looked for ways to strengthen local identity, and cultural tourism has also been engaged as a strategy to achieve this purpose. Being essentially place-based, cultural tourism is driven by an interest to experience and engage with culture first-hand. It is backed by a desire to discover, learn about and enjoy the tangible and intangible cultural assets offered in a tourism destination, ranging from heritage, performing arts, handicrafts, rituals and gastronomy, among others.
Cultural tourism is a leading priority for the majority of countries around the world -featuring in the tourism policy of 90% of countries, based on a 2016 UNWTO global survey . Most countries include tangible and intangible heritage in their definition of cultural tourism, and over 80% include contemporary culture - film, performing arts, design, fashion and new media, among others. There is, however, greater need for stronger localisation in policies, which is rooted in promoting and enhancing local cultural assets, such as heritage, food, festivals and crafts. In France, for instance, the Loire Valley between Sully-sur-Loire and Chalonnes , a UNESCO World Heritage site, has established a multidisciplinary team that defends the cultural values of the site, and advises the authorities responsible for the territorial development of the 300 km of the Valley.
While cultural tourism features prominently in policies for economic growth, it has diverse benefits that cut across the development spectrum – economic, social and environmental. Cultural tourism expands businesses and job opportunities by drawing on cultural resources as a competitive advantage in tourism markets. Cultural tourism is increasingly engaged as a strategy for countries and regions to safeguard traditional cultures, attract talent, develop new cultural resources and products, create creative clusters, and boost the cultural and creative industries. Cultural tourism, particularly through museums, can support education about culture. Tourist interest can also help ensure the transmission of intangible cultural heritage practices to younger generations.

StockSnap, Pixabay
Cultural tourism can help encourage appreciation of and pride in local heritage, thus sparking greater interest and investment in its safeguarding. Tourism can also drive inclusive community development to foster resiliency, inclusivity, and empowerment. It promotes territorial cohesion and socioeconomic inclusion for the most vulnerable populations, for example, generating economic livelihoods for women in rural areas. A strengthened awareness of conservation methods and local and indigenous knowledge contributes to long-term environmental sustainability. Similarly, the funds generated by tourism can be instrumental to ensuring ongoing conservation activities for built and natural heritage.
The growth of cultural tourism has reshaped the global urban landscape over the past decades, strongly impacting spatial planning around the world. In many countries, cultural tourism has been leveraged to drive urban regeneration or city branding strategies, from large-sized metropolises in Asia or the Arab States building on cultural landmarks and contemporary architecture to drive tourism expansion, to small and middle-sized urban settlements enhancing their cultural assets to stimulate local development. At the national level, cultural tourism has also impacted planning decisions, encouraging coastal development in some areas, while reviving inland settlements in others. This global trend has massively driven urban infrastructure development through both public and private investments, impacting notably transportation, the restoration of historic buildings and areas, as well as the rehabilitation of public spaces. The expansion of cultural city networks, including the UNESCO World Heritage Cities programme and the UNESCO Creative Cities Network, also echoes this momentum. Likewise, the expansion of cultural routes, bringing together several cities or human settlements around cultural commonalities to stimulate tourism, has also generated new solidarities, while influencing economic and cultural exchanges between cities across countries and regions.
Despite tourism’s clear potential as a driver for positive change, challenges exist, including navigating the space between economic gain and cultural integrity. Tourism’s crucial role in enhancing inclusive community development can often remain at the margins of policy planning and implementation. Rapid and unplanned tourism growth can trigger a range of negative impacts, including pressure on local communities and infrastructure from overtourism during peak periods, gentrification of urban areas, waste problems and global greenhouse gas emissions. High visitor numbers to heritage sites can override their natural carrying capacity, thus undermining conservation efforts and affecting both the integrity and authenticity of heritage sites. Over-commercialization and folklorization of intangible heritage practices – including taking these practices out of context for tourism purposes - can risk inadvertently changing the practice over time. Large commercial interests can monopolize the benefits of tourism, preventing these benefits from reaching local communities. An excessive dependency on tourism can also create localized monoeconomies at the expense of diversification and alternative economic models. When mismanaged, tourism can, therefore, have negative effects on the quality of life and well-being of local residents, as well as the natural environment.
These fault lines became more apparent when the pandemic hit – revealing the extent of over-dependence on tourism and limited structures for crisis prevention and response. While the current situation facing tourism is unpredictable, making it difficult to plan, further crises are likely in the years to come. Therefore, the pandemic presents the opportunity to experiment with new models to shape more effective and sustainable alternatives for the future.

hxdyl, Getty Images Pro
Harnessing cultural tourism in policy frameworks
From a policy perspective, countries around the world have employed cultural tourism as a vehicle to achieve a range of strategic aims. In Panama, cultural tourism is a key component of the country’s recently adopted Master Plan for Sustainable Tourism 2020-2025 that seeks to position Panama as a worldwide benchmark for sustainable tourism through the development of unique heritage routes. Cultural tourism can be leveraged for cultural diplomacy as a form of ‘soft power’ to build dialogue between peoples and bolster foreign policy. For instance, enhancing regional cooperation between 16 countries has been at the heart of UNESCO’s transnational Silk Roads Programme, which reflects the importance of culture and heritage as part of foreign policy. UNESCO has also partnered with the EU and National Geographic to develop World Heritage Journeys, a unique travel platform that deepens the tourism experience through four selected cultural routes covering 34 World Heritage sites. Also in Europe, cultural tourism has been stimulated through the development of cultural routes linked to food and wine , as well as actions to protect local food products, such as through labels and certificates of origin. The Emilia-Romagna region in Italy, for example, produces more origin-protected food and drink than any other region in the country. One of the regions' cities Parma - a UNESCO Creative City (Gastronomy) and designated Italian Capital for Culture (2020-2021) - plans to resume its cultural activities to boost tourism once restrictions have eased. Meanwhile, Spain has recently taken steps to revive its tourism industry through its cities inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List . In this regard, the Group of the 15 Spanish World Heritage Cities met recently to discuss the country's Modernization and Competitiveness Plan for the tourism sector. Cultural tourism has progressively featured more prominently in the policies of Central Asian and Eastern European countries, which have sought to revive intangible heritage and boost the creative economy as part of strategies to strengthen national cultural identity and open up to the international community. In Africa, cultural tourism is a growing market that is driven by its cultural heritage, crafts, and national and regional cultural events. Major festivals such as Dak-Art in Senegal, Bamako Encounters Photography Biennial in Mali, Sauti za Busara in United Republic of Tanzania, Pan-African Festival of Cinema and Television of Ouagadougou in Burkina Faso, and Chale Wote Street Art Festival in Ghana are just a handful of vibrant and popular platforms in the continent that share cultural expressions, generate income for local economies and strengthen Pan-African identity.
Countries are increasingly seeking alliances with international bodies to advance tourism. National and local governments are working together with international entities, such as UNESCO, UNWTO and OECD in the area of sustainable tourism. In 2012, UNESCO’s Sustainable Tourism Programme was adopted, thereby breaking new ground to promote tourism a driver for the conservation of cultural and natural heritage and a vehicle for sustainable development. In 2020, UNESCO formed the Task Force on Culture and Resilient Tourism with the Advisory Bodies to the 1972 World Heritage Convention (ICOMOS, IUCN, ICCROM) as a global dialogue platform on key issues relating to tourism and heritage management during and beyond the crisis. UNESCO has also collaborated with the UNWTO on a set of recommendations for inclusive cultural tourism recovery from the COVID-19 crisis. In response to the crisis, the Namibian Government, UNESCO and UNDP are working together on a tourism impact study and development strategy to restore the tourism sector, especially cultural tourism.
UNESCO has scaled up work in cultural tourism in its work at field level, supporting its Member States and strengthening regional initiatives. In the Africa region, enhancing cultural tourism has been reported as a policy priority across the region. For example, UNESCO has supported the Government of Ghana in its initiative Beyond the Return, in particular in relation to its section on cultural tourism. In the Pacific, a Common Country Assessment (CCA) has been carried out for 14 SIDS countries, with joint interagency programmes to be created building on the results. Across the Arab States, trends in tourism after COVID, decent jobs and cultural and creative industries are emerging as entry points for different projects throughout the region. In Europe, UNESCO has continued its interdisciplinary work on visitor centres in UNESCO designated sites, building on a series of workshops to strengthen tourism sustainability, community engagement and education through heritage interpretation. In the Latin America and the Caribbean region, UNESCO is working closely with Member States, regional bodies and the UN system building on the momentum on the International Year of Creative Economy for Sustainable Development, including through Creative Cities, and the sustainable recovery of the orange economy, among others.

BS1920, Pixabay
In the context of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, tourism has the potential to contribute, directly or indirectly, to all of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Tourism is directly mentioned in SDGs 8, 12 and 14 on inclusive and sustainable economic growth, sustainable consumption and production (SCP) and the sustainable use of oceans and marine resources, respectively. This is mirrored in the VNRs put forward by countries, who report on cultural tourism notably through the revitalization of urban and rural areas through heritage regeneration, festivals and events, infrastructure development, and the promotion of local cultural products. The VNRs also demonstrate a trend towards underlining more sustainable approaches to tourism that factor in the environmental dimensions of tourism development.
Several countries have harnessed cultural tourism as a policy panacea for economic growth and diversification. As part of Qatar's National Vision 2030 strategy, for example, the country has embarked on a development plan that includes cultural tourism through strengthening its culture-based industries, including calligraphy, handicrafts and living heritage practices. In the city of Abu Dhabi in the UAE, cultural tourism is part of the city’s plan for economic diversification and to steer its domestic agenda away from a hydrocarbon-based economy. The Plan Abu Dhabi 2030 includes the creation of a US$27 billion cultural district on Saadiyat Island, comprising a cluster of world-renowned museums, and cultural and educational institutions designed by international star architects to attract tourism and talent to the city. Since 2016, Saudi Arabia has taken decisive action to invest in tourism, culture and entertainment to reduce the country’s oil dependency, while also positioning the country as a global cultural destination. Under the 2020 G20 Saudi Presidency, the UNWTO and the G20 Tourism Working Group launched the AlUla Framework for Inclusive Community Development through Tourism to better support inclusive community development and the SDGs. The crucial role of tourism as a means of sustainable socio-economic development was also underlined in the final communique of the G20 Tourism Ministers in October last.

Siem Reap, Cambodia by nbriam
On the other hand, cultural tourism can catalyse developments in cultural policy. This was the case in the annual Festival of Pacific Arts (FestPac) that triggered a series of positive policy developments following its 2012 edition that sought to strengthen social cohesion and community pride in the context of a prolonged period of social unrest. The following year, Solomon Islands adopted its first national culture policy with a focus on cultural industries and cultural tourism, which resulted in a significant increase in cultural events being organized throughout the country.
When the pandemic hit, the geographic context of some countries meant that many of them were able to rapidly close borders and prioritize domestic tourism. This has been the case for countries such as Australia and New Zealand. However, the restrictions have been coupled by significant economic cost for many Small Island Developing States (SIDS) whose economies rely on tourism and commodity exports. Asia Pacific SIDS, for example, are some of the world’s leading tourist destinations. As reported in the Tracker last June , in 2018, tourism earnings exceeded 50% of GDP in Cook Islands, Maldives and Palau and equaled approximately 30% of GDP in Samoa and Vanuatu. When the pandemic hit in 2020, the drop in British tourists to Spain’s Balearic Islands resulted in a 93% downturn in visitor numbers , forcing many local businesses to close. According to the World Economic Outlook released last October, the economies of tourism-dependent Caribbean nations are estimated to drop by 12%, while Pacific Island nations, such as Fiji, could see their GDP shrink by a staggering 21% in 2020.
Socially-responsible travel and ecotourism have become more of a priority for tourists and the places they visit. Tourists are increasingly aware of their carbon footprint, energy consumption and the use of renewable resources. This trend has been emphasized as a result of the pandemic. According to recent survey by Booking.com, travelers are becoming more conscientious of how and why they travel, with over two-thirds (69%) expecting the travel industry to offer more sustainable travel options . Following the closures of beaches in Thailand, for example, the country is identifying ways to put certain management policies in place that can strike a better balance with environmental sustainability. The UNESCO Sustainable Tourism Pledge launched in partnership with Expedia Group focuses on promoting sustainable tourism and heritage conservation. The pledge takes an industry-first approach to environmental and cultural protection, requiring businesses to introduce firm measures to eliminate single-use plastics and promote local culture. The initiative is expanding globally in 2021 as a new, more environmentally and socially conscious global travel market emerges from the COVID-19 context.

Senja, Norway by Jarmo Piironen
Climate change places a heavy toll on heritage sites, which exacerbates their vulnerability to other risks, including uncontrolled tourism. This was underlined in the publication “World Heritage and Tourism in a Changing Climate” , published by UNESCO, UNEP and the Union of Concerned Scientists, which analyses the consequences of climate change on heritage, and its potential to permanently change or destroy a site’s integrity and authenticity. Extreme weather events, safety issues and water shortages, among others, can thwart access to sites and hurt the economic livelihoods of tourism service providers and local communities. Rising sea levels will increasingly impact coastal tourism, the largest component of the sector globally. In particular, coral reefs - contributing US$11.5 billion to the global tourism economy – are at major risk from climate change.
Marine sites are often tourist magnets where hundreds of thousands of annual visitors enjoy these sites on yachts and cruise ships. In the case of UNESCO World Heritage marine sites – which fall under the responsibility of governments - there is often a reliance on alternative financing mechanisms, such as grants and donations, and partnerships with non-governmental organizations and/or the private sector, among others. The West Norwegian Fjords – Geirangerfjord and Nærøyfjord in Norway derives a substantial portion of its management budget from sources other than government revenues. The site has benefited from a partnership with the private sector company Green Dream 2020, which only allows the “greenest” operators to access the site, and a percentage of the profits from tours is reinjected into the long-term conservation of the site. In iSimangaliso in South Africa, a national law that established the World Heritage site’s management system was accompanied by the obligation to combine the property’s conservation with sustainable economic development activities that created jobs for local people. iSimangaliso Wetland Park supports 12,000 jobs and hosts an environmental education programme with 150 schools. At the Great Barrier Reef in Australia, where 91% of all local jobs are linked to the Reef, the Coral Nurture Programme undertakes conservation through planting coral, and promotes local stewardship and adaptation involving the whole community and local tourist businesses.

Grafner, Getty Images
With borders continuing to be closed and changeable regulations, many countries have placed a focus on domestic tourism and markets to stimulate economic recovery. According to the UNWTO, domestic tourism is expected to pick up faster than international travel, making it a viable springboard for economic and social recovery from the pandemic. In doing so it will serve to better connect populations to their heritage and offer new avenues for cultural access and participation. In China, for example, the demand for domestic travel is already approaching pre-pandemic levels. In Russian Federation, the Government has backed a programme to promote domestic tourism and support small and medium-sized enterprises, as well as a cashback scheme for domestic trips, which entitles tourists to a 20% refund for their trip. While supporting domestic tourism activities, the Government of Palau is injecting funds into local businesses working in reforestation and fishing in the spirit of building new sustainable models. The measures put in place today will shape the tourism to come, therefore the pandemic presents an opportunity to build back a stronger, more agile and sustainable tourism sector.
Local solutions at the helm of cultural tourism
While state-led policy interventions in cultural tourism remain crucial, local authorities are increasingly vital stakeholders in the design and implementation of cultural tourism policies. Being close to the people, local actors are aware of the needs of local populations, and can respond quickly and provide innovative ideas and avenues for policy experimentation. As cultural tourism is strongly rooted to place, cooperating with local decision-makers and stakeholders can bring added value to advancing mutual objectives. Meanwhile, the current health crisis has severely shaken cities that are struggling due to diminished State support, and whose economic basis strongly relies on tourism. Local authorities have been compelled to innovate to support local economies and seek viable alternatives, thus reaffirming their instrumental role in cultural policy-making.

Venice, Oliver Dralam/Getty Images
Cultural tourism can be a powerful catalyst for urban regeneration and renaissance, although tourism pressure can also trigger complex processes of gentrification. Cultural heritage safeguarding enhances the social value of a place by boosting the well-being of individuals and communities, reducing social inequalities and nurturing social inclusion. Over the past decade, the Malaysian city of George Town – a World Heritage site – has implemented several innovative projects to foster tourism and attract the population back to the city centre by engaging the city’s cultural assets in urban revitalization strategies. Part of the income generated from tourism revenues contributes to conserving and revitalizing the built environment, as well as supporting housing for local populations, including lower-income communities. In the city of Bordeaux in France , the city has worked with the public-private company InCité to introduce a system of public subsidies and tax exemption to encourage the restoration of privately-owned historical buildings, which has generated other rehabilitation works in the historic centre. The city of Kyoto in Japan targets a long-term vision of sustainability by enabling local households to play an active role in safeguarding heritage by incrementally updating their own houses, thus making the city more resilient to gentrification. The city also actively supports the promotion of its intangible heritage, such as tea ceremonies, flower arrangement, seasonal festivals, Noh theatre and dance. This year marks the ten-year anniversary of the adoption of the UNESCO Recommendation on the Historic Urban Landscape (HUL). The results of a UNESCO survey carried out among Member States in 2019 on its implementation show that 89% of respondents have innovative services or tourism activities in place for historic areas, which demonstrates a precedence for countries to capitalize on urban cultural heritage for tourism purposes.
Cultural tourism has been harnessed to address rural-urban migration and to strengthen rural and peripheral sub-regions. The city of Suzhou – a World Heritage property and UNESCO Creative City (Crafts and Folk Art) - has leveraged its silk embroidery industry to strengthen the local rural economy through job creation in the villages of Wujiang, located in a district of Suzhou. Tourists can visit the ateliers and local museums to learn about the textile production. In northern Viet Nam, the cultural heritage of the Quan họ Bắc Ninh folk songs, part of the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, is firmly rooted in place and underlined in its safeguarding strategies in 49 ancient villages, which have further inspired the establishment of some hundreds of new Quan họ villages in the Bắc Ninh and Bắc Giang provinces.

Many top destination cities are known for their iconic cultural landmarks. Others create a cultural drawcard to attract visitors to the city. France, the world's number one tourist destination , attracts 89 million visitors every year who travel to experience its cultural assets, including its extensive cultural landmarks. In the context of industrial decline, several national and local governments have looked to diversify infrastructure by harnessing culture as a new economic engine. The Guggenheim museum in Bilbao in Spain is one such example, where economic diversification and unemployment was addressed through building a modern art museum as a magnet for tourism. The museum attracts an average of 900,000 visitors annually, which has strengthened the local economy of the city. A similar approach is the Museum of Old and New Art (MONA), established in 2011 by a private entrepreneur in the city of Hobart in Australia, which has catalysed a massive increase of visitors to the city. With events such as MONA FOMA in summer and Dark MOFO in winter, the museum staggers visitor volumes to the small city to avoid placing considerable strain on the local environment and communities. Within the tourism sector, cultural tourism is also well-positioned to offer a tailored approach to tourism products, services and experiences. Such models have also supported the wider ecosystems around the iconic cultural landmarks, as part of “destination tourism” strategies.
Destination tourism encompasses festivals, live performance, film and festive celebrations as drawcards for international tourists and an economic driver of the local economy. Over the past three decades, the number of art biennials has proliferated. Today there are more than 300 biennials around the world , whose genesis can be based both on artistic ambitions and place-making strategies to revive specific destinations. As a result of COVID-19, many major biennials and arts festivals have been cancelled or postponed. Both the Venice Architecture and Art Biennales have been postponed to 2022 due to COVID-19. The Berlin International Film Festival will hold its 2021 edition online and in selected cinemas. Film-induced tourism - motivated by a combination of media expansion, entertainment industry growth and international travel - has also been used for strategic regional development, infrastructure development and job creation, as well to market destinations to tourists. China's highest-grossing film of 2012 “Lost in Thailand”, for example, resulted in a tourist boom to Chiang Mai in Thailand, with daily flights to 17 Chinese cities to accommodate the daily influx of thousands of tourists who came to visit the film’s location. Since March 2020, tourism-related industries in New York City in the United States have gone into freefall, with revenue from the performing arts alone plunging by almost 70%. As the city is reliant on its tourism sector, the collapse of tourism explains why New York’s economy has been harder hit than other major cities in the country. Meanwhile in South Africa, when the first ever digital iteration of the country’s annual National Arts Festival took place last June, it also meant an estimated US$25.7 million (R377 million) and US$6.4 million (R94 million) loss to the Eastern Cape province and city of Makhanda (based on 2018 figures), in addition to the US$1.4 million (R20 million) that reaches the pockets of the artists and supporting industries. The United Kingdom's largest music festival, Glastonbury, held annually in Somerset, recently cancelled for the second year running due to the pandemic, which will have ripple effects on local businesses and the charities that receive funding from ticket sales.
Similarly, cancellations of carnivals from Santa Cruz de Tenerife in the Canary Islands to Binche in Belgium has spurred massive losses for local tourism providers, hotels, restaurants, costume-makers and dance schools. In the case of the Rio de Janeiro Carnival in Brazil, for instance, the city has amassed significant losses for the unstaged event, which in 2019 attracted 1.5 million tourists from Brazil and abroad and generated revenues in the range of US$700 million (BRL 3.78 billion). The knock-on effect on the wider economy due to supply chains often points to an estimated total loss that is far greater than those experienced solely by the cultural tourism sector.

Guggenheim Museum Bilbao, Spain by erlucho
Every year, roughly 600 million national and international religious and spiritual trips take place , generating US$18 billion in tourism revenue. Pilgrimages, a fundamental precursor to modern tourism, motivate tourists solely through religious practices. Religious tourism is particularly popular in France, India, Italy and Saudi Arabia. For instance, the Hindu pilgrimage and festival Kumbh Mela in India, inscribed in 2017 on the UNESCO Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, attracts over 120 million pilgrims of all castes, creeds and genders. The festival is held in the cities of Allahabad, Haridwar, Ujjain and Nasik every four years by rotation. Sacred and ceremonial sites have unique significance for peoples and communities, and are often integral to journeys that promote spiritual well-being. Mongolia, for example, has around 800 sacred sites including 10 mountains protected by Presidential Decree, and lakes and ovoos, many of which have their own sutras. In the case of Mongolia, the environmental stewardship and rituals and practices connected with these sacred places also intersects with longstanding political traditions and State leadership.
Cities with a vibrant cultural scene and assets are not only more likely to attract tourists, but also the skilled talent who can advance the city’s long-term prospects. Several cities are also focusing on developing their night-time economies through the promotion of theatre, concerts, festivals, light shows and use of public spaces that increasingly making use of audio-visual technologies. Situated on Chile’s Pacific coast, the city of Valparaíso, a World Heritage site, is taking steps to transform the city’s night scene into a safe and inclusive tourist destination through revitalizing public spaces. While the economies of many cities have been weakened during the pandemic, the night-time economy of the city of Chengdu in China, a UNESCO Creative City for Gastronomy, has flourished and has made a significant contribution to generating revenue for the city, accounting for 45% of citizen’s daily expenditure.
The pandemic has generated the public’s re-appropriation of the urban space. People have sought open-air sites and experiences in nature. In many countries that are experiencing lockdowns, public spaces, including parks and city squares, have proven essential for socialization and strengthening resilience. People have also reconnected with the heritage assets in their urban environments. Local governments, organizations and civil society have introduced innovative ways to connect people and encourage creative expression. Cork City Council Arts Office and Creative Ireland, for example, jointly supported the art initiative Ardú- Irish for ‘Rise’ – involving seven renowned Irish street artists who produced art in the streets and alleyways of Cork.

Chengdu Town Square, China by Lukas Bischoff
Environment-based solutions support integrated approaches to deliver across the urban-rural continuum, and enhance visitor experiences by drawing on the existing features of a city. In the city of Bamberg, a World Heritage site in Germany, gardens are a key asset of the city and contribute to its livability and the well-being of its local population and visitors. More than 12,000 tourists enjoy this tangible testimony to the local history and environment on an annual basis. Eighteen agricultural businesses produce local vegetables, herbs, flowers and shrubs, and farm the inner-city gardens and surrounding agricultural fields. The museum also organizes gastronomic events and cooking classes to promote local products and recipes.
In rural areas, crafts can support strategies for cultural and community-based tourism. This is particularly the case in Asia, where craft industries are often found in rural environments and can be an engine for generating employment and curbing rural-urban migration. Craft villages have been established in Viet Nam since the 11th century, constituting an integral part of the cultural resources of the country, and whose tourism profits are often re-invested into the sustainability of the villages. The craft tradition is not affected by heavy tourist seasons and tourists can visit all year round.
Indigenous tourism can help promote and maintain indigenous arts, handicrafts, and culture, including indigenous culture and traditions, which are often major attractions for visitors. Through tourism, indigenous values and food systems can also promote a less carbon-intensive industry. During COVID-19, the Government of Canada has given a series of grants to indigenous tourism businesses to help maintain livelihoods. UNESCO’s Intergovernmental Committee for the Protection and Promotion of the Diversity of Cultural Expressions announced that it will grant, through the International Fund for Creative Diversity (IFCD), US$70,000 dollars to Mexican indigenous cultural enterprises, which will support indigenous enterprises through training programmes, seed funding, a pre-incubation process and the creation of an e-commerce website.
Tourism has boosted community pride in living heritage and the active involvement of local communities in its safeguarding. Local authorities, cultural associations, bearers and practitioners have made efforts to safeguard and promote elements as they have understood that not only can these elements strengthen their cultural identity but that they can also contribute to tourism and economic development. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the role of intellectual property and in the regulation of heritage. In the field of gastronomy, a lot of work has been done in protecting local food products, including the development of labels and certification of origin. Member States are exploring the possibilities of geographical indication (GI) for cultural products as a way of reducing the risk of heritage exploitation in connection to, for example, crafts, textiles and food products, and favouring its sustainable development.
The pandemic has brought to the forefront the evolving role of museums and their crucial importance to the life of societies in terms of health and well-being, education and the economy. A 2019 report by the World Health Organization (WHO) examined 3,000 studies on the role of the arts in improving health and well-being, which indicated that the arts play a major role in preventing, managing and treating illness. Over the past decade the number of museums has increased by 60%, demonstrating the important role that museums have in national cultural policy. Museums are not static but are rather dynamic spaces of education and dialogue, with the potential to boost public awareness about the value of cultural and natural heritage, and the responsibility to contribute to its safeguarding.
Data presented in UNESCO's report "Museums Around the World in the Face of COVID-19" in May 2020 show that 90% of institutions were forced to close, whereas the situation in September-October 2020 was much more variable depending on their location in the world. Large museums have consistently been the most heavily impacted by the drop in international tourism – notably in Europe and North America. Larger museums, such as Amsterdam’s Rijksmuseum and Vienna’s Kunsthistorisches Museum have reported losses between €100,000 and €600,000 a week. Smaller museums have been relatively stable, as they are not as reliant on international tourism and have maintained a closer connection to local communities. In November, the Network of European Museum Organisations (NEMO) released the results of a survey of 6,000 museums from 48 countries. Of the responding museums, 93% have increased or started online services during the pandemic. Most larger museums (81%) have increased their digital capacities, while only 47% of smaller museums indicated that they did. An overwhelming majority of respondents (92.9%) confirm that the public is safe at their museum. As reported in the Tracker last October, the world’s most visited museum, the Louvre in France (9.3 million visitors annually) witnessed a ten-fold increase in traffic to its website. Yet while digital technologies have provided options for museums to remain operational, not all have the necessary infrastructure, which is the case for many museums in Africa and SIDS.

New technologies have enabled several new innovations that can better support cultural tourism and digital technologies in visitor management, access and site interpretation. Cultural tourists visiting cultural heritage sites, for example, can enjoy educational tools that raise awareness of a site and its history. Determining carrying capacity through algorithms has helped monitor tourist numbers, such as in Hạ Long Bay in Viet Nam. In response to the pandemic, Singapore’s Asian Civilizations Museum is one of many museums that has harnessed digital technologies to provide virtual tours of its collections, thus allowing viewers to learn more about Asian cultures and histories. The pandemic has enhanced the need for technology solutions to better manage tourism flows at destinations and encourage tourism development in alternative areas.
Shaping a post-pandemic vision : regenerative and inclusive cultural tourism
As tourism is inherently dependent on the movement and interaction of people, it has been one of the hardest-hit sectors by the pandemic and may be one of the last to recover. Travel and international border restrictions have led to the massive decline in tourism in 2020, spurring many countries to implement strategies for domestic tourism to keep economies afloat. Many cultural institutions and built and natural heritage sites have established strict systems of physical distancing and hygiene measures, enabling them to open once regulations allow. Once travel restrictions have been lifted, it will enable the recovery of the tourism sector and for the wider economy and community at large.
While the pandemic has dramatically shifted the policy context for cultural tourism, it has also provided the opportunity to experiment with integrated models that can be taken forward in the post-pandemic context. While destinations are adopting a multiplicity of approaches to better position sustainability in their plans for tourism development, there is no one-size-fits-all solution.
A comprehensive, integrated approach to the cultural sector is needed to ensure more sustainable cultural tourism patterns. Efforts aimed at promoting cultural tourism destinations should build on the diversity of cultural sub-sectors, including cultural and heritage sites, museums, but also the creative economy and living heritage, notably local practices, food and crafts production. Beyond cultural landmarks, which act as a hotspot to drive the attractiveness of tourism destinations, and particularly cities, cultural tourism should also encompass other aspects of the cultural value chain as well as more local, community-based cultural expressions. Such an integrated approach is likely to support a more equitable distribution of cultural tourism revenues, also spreading tourism flows over larger areas, thus curbing the negative impacts of over-tourism on renowned cultural sites, including UNESCO World Heritage sites. This comprehensive vision also echoes the growing aspiration of visitors around the world for more inclusive and sustainable tourism practices, engaging with local communities and broadening the understanding of cultural diversity.
As a result of the crisis, the transversal component of cultural tourism has been brought to the fore, demonstrating its cross-cutting nature and alliance with other development areas. Cultural tourism – and tourism more broadly – is highly relevant to the 2030 for Sustainable Development and its 17 SDGs, however, the full potential of cultural tourism for advancing development – economic, social and environmental - remains untapped. This is even though cultural tourism is included in a third of all countries’ VNRs, thus demonstrating its priority for governments. Due the transversal nature of cultural tourism, there is scope to build on these synergies and strengthen cooperation between ministries to advance cooperation for a stronger and more resilient sector. This plays an integral role in ensuring a regenerative and inclusive cultural tourism sector. Similarly, tourism can feature as criteria for certain funding initiatives, or as a decisive component for financing cultural projects, such as in heritage or the cultural and creative industries.

Houses in Amsterdam, adisa, Getty, Images Pro
Several countries have harnessed the crisis to step up actions towards more sustainable models of cultural tourism development by ensuring that recovery planning is aligned with key sustainability principles and the SDGs. Tourism both impacts and is impacted by climate change. There is scant evidence of integration of climate strategies in tourism policies, as well as countries’ efforts to develop solid crisis preparedness and response strategies for the tourism sector. The magnitude and regional variation of climate change in the coming decades will continue to affect cultural tourism, therefore, recovery planning should factor in climate change concerns. Accelerating climate action is of utmost importance for the resilience of the sector.
The key role of local actors in cultural tourism should be supported and developed. States have the opportunity to build on local knowledge, networks and models to forge a stronger and more sustainable cultural tourism sector. This includes streamlining cooperation between different levels of governance in the cultural tourism sector and in concert with civil society and private sector. Particularly during the pandemic, many cities and municipalities have not received adequate State support and have instead introduced measures and initiatives using local resources. In parallel, such actions can spur new opportunities for employment and training that respond to local needs.
Greater diversification in cultural tourism models is needed, backed by a stronger integration of the sector within broader economic and regional planning. An overdependence of the cultural sector on the tourism sector became clear for some countries when the pandemic hit, which saw their economies come to a staggering halt. This has been further weakened by pre-existing gaps in government and industry preparedness and response capacity. The cultural tourism sector is highly fragmented and interdependent, and relies heavily on micro and small enterprises. Developing a more in-depth understanding of tourism value chains can help identify pathways for incremental progress. Similarly, more integrated – and balanced – models can shape a more resilient sector that is less vulnerable to future crises. Several countries are benefiting from such approaches by factoring in a consideration of the environmental and socio-cultural pillars of sustainability, which is supported across all levels of government and in concert with all stakeholders.

abhishek gaurav, Pexels
Inclusion must be at the heart of building back better the cultural tourism sector. Stakeholders at different levels should participate in planning and management, and local communities cannot be excluded from benefitting from the opportunities and economic benefits of cultural tourism. Moreover, they should be supported and empowered to create solutions from the outset, thus forging more sustainable and scalable options in the long-term. Policy-makers need to ensure that cultural tourism development is pursued within a wider context of city and regional strategies in close co-operation with local communities and industry. Businesses are instrumental in adopting eco-responsible practices for transport, accommodation and food. A balance between public/ private investment should also be planned to support an integrated approach post-crisis, which ensures input and support from industry and civil society.
The COVID-19 crisis has highlighted the essential role of museums as an integral component of societies in terms of well-being, health, education and the economy. Digitalization has been a game-changer for many cultural institutions to remain operational to the greatest extent possible. Yet there are significant disparities in terms of infrastructure and resources, which was underscored when the world shifted online. Museums in SIDS have faced particular difficulties with lack of access to digitalization. These imbalances should be considered in post-crisis strategies.
The pandemic presents an occasion to deeply rethink tourism for the future, and what constitutes the markers and benchmarks of “success”. High-quality cultural tourism is increasingly gaining traction in new strategies for recovery and revival, in view of contributing to the long-term health and resilience of the sector and local communities. Similarly, many countries are exploring ways to fast track towards greener, more sustainable tourism development. As such, the pandemic presents an opportunity for a paradigm shift - the transformation of the culture and tourism sectors to become more inclusive and sustainable. Moreover, this includes incorporating tourism approaches that not only avoid damage but have a positive impact on the environment of tourism destinations and local communities. This emphasis on regenerative tourism has a holistic approach that measures tourism beyond its financial return, and shifts the pendulum towards focusing on the concerns of local communities, and the wellbeing of people and planet.

Entabeni Game Reserve in South Africa by SL_Photography
Related items
More on this subject.

Other recent news

What is cultural tourism and why is it growing?
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Cultural tourism is big business. Some people seek to embark on their travels with the sole intention of having a ‘cultural’ experience, whereas others may experience culture as a byproduct of their trip. We can argue that there is some form of cultural tourism in most holidays (even when taking an all-inclusive holiday you might try to local beer, for example).
But what do we mean by the term ‘cultural tourism’? What’s it all about? In this post I will explain what is meant by the term cultural tourism, providing a range of academic definitions. I will also explain what the different types of cultural tourists are, give examples of cultural tourism activities and discuss the impacts of cultural tourism. Lastly, I will provide a brief summary of some popular cultural tourism destinations.
What is cultural tourism?
Cultural tourism is the act of travellers visiting particular destinations in order to experience and learn about a particular culture . This can include many activities such as; attending events and festivals, visiting museums and tasting the local food and drinks.
Cultural tourism can also be an unintentional part of the tourism experience, whereby cultural immersion (with the local people, their language, customs, cuisine etc) is an inevitable part of a person’s holiday.
Cultural tourism definitions
It has been suggested that tourism is the ideal arena in which to investigate the nature of cultural production (MacCannell, 1976). Tourism provides endless opportunities to learn about the way other people live, about their society and their traditions. Whether you are attending the Running of the Bulls Festival in Pamplona , visiting the pyramids in ancient Egypt , taking a tour of the tea plantations in China or enjoying the locally brewed Ouzo on your all-inclusive holiday to Greece, you will inevitably encounter some form of cultural tourism as part of your holiday experience.
The World Tourism Organisation (WTO) (1985) broadly define cultural tourism as the movements of persons who satisfy the human need for diversity, tending to raise the cultural level of the individual and giving rise to new knowledge, experience and encounters. Cultural tourism is commonly associated with education in this way, some describing it more narrowly as educational cultural tourism (e.g. Bualis and Costa, 2006; Harner and Swarbrooke, 2007; Richards, 2005).
Although a common, more specific definition has not been agreed amongst academics due to the complexity and subjectivity of the term, there do appear to be two distinct viewpoints. The first focusses upon the consumption of cultural products such as sites or monuments (Bonink, 1992; Munsters, 1994), and the second comprises all aspects of travel, where travellers learn about the history and heritage of others or about their contemporary ways of life or thought (MacIntosh and Goeldner, 1986).
Csapo (2012) pertains that the umbrella term of cultural tourism can encompass a number of tourism forms including heritage (material e.g. historic buildings and non-material e.g. literature, arts), cultural thematic routes (e.g. spiritual, gastronomic, linguistic), cultural city tourism, traditions/ethnic tourism, events and festivals, religious tourism and creative culture (e.g. performing arts, crafts).
Types of cultural tourists
In attempt to understand the scope of cultural tourism academics have developed a number of typologies, usually based upon the tourist’s level of motivation.
Bywater (1993) differentiated tourists according to whether they were culturally interested, motivated or inspired.
Culturally interested tourists demonstrate a general interest in culture and consume cultural attractions casually as part of a holiday rather than consciously planning to do so.
Culturally motivated tourists consume culture as a major part of their trip, but do not choose their destination on the basis of specific cultural experiences, whereas for culturally inspired tourists culture is the main goal of their holiday.
A more complex typology was proposed by McKercher and Du Cros (2002), who defined tourists based upon the depth of the cultural experience sought, distinguishing them in to one of five hierarchical categories.
The first is the purposeful cultural tourist for whom cultural tourism is their primary motive for travel. These tourists have a very deep cultural experience.
The second category is the sightseeing cultural tourist for whom cultural tourism is a primary reason for visiting a destination, but the experience is more shallow in nature.
The serendipitous cultural tourist does not travel for cultural reasons, but who, after participating, ends up having a deep cultural tourism experience, whilst the casual cultural tourist is weakly motivated by culture and subsequently has a shallow experience.
Lastly, the incidental cultural tourist is one who does not travel for cultural tourism reasons but nonetheless participates in some activities and has shallow experiences.
Adapting this theory, Petroman et al (2013) segments tourists based upon their preferred cultural activities.
The purposeful cultural tourist, described as according to Mckercher and Du Cros (2002), enjoys learning experiences that challenge them intellectually and visits history museums, art galleries, temples and heritage sites that are less known.
The tour-amateur cultural tourist is akin with the sightseeing cultural tourist above and they often travel long distances, visit remote areas, enjoy tours and wandering through the streets.
The occasional cultural tourist plays a moderate role in the decision of travelling and enjoys an insignificant cultural experience, their preferred activities being to visit attractions and temples that are easy to reach and to explore, although not to the extent that the tour-amateur cultural tourist does.
The incidental cultural tourist plays a small or no role in the decision to travel and enjoys an insignificant cultural experience, whilst visiting attractions that area within easy reach and heritage theme parks.
The last segment is the accidental cultural tourist, who plays a small or no role in the decision to travel but enjoys a deep cultural experience. This tourist type is diverse and as such has no preferred activities attributed to it.
Importance of cultural tourism
Cultural tourism is important for many reasons. Perhaps the most prominent reason is the social impact that it brings.
Cultural tourism can help reinforce identities, enhance cross cultural understanding and preserve the heritage and culture of an area. I have discussed these advantages at length in my post The Social Impacts of Tourism , so you may want to head over there for more detail.
Cultural tourism can also have positive economic impacts . Tourists who visit an area to learn more about a culture or who visit cultural tourism attraction, such as museums or shows, during their trip help to contribute to the economy of the area. Attractions must be staffed, bringing with it employment prospects and tertiary businesses can also benefit, such as restaurants, taxi firms and hotels.
Furthermore, for those seeking a deep cultural experience, options such as homestays can have positive economic benefits to the members of the community who host the tourists.
Read also: Overtourism explained: What, why and where
Personally, I think that one of the most important benefits of cultural tourism is the educational aspect. Tourists and hosts alike can learn more about different ways of life. This can help to broaden one’s mind, it can help one to think differently and to be more objective. These are qualities that can have many positive effects on a person and which can contribute to making them more employable in the future.
Cultural tourism activities
Whether a tourist is seeking a deep cultural experience or otherwise, there are a wide range of activities that can be classified as cultural tourism. Here are a few examples:
- Staying with a local family in a homestay
- Having a tour around a village or town
- Learning about local employment, for example through a tour of a tea plantation or factory
- Undertaking volunteer work in the local community
- Taking a course such as cooking, art, embroidery etc
- Visiting a museum
- Visiting a religious building, such as a Mosque
- Socialising with members of the local community
- Visiting a local market or shopping area
- Trying the local food and drink
- Going to a cultural show or performance
- Visiting historic monuments
Impacts of cultural tourism
There are a range of impacts resulting from cultural tourism activities, both good and bad. Here are some of the most common examples:
Positive impacts of cultural tourism
Revitalisation of culture and art.
Some destinations will encourage local cultures and arts to be revitalised. This may be in the form of museum exhibitions, in the way that restaurants and shops are decorated and in the entertainment on offer, for example.
This may help promote traditions that may have become distant.
Preservation of Heritage
Many tourists will visit the destination especially to see its local heritage. It is for this reason that many destinations will make every effort to preserve its heritage.
This could include putting restrictions in place or limiting tourist numbers, if necessary. This is often an example of careful tourism planning and sustainable tourism management.
This text by Hyung You Park explains the principles of heritage tourism in more detail.
Negative impacts of cultural tourism
Social change.
Social change is basically referring to changes in the way that society acts or behaves. Unfortunately, there are many changes that come about as a result of tourism that are not desirable.
There are many examples throughout the world where local populations have changed because of tourism. Perhaps they have changed the way that they speak or the way that they dress. Perhaps they have been introduced to alcohol through the tourism industry or they have become resentful of rich tourists and turned to crime. These are just a few examples of the negative social impacts of tourism.
Read also: Business tourism explained: What, why and where
Globalisation and the destruction of preservation and heritage.
Globalisation is the way in which the world is becoming increasingly connected. We are losing our individuality and gaining a sense of ‘global being’, whereby we more and more alike than ever before.
Globalisation is inevitable in the tourism industry because of the interaction between tourists and hosts, which typically come from different geographic and cultural backgrounds. It is this interaction that encourage us to become more alike.
Standardisation and Commercialisation
Similarly, destinations risk standardisation in the process of satisfying tourists’ desires for familiar facilities and experiences.
While landscape, accommodation, food and drinks, etc., must meet the tourists’ desire for the new and unfamiliar, they must at the same time not be too new or strange because few tourists are actually looking for completely new things (think again about the toilet example I have previously).
Tourists often look for recognisable facilities in an unfamiliar environment, like well-known fast-food restaurants and hotel chains. Tourist like some things to be standardised (the toilet, their breakfast, their drinks, the language spoken etc), but others to be different (dinner options, music, weather, tourist attractions etc).
Loss of Authenticity
Along similar lines to globalisation is the loss of authenticity that often results from tourism.
Authenticity is essentially something that is original or unchanged. It is not fake or reproduced in any way.
The Western world believe that a tourist destination is no longer authentic when their cultural values and traditions change. But I would argue is this not natural? Is culture suppose to stay the same or it suppose to evolve throughout each generation?
Take a look at the likes of the long neck tribe in Thailand or the Maasai Tribe in Africa. These are two examples of cultures which have remained ‘unchanged’ for the sole purpose of tourism. They appear not to have changed the way that they dress, they way that they speak or the way that they act in generations, all for the purpose of tourism.
You can learn more about what is authenticity in tourism here or see some examples of staged authenticity in this post.
Culture clashes
Because tourism involves movement of people to different geographical locations cultural clashes can take place as a result of differences in cultures, ethnic and religious groups, values, lifestyles, languages and levels of prosperity.
Read also: Environmental impacts of tourism
The attitude of local residents towards tourism development may unfold through the stages of euphoria, where visitors are very welcome, through apathy, irritation and potentially antagonism when anti-tourist attitudes begin to grow among local people. This is represented in Doxey’s Irritation Index, as shown below.
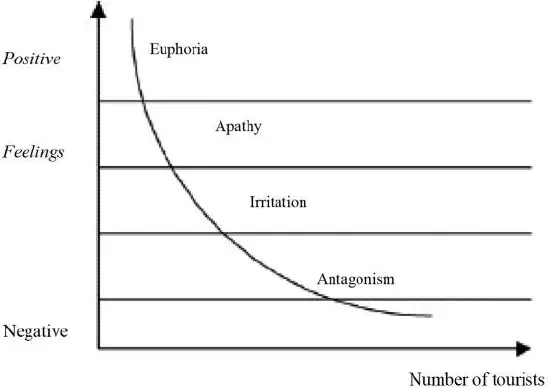
Tourist-host relationships
Culture clashes can also be exasperated by the fundamental differences in culture between the hosts and the tourists.
There is likely to be economic inequality between locals and tourists who are spending more than they usually do at home. This can cause resentment from the hosts towards the tourists, particularly when they see them wearing expensive jewellery or using plush cameras etc that they know they can’t afford themselves.
Further to this, tourists often, out of ignorance or carelessness, fail to respect local customs and moral values.
There are many examples of ways that tourists offend the local population , often unintentionally. Did you know that you should never put your back to a Buddha? Or show the sole of your feet to a Thai person? Or show romantic affection in public in the Middle East?
Cultural tourism destinations
Whilst many would argue that cultural tourism is ingrained to some extent in travel to any country, there are some particular destinations that are well-known for their ability to provide tourists with a cultural experience.
Cultural tourism in India
It is impossible not to visit India and experience the culture. Even if you are staying in a 5 star Western all-inclusive hotel in Goa, you will still test Indian curries, be spoken to by Indian workers and see life outside of the hotel on your transfer to and from the airport.
For most people who travel to India, however, cultural tourism is far more than peeking outside of the enclave tourism bubble of their all-inclusive hotel.
Thousands of international tourists visit the Taj Mahal each year. Many more people visit the various Hindu and Buddhist temples scattered throughout the country as well as the various Mosques. Some visit the famous Varanassi to learn about reincarnation.
Most tourists who visit India will try the local dal, eat the fresh mutton and taste chai.
All of these activities are popular cultural tourism activities.
Cultural tourism in Thailand
Thailand is another destination that offers great cultural tourism potential. From the Buddhist temples and monuments and the yoga retreats to homestays and village tours, there are ample cultural tourism opportunities in Thailand .
Cultural tourism in Israel
Israel is popular with religious tourists and those who are taking a religious pilgrimage, as well as leisure tourists. I visited Israel and loved travelling around to see the various sights, from Bethlehem to Jerusalem . I’m not religious in any way, but I loved learning about the history, traditions and cultures.
Cultural tourism in New York
New York is a city that is bustling with culture. It is world famous for its museums and you can learn about anything from World War Two to the Twin Towers here.
Many would argue that shopping is ingrained in the culture of those who live in New York and many tourists will take advantage of the wide selection of products on offer and bargains to be had on their travels to New York.
You can also treat yourself to watching a traditional West End show, trying some of the famous New York Cheesecake and enjoying a cocktail in Times Square!
Cultural tourism in Dubai
Dubai might not be the first destination that comes to mind when you think of cultural tourism, but it does, in fact, have a great offering.
What I find particular intriguing about Dubai is the mix of old and new. One minute you can be exploring the glitz and glamour of the many high-end shopping malls and skyscrapers and the next you can be walking through a traditional Arabian souk.
Cultural tourism: Conclusion
As you can see, there is big business in cultural tourism. With a wide range of types of cultural tourists and types of cultural tourism experiences, this is a tourism sector that has remarkable potential. However, as always, it is imperative to ensure that sustainable tourism practices are utilised to mitigate any negative impacts of cultural tourism.
If you are interested in learning more about topics such as this subscribe to my newsletter ! I send out travel tips, discount coupons and some material designed to get you thinking about the wider impacts of the tourism industry (like this post)- perfect for any tourism student or keen traveller!
Further reading
Want to learn more about cultural tourism? See my recommended reading list below.
- Cultural Tourism – A textbook illustrating how heritage and tourism goals can be integrated in a management and marketing framework to produce sustainable cultural tourism.
- Deconstructing Travel: Cultural Perspectives on Tourism – This book provides an easily understood framework of the relationship between travel and culture in our rapidly changing postmodern, postcolonial world.
- Re-Investing Authenticity: Tourism, Place and Emotions – This ground-breaking book re-thinks and re-invests in the notion of authenticity as a surplus of experiential meaning and feeling that derives from what we do at/in places.
- The Business of Tourism Management – an introduction to key aspects of tourism, and to the practice of managing a tourism business.
- Managing Sustainable Tourism – tackles the tough issues of tourism such as negative environmental impact and cultural degradation, and provides answers that don’t sacrifice positive economic growth.
- Tourism Management: An Introduction – An introductory text that gives its reader a strong understanding of the dimensions of tourism, the industries of which it is comprised, the issues that affect its success, and the management of its impact on destination economies, environments and communities.
- Responsible Tourism: Using tourism for sustainable development – A textbook about the globally vital necessity of realising sustainable tourism.
Liked this article? Click to share!
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Politics of Development
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >
Heritage Tourism
The late Alan Gordon was professor of history at the University of Guelph. He authored three books: Making Public Pasts: The Contested Terrain of Montreal’s Public Memories, 1891–1930, The Hero and the Historians: Historiography and the Uses of Jacques Cartier and Time Travel: Tourism and the Rise of the Living History Museum in Mid-Twentieth Century Canada.
- Published: 18 August 2022
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Heritage tourism is a form of cultural tourism in which people travel to experience places, artifacts, or activities that are believed to be authentic representations of people and stories from the past. It couples heritage, a way of imagining the past in terms that suit the values of the present, with travel to locations associated with enshrined heritage values. Heritage tourism sites are normally divided into two often overlapping categories: natural sites and sites related to human culture and history. By exploring the construction of heritage tourism destinations in historical context, we can better understand how and through what attributes places become designated as sites of heritage and what it means to have an authentic heritage experience. These questions are explored through heritage landscapes, national parks, battlefield tourism, architectural tourism, and the concept of world heritage.
Heritage is one of the most difficult, complex, and expansive words in the English language because there is no simple or unanimously accepted understanding of what heritage encompasses. 1 We can pair heritage with a vast range of adjectives, such as cultural, historical, physical, architectural, or natural. What unites these different uses of the term is their reference to the past, in some way or another, while linking it to present-day needs. Heritage, then, is a reimagining of the past in terms that suit the values of the present. It cannot exist independently of human attempts to make the past usable because it is the product of human interpretation of not only the past, but of who belongs to particular historical narratives. At its base, heritage is about identity, and the inclusion and exclusion of peoples, stories, places, and activities in those identities. The use of the word “heritage” in this context is a postwar phenomenon. Heritage and heritage tourism, although not described in these terms, has a history as long as the history of modern tourism. Indeed, a present-minded use of the past is as old as civilization itself, and naturally embedded itself in the development of modern tourism. 2 The exploration of that history, examining the origins and development of heritage tourism, helps unpack some of the controversies and dissonance it produces.
Heritage in Tourism
Heritage tourism sites are normally divided into two categories: natural sites and sites of human, historical, or cultural heritage. the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) separates its list of world heritage sites in this manner. Sites of natural heritage are understood to be places where natural phenomena such as wildlife, flora, geological features, or ecosystems, are generally deemed to be of exceptional beauty or significance. Cultural heritage sites, which represent over three quarters of UNESCO-recognized sites, are places where human activity has left a lasting and substantial physical impact that reveals important features of a culture or cultures. Despite the apparent simplicity of this division, it is not always easy to categorize individual sites. UNESCO thus allows for a category of “mixed” heritage sites. But official recognition is not necessary to mark a place as a heritage destination and, moreover, some authors point to versions of heritage tourism that are not tightly place-specific, such as festivals of traditional performances or foodways. 3
The central questions at the heart of heritage tourism ask what it is that designates something as “heritage” and whether tourists have an “authentic” heritage experience there. At its simplest, heritage tourism is a form of cultural tourism in which people travel to experience places, artifacts, or activities that are authentic representations of people and stories from the past. Yet this definition encompasses two, often competing, motivations. Heritage tourism is both a cultural phenomenon through which people attempt to connect with the past, their ancestors, and their identity, and it is an industry designed to profit from it. Another question surrounds the source of the “heritage” in heritage tourism. Many scholars have argued that heritage does not live in the destinations or attractions people seek. Heritage is not innate to the destination, but is rather based on the tourist’s motivations and expectations. Thus, heritage tourism is a form of tourism in which the main motivation for visiting a site is based on the traveler’s perceptions of its heritage characteristics. Following the logic of this view, the authenticity of the heritage experience depends on the traveler rather than the destination or the activity. Heritage features, as well as the sense of authenticity they impart, are democratized in what might be called a consumer-based model of authenticity. 4 This is a model that allows for virtually anything or any place to be a heritage destination. Although such an approach to understanding heritage tourism may well serve present-day studies, measuring motivations is more complicated for historical subjects. Long-departed travelers are not readily surveyed about their expectations; motivations have to be teased out of historical records. In a contrasting view, John Tunbridge and Gregory Ashworth argue that heritage attractions are created through marketing: they are invented to be heritage attractions and sold to a traveling public as such. Yet, heritage attractions, in this understanding, are still deemed authentic when they satisfy consumer expectations about heritage. 5 This insight also implies that heritage tourism destinations might be deceptions, and certainly there are examples of the fabrication of heritage sites. However, if motivations and expectations are arbiters of heritage, then even invented heritage can become authentic through its acceptance by a public. While not ignoring the motivations and expectations of travelers, for historians, any understanding of heritage tourism must include the process by which sites become designated as a places of heritage. It must encompass the economic aspects of tourism development, tourism’s role in constructing narratives of national or group identity, and the cultural phenomenon of seeking authentic representations of those identities, regardless of their origins. Such a practice might include traveling to sites connected to diasporas, places of historical significance, sites of religious pilgrimages, and landscapes of scenic beauty or cultural importance.
Scholarly interest in heritage, at least in the English-speaking world, dates from the 1980s reaction to the emergence of new right-wing political movements that used the past as a tool to legitimize political positions. Authors such as David Lowenthal, Robert Hewison, and Patrick Wright bemoaned the recourse to “heritage” as evidence of a failing society that was backward-looking, fearful, and resentful of modern diversity. 6 Heritage, they proclaimed, was elitist and innately conservative, imposed on the people from above in ways that distanced them from an authentic historical consciousness. Although Raphael Samuel fired back that the critique of heritage was itself elitist and almost snobbish, this line continued in the 1990s. Works by John Gillis, Tony Bennett, and Eric Hobsbawm, among others, concurred that heritage was little more than simplified history used as a weapon of social and political control.
At about the same time, historians also began to take tourism seriously as a subject of inquiry, and they quickly connected leisure travel to perceived evils in the heritage industry. Historians such as John K. Walton in the United Kingdom and John Jakle in the United States began investigating patterns of tourism’s history in their respective countries. Although not explicitly concerned with heritage tourism, works such as Jakle’s The Tourist explored the infrastructure and experience of leisure travel in America, including the different types of attractions people sought. 7 In Sacred Places , John Sears argued that tourism helped define America in the nineteenth century through its landscape and natural wonders. Natural tourist attractions, such as Yosemite and Yellowstone parks became sacred places for a young nation without unifying religious and national shrines. 8 Among North America’s first heritage destinations was Niagara Falls, which drew Americans, Europeans, Britons, and Canadians to marvel at its beauty and power. Tourist services quickly developed there to accommodate travelers and, as Patricia Jasen and others note, Niagara became a North American heritage destination at the birth of the continent’s tourism trade. 9
As the European and North American travel business set about establishing scenic landscapes as sites worthy of the expense and difficulty of travel to them, they rarely used a rhetoric of heritage. Sites were depicted as places to embrace “the sublime,” a feeling arising when the emotional experience overwhelms the power of reason to articulate it. Yet as modern tourism developed, promoters required more varied attractions to induce travelers to visit specific destinations. North America’s first tourist circuits, well established by the 1820s, took travelers up the Hudson River valley from New York to the spas of Saratoga Springs, then utilizing the Erie Canal even before its completion, west to Niagara Falls. Tourist guidebooks were replete with vivid depictions of the natural wonders to be witnessed, and very quickly Niagara became heavily commercialized. As America expanded beyond the Midwest in the second half of the nineteenth century, text and image combined to produce a sense that these beautiful landscapes were a common inheritance of the (white and middle-class) American people. Commissioned expeditions, such as the Powell Expedition of 1869–1872, produced best-selling travel narratives revealing the American landscape to enthralled readers in the eastern cities (see Butler , this volume). John Wesley Powell’s description of his voyage along the Colorado River combined over 450 pages of written description with 80 prints, mostly portraying spectacular natural features. American westward exploration, then, construed the continent’s natural wonders as its heritage.
In America, heritage landscapes often obscured human activity and imagined the continent as nature untouched. But natural heritage also played a role in early heritage tourism in Britain and Europe. Many scholars have investigated the connection between national character and the depiction of topographical features, arguing that people often implant their communities with ideas of landscape and associate geographical features with their identities. In this way, landscape helps embed a connection between places and particular local and ethnic identities. 10 Idealized landscapes become markers of national identity (see Noack , this volume). For instance, in the Romantic era, the English Lake District and the mountains of the Scottish Highlands became iconic national representations of English, Scottish, or British nationalities. David Lowenthal has commented on the nostalgia inherent in “landscape-as-heritage.” The archetypical English landscape, a patchwork of fields divided by hedgerows and sprinkled with villages, was a relatively recent construction when the pre-Raphaelite painters reconfigured it as the romantic allure of a medieval England. It spoke to the stability and order inherent in English character. 11
Travel literature combined with landscape art to develop heritage landscapes and promote them as tourist attractions. Following the 1707 Act of Union, English tourists became fascinated with Scotland, and in particular the Scottish Highlands. Tourist guidebooks portrayed the Highlands as a harsh, bleak environment spectacular for its beauty as well as the quaintness of its people and their customs (see Schaff , this volume). Over the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, tourist texts cemented the image of Highland culture and heritage. Scholars have criticized this process as a “Tartanization” or “Balmoralization” of the country by which its landscape and culture was reduced to a few stereotypes appealing to foreign visitors. Nevertheless, guidebook texts described the bens, lochs, and glens with detail, helping create and reinforce a mental picture of a quintessential Highland landscape. 12 The massacre of members of the Clan MacDonald at Glencoe, killed on a winter night in 1692 for insufficient loyalty to the monarchy, added romance. Forgotten for over a century, the event was recalled in the mid-nineteenth century by the historian Thomas Babington Macaulay, and quickly became a tragic tale associated with the scenic valley. At the same time the Highlands were being re-coded from a dangerous to a sublime landscape, its inhabitants became romanticized as an untainted, simple, premodern culture. The natural beauty of the landscape at Glencoe and its relative ease of access, being close to Loch Lomond and Glasgow, made it an attraction with a ready-made tragic tale. Highlands travel guides began to include Glencoe in their itineraries, combining a site of natural beauty with a haunting human past. Both natural and cultural heritage, then, are not inherent, but represent choices made by people about what and how to value the land and the past. On France’s Celtic fringe, a similar process unfolded. When modern tourism developed in Brittany in the mid-nineteenth century, guidebooks such as Joanne’s defined the terms of an authentic Breton experience. Joanne’s 1867 guide coupled the region’s characteristic rugged coastlines with the supposedly backward people, their costumes, habitudes, beliefs, and superstitions, who inhabited it. 13 Travel guides were thus the first contributors in the construction of heritage destinations. They began to highlight the history, real and imagined, of destinations to promote their distinctions. And, with increasing interest in the sites of national heritage, people organized to catalog, preserve, and promote heritage destinations.
Organizing Heritage Tourism
Among the world’s first bodies dedicated to preserving heritage was the Society for the Protection of Ancient Buildings (SPAB), organized in England in 1877. Emerging as a result of particular debates about architectural practices, this society opposed a then-popular trend of altering buildings to produce imaginary historical forms. This approach, which was most famously connected to Eugène-Emmanuel Viollet-le-Duc’s French restorations, involved removing or replacing existing architectural features, something renounced by the SPAB. The society’s manifesto declared that old structures should be repaired so that their entire history would be protected as part of cultural heritage. The first heritage preservation legislation, England’s Ancient Monuments Protection Act of 1882, provided for the protection initially of 68 prehistoric sites and appointed an inspector of ancient monuments. 14 By 1895, movements to conserve historic structures and landscapes had combined with the founding of the National Trust, officially known as the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, as a charitable agency. Much of the Trust’s early effort protected landscapes: of twenty-nine properties listed in 1907, seventeen were acreages of land and other open spaces. 15 Over the twentieth century, however, the Trust grew more and more concerned with protecting country houses and gardens, which now constitute the majority of its listed properties.
British efforts were duplicated in Europe. The Dutch Society for the Preservation of Natural Landmarks was established in 1904; France passed legislation to protect natural monuments in 1906. And in Sweden, the Society for the Protection of Nature was established in 1909, to name only a few examples. Nature was often connected to the spirit of “the folk,” an idea that encompassed a notion of an original ethnic core to the nation. Various European nationalisms of the period embraced the idea of an “authentic” national folk, with each folk considered unique due to its connection with a specific geography. Folklore and the celebration of folk culture offered Europeans links to imagined national heritages in a rapidly modernizing world, as modern, middle-class Europeans turned their attention to the romanticized primitive life of so-called simple peasants and linked notions of natural and human heritage. Through the concept of the folk, natural and human heritage combined to buttress emerging expressions of nationalism. 16
Sweden provides an instructive example. As early as the seventeenth century, Swedish antiquarians were intrigued by medieval rune stones, burial mounds, and cairns strewn across the country, but also saw these connected to natural features. Investigations of these relics of past Nordic culture involved a sense of the landscape in which they were found. This interest accelerated as folk studies grew in popularity, in part connected to nationalist political ambitions of Swedes during the growing tensions within the Kingdom of Sweden and Norway, which divided in 1905. Sweden’s preservation law required research into the country’s natural resources to create an inventory of places. Of particular interest were features considered to be “nature in its original state.” The intent was to preserve for future generations at least one example of Sweden’s primordial landscape features: primeval forests, swamps, peat bogs, and boulders. But interest was also drawn to natural landmarks associated with historical or mythical events from Sweden’s past. Stones or trees related to tales from the Nordic sagas, for example, combined natural with cultural heritage. 17
Although early efforts to protect heritage sites were not intended to support tourism, the industry quickly benefited. Alongside expanding tours to the Scottish Highlands and English Lake District, European landscapes became associated with leisure travel. As Tait Kellar argues for one example, the context of the landscape is crucial in understanding the role of tourism in the German Alps. 18 Guidebooks of the nineteenth and early twentieth century did not use the term “heritage,” but they described its tenets to audiences employing a different vocabulary. Baedeker’s travel guides, such as The Eastern Alps , guided bourgeois travelers through the hiking trails and vistas of the mountains and foothills, offering enticing descriptions of the pleasures to be found in the German landscape. Beyond the land, The Eastern Alps directed visitors to excursions that revealed features of natural history, human history, and local German cultures. 19
Across the Atlantic people also cherished escapes to the countryside for leisure and recreation and, as economic and population growth increasingly seemed to threaten the idyllic tranquility of scenic places, many banded together to advocate for their conservation. Yet, ironically, by putting in place systems to mark and preserve America’s natural heritage, conservationists popularized protected sites as tourist destinations. By the second half of the nineteenth century, the conservation movement encouraged the US government to set aside massive areas of American land as parks. For example, Europeans first encountered the scenic beauty of California’s Yosemite Valley at midcentury. With increasing settler populations following the California Gold Rush, tourists began arriving in ever larger numbers and promoters began building accommodations and roads to encourage them. Even during the Civil War, the US government recognized the potential for commercial overdevelopment and the desire of many to preserve America’s most scenic places. 20 In 1864, President Abraham Lincoln signed the Yosemite Grant, designating acres of the valley protected wilderness. This set a precedent for the later creation of America’s first national park. In 1871, the Hayden Geological Survey recommended the preservation of nearly 3,500 square miles of land in the Rocky Mountains, in the territories of Montana, Wyoming, and Idaho. Ferdinand V. Hayden was concerned that the pristine mountain region might soon be as overrun with tourists as Niagara Falls had by then become. 21 The following year, Congress established Yellowstone National Park, the world’s first designated “heritage” site. Yet, from the beginning, Yellowstone and subsequent parks were assumed to be tourist attractions. By 1879, tourists to Yellowstone had established over 200 miles of trails that led them to the park’s most famous attractions. Although thought of as nature preserves, parks were often furnished with railway access, and amenities and accommodations appeared, often prior to official designation. National parks were immediately popular tourist attractions. Even before it had established a centralized bureaucracy to care for them, the United States government had established nine national parks and nearly two dozen national monuments. Canada lagged, but established Rocky Mountain National Park (now Banff) in 1885 to balance interests of resource extraction and conservation. (The world’s second national park was Australia’s Royal National Park, established by the colony of New South Wales in 1879.) By the outbreak of the Great War, Canada and the United States had established fifteen national parks, all but one west of the Mississippi River.
Establishing parks was one component of building a heritage tourism infrastructure. Another was the creation of a national bureaucracy to organize it. The Canadian example reveals how heritage and tourism drove the creation of a national parks service. Much of the mythology surrounding Canada’s national parks emphasized the role of nature preservationists, yet the founder of the parks system, J. B. Harkin, was deeply interested in building a parks network for tourists. 22 Indeed, from early in the twentieth century, Canada’s parks system operated on the principle that parks should be “playgrounds, vacation destinations, and roadside attractions that might simultaneously preserve the fading scenic beauty and wildlife populations” of a modernizing nation. 23 Although Canada had established four national parks in the Rocky Mountains in the 1880s, the administration of those parks was haphazard and decentralized. It was not until the approaching third centennial of the founding of Quebec City (now a UNESCO World Heritage Site) that the Canadian government began thinking actively about administering its national heritage. In 1908, Canada hosted an international tourist festival on the Plains of Abraham, the celebrated open land where French and British armies had fought the decisive battle for supremacy in North America in 1759. The event so popularized the fabled battlefield that the government was compelled to create a National Battlefield Commission to safeguard it. This inspired the creation of the Dominion Parks Branch three years later to manage Canada’s natural heritage parks, the world’s first national parks service. By 1919 the system expanded to include human history—or at least European settler history—through the creation of national historic parks. These parks were even more explicitly designed to attract tourists, automobile tourists in particular. In 1916, five years after Canada, the United States established the National Parks Service with similar objectives.
As in Europe, nationalism played a significant role in developing heritage tourism destinations in America. The first national parks were inspired by the series of American surveying expeditions intended to secure knowledge of the landscape for political control. Stephen Pyne connects the American “discovery” of the Grand Canyon, for example, to notions of manifest destiny following the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848) that ended the Mexican-American War and ceded over 500,000 square miles of what is today the western United States. Popularized by the report of John Wesley Powell (1875) , the canyon began attracting tourists in the 1880s, although Congress failed to establish it as a national park. 24 Tourism was central to developing the Grand Canyon as a national heritage destination. Originally seen by Spanish explorers as an obstacle, and as a sacred place by the Navajo, Hopi, Hualapai, and Havasupai peoples, the canyon came to mark American exceptionalism. Piece by piece, sections of the canyon were set aside as reserves and finally declared a national park in 1919. By then, the park had been serviced by a railway (since 1901) and offered tourists a luxury hotel on the canyon’s south rim.
Archaeology also entered into the construction of American heritage. Almost as soon as it was annexed to the United States, the American southwest revealed to American surveyors a host of archaeological remains. For residents of the southwest, the discovery of these ancient ruins of unknown age pointed to the nobility of a lost predecessor civilization. By deliberately construing the ruins as being of an unknown age, Anglo-American settlers were able to draw distinctions between the ancients and contemporary Native Americans in ways that validated their own occupation of the territory. The ruins also had commercial potential. In Colorado, President Theodore Roosevelt established Mesa Verde National Park in 1906 to protect and capitalize on the abandoned cliff dwellings located there. These ruins had been rediscovered in the 1880s when ranchers learned of them from the local Ute people. By the turn of the century, the ruins had attracted so many treasure seekers that they needed protection. This was the first national park in America designated to protect a site of archaeological significance and linked natural and human heritage in the national parks system. 25
If, as many argue, heritage is not innate, how is it made? Part of the answer to this question can be found in the business of tourism. Commercial exploitation of heritage tourism emerged alongside heritage tourism, but was particularly active in the postwar years. Given their association with tourism, it is not surprising that railways and associated businesses played a prominent role in promoting heritage destinations. Before World War II, the most active heritage tourism promoter was likely the Fred Harvey Company, which successfully marketed, and to a great degree created, much of the heritage of the American southwest. The Fred Harvey Company originated with the opening of a pair of cafés along the Kansas Pacific Railway in 1876. After a stuttering beginning, Harvey’s chain of railway eateries grew in size. Before dining cars became regular features of passenger trains, meals on long-distance trips were provided by outside business such as Harvey’s at regular stops. With the backing of the Santa Fe Railroad, the company also developed attractions based on the Southwest region’s unique architectural and cultural features. The image capitalized on the artistic traditions of Native Americans and early Spanish traditions to create, in particular, the Adobe architectural style now associated with Santa Fe and New Mexico. 26 These designs were also incorporated into tourist facilities on the South Rim of the Grand Canyon, including the El Tovar hotel and the Hopi House souvenir and concession complex, designed to resemble a Hopi pueblo.
Relying on existing and manufactured heritage sites, North American railways popularized attractions as heritage sites. The Northern Pacific Railroad financed a number of hotels in Yellowstone Park, including the Old Faithful Inn in 1904. In 1910, the Great Northern Railroad launched its “See America First” campaign to attract visitors (and new investments) to its routes to the west’s national parks. In Canada, the Dominion Atlantic Railway rebuilt Grand Pré, a Nova Scotia Acadian settlement to evoke the home of the likely fictional character Evangeline from Henry Wadsworth Longfellow’s 1848 poem by the same name. In the poem, Evangeline was deported from Acadia in 1755 and separated from her betrothed. By the 1920s, the railway was transporting tourists to Grand Pré, christened “Land of Evangeline,” where reproductions stood in for sites mentioned in the poem. 27 However, following World War I, heritage tourism in North America became increasingly dependent on automobile travel and the Dominion Atlantic eventually sold its interest to the Canadian government.
Conflict as Cultural Heritage
Tourism to sites of military history initially involved side trips from more popular, usually natural, attractions. Thomas Chambers notes that the sites of battles of the Seven Years’ War, Revolutionary War, and War of 1812 became tourist attractions as side trips from more established itineraries, such as the northern or fashionable tours. War of 1812 battlefields, many of them in the Niagara theater of the war, were conveniently close to the natural wonders people already came to see. By visiting the places where so many had sacrificed for their country, tourists began attaching new meaning to the sites. Ease of access was essential. Chambers contrasts sites in southern states with those in the north. In the south, the fields of important American Revolution victories at Cowpens and King’s Mountain were too remote to permit easy tourist access and long remained undeveloped. 28 In a contrary example, the Plains of Abraham, the scene of General Wolfe’s dramatic victory over France that led to the Conquest of Canada, was at first a curiosity. The visit to Quebec, a main destination on the northern tour, was originally based on its role as a major port and the attraction of the scenic beauty of the city on the cliffs, compared favorably to Cintra in Portugal. 29 Ease of access helped promoters convert an empty field near the city into the “hallowed Plains.”
Access to battlefields increased at almost the exact moment that one of the nineteenth century’s most devastating wars, the American Civil War, broke out. Railway travel was essential to both the success of the Union Army in reconquering the rebelling Confederacy, and in developing tourism to the sites of the slaughter. Railway travel made sites accessible for urban travelers and new technologies, such as photography and the telegraph, sped news of victories and defeats quickly around the nation. Gettysburg, the scene of a crucial Union victory in July 1863, became a tourist attraction only a few days later. Few would call the farmland of southeastern Pennsylvania sublime, but dramatic human history had unfolded there. The battle inspired the building of a national memorial on the site only four months later, the Soldiers’ National Cemetery. At the inauguration of the cemetery Abraham Lincoln delivered his “Gettysburg Address,” calling on the nation to long remember and cherish the “hallowed ground” where history had been made.
Gettysburg sparked a frenzy of marking sites of Civil War battles and events. Battle sites became important backdrops for political efforts at reunion and reconciliation after the war and attracted hundreds and later thousands of tourists for commemorative events and celebrations. Ten thousand saw President Rutherford Hayes speak at Gettysburg in 1878 and, for the 50th anniversary of Gettysburg, some 55,000 veterans returned to Pennsylvania in July 1913. What had once been a site of bloody, brutal combat had been transformed into a destination where tourists gathered to embrace their shared heritage, north and south. As the years progressed, more attractions were added as tourists began to see their heritage on the battlefield. 30
The conflict that most clearly created tourist attractions out of places of suffering was the World War I. Soon after the war ended, its sites of slaughter also became tourist attractions. As with the Civil War in America, World War I tourists were local people and relatives of the soldiers who had perished on the field of battle. By one estimate 60,000 tourists visited the battlefields of the Western Front by the summer of 1919, the same year that Michelin began publishing guidebooks to them. Numbers grew in the decades following the war. Over 140,000 tourists took in the sites of the war in 1931, which grew to 160,000 for 1939. Organizations such as the Workers’ Travel Association hoped that tourism to battle sites would promote peace, but the travel business also benefited. Travel agencies jumped at the chance to offer tours and publishers produced travel guides to the battlefields. At least thirty English guidebooks were published by 1921. 31
This interest in a conflict that killed, often in brutal fashion, so many might seem a ghoulish form of heritage tourism. Yet Peter Slade argues that people do not visit battlefields for the love for death and gore. They attend these sites out of a sense of pilgrimage to sites sacred to their national heritage. Organized pilgrimages reveal this sense of belonging most clearly. The American Legion organized a pilgrimage of 15,000 veterans in 1927 to commemorate the decade anniversary of America’s entry to the war. The following year 11,000 Britons, including 3,000 women, made a pilgrimage of their own. Canada’s first official pilgrimage involved 8,000 pilgrims (veterans and their families) to attend the inauguration of the Vimy Ridge Memorial, marking a site held by many as a place sacred to Canadian identity. Australians and New Zealanders marched to Gallipoli in Turkey for similar reasons. 32 As with the sites of the Western Front, Gallipoli and pilgrimages to it generated travel accounts and publishers assembled guidebooks to help travelers navigate its attractions and accommodations. In these episodes, tourism was used to construct national heritage. In the interwar years, tourist activity popularized the notion that sites of national heritage existed on the battlefields of foreign lands, where “our” nation’s history was forged. National heritage tourism, then, became transnational.
Since the end of World War II, battlefield tourism has become an important projection of heritage tourism. Commercial tour operators organize thousands of tours of European World War I and World War II battlefields for Americans and Canadians, as for other nationalities. The phenomenon seems particularly pronounced among North Americans. The motivation behind modern battlefield tourism reveals its connection to heritage tourism. If heritage is an appeal to the past that helps establish a sense of identity and belonging, the feelings of national pride and remorse for sacrifice of the fallen at these sites helps define them as sacred to a particular vision of a national past. The sanctity of the battle site makes the act of consuming it as a tourist attraction an act of communion with heritage.
Built Heritage and Tourism
During the upheaval of the Civil War, some Americans began to recognize historic houses as elements of their heritage worthy of preservation. These houses were initially not seen as tourist attractions, but as markers of national values. Their heritage value preceded their value as tourist attractions. The first major preservation initiative launched in 1853 to save George Washington’s tomb and home from spoliation. Behind overt sectional divisions of north and south was an implied vesting of republican purity among the patrician families that could trace their ancestors to the revolutionary age and who could restore American culture to its proper deferential state. The success of preserving Mount Vernon led to a proliferation of similar house museums. By the 1930s, the American museum association even produced a guide for how to establish new examples and promote them as sites of heritage for tourist interest. Historic houses provided tangible, physical evidence of heritage. Like scenic landscapes attached to the stories of history, buildings connected locations to significant events and people of the past. Architectural heritage came to be closely associated with tourism. Architectural monuments are easily identified, easy to promote, and, as physical structures, easily reproduced in souvenir ephemera. Although the recognition of architectural monuments as tourist draws could be said to have originated with the Grand Tour, or at least with the publication of John Ruskin’s “Seven Lamps of Architecture” (1849), which singled out the monuments of Venice for veneration, twentieth century mobility facilitated a greater desire to travel to see historic structures. Indeed, mobility, especially automobility, prompted the desire to preserve or even reinvent the structural heritage of the past.
A driving factor behind the growth of tourism to sites associated with these structural relics was a feeling that the past—and especially the social values of the past—was being lost. For example, Colonial Williamsburg developed in reaction to the pace of urban and social change brought about by automobile travel in the 1920s. Williamsburg was once a community of colonial era architecture, but had become just another highway town before John D. Rockefeller lent his considerable wealth to its preservation and reconstruction. 33 Rockefeller had already donated a million dollars for the restoration of French chateaux at Versailles, Fontainebleu, and Rheims. 34 At Williamsburg, his approach was to remove structures from the post-Colonial period to create a townscape from the late eighteenth century. By selecting a cut-off year of 1790, Rockefeller and his experts attempted to freeze Williamsburg in a particular vision of the past. The heritage envisioned was not that of ordinary Americans, but that of colonial elites. Conceived to be a tourist attraction, Colonial Williamsburg offered a tourist-friendly lesson in American heritage. Rockefeller, and a host of consultants convinced the (white) people of Williamsburg to reimagine their heritage and their past. America’s heritage values were translated to the concepts of self-government and individual liberty elaborated by the great patriots, Washington, Madison, Henry, and Jefferson. The town commemorated the planter elites that had dominated American society until the Jacksonian era, and presented them as progenitors of timeless ideals and values. They represented the “very cradle of that Americanism of which Rockefeller and the corporate elite were the inheritors and custodians.” 35
Rockefeller’s Williamsburg was not the only American heritage tourist reconstruction. Canada also underwent reconstruction projects for specifically heritage tourism purposes, such as the construction of “Champlain’s Habitation” at Port Royal, Nova Scotia or the attempt to draw tourists to Invermere, British Columbia with a replica fur trade fort. 36 Following World War I and accelerating after World War II, the number and nature of places deemed heritage attractions grew. Across North America, all levels of governments and private corporations built replica heritage sites with varying degrees of “authenticity.” Although these sites often made use of existing buildings and landscapes, they also manufactured an imaginary environment of the past. The motivation behind these sites was almost always diversification of the local economy through increased tourism. Canada’s Fortress of Louisbourg National Historic Site is perhaps the most obvious example. It is a reconstructed section of the French colonial town, conquered and destroyed in 1758, built on the archaeological remains of the original. Constructed by the government of Canada as a means to diversify the failing resource economy of its Atlantic provinces, the tourist attraction was also designated a component of Canada’s national heritage. The US government also increased its interest in the protection of heritage destinations, greatly expanding the list of national historic landmarks, sites, parks, and monuments. As postwar governments became more concerned with managing their economies, tourism quickly came to be seen as a key economic sector. The language of national heritage helped build public support for state intervention in natural and historic artifacts and sites that could be presented as sacred national places.
In Europe, many historic sites were devastated by bombardment during World War II. Aside from pressing humanitarian issues, heritage concerns also had to be addressed. In France, the war had destroyed nearly half a million buildings, principally in the northern cities, many of which were of clear heritage value. The French government established a commission to undertake the reconstruction of historic buildings and monuments and, in some cases, entire towns. Saint-Malo, in Brittany, had been completely destroyed, but the old walled town was rebuilt to its seventeenth century appearance. Already a seaside resort, the town added a heritage site destination. In the 1920s and 1930s, European fascist states had also employed heritage tourism. In Mussolini’s Italy and Nazi Germany, workers’ leisure time was to be organized to prevent ordinary Italians and Germans from falling into unproductive leisure activities. Given the attachment to racialized views of purity and identity, organized tourism was encouraged to allow people to bond with their national heritage. Hiking in the Black Forest or the alpine Allgau might help connect Germans to the landscape and reconnect them to the traditional costumes and folkways of rural Germany. As Kristin Semmens argues, most studies of the Nazi misappropriation of the past ignore the displays of history aimed toward tourists at Germany’s heritage sites. Many museums and historic sites twisted their interpretations to fit the Nazi present. 37 In ways that foreshadowed the 1980s British left’s critique of heritage, fascist regimes made use of heritage tourism to control society. After the war, a vigorous program of denazification was undertaken to remove public relics of the Nazi regime and in formerly occupied territories, as was a program of reconstruction. In the communist east, blaming the Nazis for the destruction of German heritage was an ideological gift. It allowed the communist regime to establish itself as the true custodian of German identity and heritage. 38 In the capitalist west, tourism revived quickly. By early 1947, thirteen new tourist associations were active in the Allied occupation zone. Tourism rhetoric in the postwar years attempted to distance German heritage from the Nazi regime to reintroduce foreign travelers to the “real Germany.” Despite this objective, Alon Confino notes that traces of the Nazi past can be located in postwar tourist promotions that highlighted Nazi-era infrastructure. 39
Postwar Heritage Tourism
As tourism became a more global industry, thanks in no small part to the advent of affordable air travel in the postwar era, heritage tourism became transnational. Ethnic heritage tourism became more important, and diaspora or roots tourism, which brought second- and third-generation migrants back to the original home of their ancestors, accelerated. Commodifying ethnic heritage has been one of the most distinctive developments in twenty-first century tourism. Ethnic heritage tourism can involve migrants, their children, or grandchildren returning to their “home” countries as visitors. In this form of tourism, the “heritage” component is thus expressed in the motivations and self-identifications of the traveler. It involves a sense of belonging that is rooted in the symbolic meanings of collective memories, shared stories, and the sense of place embodied in the physical locations of the original homeland. Paul Basu has extensively studied the phenomenon of “roots tourism” among the descendants of Scottish Highlanders. He suggests that in their trips to Scotland to conduct genealogical research, explore sites connected to their ancestors, or sites connected to Scottish identity, they construct a sense of their heritage as expatriate Scots. 40 Similar “return” movements can be found in the migrant-descended communities of many settler colonial nations. For second-generation Chinese Americans visiting China, their search for authentic experiences mirrored those of other tourists. Yet, travel to their parents’ homeland strengthened their sense of family history and attachment to Chinese cultures. 41 On the other hand, Shaul Kellner examines the growing trend of cultivating roots tourism through state-sponsored homeland tours. In Tours that Bind , Kellner explores the State of Israel and American Jewish organizations’ efforts to forge a sense of Israeli heritage among young American Jews. However, Kellner cautions, individual experiences and human agency limit the hosts’ abilities to control the experience and thus control the sense of heritage. 42
Leisure tourism also played a role in developing heritage sites, as travelers to sunshine destinations began looking for more interesting side trips. Repeating the battlefield tourism of a century before, by the 1970s access to historic and prehistoric sites made it possible to add side trips to beach vacations. Perhaps the best example of this was the development of tourism to sites of Mayan heritage by the Mexican government in the 1970s. The most famous heritage sites, at least for Westerners, were the Mayan sites of Yucatan. First promoted as destinations by the American travel writer John Lloyd Stephens in the 1840s, their relative inaccessibility (as well as local political instabilities) made them unlikely tourist attractions before the twentieth century. By 1923, the Yucatan government had opened a highway to the site of the Chichén Itzá ruins, and local promoters began promotions in the 1940s. It was not until after the Mexican government nationalized all archaeological ruins in the 1970s that organized tours from Mexican beach resorts began to feature trips to the ruins themselves. 43
Mexico’s interest in the preservation and promotion of its archaeological relics coincided with one of the most important developments in heritage tourism in the postwar years: the emergence of the idea of world heritage. The idea was formalized in 1972 with the creation of UNESCO’s designation of World Heritage Sites. The number of sites has grown from the twelve first designated in 1978 to well over 1,000 in 167 different countries. In truth, the movement toward recognizing world heritage began with the Society for the Protection of Ancient Buildings, which did not limit its activities to preserving only England’s architectural heritage. Out of its advocacy, European architects and preservationists drafted a series of accords, such as the Athens Charter of 1931, and the later Venice Charter of 1964, both of which emerged from a growing sense of cultural internationalism. These agreements set guidelines for the preservation and restoration of buildings and monuments. What UNESCO added was the criterion of Outstanding Universal Value for the designation of a place as world heritage. It took until 1980 to work out the first iteration of Outstanding Universal Value and the notion has never been universally accepted, although UNESCO member countries adhere to it officially. Once a site has been named to the list, member countries are expected to protect it from deterioration, although this does not always happen. As of 2018, 54 World Heritage Sites are considered endangered. This growth mirrored the massive expansion of tourism as a business and cultural phenomenon in the late twentieth century. As tourism became an increasingly important economic sector in de-colonizing states of Asia and Latin America, governments became more concerned with its promotion by seeking out World Heritage designation.
Ironically, World Heritage designation itself has been criticized as an endangerment of heritage sites. Designation increases the tourist appeal of delicate natural environments and historic places, which can lead to problems with maintenance. Designation also affects the lives of people living within the heritage destination. Luang Prabang, in Laos, is an interesting example. Designated in 1995 as one of the best-preserved traditional towns in Southeast Asia, it represents an architectural fusion of Lao temples and French colonial villas. UNESCO guidelines halted further development of the town, except as it served the tourist market. Within the designated heritage zone, buildings cannot be demolished or constructed, but those along the main street have been converted to guest houses, souvenir shops, and restaurants to accommodate the growing tourist economy. Critics claim this reorients the community in non-traditional ways, as locals move out of center in order to rent to foreign tourists. 44 While heritage tourism provided jobs and more stable incomes, it also encouraged urban sprawl and vehicle traffic as local inhabitants yielded their town to the influx of foreign, mostly Western, visitors.
Heritage tourism may hasten the pace of change by making destinations into attractions worth visiting. To accommodate the anticipated influx of global tourists, Luang Prabang airport was renovated and its runway extended to handle larger jets in between 2008 and 2013. The influx of tourists at Machu Picchu in Peru has repeatedly led the Peruvian government to attempt to control access to the site, yet dependent on tourism’s economic contribution, such restrictions are difficult. The temple at Borobudur in Indonesia undergoes near continuous maintenance work to repair the wear and tear caused by thousands of tourists walking its steps every day. Indeed, the preserved ruins are said to be under greater threat than when they were discovered in the early nineteenth century, overgrown by the jungle.
Another colonial aspect of world heritage designation stems from the narratives of the sites themselves. Many critics accuse UNESCO of a Eurocentric conception of Outstanding Universal Value and world heritage. 45 Cultural heritage destinations in non-Western countries are often associated with sites made famous by the projects of European imperialism. The fables of discovering ancient ruins, for instance, prioritize the romance of discovery. Many of the most famous non-Western sites were “discovered” by imperial agents in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. Angkor Wat in Cambodia was introduced to the world by the French explorer Henri Muhot in 1860. Machu Picchu, the Mayan sites of Yucatan, and the ancestral Anasazi sites of the American southwest were excavated, in some cases purchased, and their narratives constructed by American and European adventurers. The cultural relics of these ancient places were looted and assembled in Western museums, the stories of adventure and discovery published for Western audiences, and eventually a travel infrastructure was established to bring mostly Western tourists to the destinations. Western tourism thus forms another kind of imperialism, as the heritage of a destination is determined to suit the expectations and motivations of the visitors. This tends to obscure other features of local history, leaving those features of heritage not suitable to the tourist trade less valuable.

Made or Experienced?
Heritage is both made and experienced. Critics of heritage tourism rightly point to the ways in which heritage promotions can manipulate the past to defend specific ideological or commercial values. Yet, at the same time, heritage experiences are honestly felt and fundamental in the shaping of modern national or cultural identities. Thus, the questions of what constitutes “heritage” in a tourist attraction and whether or not the experience is “authentic” are fundamentally connected and contradictory. Neither heritage nor authenticity can be separated from both the process of their construction and the motivations and expectations of visitors. This makes heritage tourism a slippery subject for study. It involves numerous contradictions and complications. Indeed, contradiction and dissonance are at the heart of any notion of heritage tourism; what might be heritage for some is merely leisure and consumption for others. The dissonance comes from this dichotomy: the consumer exploitation of a destination that is held by many to have sacred properties. Yet, as this chapter suggests, the construction of those sacred properties is at times dependent on the consumer culture of the tourism industry.
Further Reading
Ashworth, Gregory J. , and John E. Tunbridge . The Tourist-Historic City: Retrospect and Prospect of Managing the Heritage City . London: Routledge, 2001 .
Google Scholar
Google Preview
Basu, Paul. Highland Homecomings: Genealogy and Heritage Tourism in the Scottish Diaspora . London: Routledge, 2006 .
Dearborn, Lynne M. , and John C. Stallmeyer . Inconvenient Heritage: Erasure and Global Tourism in Luang Prabang . Walnut Creek, CA: Left Coast Press, 2010 .
Hall, Melanie , ed. Towards World Heritage: International Origins of the Preservation Movement, 1880–1930 . Farnham: Ashgate, 2011 .
Hewison, Robert. The Heritage Industry: Britain in a Climate of Decline . London: Methuen, 1987 .
Harrison, Rodney. Heritage: Critical Approaches . New York: Routledge, 2013 .
Kirshenblatt-Gimblett, Barbara. Destination Culture: Tourism, Museums, and Heritage . Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 1998 .
Lowenthal, David. The Past Is a Foreign Country: Revisited . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2015 .
Miles, Stephen. The Western Front: Landscape, Tourism and Heritage . Barnsley: Pen and Sword, 2017 .
Macdonald, Sharon. Memorylands: Heritage and Identity in Europe Today . London: Routledge, 2013 .
Park, Hyung Yu. Heritage Tourism . London: Routledge, 2014 .
Shaffer, Marguerite S. See America First: Tourism and National Identity, 1880–1940 . Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution Press, 2001 .
Schama, Simon. Landscape and Memory . New York: Alfred A Knopf, 1995 .
Sears, John F. Sacred Places: American Tourist Attractions in the Nineteenth Century . Amherst, MA: University of Massachusetts Press, 1998 .
Timothy, Dallen J. Cultural Heritage and Tourism: An Introduction . Bristol: Channel View, 2011 .
Winter, Tim. Post-Conflict Heritage, Postcolonial Tourism: Culture, Politics and Development at Angkor . London: Routledge, 2007 .
1 Peter J. Larkham , “Heritage As Planned and conserved,” in Heritage, Tourism and Society , ed. David T. Herbert (London: Mansell, 1995), 85 ; Peter Johnson and Barry Thomas , “Heritage As Business,” in Heritage, Tourism and Society , ed. David T. Herbert (London: Mansell, 1995), 170 ; David Lowenthal , The Heritage Crusade and the Spoils of History (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1998), 94.
2 David C. Harvey , “The History of Heritage,” in Ashgate Research Companion to Heritage and Identity , eds. Brian Graham and Peter Howard (Aldershot: Ashgate, 2008), 22.
3 Deepak Chhabra , Robert Healy , and Erin Sills , “Staged Authenticity and Heritage Tourism,” Annals of Tourism Research 30, no. 3 (2003): 702–719.
4 Tomaz Kolar and Vesna Zabkar , “A Consumer-Based Model of Authenticity: An Oxymoron or the Foundation of Cultural Heritage Marketing?” Tourism Management 31, no. 5 (2010): 652–664.
5 John Tunbridge and Gregory Ashworth , Dissonant Heritage: The Management of the Past as a Resource in Conflict (Chichester: J. Wiley, 1996), 10–13.
6 See Lowenthal, The Heritage Crusade and the Spoils of History ; Robert Hewison , The Heritage Industry: Britain in a Climate of Decline (London: Methuen London, 1987) ; Patrick Wright , On Living in an Old Country: The National Past in Contemporary Britain (London: Verso, 1985).
7 John A. Jakle , The Tourist: Travel in Twentieth-Century North America (Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press, 1985).
8 John F. Sears , Sacred Places: American Tourist Attractions in the Nineteenth Century (Amherst, MA: University of Massachusetts Press, 1998).
9 Patricia Jasen , Wild Things: Nature, Culture, and Tourism in Ontario, 1790–1914 (Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 1995).
10 Simon Schama , Landscape and Memory (New York: Alfred A Knopf, 1995), 6–19 ; Pamela J. Stewart and Andrew Strathan (eds.), Landscape, Memory and History: Anthropological Perspectives (London and Sterling: Pluto, 2003), 2–3.
11 David Lowenthal , “European and English Landscapes as National Symbols,” in Geography and National Identity , ed. David Hoosen (Oxford: Blackwell, 1994), 21–24 ; and David Lowenthal , “Landscape as Heritage,” in Heritage: Conservation, Interpretation and Enterprise , eds. J. D. Fladmark (London: Routledge, 1993), 10–11.
12 Katherine Grenier , Tourism and Identity in Scotland, 1770–1914: Creating Caledonia (London: Routledge, 2005), 5–11.
13 Patrick Young , Enacting Brittany: Tourism and Culture in Provincial France, 1871–1939 (Farnham; Burlington: Ashgate, 2012).
14 Christopher Chippindale , “The Making of the First Ancient Monuments Act, 1882, and Its Administration Under General Pitt-Rivers,” Journal of the British Archaeological Association 86 (1983): 1–55 ; Tim Murray , “The History, Philosophy, and Sociology of Archaeology: The Case of the Ancient Monuments Protection Act (1882),” in Histories of Archaeology: A Reader in the History of Archaeology , eds. Tim Murray and Christopher Evans (New York: Oxford University Press, 2008), 145–176.
National Trust Act, 1907 . 7 Edward 7, Ch cxxxvi, first schedule.
Other countries developed similar programs, especially after World War II: Australia, 1947; United States, 1949; Japan, 1964; and Italy, 1975.
17 Bosse Sundin , “Nature as Heritage: The Swedish Case,” International Journal of Heritage Studies 11, no. 1 (2005): 9–20.
18 Tait Keller , Apostles of the Alps: Mountaineering and Nation Building in Germany and Austria, 1860–1939 (Chapel Hill, NC: UNC Press Books, 2015).
19 See Karl Baedeker , The Eastern Alps, Including the Bavarian Highlands, The Tyrol, Salzkammergut, Styria, and Carinthia (Leipsic: K. Baedeker, 1879).
20 Eric Zuelow , A History of Modern Tourism (New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2016), 108–109.
21 M. D. Merrill (ed.), Yellowstone and the Great West: Journals, Letters, and Images from the 1871 Hayden Expedition (Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press, 2003), 210–211.
22 Alan Gordon , Making Public Pasts: The Contested Terrain of Montreal’s Public Memories (Montreal: McGill-Queen’s University Press, 2001).
23 John Sandlos , “Nature’s Playgrounds: The Parks Branch and Tourism Promotion in the National Parks, 1911–1929,” in A Century of Parks Canada, 1911–2011 , ed. Claire Elizabeth Campbell (Calgary: University of Calgary Press, 2011).
24 Stephen Pyne , How the Canyon Became Grand (New York: Viking, 1998), 25–26, 55–60 ; J. W. Powell , The Exploration of the Colorado River and Its Canyons (New York: Dover Press, 1875).
25 Linda Rancourt , “Cultural Celebration,” National Parks 80, no. 1 (2006): 4.
26 Charles Wilson , The Myth of Santa Fe: Creating a Modern Regional Tradition (Albuquerque, NM: University of New Mexico Press, 1997).
27 Ian McKay and Robin Bates , In the Province of History: The Making of the Public Past in Twentieth-Century Nova Scotia (Montreal: McGill-Queen’s University Press, 2010), 71–129.
28 Thomas A. Chambers , Memories of War Visiting Battlegrounds and Bonefields in the Early American Republic (Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press 2012).
29 See Alan Gordon, “Where Famous Heroes Fell: Tourism, History, and Liberalism in old Quebec,” 58–81 and J. I. Little , “In Search of the Plains of Abraham: British, American, and Canadian Views of a Symbolic Landscape, 1793–1913,” in Remembering 1759: The Conquest of Canada in Historical Memory , eds. Phillip Buckner and John G. Reid (Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2011), 82–109.
30 John S. Patterson , “A Patriotic Landscape: Gettysburg, 1863–1913,” Prospects 7 (1982): 315–333.
31 David Lloyd , Battlefield Tourism: Pilgrimage and the Commemoration of the Great War in Britain, Australia and Canada, 1919–1939 (Oxford and New York: Berg, 1998), 100–111.
Lloyd, Battlefield Tourism , 98–100.
33 George Humphrey Yetter , Williamsburg Before and After: The Rebirth of Virginia’s Colonial Capital (Colonial Williamsburg, 1988), 49–52 ; Stephen Conn , Museums and American intellectual life, 1876–1926 (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2000), 155.
34 Raymond B. Fosdick , John D. Rockefeller Jr.: A Portrait (New York: Harper, 1956), 356–357.
35 Michael Wallace , “Visiting the Past: History Museums in the United States,” in A Living History Reader , ed. Jay Anderson (Nashville: American Association of State and Local History, 1991), 190.
36 Alan Gordon , Time Travel: Tourism and the Rise of the Living History Museum in Mid-Twentieth-Century Canada (Vancouver: UBC Press, 2016), 65–70 ; Ben Bradley , “The David Thompson Memorial Fort: An Early Outpost of Historically Themed Tourism in Western Canada,” Histoire sociale/Social History 49, no. 99 (2016): 409–429.
37 Kristen Semmens , Seeing Hitler’s Germany: Tourism in the Third Reich (Basingstoke and New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2005).
38 Gregory Ashworth and Peter Larkham , “A Heritage for Europe: The Need, the Task, the Contribution,” in Building a New Heritage , ed. Gregory Ashworth and Peter Larkham (London: Routledge, 1994), 127–129.
39 Alon Confino , “Traveling as a Culture of Remembrance: Traces of National Socialism in West Germany, 1945–1960,” History & Memory 12, no. 2 (2000): 92–121.
40 See, for example, Paul Basu , Highland Homecomings: Genealogy and Heritage Tourism in the Scottish Diaspora (London: Routledge, 2007).
41 Huang, Wei-Jue , Gregory Ramshaw , and William C. Norman . “Homecoming or Tourism? Diaspora Tourism Experience of Second-Generation Immigrants,” Tourism Geographies 18, no. 1 (2016): 59–79.
42 Shaul Kelner , Tours That Bind: Diaspora, Pilgrimage, and Israeli Birthright Tourism (New York: New York University Press, 2010).
43 Dina Berger , The Development of Mexico’s Tourism Industry: Pyramids by Day, Martinis by Night (New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2006).
44 See, for example, Dawn Starin , “Letter From Luang Prabang: World Heritage Designation, Blessing or Curse?” Critical Asian Studies 40, no. 4 (December 2008): 639–652.
45 Tim Winter , “Heritage Studies and the Privileging of Theory,” International Journal of Heritage Studies 20, no. 5 (2014): 556–572.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Ethics, culture and social responsibility.
- Global Code of Ethics for Tourism
- Accessible Tourism
Tourism and Culture
- Women’s Empowerment and Tourism
share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
The convergence between tourism and culture, and the increasing interest of visitors in cultural experiences, bring unique opportunities but also complex challenges for the tourism sector.
“Tourism policies and activities should be conducted with respect for the artistic, archaeological and cultural heritage, which they should protect and pass on to future generations; particular care should be devoted to preserving monuments, worship sites, archaeological and historic sites as well as upgrading museums which must be widely open and accessible to tourism visits”
UN Tourism Framework Convention on Tourism Ethics
Article 7, paragraph 2
This webpage provides UN Tourism resources aimed at strengthening the dialogue between tourism and culture and an informed decision-making in the sphere of cultural tourism. It also promotes the exchange of good practices showcasing inclusive management systems and innovative cultural tourism experiences .
About Cultural Tourism
According to the definition adopted by the UN Tourism General Assembly, at its 22nd session (2017), Cultural Tourism implies “A type of tourism activity in which the visitor’s essential motivation is to learn, discover, experience and consume the tangible and intangible cultural attractions/products in a tourism destination. These attractions/products relate to a set of distinctive material, intellectual, spiritual and emotional features of a society that encompasses arts and architecture, historical and cultural heritage, culinary heritage, literature, music, creative industries and the living cultures with their lifestyles, value systems, beliefs and traditions”. UN Tourism provides support to its members in strengthening cultural tourism policy frameworks, strategies and product development . It also provides guidelines for the tourism sector in adopting policies and governance models that benefit all stakeholders, while promoting and preserving cultural elements.
Recommendations for Cultural Tourism Key Players on Accessibility
UN Tourism , Fundación ONCE and UNE issued in September 2023, a set of guidelines targeting key players of the cultural tourism ecosystem, who wish to make their offerings more accessible.
The key partners in the drafting and expert review process were the ICOMOS International Cultural Tourism Committee and the European Network for Accessible Tourism (ENAT) . The ICOMOS experts’ input was key in covering crucial action areas where accessibility needs to be put in the spotlight, in order to make cultural experiences more inclusive for all people.
This guidance tool is also framed within the promotion of the ISO Standard ISO 21902 , in whose development UN Tourism had one of the leading roles.
Download here the English and Spanish version of the Recommendations.
Compendium of Good Practices in Indigenous Tourism

The report is primarily meant to showcase good practices championed by indigenous leaders and associations from the Region. However, it also includes a conceptual introduction to different aspects of planning, management and promotion of a responsible and sustainable indigenous tourism development.
The compendium also sets forward a series of recommendations targeting public administrations, as well as a list of tips promoting a responsible conduct of tourists who decide to visit indigenous communities.
For downloads, please visit the UN Tourism E-library page: Download in English - Download in Spanish .
Weaving the Recovery - Indigenous Women in Tourism

This initiative, which gathers UN Tourism , t he World Indigenous Tourism Alliance (WINTA) , Centro de las Artes Indígenas (CAI) and the NGO IMPACTO , was selected as one of the ten most promising projects amoung 850+ initiatives to address the most pressing global challenges. The project will test different methodologies in pilot communities, starting with Mexico , to enable indigenous women access markets and demonstrate their leadership in the post-COVID recovery.
This empowerment model , based on promoting a responsible tourism development, cultural transmission and fair-trade principles, will represent a novel community approach with a high global replication potential.
Visit the Weaving the Recovery - Indigenous Women in Tourism project webpage.
Inclusive Recovery of Cultural Tourism

The release of the guidelines comes within the context of the International Year of Creative Economy for Sustainable Development 2021 , a UN initiative designed to recognize how culture and creativity, including cultural tourism, can contribute to advancing the SDGs.
UN Tourism Inclusive Recovery Guide, Issue 4: Indigenous Communities

Sustainable Development of Indigenous Tourism
The Recommendations on Sustainable Development of Indigenous Tourism provide guidance to tourism stakeholders to develop their operations in a responsible and sustainable manner within those indigenous communities that wish to:
- Open up to tourism development, or
- Improve the management of the existing tourism experiences within their communities.
They were prepared by the UN Tourism Ethics, Culture and Social Responsibility Department in close consultation with indigenous tourism associations, indigenous entrepreneurs and advocates. The Recommendations were endorsed by the World Committee on Tourism Ethics and finally adopted by the UN Tourism General Assembly in 2019, as a landmark document of the Organization in this sphere.
Who are these Recommendations targeting?
- Tour operators and travel agencies
- Tour guides
- Indigenous communities
- Other stakeholders such as governments, policy makers and destinations
The Recommendations address some of the key questions regarding indigenous tourism:

Download PDF:
- Recommendations on Sustainable Development of Indigenous Tourism
- Recomendaciones sobre el desarrollo sostenible del turismo indígena, ESP
UN Tourism/UNESCO World Conferences on Tourism and Culture
The UN Tourism/UNESCO World Conferences on Tourism and Culture bring together Ministers of Tourism and Ministers of Culture with the objective to identify key opportunities and challenges for a stronger cooperation between these highly interlinked fields. Gathering tourism and culture stakeholders from all world regions the conferences which have been hosted by Cambodia, Oman, Türkiye and Japan have addressed a wide range of topics, including governance models, the promotion, protection and safeguarding of culture, innovation, the role of creative industries and urban regeneration as a vehicle for sustainable development in destinations worldwide.
Fourth UN Tourism/UNESCO World Conference on Tourism and Culture: Investing in future generations. Kyoto, Japan. 12-13 December 2019 Kyoto Declaration on Tourism and Culture: Investing in future generations ( English, French, Spanish, Arabic, Russian and Japanese )
Third UN Tourism/UNESCO World Conference on Tourism and Culture : For the Benefit of All. Istanbul, Türkiye. 3 -5 December 2018 Istanbul Declaration on Tourism and Culture: For the Benefit of All ( English , French , Spanish , Arabic , Russian )
Second UN Tourism/UNESCO World Conference’s on Tourism and Culture: Fostering Sustainable Development. Muscat, Sultanate of Oman. 11-12 December 2017 Muscat Declaration on Tourism and Culture: Fostering Sustainable Development ( English , French , Spanish , Arabic , Russian )
First UN Tourism/UNESCO World Conference’s on Tourism and Culture: Building a new partnership. Siem Reap, Cambodia. 4-6 February 2015 Siem Reap Declaration on Tourism and Culture – Building a New Partnership Model ( English )
UN Tourism Study on Tourism and Intangible Cultural Heritage
The first UN Tourism Study on Tourism and Intangible Cultural Heritage provides comprehensive baseline research on the interlinkages between tourism and the expressions and skills that make up humanity’s intangible cultural heritage (ICH).

Through a compendium of case studies drawn from across five continents, the report offers in-depth information on, and analysis of, government-led actions, public-private partnerships and community initiatives.
These practical examples feature tourism development projects related to six pivotal areas of ICH: handicrafts and the visual arts; gastronomy; social practices, rituals and festive events; music and the performing arts; oral traditions and expressions; and, knowledge and practices concerning nature and the universe.
Highlighting innovative forms of policy-making, the UN Tourism Study on Tourism and Intangible Cultural Heritage recommends specific actions for stakeholders to foster the sustainable and responsible development of tourism by incorporating and safeguarding intangible cultural assets.
UN Tourism Study on Tourism and Intangible Cultural Heritage
- UN Tourism Study
- Summary of the Study
Studies and research on tourism and culture commissioned by UN Tourism
- Tourism and Culture Synergies, 2018
- UN Tourism Study on Tourism and Intangible Cultural Heritage, 2012
- Big Data in Cultural Tourism – Building Sustainability and Enhancing Competitiveness (e-unwto.org)
Outcomes from the UN Tourism Affiliate Members World Expert Meeting on Cultural Tourism, Madrid, Spain, 1–2 December 2022
UN Tourism and the Region of Madrid – through the Regional Ministry of Culture, Tourism, and Sports – held the World Expert Meeting on Cultural Tourism in Madrid on 1 and 2 December 2022. The initiative reflects the alliance and common commitment of the two partners to further explore the bond between tourism and culture. This publication is the result of the collaboration and discussion between the experts at the meeting, and subsequent contributions.
Relevant Links
- 3RD UN Tourism/UNESCO WORLD CONFERENCE ON TOURISM AND CULTURE ‘FOR THE BENEFIT OF ALL’
Photo credit of the Summary's cover page: www.banglanatak.com
Journal of Heritage Tourism
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 26 October 2020
- pp 6197–6198
- Cite this reference work entry

- Dallen J. Timothy 2
22 Accesses
Introduction
Tourism based on living traditions, built heritage resources, and intangible culture is one of the most pervasive forms of tourism. It involves many different resources, and people’s motivations for visiting are manifold (McKercher and du Cros 2014 ; Timothy 2011 ). Many places depend almost entirely upon the cultural past for their tourism-based economies, resulting in many political, social, ecological, and fiscal implications (Timothy 2011 , 2016 ). This condition has resulted in considerable academic interest in heritage tourism since the late 1980s. While cultural/heritage tourism specialists have published for many years in a wide array of social science journals, the Journal of Heritage Tourism (JHT) was established in 2006 to provide an international, peer-reviewed outlet for the dissemination of scholarly research specific to this subfield. JHT publishes full-length research articles, shorter pieces/research notes, and book reviews of tomes relevant to all aspects of...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
McKercher, Bob, and Hilary du Cros. 2014. Cultural tourism . 2nd ed. London: Routledge.
Google Scholar
Timothy, Dallen J. 2011. Cultural heritage and tourism: An introduction . Bristol: Channel View Publications.
Timothy, Dallen J., ed. 2016. Heritage cuisines: Traditions, identities and tourism . London: Routledge.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Community Resources and Development, Arizona State University, Phoenix, AZ, USA
Dallen J. Timothy
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Dallen J. Timothy .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
College of Humanities, Arts and Social Sciences, Flinders University, Adelaide, SA, Australia
Claire Smith
Section Editor information
Department of Archaeology, Silpakorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
Thanik Lertcharnrit
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Timothy, D.J. (2020). Journal of Heritage Tourism. In: Smith, C. (eds) Encyclopedia of Global Archaeology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-30018-0_1244
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-30018-0_1244
Published : 26 October 2020
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-30016-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-30018-0
eBook Packages : History Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Humanities
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

- GENERAL TRAVEL

Heritage Travel: What it is & How it Can Benefit You

Madison Jackson lives in Pittsburgh, PA and is the Director of Jewish Student Life at Carne...
- button]:border-none [&>button]:bg-white [&>button]:hover:cursor-pointer [&>button]:hover:text-cyan-400"> button]:hover:text-cyan-400 [&>button]:bg-white hover:cursor-pointer" height="1em" width="1em" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
Door post after door post was pointed out to me. We stopped in a court yard that had tenement style houses surrounding it on all sides. We stepped inside what seemed nothing more than a run down, dingy entrance looking practically near collapse. Peering closely at the entrances, I saw an empty carved out space, diagonal in the shape of a mezuzah (a scroll with Hebrew verses on it from the Torah, inside a decorated case). I saw two circles placed perfectly across from each other, showing where once a mezuzah had hung.

Learn about your family history & heritage while doing programs abroad—you’ll love the experience!
This was Praga. Located across the Vistula River opposite Warsaw’s Old Town, this area, sometimes referred to as “alternative Warsaw,” has been called dangerous. But, in years past, this was also the home of Warsaw’s Jews. As a Jew myself, I didn’t expect to learn about this place while interning abroad in Warsaw—a place where the majority of my people once lived. We walked through Praga and our tour guide pointed out different types of traces on doorposts of former Jewish family homes. Unlike the rest of the city, this area was barely destroyed during the war, leaving the homes of families in tact and the authentic representation of Jewish life in Warsaw prior to the war still in existence.
Exploring the mezuzah traces through heritage travel allowed me to learn the stories of Jewish families who had lived in Warsaw, not from the structure of something that was rebuilt, but from the actual traces of what remained.
There’s never been a better time to participate in heritage travel—and participating in historical travel during travel programs abroad just makes sense. Read on to learn how YOU can incorporate heritage tourism into your next great international adventure, like I did.
FAQs on heritage travel

Get up close and personal with hundreds of years of history.
What is Heritage Tourism?
According to the National Trust for Historic Preservation, Heritage Tourism is “traveling to experience the places, artifacts and activities that authentically represent the stories and people of the past and present. It includes cultural, historic, and natural resources.” In other words, Heritage Tourism is a type of travel where you search for an authentic understanding of how something, or a people, was like.
The three main types of Heritage Tourism sites are natural, cultural, and built. Natural heritage sites include landforms and rural scenery, cultural heritage tourism involves attending festivals or a place that sells traditional products, and built heritage sites encompass places such as monuments and historic homes. Through studying, volunteering, interning and teaching abroad there are several different ways in which you can engage with the different types of historic travel and heritage tourism.
- Study Abroad . Studying abroad provides a unique opportunity to live what you are studying. For example, instead of sitting in school reading about the Holocaust, if you study abroad in Europe, your classroom becomes your surroundings and you can visit places from a textbook firsthand. You can walk on the natural grounds where your ancestors once lived and enter still standing historic synagogues and other places of worship. Study abroad is a great time to explore cultural heritage tourism!
- Volunteer Abroad . Protecting special places is valuable to humanity. If you hope to spend time volunteering abroad maybe consider volunteering on a conservation project anywhere in the world, that assists in protecting a heritage site for generations of travelers to come. This type of volunteering will be beneficial as it ensures that heritage travel can continue to provide meaningful experiences for others.
- Intern Abroad . During my time doing an internship in Warsaw, I went with the office I worked for to a cemetery clean up at the Jewish cemetery in Warsaw, to a day of memorial ceremonies in Jedwabne, Poland at seven different memorials, and on a bike ride from the gates of Auschwitz-Birkenau to the Jewish Community Center in Krakow. Naturally, internships you do abroad will come with similar opportunities to visit heritage sites as part of your work hours. Additionally, you can take advantage of your temporary backyard to spend weekends traveling to visit heritage sites and learning as much as possible about the people who live or lived in the country you are working in. You will benefit from seeing a full dimension view of the country.
- Teach Abroad . You can learn about your own heritage by fully integrating into a local community! In teaching abroad you can craft your own experience by specifically signing up for an English teaching program that places you with indigenous people at a heritage site. There, you can preserve their culture and help to sustain their local environment, while also getting to know your own family history through cultural heritage tourism.
Who participates in heritage travel?

Add more context to some of those random traditions grandma forces around the holidays.
Anyone and everyone with a desire to learn can participate in heritage travel! People of all ages and backgrounds can think about doing heritage tourism during short school breaks, gap years, or family trips.
Popular examples of heritage tourism involve religious travel or pilgramages. For instance, many Catholic students might enjoy visiting the Vatican while studying abroad in Italy, or some Muslim volunteers might tack on a hajj to Mecca while volunteering abroad in the Middle East. If you're a first generation immigrant from Latin America or East Asia, you might double-dip your internship abroad to learn your family's native tongue or get to know your family's culture or history in a new way. As a Jewish student abroad, I was keen to learn more about Jewish history—visiting pre-war synagogues and learning the stories of Jewish families past.
The major benefits of heritage travel
1. memorability.
Whenever you return from a trip, you are bound to face the question: So, what did you do on your trip? Usually, people are looking for more than just a general answer, but want an example of something specific you experienced and why you enjoyed it. Heritage travel will provide you with an instant, and ongoing, answer! Travelers say that trips with heritage activities are more memorable than trips without them, because they learn something concrete and new.
2. Strengthens local economies

Heritage tourism isn’t always pretty, but it always has an important impact.
A study conducted by the Travel Industry Association showed that heritage travelers spend more time and money at their destinations than other types of travelers. This helps to develop sustainable local economies which often don’t get as much popularity as large tourist attractions. Visiting heritage sites creates jobs in local organizations while simultaneously promoting community pride through the opportunities locals have to work together to improve cultural development.
3. Diversifies the tourism experience
Relaxing at the beach is nice, but think how many more stories there are to tell when there is content and substance involved in a trip. Beyond the traditional ocean and sand vacation, heritage travel allows you to expand your horizons and spread the places people visit beyond a few locations.
4. Reinforces identity and creates understanding
Heritage tourism provides a whole new angle to traveling and can make an experience both fun and educational. You can learn more about yourself, your ancestors, and people of your race, religion, or culture, while also learning more about cultures and backgrounds different than your own. What we learn in a classroom can be difficult to understand; when you interact with sites in person you have the opportunity to really comprehend what a specific identity means.

You might even find new things to love and appreciate about your personal history!
5. Increases your learning capacity—especially when done in conjunction with a program abroad
The best part of formal programs abroad isn’t that your itinerary is taken care of (although being free of planning those logistics IS pretty great!), it’s the fact that you have the right container for doing deep thinking and reflecting on what you’re learning. Instead of just witnessing and observing during culture heritage tourism, a program abroad might be able to offer you a stronger framework to participate in the culture. Translating interactions into hard-won lessons is much easier with the help of a trusty mentor or dedicated time for reflection.
That’s why pairing heritage tourism with a program abroad can be a win-win on all fronts!
Walk the footsteps of your family

Get to know yourself—and your family—on a whole new level through heritage travel.
Soon, I started looking for mezuzah traces wherever I went in Europe. I didn't want to ever again walk by a place that had so many hidden stories—that could have been my relatives’ home, or the home of my friends grandparents. Each mezuzah trace told a story that came to life through the Jewish item.
Looking for mezuzah traces throughout Europe was just one way I was able to connect to the heritage of the Jewish people and learn what Jewish life was like in countries prior to World War II. There are so many ways that heritage travel can enhance your time on programs abroad, even for a short trip, and it will make a difference in how you remember a place once you return home.
Get Matched with 5 Programs to Enhance Heritage Travel Today
KAHAL Your Jewish Home Abroad is a non-profit organization which connects Jewish students studying abroad to Jewish opportunities, resources and connections abroad. KAHAL aims to create meaningful Jewish experiences for study abroad students, allowing them to interact with local Jewish communities and deepen their Jewish identities. Wherever students travel, KAHAL arranges chances to attend Shabbat dinners, meet Jewish students, attend holiday meals, volunteer and advocate, and provides grant funding and travel assistance.

Explore Programs on GoAbroad.com
Related Articles

By GoAbroad Writing Team | 6 days ago

By Megan Lee | 6 days ago

By Sydney E. Lutz | 6 days ago

By Lauren Kubik | 6 days ago
Popular Searches
Study abroad programs in italy, study abroad programs in spain, marine biology study abroad programs, study psychology abroad, fall study abroad 2024, spring study abroad programs, recommended programs.

1686 reviews
International Volunteer HQ [IVHQ]

1961 reviews
MAXIMO NIVEL

564 reviews
Intern Abroad HQ

2731 reviews
African Impact
For Travelers
Travel resources, for partners.

© Copyright 1998 - 2024 GoAbroad.com ®
- Study Abroad
- Volunteer Abroad
- Intern Abroad
- Teach Abroad
- TEFL Courses
- Degrees Abroad
- High School Abroad
- Language Schools
- Adventure Travel
- Jobs Abroad
- Online Study Abroad
- Online Volunteer Programs
- Online Internships
- Online Language Courses
- Online Teaching Jobs
- Online Jobs
- Online TEFL Courses
- Online Degree Programs
Select your language
Official eu languages.
- slovenščina
Culture and Creativity
Sustainable cultural tourism

Europe’s cultural heritage is a valuable resource in the fields of tourism, education, employment and sustainable development. Sustainable cultural tourism is a vital part of regional and macro-regional development strategies. In this regard, culture is both a driver and an enabler of sustainable development.
Tourism: the balance between development and the protection of cultural heritage
Tourism is an excellent way to encourage and provide access to cultural heritage, but it also brings with it challenges related to overcrowding, cultural appropriation and the loss of authenticity. Tourism brings money and jobs to cities and regions, but it can also damage residents’ day-to-day lives, as well as the area’s culture and heritage.
Given the possible negative effects of over-tourism and its impact on cultural heritage, some local communities and heritage experts have at times opposed tourism and its associated development.
Sustainable cultural tourism offers a new perspective, as it places cultural heritage and local communities at the centre of decision-making processes.
Involving local communities and other stakeholders in the decision-making processes is key to ensuring results benefit both cultural heritage and the local population. The objective of sustainable cultural tourism is to ensure good conservation practices along with authentic interpretation that supports the local economy.
Find out more about what the European Commission is doing to encourage sustainable cultural tourism .
Sustainable cultural tourism Open Method of Coordination working group
The Work Plan for Culture adopted by EU Member States for the period 2015-2018 included a working group composed of European experts on sustainable cultural tourism under the Open Method of Coordination approach.
The resulting report includes the first definition of sustainable cultural tourism, as well as recommendations and guidelines for policymakers and 27 case studies illustrating best practices in both tangible and intangible cultural heritage.
Read the Sustainable cultural tourism report .
Selected projects
Spot project.
Funded under the Horizon 2020 programme, this project aims to develop a new approach to understanding and addressing cultural tourism and to promote the development of disadvantaged areas.
Find out more about the SPOT project .
SmartCulTour
Funded under Horizon 2020, this project supports development in European regions with important cultural assets, both tangible and intangible, through sustainable cultural tourism.
Find out more about SmartCulTour .
Funded under Horizon 2020, this project connects cultural tourism stakeholders and researchers who have new approaches and methods to support European cultural tourism. The aim of the project is to reinforce a feeling of belonging and to value minority cultures.
Find out more about the IMPACTOUR project .
The European Destinations of Excellence (EDEN)
EDEN promotes models of sustainable tourism across the EU. Through this initiative, partnering countries select and promote “destinations of excellence”.
EDEN draws attention to emerging, non-traditional European destinations, highlighting their values and character. It also works as a platform for sharing good practices between awarded destinations. The European Commission and the National Tourism Bodies choose a theme every year. Cultural tourism was the EDEN theme in 2017 .
Discover the winning destinations on the EDEN website .
Thanks for your feedback
We are happy to see that your experience was positive. Don't forget to share the pages you like with your friends and colleagues.
If you need to ask a question, please contact Europe direct .

19 Top World Heritage Sites
Written by Lana Law Updated May 11, 2023
Author Lana Law has visited many of the top World Heritage Sites on her global journeys.
For centuries, or even millennia, some of the most astounding sites of ancient times were forgotten or hidden from the world, buried under jungles, deserts, or farmers' fields around the globe. Rumors of lost cities or chance discoveries by people going about their everyday lives have led to unimaginable finds that are today open for the world to see. Many of these have been designated UNESCO World Heritage Sites.

Some of these incredible sites have been attracting tourists for hundreds of years and are as fascinating now as they were when they were first uncovered. It may be a cliché to say there has never been a better time to explore the greatest sites on the planet, but it is also true. While they're all significant, some are arguably more impressive than others.
Explore ancient wonders with our list of the best World Heritage Sites.
1. Machu Picchu, Peru
2. pyramids of giza, egypt, 3. bagan, myanmar, 4. angkor wat, cambodia, 5. great wall of china, 6. roman colosseum, italy, 7. acropolis of athens, greece, 8. stonehenge, england, 9. borobudur, indonesia, 10. mesa verde, usa, 11. terracotta army, china, 12. petra, jordan, 13. mayan ruins of tikal, guatemala, 14. lascaux and lascaux ii, france, 15. chichen itza, mexico, 16. leshan giant buddha, china, 17. easter island, 18. cappadocia, 19. taj mahal, map of world heritage sites.

Highlights : An ancient 15th-century city high in the Andes with breathtaking views
Built in lush, mountainous terrain high above the Urubamba River, Machu Picchu lies in one of the most stunning settings of any archeological site in the world. This ancient city of Incas cascades down steep walls on each side of the mountain, with terraced steps that disappear over cliff edges into the valley below.
These incredible ruins have been restored and are well-maintained, giving visitors a good indication of what the city might have looked like when it was occupied during the 15th and 16th centuries.
Many people visit Peru for the sole purpose of seeing Machu Picchu, and the journey to the ruins can be an adventure in and of itself, depending on how travelers choose to reach the site.
Adventurous souls can opt for a guided, multi-day hike and camping trip along the famous Inca Trail to reach the site, or choose the easier option of accessing the ruins by bus from the small town of Aguas Calientes at the base of the hill, which most visitors get to by train from Cusco or the Sacred Valley .

Highlights : Majestic monuments set in the desert plains speak to human ingenuity
One of the most iconic sites in the world, the Pyramids of Giza, just outside Cairo , is a surreal sight rising from the barren desert landscape. Standing guard nearby, and almost as impressive, is the Sphinx , gazing blankly out over the land.
The pyramids were built as tombs for the Pharaohs, the largest of which was constructed between 2560 and 2540 BCE. To put their age in perspective, they were already more than 2,600 years old when the Colosseum in Rome was being built. Today, these giant monuments are the sole surviving member of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World .
For a memorable experience, take a sunset camel ride in front of the pyramids, one of the top things to do in Egypt. Also, be sure to follow the inner tunnels in the Pyramid of Chephren or the Pyramid of Cheops to the burial chamber deep inside.
- Read More: Pyramids of Giza: Attractions, Tips & Tours

Highlights : Countless thousand-year-old temples spread across an enchanting landscape
Thousands of ancient temples and stupas stretch endlessly across the landscape at Bagan, where the silhouette of the temple spires against the sky in the early morning or late day is a magical sight. The area is known for having the largest concentration of Buddhist temples in the world , many of which were built in the 1000s and 1100s, when it was the capital of the Pagan Kingdom.

Some of these have been restored, and others are little more than ruins. They also range in size and level of sophistication, creating an intriguing mix of structures that make visitors want to keep exploring the site. You can tour the area on rickety old bicycles, hire a horse and cart, take a hot air balloon ride over the site, or simply hire a taxi. Each of these methods has its own appeal.
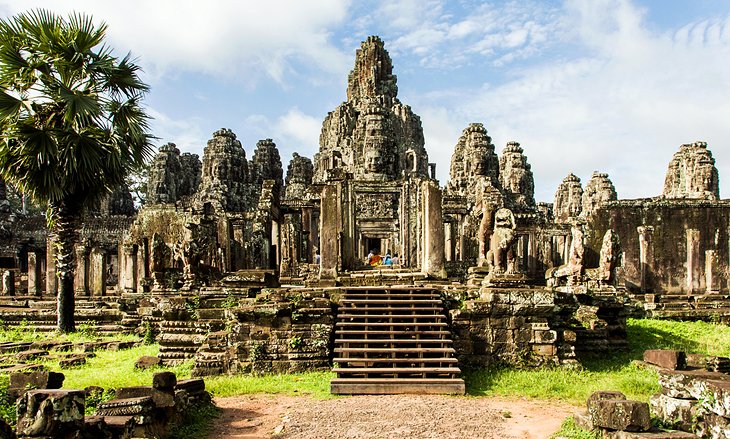

Highlights : Ruins from the 12th century showcase the architectural mastery of the ancient Khmers
In a unique jungle setting, not far from the city of Siem Reap, Angkor Wat is known for being the world's largest religious monument , but it is more than sheer size that makes the Angkor complex so interesting. The site was built by the Khmers in the 12th century, and the architecture is nothing less than stunning.
The site has an intriguing mix of excavated and unexcavated temples in varying shapes, sizes, and states of decay, with some buildings taking on a mystical appearance as they're swallowed up by trees and roots. Huge stone carved faces peer out in all directions. Extensive and intricate bas-reliefs line the walls and doorways. Crumbling passageways and steep stone stairs call out for exploration.
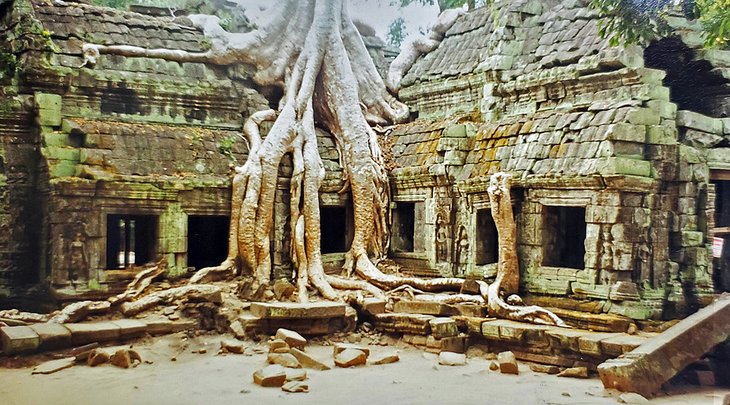

Before its fall in the 15th century, Angkor Wat was the largest city in the world. The complex is huge, and you may want to spend a couple of days taking in the site.

Highlights : Wonderful views from atop this Ming Dynasty marvel, cultural history
Stretching almost 6,000 kilometers as it snakes its way through forests and mountains, the Great Wall of China is one of those undeniable bucket list sites that have long inspired great adventures. This massive wall, connecting battlements and watchtowers, was built over the centuries, with the oldest sections dating back to the 7th century BCE.
Today, you can opt to simply visit the wall on a day trip from Beijing , or tackle whole sections of it on organized, multi-day trips. Some sections of the wall have been restored, while other sections are badly in need of repair.
The Great Wall of China is one of China's most photographed attractions.
Read More: Top-Rated Tourist Attractions in Beijing

Highlights : An iconic 50,000-seat ancient amphitheater that is a must-see when visiting Rome
One of the most recognizable structures in the world, the Roman Colosseum is the largest building remaining from Roman times . Its imposing presence in the city center of modern-day Rome is a testament to the incredible history of the city and the achievements of the Roman Empire.
Visitors popping up from the nearest subway stop or turning a corner and seeing it for the first time can't help but be stunned by its immense presence. Construction began on the structure in 72 CE, and today, it is still one of the greatest tourist attractions in the world.
The Italian Government has recently announced that the floor of the Colosseum, once the battlegrounds of brave gladiators, will be restored to its former glory. This will allow the Colosseum to be used for cultural and other special events and for visitors to imagine what it would have been like to stand and look up at the roaring crowds. This work is expected to be completed in 2023.
- Read More: Visiting the Colosseum: Highlights, Tips & Tours

Highlights : Ancient monuments dating from the 4th century BCE, fantastic views over Athens
Towering over the city of Athens from its hilltop perch, the Acropolis stands as a proud monument to Ancient Greece. Dating from between the 5th and 4th century BCE and dominating the site, the Parthenon is the largest and most recognizable structure from this period and symbolizes the extensive history of this country.
Just steps away from modern-day Athens, the Acropolis is a powerful sight, glistening in the Mediterranean sun during the day and lit for dramatic effect at night. For first-time visitors to the city, it is an awe-inspiring sight and sets the stage for travelers carrying on to other parts of Greece .
- Read More: Visiting the Acropolis in Athens: The Essential Guide

Highlights : Mysterious stones over 4,000 years old give the site a mystical air
This incredible prehistoric monument is one of the United Kingdom's most visited attractions and certainly one of its most unique places to visit, drawing huge numbers of visitors each year. The monument is thought to have been erected between 3000-1500 BCE, but there is no record of its origin or purpose, leading to all kinds of speculation and myths, some of which suggest religious or astronomical significance.
As a result, the Bronze Age ring of standing stones holds an almost mystical fascination, particularly around the summer and winter solstices, when the light from the sunrise and sunset is aligned with the stones. Located near the city of Salisbury , and not far from Bath , Stonehenge can be easily visited on a day trip from London .
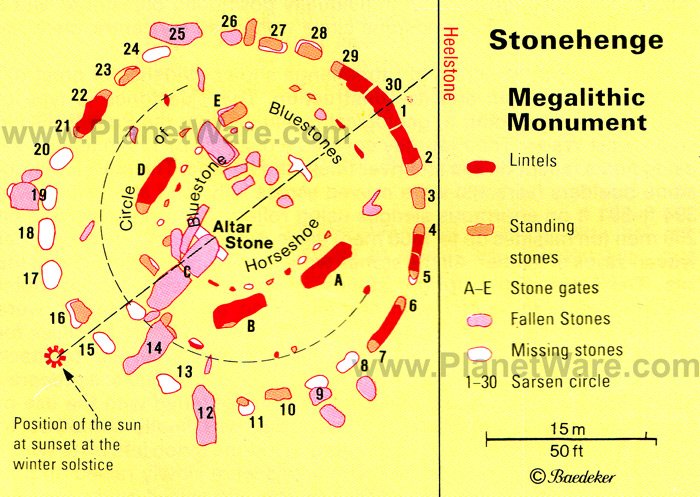
Highlights : A massive temple site nearly 1,400 years old, stunning views of volcanoes in the distance
Borobudur is one of the most important Buddhist sites in the world and certainly one of Indonesia's most famous landmarks. Set in lush, tropical surroundings, with mountains and volcanoes rising in the distance, the site is visually stunning and soothingly peaceful.
Located on the island of Java, near Yogyakarta, this massive temple complex was constructed in the 700s, but two to three hundred years later, the site was abandoned, possibly due to volcanic eruptions in the area, and went relatively undisturbed for centuries. The site was uncovered in the 1800s by the British and later restored. Today, it is one of the most important tourist attractions in Indonesia and one of the best places to photograph in the country .

Highlights : Fascinating cliff dwellings perched under massive rock ledges
Mesa Verde is home to one of the most visually stunning archeological sites in the USA and some of the most well-preserved Indian ruins in North America. The most impressive sites are the cliff dwellings tucked precariously into the canyon walls, but the entire area, including the forest-covered plateau, contains a vast array of ruins.
The Ancestral Puebloans inhabited this area of what is now Colorado for hundreds of years, living on top of the plateau between the 6th and 12th centuries and then in the cliff dwellings until the late 13th century. The drive up to the site is along a gently twisting road to the top of the mesa, where you can tour the sites on the plateau by car to see pit houses and other ruins, and enjoy stunning views of the dwellings in the canyon walls.
Those who are up for a slight physical challenge can take a guided tour through some of the cliff dwellings, climbing up ladders and exploring the site in detail.
- Read More: Exploring the Top Attractions of Mesa Verde National Park

Highlights : An incredible display of nearly 8,000 intricately carved clay warriors
Standing guard over the first emperor of China, Qin Shi Huang, the Terracotta Army is like no other archeological site in the world.
Thousands upon thousands of life-sized warriors , each with a unique face, stand in rows, where they have stood since they were buried here in the 3rd century BCE. It is estimated that some 700,000 workers were involved in the creation of the site, which is thought to have approximately 8,000 clay warriors.
The site remained undiscovered for millennia, until a farmer was digging a well in the 1970s and uncovered the treasure. Some of the site remains intentionally not excavated, but you can't help but be more than impressed by the massive army that stands before you.

Highlights : A 5,000-year-old city carved out of rose-red stone, reached via a secret passageway
A dramatic, narrow rock gorge allows entrance to the ancient city of Petra, a stone city with dwellings hewn into sandstone walls . This ancient capital city of the Nabataeans has roots that trace back to as early as the 4th or 5th century BCE. Discovered by the West in the early 1800s, it has been referred to as "the rose city" for the color of the rock, and for obvious reasons, "the carved city."
Situated in a mountainous area with limited access, it held a strategic position on an important trade route in the region. Today, Petra is the most important tourist attraction in Jordan .
Read More: Visiting Petra: Attractions, Tips & Tours

Highlights : A partially restored ancient city buried in the Guatemalan jungle with more than 3,000 structures
The ancient Mayan city of Tikal is one of the greatest archeological sites in Central America. Located in northern Guatemala and surrounded by jungle, the site comprises more than 3,000 structures from a city that existed between 600 BCE and 900 CE. Ancient pyramids, temples, plazas, and foundations of all kinds of buildings reveal a complex society that housed tens of thousands of people.
The site was rediscovered in the mid-1800s and opened to the public in the 1950s. Some of the site has been restored, but work continues, with some areas not yet mapped or excavated at all. The ruins are in Tikal National Park, a biosphere reserve protecting the forest and wildlife in the area, considered one of the best places to photograph in Guatemala

Highlights : Incredible cave artwork more than 17,000 years old
The Lascaux Cave in the Dordogne region of France contains extraordinary cave paintings , thought to be some of the finest in the world from the Paleolithic period. These detailed paintings from more than 17,000 years ago primarily depict animals that are believed to have lived here during that time frame.
The paintings were discovered in 1940 but were later recreated at an adjacent site known as Lascaux II, 200 meters away, to protect the original site from damage. Painstaking care was taken in the construction of Lascaux II to create a detailed, accurate reproduction of the original cave and the paintings.

Highlight: Mexico's best restored ancient Mayan city
In the flat jungle interior of Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula, within easy day-tripping distance of Cancun and the Mayan Riviera , is the ancient Mayan city of Chichen Itza. This great city of the Mayans was an important center from the 7th to the 13th centuries and was, for a time, the regional capital.
Today, it is one of the most well-restored Mayan sites in Mexico , offering an astounding glimpse into this culture. It is also one of Mexico's biggest tourist attractions. The huge pyramid is the most recognizable symbol of Chichen Itza, but the site is very large, with many ruins to explore.
- Read More: Visiting Chichén Itzá from Cancún: Highlights, Tips & Tours

Highlight : A giant Buddha carved into a cliff wall standing over 300 feet tall
Carved out of a red sandstone cliff wall, the Leshan Giant Buddha stands 71 meters and is the tallest stone Buddha in the world . Started by a single monk in 713 CE and completed 90 years later by his followers in 803 CE, the statue looks out over the confluence of the Minjiang, Dadu, and Qingyi Rivers. It was built with the hope that it would bestow calm waters for the boats that ply this waterway.
The statement "The mountain is a Buddha and the Buddha is a mountain" is said to be attributed to this enormous statue. You can view the Leshan Giant Buddha from very close range at either the base or near the head, each offering very different perspectives.

Highlights : Giant stone monuments from the 12th century stand as silent sentinels
Easter Island is a Chilean island in the South Pacific Ocean, famous for the giant statues known as Moais , which dot the landscape. Created by the Rapa Nui people, who are thought to have inhabited the island from the 12th century onward, hundreds of Moais are spread around the island.
Some are partially toppled, while others stand erect; some stand on ahu (stone platforms), and many still remain at the quarry where they were created. Ranging in size from a meter to 20 meters, each carving is unique and thought to symbolize an ancestor.

Highlights : 5,000-year-old caves carved out of strange rock formations, sunrise balloon tours
Perhaps one of the more bizarre World Heritage Sites, Cappadocia is a place of flowing rock formations and stone-capped chimneys that just beg to be photographed. Many of the formations are located in the Monks Valley and Goreme. Consider taking one of the many hiking trails that allow you to get up close.
Nearby, in the village of Uchisar, and equally unusual, are the ancient cave homes built by the people of the Bronze Age, some 5,000 years ago. Carved out of the soft rock, the caves were later used by Christians escaping religious persecution.
One of the highlights of a trip is a sunrise hot air balloon ride over Cappadocia . Even if you don't take a ride, the sight of a multitude of balloons rising over the crazy landscape is well worth a photo or two.

Highlights : White marble that glows and shimmers in the sun, intricate workmanship and detail work
An incredible testament to one man's love for his wife is embodied in the fantastic architecture of the Taj Mahal. Standing proudly for nearly 400 years, this site tops the list of India's tourist attractions , drawing millions each year.
Glowing white in the hot Indian sun, the marble seems to shimmer and glow in the heat and makes for beautiful photos. Up close, the intricate carving and inlaid stones are fascinating and show the level of craftsmanship that went into creating the building.
Pleasant walking trails, fountains, and gardens surround the monument. On the far side, the Yamuna River flows slowly by.
More Related Articles on PlanetWare.com

Natural World Heritage Sites: While many people think of World Heritage Sites as being cultural, UNESCO also designates Natural World Heritage Sites. For information on these, see our articles on the underwater wonders of the Great Barrier Reef in Australia or the mountainous landscape of Banff National Park in the Canadian Rockies .
In the United States , have a look at Yosemite National Park to discover one of the most famous landscapes in America, or Yellowstone National Park to discover the geysers and other geothermal attractions. Lastly, don't miss a chance to see the Grand Canyon in Arizona, or walk below the giant redwoods in Redwoods National and State Parks .

More on Peru

32 Cultural Tourism Destinations for Unique Cultural Trips
Disclaimer: This article includes affiliate links to the products we earnestly love and recommend, meaning at no extra cost to you, we might make a teeny-weeny commission if you click on the link and decide to buy something. The money will be used to sustain this little cozy blog we call our virtual home.
As a cultural traveler, I always look for unique cultural experiences wherever I travel. Do you also believe in cultural travel or immersive travel? That being so, this round-up of the very best cultural tourism destinations in the world is sure to help you plan a soulful cultural trip.
Cultural Tourism: Introduction
I’m a sucker for meaningful travel experiences. Beach vacations don’t excite me as much as cultural trips.
What exactly is a cultural trip?
To put it simply, a cultural trip is a trip with a purpose or a goal.
It’s about experiencing, understanding, appreciating, embracing, and preserving different cultures and traditions worldwide.
It’s about getting off the beaten path & stepping out of your comfort zone.
It’s about meeting natives and forming meaningful connections.
It’s about eating local delicacies and staying in homestays.
It’s about being a part of cultural events, local festivals, and rituals .
It’s about gaining knowledge or learning a new skill.
It’s about volunteering and helping local communities thrive.
It’s about challenging preconceptions and bringing in fresh perspectives.
It’s about traveling slowly, sensibly, sustainably, and responsibly, not leaving footprints, and treading a little lighter on the planet.
It’s about not just thinking about yourself but caring about the world @ large.
Culturally immersive travel is all the more important in present times to deal with the dynamic challenges of globalization and multiculturalism.
Cultural tourism is vital in preserving culture and heritage to build a beautiful world and we, as travelers, have a social responsibility to make a positive impact on the local economy, environment, and communities whenever and wherever we travel and inspire others to do that too.
To get on with it, I collaborated with seasoned cultural travelers to bring together this guide to the best cultural destinations in the world that include exciting cultural countries that put forward experiential cultural travel experiences.
Cultural Tourism Destinations for the Best Cultural Experiences in the World
Needless to say, you can have a culturally immersive travel experience anywhere and everywhere in the world.
Each destination has a culture different than yours waiting to be explored and thus, it’s tough to choose a few, however, I’ve cherry-picked the countries that catch the eye for their strong culture and heritage and intrigue a cultural tourist.
Top Cultural Tourist Destinations in Asia
Nele van Hout from The Navigatio
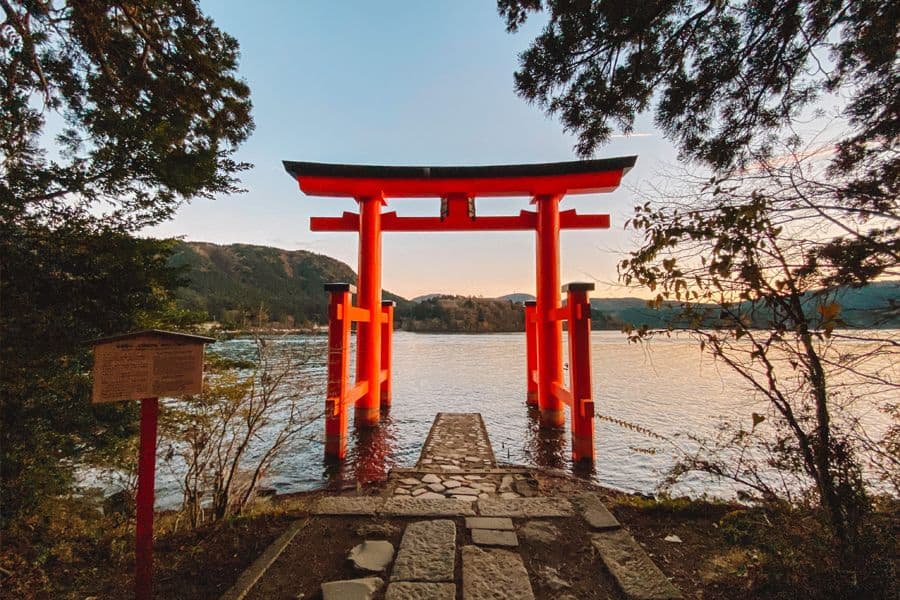

Japan is one of the most unique and culture-rich countries in the world. It’s counted as one of the leading cultural destinations in the world for a reason.
Being an island, Japan was isolated from other countries for centuries, allowing it to develop its very own unique customs and traditions.
While many influences from outside are now being introduced in the country, Japan remains a travel destination like no other.
Japan is known as a country of many contrasts. The hyper-modern side can be enjoyed in big metropolitan cities like Tokyo, where you can play video games in arcades, be checked into a hotel by a robot, sing karaoke or ride the fastest train in the world (the Shinkansen).
But it’s the traditional side where Japan really differentiates itself from the rest of the world. When visiting, you can dress up in traditional wear, the kimono, before heading over to temples there were built over a thousand years ago – some of the most famous ones can even be found inside the big cities.
In Kyoto, the cultural capital of Japan, you can still find geishas to this day – these are women dressed in kimonos wearing unique white make-up who specialize in tea ceremonies and performance arts.
Here, you can (must) also take part in an official tea ceremony . Matcha (Japanese green tea) plays a big role in Japanese culture and Kyoto is the perfect place to learn about it.
When in Japan, you should consider staying in a ryokan for at least one night. This is a traditional Japanese inn, usually equipt with tatami floors (traditional straw floors) and sometimes they even have an onsen (Japanese hot springs).
They can be found all across the country, but the city of Hakone has a lot of them , including onsen. Some even come with a view of the majestic Mount Fuji .
De Wet & Jin of the Museum of Wander

One of the top choices for cultural trips around the world, few places can compete with the cultural magnificence of China.
The country has a rich and diverse history that spans over 5,000 years, making it one of the oldest continuous civilizations in the world.
The staggering wealth of cultural heritage scattered across the country can make deciding where to go in China challenging. Whether looking for historical landmarks, tea culture , fantastic food, ancient and modern art, traditional medicine, minority cultures, or unique cultural experiences, China delivers like a few others.
First-time visitors to China can experience the best of Chinese culture and history in the capital, Beijing. Besides seeing the famous historical landmarks like the Forbidden City, the Great Wall, the Temple of Heaven, and the Summer Palace, they’ll also have many opportunities for a slice of authentic Beijing life.
Join the rest of Beijing and ride a bike along the wide and leafy bike lanes, or head to one of the parks to see people play chess, practice calligraphy or opera singing, or do ballroom dancing.
No visit to China is complete without indulging in its incredible cuisine. In Beijing, that means Peking duck. For the best roast duck in Beijing, you must not miss Quanjude restaurant.
Art lovers, collectors, or those looking for a unique souvenir from China should visit Beijing’s antique market. Panjiayuan Antique Market is home to hundreds of vendors dealing in authentic Chinese antiques and replicas – the fun is finding the difference and bargaining until the price is right.
While Beijing has accommodations to suit every budget and taste, staying in a traditional hutong courtyard hotel is best if you want to immerse yourself in the real Beijing. The Double Happiness Courtyard Hotel in the Dongcheng district is the perfect base to see and experience the local side of Beijing.
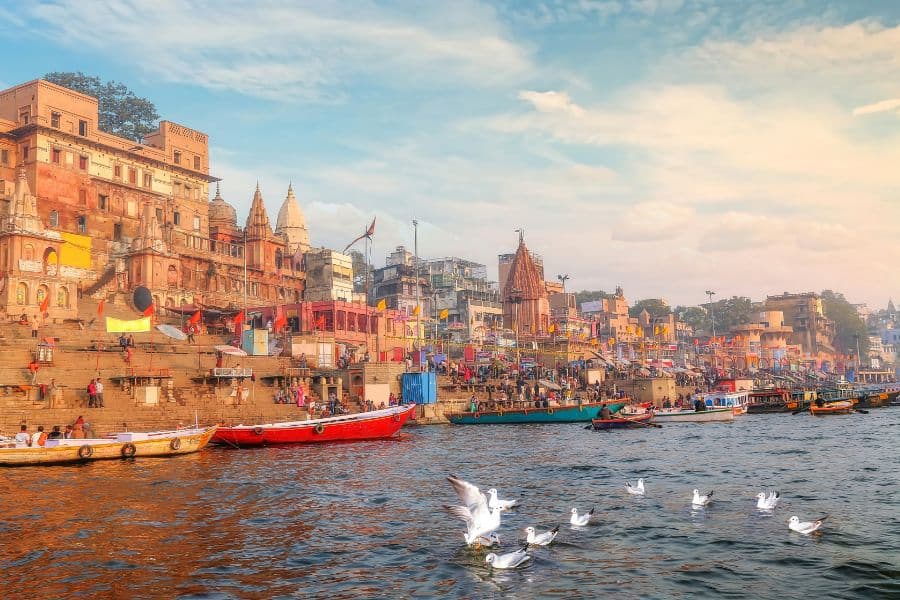

One of the oldest civilizations in the world, India has a rich, vibrant, and diverse cultural legacy that makes it the ultimate cultural tourism destination.
Over the centuries, India has been invaded several times by diverse rulers leaving an indelible mark on its cultural fabric. You can see and feel the influence of diverse cultures in architecture, traditional customs, food, dance, music, festivities, and languages. It, without a doubt, is one of the best places for culture in the world.
The Indian cultural heritage, values, and traditions have shaped the history of Asia and the world for that matter.
From ancient temples and royal palaces to majestic forts and historical monuments, the plethora of heritage sites in India showcases the cultural vitality of the country.
Each Indian state with its distinctive cultural heritage deserves a special place among beautiful cultural destinations in India, however, some states and cities take a lead for their cultural and historic stature on the world stage like Varanasi, Jaipur , Delhi , Amritsar , Madurai, Hampi, Mysore, Khajuraho, Kochi , and Rishikesh.
Among the various destinations for cultural tourism in India, Varanasi (Benaras or Kashi) is indeed the symbol of Indian culture. “Benaras is older than history, older than tradition, older even than legend, and looks twice as old as all of them put together,” penned Mark Twain.
One of the oldest living cities in the world, this sacred city on the banks of the Holy River Ganges is where people from across the world come to attain moksha (salvation). Its ancient temples, historic ghats, and revered Ganga Aarti offer unmissable cultural experiences. Without a doubt, Varanasi is one of the best cultural cities in the world.
With magnificent palaces, invincible forts, folk music, colorful festivals, and fairs – the royal cities of Rajasthan narrate the grandeur of erstwhile royals.
The unique temples of Tamil Nadu have great mythological and historical significance in Indian culture. The Meenakshi Temple in Madurai is the epitome of beauty and architecture and a must-visit for cultural buffs.
Khajuraho, a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Madhya Pradesh beautifully mirrors the art and creativity of ancient India. One of a kind in the world!
Kerala is a melting pot of different cultures and traditions. You can sense the Arab, Chinese, and European influences, especially in Fort Kochi. You can visit Kerala Kathakali Centre to witness traditional dances such as the Kathakali or the classic martial arts form of Kalaripayattu. Art lovers can plan around Kochi-Muziris Biennale, the biggest contemporary art festival in Asia.
No cultural trip to India is complete without taking part in one of the colorful Indian festivals . Holi and Diwali are hit among cultural tourists. And of course, gorging on traditional Indian food is part and parcel of an immersive travel experience in India.
The Mughal monuments of Delhi , the Golden Temple of Amritsar, the Indo-Portuguese architecture of Goa, the Awadhi heritage of Lucknow, the artistic and literary heritage of Kolkata, the historic temples of Bhubaneswar, the Buddhist pilgrimage of Bodh Gaya, ancient ruins of Hampi, palaces and pilgrim sites of Mysore, and on and on – India is your answer to culture fix.
And how can I talk about Indian culture and not mention its ancient healing traditions – Yoga and Ayurveda that make India a leader in holistic wellness? From Rishikesh and Narendra Nagar to Kottayam, Allepey, Palakkad, and Mysore – there are endless Yoga and Ayurveda Ashrams & Resorts in India.
For an immersive Indian culture experience, book a stay at one of the unique heritage hotels or local homestays or wellness retreats in India.
Ami Bhat of Thrilling Travel
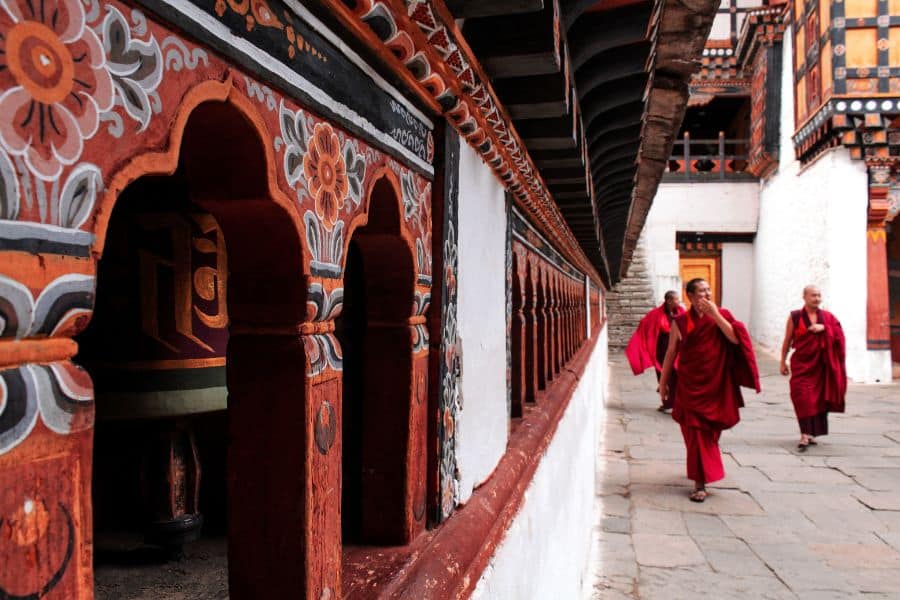

Known for its commitment to Gross National Happiness, Bhutan is a place where you will find how well-balanced the concepts of well-being and spiritual values are alongside economic development. The small landlocked country located in the eastern Himalayas is a perfect combination of culture, heritage, and nature.
The history of Bhutan dates back to the 8th century when Guru Rinpoche, also known as Padmasambhava, introduced Buddhism to the region. The country’s early history is characterized by the establishment of local chieftaincies, with the emergence of the Wangchuck dynasty in the early 20th century leading to the unification of the country.
It was in 2008, the country made the transition to a constitutional monarchy, with the king remaining the head of state but with a democratically elected government.
Every major town in Bhutan has a central Dzong (fort) which is not just a center of governance but also, a religious and cultural hot spot. A visit here not only allows you to appreciate the traditional Bhutanese architecture but gets you familiarized with the key customs and traditions of the country.
Besides these, there are several ancient monasteries and temples like Taktsang Monastery, Chimi Lhakhang ( the fertility temple), and the Gangtey Monastery that one can visit.
No cultural experience is complete without a taste of the local meals. Bhutanese cuisine is known for its spiciness and use of chilies, and traditional dishes include ema datshi (chilies and cheese), phaksha paa (pork with vegetables), and momos (dumplings).
It is highly recommended that one experiences a stay in one of their traditional villages located in peaceful valleys like the Haa Valley and Phobjikha Valley. There are several farmhouses that provide authentic experiences including traditional stone baths.
Kaitlyn from Carry On Only

Vietnam is an ideal destination in South East Asia for those who wish to experience a diverse and fascinating culture. It’s a beautiful country brimming with endless cultural tourism attractions and thus, offers some of the best cultural vacations in the world.
The history of Vietnam is complex and includes significant events such as a 1000-year-long period of Chinese rule over northern and central Vietnam, a 1st century AD rebellion led by the Trung Sisters against Chinese domination, successful defense against Mongol invasion, French colonization during the 19th century, and the widely known Vietnam War.
Vietnam has a wide range of attractions that would interest culture buffs. These include the My Son Sanctuary, Cu Chi Tunnels, The Ancient Town of Hoi An (which features the Precious Heritage Art Gallery Museum , War Remnants Museum and the Independence Palace in Ho Chi Minh City , the imperial city of Hue, Bac Ha Market in Lao Cai, Water Puppet Theatre in Hanoi , and floating markets along the Mekong Delta.
If you want to have a complete cultural experience, then choosing a Homestay in the Sapa area is the optimal way to do it. You can get an authentic taste of the daily life of the Black Hmong by staying in The Little Hmong House .
Vietnamese locals are renowned for their friendliness and hospitality towards tourists, making it easy for visitors to connect with them and learn about their vibrant culture and way of life.
If you want to experience a magnificent culture, visiting Vietnam is a must-do on your bucket list!
Alex and Leah of Alex and Lean on Tour
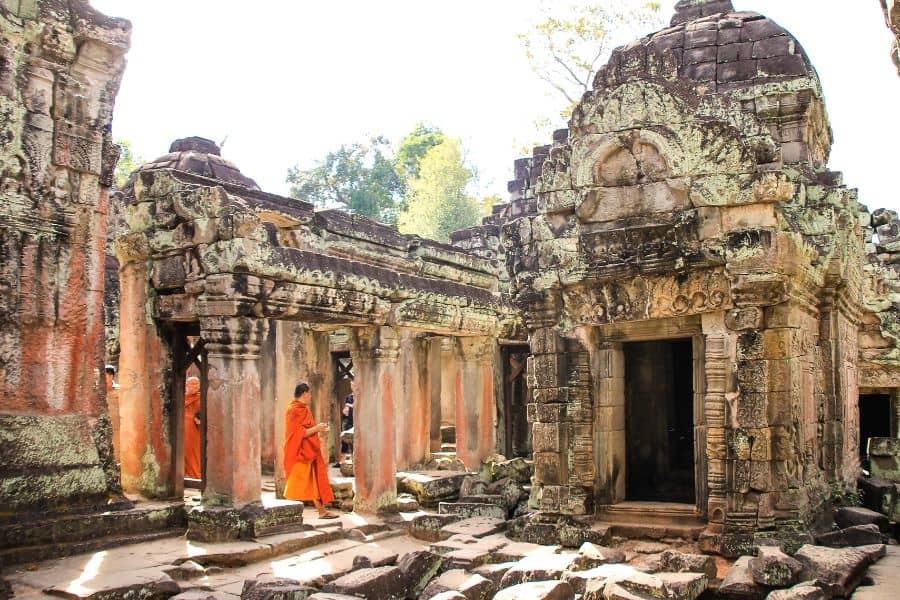

If you’re looking for an explosion of culture, look no further than Cambodia, one of the very best cultural places in the world.
The country has endless cultural attractions that you absolutely must visit. Whether it’s the famous sunset at Angkor Wat near Siem Reap or lesser-known gems such as the Battambang Bamboo train, there’s so much to experience in Cambodia.
Angkor Wat is an absolute must-visit for anyone traveling to Cambodia. The region has tons of temples, all representing something different about Cambodian culture.
If you’re looking to explore off the traditional touristy track, make sure to visit Battambang and stay at the beautiful Sanctuary Villa which fully blends into the environment perfectly yet still has amazing facilities!
Similarly, if you love the hustle and bustle of a city that has an abundance of great food places, Phnom Penh’s the place to be. Full of every food imaginable
Cambodia has a very fraught history and has only recently managed to dispose of the Khmer Rouge. This truly horrific regime attempted to restructure Cambodian society which ended up slaughtering millions of innocent people in prison and killing fields. It’s still a very poor country so make sure to be conscious and respectful when you visit!
If you’re looking to relax Cambodian-style then why not also visit the beautiful Koh Rong islands in the southwest? You’ll have the chance to swim in the turquoise sea by day and bio-illuminant plankton by night!
Dotti from Travel Oasis

Sri Lanka is a fabulous destination for culture lovers. This little island is overflowing with cultural attractions due to its extensive history dating back millennia.
The most obvious place to get a cultural fix in Sri Lanka is the cultural triangle. This region, in the center of the country, is where the Sinhalese civilization was born. It’s also where the bulk of Sri Lanka’s cultural attractions are: the ancient cities of Anuradhapura and Polonnaruwa, Mihintale, the Dambulla cave temples, and the famous rock citadel of Sigiriya.
The largest of these is Anuradhapura , Sri Lanka’s first capital. It was one of the ancient world’s great metropolises at the time, with monasteries, massive dagobas, elaborate palaces, and water tanks. Many of these monuments still remain, not only as popular tourist attractions but as important Buddhist religious sites, so it’s common to see pilgrims paying visits.
Just south of the cultural triangle is Kandy , the second-largest city in the country. Kandy is known as the cultural capital of Sri Lanka due to housing the famous Temple of the Tooth. This temple, which is open to the public, is said to hold a tooth from the Buddha and is of utmost importance to Buddhists worldwide.
In the north of Sri Lanka is Jaffna, home to the majority of the country’s Tamil population. Jaffna is a great place to experience Sri Lanka’s Hindu culture, with shrines peppered throughout the region. The most famous is Nallur Kandaswamy Kovil, which dates back to the 13th century.
There’s no better place to stay than Ceylonima Home Stay in Anuradhapura. Run by an incredibly welcoming family who goes out of their way to provide the best experience for their guests. From giving local tips to informal cooking classes in their own kitchen, this is a cultural experience not to miss.
Linda of Muy Linda Travels

Indonesia is an archipelago in Southeast Asia comprising five main islands and more than 18,000 smaller islands located on ancient trading routes between Asia, and the Middle East.
With more than 300 ethnic groups, Indonesian culture is a blend of traditions, religions, and cultural practices. More than 85% of Indonesians are Muslim with Hinduism, Buddhism, and Christianity making up the remaining numbers.
Indonesia’s ancient religious monuments are a great place to start exploring the country’s rich history and culture. The Island of Bali has more than 10,000 Hindu shrines.
But Indonesia’s most beautiful temples can be found in Java. Majestic Borobudur, the largest Buddhist Temple in the world, and Prambanan Temple, the oldest and the largest of Indonesia’s Hindu Temples lie near Yogyakarta in Central Java. Both famous monuments are UNESCO world-heritage listed and recognized for their historical importance and cultural significance.
In Central Java, the Sarasvati Hotel in Borobudur is a lovely place to stay. The elegant Dutch colonial-era building has a superb location near the entrance to the Borobudur Temple grounds.
Indonesia has a history of Sultans that ruled local areas before and during the Dutch colonial rule. Royal Courts can be visited in Java, Bali, Borneo, and the Spice Islands. The Sultans were revered for their refinement and high culture. A highlight of visiting the Royal Palace in Yogyakarta is watching a live Gamelan and shadow puppet performance.
In Java, the Batik Museum in Solo has a beautiful collection of traditional Indonesian Batik fabrics and sarongs, and in Bali, traditional Dance is performed regularly with evening performances in Ubud and around the island.
Traditional Indonesian food is another way to explore the culture with dishes like, sate chicken and peanut sauce, Gado Gado, Babi Guling, Nasi Goreng, and Mi Goreng.
Indonesia has much to offer and is a great destination for culture lovers.
Emily from Emixglobe

With a long history of colonialism blended with rich aboriginal culture, Taiwan has an extremely colorful fusion of cultural heritage unique from all its East Asian counterparts.
One of the best ways to experience the various forms of Taiwanese culture is to visit the many historic streets scattered throughout Taiwan. Each historic street has its own unique history and culture associated with it.
From these streets, you’ll be able to get a glimpse of how Taiwanese people have lived throughout the centuries; from well-preserved buildings left from the Japanese colonial period to the fascinating and unique Hakka culture of Taiwan.
Some of the most beautiful and notable historic streets in Taiwan include Jiufen and Lukang Old Street, both dating back to the Qing dynasty.
Jiufen was once a prosperous mining town and many have speculated it to be the inspiration for Ghibli’s spirited away due to striking similarities. Lukang used to be the second most prominent town in Taiwan and an important seaport rich in Hakka culture.
The Aboriginal culture is also an important part of Taiwanese culture. The Aborigines have lived in Taiwan for 6000 years, and there are officially 16 recognized tribes in Taiwan, each with its own unique language and culture.
The best way to experience the Aboriginal culture is to take their villages and immerse yourself in their daily way of life and participate in festivals and events.
South Korea
Mayi from SecretMoona

In recent years, South Korea has undergone tremendous cultural change. Thus when considering the country, we often think of K-Pop, K-Drama, K-Food, and high-tech.
But South Korea also offers something for those interested in history and culture. A trip to South Korea is an invitation to discover 5,000 years of history, art, and culture.
Here, Chinese and Japanese influences can be seen in the rich heritage, but Korean culture displays a particular style. Starting with Seoul, a bubbling capital where futuristic architecture brushes shoulders with ancient palaces.
You can explore Bukchon Hanok Village. Surrounded by Gyeongbokgung Palace, Changdeokgung Palace, and Jongmyo Shrine, Bukchon Hanok Village is home to hundreds of traditional houses called hanok, which date back to the Joseon Dynasty.
After the capital, I invite you to visit the other major places: Busan, the maritime, Gyeongju, the historic, Andong, the traditional…
The historical treasures of Gyeongju, in particular, will take you back in time. As the ancient capital of the kingdom of Silla and often referred to as ‘ the museum without walls ,’ the city displays neither tall buildings nor modern architecture.
While there, explore the city’s royal past at Tumuli Park, a peaceful park full of tumuli (large round grassy tombs), and visit the Gyeongju National Museum. As an important cultural center, it preserves and exhibits Silla’s rich history and culture.
Other must-sees are Cheomseongdae, the oldest astronomical observatory in Asia, and the Bulguksa Temple. As a UNESCO World Heritage Site, Bulguksa Temple is home to the oldest cave temple in the country.
If you want to experience monastic life firsthand, you can stay there as part of a temple stay program and learn sunmudo, a traditional Buddhist Korean martial art, among other things.
Another place to explore South Korea’s cultural and historical sights is Andong. The town is known for its traditional culture, and the main attraction is the Hahoe Folk Village, a Unesco World Heritage site.
The village has large tile-roofed residences, thatched roofs houses, and old pavilions. Stroll through the narrow streets, visit the traditional houses, and explore the Hahoe Mask Museum, with its intriguing collection of Korean and international masks.
Caroline of Veggie Wayfarer

A colorful treasure trove for cultural aficionados is located along the silk road in Central Asia. Uzbekistan was once at the very heart of trade between East and West, it comes therefore as no surprise that modern-day Uzbek culture is an eclectic mix of different civilizations which is reflected in the country’s architecture, music, and even cuisine.
Originally inhabited by nomadic tribes, and later ruled by a myriad of empires and kingdoms including the Samanids, Timurids, and the Khanate of Bukhara. The country was folded into the Soviet Union in the 20 th century but regained its independence in 1991.
Luckily the gargantuan tiled mosques and traditional architecture were carefully preserved despite being depictions of an outlawed religion. Hospitality is of the utmost importance in Uzbek culture, being invited into someone’s home for a meal or a cup of tea is a common occurrence, although you might want to brush up on your Uzbek before attending.
While tourism in Uzbekistan has gained momentum in recent years, it still remains a wonderfully authentic place to visit.
Start your trip by exploring Samarkand , with the majestic Registan Square being an absolute must-visit. Next hop on a train to Bukhara and stay with a local family at the Komil Bukhara Boutique Hotel .
End your cultural trip to Uzbekistan with little Khiva, which once held the largest slave market in all of Central Asia and was rivaled only by Bukhara in importance.
The night train from Khiva to Tashkent will bring you back to the capital, where all international airfare departs from.
Carine from We Did It Our Way

Armenia, a small country in the Caucasus, is a beautiful place with a long history & rich culture. Armenia has been on maps since the Bronze Age under different dynasties and kingdoms.
Being the first Christian nation, adopting the religion in 301 AD, many of the cultural sites in Armenia are churches.
With over 4,000 to choose from, the most notable ones are the Holy City of Etchmiadzin, where the Armenian equivalent of the pope resides, and Khor Virap, where the father of Christianity in Armenia was held captive for years.
But there’s more to do in Armenia than visit churches ! Visit the Genocide Museum to learn about the horrific genocide perpetrated by the Turks in 1915. The Areni-1 Caves, are archaeological digs where there are relics that pin Armenia as one of the birthplaces of wine-making.
The world’s oldest leather shoe was also found here, currently kept at the History Museum of Armenia in Yerevan, where there are many other museums.
Other amazing places to visit in Armenia are the Garni temple, the only pagan temple in the country, dating back to the 1st century.
Karahunj, or Zorats Karer, is suspected to be the oldest astronomical observatory in the world. Khndzoresk is an old village that has been built into the side of the mountain, with caves and ruins to explore.
Almost every night, you can attend a concert or dance show in Yerevan or Gyumri. There are also a ton of festivals and events happening almost every weekend.
A great heritage hotel is the Tufenkian Old Dilijan Guest Rooms in Dilijan. They kept the allure of the architecture of the 1800s when the city of Dilijan was known as a blossoming center of culture, commerce, and cuisine.
There are also plenty of homestays to choose from . Just be careful as your hosts will likely feed you constantly, just a little sign of how much they appreciate you!
For these reasons and so many others, Armenia is a great place to visit for culture buffs. In 2 weeks, you can easily take in the best sights in the country.
Best Cultural Travel Destinations in Europe
Raksha Nagaraj of Solopassport

Located at the eastern end of the Black Sea between Russia and Armenia, Georgia is a transcontinental country belonging to both Europe and Asia.
As per Georgia’s history, the country has gone through many political changes/rulers, including the rule of the Soviet Union and it was declared independent (again) in 1991.
Georgia is especially famous for its wine culture, as the country is the oldest wine-making country in the world that dates back to 6000 years B.C.
With more than 80% of the population practicing Orthodox Christianity, Georgia is one of the most traditional and religious countries to visit.
Georgia was also the site of the Golden Fleece sought by Jason and the Argonauts in the Greek mythological tale of Argonautica. There are many medieval churches around the country, including UNESCO World Heritage sites Jvari Monastery and Bagrati Cathedral.
In fact, Georgia’s language, Mkhedruli script (alphabets), and dance are also recognized by UNESCO.
What makes the Georgians stand out is their hospitality and their respect for women. They believe that guests are Gods and make everyone feel at home and comfortable. The food in Georgia is also unique and they love their wine.
Their culture is best observed during their feast/festival called supra. During the feast, the role of the tamada/toastmaster is significant, and the culture of drinking the wine bottoms up irrespective of how big the glass/drinking horns called khantsi is.
One of the best ways to enjoy Georgian culture is by staying at a local hotel or homestay. Musmore Boutique Hotel , situated close to Liberty Square, is a budgeted hotel run by locals and is a great opportunity to interact and learn from them. The guests can also taste and try the local cuisine at the hotel.
Tamar of World by Weekend

If you’re looking for a travel destination rich in cultural heritage, then look no further than Turkey (Türkiye). One of the best cultural vacation destinations, Turkey has been at a cultural crossroads for millennia, giving the country its unique east-meets-west mix of cultures.
While visiting Turkey you’ll have the opportunity to explore ancient Greek ruins, explore Byzantine rock churches, and see the world’s best examples of Ottoman architecture.
Culture buffs should be sure to visit Istanbul , where Europe and Asia collide into one mega-city. Current-day Istanbul was the seat of power for the Ottoman sultans, who ruled for 600 years and whose empire spanned across southern Europe and the Middle East.
You can learn about the Ottoman Empire by visiting Topkapi and Dolmabahçe Palaces. While touring these two stunning palaces you will enter former bedrooms, private prayer rooms, and grand rooms for entertaining, giving you a sense of the lavish lifestyle of the sultans.
Turkey’s cultural significance, however, extends far beyond the busy streets of Istanbul. The ancient city of Ephesus , near current-day Izmir, was once an important Roman city and home to roughly a quarter of a million people.
The city was most famous for the Temple of Artemis, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Today, the temple is in ruins aside from one free-standing column. However, the ancient city of Ephesus still contains many exemplary well-preserved ruins, making it a must-visit for travelers interested in ancient history.
Not to be overlooked by culture buffs visiting Turkey is the region of Cappadocia . Nearly 2,000 years ago, this picturesque land of fairy chimneys became home to early Christian settlers.
The settlers built churches into the rocks, chiseling out the rooms by hand. They also painted beautiful religious frescoes on the walls and ceilings, many of which can still be viewed today. The best place to see these Byzantine Christian creations is the Goreme Open Air Museum , which contains 15 rock churches.
For a unique and immersive accommodation experience in Cappadocia , be sure to stay at a cave hotel . Traditionally, many inhabitants of the valley resided in cave dwellings carved into the rocks. Today, you can experience this traditional local lifestyle, without the risk of erosion, by staying in a cave yourself!
Cris from LooknWalk

Located in Southern Europe, La Bella Italia, together with Greece, is considered the birthplace of Western civilization. Home to 53 cultural and 5 natural UNESCO Heritage sites, as well as 14 traditions recognized as intangible cultural heritage, the largest number in the world, Italy is a must on your itinerary if you are a culture buff.
Between historical sites, art museums, and colorful traditions, your trip to Italy will be an immersive experience of its history and culture.
Italy’s history spans eons. Rome started its life as a small village in the 8 th century BC. It grew into a republic, then an empire, spanning the entire Mediterranean basin, going as far north as Scotland and as far east as Mesopotamia and Arabia.
Reminders of this period dot Rome’s streets. Decades of war and the changes happening in nearby territories, eventually lead to the emergence of modern Italy.
When the Kingdom of Italy was proclaimed in 1861, its capital was Turin. It took 9 more years until Rome became the capital. But it wasn’t until after World War II that Italy became a republic again (1946).
Today, it’s one of the most popular travel destinations in the world and most travelers choose to discover Rome’s cultural and historical heritage.
Without a doubt, your cultural itinerary in Italy should start with visiting Rome’s Colosseum. And while you are here, tour the Vatican’s Museums, and go on a day trip to explore the ancient city of Pompeii .
If you are also into art, plan a trip to Florence, home to a large concentration of world-famous masterpieces. Visit the Uffizi Gallery, Ponte Vecchio, the Cathedral of Santa Maria del Fiore, and Palazzo Vecchio. And while in the area, make sure to also check out Pisa with its famous Leaning Tower.
No cultural exploration of Italy is complete without getting to know its cuisine. Learn to make pizza in Naples or discover the secrets of orecchiette in Puglia.
When it comes to accommodation, farm stays will allow you to get immersed in the Italian lifestyle. Agriturismo Podere Campriano in the heart of Chianti, close to both Florence and Siena, is a family-owned farm that produces fantastic wine and olive oil. Aside from wonderful accommodations, they also offer cooking classes and wine tours.
Elle of Only in Germany

Dating back thousands of years, Germany or Deutschland was a pagan nation and an important center of the Holy Roman Empire . It played a significant part in the history of Europe.
Germany is a hub for culture enthusiasts, with museums, art houses, and collection centers scattered across the country. All these places narrate the story of Germany and have significant cultural importance. They are perfect for witnessing the magic of art, history, and culture.
If you are a culture enthusiast, Berlin, the capital city of Germany is one of the best cities to visit in Germany.
The Pergamon Museum on the UNESCO World Heritage Site of Museum Island in Berlin houses long-buried treasures and monumental works worldwide, including Greek and Roman collections.
The Museum Brandhorst in Munich is the central venue for contemporary art, showcasing masterpieces from all over the world from the 1960s to the present.
With a host of musical theaters, opera houses, and live venues, Munich is a hub for performing arts and cultures. One must plan an evening catching traditional and classical performances at Deutsches Theater in Munich to get a dose of culture.
The Hamburg Art Hall is characterized by striking architecture, such as a historical staircase, study hall, or the atrium of the Gallery of Contemporary Art. It houses more than 150 works, including Meister Bertram and Caspar David Friedrich, and also offers a virtual tour.
The Museum Ludwig in Cologne covers major approaches in contemporary art and the 20th century. It boasts the most extensive pop art collection in Europe, the third biggest Picasso collection in the world, one of the best collections of German Expressionism, and one of the most important collections of photography.
The Ruhr Museum in Essen is located in the former coal preparation plant of the Zollverein colliery and provides information about the coal age to its visitors, focusing on the technical, historical, and cultural dimensions of the coal cage. Visitors can take a virtual tour of the museum and understand its history and its significance in real time.
Germany’s museums have preserved culturally and historically significant memorabilia with the utmost care, allowing visitors to cherish a sneak peek into the world and era that went by.
Apart from museums and art galleries, palaces, castles, cathedrals, and monuments also display Germany’s rich cultural heritage. The world-famous cathedral in Cologne is a beautiful reminder of Germany’s glorious past.
Milijana from World Travel Connector

Spain is one of the top countries in the world for its rich cultural heritage.
Spain has 49 World Heritage sites! Only Italy, China, and Germany have more World Heritage sites than Spain.
The cultural heritage of Spain goes back to prehistoric times. The Cave of Altamira near Santillana del Mar in northern Spain and its paleolithic cave painting is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
But, the highest number of World Heritage Sites in Spain is related to medieval Spain.
The Old Cities of Santiago de Compostela, Avila, Salamanca, Toledo, and the historic center of Cordoba are among the prettiest places in Spain and are World Heritage Sites. Gorgeous Seville is among the most beautiful cities in Spain as well.
UNESCO declared Seville’s Cathedral, Alcázar, and Archivo de Indias a UNESCO World Heritage site, too. Besides that, UNESCO’s protected Alhambra Place in Granada is the most visited site in Spain. The Alhambra Palace receives 2 million visitors a year.
For a highly culturally immersive experience, Spain visitors can sleep in Paradors (historic buildings converted into luxury hotels). The first Parador in Spain was the Hostal de los Reyes Catolicos in Santiago de Compostela.
However, hiking Camino de Santiago is the top culturally immersive experience in Spain to seek for. Most of the mentioned World Heritage sites are on the Camino de Santiago routes. Camino de Santiago, or St James Way, is among the most famous world pilgrimage and hiking trails.
Camino de Santiago is a net of medieval routes across Spain and Europe that lead to the tomb of Apostle James the Greater in Santiago Cathedral in Spain. UNESCO proclaimed the French Route and Routes of Northern Spain of Camino de Santiago a World Heritage Site.
Camino pilgrims visit historical places. Those places hold the finest examples of Romanesque, Gothic, Renaissance, and Baroque architecture in Europe. In the last decade, over 200,000 pilgrims hiked Camino de Santiago.
So, if you seek one of the top culturally immersive experiences in a lifetime, prepare your Camino de Santiago packing list and head to Spain!
Aixoise from All About Aix

France is widely regarded as one of the best destinations for culture lovers due to its rich history, stunning architecture, world-class art, and gastronomy.
It has a long and rich history, from the Roman Empire to the Enlightenment, the French Revolution, and the modern era.
The country is home to some of the world’s most renowned museums, including the Louvre Museum in Paris, which houses some of the most famous works of art in history, such as the Mona Lisa and the Venus de Milo.
France has numerous historic sites, such as the Palace of Versailles, Notre-Dame Cathedral, and Eiffel Tower. And that is just in Paris.
Beyond the capital region, other ancient cities with significant contributions to French culture and heritage include Lyon, Marseille, Strasbourg, Bordeaux, Avignon, and Nice, to name just a few. Each of these cities has its own unique features.
Lyon is known for its gastronomic scene, Marseille for its seafood, Strasbourg for its architecture and Christmas markets, Bordeaux for its wine culture and architecture, Avignon for its papal palace and annual theater festival, and Nice for its beaches, art museums, and markets.
And for an art-inspired stay that combines art, relaxation, and gastronomy, I highly recommend visiting the region of Provence in the south of France , the birthplace of Paul Cézanne, a world-renowned Impressionist painter.
Just 15 km north of Aix-en-Provence and 49 km north of Marseille, you can stay at Château La Coste , renowned for its impressive contemporary art and architecture collection. This heritage hotel offers guests a scenic location amidst vineyards and olive groves, all the while providing an exceptional culinary experience, wine tastings, spa treatments, and relaxation. The French are known for their “ joie de vivre” and the south of France is the perfect place to experience it.
Jo Koni from World Wild Schooling

Welcome to Greece, a country rich in history and culture that has captivated travelers for centuries.
Greece is located in southeastern Europe, on the southern end of the Balkan Peninsula. The country has a long and fascinating history that dates back to ancient times, and its culture has influenced the world in many ways.
Greece is known for its breathtaking natural beauty, from its idyllic islands to its rugged mountains and stunning beaches. But what really makes Greece stand out is its incredible cultural heritage.
Greece has been the birthplace of some of the most important figures in art, science, and philosophy, and its ancient ruins and monuments are some of the most impressive in the world.
For visitors to Athens, the Acropolis is a must-see attraction. This ancient citadel is home to the Parthenon, one of the most iconic buildings in Greece. The Temple of Poseidon in Sounion , just a short drive from Athens, is another must-visit destination. This temple sits atop a cliff overlooking the Aegean Sea, and the views are absolutely stunning.
But there’s much more to Greece than just Athens. The island of Delos, located just a short boat ride from Mykonos, is an incredible archaeological site that was once a thriving city.
The ancient theater of Epidaurus, located in the Peloponnese, is another must-see attraction. And the ancient palace of Knossos on the island of Crete is a fascinating glimpse into the world of the Minoan civilization.
For an immersive cultural experience in Greece, we recommend staying at the Kyrimai Hotel , located in the small town of Gerolimenas in the Mani region of the Peloponnese. This historic hotel has been beautifully restored and offers guests a chance to experience the traditional architecture and way of life in this part of Greece. The hotel’s restaurant serves traditional Greek cuisine made with locally-sourced ingredients.
Whether you’re interested in ancient history, breathtaking landscapes, or simply relaxing on the beach, Greece has something for everyone.
With its rich cultural heritage and welcoming people, it’s no wonder that Greece remains one of the most popular destinations in the world.
Czech Republic
Joanna from The World in My Pocket

The Czech Republic might be a small country in Europe, but it has such a rich culture and history.
The Czech Republic gave some very important people to the world: Frank Kafka, Sigmund Freud, and Gregor Mendel among many other notable novelists, philosophers, composers, and sportspeople.
The Czech Republic has a long history that saw the country divided between Bohemia and Moravia, as well as part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Because of its history, the cultures blended and influenced the way the country is now.
In the South of the country, in Moravia, you can visit the Lednice-Vatice domain with the two castles which belonged to the Liechtenstein family. Here you can also notice the English-style landscaped gardens, which are unique in the Czech Republic.
If you are into science, it’s always a great idea to take a day trip to Brno and visit the museum dedicated to Mendel and his work in genetics. You will find out there that Mendel was an Augustinian friar at St Thomas Abbey, where you can see an incredible exhibition of his personal belongings.
In the West of the country, you will find the spa towns, which are now on the UNESCO Heritage list. In Marianske Lazne, you can stay at the same hotel where King Edward VII of England used to often come for treatments. You can ask at the reception of Nove Lazne to see his cabin, which has the original chair he used in the spa treatment rooms.
Diana of Travels in Poland

Poland has a rich cultural heritage that spans centuries and has influenced the world in countless ways.
Poland has a long and storied history, dating back to the Piast dynasty that ruled the country. Even before then, the legend of Lech is well known in Polish history.
Over the centuries, Poland has experienced numerous invasions, wars, and political upheavals, including the partitions of Poland in the late 18th century when the country was divided between Russia, Prussia, and Austria.
During World War II, Poland was the center of some of the deadliest concentration camps, including Auschwitz Birkenau , which can still be visited today.
Despite this, Poland has managed to preserve its cultural identity through its traditions, customs, and artistic expressions.
Poland’s culture is a fusion of Slavic, Germanic, and Jewish influences. One of the most impressive cultural aspects of Poland is its architecture, with many historic buildings and landmarks still standing today.
The Old Town of Kraków, the Wawel Castle, and the Royal Castle in Warsaw are all excellent examples of Poland’s rich architectural heritage.
Poland offers an array of experiences that celebrate its rich cultural heritage. The Wieliczka Salt Mine, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a must-visit attraction. The mine is a fascinating underground labyrinth of salt chambers, tunnels, and sculptures carved out of rock salt.
Poland is also known for famous individuals including Marie Curie, Nicholas Copernicus, and Chopin. Visitors can also explore Poland’s museums and galleries showcasing these individuals. The Chopin Museum in Warsaw is a great example of a museum dedicated to the famous composer.
Hotel Pugetow is an ideal place to stay when in Krakow. It is a heritage hotel that was built in 1874 and is part of the Puget Palace complex and has rooms where duchesses and dukes had once stayed.
Poland’s rich cultural heritage is a testament to its resilience and creativity throughout its complex history and offers a wealth of cultural experiences that are sure to captivate and inspire visitors from around the world.
Abbey of Trips on Abbey Road

Croatia is considered a cultural gem in Europe, known for its rich history, stunning architecture, and beautiful natural scenery, as well as its lively music, dance, and culinary traditions.
There are countless museums, galleries, and even UNESCO heritage sites around celebrating this beautiful Baltic country. The history here spans back over 13 centuries, at least so you just know that there are some juicy stories and history around.
One of the best things about Croatia’s cultural history is the rich tradition of folk dance. These dances vary from region to region. One of the most popular types of folk dance in Croatia is the kolo or circle dance, which is performed during religious holidays and other special occasions.
If you are visiting during one of the major holidays you may get lucky enough to see this dance performed in the town squares. Most of the time they wear traditional clothing as well. Women with big white hats and beautiful gowns, and the men keep it simple with black suits and traditional hats.
For places to go in Croatia for a cultural experience one of the most visited destinations is Dubrovnik , with its well-preserved medieval walls that surround the old town.
Another popular city in Croatia is Zadar . Here you will find a mix of Roman, modern, and medieval structures throughout the beautiful southern city. And if you are looking to get outside and explore the Plitvice Lakes National Park is amazing with dozens of cascading waterfalls and hiking paths to explore.
Plitvice Panta Rei is near the waterfalls and would be a perfect place to get an authentic and cultural stay in Croatia.
Amber from Amber Everywhere

Culture lovers will quickly fall head over heels for Sweden, a Scandinavian country in Europe known for its coffee breaks, an affinity for the outdoors, and lively music scene.
Although Sweden shares some similarities with its Scandinavian neighbors, you’ll find many distinct cultural practices, many of which are apparent even to a first-time visitor.
Perhaps the most popular among Swedes and visitors alike is the fika or coffee break. Often, coffee is enjoyed with chokladboll, a small, round chocolate treat.
You’ll notice immediately that most people in Sweden speak Swedish, although they tend to also speak other languages fluently. While you may not need to speak Swedish to navigate the country as a tourist, you’ll certainly experience more of Swedish culture if you have some experience with the language.
Try to learn a few words and phrases before you go to maximize your exposure to Swedish culture on your trip.
If you have a chance to meet or get to know Swedish people, you’ll notice that they value egalitarianism and tend to dislike boasting. Additionally, the country values the environment and the outdoors, so you’ll tend to see more organic, sustainable, or eco-friendly products in Sweden.
You’ll also find plenty of people spending their holidays exploring the outdoors, from parks near Stockholm to longer trips to Abisko.
You can experience Swedish culture and the beautiful landscapes of Lapland by staying in the STF Abisko Turiststation in the Arctic Circle. From the Turiststation, you can see the northern lights, hike in Lapland, ice climb, and generally enjoy the beautiful outdoor scenery.
Scotland, United Kingdom
Kristine of Scotland Less Explored

The first images that come to mind when thinking of Scotland are kilts, bagpipes, castles, and whisky. And yes, this is part of Scotland’s culture and history but there is so much more to the country. Just like there are so many more places to explore in Scotland than in Edinburgh and Glasgow.
However, these are still great cities to visit and the Edinburgh Festival and Military Tattoo are worthy of specifically arranging a trip around. Both cities have many museums and theatre performances but to better understand Scottish culture you should also visit the highlands and islands.
Accounts of Scotland’s history often start with, unlike England, Scotland was not invaded by the Romans in the 1 st Century AD. But sites such as Skara Brae (ruins of a village) in the Orkneys and the Callanish standing stones in the Outer Hebrides pre-date Stonehenge and even the pyramids in Egypt!
The Vikings also influenced Scotland which can be seen from the names of villages and locations. One of the most remarkable artifacts from this time is the Uig chessmen. The chess pieces are carved from walrus tusks and were found on a beach in Uig in 1831. They are on display at the National Museum in Edinburgh and Museum Nan Eilean in Stornoway.
Traveling through Scotland between May and September you can attend Highland Games with traditional sports such as cable toss and arts such as highland dancing accompanied by bagpipes.
In the more remote parts of the country, you will find most of Scotland’s 1,000 castles. Many can be visited on a guided tour but the most intimate way to experience one is to stay overnight.
One of the best is Glenapp Castle Hotel south of Glasgow. As well as beautiful grounds the hotel offers great dining options and a fascinating whisky-tasting experience can be arranged. You will find whisky distilleries all over Scotland but the most authentic are on Islay or Speyside.
Top Cultural Heritage Tourism Destinations in North America
United states of america.
Dawn Robson from Culture Feasting

The United States is a cultural destination like no other. As the country grew and expanded through immigration, so did its abundant culture .
In the Northeast, you’ll find that New York City is a tightly condensed metropolis filled with music, art, and theater. Carnegie Hall or Lincoln Center will satisfy the music aficionado and there is Broadway for theater enthusiasts. With more than 6 million visitors each year, the Metropolitan Museum of Art should not be missed.
Music lovers should head South to New Orleans, Louisiana, known as the birthplace of Jazz, where every spring the New Orleans Jazz & Heritage Festival is held.
For more live music make your way to Nashville, Tennessee, the Music City, to discover Country, Bluegrass, and Blues music at its source. Stroll through Music Row to see the recording studios of famous musicians such as Elvis Presley and Dolly Parton.
Plan a visit to Sante Fe, New Mexico, known for its abundant art scene and festivals. Uncover the culture of the indigenous people in the Southwest by visiting the Native American History Museum of Contemporary Native Arts in downtown Santa Fe. Explore the works and life of American artist Georgia O’Keefe.
To experience the art and history of the American cowboy culture visit The National Cowboy and Western Heritage Museum in Oklahoma City.
Stay in a log cabin at Meadowlake Ranch just outside of Tulsa Oklahoma and participate in the many ranch activities such as horse riding and rope throwing.
From east to west, the United States is a country filled with cultural destinations waiting for you to discover.
Mal from Raw Mal Roams

With a complex history and fascinating Mayan heritage intertwined with the colonial past, Mexico is one of the most captivating countries to visit today.
Before the Spanish colonization in the early 16th century, Mexico was home to many brilliant pre-Colombian civilizations. First was the great civilization of Teotihuacán, built between 100 B.C. and 700 A.D. near what’s today Mexico City.
Later on, came the Mayans, which were considered the most sophisticated and advanced civilization of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica. The influence of their culture, language, and architecture is still present today in places like Chichén Itzá, Palenque, and Tulum.
Aztecs were the last great rulers when the Spaniards arrived. During colonial times, the Spanish left their mark on Mexico by constructing grand cities, ornate monasteries, and breathtakingly beautiful churches representing a unique blend of European style and Mesoamerican influence.
Today, the rich Mayan and colonial heritage merges with the vibrant modern culture, creating a unique blend unlike any other. There are many ways you can immerse yourself in Mexican culture. Start your journey by exploring Chichen Itza – the ruins of the most important Mayan city. If you a history buff, go ahead and also visit other grand structures such as Palenque, Coba, and Uxmal.
Delve into majestic cities such as Merida and Izamal, adorned with delightful colonial architecture, and stay in the converted haciendas such as San Miguel Arcángel Izamal.
Explore the mystical cenotes that were sacred to the Mayans. Indulge in the Mexican food that varies from region to region as you traverse this stunning country! And experience Mexico’s most important festivities, such as Dia de Los Muertos (Day of the Dead) and Semana Santa (Easter).
Nikki of She Saves She Travels

Located in Central America along the Caribbean Sea, Belize is a phenomenal country to experience for those interested in history and the Mayan civilization. The Maya lived in the Yucatan Peninsula of Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, and Belize.
A few of the most culturally significant sites in Belize are the Caracol Ruins, Actun Tunichil Muknal Cave, and Xunantunich Mayan Ruins , which are all located on the western edge of Belize near San Ignacio. Visitors can spend a day exploring each of these sites. Caracol and Xunantunich are Mayan cities with rich histories. Climb the pyramids and temples and let your tour guide explain the most important plazas and structures.
Actun Tunichil Muknal Cave (also known as the ATM Cave) is a sacred and spiritual site for the Mayans. To see the ancient artifacts, you’ll need to wade in waist-to-shoulder deep water and trek through narrow passages within the cave.
The ancient Mayan civilization is also known for a modern-day discovery: chocolate! Visitors to Belize can find a chocolate-making tour in many of the major tourist areas and large cities. Cacao farms will even show you how to make chocolate as the Mayans did, and how it’s been converted in recent history to a much sweeter version of the original.
For a unique stay in Belize, consider the Sleeping Giant Rainforest Lodge . Experience the lush, tropical rainforest with options to hike and discover hanging bridges along the way. Located in the heart of Belize, this 600-acre property is the right mix of relaxation and adventure for your Belize vacation!
Carley Rojas Avila of Home to Havana

Once considered an off-limits travel destination for travelers from the United States, policy changes in the past decade have made it easier than ever for travelers from the United States and beyond to visit Cuba.
One of the most complex and rich travel destinations in Latin America, Cuba offers everything from lush rainforests and soaring mountains to white sand beaches and world-class resorts.
One of the most interesting things to do in Havana, Cuba is to visit the Museo de la Revolución – Museum of the Revolution. Housed in the lavish former presidential palace, this museum houses important exhibits about the Cuban Revolution.
You can still see bullet holes on the outside of the building, maintained as a sign of the history of the taking of the palace during the Cuban Revolution. The museum’s outside patio area is home to a full-scale replica of the Granma, the ship Fidel Castro used to arrive in Cuba with a band of revolutionaries at the start of the Cuban Revolution.
While Havana is a must on any traveler’s itinerary, make sure to head outside of Havana as well to experience another side of Cuba. The Viñales Valley is a perfect choice just a few hours west of Havana.
Stay at Finca Media Luna , an eco-farm with beautiful accommodations and delicious home-cooked Cuban food, for a great way to connect with locals and see a stunning part of Cuba.
If you’d prefer a beach getaway, the people beach resort town of Varadero is a great choice with plenty of amenities, while more remote, untouched beaches like Cayo Jutias and Playa Maguana outside of Baracoa are other great options.
Top Cultural Destinations in South America
Martha from May Cause Wanderlust

Peru is a beautiful country for culture lovers because it has such a rich and varied cultural history. And the good news is you can explore a lot of Peru’s cultural tapestry in two weeks in Peru .
It has been home to ancient civilizations, including the Incas, who conquered the high altitude of Peru’s mountains and plateaus with stone steps, agricultural terraces, and impressive landmarks. The most well-known is, of course, Machu Picchu, a stone citadel perched high in the Andes. But there are many other Inca ruins around Cusco and the Sacred Valley of the Incas.
Then there’s the Nazca – an older civilization than the Incas, and more mysterious. Their legacy is the impressive Nazca lines, markings, and hieroglyphs on the desert floor, best seen from above. Scientists only have theories about their purpose and how they were constructed with such geometric regularity.
But the culture in Peru is not all a history lesson. To this day, there are pockets of preserved traditional culture, and one of the best places to experience this is Lake Titicaca. Here, island communities, still relatively isolated from the mainland, have preserved their traditional way of life.
A great way to immerse yourself in one of these cultures is a homestay on Amantani island , which is the most populated island, and known for its textiles and ceramics.
You can also do day trips from Puno to Taquile Island, also known for its textiles and its pretty archways, and the floating Uros islands, which are literally floating islands made from totara reeds.
And if you still haven’t had enough culture in Peru, modern Peru is known as a great foodie destination, with fresh, inventive cuisine and world-class restaurants.
Carley Rojas Avila of Explorers Away

Don’t let the dark periods of Colombia’s recent history weigh on you; Colombia is a vibrant and rich travel destination you’ll love exploring. With its delicious and varied regional cuisines, incredible dance and music traditions, and an array of natural and man-made attractions, it’s a destination anyone can love.
One of the highlights of a trip to Colombia is a visit to Ciudad Perdida, a “lost city” deep in the mountainous jungle near Colombia’s Caribbean coast. While would-be visitors have to embark on a four-day trek through the jungle to reach the expansive ruins and terraces of this indigenous city, it’s an adventure well worth the effort.
For a slightly less adventurous itinerary but just as memorable of an experience, head to Cartagena on Colombia’s northern coast. This historic city has impressive walls and forts dating back to the Spanish colonial era, as well as glimmering new skyscrapers and white sand beaches.
Make sure to stay in one of the restored colonial boutique hotels in Cartagena, such as Casa Pestagua , considered among the best places to stay in Cartagena after undergoing extensive refurbishing.
Best Cultural Tourism Destinations in Africa
Andy from Explore with Finesse

Kenya is a great destination for culture lovers due to its rich and diverse history. Located in East Africa, Kenya has been inhabited by humans for millions of years. Today, it is home to 42 different ethnic groups, each with its own unique traditions, language, and customs.
The Maasai people, for example, are known for their vibrant traditional dress, intricate beadwork, and their distinct way of life centered around cattle herding. Other ethnic groups include the Kikuyu, Luhya, and Luo.
Kenya was colonized by the British in the late 19th century and gained independence in 1963. Because of this, many Kenyans speak English in addition to the country’s other official language, Swahili. Today, Kenya is known for its stunning landscapes, wildlife, and diverse cultural heritage.
For culture buffs, a visit to the Maasai Mara National Reserve offers an opportunity to experience the Maasai culture firsthand. Visitors can witness traditional dance performances, participate in beadwork workshops, and even stay in a traditional Maasai homestay.
Another cultural attraction in Kenya that is worth visiting is Diani , a coastal town located south of Mombasa. Diani is known for its beautiful beaches and unique blend of Swahili and European cultures. One of the oldest mosques in Kenya, the Kongo Mosque, can be found in Diani. This was built in the 14th century by Arab explorers and is still in use today.
For an immersive cultural experience, consider staying at the Giraffe Manor . Located in Nairobi, the hotel is set on 140 acres of indigenous forest and offers guests the opportunity to interact with endangered Rothschild’s giraffes that frequently visit the property.
Trisha Agrawal from Try Wandering More

Egypt is home to the only remaining Wonder of the Ancient World, the Pyramids of Giza, one of the best cultural attractions. Being an ancient civilization, its history and culture date back to 3200 BC – over 5000 years ago. Mind-boggling!
The best bit is that one can see remnants of that age today through grand Egyptian temples dedicated to multiple gods, gigantic Pyramids, towering statues of Pharaohs, beautifully painted tombs, well-preserved mummies, and fascinating hieroglyphics. You’ll be completely drawn in and dazzled!
To immerse yourself in ancient architecture, head to the Pyramids around Cairo; the marvelous temples around Luxor, especially Karnak Temple (the second largest temple in the world); the tombs at the Valley of the Kings near Luxor, and Abu Simbel near Aswan.
To see the mummies of the pharaohs and the treasures hidden in the royal tombs, visit the National Museum of Egyptian Civilization and the Grand Egyptian Museum in Cairo.
Egypt is, however, more than just the Pharaonic era. It’s also about all those that came after – Persians, Greeks, Romans, Caliphates, Mamluks, Ottomans, the French, and the English.
Egypt is, therefore, a blend of cultures while being primarily Islamic. This is very noticeable in the food and architecture. Visit Alexandria and the temples of Dendera, Edfu, and Philae to learn about the Greco-Roman era. Walk through the markets and mosques in Islamic Cairo to learn about the Islamic age.
Egypt also has biblical significance. It is where Moses grew up and eventually received the Ten Commandments. It is also where the Holy Family took refuge after fleeing Bethlehem. Visit the churches and synagogues at Coptic Cairo and climb Mount Sinai to see biblical stories come to life.
While planning your trip to Egypt , add a felucca ride or a cruise down the Nile to your itinerary to experience life along the river. Don’t miss staying at a historic hotel like Marriott Mena House in Giza that overlooks the Pyramids.
Whether you are a seasoned cultural traveler or a newbie who wants to embrace culturally conscious travel or a traveler who’s looking for a one-off-out-of-the-ordinary experience – we hear you. This hand-picked list of the best cultural holiday destinations is sure to inspire each one of you to plan your next cultural getaway.
Did we miss a destination you feel should grace this compilation? Let us know in the comments below!
Save the Best Cultural Trips Guide to Pinterest

Anjali Chawla
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
© 2024 Travel Melodies. All Rights Reserved.
As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases.
Cultural Tourism: Definitions, Types, Advantages & Disadvantages, or Stakeholders of Cultural Tourism
Cultural tourism is a rapidly growing segment within the global travel industry, catering to individuals seeking to immerse themselves in local populations’ customs, traditions, and lifestyles. It combines the elements of leisure with an authentic experience of a destination’s unique historical, architectural, artistic, and culinary aspects. As a result, this form of tourism allows travellers to gain a deeper appreciation and understanding of different societies and their cultural characteristics.
In recent years, the demand for cultural tourism has been on the rise as more people are interested in exploring foreign customs and cultural experiences beyond the typical tourist attractions. This trend fosters cross-cultural connections and mutual understanding and creates positive economic and social impacts on local communities. By preserving and showcasing their traditions, local people have the opportunity to generate income and employment while maintaining a sense of pride in their cultural heritage.
With the increasing focus on sustainability and responsible tourism practices, cultural tourism sets itself apart by emphasizing the importance of engaging with local communities, adhering to ethical standards and minimizing negative impacts on the environment. As such, it presents a viable option for tourists who wish to expand their horizons while also contributing positively to the places they visit.
Table of Contents
Understanding cultural tourism.

Cultural tourism is a significant and growing aspect of the global tourism industry. The United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO ) defines cultural tourism as the movement of people to cultural attractions away from their normal residence, with the intention of gathering new information and experiences that satisfy their cultural needs. It encompasses various activities undertaken by tourists to explore and experience different cultures, customs, and traditions.
One of the key aspects of cultural tourism is the opportunity it provides visitors to learn and engage with local communities, their history, and their way of life. This tourism is more than just visiting heritage sites or attending cultural events; it involves understanding and experiencing how people from different cultures live, express themselves through art, and maintain their traditions.
Cultural tourism fosters mutual understanding and respect between people from different cultural backgrounds. It encourages dialogue and exchange, breaking down social and cultural barriers and contributing to more tolerant societies. This form of tourism is an essential aspect of sustainable tourism development, as it seeks to preserve precious heritage for future generations while supporting economic growth for local communities.
As the tourism industry continues to grow, the demand for unique and authentic experiences increases. Cultural tourism serves to meet this demand by offering visitors the opportunity to immerse themselves in various cultural settings, fostering a deeper understanding of the world and its diverse cultures.
Importance of Cultural Tourism
Cultural tourism plays a significant role in society as it helps preserve and promote the values, beliefs, traditions, and heritage that define a particular culture. It allows individuals and communities to exhibit unique perspectives on arts, rituals, folklore, music, literature, language, oral traditions, and other cultural elements. Cultural tourism serves as a bridge between societies, aiding in fostering mutual respect, tolerance, and understanding among various cultures.
Economic benefits are also apparent through cultural tourism. Visitors contribute to the local economy, supporting local businesses and sustaining host communities’ cultural products and experiences. By engaging in cultural tourism, visitors gain an authentic understanding of indigenous and local cultures, empowering them to appreciate the rich diversity and uniqueness of the world.
Furthermore, cultural tourism helps preserve cultural heritage, vital for maintaining a sense of identity and continuity for future generations. This preservation and promotion of different cultures provide a sense of pride and belonging for people who are part of those traditions. In turn, this enhances cultural exchange, allowing individuals to learn about other ways of life while appreciating their values and beliefs.
Cultural tourism also supports the sustainability of performing arts and other creative industries. Through various interactions with artists and performers, visitors can develop an appreciation for a wide range of artistic expressions, contributing to the overall vitality of the art world.
Through the development of cultural tourism, a society can showcase its cultural heritage while contributing to its economic prosperity. By embracing the importance of cultural tourism, we can foster a greater understanding, appreciation, and celebration of the rich tapestry of customs, beliefs, and traditions that make up the world’s diverse cultures.
Types of Cultural Tourism

Cultural tourism allows travellers to immerse themselves in the history, heritage, and traditions of different places around the world. This form of tourism can be categorized into several types, each offering a unique way for visitors to experience and appreciate local cultures.
One type of cultural tourism is Historical and Heritage Tourism . This focuses on exploring sites related to a region’s past, such as ancient archaeological sites, monuments, and museums. It can instil a sense of wonder and appreciation for past civilizations’ achievements and teach travellers about the history of the places they visit.
Moving to the artistic side, Arts Tourism highlights the creative aspects of a culture. Tourists visit galleries, theatres, and concerts to experience local art, music, dance, and drama. It allows them to understand different communities’ aesthetic and expressive tendencies, opening their minds to new perspectives and forms of creativity.
Religious and Spiritual Tourism is another common form, where tourists visit religious sites, such as temples, churches, and mosques, or engage in spiritual practices like meditation and yoga. This type of cultural tourism can provide insights into various societies’ belief systems and rituals, fostering understanding and tolerance among people of different faiths.
However, culture isn’t just about history, arts, and religion but also daily life. Ethno and Indigenous Tourism involves tourists visiting and interacting with indigenous communities to learn about their customs, way of life, and unique perspectives on the world. This type of cultural tourism encourages empathy and cross-cultural understanding while emphasising respect for indigenous people’s rights and dignity.
Lastly, Culinary and Agritourism put emphasis on local food and drink traditions, as well as the agricultural practices that underpin them. This type of tourism can include attending food festivals, partaking in cooking classes or workshops, and visiting farms, vineyards, or breweries. Culinary experiences help tourists understand the richness of a region’s flavours and the relationship between local communities and their land and resources.
In summary, cultural tourism comes in various forms, appealing to different interests and tastes. It offers travellers a chance to explore and interact with diverse cultures, fostering connections and understanding among people around the world.
Forms of Cultural Tourism
Cultural tourism offers a wide range of experiences for travellers who seek to immerse themselves in different cultures, traditions, and ways of life. Various forms of cultural tourism cater to different interests and preferences.
Museums and galleries play a significant role in cultural tourism as they showcase a certain location’s history, art, and culture. Examples include art galleries displaying local and international masterpieces and museums featuring exhibits about the history and development of a specific region or theme.
Monuments and historic sites attract cultural tourists interested in exploring the past. Famous landmarks, archaeological sites, and heritage buildings tell the stories of civilizations and cultures that once thrived. UNESCO World Heritage Sites are often at the top of travellers’ lists, representing the world’s most significant cultural and natural heritage.
Architecture as a form of cultural tourism exposes tourists to varying architectural styles and meanings. Walking tours, cityscapes, and visits to iconic buildings provide a deeper understanding of a city’s architectural design’s cultural, social, and political influences.
Festivals and special events are another important aspect of cultural tourism, highlighting a particular community’s local customs and practices. These may include carnivals, parades, performances, traditional dances, and food festivals that provide a unique insight into the cultural identity of a place.
Gastronomy and cuisine play an integral role in the cultural tourism experience, as they allow tourists to savour the flavours and ingredients unique to a location. Local markets, food tours, cooking classes, and traditional restaurants all offer opportunities to appreciate the culinary heritage of a destination.
Shopping for crafts and textiles is a popular form of cultural tourism, as it allows travellers to bring home tangible memories of their journeys. Local artisans may showcase their talents through handmade textiles, pottery, jewellery, and other crafts, reflecting their community’s cultural heritage and artistic expression.
Cultural tourism encompasses diverse experiences, enabling travellers to engage with their chosen destination’s rich history, art, architecture, events, cuisine, and crafts. By exploring these varied aspects, visitors can deepen their understanding and appreciation of the world’s unique cultural landscapes.
Tangible and Intangible Cultural Attractions

Cultural tourism often focuses on two major aspects: tangible and intangible cultural attractions. These attractions shape a destination’s identity, providing depth and context for visitors and facilitating cultural exchange. This section will explore various facets of tangible and intangible attractions, comprehensively understanding their significance and diversity.
Tangible cultural attractions encompass elements of history, arts, and architecture that visitors can physically experience. Notable examples include monuments, visual art, and crafts that showcase local communities’ unique skills and traditions. Such attractions often reflect centuries of evolution and showcase the ingenuity of a region’s inhabitants. By visiting these sites and engaging with these art forms, travellers gain firsthand insights into the cultural heritage of their destination.
On the other hand, intangible cultural attractions comprise the non-material aspects of a culture that contribute to its unique characteristics and traditions. Music, social practices, festive events, and customs are some of the intangible elements that enrich the cultural landscape of a tourist destination. Interaction with local people plays a crucial role in understanding the region’s intangible cultural attractions, as they act as custodians of these traditions and their oral histories.
A dynamic interplay exists between tangible and intangible cultural attractions, creating a vibrant, multi-dimensional experience for tourists. For instance, the physical structure in architectural landmarks represents the tangible aspect, while the stories, legends, and rituals connected to the site contribute to its intangible allure. This symbiotic relationship reflects the essential interdependence between culture’s material and immaterial aspects.
In conclusion, tangible and intangible cultural attractions are indispensable pillars of cultural tourism. They provide an enriching experience for visitors and play a vital role in preserving and promoting a destination’s unique cultural heritage. Both aspects should be regarded with equal importance and cultivated to ensure a comprehensive and engaging experience for travellers seeking to explore a destination’s cultural offerings.
Advantages of Cultural Tourism
Cultural tourism provides a unique opportunity for individuals to immerse themselves in a particular society’s history, traditions, and customs. In doing so, they can develop a deeper understanding and appreciation of the diverse cultures that make up the world.
One significant advantage of cultural tourism is its potential to boost local economies. Tourist expenditures in local businesses such as hotels , restaurants, and shops can contribute to the growth and development of a region. Additionally, cultural tourism can create jobs, especially for local artisans, performers, and guides who offer authentic cultural experiences to visitors.
Another benefit of cultural tourism is the preservation and revitalization of cultural heritage. By attracting tourists interested in learning about and experiencing different traditions, communities are encouraged to preserve and maintain their cultural assets, such as historic sites, museums, and festivals. This helps ensure that future generations can continue to enjoy and learn from these valuable resources.
Cultural tourism also fosters cross-cultural understanding and appreciation. As people engage with diverse cultures, they may develop a broader perspective and a greater respect for cultural differences. This can lead to increased tolerance and harmony among different societies.
However, it is important to be aware of the potential disadvantages of cultural tourism. For instance, there may be issues related to overcrowding, environmental impact, or the commodification of cultural traditions. This makes it crucial to manage cultural tourism responsibly, ensuring it benefits both the tourists and the host communities.
Disadvantages of Cultural Tourism
Cultural tourism has gained popularity in recent years, drawing visitors from around the globe to experience and appreciate diverse cultures. However, this type of tourism also brings several disadvantages that must be considered.
One significant drawback of cultural tourism is the potential for commodification of cultures. As communities open their doors to tourists, they risk losing the authenticity and uniqueness of their cultural identity. Traditional practices and artefacts may be tailored to appeal to the tourist market, diluting their cultural significance.
Moreover, cultural tourism can put pressure on resources and spaces used by local communities. The influx of tourists may lead to overcrowding and increased competition for essential amenities. This could negatively impact the quality of life for local residents and strain the available infrastructure.
Another issue is the potential for environmental degradation resulting from cultural tourism. Some tourist activities may involve access to sensitive natural areas, leading to erosion, pollution, or disturbance of wildlife habitats. The construction of tourist facilities and infrastructure can also threaten the environment.
Lastly, cultural tourism can contribute to the unequal distribution of economic benefits. While some members of the community may profit from tourism-related businesses, others may not be able to participate in or benefit from these enterprises. This could exaggerate income disparities and create economic imbalances within communities.
In conclusion, despite cultural tourism’s numerous benefits to travellers and host communities, it is crucial to acknowledge and address its potential negative aspects. To ensure the long-term success of cultural tourism, policies and practices must be implemented that prioritize the protection of cultural and environmental resources and promote equitable distribution of economic benefits.
Cultural Tourism Destinations

Cultural tourism is a popular type of travel that allows visitors to immerse themselves in various destinations’ history, heritage, and traditions. Throughout the world, numerous places provide rich cultural experiences for travellers. Here, we explore a few notable cultural tourism destinations.
China is a vast and diverse country with a history dating back thousands of years. One can explore the architectural wonders of the Great Wall, the Terracotta Army in Xi’an, or the magnificent Forbidden City in Beijing. Visiting local markets and trying traditional cuisine also adds to the cultural experience in China.
India is another top destination for cultural tourism, offering many historical sites and vibrant traditions. The Taj Mahal in Agra, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a must-see with its iconic marble mausoleum. Another popular destination is Rajasthan , where the colourful cities and the royal palaces, such as the spectacular City Palace of Jaipur, offer a glimpse into the past.
France , specifically Paris , provides visitors with rich art, architecture, and cuisine. Iconic sites such as the Louvre, Notre Dame Cathedral, and the Eiffel Tower showcase the country’s artistic and architectural achievements throughout history.
Similarly, Spain is renowned for its rich cultural heritage with attractions such as the Alhambra in Granada, the Park Güell in Barcelona, designed by Gaudí, and the Prado Museum in Madrid.
Turkey , especially Istanbul , offers an intricate blend of European and Asian influences, with historic sites such as the Hagia Sophia, the Blue Mosque, and the Topkapı Palace. Moreover, the open-air bazaars and Turkish baths deliver an authentic cultural experience.
Italy , the birthplace of the Renaissance, is brimming with artistic and architectural masterpieces. Cities like Rome, Florence, and Venice are steeped in history, allowing visitors to marvel at landmarks like the Colosseum, St. Peter’s Basilica, or the Uffizi Gallery.
The beautiful island of Bali in Indonesia is known for its lush landscapes, Hindu temples, and vibrant arts scene, making it an excellent location for immersing oneself in the culture of the region.
Uzbekistan has gained attention recently as tourism grows along the Silk Road route. Visitors can admire the stunning architecture and mosaics of cities such as Samarkand, Bukhara, and Khiva, which capture the rich heritage of the ancient trading route.
In conclusion, cultural tourism invites travellers to explore fascinating destinations across the globe. While each location offers unique experiences, they provide a deeper understanding of human history, traditions, and heritage.
Stakeholders of Cultural Tourism

Cultural tourism is a multi-faceted industry that brings value to travellers in search of authentic experiences and to a myriad of stakeholders. From local communities to government bodies and from small businesses to environmental conservation efforts, cultural tourism can shape economies and lifestyles in both positive and negative ways. This guide delves into the key stakeholders in the cultural tourism sector, exploring their roles, impacts, and interconnected interests.
Tourists: The Heart of the Industry
Arguably, tourists are the backbone of cultural tourism. Whether they are history enthusiasts seeking out ancient ruins or gastronomes on the hunt for authentic local cuisine, tourists drive demand and shape the landscape of the tourism industry. They often seek enriching experiences that can offer a deep understanding of local cultures.
Local Communities: The Soul of the Destination
Local communities provide the lived experience that many cultural tourists seek. These people preserve the traditions, language, and heritage sites that form the basis of cultural tourism. Unfortunately, they can also bear the brunt of poorly managed tourism through cultural commodification and environmental degradation.
Government Bodies: The Framework Providers
Local and national governments play an instrumental role in regulating and promoting cultural tourism. They invest in infrastructure, enforce zoning laws, and facilitate public services like safety and sanitation that are vital to the tourism industry.
Tourism Boards and Agencies: The Promoters
Tourism boards, often funded by governments, are responsible for marketing a destination’s cultural assets to the world. These bodies work closely with other stakeholders to develop tourism packages, advertise local attractions, and even set guidelines for responsible tourism.
Tour Operators and Travel Agents: The Experience Curators
Specializing in delivering personalized experiences, these businesses are intermediaries between tourists and destinations. They can make or break the quality of the cultural tourism experience through their choices of local partnerships, itineraries, and guides.
Cultural Institutions: The Keepers of Heritage
Museums, art galleries, and historical sites are essential touchpoints for cultural tourists. They collaborate closely with various stakeholders to ensure that cultural assets are preserved and made accessible to the public.
Artisans and Performers: The Artistic Impressions
Artisans and performers add texture to the cultural fabric of a destination. These stakeholders benefit from increased visibility and economic opportunities , providing tourists a gateway to the authentic local culture.
Small Business Owners: The Local Economy Boosters
From restaurants and cafes to souvenir shops, small businesses see a surge in revenue when cultural tourism is thriving. They form a vital part of the local economy, providing services that enrich the tourist experience.
Academics and Researchers: The Thought Leaders
Cultural tourism is a field ripe for academic inquiry, touching upon anthropology, economics, and sociology disciplines. Research in this area can help shape policies that benefit tourists and local communities.
NGOs: The Advocates of Sustainability
Organizations that focus on cultural or environmental conservation often align with the interests of responsible cultural tourism. They act as watchdogs and advocates, ensuring that tourism practices are sustainable and ethical.
Real Estate Developers: The Infrastructure Builders
Though not directly related to the culture, real estate is essential in accommodating the influx of tourists, especially in booming destinations. They must balance business interests with responsible development.
Media: The Influencers
Media outlets, including travel bloggers and journalists, have a significant role in shaping public perception of a destination. Their storytelling can amplify the benefits or expose the pitfalls of cultural tourism.
The Environment: The Unspoken Stakeholder
Although not a traditional “stakeholder,” the environment stands to be significantly affected by tourism activities. Sustainable practices must be adopted to preserve the natural and cultural landscapes that attract visitors in the first place.
Understanding the intricate web of stakeholders in cultural tourism is the first step in creating an industry that benefits all. As cultural tourism evolves, stakeholders must actively dialogue to ensure sustainable and enriching experiences for everyone involved.
Cultural Tourism Experience
Cultural tourism experiences provide a unique opportunity for travellers to immerse themselves in the local culture, customs, and traditions of the places they visit. These immersive travel experiences enable tourists to understand the heritage and identity of the communities they encounter.
One popular way to experience cultural tourism is through homestays. These accommodations offer the chance to live with a local family, providing a firsthand glimpse into their daily lives and customs. The cultural exchange within a homestay environment can be transformative, offering insights that would otherwise remain veiled during a typical sightseeing vacation.
Another important aspect of cultural tourism is engaging with the local communities, participating in their events and festivals, and learning about their history and heritage through interactions with the people there. These experiences enable travellers to connect meaningfully with locals, fostering mutual appreciation and understanding of different cultures.
Cultural experiences often focus on different dimensions, such as:
- Arts and crafts: Exploring local artisans’ craftsmanship and heritage by visiting workshops, galleries, and markets.
- Cuisine: Sampling regional culinary specialities can offer a taste of local culture, traditions, and history.
- Religious sites: Visiting places of worship offers insight into the spiritual beliefs and practices of the area.
- Performing arts: Engaging with local music, dance, and theatre performances can reveal unique cultural perspectives and expressions.
Cultural tourism emphasizes responsible travel and encourages visitors to respect and appreciate the local customs, traditions, and the natural environment while exploring new destinations. Tourists can create unforgettable memories by connecting with people from different backgrounds and gaining a deeper understanding of their practices and values, fostering greater global empathy and cultural appreciation.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Cultural Heritage Tourism: Best Practices and Key Concepts for Regional Initiatives

Related Papers
Historical Archaeology
Paul Shackel
Breaking barriers - The Future is Heritage
Jesper de Raad
“You are the future!” is a commonly heard exclamation by cultural heritage policy makers aimed at young people engaged in the heritage field. Organizations like UNESCO and Europa Nostra try hard to involve young professionals in their policy. Likewise, cultural corporations like museums, heritage institutions and cultural policy makers are quite keen to involve youngsters as their audience and as participators. Or so it seems. Young people are seen as the cultural heritage policymakers, museum visitors, employees and investors of the future. But what is the common view of the value of youth participation for young people now? From the 19th of June until the 22th of June, The Future is Heritage Summit took place during the European Year of Cultural Heritage (2018). Young heritage professionals from all over Europe responded to the call for papers on how they viewed cultural heritage and it future in their country and Europe. The entire program of the summit was set up, developed and finalized by these young participants and in Berlin they literally took the stage. With a broad intercultural and European context, the young heritage professionals addressed topics in the cultural heritage sector and with this, they exchanged their thoughts and learned about each other’s history and backgrounds. The Future is Heritage Summit gave young heritage professionals a change to share their thoughts and work. Without premeditation, the summit gave a stage to talk and listen professionally, to create a dialogue. The summit was there to get influenced and changed by what others had to tell. To charge the participant with new energy and to create a network. There were vivid discussions, interesting workshops and inspiring visits to museums and heritage sites in the city of Berlin. It was a tremendous success. In this article, we explore the challenges we and other young heritage professionals experience in starting our careers in the European heritage field. We’ll talk about how and why we organized The Future is Heritage, and how it was shaped through participating with young professionals. Also, we explore community participation in general. For those who didn’t attend The Future is Heritage, we made an overview of our program. We conclude this article by talking about the aftermath of The Future is Heritage and our lessons learned by participating in this extraordinary event.
Katja Mäkinen
Emma Waterton
Academics did not create heritage, but they disciplined it, so to speak, in the late 20 th century. Heritage was already happening in the context of multiculturalism and globalization as " people all over the world … turned to ethnic and cultural identity as a means of mobilizing themselves for the defense of their social and political-economic interests " (Turner, 1993, p. 423). It was also happening via the mechanisms of UNESCO's World Heritage List, which were beginning to operate as early as 1978, and as mass tourism opened up new horizons for that industry. Indeed, cultural heritage was – and is – on the move: heritage is in action. One clear demonstration of this is the " overproduction " of heritage. Whether it is the expansion of the World Heritage List (1,031 inscriptions as of 2015 with no end in sight/sites, if we may be permitted the pun), the proliferation of museums, individual and community heritagizing actions, business sector appropriations of heritage discourse and imagery, the new European Heritage Label, or heritage-justified internal and international ethnic strife—it seems that everything and anything is being declared, contested and/or performed as heritage. Moreover, heritage now travels with a mobile population – temporary, permanent and along a scale between those extremes – and it (re)creates and reconfigures itself in its destinations. Heritage is produced and mobilized by individuals and communities in any number of actions, including remembering, forgetting, generating, adapting and performing. Heritage shapes and reshapes people's sense of place, sense of belonging and cultural identities locally and nationally. Clearly, then, heritage does " work " (Smith, 2006). And as work, cultural heritage is a tool that is deployed broadly in society today. It is at work in indigenous and vernacular communities, in urban development and regeneration schemes, in expressions of community, in acts of memorialization and counteracts of forgetting, in museums and other spaces of representation, in tourism, in the offices of those making public policy and, all too frequently, in conflicts over identity and the goals of those politics of identification. Thus, heritage is not simply an inert " something " to be looked at, passively experienced or a point of entertainment; rather, it is always bringing the past into the present through historical contingency and strategic appropriations, deployments, redeployments, and the creation of connections and reconnections. It implicates how memory is produced, framed, articulated and inscribed upon spaces in a locale, across regions, nationally and, ultimately, transnationally. It enables us to critically engage with contemporary social and political issues of grand import while also being a familiar prop drawn upon to make sense of more mundane processes of negotiating self, place, home and community.
Journal of Sustainable Tourism
Cheryl Hargrove
Museum and Society
Kristina Dziedzic Wright
Bill Mulligan
Keynote address: Minnesota Historical Organizations, Annual Meeting, St. Paul, MN, October 17, 1997
Cadernos do LEPAARQ
TIAGO MUNIZ , Cornelius Holtorf
What is the role of cultural heritage in constructing futures? How can a UNESCO Chair provide tools for creative futures thinking and future-making? And how does archaeology relate to that? This interview develops the concept of heritage futures and calls the attention of the “heritage sector” to broad interdisciplinarity and open-minded collaborations with partners outside of academia and industry, among others. Here, Dr. Cornelius Holtorf, archaeologist, Professor of Archaeology, Director of the Graduate School in Contract Archaeology (GRASCA) and UNESCO Chair on Heritage Futures at Linnaeus University talks about his ongoing projects/ideas and comments on the impact of tourism and covid-19 on cultural heritage, heritage futures and future literacy.
International Journal of Heritage Studies
Bryony Onciul
Cambridge University Press eBooks
Hannu I Heikkinen
20 Best Cultural Cities In The World
Here are the best cultural tourism destinations that you ought to visit if you want to do more than just travel. Learn a thing or two about the culture of these places.
- Paris – An Epitome Of Love, Romance, And Modern Art
- Milan – The Fashion Capital Of The World
- London – A Flawless Combo Of Cosmopolitan Culture & Old-World Charm
- Rome – A City That Oozes Royalty, Romance, And Ruins
- Jerusalem – An United Abode Of Judaism, Islam, And Christianity
- Bangkok – A Fantasy Land Of Temples, Bars, And Buzzing Nightlife
- Toronto – A True Showcase Of Unity In Diversity
- Miami – A Dazzling City Where Beach Scenes Are Done Right
- Singapore – A Cuisine Hybrid That Brings Flavors Of The World Together
- Madrid – A City That Cannot Survive Without Flamenco
- Dubai – A Skyscraper-City That Is Synonymous With Luxury
- Rio de Janeiro – The La La Land Of Festivals & Carnivals
- Barcelona – A City That Speaks Architecture
- Varanasi – The Spiritual Capital Of India
- São Paulo – An Owl City That Has Over 2000 Nightclubs
- New York – Shining With The Empire State Of Mind
- Tokyo – The Food Capital Of The World
- Vienna – A City That Breathes Music, In & Out
- Istanbul – A City That Brings Ancient Relics Back To Life
- Shanghai – The Museum City
20. Shanghai – The Museum City

Shanghai, also known as the global financial hub, is the largest city of China, and also the most populous city in the world. It is the birthplace of Chinese cinema, and boasts of numerous cultural attractions such as national as well as regional museums, diverse architecture, fascinating art galleries, sybaritic restaurants and cafes, and a vibrant nightlife.
Major Attractions: Shanghai Museum, The Bund, Shanghai World Financial Centre, Oriental Pearl Tower, Yu Garden, and more. Best Things To Do: Experience speed on the world’s fastest train – the Maglev, rejuvenate at Disneyland Park, enjoy a peaceful walk at the Bund, and more. Best Time To Visit: October to November.
Must Read: Crazy Adventures You Need To Try At The Great Wall of China
Looking To Book An International Holiday?
Book memorable holidays on TravelTriangle with 650+ verified travel agents for 65+ domestic and international destinations.

Trip to Sri Lanka at Rs 13,500/-
Plan Your Vacation Today!
Trip to Singapore at Rs 20,499/-
Get Quotes From Local Experts

Mauritius Holiday Starting at Rs 65,000/-
Talk to Our Experts Today

Maldives Honeymoon Trip at Rs 39,800/-
Pay with easy EMI Option

Europe Trip at Rs 89,999/-
All Inclusive Deals

Vacation in Dubai at Rs 27,499/-

Hong Kong Holiday at Rs 24,999/-
Money Safe Guarantee

Thailand Holiday at Rs 7,999/-
Flights Excluded

See more at TRAVELTRIANGLE.COM
19. Istanbul – A City That Brings Ancient Relics Back To Life

Witness the old world charm while traversing through the empire city of Istanbul. Straddling across Europe and Asia, Istanbul is the world’s only transcontinental city with an amalgamation of Asian and European culture . The relics of antiquity, historical museum, bustling markets, medieval ruins, upmarket restaurants, and peppy nightclubs form a major part of cultural tourism in Istanbul.
Major Attractions: Hagia Sophia, Topkapi Palace, Sultan Ahmed Mosque, Bosphorus, and more. Best Things To Do: Take a tour of the Bosphorous Cruise, shopping at the Grand Bazar, explore the Basilica Cistern, and more. Best Time To Visit: April to May or September to November
Suggested Read: 26 Places To Visit In Germany That Will Compel You To Stay Here Forever
18. Vienna – A City That Breathes Music, In & Out

Vienna is another city which adds to the charm of elegant European culture . The city of canals is known for its artistic legacy, imperial architecture, and majestic museums. Vienna’s long-lived culture of music, theatre, and opera is now accompanied by a contemporary trend of opulent coffee houses and elegant restaurants.
Major Attractions: Schonbrunn Palace, Hofburg, St. Stephen’s Cathedral, Belvedere, Albertina, and more. Best Things To Do: Visit the State Opera House, explore the Tiergarten Schönbrunn zoo, enjoy riding on the Wiener Riesenrad Ferris wheel, and more. Best Time To Visit: April to May or September to October
Suggested Read: 5 Best Ways To Convert INR To Euro On Your Europe Holiday
17. Tokyo – The Food Capital Of The World
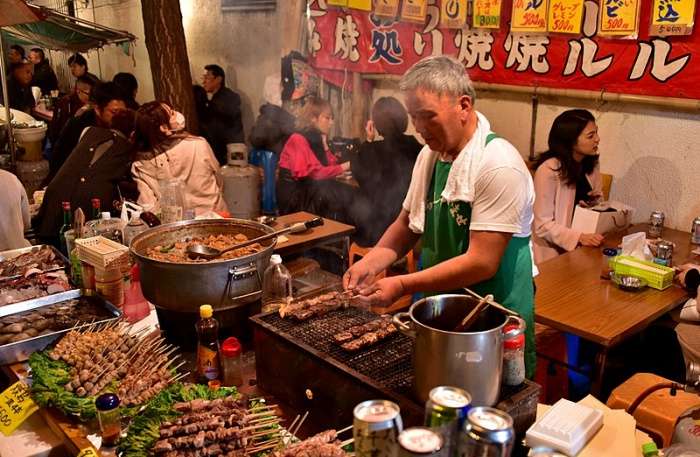

Image Source
Unlike other cultural destinations of the world, Tokyo’s culture is not only limited to ancient art and architecture. This metropolitan city depicts a unique blend of futuristic and traditional world with architecture ranging from historical temples to neon-lit skyscrapers. The most beckoning part of Japanese culture is their food. Tokyo has the most number of Michelin-starred restaurant than any other city in the world, thus, earning the title of ‘food capital of the world’.
Major Attractions: Tokyo SkyTree, Imperial Palace, Tokyo National Museum, Odaiba, Shinjuku Gyoen, and more. Best Things To Do: Spectate a game of Sumo Wrestling, dine out at the finest restaurants, visit the Tokyo Disneyland, and more. Best Time To Visit: March to May and October to December
Suggested Read: 15 Magical Autumn Honeymoon Places For Newlywed Couples
16. New York – Shining With The Empire State Of Mind

New York, the most lively city of United States, is also a popular commercial, financial, and cultural cities of the world . The city houses ultramodern architectural buildings, highest number of theaters, musical concerts, and a bustling nightlife which beckon every traveler to visit this place once in a lifetime.
Major Attractions: Central Park, Empire State Building, Statue Of Liberty, Rockefeller Center, Metropolitan Museum of Art, and more. Best Things To Do: Attend a broadway show at Times Square, visit the Brooklyn Bridge, explore the High Line, visit the Bryant Park, and more. Best Time To Visit: April to June and September to November
Suggested Read: 8 Salzburg Hotels That Let You Experience The City’s Fine Hospitality On Your Trip
15. São Paulo – An Owl City That Has Over 2000 Nightclubs

Holding a record of maximum number of nightclubs, Sao Paulo is a city that never sleeps. The city witnesses a vast cultural diversity with sophisticated art and architecture on side and an uproaring party culture on the other. Keeping aside cultural places to visit , the Paulistanos possess an eternal love for music and theatre which reflects brightly from their culture.
Major Attractions: Ibirapuera Park, Sao Paulo Museum of Art, Sao Paulo Cathedral, and more. Best Things To Do: Witness the Samba Saturdays, watch a play at the Theatro Municipal de Sao Paulo, and more. Best Time To Visit: September to March
Suggested Read: 13 Best Places To Visit In Brussels That Highlight The Charm Of The City
14. Varanasi – The Spiritual Capital Of India
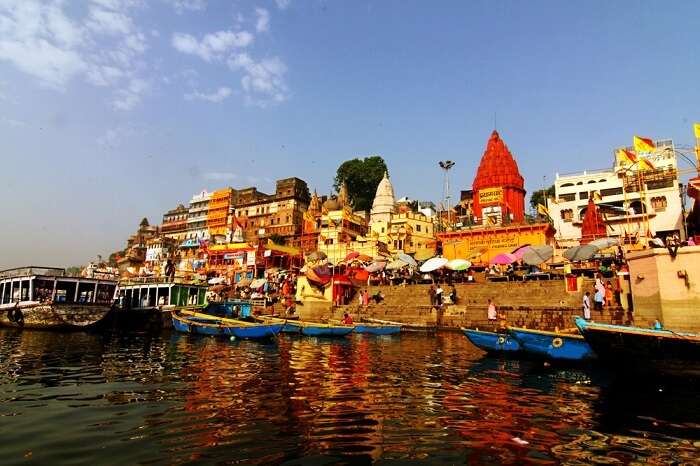

Varanasi, a major pilgrimage city in India, is one of the most visited cultural travel destinations of the country. Situated on the banks of the divine Ganges river, Varanasi is one of the oldest civilised city of the world which can be best explored with personalized India tour packages . This mystical city is considered as an abode of Lord Shiva, and is of great religious importance to the Hindus who visit this place in order to repent, seek forgiveness, and to pay final respects to the departed family members.
Major Attractions: Kashi Vishwanath Temple, Panchganga Ghat, Dashashwamedh Ghat, Ramnagar Fort, Chaukhandi Stupa, and more. Best Things To Do: Witness the evening prayer ceremony at Ganga Ghat, River Rafting, explore the Chandra Prabha Wildlife Sanctuary, and more. Best Time To Visit: November To February
Suggested Read: 39 Places To Visit In Varanasi: The Best Of Culture, History, & Spirituality
13. Barcelona – A City That Speaks Architecture

This Spanish seaside city possesses a rich cultural heritage in the form of art and architecture which dates back to the middle ages. Barcelona is one of the most visited cultural places in the world which is not only famous for its historical past but also for its Catalan cuisine and elegant wine and dine restaurants. It is one of the most interesting cultural tourism places to visit if you want to have a holistic experience.
Major Attractions: Sagrada Familia, Park Guell, Casa Mila, Gothic Quarter, La Boqueria, Museu Picasso, and more. Best Things To Do: Explore La Boqueria food market, enjoy Tibidabo Amusement Park, trek to Montjuic, cable car ride at Montserrat, and more. Best Time To Visit: May to June or September to October
Suggested Read: This Winter, Escape To The Best Honeymoon Destinations In Europe In Winter
12. Rio de Janeiro – The La La Land Of Festivals & Carnivals

The first thing that comes to one’s mind upon hearing Rio de Janeiro is the famous ‘Christ The Redeemer’ statue. The ‘Marvellous City’ is an important part of cultural tourism famous for its colourful lifestyle, high-spirited nightlife with music in the veins of every Carioca. The enthusiastic lifestyle of the people coupled with the golden sand beaches, and picturesque mountains make the city even more enticing.
Major Attractions: Christ The Redeemer Statue, Sugarloaf Mountain, Copacabana, Corcovado, and more. Best Things To Do: Santa Teresa tour, hike the Sugarloaf mountain, shopping at Ipanema, nightlife at Botafogo, and more. Best Time To Visit: December to March
Suggested Read: Guide To Budapest: The Most Stunning City In Europe
Planning your holiday but confused about where to go? These travel stories help you find your best trip ever!
Real travel stories. Real stays. Handy tips to help you make the right choice.

Ramya Narrates The Story Of 6 Girls On An Extraordinary Trip To Thailand
Bangkok. Phi Phi. Krabi. Why should guys have all the fun?

Sandeep Illustrates On The Best Activities For A Family Trip To Mauritius
Water sports. Cocktail parties. And unlimited fun at Casela.
Nisarg Can't Stop Praising His Honeymoon Trip To Maldives
There was snorkeling, sightseeing, luxury, comfort, & much more!

Sabyacsachi's Romantic Trip Proves Europe To Be The Mother Of All Vacations
For Art, Culture, Luxury, & more...

Srishti Talks Of Her Amazing Trip To Singapore With Her Mother & Niece
A fun-filled destination for ages indeed!

67-Year Old Sridhar Tells How He Beat The Odds & Took A Solo Trip To Dubai
Desert safari. Burj Khalifa. Welcoming locals. Tell me more!

Not Adventure Lovers? Saurabh's Family Trip Proves Hong Kong To Still Be Full Of Fun
Your kids will love Disney Land & Ocean Park!

Ravi's Tale Of A Sri Lanka Family Tour Is All You Need To Know About Ramayana Tour
For the love of Ramayana & Travel!
11. Dubai – A Skyscraper-City That Is Synonymous With Luxury

Dubai, the most sumptuous cultural tourism city, is a synonym of luxury. The lavish culture of the Emirati people reflects in their ornate architecture, extravagant hotels and resorts, and expansive malls. Being an epitome of development, Dubai is one of the most futuristic cities of the world in terms of technology, and architecture.
Major Attractions: Burj Khalifa, Burj Al Arab, Palm Jumeirah, The Ferrari Museum, Aquaventure Waterpark, and more. Best Things To Do: Desert Safari, Shopping at Dubai Mall, dune bashing, cruise the Dubai Creek, quad-biking, and more. Best Time To Visit: November to March
Suggested Read: Spending Winter In Dubai This Year Would Be The Best Decision You’d Ever Make With This Guide!
10. Madrid – A City That Cannot Survive Without Flamenco

Madrid, the capital of Spain, is another city which depicts the majestic grandeur of European culture . The city’s culture is beautifully moulded in the artistic and architectural masterpieces, which is further enhanced by the culinary delights where fine art meets fine dining on the bustling streets of the city which become even more lit during the night.
Major Attractions: Buen Retiro Park, Plaza Mayor, Royal Palace Of Madrid, Museo Nacional Del Prado, Puerta del Sol, and more. Best Things To Do: Visit the Temple of Debod, do the flamenco, shopping at the flea market, explore the Almudena Cathedral, attend a theatre performance at Gran Vía, and more. Best Time To Visit: September to November and March to May
Suggested Read: 20 Remarkable Places To Visit In Madrid That Give You A Taste Of The Good Life In Spain!
9. Singapore – A Cuisine Hybrid That Brings Flavors Of The World Together

One of the most tourist-friendly cities in the world, Singapore is an indispensable part of cultural tourism . This island city is one of the most culturally diverse cities in the world in terms of lifestyle, language, and cuisine. It is a global financial with the most efficient transport system in the world, eco-friendly business hubs, and a plethora of national parks in Singapore .
Major Attractions: Gardens By The Bay, Sentosa, Universal Studios, Singapore Botanic Gardens, Merlion Park, and more. Best Things To Do: Enjoy the Night Safari, go on a Singapore Zoo tour, experience the River Safari, enjoy riding on the Singapore Flyer, and more. Best Time To Visit: February to April
Suggested Read: 22 Chilling Winter Destinations In Europe That’ll Melt Your Heart
8. Miami – A Dazzling City Where Beach Scenes Are Done Right

One of the leading cities of cultural tourism , Miami lures culture lovers to visit its white sand beaches, artistic beauty, and architectural jewels. This culturally diverse city is one of beckons you to capture a glimpse of its exuberant culture which reflects through its dazzling nightlife, innovative cuisines, and thrilling adventure sports.
Major Attractions: Miami Seaquarium, Jungle Island, Coral Castle, Vizcaya Museum and Gardens, and more. Best Things To Do: Shopping at Lincoln Road, swim at the Venetian Pool, go bowling at the Dolphin Mall, experience skydiving, and more. Best Time To Visit: March to May
Suggested Read: 10 Exciting Things To Do In Helsinki For Unforgettable Finnish Experiences
7. Toronto – A True Showcase Of Unity In Diversity

Toronto, often called the capital of language diversity, is one of the finest example of cultural tourism . This culturally and linguistically diverse city is an exceptional example of hospitality and the number of ethnic groups that it accommodates. Other than that, Toronto is also known for its freezing winters, prodigious skyscrapers, and extensive culinary delights.
Major Attractions: CN Tower, Lake Ontario, Royal Ontario Museum, Ripley’s Aquarium of Canada, Casa Loma, and more. Best Things To Do: Dine at the CN Tower, enjoy sailing at Lake Ontario, explore the Canada’s Wonderland, visit the Toronto Islands, shopping at Eaton Centre, and more. Best Time To Visit: April to May and September to October
Suggested Read: 40 Best Places To Visit In Canada That Will Leave You Spellbound!
6. Bangkok – A Fantasy Land Of Temples, Bars, And Buzzing Nightlife

One of the most budget-friendly cultural tourism destinations , Bangkok is famous for its iconic temples, vibrant cuisine, and lively bars all over the world. The Thai culture resides in each and every aspect of the city, be it ultramodern architecture, tropical beaches, the traditional martial arts, or the much-hyped go-go bars. Apart from this, this temple land is also popular among the honeymooners who flock to Bangkok, Thailand all around the year. It is also one of the most popular cultural tourism destinations .
Major Attractions: Phi Phi Islands, Chiang Mai, Bangkok, Pattaya, Railay Beach, Wat Arun, Ko Pha Ngan, and more. Best Things To Do: Island hopping at Phi Phi Islands, scuba diving and snorkelling at Similan Islands, nightlife at Pattaya, and more. Best Time To Visit: November to April
Suggested Read: Top 18 Places To Visit In Switzerland During Winters
5. Jerusalem – An United Abode Of Judaism, Islam, And Christianity

Jerusalem, in true sense, is the quintessence of cultural tourism . It might be the only city in the world where one can hear church bells in consonance with Namaz, and the sound of the Shofar. The city’s cultural diversity is accompanied by its contrasting ancient and newfangled architecture, lifestyle, and beliefs. This city offers captivating tourist attractions ranging from museums to buildings, and restaurants and bars.
Major Attractions: Church Of The Holy Sepulchre, Dome Of The Rock, Western Wall, Mount Zion, and more. Best Things To Do: Hike the Israel National Trail, visit the Yad Vashem, shopping at Old City Market, explore the Monastery of the Cross, and more. Best Time To Visit: April to May or October to November
Suggested Read: 10 Most Beautiful Rivers In Europe For Cruise Journeys
4. Rome – A City That Oozes Royalty, Romance, And Ruins

Rome, also known as the Eternal City, is the epitome of European culture . Traversing through this city feels like travelling back in time to the middle ages. The cultural heritage of the city is restored in the ancient ruins like the age-old Colosseum, Roman Forum, and Piazza Venezia. The mesmerizing art and the bustling city life of this city render it one of the most romantic destinations in the world. It is also one of the must-see tourist places in Italy .
Major Attractions: Colosseum, Trevi Fountain, Roman Forum, Vatican Museum’s, St. Peter’s Basilica, Pantheon, and more. Best Things To Do: Shop at the Spanish Steps, savour the Gelatos at Giolitti, explore the Piazza Navona, visit the museum of Castel Sant’Angelo, and more. Best Time To Visit: October to April
Suggested Read: 15 Unique Things To Do In Copenhagen To Experience The City Like A Local
3. London – A Flawless Combo Of Cosmopolitan Culture & Old-World Charm

London, the capital city of England, depicts an amalgamation of both ancient and modern European culture . The cosmopolitan culture of the city can be estimated by the fact that one in every 3 Londoners is a foreign born. Other than that, the royal city is also known for its heritage architecture, creative art, film festivals, performing arts, and delectable cuisines.
Major Attractions: Big Ben, Buckingham Palace, Trafalgar Square, Tower Of London, British Museum, Tower Bridge, Palace of Westminster, and more. Best Things To Do: Boating at River Thames, visit St. Paul’s Cathedral, witness the best skyline views from The Shard, explore the London Dungeon, and more. Best Time To Visit: May to September
Suggested Read: Christmas Celebration In Delhi: 18 Best Places To Embrace The Festive Vibes In The Capital!
2. Milan – The Fashion Capital Of The World

Take a bus tour around the streets of Milan to absorb the rich history associated with its architecture, people, and food. Dressing to impress is a way of life and a given in the fashion capital of the world. Be prepared for a classy experience in a city that’s had more than its fair share of scandals, historic moments, and iconic people who have made a big imprint on human civilization, making it a significant cultural tourism destination .
Major Attractions: Milan Cathedral, Galleria Vittorio Emanuele II, Sforza Castle, Santa Maria delle Grazie, Palazzo dell’Arengario, and more. Best Things To Do: Watch an Italian classic at Teatro alla Scala, explore Royal Palace of Milan, admire the modern art at Pinacoteca di Brera, and more. Best Time To Visit: April to May and September to October
Suggested Read: Two Weeks In Europe: Music Festival, Austrian Beer & Unforgettable Madness With Friends
1. Paris – An Epitome Of Love, Romance, And Modern Art

Paris is a city overloaded with European culture . It is the most romantic destination of the world and a hub of modern art, fashion, film festivals, cinemas, shopping and gastronomy. Another important part of Parisian culture is the French cuisine which is served in iconic restaurants and blissful bakeries.
Major Attractions: Eiffel Tower, Arc De Triomphe, The Louvre, Notre-Dame de Paris, Sacré-Cœur, Paris, and more. Best Things To Do: Visit Disneyland Paris, dine at the Eiffel Tower, explore the Tuileries Garden, shopping at Champs-Élysées, and more. Best Time To Visit: June to August and September to October
Further Read: In Pictures: 35 Most Beautiful Cities In Europe That Will Make You Want To Take The EuroTrip Now!
Are you a culture vulture? Then wait no more! Book an international holiday package with TravelTriangle to one of the most cultural cities in the world and experience the best of cultural tourism.
Disclaimer: TravelTriangle claims no credit for images featured on our blog site unless otherwise noted. All visual content is copyrighted to its respectful owners. We try to link back to original sources whenever possible. If you own the rights to any of the images, and do not wish them to appear on TravelTriangle, please contact us and they will be promptly removed. We believe in providing proper attribution to the original author, artist or photographer.
Please Note: Any information published by TravelTriangle in any form of content is not intended to be a substitute for any kind of medical advice, and one must not take any action before consulting a professional medical expert of their own choice.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cultural Tourism
Which are the most famous cities in europe.
Paris, Rome, London, Madrid, Spain, and Vienna are some of the most popular cities in Europe that travellers often add to their itinerary. If you are planning a backpacking trip, you can add several more destinations from the surrounding countries.
Which is the most populous city in the world?
Tokyo is the most populous city in the world which has a population of approximately 9 million people. It is also one of the fastest developing cities in the world.
Which are the most popular cultural cities of South America?
Sao Paulo and Rio de Janeiro are the most popular cultural cities of South America. Most travellers explore these capitals before exploring other destinations in the country.
Which city is known as the fashion capital of the world?
Paris, Milan, London, and New York are known as the fashion capitals of the world.
Which city is known as the spiritual capital of India?
Varanasi is known as the spiritual capital of India. Home to some of the most popular temples and pilgrimage sites, many devotees travel to Varanasi for spiritual gatherings every year.
Looking To Book A Holiday Package?
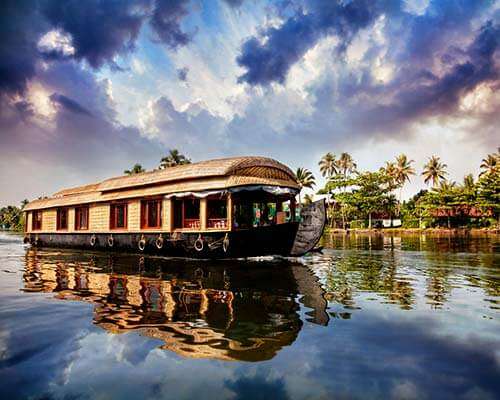

Spellbinding Cochin Family Tour 2D/1N Package @ Rs 2,750
Plan your trip today!

Himachal Family Tour Package 4D/3N @ Rs 8,750
Get quotes from multiple travel experts.

Exciting Andaman Family Trip 5D/4N @ Rs 10,250
Compare & customize quotes before booking.

Gangtok & Darjeeling Tour Package 5D/4N @ Rs 13,000
Have Questions? Talk to our travel experts today.

Wonderful Goa Family Package 3D/2N @ Rs 6,500
Best prices guaranteed.

Riveting Rajasthan Vacation 3D/2N Package @ Rs 6,499
EMI option available.

Enchanting Uttarakhand Tour 4D/3N Package @ Rs 7,199
Explore best destinations with our experts.

Delightful South Weekend Tour 3D/2N Package @ Rs 4,999
Thrilling weekend full of fun.

Marvelous Gujarat Tour 3D/2N Package @ Rs 4,999
Talk to our experts today.
People Also Read
Indian Cultural Heritage Unique Cultural Experience Sarawak Cultural Village
Recent Posts

Exploring Rich Cultural History: Heritage Sites In Europe
Top 10 Bucket List For Families In The World That You Must Include

2024 में 32 दुनिया में सितंबर में घूमने की जगहें जो आपको एक शांत छुट्टी

10 Meilleurs endroits à visiter en juin dans le monde pendant vos vacances d’été en 2024.

Ultimate Travel Bucket List For Teens To Unleash Your Inner Adventurer

11 Spectacular Bucket List Ideas For Couples
Trending Blogs

20 Mysterious Places In India To Visit In 2023 More Bizarre Than The Bermuda Triangle

10 Scariest Roads In India That Are A Driver’s Nightmare

101 Places To Visit In India Before You Turn 30 in 2024

35 Exotic Places To Visit In December In India 2024 To Enjoy A Surreal Vacation

60 Best Honeymoon Destinations In India In 2024

95 Best Honeymoon Destinations In The World In 2023 For A Romantic Escape!
Best Places To Visit In India By Month
Best places to visit outside india by month.
- TravelTriangle
- Worldwide »
- Tour Packages
- Honeymoon Packages
- Family Packages
- Budget Tour Packages
- Luxury Tour Packages
- Adventure Tour Packages
- Group Tour Packages
- Kerala Tour Packages
- Goa Tour Packages
- Andaman Tour Packages
- Sikkim Tour Packages
- Himachal Tour Packages
- Uttarakhand Tour Packages
- Rajasthan Tour Packages
- Tour Packages From Delhi
- Tour Packages From Mumbai
- Tour Packages From Bangalore
- Tour Packages From Chennai
- Tour Packages From Kolkata
- Tour Packages From Hyderabad
- Tour Packages From Ahmedabad
- Kerala Tourism
- Goa Tourism
- Sikkim Tourism
- Andaman Tourism
- Himachal Tourism
- Uttarakhand Tourism
- Rajasthan Tourism
- Hotels in Kerala
- Hotels in Goa
- Hotels in Sikkim
- Hotels in Andaman
- Hotels in Himachal
- Hotels in Uttarakhand
- Hotels in Rajasthan

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Cultural tourism helps to encourage the preservation of culture and heritage by keeping endangered traditions alive. There might be little demand for heritage handicraft skills, for example, but outside interest (and an opportunity to earn an income) could be enough to safeguard a tradition that might otherwise have been lost.
Heritage tourism. Cultural heritage tourism is a form of non-business travel whereby tourists engage with the heritage, tangible and intangible, moveable and immovable, of a region through activities, experiences, and purchases which facilitate a connection to the people, objects, and places of the past associated with the locations being ...
Each year, millions of travelers visit America's historic places. The National Trust for Historic Preservation defines heritage tourism as "traveling to experience the places, artifacts, and activities that authentically represent the stories and people of the past and present." A high percentage of domestic and international travelers participate in cultural and/or heritage activities ...
on Advancing Sustainable Tourism at Natural and Cultural Heritage Sites . Policy orientations: defining the relationship between World Heritage and tourism. 1. ... While there are many excellent examples of World Heritage properties successfully managing their relationship to tourism, it is also clear that many properties could improve: ...
6 • Cultural Heritage Tourism CULTURAL HERITAGE TOURISM As the term implies, cultural heritage tourism involves visiting places that are significant to the past or present cultural identity of a particular group of people. In the United States, America's rich history has created a vibrant and complex patchwork of cultural heritages.
The action of the International Coordinating Committee (link is external) (ICC-Angkor) for the safeguarding and development of this exceptional cultural site is a striking example of international solidarity and testifies to one of UNESCO's most impressive achievements for heritage. Thirty countries and an ad hoc experts group for scientific ...
Bringing cultural tourism back in the game The COVID-19 pandemic has stopped cultural tourism in its tracks. Throughout 2020 international arrivals plunged by 74% worldwide, dealing a massive blow to the sector, which faces ongoing precarity and unpredictability. Amidst international travel restrictions, border closures and physical distancing measures, countries have been forced to impose ...
The World Tourism Organisation (WTO) (1985) broadly define cultural tourism as the movements of persons who satisfy the human need for diversity, tending to raise the cultural level of the individual and giving rise to new knowledge, experience and encounters. Cultural tourism is commonly associated with education in this way, some describing ...
Cultural and heritage tourism isn't just a niche; it's a window to the soul of nations, offering a richer, fuller understanding of the world we live in. Every dance, every monument, every folk song carries the weight of history and the spirit of its people. To travel this way is to honor, celebrate, and immerse in the grand tapestry of human ...
Heritage tourism is a form of cultural tourism in which people travel to experience places, artifacts, or activities that are believed to be authentic representations of people and stories from the past. ... Stones or trees related to tales from the Nordic sagas, for example, combined natural with cultural heritage. 17. Although early efforts ...
Over the past two days in Japan's capital of culture, delegates debated how to keep the appreciation of heritage and contemporary cultural expression at the heart of tourism for generations to come. Intercultural dialogue, local communities and innovative measurement systems are at the core of the conference conclusions laid down in the Kyoto ...
This webpage provides UN Tourism resources aimed at strengthening the dialogue between tourism and culture and an informed decision-making in the sphere of cultural tourism. It also promotes the exchange of good practices showcasing inclusive management systems and innovative cultural tourism experiences.. About Cultural Tourism. According to the definition adopted by the UN Tourism General ...
Tourism based on living traditions, built heritage resources, and intangible culture is one of the most pervasive forms of tourism. It involves many different resources, and people's motivations for visiting are manifold (McKercher and du Cros 2014; Timothy 2011).Many places depend almost entirely upon the cultural past for their tourism-based economies, resulting in many political, social ...
Beyond the traditional ocean and sand vacation, heritage travel allows you to expand your horizons and spread the places people visit beyond a few locations. 4. Reinforces identity and creates understanding. Heritage tourism provides a whole new angle to traveling and can make an experience both fun and educational.
Cultural tourism in Egypt in the 19th century. Tourists at Hearst Castle, California. Tourists taking pictures at the khmer Pre Rup temple ruins, an example of cultural tourism.. Cultural tourism is a type of tourism in which the visitor's essential motivation is to learn, discover, experience and consume the cultural attractions and products offered by a tourist destination.
Tourism: the balance between development and the protection of cultural heritage. Tourism is an excellent way to encourage and provide access to cultural heritage, but it also brings with it challenges related to overcrowding, cultural appropriation and the loss of authenticity. Tourism brings money and jobs to cities and regions, but it can ...
19. Taj Mahal. Map of World Heritage Sites. 1. Machu Picchu, Peru. Machu Picchu, Peru. Highlights: An ancient 15th-century city high in the Andes with breathtaking views. Built in lush, mountainous terrain high above the Urubamba River, Machu Picchu lies in one of the most stunning settings of any archeological site in the world.
Cultural heritage tourism development has evolved 112 riad hotels between 1997 and 2016 (Alami, El Khazzan, and Souab Citation 2017), ... The examples of success stories of cultural heritage tourism worldwide come with the care, continuity and development of heritage resources. It remains a possible outcome that when the cultural aspect is ...
For example there are a growing number of public-private partnerships formed to develop and promote cultural tourism, such as heritage hotels in Rajasthan, many cultural routes in Europe, and Cultural Tourism Enterprises in Tanzania (UNWTO, 2018). But we know relatively little about how these bodies function, or the effect that they have on ...
The Meenakshi Temple in Madurai is the epitome of beauty and architecture and a must-visit for cultural buffs. Khajuraho, a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Madhya Pradesh beautifully mirrors the art and creativity of ancient India. One of a kind in the world! Kerala is a melting pot of different cultures and traditions.
One type of cultural tourism is Historical and Heritage Tourism. This focuses on exploring sites related to a region's past, such as ancient archaeological sites, monuments, and museums. ... Notable examples include monuments, visual art, and crafts that showcase local communities' unique skills and traditions. Such attractions often ...
Cultural and Heritage Tourism is a tool of economic development that achieves. economic growth through attracting visitors from outside a host community, who. are motivated wholly or in part b y ...
Academics did not create heritage, but they disciplined it, so to speak, in the late 20 th century. Heritage was already happening in the context of multiculturalism and globalization as " people all over the world … turned to ethnic and cultural identity as a means of mobilizing themselves for the defense of their social and political-economic interests " (Turner, 1993, p. 423).
Learn about cultural heritage through its definition, examples, and main types (tangible and intangible), as well as understand its significance in society and tourism. Updated: 11/21/2023 Table ...
Cultural tourism relates to a city's majestic art, fascinating architecture, age-old customs, impeccable hospitality, authentic cuisines, thriving nightlife, and many more facets. These compelling aspects make up the culture of a place that plays an influential role in developing and boosting the tourism of a particular destination.
Tourism development planning must balance economic growth with the need to protect the integrity of the region's cultural attributes. When promoting an area as a destination spot known for its cultural heritage, residents need to play a starring role. They are the ambassadors and storytellers who represent the region's heritage and are ...