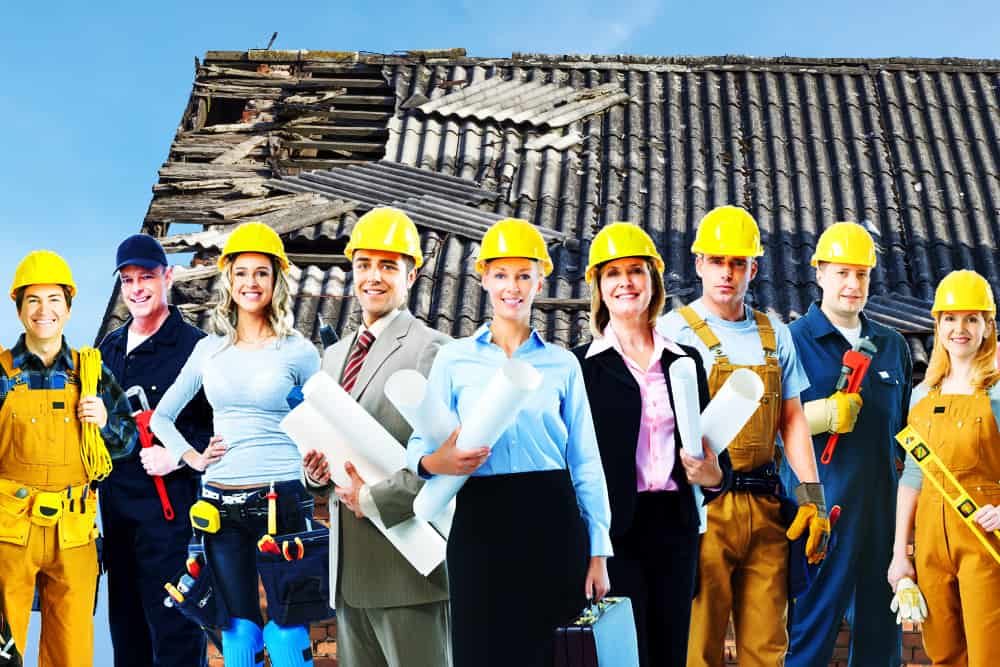
Slips, Trips, and Falls toolbox talk
A simple, 5 minute outline of what to cover in a toolbox talk on Slips, Trips, and Falls.
Download a Slips, Trips, and Falls toolbox talk pdf
Slips, trips and falls are a common reason for many of the injuries in workplaces. They can cause minor injuries but can also lead to serious, long-term injuries. Many slip, trips and falls are avoidable and there are usually easy solutions a workplace can apply to control the risk, either by eliminating or minimising it. It could be as simple as cleaning up a spillage straight away, or moving a cord off a walkway which can prevent injuries from occurring.

Why run a Slips, Trips, and Falls Toolbox Talk?
- Prevent unnecessary injury from slip, trips and falls by improving awareness and training
- Fewer injuries means higher productivity
- Makes sure workers know what to look for and what to do about it to reduce the risk of an injury occurring
What to watch out for that are common causes of slip, trips and falls?
- Poor housekeeping & messy sites
- Poor lighting
- Uneven walking surfaces
- Clutter on site
- Uncovered cords and cables
- Weather conditions (e.g. rain, ice, dust)
- Obstructed views
- Unsuitable footwear
- Distractions (e.g. cell phone, other workers)
What can you do to help prevent slips, trips and falls occurring?
- Keeping work areas clear & tidy from clutter, obstructions and rubbish
- Any waste placed in designated bins
- Clean up any leaks or spills immediately
- Put tools and equipment away
- Wear suitable footwear (e.g. grippy, anti-slip)
- Ensure work areas are well lit and sufficient light for work
- Keep cords and cables out of walkways, covered or secured
- Be aware of your surroundings and focus on what you are doing
- Work to the weather conditions
What if a slip, trip or fall occurs or nearly occurs?
- Report all slip, trip and fall accidents and near misses, with or without injury, this will help identify the hazards and implement control measures to prevent reoccurrence
Key takeaways
- Simply cleaning up your work area as you go, can help reduce slip, trips and falls
- Make sure you are always aware of your surroundings and look where you are walking
If you see a hazard that has the potential to cause a slip, trip or fall then pick it up or fix it – don’t wait for someone else to do it. Do it yourself!
Sales and Support Inquiries:
- [email protected]
- Help Centre
- Media Enquiries
- Toolbox Talk Topic Tool
- Health & Safety Consultant Directory
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Account Owner Terms
- Facebook logo to SaferMe FACEBOOK PAGE
- Twitter logo to SaferMe twitter PAGE

- Weill Cornell Medicine

Slips, Trips, and Falls: Understanding, Preventing, and Mitigating Risks
By Gian Joseph, Safety Advisor
As we enter the rainy and cold season, we face several risks , which include slips , trips, and fall s in our day-to-day activities. It is important t o be aware of hazards around us and learn how to properly identify and assess any risks with each step.
Slips, trips, and falls (STFs) are common accidents that can lead to severe injuries. These incidents occur in various settings, from homes and workplaces to public spaces , and i t is essential to understand the causes, consequences, and , most importantly, strategies for prevention and mitigation.
1. Understanding the Dynamics of STFs. STFs are caused by the following .
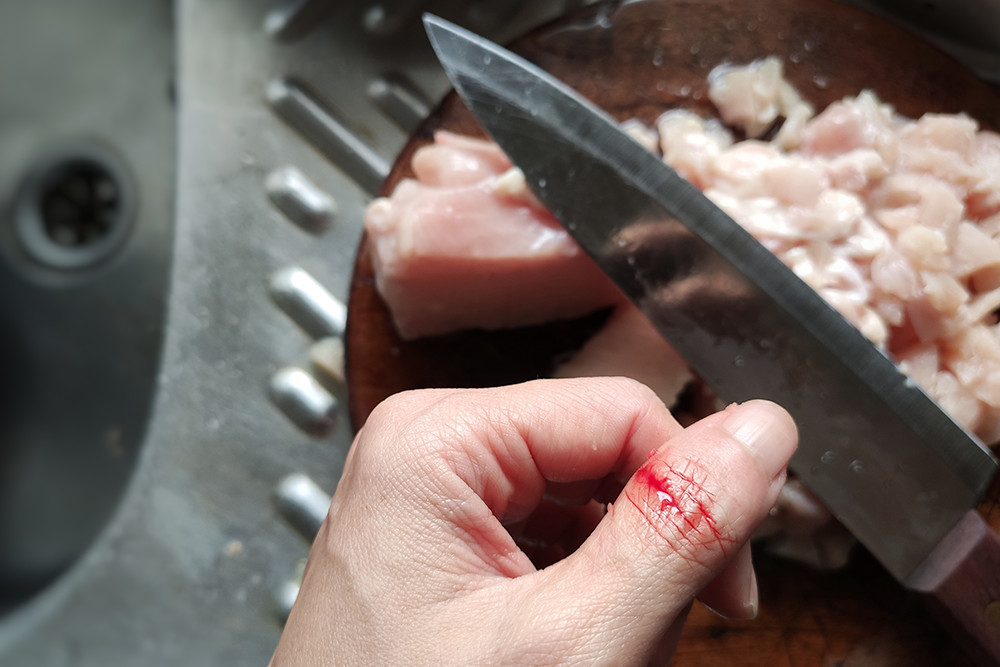
Insu fficient friction between the shoe and the walking surface. Common causes include wet or greasy floors, spills, and loose debris (Slip and Fall Accidents, 2021).
When a person's foot collides with an object or an uneven surface, it caus es them to lose balance. Typical trip hazards include cluttered walkways, electrical cords, uneven flooring, and damaged or upturned mats (Slip and Fall Accidents, 2021).
2. The Impact of STFs
Slips, trips, and falls have far-reaching effects, affecting individuals and society . Personal i njuries range from minor cuts , bruises, sprains , and abrasions to fractures, dislocations, and head injuries (National Safety Council, 2021). The medical expenses associated with treating STF-related injuries can be substantial , including hospital stays, surgeries, rehabilitation, and ongoing care (National Safety Council, 2021). STFs can result in missed workdays and reduced productivity for both individuals and employers. Workers' compensation claims and absenteeism contribute to economic costs (National Safety Council, 2021). Lastly, t he physical and psychological consequences of STFs can limit mobility, independence, and overall quality of life, especially among older adults ( Sahyoun et al., 2020).
3. Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Preventing and mitigating STFs involves a combination of awareness, environmental modifications, and education . H ere are some ways you can take precaution s against STFs in your daily activities;
Clear Pathways: Maintain clear, unobstructed walkways by removing clutter and tripping hazards such as cords, toys, and loose rugs (Occupational Safety and Health Administration [OSHA], 2002).
Adequate Lighting: Ensure proper lighting in all areas, both indoors and outdoors, to improve visibility and reduce the risk of tripping over obstacles (OSHA, 2002).
Slip-Resistant Flooring: Install slip-resistant flooring materials, especially in areas prone to moisture, like bathrooms and kitchens (OSHA, 2002).
Footwear: Encourage the use of proper footwear with good traction, especially in environments where slip hazards are prevalent ( Sahyoun et al., 2020).
Handrails and Guardrails: Install and maintain handrails and guardrails on stairs, ramps, and elevated platforms to provide support and prevent falls (OSHA, 2002).
Warning Signs: Use signage to alert individuals to potential hazards, such as wet floors or uneven surfaces (OSHA, 2002).
Education and Training: Promote awareness and provide training to individuals on recognizing and avoiding STF hazards (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health [NIOSH], 2015).
Workplace Safety: Employers should implement safety protocols and conduct risk assessments in the workplace, addressing potential STF risks (NIOSH, 2015).
Regular Maintenance: Routinely inspect and maintain buildings, walkways, and outdoor areas to identify and address potential hazards promptly (NIOSH, 2015).
4. A Holistic Approach to STF Prevention
Preventing and mitigating STFs require a collaborative approach involving individuals, organizations, and communities:
Individuals : Exercise caution when walking, especially in unfamiliar or potentially hazardous environments. Wear appropriate footwear and take your time, especially in wet or slippery conditions ( Sahyoun et al., 2020).
Employers: Create a safe work environment by identifying and mitigating STF risks. Provide training to employees on safety protocols and the proper use of equipment (OSHA, 2002).
Property Owners and Managers: Ensure properties are well-maintained and free from hazards. Regularly inspect and address issues promptly (NIOSH, 2015).
Government and Local Authorities: Enforce building codes and regulations that promote safety, especially in public spaces and commercial buildings (OSHA, 2002).
Conclusion
Slips, trips, and falls are preventable accidents that carry substantial personal, economic, and societal costs. By comprehending the causes, consequences, and prevention strategies, we can significantly reduce the incidence of STFs and mitigate their impact. Whether at home, at work, or in public spaces, prioritizing safety and fostering awareness about STFs is crucial for the well-being of individuals and communities. Let us strive collectively to create environments where everyone can move safely and confidently, free from the fear of falling.
References:
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). (2015). Preventing Slips, Trips, and Falls in Wholesale and Retail Trade Establishments. https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/2015-100/pdfs/2015-100.pdf
National Safety Council. (2021). Injury Facts. https://injuryfacts.nsc.org/work/overview/work-safety-introduction/work-...
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). (2002). OSHA Publication 3151-12R. Preventing Slips, Trips, and Falls in Wholesale and Retail Trade Establishments. https://www.osha.gov/Publications/osha3151.pdf
Sahyoun , N. R., Pratt, L. A., & Lentzner , H. (2020). The Changing Profile of Nursing Home Residents: 1985-1997. Journal of Aging and Health, 12(3), 336-363.
Slip and Fall Accidents. (2021). InjuryClaimCoach.com. https://www.injuryclaimcoach.com/slip-and-fall-accidents.html
Please note that the sources cited are accurate as of the time of writing this article. For the most current information, consult authoritative sources and local health authorities.
Go to the staff directory for individual contacts within EHS. You may also use the Weill Cornell Medicine online directory to search for faculty and staff.
Create an EHS Incident
Weill Cornell Medicine Environmental Health and Safety 402 East 67th Street Room LA-0020 New York, NY 10065 Phone: (646) 962-7233 Fax: (646) 962-0288
- +1 (800) 826-0777
- VIRTUAL TOUR
- Mass Notification
- Threat Intelligence
- Employee Safety Monitoring
- Travel Risk Management
- Emergency Preparedness
- Remote Workforce
- Location and Asset Protection
- Critical Communication
- Business Continuity
- Why AlertMedia
- Who We Serve
- Customer Spotlights
- Resource Library
- Downloads & Guides

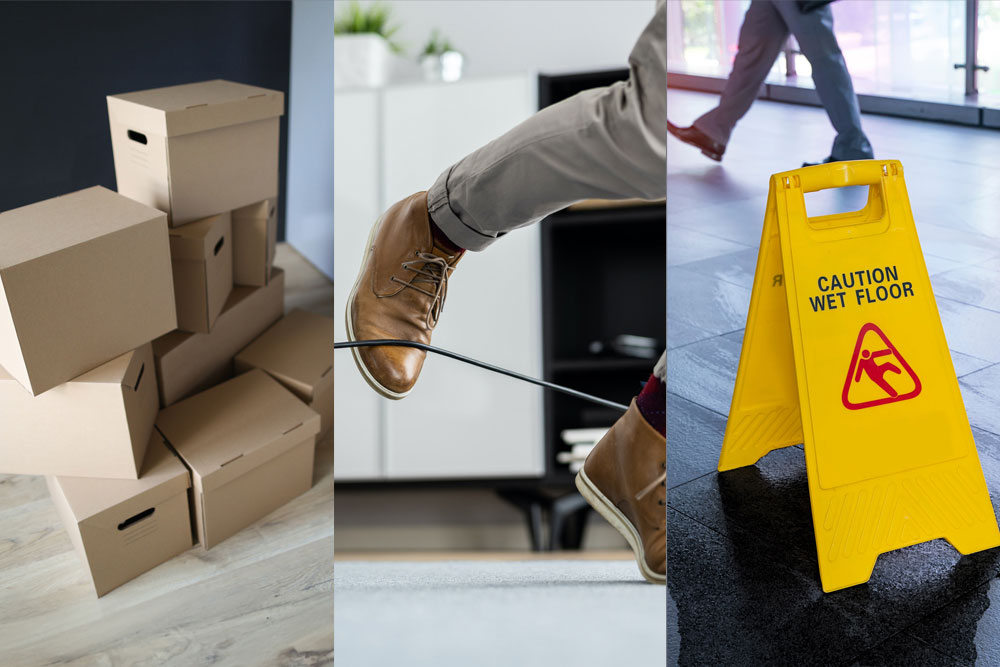
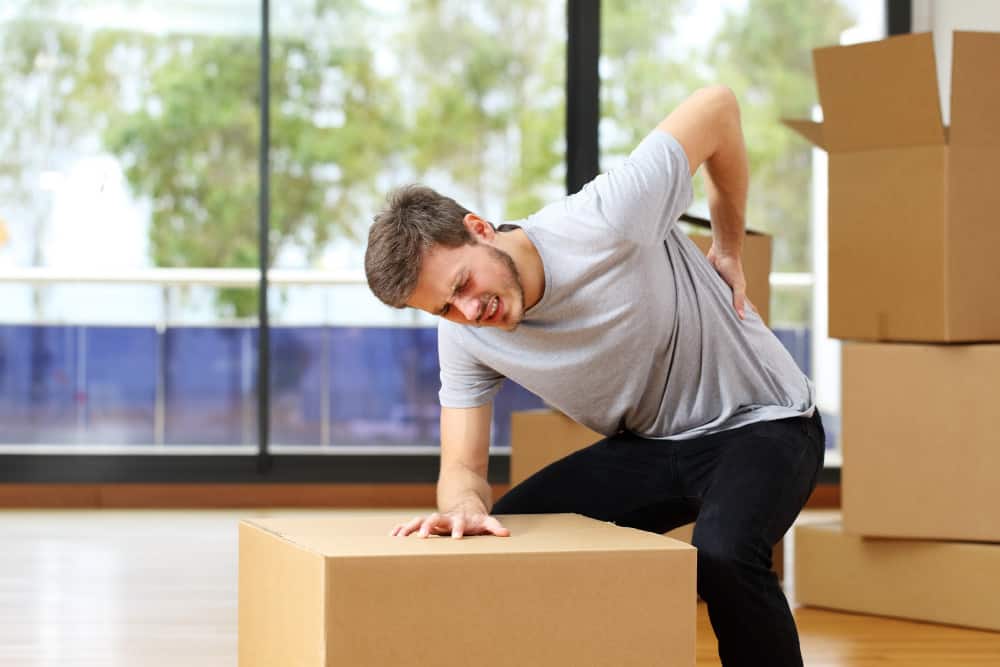
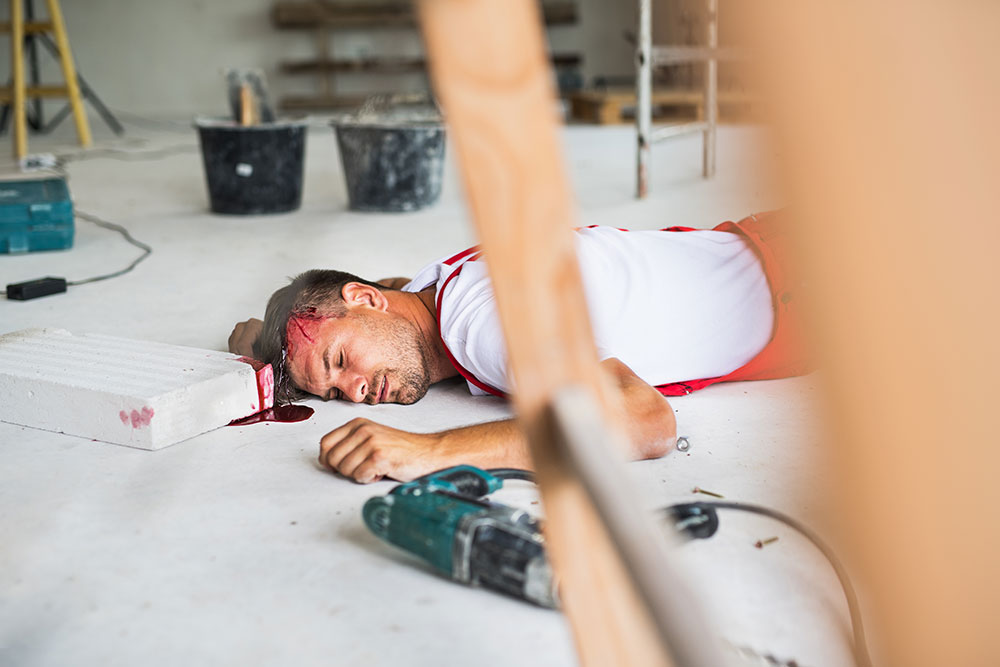
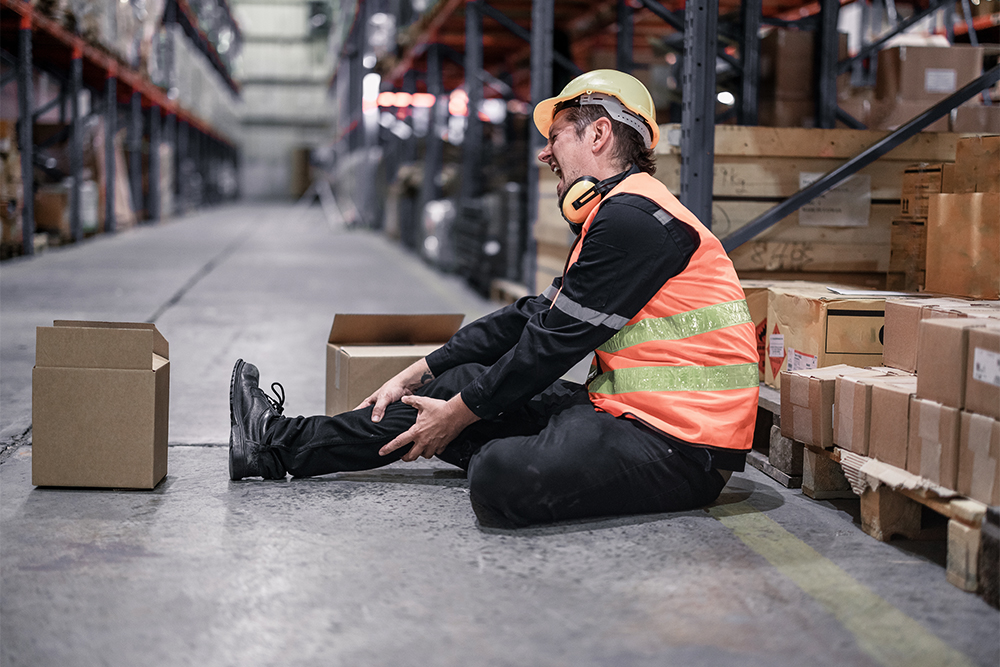
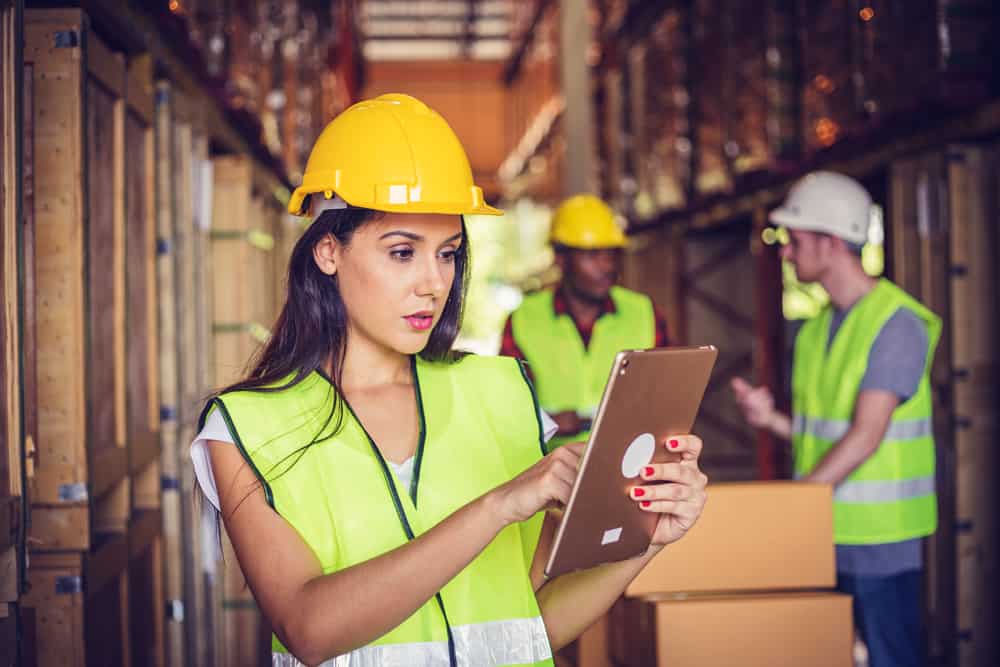
Prevent Workplace Slips, Trips, and Falls—8 Safety Tips
Mopping up a spill or double-checking a guardrail might seem like simple common sense, but slips, trips, and falls are the second most common cause of death at work. These are life-saving procedures. Keep reading for practical tips to prevent workplace accidents.
- Slip, Trip, and Fall Hazards Listed
- Clarifying OSHA Standards
- Prevent Workplace Slips, Trips, and Falls
These are familiar scenarios at home: slipping on a wet floor in the kitchen and tripping over a toy left out by the kids. While annoying, these accidents are typically minor hazards in the home. You might stub your toe, but rarely are there severe consequences.
In the workplace, it’s a different and far more serious story. Slips, trips, and falls account for over 200,000 workplace injuries per year. In 2020, nearly one in five accidents leading to missed work was due to a slip, trip, or fall. They’re also the second-leading cause of workplace fatalities.
As a safety leader, you’re responsible for your company’s duty of care and for providing a safe workplace . This blog post will examine common hazards leading to slips, trips, and falls and the steps you can take to minimize injury risks for your team.
Download Our Workplace Safety Checklist
What are slip, trip, and fall hazards in the workplace.
Accidents involving slips, trips, and falls are often grouped together. While they’re similar, it’s important to understand the distinction since they each have different causes and consequences.
Slips occur when someone’s footwear loses traction with the surface they’re on, causing a loss of balance. Under some circumstances, slipping can lead to a fall.
Trips happen when someone hits their foot or lower leg on an object. As their upper body continues moving forward while their lower body remains stationary, the person may lose their balance in the process.
Falls often result from slips or trips, but they can also happen on their own. For example, a worker on a ladder or scaffolding can lose their balance and fall without slipping or tripping. Falls are also possible on flat surfaces and can still cause serious injuries.
Once you understand the hazards that lead to each type of accident, you can identify and mitigate risks in your workplace. Here are some of the most common causes of slips, trips, and falls in the workplace:

Slip Hazards
- Spills of wet or dry substances
- The cleaning process during spill removal
- Employees rushing or not paying attention to workplace conditions, especially while carrying objects
- Slippery floor surfaces such as marble or laminate
- Wet surfaces
- Poor lighting that obscures hazards
- Inappropriate footwear for the environment
- Transitioning between different types of surfaces
Trip Hazards
- Objects or obstructions in walkways
- Uneven surfaces on flooring or concrete
- Cables, cords, and hoses that aren’t properly secured or organized
- Unmarked steps or ramps
- Irregular stairs or stairs without railings
- Carpet, rugs, or mats with wrinkles or lifted edges
Fall Hazards
- Improperly used or poorly maintained ladders
- Elevated surfaces without guardrails
- Floor and wall openings
- Working in elevated environments without a safety harness
- Ill-fitting or improperly used PPE, such as helmets and safety lines
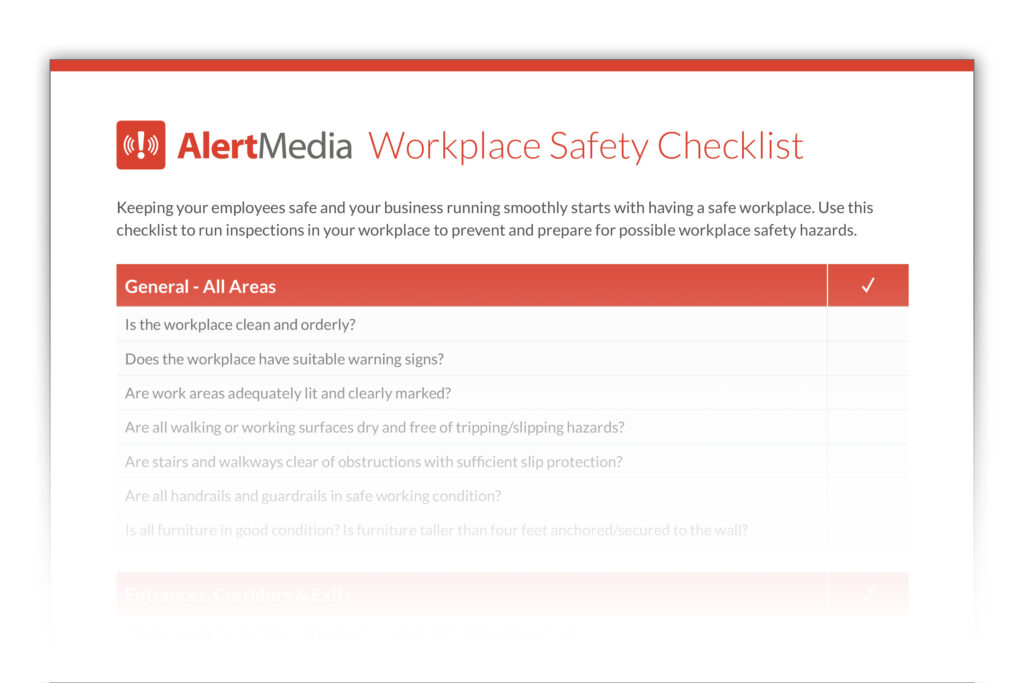
Preview the Workplace Safety Checklist
Are There OSHA Standards Related to Slips, Trips, and Falls?
Despite how common these injuries are, there is no specific OSHA standard on slips, trips, and falls. However, several OSHA rules indirectly address the same hazards.
The most important regulation to be aware of is 29 CFR 1910 Subpart D, which covers walking and working surfaces. OSHA updated the standard in 2017, introducing many upgrades to fall protection system requirements, improved employer-provided inspection guidelines, and a greater emphasis on safety training for employees.
For the construction industry, 29 CFR 1916 contains numerous fall-related regulations. Subpart M specifically addresses fall prevention, but other sections, such as Subpart L (scaffolds) and Subpart E (personal protective and lifesaving equipment), are also relevant. OSHA used 29 CFR 1916 as guidance when revising 29 CFR 1910, so the two guidelines now reflect many of the same OSHA violations .
As with any other workplace hazard or accident, OSHA recordkeeping requirements still apply in the event of a slip, trip, or fall incident. Internally, the reporting process is also an opportunity to review the details of the incident and determine how you can update your workplace safety policy to prevent similar accidents in the future.
How to Prevent Slips, Trips, and Falls in the Workplace
Many hazards that cause slips, trips, and falls are inevitable. However, injuries and accidents are not. To prevent slips, trips, and falls, train your employees to follow a three-step process:
- Recognize the hazard: Identify conditions that could lead to a slip, trip, or fall.
- Evaluate the hazard: Examine the situation and determine what level of risk it presents and who it affects.
- Control the hazard: Avoid the risk by removing the hazard (such as mopping up a spill) or implementing safety equipment and procedures (such as installing handrails on an elevated platform).
Here are eight workplace safety tips to prevent falls, trips, and slips.
1. Teach situational awareness
Since many causes of slips, trips, and falls are foreseeable, situational awareness in the workplace is one of the best preventative measures. Encourage your employees to pay attention to their surroundings and the risks they present:
- Look at walking surfaces for spills, obstacles, or other potential hazards
- Watch for signage that warns of increased hazards
- Be aware of conditions such as weather or time of day that might increase the risk of an accident
- Take shorter and more cautious steps on slippery surfaces
2. Encourage proper footwear
Like any other form of PPE, proper footwear can significantly reduce the risk of accidents. Research has found that slip-resistant shoes can reduce injury claims by 67% in environments with slippery work surfaces.
Employees should regularly inspect their shoes and make sure the soles aren’t worn out, as the lack of tread increases the danger of slipping. Additionally, anyone who works in conditions exposed to winter weather hazards should wear insulated boots. Cold temperatures can decrease muscle function, increasing the risk of slipping, tripping, or falling.
3. Utilize signage
Signage is an effective warning system for many workplace risks, but it can be especially effective in preventing slips, trips, and falls. There are two types of signs you can use to increase occupational safety:
- Temporary: Use warning signs while addressing a new hazard, such as cleaning up a spill, repairing a handrail, or replacing a ripped carpet. While temporary signage can help prevent injuries, you still need to address the actual hazard as quickly as possible.
- Permanent: For unavoidable hazards, such as slippery surfaces, a permanent sign can help warn employees to be careful. Use these sparingly, though, as it’s easy for people to ignore signs they see every day.
4. Keep floors clear and clean
Good housekeeping can help prevent most slips, trips, and falls. The details of keeping walking areas clean will vary widely by work environment, but there are a few common themes to encourage workplace safety:
- Report spills immediately, and warn nearby employees until someone can clean the contaminated surface
- Keep walkways clear of obstacles, loose objects, and anything that someone could trip over
- Place mats at entrances and exits so people can dry their shoes and avoid tracking water or other substances around the workplace
- Install handrails on stairways and elevated walkways
5. Apply non-slip mats and coatings
In some situations, keeping floors from becoming slippery is nearly impossible. Whether it’s liquid splashing or steam condensing, you must focus on mitigating the risk rather than avoiding it altogether.
For smaller or less demanding settings, non-slip mats can help employees maintain traction while walking around. In other cases, treating the floor with a permanent coating can help reduce slipping risks, even in the constant presence of liquids.
Who is at risk for slips, trips, and falls?
While all industries have some level of risk for a slip, trip, or fall, there are some industries where the risk is much higher, and the potential result could be much more dangerous. Here are some of the highest-risk industries:
- Construction
- Manufacturing
- Transportation/shipping/logistics
- Outdoor maintenance/groundskeeping
- Foodservice/hospitality
6. Ensure proper lighting
To identify slip, trip, and fall hazards, your employees need to be able to see their surroundings. Make sure that all of your work areas have proper lighting, especially in areas that are more prone to unsafe conditions.
While this can be a challenge in outdoor work environments, especially at night, it’s even more critical in those situations. Environmental conditions can lead to increased risks, and employees need to be able to see and avoid them. Adequate lighting should also extend to parking lots and walking areas around your facilities.
7. Develop safety programs
Your company’s safety plans and programs should include specific guidelines for preventing slips, trips, and falls. There are a few key topics to consider when developing these policies:
- The types of surfaces employees work and walk on and whether they present extra risks
- Seasonal or regional conditions that could heighten hazards, such as winter weather threats
- Specific OSHA regulations that apply to your workplace
- Potentially hazardous equipment training such as ladder safety
- Regular inspection plans to ensure your team is maintaining a safe work environment
- Policies to report hazards using your company’s two-way communication platform
- First aid training , so employees are prepared to respond safely should injuries occur
8. Provide Slips, Trips, and Falls Training
Lastly, training your employees to avoid slips, trips, and falls will help keep them safe. Provide specific guidance on the environments they’ll work in and the hazards they’ll face. For example, a slips, trips, and falls safety talk for food service workers should focus on wet floors and walking safely in crowded, fast-paced environments. Conversely, office workers could use extra reminders to watch for stray power cords and keep walkways clear of boxes, files, and other tripping hazards.
Working slips, trips, and falls into your safety topics for meetings is also helpful. Regular safety talks or safety moments are an excellent opportunity to remind your team about seasonal risks or update them on newly installed safety measures.
Don’t Let Your Safety Standards Slip
Slips, trips, and falls are some of the most common workplace injuries. Fortunately, you can usually prevent them with proper planning and safety measures.
By making slip, trip, and fall prevention a part of your company’s safety culture, you can ensure your employees are aware of their surroundings and ready to look out for each other’s safety. Enable them to report hazards easily, address risks quickly, and train them to avoid situations that are likely to cause injury.
With the right planning and prevention, even the most intense work environments can be as safe as a walk in the park.
More Articles You May Be Interested In

Workplace Safety Checklist
Please complete the form below to receive this resource.
Check Your Inbox!
The document you requested has been sent to your provided email address.
Cookies are required to play this video.
Click the blue shield icon on the bottom left of your screen to edit your cookie preferences.


Slips, Trips, And Falls Hazards | How To Prevent Them
Every year, countless individuals experience the unexpected mishap of a slip, trip, or fall. These incidents occur across all age groups and settings, from homes and public spaces to workplaces. While often brushed off as minor inconveniences or embarrassments, slips, trips, and falls can lead to serious injuries and significant financial and emotional costs.
The key to tackling this pervasive issue lies in understanding the factors contributing to these accidents and implementing effective prevention measures. In this blog, we delve into the causes of slips, trips, and falls, their impact, and, most importantly, how we can prevent them.
By understanding these risks, we empower ourselves to create safer environments, whether looking at the comfort of our homes, the safety of public spaces, or the well-being of employees in a workplace. This guide aims to heighten awareness, encourage preventive action, and highlight our shared responsibility in reducing the risks and consequences of slips, trips, and falls. Join us as we navigate through this important topic step by carefully step.
The Importance of Preventing Slips, Trips, and Falls
The impact of slips, trips, and falls can be highly significant, from bruised shins to broken bones. These incidents aren’t just about physical injury. The repercussions can ripple outwards, affecting an individual’s quality of life, workability, and mental well-being. In the workplace, such accidents can lead to significant downtime, loss of productivity, and even legal implications for businesses. It’s estimated that the annual costs associated with occupational falls run into billions of dollars globally, impacting not just individuals but entire economies. Therefore, it’s clear that these everyday accidents are anything but trivial and that preventing them should be a top priority for everyone.
Basic Understanding of Slips, Trips, and Falls
To prevent these incidents, we first need to understand them. So, what exactly are slips, trips, and falls? A slip occurs when there is too little friction or traction between your footwear and the walking surface, leading to a loss of balance. A trip happens when your foot or lower leg hits an object, and your upper body continues moving, resulting in loss of balance. A fall can result from a slip or trip but can also occur due to other factors, like poor lighting, lack of handrails, or sudden illness.
Each of these incidents can occur under various circumstances. While some common causes include wet or uneven surfaces, poor footwear, and cluttered walkways, there can also be less obvious contributors, like insufficient training or awareness. This article aims to delve deeper into the world of slips, trips, and falls, elucidating their causes, impacts, and, most importantly, the strategies for prevention. The goal is not to instill fear but to inspire a culture of safety, vigilance, and proactive measures to keep everyone safe.

Definition and Differences: Slips, Trips, and Falls
While the terms ‘slips,’ ‘trips,’ and ‘falls’ are often used interchangeably, they refer to distinct occurrences. As we’ve already discussed, a slip occurs when there is insufficient traction between your foot and the walking surface. This lack of grip may cause an imbalance, leading you to fall.
Trips, on the other hand, occur when your foot contacts an object in its path or drops unexpectedly, causing you to lose balance. A trip might occur due to clutter, an obstacle in the pathway, or an uneven walking surface.
Finally, a fall is a sudden, uncontrolled descent for various reasons, including slips, trips, loss of consciousness, or other health-related issues. Falls can occur on the same level (for example, falling on the floor) or from one level to another (like falling down the stairs or from a ladder).
Common Causes of Slips, Trips, and Falls
Understanding the common causes of these incidents is the first step toward prevention. Below are some major factors that often contribute to slips, trips, and falls.
- Wet or Oily Surfaces: One of the most common causes of slips is the presence of wet or oily surfaces. This might occur in areas prone to spills or leaks, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and certain industrial environments.
- Uneven Surfaces, Irregularities, and Obstacles: Uneven walking surfaces or irregularities such as potholes, cracks, or abrupt transitions can cause trips. Obstacles might include clutter, cords, open drawers, and other items that haven’t been stored properly.
- Poor Lighting Conditions: Inadequate lighting can make it difficult to see and avoid potential hazards like spills, obstacles, or changes in level. This can lead to both trips and falls.
- Weather Hazards: Outdoor slips and falls often increase during bad weather conditions such as rain, snow, or ice, which make surfaces slippery and vision less clear.
- Human Factors: Rushing, distraction, fatigue, or lack of proper training can also contribute to slips, trips, and falls. These can often be mitigated through awareness and training.
- Improper Footwear: Footwear unsuitable for the work environment or the current weather conditions can increase the risk of slips, trips, and falls. For example, smooth-soled shoes might not provide enough traction on a wet or oily surface, leading to slips.
- Loose or Unsecured Mats or Rugs: Unsecured mats, rugs, or carpets can shift underfoot or present tripping hazards with their edges.
- Improper Use of Equipment: This might involve using chairs instead of ladders, climbing on shelves, or not using safety equipment correctly, all of which can lead to falls.
- Poor Housekeeping: If work and walkway areas are not kept clean and orderly, they can contribute significantly to slips, trips, and falls. Examples include cluttered workspaces, cables across walkways, or spills not promptly cleaned up.
- Lack of Safety Training: Employees not properly trained on the correct job procedures, including safety equipment, can be at higher risk for accidents.
- Inadequate Maintenance: Neglecting maintenance can lead to hazards such as leaky pipes (leading to wet surfaces), potholes, or uneven flooring, which can cause slips, trips, and falls.
- Poorly Designed Walkways: Walkways with sudden drops, absence of handrails, sharp turns, or inadequate space can increase the risk of falls.
- Medical Conditions: Certain conditions like poor vision, balance disorders, or mobility problems can also increase the risk of slips, trips, and falls.
- Age: Both the very young and the elderly are at an increased risk for falls, partly due to factors such as lack of coordination, decreased strength, or reduced balance.
Remember, while this list of causes is extensive, it is not exhaustive. There may be other contributing factors depending on the specific circumstances or environment. That’s why it’s crucial to carry out regular risk assessments to promptly identify and address potential hazards.

Impact and Consequences Of Slips, Trips, And Falls
The impacts of slips, trips, and falls extend beyond the immediate event and can have lasting effects on the individuals involved and the organizations they belong to. These incidents can result in physical injuries, financial costs, and psychological distress.
Physical Injuries: From Minor to Severe
Physical injuries resulting from slips, trips, and falls can range from minor to severe. Minor injuries may include bruises, abrasions, or sprains. At the same time, more severe cases can lead to fractures, concussions, or even life-threatening injuries such as traumatic brain injuries or spinal cord damage.
In some cases, these incidents can lead to chronic pain or long-term disability, affecting the individual’s ability to perform daily activities or return to work. Falls, in particular, can be especially dangerous for older adults, leading to hip fractures or other serious injuries that significantly impact their independence and quality of life.
Financial Implications: Costs of Accidents
The financial implications of these incidents are also considerable. For individuals, this can include medical expenses, rehabilitation costs, and lost wages during recovery. Additionally, they might face expenses related to modifying their home for accessibility if the fall leads to a long-term disability.
For businesses, the financial costs can be substantial. There are indirect costs besides direct costs like medical expenses and workers’ compensation claims. These can include lost productivity due to employee absence, costs related to training replacement employees, and potential increases in insurance premiums. In severe cases, businesses may also face legal fees if they are negligent in providing a safe environment.
Psychological Implications: Fear and Anxiety After a Fall
The psychological impacts of slips, trips, and falls should not be underestimated. People who have experienced such an incident may develop a fear of falling again. This fear can limit their activities, reduce their independence, and decrease their quality of life.
Anxiety, depression, and social isolation can also result from the fear of falling or the consequences of an injury, such as disability. Employees may experience stress or anxiety about returning to work, especially if they feel the environment is unsafe.
Understanding these impacts highlights the importance of preventive measures to ensure safe environments, reducing the risk of slips, trips, and falls. The following sections will explore strategies to identify potential hazards and implement effective control measures.

Slips, Trips, And Falls Hazards Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is critical in preventing slips, trips, and falls. It involves identifying potential hazards, evaluating their risks, and determining appropriate control measures. A thorough risk assessment should consider all areas and activities in a given environment, from the home to the workplace.
Identifying High-Risk Areas in the Home or Workplace
High-risk areas vary depending on the setting. These might include staircases, bathrooms, and kitchens in the home, where wet surfaces are common. Outdoor areas like driveways or walkways can also present risks, especially in adverse weather conditions. Any area without sufficient support structures could be risky for older adults or those with mobility issues.
In the workplace, high-risk areas could be those with heavy foot traffic, wet or uneven surfaces, or places with lots of equipment and machinery. Industrial kitchens, construction sites , warehouses, and healthcare facilities are examples of workplace environments that often have high-risk areas.
Key Considerations for Risk Assessment
A comprehensive risk assessment should consider various factors. These include:
- The Environment: Assess the condition of the floors, lighting, staircases, and walkways. Look for hazards like wet surfaces, uneven floors, poor lighting, or lack of handrails.
- Human Factors: Consider the behavior and health of individuals in the environment. Are they rushing? Are they carrying heavy items that may obstruct their view? Do they have any health conditions that increase their risk?
- Tasks: Evaluate the tasks being performed. Does the job involve working at height, handling hazardous substances, or heavy physical labor? Are workers exposed to distractions or time pressure?
- Footwear and Clothing: Assess whether appropriate footwear and clothing are worn for specific environments and tasks.
- Previous Incidents: Look at the history of slips, trips, and falls in the environment. A pattern might indicate a persistent problem that needs addressing.
Importance of Regular Safety Audits
Regular safety audits are essential to maintain a safe environment. These audits involve routinely inspecting the environment and practices to ensure that safety measures are up-to-date and effectively implemented. They help identify new or overlooked hazards and assess the effectiveness of current control measures.
Regular audits also demonstrate a commitment to safety, which can encourage individuals to take responsibility for their safety and that of others. This fosters a proactive safety culture where hazards are promptly reported and addressed, further reducing the risk of slips, trips, and falls.

Prevention and Control Measures For Slips, Trips, And Falls
Once potential hazards have been identified through risk assessment, it’s crucial to implement prevention and control measures to mitigate these risks. This involves a range of strategies, from good housekeeping practices to installing safety features.
Housekeeping Best Practices
Proper housekeeping is one of the most effective ways to prevent slips, trips, and falls. Here are some best practices:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean floors regularly and immediately clean up any spills. Ensure to put up “wet floor” signs until the area is dry.
- Declutter: Keep walkways and work areas clear of clutter and obstacles.
- Proper Storage: Store materials and equipment properly when not in use.
- Maintenance: Promptly repair any damages to walkways and work areas, like cracks or uneven surfaces.
Installing Safety Features (Handrails, Non-Slip Mats, etc.)
Installing safety features can greatly reduce the risk of accidents. Here are a few examples:
- Handrails: Install sturdy handrails on all staircases and other areas where individuals may need extra support.
- Non-slip Mats: Use non-slip mats in areas prone to wet or slippery conditions.
- Guard Rails: Install guardrails around elevated platforms, mezzanines, and other fall hazards.
- Visible Markings: Use reflective tape or other visible markings to highlight changes in floor level or other hazards.
Appropriate Footwear for Different Surfaces
Wearing the right footwear can significantly reduce the risk of slips, trips, and falls. Choose shoes with good traction, especially for wet or slippery surfaces. Protective footwear should be worn in workplaces where specific hazards are present, such as construction sites.
Prompt Removal or Correction of Identified Hazards
Address identified hazards as quickly as possible to prevent accidents. If a hazard cannot be immediately removed or corrected, ensure it is clearly marked, and individuals are informed about it until it can be addressed.
Adequate Lighting
Ensure all areas have sufficient lighting to allow individuals to see and avoid potential hazards. This is particularly important for stairways, hallways, and outdoor paths. Replace burnt-out bulbs promptly and consider installing automatic lights in often-used areas.
By implementing these prevention and control measures, you can greatly reduce the risk of slips, trips, and falls, promoting a safer environment for everyone. In the next section, we’ll explore additional strategies and considerations specific to the workplace.

Workplace-Specific Considerations
While many of the principles of slips, trips, and falls prevention apply universally, certain considerations are particularly relevant to workplaces. These involve safety training, employer responsibilities, and industry-specific hazards.
Importance of Safety Training and Awareness Programs
Safety training is vital to workplace safety . Regular training sessions can ensure that employees are aware of potential hazards and the best practices for avoiding them. Training should cover topics such as proper use of equipment, safe handling of materials, and emergency procedures.
Awareness programs, too, can play a crucial role in maintaining a safe work environment. These programs could include regular safety reminders via bulletins, emails, or meetings, encouraging employees to be vigilant and proactive about safety.
Employer Responsibilities and Employee Rights
Employers have a responsibility to provide a safe work environment. This involves conducting regular risk assessments, addressing identified hazards promptly, and providing necessary safety training and equipment. They should also have procedures in place for reporting accidents or hazards and ensure that employees feel comfortable using these procedures without fear of retaliation.
Employees, on the other hand, have the right to a safe workplace and the right to speak up about safety concerns. They also have a role in maintaining safety by following established procedures, using provided safety equipment, and promptly reporting any hazards or incidents.
Industry-Specific Hazards and Control Measures
Every industry has its unique set of hazards, so it’s important to consider these when planning prevention and control measures. For example, spills and hot surfaces might be major hazards in a restaurant kitchen. Measures could include non-slip mats, appropriate footwear, and caution signs. In a construction site, falls from a height might be the primary concern, necessitating guardrails, safety harnesses, and fall arrest systems.
In conclusion, slips, trips, and falls are common but preventable incidents. By understanding their causes and impacts, conducting regular risk assessments, and implementing effective prevention and control measures, we can significantly reduce these accidents, fostering safer homes, workplaces, and communities.

The Role of Training in Preventing Slips, Trips , and Falls
Proper training programs are essential to educate employees on recognising hazards and taking preventive measures. Key training includes:
- Slips, Trips , and Falls Training: This program focuses on identifying potential slip, trip, and fall hazards, understanding the causes and learning preventive measures. Through online slips, trips, and falls training , employees can learn how to recognize and mitigate these risks effectively and promptly report such incidents.
- Hazard Awareness Training: General hazard awareness training helps employees recognize various workplace hazards, including those that could lead to slips, trips and falls. It promotes a culture of safety and vigilance.
- Housekeeping and Workplace Organi z ation: Training on maintaining a clean and organized workplace can prevent many trip hazards. This includes proper material storage, cable management and clear walkways.
- Emergency Response Training: Knowing how to respond in the event of a slip, trip or fall is crucial. This training covers first aid, emergency procedures and reporting protocols to ensure quick and effective response to incidents.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Training: Employees must know how to select, use and maintain their PPE. PPE training includes instructions on wearing non-slip footwear, gloves and other protective gear to minimize the risk of slips, trips and falls.
- Work at Height Training: Work at height course educates employees on the risks of working at heights and teaches safe practices for performing such tasks. This specialized training helps prevent severe injuries resulting from fall incidents.
Preventing slips, trips, and falls is no small task, but it is a crucial one. As we’ve explored in this guide, these incidents are far from trivial, carrying the potential for serious physical injuries, significant financial costs, and profound psychological impacts. Yet, armed with the knowledge of what causes these incidents and understanding their impacts, we’re already halfway towards prevention.
The steps to creating safer environments—at home, in public spaces, or at workplaces—aren’t overly complex. They begin with recognizing the potential hazards and involve a thoughtful blend of risk assessment, implementing practical measures, and fostering a culture of safety awareness. From basic housekeeping to installing safety features, each action reduces the risk.
It’s important to remember that the responsibility of preventing slips, trips, and falls doesn’t rest on a single individual or group—it’s a collective effort. Employers, employees, homeowners, and public facility managers all have roles to play. And in our various roles, we all contribute to a larger, shared goal: creating safer environments for everyone.
Preparing for and preventing these incidents can seem daunting in a world where the unexpected is expected. But, as we’ve seen, it’s not only possible; it’s a critical part of our commitment to safety for ourselves and others. Let this guide serve as a reminder and resource for that commitment, helping us make each step we take a safer one. Thank you for joining us on this journey towards safer environments and greater awareness. Let’s continue to take steps, big and small, toward a safer tomorrow.

Sorry, we're unable to complete your request
We cannot complete your request due to a technical difficulty. You may return to the previous page or go to the homepage and explore other options. For immediate assistance please call us.
Error Ref: %26%2332%3b%26%2335%3b18%26%2346%3b456a645f%26%2346%3b1727331656%26%2346%3ba2ddf65
- SafetySign.com
- Help Center
Prevent Slips, Trips, and Falls
JavaScript is not enabled.
This site requires the use of JavaScript. Please enable JavaScript .
10 Simple Ways to Prevent Slips, Trips, and Falls

Slips, trips, and falls are the leading causes of time lost in the workplace. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has cited fall protection standard violations more frequently than any other standard.
These types of hazards are serious issues for workers and employers, but their risk can be minimized with 10 simple ways to prevent slips, trips, and falls. With the risk of injury ranging from a simple sprained ankle to serious injury or death, fall protection and prevention should be everyone’s top priority.
These 10 ways to prevent injury should be considered best practices in every industry.
Like any other safety hazard, slips, trips, and falls can be highlighted during safety training. Make sure that everyone can recognize and avoid slip, trip, and fall hazards and that they use PPE correctly when necessary.
With these types of hazards being common to every type of work environment, it is important to notify supervisors or maintenance crews of slip, trip, and fall hazards when they are present. With so many ways to avoid or lessen the severity of slip, trip, and fall hazards, hopefully businesses will take steps to abate this hazards and less time will be lost by workers.
Your cart is empty.
- Health & Safety
- Hazards & exposures
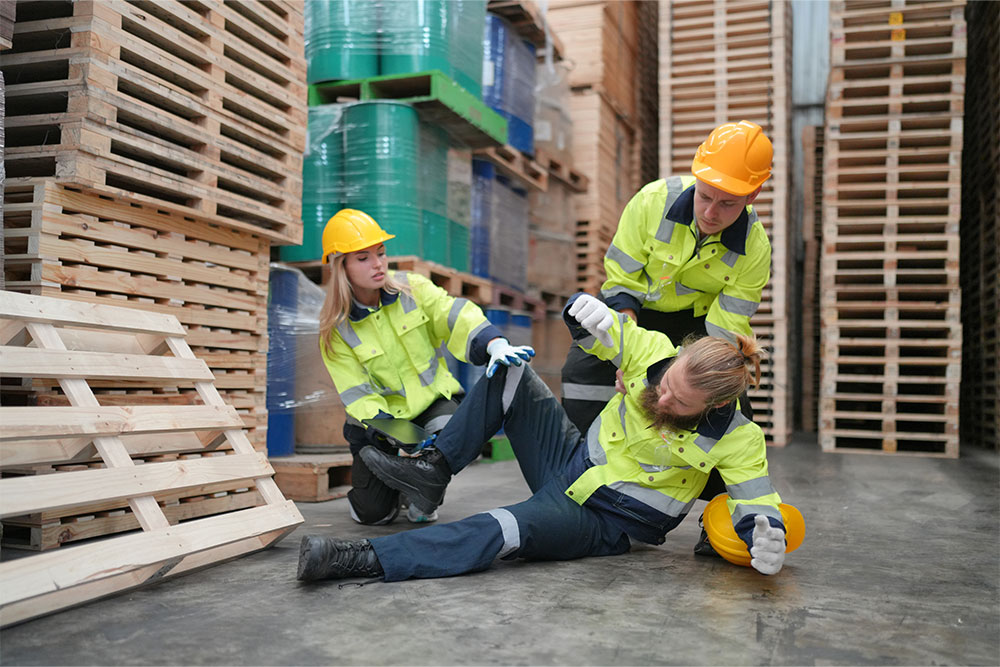
Slips, trips & falls
Slips, trips, and falls put workers at risk of sprains, strains, bruises, concussions, and fractures. Falls often result from slipping or tripping.
Slips happen where there is not enough grip or traction between the footwear and the walking surface. This can be a result of water, oil, grease, or dust on the floor. Loose rugs or mats, floors with varying traction, and the wrong footwear can also cause slips.
Trips and falls can happen when people lose their balance after their feet collide with objects. Common tripping hazards in the workplace include:
- Damaged or worn carpets, rugs, and mats
- Uneven flooring
- Cluttered walkways
- Uncovered cables
- Poor lighting
- Obstructed views
See our resources for information about reducing the risk of slips, trips, and falls.

Preventing Slips, Trips, and Falls in the Workplace
This book, written for employers and joint health and safety committees, describes common misconceptions about slips, trips, and falls as well as the factors that contribute to their causes. It also...

Kitchen Safety: Preventing Slips, Trips, and Falls
Slips, trips, and falls due to wet or greasy floors are common occurrences in kitchens. This video demonstrates safe work procedures to prevent injuries caused by slips, trips, and falls.

Safe in the Hall
Firefighter safety training routinely focuses on fire-related safety issues. However, at least one-third of all injuries to firefighters occur in fire halls. This video uses three scenarios to illustrate...
- Slips, trips, and falls are B.C.’s costliest workplace incidents: WorkSafeBC Published on: October 24, 2023

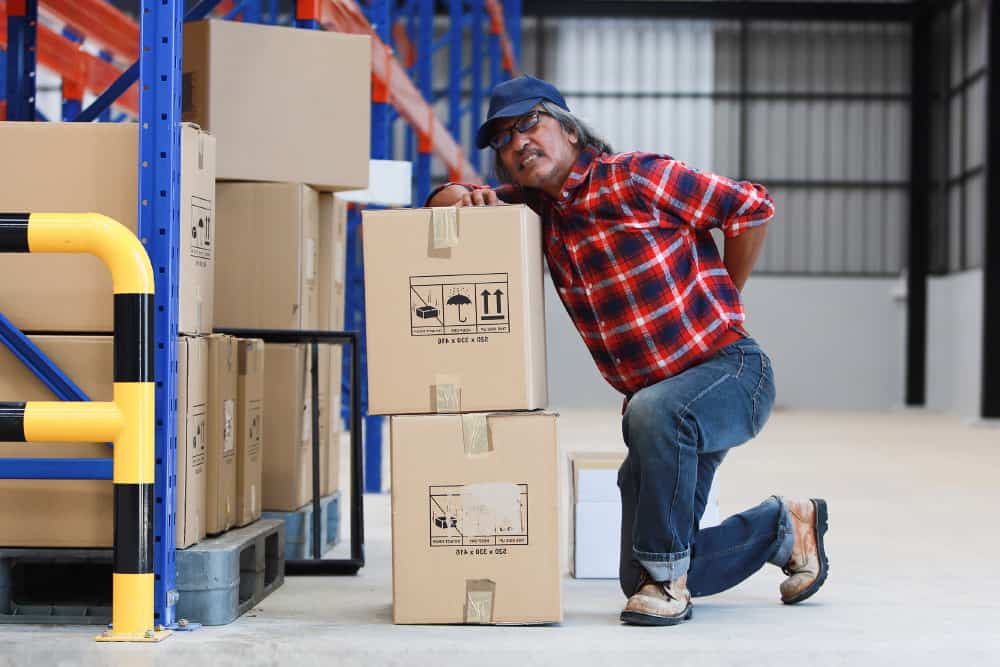
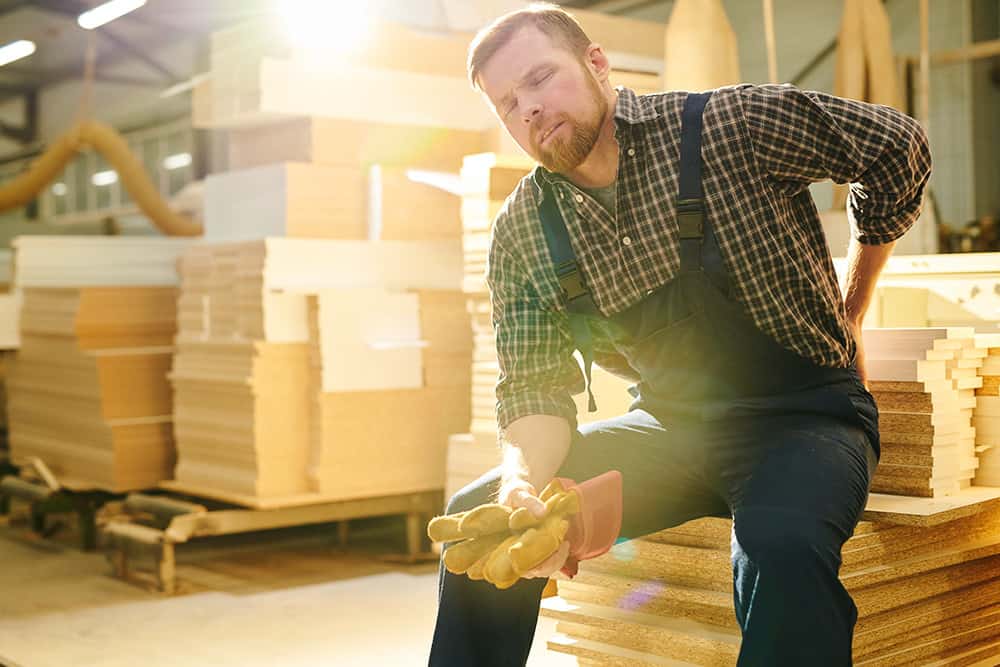
Common Causes of Slip and Fall Accidents at Work

Slips, trips and falls are the most common work-related accidents. And when workers do fall, the consequences can be severe. Fortunately, most incidents can be prevented with simple, low-cost control measures.
So, whether you run an office, warehouse or industrial site, it’s important to identify and address the hazards that lead to slips and falls.
In this blog, we’ll explore the leading causes of slip and fall accidents and share practical tips to help you prevent these incidents in your workplace.
How Often Slips, Trips and Falls Happen at Work
According to the Health and Safety Executive (HSE), slips, trips and falls on the same level are the leading workplace accidents. They make up 32% of all non-fatal work-related injuries , nearly double the number caused by manual handling, which accounts for 17%.
And every one of the work-related slips, trips and falls recorded in these statistics resulted in serious harm.
Under the Reporting of Injuries, Diseases, and Dangerous Occurrences Regulations (RIDDOR), employers must report specified (i.e. severe) injuries and injuries that keep an employee off work for seven days or more.
Each slip, trip and fall recorded by the HSE came from a RIDDOR report. This means that every incident caused a seven-day absence or severe injury, such as a broken bone or concussion.
In addition to the personal impact, slip, trip and fall accidents place a heavy financial burden on businesses. They cost UK companies over £500 million each year, including direct costs like compensation and insurance claims, and indirect costs, such as lost productivity.
Given these figures, preventing slips, trips and falls is essential to maintaining a safe and efficient workplace.
What the Law Says
As an employer, you’re legally required to provide a safe working environment, and that includes preventing slip, trip and fall accidents .
There are three key pieces of legislation you must comply with:
- The Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 places a general duty on employers to ensure the health, safety and welfare of employees and anyone else affected by work activities. This means you must take reasonable steps to protect workers from hazards, including those that lead to slips, trips and falls.
- The Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999 requires employers to carry out regular risk assessments to identify potential dangers in the workplace. You must evaluate the risks of slips, trips and falls and put control measures in place to minimise them. Additionally, employees must be given appropriate training to ensure they can recognise and manage work-related risks.
- The Workplace (Health, Safety and Welfare) Regulations 1992 covers the condition of floors and walkways. Employers must ensure that floors are kept in good repair and free from obstructions to allow safe movement around the workplace.
Slips Trips and Falls Training
Our comprehensive Slips, Trips and Falls Training course helps prevent slip, trip and fall incidents by equipping trainees with the knowledge to effectively recognise and reduce associated risks across different work settings. Trainees also learn about their role in maintaining a safe workplace free from slips, trips and falls.
Common Causes of Slip and Fall Accidents
Slips, trips and falls can happen in any workplace but can often be prevented with simple, low-cost control measures.
The first step is identifying the common causes of slip and fall accidents present in your workplace.
Slips occur when there is not enough traction between footwear and the walking surface. Most slips occur on wet floors.
Wet floors are slippery floors. Spills, rainwater brought in from outside or recently mopped surfaces all cause floors to become slick.
So, you have to implement measures that minimise the time floors are wet or prevent them from becoming wet in the first place. Common solutions include:
- Extending canopies or rain covers over entranceways
- Placing water-absorbent mats in entranceways
- Scheduling wet mopping out of hours
- Isolating areas being cleaned and using safety signs to warn of wet floors
- Using dry mopping or spot cleaning with absorbent towels during the workday
Contaminated Floors
Grease, oil, drinks and other liquids can spill and “contaminate” floors, creating slick surfaces that lead to slips. Dust and other solid debris can also create slipping hazards.
These contaminants are often found in industrial settings, areas where machinery is used or kitchens where food and drink are prepared.
Effective control measures against contamination include:
- Fixing leaks in faulty machinery or building features
- Installing drip trays, drains or screens around leaky machinery
- Providing slip-resistant footwear for areas that can’t be reliably kept clean and dry
- Planning walkways around areas that are often contaminated
- Ensuring workers have the motivation, knowledge and resources to spot clean drips or sweep up dry materials

Trips happen when your foot strikes an object or uneven surface, causing you to lose balance.
Unsafe Walkways
Most trips are caused by obstructed walkways, so keeping these routes clear is critical.
You must also ensure sufficient lighting in all walkways, particularly if there are hidden steps or subtle slopes. It also helps to warn workers of these hazards with safety signs or contrasting colours along edges.
Poor Housekeeping
Obstructions will be a consistent problem if employees don’t tidy up their workspaces. Trailing cables, abandoned boxes or leftover rubbish are all common tripping hazards.
Encourage a “see it, sort it” mindset. All workers should clear away clutter (and tidy up spills), no matter who made the mess. Provide the training, storage and resources necessary for this.
Inadequate Flooring
Damaged or uneven flooring can catch a person’s foot and lead to a fall. So, you must ensure that floors are kept in good condition.
Look out for:
- Upturned carpet edges
- Raised or sunken tiling
- Cracked concrete
Again, a “see it, sort it” mentality among workers is helpful. Encourage employees who notice these issues to report them immediately (but don’t expect them to attempt a fix).
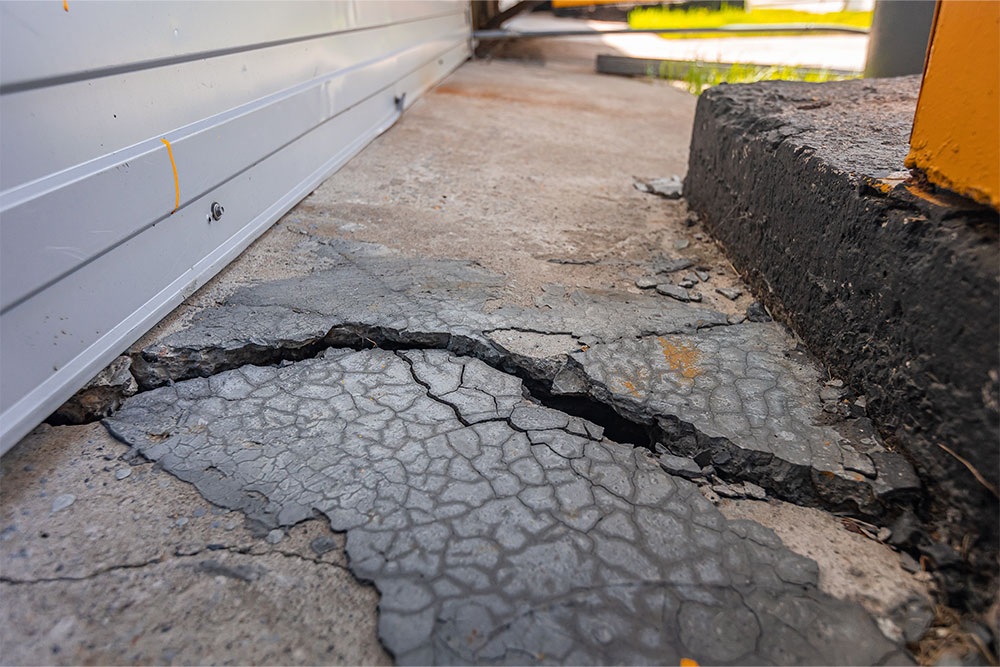

A fall describes when a person loses their balance and hits the ground or a lower level.
Falls on the same level are the result of a slip or trip, so they share common causes.
Falls while working at height are considered a separate accident type with distinct causes and controls .
Common Causes of Slip and Fall Accidents – Key Takeaways
- Slips, trips and falls are the most common workplace accidents but can often be prevented with simple control measures.
- Wet floors, obstructed walkways and poor housekeeping are the leading causes of slips and trips.
- Employers must assess and manage slip, trip and fall risks to ensure a safe working environment.
- Regular maintenance, effective cleaning and employee training are essential to preventing slip, trip and fall hazards.
Preventing Slips, Trips and Falls at Work
While understanding the common causes of slip and fall accidents at work is important, effective prevention requires ongoing effort and awareness.
That’s where our online Slips, Trips and Falls Training course can help. It covers essential strategies for preventing these accidents, so your team can stay safe and compliant. By investing in this training, you’ll equip your employees with the knowledge they need to spot potential hazards and act to reduce slip and fall risks.
About the author(s)

Jonathan Goby
Share with others
You might also like.
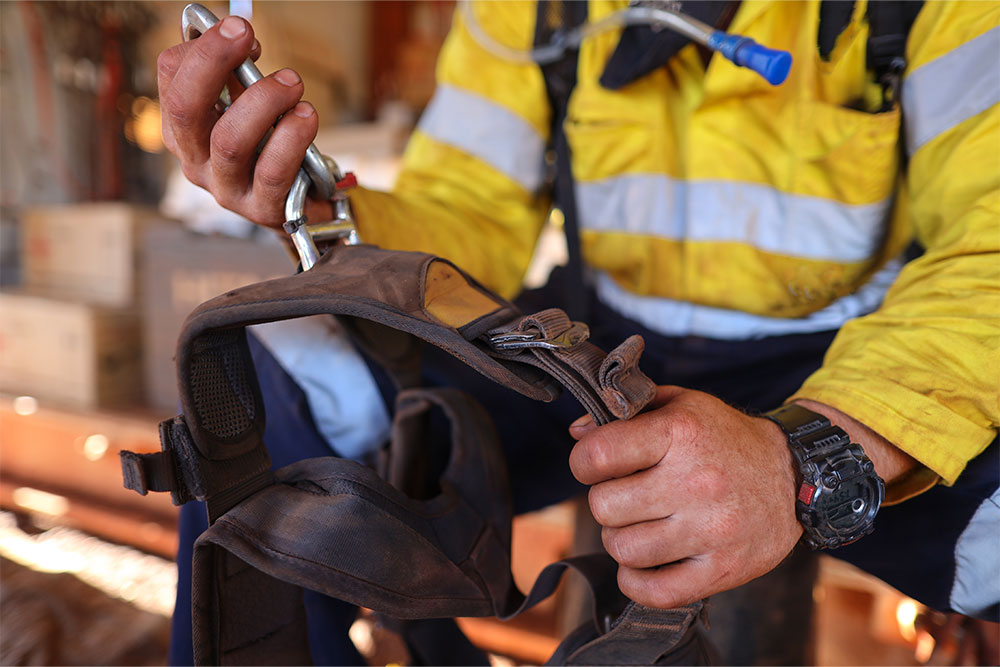

Common Mistakes in Harness and Lanyard Use

Construction Site Signs – A Complete Guide

What are the Roles and Responsibilities of Safety Officer in Construction?

Why is Communication Important in the Workplace?

How to Set a Table: Basic, Casual & Formal Dinner Setting

What is a fire door?

How Human Focus Helped Drainline Up Their Health & Safety & Training Game

Risk Assessment for Working from Home

When is an Accident Book Required in the Workplace?

How Many Fire Wardens Should There Be in Your Workplace?

Grinding Wheels – Types, Purposes and Uses

Acrophobia: Understanding the Fear of Heights

The New Building Safety Regulator – A Review of Where We Are 1 Year In

Can RAAC Cause Buildings to Collapse?

10 Fire Hazards in the Workplace

How to Prevent Fire Spreading Through the Workplace

Fire Triangle vs Fire Tetrahedron: What’s the Difference?

Who Enforces Health and Safety Law?

15 Common Construction Site Hazards

Fire Safety (England) Regulations 2022

Who is at Risk of Asbestos Exposure?

When Should a Safety Harness be Replaced?
Epilepsy or Seizure First Aid: What to Do

Personal Emergency Evacuation Plans Explained

Understanding Psychosocial Risks at Work

Abrasive Wheels Regulations – Everything You Need to Know

PUWER Compliance: 8 Questions to Ask Operators & Supervisors

Keys to Mental Resilience #5: Learning

Menopause at Work – Why You Need to Care

A Complete Guide to the Working at Height Regulations 2005

What is Mental Health First Aid?

Managing Health and Safety Concerns at Work

Stricter Laws on Using a Phone While Driving Coming March 2022

10 Common Health and Safety Hazards

What Happens if You Fail to Follow LOLER?

The Role of Duty Holders Under the CDM Regulations 2015

What Does HACCP Stand For?

Can Stress Cause Vertigo?

Equality Act 2010 Updates | Changes to Sexual Harassment Law
What are the Three Main Considerations for Moving and Handling?
Who Does GDPR Apply To?

What Is the Purpose of a PUWER Inspection?

Why Is Password Security Important for Your Business?

6 Ways to Get Better Mental Health at Work and at Home

What is the Purpose of a Risk Assessment?

What is Inclusive Practice?

What Are Preliminaries in Construction?

What is Intervention in Education? Types and Examples

Why Staff Health and Safety Should Be Your Business Priority

How Many Hinges on a Fire Door Are Required?

What is Manual Handling – Everything You Need to Know
Asbestosis Symptoms and other Common Diseases and Health Concerns after Asbestos Exposure
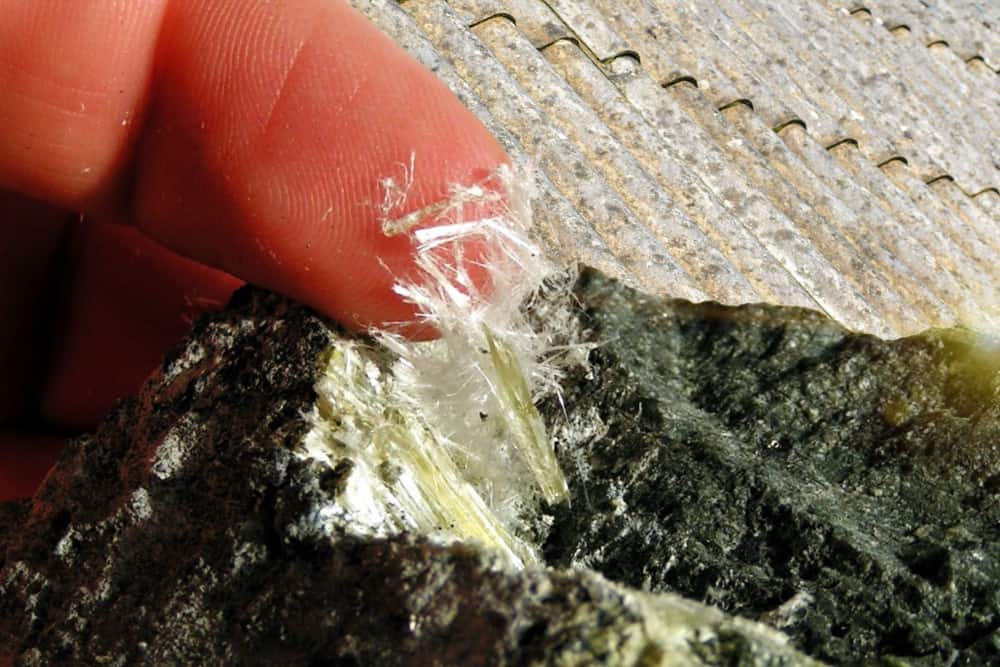

How Dangerous Is Asbestos in Common ACMs and Products?

Health and Safety Responsibilities of Sub-Contractors

Mental Health Crisis – What Can Be Done?

The Importance of a Good Communication Strategy

HSE Inspection Initiative – Dust Kills

5 Key Principles of Manual Handling

What is Personal Data? – a Simple Explanation
How Many First Aiders Do I Need?
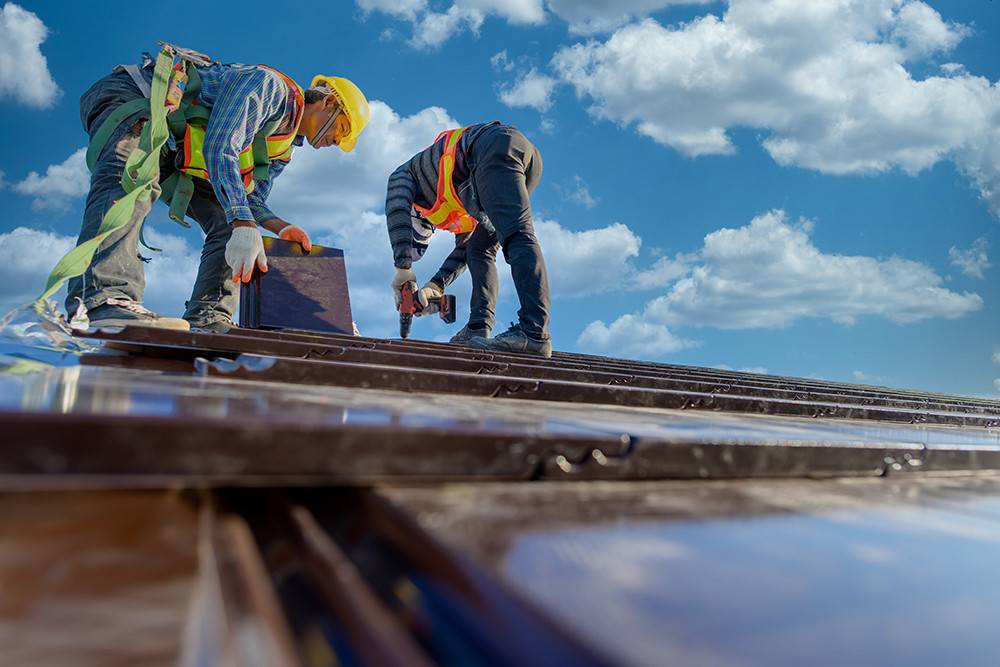

What Are the Hazards of Working at Height?

What Is Ergonomic Approach to Manual Handling?

NEBOSH or IOSH – How to Choose the Right Certification?

Who Is Responsible for the Safeguarding of Children?

Annual Asbestos-Related Deaths Still High, Report Finds

10 Safety Training Required in the Workplace

What Is Hybrid Working? A Quick Guide for Businesses

Is There a Difference Between a Chef and a Cook?

Is Portable Appliance Testing Mandatory?

7 Strategies for Effective Communication in the Classroom

What Does PUWER Stand For In Construction?

What is Hot Work and Do I Need a Permit?

What is Near Miss Reporting in the Workplace

Are Online Training Certificates as Good as Certificates Earned in Classroom Training?

Can Stress Cause High Blood Pressure? Stress and Your Health

PU Adhesives and Sealant Products Mandatory Training

First Aid Qualifications – Different Between EFAW and FAW

How to Do a Plumbing Risk Assessment

What Is the Most Painful Mental Illness?

Can Stress Cause Miscarriage?

Christmas Things to do at Work to Make it Stress-Free for Employees

What Is the Role of a Mental Health First Aider?

What Are The 6 Lawful Bases for Processing Data?

5 Different Methods of Communication

10 Common Causes of Slips, Trips and Falls at Work

What Are RAMS In Construction?

How to Stop Worrying About Asbestos

How to Use a Fire Risk Assessment Template

GDPR and Third-Party Data Processors in the UK

What is Cyber Security? What You Need to Know to Protect Your Business

Why Good Training is Crucial to Enable Employees to Manage Violence and Aggression Effectively

Keys to Mental Resilience #3: Assertiveness

Understanding Common Types of Mental Illness

World Mental Health Day – Our Minds, Our Rights

What Equipment Does LOLER Cover?

Completing Your First Aid Needs Assessment

Fire Safety in Schools: Key Principles for Administration

GDPR for Small Businesses – A Complete Guide for 2023

Hot Work Fires: How to Reduce Risks

7 Reasons You Need an Equality, Diversity & Inclusion Policy

How Often Should Pat Testing Be Done?

The Secret to Good Mental Health & The 12 Spokes of Mental Resilience

Making Tall Buildings in England Safer – New BSR Campaign

Making Your Health and Safety Policy Statement Effective

What Should a Safeguarding Policy Include?

Intermittent Fire Alarm: What Should You Do?

What is a Spill Kit – Everything You Need to Know

What is TILE Manual Handling?

Interpersonal Communication Skills Improve Relationships

What Is A DSE Assessment?

What is a Tender in Construction?
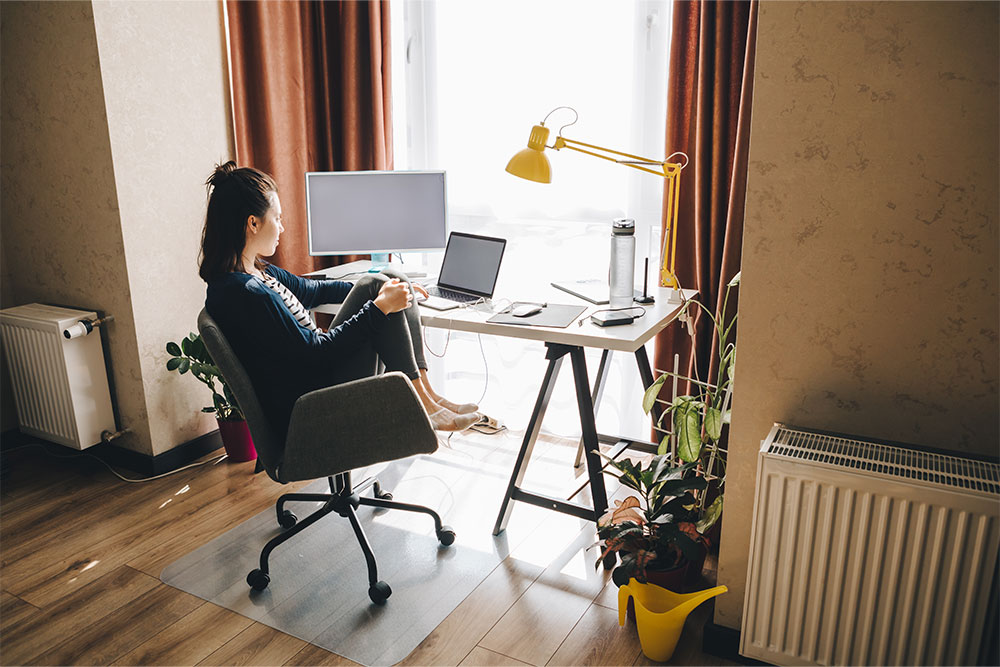

How to Manage the Health & Safety of Remote Workers

A Fast and Easy Fire Door Inspection Checklist
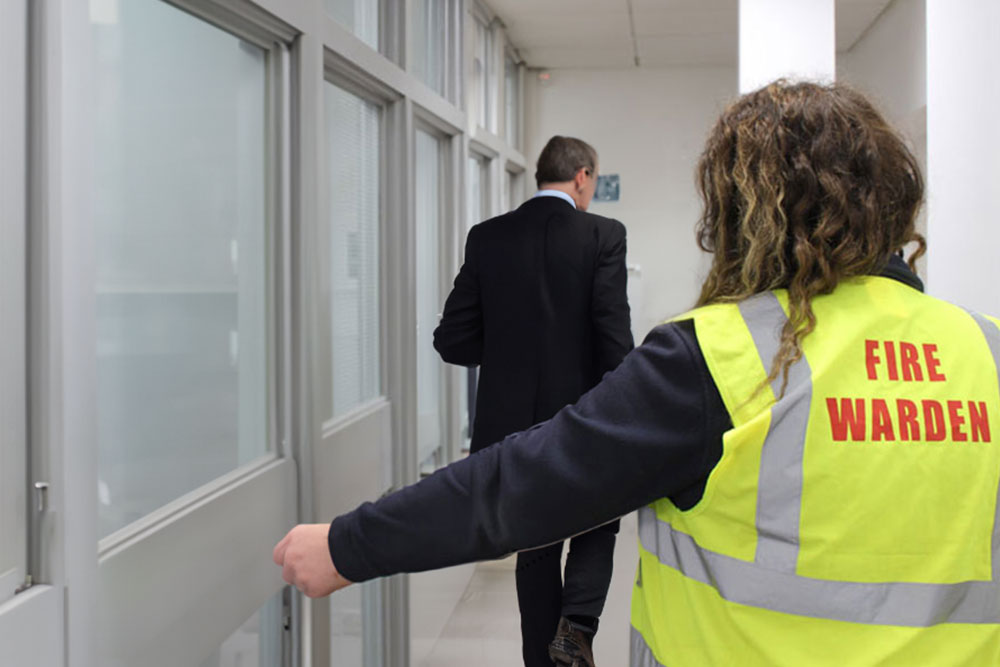

How to Conduct a Fire Drill in the Workplace
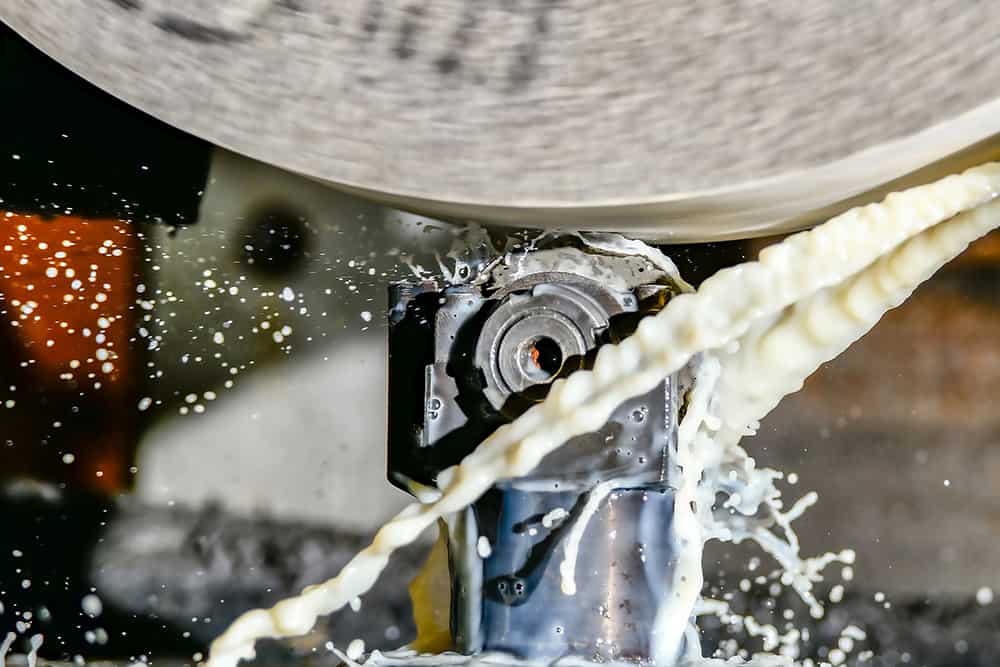

How to Dress a Grinding Wheel
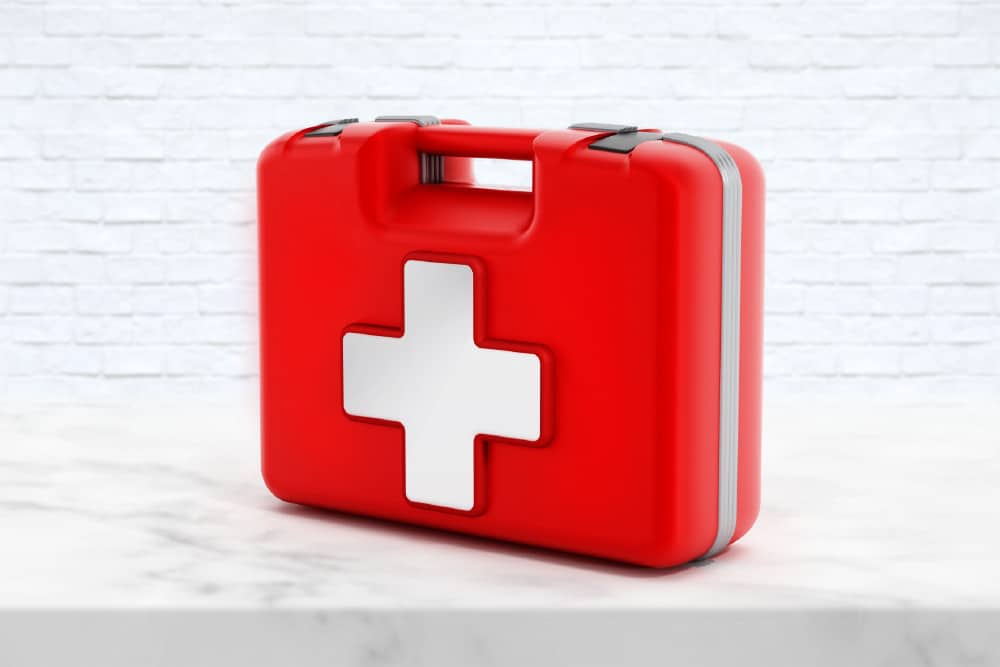

Health And Safety First Aid Regulations 1981 – Are You Risk Ready?

Who is Responsible for Completing a Fire Risk Assessment at Work?

Grenfell Report: What it Means for Building Safety

5 Examples of Personal Development Goals

Asbestos in Schools – Has Anything Improved?
Returning to the Office May Increase Cybersecurity Risks

How to Safely Handle, Store & Dispose of Hazardous Substances at Work

Natasha’s Law: How Does It Impact My Business?
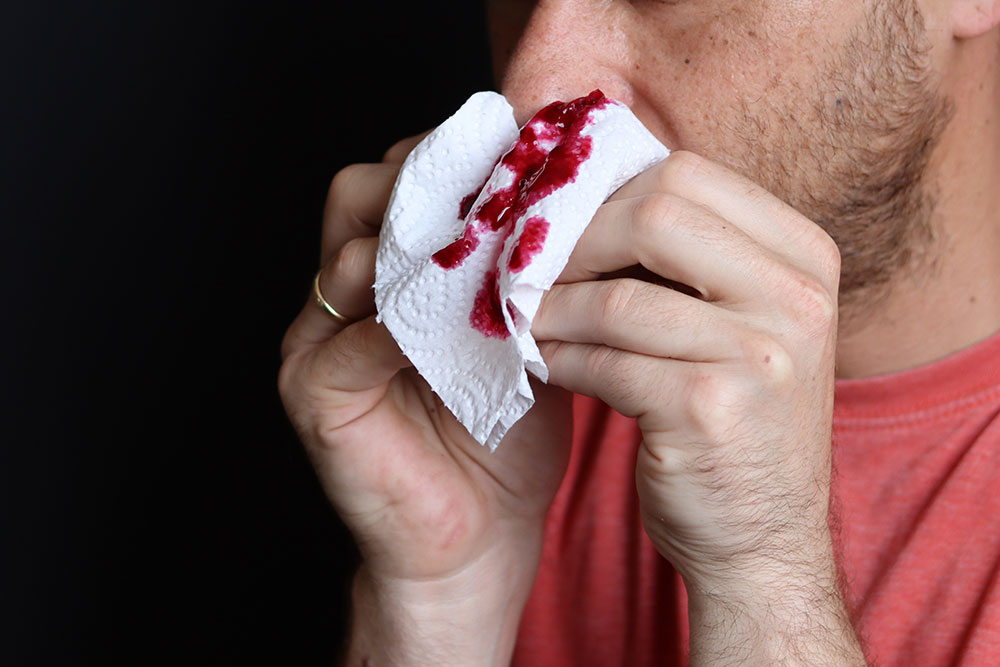

How to Provide First Aid for a Bleeding Nose

What is LOLER – Lifting Operations and Lifting Equipment Regulations 1998?

What Is Resident Engagement in the Building Safety Bill?

The Value of ESG Credentials: What You Need to Know

Coaching vs. Mentoring: Differences, Benefits & Opportunities

How to Improve Active Listening in Communication
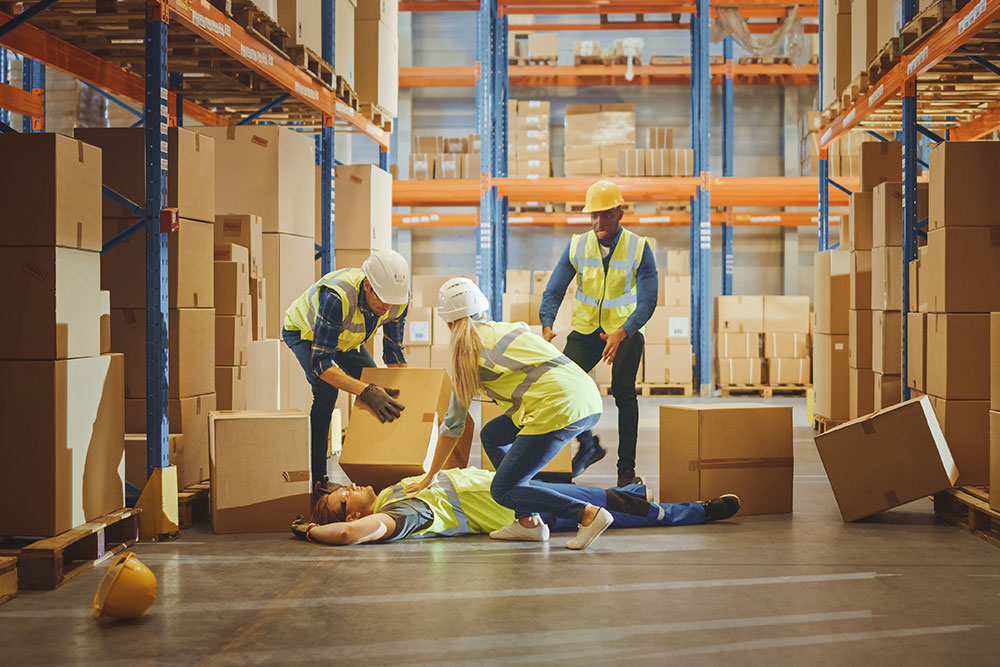

What Should You Do If an Accident or Sudden Illness Occurs at Work?

GDPR: A Guide to the Key Changes
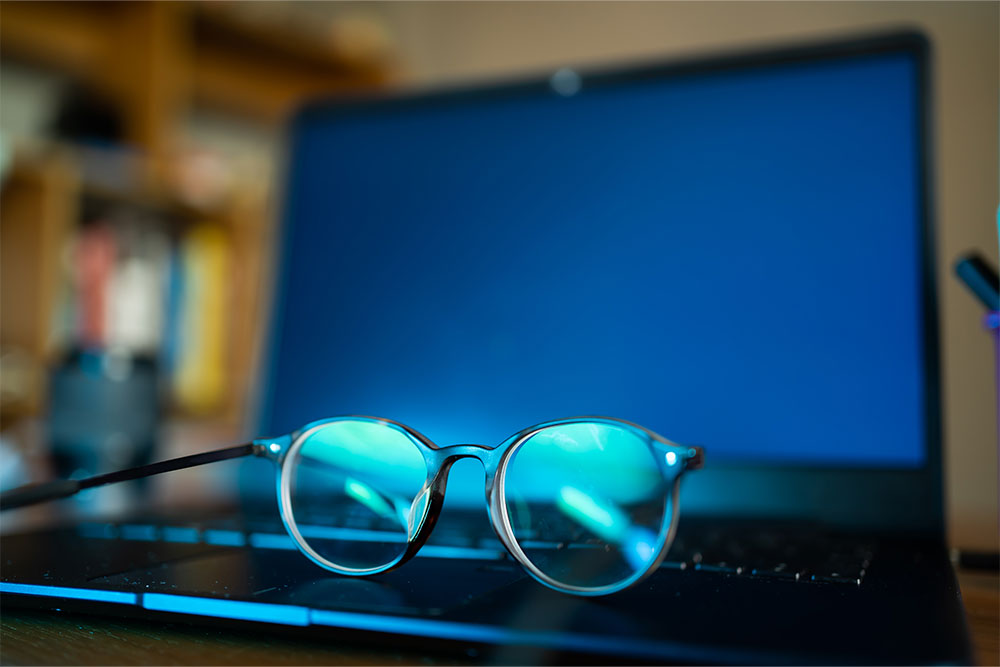

How the 20-20-20 Rule Helps To Prevent Eyestrain at Work
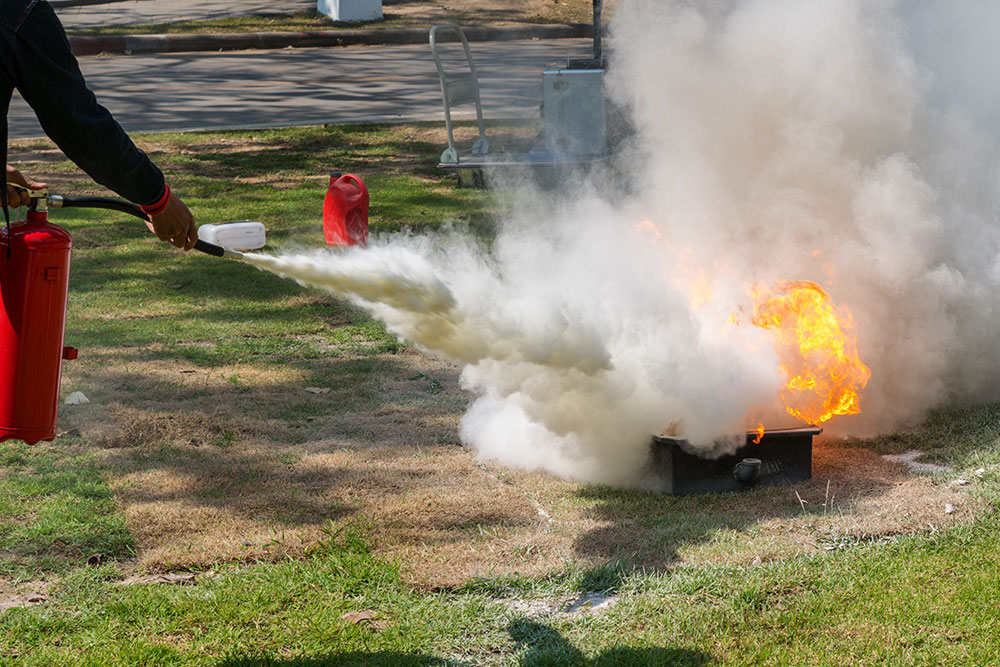

What Does PASS Stand for In Fire Safety?
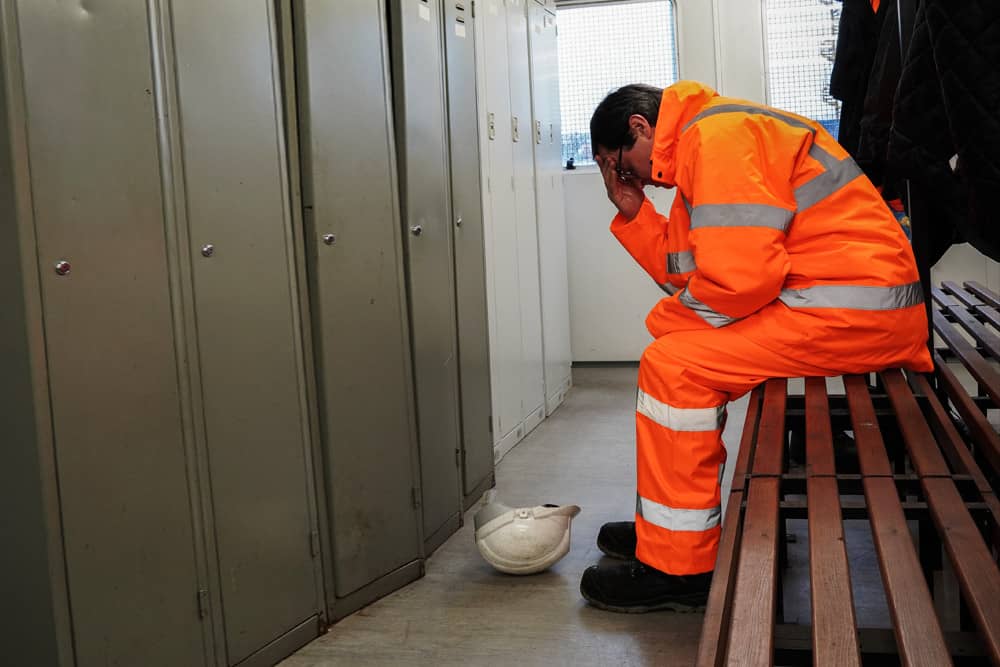

Importance of Mental Health in Construction

What Is the Data Protection Act 2018?

How to Conduct a Kitchen Risk Assessment for Restaurants and Catering Businesses

What is PUWER Machinery Guarding?

Human Focus Now Includes IIRSM approved Courses

Control of Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations 2002

How To Gauge Your Own Violence & Aggression Training Needs – Perspectives From Real Life Scenarios

How to Use Assessment for Learning

10 Effective Ways to Boost Employee Morale
Understanding the Risk Matrix: A Quick Guide

Choosing the Right Full Body Harness

What is Nonverbal Communication? Types and Examples

How to Comply with PUWER

Fire Safety Policy for UK Workplaces

How to Seek Help for Mental Health Support?

Understanding the Purposes of GDPR

The 4 Types of Food Safety Hazards

Hard Hat Colour Codes in Construction: What Do They Mean?

How an AED Can Save Lives

The History of Asbestos

Manual Handling – HSE Campaign 2023

A Guide to PUWER Main Features and Legal Requirements

Types of Asbestos Survey Explained

Ladder Safety in Work Environments – A Practical Guide

What Legislation Applies to Manual Handling in the UK?

What is ISO 14001 and How Can it Help Your Business?

Key Types of Fire Hazards on a Construction Site
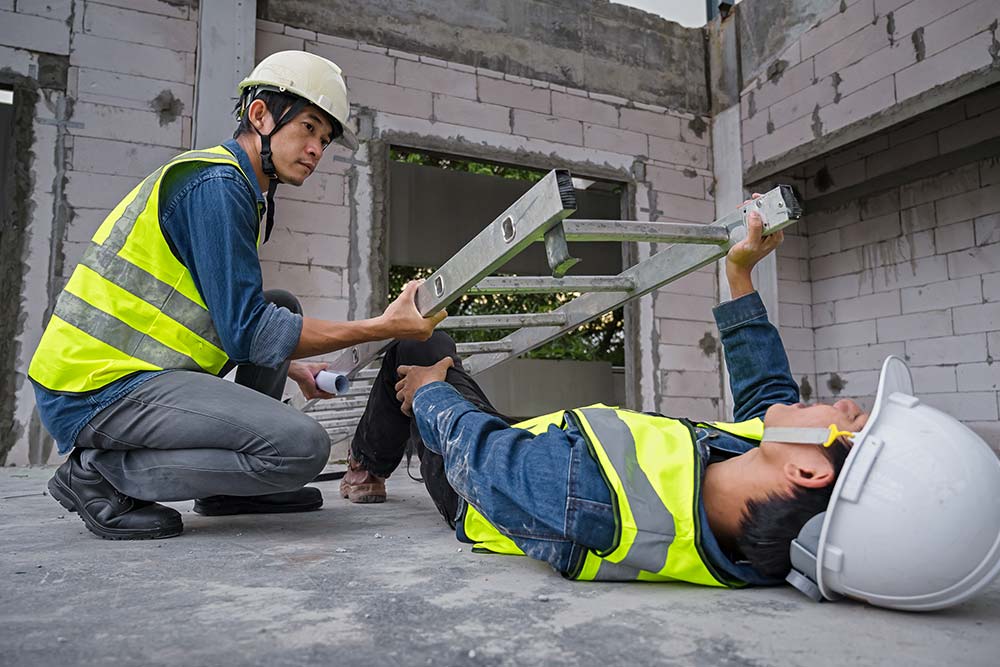

Fall from Height – the Leading Cause of Workplace Death

What is a Health and Safety File?

The Healthy Eating Food Pyramid – A Guide to Eating Well
The Four Types of Communication and When to Use Them
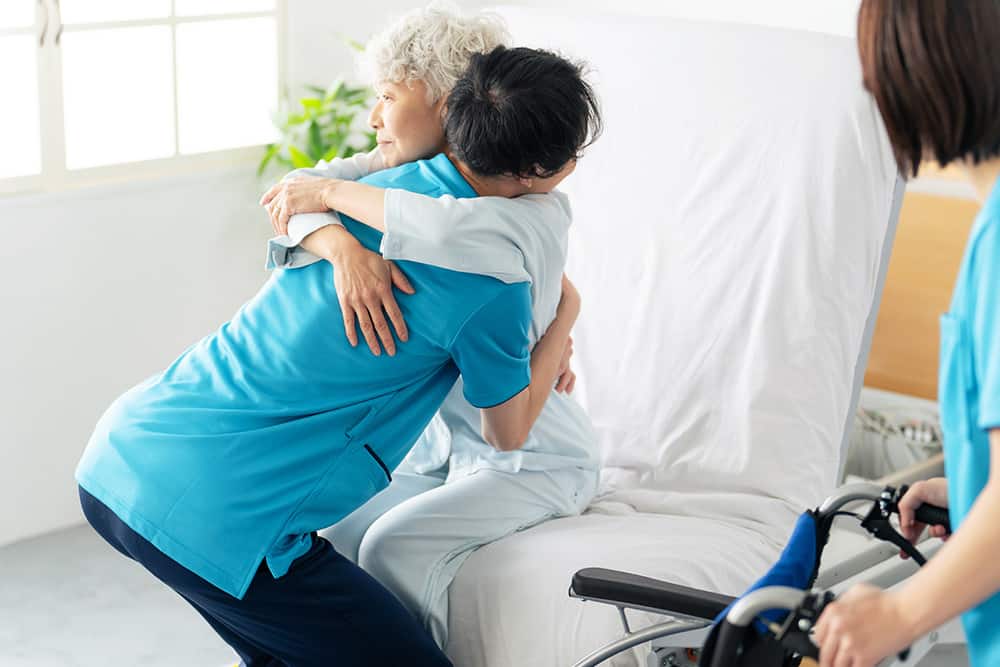

Principles for Safe Moving and Handling in Health and Social Care

How to Build Resilience in Healthcare Professionals

What is the Purpose of a Fire Door?

Why Competency is Vital on a Construction Site?

Data Protection in Schools – Everything You Need To Know

Slips, Trips and Falls – Everything You Need to Know
Employees Responsibilities for COSHH – A Complete Guide

How Often Should a Fire Risk Assessment Be Reviewed?

The Key Difference Between Fire Marshal and Fire Warden

Language Translation for online courses

How To Become a PAT Tester

What Is Corporate Social Responsibility?

What is Construction Design & Management Regulations 2015

Workplace Health Safety and Welfare Regulations 1992 – A Complete Guide

Can Stress Cause Chest Pain?

Working at Height Toolbox Talk

Refusal to Wear PPE: An Employer’s Guide

Fire Safety Poster – A Simple Way to Improve Fire Safety

Can I PAT Test My Own Equipment?

Where Are Fire Doors Required in a Building?

Do You Need To Worry About Silica Dust?

What Causes Sleepwalking?

What is a Fire Risk Assessment?

What to Include in a Hybrid Working Policy

Understanding the 4 Cs of Food Safety

What Are the Different Classes of Fire? A Short Guide to Fire Types

How to Conduct a DSE Workstation Assessment
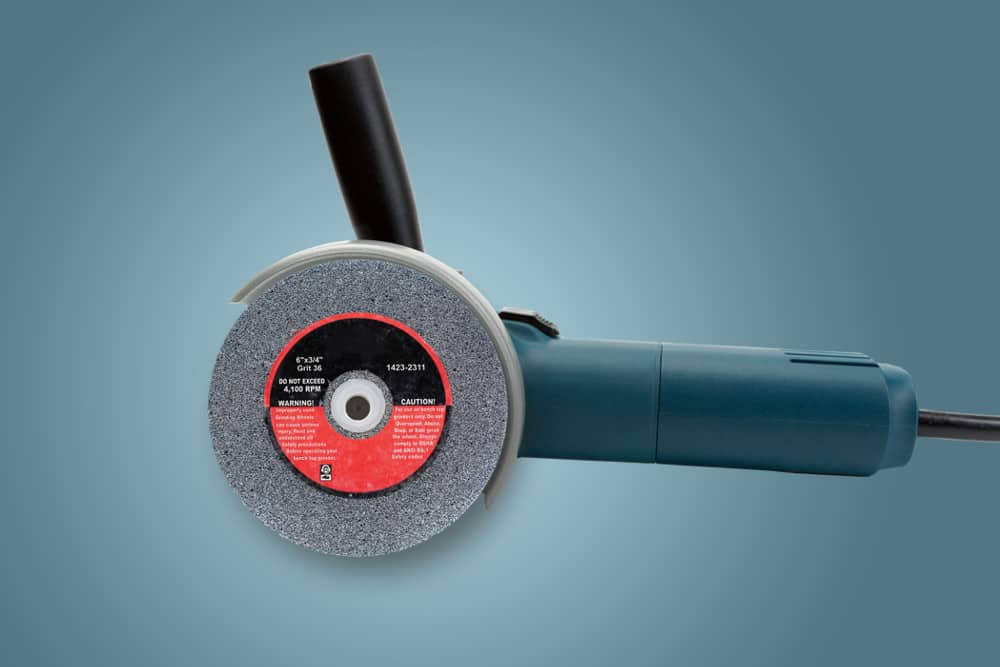

What Does the Code Number on an Abrasive Wheel Show?
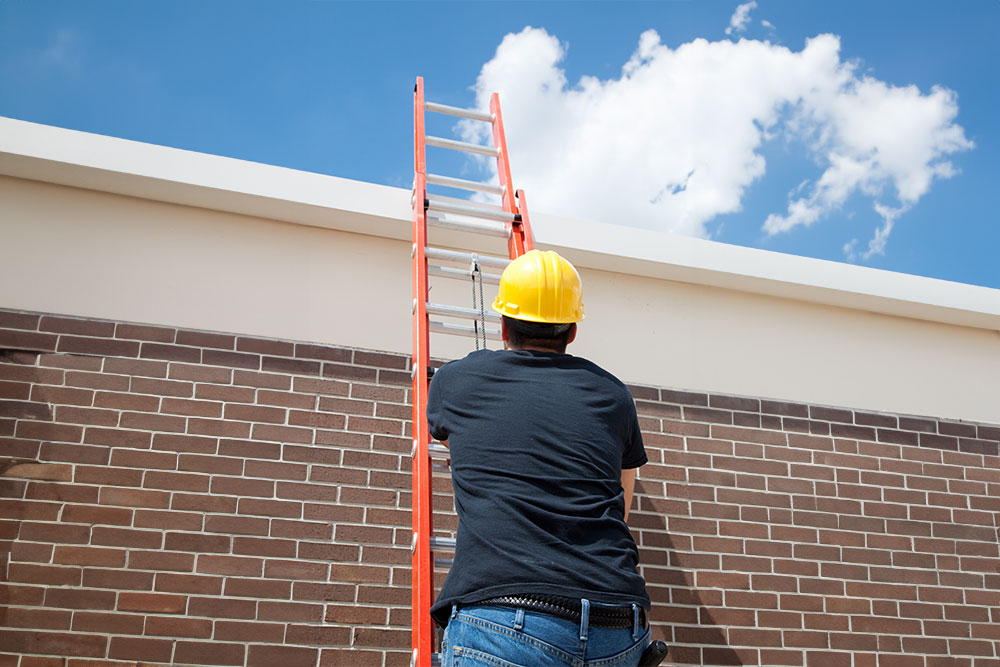

What Size Ladder Do You Need for a Two-Storey House?

Higher-Risk Residential Buildings: Accountable Persons

The Health and Safety Regulations You Must Comply With

Can Stress Cause Elevated Liver Enzymes?

What Level Is IOSH Managing Safely?

Types of Fire Alarm Systems for Your Business

What Is a COSHH Assessment?

Recognising and Overcoming Types of Bias

How to Conduct an Abrasive Wheels Risk Assessment

Food Preservation Methods and Guidance

Asbestos Insulation: The Vital Facts You Must Know

Mental Health VS Physical Health – What You Need to Know

What is GDPR? Why the GDPR Matters for Your Business

How to Put Out an Electrical Fire
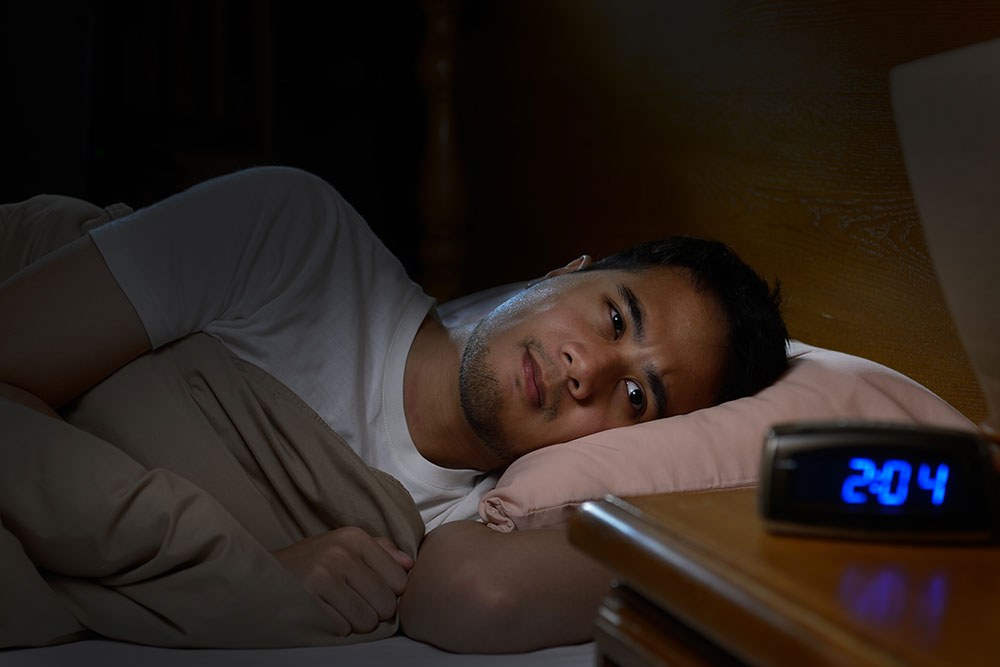

Why Sleep Is Important for Mental Health

4 Reasons Why Fire Safety Is Important for Employers

What Is the Difference Between Equality and Diversity?

Health and Safety Policy Template – Responsible Parties

What Is Environmental Health and Safety?

How to Use a Defibrillator

How Often Should Fire Warden Training Be Refreshed?

What are the 4 Types of Food Contamination?

Asbestos-Related Disease Deaths 2024

Work-related Accidents – 135 UK Fatal Injuries in 2022/23

Is Induction Training Required in Health and Safety Policy?

What are the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992

The Construction Phase Plan – Why Does It Matter?

What Is Working at Height?

Contagious behaviours and how we can use this to improve coronavirus safety?

How to Improve Near Miss Reporting

The Importance of GDPR In Healthcare

What Does LOLER Stand For?

Is PAT Testing a Legal Requirement?
When Should a Risk Assessment be Carried Out?

How to Improve Communication Skills

What Is a Food Temperature Danger Zone? Free Safety Chart

A Comprehensive List of Construction Vehicles Used in UK

What Does Health & Safety Training For Cleaners Need to Cover?

How to Become a Health and Safety Professional

What is an Asbestos Testing Kit?

Are You Making These 7 Common Ladder Safety Mistakes?

What is Health and Safety Audit & How to Conduct it?

Do You Have to Wear a Harness in a MEWP?

GDPR Compliance – 10 Rules for Managing Data Consent

When to Use a Fire Blanket

How Often Should a Fire Alarm Be Tested?

Human Focus Achieves Recertification in Cyber Essentials Scheme 2024

Communication Techniques to Help You at Work

Everything You Need to Know About Separation Anxiety in Adults

The Role of Violence & Aggression Training Online – A Perspective from The UK’s Leading Violence and Aggression Trainer

What is a CHAS Accreditation?

Recognising Common Cyber Security Threats

15 Stress Busters – What You Can Do to Address Stress

Who is Responsible for Enforcing Fire Safety Legislation?

What is an Abrasive Wheel?

Metacognition in the Classroom: Teaching Strategies & Benefits

7 Powerful Habits for Effective Teaching

Human Focus Fire Stopping Course Earns IFSM Approval

International Building Safety Month 2024

What Are The 7 Principles of GDPR?

Why is Health and Safety Important in the Workplace

8 Effective Stress Management Techniques

How to Foot a Ladder & What You Must Try First

How ASCONE Can Prevent Shoplifting & Avoid Wrongful Arrests

What Type of Accident Kills Most Construction Workers?

Mental Health in the Workplace – Everything You Need to Know

What Is a Banksman?

Stress Bucket – a Tool for Better Mental Health

Reduce the Time & Cost of Mandatory Equipment Inspections

How to Deal with Stress at Work

What Is Microbial Contamination?

Who Are the Duty Holders Under the New Building Safety Bill?

BBQ Fire Safety: A Complete Guide

How to Develop a First Aid Policy for Your Business

Good Fire Safety Housekeeping Practices in the Workplace

10 Common Manual Handling Injuries in the Workplace and How to Prevent Them

Manual Handling Equipment in the Workplace
Positive Mental Health for Healthcare Workers

What is Equality and Diversity?

Which White Goods Can Be a Fire Risk?

Three-quarters of All Fire Doors Are Not Fit For Purpose

Understanding Mental Health Continuum Model
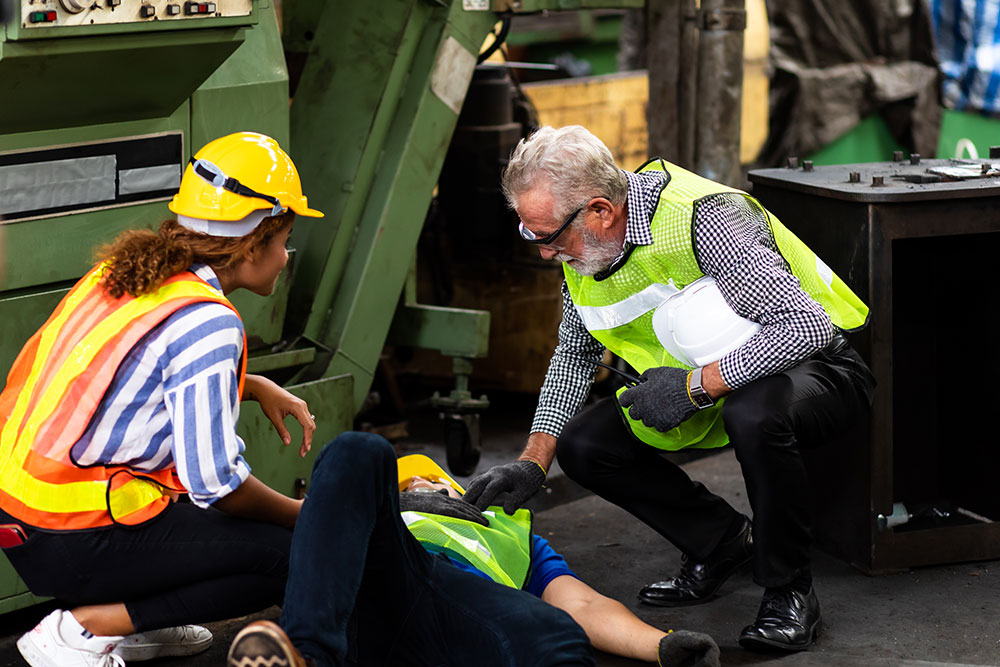

What Are the Responsibilities of a First Aider in the Workplace?
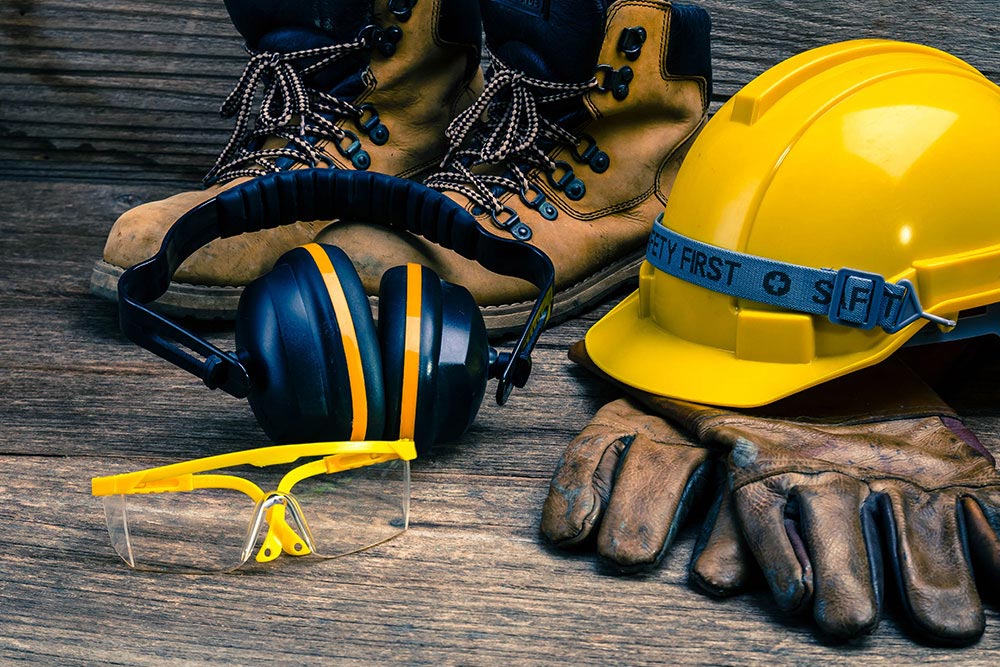

Types of PPE

Why You Should Do Legionella Testing and Water Analysis

What is Safeguarding & Why is it Important?

How Long Does Food Poisoning Last?

A Workplace Stress Risk Assessment Can Reduce Absenteeism

The 10 Golden Rules of COSHH and Why They Matter for Your Workplace

Warehouse Safety: The 5 Biggest Hazards

What is the Difference Between Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and COSHH Assessments?

Who Does the Control of Asbestos Regulations Apply To?

Can You Remove Asbestos Yourself?

Resilience in the Workplace: 4 Ways to Develop It

PAT Testing Checklist

Using ABC Charts for Challenging Behaviour: Free Template

How Important is Mental Health in the Education System?

How Many People Suffer from Slips, Trips and Falls at Work?

Floor Safety Tips: Reduce Slip, Trip and Fall Risks at Work

Manual Handling Tips for Construction Sites

What are an Employer’s Legal Duties in Respect to PUWER Risk Assessment?

The Importance of Defibrillators in the Workplace

What Are the Rules for Working at Height?

What is Human Resources (HR)? Duties and Responsibilities

What Needs PAT Testing – A Complete Guide

First Aid Signs and Symbols

What is DSEAR and Its Regulations? – A Complete Guide

Understanding Your Child Development Stages

Mental Health Stigma – Why We Avoid Mental Health Issues

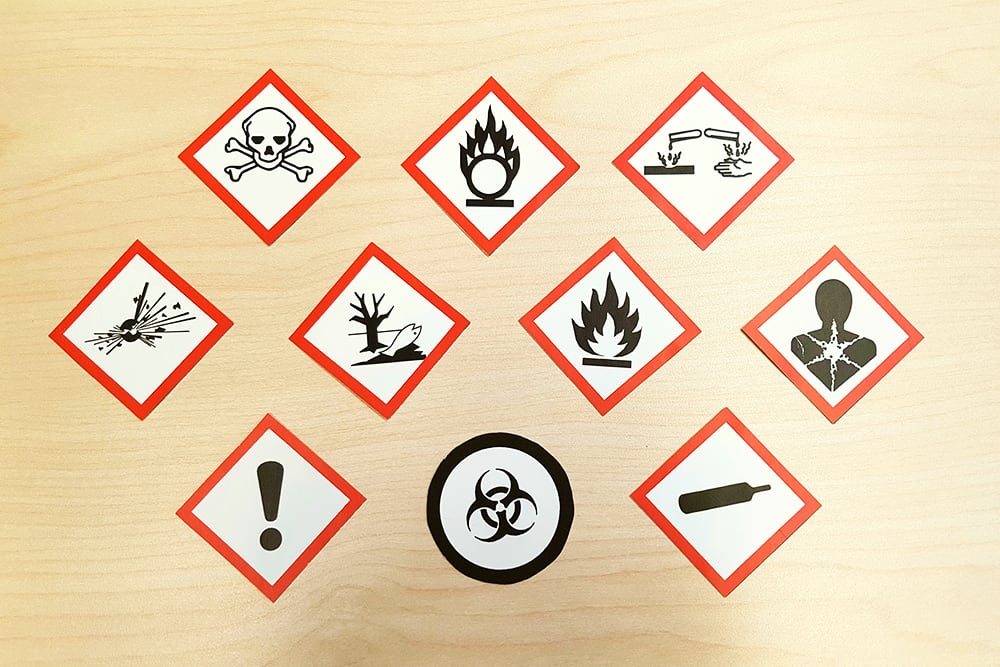
9 COSHH Hazard Symbols – What Does COSHH Mean

How to Implement an Effective Near Miss Reporting System

How to Become a Construction Worker

Free Workplace Fire Safety Checklist

Is COSHH a Legal Requirement – Everything You Must Know

Mental Health First Aid in The Workplace

A Short Guide to the UK’s Legionella Regulations

What is First Aid and How Can It Benefit Your Business?

Common Types of Working at Heights Equipment

First Aid Kits – What Should They Contain?

Manual Handling at Work – Everything You Need to Know

HSE Releases New Asbestos Statistics for 2021

Is Depression a Disability? Know Your Rights and Benefits

PUWER Regulations Guide – What Does PUWER Stand For?

AVPU in First Aid – Everything You Need to Know

What Is Due Diligence in Food Safety? Why Due Diligence Matters in Hospitality

What is Verbal Communication?

Why You Need a Fire Safety Course

Upgrade Your Accident Lessons Learnt Training

Supporting Mental Health in Schools

Using Electrical Safety Signs in the Workplace

Use By and Best Before Dates: What Is the Difference?

Pre-construction Information for CDM Regulations 2020

Mental Health at Work – Everything You Need to Know

COSHH Storage Requirements – Everything You Need to Know

Christmas Events & Covid-19: Updates on the UK Situation

The 3 Ps of First Aid Explained

Duty of Candour in Healthcare

World Lung Cancer Month 2023

What Are Types of Fire Extinguishers, Colours and Codes?

10 Fire Safety Tips for the Home and Workplace

Who is Responsible for Health and Safety in the Workplace

What Is Transgender Awareness Week 2023?

The UK Health and Safety Legislation Framework

What is Asbestos – Types, Hazards and Safety

Essential Safe Lifting Techniques for Manual Handling

6 Types of Mental Health Therapy

Keys to Mental Resilience #4: Being Active

Fire Safety in Care Homes – The 2023 Guide

What is Thalassophobia?

Working from Home: Health and Safety Compliance

The Cost of Non-Compliance: Why Regulations Matter

The Importance of a Working at Height Rescue Plan

How to Perform a Risk Assessment for Cleaning Work

What Are the Document Requirements Under CDM Regs?

Is My Incident Reportable Under RIDDOR?

What are the Principles of Equality and Diversity?

Why Are Risk Assessments Important?

Free GDPR Policy Template and Instructions

The Consequences of Poor Manual Handling in the Workplace

Equipment Maintenance Regulations for PUWER Compliance

Data Breach Reporting – How and When You Need to Do It

What Is a Defibrillator?

Mental Health Awareness Week 2024

Keys to Mental Resilience #1: Strong Connections

Active vs Passive Fire Protection

5 Essential Communication Skills for Nurses

Data Protection Licence – What It Is and How to Apply

Fire Safety Signs – A Complete Guide with UK Regulations

How to Prevent Slips, Trips and Falls in the Workplace

The GDPR Glossary of Terms Explained

How to Measure Regulatory Compliance in Health & Safety
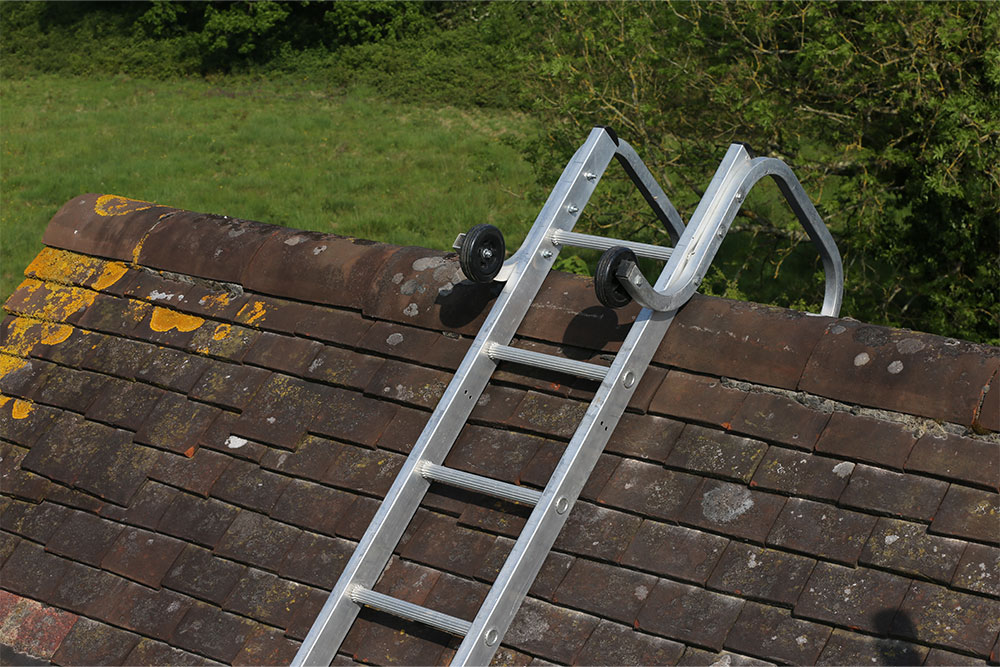

How to Use a Roof Ladder at Work

How Often Should Health and Safety Policies be Reviewed?

Flexible Working – What Are Your Rights and Responsibilities?

PAT Testing for Landlords – What You Need to Know

How Health And Safety In Film And TV Can Improve

Team Manual Handling – When and How to Do It Safely

CDM Regulations – A Complete Summary with 4 Examples

What is a Health and Safety Policy?

What is the Difference Between a Hazard and a Risk

How a Project Works Under a CDM Coordinator

Defibrillators In Schools Campaign

What is a Safety Data Sheet and Why it is important?

What Is PPE and Why Is It Important in the Workplace?

Fire Wardens in the Workplace – Why Do We Need Them?

The Employee Value Proposition – Why the EVP Is a Big Deal for Businesses

Revolutionising Manual Handling Training: From Theory to Practice

What is Prader-Willi Syndrome?

University Mental Health – Role of Students

What is a Confined Space?

The Importance of Mental Health in Hospitality

What is Catastrophising and How Can it be Managed?

Mental Health at Work: What Resilience Can Do For You

What is a Risk Assessment? – Here’s A Brief Description

When Did GDPR Come into Force?

How to Reduce the Time & Costs of ISO 45001 Compliance

What are the COSHH Requirements in a School?

Workplace Verbal Abuse Quiz: How Sensitive Are You to Verbal Abuse?

How Often Should LOLER Testing Be Done?

What is the Regulatory Reform Fire Safety Order 2005

Who is Responsible for Health and Safety in the Workplace?

What is the Hierarchy of Manual Handling?
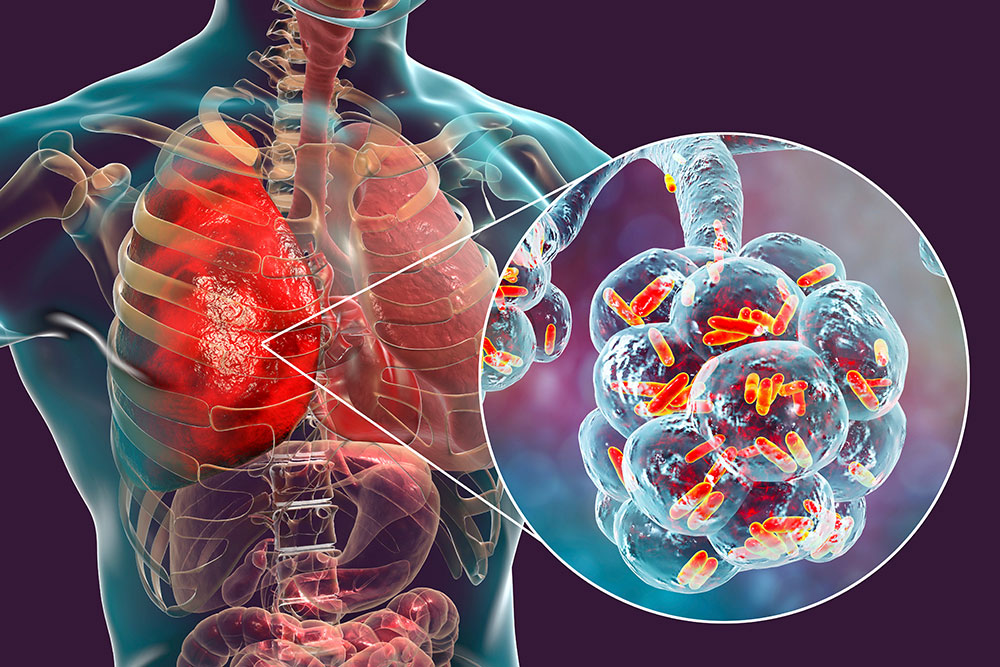
Legionnaires’ Disease – Causes, Symptoms & Treatments

Health and Safety Legislation in Schools

Understanding Mental Ill-Health

How to Prevent Human Error in Workplace

New Duty to Manage Asbestos Guidance – Are You Compliant?

PPE Regulations – Everything You Need to Know

How to Talk About Mental Health

What Are the GDPR Consent Requirements?

What is RACE Fire Safety?

10 Types of Fire Hazard in the Workplace

What is a Dynamic Risk Assessment?

Data Protection Act 2018 Summary – What You Need to Know

How to Lead a Manual Handling Toolbox Talk

7 Reasons Why Workers Don’t Report Near Misses

Guidance for Defibrillator Sign Standards

Health and Safety at Work Act 1974

What Does FED Stand for in Fire Safety?

Using the Power Zone for Safer Manual Handling

How to Use a Safety Harness on a Roof

Why is health and safety important for all workplaces?

What Are The 6 Principles of Safeguarding?

How to Report Health and Safety Concerns?

Food Hygiene Rating Scheme Explained

8 Ladder Hazards Most Workers Miss

Caldicott Principles – A Complete Guide

New Mandatory Training for The Safe Use of Diisocyanates

What is Bullying in the Workplace?

Why is RIDDOR Important?

Why is a Legionella Management Plan Important for Employers

What is Nyctophobia?

How Many Fire Extinguishers Do I Need for My Workplace?

Business Letter Format: How to Write a Business Letter

What Skills Do Mental Health First Aiders Need?

What Are the Six Stages of Cleaning?

Duties in the Fire Safety Act 2021 – A Complete Overview

What Is Sexual Harassment?

The Biggest GDPR Fines of 2023

Accident Investigation Questions: Uncovering Root Causes

What is Safeguarding Adults and What are the Legal Responsibilities of Caregivers?

How to Measure Stress Levels

Can Stress Cause Nosebleeds?

Keys to Mental Resilience #2: Relaxation

Manual Handling in Healthcare – Why it is Important

Food Safety for Small Businesses

Who Is Responsible for Fire Safety in the Workplace?

What is a Method Statement?

Safety Harness Regulations You Must Know

When is it Permissible to Paint a Ladder?

The Role of Universities In Student Mental Health Support

What is PAT Testing and Why Should You Do It?

What Are the Benefits of Effective Communication Skills in the Workplace?

How to Use a Fire Extinguisher to Stay Safe at Work

What is the Golden Thread? | Building Safety Act 2022

What is Health and Safety Competence?

Why a Near Miss Form is Essential for Workplace Safety

Difference Between Flammable and Combustible Materials

What is COSHH? | An Introduction

Display Screen Equipment Regulations 1992– What They Are & Why They Matter

Hierarchy of Control: Working at Height – A Complete Guide

Can Manual Handling be Avoided Completely?

How to Do the Primary Survey in First Aid with DRABC Steps

Why Communication Models Are Important in the Workplace

IOSH Membership – Types and Benefits

Mental Health Discrimination at Work – All You Must Know

Building Safety Act 2022: How to Register A High-Rise Building
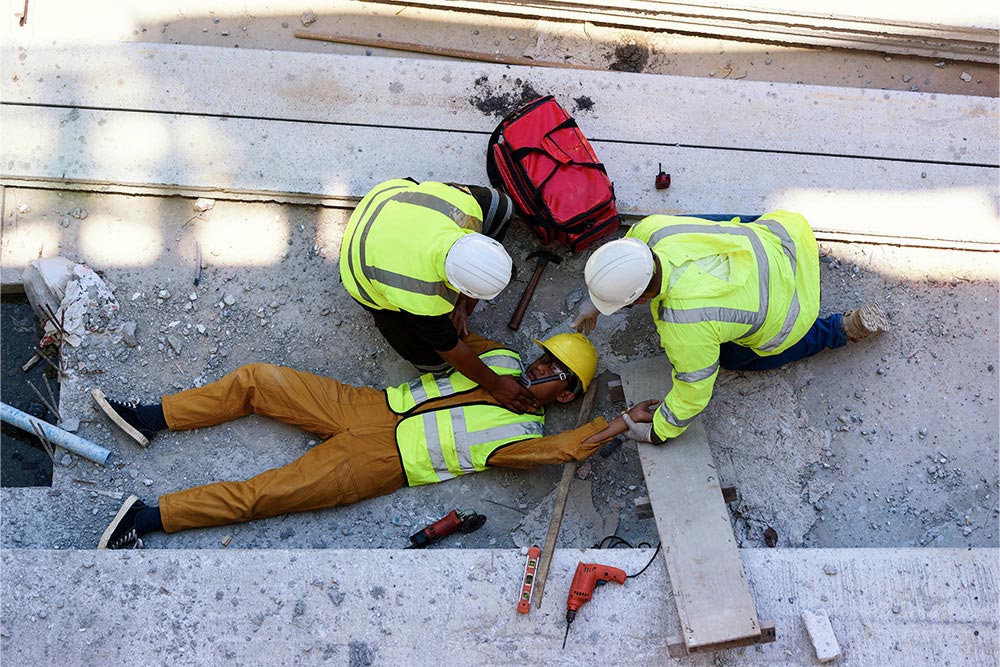

What is a First Aid Secondary Survey?

HSE Statistics – Work-Related Fatal Injuries 2023/24

5 Ways to Promote Equality and Diversity in The Workplace

How to Test for Asbestos

HSE Asbestos Services Surveys

Coronavirus Safety – A Behavioural Nudge

Food Allergy – Causes, Symptoms & Treatments

What Is Legionella Risk Assessment?
PAT Testing Risk Assessment

What are the Benefits of Staff Fire Awareness?

The Importance of COSHH in Care Homes

How Long Does PAT Testing Last? Everything You Must Know

A Personal Development Plan (PDP) Guide & Template

What Are the Four Ways in Which Fire Can Spread?

Women in Construction

What Temperature Kills Legionella?

How to Manage the Health & Safety of Homeworkers

Key Ingredients of an Effective Permit to Work System

Control of Noise at Work Regulations 2005

List of Construction Training Courses

How to Improve Mental Health by Making Lifestyle Changes

What is Dementia? Signs, Treatment & Prevention

The Importance of ISO 45003 in the Workplace

What Is Diversity in Health and Social Care?

Who is Responsible for Using a Fire Extinguisher?

New Fire Safety Duties for Responsible Persons

15 Types of Cyber Attack

Valentine’s Day Tips for Mental Health

What Does ELITE Stand For in Moving and Handling?

PAT Testing Regulations UK – Explained

How Often Should You Service Fire Extinguishers?

How to Support Someone with Mental Health Issues

Can Stress Cause Diarrhoea? What You Can Do to Avoid Anxiety-Induced Diarrhoea

How to Conduct a Fire Risk Assessment for a Hotel

Why Many Don’t Take Workplace Verbal Abuse Seriously & What You Can Do If It Happens to You

How to Defrost a Freezer

6 Key Fire Marshal Responsibilities You Should Know

The HSE’s ‘Work Right’ Campaign Focuses on Construction Dusts
The Fundamentals of Risk Assessments in the Workplace

How to Maintain Confidentiality in Health and Social Care

What is the Role of a Fire Warden?

How to Stand at a Standing Desk

How to Manage Mental Health at Christmas

What Does Asbestos Look Like – Common Uses

Chopping Board Colours – What Do I Need?

Building Resilience in Children

Mental Health Act Reform – Why is it Needed?

Violating Fire Safety Regulations Could Lead to Unlimited Fines

What is Near Miss Incident?

Food Safety Act 1990 – A Complete Guide for Food Businesses

Manual Handling Tasks: What You Must Do to Reduce Risks

Why Fire Training for Schools is Critical

Scaffolding Safety – Regulations and Requirements

How to Help Someone Struggling with Mental Health

What is the Children Act 2004?

Ladder Angle: What is the Rule for Safe Ladder Work?

What Is Mental Health – Your Questions Answered Here
What are High Risk Foods

The Shannon and Weaver Model of Communication at Work

How to Make Workplaces Safer for Employees

Fire Evacuation Plan For 2023

What is Time Management? – 5 Common Faults and Fixes

Fire Safety Tips for Christmas 2023

What are Permit to Work Systems?

Changes to the Higher-Risk Buildings Regulations

What is a Hazardous Substance?

What Needs to Be in Your Health and Safety Policy?

10 Manual Handling Techniques for Your Workplace

What Is Display Screen Equipment?

Recycling Symbols in UK – A Guide for Businesses

What Is Mental Health and Why It Is Important?

The Risks of Hand Arm Vibration

How to Write a Cyber Security Policy

Regulation vs Legislation – How Do They Differ and Why Does it Matter for Your Business?

How to use PPE Signs in the Workplace

Manual Handling Weight Limits – Why They Are Important

The Equality Act 2010 Explained

World Day for Safety and Health at Work 2023

Protecting the Public During Construction Work

How Many Steps Are There to COSHH Compliance?

Why is Workplace First Aid Important?

Top 10 Mental Health Journal Prompts

Ladder Inspection Checklist – Legal Requirement To Inspect Your Ladders

The 5 Principles of Mental Capacity Act

10 Vital Data Protection Methods

LOTOTO – Why You Need to Upgrade Your LOTO System to LOTOTO

Mental Health Myths and Facts – What’s the difference?

The 5 Steps in Risk Assessment Business Owners Must Know

What Is an Appointed Person for Lifting Operations?

Types of Lifting Operations

Sickness Absence Management

Mental Health in Construction – Everything You Need to Know

What is a Subject Access Request GDPR?
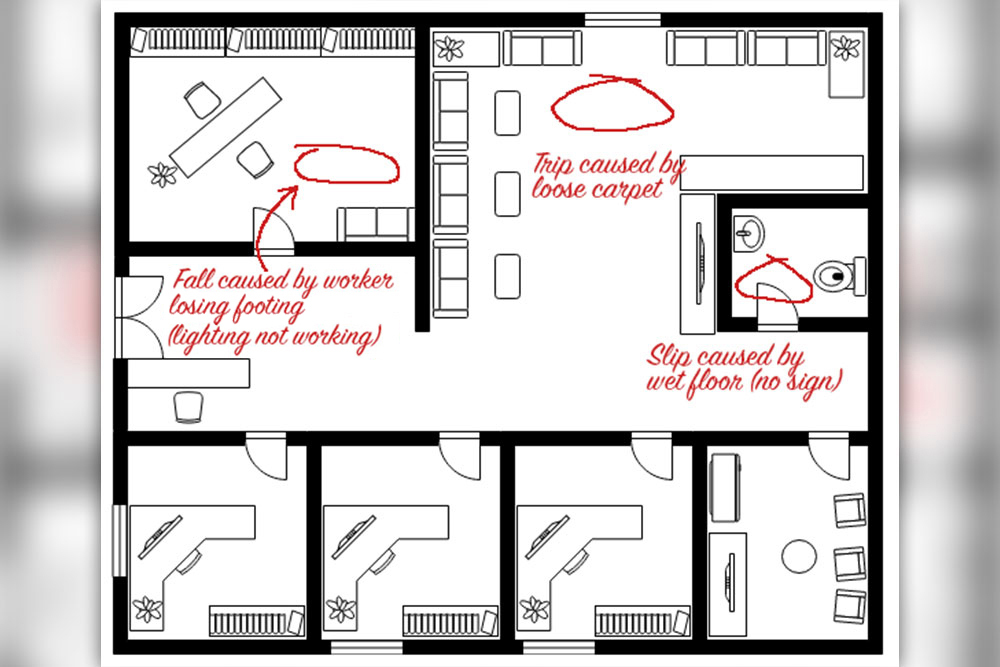
What is Slip and Trip Mapping Used For?

Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999

Fire Safety Risk Assessment – Everything You Need to Know

Why You Need Fire Extinguisher Signs and How to Use Them

A Short Guide to Warning Signs in the UK

Hazard Perception – Why Does This Matter?

How to Check if CDM 2015 Applies to Your Project

Stress & Anxiety: How Alcohol Affects Your Mental Health
New Fire Safety (England) Regulations 2022 – Duties from January 2023

How to Turn Off a Fire Alarm
Popular Courses

Recent Articles

Current Offers

£ 895.00 Original price was: £895.00. £ 595.00 Current price is: £595.00. +VAT

£ 100.00 Original price was: £100.00. £ 49.00 Current price is: £49.00. +VAT

£ 100.00 Original price was: £100.00. £ 60.00 Current price is: £60.00. +VAT
£ 25.00 Original price was: £25.00. £ 15.00 Current price is: £15.00. +VAT
Slips, Trips, and Falls
Members can click here for an ad-free version of this talk!
Slips, Trips, and Falls Safety Talk
Slips, trips, and falls are one of the leading causes of injuries and fatalities in the workplace. According to OSHA, slip, trip, and fall incidents cause 15% of all accidental deaths and are second only to motor vehicle incidents as a cause of fatalities on the job. These types of incidents can result in life-changing injuries to the employees who suffer them.
Common Slip, Trip, and Fall Incidents
- Falls from elevation are often deadly or result in serious injury and may include falls from ladders, falls off of mobile equipment, falls from roofs or other elevated structures, etc.
- Slip incidents on slippery surfaces such as snow and ice are common in colder geographical areas in the U.S. Wet floor conditions or spilled liquids are also common causes of slip incidents at work.
- Trips can be caused by a multitude of reasons, including poor housekeeping , changes in elevation, poor lighting conditions, improper footwear, etc.
Mitigation Actions to Prevent Slip, Trip, and Fall Incidents
- Always use fall prevention or protection for work over 4ft in general industry work and 6ft in the construction industry. Protect workers by using proper guarding of any holes or open windows and use guardrails to prevent falls. Where guardrails are not feasible, use adequate fall protection. An example of adequate fall protection is a full-body harness and a self-retracting lanyard attached to an approved anchor point with 100% tie-off.
- Proper housekeeping is very important in preventing slip, trip, and falls incidents. Objects on the ground create a hazard for anyone walking or working in the area. Maintain clearly defined paths for walking in the work area. Maintain organized laydown yards for tools and equipment out of the way of employee foot traffic.
- Address any wet, slippery, or icy walking surfaces in your work area. Post signs of any hazardous surfaces until the situation is taken care of completely.
- When climbing up or down a portable or fixed ladder, ensure that you use proper techniques, such as using three points of contact and keeping your belt buckle within the sides of the ladder. Do not lean to reach objects- this can throw off your balance, and you could fall.
Discussion points:
-Are there trip hazards due to improperly placed objects in your work area?
-Has anyone or a close family member of yours experienced a severe fall? How has it affected you/ them?
-What are other ways we can protect ourselves from slips, trips, and falls here at our site?
Slip, Trip, and Fall Safety Presentation
Looking for a complete safety meeting on slips, trips, and falls? This safety meeting focuses on injury statistics, common slips/trips/fall hazards, and best practices to reduce the risk of injuries.
This product bundle includes an editable 10-slide PowerPoint presentation, an editable 7-question quiz, an answer sheet, three related safety talks , and a sign-in sheet.
This product provides everything you need to have a safety meeting and the supporting materials to create a longer safety campaign to keep safety at the top of your employees’ minds.
Save your time by purchasing this slips, trips, and falls safety bundle!

Do you want downloadable PDFs of all of the talks? Join as a member and get all of the 250+ free talks as well as 300+ additional talks in PDFs that are easy to download and print!
One thought on “Slips, Trips, and Falls”
How do i get free safety talks from your site i am needing industrial construction safety talks oil and gas rigging installing piping etc
Comments are closed.

- CAHF History
- Meet the CEO
- CAHF Leadership
- East Bay Chapter
- Golden Gate Chapter
- Redwood Empire Chapter
- Santa Clara Chapter
- Delta Chapter
- Progress Valley Chapter
- Sacramento Chapter
- Sierra Chapter
- Central Valley Chapter
- Central Coast Chapter
- Channel Islands Chapter
- Kern County Chapter
- Long Beach / South Bay Chapter
- Los Angeles Chapter
- Pasadena/San Gabriel Chapter
- San Fernando Chapter
- Orange County Chapter
- San Bernardino / Riverside Chapter
- San Diego Chapter
- Consumer Help
- Legacy Partner Program
- AHCA Member Savings Program Participants
- 2023 Patrons of the Association
- Advertising with CAHF
- CAHF Code of Conduct
- Contact CAHF
- A Scholarship Opportunity
- CE Instructions
- On-Demand Course Catalog
- Program Services
- Restorative Nursing Program
- 2024 Table-Top Shows (Associate Members ONLY)
- National Association of Health Care Assistants (NAHCA)
- Request CEs
- Sponsorships
- CAHF 2024 Annual Convention & Expo
- 2024 Exhibitor Prospectus
- 2024 Expo Booth Reservations
- 2024 Expo Floor Plan
- More Resources
- Vaccine Information
- Associate Member Brochure
- Career Center
- Elder Care California
- Helpful Links
- 2022 Quality Report
- CAHF on Social Media
- Next Steps in Your Care Materials
- Five Year Quality Snapshot
- 2018 Annual Report
- Shopping Cart
- Facility Search
- Facility Directory
- Vendor/Associate Member Search
- Vendor Directory
- Buyers Guide
- 2020 Award Recipients
- 2023 AHCA Quality Award Winners
- CAHF Disaster Preparedness
- Planning Emergency Response - Disaster Preparation
- Pre-Employment Criminal Background Screening
- The Role of the QIDP
- Legislation
- CAHF PAC - Contribute to Candidate Campaigns
- Be a Long-Term Care Advocate
- Advocacy Tools
- Antipsychotic Reduction
- CNA Training Kickstarter Project
- Dietary Services Project
- Facility Faces of California Photo Contest
- Music and Memory
- Nursing Home Leader Academy (NHLA)
- Nurses Council
- Volunteer Engagement Project
- Become An Associate Member
- Facility Membership Information
- Add Buyer's Guide to Your Phone

Fall & Alarm Reduction Empira
Secrets of the Stars: A Blueprint for a Fall Prevention Program
Questions at the Time a Resident Falls
Family & Friends: Fall Prevention - How You Can Help!
Fall Scene Investigation Report
Hourly Needs for the "4 Ps"
Fall Risk Assessment & Prevention Tools
- Competencies: Fall Management
- Tinetti Balance Assessment Tool
Fall Risk Assessment: Hendrich II Scale
Fall Investigation Report
Fall Risk Predictive Factors Assessment
Slips, Trips and Falls Checklist
SAMPLE Fall Prevention Program Work Plan with Resources
SAMPLE Fall Prevention Program Work Plan Template
Quality Measure (QM) Drilldown Quick Reference Tool
Alarm Reduction
Reducing and Discontinuing Resident Alarms
Case Study: Nursing Home Alarm Elimination Program
Rethinking the Use of Position Change Alarms
Other Tools & Resources
Health Care Association of New Jersey: Fall Management Guideline
Ontario Shores Falls Risk Assessment, Prevention and Management Self Learning Package
QAPI Goal Setting Worksheet
Falls: Are We Really Doing Everything To Prevent Them?
Increase Resident Mobility-Resident Fact Sheet
Increase Resident Mobility-Leadership Fact Sheet
Increase Resident Mobility- Staff Fact Sheet
Calming Interventions
Engineer/Maintenance Inspection List
Huddles Tip Sheet
Sample Fall QA Form
Case Study: Luna Lights Pilot Program
Sample Fall Committee Minutes
Individualized Restraint Reduction Process
Restraint/Device/Enabler Flow Chart
- sidewalk obligations and liabilities california
Sidewalk Obligations And Liabilities In California
Introduction:
It comes as a surprise to many property owners in California when they discover that under State law the public sidewalks next to their property are their responsibility to maintain in safe condition.
Liability between municipalities and landowners for condition of the sidewalk and for injuries sustained by those using the sidewalk due to defective sidewalk conditions is the subject of lawsuits and statutory provisions. In California, municipalities and counties usually own the sidewalks next to private property, but California state law long enacted states that the landowners are responsible for maintaining the sidewalk fronting their property in a safe and usable manner.
According to Streets and Highways Code 5610:
“The owners of lots or portions of lots fronting on any portion of a public street or place when that street or place is improved or if and when the area between the property line of the adjacent property and the street line is maintained as a parking or a parking strip, shall maintain any sidewalk in such condition that the sidewalk will not endanger persons or property and maintain it in a condition which will not interfere with the public convenience…”
This article shall discuss the ramifications of this law in California.
The Basic Law:
The Cost of Repair:
California state law provides that a municipality may assess landowners for the cost the municipality incurs to maintain sidewalks if the landowner fails to perform his/her duty. Note that this is a choice available to the municipality and not all so assess.
The Issue of Liability:
The law is clear: the property owner must maintain the sidewalks in a safe condition. What happens if the owner does not and there is injury to a third party?
Note that the municipality is required to pass local law if it wants to imposed liability for injuries upon the owner. Although state law provides that abutting landowners are responsible for sidewalk maintenance and may be assessed the cost of repairs, they may not be liable for injuries or damages to third persons who use the sidewalk, unless the municipality enacts an ordinance that addresses liability. Williams v. Foster (1989). The Williams case occurred after the plaintiff, Dennis Williams, tripped on a raised portion of the sidewalk in the City of San Jose, and thereafter sued the City. In its defense, San Jose argued that under Section 5610, the owner of the property fronting the sidewalk in question was solely liable. Rejecting this contention, the court held that Foster (landowner) owed no legal duty at all to the injured plaintiff.
In reaching the Williams decision, the court held that imposing upon abutting owners a duty of care in favor of third persons “would require clear and unambiguous language,” which according to the court, is not contained in 5610. Notably, the court went on to state that the City, “could have enacted an ordinance which expressly made abutting owners liable to members of the public for failure to maintain the sidewalk but did not.” Following the Williams decision, the City of San Jose amended its sidewalk ordinance to include language similar to that suggested by the Williams Court. It is vital for property owners to check the local ordinance to see their level of liability.
In 2001, after adopting a sidewalk liability ordinance that addressed the issues raised in Williams, San Jose was sued by Joanne Gonzalez, who alleged she was injured when she tripped and fell over a raised portion on a public sidewalk. Gonzalez also sued Charles Huang, who owned the property adjacent to the sidewalk on which she fell. Huang was sued on the theory that he had a common law duty to the plaintiff to maintain the sidewalk in a non-dangerous condition, as well as a duty under the San Jose Municipal Code.
The City of San Jose argued that the adjacent property owner was partially liable because he had not maintained the sidewalk as required by the local ordinance. Huang filed a motion for summary judgment arguing in part that the sidewalk liability ordinance enacted by the City of San Jose was unconstitutional. The trial court agreed with Huang and granted his Motion for Summary Judgment. Both Gonzalez and the City of San Jose appealed.
The case proceeded to the Court of Appeal which in 2004 ruled in San Jose’s favor. (Gonzales v. City of San Jose (2004.) The primary issue before the court was whether the state law preempted the local measure. The court found that the ordinance was constitutional and was not preempted by state law.
In its holding, the Gonzales court noted that cities are empowered under the California Constitution to enact ordinances and regulations deemed necessary to protect the public health, safety, and welfare, and that the City of San Jose’s ordinance was a permissible exercise of that power. Without such an ordinance, the court noted, landowners would have no incentive to maintain adjacent sidewalks in a safe manner.
The court emphasized that the ordinance did not serve to absolve the city of liability for dangerous conditions on city-owned sidewalks when the city created the dangerous condition, knew of its existence and failed to remedy it.
Since the Gonzales ruling, many municipalities have enacted liability shifting ordinances. Check your local law!
Note that even in jurisdictions which have enacted liability shifting ordinances, one must determine the cause of the defective sidewalk condition. In some ordinances, liability does not shift to the landowner if the landowner did not cause the defective condition to exist.
The city, and sometimes additionally the adjacent property owner, may be generally liable for negligence in causing a dangerous and defective public sidewalk that causes personal injuries. Others might, and times, also be liable. Consider, for example, a builder or hired contractor negligently repairs a sidewalk resulting in injuries or a landscape architect negligently plants a tree that distorts the sidewalk. Those are parties that may also be brought into the action.
And if the government is at fault, it remains liable despite the duty to maintain imposed upon the landowner. A public entity (typically a city or municipality) is liable for foreseeable injuries caused by a dangerous condition on the public sidewalk negligently (unreasonably) created their employee. Government Code Section 830, 835(a) and 835.4.
Further, a public entity is liable for foreseeable injuries caused by a dangerous condition on the public sidewalk negligently (unreasonably) created by an adjacent/abutting landowner or other third party if the public entity had actual or constructive notice (knew or should have known) of the dangerous condition for a sufficient time before the injury to have taken measures to protect against the danger. See Government Code Section 830, 835(b), 835.2 and 835.4. Peters v. City and County of San Francisco (1953) 41 Cal. 2d 419, 429. A “dangerous condition” is one that creates a substantial risk of injury when the property is used with due care in a reasonably foreseeable manner. Government Code Section 830(a). Minor, trivial or insignificant defects are not deemed as dangerous. Government Code Section 830(a) and 830.2.
Note that the owner is liable for conditions of danger created by the owner even if on the public sidewalk.
“An abutting owner has always had a duty to refrain from affirmative conduct which would render the sidewalk itself or use of the sidewalk dangerous to the public.” ( Selger v. Steven Brothers, Inc. (1990) 222 Cal.App.3d 1585, 1592, 1594; see also Swanberg v. O’Mectin (1984) 157 Cal.App.3d 325, 330; Lompoc Unified School Dist. v. Superior Court ( 1993) 20 Cal.App.4th 1688, 1693; Peters v. City & County of San Francisco ( 1953) 41 Cal.2d 419, 423.
But if there is no negligence on the part of the owner and no local ordinance imposing a duty to repair, California Streets and Highways Code § 5610 does not impose on owners tort liability or a duty to indemnify municipalities for pedestrian injuries, except where a property owner created the defect or exercised dominion or control over the abutting sidewalk. Williams v. Foster (1989) 216 Cal.App.3d 510, 516-517 & fn. 8; Schaefer v. Lenahan (1944) 63 Cal.App.324, 327-328, 331-332; see Gonzales v. City of San Jose (2004) 125 Cal.App.4th 1127, 1137.
The lack of tort liability to property owners for injuries to sidewalk travelers unless the injuries are caused by the property owner is often referred to as the “Sidewalk Accident Decisions Doctrine.” Contreras v. Anderson (1997) 59 Cal.App.4th 188, 195, fn. 6.
- A property owner may be liable if he or she alters the sidewalk for the benefit of the owner's property. Sexton v. Brooks (1952) 39 Cal. 2d 153, 157.
- A property owner may also be liable if he or she negligently damages the sidewalk. Moeller v. Fleming (1982) 136 Cal. App. 3d 241, 245 (break in sidewalk caused by the property owner’s tree); Alpert v. Villa Romano Homeowners Association (2000) 81 Cal.App.4th 1320, 1335-1336 (issue of liability created where owner planted plants and trees on both sides of the sidewalk allegedly causing a sidewalk trip hazard that injured a person).
- An abutting owner can be found liable for negligence in creating a special hazard on the sidewalk. Kopfinger v. Grand Central Pub. Market (1964) 60 Cal. 2d 852, 857 (Meat product left on the sidewalk for deliveries can create liability to the market even if caused by third persons because it was connected with the business). Lee v. Ashizawa (1964) 60 Cal. 2d 862, 865 (Oil on sidewalk from owner’s business activities creates a triable issue for the jury). Compare Jamison v. Mark C. Bloome Co . (1980) 112 Cal. App. 3d 570, 577 (Property owner was not liable for oil on sidewalk caused by vandals after close of business).
Defenses to Sidewalk Injuries;
In some locales, the doctrine of governmental immunity from civil liability often shields municipal bodies from liability to sidewalk injury claims. Governmental immunity is not an "all or nothing" proposition. Some states, such as Michigan, have carved out exceptions to governmental immunity when a sidewalk defect is greater than two inches in size. Again, local ordinances must be reviewed to determine if governmental immunity has been sought.
Another common defense to sidewalk injuries is the "open and obvious doctrine," which pins some amount of liability on the injured person if the sidewalk hazard was open, obvious, and easily avoided. Open and obvious law changes from state to state and is constantly in flux. In California, with comparative negligence as a doctrine, the liability is divided among all those who were at fault and would reduce the liability of the owner if the injured party was found negligent.
Common Sense:
If you own property in California, you should take the time to learn the applicable municipal ordinances that possibly impose liability upon you for the condition of the sidewalk. But whether such liability is imposed or not, note that you are required to keep it in good repair. That is a duty every bit as important as making sure your own home or commercial property is in good condition. Ultimately, this will improve the property value as well, so this is one of those instances where your own self-interest and that of the local municipality correspond.
Where it gets complicated is if local property owners are not taking their own responsibility seriously and the aesthetics of the neighborhood as well as safety of the sidewalks suffer due to the irresponsibility of one or two owners on a block. At times, they simply do not have adequate resources to maintain the sidewalk. It is possible they are unaware of the legal duty imposed.
In such instances, communication with neighbors is a good first step. If that does not work, and the condition is dangerous, contacting the municipality so they are on notice will at least force them to remedy the situation or face their own liability.
What one cannot do is pretend that this is not a duty imposed. Sooner or later, a broken sidewalk will create a problem for the owner of property and the sooner it is handled, the better.
Founded in 1939, our law firm combines the ability to represent clients in domestic or international matters with the personal interaction with clients that is traditional to a long established law firm.
Read more about our firm
© 2024, Stimmel, Stimmel & Roeser, All rights reserved | Terms of Use | Site by Bay Design
- Doctors, Clinics & Locations, Conditions & Treatments
- Patients & Visitors
- Medical Records
- Support Groups
- Help Paying Your Bill
- COVID-19 Resource Center
- Locations and Parking
- Visitor Policy
- Hospital Check-in
- Video Visits
- International Patients
View the changes to our visitor policy
View information for Guest Services
New to MyHealth?
Manage Your Care From Anywhere.
Access your health information from any device with MyHealth. You can message your clinic, view lab results, schedule an appointment, and pay your bill.
ALREADY HAVE AN ACCESS CODE?
Don't have an access code, need more details.
Learn More about MyHealth Learn More about Video Visits
MyHealth for Mobile
Get the iPhone MyHealth app Get the Android MyHealth app
WELCOME BACK
Trauma service.
Serving over 2.6 million people, Stanford Medicine is the only Level 1 Adult and Level 1 Pediatric Trauma Center verified by the American College of Surgeons (ASC) on the peninsula of the San Francisco Bay Area. We provide specialized care to over 3700 patients per year and handle 20-25 consults daily. We offer exceptional 24-hours-a-day onsite trauma specialists in a state-of-the art facility, fully equipped to handle any medical or surgical emergency.

Our Doctors
Our advanced practice providers, care and treatment, fall prevention for older adults.

An estimated one in three older adults, 65 years and older, fall each year. That number increases to an estimated one in two for those over 80. The good news is that there are ways to reduce falls and stay independent, including:
- Exercise – Improve your gait (manner of walking), strength, and balance
- Medication review – Ask your doctor or pharmacist to review your prescriptions, over-the-counter medications, and vitamins and minerals in order to look at side effects, such as dizziness and drowsiness.
- Home safety – About 50% of falls by older adults happen in the home. Go through your home thoroughly to remove hazards, such as clutter and things to trip on. Consider adding supports like grab bars in your bathroom and using night lights and better lighting in your home.
- Check your vision – Get annual eye exams
Download our Home Safety Checklist to learn more.
Stanford Health Care offers four fall prevention programs:
Farewell to falls.

This free, home-based, fall prevention education program sends an occupational therapist to the home to look at the multi-faceted risk factors associated with falls. The therapist assesses strength and balance, and a home safety evaluation with recommendations is completed. Medications are reviewed by a Stanford Health Care pharmacist, home exercises are recommended, and information and education on other risk factors are provided. This program offers two visits, and follow-up phone calls are made monthly. After one year, the occupational therapist returns to the home for a third visit and re-evaluation.
Eligibility requirements:
- 65 years or older
- Lives in Santa Clara or San Mateo County
- Ambulatory (cane or walker ok)
- Lives in own home or apartment
- Interested in participating in a full multi-faceted visit
- Cognitively able to provide health history and fully participate
- No alcohol dependency
Self-referrals are welcome. To enroll or get more information about Farewell to Falls, please email [email protected] or call 650-724-9369
A Matter of Balance

A Matter of Balance is an evidence-based program for older adults. 10 to 12 older adults meet for 8 two-hour sessions either once or twice weekly in senior centers and other community settings in Santa Clara and San Mateo Counties. Through facilitated discussions, group activities and exercise, older adults learn strategies to help reduce fear of falling and fall risks. Program dates and sites vary.
To enroll in A Matter of Balance class or get more information please email [email protected] or call 650-724-9369 .
Stepping On
Stepping On is an evidence-based program developed in Australia and has been shown to decrease falls by 31%. Older adults meet in a group setting for two hours once a week for seven weeks. Sessions include facilitated discussions and guest speakers, including a physical or occupational therapist, pharmacist, vision specialist, and community safety expert. Exercises are taught and practiced each week. A home visit is offered at the end of the seven weeks, and participants come together for a "booster session" three months later.
To enroll in a Stepping On class or get more information please email [email protected] or call 650-724-9369 .
Bingocize is an evidence-based fall prevention program that can be offered in-person or virtually. BINGO + EXERCISE = BINGOCIZE! 10 to 20 older adults, aged 65 years and older, gather two times/week for one hour for 10 weeks to play Bingo, learn fall prevention information and exercise together.
To enroll in a Bingocize class or get more information please email [email protected] or call 650-724-9369 .
More on Fall Prevention
Experts on fall prevention may be available to present to groups of at least 12 older adults or professionals in Santa Clara or San Mateo County. For more information, please email [email protected] or call 650-724-9369 .
For more information on fall prevention, visit:
- www.smcfallprevention.org
- www.svhap.org
- www.cdc.gov
- www.ncoa.org
Stanford Health Care Now

Stanford Hospital & Clinics and Lucile Packard Children's Hospital at Stanford Re-verified as a Level I Trauma Center
When plane-crash victims arrived at stanford hospital, medical teams were ready, for patients.
Patients may be transferred using Stanford Life Flight air or ground transport.
Stanford Health Care is known worldwide for the advanced patient care provided by its doctors and staff. We also provide a wide range of guest services and amenities to our patients and visitors. Learn more about preparing for a hospital stay, billing and financial services, and our other support programs in Patients & Visitors .
International Patients Phone: +1 650-723-8561 Email: [email protected]
IF YOU ARE EXPERIENCING A MEDICAL EMERGENCY, DIAL 9-1-1
- Billing and insurance
For Health Care Professionals
Physician helpline.
Phone: 1-866-742-4811 Fax: 650-320-9443 Monday – Friday, 8:30 a.m. – 5 p.m.
TRANSFER CENTER
Phone: 1-800-800-1551, 24 hours - 7 days a week
Stanford Health Care provides comprehensive services to refer and track patients, as well as provides the latest information and news for physicians and office staff. For help with all referral needs and questions, visit Referral Information .
- Send referrals online
- Place radiology and lab orders
- View referral status
- Access medical records
Learn More About MedLink

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
OSHA Walking & Working Surfaces Training Course. Get Certified in 2 Hours - $20. No Classroom Attendance Required. Support Available 7 Days a Week. Limited Time Savings.
Non-Fatal Injuries - Slips, trips, and falls cases ranked third among the top employer-reported workplace injuries in 2022, involving days away from work. Common Causes and Risk Factors. Slips, trips, and falls can happen due to many reasons—from uneven working surfaces to unsafe ladder positions. Knowing the causes can help managers assess ...
That means preventing slips, trips, and falls is an ongoing process that relies heavily on employees being able to recognize related hazards. What Are OSHA's Trip Hazard Regulations? OSHA's primary standard for slip, trip, and fall hazards is the General Industry Walking-Working Surface standard (29 CFR 1910 Subpart D, which includes §1910.21-30).
Hazards in the Workplace. In 2022, 865 workers died in falls, and hundreds of thousands were injured badly enough to require days off of work. A worker doesn't have fall from a high level to suffer fatal injuries; 144 workers were killed in falls on the same level in 2022, according to Injury Facts. Construction workers are most at risk for ...
Slips, trips, and falls cause nearly 700 fatalities per year and many more injurious accident in the workplace according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. There are three physical factors involved in slips, trips, and falls: friction, momentum, and gravity. Each one plays a role. Friction is the resistance between objects, momentum is affected ...
Download a Slips, Trips, and Falls toolbox talk pdf. Slips, trips and falls are a common reason for many of the injuries in workplaces. They can cause minor injuries but can also lead to serious, long-term injuries. Many slip, trips and falls are avoidable and there are usually easy solutions a workplace can apply to control the risk, either by ...
Slips, trips, and falls are preventable accidents that carry substantial personal, economic, and societal costs. By comprehending the causes, consequences, and prevention strategies, we can significantly reduce the incidence of STFs and mitigate their impact. Whether at home, at work, or in public spaces, prioritizing safety and fostering awareness about STFs is crucial for the well-being of ...
Young workers can slip when they lose their footing. They can trip when catching their foot on or in something, and they can fall when using a ladder. Common causes of slips, trips, and falls include: Did you know? Falls from portable ladders are one of the leading causes of work-related deaths and injuries.
Slips, trips and falls can result in injuries with lasting effects and even death. It is important to understand how slips, trips and falls happen, how to identify hazards and how to eliminate or minimize the hazards. Slips happen because of a lack of friction or traction between a person's footwear and the walking
Slips, Trips and Falls Tip sheet We may not consider slipping at home or tripping on the sidewalk to be serious risks, but they can be deadly. Falls are the second leading cause of unintentional-injury-related deaths overall in the U.S. and the number one cause of death for those 68 and older, according to Injury Facts® (injuryfacts.nsc.org).
In the workplace, it's a different and far more serious story. Slips, trips, and falls account for over 200,000 workplace injuries per year. In 2020, nearly one in five accidents leading to missed work was due to a slip, trip, or fall. They're also the second-leading cause of workplace fatalities.
Appropriate Footwear for Different Surfaces. Wearing the right footwear can significantly reduce the risk of slips, trips, and falls. Choose shoes with good traction, especially for wet or slippery surfaces. Protective footwear should be worn in workplaces where specific hazards are present, such as construction sites.
Importance. Slips, trips, and falls are common workplace accidents that can lead to injuries and financial losses for businesses. Most commonly, this training aims to protect lives and comply with safety regulations such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration ().Proper safety training helps organizations identify and prevent hazards, which protects both of its employees and helps ...
A stumble down a stairway. A trip over an uneven surface. Slipping on the ice. It can lead to a variety of regrettable events ranging from a simple bruised shin to an extremely serious injury. It's just one of a number of conditions and situations that set the stage for slips, trips and falls in the workplace. According to the U.S. Department ...
Slip, Trip, and Fall Prevention | 5 Table 1. Slip, trip and fall (STF) workers' compen-sation claims by body part injured, 1996-2005. Body part n % of total STF claims Lower extremities 185 44.9 Upper extremities 69 16.7 Multiple body parts 67 16.7 Back/trunk 73 16.2 Head/neck 18 4.3 Unknown 60 12.7 Total 472 100.0 Source: Bell et al. 2008 ...
Slips, trips, and falls are the leading causes of time lost in the workplace. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has cited fall protection standard violations more frequently than any other standard. These types of hazards are serious issues for workers and employers, but their risk can be minimized with 10 simple ways to ...
Falls are when you lose contact with the walking or working surface and fall. Falls can occur either on the same level or from an elevated surface. Falls from an elevated surface are second only to motor vehicle accidents in the cause of work place fatalities. The hazards which result in slips, trips and falls generally can be grouped into ...
Slips, trips & falls. Slips, trips, and falls put workers at risk of sprains, strains, bruises, concussions, and fractures. Falls often result from slipping or tripping. The risks Slips happen where there is not enough grip or traction between the footwear and the walking surface. This can be a result of water, oil, grease, or dust on the floor.
Workplace injuries from slips, trips and falls result in more than 260,000 missed workdays a year. The average worker misses 11 days of work following such injuries. And these injuries cost employers an average of $20,000 per incident, according to EHS Today, a trade magazine for environmental health and safety professionals.
According to the Health and Safety Executive (HSE), slips, trips and falls on the same level are the leading workplace accidents. They make up 32% of all non-fatal work-related injuries, nearly double the number caused by manual handling, which accounts for 17%.. And every one of the work-related slips, trips and falls recorded in these statistics resulted in serious harm.
Slips, trips, and falls are one of the leading causes of injuries and fatalities in the workplace. According to OSHA, slip, trip, and fall incidents cause 15% of all accidental deaths and are second only to motor vehicle incidents as a cause of fatalities on the job. These types of incidents can result in life-changing injuries to the employees ...
Competencies: Fall Management. Tinetti Balance Assessment Tool. Fall Risk Assessment: Hendrich II Scale. Fall Investigation Report. Fall Risk Predictive Factors Assessment. Slips, Trips and Falls Checklist. SAMPLE Fall Prevention Program Work Plan with Resources. SAMPLE Fall Prevention Program Work Plan Template.
The Basic Law: The Cost of Repair: California state law provides that a municipality may assess landowners for the cost the municipality incurs to maintain sidewalks if the landowner fails to perform his/her duty. Note that this is a choice available to the municipality and not all so assess. The Issue of Liability: The law is clear: the ...
BINGO + EXERCISE = BINGOCIZE! 10 to 20 older adults, aged 65 years and older, gather two times/week for one hour for 10 weeks to play Bingo, learn fall prevention information and exercise together. To enroll in a Bingocize class or get more information please email [email protected] or call 650-724-9369.
Slip and Fall Accident Lawyer Licensed for 20 years. Practice Areas: Slip and Fall Accident, Personal Injury, Workers Compensation and more. Quality, aggressive and honest representation for your work injury or auto accident. Rating: 8.6. Call for a consultation (408) 628-1070. Profile.