Flow through your inbox
Flowrite turns your instructions into ready-to-send emails and messages across your browser.
.png)
For companies
Mar 1, 2023

How to write a reimbursement email with 7 samples and template
Whatever your expense, this guide to reimbursement emails will ensure you're never short-changed or out of pocket.

Lawrie Jones
Table of contents
Reimbursement emails are professional correspondence to ensure you get paid for outgoings and expenses.
For example, you may have incurred costs for everyday expenses, run up medical bills, or be asking for a payout for lost or damaged items. Whatever your expense, our guide to reimbursement emails will ensure you're never short-changed or out of pocket.
Every reimbursement email must be clear about your costs, what they're for, and how you want to get paid. We can show you how to write an effective reimbursement email, including the correct format, suitable subject lines, and several samples to help you.
So stop waiting for the cash, and let's start writing...
How to write a reimbursement email
Reimbursement emails are formal emails that you'll write to get paid for expenses you’ve run up. The first lesson is, you must be clear and concise in every request for reimbursement. This isn’t the time to beat around the bush or go light on the details.
Firstly, start with an introduction about who you are and why you're getting in touch. Of course, this will differ if you're an internal team member or from the outside, but it always pays to be positive!
You'll want to justify why you're due a reimbursement. Basically, you have to be clear about what you are asking for repayment for any why. You'll also need to prove your expenses by providing all the necessary details and documentation.
Reimbursement email format
Reimbursement emails are based on a format that should be familiar to anyone in business. It's all based on three core parts: the subject line, body copy, and sign-off.
Remember to include attachments of relevant documentation, including invoices and receipts!
1. Reimbursement email subject line
We kick off with a professional and formal subject line. You want to ensure that it's clear and relevant to the request but also that it's attention-grabbing.
Why? Because reimbursement requests are easy to ignore. Don't give them a chance by ensuring your subject line stands out.
- Reimbursement request – (add details)
- Reimbursement claim attached – date
- Request for payment – (add details)
- Expenses attached – please confirm receipt
2. Reimbursement email body
Reimbursement emails are pretty simple to crack. You'll start by introducing yourself , explaining the purpose of your message, and providing any relevant background.
- My name is (your name), and I'm contacting you from (where you're from). I'm emailing you to request reimbursement for (include details).
Next, list out what you're asking to be paid for. Your request for reimbursement should be explicit and document everything. Use bullet points in your request for reimbursement to include all the details to make payment as simple as possible.
- I'm requesting reimbursement for the following:
- Include details...
You should add some relevant background to your message to provide context. This can act as a justification for reimbursement.
- The expenses were incurred while I worked for you on (insert details of costs).
You can expect anyone to pay out without proof, so always provide attachments, including all relevant documentation. You can attach copies of receipts and anything else required to process your payment.
You can end your reimbursement emails here or add a clear call to action and potentially a deadline.
- I have attached copies of my receipts to this email. I understand your payment terms are 28 days. Can you confirm that this is correct?
3. How to end reimbursement email
As a piece of professional business correspondence, you'll need a professional closing (here are 40 more) ! We always recommend adding a polite thank you before providing the following steps to ensure your expenses are reimbursed.
- Please confirm that you have received this message and provide details of when I can expect payment.
It's essential to add contact details so the recipient can clarify any details and confirm your payment.
- You can reach me at (insert details) if you need to contact me.
Finish with a suitable sign-off (kind regards, many thanks, etc.), and you're ready to send.
7 reimbursement email examples
We all love the theory, but sometimes you must see some examples to understand how it fits together.
So here we provide 7 reimbursement email examples that focus on using clear and concise language to get your cash!
Of course, we strike the right professional tone – friendly but formal. We've also provided spaces to slot in relevant details and tag receipts.
Ready to go? Here are reimbursement emails we can all use to make getting paid a priority!
1. Asking for reimbursement email sample
This simple reimbursement sample does everything we've outlined above (in some style!). We start by saying hi and following up with some introduction and background before laying out our request for reimbursement.
Next, we provide details of all expenses and, naturally, highlight the attachments of relevant documentation. Finally, we conclude with a clear call to action.
If you need one reimbursement sample that can do it all, it's this one.
- You can list your expenses here...
2. Sample email for reimbursement of travel expenses
Travel expenses are a common cause for a reimbursement email, so keep this sample ready for when it's required.
When it comes to expense reimbursement emails, include all details (dates, times, and travel methods) to make it as easy as possible for your claim to be paid. (It's worth checking out your company's rules on reimbursement before submitting a claim to ensure you include everything you need.)
Being as straightforward as possible is the most effective strategy for securing your reimbursement.
3. Sample email for reimbursement of travel expenses for the interview
Not all businesses will pay expenses for an interview, but if this one does – be sure to claim it!
You're not going to be familiar to the company, so you'll need to include lots of proof. Include dates, times, and details of the interview – and even consider copying the recruiting manager into your email.
Then, follow all the advice above, including stating who you are, why you're messaging, and the purpose (getting paid!).
OK, so you may not get the job – but with our interview expenses reimbursement template, you'll get your travel expenses back at least!
- You may want to call to share your bank details, but you have the option!
4. Reimbursement request email for lost or damaged items
Requesting reimbursement for lost or damaged items isn't easy. You need to prove you owned the items, describe the loss or damage, and push for payment.
In this example, we're claiming for damage to a phone. We include the contract as proof of purchase and images of the damage. We mention the insurance policy we have and our preferred method of compensation.
Be prepared to answer questions and offer more information, but keep going!
- Bullet points are a helpful way to provide lots of detail.
5. Sample email for reimbursement of medical expenses
Claiming repayment for medical expenses is familiar to our US cousins, and there are strict rules. Start by providing details of your insurance policy and coverage.
Next, you'll need to make a clear request for reimbursement and provide details of all medical expenses. Including receipts and details of all parties involved is critical to ensure rapid repayment.
Get well soon!
6. Request for reimbursement of advance payment email
In some cases, such as buying a travel ticket or equipment for work, you may request advance payment.
First, you'll need to provide a clear and convincing claim why you should receive an advance payment.
After this justification, you must confirm the agreement (including what's being paid for, when, and why). Finally, you'll want to set out any conditions for payment.
7. Follow-up email for reimbursement status
Sometimes (sadly) reimbursement emails aren't processed and paid. Often, they can be ignored as they're not usually a priority. If this happens, this follow-up email is for you.
It pays (literally!) to be polite and request the reimbursement status. After that, hit them up with a request for payment confirmation. Finally, request that they send an update and provide you with a deadline for payment.
Expense reimbursement email template
The samples above are great examples of how to create reliable reimbursement emails, but if they don't hit the spot, use this template. This template is entirely customizable, so just cut and paste the bits you need, and bin the rest. Here's how it works...
The template works through each part of the professional and formal format. It begins with some introduction and background, then goes straight in with a request for reimbursement.
Subsequent steps include details of expenses and a justification for reimbursement. We've also added all vital information and attachments, like invoices, receipts, and payment confirmations.
There's a professional closing and a clear call to action!
- Add details
Send reimbursement emails using Flowrite
If you're struggling with writing emails or want to get to inbox zero, Flowrite is your best help.
We developed an artificial intelligence tool that writes your emails for you, like this:
Final words on reimbursement emails
You should be bossing cashback claims by now, but we'll summarise the key tips for effective reimbursement emails.
Understand and follow the format, including introductions, information, and attachments. Always understand the rules around reimbursement, and follow them.
If we're owed money, we tend to get pushy – but we must always stay polite and professional. So focus on striking the right tone and take your time. It will pay off in the end!
Supercharge your communication with Flowrite
Write emails and messages faster across Google Chrome.
Explore Flowrite
.png)
Start using Flowrite today
Try it yourself

Payment reminder
Reply to: "
Received message
couldn’t charge your account update payment method subscription will be cancelled by the end of billing cycle
Generate a reply
Generate an outreach
Share this article
Related articles

Ask for approval by email – with 7 samples and a template
We've made it easier to get a 'yes' with our tips and 7 email approval samples suitable for professional use.

Vacation request email — 15 samples and template
Time to book a holiday? Here’s how to write a vacation request email to make sure you’re good to go (with 15 examples).

How to ask for something in an email with 9 examples
Learn how to write request emails that get results with our in-depth guide. This article breaks down the process of writing request emails for information, documents, contact details, favors and more.

We use cookies to analyze site performance and deliver a better experience for visitors.
%20(1).png)
Product updates
Read the latest →
%20(1).png)
About Flowrite
Get to know us →
Productivity

© 2023 Flowrite
Writing a Reimbursement Email – 7 Examples and Templates
- August 14, 2023
Ready to sail the choppy waters of crafting that flawless reimbursement email?
Well, grab your virtual pen (and maybe a pirate hat), because we’re about to dive deep.
Forget the days of boring templates and yawn drab emails; it’s time to mix a pinch of humor , a dash of expertise, and create an email cocktail that’s both persuasive and delightful.
Whether you’re looking to reclaim travel expenses or those sneaky extra charges, fear not!
This guide is your treasure map. Let’s set sail!
What is Reimbursement?
Reimbursement is a term you might have come across when dealing with expenses, especially if you’ve been in a situation where you’ve had to request reimbursement or send a reimbursement of expenses letter.
Picture this: you’ve traveled for a company event, and now you want to get back the money you spent . You’d write a request for a reimbursement letter or perhaps a more casual reimbursement email to your boss or finance department.
This process means you’re asking the company to cover the costs you’ve incurred – be it for travel, medical bills, or other professional expenses.
It’s like telling your company, “Hey, I’ve got this bill, so can you reimburse me?” And when they agree, it’s them essentially saying, “Sure, here’s your reimbursement for expenses.”
It’s essential, however, to always provide the necessary documentation , like receipts, when asking for reimbursement to ensure the process goes smoothly.
Key Elements of a Reimbursement Letter/Email
When you’re gearing up to send that crucial reimbursement email or letter, you’ll want to ensure you’ve got all the key elements in place. You know, those parts that make the difference between a smooth, quick reimbursement process and a back-and-forth headache.
Here are some essentials you’ll need:
Subject Line
The subject line is like the crow’s nest of our ship – the first thing that’s spotted from a distance. A clear and direct subject line , such as “Request for Travel Expense Reimbursement” or “Medical Expense Claim for October” , ensures your email isn’t lost in the vast ocean of an inbox.
It gives the recipient a heads-up about the content , making sure your email is opened and read.
Recipient's Details
When it comes to your reimbursement letter, addressing the right individual professionally is pivotal. It marks the initial step to ensure your request is both seen and acknowledged.
A little insider tip: always double-check names for the correct spelling . Including official designations can also make a world of difference, adding that extra layer of professionalism. And if you’re leaning towards a digital mode of communication, verifying the email addresses can save you from potential mishaps.
Purpose Statement
Every effective letter has a clear intent , and your reimbursement request is no different. Clearly stating your purpose right from the get-go cuts through any potential confusion and prepares the reader for your request’s specifics .
Here’s a simple pro tip for you: phrases like “I am writing to request reimbursement…” or “This is a formal request for reimbursement…” are your best friends. They’re straightforward , and they work wonders in setting the right tone.
Detailed Breakdown of Expenses
This is the heart of your reimbursement email. Consider it a blueprint of your claim . It’s where you list out the various expenses incurred, ideally in a tabulated format or as a summary.
Including specifics like date, amount, and nature of the expense (e.g., “Hotel Stay on 5th June – $150”) ensures transparency. This breakdown acts as a quick reference, making it easier for the processing team to validate your claims.
Documentation and Proof
Ever heard of the saying, “Seeing is believing” ? It stands true, especially when you’re making a reimbursement claim. Providing concrete evidence of your expenses can turn the tide in your favor. Always retain all your receipts; they’re the backbone of your claim.
For those who prefer the digital route, screenshots or PDFs of transactions come in handy. And if you’re looking for an organized approach, using a standardized reimbursement receipt template is a game-changer.
Total Amount
Now, onto one of the most vital parts: the amount. Clear and transparent communication about the funds you’re seeking not only helps maintain transparency but can also expedite the entire process .
Offering a detailed breakdown of expenses can be invaluable, especially when there are multiple items on the list. Always double-check your figures for accuracy. And a neat trick? Present your totals in both words and numerals—it leaves no room for ambiguity.
A Call to Action
The grand finale of your reimbursement letter should pack a punch. Drawing your letter to a close with a precise expectation of the next steps can be the gentle nudge that spurs quicker action. While you want to be assertive, always remember the golden rule of staying polite.
Phrases like “I kindly request timely processing…” or “I appreciate your prompt attention to this matter…” strike the perfect balance between assertiveness and courtesy.
7 Examples and Templates for Reimbursement Emails
Reimbursements are an essential aspect of professional and personal dealings. With the right approach, you can seamlessly request and receive the funds you’ve spent. Here are detailed insights into various reimbursement situations:
General Reimbursement Letter
There are times when you make expenditures on behalf of the company or someone else. Perhaps you purchased office supplies or paid for a subscription. A General Reimbursement Letter is perfect for these generic situations.
Our sample letter requesting reimbursement of expenses ensures you communicate effectively, outlining the nature of the expense, the total amount, and any relevant documentation. Remember, clarity is key , and with our email template , your request is bound to be straightforward and well-received .
Here’s an email template:
Subject: Request for Reimbursement for [specific expense]
Dear [Recipient’s Name],
I hope this email finds you well. I am writing to request reimbursement for expenses incurred on behalf of the company. The details are as follows:
Date of Purchase: [Date] Item/Service Purchased: [Specific item or service] Total Amount: [Amount] Purpose: [Brief description]
Attached are the receipts and any relevant documentation.
Thank you for your prompt attention to this request.
Warm regards,
[Your Name]
Requesting Travel Expenses
Business trips, training, or corporate meetings often mean travel. Once you return, you’ll want to reclaim the funds spent on flights, accommodation, and other related costs. This is where our template shines.
It’s crafted to address specifics like dates, locations, and the breakdown of expenses. Plus, there’s room to attach receipts or invoices , ensuring transparency and swift processing.
Subject: Reimbursement Request for Travel Expenses
I am reaching out to request reimbursement for travel expenses from my recent trip to [Destination]. Here are the details:
Travel Date: [Starting Date] to [Ending Date] Total Amount: [Amount] Breakdown: [Flight, Hotel, Meals, etc.]
I’ve attached all relevant invoices and receipts.
Thanks for your prompt attention.
Best regards,
Email to Insurance Company
Insurance claims often come with their own set of complexities. Whether you’re dealing with property, health, or vehicle insurance, ensuring you have a well-drafted letter can streamline the process .
Our reimbursement letter for insurance captures all necessary details — policy number, claim amount, and the nature of the claim. Designed to cut through the red tape, this template ensures your claim gets the attention it deserves.
Subject: Claim Request – Policy Number: [Your Policy Number]
Dear [Insurance Company Name],
I am writing to claim reimbursement as per my policy [Policy Number]. Details of my claim are as follows:
Nature of Claim: [e.g., Medical treatment, vehicle repair] Total Amount: [Amount]
Attached are all necessary documents, bills, and proof of the incident.
Looking forward to a swift resolution.
Asking for Additional Charges
Life’s unpredictable. You might encounter unexpected costs, be it in a project, a service, or a purchase. When you need to communicate these extra charges, clarity and tact are crucial .
Our sample email for additional charges does just that, detailing the reasons for the added costs, providing a breakdown, and requesting timely reimbursement . This way, you tackle the situation head-on without any misunderstandings.
Subject: Notification of Additional Charges – [Specific reason]
I’d like to bring to your attention additional charges incurred due to [specific reason]. Here’s the breakdown:
Original Amount: [Amount] Additional Charges: [Amount]
The total amount now stands at [New Total Amount]. Attached are the relevant bills and a detailed explanation.
Thank you for understanding.
Medical Reimbursement
Medical expenses, whether expected or sudden, can be hefty. If you’re part of a health plan or if your workplace offers medical benefits, you’ll need to request a refund of these bills.
With our medical reimbursement templates, you can effectively list out treatments , medicines , and other costs . Accompanied by the right documentation, such as medical receipts and prescriptions, this guide simplifies the daunting process of claiming medical expenses.
Subject: Medical Reimbursement Request
Dear [HR/Insurance Provider’s Name],
I hope this message finds you well. I’m writing to request reimbursement for recent medical expenses.
Treatment Date: [Date] Medical Facility: [Hospital/Clinic Name] Total Amount: [Amount]
Please find attached the medical bills, prescriptions, and any other supporting documents.
Thank you for your prompt attention.
Transportation Costs
Whether you’re commuting for work, attending meetings, or undertaking longer business journeys, transportation can be a significant expense . The transportation email template we offer covers various types of commutes — from daily local travels to longer out-of-town journeys.
By detailing distances, modes of transport, and associated costs, you present a comprehensive claim , making the reimbursement process smooth.
Subject: Request for Transportation Cost Reimbursement
I am writing to request reimbursement for transportation expenses incurred during [specific time period/task]. Here’s a summary:
Total Distance: [X miles/km] Mode of Transport: [Car, Train, etc.] Total Amount: [Amount]
Attached are the travel logs and receipts.
Thanks for your understanding.
Job Interview Travel Reimbursement
It’s always exciting when a company considers you worth flying out for an interview. While it’s a great sign, you shouldn’t be left covering the travel costs.
Our guide on how to ask for travel reimbursement for a job interview ensures you’re polite, clear, and precise . Detail your travel, stay, and even meal costs, so you can focus on acing the interview instead of worrying about the expenses.
Subject: Travel Reimbursement Request Post Interview on [Date]
Dear [HR Name/Interviewer’s Name],
Thank you for the opportunity to interview at [Company Name]. I’m reaching out to request reimbursement for my travel expenses:
Journey Date: [Date] Transport Mode: [Flight, Train, etc.] Total Amount: [Amount]
Attached are all the receipts and relevant documents.
Thank you for facilitating this process.
Potential Challenges in Reimbursement Process
Navigating the reimbursement process isn’t always a breeze. In fact, when you dive into the world of requesting reimbursement, you might stumble upon several potential pitfalls.
Whether you’re drafting a reimbursement email or submitting a detailed reimbursement request letter, being aware of these hurdles can make all the difference. Let’s break down some of the common challenges you might face:
- Incomplete Documentation : Perhaps the biggest hiccup is not having all your receipts or proofs. Without these, it's tough to validate your reimbursement request.
- Delay in Approvals : Sometimes, your reimbursement of expenses letter might get stuck in the bureaucratic maze, leading to frustrating waits.
- Unclear Company Policies : Not every company has a crystal-clear reimbursement policy. This ambiguity can lead to confusion about what's reimbursable and what's not.
- Errors in Submission : A minor oversight, like filling out a wrong date or amount, can hold up the entire process.
- Lost Receipts : It's all too easy to misplace a crucial receipt, making your reimbursement letter for expenses incomplete.
- Change in Rates : Especially with travel, rates might vary. If you're asking for reimbursement of travel expenses, you might face discrepancies between estimated and actual costs.
Remember, while these challenges might seem daunting, being meticulous and organized can help you navigate the reimbursement journey with relative ease. Always double-check your documentation, be patient, and stay proactive in following up on your requests.
Frequently Asked Questions on Reimbursement Emails
Diving into the realm of reimbursement emails, it’s only natural to be brimming with questions. And you’re not alone! Many individuals, just like you, often find themselves pondering the ins and outs of such correspondence.
To help shed some light, let’s tackle a few of the frequently asked questions that might be on your mind:
How long should I wait before following up on a reimbursement email?
While it’s tempting to expect immediate responses, especially when money is involved, patience is key . Typically, it’s courteous to give the recipient about a week to process your reimbursement request letter or email. Remember, there might be several internal processes or checks they have to go through.
However, if you haven’t heard back in a week or two, it’s perfectly okay to send a gentle follow-up email . It’s a balancing act between being assertive about your reimbursement request and understanding potential administrative delays.
Should I include original receipts in my reimbursement email?
This is a common concern when drafting a reimbursement email. Generally, it’s best to attach scanned copies or clear photos of your receipts . This provides proof without risking the loss of the original document.
But always keep the originals safe, as some companies might request to see them later, especially when large amounts are involved or if there’s a discrepancy in the reimbursement of expenses format.
How do I ensure the confidentiality of personal information in reimbursement emails?
When you’re sharing sensitive data, like bank account details or personal expenses, security becomes paramount . Ensure that the recipient’s email address is correct before hitting ‘send’.
Use a secure email platform and avoid sending such details through public Wi-Fi networks. If the information is highly sensitive, consider using encrypted email services or communicate the details through a more secure channel, like a secure company portal or encrypted messaging service .
Key Takeaways on Reimbursement Emails
Navigating the maze of reimbursement emails is more than just crafting a message; it’s about understanding the nuances , anticipating potential challenges, and addressing common queries.
Throughout our deep dive, we uncovered the essential components of a standout reimbursement letter and provided tailored templates for various scenarios , from general expense claims to specific ones like travel or medical reimbursements.
We also delved into potential hiccups in the reimbursement journey, emphasizing the importance of documentation and patience . Moreover, we addressed some burning questions that many face while dealing with such correspondence, offering insights into the ideal wait time for follow-ups and ensuring data confidentiality .
In essence, mastering the art of reimbursement emails boils down to being meticulous, patient, and proactive. And with the knowledge we’ve unpacked, you’re well-equipped to sail through your reimbursement requests with confidence and ease .
So, the next time you find yourself drafting that crucial email, remember these insights and make every word count!
To achieve the best results with email outreach, we recommend using a professional email automation software
13 best cold email platforms rated and compared
Edgar Abong
Table of contents.
Influno © 2024 All rights reserved
- Our story & team
- Contact & support
- Features & pricing
- Outreach guides
- Privacy policy
- Terms of service
Last Updated on August 14, 2023 by Edgar Abong
How To Write A Reimbursement Request Email
Welcome to this article on how to write a reimbursement email. In this article, we will provide you with a step-by-step guide on what to do before writing the email, what to include in the email, and even provide you with sample templates that you can customize and use.
So, if you’re wondering how to write an effective reimbursement email, you’re in the right place!
Here’s how to write a reimbursement email:
Table of Contents
What To Do Before Writing the Email
Before you sit down to compose your reimbursement email, it’s essential to gather all the necessary information and take a few important actions:
- Collect Receipts: Make sure you have all the relevant receipts and documentation to support your reimbursement request. This includes itemized bills, invoices, or any other proof of purchase.
- Review Company Policy: Familiarize yourself with your company’s reimbursement policy. Pay attention to any specific guidelines or requirements that must be followed when submitting a reimbursement request.
- Calculate Expenses: Calculate the total amount of expenses you are requesting to be reimbursed. Make sure to double-check your calculations to avoid any discrepancies.
- Identify the Recipient: Determine who the appropriate person or department is to address your reimbursement request. It could be your manager, supervisor, or someone from the finance department.
What to Include In the Email
When writing a reimbursement email, it’s crucial to include all relevant information to ensure a smooth and efficient reimbursement process. Here are the key elements to include:
Subject Line
In the subject line of your email, clearly state your request for reimbursement. Be concise and specific.
Start your email with a polite and professional greeting. Address the recipient by their appropriate title or name.
Introduction
In the opening paragraph, briefly introduce yourself and explain the purpose of the email. Clearly state that you are submitting a reimbursement request.
Expense Details
Provide a comprehensive breakdown of each expense you are seeking reimbursement for. Include the date, description, and amount for each item. Attach copies of receipts or supporting documentation if required.
Total Amount
Calculate the total amount of expenses and indicate it clearly in your email. Ensure that the amount is accurate and matches the supporting documentation.
Payment Method
Specify your preferred method of payment. This could be through direct deposit, a physical check, or any other payment option available within your company’s reimbursement policies.
Additional Notes
If there are any additional notes or comments you would like to include, do so in this section. Keep it concise and relevant to the reimbursement request.
End your email with a polite closing remark, followed by your name, job title, and contact information. Thank the recipient for their attention and express your willingness to provide any further information if necessary.
Email Template – Reimbursement Request Email
Subject: Reimbursement Request – [Your Name] Dear [Recipient’s Name], I hope this email finds you well. I am writing to request reimbursement for the following expenses: Date: [Expense Date], Description: [Expense Description], Amount: $[Expense Amount] Date: [Expense Date], Description: [Expense Description], Amount: $[Expense Amount] Date: [Expense Date], Description: [Expense Description], Amount: $[Expense Amount] The total amount of expenses is $[Total Amount]. I have attached all the necessary receipts and supporting documents for your review. Please process the reimbursement through direct deposit to the following account: Account Name: [Your Name] Account Number: [Your Account Number] If you require any additional information or documentation, please let me know, and I will be happy to provide it promptly. Thank you for your attention to this matter. I look forward to a favorable response. Best regards, [Your Name] [Your Job Title] Contact Information: [Your Phone Number / Email Address]
Writing a reimbursement email can be straightforward if you follow these guidelines. Remember to gather all necessary information, compose a clear and concise email, and submit your reimbursement request to the appropriate recipient.
Lastly, keep in mind that each company may have its own unique reimbursement policy and procedures. Adjust the templates provided accordingly to align with your specific requirements.
Good luck with your reimbursement request!

Team portal
Try for free
Talk to sales
How to Write Professional Reimbursement Emails
Sep 4, 2023
As a business owner, manager, or employee, there will be times when you'll need to reconcile expenses incurred on behalf of the company, which prompts the need for a 'reimbursement email'. This article is here to guide you on the art of formulating the perfect reimbursement emails that are both professional and effective, ensuring you have no bias or misunderstanding in your communications.
What is a reimbursement email?
A reimbursement email is a written communication requesting refunds for expenditures incurred. These are payments that an individual or organization has made and is requesting repayment from another party. Typically, employees write these emails to their HR or finance departments seeking refunds for expenses made on behalf of the company such as travel expenses, purchasing materials, or conducting client meetings.
Reimbursement emails serve several significant roles. Firstly, they're crucial in maintaining transparent financial transactions within an organization. Secondly, they reassure employees that the organization values their contributions and is ready to refund any personal expenses made on its behalf. Thirdly, they represent a vital record, should there be any need for audits or financial checks in the future.

Key points in writing effective reimbursement emails:
Be professional: Treat your reimbursement email as any business correspondence. Stick to a clear, concise, and professional tone.
Attach supporting documents: Always attach receipts or any additional supporting documents that corroborate your claim for reimbursement.
Follow the company policy: Understand your company's reimbursement policies and follow them while crafting your email.
Want a simple solution for drafting your reimbursement emails? Look no further than MailMaestro!
Writing the perfect reimbursement email can sometimes be challenging. However, with MailMaestro you can craft professional emails effortlessly. With MailMaestro you can choose to enhance an already existing draft or start an entirely new one , using MailMaestro feels like having your personal email assistant.
But there's more to it. MailMaestro's new release features Improve with AI which allows you to fine-tune specific sections without affecting the entire content. Once the draft is created, you can highlight a section or the entire text, then adjust it to meet your specific needs. Here's how it works:
Sample instructions for MailMaestro:
Resulting email from mailmaestro:.
Don't wait any longer - experience the convenience and professionalism of MailMaestro today. Download now and transform your email composition process!
Sample situations for reimbursement and how to approach them:
Different scenarios require unique approaches to writing reimbursement emails. Here are five possibilities with template examples:
Travel Expenses
When an employee travels for business purposes, they may require a refund for transportation, accommodation, or meals. An efficient approach will be to detail the nature of the journey, summarize the costs incurred, and adhere to the company’s travel policy.
Subject: Reimbursement Request – [Your Name] Business Travel Expenses
Dear [Recipient's Name],
Following my recent business trip for the sales meeting held in Toronto, I am writing to request reimbursement for my travel-related expenses as per our company's travel policy. The total expense for the trip is $500. I have attached all relevant receipts for your reference.
Best regards, [Your Name]
Client Meeting
Servicing clients effectively often requires creating a conducive atmosphere for business discussions, which may include hosting lunch, dinner, or other meet-up sessions. When you incur expenses during these client engagements, you may need to request reimbursement from your employer. In such a situation, you want to clearly state the nature of the engagement, including the client's name, the location, and the total expenses incurred for easy reference and verification.
Subject: Reimbursement Request – [Your Name] Client Meeting Expenses
I am writing to request a reimbursement for the expenses incurred during the client meeting with [Client's Name]. The total cost came to be $200, and I have attached detailed receipts to this mail.

Office Supplies
There are instances when you may have to purchase office supplies using your personal funds. This could be due to an emergency need or a lack of immediate funds in the petty cash. When requesting a refund, it's important to provide details about what the supplies are, why they were necessary, and provide an invoice or receipt as proof of purchase.
Subject: Reimbursement Request – [Your Name] Office Supplies Expenses
I've recently purchased some office supplies for our department, and I'd like to request a reimbursement of $120 for the same. I am attaching the relevant invoice.
Best, [Your Name]
Training and Conferences
Employee development and continuous learning are vital for business growth and competitiveness. So, when an employee attends a conference or training session, the fees for which they may have paid out of pocket, they can request a reimbursement from the company. It's important to explicitly describe the nature of the conference or training, the costs borne, and why such expenses should be covered by the company. Remember to attach the receipt or proof of the payment made for the courses or conference.
Subject: Reimbursement Request – [Your Name] Training Expenses
I have recently attended a training course on [Name of the Course] and have borne the expenditure of $400. I am writing to request a refund. I am attaching the necessary receipts for reference.
Medical Expenses
Healthcare benefits are an integral part of employee welfare. If your company includes a healthcare plan that covers certain medical expenses, you might need to apply for a reimbursement when you spend out of pocket for such eligible medical services. In such a case, ensure to fully describe the nature of the medical services you received, how much you spent, that it falls within the scope of the company's health benefits, and attach all necessary receipts or bills for confirmation.
Subject: Reimbursement Request – [Your Name] Medical Expenses
I am writing to request reimbursement for my recent medical expenses, which is covered under our company's health policy. The total cost incurred is $500; I am attaching the necessary documents for your perusal.
Warm regards, [Your Name]

Effective reimbursement emails are key to maintaining trust and financial clarity within your organization. With MailMaestro, crafting these emails becomes effortless and efficient. Download MailMaestro today and revolutionize your email drafting process.
How to Write a Letter Requesting Reimbursement Examples Included

A letter requesting reimbursement is a letter written to repay you for out-of-pocket expenses. When writing reimbursement letters, it is important that you follow the right steps and tick all the appropriate boxes. If a reimbursement letter isn’t written properly, there’s a chance you may be required to write the letter more than once, or worse, do not get reimbursed.
In this article, we are going to discuss what a reimbursement letter is, everything you need to know to write a reimbursement letter and the types. We’re going to round it up by providing different reimbursement letter samples to help you better understand how to write your own reimbursement letters.
Without further ado:
What is a Letter Requesting Reimbursement?
A reimbursement letter is a letter written to request compensation for out-of-pocket expenses by an employee. It could also be to request overpayment or refunds. While most reimbursement mainly deals with out-of-pocket expenses, it also cuts across other sections. For instance, there are reimbursements for payments such as insurance, taxes, etc.
Unlike other compensations, one of the perks of reimbursement is that it is not subject to taxation.
Reimbursements is generally for business expenses, so, before attending to your company’s needs out-of-pocket, ensure to read the company policy on these matters, or simply reach out to your manager or HR to ensure you’ll be reimbursed for your troubles.
Some of these business-related expenses may include travel-related expenses such as hotels, food, transportation, flights, etc. In some not-so-common cases, your company may even refund you for taking personal development training. This can be anything from getting a degree to a certification course.
As said earlier, do not assume your company is automatically going to reimburse you for all your business-related expenses. It is always good to have this information beforehand.
There are different avenues where you’re entitled to receive a reimbursement, such as tax refunds, insurance reimbursements, etc. The difference in most of these cases is that the reimbursements are done automatically. This means there’s usually no need to send any letter reminding the institution of the reimbursement.
How to Write Payment Received Emails: Samples Included
How to Write Reimbursement Letters
When writing reimbursement letters, you need to take extra caution than you would when writing other professional letters. If not done properly, reimbursement could open a can of worms and lead to disagreement. As such, when writing these kinds of letters, you need to make sure you follow the guidelines to the letter to ensure you’re reimbursed without much hassle.
In this section of this article, we’re going to look at some of the most important guidelines to follow when writing these kinds of letters.
1. Remember You’re Writing a Professional Letter
When writing a reimbursement letter, you need to remember you’re writing a professional letter. This means it must follow all professional writing etiquette. This includes using the right subject, addressing it with the appropriate honorifics, signing the letter off appropriately, etc.
2. Your Letter Should Be Straight to The Point
Like all professional letters, reimbursement letters should go straight to the point and not waste time with any unnecessary information. This means you shouldn’t include any information that doesn’t serve the general purpose of the letter. The first paragraph should go straight to the point and explain to your recipient what the letter is all about.
3. Include All the Appropriate Documents
Reimbursement letters are letters written to ask for repayment of any out-of-pocket expense. This means you’re presenting a case to your company telling them how much you spent and how much you want to be reimbursed. This means your letter should include all the documents that help your case. This should include all the invoices you paid out-of-pocket, all the hotel bills, taxi fees, and anything you spent during the course of the event.
4. Tally the Experience
You could also decide to take things up a notch by giving a brief description of each receipt you included. This is more important when you’re requesting reimbursement for activities that span through the course of days or weeks. If you’re reimbursed for a one-time event, you do not need to tally your experiences.
5. Send to The Right Party
Before sending a reimbursement letter, reach out to HR or your manager to find out who’s in a better position to receive your letter. When doing this, also remember to CC or Bcc the appropriate recipients. Doing this saves you the stress of having to send multiple emails and also ensures your reimbursement request gets the attention it deserves and is acted upon swiftly.
6. State how You’d Like to Receive the Refund
Before closing the letter, you can decide to include how you’d like to receive the reimbursement. If you feel unsure about this, you could simply ask that the recipient of the letter get back to you on how best to proceed.
Sample Reimbursement Letters
In this section of this article, we’re going to list out multiple samples of reimbursement letters for various instances to help you write the best reimbursement letters.
Reimbursement Letter Sample for Waste Charge
Reimbursement letter sample for electricity bill, reimbursement letter sample for expenses incurred on a trip, sample request reimbursement office expense, reimbursement mail to hr.
We have included everything you need to know to write a reimbursement letter in this article. When writing a letter of this kind, it is important to ensure all the necessary receipts are attached to save both you and the receipt from any unnecessary back and forth. Also, ensure that you communicate with the recipient before writing the letter to ensure they expect it.
About The Author
Jim Blessed
Related posts.

9 Tips You Need to Write and Respond to Emails Professionally

12 Rules of Writing Emails Professionally and Effectively

How to Write Professional Emails: 7 Critical Ingredients

8 Simple Lessons for Writing Irresistible Business to Business Emails
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Home » Email » Write an Email to HR for Travel Reimbursement – Sample Email for Reimbursement of Travel Expenses
Write an Email to HR for Travel Reimbursement – Sample Email for Reimbursement of Travel Expenses
Table of Contents:
- Sample Letter
Live Editing Assistance
How to use live assistant, additional template options, download options, share via email, share via whatsapp, copy to clipboard, print letter, sample request email for travel expense reimbursement.
To: __________@________.___ , [Receiver’s Email Address] From: ___________@________.___ , [Sender’s Email Address]
Date: __/__/____ (Date)
Subject: Request for travel reimbursement
Respected Sir/Madam,
Respected, my name is __________ (Name) and I work in ___________ (Department) department of your reputed company i.e. _________ (Company Name). My employee ID is ________ (Employee ID) and I work as _________ (Designation).
I want to state that I visited _________ (Location) for ____________ (Personal/ Professional work). This visit was done on __/__/____ (Date). Therefore, I request you to kindly reimburse the amount of the expense of __________ (Amount) which I spent. I am attaching a copy of the ________ (cab booking/ hotel reservation/ ticket/ invoice/ boarding pass) for your reference.
I shall be highly thankful for your kind support.
Thanking you, ___________ (Signature), ___________ (Name), ___________ (Employee ID)
Live Preview
The Live Assistant feature is represented by a real-time preview functionality. Here’s how to use it:
- Start Typing: Enter your letter content in the "Letter Input" textarea.
- Live Preview: As you type, the content of your letter will be displayed in the "Live Preview" section below the textarea. This feature converts newline characters in the textarea into <br> tags in HTML for better readability.
The letter writing editor allows you to start with predefined templates for drafting your letters:
- Choose a Template: Click one of the template buttons ("Start with Sample Template 1", "Start with Sample Template 2", or "Start with Sample Template 3").
- Auto-Fill Textarea: The chosen template's content will automatically fill the textarea, which you can then modify or use as is.
Click the "Download Letter" button after composing your letter. This triggers a download of a file containing the content of your letter.
Click the "Share via Email" button after composing your letter. Your default email client will open a new message window with the subject "Sharing My Draft Letter" and the content of your letter in the body.
Click the "Share via WhatsApp" button after you've composed your letter. Your default browser will open a new tab prompting you to send the letter as a message to a contact on WhatsApp.
If you want to copy the text of your letter to the clipboard:
- Copy to Clipboard: Click the "Copy to Clipboard" button after composing your letter.
- Paste Anywhere: You can then paste the copied text anywhere you need, such as into another application or document.
For printing the letter directly from the browser:
- Print Letter: Click the "Print Letter" button after composing your letter.
- Print Preview: A new browser window will open showing your letter formatted for printing.
- Print: Use the print dialog in the browser to complete printing.
- A: Address the recipient with "Dear Sir/Madam" or "Respected Sir/Madam" to maintain a professional tone.
- A: Ensure to include your name, department, employee ID, purpose of travel, dates, and total expenses incurred, along with any supporting documentation.
- A: Yes, it's important to attach copies of relevant documents such as cab bookings, hotel reservations, tickets, or invoices to support your reimbursement request.
- A: Sign off with "Thank you" or "Sincerely," followed by your signature, name, and employee ID.
- A: If you have any questions or need assistance, don't hesitate to reach out to the HR department or the designated contact person for reimbursement inquiries.
Incoming Search Terms:
- sample email for reimbursement of expenses
- email to hr for reimbursement of expenses
By lettersdadmin
Related post, write an email to decline job offer – sample email to decline job offer.
Write an mail to HR for attendance issue – Attendance Issue Email Sample
Sample maternity leave request email – sample email template requesting maternity leave from company, leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Sample Job Joining Application for House Job – House Job Joining Application Sample
Complaint letter to employer about discrimination – complaint letter about discrimination at work, letter to editor complaining about loudspeaker nuisance – write a letter to the editor complaining about loudspeaker nuisance, write a letter to the editor about the noise pollution during the festival, privacy overview.

Emails In English
Email Sample, Free to Use Email Templates

Request Email for Reimbursement – Sample Email Requesting Travel Expense Reimbursement
To: _________@____.__ (Receiver’s email address) Bcc/Cc: _________@____.__ (Bcc/ Cc receiver’s email address)
From: _________@____.__ (Sender’s email address)
Subject: Request for Reimbursement of Travel Expenses
Respected Sir/Madam,
With due respect, I would like to inform you that my name is ____________(name) and I am an employee of your esteemed organization with employee ID __________ (mention your ID).
I am writing this email to bring to your notice that on __/__/____ (date), I had to visit for _________(site inspection/office-related work/mention purpose of visit) at __________(location). In this regard, I hereby request you to kindly reimburse the expenses incurred during this trip. The total amount spent was ________ (amount), and I have already attached the invoice for your reference.
I kindly request you to consider my reimbursement request and facilitate the necessary process. If in case you have any inquiries or require additional information, please feel free to contact me at ________(contact details).
Yours Truly, ____________ (Name), ____________ (Employee ID), ____________ (Contact details)
Incoming Search Terms:
- Sample Email for Requesting Travel Expense Reimbursement
- Email Template for Reimbursement of Business Travel Expenses
- Request for Travel Expense Refund - Email Format
- Email Request for Expense Reimbursement After Official Travel
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Privacy Overview

Tax Resources for Accountants and Small Businesses (U.S.)
- Expense Reimbursements / IRS / Meals and Incidental Expenses / Mileage / Payroll / Per Diem Rates / Small business
- Complete Guide to Reimbursing Employees for Travel Expenses
Published September 2, 2020 · Updated April 21, 2021
When an employee travels away from the office and incurs expenses, the company should reimburse them. Whether travelling across the world or just driving their car to a client’s location, getting the reimbursement right isn’t hard.
Keep reading to learn how to make proper employee reimbursements.
Accountable Plans
You’ll first need to decide if you will implement an accountable or nonaccountable plan. This is just as it sounds; either you’ll have employees be accountable for business expense reimbursements or not.
All businesses should have an expense reimbursement plan in writing. This includes corporations, sole proprietors, the self-employed, and non-profits. Non-profits should be extremely careful when reimbursing disqualified persons because nonaccountable plan reimbursements not properly approved or recorded can cause significant tax exposure to the charitable organization.
An accountable plan must follow the IRS guidelines for expense reimbursement. To qualify, the following rules must be met:
- Expenses must be for business purposes.
- Expenses must be adequately reported to the company in reasonable time.
- Any excess reimbursement or allowance must be returned in a reasonable amount of time.
Any expense that doesn’t meet these three criteria is considered a reimbursement under a nonaccountable plan.
This distinction between these two types of plans is important because accountable plan reimbursements are not taxable to the employee, whereas nonaccountable plans are taxable.
Business Purpose
Expenses incurred as an employee while completing work for an employer have a business purpose. Examples include things like registration fees for a conference, taxi rides to the airport for a business trip, or meals while away on a business trip.
If however, an employer reimburses an employee for dinner when the employee works late, this does not qualify as a business purpose. This reimbursement would be taxable to the employee because it was made under a nonaccountable plan.
Reporting in a Reasonable Time
While what is considered a reasonable amount of time is subjective, the general rule is that all reimbursable expenses must be submitted within 60 days of when they were incurred.
Adequate reporting involves providing a record, like an expense report, of all expenses incurred and providing evidence, like receipts, to support the expenses.
Excess Reimbursement
If an employee receives a travel advance to cover travel expenses but spends less than the advance, the difference is an excess reimbursement and must be returned to the employer to not be taxable. If the excess isn’t returned in a reasonable amount of time, it’s taxable.
A reasonable period of time in this instance is generally deemed to be within 120 days of when the expense was incurred.
With a travel advance, employees should submit an expense report and receipts to substantiate all expenses.
Mileage and Business Use of Personal Vehicle
When an employee uses their personal vehicle for company business, you’ll need to reimburse them. You have three options.
- Standard mileage rate
- Actual costs
- Monthly allowance
Standard Mileage Rate
If you use the standard mileage rate, it is 57.5 cents per mile for 2020.
You can pay more, but the IRS’ safe-harbor threshold of 57.5 cents per mile will allow you a tax deduction without having to substantiate the rate.
Note that the IRS typically updates rates in December. So, you can expect to see the 2021 rate announced in December 2020. IRS 2021 Mileage Rates are here.
IRS Standard Mileage Rates 2020
Actual Costs
Instead of using the standard rate, you can reimburse employees for actual expenses.
The employee will sum up all the costs of owning the vehicle including everything from fuel, maintenance, tolls, registration, and insurance. And based upon the percentage of business miles driven, that portion of the total actual costs is reimbursed.
Monthly Allowance
Using the monthly allowance method is relatively easy. Each month you provide a set dollar amount to the employee.
If you require the employee to provide a mileage log at the end of the month, this will determine if any part of the allowance is taxable. If no mileage log is required, the entire allowance is taxable under an unaccountable plan.
If a mileage log is provided and the employee drove less than expected, they should return the excess allowance within 30 days. If they don’t, the excess becomes taxable to them.
An employee’s commute from their home to their normal place of business is not a reimbursable expense. Any business miles driven in excess of the commute miles is reimbursable.
For example, an employee’s normal round-trip commute is 20 miles. On Fridays, the employee works on-site at a client’s office that is 30 miles away from the employee’s home. So, the employee drives 60 miles round-trip on Fridays. Since this is longer than he would drive if he commuted to the office, you’ll want to reimburse the employee for 40 miles (60 miles – 20 miles).
Mileage Logs
Employees should keep mileage logs when using a personal vehicle for business use. The log should include:
- Employee’s name
- Description of vehicle
- Date of business use
- Purpose of business use
- Starting mileage on odometer
- Ending mileage on odometer
- Approval authorization
Here’s an example of a mileage log using Microsoft Excel.
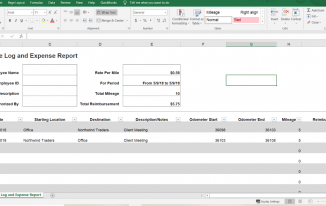
Mileage log and expense report – employee reimbursement
Note that in this example, the employee drove from the office to a client and then back to the office. Therefore, there is no need to deduct commuting mileage.
But suppose, like in our example from above, that on Fridays the employee drives from home to the client’s location and back home. His mileage log would look like this:
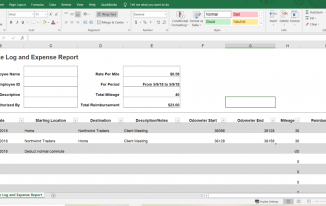
Mileage log and expense report example – employee reimbursement
But what if in this example, the drive to the client’s office from the employee’s home was shorter than his regular commute? In this case there is nothing to reimburse and the employee enjoys the benefit of less driving.
What would happen if this same employee didn’t normally work on Fridays or he always worked from home on Fridays? Then the entire drive to the client’s office would be reimbursable since the employee’s normal work schedule didn’t require him to commute on Fridays.
Many employees will forget to deduct their normal commute from mileage reimbursement requests. You’ll want to remind them.
Direct Expense Reimbursement of Travel Expenses
For employees who travel frequently, providing them with a company credit card is ideal. But for those times when an employee must use their own money for business expenses, you’ll want to reimburse employees quickly.
For easy recordkeeping, have employees complete expense reports when seeking reimbursements. Like the mileage log, it will detail who incurred the expense and when, what it was for, and the amount.
You can reimburse your employees with cash; however best practices would be to pay with check or some other trackable means, like ACH.
Here’s an example of an easy expense report in Excel.
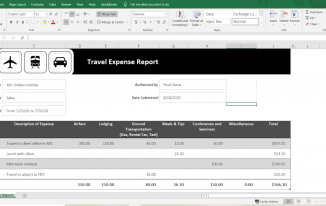
Travel expense report example – employee reimbursement
For each expense, the employee should include receipts to support the amounts requested.
Receipts for purchases should contain the amount, date, place, and a brief description of the expense.
For example, hotel receipts should include:
- The name and location of the hotel.
- The dates stayed.
- Separate amounts for charges (i.e. lodging, meals, or food).
Restaurant and meal receipts should include:
- The name and location of the restaurant.
- The names of people in attendance.
- The date and amount of the meal.
You may choose to reimburse employees for meal tips. Be sure to have a clear policy of what will be reimbursed and what will not. For example, you’ll reimburse up to 20% for tips. Anything above that will not be reimbursed.
You’ll also need to consider your policy for lost receipts. You can still reimburse but have the employee fill out a missing receipt form to document the expense.
In lieu of direct expense reimbursement, consider using a per diem.
A per diem provides the employee with a specified dollar amount per day to use on meals, snacks, lodging, or other miscellaneous purchases. Larger expenses like airfare would be paid using the direct expense reimbursement method or paid for directly by the company.
Per diems should be prorated for partial days of travel. Acceptable methods include the ¾’s method or any other method you choose that is reasonable. The ¾’s method adds ¾ of a daily per diem rate on departure days and another ¾’s on return days.
The IRS sets per diem rates for cities and metropolitan areas. More expensive locales have higher daily rates than cheaper cities. For example, the daily rate for high cost cities like San Francisco, Vail, Colorado, and Nashville, Tennessee is $297. And many cities are designated high cost for only portions of the year. Miami and Park City, Utah are considered high cost only from December 1 – March 31.
And if you’re not in a high cost city, the daily rate is $200. These per diem rates are often updated each year. So you’ll always want to check for the current rates.
For example, Dave is travelling to Seattle for business. Seattle is a high cost locale. He’s leaving on Monday and returning on Thursday. Seattle’s maximum per diem rate is $297 per day. Dave will receive $222.75 ($297 x ¾) for Monday and Thursday and the full $297 for Tuesday and Wednesday.
Per diems are not taxable income to your employee if you use the IRS rates and your employee provides an expense report with receipts. However, using higher rates will create taxable income for the amount above the federal rate. And not submitting an expense report and receipts will make the entire per diem taxable because you’ll have an unaccountable plan and your company will not have the required receipts to support the tax deduction.
If your business operates in the transportation sector (i.e. shipping, trucking, or rail, etc…), it’s important to note that there are different per diem limits and rules you must follow.
Entertainment Expenses
With the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, entertainment expenses are no longer tax deductible for companies.
As an employer, you may still reimburse your employees for entertainment expenses; however, these reimbursements will need to be segregated so that they are not included on your tax return. Examples of entertainment expenses include tickets to entertain clients at sporting events or country club fees for golf memberships.
What documentation you require for entertainment reimbursements is up to you but best practices suggest following the same requirements for travel or mileage reimbursements.
Commingling
If travel or meals involve both a business and personal aspect, only the portion of the expense that is business related is reimbursable. Expense reports and receipts should indicate whether there are any personal expenses.
For example, an employee makes a business trip to California from Georgia and elects to stay two days after business is finished for a mini-vacation. Best practices would have the employee check out of his hotel room and check back in using his personal credit card to pay the hotel bill for his extended stay. This way he has two different receipts; one for business and one for pleasure. However, if he doesn’t do that and the entire hotel stay is charged on the same receipt, you’ll need to back out the charges related to his personal stay.
None of this information should be taken as legal or financial advice, nor should it deter you from seeking the assistance of a licensed attorney, accountant, or financial services professional. But if you want to make sure your company’s policies for employee reimbursements are consistent with best practices, implementing these policies is a great place to start!
Tags: Business Use of Personal Vehicle Commingling Direct Expense Reimbursement employee Commuting reimbursement Employee Expense Reimbursement employee Monthly Allowance employees reimbursements entertainment expenses Excess Reimbursement Expense Reimbursement IRS Accountable Plans IRS Expense Reimbursement Mileage log and expense report Mileage Logs mileage on odometer Per Diem reimbursed expenses Reimbursing Employees Standard Mileage Rate travel expenses
- Next story 11 Facts about Employee Reimbursements Taxation
- Previous story Late Payment Calculator
- 2020 Mileage rates
- 2021 Mileage Rates
- Employee Reimbursements Taxation
- Gross from Net Calculator
- Reverse Sales Tax Calculator
- Taxation of Fringe Benefits
- IRS Mileage
Useful links
- Chamber of Commerce
Bistvo.com – Daily Inspiration
- 2020 Tax Calculator
- Accounting books
- Accounting education
- Accounting Jobs
- Accounting links
- Accounting software
- Accounting Software
- Accounting tutorials
- Additional Medicare Tax
- Annual Reports
- Calculators
- Chart of accounts
- Coronavirus
- Court decisions
- Depreciation
- EU Electronic Services
- European VAT on digital services
- Expense Reimbursements
- Federal income tax
- Federal Tax
- Financial statements
- FLSA – Fair Labor Standards Act
- Fringe Benefits
- Invoicing software
- Local Taxes
- Massachusetts
- Meals and Incidental Expenses
- Minimal Wage
- Minimum Wage
- Mississippi
- Net investment tax
- Nonprofits & Activism
- North Carolina
- OVDI Offshore Voluntary Disclosure Initiative
- Overtime pay
- Partnerships
- Payroll outsourcing
- Payroll software
- Penality and Interest
- Pennsylvania
- Per Diem Rates
- Principal business codes
- Professional tax software
- Retirement planning
- Self-Employed
- Small business
- Social Security and Medicare
- Sole Proprietorship
- State Licenses and Permits
- State Sales Tax
- Tax and Accounting Dictionary
- Tax calculators
- Tax court cases
- Tax Preparation Software
- Tax websites
- Title 26 – Internal Revenue Code
- U.S. Department of Labor (DOL)
- Underpayment Interest Rates
- Washinghton
- West Virginia
- West Viriginia


"Shoeboxed makes it stupid simple to scan receipts...”
What to know about travel expense reimbursement + templates.
The best way to establish an accurate reimbursement strategy for your employee and your company is to ensure that you have an expense reimbursement policy in place and that it is covered with all applicable employees during the onboarding process.

Caryl Ramsey
Published on
June 2nd, 2023
Shoeboxed is an expense & receipt tracking app that helps you get reimbursed quickly, maximize tax deductions, and reduce the hassle of doing accounting.
Employers and employees should understand the business’s guidelines for T&E or travel expense reimbursement policies so that neither runs into any issues over business-related expenses down the road.
The IRS is pretty flexible with employers when it comes to employee reimbursement for business travel expenses while away on a company trip.
Table of Contents
Does travel expense reimbursement qualify as a deductible travel expense?
What the IRS is not flexible about is whether or not the travel-related expenses incurred on the business trip qualify as a deductible travel expense.
Employers can deduct “ordinary and necessary expenses” of employees traveling away from their tax home.
According to the IRS, any reimbursement that does not qualify as a deductible travel expense is considered employee wages.
What are “accountable” and “non-accountable” plans?
There are two methods for reimbursing workers for expenses incurred when traveling for business. These are the “accountable plan” and the “non-accountable” plan.
An “accountable plan” is based on the Internal Revenue Service’s guidelines for reimbursing employees for the actual travel costs so that the reimbursable expenses incurred are not counted as income.
This means that the reimbursements are not subject to W-2 reporting or withholding taxes.
The expenses, however, must be business-related. To qualify for the “accountable plan,” expenses must be business-related, reported accurately, and excess reimbursements issued.
If the company’s reimbursement process doesn’t meet the guidelines under federal law for the “accountable plan,” then the expenses fall under the “non-accountable plan.”
If a reimbursed cost is non-accountable, then it is subject to being taxed as part of the employee’s compensation, therefore, it must be reported on the W-2 form and is subject to withholding.
What is travel expense reimbursement?
Travel expense reimbursement is when you pay employees back for business expenses incurred while traveling.
The expenses that are reimbursed are dependent upon the reimbursement policies determined by your business.
A travel reimbursement policy should be set up by your business that specifies the rules and procedures regarding reimbursement for travel-related expenses.
Many companies are using traditional expense management systems where staff can use a credit card and submit refunded trip expenses after the trip ends.
Hit the road with Shoeboxed 🚗
Stuff receipts into the Magic Envelope while on the road. Then send them in once a month to get scanned. Expense reports don’t get easier than this! 💪🏼 Try free for 30 days!
What common types of travel expenses qualify for deductible expense reimbursement?
As an optional reimbursement provider, you have a choice on whether or not to reimburse employees for travel expenses .
Regardless, a clear reimbursement policy should be established within the company.
Some of the most typical reimbursable expenses include the following:
Transportation costs between your home and the business destination
Transportation between airport/station and hotel
Transportation between the hotel and the work location
Sending company-related supplies from your regular work location to your travel work destination
Business use of a rental car or the actual expenses of operating your personal vehicle when traveling away from home on business such as mileage reimbursement
The cost of parking your rental car can vary significantly depending on factors such as location, duration, and demand. Urban areas and popular tourist destinations often have higher parking fees, while off-peak times or less crowded areas may offer more affordable options
Lodging and meal expenses
Dry cleaning and laundry
Business communication expenses
Business related tips
Parking fees and tolls
How do expense reports play a role in a business’s expense reimbursement policy?
To prevent fraud and to keep company records updated and accurate, companies should use expense reports as part of their expense reimbursement policy.
The expense report should be used by employees to report incidental expenses such as travel expenses , business meals, and small purchases of supplies or equipment for the office.
Employees fill out these expense reports, which require the information of a typical transaction.
Some of the information found on an expense report include the vendor’s name, date paid, expense description, amount paid, and totals for each expense category .
Then the expense report is submitted to the company and according to the reimbursement policy, the employee is reimbursed.
See also: Expense Report Template Google Sheets: 4 Free Templates
Receipt requirements
It’s important to always have proof or documentation of the expenses that you incurred. The best proof is to provide the original receipt from the store, merchant, or a receipt book .
Therefore, when turning in an expense report, always attach any supporting documentation such as your receipts to the expense report.
This safeguards the company against expense fraud and ensures that the company will have the documentation needed for tax deductions and any audits if requested.
Processing expense reports for travel reimbursements
Once expense reports are submitted to the company, the company is responsible for the accuracy of the expense reports.
The company has an obligation to check the expense report against its business travel and reimbursement policies.
This is meant as an assurance system for ensuring accurate compliance with corporate policies.
Deadlines for expense reimbursement
Businesses should establish monthly or quarterly deadlines for expense reports. This ensures that the business can claim the expense as a tax deduction.
It also ensures that records are kept more accurate and up-to-date, that an expense doesn’t fall through the cracks, and that the company maintains a more efficient cash flow.
Not only should there be a deadline for the employee to submit an expense report, but there also should be a deadline for when the employee will be reimbursed by the company.
See also: Travel Nurse Expenses: Put Money Back in Your Pocket
4 Free travel expense reimbursement form templates
Whether you’re a new business looking for an easy way to keep up with eligible travel reimbursements or an employee that often travels for work, these free travel expense reimbursement form templates are a great way to record travel expenses and separate them from non travel reimbursements.
1. Hloom free travel expense reimbursement spreadsheet
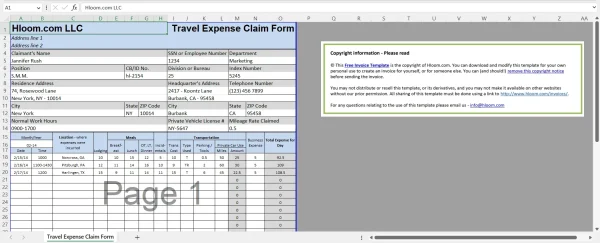
Hloom free travel expense reimbursement spreadsheet for Excel.
Hloom offers a free travel expense reimbursement spreadsheet that you can use to report any travel expenses made while away on a business trip.
Employees’ travel expenses should be recorded in a concise, organized template so it’s easy to categorize eligible reimbursement claims, see if expenditures were within spending limits, and receive reimbursement all by looking at a single form.
Use this template to record:
The date, time, and location you traveled to
The meals you ate
The cost of lodging
Cost of transportation
Private vehicle license
This template is 100% free and customizable, so you can adjust the columns as needed to suit your company.
2. GeneralBlue simple free travel expense reimbursement form
This free travel expense reimbursement form by GeneralBlue is as easy as it gets. It’s an Excel template with 8 columns for recording the expenses incurred traveling for business.
With this straightforward form, you can record:
The date you traveled
A description of your trip
The cost of transportation
The cost of hotels
The cost of meals
Miscellaneous expenses
The total amount of travel expenses
There is also a line for employee and approval signatures so you have an official record of travel expenses and reimbursements.
3. U.S. General Services Administration travel expense reimbursement template
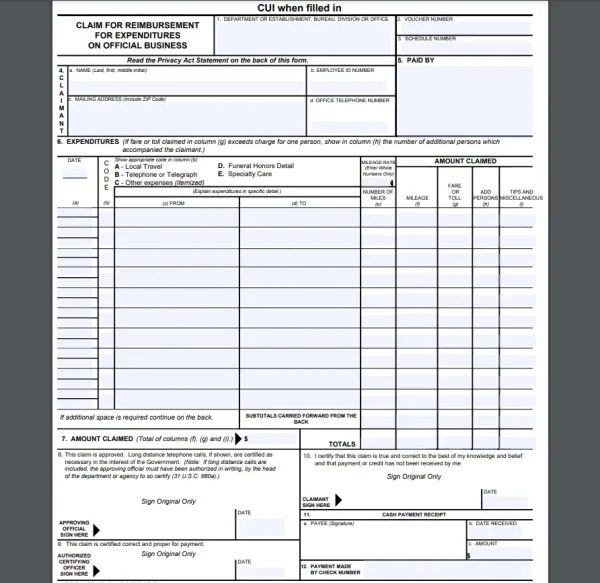
Travel expense reimbursement template from the U.S. General Services Administration.
For state employees, the U.S. GSA offers a free travel expense reimbursement template that you can use to record spending while out on state business.
This template has everything an employee would need to record official business expenses, including:
Department or establishment
Official business categories
Mileage, including fare or toll
Date traveled
Additional persons
Tips and miscellaneous expenses
Spaces for authorizing signatures
The U.S. GSA travel expense template has to be printed and written as a paper copy.
4. Vertex42 travel expense reimbursement sheet
The Vertex42 travel expense reimbursement sheet is available for free and can be downloaded as an Excel file or Google Sheet .
This expense report includes:
Description of travel
Air and transportation costs
Fuel and mileage costs
Conferences and seminars
Meals and tip costs
Entertainment
Other expenses
The total cost of expenses
There’s also a place for authorized signatures, department, manager name, employee ID, and more.
Bonus: Shoeboxed for receipt tracking and expense reports
Use Shoeboxed to capture your receipts and create detailed expense reports for reimbursement.
If you don’t want to deal with the hassle of keeping up with your receipts, manually inputting the expenses into a spreadsheet, or printing out an expense report for your boss, Shoeboxed can help!
Tracking receipts with Shoeboxed
Shoeboxed is a great travel management software that allows you to snap photos of your receipts, digitally extract the important information, and categorize the expenses so that they’re easy to find and manage in your Shoeboxed account.
Break free from manual data entry ✨
Use Shoeboxed’s Magic Envelope to ship off your receipts and get them back as scanned data in a private, secure cloud-based account. 📁 Try free for 30 days!
Creating expense reports for business travel expenses
Once your receipt details are uploaded to your Shoeboxed account , you can select the receipts you want to put in your expense report and either export, print, or email them to the appropriate authority.
Shoeboxed will then create a detailed and organized expense report with images of your receipts attached so you can get reimbursed!
And if you didn’t think it could get any better, Shoeboxed also offers a free mileage tracker so you can effortlessly calculate business mileage and add it to your expense report.
Frequently asked questions
Can i get reimbursed for travel expenses.
The IRS offers two plans for reimbursing workers for travel expenses that are deductible: 1. Employers don’t have to pay employment tax by not including the reimbursement for travel-related expenses from the worker’s wages with the accountable plan; or 2. Employers will have to count all payments to workers as wages under a non-accountable plan.
What are travel reimbursements?
Travel compensation consists of reimbursements for out-of-pocket expenses by employees when they travel for work. The employee typically fills out an expense report and turns it in to the employer. Your employee’s costs will be affected according to your company and reimbursement policies. Travel insurance policies provide you with guidelines for reimbursement of travel expenses.
How much travel expense can I claim?
During business travel the actual cost of transport is 100% deducted—whether it is a flight ticket, train ticket, or bus ticket. Similarly, renting a motor vehicle can make your travel expenses deductible.
In conclusion
The best way to establish an accurate reimbursement strategy for your employee and your company is to ensure that you have an expense reimbursement policy in place and that it is covered by all applicable employees during the onboarding process.
Providing an expense report template makes it much easier for the employees and for those processing the expense reports.
The expense reports will also help to maximize tax deductions, make the audit process much smoother, and ensure that the employee is being reimbursed the correct amount.
Caryl Ramsey has years of experience assisting in different aspects of bookkeeping, taxes, and customer service. She uses a variety of accounting software for setting up client information, reconciling accounts, coding expenses, running financial reports, and preparing tax returns. She is also experienced in setting up corporations with the State Corporation Commission and the IRS.
About Shoeboxed!
Shoeboxed is a receipt scanning service with receipt software that supports multiple methods for receipt capture: send, scan, upload, forward, and more!
You can stuff your receipts into one of our Magic Envelopes (prepaid postage within the US). Use our receipt tracker + receipt scanner app ( iPhone , iPad and Android ) to snap a picture while on the go. Auto-import receipts from Gmail. Or forward a receipt to your designated Shoeboxed email address.
Turn your receipts into data and deductibles with our expense reports that include IRS-accepted receipt images.
Join over 1 million businesses scanning & organizing receipts, creating expense reports and more—with Shoeboxed.
Try Shoeboxed today!
Turn business receipts into data & deductibles
Join over 1 million businesses scanning receipts, creating expense reports, and reclaiming multiple hours every week—with Shoeboxed.
- Email Letter to Request Travelling Allowance
Email 1: Request for Travelling Allowance for Business Trip
Subject: Request for Travelling Allowance for Business Trip
Dear [Manager's Name],
I am writing to request for reimbursement of travel expenses incurred during my recent business trip to [destination]. As per the company's policy, employees are eligible for reimbursement of travel expenses when travelling for business purposes.
I have attached the receipts for airfare, hotel accommodation, meals, and transportation for your reference. The total expenses incurred during my trip amount to [amount]. I would appreciate if you could approve my request for reimbursement of these expenses.
Thank you for your attention to this matter.
[Your Name]
Email 2: Request for Travelling Allowance for Job Interview
Subject: Request for Travelling Allowance for Job Interview
Dear [HR Manager's Name],
I am writing to request for reimbursement of travel expenses incurred during my recent job interview for the position of [position] at your company. I appreciate the opportunity to interview for the position, but I had to travel from [location] to [destination] for the interview.
Email 3: Request for Travelling Allowance for Conference
Subject: Request for Travelling Allowance for Conference
I am writing to request for reimbursement of travel expenses incurred during my recent attendance at [conference name] held at [destination]. As per the company's policy, employees are eligible for reimbursement of travel expenses when attending conferences.
Email 4: Request for Travelling Allowance for Training
Subject: Request for Travelling Allowance for Training
I am writing to request for reimbursement of travel expenses incurred during my recent training program at [location]. As per the company's policy, employees are eligible for reimbursement of travel expenses when attending training programs.
Email 5: Request for Travelling Allowance for Sales Visit
Subject: Request for Travelling Allowance for Sales Visit
I am writing to request for reimbursement of travel expenses incurred during my recent sales visit to [customer name] at [location]. As per the company's policy, employees are eligible for reimbursement of travel expenses when visiting customers for sales purposes.
We are delighted to extend our professional proofreading and writing services to cater to all your business and professional requirements, absolutely free of charge at Englishtemplates.com . Should you need any email, letter, or application templates, please do not hesitate to reach out to us at englishtemplates.com. Kindly leave a comment stating your request, and we will ensure to provide the necessary template at the earliest.
Posts in this Series
- Causes Of Corruption, And Their Solutions Letter To Editor
- Chair Request Letter For Office, Teacher, Employee
- Change Of Address Letter For Customers
- Change Of Engineer Of Record Letter, Change Engineer Of Record Florida
- Change Of Residential Address Letter Sample
- Character Reference Letter From Mother To Judge
- Character Reference Letter Sample For Jobs
- Cheque Date Correction Letter Request Format
- Clarification Letter From Shipper On Mistake To Customs
- Closure Letter To Someone You Love
- Clothing Store Manager Cover Letter
- Company Address Change Letter To Bank
- Compensation Letter For Damages
- Complaint Letter About A Rude Staff
- Complaint Letter Against Father In Law
- Disability Insurance Recovery Letter
- Disappointment Letter To Boss On Appraisal
- Disappointment Letter To Client
- Disappointment Letter To My Wife
- Dishonoured Cheque Letter Before Action
- Diwali Holiday Announcement Email To Employees, Customers
- Donation Letter For Football Team
- Donation Request Letter For Laptop
- Donation Request Letter For Orphanage
- Donor Meeting Request Letter
- Down Payment Request Letter Sample
- Draft A Letter Of Interest To Contract, Or Lent Cars To Government Departments, And Agencies
- Early Payment Discount Letter Sample
- Early Retirement Letter Due To Illness
- Early Retirement Letter Of Resignation
- Early Retirement Request Letter For Teachers
- Eid Greetings Letter From Company To Staff Members, Employees And Students
- Electrical Engineer Experience Letter Sample
- Employee Encouragement Letter Sample
- Employee Not Returning Uniforms
- Employee Recognition Letters Sample
- Employee Warning Letter Sample For Employers
- Best Thank You Letter After Interview 2023
- Beautiful Apology Letter To Girlfriend
- Babysitter Cover Letter No Experience
- Babysitter Letter Of Payment
- Babysitting Letter To Parents
- Back To School Letter From Principal In Florida
- Balance Confirmation Letter Format For Banks And Companies
- Bank Account Maintenance Certificate Request Letter
- Bank Balance Confirmation Letter Sample
- Bank Internship Letter Format, And Sample
- Bank Loan Repayment Letter Format
- Authorization Letter To Collect Money On My Behalf
- Authorized Signatory Letter Format For Bank
- Aviation Management Cover Letter Example
- Attestation Letter For Employee
- Attestation Letter Of A Good Character
- Audit Document Request Letter
- Authority Letter For Degree Attestation Sample
- Authority Letter For Issuing Degree
- Authority Letter For Receiving Degree
- Authority Letter To Collect Documents
- Authority Letter To Collect Passport
- Authorization Letter For Air Ticket Refund
- Authorization Letter For Car Insurance Claim
- Authorization Letter For Driver License Renewal
- Authorization Letter For Getting Driver License
- Authorization Letter For Student Driver License
- Authorization Letter For Tree Cutting Permit
- Ask Permission From My Boss For Straight Afternoon
- Asking For Compensation In A Complaint Letter Example
- Appointment Letter With Probation Period
- Appreciation Letter For Good Performance On Duty
- Appreciation Letter For Hosting An Event
- Appreciation Letter For Manager
- Appreciation Letter From Hotel To Guest
- Appreciation Letter To Employee For Good Performance
- Apprenticeship Result Letter By Principal
- Approval Letter For Job Transfer
- Approval Letter For Laptop
- Approval Request To Govt Authorities For Sports Shop Approval
- Ask For A Letter Of Recommendation Taxas
- Apply For Government Contracts Letter
- Appointment Letter Daily Wages
- Appointment Letter For A Medical Representative Job
- Appointment Letter For Job In Word Free Download
- Appointment Letter For Patient
- Credit Card Address Change Request Letter To Hdfc Bank
- Customer Request Letter For Insurance Policy Pending
- Data Collection Application Letter Request From University
- Dealership Cancellation Request Letter
- Death Intimation Letter Format To Bank
- Debit Card Cancellation Letter Format
- Demand For Assurance Letter
- Demand Letter For Attorney Fees
- Demand Letter For Mortgage Payment
- Demand Letter For Property Return
- Demand Letter For Return Of Items
- Demanding Letter For The Competition Exams Books For Your College Library
- Denial Letter For Insurance Claim
- Compliment Letter To Hotel Staff
- Compromise Agreement Sample Letter
- Compromise Letter For The Reason Of Disturbance
- Compromise Letter To Police Station
- Computer Repair, And Replacement Complaining Letter
- Condolence Letter For Death Of Friend
- Condolence Letter For Death Of Mother
- Condolence Letter For Loss Of Child
- Condolence Letter For The Death Of Father, Mother, Or Someone Else
- Condolence Letter On Death Of Father In English
- Condolence Letter To A Friend Who Lost His Brother
- Condolence To My Player Lost A Parent
- Condolences Letter On Loss Of Wife
- Confessional Letter To Church
- Confirm Meeting Appointment Letter Sample
- Confirmation Letter For Airport Pick Up
- Confirmation Letter For Appointment In Email
- Confirmation Letter For Bank Account
- Confirmation Letter For Completion Of Training
- Confirmation Letter For Teacher After Completion Of 1 Year Of Probation With Necessary Terms, And Conditions
- Conflict Resolution Letter For Employees
- Congratulation Letter After Job Interview
- Congratulation Letter Business Success
- Congratulation Letter For Passing Board Exam
- Congratulation Letter For Promotion
- Congratulations Letter Receiving Award
- Consent Letter For Children Travelling Abroad
- Consent Letter For Guarantor
- Construction Contract Approval Letter
- Construction Delay Claim Letter Sample
- Contract Approval Letter Example
- Contract Extension Approval Letter
- Contract Renewal Letter To Manager
- Contract Termination Letter Due To Poor Performance
- Contract Termination Letter To Vendor
- Contractor Recommendation Letter Format
- Convert Residential To Commercial Property
- Courtesy Call Letter Sample
- Work From Home After Accident Letter Format
- Uniform Exemption Letter For Workers, Students, Employees
- Thanks Letter For Visitors Free Download
- Thanks Letter To Chief Guest And Guest Of Honor
- Apology For Resignation Letter
- Apply For Funds For Ngo Dealing With Disabled People, We Have A Land, And Want To Build The Proper Shelter
- Allow Vehicles For Lifting Auction Material Letter Format
- Address Change Request Letter For Credit Card
- Address Proof Letter Format
- Admission Confirmation Letter Format
- Admission Rejection Letter Samples
- Accreditation Letter For School
- Accreditation Letter For Travel Agency
- Accountant Letter For Visa
- Accreditation Letter For Organization
- Absence Excuse Letter For Professor-Lecturer
- Acceptance Letter By Auditor
- A Letter Of Support For A Graduation
- School Timing Change Notice
- Thank You Letter For Sponsoring An Event
- Sample Letter Of Data Collection, And Research Work
- Sample Letter Of Request For Borrowing Materials
- Sample Letter Of Thank You For Participation
- Sample Letter To Bank Manager For Unblock Atm Card
- Sample Letter To Claim Car Insurance
- Sample Letter To Close Bank Account Of Company
- Sample Letter To Parents About Fee Increase
- Sample Letter To Parents For School Fees Submission
- Sample Letter To Return Products, Or Ordered Items Or Replacement
- Sample Nomination Letter To Attend Training
- Sample Notice For Parent Teacher Meeting (Ptm)
- Sample Authority Letter For Cheque Collection
- Sample Experience Letter For Hotel Chef Or Cook
- Sample Experience Letter For Nurses
- Sample Holiday Notification Letter Format For Office
- Sample Invitation Letter To Chief Guest
- Sample Letter Asking Permission To Conduct Seminar
- Sample Letter For Acknowledging Delivery Of Goods, Or Services
- Sample Letter For Leave Without Permission
- Sample Letter For Requesting Quotations
- Sample Letter For Urgent Visa Request
- Salary Deduction Letter To Employee
- Request Letter For Any Suitable Job - Covering Letter Format
- Request Letter For Change Of Name In School Records
- Reply To Employment Verification Letter
- Request Application Letter To The College Principal -Vice-Chancellor -Admission Office For Taking Admission
- Request Final Payment Settlement After The Resignation
- Request For Fuel Allowance To Company-Employer
- Request For Meeting Appointment With Seniors - Other Employees-Clients Sample Letter
- Request For Office Supplies Templates
- Request Letter For Accommodation In University
- Request Letter For An Online Interview
- New Email Address Change Notification Letter
- Notice On Cleanliness In Your Office Compound
- Office Closing Reason For Business Loss Letter Format
- One Hour Leave Application Request Letter
- Permission Letter For Blood Donation Camp
- Promotion Request Letter And Application Format
- Proposal Letter For School Events And Activities
- Quotation Approval Request Letter With Advance Payment
- Recommendation Letter For Visa Application From Employer
- Remaining Payment Request Letter Sample For Clients, Customers
- Letter To Principal For Change Of School Bus Route
- Letter To Principal From Teacher About Misbehavior of a Student
- Letter To Remove Name From Joint Bank Account
- Letter To Renew Employment Contract Sample
- Letter To Subcontractor For Work Delay By The Contractor
- Letter To Your Friend About An Exhibition You Have Seen Recently
- Loan Cancellation Letter Sample
- Marriage Leave Extension Letter To Office-Manager Or Company
- Letter Of Introduction From A Company To An Employee For Visa
- Letter Of Recommendation For Further Studies By Employer
- Letter Regarding Visa Delay To Embassy
- Letter Requesting School Principal To Issue A New Student Identity Card
- Letter Requesting Sponsorship For Education From Ngo-Spouse-Court
- Letter To Airline For Refund Due To Illness, Death, Or Medical Grounds
- Letter To Cancel The Approved Leave Of Employee Due To Work In Office
- Letter To Customs Officer To Release Goods-Cargo
- Letter To Friend Telling About Your New School
- Letter To Friend Thanking Him For The Books He Lent To You
- Letter To Increase PF(Provident Fund) Contribution
- Letter To Inform Change Of Bank Account
- Letter To Insurance Company For Change Of Address
- Letter To Municipal Commissioner For Street Lights
- Letter To Municipal Corporation For Road Repair
- Letter To Parents Asking For Money
- 10 Examples of Letters of Recommendations
- English (UK)
- English (CA)
- Deutsch (DE)
- Deutsch (CH)
2024 guide to travel and expense management
Expense reimbursement policy best practices, what is an expense reimbursement policy.
?)
Download your expense reimbursement policy template now
How to create an expense reimbursement policy, create guidelines for what counts as reimbursable expenses.
- Is the expense travel-related? If yes, refer to your travel guidelines for employees . You should have guidelines for what does and doesn’t count as a travel-related expense in there. For example, meals eaten while traveling, would be reimbursable so long as they adhere to your company’s per diem rates .
- Expenses that aren’t travel-related can be reimbursed if they meet the criteria for accountable plan rules. The IRS creates guidelines for reimbursing employees so that these expenses don’t count as taxable income. For expenses to meet accountable plan rules they must be work-related expenses and reported to employers in a timely manner.
Outline how employees should report expenses
How to document and implement your employee expense policy.
- Making your company’s expense reimbursement policy clear and specific. Define any potentially confusing jargon so that employees won’t misunderstand the rules.
- Testing it out on employees. When you know the ins and outs of accounting, it’s easy to assume that everyone else does too. Test your new policy on a focus group before rolling it out to the entire company to see what you need to explain or simplify. Does everyone understand what an accountable plan is? Are “work-related expenses” clearly defined? Can employees get access to the company credit card instead of paying out of pocket? Get feedback to determine whether or not the policy has clauses that can be misinterpreted. Make adjustments as needed.
- Announcing the new policy and making it easily available through your company's communication tool, Slack, intranet, etc. Make the policy available in a cloud-based drive so that employees can review it on the go. This accessibility is especially important for your business travelers.
- Including the expense reimbursement policy in your corporate travel policy to make it even more accessible.
- Equipping employees with travel and expense software to enforce the policy. Give them an expense management tool to help collect receipts and file expense reports and travel booking software to track travel expenses.
Seamlessly integrate your expense tool with TravelPerk
Tips for enforcing an expense reimbursement policy.
- Ask employees for receipts that include the vendor’s name, date and time of purchase, and list of items bought.
- Scrutinize receipts. Are they forged? Do the purchases make sense? Is the employee trying to get reimbursed for a tip although gratuity was included in the meal? Does the receipt have a bunch of business-related expenses and several personal purchases hidden amongst them? Play detective.
- Create consequences for fraud. Firing employees who commit fraud will set an example and discourage others from following suit.
- Create consequences for overspending. If employees spend over the per diem rate for their trip, reimburse them up to the allowed amount, but don’t let them get away with anything more. If a certain employee consistently overspends on business trips, consider giving them fewer travel opportunities.
- Use tools that enforce the company’s spending policy. Adopt a travel management tool that shows which options are on-policy and which aren’t. Technology makes it easier than ever to identify and prevent expense reimbursement policy fraud.
- Grant employees access to virtual corporate cards. These cards give administrators the ability to track spending in real time. If a finance team member sees a business traveler making suspicious purchases, they can send the employee a warning or email them a copy of the expense policy as a reminder.
?)
Make business travel simpler. Forever.
- See our platform in action . Trusted by thousands of companies worldwide, TravelPerk makes business travel simpler to manage with more flexibility, full control of spending with easy reporting, and options to offset your carbon footprint.
- Find hundreds of resources on all things business travel, from tips on traveling more sustainably, to advice on setting up a business travel policy, and managing your expenses. Our latest e-books and blog posts have you covered.
- Never miss another update. Stay in touch with us on social for the latest product releases, upcoming events, and articles fresh off the press.
- Business Travel Management
- Offset Carbon Footprint
- Flexible travel
- Travelperk Sustainability Policy
- Corporate Travel Resources
- Corporate Travel Glossary
- For Travel Managers
- For Finance Teams
- For Travelers
- Thoughts from TravelPerk
- Careers Hiring
- User Reviews
- Integrations
- Privacy Center
- Help Center
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Modern Slavery Act | Statement
- Supplier Code of Conduct
An official website of the United States Government
- Kreyòl ayisyen
- Search Toggle search Search Include Historical Content - Any - No Include Historical Content - Any - No Search
- Menu Toggle menu
- INFORMATION FOR…
- Individuals
- Business & Self Employed
- Charities and Nonprofits
- International Taxpayers
- Federal State and Local Governments
- Indian Tribal Governments
- Tax Exempt Bonds
- FILING FOR INDIVIDUALS
- How to File
- When to File
- Where to File
- Update Your Information
- Get Your Tax Record
- Apply for an Employer ID Number (EIN)
- Check Your Amended Return Status
- Get an Identity Protection PIN (IP PIN)
- File Your Taxes for Free
- Bank Account (Direct Pay)
- Payment Plan (Installment Agreement)
- Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS)
- Your Online Account
- Tax Withholding Estimator
- Estimated Taxes
- Where's My Refund
- What to Expect
- Direct Deposit
- Reduced Refunds
- Amend Return
Credits & Deductions
- INFORMATION FOR...
- Businesses & Self-Employed
- Earned Income Credit (EITC)
- Child Tax Credit
- Clean Energy and Vehicle Credits
- Standard Deduction
- Retirement Plans
Forms & Instructions
- POPULAR FORMS & INSTRUCTIONS
- Form 1040 Instructions
- Form 4506-T
- POPULAR FOR TAX PROS
- Form 1040-X
- Circular 230
Future Developments
Who should use this publication.
Users of employer-provided vehicles.
Who doesn’t need to use this publication.
Volunteers.
Comments and suggestions.
Getting answers to your tax questions.
Getting tax forms, instructions, and publications.
Ordering tax forms, instructions, and publications.
- Useful Items - You may want to see:
Travel expenses defined.
Members of the Armed Forces.
Main place of business or work.
No main place of business or work.
Factors used to determine tax home.
Tax Home Different From Family Home
Temporary assignment vs. indefinite assignment.
Exception for federal crime investigations or prosecutions.
Determining temporary or indefinite.
Going home on days off.
Probationary work period.
Separating costs.
Travel expenses for another individual.
Business associate.
Bona fide business purpose.
Lavish or extravagant.
50% limit on meals.
Actual Cost
Incidental expenses.
Incidental-expenses-only method.
50% limit may apply.
Who can use the standard meal allowance.
Use of the standard meal allowance for other travel.
Amount of standard meal allowance.
Federal government's fiscal year.
Standard meal allowance for areas outside the continental United States.
Special rate for transportation workers.
Travel for days you depart and return.
Trip Primarily for Business
Trip primarily for personal reasons.
Public transportation.
Private car.
Travel entirely for business.
Travel considered entirely for business.
Exception 1—No substantial control.
Exception 2—Outside United States no more than a week.
Exception 3—Less than 25% of time on personal activities.
Exception 4—Vacation not a major consideration.
Travel allocation rules.
Counting business days.
Transportation day.
Presence required.
Day spent on business.
Certain weekends and holidays.
Nonbusiness activity on the way to or from your business destination.
Nonbusiness activity at, near, or beyond business destination.
Other methods.
Travel Primarily for Personal Reasons
Daily limit on luxury water travel.
Meals and entertainment.
Not separately stated.
Convention agenda.
North American area.
Reasonableness test.
Cruise Ships
Deduction may depend on your type of business.
Exceptions to the Rules
Entertainment events.
Entertainment facilities.
Club dues and membership fees.
Gift or entertainment.
Other rules for meals and entertainment expenses.
Costs to include or exclude.
Application of 50% limit.
When to apply the 50% limit.
Taking turns paying for meals.
1—Expenses treated as compensation.
2—Employee's reimbursed expenses.
3—Self-employed reimbursed expenses.
4—Recreational expenses for employees.
5—Advertising expenses.
6—Sale of meals.
Individuals subject to “hours of service” limits.
Incidental costs.
Exceptions.
- Illustration of transportation expenses.
Temporary work location.
No regular place of work.
Two places of work.
Armed Forces reservists.
Commuting expenses.
Parking fees.
Advertising display on car.
Hauling tools or instruments.
Union members' trips from a union hall.
Office in the home.
Examples of deductible transportation.
Choosing the standard mileage rate.
Standard mileage rate not allowed.
Five or more cars.
Personal property taxes.
Parking fees and tolls.
Sale, trade-in, or other disposition.
Business and personal use.
Employer-provided vehicle.
Interest on car loans.
Taxes paid on your car.
Sales taxes.
Fines and collateral.
Casualty and theft losses.
Depreciation and section 179 deductions.
Car defined.
Qualified nonpersonal use vehicles.
More information.
More than 50% business use requirement.
Limit on the amount of the section 179 deduction.
Limit for sport utility and certain other vehicles.
Limit on total section 179 deduction, special depreciation allowance, and depreciation deduction.
Cost of car.
Basis of car for depreciation.
When to elect.
How to elect.
Revoking an election.
Recapture of section 179 deduction.
Dispositions.
Combined depreciation.
Qualified car.
Election not to claim the special depreciation allowance.
Placed in service.
Car placed in service and disposed of in the same year.
Methods of depreciation.
More-than-50%-use test.
Qualified business use.
Use of your car by another person.
Business use changes.
Use for more than one purpose.
Change from personal to business use.
Unadjusted basis.
Improvements.
Car trade-in.
Effect of trade-in on basis.
Traded car used only for business.
Traded car used partly in business.
Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS).
Recovery period.
Depreciation methods.
MACRS depreciation chart.
Depreciation in future years.
Disposition of car during recovery period.
How to use the 2023 chart.
Trucks and vans.
Car used less than full year.
Reduction for personal use.
Section 179 deduction.
Deductions in years after the recovery period.
Unrecovered basis.
The recovery period.
How to treat unrecovered basis.
- Table 4-1. 2023 MACRS Depreciation Chart (Use To Figure Depreciation for 2023)
Qualified business use 50% or less in year placed in service.
Qualified business use 50% or less in a later year.
Excess depreciation.
Deductible payments.
Fair market value.
Figuring the inclusion amount.
Leased car changed from business to personal use.
Leased car changed from personal to business use.
Reporting inclusion amounts.
Casualty or theft.
Depreciation adjustment when you used the standard mileage rate.
Depreciation deduction for the year of disposition.
Documentary evidence.
Adequate evidence.
Canceled check.
Duplicate information.
Timely kept records.
Proving business purpose.
Confidential information.
Exceptional circumstances.
Destroyed records.
Separating expenses.
Combining items.
Car expenses.
Gift expenses.
Allocating total cost.
If your return is examined.
Reimbursed for expenses.
Examples of Records
Self-employed.
Both self-employed and an employee.
Statutory employees.
Reimbursement for personal expenses.
Income-producing property.
Value reported on Form W-2.
Full value included in your income.
Less than full value included in your income.
No reimbursement.
Reimbursement, allowance, or advance.
Reasonable period of time.
Employee meets accountable plan rules.
Accountable plan rules not met.
Failure to return excess reimbursements.
Reimbursement of nondeductible expenses.
Adequate Accounting
Related to employer.
The federal rate.
Regular federal per diem rate.
The standard meal allowance.
High-low rate.
Prorating the standard meal allowance on partial days of travel.
The standard mileage rate.
Fixed and variable rate (FAVR).
Reporting your expenses with a per diem or car allowance.
Allowance less than or equal to the federal rate.
Allowance more than the federal rate.
Travel advance.
Unproven amounts.
Per diem allowance more than federal rate.
Reporting your expenses under a nonaccountable plan.
Adequate accounting.
How to report.
Contractor adequately accounts.
Contractor doesn’t adequately account.
High-low method.
Regular federal per diem rate method.
Federal per diem rate method.
Information on use of cars.
Standard mileage rate.
Actual expenses.
Car rentals.
Transportation expenses.
Employee business expenses other than nonentertainment meals.
Non-entertainment-related meal expenses.
“Hours of service” limits.
Reimbursements.
Allocating your reimbursement.
After you complete the form.
Limits on employee business expenses.
1. Limit on meals and entertainment.
2. Limit on total itemized deductions.
Member of a reserve component.
Officials Paid on a Fee Basis
Special rules for married persons.
Where to report.

Impairment-Related Work Expenses of Disabled Employees
Preparing and filing your tax return.
Free options for tax preparation.
Using online tools to help prepare your return.
Need someone to prepare your tax return?
Employers can register to use Business Services Online.
IRS social media.
Watching IRS videos.
Online tax information in other languages.
Free Over-the-Phone Interpreter (OPI) Service.
Accessibility Helpline available for taxpayers with disabilities.
Getting tax forms and publications.
Getting tax publications and instructions in eBook format.
Access your online account (individual taxpayers only).
Get a transcript of your return.
Tax Pro Account.
Using direct deposit.
Reporting and resolving your tax-related identity theft issues.
Ways to check on the status of your refund.
Making a tax payment.
What if I can’t pay now?
Filing an amended return.
Checking the status of your amended return.
Understanding an IRS notice or letter you’ve received.
Responding to an IRS notice or letter.
Contacting your local TAC.
What Is TAS?
How can you learn about your taxpayer rights, what can tas do for you, how can you reach tas, how else does tas help taxpayers, low income taxpayer clinics (litcs), appendix a-1. inclusion amounts for passenger automobiles first leased in 2018, appendix a-2. inclusion amounts for passenger automobiles first leased in 2019, appendix a-3. inclusion amounts for passenger automobiles first leased in 2020, appendix a-4. inclusion amounts for passenger automobiles first leased in 2021, appendix a-5. inclusion amounts for passenger automobiles first leased in 2022, appendix a-6. inclusion amounts for passenger automobiles first leased in 2023, publication 463 - additional material, publication 463 (2023), travel, gift, and car expenses.
For use in preparing 2023 Returns
Publication 463 - Introductory Material
For the latest information about developments related to Pub. 463, such as legislation enacted after it was published, go to IRS.gov/Pub463 .
Standard mileage rate. For 2023, the standard mileage rate for the cost of operating your car for business use is 65.5 cents ($0.655) per mile. Car expenses and use of the standard mileage rate are explained in chapter 4.
Depreciation limits on cars, trucks, and vans. The first-year limit on the depreciation deduction, special depreciation allowance, and section 179 deduction for vehicles acquired before September 28, 2017, and placed in service during 2023, is $12,200. The first-year limit on depreciation, special depreciation allowance, and section 179 deduction for vehicles acquired after September 27, 2017, and placed in service during 2023 increases to $20,200. If you elect not to claim a special depreciation allowance for a vehicle placed in service in 2023, the amount increases to $12,200. Depreciation limits are explained in chapter 4.
Section 179 deduction. The maximum amount you can elect to deduct for section 179 property (including cars, trucks, and vans) you placed in service in tax years beginning in 2023 is $1,160,000. This limit is reduced by the amount by which the cost of section 179 property placed in service during the tax year exceeds $2,890,000. Section 179 deduction is explained in chapter 4.Also, the maximum section 179 expense deduction for sport utility vehicles placed in service in tax years beginning in 2023 is $28,900.
Temporary deduction of 100% business meals. The 100% deduction on certain business meals expenses as amended under the Taxpayer Certainty and Disaster Tax Relief Act of 2020, and enacted by the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021, has expired. Generally, the cost of business meals remains deductible, subject to the 50% limitation. See 50% Limit in chapter 2 for more information.
Photographs of missing children. The IRS is a proud partner with the National Center for Missing & Exploited Children® (NCMEC) . Photographs of missing children selected by the Center may appear in this publication on pages that would otherwise be blank. You can help bring these children home by looking at the photographs and calling 800-THE-LOST (800-843-5678) if you recognize a child.
Per diem rates. Current and prior per diem rates may be found on the U.S. General Services Administration (GSA) website at GSA.gov/travel/plan-book/per-diem-rates .
Introduction
You may be able to deduct the ordinary and necessary business-related expenses you have for:
Non-entertainment-related meals,
Transportation.
This publication explains:
What expenses are deductible,
How to report them on your return,
What records you need to prove your expenses, and
How to treat any expense reimbursements you may receive.
You should read this publication if you are an employee or a sole proprietor who has business-related travel, non-entertainment-related meals, gift, or transportation expenses.
If an employer-provided vehicle was available for your use, you received a fringe benefit. Generally, your employer must include the value of the use or availability of the vehicle in your income. However, there are exceptions if the use of the vehicle qualifies as a working condition fringe benefit (such as the use of a qualified nonpersonal use vehicle).
A working condition fringe benefit is any property or service provided to you by your employer, the cost of which would be allowable as an employee business expense deduction if you had paid for it.
A qualified nonpersonal use vehicle is one that isn’t likely to be used more than minimally for personal purposes because of its design. See Qualified nonpersonal use vehicles under Actual Car Expenses in chapter 4.
For information on how to report your car expenses that your employer didn’t provide or reimburse you for (such as when you pay for gas and maintenance for a car your employer provides), see Vehicle Provided by Your Employer in chapter 6.
Partnerships, corporations, trusts, and employers who reimburse their employees for business expenses should refer to the instructions for their required tax forms, for information on deducting travel, meals, and entertainment expenses.
If you are an employee, you won’t need to read this publication if all of the following are true.
You fully accounted to your employer for your work-related expenses.
You received full reimbursement for your expenses.
Your employer required you to return any excess reimbursement and you did so.
There is no amount shown with a code L in box 12 of your Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement.
If you perform services as a volunteer worker for a qualified charity, you may be able to deduct some of your costs as a charitable contribution. See Out-of-Pocket Expenses in Giving Services in Pub. 526, Charitable Contributions, for information on the expenses you can deduct.
We welcome your comments about this publication and suggestions for future editions.
You can send us comments through IRS.gov/FormComments . Or, you can write to the Internal Revenue Service, Tax Forms and Publications, 1111 Constitution Ave. NW, IR-6526, Washington, DC 20224.
Although we can’t respond individually to each comment received, we do appreciate your feedback and will consider your comments and suggestions as we revise our tax forms, instructions, and publications. Don’t send tax questions, tax returns, or payments to the above address.
If you have a tax question not answered by this publication or the How To Get Tax Help section at the end of this publication, go to the IRS Interactive Tax Assistant page at IRS.gov/Help/ITA where you can find topics by using the search feature or viewing the categories listed.
Go to IRS.gov/Forms to download current and prior-year forms, instructions, and publications.
Go to IRS.gov/OrderForms to order current forms, instructions, and publications; call 800-829-3676 to order prior-year forms and instructions. The IRS will process your order for forms and publications as soon as possible. Don’t resubmit requests you’ve already sent us. You can get forms and publications faster online.
Useful Items
Publication
946 How To Depreciate Property
Form (and Instructions)
Schedule A (Form 1040) Itemized Deductions
Schedule C (Form 1040) Profit or Loss From Business (Sole Proprietorship)
Schedule F (Form 1040) Profit or Loss From Farming
2106 Employee Business Expenses
4562 Depreciation and Amortization (Including Information on Listed Property)
See How To Get Tax Help for information about getting these publications and forms.
If you temporarily travel away from your tax home, you can use this chapter to determine if you have deductible travel expenses.
This chapter discusses:
Traveling away from home,
Temporary assignment or job, and
What travel expenses are deductible.
For tax purposes, travel expenses are the ordinary and necessary expenses of traveling away from home for your business, profession, or job.
An ordinary expense is one that is common and accepted in your trade or business. A necessary expense is one that is helpful and appropriate for your business. An expense doesn’t have to be required to be considered necessary.
You will find examples of deductible travel expenses in Table 1-1 .
Traveling Away From Home
You are traveling away from home if:
Your duties require you to be away from the general area of your tax home (defined later) substantially longer than an ordinary day's work, and
You need to sleep or rest to meet the demands of your work while away from home.
You are a railroad conductor. You leave your home terminal on a regularly scheduled round-trip run between two cities and return home 16 hours later. During the run, you have 6 hours off at your turnaround point where you eat two meals and rent a hotel room to get necessary sleep before starting the return trip. You are considered to be away from home.
You are a truck driver. You leave your terminal and return to it later the same day. You get an hour off at your turnaround point to eat. Because you aren’t off to get necessary sleep and the brief time off isn’t an adequate rest period, you aren’t traveling away from home.
If you are a member of the U.S. Armed Forces on a permanent duty assignment overseas, you aren’t traveling away from home. You can’t deduct your expenses for meals and lodging. You can’t deduct these expenses even if you have to maintain a home in the United States for your family members who aren’t allowed to accompany you overseas. If you are transferred from one permanent duty station to another, you may have deductible moving expenses, which are explained in Pub. 3, Armed Forces' Tax Guide.
A naval officer assigned to permanent duty aboard a ship that has regular eating and living facilities has a tax home (explained next) aboard the ship for travel expense purposes.
To determine whether you are traveling away from home, you must first determine the location of your tax home.
Generally, your tax home is your regular place of business or post of duty, regardless of where you maintain your family home. It includes the entire city or general area in which your business or work is located.
If you have more than one regular place of business, your tax home is your main place of business. See Main place of business or work , later.
If you don’t have a regular or a main place of business because of the nature of your work, then your tax home may be the place where you regularly live. See No main place of business or work , later.
If you don’t have a regular or main place of business or post of duty and there is no place where you regularly live, you are considered an itinerant (a transient) and your tax home is wherever you work. As an itinerant, you can’t claim a travel expense deduction because you are never considered to be traveling away from home.
If you have more than one place of work, consider the following when determining which one is your main place of business or work.
The total time you ordinarily spend in each place.
The level of your business activity in each place.
Whether your income from each place is significant or insignificant.
You live in Cincinnati where you have a seasonal job for 8 months each year and earn $40,000. You work the other 4 months in Miami, also at a seasonal job, and earn $15,000. Cincinnati is your main place of work because you spend most of your time there and earn most of your income there.
You may have a tax home even if you don’t have a regular or main place of work. Your tax home may be the home where you regularly live.
If you don’t have a regular or main place of business or work, use the following three factors to determine where your tax home is.
You perform part of your business in the area of your main home and use that home for lodging while doing business in the area.
You have living expenses at your main home that you duplicate because your business requires you to be away from that home.
You haven’t abandoned the area in which both your historical place of lodging and your claimed main home are located; you have a member or members of your family living at your main home; or you often use that home for lodging.
If you satisfy all three factors, your tax home is the home where you regularly live. If you satisfy only two factors, you may have a tax home depending on all the facts and circumstances. If you satisfy only one factor, you are an itinerant; your tax home is wherever you work and you can’t deduct travel expenses.
You are single and live in Boston in an apartment you rent. You have worked for your employer in Boston for a number of years. Your employer enrolls you in a 12-month executive training program. You don’t expect to return to work in Boston after you complete your training.
During your training, you don’t do any work in Boston. Instead, you receive classroom and on-the-job training throughout the United States. You keep your apartment in Boston and return to it frequently. You use your apartment to conduct your personal business. You also keep up your community contacts in Boston. When you complete your training, you are transferred to Los Angeles.
You don’t satisfy factor (1) because you didn’t work in Boston. You satisfy factor (2) because you had duplicate living expenses. You also satisfy factor (3) because you didn’t abandon your apartment in Boston as your main home, you kept your community contacts, and you frequently returned to live in your apartment. Therefore, you have a tax home in Boston.
You are an outside salesperson with a sales territory covering several states. Your employer's main office is in Newark, but you don’t conduct any business there. Your work assignments are temporary, and you have no way of knowing where your future assignments will be located. You have a room in your married sister's house in Dayton. You stay there for one or two weekends a year, but you do no work in the area. You don’t pay your sister for the use of the room.
You don’t satisfy any of the three factors listed earlier. You are an itinerant and have no tax home.
If you (and your family) don’t live at your tax home (defined earlier), you can’t deduct the cost of traveling between your tax home and your family home. You also can’t deduct the cost of meals and lodging while at your tax home. See Example 1 , later.
If you are working temporarily in the same city where you and your family live, you may be considered as traveling away from home. See Example 2 , later.
You are a truck driver and you and your family live in Tucson. You are employed by a trucking firm that has its terminal in Phoenix. At the end of your long runs, you return to your home terminal in Phoenix and spend one night there before returning home. You can’t deduct any expenses you have for meals and lodging in Phoenix or the cost of traveling from Phoenix to Tucson. This is because Phoenix is your tax home.
Your family home is in Pittsburgh, where you work 12 weeks a year. The rest of the year you work for the same employer in Baltimore. In Baltimore, you eat in restaurants and sleep in a rooming house. Your salary is the same whether you are in Pittsburgh or Baltimore.
Because you spend most of your working time and earn most of your salary in Baltimore, that city is your tax home. You can’t deduct any expenses you have for meals and lodging there. However, when you return to work in Pittsburgh, you are away from your tax home even though you stay at your family home. You can deduct the cost of your round trip between Baltimore and Pittsburgh. You can also deduct your part of your family's living expenses for non-entertainment-related meals and lodging while you are living and working in Pittsburgh.
Temporary Assignment or Job
You may regularly work at your tax home and also work at another location. It may not be practical to return to your tax home from this other location at the end of each workday.
If your assignment or job away from your main place of work is temporary, your tax home doesn’t change. You are considered to be away from home for the whole period you are away from your main place of work. You can deduct your travel expenses if they otherwise qualify for deduction. Generally, a temporary assignment in a single location is one that is realistically expected to last (and does in fact last) for 1 year or less.
However, if your assignment or job is indefinite, the location of the assignment or job becomes your new tax home and you can’t deduct your travel expenses while there. An assignment or job in a single location is considered indefinite if it is realistically expected to last for more than 1 year, whether or not it actually lasts for more than 1 year.
If your assignment is indefinite, you must include in your income any amounts you receive from your employer for living expenses, even if they are called “travel allowances” and you account to your employer for them. You may be able to deduct the cost of relocating to your new tax home as a moving expense. See Pub. 3 for more information.
If you are a federal employee participating in a federal crime investigation or prosecution, you aren’t subject to the 1-year rule. This means you may be able to deduct travel expenses even if you are away from your tax home for more than 1 year provided you meet the other requirements for deductibility.
For you to qualify, the Attorney General (or their designee) must certify that you are traveling:
For the federal government;
In a temporary duty status; and
To investigate, prosecute, or provide support services for the investigation or prosecution of a federal crime.
You must determine whether your assignment is temporary or indefinite when you start work. If you expect an assignment or job to last for 1 year or less, it is temporary unless there are facts and circumstances that indicate otherwise. An assignment or job that is initially temporary may become indefinite due to changed circumstances. A series of assignments to the same location, all for short periods but that together cover a long period, may be considered an indefinite assignment.
The following examples illustrate whether an assignment or job is temporary or indefinite.
You are a construction worker. You live and regularly work in Los Angeles. You are a member of a trade union in Los Angeles that helps you get work in the Los Angeles area. Your tax home is Los Angeles. Because of a shortage of work, you took a job on a construction project in Fresno. Your job was scheduled to end in 8 months. The job actually lasted 10 months.
You realistically expected the job in Fresno to last 8 months. The job actually did last less than 1 year. The job is temporary and your tax home is still in Los Angeles.
The facts are the same as in Example 1 , except that you realistically expected the work in Fresno to last 18 months. The job was actually completed in 10 months.
Your job in Fresno is indefinite because you realistically expected the work to last longer than 1 year, even though it actually lasted less than 1 year. You can’t deduct any travel expenses you had in Fresno because Fresno became your tax home.
The facts are the same as in Example 1 , except that you realistically expected the work in Fresno to last 9 months. After 8 months, however, you were asked to remain for 7 more months (for a total actual stay of 15 months).
Initially, you realistically expected the job in Fresno to last for only 9 months. However, due to changed circumstances occurring after 8 months, it was no longer realistic for you to expect that the job in Fresno would last for 1 year or less. You can deduct only your travel expenses for the first 8 months. You can’t deduct any travel expenses you had after that time because Fresno became your tax home when the job became indefinite.
If you go back to your tax home from a temporary assignment on your days off, you aren’t considered away from home while you are in your hometown. You can’t deduct the cost of your meals and lodging there. However, you can deduct your travel expenses, including meals and lodging, while traveling between your temporary place of work and your tax home. You can claim these expenses up to the amount it would have cost you to stay at your temporary place of work.
If you keep your hotel room during your visit home, you can deduct the cost of your hotel room. In addition, you can deduct your expenses of returning home up to the amount you would have spent for meals had you stayed at your temporary place of work.
If you take a job that requires you to move, with the understanding that you will keep the job if your work is satisfactory during a probationary period, the job is indefinite. You can’t deduct any of your expenses for meals and lodging during the probationary period.
What Travel Expenses Are Deductible?
Once you have determined that you are traveling away from your tax home, you can determine what travel expenses are deductible.
You can deduct ordinary and necessary expenses you have when you travel away from home on business. The type of expense you can deduct depends on the facts and your circumstances.
Table 1-1 summarizes travel expenses you may be able to deduct. You may have other deductible travel expenses that aren’t covered there, depending on the facts and your circumstances.
If you have one expense that includes the costs of non-entertainment-related meals, entertainment, and other services (such as lodging or transportation), you must allocate that expense between the cost of non-entertainment-related meals, and entertainment and the cost of other services. You must have a reasonable basis for making this allocation. For example, you must allocate your expenses if a hotel includes one or more meals in its room charge.
If a spouse, dependent, or other individual goes with you (or your employee) on a business trip or to a business convention, you generally can’t deduct their travel expenses.
You can deduct the travel expenses of someone who goes with you if that person:
Is your employee,
Has a bona fide business purpose for the travel, and
Would otherwise be allowed to deduct the travel expenses.
If a business associate travels with you and meets the conditions in (2) and (3) above, you can deduct the travel expenses you have for that person. A business associate is someone with whom you could reasonably expect to actively conduct business. A business associate can be a current or prospective (likely to become) customer, client, supplier, employee, agent, partner, or professional advisor.
Table 1-1. Travel Expenses You Can Deduct
A bona fide business purpose exists if you can prove a real business purpose for the individual's presence. Incidental services, such as typing notes or assisting in entertaining customers, aren’t enough to make the expenses deductible.
You drive to Chicago on business and take your spouse with you. Your spouse isn’t your employee. Your spouse occasionally types notes, performs similar services, and accompanies you to luncheons and dinners. The performance of these services doesn’t establish that your spouse’s presence on the trip is necessary to the conduct of your business. Your spouse’s expenses aren’t deductible.
You pay $199 a day for a double room. A single room costs $149 a day. You can deduct the total cost of driving your car to and from Chicago, but only $149 a day for your hotel room. If both you and your spouse use public transportation, you can only deduct your fare.
You can deduct a portion of the cost of meals if it is necessary for you to stop for substantial sleep or rest to properly perform your duties while traveling away from home on business. Meal and entertainment expenses are discussed in chapter 2 .
You can't deduct expenses for meals that are lavish or extravagant. An expense isn't considered lavish or extravagant if it is reasonable based on the facts and circumstances. Meal expenses won't be disallowed merely because they are more than a fixed dollar amount or because the meals take place at deluxe restaurants, hotels, or resorts.
You can figure your meal expenses using either of the following methods.
Actual cost.
If you are reimbursed for the cost of your meals, how you apply the 50% limit depends on whether your employer's reimbursement plan was accountable or nonaccountable. If you aren’t reimbursed, the 50% limit applies even if the unreimbursed meal expense is for business travel. Chapter 2 discusses the 50% Limit in more detail, and chapter 6 discusses accountable and nonaccountable plans.
You can use the actual cost of your meals to figure the amount of your expense before reimbursement and application of the 50% deduction limit. If you use this method, you must keep records of your actual cost.
Standard Meal Allowance
Generally, you can use the “standard meal allowance” method as an alternative to the actual cost method. It allows you to use a set amount for your daily meals and incidental expenses (M&IE), instead of keeping records of your actual costs. The set amount varies depending on where and when you travel. In this publication, “standard meal allowance” refers to the federal rate for M&IE, discussed later under Amount of standard meal allowance . If you use the standard meal allowance, you must still keep records to prove the time, place, and business purpose of your travel. See the recordkeeping rules for travel in chapter 5 .
The term “incidental expenses” means fees and tips given to porters, baggage carriers, hotel staff, and staff on ships.
Incidental expenses don’t include expenses for laundry, cleaning and pressing of clothing, lodging taxes, costs of telegrams or telephone calls, transportation between places of lodging or business and places where meals are taken, or the mailing cost of filing travel vouchers and paying employer-sponsored charge card billings.
You can use an optional method (instead of actual cost) for deducting incidental expenses only. The amount of the deduction is $5 a day. You can use this method only if you didn’t pay or incur any meal expenses. You can’t use this method on any day that you use the standard meal allowance. This method is subject to the proration rules for partial days. See Travel for days you depart and return , later, in this chapter.
The incidental-expenses-only method isn’t subject to the 50% limit discussed below.
If you use the standard meal allowance method for non-entertainment-related meal expenses and you aren’t reimbursed or you are reimbursed under a nonaccountable plan, you can generally deduct only 50% of the standard meal allowance. If you are reimbursed under an accountable plan and you are deducting amounts that are more than your reimbursements, you can deduct only 50% of the excess amount. The 50% Limit is discussed in more detail in chapter 2, and accountable and nonaccountable plans are discussed in chapter 6.
You can use the standard meal allowance whether you are an employee or self-employed, and whether or not you are reimbursed for your traveling expenses.
You can use the standard meal allowance to figure your meal expenses when you travel in connection with investment and other income-producing property. You can also use it to figure your meal expenses when you travel for qualifying educational purposes. You can’t use the standard meal allowance to figure the cost of your meals when you travel for medical or charitable purposes.
The standard meal allowance is the federal M&IE rate. For travel in 2023, the rate for most small localities in the United States is $59 per day.
Most major cities and many other localities in the United States are designated as high-cost areas, qualifying for higher standard meal allowances.
If you travel to more than one location in one day, use the rate in effect for the area where you stop for sleep or rest. If you work in the transportation industry, however, see Special rate for transportation workers , later.
Per diem rates are listed by the federal government's fiscal year, which runs from October 1 to September 30. You can choose to use the rates from the 2022 fiscal year per diem tables or the rates from the 2023 fiscal year tables, but you must consistently use the same tables for all travel you are reporting on your income tax return for the year. See Transition Rules , later.
The standard meal allowance rates above don’t apply to travel in Alaska, Hawaii, or any other location outside the continental United States. The Department of Defense establishes per diem rates for Alaska, Hawaii, Puerto Rico, American Samoa, Guam, Midway, the Northern Mariana Islands, the U.S. Virgin Islands, Wake Island, and other non-foreign areas outside the continental United States. The Department of State establishes per diem rates for all other foreign areas.
You can use a special standard meal allowance if you work in the transportation industry. You are in the transportation industry if your work:
Directly involves moving people or goods by airplane, barge, bus, ship, train, or truck; and
Regularly requires you to travel away from home and, during any single trip, usually involves travel to areas eligible for different standard meal allowance rates.
Using the special rate for transportation workers eliminates the need for you to determine the standard meal allowance for every area where you stop for sleep or rest. If you choose to use the special rate for any trip, you must use the special rate (and not use the regular standard meal allowance rates) for all trips you take that year.
For both the day you depart for and the day you return from a business trip, you must prorate the standard meal allowance (figure a reduced amount for each day). You can do so by one of two methods.
Method 1: You can claim 3 / 4 of the standard meal allowance.
Method 2: You can prorate using any method that you consistently apply and that is in accordance with reasonable business practice.
You are employed in New Orleans as a convention planner. In March, your employer sent you on a 3-day trip to Washington, DC, to attend a planning seminar. You left your home in New Orleans at 10 a.m. on Wednesday and arrived in Washington, DC, at 5:30 p.m. After spending 2 nights there, you flew back to New Orleans on Friday and arrived back home at 8 p.m. Your employer gave you a flat amount to cover your expenses and included it with your wages.
Under Method 1 , you can claim 2½ days of the standard meal allowance for Washington, DC: 3 / 4 of the daily rate for Wednesday and Friday (the days you departed and returned), and the full daily rate for Thursday.
Under Method 2 , you could also use any method that you apply consistently and that is in accordance with reasonable business practice. For example, you could claim 3 days of the standard meal allowance even though a federal employee would have to use Method 1 and be limited to only 2½ days.
Travel in the United States
The following discussion applies to travel in the United States. For this purpose, the United States includes the 50 states and the District of Columbia. The treatment of your travel expenses depends on how much of your trip was business related and on how much of your trip occurred within the United States. See Part of Trip Outside the United States , later.
You can deduct all of your travel expenses if your trip was entirely business related. If your trip was primarily for business and, while at your business destination, you extended your stay for a vacation, made a personal side trip, or had other personal activities, you can deduct only your business-related travel expenses. These expenses include the travel costs of getting to and from your business destination and any business-related expenses at your business destination.
You work in Atlanta and take a business trip to New Orleans in May. Your business travel totals 900 miles round trip. On your way home, you stop in Mobile to visit your parents. You spend $2,165 for the 9 days you are away from home for travel, non-entertainment-related meals, lodging, and other travel expenses. If you hadn’t stopped in Mobile, you would have been gone only 6 days, and your total cost would have been $1,633.50. You can deduct $1,633.50 for your trip, including the cost of round-trip transportation to and from New Orleans. The deduction for your non-entertainment-related meals is subject to the 50% limit on meals mentioned earlier.
If your trip was primarily for personal reasons, such as a vacation, the entire cost of the trip is a nondeductible personal expense. However, you can deduct any expenses you have while at your destination that are directly related to your business.
A trip to a resort or on a cruise ship may be a vacation even if the promoter advertises that it is primarily for business. The scheduling of incidental business activities during a trip, such as viewing videotapes or attending lectures dealing with general subjects, won’t change what is really a vacation into a business trip.
Part of Trip Outside the United States
If part of your trip is outside the United States, use the rules described later in this chapter under Travel Outside the United States for that part of the trip. For the part of your trip that is inside the United States, use the rules for travel in the United States. Travel outside the United States doesn’t include travel from one point in the United States to another point in the United States. The following discussion can help you determine whether your trip was entirely within the United States.
If you travel by public transportation, any place in the United States where that vehicle makes a scheduled stop is a point in the United States. Once the vehicle leaves the last scheduled stop in the United States on its way to a point outside the United States, you apply the rules under Travel Outside the United States , later.
You fly from New York to Puerto Rico with a scheduled stop in Miami. Puerto Rico isn’t considered part of the United States for purposes of travel. You return to New York nonstop. The flight from New York to Miami is in the United States, so only the flight from Miami to Puerto Rico is outside the United States. Because there are no scheduled stops between Puerto Rico and New York, all of the return trip is outside the United States.
Travel by private car in the United States is travel between points in the United States, even though you are on your way to a destination outside the United States.
You travel by car from Denver to Mexico City and return. Your travel from Denver to the border and from the border back to Denver is travel in the United States, and the rules in this section apply. The rules below under Travel Outside the United States apply to your trip from the border to Mexico City and back to the border.
Travel Outside the United States
If any part of your business travel is outside the United States, some of your deductions for the cost of getting to and from your destination may be limited. For this purpose, the United States includes the 50 states and the District of Columbia.
How much of your travel expenses you can deduct depends in part upon how much of your trip outside the United States was business related.
Travel Entirely for Business or Considered Entirely for Business
You can deduct all your travel expenses of getting to and from your business destination if your trip is entirely for business or considered entirely for business.
If you travel outside the United States and you spend the entire time on business activities, you can deduct all of your travel expenses.
Even if you didn’t spend your entire time on business activities, your trip is considered entirely for business if you meet at least one of the following four exceptions.
Your trip is considered entirely for business if you didn’t have substantial control over arranging the trip. The fact that you control the timing of your trip doesn’t, by itself, mean that you have substantial control over arranging your trip.
You don’t have substantial control over your trip if you:
Are an employee who was reimbursed or paid a travel expense allowance, and
Aren’t related to your employer, or
Aren’t a managing executive.
“Related to your employer” is defined later in chapter 6 under Per Diem and Car Allowances .
A “managing executive” is an employee who has the authority and responsibility, without being subject to the veto of another, to decide on the need for the business travel.
A self-employed person generally has substantial control over arranging business trips.
Your trip is considered entirely for business if you were outside the United States for a week or less, combining business and nonbusiness activities. One week means 7 consecutive days. In counting the days, don’t count the day you leave the United States, but do count the day you return to the United States.
You traveled to Brussels primarily for business. You left Denver on Tuesday and flew to New York. On Wednesday, you flew from New York to Brussels, arriving the next morning. On Thursday and Friday, you had business discussions, and from Saturday until Tuesday, you were sightseeing. You flew back to New York, arriving Wednesday afternoon. On Thursday, you flew back to Denver.
Although you were away from your home in Denver for more than a week, you weren’t outside the United States for more than a week. This is because the day you depart doesn’t count as a day outside the United States.
You can deduct your cost of the round-trip flight between Denver and Brussels. You can also deduct the cost of your stay in Brussels for Thursday and Friday while you conducted business. However, you can’t deduct the cost of your stay in Brussels from Saturday through Tuesday because those days were spent on nonbusiness activities.
Your trip is considered entirely for business if:
You were outside the United States for more than a week, and
You spent less than 25% of the total time you were outside the United States on nonbusiness activities.
You flew from Seattle to Tokyo, where you spent 14 days on business and 5 days on personal matters. You then flew back to Seattle. You spent 1 day flying in each direction.
Because only 5 / 21 (less than 25%) of your total time abroad was for nonbusiness activities, you can deduct as travel expenses what it would have cost you to make the trip if you hadn’t engaged in any nonbusiness activity. The amount you can deduct is the cost of the round-trip plane fare and 16 days of non-entertainment-related meals (subject to the 50% Limit ), lodging, and other related expenses.
Your trip is considered entirely for business if you can establish that a personal vacation wasn’t a major consideration, even if you have substantial control over arranging the trip.
Travel Primarily for Business
If you travel outside the United States primarily for business but spend some of your time on other activities, you generally can’t deduct all of your travel expenses. You can only deduct the business portion of your cost of getting to and from your destination. You must allocate the costs between your business and other activities to determine your deductible amount. See Travel allocation rules , later.
If your trip outside the United States was primarily for business, you must allocate your travel time on a day-to-day basis between business days and nonbusiness days. The days you depart from and return to the United States are both counted as days outside the United States.
To figure the deductible amount of your round-trip travel expenses, use the following fraction. The numerator (top number) is the total number of business days outside the United States. The denominator (bottom number) is the total number of business and nonbusiness days of travel.
Your business days include transportation days, days your presence was required, days you spent on business, and certain weekends and holidays.
Count as a business day any day you spend traveling to or from a business destination. However, if because of a nonbusiness activity you don’t travel by a direct route, your business days are the days it would take you to travel a reasonably direct route to your business destination. Extra days for side trips or nonbusiness activities can’t be counted as business days.
Count as a business day any day your presence is required at a particular place for a specific business purpose. Count it as a business day even if you spend most of the day on nonbusiness activities.
If your principal activity during working hours is the pursuit of your trade or business, count the day as a business day. Also, count as a business day any day you are prevented from working because of circumstances beyond your control.
Count weekends, holidays, and other necessary standby days as business days if they fall between business days. But if they follow your business meetings or activity and you remain at your business destination for nonbusiness or personal reasons, don’t count them as business days.
Your tax home is New York City. You travel to Quebec, where you have a business meeting on Friday. You have another meeting on the following Monday. Because your presence was required on both Friday and Monday, they are business days. Because the weekend is between business days, Saturday and Sunday are counted as business days. This is true even though you use the weekend for sightseeing, visiting friends, or other nonbusiness activity.
If, in Example 1 , you had no business in Quebec after Friday, but stayed until Monday before starting home, Saturday and Sunday would be nonbusiness days.
If you stopped for a vacation or other nonbusiness activity either on the way from the United States to your business destination, or on the way back to the United States from your business destination, you must allocate part of your travel expenses to the nonbusiness activity.
The part you must allocate is the amount it would have cost you to travel between the point where travel outside the United States begins and your nonbusiness destination and a return to the point where travel outside the United States ends.
You determine the nonbusiness portion of that expense by multiplying it by a fraction. The numerator (top number) of the fraction is the number of nonbusiness days during your travel outside the United States, and the denominator (bottom number) is the total number of days you spend outside the United States.
You live in New York. On May 4, you flew to Paris to attend a business conference that began on May 5. The conference ended at noon on May 14. That evening, you flew to Dublin where you visited with friends until the afternoon of May 21, when you flew directly home to New York. The primary purpose for the trip was to attend the conference.
If you hadn’t stopped in Dublin, you would have arrived home the evening of May 14. You don’t meet any of the exceptions that would allow you to consider your travel entirely for business. May 4 through May 14 (11 days) are business days and May 15 through May 21 (7 days) are nonbusiness days.
You can deduct the cost of your non-entertainment-related meals (subject to the 50% Limit ), lodging, and other business-related travel expenses while in Paris.
You can’t deduct your expenses while in Dublin. You also can’t deduct 7 / 18 of what it would have cost you to travel round trip between New York and Dublin.
You paid $750 to fly from New York to Paris, $400 to fly from Paris to Dublin, and $700 to fly from Dublin back to New York. Round-trip airfare from New York to Dublin would have been $1,250.
You figure the deductible part of your air travel expenses by subtracting 7 / 18 of the round-trip airfare and other expenses you would have had in traveling directly between New York and Dublin ($1,250 × 7 / 18 = $486) from your total expenses in traveling from New York to Paris to Dublin and back to New York ($750 + $400 + $700 = $1,850).
Your deductible air travel expense is $1,364 ($1,850 − $486).
If you had a vacation or other nonbusiness activity at, near, or beyond your business destination, you must allocate part of your travel expenses to the nonbusiness activity.
The part you must allocate is the amount it would have cost you to travel between the point where travel outside the United States begins and your business destination and a return to the point where travel outside the United States ends.
None of your travel expenses for nonbusiness activities at, near, or beyond your business destination are deductible.
Assume that the dates are the same as in the previous example but that instead of going to Dublin for your vacation, you fly to Venice, Italy, for a vacation.
You can’t deduct any part of the cost of your trip from Paris to Venice and return to Paris. In addition, you can’t deduct 7 / 18 of the airfare and other expenses from New York to Paris and back to New York.
You can deduct 11 / 18 of the round-trip plane fare and other travel expenses from New York to Paris, plus your non-entertainment-related meals (subject to the 50% Limit ), lodging, and any other business expenses you had in Paris. (Assume these expenses total $4,939.) If the round-trip plane fare and other travel-related expenses (such as food during the trip) are $1,750, you can deduct travel costs of $1,069 ( 11 / 18 × $1,750), plus the full $4,939 for the expenses you had in Paris.
You can use another method of counting business days if you establish that it more clearly reflects the time spent on other than business activities outside the United States.
If you travel outside the United States primarily for vacation or for investment purposes, the entire cost of the trip is a nondeductible personal expense. However, if you spend some time attending brief professional seminars or a continuing education program, you can deduct your registration fees and other expenses you have that are directly related to your business.
The university from which you graduated has a continuing education program for members of its alumni association. This program consists of trips to various foreign countries where academic exercises and conferences are set up to acquaint individuals in most occupations with selected facilities in several regions of the world. However, none of the conferences are directed toward specific occupations or professions. It is up to each participant to seek out specialists and organizational settings appropriate to their occupational interests.
Three-hour sessions are held each day over a 5-day period at each of the selected overseas facilities where participants can meet with individual practitioners. These sessions are composed of a variety of activities including workshops, mini-lectures, roleplaying, skill development, and exercises. Professional conference directors schedule and conduct the sessions. Participants can choose those sessions they wish to attend.
You can participate in this program because you are a member of the alumni association. You and your family take one of the trips. You spend about 2 hours at each of the planned sessions. The rest of the time you go touring and sightseeing with your family. The trip lasts less than 1 week.
Your travel expenses for the trip aren’t deductible since the trip was primarily a vacation. However, registration fees and any other incidental expenses you have for the five planned sessions you attended that are directly related and beneficial to your business are deductible business expenses. These expenses should be specifically stated in your records to ensure proper allocation of your deductible business expenses.
Luxury Water Travel
If you travel by ocean liner, cruise ship, or other form of luxury water transportation for business purposes, there is a daily limit on the amount you can deduct. The limit is twice the highest federal per diem rate allowable at the time of your travel. (Generally, the federal per diem is the amount paid to federal government employees for daily living expenses when they travel away from home within the United States for business purposes.)
The highest federal per diem rate allowed and the daily limit for luxury water travel in 2023 are shown in the following table.
You are a travel agent and traveled by ocean liner from New York to London, England, on business in May. Your expense for the 6-day cruise was $6,200. Your deduction for the cruise can’t exceed $4,776 (6 days × $796 daily limit).
If your expenses for luxury water travel include separately stated amounts for meals or entertainment, those amounts are subject to the 50% limit on non-entertainment-related meals and entertainment before you apply the daily limit. For a discussion of the 50% Limit , see chapter 2.
In the previous example, your luxury water travel had a total cost of $6,200. Of that amount, $3,700 was separately stated as non-entertainment-related meals and $1,000 was separately stated as entertainment. Considering that you are self-employed, you aren’t reimbursed for any of your travel expenses. You figure your deductible travel expenses as follows.
If your meal or entertainment charges aren’t separately stated or aren’t clearly identifiable, you don’t have to allocate any portion of the total charge to meals or entertainment.
The daily limit on luxury water travel (discussed earlier) doesn’t apply to expenses you have to attend a convention, seminar, or meeting on board a cruise ship. See Cruise Ships , later, under Conventions.
Conventions
You can deduct your travel expenses when you attend a convention if you can show that your attendance benefits your trade or business. You can’t deduct the travel expenses for your family.
If the convention is for investment, political, social, or other purposes unrelated to your trade or business, you can’t deduct the expenses.
The convention agenda or program generally shows the purpose of the convention. You can show your attendance at the convention benefits your trade or business by comparing the agenda with the official duties and responsibilities of your position. The agenda doesn’t have to deal specifically with your official duties and responsibilities; it will be enough if the agenda is so related to your position that it shows your attendance was for business purposes.
Conventions Held Outside the North American Area
You can’t deduct expenses for attending a convention, seminar, or similar meeting held outside the North American area unless:
The meeting is directly related to the active conduct of your trade or business, and
It is as reasonable to hold the meeting outside the North American area as within the North American area. See Reasonableness test , later.
The North American area includes the following locations.
The following factors are taken into account to determine if it was as reasonable to hold the meeting outside the North American area as within the North American area.
The purpose of the meeting and the activities taking place at the meeting.
The purposes and activities of the sponsoring organizations or groups.
The homes of the active members of the sponsoring organizations and the places at which other meetings of the sponsoring organizations or groups have been or will be held.
Other relevant factors you may present.
You can deduct up to $2,000 per year of your expenses of attending conventions, seminars, or similar meetings held on cruise ships. All ships that sail are considered cruise ships.
You can deduct these expenses only if all of the following requirements are met.
The convention, seminar, or meeting is directly related to the active conduct of your trade or business.
The cruise ship is a vessel registered in the United States.
All of the cruise ship's ports of call are in the United States or in territories of the United States.
You attach to your return a written statement signed by you that includes information about:
The total days of the trip (not including the days of transportation to and from the cruise ship port),
The number of hours each day that you devoted to scheduled business activities, and
A program of the scheduled business activities of the meeting.
You attach to your return a written statement signed by an officer of the organization or group sponsoring the meeting that includes:
A schedule of the business activities of each day of the meeting, and
The number of hours you attended the scheduled business activities.
2. Meals and Entertainment
You can no longer take a deduction for any expense related to activities generally considered entertainment, amusement, or recreation. You can continue to deduct 50% of the cost of business meals if you (or your employee) are present and the food or beverages aren't considered lavish or extravagant.
Entertainment
Entertainment—defined.
Entertainment includes any activity generally considered to provide entertainment, amusement, or recreation. Examples include entertaining guests at nightclubs; at social, athletic, and sporting clubs; at theaters; at sporting events; on yachts; or on hunting, fishing, vacation, and similar trips. Entertainment may also include meeting personal, living, or family needs of individuals, such as providing meals, a hotel suite, or a car to customers or their families.
Your kind of business may determine if a particular activity is considered entertainment. For example, if you are a dress designer and have a fashion show to introduce your new designs to store buyers, the show generally isn’t considered entertainment. This is because fashion shows are typical in your business. But, if you are an appliance distributor and hold a fashion show for the spouses of your retailers, the show is generally considered entertainment.
If you have one expense that includes the costs of entertainment and other services (such as lodging or transportation), you must allocate that expense between the cost of entertainment and the cost of other services. You must have a reasonable basis for making this allocation. For example, you must allocate your expenses if a hotel includes entertainment in its lounge on the same bill with your room charge.
In general, entertainment expenses are nondeductible. However, there are a few exceptions to the general rule, including:
Entertainment treated as compensation on your originally filed tax returns (and treated as wages to your employees);
Recreational expenses for employees such as a holiday party or a summer picnic;
Expenses related to attending business meetings or conventions of certain exempt organizations such as business leagues, chambers of commerce, professional associations, etc.; and
Entertainment sold to customers. For example, if you run a nightclub, your expenses for the entertainment you furnish to your customers, such as a floor show, aren’t subject to the nondeductible rules.
Examples of Nondeductible Entertainment
Generally, you can't deduct any expense for an entertainment event. This includes expenses for entertaining guests at nightclubs; at social, athletic, and sporting clubs; at theaters; at sporting events; on yachts; or on hunting, fishing, vacation, and similar trips.
Generally, you can’t deduct any expense for the use of an entertainment facility. This includes expenses for depreciation and operating costs such as rent, utilities, maintenance, and protection.
An entertainment facility is any property you own, rent, or use for entertainment. Examples include a yacht, hunting lodge, fishing camp, swimming pool, tennis court, bowling alley, car, airplane, apartment, hotel suite, or home in a vacation resort.
You can’t deduct dues (including initiation fees) for membership in any club organized for business, pleasure, recreation, or other social purposes.
This rule applies to any membership organization if one of its principal purposes is either:
To conduct entertainment activities for members or their guests; or
To provide members or their guests with access to entertainment facilities, discussed later.
The purposes and activities of a club, not its name, will determine whether or not you can deduct the dues. You can’t deduct dues paid to:
Country clubs,
Golf and athletic clubs,
Airline clubs,
Hotel clubs, and
Clubs operated to provide meals under circumstances generally considered to be conducive to business discussions.
Any item that might be considered either a gift or entertainment will generally be considered entertainment. However, if you give a customer packaged food or beverages that you intend the customer to use at a later date, treat it as a gift.
As discussed above, entertainment expenses are generally nondeductible. However, you may continue to deduct 50% of the cost of business meals if you (or an employee) is present and the food or beverages are not considered lavish or extravagant. The meals may be provided to a current or potential business customer, client, consultant, or similar business contact.
Food and beverages that are provided during entertainment events are not considered entertainment if purchased separately from the entertainment, or if the cost of the food and beverages is stated separately from the cost of the entertainment on one or more bills, invoices, or receipts. However, the entertainment disallowance rule may not be circumvented through inflating the amount charged for food and beverages.
Any allowed expense must be ordinary and necessary. An ordinary expense is one that is common and accepted in your trade or business. A necessary expense is one that is helpful and appropriate for your business. An expense doesn't have to be required to be considered necessary. Expenses must not be lavish or extravagant. An expense isn't considered lavish or extravagant if it is reasonable based on the facts and circumstances.
For each example, assume that the food and beverage expenses are ordinary and necessary expenses under section 162(a) paid or incurred during the tax year in carrying on a trade or business and are not lavish or extravagant under the circumstances. Also assume that the taxpayer and the business contact are not engaged in a trade or business that has any relation to the entertainment activity.
Taxpayer A invites B, a business contact, to a baseball game. A purchases tickets for A and B to attend the game. While at the game, A buys hot dogs and drinks for A and B. The baseball game is entertainment as defined in Regulations section 1.274-11(b)(1)(i) and, thus, the cost of the game tickets is an entertainment expense and is not deductible by A. The cost of the hot dogs and drinks, which are purchased separately from the game tickets, is not an entertainment expense and is not subject to the section 274(a)(1) disallowance. Therefore, A may deduct 50% of the expenses associated with the hot dogs and drinks purchased at the game.
Taxpayer C invites D, a business contact, to a basketball game. C purchases tickets for C and D to attend the game in a suite, where they have access to food and beverages. The cost of the basketball game tickets, as stated on the invoice, includes the food and beverages. The basketball game is entertainment as defined in Regulations section 1.274-11(b)(1)(i) and, thus, the cost of the game tickets is an entertainment expense and is not deductible by C. The cost of the food and beverages, which are not purchased separately from the game tickets, is not stated separately on the invoice. Thus, the cost of the food and beverages is also an entertainment expense that is subject to the section 274(a)(1) disallowance. Therefore, C may not deduct any of the expenses associated with the basketball game.
Assume the same facts as in Example 2 , except that the invoice for the basketball game tickets separately states the cost of the food and beverages. As in Example 2 , the basketball game is entertainment as defined in Regulations section 1.274-2(b)(1)(i) and, thus, the cost of the game tickets, other than the cost of the food and beverages, is an entertainment expense and is not deductible by C. However, the cost of the food and beverages, which is stated separately on the invoice for the game tickets, is not an entertainment expense and is not subject to the section 274(a)(1) disallowance. Therefore, C may deduct 50% of the expenses associated with the food and beverages provided at the game.
In general, you can deduct only 50% of your business-related meal expenses, unless an exception applies. (If you are subject to the Department of Transportation's “hours of service” limits, you can deduct 80% of your business-related meal expenses. See Individuals subject to hours of service limits , later.)
The 50% limit applies to employees or their employers, and to self-employed persons (including independent contractors) or their clients, depending on whether the expenses are reimbursed.
Examples of meals might include:
Meals while traveling away from home (whether eating alone or with others) on business, or
Meal at a business convention or business league meeting.
Figure A. Does the 50% Limit Apply to Your Expenses?
There are exceptions to these rules. See Exceptions to the 50% Limit for Meals , later.
Figure A. Does the 50% limit apply to Your Expenses?TAs for Figure A are: Notice 87-23; Form 2106 instructions
Summary: This is a flowchart used to determine if employees and self-employed persons need to put a 50% limit on their business expense deductions.
This is the starting of the flowchart.
Decision (1)
Were your meal and entertainment expenses reimbursed? (Count only reimbursements your employer didn’t include in box 1 of your Form W-2. If self-employed, count only reimbursements from clients or customers that aren’t included on Form 1099-MISC, Miscellaneous Income.)
Decision (2)
If an employee, did you adequately account to your employer under an accountable plan? If self-employed, did you provide the payer with adequate records? (See Chapter 6.)
Decision (3)
Did your expenses exceed the reimbursement?
Decision (4)
Process (a)
Your meal and entertainment expenses are NOT subject to the limitations. However, since the reimbursement wasn’t treated as wages or as other taxable income, you can’t deduct the expenses.
Process (b)
Your nonentertainment meal expenses ARE subject to the 50% limit. Your entertainment expenses are nondeductible.
This is the ending of the flowchart.
Please click here for the text description of the image.
Taxes and tips relating to a business meal are included as a cost of the meal and are subject to the 50% limit. However, the cost of transportation to and from the meal is not treated as part of the cost and would not be subject to the limit.
The 50% limit on meal expenses applies if the expense is otherwise deductible and isn’t covered by one of the exceptions discussed later. Figure A can help you determine if the 50% limit applies to you.
The 50% limit also applies to certain meal expenses that aren’t business related. It applies to meal expenses you have for the production of income, including rental or royalty income. It also applies to the cost of meals included in deductible educational expenses.
The 50% limit will apply after determining the amount that would otherwise qualify for a deduction. You first have to determine the amount of meal expenses that would be deductible under the other rules discussed in this publication.
If a group of business acquaintances takes turns picking up each others' meal checks primarily for personal reasons, without regard to whether any business purposes are served, no member of the group can deduct any part of the expense.
You spend $200 (including tax and tip) for a business meal. If $110 of that amount isn’t allowable because it is lavish and extravagant, the remaining $90 is subject to the 50% limit. Your deduction can’t be more than $45 (50% (0.50) × $90).
You purchase two tickets to a concert for $200 for you and your client. Your deduction is zero because no deduction is allowed for entertainment expenses.
Exception to the 50% Limit for Meals
Your meal expense isn’t subject to the 50% limit if the expense meets one of the following exceptions.
In general, expenses for goods, services, and facilities, to the extent the expenses are treated by the taxpayer, with respect to entertainment, amusement, or recreation, as compensation to an employee and as wages to the employee for tax purposes.
If you are an employee, you aren’t subject to the 50% limit on expenses for which your employer reimburses you under an accountable plan. Accountable plans are discussed in chapter 6.
If you are self-employed, your deductible meal expenses aren’t subject to the 50% limit if all of the following requirements are met.
You have these expenses as an independent contractor.
Your customer or client reimburses you or gives you an allowance for these expenses in connection with services you perform.
You provide adequate records of these expenses to your customer or client. (See chapter 5 .)
In this case, your client or customer is subject to the 50% limit on the expenses.
You are a self-employed attorney who adequately accounts for meal expenses to a client who reimburses you for these expenses. You aren’t subject to the limitation on meal expenses. If the client can deduct the expenses, the client is subject to the 50% limit.
If you (as an independent contractor) have expenses for meals related to providing services for a client but don’t adequately account for and seek reimbursement from the client for those expenses, you are subject to the 50% limit on non-entertainment-related meals and the entertainment-related meal expenses are nondeductible to you.
You aren't subject to the 50% limit for expenses for recreational, social, or similar activities (including facilities) such as a holiday party or a summer picnic.
You aren’t subject to the 50% limit if you provide meals to the general public as a means of advertising or promoting goodwill in the community. For example, neither the expense of sponsoring a television or radio show nor the expense of distributing free food and beverages to the general public is subject to the 50% limit.
You aren’t subject to the 50% limit if you actually sell meals to the public. For example, if you run a restaurant, your expense for the food you furnish to your customers isn’t subject to the 50% limit.
You can deduct a higher percentage of your meal expenses while traveling away from your tax home if the meals take place during or incident to any period subject to the Department of Transportation's “hours of service” limits. The percentage is 80%.
Individuals subject to the Department of Transportation's “hours of service” limits include the following persons.
Certain air transportation workers (such as pilots, crew, dispatchers, mechanics, and control tower operators) who are under Federal Aviation Administration regulations.
Interstate truck operators and bus drivers who are under Department of Transportation regulations.
Certain railroad employees (such as engineers, conductors, train crews, dispatchers, and control operations personnel) who are under Federal Railroad Administration regulations.
Certain merchant mariners who are under Coast Guard regulations.
If you give gifts in the course of your trade or business, you may be able to deduct all or part of the cost. This chapter explains the limits and rules for deducting the costs of gifts.
You can deduct no more than $25 for business gifts you give directly or indirectly to each person during your tax year. A gift to a company that is intended for the eventual personal use or benefit of a particular person or a limited class of people will be considered an indirect gift to that particular person or to the individuals within that class of people who receive the gift.
If you give a gift to a member of a customer's family, the gift is generally considered to be an indirect gift to the customer. This rule doesn’t apply if you have a bona fide, independent business connection with that family member and the gift isn’t intended for the customer's eventual use.
If you and your spouse both give gifts, both of you are treated as one taxpayer. It doesn’t matter whether you have separate businesses, are separately employed, or whether each of you has an independent connection with the recipient. If a partnership gives gifts, the partnership and the partners are treated as one taxpayer.
You sell products to a local company. You and your spouse gave the local company three gourmet gift baskets to thank them for their business. You and your spouse paid $80 for each gift basket, or $240 total. Three of the local company's executives took the gift baskets home for their families' use. You and your spouse have no independent business relationship with any of the executives' other family members. You and your spouse can deduct a total of $75 ($25 limit × 3) for the gift baskets.
Incidental costs, such as engraving on jewelry, or packaging, insuring, and mailing, are generally not included in determining the cost of a gift for purposes of the $25 limit.
A cost is incidental only if it doesn’t add substantial value to the gift. For example, the cost of gift wrapping is an incidental cost. However, the purchase of an ornamental basket for packaging fruit isn’t an incidental cost if the value of the basket is substantial compared to the value of the fruit.
The following items aren’t considered gifts for purposes of the $25 limit.
An item that costs $4 or less and:
Has your name clearly and permanently imprinted on the gift, and
Is one of a number of identical items you widely distribute. Examples include pens, desk sets, and plastic bags and cases.
Signs, display racks, or other promotional material to be used on the business premises of the recipient.
Figure B. When Are Transportation Expenses Deductible?
Most employees and self-employed persons can use this chart. (Don’t use this chart if your home is your principal place of business. See Office in the home , later.)
Figure B. When Are Local Transportation Expenses Deductible?TAs for Figure B are: Reg 1.162-1(a); RR 55–109; RR 94–47
Summary: This illustration depicts the rules used to determine if transportation expenses are deductible.
The image then lists definitions for words used in the graphic:
Any item that might be considered either a gift or entertainment will generally be considered entertainment. However, if you give a customer packaged food or beverages you intend the customer to use at a later date, treat it as a gift.
4. Transportation
This chapter discusses expenses you can deduct for business transportation when you aren’t traveling away from home , as defined in chapter 1. These expenses include the cost of transportation by air, rail, bus, taxi, etc., and the cost of driving and maintaining your car.
Transportation expenses include the ordinary and necessary costs of all of the following.
Getting from one workplace to another in the course of your business or profession when you are traveling within the city or general area that is your tax home. Tax home is defined in chapter 1.
Visiting clients or customers.
Going to a business meeting away from your regular workplace.
Getting from your home to a temporary workplace when you have one or more regular places of work. These temporary workplaces can be either within the area of your tax home or outside that area.
Daily transportation expenses you incur while traveling from home to one or more regular places of business are generally nondeductible commuting expenses. However, there may be exceptions to this general rule. You can deduct daily transportation expenses incurred going between your residence and a temporary work station outside the metropolitan area where you live. Also, daily transportation expenses can be deducted if (1) you have one or more regular work locations away from your residence; or (2) your residence is your principal place of business and you incur expenses going between the residence and another work location in the same trade or business, regardless of whether the work is temporary or permanent and regardless of the distance.
Illustration of transportation expenses.
Figure B above illustrates the rules that apply for deducting transportation expenses when you have a regular or main job away from your home. You may want to refer to it when deciding whether you can deduct your transportation expenses.
If you have one or more regular work locations away from your home and you commute to a temporary work location in the same trade or business, you can deduct the expenses of the daily round-trip transportation between your home and the temporary location, regardless of distance.
If your employment at a work location is realistically expected to last (and does in fact last) for 1 year or less, the employment is temporary unless there are facts and circumstances that would indicate otherwise.
If your employment at a work location is realistically expected to last for more than 1 year or if there is no realistic expectation that the employment will last for 1 year or less, the employment isn’t temporary, regardless of whether it actually lasts for more than 1 year.
If employment at a work location initially is realistically expected to last for 1 year or less, but at some later date the employment is realistically expected to last more than 1 year, that employment will be treated as temporary (unless there are facts and circumstances that would indicate otherwise) until your expectation changes. It won’t be treated as temporary after the date you determine it will last more than 1 year.
If the temporary work location is beyond the general area of your regular place of work and you stay overnight, you are traveling away from home. You may have deductible travel expenses, as discussed in chapter 1 .
If you have no regular place of work but ordinarily work in the metropolitan area where you live, you can deduct daily transportation costs between home and a temporary work site outside that metropolitan area.
Generally, a metropolitan area includes the area within the city limits and the suburbs that are considered part of that metropolitan area.
You can’t deduct daily transportation costs between your home and temporary work sites within your metropolitan area. These are nondeductible commuting expenses.
If you work at two places in 1 day, whether or not for the same employer, you can deduct the expense of getting from one workplace to the other. However, if for some personal reason you don’t go directly from one location to the other, you can’t deduct more than the amount it would have cost you to go directly from the first location to the second.
Transportation expenses you have in going between home and a part-time job on a day off from your main job are commuting expenses. You can’t deduct them.
A meeting of an Armed Forces reserve unit is a second place of business if the meeting is held on a day on which you work at your regular job. You can deduct the expense of getting from one workplace to the other as just discussed under Two places of work .
You usually can’t deduct the expense if the reserve meeting is held on a day on which you don’t work at your regular job. In this case, your transportation is generally a nondeductible commuting expense. However, you can deduct your transportation expenses if the location of the meeting is temporary and you have one or more regular places of work.
If you ordinarily work in a particular metropolitan area but not at any specific location and the reserve meeting is held at a temporary location outside that metropolitan area, you can deduct your transportation expenses.
If you travel away from home overnight to attend a guard or reserve meeting, you can deduct your travel expenses. These expenses are discussed in chapter 1 .
If you travel more than 100 miles away from home in connection with your performance of services as a member of the reserves, you may be able to deduct some of your reserve-related travel costs as an adjustment to gross income rather than as an itemized deduction. For more information, see Armed Forces Reservists Traveling More Than 100 Miles From Home under Special Rules in chapter 6.
You can’t deduct the costs of taking a bus, trolley, subway, or taxi, or of driving a car between your home and your main or regular place of work. These costs are personal commuting expenses. You can’t deduct commuting expenses no matter how far your home is from your regular place of work. You can’t deduct commuting expenses even if you work during the commuting trip.
You sometimes use your cell phone to make business calls while commuting to and from work. Sometimes business associates ride with you to and from work, and you have a business discussion in the car. These activities don’t change the trip from personal to business. You can’t deduct your commuting expenses.
Fees you pay to park your car at your place of business are nondeductible commuting expenses. You can, however, deduct business-related parking fees when visiting a customer or client.
Putting display material that advertises your business on your car doesn’t change the use of your car from personal use to business use. If you use this car for commuting or other personal uses, you still can’t deduct your expenses for those uses.
You can’t deduct the cost of using your car in a nonprofit car pool. Don’t include payments you receive from the passengers in your income. These payments are considered reimbursements of your expenses. However, if you operate a car pool for a profit, you must include payments from passengers in your income. You can then deduct your car expenses (using the rules in this publication).
Hauling tools or instruments in your car while commuting to and from work doesn’t make your car expenses deductible. However, you can deduct any additional costs you have for hauling tools or instruments (such as for renting a trailer you tow with your car).
If you get your work assignments at a union hall and then go to your place of work, the costs of getting from the union hall to your place of work are nondeductible commuting expenses. Although you need the union to get your work assignments, you are employed where you work, not where the union hall is located.
If you have an office in your home that qualifies as a principal place of business, you can deduct your daily transportation costs between your home and another work location in the same trade or business. (See Pub. 587, Business Use of Your Home, for information on determining if your home office qualifies as a principal place of business.)
The following examples show when you can deduct transportation expenses based on the location of your work and your home.
You regularly work in an office in the city where you live. Your employer sends you to a 1-week training session at a different office in the same city. You travel directly from your home to the training location and return each day. You can deduct the cost of your daily round-trip transportation between your home and the training location.
Your principal place of business is in your home. You can deduct the cost of round-trip transportation between your qualifying home office and your client's or customer's place of business.
You have no regular office, and you don’t have an office in your home. In this case, the location of your first business contact inside the metropolitan area is considered your office. Transportation expenses between your home and this first contact are nondeductible commuting expenses. Transportation expenses between your last business contact and your home are also nondeductible commuting expenses. While you can’t deduct the costs of these trips, you can deduct the costs of going from one client or customer to another.
Car Expenses
If you use your car for business purposes, you may be able to deduct car expenses. You can generally use one of the two following methods to figure your deductible expenses.
Actual car expenses.
The cost of using your car as an employee, whether measured using actual expenses or the standard mileage rate, will no longer be allowed to be claimed as an unreimbursed employee travel expense as a miscellaneous itemized deduction due to the suspension of miscellaneous itemized deductions that are subject to the 2% floor under section 67(a). The suspension applies to tax years beginning after December 2017 and before January 2026. Deductions for expenses that are deductible in determining adjusted gross income are not suspended. For example, Armed Forces reservists, qualified performing artists, and fee-basis state or local government officials are allowed to deduct unreimbursed employee travel expenses as an adjustment to total income on Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 12.
If you use actual expenses to figure your deduction for a car you lease, there are rules that affect the amount of your lease payments you can deduct. See Leasing a Car , later.
In this publication, “car” includes a van, pickup, or panel truck. For the definition of “car” for depreciation purposes, see Car defined under Actual Car Expenses , later.
Standard Mileage Rate
For 2023, the standard mileage rate for the cost of operating your car for business use is 65.5 cents ($0.655) per mile.
You can generally use the standard mileage rate whether or not you are reimbursed and whether or not any reimbursement is more or less than the amount figured using the standard mileage rate. See chapter 6 for more information on reimbursements .
If you want to use the standard mileage rate for a car you own, you must choose to use it in the first year the car is available for use in your business. Then, in later years, you can choose to use either the standard mileage rate or actual expenses.
If you want to use the standard mileage rate for a car you lease, you must use it for the entire lease period. For leases that began on or before December 31, 1997, the standard mileage rate must be used for the entire portion of the lease period (including renewals) that is after 1997.
You must make the choice to use the standard mileage rate by the due date (including extensions) of your return. You can’t revoke the choice. However, in later years, you can switch from the standard mileage rate to the actual expenses method. If you change to the actual expenses method in a later year, but before your car is fully depreciated, you have to estimate the remaining useful life of the car and use straight line depreciation for the car’s remaining estimated useful life, subject to depreciation limits (discussed later).
For more information about depreciation included in the standard mileage rate, see Exception under Methods of depreciation , later.
You can’t use the standard mileage rate if you:
Use five or more cars at the same time (such as in fleet operations);
Claimed a depreciation deduction for the car using any method other than straight line for the car’s estimated useful life;
Used the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) (as discussed later under Depreciation Deduction );
Claimed a section 179 deduction (discussed later) on the car;
Claimed the special depreciation allowance on the car; or
Claimed actual car expenses after 1997 for a car you leased.
You can elect to use the standard mileage rate if you used a car for hire (such as a taxi) unless the standard mileage rate is otherwise not allowed, as discussed above.
If you own or lease five or more cars that are used for business at the same time, you can’t use the standard mileage rate for the business use of any car. However, you may be able to deduct your actual expenses for operating each of the cars in your business. See Actual Car Expenses , later, for information on how to figure your deduction.
You aren’t using five or more cars for business at the same time if you alternate using (use at different times) the cars for business.
The following examples illustrate the rules for when you can and can’t use the standard mileage rate for five or more cars.
A salesperson owns three cars and two vans that they alternate using for calling on their customers. The salesperson can use the standard mileage rate for the business mileage of the three cars and the two vans because they don’t use them at the same time.
You and your employees use your four pickup trucks in your landscaping business. During the year, you traded in two of your old trucks for two newer ones. You can use the standard mileage rate for the business mileage of all six of the trucks you owned during the year.
You own a repair shop and an insurance business. You and your employees use your two pickup trucks and van for the repair shop. You alternate using your two cars for the insurance business. No one else uses the cars for business purposes. You can use the standard mileage rate for the business use of the pickup trucks, the van, and the cars because you never have more than four vehicles used for business at the same time.
You own a car and four vans that are used in your housecleaning business. Your employees use the vans, and you use the car to travel to various customers. You can’t use the standard mileage rate for the car or the vans. This is because all five vehicles are used in your business at the same time. You must use actual expenses for all vehicles.
If you are an employee, you can’t deduct any interest paid on a car loan. This applies even if you use the car 100% for business as an employee.
However, if you are self-employed and use your car in your business, you can deduct that part of the interest expense that represents your business use of the car. For example, if you use your car 60% for business, you can deduct 60% of the interest on Schedule C (Form 1040). You can’t deduct the part of the interest expense that represents your personal use of the car.
If you itemize your deductions on Schedule A (Form 1040), you can deduct on line 5c state and local personal property taxes on motor vehicles. You can take this deduction even if you use the standard mileage rate or if you don’t use the car for business.
If you are self-employed and use your car in your business, you can deduct the business part of state and local personal property taxes on motor vehicles on Schedule C (Form 1040), or Schedule F (Form 1040). If you itemize your deductions, you can include the remainder of your state and local personal property taxes on the car on Schedule A (Form 1040).
In addition to using the standard mileage rate, you can deduct any business-related parking fees and tolls. (Parking fees you pay to park your car at your place of work are nondeductible commuting expenses.)
If you sell, trade in, or otherwise dispose of your car, you may have a gain or loss on the transaction or an adjustment to the basis of your new car. See Disposition of a Car , later.
Actual Car Expenses
If you don’t use the standard mileage rate, you may be able to deduct your actual car expenses.
Actual car expenses include:
If you have fully depreciated a car that you still use in your business, you can continue to claim your other actual car expenses. Continue to keep records, as explained later in chapter 5 .
If you use your car for both business and personal purposes, you must divide your expenses between business and personal use. You can divide your expense based on the miles driven for each purpose.
You are a contractor and drive your car 20,000 miles during the year: 12,000 miles for business use and 8,000 miles for personal use. You can claim only 60% (12,000 ÷ 20,000) of the cost of operating your car as a business expense.
If you use a vehicle provided by your employer for business purposes, you can deduct your actual unreimbursed car expenses. You can’t use the standard mileage rate. See Vehicle Provided by Your Employer in chapter 6.
If you are an employee, you can’t deduct any interest paid on a car loan. This interest is treated as personal interest and isn’t deductible. If you are self-employed and use your car in that business, see Interest , earlier, under Standard Mileage Rate.
If you are an employee, you can deduct personal property taxes paid on your car if you itemize deductions. Enter the amount paid on Schedule A (Form 1040), line 5c.
Generally, sales taxes on your car are part of your car's basis and are recovered through depreciation, discussed later.
You can’t deduct fines you pay or collateral you forfeit for traffic violations.
If your car is damaged, destroyed, or stolen, you may be able to deduct part of the loss not covered by insurance. See Pub. 547, Casualties, Disasters, and Thefts, for information on deducting a loss on your car.
Generally, the cost of a car, plus sales tax and improvements, is a capital expense. Because the benefits last longer than 1 year, you generally can’t deduct a capital expense. However, you can recover this cost through the section 179 deduction (the deduction allowed by section 179 of the Internal Revenue Code), special depreciation allowance, and depreciation deductions. Depreciation allows you to recover the cost over more than 1 year by deducting part of it each year. The section 179 deduction , special depreciation allowance , and depreciation deductions are discussed later.
Generally, there are limits on these deductions. Special rules apply if you use your car 50% or less in your work or business.
You can claim a section 179 deduction and use a depreciation method other than straight line only if you don’t use the standard mileage rate to figure your business-related car expenses in the year you first place a car in service.
If, in the year you first place a car in service, you claim either a section 179 deduction or use a depreciation method other than straight line for its estimated useful life, you can’t use the standard mileage rate on that car in any future year.
For depreciation purposes, a car is any four-wheeled vehicle (including a truck or van) made primarily for use on public streets, roads, and highways. Its unloaded gross vehicle weight (for trucks and vans, gross vehicle weight) must not be more than 6,000 pounds. A car includes any part, component, or other item physically attached to it or usually included in the purchase price.
A car doesn’t include:
An ambulance, hearse, or combination ambulance-hearse used directly in a business;
A vehicle used directly in the business of transporting persons or property for pay or hire; or
A truck or van that is a qualified nonpersonal use vehicle.
These are vehicles that by their nature aren’t likely to be used more than a minimal amount for personal purposes. They include trucks and vans that have been specially modified so that they aren’t likely to be used more than a minimal amount for personal purposes, such as by installation of permanent shelving and painting the vehicle to display advertising or the company's name. Delivery trucks with seating only for the driver, or only for the driver plus a folding jump seat, are qualified nonpersonal use vehicles.
See Depreciation Deduction , later, for more information on how to depreciate your vehicle.
Section 179 Deduction
You can elect to recover all or part of the cost of a car that is qualifying section 179 property, up to a limit, by deducting it in the year you place the property in service. This is the section 179 deduction. If you elect the section 179 deduction, you must reduce your depreciable basis in the car by the amount of the section 179 deduction.
You can claim the section 179 deduction only in the year you place the car in service. For this purpose, a car is placed in service when it is ready and available for a specifically assigned use in a trade or business. Even if you aren’t using the property, it is in service when it is ready and available for its specifically assigned use.
A car first used for personal purposes can’t qualify for the deduction in a later year when its use changes to business.
In 2022, you bought a new car and used it for personal purposes. In 2023, you began to use it for business. Changing its use to business use doesn’t qualify the cost of your car for a section 179 deduction in 2023. However, you can claim a depreciation deduction for the business use of the car starting in 2023. See Depreciation Deduction , later.
You must use the property more than 50% for business to claim any section 179 deduction. If you used the property more than 50% for business, multiply the cost of the property by the percentage of business use. The result is the cost of the property that can qualify for the section 179 deduction.
You purchased a new car in April 2023 for $24,500 and used it 60% for business. Based on your business usage, the total cost of your car that qualifies for the section 179 deduction is $14,700 ($24,500 cost × 60% (0.60) business use). But see Limit on total section 179, special depreciation allowance, and depreciation deduction , discussed later.
There are limits on:
The amount of the section 179 deduction;
The section 179 deduction for sport utility and certain other vehicles; and
The total amount of the section 179 deduction, special depreciation allowance, and depreciation deduction (discussed later ) you can claim for a qualified property.
For tax years beginning in 2023, the total amount you can elect to deduct under section 179 can’t be more than $1,160,000.
If the cost of your section 179 property placed in service in tax years beginning in 2023 is over $2,890,000, you must reduce the $1,160,000 dollar limit (but not below zero) by the amount of cost over $2,890,000. If the cost of your section 179 property placed in service during tax years beginning in 2023 is $4,050,000 or more, you can’t take a section 179 deduction.
The total amount you can deduct under section 179 each year after you apply the limits listed above cannot be more than the taxable income from the active conduct of any trade or business during the year.
If you are married and file a joint return, you and your spouse are treated as one taxpayer in determining any reduction to the dollar limit, regardless of which of you purchased the property or placed it in service.
If you and your spouse file separate returns, you are treated as one taxpayer for the dollar limit. You must allocate the dollar limit (after any reduction) between you.
For more information on the above section 179 deduction limits, see Pub. 946, How To Depreciate Property.
You cannot elect to deduct more than $28,900 of the cost of any heavy sport utility vehicle (SUV) and certain other vehicles placed in service during the tax years beginning in 2023. This rule applies to any four-wheeled vehicle primarily designed or used to carry passengers over public streets, roads, or highways that isn’t subject to any of the passenger automobile limits explained under Depreciation Limits , later, and that is rated at more than 6,000 pounds gross vehicle weight and not more than 14,000 pounds gross vehicle weight. However, the $28,900 limit doesn’t apply to any vehicle:
Designed to have a seating capacity of more than nine persons behind the driver's seat;
Equipped with a cargo area of at least 6 feet in interior length that is an open area or is designed for use as an open area but is enclosed by a cap and isn’t readily accessible directly from the passenger compartment; or
That has an integral enclosure, fully enclosing the driver compartment and load carrying device, doesn’t have seating rearward of the driver's seat, and has no body section protruding more than 30 inches ahead of the leading edge of the windshield.
The first-year limit on the depreciation deduction, special depreciation allowance, and section 179 deduction for vehicles acquired before September 28, 2017, and placed in service during 2023, is $12,200. The first-year limit on depreciation, special depreciation allowance, and section 179 deduction for vehicles acquired after September 27, 2017, and placed in service during 2023 increases to $20,200. If you elect not to claim a special depreciation allowance for a vehicle placed in service in 2023, the amount increases to $12,200. The limit is reduced if your business use of the vehicle is less than 100%. See Depreciation Limits , later, for more information.
In the earlier example under More than 50% business use requirement , you had a car with a cost (for purposes of the section 179 deduction) of $14,700. However, based on your business usage of the car, the total of your section 179 deduction, special depreciation allowance, and depreciation deductions is limited to $12,120 ($20,200 limit x 60% (0.60) business use) because the car was acquired after September 27, 2017, and placed in service during 2023.
For purposes of the section 179 deduction, the cost of the car doesn’t include any amount figured by reference to any other property held by you at any time. For example, if you buy a car as a replacement for a car that was stolen or that was destroyed in a casualty loss, and you use section 1033 to determine the basis in your replacement vehicle, your cost for purposes of the section 179 deduction doesn’t include your adjusted basis in the relinquished car. In that case, your cost includes only the cash you paid.
The amount of the section 179 deduction reduces your basis in your car. If you choose the section 179 deduction, you must subtract the amount of the deduction from the cost of your car. The resulting amount is the basis in your car you use to figure your depreciation deduction.
If you want to take the section 179 deduction, you must make the election in the tax year you place the car in service for business or work.
Employees use Form 2106, Employee Business Expenses, to make the election and report the section 179 deduction. All others use Form 4562, Depreciation and Amortization, to make an election.
File the appropriate form with either of the following.
Your original tax return filed for the year the property was placed in service (whether or not you file it timely).
An amended return filed within the time prescribed by law. An election made on an amended return must specify the item of section 179 property to which the election applies and the part of the cost of each such item to be taken into account. The amended return must also include any resulting adjustments to taxable income.
An election (or any specification made in the election) to take a section 179 deduction for 2023 can only be revoked with the Commissioner's approval.
To be eligible to claim the section 179 deduction, you must use your car more than 50% for business or work in the year you acquired it. If your business use of the car is 50% or less in a later tax year during the recovery period, you have to recapture (include in income) in that later year any excess depreciation. Any section 179 deduction claimed on the car is included in figuring the excess depreciation. For information on this calculation, see Excess depreciation , later in this chapter under Car Used 50% or Less for Business. For more information on recapture of a section 179 deduction, see Pub. 946.
If you dispose of a car on which you had claimed the section 179 deduction, the amount of that deduction is treated as a depreciation deduction for recapture purposes. You treat any gain on the disposition of the property as ordinary income up to the amount of the section 179 deduction and any allowable depreciation (unless you establish the amount actually allowed). For information on the disposition of a car, see Disposition of a Car , later. For more information on recapture of a section 179 deduction, see Pub. 946.
Special Depreciation Allowance
You may be able to claim the special depreciation allowance for your car, truck, or van if it is qualified property and was placed in service in 2023. The allowance for 2023 is an additional depreciation deduction for 100% of the car's depreciable basis (after any section 179 deduction, but before figuring your regular depreciation deduction under MACRS) if the vehicle was acquired after September 27, 2017, and placed in service during 2023. Further, while it applies to a new vehicle, it also applies to a used vehicle only if the vehicle meets the used property requirements. For more information on the used property requirements, see section 168(k)(2)(E)(ii). To qualify for the allowance, more than 50% of the use of the car must be in a qualified business use (as defined under Depreciation Deduction , later).
The first-year limit on the depreciation deduction, special depreciation allowance, and section 179 deduction for vehicles acquired before September 28, 2017, and placed in service during 2023, is $12,200. Your combined section 179 depreciation, special depreciation allowance, and regular MACRS depreciation deduction is limited to the maximum allowable depreciation deduction for vehicles acquired after September 27, 2017, and placed in service during 2023 is $20,200. If you elect not to claim a special depreciation allowance for a vehicle placed in service in 2023, the amount is $12,200. See Depreciation Limits , later in this chapter.
To be qualified property, the car (including the truck or van) must meet all of the following tests.
You acquired the car after September 27, 2017, but only if no written binding contract to acquire the car existed before September 28, 2017.
You acquired the car new or used.
You placed the car in service in your trade or business before January 1, 2027.
You used the car more than 50% in a qualified business use during the tax year.
You can elect not to claim the special depreciation allowance for your car, truck, or van that is qualified property. If you make this election, it applies to all 5-year property placed in service during the year.
To make this election, attach a statement to your timely filed return (including extensions) indicating the class of property (5-year for cars) for which you are making the election and that you are electing not to claim the special depreciation allowance for qualified property in that class of property.
Depreciation Deduction
If you use actual car expenses to figure your deduction for a car you own and use in your business, you can claim a depreciation deduction. This means you can deduct a certain amount each year as a recovery of your cost or other basis in your car.
You generally need to know the following things about the car you intend to depreciate.
Your basis in the car.
The date you place the car in service.
The method of depreciation and recovery period you will use.
Your basis in a car for figuring depreciation is generally its cost. This includes any amount you borrow or pay in cash, other property, or services.
Generally, you figure depreciation on your car, truck, or van using your unadjusted basis (see Unadjusted basis , later). However, in some situations, you will use your adjusted basis (your basis reduced by depreciation allowed or allowable in earlier years). For one of these situations, see Exception under Methods of depreciation , later.
If you change the use of a car from personal to business, your basis for depreciation is the lesser of the fair market value or your adjusted basis in the car on the date of conversion. Additional rules concerning basis are discussed later in this chapter under Unadjusted basis .
You generally place a car in service when it is available for use in your work or business, in an income-producing activity, or in a personal activity. Depreciation begins when the car is placed in service for use in your work or business or for the production of income.
For purposes of figuring depreciation, if you first start using the car only for personal use and later convert it to business use, you place the car in service on the date of conversion.
If you place a car in service and dispose of it in the same tax year, you can’t claim any depreciation deduction for that car.
Generally, you figure depreciation on cars using the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery (MACRS) discussed later in this chapter.
If you used the standard mileage rate in the first year of business use and change to the actual expenses method in a later year, you can’t depreciate your car under the MACRS rules. You must use straight line depreciation over the estimated remaining useful life of the car. The amount you depreciate can’t be more than the depreciation limit that applies for that year. See Depreciation Limits , later.
To figure depreciation under the straight line method, you must reduce your basis in the car (but not below zero) by a set rate per mile for all miles for which you used the standard mileage rate. The rate per mile varies depending on the year(s) you used the standard mileage rate. For the rate(s) to use, see Depreciation adjustment when you used the standard mileage rate under Disposition of a Car , later.
This reduction of basis is in addition to those basis adjustments described later under Unadjusted basis . You must use your adjusted basis in your car to figure your depreciation deduction. For additional information on the straight line method of depreciation, see Pub. 946.
Generally, you must use your car more than 50% for qualified business use (defined next) during the year to use MACRS. You must meet this more-than-50%-use test each year of the recovery period (6 years under MACRS) for your car.
If your business use is 50% or less, you must use the straight line method to depreciate your car. This is explained later under Car Used 50% or Less for Business .
A qualified business use is any use in your trade or business. It doesn’t include use for the production of income (investment use), or use provided under lease to, or as compensation to, a 5% owner or related person. However, you do combine your business and investment use to figure your depreciation deduction for the tax year.
Don’t treat any use of your car by another person as use in your trade or business unless that use meets one of the following conditions.
It is directly connected with your business.
It is properly reported by you as income to the other person (and, if you have to, you withhold tax on the income).
It results in a payment of fair market rent. This includes any payment to you for the use of your car.
If you used your car more than 50% in qualified business use in the year you placed it in service, but 50% or less in a later year (including the year of disposition), you have to change to the straight line method of depreciation. See Qualified business use 50% or less in a later year under Car Used 50% or Less for Business , later.
If you use your car for more than one purpose during the tax year, you must allocate the use to the various purposes. You do this on the basis of mileage. Figure the percentage of qualified business use by dividing the number of miles you drive your car for business purposes during the year by the total number of miles you drive the car during the year for any purpose.
If you change the use of a car from 100% personal use to business use during the tax year, you may not have mileage records for the time before the change to business use. In this case, you figure the percentage of business use for the year as follows.
Determine the percentage of business use for the period following the change. Do this by dividing business miles by total miles driven during that period.
Multiply the percentage in (1) by a fraction. The numerator (top number) is the number of months the car is used for business, and the denominator (bottom number) is 12.
You use a car only for personal purposes during the first 6 months of the year. During the last 6 months of the year, you drive the car a total of 15,000 miles of which 12,000 miles are for business. This gives you a business use percentage of 80% (12,000 ÷ 15,000) for that period. Your business use for the year is 40% (80% (0.80) × 6 / 12 ).
The amount you can claim for section 179, special depreciation allowance, and depreciation deductions may be limited. The maximum amount you can claim depends on the year in which you placed your car in service. You have to reduce the maximum amount if you did not use the car exclusively for business. See Depreciation Limits , later.
You use your unadjusted basis (often referred to as your basis or your basis for depreciation) to figure your depreciation using the MACRS depreciation chart, explained later under Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) . Your unadjusted basis for figuring depreciation is your original basis increased or decreased by certain amounts.
To figure your unadjusted basis, begin with your car's original basis, which is generally its cost. Cost includes sales taxes (see Sales taxes , earlier), destination charges, and dealer preparation. Increase your basis by any substantial improvements you make to your car, such as adding air conditioning or a new engine. Decrease your basis by any section 179 deduction, special depreciation allowance, gas guzzler tax, and vehicle credits claimed. See Pub. 551, Basis of Assets, for further details.
If you acquired the car by gift or inheritance, see Pub. 551, Basis of Assets, for information on your basis in the car.
A major improvement to a car is treated as a new item of 5-year recovery property. It is treated as placed in service in the year the improvement is made. It doesn’t matter how old the car is when the improvement is added. Follow the same steps for depreciating the improvement as you would for depreciating the original cost of the car. However, you must treat the improvement and the car as a whole when applying the limits on the depreciation deductions. Your car's depreciation deduction for the year (plus any section 179 deduction, special depreciation allowance, and depreciation on any improvements) can’t be more than the depreciation limit that applies for that year. See Depreciation Limits , later.
If you traded one car (the “old car”) for another car (the “new car”) in 2023, you must treat the transaction as a disposition of the old car and the purchase of the new car. You must treat the old car as disposed of at the time of the trade-in. The depreciable basis of the new car is the adjusted basis of the old car (figured as if 100% of the car’s use had been for business purposes) plus any additional amount you paid for the new car. You then figure your depreciation deduction for the new car beginning with the date you placed it in service. You must also complete Form 2106, Part II, Section D. This method is explained later, beginning at Effect of trade-in on basis .
The discussion that follows applies to trade-ins of cars in 2023, where the election was made to treat the transaction as a disposition of the old car and the purchase of the new car. For information on how to figure depreciation for cars involved in a like-kind exchange (trade-in) in 2023, for which the election wasn’t made, see Pub. 946 and Regulations section 1.168(i)-6(d)(3).
Like‐kind exchanges completed after December 31, 2017, are generally limited to exchanges of real property not held primarily for sale. Regulations section 1.168(i)-6 doesn't reflect this change in law.
If you trade in a car you used only in your business for another car that will be used only in your business, your original basis in the new car is your adjusted basis in the old car, plus any additional amount you pay for the new car.
You trade in a car that has an adjusted basis of $5,000 for a new car. In addition, you pay cash of $20,000 for the new car. Your original basis of the new car is $25,000 (your $5,000 adjusted basis in the old car plus the $20,000 cash paid). Your unadjusted basis is $25,000 unless you claim the section 179 deduction, special depreciation allowance, or have other increases or decreases to your original basis, discussed under Unadjusted basis , earlier.
If you trade in a car you used partly in your business for a new car you will use in your business, you must make a “trade-in” adjustment for the personal use of the old car. This adjustment has the effect of reducing your basis in your old car, but not below zero, for purposes of figuring your depreciation deduction for the new car. (This adjustment isn’t used, however, when you determine the gain or loss on the later disposition of the new car. See Pub. 544, Sales and Other Dispositions of Assets, for information on how to report the disposition of your car.)
To figure the unadjusted basis of your new car for depreciation, first add to your adjusted basis in the old car any additional amount you pay for the new car. Then subtract from that total the excess, if any, of:
The total of the amounts that would have been allowable as depreciation during the tax years before the trade if 100% of the use of the car had been business and investment use, over
The total of the amounts actually allowed as depreciation during those years.
MACRS is the name given to the tax rules for getting back (recovering) through depreciation deductions the cost of property used in a trade or business or to produce income.
The maximum amount you can deduct is limited, depending on the year you placed your car in service. See Depreciation Limits , later.
Under MACRS, cars are classified as 5-year property. You actually depreciate the cost of a car, truck, or van over a period of 6 calendar years. This is because your car is generally treated as placed in service in the middle of the year, and you claim depreciation for one-half of both the first year and the sixth year.
For more information on the qualifications for this shorter recovery period and the percentages to use in figuring the depreciation deduction, see chapter 4 of Pub. 946.
You can use one of the following methods to depreciate your car.
The 200% declining balance method (200% DB) over a 5-year recovery period that switches to the straight line method when that method provides an equal or greater deduction.
The 150% declining balance method (150% DB) over a 5-year recovery period that switches to the straight line method when that method provides an equal or greater deduction.
The straight line method (SL) over a 5-year recovery period.
Before choosing a method, you may wish to consider the following facts.
Using the straight line method provides equal yearly deductions throughout the recovery period.
Using the declining balance methods provides greater deductions during the earlier recovery years with the deductions generally getting smaller each year.
A 2023 MACRS Depreciation Chart and instructions are included in this chapter as Table 4-1 . Using this table will make it easy for you to figure the 2023 depreciation deduction for your car. A similar chart appears in the Instructions for Form 2106.
You must use the Depreciation Tables in Pub. 946 rather than the 2023 MACRS Depreciation Chart in this publication if any one of the following three conditions applies to you.
You file your return on a fiscal year basis.
You file your return for a short tax year (less than 12 months).
During the year, all of the following conditions apply.
You placed some property in service from January through September.
You placed some property in service from October through December.
Your basis in the property you placed in service from October through December (excluding nonresidential real property, residential rental property, and property placed in service and disposed of in the same year) was more than 40% of your total bases in all property you placed in service during the year.
If you use the percentages from the chart, you generally must continue to use them for the entire recovery period of your car. However, you can’t continue to use the chart if your basis in your car is adjusted because of a casualty. In that case, for the year of the adjustment and the remaining recovery period, figure the depreciation without the chart using your adjusted basis in the car at the end of the year of the adjustment and over the remaining recovery period. See Figuring the Deduction Without Using the Tables in chapter 4 of Pub. 946.
If you dispose of the car before the last year of the recovery period, you are generally allowed a half-year of depreciation in the year of disposition. This rule applies unless the mid-quarter convention applies to the vehicle being disposed of. See Depreciation deduction for the year of disposition under Disposition of a Car , later, for information on how to figure the depreciation allowed in the year of disposition.
To figure your depreciation deduction for 2023, find the percentage in the column of Table 4-1 based on the date that you first placed the car in service and the depreciation method that you are using. Multiply the unadjusted basis of your car (defined earlier) by that percentage to determine the amount of your depreciation deduction. If you prefer to figure your depreciation deduction without the help of the chart, see Pub. 946.
You bought a used truck in February 2022 to use exclusively in your landscape business. You paid $9,200 for the truck with no trade-in. You didn’t claim any section 179 deduction, the truck didn’t qualify for the special depreciation allowance, and you chose to use the 200% DB method to get the largest depreciation deduction in the early years.
You used the MACRS Depreciation Chart in 2022 to find your percentage. The unadjusted basis of the truck equals its cost because you used it exclusively for business. You multiplied the unadjusted basis of the truck, $9,200, by the percentage that applied, 20%, to figure your 2022 depreciation deduction of $1,840.
In 2023, you used the truck for personal purposes when you repaired your parent’s cabin. Your records show that the business use of the truck was 90% in 2023. You used Table 4-1 to find your percentage. Reading down the first column for the date placed in service and across to the 200% DB column, you locate your percentage, 32%. You multiply the unadjusted basis of the truck, $8,280 ($9,200 cost × 90% (0.90) business use), by 32% (0.32) to figure your 2023 depreciation deduction of $2,650.
Depreciation Limits
There are limits on the amount you can deduct for depreciation of your car, truck, or van. The section 179 deduction and special depreciation allowance are treated as depreciation for purposes of the limits. The maximum amount you can deduct each year depends on the date you acquired the passenger automobile and the year you place the passenger automobile in service. These limits are shown in the following tables for 2023.
Maximum Depreciation Deduction for Passenger Automobiles (Including Trucks and Vans) Acquired Before September 28, 2017, and Placed in Service During 2018–2023
Maximum depreciation deduction for passenger automobiles (including trucks and vans) acquired after september 27, 2017, and placed in service during 2018 or later.
The maximum amount you can deduct each year depends on the year you place the car in service. These limits are shown in the following tables for prior years.
Maximum Depreciation Deduction for Cars Placed in Service Prior to 2018
For tax years prior to 2018, the maximum depreciation deductions for trucks and vans are generally higher than those for cars. A truck or van is a passenger automobile that is classified by the manufacturer as a truck or van and rated at 6,000 pounds gross vehicle weight or less.
Maximum Depreciation Deduction for Trucks and Vans Placed in Service Prior to 2018
The depreciation limits aren’t reduced if you use a car for less than a full year. This means that you don’t reduce the limit when you either place a car in service or dispose of a car during the year. However, the depreciation limits are reduced if you don’t use the car exclusively for business and investment purposes. See Reduction for personal use next.
The depreciation limits are reduced based on your percentage of personal use. If you use a car less than 100% in your business or work, you must determine the depreciation deduction limit by multiplying the limit amount by the percentage of business and investment use during the tax year.
The section 179 deduction is treated as a depreciation deduction. If you acquired a passenger automobile (including trucks and vans) after September 27, 2017, and placed it in service in 2023, use it only for business, and choose the section 179 deduction, the special depreciation allowance and depreciation deduction for that vehicle for 2023 is limited to $20,200.
On September 4, 2023, you bought and placed in service a used car for $15,000. You used it 80% for your business, and you choose to take a section 179 deduction for the car. The car isn’t qualified property for purposes of the special depreciation allowance.
Before applying the limit, you figure your maximum section 179 deduction to be $12,000. This is the cost of your qualifying property (up to the maximum $1,160,000 amount) multiplied by your business use ($15,000 × 80% (0.80)).
You then figure that your section 179 deduction for 2023 is limited to $9,760 (80% of $12,200). You then figure your unadjusted basis of $2,440 (($15,000 × 80% (0.80)) − $9,760) for determining your depreciation deduction. You have reached your maximum depreciation deduction for 2023. For 2024, you will use your unadjusted basis of $2,440 to figure your depreciation deduction.
If the depreciation deductions for your car are reduced under the passenger automobile limits (discussed earlier), you will have unrecovered basis in your car at the end of the recovery period. If you continue to use your car for business, you can deduct that unrecovered basis (subject to depreciation limits) after the recovery period ends.
This is your cost or other basis in the car reduced by any clean-fuel vehicle deduction (for vehicles placed in service before January 1, 2006), alternative motor vehicle credit, electric vehicle credit, gas guzzler tax, and depreciation (including any special depreciation allowance , discussed earlier, unless you elect not to claim it) and section 179 deductions that would have been allowable if you had used the car 100% for business and investment use.
For 5-year property, your recovery period is 6 calendar years. A part year's depreciation is allowed in the first calendar year, a full year's depreciation is allowed in each of the next 4 calendar years, and a part year's depreciation is allowed in the 6th calendar year.
Under MACRS, your recovery period is the same whether you use declining balance or straight line depreciation. You determine your unrecovered basis in the 7th year after you placed the car in service.
If you continue to use your car for business after the recovery period, you can claim a depreciation deduction in each succeeding tax year until you recover your basis in the car. The maximum amount you can deduct each year is determined by the date you placed the car in service and your business-use percentage. For example, no deduction is allowed for a year you use your car 100% for personal purposes.
In April 2017, you bought and placed in service a car you used exclusively in your business. The car cost $31,500. You didn’t claim a section 179 deduction or the special depreciation allowance for the car. You continued to use the car 100% in your business throughout the recovery period (2017 through 2022). For those years, you used the MACRS Depreciation Chart (200% DB method), the Maximum Depreciation Deduction for Cars Placed in Service Prior to 2018 table and Maximum Depreciation Deduction for Passenger Automobiles (Including Trucks and Vans) Acquired Before September 28, 2017, and Placed in Service During 2018–2023 table, earlier, for the applicable tax year to figure your depreciation deductions during the recovery period. Your depreciation deductions were subject to the depreciation limits, so you will have unrecovered basis at the end of the recovery period as shown in the following table.
At the end of 2022, you had an unrecovered basis in the car of $14,626 ($31,500 – $16,874). If you continued to use the car 100% for business in 2023 and later years, you can claim a depreciation deduction equal to the lesser of $1,875 or your remaining unrecovered basis.
If your business use of the car was less than 100% during any year, your depreciation deduction would be less than the maximum amount allowable for that year. However, in determining your unrecovered basis in the car, you would still reduce your original basis by the maximum amount allowable as if the business use had been 100%. For example, if you had used your car 60% for business instead of 100%, your allowable depreciation deductions would have been $10,124 ($16,874 × 60% (0.60)), but you still would have to reduce your basis by $16,874 to determine your unrecovered basis.
Table 4-1. 2023 MACRS Depreciation Chart (Use To Figure Depreciation for 2023)
Car used 50% or less for business.
If you use your car 50% or less for qualified business use (defined earlier under Depreciation Deduction ) either in the year the car is placed in service or in a later year, special rules apply. The rules that apply in these two situations are explained in the following paragraphs. (For this purpose, “car” was defined earlier under Actual Car Expenses and includes certain trucks and vans.)
If you use your car 50% or less for qualified business use, the following rules apply.
You can’t take the section 179 deduction.
You can’t take the special depreciation allowance.
You must figure depreciation using the straight line method over a 5-year recovery period. You must continue to use the straight line method even if your percentage of business use increases to more than 50% in a later year.
Instead of making the computation yourself, you can use column (c) of Table 4-1 to find the percentage to use.
In May 2023, you bought and placed in service a car for $17,500. You used it 40% for your consulting business. Because you didn’t use the car more than 50% for business, you can’t take any section 179 deduction or special depreciation allowance, and you must use the straight line method over a 5-year recovery period to recover the cost of your car.
You deduct $700 in 2023. This is the lesser of:
$700 (($17,500 cost × 40% (0.40) business use) × 10% (0.10) recovery percentage (from column (c) of Table 4-1 )), or
$4,880 ($12,200 maximum limit × 40% (0.40) business use).
If you use your car more than 50% in qualified business use in the tax year it is placed in service but the business use drops to 50% or less in a later year, you can no longer use an accelerated depreciation method for that car.
For the year the business use drops to 50% or less and all later years in the recovery period, you must use the straight line depreciation method over a 5-year recovery period. In addition, for the year your business use drops to 50% or less, you must recapture (include in your gross income) any excess depreciation (discussed later). You also increase the adjusted basis of your car by the same amount.
In June 2020, you purchased a car for exclusive use in your business. You met the more-than-50%-use test for the first 3 years of the recovery period (2020 through 2022) but failed to meet it in the fourth year (2023). You determine your depreciation for 2023 using 20% (from column (c) of Table 4-1 ). You will also have to determine and include in your gross income any excess depreciation, discussed next.
You must include any excess depreciation in your gross income and add it to your car's adjusted basis for the first tax year in which you don’t use the car more than 50% in qualified business use. Use Form 4797, Sales of Business Property, to figure and report the excess depreciation in your gross income.
Excess depreciation is:
The amount of the depreciation deductions allowable for the car (including any section 179 deduction claimed and any special depreciation allowance claimed) for tax years in which you used the car more than 50% in qualified business use, minus
The amount of the depreciation deductions that would have been allowable for those years if you hadn’t used the car more than 50% in qualified business use for the year you placed it in service. This means the amount of depreciation figured using the straight line method.
In September 2019, you bought a car for $20,500 and placed it in service. You didn’t claim the section 179 deduction or the special depreciation allowance. You used the car exclusively in qualified business use for 2019, 2020, 2021, and 2022. For those years, you used the appropriate MACRS Depreciation Chart to figure depreciation deductions totaling $13,185 ($3,160 for 2019, $5,100 for 2020, $3,050 for 2021, and $1,875 for 2022) under the 200% DB method.
During 2023, you used the car 30% for business and 70% for personal purposes. Since you didn’t meet the more-than-50%-use test, you must switch from the 200% DB depreciation method to the straight line depreciation method for 2023, and include in gross income for 2023 your excess depreciation determined as follows.
In 2023, using Form 4797, you figure and report the $2,110 excess depreciation you must include in your gross income. Your adjusted basis in the car is also increased by $2,110. Your 2023 depreciation is $1,230 ($20,500 (unadjusted basis) × 30% (0.30) (business-use percentage) × 20% (0.20) (from column (c) of Table 4-1 on the line for Jan. 1–Sept. 30, 2019)). However, your depreciation deduction is limited to $563 ($1,875 x 30% (0.30) business use).
Leasing a Car
If you lease a car, truck, or van that you use in your business, you can use the standard mileage rate or actual expenses to figure your deductible expense. This section explains how to figure actual expenses for a leased car, truck, or van.
If you choose to use actual expenses, you can deduct the part of each lease payment that is for the use of the vehicle in your business. You can’t deduct any part of a lease payment that is for personal use of the vehicle, such as commuting.
You must spread any advance payments over the entire lease period. You can’t deduct any payments you make to buy a car, truck, or van even if the payments are called “lease payments.”
If you lease a car, truck, or van for 30 days or more, you may have to reduce your lease payment deduction by an “inclusion amount,” explained next.
Inclusion Amounts
If you lease a car, truck, or van that you use in your business for a lease term of 30 days or more, you may have to include an inclusion amount in your income for each tax year you lease the vehicle. To do this, you don’t add an amount to income. Instead, you reduce your deduction for your lease payment. (This reduction has an effect similar to the limit on the depreciation deduction you would have on the vehicle if you owned it.)
The inclusion amount is a percentage of part of the fair market value of the leased vehicle multiplied by the percentage of business and investment use of the vehicle for the tax year. It is prorated for the number of days of the lease term in the tax year.
The inclusion amount applies to each tax year that you lease the vehicle if the fair market value (defined next) when the lease began was more than the amounts shown in the following tables.
All vehicles are subject to a single inclusion amount threshold for passenger automobiles leased and put into service in 2023. You may have an inclusion amount for a passenger automobile if:
Passenger Automobiles (Including Trucks and Vans)
For years prior to 2018, see the inclusion tables below. You may have an inclusion amount for a passenger automobile if:
Cars (Except for Trucks and Vans)
Trucks and Vans
Fair market value is the price at which the property would change hands between a willing buyer and seller, neither having to buy or sell, and both having reasonable knowledge of all the necessary facts. Sales of similar property around the same date may be helpful in figuring the fair market value of the property.
Figure the fair market value on the first day of the lease term. If the capitalized cost of a car is specified in the lease agreement, use that amount as the fair market value.
Inclusion amounts for tax years 2018–2023 are listed in Appendices A-1 through A-6 for passenger vehicles (including trucks and vans). If the fair market value of the vehicle is $100,000 or less, use the appropriate appendix (depending on the year you first placed the vehicle in service) to determine the inclusion amount. If the fair market value is more than $100,000, see the revenue procedure(s) identified in the footnote of that year’s appendix for the inclusion amount.
For each tax year during which you lease the car for business, determine your inclusion amount by following these three steps.
Locate the appendix that applies to you. To find the inclusion amount, do the following.
Find the line that includes the fair market value of the car on the first day of the lease term.
Go across the line to the column for the tax year in which the car is used under the lease to find the dollar amount. For the last tax year of the lease, use the dollar amount for the preceding year.
Prorate the dollar amount from (1b) for the number of days of the lease term included in the tax year.
Multiply the prorated amount from (2) by the percentage of business and investment use for the tax year. This is your inclusion amount.
On January 17, 2023, you leased a car for 3 years and placed it in service for use in your business. The car had a fair market value of $62,500 on the first day of the lease term. You use the car 75% for business and 25% for personal purposes during each year of the lease. Assuming you continue to use the car 75% for business, you use Appendix A-6 to arrive at the following inclusion amounts for each year of the lease. For the last tax year of the lease, 2026, you use the amount for the preceding year.
2024 is a leap year and includes an extra calendar day, February 29, 2024.
For each year of the lease that you deduct lease payments, you must reduce your deduction by the inclusion amount figured for that year.
If you lease a car for business use and, in a later year, change it to personal use, follow the rules explained earlier under Figuring the inclusion amount . For the tax year in which you stop using the car for business, use the dollar amount for the previous tax year. Prorate the dollar amount for the number of days in the lease term that fall within the tax year.
On August 16, 2022, you leased a car with a fair market value of $64,500 for 3 years. You used the car exclusively in your data processing business. On November 6, 2023, you closed your business and went to work for a company where you aren’t required to use a car for business. Using Appendix A-5 , you figured your inclusion amount for 2022 and 2023 as shown in the following table and reduced your deductions for lease payments by those amounts.
If you lease a car for personal use and, in a later year, change it to business use, you must determine the car's fair market value on the date of conversion. Then figure the inclusion amount using the rules explained earlier under Figuring the inclusion amount . Use the fair market value on the date of conversion.
In March 2021, you leased a truck for 4 years for personal use. On June 1, 2023, you started working as a self-employed advertising consultant and started using the leased truck for business purposes. Your records show that your business use for June 1 through December 31 was 60%. To figure your inclusion amount for 2023, you obtained an appraisal from an independent car leasing company that showed the fair market value of your 2021 truck on June 1, 2023, was $62,650. Using Appendix A-6 , you figured your inclusion amount for 2023 as shown in the following table.
For information on reporting inclusion amounts, employees should see Car rentals under Completing Forms 2106 in chapter 6. Sole proprietors should see the Instructions for Schedule C (Form 1040), and farmers should see the Instructions for Schedule F (Form 1040).
Disposition of a Car
If you dispose of your car, you may have a taxable gain or a deductible loss. The portion of any gain that is due to depreciation (including any section 179 deduction, clean-fuel vehicle deduction (for vehicles placed in service before January 1, 2006), and special depreciation allowance) that you claimed on the car will be treated as ordinary income. However, you may not have to recognize a gain or loss if you dispose of the car because of a casualty or theft.
This section gives some general information about dispositions of cars. For information on how to report the disposition of your car, see Pub. 544.
Like‐kind exchanges completed after December 31, 2017, are generally limited to exchanges of real property not held primarily for sale.
For a casualty or theft, a gain results when you receive insurance or other reimbursement that is more than your adjusted basis in your car. If you then spend all of the proceeds to acquire replacement property (a new car or repairs to the old car) within a specified period of time, you don’t recognize any gain. Your basis in the replacement property is its cost minus any gain that isn’t recognized. See Pub. 547 for more information.
When you trade in an old car for a new one, the transaction is considered a like-kind exchange. Generally, no gain or loss is recognized. (For exceptions, see chapter 1 of Pub. 544.) In a trade-in situation, your basis in the new property is generally your adjusted basis in the old property plus any additional amount you pay. (See Unadjusted basis , earlier.)
If you used the standard mileage rate for the business use of your car, depreciation was included in that rate. The rate of depreciation that was allowed in the standard mileage rate is shown in the Rate of Depreciation Allowed in Standard Mileage Rate table, later. You must reduce your basis in your car (but not below zero) by the amount of this depreciation.
If your basis is reduced to zero (but not below zero) through the use of the standard mileage rate, and you continue to use your car for business, no adjustment (reduction) to the standard mileage rate is necessary. Use the full standard mileage rate (65.5 cents ($0.655) per mile from January 1–December 31 for 2023) for business miles driven.
Rate of Depreciation Allowed in Standard Mileage Rate
In 2018, you bought and placed in service a car for exclusive use in your business. The car cost $25,500. From 2018 through 2023, you used the standard mileage rate to figure your car expense deduction. You drove your car 14,100 miles in 2018, 16,300 miles in 2019, 15,600 miles in 2020, 16,700 miles in 2021, 15,100 miles in 2022, and 14,900 miles in 2023. The depreciation portion of your car expense deduction is figured as follows.
If you deduct actual car expenses and you dispose of your car before the end of the recovery period (years 2 through 5), you are allowed a reduced depreciation deduction in the year of disposition.
Use the depreciation tables in Pub. 946 to figure the reduced depreciation deduction for a car disposed of in 2023.
The depreciation amounts computed using the depreciation tables in Pub. 946 for years 2 through 5 that you own your car are for a full year’s depreciation. Years 1 and 6 apply the half-year or mid-quarter convention to the computation for you. If you dispose of the vehicle in years 2 through 5 and the half-year convention applies, then the full year’s depreciation amount must be divided by 2. If the mid-quarter convention applies, multiply the full year’s depreciation by the percentage from the following table for the quarter that you disposed of the car.
If the car is subject to the Depreciation Limits , discussed earlier, reduce (but do not increase) the computed depreciation to this amount. See Sale or Other Disposition Before the Recovery Period Ends in chapter 4 of Pub. 946 for more information.
5. Recordkeeping
If you deduct travel, gift, or transportation expenses, you must be able to prove (substantiate) certain elements of expense. This chapter discusses the records you need to keep to prove these expenses.
How To Prove Expenses
Table 5-1 is a summary of records you need to prove each expense discussed in this publication. You must be able to prove the elements listed across the top portion of the chart. You prove them by having the information and receipts (where needed) for the expenses listed in the first column.
You should keep adequate records to prove your expenses or have sufficient evidence that will support your own statement. You must generally prepare a written record for it to be considered adequate. This is because written evidence is more reliable than oral evidence alone. However, if you prepare a record on a computer, it is considered an adequate record.
What Are Adequate Records?
You should keep the proof you need in an account book, diary, log, statement of expense, trip sheets, or similar record. You should also keep documentary evidence that, together with your record, will support each element of an expense.
You must generally have documentary evidence such as receipts, canceled checks, or bills, to support your expenses.
Documentary evidence isn’t needed if any of the following conditions apply.
You have meals or lodging expenses while traveling away from home for which you account to your employer under an accountable plan, and you use a per diem allowance method that includes meals and/or lodging. ( Accountable plans and per diem allowances are discussed in chapter 6.)
Your expense, other than lodging, is less than $75.
You have a transportation expense for which a receipt isn’t readily available.
Documentary evidence will ordinarily be considered adequate if it shows the amount, date, place, and essential character of the expense.
For example, a hotel receipt is enough to support expenses for business travel if it has all of the following information.
The name and location of the hotel.
The dates you stayed there.
Separate amounts for charges such as lodging, meals, and telephone calls.
A restaurant receipt is enough to prove an expense for a business meal if it has all of the following information.
The name and location of the restaurant.
The number of people served.
The date and amount of the expense.
A canceled check, together with a bill from the payee, ordinarily establishes the cost. However, a canceled check by itself doesn’t prove a business expense without other evidence to show that it was for a business purpose.
You don‘t have to record information in your account book or other record that duplicates information shown on a receipt as long as your records and receipts complement each other in an orderly manner.
You don’t have to record amounts your employer pays directly for any ticket or other travel item. However, if you charge these items to your employer, through a credit card or otherwise, you must keep a record of the amounts you spend.
You should record the elements of an expense or of a business use at or near the time of the expense or use and support it with sufficient documentary evidence. A timely kept record has more value than a statement prepared later when there is generally a lack of accurate recall.
You don’t need to write down the elements of every expense on the day of the expense. If you maintain a log on a weekly basis that accounts for use during the week, the log is considered a timely kept record.
If you give your employer, client, or customer an expense account statement, it can also be considered a timely kept record. This is true if you copy it from your account book, diary, log, statement of expense, trip sheets, or similar record.
You must generally provide a written statement of the business purpose of an expense. However, the degree of proof varies according to the circumstances in each case. If the business purpose of an expense is clear from the surrounding circumstances, then you don’t need to give a written explanation.
If you are a sales representative who calls on customers on an established sales route, you don’t have to give a written explanation of the business purpose for traveling that route. You can satisfy the requirements by recording the length of the delivery route once, the date of each trip at or near the time of the trips, and the total miles you drove the car during the tax year. You could also establish the date of each trip with a receipt, record of delivery, or other documentary evidence.
You don’t need to put confidential information relating to an element of a deductible expense (such as the place, business purpose, or business relationship) in your account book, diary, or other record. However, you do have to record the information elsewhere at or near the time of the expense and have it available to fully prove that element of the expense.
What if I Have Incomplete Records?
If you don’t have complete records to prove an element of an expense, then you must prove the element with:
Your own written or oral statement containing specific information about the element, and
Other supporting evidence that is sufficient to establish the element.
If the element is the description of a gift, or the cost, time, place, or date of an expense, the supporting evidence must be either direct evidence or documentary evidence. Direct evidence can be written statements or the oral testimony of your guests or other witnesses setting forth detailed information about the element. Documentary evidence can be receipts, paid bills, or similar evidence.
If the element is either the business relationship of your guests or the business purpose of the amount spent, the supporting evidence can be circumstantial rather than direct. For example, the nature of your work, such as making deliveries, provides circumstantial evidence of the use of your car for business purposes. Invoices of deliveries establish when you used the car for business.
Table 5-1. How To Prove Certain Business Expenses
You can keep an adequate record for parts of a tax year and use that record to prove the amount of business or investment use for the entire year. You must demonstrate by other evidence that the periods for which an adequate record is kept are representative of the use throughout the tax year.
You use your car to visit the offices of clients, meet with suppliers and other subcontractors, and pick up and deliver items to clients. There is no other business use of the car, but you and your family use the car for personal purposes. You keep adequate records during the first week of each month that show that 75% of the use of the car is for business. Invoices and bills show that your business use continues at the same rate during the later weeks of each month. Your weekly records are representative of the use of the car each month and are sufficient evidence to support the percentage of business use for the year.
You can satisfy the substantiation requirements with other evidence if, because of the nature of the situation in which an expense is made, you can’t get a receipt. This applies if all the following are true.
You were unable to obtain evidence for an element of the expense or use that completely satisfies the requirements explained earlier under What Are Adequate Records .
You are unable to obtain evidence for an element that completely satisfies the two rules listed earlier under What if I Have Incomplete Records .
You have presented other evidence for the element that is the best proof possible under the circumstances.
If you can’t produce a receipt because of reasons beyond your control, you can prove a deduction by reconstructing your records or expenses. Reasons beyond your control include fire, flood, and other casualties.
Separating and Combining Expenses
This section explains when expenses must be kept separate and when expenses can be combined.
Each separate payment is generally considered a separate expense. For example, if you entertain a customer or client at dinner and then go to the theater, the dinner expense and the cost of the theater tickets are two separate expenses. You must record them separately in your records.
You can make one daily entry in your record for reasonable categories of expenses. Examples are taxi fares, telephone calls, or other incidental travel costs. Nonentertainment meals should be in a separate category. You can include tips for meal-related services with the costs of the meals.
Expenses of a similar nature occurring during the course of a single event are considered a single expense.
You can account for several uses of your car that can be considered part of a single use, such as a round trip or uninterrupted business use, with a single record. Minimal personal use, such as a stop for lunch on the way between two business stops, isn’t an interruption of business use.
You make deliveries at several different locations on a route that begins and ends at your employer's business premises and that includes a stop at the business premises between two deliveries. You can account for these using a single record of miles driven.
You don’t always have to record the name of each recipient of a gift. A general listing will be enough if it is evident that you aren’t trying to avoid the $25 annual limit on the amount you can deduct for gifts to any one person. For example, if you buy a large number of tickets to local high school basketball games and give one or two tickets to each of many customers, it is usually enough to record a general description of the recipients.
If you can prove the total cost of travel or entertainment but you can’t prove how much it costs for each person who participated in the event, you may have to allocate the total cost among you and your guests on a pro rata basis. To do so, you must establish the number of persons who participated in the event.
If your return is examined, you may have to provide additional information to the IRS. This information could be needed to clarify or to establish the accuracy or reliability of information contained in your records, statements, testimony, or documentary evidence before a deduction is allowed.
How Long To Keep Records and Receipts
You must keep records as long as they may be needed for the administration of any provision of the Internal Revenue Code. Generally, this means you must keep records that support your deduction (or an item of income) for 3 years from the date you file the income tax return on which the deduction is claimed. A return filed early is considered filed on the due date. For a more complete explanation of how long to keep records, see Pub. 583, Starting a Business and Keeping Records.
You must keep records of the business use of your car for each year of the recovery period. See More-than-50%-use test in chapter 4 under Depreciation Deduction.
Employees who give their records and documentation to their employers and are reimbursed for their expenses generally don’t have to keep copies of this information. However, you may have to prove your expenses if any of the following conditions apply.
You claim deductions for expenses that are more than reimbursements.
Your expenses are reimbursed under a nonaccountable plan.
Your employer doesn’t use adequate accounting procedures to verify expense accounts.
You are related to your employer as defined under Per Diem and Car Allowances in chapter 6.
Table 5-2 and Table 5-3 are examples of worksheets that can be used for tracking business expenses.
Table 5-2. Daily Business Mileage and Expense Log
Table 5-3. Weekly Traveling Expense Record
6. How To Report
This chapter explains where and how to report the expenses discussed in this publication. It discusses reimbursements and how to treat them under accountable and nonaccountable plans. It also explains rules for independent contractors and clients, fee-basis officials, certain performing artists, Armed Forces reservists, and certain disabled employees. The chapter ends with illustrations of how to report travel, gift, and car expenses on Forms 2106.
Where To Report
This section provides general information on where to report the expenses discussed in this publication.
You must report your income and expenses on Schedule C (Form 1040) if you are a sole proprietor, or on Schedule F (Form 1040) if you are a farmer. You don’t use Form 2106.
If you claim car or truck expenses, you must provide certain information on the use of your vehicle. You provide this information on Schedule C (Form 1040) or Form 4562.
If you file Schedule C (Form 1040):
Report your travel expenses, except meals, on line 24a;
Report your deductible non-entertainment-related meals (actual cost or standard meal allowance) on line 24b;
Report your gift expenses and transportation expenses, other than car expenses, on line 27a; and
Report your car expenses on line 9. Complete Part IV of the form unless you have to file Form 4562 for depreciation or amortization.
If you file Schedule F (Form 1040), do the following.
Report your car expenses on line 10. Attach Form 4562 and provide information on the use of your car in Part V of Form 4562.
Report all other business expenses discussed in this publication on line 32. You can only include 50% of your non-entertainment-related meals on that line.
If you are both self-employed and an employee, you must keep separate records for each business activity. Report your business expenses for self-employment on Schedule C (Form 1040), or Schedule F (Form 1040), as discussed earlier. Report your business expenses for your work as an employee on Form 2106, as discussed next.
If you are an employee, you must generally complete Form 2106 to deduct your travel and transportation expenses.
You are an employee deducting expenses attributable to your job.
You weren’t reimbursed by your employer for your expenses (amounts included in box 1 of your Form W-2 aren’t considered reimbursements).
If you claim car expenses, you use the standard mileage rate.
For more information on how to report your expenses on Form 2106, see Completing Form 2106 , later.
If you didn’t receive any reimbursements (or the reimbursements were all included in box 1 of your Form W-2), the only business expense you are claiming is for gifts, and the special rules discussed later don’t apply to you, don’t complete Form 2106.
If you received a Form W-2 and the “Statutory employee” box in box 13 was checked, report your income and expenses related to that income on Schedule C (Form 1040). Don’t complete Form 2106.
Statutory employees include full-time life insurance salespersons, certain agent or commission drivers, traveling salespersons, and certain homeworkers.
If your employer reimburses you for nondeductible personal expenses, such as for vacation trips, your employer must report the reimbursement as wage income in box 1 of your Form W-2. You can’t deduct personal expenses.
If you have travel or transportation expenses related to income-producing property, report your deductible expenses on the form appropriate for that activity.
For example, if you have rental real estate income and expenses, report your expenses on Schedule E (Form 1040), Supplemental Income and Loss. See Pub. 527, Residential Rental Property, for more information on the rental of real estate.
Vehicle Provided by Your Employer
If your employer provides you with a car, you may be able to deduct the actual expenses of operating that car for business purposes. The amount you can deduct depends on the amount that your employer included in your income and the business and personal miles you drove during the year. You can’t use the standard mileage rate.
Your employer can figure and report either the actual value of your personal use of the car or the value of the car as if you used it only for personal purposes (100% income inclusion). Your employer must separately state the amount if 100% of the annual lease value was included in your income. If you are unsure of the amount included on your Form W-2, ask your employer.
You may be able to deduct the value of the business use of an employer-provided car if your employer reported 100% of the value of the car in your income. On your 2023 Form W-2, the amount of the value will be included in box 1, Wages, tips, other compensation; and box 14, Other.
To claim your expenses, complete Form 2106, Part II, Sections A and C. Enter your actual expenses on line 23 of Section C and include the entire value of the employer-provided car on line 25. Complete the rest of the form.
If less than the full annual lease value of the car was included on your Form W-2, this means that your Form W-2 only includes the value of your personal use of the car. Don’t enter this value on your Form 2106 because it isn’t deductible.
If you paid any actual costs (that your employer didn’t provide or reimburse you for) to operate the car, you can deduct the business portion of those costs. Examples of costs that you may have are gas, oil, and repairs. Complete Form 2106, Part II, Sections A and C. Enter your actual costs on line 23 of Section C and leave line 25 blank. Complete the rest of the form.
Reimbursements
This section explains what to do when you receive an advance or are reimbursed for any of the employee business expenses discussed in this publication.
If you received an advance, allowance, or reimbursement for your expenses, how you report this amount and your expenses depends on whether your employer reimbursed you under an accountable plan or a nonaccountable plan.
This section explains the two types of plans, how per diem and car allowances simplify proving the amount of your expenses, and the tax treatment of your reimbursements and expenses. It also covers rules for independent contractors.
You aren’t reimbursed or given an allowance for your expenses if you are paid a salary or commission with the understanding that you will pay your own expenses. In this situation, you have no reimbursement or allowance arrangement, and you don’t have to read this section on reimbursements. Instead, see Completing Form 2106 , later, for information on completing your tax return.
A reimbursement or other expense allowance arrangement is a system or plan that an employer uses to pay, substantiate, and recover the expenses, advances, reimbursements, and amounts charged to the employer for employee business expenses. Arrangements include per diem and car allowances.
A per diem allowance is a fixed amount of daily reimbursement your employer gives you for your lodging and M&IE when you are away from home on business. (The term “incidental expenses” is defined in chapter 1 under Standard Meal Allowance. ) A car allowance is an amount your employer gives you for the business use of your car.
Your employer should tell you what method of reimbursement is used and what records you must provide.
If you are an employer and you reimburse employee business expenses, how you treat this reimbursement on your employee's Form W-2 depends in part on whether you have an accountable plan. Reimbursements treated as paid under an accountable plan, as explained next, aren’t reported as pay. Reimbursements treated as paid under nonaccountable plans , as explained later, are reported as pay. See Pub. 15 (Circular E), Employer's Tax Guide, for information on employee pay.
Accountable Plans
To be an accountable plan, your employer's reimbursement or allowance arrangement must include all of the following rules.
Your expenses must have a business connection—that is, you must have paid or incurred deductible expenses while performing services as an employee of your employer.
You must adequately account to your employer for these expenses within a reasonable period of time.
You must return any excess reimbursement or allowance within a reasonable period of time.
Adequate accounting and returning excess reimbursements are discussed later.
An excess reimbursement or allowance is any amount you are paid that is more than the business-related expenses that you adequately accounted for to your employer.
The definition of reasonable period of time depends on the facts and circumstances of your situation. However, regardless of the facts and circumstances of your situation, actions that take place within the times specified in the following list will be treated as taking place within a reasonable period of time.
You receive an advance within 30 days of the time you have an expense.
You adequately account for your expenses within 60 days after they were paid or incurred.
You return any excess reimbursement within 120 days after the expense was paid or incurred.
You are given a periodic statement (at least quarterly) that asks you to either return or adequately account for outstanding advances and you comply within 120 days of the statement.
If you meet the three rules for accountable plans, your employer shouldn’t include any reimbursements in your income in box 1 of your Form W-2. If your expenses equal your reimbursements, you don’t complete Form 2106. You have no deduction since your expenses and reimbursements are equal.
Even though you are reimbursed under an accountable plan, some of your expenses may not meet all three rules. All reimbursements that fail to meet all three rules for accountable plans are generally treated as having been reimbursed under a nonaccountable plan (discussed later).
If you are reimbursed under an accountable plan, but you fail to return, within a reasonable time, any amounts in excess of the substantiated amounts, the amounts paid in excess of the substantiated expenses are treated as paid under a nonaccountable plan. See Reasonable period of time , earlier, and Returning Excess Reimbursements , later.
You may be reimbursed under your employer's accountable plan for expenses related to that employer's business, some of which would be allowable as employee business expense deductions and some of which would not. The reimbursements you receive for the nondeductible expenses don’t meet rule (1) for accountable plans, and they are treated as paid under a nonaccountable plan.
Your employer's plan reimburses you for travel expenses while away from home on business and also for meals when you work late at the office, even though you aren’t away from home. The part of the arrangement that reimburses you for the nondeductible meals when you work late at the office is treated as paid under a nonaccountable plan.
One of the rules for an accountable plan is that you must adequately account to your employer for your expenses. You adequately account by giving your employer a statement of expense, an account book, a diary, or a similar record in which you entered each expense at or near the time you had it, along with documentary evidence (such as receipts) of your travel, mileage, and other employee business expenses. (See Table 5-1 in chapter 5 for details you need to enter in your record and documents you need to prove certain expenses.) A per diem or car allowance satisfies the adequate accounting requirement under certain conditions. See Per Diem and Car Allowances , later.
You must account for all amounts you received from your employer during the year as advances, reimbursements, or allowances. This includes amounts you charged to your employer by credit card or other method. You must give your employer the same type of records and supporting information that you would have to give to the IRS if the IRS questioned a deduction on your return. You must pay back the amount of any reimbursement or other expense allowance for which you don’t adequately account or that is more than the amount for which you accounted.
Per Diem and Car Allowances
If your employer reimburses you for your expenses using a per diem or a car allowance, you can generally use the allowance as proof for the amount of your expenses. A per diem or car allowance satisfies the adequate accounting requirements for the amount of your expenses only if all the following conditions apply.
Your employer reasonably limits payments of your expenses to those that are ordinary and necessary in the conduct of the trade or business.
The allowance is similar in form to and not more than the federal rate (defined later).
You prove the time (dates), place, and business purpose of your expenses to your employer (as explained in Table 5-1 ) within a reasonable period of time.
You aren’t related to your employer (as defined next). If you are related to your employer, you must be able to prove your expenses to the IRS even if you have already adequately accounted to your employer and returned any excess reimbursement.
You are related to your employer if:
Your employer is your brother or sister, half brother or half sister, spouse, ancestor, or lineal descendant;
Your employer is a corporation in which you own, directly or indirectly, more than 10% in value of the outstanding stock; or
Certain relationships (such as grantor, fiduciary, or beneficiary) exist between you, a trust, and your employer.
The federal rate can be figured using any one of the following methods.
For per diem amounts:
The regular federal per diem rate.
The high-low rate.
For car expenses:
A fixed and variable rate (FAVR).
The regular federal per diem rate is the highest amount that the federal government will pay to its employees for lodging and M&IE (or M&IE only) while they are traveling away from home in a particular area. The rates are different for different localities. Your employer should have these rates available. You can also find federal per diem rates at GSA.gov/travel/plan-book/per-diem-rates .
The standard meal allowance is the federal M&IE rate. For travel in 2023, the rate for most small localities in the United States is $59 per day. Most major cities and many other localities qualify for higher rates. You can find this information at GSA.gov/travel/plan-book/per-diem-rates .
You receive an allowance only for M&IE when your employer does one of the following.
Provides you with lodging (furnishes it in kind).
Reimburses you, based on your receipts, for the actual cost of your lodging.
Pays the hotel, motel, etc., directly for your lodging.
Doesn’t have a reasonable belief that you had (or will have) lodging expenses, such as when you stay with friends or relatives or sleep in the cab of your truck.
Figures the allowance on a basis similar to that used in figuring your compensation, such as number of hours worked or miles traveled.
This is a simplified method of figuring the federal per diem rate for travel within the continental United States. It eliminates the need to keep a current list of the per diem rates for each city.
Under the high-low method, the per diem amount for travel during January through September of 2023 is $297 (which includes $74 for M&IE) for certain high-cost locations. All other areas have a per diem amount of $204 (which includes $64 for M&IE). For more information, see Notice 2022-44, which can be found at IRS.gov/irb/2022-41_IRB#NOT-2022-44 .
Effective October 1, 2023, the per diem rate for certain high-cost locations increased to $309 (which includes $74 for M&IE). The rate for all other locations increased to $214 (which includes $64 for M&IE). For more information, see Notice 2023-68, which can be found at IRS.gov/irb/2023-41_IRB#NOT-2023-68 , and Revenue Procedure 2019-48 at IRS.gov/irb/2019-51_IRB#REV-PROC-2019-48 .
The standard meal allowance is for a full 24-hour day of travel. If you travel for part of a day, such as on the days you depart and return, you must prorate the full-day M&IE rate. This rule also applies if your employer uses the regular federal per diem rate or the high-low rate.
You can use either of the following methods to figure the federal M&IE for that day.
For the day you depart, add 3 / 4 of the standard meal allowance amount for that day.
For the day you return, add 3 / 4 of the standard meal allowance amount for the preceding day.
Method 2: Prorate the standard meal allowance using any method you consistently apply in accordance with reasonable business practice. For example, an employer can treat 2 full days of per diem (that includes M&IE) paid for travel away from home from 9 a.m. of one day to 5 p.m. of the next day as being no more than the federal rate. This is true even though a federal employee would be limited to a reimbursement of M&IE for only 1½ days of the federal M&IE rate.
This is a set rate per mile that you can use to figure your deductible car expenses. For 2023, the standard mileage rate for the cost of operating your car for business use is 65.5 cents ($0.655) per mile.
This is an allowance your employer may use to reimburse your car expenses. Under this method, your employer pays an allowance that includes a combination of payments covering fixed and variable costs, such as a cents-per-mile rate to cover your variable operating costs (such as gas, oil, etc.) plus a flat amount to cover your fixed costs (such as depreciation (or lease payments), insurance, etc.). If your employer chooses to use this method, your employer will request the necessary records from you.
If your reimbursement is in the form of an allowance received under an accountable plan, the following facts affect your reporting.
Whether the allowance or your actual expenses were more than the federal rate.
If your allowance is less than or equal to the federal rate, the allowance won’t be included in box 1 of your Form W-2. You don’t need to report the related expenses or the allowance on your return if your expenses are equal to or less than the allowance.
However, if your actual expenses are more than your allowance, you can complete Form 2106. If you are using actual expenses, you must be able to prove to the IRS the total amount of your expenses and reimbursements for the entire year. If you are using the standard meal allowance or the standard mileage rate, you don’t have to prove that amount.
In April, a member of a reserve component of the Armed Forces takes a 2-day business trip to Denver. The federal rate for Denver is $278 ($199 lodging + $79 M&IE) per day. As required by their employer's accountable plan, they account for the time (dates), place, and business purpose of the trip. Their employer reimburses them $278 a day ($556 total) for living expenses. Their living expenses in Denver aren’t more than $278 a day.
Their employer doesn’t include any of the reimbursement on their Form W-2 and they don’t deduct the expenses on their return.
In June, a fee-basis local government official takes a 2-day business trip to Boston. Their employer uses the high-low method to reimburse employees. Because Boston is a high-cost area, they are given an advance of $297 (which includes $74 for M&IE) a day ($594 total) for their lodging and M&IE. Their actual expenses totaled $700.
Since their $700 of expenses are more than their $594 advance, they include the excess expenses when they itemize their deductions. They complete Form 2106 (showing all of their expenses and reimbursements). They must also allocate their reimbursement between their meals and other expenses as discussed later under Completing Form 2106 .
A fee-basis state government official drives 10,000 miles during 2023 for business. Under their employer's accountable plan, they account for the time (dates), place, and business purpose of each trip. Their employer pays them a mileage allowance of 40 cents ($0.40) a mile.
Because their $6,550 expense figured under the standard mileage rate (10,000 miles x 65.5 cents ($0.655) per mile) is more than their $4,000 reimbursement (10,000 miles × 40 cents ($0.40)), they itemize their deductions to claim the excess expense. They complete Form 2106 (showing all their expenses and reimbursements) and enter $2,550 ($6,550 − $4,000) as an itemized deduction.
If your allowance is more than the federal rate, your employer must include the allowance amount up to the federal rate under code L in box 12 of your Form W-2. This amount isn’t taxable. However, the excess allowance will be included in box 1 of your Form W-2. You must report this part of your allowance as if it were wage income.
If your actual expenses are less than or equal to the federal rate, you don’t complete Form 2106 or claim any of your expenses on your return.
However, if your actual expenses are more than the federal rate, you can complete Form 2106 and deduct those excess expenses. You must report on Form 2106 your reimbursements up to the federal rate (as shown under code L in box 12 of your Form W-2) and all your expenses. You should be able to prove these amounts to the IRS.
Sasha, a performing artist, lives and works in Austin. In July, the employer sent Sasha to Albuquerque for 4 days on business. The employer paid the hotel directly for Sasha’s lodging and reimbursed $80 a day ($320 total) for M&IE. Sasha’s actual meal expenses weren’t more than the federal rate for Albuquerque, which is $69 per day.
The employer included the $44 that was more than the federal rate (($80 − $69) × 4) in box 1 of Sasha’s Form W-2. The employer shows $276 ($69 a day × 4) under code L in box 12 of Form W-2. This amount isn’t included in income. Sasha doesn’t have to complete Form 2106; however, Sasha must include the $44 in gross income as wages (by reporting the total amount shown in box 1 of their Form W-2).
Another performing artist, Ari, also lives in Austin and works for the same employer as in Example 1 . In May, the employer sent Ari to San Diego for 4 days and paid the hotel directly for the hotel bill. The employer reimbursed Ari $75 a day for M&IE. The federal rate for San Diego is $74 a day.
Ari can prove that actual non-entertainment-related meal expenses totaled $380. The employer's accountable plan won’t pay more than $75 a day for travel to San Diego, so Ari doesn’t give the employer the records that prove that the amount actually spent was $380. However, Ari does account for the time (dates), place, and business purpose of the trip. This is Ari’s only business trip this year.
Ari was reimbursed $300 ($75 × 4 days), which is $4 more than the federal rate of $296 ($74 × 4 days). The employer includes the $4 as income on the employee’s Form W-2 in box 1. The employer also enters $296 under code L in box 12 of the employee’s Form W-2.
Ari completes Form 2106 to figure deductible expenses and enters the total of actual expenses for the year ($380) on Form 2106. Ari also enters the reimbursements that weren’t included in income ($296). Ari’s total deductible meals and beverages expense, before the 50% limit, is $96. Ari will include $48 as an itemized deduction.
Palmer, a fee-basis state government official, drives 10,000 miles during 2023 for business. Under the employer's accountable plan, Palmer gets reimbursed 70 cents ($0.70) a mile, which is more than the standard mileage rate. The total reimbursement is $7,000.
The employer must include the reimbursement amount up to the standard mileage rate, $6,550 (10,000 miles x 65.5 cents ($0.655) per mile), under code L in box 12 of the employee’s Form W-2. That amount isn’t taxable. The employer must also include $450 ($7,000 − $6,550) in box 1 of the employee's Form W-2. This is the reimbursement that is more than the standard mileage rate.
If the expenses are equal to or less than the standard mileage rate, Palmer wouldn’t complete Form 2106. If the expenses are more than the standard mileage rate, Palmer would complete Form 2106 and report total expenses and reimbursement (shown under code L in box 12 of their Form W-2). Palmer would then claim the excess expenses as an itemized deduction.
Returning Excess Reimbursements
Under an accountable plan, you are required to return any excess reimbursement or other expense allowances for your business expenses to the person paying the reimbursement or allowance. Excess reimbursement means any amount for which you didn’t adequately account within a reasonable period of time. For example, if you received a travel advance and you didn’t spend all the money on business-related expenses or you don’t have proof of all your expenses, you have an excess reimbursement.
Adequate accounting and reasonable period of time were discussed earlier in this chapter.
You receive a travel advance if your employer provides you with an expense allowance before you actually have the expense, and the allowance is reasonably expected to be no more than your expense. Under an accountable plan, you are required to adequately account to your employer for this advance and to return any excess within a reasonable period of time.
If you don’t adequately account for or don't return any excess advance within a reasonable period of time, the amount you don’t account for or return will be treated as having been paid under a nonaccountable plan (discussed later).
If you don’t prove that you actually traveled on each day for which you received a per diem or car allowance (proving the elements described in Table 5-1 ), you must return this unproven amount of the travel advance within a reasonable period of time. If you don’t do this, the unproven amount will be considered paid under a nonaccountable plan (discussed later).
If your employer's accountable plan pays you an allowance that is higher than the federal rate, you don’t have to return the difference between the two rates for the period you can prove business-related travel expenses. However, the difference will be reported as wages on your Form W-2. This excess amount is considered paid under a nonaccountable plan (discussed later).
Your employer sends you on a 5-day business trip to Phoenix in March 2023 and gives you a $400 ($80 × 5 days) advance to cover your M&IE. The federal per diem for M&IE for Phoenix is $69. Your trip lasts only 3 days. Under your employer's accountable plan, you must return the $160 ($80 × 2 days) advance for the 2 days you didn’t travel. For the 3 days you did travel, you don’t have to return the $33 difference between the allowance you received and the federal rate for Phoenix (($80 − $69) × 3 days). However, the $33 will be reported on your Form W-2 as wages.
Nonaccountable Plans
A nonaccountable plan is a reimbursement or expense allowance arrangement that doesn’t meet one or more of the three rules listed earlier under Accountable Plans .
In addition, even if your employer has an accountable plan, the following payments will be treated as being paid under a nonaccountable plan.
Excess reimbursements you fail to return to your employer.
Reimbursement of nondeductible expenses related to your employer's business. See Reimbursement of nondeductible expenses , earlier, under Accountable Plans.
If you aren’t sure if the reimbursement or expense allowance arrangement is an accountable or nonaccountable plan, ask your employer.
Your employer will combine the amount of any reimbursement or other expense allowance paid to you under a nonaccountable plan with your wages, salary, or other pay. Your employer will report the total in box 1 of your Form W-2.
You must complete Form 2106 and itemize your deductions to deduct your expenses for travel, transportation, or non-entertainment-related meals. Your meal and entertainment expenses will be subject to the 50% Limit discussed in chapter 2.
Your employer gives you $1,000 a month ($12,000 total for the year) for your business expenses. You don’t have to provide any proof of your expenses to your employer, and you can keep any funds that you don’t spend.
You are a performing artist and are being reimbursed under a nonaccountable plan. Your employer will include the $12,000 on your Form W-2 as if it were wages. If you want to deduct your business expenses, you must complete Form 2106 and itemize your deductions.
You are paid $2,000 a month by your employer. On days that you travel away from home on business, your employer designates $50 a day of your salary as paid to reimburse your travel expenses. Because your employer would pay your monthly salary whether or not you were traveling away from home, the arrangement is a nonaccountable plan. No part of the $50 a day designated by your employer is treated as paid under an accountable plan.
Rules for Independent Contractors and Clients
This section provides rules for independent contractors who incur expenses on behalf of a client or customer. The rules cover the reporting and substantiation of certain expenses discussed in this publication, and they affect both independent contractors and their clients or customers.
You are considered an independent contractor if you are self-employed and you perform services for a customer or client.
Accounting to Your Client
If you received a reimbursement or an allowance for travel, or gift expenses that you incurred on behalf of a client, you should provide an adequate accounting of these expenses to your client. If you don’t account to your client for these expenses, you must include any reimbursements or allowances in income. You must keep adequate records of these expenses whether or not you account to your client for these expenses.
If you don’t separately account for and seek reimbursement for meal and entertainment expenses in connection with providing services for a client, you are subject to the 50% limit on those expenses. See 50% Limit in chapter 2.
As a self-employed person, you adequately account by reporting your actual expenses. You should follow the recordkeeping rules in chapter 5 .
For information on how to report expenses on your tax return, see Self-employed at the beginning of this chapter.
Required Records for Clients or Customers
If you are a client or customer, you generally don’t have to keep records to prove the reimbursements or allowances you give, in the course of your business, to an independent contractor for travel or gift expenses incurred on your behalf. However, you must keep records if:
You reimburse the contractor for entertainment expenses incurred on your behalf, and
The contractor adequately accounts to you for these expenses.
If the contractor adequately accounts to you for non-entertainment-related meal expenses, you (the client or customer) must keep records documenting each element of the expense, as explained in chapter 5 . Use your records as proof for a deduction on your tax return. If non-entertainment-related meal expenses are accounted for separately, you are subject to the 50% limit on meals. If the contractor adequately accounts to you for reimbursed amounts, you don’t have to report the amounts on an information return.
If the contractor doesn’t adequately account to you for allowances or reimbursements of non-entertainment-related meal expenses, you don’t have to keep records of these items. You aren’t subject to the 50% limit on meals in this case. You can deduct the reimbursements or allowances as payment for services if they are ordinary and necessary business expenses. However, you must file Form 1099-MISC to report amounts paid to the independent contractor if the total of the reimbursements and any other fees is $600 or more during the calendar year.
How To Use Per Diem Rate Tables
This section contains information about the per diem rate substantiation methods available and the choice of rates you must make for the last 3 months of the year.
The Two Substantiation Methods
IRS Notices list the localities that are treated under the high-low substantiation method as high-cost localities for all or part of the year. Notice 2022-44, available at IRS.gov/irb/2022-41_IRB#NOT-2022-44 , lists the high-cost localities that are eligible for $297 (which includes $74 for meals and incidental expenses (M&IE)) per diem, effective October 1, 2022. For travel on or after October 1, 2022, all other localities within the continental United States (CONUS) are eligible for $204 (which includes $64 for M&IE) per diem under the high-low method.
Notice 2023-68, available at IRS.gov/irb/2023-41_IRB#NOT-2023-68 , lists the high-cost localities that are eligible for $309 (which includes $74 for M&IE) per diem, effective October 1, 2023. For travel on or after October 1, 2023, the per diem for all other localities increased to $214 (which includes $64 for M&IE).
Regular federal per diem rates are published by the General Services Administration (GSA). Both tables include the separate rate for M&IE for each locality. The rates listed for FY2023 at GSA.gov/travel/plan-book/per-diem-rates are effective October 1, 2022, and those listed for FY2024 are effective October 1, 2023. The standard rate for all locations within CONUS not specifically listed for FY2023 is $157 ($98 for lodging and $59 for M&IE). For FY2024, this rate increases to $166 ($107 for lodging and $59 for M&IE).
Transition Rules
The transition period covers the last 3 months of the calendar year, from the time that new rates are effective (generally, October 1) through December 31. During this period, you may generally change to the new rates or finish out the year with the rates you had been using.
If you use the high-low substantiation method, when new rates become effective (generally, October 1), you can either continue with the rates you used for the first part of the year or change to the new rates. However, you must continue using the high-low method for the rest of the calendar year (through December 31). If you are an employer, you must use the same rates for all employees reimbursed under the high-low method during that calendar year.
The new rates and localities for the high-low method are included each year in a notice that is generally published in mid to late September. You can find the notice in the weekly Internal Revenue Bulletin (IRB) at IRS.gov/IRB , or visit IRS.gov and enter “Special Per Diem Rates” in the search box.
New CONUS per diem rates become effective on October 1 of each year and remain in effect through September 30 of the following year. Employees being reimbursed under the per diem rate method during the first 9 months of a year (January 1–September 30) must continue under the same method through the end of that calendar year (December 31). However, for travel by these employees from October 1 through December 31, you can choose to continue using the same per diem rates or use the new rates.
The new federal CONUS per diem rates are published each year, generally early in September. Go to GSA.gov/travel/plan-book/per-diem-rates .
Completing Form 2106
For tax years beginning after 2017, the Form 2106 will be used by Armed Forces reservists, qualified performing artists, fee-basis state or local government officials, and employees with impairment-related work expenses. Due to the suspension of miscellaneous itemized deductions subject to the 2% floor under section 67(a), employees who do not fit into one of the listed categories may not use Form 2106.
This section briefly describes how employees complete Forms 2106. Table 6-1 explains what the employer reports on Form W-2 and what the employee reports on Form 2106. The instructions for the forms have more information on completing them.
Table 6-1. Reporting Travel, Nonentertainment Meal, Gift, and Car Expenses and Reimbursements
If you used a car to perform your job as an employee, you may be able to deduct certain car expenses. These are generally figured on Form 2106, Part II, and then claimed on Form 2106, Part I, line 1, column A.
If you claim any deduction for the business use of a car, you must answer certain questions and provide information about the use of the car. The information relates to the following items.
Date placed in service.
Mileage (total, business, commuting, and other personal mileage).
Percentage of business use.
After-work use.
Use of other vehicles.
Whether you have evidence to support the deduction.
Whether or not the evidence is written.
If you claim a deduction based on the standard mileage rate instead of your actual expenses, you must complete Form 2106, Part II, Section B. The amount on line 22 (Section B) is carried to Form 2106, Part I, line 1. In addition, on Part I, line 2, you can deduct parking fees and tolls that apply to the business use of the car. See Standard Mileage Rate in chapter 4 for information on using this rate.
If you claim a deduction based on actual car expenses, you must complete Form 2106, Part II, Section C. In addition, unless you lease your car, you must complete Section D to show your depreciation deduction and any section 179 deduction you claim.
If you are still using a car that is fully depreciated, continue to complete Section C. Since you have no depreciation deduction, enter zero on line 28. In this case, don’t complete Section D.
If you claim car rental expenses on Form 2106, line 24a, you may have to reduce that expense by an inclusion amount , as described in chapter 4. If so, you can show your car expenses and any inclusion amount as follows.
Figure the inclusion amount without taking into account your business-use percentage for the tax year.
Report the inclusion amount from (1) on Form 2106, Part II, line 24b.
Report on line 24c the net amount of car rental expenses (total car rental expenses minus the inclusion amount figured in (1)).
Show your transportation expenses that didn’t involve overnight travel on Form 2106, line 2, column A. Also include on this line business expenses you have for parking fees and tolls. Don’t include expenses of operating your car or expenses of commuting between your home and work.
Show your other employee business expenses on Form 2106, lines 3 and 4, column A. Don’t include expenses for nonentertainment meals on those lines. Line 4 is for expenses such as gifts, educational expenses (tuition and books), office-in-the-home expenses, and trade and professional publications.
Show the full amount of your expenses for nonentertainment business-related meals on Form 2106, line 5, column B. Include meals while away from your tax home overnight and other business meals. Enter 50% of the line 8, column B, meal expenses on line 9, column B.
If you are subject to the Department of Transportation's “hours of service” limits (as explained earlier under Individuals subject to hours of service limits in chapter 2), use 80% instead of 50% for meals while away from your tax home.
Enter on Form 2106, line 7, the amounts your employer (or third party) reimbursed you that weren’t reported to you in box 1 of your Form W-2. This includes any amount reported under code L in box 12 of Form W-2.
If you were reimbursed under an accountable plan and want to deduct excess expenses that weren’t reimbursed, you may have to allocate your reimbursement. This is necessary when your employer pays your reimbursement in the following manner.
Pays you a single amount that covers non-entertainment-related meals and/or entertainment, as well as other business expenses.
Doesn’t clearly identify how much is for deductible non-entertainment-related meals.
Your employer paid you an expense allowance of $12,000 this year under an accountable plan. The $12,000 payment consisted of $5,000 for airfare and $7,000 for non-entertainment-related meals, and car expenses. Your employer didn’t clearly show how much of the $7,000 was for the cost of deductible non-entertainment-related meals. You actually spent $14,000 during the year ($5,500 for airfare, $4,500 for non-entertainment-related meals, and $4,000 for car expenses).
Since the airfare allowance was clearly identified, you know that $5,000 of the payment goes in column A, line 7, of Form 2106. To allocate the remaining $7,000, you use the worksheet from the Instructions for Form 2106. Your completed worksheet follows.
Reimbursement Allocation Worksheet (Keep for your records.)
If you are a government official paid on a fee basis, a performing artist, an Armed Forces reservist, or a disabled employee with impairment-related work expenses, see Special Rules , later.
Your employee business expenses may be subject to either of the limits described next. They are figured in the following order on the specified form.
Certain non-entertainment-related meal expenses are subject to a 50% limit. Generally, entertainment expenses are nondeductible if paid or incurred after December 2017. If you are an employee, you figure this limit on line 9 of Form 2106. (See 50% Limit in chapter 2.)
Limitations on itemized deductions are suspended for tax years beginning after 2017 and before tax year January 2026, per section 68(g).
Special Rules
This section discusses special rules that apply only to Armed Forces reservists, government officials who are paid on a fee basis, performing artists, and disabled employees with impairment-related work expenses. For tax years beginning after 2017, they are the only taxpayers who can use Form 2106.
Armed Forces Reservists Traveling More Than 100 Miles From Home
If you are a member of a reserve component of the Armed Forces of the United States and you travel more than 100 miles away from home in connection with your performance of services as a member of the reserves, you can deduct your travel expenses as an adjustment to gross income rather than as a miscellaneous itemized deduction. The amount of expenses you can deduct as an adjustment to gross income is limited to the regular federal per diem rate (for lodging and M&IE) and the standard mileage rate (for car expenses) plus any parking fees, ferry fees, and tolls. See Per Diem and Car Allowances , earlier, for more information.
You are a member of a reserve component of the Armed Forces of the United States if you are in the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, Air Force, or Coast Guard Reserve; the Army National Guard of the United States; the Air National Guard of the United States; or the Reserve Corps of the Public Health Service.
If you have reserve-related travel that takes you more than 100 miles from home, you should first complete Form 2106. Then include your expenses for reserve travel over 100 miles from home, up to the federal rate, from Form 2106, line 10, in the total on Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 12.
You can’t deduct expenses of travel that doesn’t take you more than 100 miles from home as an adjustment to gross income.
Certain fee-basis officials can claim their employee business expenses on Form 2106.
Fee-basis officials are persons who are employed by a state or local government and who are paid in whole or in part on a fee basis. They can deduct their business expenses in performing services in that job as an adjustment to gross income rather than as a miscellaneous itemized deduction.
If you are a fee-basis official, include your employee business expenses from Form 2106, line 10, in the total on Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 12.
Expenses of Certain Performing Artists
If you are a performing artist, you may qualify to deduct your employee business expenses as an adjustment to gross income. To qualify, you must meet all of the following requirements.
During the tax year, you perform services in the performing arts as an employee for at least two employers.
You receive at least $200 each from any two of these employers.
Your related performing-arts business expenses are more than 10% of your gross income from the performance of those services.
Your adjusted gross income isn’t more than $16,000 before deducting these business expenses.
If you are married, you must file a joint return unless you lived apart from your spouse at all times during the tax year. If you file a joint return, you must figure requirements (1), (2), and (3) separately for both you and your spouse. However, requirement (4) applies to your and your spouse's combined adjusted gross income.
If you meet all of the above requirements, you should first complete Form 2106. Then you include your performing-arts-related expenses from Form 2106, line 10, in the total on Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 12.
If you don’t meet all of the above requirements, you don’t qualify to deduct your expenses as an adjustment to gross income.
If you are an employee with a physical or mental disability, your impairment-related work expenses aren’t subject to the 2%-of-adjusted-gross-income limit that applies to most other employee business expenses. After you complete Form 2106, enter your impairment-related work expenses from Form 2106, line 10, on Schedule A (Form 1040), line 16, and identify the type and amount of this expense on the line next to line 16.
Impairment-related work expenses are your allowable expenses for attendant care at your workplace and other expenses in connection with your workplace that are necessary for you to be able to work.
You are disabled if you have:
A physical or mental disability (for example, blindness or deafness) that functionally limits your being employed; or
A physical or mental impairment (for example, a sight or hearing impairment) that substantially limits one or more of your major life activities, such as performing manual tasks, walking, speaking, breathing, learning, or working.
You can deduct impairment-related expenses as business expenses if they are:
Necessary for you to do your work satisfactorily;
For goods and services not required or used, other than incidentally, in your personal activities; and
Not specifically covered under other income tax laws.
You are blind. You must use a reader to do your work. You use the reader both during your regular working hours at your place of work and outside your regular working hours away from your place of work. The reader's services are only for your work. You can deduct your expenses for the reader as business expenses.
You are deaf. You must use a sign language interpreter during meetings while you are at work. The interpreter's services are used only for your work. You can deduct your expenses for the interpreter as business expenses.
How To Get Tax Help
If you have questions about a tax issue; need help preparing your tax return; or want to download free publications, forms, or instructions, go to IRS.gov to find resources that can help you right away.
After receiving all your wage and earnings statements (Forms W-2, W-2G, 1099-R, 1099-MISC, 1099-NEC, etc.); unemployment compensation statements (by mail or in a digital format) or other government payment statements (Form 1099-G); and interest, dividend, and retirement statements from banks and investment firms (Forms 1099), you have several options to choose from to prepare and file your tax return. You can prepare the tax return yourself, see if you qualify for free tax preparation, or hire a tax professional to prepare your return.
Your options for preparing and filing your return online or in your local community, if you qualify, include the following.
Free File. This program lets you prepare and file your federal individual income tax return for free using software or Free File Fillable Forms. However, state tax preparation may not be available through Free File. Go to IRS.gov/FreeFile to see if you qualify for free online federal tax preparation, e-filing, and direct deposit or payment options.
VITA. The Volunteer Income Tax Assistance (VITA) program offers free tax help to people with low-to-moderate incomes, persons with disabilities, and limited-English-speaking taxpayers who need help preparing their own tax returns. Go to IRS.gov/VITA , download the free IRS2Go app, or call 800-906-9887 for information on free tax return preparation.
TCE. The Tax Counseling for the Elderly (TCE) program offers free tax help for all taxpayers, particularly those who are 60 years of age and older. TCE volunteers specialize in answering questions about pensions and retirement-related issues unique to seniors. Go to IRS.gov/TCE or download the free IRS2Go app for information on free tax return preparation.
MilTax. Members of the U.S. Armed Forces and qualified veterans may use MilTax, a free tax service offered by the Department of Defense through Military OneSource. For more information, go to MilitaryOneSource ( MilitaryOneSource.mil/MilTax ).
Also, the IRS offers Free Fillable Forms, which can be completed online and then e-filed regardless of income.
Go to IRS.gov/Tools for the following.
The Earned Income Tax Credit Assistant ( IRS.gov/EITCAssistant ) determines if you’re eligible for the earned income credit (EIC).
The Online EIN Application ( IRS.gov/EIN ) helps you get an employer identification number (EIN) at no cost.
The Tax Withholding Estimator ( IRS.gov/W4App ) makes it easier for you to estimate the federal income tax you want your employer to withhold from your paycheck. This is tax withholding. See how your withholding affects your refund, take-home pay, or tax due.
The First Time Homebuyer Credit Account Look-up ( IRS.gov/HomeBuyer ) tool provides information on your repayments and account balance.
The Sales Tax Deduction Calculator ( IRS.gov/SalesTax ) figures the amount you can claim if you itemize deductions on Schedule A (Form 1040).
Go to IRS.gov/Help : A variety of tools to help you get answers to some of the most common tax questions.
Go to IRS.gov/ITA : The Interactive Tax Assistant, a tool that will ask you questions and, based on your input, provide answers on a number of tax topics.
Go to IRS.gov/Forms : Find forms, instructions, and publications. You will find details on the most recent tax changes and interactive links to help you find answers to your questions.
You may also be able to access tax information in your e-filing software.
There are various types of tax return preparers, including enrolled agents, certified public accountants (CPAs), accountants, and many others who don’t have professional credentials. If you choose to have someone prepare your tax return, choose that preparer wisely. A paid tax preparer is:
Primarily responsible for the overall substantive accuracy of your return,
Required to sign the return, and
Required to include their preparer tax identification number (PTIN).
The Social Security Administration (SSA) offers online service at SSA.gov/employer for fast, free, and secure W-2 filing options to CPAs, accountants, enrolled agents, and individuals who process Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement, and Form W-2c, Corrected Wage and Tax Statement.
Go to IRS.gov/SocialMedia to see the various social media tools the IRS uses to share the latest information on tax changes, scam alerts, initiatives, products, and services. At the IRS, privacy and security are our highest priority. We use these tools to share public information with you. Don’t post your social security number (SSN) or other confidential information on social media sites. Always protect your identity when using any social networking site.
The following IRS YouTube channels provide short, informative videos on various tax-related topics in English, Spanish, and ASL.
Youtube.com/irsvideos .
Youtube.com/irsvideosmultilingua .
Youtube.com/irsvideosASL .
The IRS Video portal ( IRSVideos.gov ) contains video and audio presentations for individuals, small businesses, and tax professionals.
You can find information on IRS.gov/MyLanguage if English isn’t your native language.
The IRS is committed to serving taxpayers with limited-English proficiency (LEP) by offering OPI services. The OPI Service is a federally funded program and is available at Taxpayer Assistance Centers (TACs), most IRS offices, and every VITA/TCE tax return site. The OPI Service is accessible in more than 350 languages.
Taxpayers who need information about accessibility services can call 833-690-0598. The Accessibility Helpline can answer questions related to current and future accessibility products and services available in alternative media formats (for example, braille, large print, audio, etc.). The Accessibility Helpline does not have access to your IRS account. For help with tax law, refunds, or account-related issues, go to IRS.gov/LetUsHelp .
Form 9000, Alternative Media Preference, or Form 9000(SP) allows you to elect to receive certain types of written correspondence in the following formats.
Standard Print.
Large Print.
Audio (MP3).
Plain Text File (TXT).
Braille Ready File (BRF).
Go to IRS.gov/DisasterRelief to review the available disaster tax relief.
Go to IRS.gov/Forms to view, download, or print all the forms, instructions, and publications you may need. Or, you can go to IRS.gov/OrderForms to place an order.
Download and view most tax publications and instructions (including the Instructions for Form 1040) on mobile devices as eBooks at IRS.gov/eBooks .
IRS eBooks have been tested using Apple's iBooks for iPad. Our eBooks haven’t been tested on other dedicated eBook readers, and eBook functionality may not operate as intended.
Go to IRS.gov/Account to securely access information about your federal tax account.
View the amount you owe and a breakdown by tax year.
See payment plan details or apply for a new payment plan.
Make a payment or view 5 years of payment history and any pending or scheduled payments.
Access your tax records, including key data from your most recent tax return, and transcripts.
View digital copies of select notices from the IRS.
Approve or reject authorization requests from tax professionals.
View your address on file or manage your communication preferences.
With an online account, you can access a variety of information to help you during the filing season. You can get a transcript, review your most recently filed tax return, and get your adjusted gross income. Create or access your online account at IRS.gov/Account .
This tool lets your tax professional submit an authorization request to access your individual taxpayer IRS online account. For more information, go to IRS.gov/TaxProAccount .
The safest and easiest way to receive a tax refund is to e-file and choose direct deposit, which securely and electronically transfers your refund directly into your financial account. Direct deposit also avoids the possibility that your check could be lost, stolen, destroyed, or returned undeliverable to the IRS. Eight in 10 taxpayers use direct deposit to receive their refunds. If you don’t have a bank account, go to IRS.gov/DirectDeposit for more information on where to find a bank or credit union that can open an account online.
Tax-related identity theft happens when someone steals your personal information to commit tax fraud. Your taxes can be affected if your SSN is used to file a fraudulent return or to claim a refund or credit.
The IRS doesn’t initiate contact with taxpayers by email, text messages (including shortened links), telephone calls, or social media channels to request or verify personal or financial information. This includes requests for personal identification numbers (PINs), passwords, or similar information for credit cards, banks, or other financial accounts.
Go to IRS.gov/IdentityTheft , the IRS Identity Theft Central webpage, for information on identity theft and data security protection for taxpayers, tax professionals, and businesses. If your SSN has been lost or stolen or you suspect you’re a victim of tax-related identity theft, you can learn what steps you should take.
Get an Identity Protection PIN (IP PIN). IP PINs are six-digit numbers assigned to taxpayers to help prevent the misuse of their SSNs on fraudulent federal income tax returns. When you have an IP PIN, it prevents someone else from filing a tax return with your SSN. To learn more, go to IRS.gov/IPPIN .
Go to IRS.gov/Refunds .
Download the official IRS2Go app to your mobile device to check your refund status.
Call the automated refund hotline at 800-829-1954.
Payments of U.S. tax must be remitted to the IRS in U.S. dollars. Digital assets are not accepted. Go to IRS.gov/Payments for information on how to make a payment using any of the following options.
IRS Direct Pay : Pay your individual tax bill or estimated tax payment directly from your checking or savings account at no cost to you.
Debit Card, Credit Card, or Digital Wallet : Choose an approved payment processor to pay online or by phone.
Electronic Funds Withdrawal : Schedule a payment when filing your federal taxes using tax return preparation software or through a tax professional.
Electronic Federal Tax Payment System : Best option for businesses. Enrollment is required.
Check or Money Order : Mail your payment to the address listed on the notice or instructions.
Cash : You may be able to pay your taxes with cash at a participating retail store.
Same-Day Wire : You may be able to do same-day wire from your financial institution. Contact your financial institution for availability, cost, and time frames.
Note. The IRS uses the latest encryption technology to ensure that the electronic payments you make online, by phone, or from a mobile device using the IRS2Go app are safe and secure. Paying electronically is quick, easy, and faster than mailing in a check or money order.
Go to IRS.gov/Payments for more information about your options.
Apply for an online payment agreement ( IRS.gov/OPA ) to meet your tax obligation in monthly installments if you can’t pay your taxes in full today. Once you complete the online process, you will receive immediate notification of whether your agreement has been approved.
Use the Offer in Compromise Pre-Qualifier to see if you can settle your tax debt for less than the full amount you owe. For more information on the Offer in Compromise program, go to IRS.gov/OIC .
Go to IRS.gov/Form1040X for information and updates.
Go to IRS.gov/WMAR to track the status of Form 1040-X amended returns.
Go to IRS.gov/Notices to find additional information about responding to an IRS notice or letter.
You can now upload responses to all notices and letters using the Document Upload Tool. For notices that require additional action, taxpayers will be redirected appropriately on IRS.gov to take further action. To learn more about the tool, go to IRS.gov/Upload .
You can use Schedule LEP (Form 1040), Request for Change in Language Preference, to state a preference to receive notices, letters, or other written communications from the IRS in an alternative language. You may not immediately receive written communications in the requested language. The IRS’s commitment to LEP taxpayers is part of a multi-year timeline that began providing translations in 2023. You will continue to receive communications, including notices and letters, in English until they are translated to your preferred language.
Keep in mind, many questions can be answered on IRS.gov without visiting a TAC. Go to IRS.gov/LetUsHelp for the topics people ask about most. If you still need help, TACs provide tax help when a tax issue can’t be handled online or by phone. All TACs now provide service by appointment, so you’ll know in advance that you can get the service you need without long wait times. Before you visit, go to IRS.gov/TACLocator to find the nearest TAC and to check hours, available services, and appointment options. Or, on the IRS2Go app, under the Stay Connected tab, choose the Contact Us option and click on “Local Offices.”
The Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS) Is Here To Help You
TAS is an independent organization within the IRS that helps taxpayers and protects taxpayer rights. TAS strives to ensure that every taxpayer is treated fairly and that you know and understand your rights under the Taxpayer Bill of Rights .
The Taxpayer Bill of Rights describes 10 basic rights that all taxpayers have when dealing with the IRS. Go to TaxpayerAdvocate.IRS.gov to help you understand what these rights mean to you and how they apply. These are your rights. Know them. Use them.
TAS can help you resolve problems that you can’t resolve with the IRS. And their service is free. If you qualify for their assistance, you will be assigned to one advocate who will work with you throughout the process and will do everything possible to resolve your issue. TAS can help you if:
Your problem is causing financial difficulty for you, your family, or your business;
You face (or your business is facing) an immediate threat of adverse action; or
You’ve tried repeatedly to contact the IRS but no one has responded, or the IRS hasn’t responded by the date promised.
TAS has offices in every state, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico . To find your advocate’s number:
Go to TaxpayerAdvocate.IRS.gov/Contact-Us ;
Download Pub. 1546, The Taxpayer Advocate Service Is Your Voice at the IRS, available at IRS.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p1546.pdf ;
Call the IRS toll free at 800-TAX-FORM (800-829-3676) to order a copy of Pub. 1546;
Check your local directory; or
Call TAS toll free at 877-777-4778.
TAS works to resolve large-scale problems that affect many taxpayers. If you know of one of these broad issues, report it to TAS at IRS.gov/SAMS . Be sure to not include any personal taxpayer information.
LITCs are independent from the IRS and TAS. LITCs represent individuals whose income is below a certain level and who need to resolve tax problems with the IRS. LITCs can represent taxpayers in audits, appeals, and tax collection disputes before the IRS and in court. In addition, LITCs can provide information about taxpayer rights and responsibilities in different languages for individuals who speak English as a second language. Services are offered for free or a small fee. For more information or to find an LITC near you, go to the LITC page at TaxpayerAdvocate.IRS.gov/LITC or see IRS Pub. 4134, Low Income Taxpayer Clinic List , at IRS.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p4134.pdf .
Appendices A-1 through A-6 show the lease inclusion amounts that you may need to report if you first leased a passenger automobile (including a truck and van) in 2018 through 2023 for 30 days or more.
If any of these apply to you, use the appendix for the year you first leased the car. (See Leasing a Car in chapter 4.)

The ABCs of Travel Expense Reimbursement: A Beginner’s Handbook
Traveling for work can be an exciting adventure, but it often comes with a myriad of expenses. Fortunately, many employers offer travel expense reimbursement to ease the financial burden on their employees. In this beginner’s handbook, we’ll explore the world of travel expense reimbursement , understanding its intricacies, and learn about Zaggle EMS which can make the process much smoother.
Understanding Travel Expense Reimbursement
Travel Expense Reimbursement is a process where an employer reimburses an employee for expenses incurred during a business trip. These expenses can include transportation, accommodation, meals, and miscellaneous costs. Employees need to understand what is eligible for reimbursement and how to track and document these expenses properly.
Common Travel Expenses
Let’s break down the common travel expenses into four categories:
A. Transportation Expenses: Transportation expenses can include airfare, train tickets, car rentals, and even parking fees. For instance, a flight from Hyderabad to Mumbai or a taxi ride to the conference venue can fall under this category.
B. Accommodation Expenses: Accommodation expenses cover the costs of staying in hotels, Airbnb rentals, or other lodging options. Whether it’s a five-star hotel in Delhi or a cozy guest house in the city, these expenses are eligible for reimbursement.
C. Meals and Dining Expenses: This category covers the cost of food and dining while on a business trip. It includes breakfast, lunch, dinner, and even snacks. Whether you’re dining at a fancy restaurant or grabbing a quick sandwich on the go, these expenses add up.
D. Miscellaneous Expenses: Miscellaneous expenses can be a bit tricky, as they encompass a wide range of costs, from conference fees and dry cleaning to business calls and internet charges. It’s essential to keep track of these smaller expenses, as they can significantly impact your reimbursement.
Expense Tracking and Documentation
One of the main challenges in the travel expense reimbursement process is proper tracking and documentation. Keeping receipts and organizing expenses can be cumbersome, and paper records are prone to loss or damage.
One of the primary difficulties lies in the proper tracking and documentation of expenses . Keeping physical receipts and records can be cumbersome, leading to potential errors, lost paperwork, or delays in reimbursement. Efficient expense tracking and reporting are key to overcoming these challenges and ensuring a smooth reimbursement process.
This is where digital tools like Zaggle EMS play a crucial role, making the process more efficient and less error-prone.
A. Submitting Expense Reports
With Zaggle EMS, employees can submit expense reports conveniently, reducing paperwork and the risk of errors. Smart Scan, a feature within Zaggle EMS, allows you to create expenses by scanning receipts using OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technology. It’s available through the Zaggle mobile application. You can even attach up to three receipts per expense, making sure you have all the necessary documentation.
B. Reimbursement Process
Zaggle EMS streamlines the reimbursement process by providing a clear and structured platform for both employees and employers. It categorizes expenses, making it easier for organizations to understand where their money is going.
C. Approval Process
The approval process is a crucial step in the travel expense reimbursement journey, ensuring that expenses are legitimate and comply with company policies
Zaggle EMS allows you to establish a hierarchical or multi-stage approval flow to ensure expenses are reviewed by the right people in the organization. In Zaggle EMS, you can configure up to 5 levels of approval in your workflow. This flexibility accommodates the unique approval structures within various organizations, from small businesses to large enterprises.
The approval process is critical to maintaining financial responsibility within an organization and adhering to established policies. By configuring hierarchical approval flows, organizations can ensure that expense reports undergo the necessary scrutiny. Moreover, the flexibility in the number of approval levels and the ability to resubmit and approve rejected reports streamline the process, making travel expense reimbursement a transparent and accountable process for both employees and employers.
Tips for a Smooth Reimbursement Process
1. Stay Organized: Keep all your receipts in one place. Using digital tools like Zaggle EMS can help you store and organize them efficiently.
2. Submit Promptly: Don’t procrastinate in submitting your expense reports. The sooner you do, the quicker you’ll get reimbursed.
3. Know Your Company’s Policy : Familiarize yourself with your company’s reimbursement policy. Some expenses may have specific limits or requirements.
4. Double-check: Before submitting an expense report, double-check all the information. Accuracy is crucial to avoid any delays.
Travel expense reimbursement doesn’t have to be a daunting process. With the right knowledge and tools, such as Zaggle EMS , you can simplify the task of tracking, documenting, and reporting your expenses. By understanding the ABCs of travel expense reimbursement , you can make your business trips financially stress-free and focus on the work at hand. Remember, the key to a smooth reimbursement process is organization and the use of efficient digital tools. Safe travels!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Zaggle Save
- Zaggle Propel
- Zaggle Edge
- Zaggle Zoyer
- Manage Cards
- Gift Cards Deals
- Partner with Us
Information
- Grievance Policy
- Refund Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Investor Relations
Download Zaggle App
© Zaggle 2023 | All rights reserved.
Ready to simplify your receipt and expense management process?
Enter your email to sign up for Expensify today!
Travel Expense Reimbursement
Travel expense reimbursement - what to know.
Going on a business trip may sound fancy, but the fun only lasts so long until you’re faced with the reimbursement of travel expenses. It doesn’t have to cause a headache, though.
With Expensify Travel, the travel expense reimbursement process is simplified and enhanced. It’s available for free for those who have an Expensify plan. And if you have the Expensify Visa® Commercial Card , our travel management system helps you seamlessly track all your business travel expenses.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know so you can focus on your business trip instead of submitting and collecting receipts.
What is travel expense reimbursement?
Travel expense reimbursement is the compensation process for employees who incur out-of-pocket expenses during business travel. Now, what are travel expenses? They include accommodation, transportation, meals, and other miscellaneous expenses related to business travel.
In the corporate world, reimbursing travel expenses promotes fairness, talent retention, and accurate financial reporting. Essentially, it recognizes that employee travel expenses should be reimbursed timely.
Make travel simple with Expensify
Enter your email or phone number below to get started.

Simplify travel expense reimbursement with Expensify
Expensify seamlessly simplifies the travel reimbursement process and expense management on the go. Employees can quickly request reimbursement, and employers can easily review and reimburse these expenses.
The following features make business travel expenses reimbursement as easy as 1, 2, 3:
Receipt scanning
With Expensify’s receipt scanning app, the analog way of receipt tracking is a thing of the past. Say goodbye to hanging on to those annoying little pieces of paper, which take up too much wallet space, and streamline the travel expense reimbursement process by simply taking a picture with your phone. Snap a photo of a receipt, submit your expense report when you’re back, and get paid stat!
Mileage tracking
If you’re using your car or renting a ride for your business trip, mileage tracking is another crucial thing to track. Rather than trying to track things in your phone’s note app or penciling in some miles on your dollar store notepad, just use Expensify to record mileage while traveling. Plus, Expensify stays up-to-date with the IRS mileage rate, so you don’t have to.
Spending limits
Want to ensure you’re never surprised by your employees’ final travel expense reimbursement request? With the Expensify Card, you can set Smart Limits. These limits let you set a cap for expenses beforehand, allowing the cardholder to spend up to the amount you’ve set before you approve them for more.
Corporate card reconciliation
Reconcile accounts without breaking a sweat by using the Expensify Corporate Card. With each swipe of a corporate card, a transaction is imported into Expensify, letting your top salesperson focus on closing the deal while having dinner with a client instead of worrying about getting a copy of the receipt. If your company is already using a corporate card they love, no worries - our credit card import feature works with several other bank cards.
Travel expense reimbursement form
When you return to the office after a business trip, filling out a travel expense reimbursement form is probably your last priority. But it’s necessary to get paid. Some companies have their internal process and forms for this, while others don’t have a standard.
If your company doesn’t have a template for travel expense reimbursement, a quick Google search will yield plenty of options to help you get reimbursed ASAP. But why not make things easy on yourself?
Expensify is the ultimate travel expense reimbursement software. It allows employees to submit expense reports in a snap to their admin and enables admins to take them from there based on the company’s processes.
Employee travel expense reimbursement guidelines
Clear travel expense reimbursement guidelines for all company staff are essential. Employees should be appropriately compensated for their business-related travel expenses.
Good guidelines typically outline the steps employees must follow to claim the categories of expenses eligible for reimbursement. When these guidelines are easy to understand and transparent, it is easier for managers to enforce them, ensuring all necessary documents are submitted and the proper steps have been taken.
Of course, having travel expense reimbursement software like Expensify takes the guesswork out of company policies for business-related travel expenses, ensuring happy team members from sales to accounting and beyond.
Common questions about travel expense reimbursement
What are the irs rules about employee travel reimbursement.
The IRS (Internal Revenue Service) has specific rules regarding employee travel reimbursement. Employers can offer employees travel reimbursement for business-related expenses, such as transportation, lodging, meals, and other incidental costs incurred while on travel for work purposes.
Note that expenses must be considered ordinary and necessary for the employee's job. If the reimbursement meets the requirements specified by the IRS , it is generally tax-free for the employee. Cha-ching! It’s recommended that employees maintain records such as receipts, invoices, and travel itineraries to be reimbursed.
Whether you’re an employee or an employer, review the specific rules and guidelines the IRS provides to stay compliant.
How do you request reimbursement for travel expenses?
It’s pretty simple to request to be reimbursed for your business travel expenses. Follow these steps to make sure you get your money back:
Gather all documentation related to your business travel (flights, accommodation, meals, transport, etc.)
Complete a reimbursement form (if provided by your employer or organization) or write a travel expense reimbursement letter.
Submit your documentation and form to the department that handles reimbursements.
And if you have an Expensify plan or the Expensify Corporate Card , you can skip the paperwork and let the app do all the work for you.
What is the travel reimbursement policy for 2024?
Regarding travel reimbursement policies, every company has its budget for business travel allowances for the year. So, check out your company or organization’s policies to understand what’s allowed and what's not.
Most companies follow standards set by the IRS, but it’s always good to read up on the rules yourself to stay on top of things. Remember to keep track of any documentation from your business trip and track your mileage if you're responsible for driving during your trip.
Can a company refuse to reimburse travel expenses?
As with almost anything, a company can refuse to reimburse travel expenses. This is usually because of an organization’s policies or guidelines. For example, if your expenses fall outside of specified limits, you don’t have the proper documentation, or a company policy has been violated, your request may be rejected.
Are reimbursed expenses considered income?
Generally speaking, travel expense reimbursement is not considered income for individuals. This protects employees from having an extra tax burden for doing their job. Of course, ensure you have followed the proper steps to request reimbursement and keep copies for yourself, just in case.
Reimbursing travel expenses has never been easier
Travel expense reimbursement is the last thing you want to deal with after a business trip. So, reduce the extra work and use Expensify to track your expenses correctly.
From helping you keep track of mileage, scanning receipts, or setting spending limits, Expensify is here to make reimbursing travel expenses a breeze so you can focus on more critical business matters.
- Expense Management
- Spend Management
- Expense Reports
- Company Card
- Receipt Scanning App
- ExpensifyApproved!
- ExpensifyHelp
- Expensify App
- About Expensify
- Expensify.org
- Investor Relations
Get Started
- Create a new account
©2008-2023 Expensify, Inc.
The Expensify Visa® Commercial Card is issued by The Bancorp Bank, N.A. pursuant to a license from Visa U.S.A. Inc. and may not be used at all merchants that accept Visa cards. Apple® and the Apple logo® are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc. Google Play and the Google Play logo are trademarks of Google LLC.
Money transmission is provided by Expensify Payments LLC (NMLS ID:2017010) pursuant to its licenses .
- Accounts Payable Software
- Accounts Receivable Software
- Travel & Expense Management
- Payment Automation
- Cash Flow Management
- Account Payable
- Account Receivable
- Travel & Expense
- Finance News
- Press Release
- Get Started
The Complete Guide to Travel and Expense Management (T&E)
Managing travel and expenses for your company can be a complex task, requiring careful attention to detail and adherence to company policies. As your business grows, so does the need for effective travel and expense management. From ensuring compliance with policy guidelines to optimizing costs, there are many factors to consider to make the process smoother for everyone involved.
In this blog post, we will explore the fundamentals of travel and expense management, offering insights into best practices that can help streamline the process. Whether you’re a small business with a handful of travelers or a large corporation with a global workforce, understanding the basics of travel and expense management is essential for maintaining control over your travel costs and ensuring compliance with your company’s policies.
What is Travel and Expense Management?
Travel and Expense Management (T&E) is the process of overseeing and controlling an organization’s spending on business-related travel and expenses. It involves documenting, processing, and monitoring the expenses to ensure they are in line with company policies and tax regulations.
T&E management includes various tasks such as booking travel arrangements, managing expenses, and ensuring compliance with corporate policies and legal requirements. The goal of travel and expense management is to optimize spending, improve efficiency, and maintain transparency in business expenses.
Key components of travel and expense management include:
- Approving travel requests
- Booking travel arrangements (such as flights and hotels)
- Managing corporate credit cards
- Submitting and approving expense claims
- Handling reimbursement
- Auditing expenses for compliance
- Guiding travel policies to employees
T&E management helps organizations save money, time, and resources by providing visibility into spending patterns and ensuring that employees only spend money on necessary expenses during business trips. It plays a crucial role in maintaining accurate financial records and ensuring compliance with tax regulations .
What is the Travel & Expense Policy?
A travel and expense policy is a set of guidelines and rules established by a company to regulate how employees spend company funds on business trips and related expenses.
These policies typically cover various aspects of travel and expenses, including:
- How and where to book travel
- Criteria for approving or rejecting travel itineraries
- Expense reimbursement process
- Guidelines for flights, trains, and class accommodations
- Approved hotels and allowable incidental expenses
- Ground transportation guidelines
- Meal allowances
T&E policies are designed to ensure that employees understand the company’s expectations regarding travel and expenses and to provide clarity and consistency in how these expenses are managed and reimbursed. They help companies control costs, ensure compliance with regulations, and provide employees with clear guidelines for managing expenses while traveling for business.
Why is Travel and Expense Management Important?
Travel and expense management is essential for controlling costs, ensuring compliance, optimizing processes, and enhancing employee satisfaction. Implementing an effective travel and expense management process can lead to significant cost savings and operational efficiencies for businesses of all sizes. Let’s take a look at the importance of T&E management:
- Cost Control: Effective management of travel and expenses helps control costs by ensuring that expenditures are in line with budgets and company policies. It allows businesses to identify areas of overspending and implement measures to reduce unnecessary expenses.
- Compliance: Compliance with company policies and regulatory requirements is crucial. A proper travel and expense management process helps ensure that expenses are incurred for legitimate business purposes and comply with tax regulations , reducing the risk of audits and penalties.
- Visibility and Reporting: A centralized process provides visibility into travel and expense data, allowing businesses to track spending, analyze trends, and generate reports. This visibility helps in making informed decisions and optimizing travel budgets.
- Streamlined Processes: Managing travel and expenses manually can be time-consuming and prone to errors. An automated system streamlines processes, reducing administrative burden, and improving efficiency.
- Policy Enforcement: A robust travel and expense management system helps enforce company policies related to travel and expenses. It ensures that employees adhere to guidelines regarding travel bookings, expense submissions, and reimbursement , promoting accountability and compliance.
- Employee Satisfaction: A well-managed travel and expense process can enhance employee satisfaction by providing a smooth and timely reimbursement process. It also ensures that employees are aware of the company’s travel policies and procedures, reducing confusion and frustration.
What are the Stages of Travel and Expense Management?
Here is a breakdown of the eight different stages of travel and expense management:
1. Developing an Expense Policy
Develop a comprehensive expense policy that covers all aspects of travel and expense management. Specify allowable expenses, limits, and procedures for requesting funds, making authorized transactions, submitting expense reports, and receiving reimbursements. Include clear guidelines for travel-related expenses to ensure consistency and compliance.
2. Streamlining Pre-Travel Processes
Use travel and expense management automation platforms to simplify the pre-travel process. These platforms enable employees to submit travel requests, which are then routed to managers for approval. Managers can quickly review and approve requests, and employees can book their travel directly through the platform, ensuring all bookings are recorded and tracked efficiently.
3. Managing Expense Incurrence
During business trips, employees will incur various expenses, such as meals, transportation, and accommodation. Companies can provide employees with cash advances, and corporate credit cards, or require them to pay out of pocket and submit expense reports for reimbursement. Clear communication and guidelines are essential to ensure employees understand the process and comply with company policies.
4. Efficient Receipt Handling
Managing receipts is a crucial aspect of expense management. Traditionally, employees would need to keep track of paper receipts and submit them along with their expense reports. However, digital solutions offer a more convenient option. Employees can use mobile apps to capture and upload receipts, which are then stored securely in the cloud. Some platforms even offer OCR capabilities, automatically extracting relevant information from receipts and eliminating manual data entry.
5. Standardizing Expense Reporting
Standardize the expense reporting process to ensure consistency and accuracy. Provide employees with easy-to-use tools, such as mobile apps or web-based forms, to submit their expense reports. Include prompts for required information, such as date, amount, and purpose of the expense, to streamline the reporting process and minimize errors.
6. Implementing an Approval Process
Implement a clear and efficient approval process for expense claims. Use expense management software to automate the workflow, allowing managers to review and approve claims quickly. Ensure that all claims are reviewed for compliance with company policies before approval to prevent unauthorized expenses.
7. Ensuring Prompt Reimbursement
Prompt reimbursement of expenses is essential to maintain employee satisfaction. Once expense claims are approved, ensure that reimbursements are processed promptly. Consider using direct deposit or other electronic payment methods to expedite the reimbursement process and reduce administrative burden.
8. Conducting Compliance Audits
Regularly audit expense reports to ensure compliance with company policies and regulations. Look for any anomalies or discrepancies that may indicate fraudulent activity. Conducting regular audits helps maintain the integrity of the expense management process and identifies areas for improvement.
What are the Challenges of Travel and Expense Management?
Managing travel and expenses poses several challenges for organizations, ranging from tracking and controlling costs to ensuring policy compliance. These challenges can impact financial health, employee satisfaction, and operational efficiency. Understanding these challenges is crucial for implementing effective solutions. Here are some common challenges of travel and expense management:
1. Trouble with Policy Compliance
A common challenge in managing travel and expenses is the lack of enforcement of policies. This often occurs due to unclear policies. When policies are ambiguous, employees may spend without regard to guidelines, leading to uncontrolled expenses and budget strain.
As businesses grow, ensuring compliance becomes more challenging. Unauthorized bookings and other policy breaches can occur due to various reasons, such as lack of awareness or attempts at internal fraud.
2. Lack of Data Management
Even with enforced expense reporting within your travel and expense management policy, there’s always a risk of misplacing receipts and losing travel documents. Ensuring comprehensive tracking of every expense can be challenging, especially when employees have to hold onto receipts until they return home to submit them.
3. Limited Visibility into Spends
One of the significant challenges in travel expense management is the lack of visibility into spending. This often occurs due to ineffective tracking of employee expenditures. Without clear visibility, it becomes challenging to control costs effectively.
While some savings might be possible, a comprehensive understanding of spending or potential savings opportunities remains unclear. Delayed submission of expense reports further complicates the situation, as neither managers nor travelers can accurately assess whether expenses align with budgetary constraints.
4. Unclear Expense Policies
Corporate travel and expense management involve many considerations, making it easy to overlook aspects when creating your expense policy. This can create confusion and ambiguity, leading to a lack of clarity for employees.
5. Complicated Expense Workflows
Managing business travel expenses often involves navigating complex workflows. Obtaining approvals from multiple stakeholders can be time-consuming, especially when quick payments are needed. Additionally, the process of filing expense reports after a trip can involve many complex steps.
6. Labor-Intensive Manual Processes and Paperwork
Many businesses use manual processes, such as spreadsheets, to track their expenses. While this may seem efficient initially, it becomes difficult to manage as the business grows. Manually inputting data into spreadsheets is time-consuming and prone to errors.
Without automation, your team will spend a lot of time on manual data entry and paperwork. It includes collecting and storing receipts, as well as entering each transaction from business trips into spreadsheets. These tasks can decrease productivity and lead to inefficiencies.
7. Expense Fraud
Expense fraud can pose a significant threat to your company’s finances, as employees may misuse company funds by submitting false expenses or using them for personal trips. To prevent such fraud, organizations must implement measures to detect and prevent fraudulent activities.
Expense fraud can take various forms, including internal fraud where employees intentionally make unauthorized transactions, or external fraud where criminals steal company funds. Not enforcing travel and expense policies or carefully controlling spending can lead to multiple fraud attempts, some of which may go unnoticed.
8. Difficulty Managing Multi-Currency Expenses
Business travel can involve transactions in different currencies, which can be complex. Managing expenses in foreign currencies requires decisions on when to convert rates, such as at the time of purchase or reimbursement.
9. Challenges with Filing Expense Reports
Filing expense reports manually can be time-consuming and tedious. Employees often find it challenging to keep track of receipts and complete the paperwork accurately and promptly. This manual process can lead to delays in reimbursement and create a frustrating experience for employees.
10. Dealing with Reimbursements
Managing reimbursements for employee travel expenses can be challenging. Without an efficient system in place, employees may experience delays in receiving their reimbursement checks, leading to frustration and dissatisfaction. Delayed reimbursements can also impact employee morale and may create financial burdens for employees who rely on timely reimbursements.
Best Practices for Travel and Expense Management
Effective travel and expense management is crucial for organizations to control costs, ensure policy compliance, and streamline processes. Here are some best practices to improve your travel and expense management:
1. Enhance Spend Visibility
Utilizing automated travel expense software and mobile tracking apps allows companies to gain real-time insights into their spending. These tools provide detailed reports on expenses, highlighting areas where costs can be optimized. By having a 360-degree view of expenses, businesses can make informed decisions, identify trends, and ensure compliance with policies. Additionally, these tools can help detect any unauthorized or non-compliant spending, allowing for prompt action to be taken. Overall, enhanced spending visibility leads to better financial management and cost control.
2. Prioritize Employee Experience
Improving the travel experience for employees can lead to higher compliance with travel policies. Offering self-booking tools and user-friendly interfaces can make the travel booking process more efficient and enjoyable for employees. This can result in higher employee satisfaction and increased productivity. By prioritizing employee experience, companies can create a positive work environment and improve overall employee morale.
3. Offer Convenient Payment Options
Providing corporate credit cards to employees for business expenses can streamline the payment process and eliminate the need for employees to use personal funds. It can reduce the administrative burden associated with expense reimbursement and ensure that employees are not out of pocket for business expenses. Alternatively, engaging a travel management company can simplify the payment process by consolidating all travel expenses into a single invoice, making it easier to track and manage expenses.
4. Embrace Paperless Processes
Digitizing expense filing and reimbursement procedures can significantly reduce the time and effort required to process expenses. By eliminating paperwork, companies can streamline their expense management processes, reduce the risk of errors, and improve efficiency. Additionally, digital processes can provide greater transparency and visibility into expenses, making it easier for companies to track and monitor spending. Overall, embracing paperless processes can lead to cost savings and improved productivity.
5. Optimize Approval Workflows
Designing workflows that facilitate quick approval for essential expenses can expedite the expense approval process. By setting up auto-approval for certain spending categories, companies can reduce the time and effort required to process expenses. This can lead to faster reimbursement for employees and improved cash flow for the company. Additionally, optimizing approval workflows can help prevent delays and bottlenecks in the approval process, ensuring that expenses are approved on time.
6. Utilize Travel Expense Policy Templates
Using pre-designed policy templates simplifies the creation of travel expense policies. These templates are often customizable, allowing companies to tailor them to their specific needs and requirements. By using templates, companies can save time and effort in developing policies from scratch. Additionally, templates ensure that policies are comprehensive and cover all necessary aspects of travel expenses. This helps to reduce the risk of misunderstandings and ensures that employees are aware of and comply with the company’s policies.
7. Implement a Paperless Policy
Integrating the travel and expense policy into digital tools makes it easily accessible to employees. This eliminates the need for physical documents, reducing paper waste and simplifying document management. A paperless policy also allows for real-time updates and changes to the policy, ensuring that employees always have access to the most up-to-date information. Additionally, a digital policy can be easily distributed to employees, ensuring that everyone is aware of and understands the policy.
8. Regularly Update Your Policy
Keeping the travel and expense policy current reflects changes in business needs and employee behaviors. Regular updates ensure that the policy remains relevant and effective in managing expenses. This helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures that employees are aware of any changes to the policy. Regular updates also demonstrate a commitment to compliance and best practices in travel and expense management.
Closing Thoughts
Implementing best practices for travel and expense management is essential for organizations to achieve greater efficiency, compliance, and cost control. By enhancing spend visibility, prioritizing employee experience, offering convenient payment options, embracing paperless processes, and optimizing approval workflows, businesses can streamline their travel and expense processes and drive better outcomes.
At Peakflo, we understand the importance of effective travel and expense management. Our Travel and Expense solution is designed to simplify and streamline the entire process. With Peakflo’s intuitive software, organizations can automate expense tracking, simplify reimbursement processes, and gain real-time insights into spending patterns. By leveraging our solution, businesses can optimize their travel and expense management, reduce administrative burden, and ensure compliance with policies, ultimately driving greater efficiency and cost savings.
Understanding Expense Claim: The Ultimate Guide
The ultimate guide to business travel process, what is per diem expense & how is per diem rate calculated, latest post, tesco accounting scandal: overstating profits by £326 million, barclays capital lost millions due to an excel error, ditching legacy systems: the key to a sustainable finance landscape, split payment: streamlining transactions for marketplaces, future-proofing b2b payments: the payment automation handbook.
- Accounts Payable
- Accounts Receivable
- Travel and Expense Management
- B2B Payment Software
- Invoice Management
- Procurement Software
- Product Tour
- Saving Calculator
© 2023 by Peakflo. All rights reserved.
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance
- Book a Speaker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Vivamus convallis sem tellus, vitae egestas felis vestibule ut.
Error message details.
Reuse Permissions
Request permission to republish or redistribute SHRM content and materials.
Travel Expense Policy
It is the policy of [Company Name] to reimburse staff for reasonable and necessary expenses incurred during approved work-related travel.
Employees seeking reimbursement should incur the lowest reasonable travel expenses and exercise care to avoid impropriety or the appearance of impropriety. Reimbursement is allowed only when reimbursement has not been, and will not be, received from other sources. If a circumstance arises that is not specifically covered in this travel policy, then the most conservative course of action should be taken.
Business travel policies are aligned with company reimbursement rules. All business-related travel paid with [Company Name] funds must comply with company expenditure policies.
Authorization and responsibility
Staff travel must be authorized. Travelers should verify that planned travel is eligible for reimbursement before making travel arrangements. Within 30 days of completion of a trip, the traveler must submit a travel reimbursement form and supporting documentation to obtain reimbursement of expenses.
An individual may not approve his or her own travel or reimbursement. The travel reimbursement form must be signed by the executive director or the director of finance (for travel over $[amount]) or by the business manager (for travel under $[amount]).
Travel and reimbursement for members of the management team must be approved by the executive director or the director of finance and will be reviewed annually by the internal auditor.
Designated approval authorities are required to review expenditures and withhold reimbursement if there is reason to believe that the expenditures are inappropriate or extravagant.
Personal funds
Travelers should review reimbursement guidelines before spending personal funds for business travel to determine if such expenses are reimbursable. See Section II: Travel Expenses/Procedures for details. [Company Name] reserves the right to deny reimbursement of travel-related expenses for failure to comply with policies and procedures.
Travelers who use personal funds to facilitate travel arrangements will not be reimbursed until after the trip occurs and proper documentation is submitted.
Vacation in conjunction with business travel
In cases in which vacation time is added to a business trip, any cost variance in airfare, car rental or lodging must be clearly identified on the travel request form. [Company Name] will not prepay any personal expenses with the intention of being "repaid" at a later time, nor will any personal expenses be reimbursed.
Occasionally it may be necessary for travelers to request exceptions to this travel policy. Requests for exceptions to the policy must be made in writing and approved by the executive director or by the director of finance. Exceptions related to the director's or the director of finance's expenses must be submitted to the opposite person or to the treasurer of the board of trustees for approval. In most instances, the expected turnaround time for review and approval is five business days.
Travel Expenses/Procedures
General information Authorized business travel for staff that includes prepayments must be pre-approved.
Reimbursement of parking, mileage, gasoline in lieu of mileage and ferry or bus passes do not require requests if they are under $[amount]. Requests for reimbursement of expenses over $[amount] are to be submitted on a travel reimbursement form.
Permissible prepaid travel expenses Before the travel, [Company Name] may issue prepayments for airfare, rail transportation, rental vehicles, conference registration fees and cash advances. Applicable policies and methods of payments for these prepayments follow.
Airfare. Travelers are expected to obtain the lowest available airfare that reasonably meets business travel needs. Airfare may be prepaid by the business office.
Travelers are encouraged to book flights at least [amount of time] in advance to avoid premium airfare pricing.
Coach class or economy tickets must be purchased for domestic or international flights with flight time totaling less than five consecutive hours excluding layovers.
A less-than-first-class ticket (i.e., business class) may be purchased at [Company Name]'s discretion for domestic or international flights with flight time exceeding five consecutive hours excluding layovers.
Airfare may be purchased with a credit card or check through the business office with a request for payment form.
Rail transportation. [Company Name] will prepay rail transportation provided that the cost does not exceed the cost of the least expensive airfare.
Rental vehicles. [Company Name] will pay for approved use of a rental vehicle. See the section on reimbursements below in this section.
Conference registration fees. Conference registration fees can be prepaid with a credit card or check through the business office with a request for payment form. Business-related banquets or meals that are considered part of the conference can be paid with the registration fees; however, such meals must be deducted from the traveler's per diem allowance.
Travel advances. Cash advances are authorized for specific situations that might cause undue financial hardship for business travelers. These situations are limited to staff traveling on behalf of [Company Name]. A maximum of 80 percent of the total estimated cost can be advanced.
Expenses associated with the travel must be reconciled and substantiated within two weeks of the return date. The traveler must repay [Company Name] for any advances in excess of the approved reimbursable expenses. The department initiating the travel is responsible for notifying the business office to deposit any excess funds into the appropriate departmental account.
Travel advances are processed by submitting a completed request for payment form and travel request form to the business office. Reimbursement for any remaining expenses is processed on a travel reimbursement form approved by the designated approval authority.
Reimbursements Requests for reimbursements of travel-related expenses are submitted on a travel reimbursement form. This form must be accompanied by supporting documentation. If the requested reimbursement exceeds 20 percent of the total pre-trip estimate, the travel reimbursement form must be signed by the executive director or the director of finance.
These forms must be submitted to the business office within two weeks after the trip is completed. Travel reimbursement forms not submitted within this time frame require exception approval from the executive director or from the director of finance.
Reimbursement of travel expenses is based on documentation of reasonable and actual expenses supported by the original, itemized receipts where required. Reimbursements that may be paid by [Company Name] are shown below.
Airfare. If the airfare was not prepaid by the business office, an original itemized airline receipt, an e-ticket receipt/statement or an Internet receipt/statement is required. The receipt must show the method of payment and indicate that payment was made.
Rail transportation. If rail transportation was not prepaid by the business office, an original itemized receipt, original e-ticket receipt/statement or Internet receipt/statement is required. The receipt must show the method of payment and indicate that payment was made.
Automobile (personally owned—domestic travel). A valid driver's license issued within the United States and personal automobile insurance are required for expenses to be reimbursed. Drivers should be aware of the extent of coverage (if any) provided by his or her automobile insurance company for travel that is business or not personal in nature.
Reimbursement for use of a personal automobile is based on the [Company Name] mileage rate.
A staff travel reimbursement form is required for reimbursement of all vehicle-related expenses, including gasoline, wear and tear, and personal auto insurance. As of [date], the rate is [$] per mile. Travelers may opt to request reimbursement for actual gasoline expenses in lieu of the [Company Name] mileage rate. In these instances original, itemized receipts are required.
Automobile (rental—domestic travel). Reimbursement for a commercial rental vehicle as a primary mode of transportation is authorized only if the rental vehicle is more economical than any other type of public transportation, or if the destination is not otherwise accessible. Vehicle rental at a destination city is reimbursable. Original receipts are required.
[Company Name] authorizes reimbursement for the most economic vehicle available. In certain circumstances larger vehicles may be rented, with supervisory approval. The rental agreement must clearly show the date and the points of departure/arrival, as well as the total cost. Drivers must adhere to the rental requirements, and restrictions must be followed. Original receipts are required.
When vehicle rentals are necessary, [Company Name] encourages travelers to purchase collision damage waiver (CDW) and loss damage waiver (LDW) coverage. [Company Name] will reimburse the cost of CDW and LDW coverage; all other insurance reimbursements will be denied.
Drivers should be aware of the extent of coverage (if any) provided by his or her automobile insurance company for travel that is business or not personal in nature.
Parking fees, tolls and other incidental costs associated with the vehicle use are not covered by the rental agreement.
Travelers are strongly encouraged to fill the gas tank before returning the vehicle to the rental agency to avoid service fees and more expensive fuel rates.
Conference registration fees. If the conference fee was not prepaid, [Company Name] will reimburse these fees, including business-related banquets or meals that are part of the conference registration. Original receipts to support the payment are required. If the conference does not provide a receipt, then a cancelled check, credit card slip/statement or documentation that the amount was paid is required for reimbursement.
A prorated amount for the meals provided must be deducted from the traveler's per diem. See Meals (per diem) for more detail. Entertainment activities such as golf outings and sightseeing tours will not be reimbursed.
Registration fees paid directly by an individual will not be reimbursed until the conference is completed.
Lodging (commercial). The cost of overnight lodging (room rate and tax only) will be reimbursed to the traveler if the authorized travel is 45 miles or more from the traveler's home or primary worksite.
Exceptions to this restriction may be approved in writing by the executive director or by the director of finance.
[Company Name] will reimburse lodging expenses at reasonable, single occupancy or standard business room rates. When the hotel or motel is the conference or convention site, reimbursement will be limited to the conference rate.
Only single room rates are authorized for payment or reimbursement unless the second party is representing the agency in an authorized capacity. If the lodging receipt shows more than a single occupancy, the single room rate must be noted. If reimbursement for more than the single room rate is requested, the name of the second person must be included.
Meals (per diem). Per diem allowances are reimbursable for in-state overnight travel that is 45 miles or more from the traveler's home or primary worksite.
Per diem allowances are applicable for all out-of-state travel that is 45 miles or more from the traveler's home or primary worksite.
[Company Name] per diem rates are based on the U.S. General Services Administration Guidelines, which vary by city location. In addition to meals these rates include incidental expenses such as laundry, dry cleaning and service tips (e.g., housekeeping or porter tips). Incidental expenses, unless specifically cited in this policy, will not be reimbursed.
Per diem reimbursements are based on departure and return times over the entire 24-hour day and are prorated accordingly.
If a free meal is served on the plane, included in a conference registration fee, built in to the standard, single hotel room rate or replaced by a legitimate business meal, the per diem allowance for that meal may not be claimed.
Receipts are not required for per diem allowances. Per diem allowances are reimbursed after the trip is completed.
Business meals. Travelers are required to follow [Company Name] expenditure policies when requesting reimbursement for business meals. Original itemized receipts are required.
Business expenses. Business expenses, including faxes, photocopies, Internet charges, data ports and business telephone calls incurred while on travel status, can be reimbursed. Original itemized receipts are required.
Parking. Original receipts are required for parking fees (including airport parking) totaling $[amount] or more. The lodging bill can be used as a receipt when charges are included as part of the overnight stay.
Telephone calls. The costs of personal telephone calls are the responsibility of the individual.
Tolls. Original receipts are required for tolls totaling $[amount] or more.
Miscellaneous transportation. Original receipts are required for taxi, bus, subway, metro, ferry and other modes of transportation if costs are $[amount] or more for each occurrence.
Visa, passport fees and immunizations. If these items are required for international travel, their reimbursement is left to the discretion of your supervisor. If approved by the designated authority, original itemized receipts are required.
Nonreimbursable Travel Expenses The following items that may be associated with business travel will not be reimbursed by [Company Name]:
- Airline club memberships.
- Airline upgrades.
- Business class for domestic flights or first class for all flights.
- Child care, babysitting, house-sitting, or pet-sitting/kennel charges.
- Commuting between home and the primary work location.
- Costs incurred by traveler's failure to cancel travel or hotel reservations in a timely fashion.
- Evening or formal wear expenses.
- Haircuts and personal grooming.
- Laundry and dry cleaning.
- Passports, vaccinations and visas when not required as a specific and necessary condition of the travel assignment.
- Personal entertainment expenses, including in-flight movies, headsets, health club facilities, hotel pay-per-view movies, in-theater movies, social activities and related incidental costs.
- Travel accident insurance premiums or purchase of additional travel insurance.
- Other expenses not directly related to the business travel.
Travel for Non-Employees Additional costs for travel, lodging, meal or other travel expenses for spouses or other family members will not be reimbursed unless the individual has a bona fide company purpose for engaging in the travel or attending the event. Such travel is generally limited to senior management and should occur infrequently.
Related Content

A 4-Day Workweek? AI-Fueled Efficiencies Could Make It Happen
The proliferation of artificial intelligence in the workplace, and the ensuing expected increase in productivity and efficiency, could help usher in the four-day workweek, some experts predict.

How One Company Uses Digital Tools to Boost Employee Well-Being
Learn how Marsh McLennan successfully boosts staff well-being with digital tools, improving productivity and work satisfaction for more than 20,000 employees.
Advertisement
Artificial Intelligence in the Workplace
An organization run by AI is not a futuristic concept. Such technology is already a part of many workplaces and will continue to shape the labor market and HR. Here's how employers and employees can successfully manage generative AI and other AI-powered systems.
HR Daily Newsletter
New, trends and analysis, as well as breaking news alerts, to help HR professionals do their jobs better each business day.
Success title
Success caption
Sample Emails for Reimbursement of Travel Expenses for Interview
Sometimes companies offer and pay travel expenses to the candidates who attend the interview. But the terms and conditions will be mentioned in the interview call letter. So before opting for going to the interview make sure to read all the terms related to travel expenses.
Whether you are selected or not selected for the job is not a matter, whenever the recruiters promise you that they will reimburse the travel expenses then they have to make the reimbursement for all the eligible travel expenses.
To claim the travel expenses you need to keep all the tickets, hotel bills, and lodging bills. Here you can find some sample email formats to request travel expenses for attending the job interview
How to Ask for Travel Reimbursement for an Interview
- Address the right person from whom you got the interview call letter. In most cases, company HRs will send those emails.
- Mention the subject line as “ Regarding reimbursement of travel expenses ”
- Write your name, date of interview, position for which you interviewed, and place of the interview.
- Attach all the required bill copies like travel bills, lodging bills, and hotel bills.
- And it is better to mention the details of travel expenses in the email.
- End the letter with thinking you note.
Sample Reimbursement Emails for Travel Expenses for Interview
Sub: Request for travel expense reimbursement.
Dear Sir/Madam,
My name is ____________(your name), attended interview on ___________(date of interview) for the position of ___________(job position) at _____________________(company name & location).
I was glad to attend the interview in an esteemed organization like yours.
As per the interview call letter you offered me to claim the travel expenses, the same you have already said after the interview.
Here I am claiming my travel expenses and attaching all the required copies of my travel and hotel bills. So please find them and kindly reimburse my travel expenses.
I hope you can make the payment soon.
Thanking you.
Sub: Regarding Travel expense reimbursement.
Dear Mr/Mrs.____________,
I am ____________(your name) has been interviewed for the post of ____________(job position) on __________(date of interview) at _______________________(company name & location), I am awaiting for the interview results.
Here I would like to request reimbursement of my travel expenses for an amount of 5800 Rs which I spent for attending the interview and please find all the bills attached with this email.
Here is the details of my travel expenses:
I shall be thankful to you in this matter.
1. Will companies really pay travel expenses for attending the interview
Yes, if the company is genuine then they will reimburse the travel expense, they will mention the information related to travel expense reimbursement in your interview call letter.
2. What if the recruiter is not paying the travel expenses.
If the recruiter is not reimbursing the travel expenses even though they offered in the interview call letter then you can contact the head of the organization.
Still, if you don’t get the reply then you can file a complaint on respect labour department or on the company’s social media platforms.
3. Are interview travel reimbursements taxable
Hence the reimbursed travel expenses are not an income to the person so they are not taxable. Companies will show it in their business expenses.
4. In how many days my travel expenses will be reimbursed
It depends on the company in which you attended the interview, in most cases, it will take 7- 30 days.
5. Can I get travel expenses before attending the interview?
No, companies generally don’t prefer to pay the travel expenses before the interview. In some rare cases, they will send you the tickets for attending the interview.
6. Why companies pay travel expenses of candidates
In general, companies spend a lot of amount on recruiting process. They will allocate a separate budget for reimbursement of travel expenses. Whenever they feel a particular candidate is worthy and suitable for the job position, then they are ready to pay the travel expenses, whether they hire him or not.
- Why should you be hired for this internship, Internshala answers?
- What is your current notice period answer?
- Download biodata formats for jobs in Word & PDF formats.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Travel and Expense
6 expense reimbursement policy best practices and why you need them.
Strong expense reimbursement policies are critical to overall organizational success, especially when you have employees who travel for business purposes. However, if you're not following expense reimbursement policy best practices, you might inadvertently create higher risks for the company and employees when you do reimburse people.
Why Do You Need a Strong Expense Reimbursement Policy?
A strong policy that governs expense reimbursements protects employees as well as the company. It communicates specifics about what can and can't be reimbursed and how to seek reimbursement. When your policy is detailed and clearly worded, it can reduce the risk of noncompliant spend.
Other benefits of effective expense reimbursement policies include:
- Helping to define the culture of your organization
- Supporting trust so employees can travel for business with confidence
- Increasing the efficiency of reimbursements, reducing the time employees may float their own expenses
- Setting parameters for control of travel and other business expenses to help maintain the budget
Initial Steps for Designing an Employee Expense Reimbursement Policy
Before you sit down to write an employee expense reimbursement policy, take some time to gather necessary information and make sure you’re creating a policy that works well for your organization.
Start by considering specific business needs. What type of budget are you working with, and do you have software solutions to help manage your expense request and reimbursement processes? You may also want to consider how investing in efficient expense management can help you save time and money in the long term.
Next, consider the company's mission and values and how expense reimbursement policies can support them. For example, if sustainability is important to your business, you may want to include parameters in your policy (this travel sustainability guide can help) that support making a sustainable choice when possible for travel arrangements and other expenses.
Finally, consider the needs and desires of your employees. Flexibility in the workplace is a global trend and preference for many people, for example. While flexibility often relates specifically to scheduling and where and how people do work, it could also relate to how travel expenses are handled. If that's important to your employees, can you build some flexibility into your expense reimbursement policy?
As you work to answer these questions and set the stage for policy creation, collaborate with stakeholders and subject-matter experts in your organization. That might include getting feedback from employees who travel frequently and are familiar with your current expense reimbursement practices.
6 Expense Reimbursement Policy Best Practices
Once you set the foundation for your employee expense reimbursement policy, you can put these best practices into action when creating it.
1. Define Qualifying Reimbursements
One of the most important purposes of your expense reimbursement policy is to set parameters on allowed spending. Your policy should define what makes an expense business-related and also provide boundaries, such as maximum allowable amounts or types of allowed purchases.
For example, it's common to set a per diem for meals for each day an employee travels. Perhaps you allow up to $55 per day for meals. As long as the employee has the receipts to back up their meal expenses, you would automatically approve up to that amount.
But you can also set parameters for other types of spending. Perhaps employees are only allowed to book certain types of hotel rooms with properties you have negotiated business rates with or economy or business class flights.
2. Require Receipts
Ensure that your expense reimbursement policy is clear about the need for receipts. Describe the types of receipts that are acceptable. That might include:
- Traditional register receipts
- Email receipts
- Printed purchase confirmation from online booking sites
Detail how receipts should be prepared for submission—digital processes may require the employee to take pictures of receipts or scan them in for adding to expense reporting software.
3. Reduce Paperwork in Your Expense Report and Reimbursement Process
Ensure your policy details the types of templates and workflows people should use to submit reimbursement requests, approve those requests, and, ultimately, fund them. When possible, remove actual hard-copy paper from the process. Digital forms support higher levels of streamlining and automation and they also reduce risks associated with paper, including the loss of paperwork and data breaches.
4. Define Expense Submission Deadlines
You might think that employees will rush to complete expense reports so they can be reimbursed. Surprisingly, however, the paperwork can get shuffled to the backburner when people are busy with other work. This can lead to employees submitting expense requests months after the expenditure occurred.
Slow expense reporting can put a burden on your accounting processes and even cause you to miss some tax opportunities. You can help speed up expense reporting processes by setting deadlines in your policy.
5. Create an Approval Workflow
Define the workflow for expense report approvals in your policy. If you're taking part in digital transformation and automating some of the expense process , define what types of expenses or dollar thresholds are eligible for auto approval.
Ensure the policy covers who must approve expenses and avoid creating policies that would allow someone (a manager, for example) to approve their own expense report.
6. Include Quality and Compliance Audits
Consider adding quality and compliance audit procedures to your expense reimbursement policy. Define who conducts the audit and how they do so. It's also important to set the parameters for auditing so that no one perceives audits as being directed to certain individuals.
You might write a policy that requires auditing of every third expense reported submitted by any given employee, for example. Or, you might set up the process so audits are triggered when expense reimbursement requests surpass a dollar threshold or include certain types of expenses.
Ready to get started on your employee expense reimbursement policy? Use the SAP Concur expense policy builder to ensure you cover all the bases.
Travel Bank Virgin America: Everything You Need To Know
- Last updated May 25, 2024
- Difficulty Intemediate
- Category Travel

Are you a frequent traveler? If so, you may want to know about a valuable tool called Travel Bank offered by Virgin America. Travel Bank is a user-friendly platform that allows you to effortlessly manage your travel funds and make the most of your flights. In this article, we will provide you with everything you need to know about Travel Bank Virgin America, from its features and benefits to tips on how to get the most out of this convenient service. So, sit back, relax, and let us take you on a journey through the world of Travel Bank Virgin America.
What You'll Learn
Introduction to travel bank: explaining its purpose and benefits.
- How to Set up and Access Travel Bank on Virgin America?
Managing and Using Travel Bank Credits for Future Bookings
Frequently asked questions about travel bank on virgin america.

Travel Bank is a unique feature offered by Virgin America Airlines that aims to make travel planning and management more convenient for its customers. It allows passengers to hold their unused flight credits in a virtual account, which can be used towards future flights and other travel-related expenses.
The purpose of Travel Bank is to provide customers with a hassle-free way to manage their flight credits and simplify the booking process. Instead of keeping track of physical vouchers or coupons, customers can store their credits digitally in their Travel Bank account.
One of the major benefits of Travel Bank is its flexibility. Customers can use their credits towards the purchase of not only flights but also other services such as baggage fees, seat upgrades, and even onboard food and beverages. This allows travelers to maximize the value of their credits and customize their travel experience according to their preferences.
Another advantage of Travel Bank is its ease of use. Customers can access their Travel Bank account through the Virgin America website or mobile app, making it convenient to check the balance and make bookings on the go. The system is designed to be user-friendly, with clear instructions and a straightforward interface.
Furthermore, Travel Bank offers a solution for customers who have to cancel or change their flights. Instead of losing the entire value of their tickets, passengers can opt to have the credit applied to their Travel Bank account. This credit can then be used towards future travel, providing flexibility and peace of mind in case of unexpected changes in plans.
In summary, Travel Bank is a valuable tool offered by Virgin America Airlines to streamline the travel experience and enhance customer satisfaction. It provides a convenient way for passengers to manage their flight credits and offers flexibility in using them towards flights and other travel-related expenses. Whether it's for booking future flights or making changes to existing reservations, Travel Bank simplifies the process and ensures that customers can make the most of their credits.
Managing Travel Expenses: How Consultants Handle Client Reimbursement
You may want to see also
How to Set up and Access Travel Bank on Virgin America
Travel Bank is a convenient feature offered by Virgin America that allows you to store and manage your travel credits in one place. If you have received credits from cancelled or changed flights, you can access and use them for future bookings using the Travel Bank system. In this blog post, we will guide you on how to set up and access Travel Bank on Virgin America.
To set up your Travel Bank account, follow these steps:
Step 1: Go to the Virgin America website
Visit the official Virgin America website using your preferred web browser.
Step 2: Access the Travel Bank page
Navigate to the Travel Bank page by clicking on the "Manage Travel" or "My Trips" section on the website's homepage.
Step 3: Create a Travel Bank account
If you don't already have a Travel Bank account, click on the "Create Account" or "Sign Up" button. You will be asked to provide your personal information such as your name, email address, and password. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the registration process.
Step 4: Link your reservation
Once you have successfully created your Travel Bank account, you will need to link your reservation to access any travel credits. To do this, enter your confirmation code and last name on the Travel Bank page and click on the "Link Reservation" or "Find Reservation" button. Your reservation will then be associated with your Travel Bank account.
Now that you have set up your Travel Bank account, here's how you can access and use your travel credits:
Step 1: Log in to your Travel Bank account
Return to the Travel Bank page and click on the "Log In" button. Enter your email address and password, and then click on the "Sign In" or "Log In" button.
Step 2: View your available travel credits
Once logged in, you will be able to see a summary of your available travel credits. This will include any unused value from cancelled or changed flights. You can also view the expiration dates and details of each credit.
Step 3: Book a flight using Travel Bank credits
To use your travel credits for a new flight booking, simply select the option to pay with Travel Bank during the booking process. The available credits will be automatically applied, and you will only need to pay for any remaining balance, taxes, and fees using a valid payment method.
Step 4: Manage your Travel Bank account
You can also use the Travel Bank portal to manage your account settings, add new travel credits, and view the history of your transactions. Additionally, you can transfer your travel credits to another person's Travel Bank account, as long as they are also a Virgin America member.
Remember to check the terms and conditions of your travel credits, as there may be certain restrictions or limitations on their use. It's also worth noting that Travel Bank credits are non-transferable to other airlines and cannot be redeemed for cash.
Using Travel Bank on Virgin America is a simple and convenient way to manage your travel credits. By following the steps outlined in this blog post, you'll be able to set up and access your Travel Bank account hassle-free. Enjoy your future travels with Virgin America!
Tips for Traveling with Ice Cream and Keeping it Solid
If you've ever flown with Virgin America, you may be familiar with their Travel Bank feature. Travel Bank is essentially a virtual account that stores any credits or funds you have with the airline. It provides an easy and convenient way to manage and use your credits for future bookings.
To start, you'll need to create a Travel Bank account on the Virgin America website. Once you have an account, any credits or funds you receive from cancelled or changed flights will be deposited into your Travel Bank. You can also choose to add funds to your Travel Bank manually.
When it comes time to book a flight, you can use your Travel Bank credits to pay for all or part of your booking. Simply select the Travel Bank payment option during the checkout process, and the cost of your booking will be deducted from your available credits. If your Travel Bank credits do not cover the full cost of your booking, you can pay the remaining balance with a credit or debit card.
One great feature of Travel Bank is that it allows you to easily manage and track your credits. You can view your Travel Bank balance at any time by logging into your account on the Virgin America website. This makes it simple to keep track of how much credit you have available for future bookings.
It's important to note that Travel Bank credits typically have an expiration date. This means that if you don't use your credits within a certain timeframe, they may expire and become unusable. Make sure to check the expiration date of your credits and plan your future bookings accordingly.
If you have a Travel Bank credit that is about to expire, there are a few options available to you. You can either book a flight for a future date before the credit expires, or you can convert the credits into Elevate points. Elevate points can be used for future bookings, and they do not have an expiration date.
To convert your Travel Bank credits into Elevate points, simply log into your Travel Bank account and select the option to convert. The conversion rate may vary, so it's important to check the current rate before making a decision.
Overall, Travel Bank is a useful tool for managing and using your credits with Virgin America. It provides a flexible and convenient way to pay for flights and helps ensure that your credits don't go to waste. Remember to keep track of your credits and their expiration dates, and make the most of your Travel Bank account for future bookings.
How Potential Employers Reimburse Interview Travel Expenses
What is Travel Bank?
Travel Bank is a virtual account that allows you to store money towards future travel with Virgin America. It is a convenient way to manage your travel funds and make bookings quickly and easily.
How does Travel Bank work?
When you receive a credit from Virgin America for a cancelled or changed flight, or if you choose to cancel a booking and opt for travel credit, the funds will be deposited into your Travel Bank account. You can then use these funds to book future flights with Virgin America.
How do I access my Travel Bank?
To access your Travel Bank, simply log in to your Virgin America account on the website or mobile app. From there, you can view your available funds, make bookings, and manage your travel credits.
Can I use my Travel Bank for any flight?
Yes, you can use your Travel Bank for any flight with Virgin America, as long as there are sufficient funds in your account. You can use it to pay for the base fare, taxes, and fees.
Can I combine Travel Bank with other forms of payment?
Yes, you can combine your Travel Bank funds with other payment methods such as credit cards or gift cards. This allows you to maximize the use of your travel credits and make bookings without any limitations.
How long is my Travel Bank credit valid for?
Your Travel Bank credit is typically valid for one year from the date of issuance. However, please keep in mind that Virgin America no longer operates flights. If you still have a credit in your Travel Bank, you should contact the Customer Support of the airline that acquired Virgin America, such as Alaska Airlines.
Can I transfer my Travel Bank credit to someone else?
No, Travel Bank credits are not transferable to another person. The funds can only be used by the account holder for their own bookings.
What happens if I don't use all my Travel Bank credit?
If you don't use all of your Travel Bank credit within the validity period, the remaining funds will expire. It is important to keep track of your credits and plan your bookings accordingly to avoid losing any money.
Can I get a refund for my Travel Bank credit?
In most cases, Travel Bank credits are non-refundable. However, you may be able to request a refund for certain circumstances, such as if the airline cancels your flight or if there are extenuating circumstances. It is best to contact Virgin America or the appropriate airline's customer support for more information.
Is Travel Bank available for all Virgin America customers?
Travel Bank is available for all customers who had an active account with Virgin America. If you are a new customer, you may need to create an account and provide the necessary information to access Travel Bank.
The Ultimate Guide on Getting to Hamburg Airport from Kiel
Frequently asked questions.
Travel Bank is a system used by Virgin America to store credits and funds that can be used towards future travel bookings.
When you cancel a flight or receive a credit from a refund or compensation, the funds are placed in your Travel Bank account. You can use these funds to book new flights or pay for extras like seat upgrades or baggage fees.
Yes, you can transfer funds from your Travel Bank account to another person's account as long as they are also a member of the Virgin America Elevate loyalty program.
The funds in your Travel Bank account will generally remain valid for one year from the date they were deposited. However, it's always a good idea to check the specific terms and conditions associated with your Travel Bank account for any exceptions or restrictions.

- Naim Haliti Author Editor Reviewer Traveller

- Arjun Yadav Author Editor Reviewer
It is awesome. Thank you for your feedback!
We are sorry. Plesae let us know what went wrong?
We will update our content. Thank you for your feedback!
Leave a comment
Travel photos, related posts.

Exploring Southeast Asia: Can Men Safely Travel to the Region while their Partner is Pregnant?
- May 15, 2024

Exploring Peru: Traveling with a US Visa Simplified
- Mar 22, 2024

Can I Travel on an F1 Visa During the Term? Exploring the Possibilities
- Mar 18, 2024

Understanding the Basics: What is a Travel Health Visa?
- May 07, 2024

A Step-by-Step Guide on Using JetBlue Travel Bank for Payments

Choosing the Ideal Size of Ziploc Bags for Travel: A Complete Guide
- May 11, 2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
2. Sample email for reimbursement of travel expenses. Travel expenses are a common cause for a reimbursement email, so keep this sample ready for when it's required. When it comes to expense reimbursement emails, include all details (dates, times, and travel methods) to make it as easy as possible for your claim to be paid.
Dear [Recipient's Name], I am writing to request reimbursement for transportation expenses incurred during [specific time period/task]. Here's a summary: Total Distance: [X miles/km] Mode of Transport: [Car, Train, etc.] Total Amount: [Amount] Attached are the travel logs and receipts. Thanks for your understanding.
Subject: Reimbursement Request - [Your Name] Dear [Recipient's Name], I hope this email finds you well. I am writing to request reimbursement for the following expenses: The total amount of expenses is $ [Total Amount]. I have attached all the necessary receipts and supporting documents for your review.
Subject: Reimbursement Request - [Your Name] Business Travel Expenses. Dear [Recipient's Name], Following my recent business trip for the sales meeting held in Toronto, I am writing to request reimbursement for my travel-related expenses as per our company's travel policy. The total expense for the trip is $500.
Reimbursement Mail to Hr Subject: Reimbursement Request Dear [HR Manager's Name], I hope this email finds you well. I am writing to request reimbursement for the expenses I incurred during [purpose of expenses, e.g., business travel, office supplies, etc.] on [date(s)]. The total amount of the expenses is [amount in currency].
Writing an effective email requesting travel reimbursement requires clarity and politeness. Ensure to include all necessary details, such as the purpose of the travel, dates, and expenses incurred, while avoiding unclear language or omitting important information.
Subject: Request for Travel Reimbursement. Dear _____ (HR Name of the Manager), I am writing to request reimbursement for travel expenses incurred during _____ (mention purpose of travel, e.g., business trip, client meeting) on _____ (mention dates of travel). Please find attached the relevant receipts and documents for your reference.
Sample email to formally request for reimbursement of travel expenses from HR Manager that incurred during official business trips. Skip to content. Emails In English Email Sample, Free to Use Email Templates ... Sample Email Requesting Travel Expense Reimbursement. August 10, 2023. To: _____@____.__ ...
A travel expense reimbursement policy is a document that outlines the rules and guidelines for reimbursing employees for business-related travel expenses. It includes details from pre-travel planning to settling reimbursable amounts. The policy specifies which travel expenses are eligible for reimbursement and which are not.
Excess Reimbursement. If an employee receives a travel advance to cover travel expenses but spends less than the advance, the difference is an excess reimbursement and must be returned to the employer to not be taxable. If the excess isn't returned in a reasonable amount of time, it's taxable. A reasonable period of time in this instance is ...
2. GeneralBlue simple free travel expense reimbursement form. This free travel expense reimbursement form by GeneralBlue is as easy as it gets. It's an Excel template with 8 columns for recording the expenses incurred traveling for business. With this straightforward form, you can record: The date you traveled.
Record and Manage Expenses. Implement a system for employees to capture and document their expenses. This could be a digital system where employees can upload photos of receipts or a manual process where employees keep physical copies of receipts. Ensure that the process is easy to use to encourage compliance. 6.
Email 1: Request for Travelling Allowance for Business Trip. Subject: Request for Travelling Allowance for Business Trip. Dear [Manager's Name], I am writing to request for reimbursement of travel expenses incurred during my recent business trip to [destination].
File a claim for general health care travel reimbursement online. General health care travel reimbursement covers these expenses for eligible Veterans and caregivers: Regular transportation, such as by car, plane, train, bus, taxi, or light rail. Approved meals and lodging expenses. You can file a claim online through the Beneficiary Travel ...
Any business in which an employee makes a purchase on behalf of the company using personal funds (cash, personal credit card, etc.) instead of a corporate credit card should have an expense reimbursement policy. Out-of-pocket business expenses are very common for event planning or travel heavy roles. An employee might pay out-of-pocket for cab ...
Free email template showing you how to ask for the reimbursement of interview travel expenses. Customise the template for your personal circumstances by replacing the [placeholder text] that's situated within square brackets. Re: interview in [location] at [time] on [date] Hi [first name], In order to attend my interview, I will need to ...
You figure the deductible part of your air travel expenses by subtracting 7 / 18 of the round-trip airfare and other expenses you would have had in traveling directly between New York and Dublin ($1,250 × 7 / 18 = $486) from your total expenses in traveling from New York to Paris to Dublin and back to New York ($750 + $400 + $700 = $1,850).
Travel Expense Reimbursement is a process where an employer reimburses an employee for expenses incurred during a business trip. These expenses can include transportation, accommodation, meals, and miscellaneous costs. Employees need to understand what is eligible for reimbursement and how to track and document these expenses properly.
Follow these steps to make sure you get your money back: Gather all documentation related to your business travel (flights, accommodation, meals, transport, etc.) Complete a reimbursement form (if provided by your employer or organization) or write a travel expense reimbursement letter. Submit your documentation and form to the department that ...
The goal of travel and expense management is to optimize spending, improve efficiency, and maintain transparency in business expenses. Key components of travel and expense management include: Approving travel requests. Booking travel arrangements (such as flights and hotels) Managing corporate credit cards.
A staff travel reimbursement form is required for reimbursement of all vehicle-related expenses, including gasoline, wear and tear, and personal auto insurance. As of [date], the rate is [$] per mile.
Mention the subject line as " Regarding reimbursement of travel expenses ". Write your name, date of interview, position for which you interviewed, and place of the interview. Attach all the required bill copies like travel bills, lodging bills, and hotel bills. And it is better to mention the details of travel expenses in the email.
Once you set the foundation for your employee expense reimbursement policy, you can put these best practices into action when creating it. 1. Define Qualifying Reimbursements. One of the most important purposes of your expense reimbursement policy is to set parameters on allowed spending.
Step 1: Go to the Virgin America website. Visit the official Virgin America website using your preferred web browser. Step 2: Access the Travel Bank page. Navigate to the Travel Bank page by clicking on the "Manage Travel" or "My Trips" section on the website's homepage. Step 3: Create a Travel Bank account.