Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution, update may 10, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |

Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Travel.State.Gov Newsroom
U.S. Passports News
International Travel News
U.S. Visas News
Intercountry Adoption News and Notices
Share this page:
Update on Change to U.S. Travel Policy Requiring COVID-19 Vaccination for nonimmigrant travel
Worldwide Visa Operations: Update
Employment-Based Fourth Preference (EB-4) Announcement
Suspension of Visa Services in Sudan
Diversity Visa 2024 Update
Nonimmigrant Visa Fee Increases to Take Effect June 17, 2023
India EB-3 Retrogression
Expiration of Covid-Era Visa Application Fee Receipts
Digital Visa Authorization (DVA) Proof of Concept
Final Rule Governing Public Charge Grounds of Visa Ineligibility
Visa Waiver Travel for Israeli Citizens
Important Update on Waivers of the Interview Requirement for Certain Nonimmigrant Visa Applicants
Department of State to Process Domestic Visa Renewals in Limited Pilot Program
Visa Information for Nationals of Haiti
Department of State/AILA Liaison Committee Meeting March 20, 2024
The Administration will end the COVID-19 vaccine requirements for international air travelers at the end of the day on May 11, the same day that the COVID-19 public health emergency ends. This means starting May 12, noncitizen nonimmigrant air passengers will no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated with an accepted COVID-19 vaccine to board a flight to the United States. CDC’s Amended Order Implementing Presidential Proclamation on Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID-19 Pandemic will no longer be in effect when the Presidential Proclamation Advancing the Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID-19 Pandemic is revoked .
Please see: https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2023/05/01/the-biden-administration-will-end-covid-19-vaccination-requirements-for-federal-employees-contractors-international-travelers-head-start-educators-and-cms-certified-facilities/
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
Fact Sheet: Biden Administration Releases Additional Detail for Implementing a Safer, More Stringent International Air Travel System
As we continue to work to protect people from COVID-19, today, the Biden Administration is releasing additional detail around implementation of the new international air travel policy requiring foreign national travelers to the United States to be fully vaccinated. This updated policy puts in place an international travel system that is stringent, consistent across the globe, and guided by public health. Starting on November 8, non-citizen, non-immigrant air travelers to the United States will be required to be fully vaccinated and to provide proof of COVID-19 vaccination status prior to boarding an airplane to fly to the U.S., with only limited exceptions. The updated travel guidelines also include new protocols around testing. To further strengthen protections, unvaccinated travelers – whether U.S. Citizens, lawful permanent residents (LPRs), or the small number of excepted unvaccinated foreign nationals – will now need to test within one day of departure. Today, the Administration is releasing the following documents to implement these requirements: 1) a Presidential Proclamation to Advance the Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID-19 Pandemic; 2) three Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Orders on vaccination, testing, and contact tracing; and 3) technical instructions to provide implementation details to the airlines and their passengers. With science and public health as our guide, the United States has developed a new international air travel system that both enhances the safety of Americans here at home and enhances the safety of international air travel. The additional detail released today provides airlines and international air travelers with time to prepare for this new policy ahead of the November 8 implementation date. As previously announced, fully vaccinated foreign nationals will also be able to travel across the Northern and Southwest land borders for non-essential reasons, such as tourism, starting on November 8. Additional detail on amendments to restrictions with respect to land borders will be available in the coming days. Travelers can find full details about today’s air travel announcement on the CDC and Department of State websites. A summary is below: Fully Vaccinated Status:
- Starting on November 8, non-citizen, non-immigrant air travelers to the United States will be required to be fully vaccinated and to provide proof of vaccination status prior to boarding an airplane to fly to the U.S.
Proof of Vaccination:
- For foreign nationals, proof of vaccination will be required – with very limited exceptions – to board the plane.
- Match the name and date of birth to confirm the passenger is the same person reflected on the proof of vaccination;
- Determine that the record was issued by an official source (e.g., public health agency, government agency) in the country where the vaccine was given;
- Review the essential information for determining if the passenger meets CDC’s definition for fully vaccinated such as vaccine product, number of vaccine doses received, date(s) of administration, site (e.g., vaccination clinic, health care facility) of vaccination.
- The Biden Administration will work closely with the airlines to ensure that these new requirements are implemented successfully.
Accepted Vaccines:
- CDC has determined that for purposes of travel to the United States, vaccines accepted will include FDA approved or authorized and World Health Organization (WHO) emergency use listed (EUL) vaccines.
- Individuals can be considered fully vaccinated ≥2 weeks after receipt of the last dose if they have received any single dose of an FDA approved/authorized or WHO EUL approved single-dose series (i.e., Janssen), or any combination of two doses of an FDA approved/authorized or WHO emergency use listed COVID-19 two-dose series (i.e. mixing and matching).
- More details are available in the CDC Annex here .
Enhanced Testing:
- Previously, all travelers were required to produce a negative viral test result within three days of travel to the United States.
- Both nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), such as a PCR test, and antigen tests qualify.
- As announced in September, the new system tightens those requirements, so that unvaccinated U.S. Citizens and LPRs will need to provide a negative test taken within one day of traveling.
- That means that all fully vaccinated U.S. Citizens and LPRs traveling to the United States should be prepared to present documentation of their vaccination status alongside their negative test result.
- For those Americans who can show they are fully vaccinated, the same requirement currently in place will apply – they have to produce a negative test result within three days of travel.
- For anyone traveling to the United States who cannot demonstrate proof of full vaccination, they will have to produce documentation of a negative test within one day of departure.
Requirements for Children:
- Children under 18 are excepted from the vaccination requirement for foreign national travelers, given both the ineligibility of some younger children for vaccination, as well as the global variability in access to vaccination for older children who are eligible to be vaccinated.
- Children between the ages of 2 and 17 are required to take a pre-departure test.
- If traveling with a fully vaccinated adult, an unvaccinated child can test three days prior to departure (consistent with the timeline for fully vaccinated adults). If an unvaccinated child is traveling alone or with unvaccinated adults, they will have to test within one day of departure.
Limited Exceptions from the Vaccination Requirement:
- There are a very limited set of exceptions from the vaccination requirement for foreign nationals. These include exceptions for children under 18, certain COVID-19 vaccine clinical trial participants, those with medical contraindications to the vaccines, those who need to travel for emergency or humanitarian reasons (with a US government-issued letter affirming the urgent need to travel), those who are traveling on non-tourist visas from countries with low-vaccine availability (as determined by the CDC), and other very narrow categories.
- Those who receive an exception will generally be required to attest they will comply with applicable public health requirements, including, with very limited exceptions, a requirement that they be vaccinated in the U.S. if they intend to stay here for more than 60 days.
Contact Tracing:
- The CDC is also issuing a Contact Tracing Order that requires all airlines flying into the United States to keep on hand – and promptly turn over to the CDC, when needed – contact information that will allow public health officials to follow up with inbound air travelers who are potentially infected or have been exposed to someone who is infected.
- This is a critical public health measure both to prevent the introduction, transmission, and spread of new variants of COVID-19 as well as to add a critical prevention tool to address other public health threats.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

COVID-19 international travel advisories
If you plan to visit the U.S., you do not need to be tested or vaccinated for COVID-19. U.S. citizens going abroad, check with the Department of State for travel advisories.
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S.
- As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
- As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
U.S. citizens traveling to a country outside the U.S.
Find country-specific COVID-19 travel rules from the Department of State.
See the CDC's COVID-19 guidance for safer international travel.
LAST UPDATED: May 23, 2024
Have a question?
Ask a real person any government-related question for free. They will get you the answer or let you know where to find it.
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Statement regarding vaccination requirements for noncitizen nonimmigrant air travelers entering the United States
Beginning November 8, 2021, all non-U.S. citizen, non-U.S. immigrants must be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 prior to traveling to the United States, to meet the President’s proclamation and CDC orders . These travelers are also required to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination and a negative test no more than three days prior to the flight’s departure. Limited exceptions apply.
According to CDC requirements , all air passengers two years of age or older traveling internationally, regardless of vaccination status, must provide a negative test to the airline before boarding the flight.
- Passengers fully vaccinated must provide a negative test no more than three days before the flight’s departure from a foreign country, in addition to showing proof of vaccination.
- Passengers over two years of age not fully vaccinated must provide a negative test no more than one day before the flight’s departure. Except in the limited circumstances allowed by CDC, unvaccinated travelers will be US citizens and legal permanent residents.
Those who recently recovered from COVID-19 may travel with documentation of recovery and a letter from a licensed healthcare provider or public health official indicating the patient is cleared for travel.
For more information on this new travel requirement, visit TSA.gov.
For more information about accepted COVID-19 vaccines and verification documents, visit https://www.cdc.gov .
Official websites use .gov
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Get Vaccinated Before You Travel
It’s important to plan ahead to get the shots required for all countries you and your family plan to visit.

Protect your child and family when traveling in the United States or abroad by:
- Getting the shots required for all countries you and your family plan to visit during your trip
- Making sure you and your family are up-to-date on all routine U.S. vaccines
- Staying informed about travel notices and alerts and how they can affect your family’s travel plans
Avoid getting sick or coming back home and spreading the disease to others.
Vaccinate at least a month before you travel
See your doctor when you start to plan your trip abroad. It’s important to do this well in advance.
- Your body needs time to build up immunity.
- You may need several weeks to get all the doses of the vaccine.
- Your primary doctor may not stock travel vaccines. Visit a travel medical clinic .
- You’ll need time to prepare for your pre-travel appointment .
- If the country you visit requires a yellow fever vaccine , only a limited number of clinics have the vaccine and will probably be some distance from where you live. You must get it at least 10 days before travel.
Find out which vaccines are recommended or required for the countries you plan to visit .
TIP : Save time by getting routine vaccines during the same doctor visit. Use the Vaccine Self-Assessment Tool and discuss the results with your doctor. It tells you which U.S. recommended vaccines you (19 years and older) or your child (birth – 18 years) might need.
Last-minute travelers
When traveling to another country be aware your doctor may not carry a travel vaccine and you may have to visit a medical clinic.
Many travel vaccines require multiple shots or take time to become fully effective. But some multiple-dose vaccines (like hepatitis A) can still give you partial protection after just one dose. Some can also be given on an “accelerated schedule,” meaning doses are given in a shorter period of time.
- Discover and learn about specific diseases that can affect you while traveling
- What to do if you get sick after traveling
- Vaccines & Immunizations
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
The independent source for health policy research, polling, and news.
Key Questions about COVID-19 Vaccine Passports and the U.S.
Anna Rouw , Jennifer Kates , and Josh Michaud Published: Apr 15, 2021
As COVID-19 vaccination rolls out in parts of the world, many countries have started to implement or are considering the use of COVID-19 “vaccine passports” – paper or digital forms certifying that a person has been vaccinated against COVID-19 – for purposes of international travel. In addition, some countries are using them for domestic travel and/or access to certain establishments, activities, and events. Such certifications are separate from but related to the issue of vaccine mandates . Where COVID-19 vaccines are mandated, there will be a need to certify vaccine status, and a vaccine passport is a potential tool for that purpose.
The U.S. government is exploring COVID-19 vaccine certifications for use internationally and domestically. The administration has said that a vaccine passport may be required in the future for international travelers entering the U.S., but it will not impose a federal requirement for domestic purposes. However, it is working with the private sector to develop standards around such certifications. Within the U.S., states are landing on different sides of what has quickly become a partisan issue with several states moving to implement passports while others have come out strongly against the idea.
This brief provides an overview of what vaccine passports are, how they are being used, and identifies a number of outstanding policy issues facing the U.S. in both the international and domestic contexts.
What are COVID-19 Vaccine Passports?
A vaccine passport is a paper or digital form certifying that a person has been vaccinated against a particular disease. There is a long history of the use of vaccine certifications for international travel, with many countries currently requiring travelers to present proof of yellow fever vaccination to enter, for example. A COVID-19 vaccine certification for international travel could be used by governments in a number of ways, such as allowing an individual to move across borders more freely by potentially bypassing travel restrictions like testing or quarantine requirements upon arrival. In addition, vaccine passports may be used for domestic purposes, such as to permit individuals access to certain businesses, locations or activities within countries.
Where are COVID-19 Vaccine Passports Being Used Now?
Several countries have already begun to use COVID-19 vaccine passports, with wide variation in policies and implementation. Israel began issuing ‘green passes’ in February 2021 to their vaccinated citizens to allow for less restricted internal movement and access to businesses such as to gyms or theaters. Other countries, such as China and Bahrain , have begun issuing digital vaccine passports to their vaccinated citizens to equip them to travel internationally. Lastly, in several countries, including Georgia , Estonia , Poland , and Seychelles , proof of COVID-19 vaccination allows incoming travelers to avoid certain travel restrictions, such as testing or quarantining. Numerous other countries are considering the use of COVID-19 vaccine passports, either for internal or international movement, including the United Kingdom , Malaysia , Singapore , Greece , Denmark , the EU , and the U.S.
Multiple international organizations have already launched efforts to set standards and coordinate the design and implementation of vaccine passports for international travel, including the World Health Organization , World Economic Forum , International Chamber of Commerce , and the International Air Travel Association . The WHO is undertaking this effort as part of its mandate under the International Health Regulations (IHR) to coordinate among member states to provide a public health response to the international spread of diseases; it is possible that COVID-19 vaccination could be included in an updated version of the IHR (at this time, yellow fever is the only disease listed in the IHR for which countries can require proof of vaccination as a condition of entry).
Will the U.S. Use COVID-19 Vaccine Passports?
There is likely to be growing demand for vaccine certifications for use in the U.S., for international travel as well as domestic purposes. Airlines and tourism groups have already called for vaccine certifications as a way to ease the process of pandemic-era travel; the CDC recently released guidance saying fully vaccinated individuals can resume non-essential travel safely within the U.S. and stating that fully vaccinated persons can consider international travel if they maintain recommended precautions. Federal officials have also indicated that vaccination may in the future be required for entry into the U.S. for incoming travelers; the U.S. currently requires all air passengers coming to the U.S. to have a negative COVID-19 test. 1 Domestically, proof of vaccination may be required for entry into certain federal facilities in the U.S., including military bases and other federal buildings, and a number of U.S. companies and universities have already announced vaccinations will be required for their employees, students, and staff, which will require some kind of certification (see this recent KFF analysis for more discussion of vaccine mandates in the U.S.). Indeed, as stated at a recent meeting of the federal Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC), “Proof of individual COVID-related health status is likely to be an important component of pandemic response” and “As more of the population becomes vaccinated, proof of immunization will likely become a major, if not the primary, form of health status validation”.
The Biden administration has made it clear it will not be the role of the federal government to issue vaccine passports or to collect and store individuals’ vaccination data at the federal level, but the government is taking on a coordination role and working with many of the international and domestic vaccine passport initiatives being developed by other parties. For example, President Biden issued an Executive Order directing the State Department to work with the World Health Organization, the International Civil Aviation Organization, the International Air Transport Association, foreign governments and others to establish international travel standards. Further, the order directs the Secretaries of the State Department, Department of Health and Human Services, and Department of Homeland Security, in coordination with relevant international organizations, to assess the feasibility of linking vaccination status with digital certificates for international travel. On the domestic side, the Administration is working with a number of privately-led vaccine passport initiatives already underway, to develop guidelines and address issues such as accessibility, privacy, and other access barriers. There are at least 17 such U.S.-based initiatives involving companies and institutions including Microsoft, IBM, MasterCard, the Mayo Clinic, and MIT. So far, these efforts remain in the development stage and none of these organizations has yet launched a vaccine passport for widespread use in the U.S. In the absence of a widely used vaccine passport system, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) “vaccination report card”, which is issued to each vaccinated individual, is being used as proof of vaccination in many cases for access to some activities and facilities. However, these cards can be falsified and lack a digital counterpart, upping the stakes on the need to develop standards and implement security measures.
Individual states are landing on different sides of the issue. Several have launched or are actively exploring the use vaccine certificates with New York being the first state to introduce a COVID-19 vaccine certification pass that would allow individuals to certify their vaccination status in order to access certain social activities. Other states, including Hawaii , are considering similar efforts. At the same time, several governors have come out strongly against vaccine passports, with some issuing executive orders banning their use, as has been done in Florida and Texas , or supporting legislation to prevent them, as in Tennessee . In the absence of a federally issued or sanctioned vaccine passport, and no nationwide private sector initiative yet being adopted, the U.S. may see more state or local level certification initiatives, which may or may not be coordinated across jurisdictions.
What are Key Implementation Issues to Consider?
There are a host of challenges and questions surrounding the design and use of vaccine passports, including issues of equity and access, a lack of uniform standards, and privacy and security.
Equity and access: There have already been significant equity challenges in vaccine roll out and access. Globally, most people in low and middle income countries (LMICs) do not have access to COVID-19 vaccines and may not until 2023 or later, and within the U.S. our analyses show that Black and Hispanic people have been vaccinated at lower rates than White people, and that high poverty and uninsured rates are associated with lower vaccination rates in many U.S. counties. In addition, non-citizen immigrants in the U.S. who, while eligible for free COVID-19 vaccination, may be reluctant to access the vaccine and/or to sign up for a vaccine passport that would require sharing of personal or other information with authorities. Further, it is still an ongoing question as to how populations that are either ineligible or unable to receive the COVID-19 vaccine, such as children under the age of 16, people with medical exceptions and those with religious objections, will be included in a COVID-19 vaccine passport system. Lastly, the process to sign up for a vaccine passport itself may present additional access issues, particularly for some groups. Given these inequities, some have cited concerns that proof of vaccination as a condition to access certain activities, such as travel or specific venues, has the potential to be discriminatory. For this reason, the World Health Organization’s Emergency Committee on the COVID-19 Pandemic officially cautioned countries against the use of requiring COVID-19 vaccine passports for international travel at this time, stating that COVID-19 vaccination should not exempt individuals from other risk-reduction measures while traveling and noting that vaccination as a requirement to travel would inequitably impact individuals in LMICs. Likewise, a coalition of travel organizations recently expressed concerns about imposing a travel-related vaccine requirement, recommending that vaccinated individuals be exempt from international testing requirements but that vaccination not be a “prerequisite to travel.” The EU, in its proposal for a Digital Green Certificate , has said that to ensure freedom of movement with the EU, it would include COVID-19 test certificates and certificates for those who have recovered from COVID-19 as part of its plan, in addition to certification of vaccination. New York state’s Excelsior Pass also allows for the use of a negative COVID-19 test (instead of vaccine certification).
Mutual recognition of passports : Countries that have begun or are considering issuing COVID-19 vaccine passports will need to establish agreements with other countries in order to have these passports recognized for international travel. Already, some of the initial passport proposals demonstrate limitations in this regard. For example, the EU’s proposal would allow for any vaccinated EU citizen to travel freely across all EU member states 2 , but not outside of the EU. Israel has signed an agreement with Cyprus and Greece to allow for international travel, while Malaysia and Singapore are considering an agreement for reciprocal recognition . The U.S. has not yet weighed in on an international standard or indicated what form of passport the government would accept for international arrivals, though such standards are being discussed and developed but have yet to be applied. This has created confusion, and a fragmented approach across countries so far. It is also likely to be an issue within the U.S. as different jurisdictions take varying approaches.
Lack of uniform digital standards : Related to the issue of mutual recognition is that of digital standards. Currently, there is no standardized guidance related to the design of COVID-19 vaccine passports, including any standards for issues such as data privacy or interoperability. One report has identified at least 12 issues that will require international guidance in order to create a universally recognized COVID-19 vaccine passport system. The WHO’s Smart Vaccination Certificate Working Group is currently working to provide such international guidance and standards. The group released its first round of guidance addressing several digital standards issues, including interoperability and minimum data standards, in March 2021. A complete set of recommendations in expected in June 2021, though in the meantime, countries are moving ahead with individual efforts. Within the U.S., the interoperability of individual organization or jurisdiction passport efforts also presents a domestic challenge.
Diverse vaccine authorization and approval landscape: Across countries, different combinations of vaccines have been authorized and administered. Some of the vaccines used in one country may not be recognized or accepted by another country, raising questions about whether and how to certify different vaccines across this landscape for purposes of a vaccine passport. For example, Iceland has stated that only vaccines approved for use by the European Medicines Agency or the WHO will be recognized in order to waive certain screening and quarantine requirements for incoming travelers, which would exclude persons who have been vaccinated with the Russian Sputnik V vaccine or one of the Chinese-developed COVID-19 vaccines. Similarly, the EU’s Digital Green Certificate proposal would also only include vaccines that have received EU-wide authorization. So far, the U.S. has not stated which vaccines it might accept for the purposes of a vaccine passport.
Scientific considerations: The WHO has stated there is a need for further scientific investigation into COVID-19 vaccine products to understand in more detail the extent vaccines reduce transmission, and the strength and duration of immunity provided. For example, Israel’s green passes are only valid for six months starting the week after vaccination, to take into consideration the potential for waning immunity over time. COVID-19 passports may need to consider each vaccine product’s unique immunity profile when issuing certification of vaccine-induced immunity over a certain period of time, a process which becomes even more complicated in the presence of variants with unknown effects on vaccine effectiveness.
Privacy and security: Among the concerns raised in the lack of uniform digital standards and COVID-19 vaccine passports is the issue of privacy and data security. Combining and storing individuals’ vaccination data in a centralized database could expose this information to data breaches and raises questions about oversight and control of that data. In fact, some vulnerabilities have already been detected in COVID-19 vaccine passports under development. Individuals and organizations are less likely to want to participate if these concerns about security and privacy are not adequately addressed.
There are a large number of as-yet uncoordinated efforts underway already to develop vaccine passports. It is not yet clear if or when the U.S. might adopt a vaccine passport standard for cross-border travel or for domestic purposes, and what form such a credential will take or what restrictions it might place on individuals. It is likely that attention to, and calls for, vaccine passports for both international and domestic use will increase over time, as more people are vaccinated and governments and employers seek to find ways to balance public health concerns while also easing a return to some level of normalcy. However, there a number of significant issues to consider related to the design, use, and ethics of vaccine passports, and many questions about how they can and should be implemented in the U.S. and elsewhere.
For incoming travel to the U.S. , individuals are currently required to either provide proof of a negative COVID-19 test within three days of departure or proof of recovery within the last 90 days. As of April 13, vaccination status does not exempt incoming travelers from these requirements.
← Return to text
The proposal would also allow Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland to opt-in to the program.
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Coronavirus
news release
- Vaccine Passports: What We Know and What to Consider
Also of Interest
- Key Questions About COVID-19 Vaccine Mandates
- How are States Addressing Racial Equity in COVID-19 Vaccine Efforts?
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Vaccines for Travelers
Vaccines protect travelers from serious diseases. Depending on where you travel, you may come into contact with diseases that are rare in the United States, like yellow fever. Some vaccines may also be required for you to travel to certain places.
Getting vaccinated will help keep you safe and healthy while you’re traveling. It will also help make sure that you don’t bring any serious diseases home to your family, friends, and community.
On this page, you'll find answers to common questions about vaccines for travelers.
Which vaccines do I need before traveling?
The vaccines you need to get before traveling will depend on few things, including:
- Where you plan to travel . Some countries require proof of vaccination for certain diseases, like yellow fever or polio. And traveling in developing countries and rural areas may bring you into contact with more diseases, which means you might need more vaccines before you visit.
- Your health . If you’re pregnant or have an ongoing illness or weakened immune system, you may need additional vaccines.
- The vaccinations you’ve already had . It’s important to be up to date on your routine vaccinations. While diseases like measles are rare in the United States, they are more common in other countries. Learn more about routine vaccines for specific age groups .
How far in advance should I get vaccinated before traveling?
It’s important to get vaccinated at least 4 to 6 weeks before you travel. This will give the vaccines time to start working, so you’re protected while you’re traveling. It will also usually make sure there’s enough time for you to get vaccines that require more than 1 dose.
Where can I go to get travel vaccines?
Start by finding a:
- Travel clinic
- Health department
- Yellow fever vaccination clinic
Learn more about where you can get vaccines .
What resources can I use to prepare for my trip?
Here are some resources that may come in handy as you’re planning your trip:
- Visit CDC’s travel website to find out which vaccines you may need based on where you plan to travel, what you’ll be doing, and any health conditions you have.
- Download CDC's TravWell app to get recommended vaccines, a checklist to help prepare for travel, and a personalized packing list. You can also use it to store travel documents and keep a record of your medicines and vaccinations.
- Read the current travel notices to learn about any new disease outbreaks in or vaccine recommendations for the areas where you plan to travel.
- Visit the State Department’s website to learn about vaccinations, insurance, and medical emergencies while traveling.
Traveling with a child? Make sure they get the measles vaccine.
Measles is still common in some countries. Getting your child vaccinated will protect them from getting measles — and from bringing it back to the United States where it can spread to others. Learn more about the measles vaccine.
Find out which vaccines you need
CDC’s Adult Vaccine Quiz helps you create a list of vaccines you may need based on your age, health conditions, and more.
Take the quiz now !
Get Immunized
Getting immunized is easy. Vaccines and preventive antibodies are available at the doctor’s office or pharmacies — and are usually covered by insurance.
Find out how to get protected .
Advertisement
Supported by
U.S. Ends Last Covid Travel Barrier, Vaccine Mandate for Foreign Arrivals

By Ceylan Yeginsu
- Share full article
International passengers traveling to the United States no longer have to show proof of vaccination against Covid as of midnight Thursday, when the coronavirus health emergency officially ended .
The Biden administration dropped its requirement for coronavirus testing last June but kept in place its vaccination policy for foreign travelers. In February, the House of Representatives voted to end the last remaining pandemic restrictions on May 11.
“As we continue to monitor the evolving state of Covid-19 and the emergence of virus variants, we have the tools to detect and respond to the potential emergence of a variant of high consequence,” President Biden said in a proclamation published on May 1.
“Considering the progress that we have made, and based on the latest guidance from our public health experts, I have determined that we no longer need the international air travel restrictions that I imposed in October 2021,” he added.

Why It Matters: Most other countries have dropped restrictions.
For 18 months during the height of the pandemic, the U.S. closed its borders to international travelers, separating families and costing the global travel industry billions of dollars.
In November 2021, those restrictions were eased, and international travelers were welcomed back to the United States with great fanfare. But foreign travelers were still required to be vaccinated and take a coronavirus test within three days of travel to all U.S. ports of entry. When the administration dropped its testing rule in June last year but kept vaccinations in place, it argued that they were still necessary to slow the spread of new variants of the virus entering the country.
As of last summer, the U.S. was one of the few remaining countries to maintain coronavirus travel restrictions, causing many travelers to choose alternative destinations that welcome them unconditionally.
The rules barred the world’s No. 1-ranked tennis player, Novak Djokovic, from competing in the U.S. Open in 2022 because he is not vaccinated.
Background: Spending by foreign travelers in the U.S. still lags.
The initial U.S. travel ban on international travel decimated the U.S. economy’s tourism sector and resulted in losses of nearly $300 billion in visitor spending and more than one million American jobs, according to the U.S. Travel Association, an industry group.
Until April last year, all passengers traveling to or within the U.S. were required to wear masks on airplanes — a contentious mandate that led to fistfights and altercations on planes and put off some international travelers from taking long-haul flights.
Even after the restrictions were eased, spending by international travelers in the U.S. was still down by 78 percent in March 2022 compared to 2019 levels and by 56 percent for business travel, the group said.
“Today’s action to lift the vaccine requirement eases a significant entry barrier for many global travelers, moving our industry and country forward,” Geoff Freeman, the chief executive of the association, said in a statement after the May 11 end date was announced.
Ceylan Yeginsu is a travel reporter. She was previously a correspondent for the International desk in Britain and Turkey, covering politics; social justice; the migrant crisis; the Kurdish conflict, and the rise of Islamic State extremism in Syria and the region. More about Ceylan Yeginsu

CDC urges meningococcal disease vaccination ahead of Hajj travel
T he US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is urging doctors to be on the lookout for potentially deadly meningococcal disease linked to travel to Saudi Arabia.
Since April, there have been 12 confirmed cases of meningococcal disease associated with travel for Umrah, an Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, the birthplace of the Prophet Muhammad in Saudi Arabia. Believers in the Muslim faith make Umrah trips to Mecca throughout the year to receive blessings. Muslims also make a longer, more ritualized pilgrimage to Mecca at least once in their lifetime during a set time of year called Hajj. This year’s Hajj is June 14 to 19.
Five of the pilgrims who got sick this year live in the United States. France has had four cases, and the United Kingdom has had three. Ten of the people who got sick had been to Mecca, and two had a close association with someone who did.
Meningococcal disease is highly contagious among unvaccinated people. Of the patients whose vaccination status is known, nine were unvaccinated.
Meningococcal disease , including meningitis, is an uncommon illness caused by the bacteria Neisseria meningitidis. It can cause infection in the lining of the brain and spinal cord that can cause a lifetime of medical problems such as memory and concentration issues, seizures, balance problems, hearing loss and blindness. The disease can also lead to a serious blood infection called septicemia or blood poisoning.
Research shows that an estimated 10% to 15% of cases end in death, even with appropriate treatment.
The number of cases in the US has been on the rise, according to the CDC. This year, 143 cases were reported as of the end of March, compared with 81 for the same period last year. There were 422 cases in all of 2023, the most since 2014, according to the CDC .
Meningococcal disease can be treated with antibiotics if it’s caught early enough. However, diagnosis is often delayed because the symptoms can mimic those of other infectious diseases like Covid-19 or the flu. Symptoms include fever, a headache, nausea or vomiting, trouble walking, a stiff neck, a skin rash, sensitivity to light and brain fog.
Tests of the bacteria in the newly confirmed cases showed that in one case in the US and one in France, it was resistant to ciprofloxacin, one of the first-line antibiotics used to treat meningococcal disease. Eight cases responded to treatment with penicillin or ciprofloxacin.
Vaccines and boosters available
Saudi Arabia requires all Umrah or Hajj pilgrims age 1 and older to have gotten the quadrivalent meningococcal vaccine, also known as the meningococcal conjugate or MenACWY vaccine. It protects against four variations of the bacteria that are in wide circulation: A, C, W, and Y. Overall, most cases in the US are related to serogroup Y.
In the US, doctors may also recommend the MenB vaccine to protect against the B-variation of the bacteria.
A shot made by Pfizer that was approved in the US last year, Penbraya, protects against all five of these most common serogroups that cause meningococcal disease.
Most of the pilgrims who got sick tested positive for the W variation. One case in the United States was caused by serogroup C.
In the US, the vaccine is routinely recommended for all preteens and teens and for some younger children and adults under specific circumstances. One such instance is before travel to countries where meningococcal disease is more common. This includes a recommendation for a booster if the last time a traveler got the shot was three to five or more years before their trip.
The CDC said Monday that health care providers should work with patients who are considering travel for Hajj or Umrah to make sure they have received the MenACWY vaccine within the past five years or get the shot at least 10 days before they leave for their trip.
In the new notice, which was issued through the CDC’s Health Alert Network, the agency also reminded providers to suspect meningococcal disease in anyone who has symptoms after recent travel for Hajj or Umrah.
The CDC told health departments and providers to consider using several of the preferred antibiotics used to treat meningococcal disease in people associated with travel to Mecca.
People who come into close contact with someone with meningococcal disease should get an antibiotic as soon as possible after exposure, regardless of their vaccination status, the CDC said, and ideally within a day after the initial patient has been identified.
The most recent outbreak connected to a mass gathering was in 2000-01, the CDC said, and it was primarily caused by the W variation of the bacteria. It’s only since 2002 that Saudi Arabia has required all pilgrims to provide proof of vaccination against meningococcal disease, but vaccination coverage among these travelers is “known to be incomplete,” the CDC said.
For more CNN news and newsletters create an account at CNN.com
Dengue fever, once confined to the tropics, now threatens the U.S.
Meg Norris was traveling in Argentina in April when the first signs of dengue fever hit her. The weather in Salta, just south of the Bolivian border, was warm, but Norris, a 33-year-old from Boulder, Colorado, zipped a fleece sweatshirt around her body to stop herself from shivering.
“I thought it was sun poisoning,” she said.
She woke that night in a sweat and spent the hours alternately burning up then freezing. In the morning, her eyes were sore and her lymph nodes were swollen. For the following week, there was nothing to do but sleep, stay hydrated and wait for the body aches that give the illness the moniker “break-bone fever” to pass.

Latin America is experiencing its worst dengue fever outbreak on record. Case numbers in the first 4 ½ months of 2024 are already 238% higher than they were by this time last year, which itself ended with a record 4.1 million cases, according to the Pan American Health Organization . Cases are more than 400% higher than the five-year average.
An unusually wet and warm summer season brought by the El Niño weather pattern has created ideal conditions for the mosquitoes that spread dengue to hatch en masse and carry higher amounts of the virus.
Experts warn this could be a preview of what dengue fever will look like in the future. Climate change is creating unusually balmy conditions, which are already expanding the range of mosquito-borne diseases.
“That’s concerning for places where dengue hasn’t occurred before in recent history: North America and Europe,” said Dr. Albert Ko, a professor of epidemiology of microbial diseases at the Yale School of Public Health.
Dengue is a viral fever caused by four different viruses and spread through mosquito bites. It’s common in many tropical regions across the globe, but has begun to appear in more temperate climates. The mosquitoes that carry dengue fever, Aedes aegypti are now regularly found in the southern parts of the U.S., but recently, the insects have been found as far north as the Bay Area and Washington, D.C. One 2019 study predicted an additional 2 billion people will be at risk for dengue fever by 2080.
“We are definitely worried,” Ko said.

Why are dengue cases rising around the world?
Dengue outbreaks have historically occurred in the Americas every three to four years, said Dr. Gabriela Paz-Bailey, dengue branch chief in the division of vector-borne diseases at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “But now we are seeing them every year,” she said.
Part of the reason for that is tied to climate change.
A warming climate expands the mosquitoes’ habitat and allows them to breed all year long, rather than only in the warmer months. The hotter temperatures also cause the viruses to replicate faster, meaning mosquitoes end up carrying many more viral copies, increasing the likelihood that a person will become infected if bitten.
“We are also seeing dengue cause outbreaks at times when they usually don’t occur,” Ko said.
South America’s dengue cases weren’t just unusually high this year, but they also came unusually early in the season. Similarly, Puerto Rico, a place where dengue outbreaks can occur in the summer and fall, declared a public health emergency in late March after the U.S. territory was overtaken by dengue fever cases and more than 400 people were hospitalized .
In recent years, the epidemic has spread to parts of southern Brazil and northern Argentina, where dengue hasn’t previously been a big problem, Ko said.
“That gives us a snapshot of what we may see here in North America in the coming decades,” Ko said.
How would dengue get a foothold in the U.S.?
The fact that Aedes aegypti mosquitoes are found in places outside their normal range doesn’t mean the mosquitoes are carrying dengue viruses, but those first insects are a warning of what may be to come, Ko added
Locally transmitted dengue fever infections — meaning the infected person didn’t get sick abroad — are still rare in the continental U.S., but have recently been seen for the first time in some states. Last October, California health officials reported the state’s first case of locally transmitted dengue in Pasadena. Local transmission has also occurred in Arizona, Florida and the southern coast of Texas. Last summer brought record-breaking heat waves to Europe, where cases of local dengue transmission were seen in France, Italy and Spain.
“I think this means dengue will become more common,” said Paz-Bailey, adding that the main concern is still the significant increase in cases where the virus is already endemic.
This summer, she does not expect to see significant dengue outbreaks on the U.S. mainland, but she said there is likely to be some people who travel to regions that have higher-than-usual cases and bring the virus back home.
“Travel-associated cases do result in small chains of outbreaks,” Paz-Bailey said.
Humans are reservoirs for dengue, so in order to have widespread transmission, enough people must be infected for the mosquitoes to reliably bite someone with the virus so that they can spread it to another person.
“That’s why we’re seeing an outbreak of dengue in Puerto Rico right now,” said Michael von Fricken, director of the One Health Center of Excellence at the University of Florida in Gainesville. “They’ve reached this tipping point where there are enough infected humans that they’re subsequently infecting other mosquitoes that are continuing to transmit disease.”
Florida has logged 176 dengue cases so far this year, the vast majority in people who were infected in other countries, most frequently Brazil or Cuba. The Florida Health Department has recorded only seven cases of locally transmitted dengue transmission in the state so far this year. In all of 2023, the department documented 173 locally transmitted cases, most of them in Miami-Dade County.
What are the symptoms of dengue fever?
Dengue fever is caused by four viruses, so a person can be infected four times in their lifetime. Only about 1 in 4 people are symptomatic the first time they’re infected, according to the CDC.
Ko said a person’s initial symptoms are usually a fever and headaches. Fatigue, nausea, vomiting, a rash that looks like measles, as well as the extremely painful body aches.
Most people recover in a week or two, but about 1 in 20 people develop severe dengue, which can be fatal. The more times a person is infected with dengue, the higher risk they are for complications.
“After you’ve had your first exposure, your risk of having dengue hemorrhagic fever or severe symptoms increases exponentially,” Von Fricken said. Dengue also becomes deadlier with each infection.
While the U.S. does have a dengue vaccine, it’s approved only for children ages 9 to 16 who live in places where dengue is endemic, including Puerto Rico, American Samoa or the U.S. Virgin Islands.
What’s more, children can get the vaccine only if they’ve previously had a dengue infection. That’s because if a person were to get vaccinated and then get their first dengue infection, they still run the risk of getting very sick, just as someone gets sicker from their second infection. Since most Americans have not had dengue, “that vaccine is not very useful” for most, Ko said.
There’s no specific drug to treat dengue. Instead, doctors just aim to treat the symptoms and keep the patient comfortable until the virus runs its course. That means resting and drinking a lot of fluids. Ko said people should try to take acetaminophen (Tylenol) for pain and fever if they can, since nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which include ibuprofen and aspirin, can make bleeding worse if someone develops hemorrhagic dengue, in which their blood vessels are damaged and become leaky.
Paz-Bailey said it’s important for people traveling to places with dengue to stay in places with air conditioning when possible, use insect-repellant and wear long sleeves and pants to avoid mosquito bites.
Bed nets can be helpful, but the mosquitoes that carry dengue typically bite during the day, so they may be less helpful than they are at preventing other mosquito-borne diseases like malaria, Ko said.
At home, people can make their yards less appealing to mosquitos by reducing the amount of standing water, especially after a bout of rain.
“It’s difficult to control the mosquito population, so we need to hit it with all we have and layer our strategies,” Paz-Bailey said. “No single strategy will be good enough.”
Kaitlin Sullivan is a contributor for NBCNews.com who has worked with NBC News Investigations. She reports on health, science and the environment and is a graduate of the Craig Newmark Graduate School of Journalism at City University of New York.
Anne Thompson is NBC News’ chief environmental affairs correspondent.
Patrick Martin is a producer in the NBC News Health & Medical Unit.
Language selection
- Français fr
Important notice
Temporary website updates are in progress to fix technical issues. For assistance, visit our Contact Us page.
Travelling with a pet
The United States (US) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced changes to the import requirements for dogs entering the United States . These changes will come into effect on August 1, 2024 and will impact dogs travelling from Canada to the United States. The CFIA is currently in the process of reviewing these requirements. Further information and guidance will be provided as soon as possible.
New import conditions for personal pet dogs and assistance dogs from countries at high-risk for dog rabies starting September 28, 2023
Personal pet dogs and assistance dogs from countries at high-risk for dog rabies will require an import permit issued by the Canadian Food Inspection Agency before travelling to Canada.
If you're planning on bringing your dog into Canada from September 28, 2023 onwards, prepare in advance and learn more about the import process .
Pets must meet specific requirements when travelling to Canada or another country. It is your responsibility to review all the requirements for your situation.
Some requirements must be completed at specific times and if not completed correctly or on time your pet may not be eligible to travel and be refused entry.
As soon as you know your travel details, contact your local veterinarian to assist with the pet travel process. Requirements could include obtaining a health certificate, updating vaccinations, testing, or administering medications.
Only dogs, cats and ferrets qualify as pets by Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA). Check requirements for other animals if you're travelling with a non-traditional pet.
Travelling to Canada from another country (import requirements)
Requirements for bringing an animal into Canada apply to the following situation:
- animals entering Canada permanently
- animals in transit through Canada on their way to a final destination
- animals entering Canada for a temporary visit
- Canadian animals returning to Canada
Travelling from Canada to another country (export requirements)
The country you're travelling to may have requirements your pet must meet before they can enter the country. Export requirements are determined by each country and can change frequently. Every time you plan to travel with your pet, it is your responsibility to check the requirements and allow enough time to get your pet ready to travel.
- Pets (dogs, cats and ferrets)
- All other animals
Related links
- Travelling to the United States with a pet
- Look up import requirements (AIRS)
Uganda Tackles Yellow Fever With New Travel Requirement, Vaccination Campaign for Millions
Uganda has rolled out a nationwide yellow fever vaccination campaign to help safeguard its population against the mosquito-borne disease that has long posed a threat

A man receives a shot of yellow fever vaccine at Kiswa Health Center III in Kampala, Uganda Tuesday, April. 2, 2024. Uganda has rolled out a nationwide yellow fever vaccination campaign to help safeguard its population against the mosquito-borne disease that has long posed a threat. (AP Photo)
KAMPALA, Uganda (AP) — Uganda has rolled out a nationwide yellow fever vaccination campaign to help safeguard its population against the mosquito-borne disease that has long posed a threat.
By the end of April, Ugandan authorities had vaccinated 12.2 million of the 14 million people targeted, said Dr. Michael Baganizi, an official in charge of immunization at the health ministry.
Uganda will now require everyone traveling to and from the country to have a yellow fever vaccination card as an international health regulation, Baganizi said.
Ugandan authorities hope the requirement will compel more people to get the yellow fever shot amid a general atmosphere of vaccine hesitancy that worries healthcare providers in the East African nation.
The single-dose vaccine has been offered free of charge to Ugandans between the ages of 1 and 60. Vaccination centers in the capital, Kampala, and elsewhere included schools, universities, hospitals and local government units.
Before this, Ugandans usually paid to get the yellow fever shot at private clinics, for the equivalent of $27.
Uganda, with 45 million people, is one of 27 countries on the African continent classified as at high risk for yellow fever outbreaks. According to the World Health Organization, there are about 200,000 cases and 30,000 deaths globally each year from the disease.
Uganda's most recent outbreak was reported earlier this year in the central districts of Buikwe and Buvuma.
Yellow fever is caused by a virus transmitted by the bite of infected mosquitoes. The majority of infections are asymptomatic. Symptoms can include fever, muscle pain, headache, loss of appetite and nausea or vomiting, according to the WHO.
Uganda’s vaccination initiative is part of a global strategy launched in 2017 by the WHO and partners such as the U.N. children's agency to eliminate yellow fever by 2026. The goal is to protect almost one billion people in Africa and the Americas.
A midterm evaluation of that strategy, whose results were published last year, found that 185 million people in high-risk African countries had been vaccinated by August 2022.
In Uganda, most people get the yellow fever shot when they are traveling to countries such as South Africa that demand proof of vaccination on arrival.
James Odite, a nurse working at a private hospital which has been designated as a vaccination center in a suburb of the capital, Kampala, told the AP that hundreds of doses remained unused after the yellow fever vaccination campaign closed. They will be used in a future mass campaign.
Among the issues raised by vaccine-hesitant people was the question of whether "the government wants to give them expired vaccines,” Odite said.
Baganizi, the immunization official, said Uganda's government has invested in community “sensitization” sessions during which officials tell people that vaccines save lives.
The Associated Press receives financial support for global health and development coverage in Africa from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Trust. The AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org .
Copyright 2024 The Associated Press . All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
Photos You Should See - May 2024

Join the Conversation
Tags: Associated Press , health , world news
America 2024

Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
The 10 worst presidents.
U.S. News Staff Feb. 23, 2024

Cartoons on President Donald Trump
Feb. 1, 2017, at 1:24 p.m.

Photos: Obama Behind the Scenes
April 8, 2022

Photos: Who Supports Joe Biden?
March 11, 2020

Key Reactions to Trump’s Guilty Verdict
Lauren Camera and Laura Mannweiler May 30, 2024

Trump's Convicted: What's Next?
Lauren Camera May 30, 2024

Trump Guilty in Historic Trial

What to Know: Human Cases of Bird Flu
Cecelia Smith-Schoenwalder May 30, 2024

How’s Biden Doing With Young Voters?

Q1 Economic Growth Revised Downward
Tim Smart May 30, 2024


An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Press Releases
DHS to Require Non-U.S. Individual Travelers Entering the United States at Land Ports of Entry and Ferry Terminals to be Fully Vaccinated Against COVID-19
New Requirements at Land Ports of Entry and Ferry Terminals Will Protect Public Health While Facilitating Cross-Border Trade and Travel
WASHINGTON – Beginning on January 22, 2022, DHS will require non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States via land ports of entry and ferry terminals at the U.S.-Mexico and U.S.-Canada borders to be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide related proof of vaccination, as COVID-19 cases continue to rise nationwide. These new restrictions will apply to non-U.S. individuals who are traveling for both essential and non-essential reasons. They will not apply to U.S. citizens, Lawful Permanent Residents, or U.S. nationals.
“Starting on January 22, 2022, the Department of Homeland Security will require that non-U.S. individuals entering the United States via land ports of entry or ferry terminals along our Northern and Southern borders be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 and be prepared to show related proof of vaccination,” said Secretary Alejandro N. Mayorkas. “These updated travel requirements reflect the Biden-Harris Administration’s commitment to protecting public health while safely facilitating the cross-border trade and travel that is critical to our economy.”
These changes – which were first announced in October 2021 and made in consultation with the White House and several federal agencies, including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – will align public health measures that govern land travel with those that govern incoming international air travel.
Non-U.S. individuals traveling to the United States via land ports of entry or ferry terminals, whether for essential or non-essential reasons, must:
- verbally attest to their COVID-19 vaccination status;
- provide proof of a CDC-approved COVID-19 vaccination, as outlined on the CDC website ;
- present a valid Western Hemisphere Travel Initiative (WHTI)-compliant document, such as a valid passport, Trusted Traveler Program card, or Enhanced Tribal Card; and,
- be prepared to present any other relevant documents requested by a U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) officer during a border inspection.
COVID-19 testing is not required for entry via a land port of entry or ferry terminal.
Although these new vaccination requirements do not apply to U.S. citizens, Lawful Permanent Residents, or U.S. nationals, all travelers are reminded to bring a WHTI -compliant document when re-entering the United States. Non-U.S. individuals attempting to enter the United States irregularly, through any illegal means or without proper documentation, will continue to be expelled pursuant to CDC’s Title 42 public health order.
To help reduce wait times, travelers can take advantage of facial biometrics and CBP One™ , which is a single portal for CBP mobile applications and services.
To learn more about the updated requirements for travelers, review the DHS fact sheet .
- Border Security
- Transportation Security
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
CMS Newsroom
Search cms.gov.
- Physician Fee Schedule
- Local Coverage Determination
- Medically Unlikely Edits
2024-05-23-MLNC

Thursday, May 23, 2024
Medicare Shared Savings Program: Apply by June 17 for January 1 Start Date
Medicare providers: deadlines for joining an accountable care organization, institutional providers: medicare enrollment & certification roadmap, improve your search results for cms content, medical services authorized by the veterans health administration: avoid duplicate payments, claims, pricers, & codes, pass-through device: correct returned claims.
MLN Matters® Articles
ICD-10 & Other Coding Revisions to National Coverage Determinations: October 2024 Update
- National Coverage Determination 110.23: Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- Hospice Claims Edits for Certifying Physicians — Revised
From Our Federal Partners
Meningococcal disease cases linked to travel to the kingdom of saudi arabia: ensure travelers are current on meningococcal vaccination, news .
The Medicare Shared Savings Program is now accepting applications through the Accountable Care Organization (ACO) Management System . Apply no later than noon ET on June 17, 2024.
ACOs interested in Advance Investment Payments (PDF) or the ACO Primary Care Flex Model must first apply to the Shared Savings Program.
To learn more about the process, register for the upcoming June 5, 2024 webinar on Completing Phase 1 of the Application and Avoiding Common Deficiencies.
More information:
- Application Types & Timeline webpage
- Application Toolkit
- Key Application Actions and Deadlines (PDF)
- Email questions to [email protected]
To participate in an Accountable Care Organization (ACO) for performance year 2025, work with an ACO to join their participant list. ACOs must submit their lists to CMS by August 1 at:
- Noon ET for the Medicare Shared Savings Program
- 11:59 pm ET for the ACO Realizing Equity, Access, and Community Health Model (ACO REACH)
Participant taxpayer identification numbers can only appear on one ACO participant list. Resolve any overlaps by September 5.
More Information:
- Email questions to [email protected] or [email protected]
Read the Provider Enrollment & Certification Roadmap (PDF) to learn about each step of the process, including timeframes and points of contact.
- Become an Institutional Provider webpage
- Medicare Enrollment for Providers & Suppliers webpage
If you’re using a search engine to find information on CMS.gov, include “CMS” in your search term to get optimal results.
In a report , the Office of the Inspector General found that Medicare paid providers for medical services authorized and paid for by the Department of Veterans Affairs’ community care programs, resulting in duplicate payments of up to $128 million. We don’t pay for services authorized under Veterans Health Administration benefits.
More information to bill correctly:
- Medicare Secondary Payer (PDF) booklet
- Medicare Overpayments (PDF) fact sheet
- Medicare Benefit Policy Manual, Chapter 16 (PDF) , Section 50.1.1
Learn how to correct pass-through device claims that CMS returned with Reason Code W7098, “Claim with pass-through device lacks required procedure (RTP).”
For claims with a pass-through device code, include the corresponding procedure code from the device offset code pairs list. If the procedure and pass-through device codes aren’t paired on the list, resubmit the claim with HCPCS C1889 in place of the pass-through device code so your Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC) can reprocess your claim.
For example: You billed HCPCS code 92920 for the procedure, but it’s not a corresponding procedure for the pass-through device HCPCS C1761. If your MAC returns the claim with Reason Code W7098, resubmit it using HCPCS code 92920 with HCPCS C1889 instead of C1761.
MLN Matters ® Articles
Learn about revisions effective October 1, 2024 (PDF) :
- Recent coding changes
National Coverage Determination 110.23: Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Learn about expanded coverage for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) effective March 6, 2024 (PDF) :
- HSCT using bone marrow, peripheral blood or umbilical cord blood stem cell products
- Other indications for stem cell transplantation not otherwise specified
Your Medicare Administrative Contractor will adjust claims that you bring to their attention.
Hospice Claims Edits for Certifying Physicians — Revised
CMS added coding information for the referring provider name (PDF) for claims you submit on or after October 7, 2024, with dates of service June 3, 2024 or later.
The CDC issued a Health Alert Network Health Advisory to alert clinicians to cases of meningococcal disease linked to travel to the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA). Since April 2024, 12 cases of meningococcal disease linked to KSA travel: United States (5 cases), France (4 cases), and the United Kingdom (3 cases).
Recommendations for Healthcare Providers
- Recommend vaccination with MenACWY conjugate vaccine for people considering travel to KSA to perform Hajj or Umrah (pilgrims) in addition to routine meningococcal vaccination for adolescents and other people at increased meningococcal disease risk
- Maintain a heightened index of suspicion for meningococcal disease among symptomatic people who have recently been in KSA and among close contacts of people who have recently been in KSA, regardless of vaccination status
- Immediately notify state, tribal, local, or territorial health departments about any suspected or confirmed cases of meningococcal disease in the United States
- Preferentially consider using rifampin, ceftriaxone, or azithromycin instead of ciprofloxacin as prophylaxis for close contacts in the United States of meningococcal disease cases associated with travel in KSA
Subscribe to the MLN Connects® newsletter, or read past editions .
View the Medicare Learning Network® Content Disclaimer and Department of Health & Human Services Disclosure .
The Medicare Learning Network®, MLN Connects®, and MLN Matters® are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services (HHS).

- Investigates
- Houston Life
- Newsletters
WEATHER ALERT
4 warnings in effect for 8 counties in the area
Uganda tackles yellow fever with new travel requirement, vaccination campaign for millions.
Risdel Kasasira
Associated Press
Copyright 2023 The Associated Press. All rights reserved
A man receives a shot of yellow fever vaccine at Kiswa Health Center III in Kampala, Uganda Tuesday, April. 2, 2024. Uganda has rolled out a nationwide yellow fever vaccination campaign to help safeguard its population against the mosquito-borne disease that has long posed a threat. (AP Photo)
KAMPALA – Uganda has rolled out a nationwide yellow fever vaccination campaign to help safeguard its population against the mosquito-borne disease that has long posed a threat.
By the end of April, Ugandan authorities had vaccinated 12.2 million of the 14 million people targeted, said Dr. Michael Baganizi, an official in charge of immunization at the health ministry.
Recommended Videos
Uganda will now require everyone traveling to and from the country to have a yellow fever vaccination card as an international health regulation, Baganizi said.
Ugandan authorities hope the requirement will compel more people to get the yellow fever shot amid a general atmosphere of vaccine hesitancy that worries healthcare providers in the East African nation.
The single-dose vaccine has been offered free of charge to Ugandans between the ages of 1 and 60. Vaccination centers in the capital, Kampala, and elsewhere included schools, universities, hospitals and local government units.
Before this, Ugandans usually paid to get the yellow fever shot at private clinics, for the equivalent of $27.
Uganda, with 45 million people, is one of 27 countries on the African continent classified as at high risk for yellow fever outbreaks. According to the World Health Organization, there are about 200,000 cases and 30,000 deaths globally each year from the disease.
Uganda's most recent outbreak was reported earlier this year in the central districts of Buikwe and Buvuma.
Yellow fever is caused by a virus transmitted by the bite of infected mosquitoes. The majority of infections are asymptomatic. Symptoms can include fever, muscle pain, headache, loss of appetite and nausea or vomiting, according to the WHO.
Uganda’s vaccination initiative is part of a global strategy launched in 2017 by the WHO and partners such as the U.N. children's agency to eliminate yellow fever by 2026. The goal is to protect almost one billion people in Africa and the Americas.
A midterm evaluation of that strategy, whose results were published last year, found that 185 million people in high-risk African countries had been vaccinated by August 2022.
In Uganda, most people get the yellow fever shot when they are traveling to countries such as South Africa that demand proof of vaccination on arrival.
James Odite, a nurse working at a private hospital which has been designated as a vaccination center in a suburb of the capital, Kampala, told the AP that hundreds of doses remained unused after the yellow fever vaccination campaign closed. They will be used in a future mass campaign.
Among the issues raised by vaccine-hesitant people was the question of whether "the government wants to give them expired vaccines,” Odite said.
Baganizi, the immunization official, said Uganda's government has invested in community “sensitization” sessions during which officials tell people that vaccines save lives.
The Associated Press receives financial support for global health and development coverage in Africa from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Trust. The AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org .
Copyright 2024 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
United States Traveler View
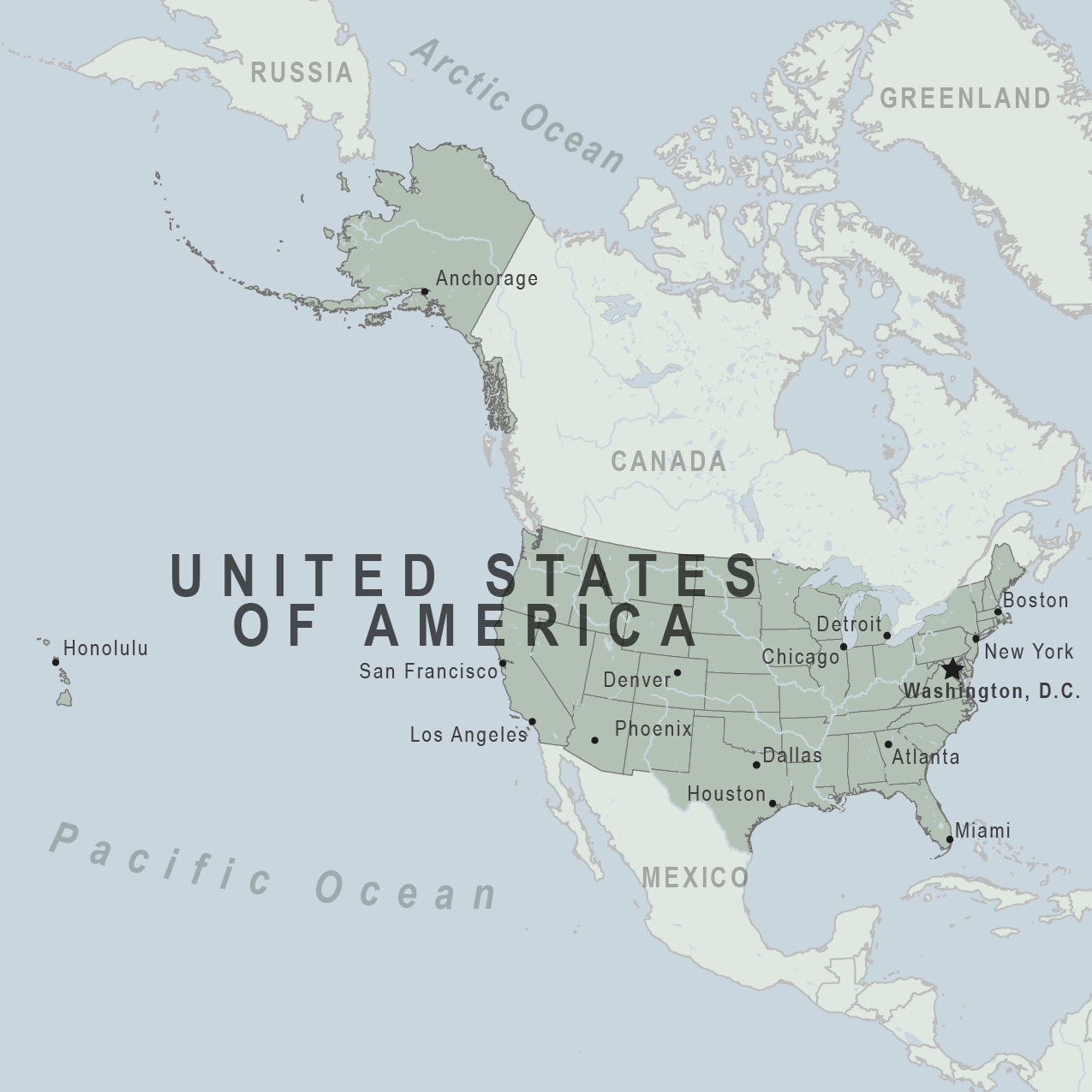
Novel Coronavirus Travel Information
- Level 3: Cruise Ship Travel
- Coronavirus and Travel in the United States
For general advice about your trip to the United States, see these additional resources:
- US Department of State’s Travel.State.gov - including information on visas for foreign citizens traveling to the United States.
- US Customs and Border Protection
- Transportation Security Administration
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Last Updated: May 4, 2023. The Administration will end the COVID-19 vaccine requirements for international air travelers at the end of the day on May 11, the same day that the COVID-19 public health emergency ends. This means starting May 12, noncitizen nonimmigrant air passengers will no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated with ...
More. Learn about CDC's Traveler Genomic Surveillance Program that detects new COVID-19 variants entering the country. Sign up to get travel notices, clinical updates, & healthy travel tips. CDC Travelers' Health Branch provides updated travel information, notices, and vaccine requirements to inform international travelers and provide ...
Q. What are the requirements for travelers entering the United States through land POEs? A: Before embarking on a trip to the United States, non-U.S. travelers should be prepared for the following: Possess proof of an approved COVID-19 vaccination as outlined on the CDC website. During border inspection, verbally attest to their COVID-19 vaccination status.
October 25, 2021. Today, the White House and CDC announced details of the new vaccination policy that will go into effect for international travelers on November 8. As of that date, foreign national air travelers to the United States will be required to be fully vaccinated and to provide proof of vaccination status prior to boarding an airplane ...
Nov. 8, 2021. On Monday, the United States lifted travel restrictions for international visitors from 33 countries who are fully vaccinated against the coronavirus, ending an 18-month ban that has ...
Starting on November 8, non-citizen, non-immigrant air travelers to the United States will be required to be fully vaccinated and to provide proof of COVID-19 vaccination status prior to boarding ...
Starting in January 2022, however, all inbound foreign national travelers seeking to enter the United States via land POEs or ferry terminals - whether for essential or non-essential reasons - must be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide related proof of vaccination. As travel begins to resume, travel volumes and wait times are ...
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S. As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19. As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
Beginning November 8, 2021, all non-U.S. citizen, non-U.S. immigrants must be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 prior to traveling to the United States, to meet the President's proclamation and CDC orders.These travelers are also required to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination and a negative test no more than three days prior to the flight's departure.
Reuters. The White House has announced that it will open its land borders with Canada and Mexico to fully vaccinated travelers starting on Nov. 8, simultaneously lifting one of the United States ...
If yellow fever vaccine is recommended or required for your destination, you'll need to go to a vaccine center authorized to give yellow fever vaccinations. Many yellow fever vaccine centers also provide other pre-travel health care services. Find an authorized US yellow fever vaccine center. Examples of Vaccines
Today, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) announced that it will extend temporary Title 19 requirements and continue to require non-U.S. travelers entering the United States via land ports of entry and ferry terminals at the U.S.-Mexico and U.S.-Canada borders to be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 and provide related proof of vaccination upon request.
Sept. 20, 2021, 7:29 AM PDT. By Shannon Pettypiece. WASHINGTON — The Biden administration will require all international travelers coming into the United States to be fully vaccinated and tested ...
Vaccination (2-dose vaccine): Recommended for most travelers. --Administer 2 doses, at least 6 months apart. --At least 1 dose should be given before travel. Consultation: Advise patient to wash hands frequently and avoid unsafe food and water. Hepatitis B. Sexual contact, contaminated needles, & blood products, vertical transmission.
Protect your child and family when traveling in the United States or abroad by: Getting the shots required for all countries you and your family plan to visit during your trip. Making sure you and your family are up-to-date on all routine U.S. vaccines. Staying informed about travel notices and alerts and how they can affect your family's ...
The U.S. government is exploring COVID-19 vaccine certifications for use internationally and domestically. The administration has said that a vaccine passport may be required in the future for ...
Vaccines for Travelers. Vaccines protect travelers from serious diseases. Depending on where you travel, you may come into contact with diseases that are rare in the United States, like yellow fever. Some vaccines may also be required for you to travel to certain places. Getting vaccinated will help keep you safe and healthy while you're ...
International passengers traveling to the United States no longer have to show proof of vaccination against Covid as of midnight Thursday, when the coronavirus health emergency officially ended ...
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is urging doctors to be on the lookout for potentially deadly meningococcal disease linked to travel to Saudi Arabia. Since April, there have been ...
Beginning May 12, 2023, DHS will no longer require non-U.S. travelers entering the United States via land ports of entry and ferry terminals to be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 and provide related proof of vaccination upon request. DHS intends to rescind these Title 19 travel restrictions in alignment with the end of the Public Health Emergency and the termination of the Presidential ...
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is urging doctors to be on the lookout for potentially deadly meningococcal disease linked to travel to Saudi Arabia. Since April, there have been ...
Latin America is experiencing its worst dengue fever outbreak on record. Case numbers in the first 4 ½ months of 2024 are already 238% higher than they were by this time last year, which itself ...
These changes will come into effect on August 1, 2024 and will impact dogs travelling from Canada to the United States. The CFIA is currently in the process of reviewing these requirements. Further information and guidance will be provided as soon as possible. Pets must meet specific requirements when travelling to Canada or another country.
AP Photo. A man receives a shot of yellow fever vaccine at Kiswa Health Center III in Kampala, Uganda Tuesday, April. 2, 2024. Uganda has rolled out a nationwide yellow fever vaccination campaign ...
Beginning on January 22, 2022, DHS will require non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States via land ports of entry and ferry terminals at the U.S.-Mexico and U.S.-Canada borders to be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide related proof of vaccination, as COVID-19 cases continue to rise nationwide. These new restrictions will apply to non-U.S. individuals who are traveling for ...
An official website of the United States government. Here's how you know ... 12 cases of meningococcal disease linked to KSA travel: United States (5 cases), France (4 cases), and the United Kingdom (3 cases). Recommendations for Healthcare Providers. Recommend vaccination with MenACWY conjugate vaccine for people considering travel to KSA to ...
Vaccination centers in the capital, Kampala, and elsewhere included schools, universities, hospitals and local government units. Before this, Ugandans usually paid to get the yellow fever shot at ...
Page last reviewed: December 15, 2023. Content source: National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID) Division of Global Migration Health (DGMH) (1-800-232-4636) Official U.S. government health recommendations for traveling. Provided by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).