Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution, update may 10, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |

Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Travel Advisory July 27, 2023
Haiti - level 4: do not travel.
Last Update: Updated to reflect the Ordered Departure of non-emergency U.S. government personnel and eligible family members for Embassy Port-au-Prince.
Do not travel to Haiti due to kidnapping, crime, civil unrest, and poor health care infrastructure. On July 27, 2023, the Department of State ordered the departure of family members of U.S. government employees and non-emergency U.S. government employees. U.S. citizens in Haiti should depart Haiti as soon as possible by commercial or other privately available transportation options, in light of the current security situation and infrastructure challenges. U.S. citizens wishing to depart Port-au-Prince should monitor local news and only do so when considered safe.
Country Summary : Kidnapping is widespread, and victims regularly include U.S. citizens. Kidnappers may use sophisticated planning or take advantage of unplanned opportunities, and even convoys have been attacked. Kidnapping cases often involve ransom negotiations and U.S. citizen victims have been physically harmed during kidnappings. Victim’s families have paid thousands of dollars to rescue their family members.
Violent crime, often involving the use of firearms, such as armed robbery, carjackings, and kidnappings for ransom that include U.S. citizens are common. Mob killings against presumed criminals have been on the rise since late April. Travelers are sometimes followed and violently attacked and robbed shortly after leaving the Port-au-Prince international airport. Robbers and carjackers also attack private vehicles stuck in heavy traffic congestion and often target lone drivers, particularly women. As a result, the U.S. Embassy requires its personnel to use official transportation to and from the airport.
Protests, demonstrations, tire burning, and roadblocks are frequent, unpredictable, and can turn violent. The U.S. government is extremely limited in its ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in Haiti – assistance on site is available only from local authorities (Haitian National Police and ambulance services). Local police generally lack the resources to respond effectively to serious criminal incidents. Shortages of gasoline, electricity, medicine, and medical supplies continue throughout much of Haiti. Public and private medical clinics and hospitals often lack qualified medical staff and even basic medical equipment and resources.
U.S. government personnel are limited only to the confined area around the Embassy and are prohibited from walking in Port-au-Prince. U.S. government personnel in Haiti are prohibited from:
- Using any kind of public transportation or taxis
- Visiting banks and using ATMs
- Driving at night
- Traveling anywhere between 1:00 a.m. and 5:00 a.m.
- Traveling without prior approval and special security measures in place.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Haiti.
The Haitian Ministry of Health and Population (MSPP) has confirmed an outbreak of cholera in the country.
If you decide to travel to Haiti:
- Avoid demonstrations and crowds. Do not attempt to drive through roadblocks.
- Arrange airport transfers and hotels in advance, or have your host meet you upon arrival.
- Do not provide personal information to unauthorized individuals (e.g. people without official uniforms or credentials) located in the immigration, customs, or other areas inside or near any airports.
- If you are being followed as you leave the airport, drive to the nearest police station immediately.
- Travel by vehicle to minimize walking in public.
- Travel in groups of at least two people.
- Always keep vehicle doors locked and windows closed when driving.
- Exercise caution and alertness, especially when driving through markets and other traffic congested areas.
- Do not physically resist any robbery attempt.
- Purchase travel insurance and medical evacuation insurance ahead of time.
- Review information on Travel to High-Risk Areas .
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report on Haiti.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
1 page per stamp
Yes, for stays over 90 days. Foreign passport holders visiting Haiti must pay a tourist fee of $10.00 at the airport
None; however, review current COVID testing and vaccination guidance
Embassies and Consulates
U.S. Embassy Port-au-Prince
Boulevard du 15 October, Tabarre 41, Route de Tabarre Port-au-Prince, Haiti Telephone: +(509) 2229-8000 / 2229-8900 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(509) 2229-8000 Fax: +(509) 2229-8027 Email: [email protected]
American Citizen Services Unit office hours are 7:00 a.m. to 3:30 p.m., Monday through Friday. Most routine services require an appointment; visit our Embassy webpage . The Embassy is closed on U.S. and local holidays.
Destination Description
Learn about the U.S. relationship to countries around the world.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
The Government of Haiti requires all non-Haiti citizens age 12 and over entering the country to be fully vaccinated against COVID-19, or to present a negative COVID test. No COVID test or vaccination is required for travelers under the age of 5 .
Requirement for Entry: Passport valid for at least six months from date of arrival. Visit the Embassy of Haiti website for the most current visa information.
HIV/AIDS Restrictions: The U.S. Department of State is unaware of any HIV/AIDS entry restrictions for visitors to or foreign residents of Haiti.
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction and customs regulations on our websites.
Safety and Security
Crime: Embassy employees are prohibited from using public transportation and visiting certain areas of Port-au-Prince due to high crime. Political violence and violent crimes are common in Haiti, including murders, kidnappings, robberies, assaults, vehicle break-ins, and home invasions. Travelers are often targeted, followed, and violently attacked and robbed shortly after leaving the Port-au-Prince international airport. For this reason, Embassy personnel are prohibited from traveling in personal vehicles to and from the airport. Also, the Embassy has procedures in place to detect surveillance and deter attacks on its employees.
Labadee, a port near Cap Haitien in the north - only accessible by cruise ship passengers - has private security and lower rates of reported crime. Travelers should exercise heightened precautions,however, due to increasing insecurity nationwide.
Safety Precautions:
- Be careful about providing your destination address in Haiti. Do not provide personal information to unauthorized individuals located in the immigration, customs, or other areas inside or near any airports in Haiti.
- As you leave the airport, make sure you are not being followed. If you notice you are being followed, drive to the nearest police station immediately.
- Be aware of your surroundings.
- Keep a low profile.
- Do not display signs of wealth, such as jewelry or watches.
- Embassy employees are prohibited from visiting banks and using ATMs. U.S. citizens are often followed, attacked and robbed soon after withdrawing money. If you must use an ATM, select one that is out of sight from the general public (such as inside your hotel), and be cautious at all times.
- Do not resist a robbery or car-jacking attempt. Criminals may kill those who resist.
- If a situation makes you feel uncomfortable, leave immediately.
- Be aware: drug traffickers have duped travelers into transporting narcotics aboard on commercial flights.
- Be aware: crime rates tend to go up during holidays, particularly in crowded street festivities.
See the Department of State and the FBI pages for information on scams.
Victims of Crime, Domestic Violence and Sexual Assault: Local authorities are responsible for investigating and prosecuting crimes. Police investigations may not meet U.S. standards and forensic medical services are very basic. While rape kits exist in Haiti, there is generally no capacity to collect or utilize samples for police investigation. Report crimes to the local police at (+509) 3838-1111 or (+509) 3733-3640, then call the U.S. Embassy at (+509) 2229-8000.
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
- Help you find appropriate medical care
- Assist you in reporting a crime to the police
- Contact relatives or friends if we receive your written consent
- Explain the local criminal justice process in general terms
- Provide a list of attorneys in Haiti
- Provide information on victim’s compensation programs in the United States
- In cases of destitution, provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical support
- Help you find hotel accommodations and arrange a flight home
- Replace a stolen or lost passport
Demonstrations occur frequently. They may take place in response to political or economic issues, on politically significant holidays, and during international events.
- Demonstrations can be unpredictable, avoid areas around protests and demonstrations.
- Past demonstrations have turned violent.
- Check local media for updates and traffic advisories.
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence are encouraged to contact the Embassy for assistance.
No formal tourism industry infrastructure is in place on any level in most locations. With the exception of Labadee, tourists are participating in activities at their own risk. Emergency response and subsequent appropriate medical treatment is not available in-country. U.S. citizens are encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage
Hurricanes: Hurricane season runs from June 1 – November 30 in the Atlantic. Roads and bridges may become impassible. Poor rescue services and weak infrastructure hamper the government’s ability to respond to storms.
For information on how to prepare and respond to storms and hurricanes:
- https://www.ready.gov/hurricanes
- Haiti Météo website
- Local media broadcasts in Creole or French
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
- U.S. Federal Emergency Management Agency
Earthquakes: Haiti is prone to earthquakes. For information on what to do before, during, and after an earthquake, visit https://www.ready.gov/earthquakes .
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to local laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Prolonged pre-trial detention is common and prison conditions do not meet U.S. standards. Individuals establishing a business or practicing a profession that requires additional permits or licensing should seek information from the competent local authorities, prior to practicing or operating a business.
Furthermore, some laws are also prosecutable in the United States, regardless of local law. For examples, see our website on crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website.
Arrest Notification: If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy immediately. See our webpage for further information.
Real Estate Investments: Be highly cautious. Property rights are irregularly enforced. Clear title to land is difficult or impossible to obtain. Consult an attorney before signing documents or closing on any real estate transactions. Undeveloped land is vulnerable to legal and physical takeover. Absentee owners may be assaulted by squatters when trying to reclaim their property. Litigation and eviction proceedings can take years. U.S. citizens involved in business/property disputes are sometimes arrested without charge and can spend months or years in pre-trial detention, waiting for their cases to be heard. The Embassy does not attend property dispute hearings but, as above, can assist U.S. citizens who have been arrested.
Firearms and Other Weapons: Possession of firearms, ammunition, and dangerous weaponry is strictly prohibited to any person, unless the individual has a Haitian license or has been specifically authorized by Haitian authorities. In order to bring a firearm into Haiti, an owner must obtain written permission in advance from the Director-General of the Haitian National Police (HNP). Contact the “Centre de Renseignement de la police”/Information Center (CRO) at [email protected] or by telephones at 509-3838-1111 /509-3837-1111/509-3839-1111 for additional information. Travelers caught entering Haiti with any type of weapon, including firearms or ammunitions, will likely face severe penalties, including prison time. U.S.-issued permits allowing an individual to carry weapons are not valid in Haiti. Visit the Department’s Traveling Abroad with Firearms webpage .
Faith-Based Travelers: See the following webpages for details:
- Faith-Based Travel Information
- International Religious Freedom Report – see country reports
- Human Rights Report – see country reports
- Hajj Fact Sheet for Travelers
- Best Practices for Volunteering Abroad
LGBTQI+ Travelers: Anti-LGBTQI+ sentiment exists. While no laws criminalize sexual orientation or consensual same-sex conduct between adults, persons identified as LGBTQI+ may be targeted for harassment, discrimination, or physical attacks. See our LGBTQI+ Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Travelers with Disabilities: The law in Haiti prohibits discrimination against persons with disabilities, but the law is not enforced. Social acceptance of persons with disabilities in public is not as prevalent as in the United States, however. Expect accessibility to be limited in public transportation, lodging, communication/information, and general infrastructure. Businesses rarely accommodate persons with disabilities and Haitian authorities do not enforce laws mandating public access for the disabled. Sidewalks, when present, are frequently congested by sidewalk commerce and parked cars.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: Domestic violence and sexual assault are unfortunately common and not always investigated or prosecuted consistently or vigorously. See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
The Government of Haiti requires all non-Haiti citizens age 12 and over entering the country to be fully vaccinated against COVID-19, or to present a negative COVID test.
Medical facilities, including ambulance services, are scarce and generally sub-standard, especially outside the capital. Life-threatening emergencies often require evacuation to a point outside of Haiti by air ambulance at the patient's expense. Lists of doctors, hospitals, and air ambulance services are available at the Embassy website.
There is no functional national emergency services line in Haiti. The Embassy maintains a list of emergency telephone contacts.
Ambulance services may not be reliable in an emergency. Injured or seriously ill travelers may prefer to take a taxi or private vehicle to the nearest major hospital rather than wait for an ambulance. Ambulance services are:
- Not widely available and training and availability of emergency responders may be below U.S. standards.
- Not equipped with state-of-the-art medical equipment.
- Often not staffed with trained paramedics and often have little or no medical equipment.
We do not pay medical bills. Be aware that U.S. Medicare/Medicaid does not apply overseas. Most hospitals and doctors overseas do not accept U.S. health insurance.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept cash payments. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage. Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information on type of insurance you should consider before you travel overseas.
We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation.
Always carry your prescription medication in original packaging, along with your doctor’s prescription. Check with the Haitian Ministry of Public Health to ensure the medication is legal in Haiti.
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Further health information:
- World Health Organization
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Health facilities in general:
- Public medical clinics often lack basic resources and supplies.
- Hospitals and doctors often require payment “up front” prior to service or admission. Credit card payment is not always available.
- Private hospitals usually require advance payment or proof of adequate insurance before admitting a patient.
- Medical staff may speak little or no English.
- Patients bear all costs for transfer to or between hospitals.
- Psychological and psychiatric services are limited, even in the larger cities.
Water Quality
In most areas, tap water is not potable. Bottled water and beverages are generally safe, although you should be aware that many restaurants and hotels serve tap water unless bottled water is specifically requested. Be aware that ice for drinks may be made using tap water.
General Health Language
The following diseases are prevalent:
- Chikungunya
- Use the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended mosquito repellents and sleep under insecticide-impregnated mosquito nets. Chemoprophylaxis is recommended for all travelers even for short stays.
- There are shortages of food, water, medicine, medical supplies, etc. throughout Haiti.
- Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information about Resources for Travelers regarding specific issues in Haiti.
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety: Traffic is extremely chaotic throughout the country and is frequently congested in urban areas. Lanes are not marked, and signs indicating the flow of traffic seldom exist. Roads are generally unmarked, and detailed, accurate maps are not widely available. GPS-based systems do usually work accurately, but the lack of road signage makes it hard to determine the indicated route. There are only a handful of stoplights in the country. Pedestrians regularly walk on the side of the road, and animals often dart into traffic. Even though driving is on the right side of the road, large potholes and flooding may cause drivers to swerve unpredictably and dangerously into the opposite lane of traffic. Speeding, aggressive driving, lack of traffic lights and signs, lack of right of way, unlit vehicles, and poor maintenance are the cause of many fatal traffic accidents in Haiti, as are overloaded vehicles on winding, mountainous and degraded roads. Motorcycles weave through traffic at high speeds. Driving under the influence is common at night. Traffic accidents are a major cause of death and injury, and extreme caution should be exercised. Those lacking knowledge of Haitian roads and traffic customs should hire a driver through a tour company or hotel. Heavy rains can cause mudslides and flooding that can quickly make conditions perilous. The Haitian government lacks adequate resources to assist drivers in distress or to clear the road of accidents or broken-down vehicles. If you are involved in an accident, do not expect medical or law enforcement assistance.
Public Transportation: Public transportation consists of “tap-taps” (collective buses), private motorcycles for hire, and public buses and taxis in some cities or inter-city routes. Embassy personnel are prohibited from using any public transportation, and U.S. citizens are advised to avoid doing so due to the risk of crime. There is a significant risk of ejection in any accident, or even rough driving, due to lack of seat belts.
See our Road Safety page for more information.
Aviation Safety Oversight:
The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed the government of Haiti’s Civil Aviation Authority as not being in compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of Haiti’s air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA’s safety assessment page .
Maritime Travel: Mariners planning travel to Haiti should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts . Information may also be posted to the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website , and the NGA broadcast warnings .
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Haiti . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Make two copies of all of your travel documents in case of emergency, and leave one with a trusted friend or relative.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Is it safe to travel to Haiti right now? What travelers should know

The State Department is urging Americans not to travel to Haiti amid fresh gang violence in the country, which declared a state of emergency last week.
While neither the warnings nor violence are entirely new – Haiti has been a Level 4: Do Not Travel destination in State Department travel advisories since before the 2021 assassination of President Jovenel Moïse – a spate of recent high-profile attacks, including an attempt by armed gangs to seize control of the country’s main international airport, has sparked renewed urgency.
“The current security situation in Haiti is unpredictable and dangerous,” the U.S. Embassy in Haiti said in a security alert issued Sunday. “We are aware that there are few or no commercial options to depart Haiti safely at this time. As they become available, we urge U.S. citizens to take advantage of them. The U.S. Embassy’s ability to assist U.S. citizens is severely limited.”
The U.S. military stepped in to airlift American personnel “into and out of the Embassy” to augment security, U.S. Southern Command said Sunday in a statement to USA TODAY. The embassy is also coordinating assisted departure flights "through non-commercial means" for U.S. citizens, according to its website .
Helicopter rides from U.S. Embassy Port-au-Prince to Santo Domingo in the Dominican Republic are available, and the country also "indicated they will allow U.S. citizens to enter" through a land border with a valid passport, according to a State Department advisory . The airport in Cap-Haitien has "limited commercial flight activity" as well, the advisory said.
Learn more: Best travel insurance
Americans in Haiti can fill out crisis intake forms and enroll in the State Department’s Smart Traveler Enrollment Program program for updates.
Here’s what airlines and cruise lines are doing about trips to Haiti:
Haiti violence: Military airlifts American personnel out of embassy as Haiti spirals into violence
Are there direct flights to Haiti?
Three U.S. airlines typically operate direct flights to Haiti: American, JetBlue and Spirit. However, all three have temporarily suspended service and issued travel waivers for the Caribbean destination.
◾ American Airlines customers with flights scheduled to, through, or from Port-au-Prince (PAP) through April 1 may modify flights without paying change fees. Changes must be made by April 1 with the same origin and destination cities as the original booking.
◾ JetBlue Airways is waiving change and cancellation fees for travelers with flights scheduled to and from Port-au-Prince through April 15. Changes can be made through April 30.
◾ Spirit Airlines is waiving change fees and fare differences on travel to, from, or through Cap Haitien (CAP) and Port-au-Prince through April 15. Travelers should rebook by April 30. After that, the airline said change fees would still be waived, but fare differences may apply.
Is Royal Caribbean still going to Haiti?
Royal Caribbean and its sister line Celebrity Cruises normally sail to Labadee, Haiti , a private destination roughly six hours away from Port-au-Prince by car. However Royal Caribbean is skipping several previously scheduled stops, in coming days.
The following sailings will not go to Labadee.
- Adventure of the Seas: 3/15 sailing
- Mariner of the Seas: 3/16 sailing
- Explorer of the Seas: 3/17 sailing
- Oasis of the Seas: 3/17, 3/24, 3/31, 4/7 and 4/14 sailings
- Symphony of the Seas: 3/17, 3/23, 3/31, 4/6, 4/14, 4/20 and 4/28 sailings
- Grandeur of the Seas: 3/18 sailing
- Independence of the Seas: 4/4, 4/8, 4/18 and 4/22 sailings
"The safety and security of our guests, crew, and communities we visit are our top priority," a Royal Caribbean spokesperson said in a statement to USA TODAY. "Our Global Security and Intel Team is closely monitoring the evolving situation in Haiti, and in an abundance of caution, we are temporarily making adjustments to sailings visiting Labadee. We will continue to monitor and reassess calls as needed, and will communicate updates with guests directly."
As recently as March 11, the cruise line had not canceled any sailings to Labadee, but was keeping a close on the situation while noting that it had private security in the area, which was closed to the public.
It doesn’t look like any Celebrity cruises are scheduled there until fall.
Contributing: Nathan Diller, USA TODAY
Eve Chen is a travel reporter for USA TODAY based in Atlanta. You can reach her at [email protected].
Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution, update may 10, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Haiti Travel Advisory
Travel advisory july 27, 2023, haiti - level 4: do not travel.
Last Update: Updated to reflect the Ordered Departure of non-emergency U.S. government personnel and eligible family members for Embassy Port-au-Prince.
Do not travel to Haiti due to kidnapping, crime, civil unrest, and poor health care infrastructure. On July 27, 2023, the Department of State ordered the departure of family members of U.S. government employees and non-emergency U.S. government employees. U.S. citizens in Haiti should depart Haiti as soon as possible by commercial or other privately available transportation options, in light of the current security situation and infrastructure challenges. U.S. citizens wishing to depart Port-au-Prince should monitor local news and only do so when considered safe.
Country Summary : Kidnapping is widespread, and victims regularly include U.S. citizens. Kidnappers may use sophisticated planning or take advantage of unplanned opportunities, and even convoys have been attacked. Kidnapping cases often involve ransom negotiations and U.S. citizen victims have been physically harmed during kidnappings. Victim’s families have paid thousands of dollars to rescue their family members.
Violent crime, often involving the use of firearms, such as armed robbery, carjackings, and kidnappings for ransom that include U.S. citizens are common. Mob killings against presumed criminals have been on the rise since late April. Travelers are sometimes followed and violently attacked and robbed shortly after leaving the Port-au-Prince international airport. Robbers and carjackers also attack private vehicles stuck in heavy traffic congestion and often target lone drivers, particularly women. As a result, the U.S. Embassy requires its personnel to use official transportation to and from the airport.
Protests, demonstrations, tire burning, and roadblocks are frequent, unpredictable, and can turn violent. The U.S. government is extremely limited in its ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in Haiti – assistance on site is available only from local authorities (Haitian National Police and ambulance services). Local police generally lack the resources to respond effectively to serious criminal incidents. Shortages of gasoline, electricity, medicine, and medical supplies continue throughout much of Haiti. Public and private medical clinics and hospitals often lack qualified medical staff and even basic medical equipment and resources.
U.S. government personnel are limited only to the confined area around the Embassy and are prohibited from walking in Port-au-Prince. U.S. government personnel in Haiti are prohibited from:
- Using any kind of public transportation or taxis
- Visiting banks and using ATMs
- Driving at night
- Traveling anywhere between 1:00 a.m. and 5:00 a.m.
- Traveling without prior approval and special security measures in place.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Haiti.
The Haitian Ministry of Health and Population (MSPP) has confirmed an outbreak of cholera in the country.
If you decide to travel to Haiti:
- Avoid demonstrations and crowds. Do not attempt to drive through roadblocks.
- Arrange airport transfers and hotels in advance, or have your host meet you upon arrival.
- Do not provide personal information to unauthorized individuals (e.g. people without official uniforms or credentials) located in the immigration, customs, or other areas inside or near any airports.
- If you are being followed as you leave the airport, drive to the nearest police station immediately.
- Travel by vehicle to minimize walking in public.
- Travel in groups of at least two people.
- Always keep vehicle doors locked and windows closed when driving.
- Exercise caution and alertness, especially when driving through markets and other traffic congested areas.
- Do not physically resist any robbery attempt.
- Purchase travel insurance and medical evacuation insurance ahead of time.
- Review information on Travel to High-Risk Areas .
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report on Haiti.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, search for travel advisories, external link.
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Haiti travel advice
Latest updates: The Need help? section was updated.
Last updated: June 5, 2024 13:33 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, haiti - avoid all travel.
The security situation remains volatile in Haiti. You should consider leaving the country by commercial means if you can do so safely.
Back to top
Security situation in Haiti
The security situation remains extremely volatile in Haiti.
On March 3, 2024, the government of Haiti declared a state of emergency in Ouest Department, including in Port-au-Prince, in response to gang violence and the deteriorating security situation.
Demonstrations are prohibited in the Ouest Department. There are frequent clashes between gangs and security forces. Kidnappings, robberies, and violent crime are increasing.
While the state of emergency is in effect:
- follow the instructions of local authorities
- always cooperate with police officers
- carry valid ID at all times and be prepared for various checkpoints
- monitor local news to stay informed on the current situation
A nightly curfew is in effect in Ouest Department from 10 pm to 5 am. You must stay indoors while the curfew is in effect. There are exceptions for certain professions, including medical personnel and journalists carrying official identification.
Your personal safety is at risk if you are currently in Haiti. You should consider leaving the country by commercial means if you can do so safely.
There are two international airports in the country which can be difficult to access due to the highly volatile security situation. The Toussaint Louverture International Airport has reopened although with limited operations. The Cap Haitian International Airport is operational.
We strongly advise against any road travel from Port-au-Prince to Cap-Haitien, given the presence of gangs and a highly volatile security situation.
Avoid all travel to Haiti. If you are in Haiti despite this advisory:
- shelter in a safe place until the situation has stabilized
- consider leaving the country if there's a safe means to do so
- ensure that you have essential supplies, including food, water and fuel
- ensure that your passport and other travel documents are up-to-date and secure at all times
- limit your movements, if you are unable to shelter in place
- avoid crossing road blockades, even if they appear unattended
- allow extra time to reach your destination
- be aware of your surroundings at all times
- maintain a low profile when going outside
- don't show signs of affluence
- register or update your personal information through the Registration of Canadians Abroad service and encourage other Canadian citizens in Haiti to do so
Canadian citizens in Haiti must register with Global Affairs Canada and contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre if they require consular assistance.
Declaration of the state of emergency – Ministry of Communication of Haiti (in French)
Border closure with the Dominican Republic
On March 5, 2024, the Government of the Dominican Republic closed its air border with Haiti. Land and sea borders between the two countries remain closed to travellers.
The Embassy of Canada to Haiti, in Port-au-Prince, cannot help you enter the Dominican Republic from Haiti.
Crime rates are high in large centres such as downtown Port-au-Prince, where armed gangs operate, as well as near the border with the Dominican Republic.
The number of violent incidents has been increasing since 2020, especially kidnappings in and around Port-au-Prince.
There has also been an increase in home invasions. These incidents generally occur in middle-class neighbourhoods, but have increased in number in affluent neighbourhoods in Port-au-Prince and outside Pétion-Ville.
Petty crime, such as pickpocketing and purse snatching, also occurs.
Criminality increases in the periods leading up to the holiday season in December, Carnival in February or March and the beginning of the school year in late August or early September.
Foreigners are viewed as wealthy and may arouse envy. To avoid becoming a target:
- don’t show signs of affluence
- avoid using your smartphone or camera in public
- be aware of your surroundings
- ensure that your personal belongings, including your passport and other travel documents, are secure at all times
- remain cautious with new acquaintances offering friendship or hospitality
- never walk alone and avoid travelling after nightfall
Greater Port-au-Prince area
Several areas in greater Port-au-Prince continue to be dangerous due to criminal activity and kidnappings. Local authorities may have difficulties assisting during an emergency in these areas:
- Artibonite Central
- Carrefour Drouillard
- Champs-de-Mars
- Cité Soleil
- Croix-des-Bouquets
- Downtown Port-au-Prince
- Portail Léogane
- Road to the airport
- Toussant Brave
Police presence is not guaranteed in these areas and your personal safety might be at risk. Due to the local environment, security forces may not be able to provide emergency assistance in due time.
If you must travel to these areas, it’s imperative that you take appropriate security precautions:
- be vigilant at all times when moving about the city, towns and country
- ensure that your local contacts know when to expect you and your travel plans within these areas
- ask your local contacts to guide you in your travels
- keep windows closed and doors locked when travelling by car
- never use public transport of any kind
- ask the organizations, institutes or hosts that are taking care of you about the latest updates on the region to which you are travelling, since the security situation can change at any moment
- avoid going out after nightfall
- follow the advice of local authorities
Pétion-Ville
Armed robberies occur regularly in Pétion-Ville. In most cases, armed thieves on motorcycles attack their victims in broad daylight. Attacks have been increasing, particularly against motorists. They usually occur in traffic jams during peak hours.
- Be vigilant at all times while travelling
- Keep windows closed and doors locked when travelling by car
Main highways and roads
Armed gangs have set up roadblocks to commit robberies and demand payments along Route Nationale 2 from Martissant to Miragoane.
Armed gangs are fighting to control the main highways connecting Port-au-Prince to northern departments.
If you must drive:
- limit your movements
Toussaint Louverture International Airport
Thieves try to distract foreigners to steal their passports at Toussaint Louverture International Airport.
- Be cautious when claiming your luggage upon arrival
- Keep your valuables and identification on you
- Have your local contacts arrange for your pick-up from the airport
- Carry only small amounts of cash
Several shooting incidents have also occurred along the road to the airport. Gangs have committed armed robberies, particularly between Delmas 33 and the airport.
- Don’t resist if you’re threatened by robbers
- Be extremely vigilant when leaving the airport
Border with the Dominican Republic
The security environment is highly volatile at the border between Haiti and the Dominican Republic.
Criminal activities are widespread near the border with the Dominican Republic. Armed gangs operate along the border controlling many of the roads leading to the border.
Border areas with the Dominican Republic are subject to gang operations, including the following areas:
- Ouanaminthe
Robberies in bank areas
Some criminals wait near banks, watching clients, and attempt to rob them when they leave.
There is also a higher risk of robbery from individuals using bank ATMs.
- Be extremely vigilant when entering or leaving a bank
- Only use ATMs inside a hotel or supermarket
- Deal directly with a teller if you are at a bank
- Avoid carrying large sums of money
Kidnappings are common in Haiti.
Kidnappers target both local people and foreigners, including dual citizens who live or travel in Haiti, regardless of rank or social class. Since September 2020, hundreds of Canadians and other foreign nationals have been abducted. Missionaries, aid workers and children can become victims. Most of the victims are released in exchange for ransom. In some exceptional cases, however, victims have disappeared or have been killed.
- Remain alert to small groups of loiterers, especially near your residence
- Keep doors and windows secure at all times
- Instruct domestic staff to permit into your home only pre-authorized visitors whose identities have been verified
- Keep all visitors under close scrutiny
- Remain extremely vigilant wherever you are in the country
Demonstrations
Demonstrations and civil unrest take place frequently.
Due to ongoing political instability, some demonstrations have turned violent. Protesters have set up roadblocks across the country and blocked the access to the airport. In those circumstances, water, food and fuel shortages could occur.
Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. They can also lead to disruptions to traffic and public transportation.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Women’s safety
Crimes committed against women frequently occur in Haiti. Reports of rape and assault against women and children have increased. Attackers sometimes act in groups.
Advice for women travellers
Service outages and supply shortages
Power outages are frequent, and shortages of essential supplies such as water and fuel occur.
Ensure that you plan adequately in case of outages and supply shortages.
Road safety
Road conditions and road safety are poor throughout the country due to:
- narrow and poorly maintained roads
- insufficient traffic signs, traffic lights and road markings
- high rates of driving while impaired, with the vehicle’s lights off
- poor vehicle maintenance
- inadequate street lighting
Heavy rains can hamper overland travel and reduce the provision of essential services. Roads may become impassable and bridges damaged.
If you need to travel within Haiti, consider hiring a driver through a reputable agency or hotel. If you must drive:
- always keep your fuel tanks at least half full, as disruptions of fuel supplies are frequent
- always carry a cell phone and a list of emergency contact numbers with you, as roadside assistance services are deficient
- keep in mind that cell phone coverage may be intermittent in some rural areas
- avoid driving at night or in bad weather, even in the city
- be cautious about abandoned vehicle beside the road
- watch out for pedestrians and stray animals on the road
Public transportation
Public transportation is unsafe and unreliable. Drivers don’t always respect traffic laws. Vehicles are often in poor condition or overloaded, which leads to serious accidents involving injuries and sometimes death.
You should avoid all public transportation in Haiti, but most specifically trucks converted into buses, known as “tap taps.”
Ferry accidents occur and are often caused by poor safety practices or extreme weather conditions.
You should avoid ferry travel. If you choose to travel by ferry:
- make sure the vessel you are boarding is carrying appropriate safety equipment
- make sure that life jackets are provided for all passengers and accessible at all times
- avoid boarding vessels that appear overloaded or unseaworthy
- verify the safety standards of ferries with your tour operator
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Haitian authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for the expected duration of your stay in Haiti.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: not required for stays up to 90 days Business visa: not required Student visa: required Work permit: required
Residency permit
You must obtain a residency permit if you intend to stay for 90 days or more. This requirement doesn’t apply to Canadians of Haitian origin.
If you plan to extend your stay beyond 90 days and are a Canadian of non-Haitian origin, you must apply to the Haitian Immigration Service before the 90 days have expired. If you fail to do so, you will need an exit visa to leave the country.
Canadian investors, exporters/importers and workers must apply to the Haitian Immigration Service for a residency permit through their employer for stays of 6 months or more. You must obtain this document before leaving Canada.
How to obtain a visa - Embassy of Haiti in Canada (in French)
Other entry requirements
Customs officials may ask you to show them a return or onward ticket and proof of sufficient funds to cover your stay.
- Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- Zika virus: Advice for travellers - 31 August, 2023
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is no risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is required if you are coming from a country where yellow fever occurs.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is not recommended.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre
* It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes.
Malaria is a risk to travellers to this destination. Antimalarial medication is recommended for most travellers to this destination and should be taken as recommended. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times:
- Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin.
- Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows.
- Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area.
- Wear permethrin-treated clothing.
If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
In this destination, rabies is commonly carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. In this destination, rabies treatment may be limited or may not be available, therefore you may need to return to Canada for treatment.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Cholera is a risk in parts of this country. Most travellers are at very low risk.
To protect against cholera, all travellers should practise safe food and water precautions .
Travellers at higher risk of getting cholera include those:
- visiting, working or living in areas with limited access to safe food, water and proper sanitation
- visiting areas where outbreaks are occurring
Vaccination may be recommended for high-risk travellers, and should be discussed with a health care professional.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
- In this country, dengue is a risk to travellers. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue.
Zika virus is a risk in this country.
Zika virus is primarily spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can also be sexually transmitted. Zika virus can cause serious birth defects.
During your trip:
- Prevent mosquito bites at all times.
- Use condoms correctly or avoid sexual contact, particularly if you are pregnant.
If you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy, you should discuss the potential risks of travelling to this destination with your health care provider. You may choose to avoid or postpone travel.
For more information, see Zika virus: Pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Tuberculosis is an infection caused by bacteria and usually affects the lungs.
For most travellers the risk of tuberculosis is low.
Travellers who may be at high risk while travelling in regions with risk of tuberculosis should discuss pre- and post-travel options with a health care professional.
High-risk travellers include those visiting or working in prisons, refugee camps, homeless shelters, or hospitals, or travellers visiting friends and relatives.
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that attacks and impairs the immune system, resulting in a chronic, progressive illness known as AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome).
High risk activities include anything which puts you in contact with blood or body fluids, such as unprotected sex and exposure to unsterilized needles for medications or other substances (for example, steroids and drugs), tattooing, body-piercing or acupuncture.
Medical services and facilities
Health care is inadequate throughout the country. There are few hospitals, and many are closed. Clinics and hospitals that are open are easily overwhelmed. Hospital services can be disrupted by gang violence
Ambulances are also limited and may not have the basic required medical supplies onboard. As a result, emergency response is not guaranteed.
Physicians and hospitals generally expect immediate cash payment for care even if you have proof of valid travel health insurance. You will have to pay the full amount of the bill before your departure.
Medications sold in Haiti may be of inferior quality to those available in Canada. Pharmacies may carry expired medications while some medications may simply not be available.
Bring a sufficient supply of medications for the duration of your stay.
Medical evacuation can be very expensive and you may need it in case of serious illness or injury.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Legal fees can be very high and judicial procedures are slow. Some Canadians have experienced an over a year detention period before being sent to trial. Prison conditions are extremely difficult. Penal facilities are overcrowded, unsanitary and under-resourced.
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe. Convicted offenders can expect lengthy legal proceedings, heavy jail sentences and fines.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is legally recognized in Haiti.
If you are a Canadian citizen, but also a citizen of Haiti, our ability to offer you consular services may be limited while you're there. You may also be subject to different entry/exit requirements .
Travellers with dual citizenship
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and Haiti.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Haiti by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Haiti to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children's Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country's judicial affairs.
- International Child Abductions: A guide for affected parents
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Request emergency assistance
2SLGBTQI+ travellers
Haitian law does not prohibit sexual acts between individuals of the same sex.
However, 2SLGBTQI+ travellers could be discriminated against based on their sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression or sex characteristics.
Travel and your sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics
In order to fight insecurity, local authorities have temporarily forbidden to drive vehicles with tinted windows throughout the country.
You may use your Canadian driver’s licence to drive in Haiti for up to 3 months. For stays of 3 months or more, you will require a Haitian driver’s permit.
You should carry an international driving permit.
International Driving Permit
Photography
People may feel exploited or insulted by being subjects of photography in poor or urban areas.
Obtain permission before photographing individuals.
Donations entering the country are subject to import rules. They could be seized and taxed in accordance with local legislation. This includes:
- new or used material goods
- personal care products
- medications
Contact the Embassy of the Republic of Haiti or one of its consulates before sending goods to Haiti.
The currency in Haiti is the Haitian gourde (HTG).
Although all prices should be in gourde since March 2018, they are still often quoted in Haitian dollars (5 gourdes = 1 Haitian dollar) or in U.S. dollars.
Canadian currency is not accepted. Most leading hotels accept major credit cards. You can also use your Canadian bank cards to access funds from some ATMs, but the withdrawal limit is much lower than in Canada. Haitian ATMs are unreliable and you should not depend upon them in emergency situations.
Make sure to have sufficient cash in case you’re unable to access an ATM or use your credit card.
Hurricane season
Hurricanes usually occur from mid-May to the end of November. During this period, even small tropical storms can quickly develop into major hurricanes.
These severe storms can put you at risk and hamper the provision of essential services.
If you decide to travel to Haiti during the hurricane season:
- know that you expose yourself to serious safety risks
- be prepared to change your travel plans on short notice, including cutting short or cancelling your trip
- stay informed of the latest regional weather forecasts
- carry emergency contact information for your airline or tour operator
- follow the advice and instructions of local authorities
- Tornadoes, cyclones, hurricanes, typhoons and monsoons
- Large-scale emergencies abroad
- Active storm tracking and hurricane watches and warnings - United States National Hurricane Center
Rainy season
The rainy season extends from April to June and from October to November. It can lead to severe flooding.
Seasonal flooding can hamper overland travel and reduce the provision of essential services. Roads may become impassable due to mudslides and landslides. Bridges, buildings, and infrastructure may be damaged.
- Monitor local media for the latest updates, including those on road conditions
- Stay away from flooded areas
- Monitor weather reports
- Follow the instructions of local authorities, including evacuation orders
Earthquakes and tsunamis
Haiti is located in an active seismic zone. Earthquakes occur. Tsunamis can also affect coastal areas.
A tsunami can occur within minutes of a nearby earthquake. However, the risk of tsunami can remain for several hours following the first tremor. If you’re staying on the coast, familiarize yourself with the region’s evacuation plans in the event of a tsunami warning.
In the event of an earthquake:
- monitor local media for the latest information
- Earthquakes - What to Do?
- Tsunami alerts - U.S. Tsunami Warning System
- Latest earthquakes - U.S. Geological Survey
Local services
In case of emergency, dial 114.
Consular assistance
For emergency consular assistance, call the Embassy of Canada to Haiti, in Port-au-Prince, and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also call the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.
Haiti Safety 2024: Is Haiti Safe to Visit?
Haiti is nestled on the second-largest Caribbean island, Hispaniola, and shares its stunning scenery with the Dominican Republic .
There’s a lot to love about Haiti—the untouched rainforest of Macaya National Park , the mesmerizing Saut Mathurine waterfall, the enchanting island Île à Rat , the grand Sans Souci Palace , the hidden gem of Grotte Marie Jeanne underground cave, and the tropical haven of Cotes des Arcadins .
Unfortunately, beyond the scenic beauty, Haiti’s turbulent sociopolitical scene makes it a highly dangerous destination —political turmoil, criminal activity, civil unrest, and the highest travel advisory warning against visiting this country. Stay with us to uncover more about Haiti.
Is Haiti Safe?
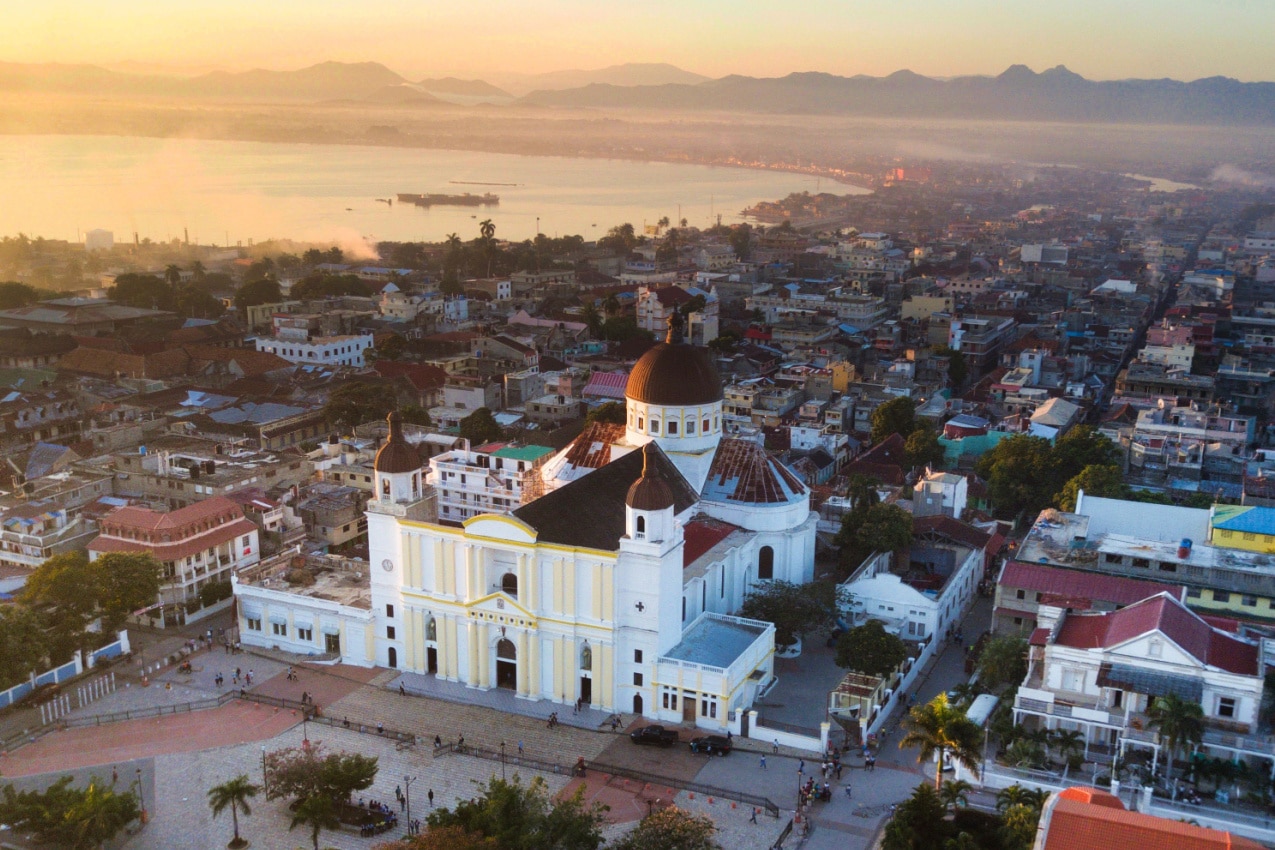

No, Haiti is not a safe destination for travelers. In imperialist times, Haiti was the most profitable colony globally due to its sugar and coffee trade. But, as usual, colonialism has taken its toll. Today, Haiti ranks among the world’s poorest countries .
Additionally, Haiti is still grappling with the aftermath of the devastating 2010 earthquake , which claimed over 300,000 lives and rendered 1.5 million people homeless.
Drive from Port-au-Prince’s international airport to the city center, and you’ll pass through slums where goats and pigs scavenge through piles of trash. Teens clean car windows in halted traffic, and hotels are guarded by armed personnel.
Why the armed guards? Well, there’s virtually no safe haven in this country. The threat of violent crime is very real and present everywhere. As a result, Haiti earned one of the lowest ranks in the 2023 Global Peace Safety Index , coming in at 129 out of 163 countries.
- International travel advisories: Level 4 (Do Not Travel); violent crime and shortage of basic necessities are widespread
- Crime rating: High, 77.88
- Most dangerous areas: Artibonite Central, Bas-Delmas, Bel Air, Carrefour, Carrefour, Drouillard, Champs-de-Mars, Cité Soleil, Croix-des-Bouquets, Downtown Port-au-Prince, Fontamara, Jalousie, Laboule 12, Martissant, Portail Léogane, Road to the airport, Santo, Tabarre, Torcelle, and Toussant Brave
- Public transportation safety: Passengers often fall victim to assault, abductions, and theft; official taxis are rare, buses are few, and minibusses lack safety features
- Safety walking alone during the day: Low
- Safety walking alone during the night: Very low
- Road safety: Roads lack proper markings, some are closed, and others have large potholes
- Beach safety: The safest beaches are located at the Labadee Resort ; take notice of the warning flags and keep an eye on your belongings
- Tap water: Unsafe to drink
- Common natural disasters: Earthquakes, hurricanes, and tsunamis
- Carbon monoxide poisoning: Possible, a portable carbon monoxide detector is advised if you plan to travel
- Police presence: Severely understaffed and may lack the resources to respond effectively to serious criminal incidents
- Medical care quality: Hospitals and clinics lack qualified doctors, basic equipment, and resources for treating patients
Travel Advisory for Haiti
Every international travel advisory echoes the same stark warning for Haiti—Do Not Travel.
The United States , the United Kingdom , Canada , Australia , and New Zealand travel advisories all place Haiti in the highest risk category— Level Four —and strongly discourage travelers from visiting due to:
- Violent Crime: Travelers are at risk of being followed and violently attacked especially after leaving the Port-au-Prince International Airport. Criminals target vehicles stuck in heavy traffic.
- Civil unrest: Ongoing political instability leads to violent demonstrations, roadblocks, and attacks by criminal organizations, impacting areas like Route Nationale 2 from Martissant to Miragoane.
- Lack of police protection: Local police often lack the resources to respond effectively to serious criminal incidents, particularly in Artibonite Central, Bas-Delmas, Bel Air, Carrefour, Carrefour, Drouillard, Champs-de-Mars, Cité Soleil, Croix-des-Bouquets, Downtown Port-au-Prince, Fontamara, Jalousie, Laboule 12, Martissant, Portail Léogane, Road to the airport, Santo, Tabarre, Torcelle, and Toussant Brave.
- Poor healthcare infrastructure: Medical clinics and hospitals lack qualified staff, basic equipment, and resources. Life-threatening emergencies may require evacuation at the patient’s expense.
- Severe shortages of basic necessities: Frequent power outages, as well as water and fuel shortages, are common. Tap water is generally unsafe to drink.
- Natural disasters: Cyclones, hurricanes, tropical storms, floods, and earthquakes continue to pose a significant risk, with limited government capacity to respond effectively.
Given these substantial risks, it is strongly advised to avoid traveling to Haiti.
A Comprehensive Look at Haiti Crime Rates
Haiti has a high crime rating of 77.88.
Data from the Haitian National Police and the UN reveal a dire situation in the first quarter of 2023 —over 1,600 reported incidents. This is a staggering rise, as the number nearly tripled from 692 incidents during the same period of the previous year (Q1 2022).
The capital Port-au-Prince and its metropolitan region face the cruelty of approximately 150 criminal groups , many affiliated with the G-Pèp and the G9 alliance . Cité Soleil has served as the main battleground for rival disputes between the G9 and the G-Pèp alliance.
With violence surging in Haiti, people are witnessing a full-blown humanitarian crisis . In 2023 , nearly 200,000 people have been displaced, around 70,000 individuals are living in makeshift settlements, 31,000 live out in the open, and another 34,000 are crammed into classrooms.
The situation demands urgent attention from authorities, and a wake-up call for you, tourists, to reserve this destination for better days.
Source : Numbeo , 2024 data, based on 50 contributors
Police Presence in Haiti
The Haitian National Police force is severely understaffed and lacks the necessary equipment to tackle the country’s widespread violence and criminality. The force is pressed rather thin , with personnel dropping from 14,772 to around 13,200 in 2023.
If you happen to visit Haiti for whatever reason—despite the warnings of the authorities—know that police protection in Haiti is not guaranteed. If you believe that you are being followed in Haiti, be it after leaving the airport or anyplace else, prioritize your safety and go to the nearest police station immediately.
Public Transportation Safety in Haiti

Public transportation in Haiti comes with a host of challenges, and safety is a major concern.
Official taxis are a rarity, buses are few and far between, and the shared “tap-tap” minibusses, although commonly used, should be avoided as they lack safety features, the drivers drive recklessly, and are often overcrowded. Reports of armed robberies and abductions associated with public transportation raise serious red flags. Adding to the list of reasons to avoid public transport, bus stations are often chaotic hotspots for pickpocketing and scams.
Road Safety in Haiti
Driving in Haiti is not safe. Many roads lack proper markings, others are closed, and a great majority have large potholes caused by massive earthquakes.
If this weren’t enough, Haiti’s roads are shared spaces with animals that are rather oblivious to the concept of cars. In urban areas, encounters with smaller animals like pigs, dogs, and goats are common, while rural roads may lead to encounters with larger animals such as cows and donkeys.
Medical Care Quality in Haiti
Healthcare in Haiti is limited and inadequate.
Fontaine Hospital Center , situated in the heart of Cité Soleil—the most densely populated and violent area of the capital—stands as one of the last bastions for medical treatment. Ambulance services are limited, and they might not be well-equipped with essential medical supplies, so effective emergency response is also not guaranteed.
When seeking medical attention, visitors should be prepared for immediate cash payments, even if they have valid travel health insurance. Pharmacies might stock expired medications, and some crucial medications may not be available.
In life-threatening situations, be aware that Haiti may not be able to provide you with sufficient medical treatment. In such cases, evacuation might be necessary, and it often comes at the patient’s own expense.
Is It Safe to Travel Solo in Haiti?
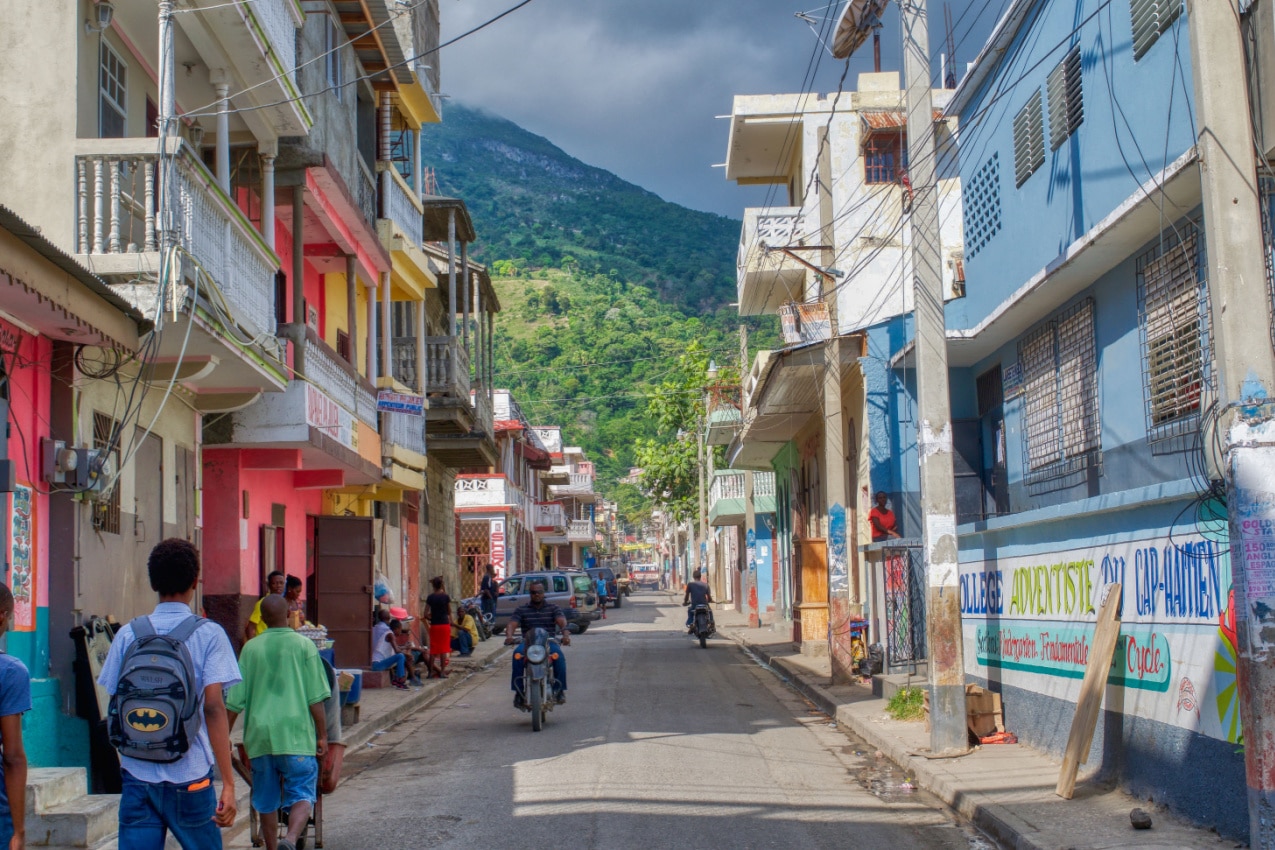

Travel advisories strongly discourage solo visits to Haiti due to a multitude of safety concerns, civil unrest, and limited healthcare facilities.
Solo travelers, in particular, are viewed as easy targets and might find themselves more susceptible to harassment and assault. Public transportation adds another layer of risk, as it’s both unreliable and unsafe, especially after nightfall. Until travel advisories change, it’s best to avoid solo trips to Haiti.
Perils of Nature: The Risk of Natural Disasters in Haiti
Haiti is at risk of a few natural disasters: hurricanes, earthquakes, and tsunamis.
Haiti lies in the Atlantic hurricane belt, making it susceptible to hurricanes and tropical storms during the hurricane season, which is from June 1 to November 30 . On average, about five such events occur each year , with the most affected regions being southeast, south, and northwest.
The latest hurricane , Franklin , reached tropical storm hurricane status with winds up to 57 mph (93 km/h) on August 24, 2023, near Dérac. The most devastating hurricane season , however, happened back in 2008 when storms Fay, Gustav, Hanna, and Ike caused widespread destruction.
In case of a hurricane or severe storm:
- Be aware of potential travel disruptions
- Flights may be delayed or suspended
- Adequate shelter might be limited
- Port access could be impacted
If a hurricane is imminent:
- Identify local shelters
- Follow the advice from local authorities
- Stay informed with updates from the US National Hurricane Center
Earthquakes
Haiti, located along the boundary of the Caribbean and North American tectonic plates, is susceptible to seismic activity.
One of the most devastating earthquakes occurred in 2010 , registering 7.0 on the Richter scale. Lasting 35 seconds, it resulted in 220,000 dead, 300,000 injured, and 1.5 million homeless.
Tragically, that wasn’t the strongest one, nor the last one to devastate the nation. The strongest earthquake in Haiti occurred in 2021 , with a magnitude of 7.2 on the Richter Scale. It claimed 2,248 lives and triggered a tsunami warning.
To this day, earthquake-damaged infrastructure, including health services, roads, telecommunications, and utilities, remains a challenge. Water and sewerage system damages have contributed to increased disease outbreaks in Haiti.
In the event of an earthquake hit in Haiti:
- Drop to the ground, take cover under something sturdy, and hold on until the shaking stops
- If outdoors, find a clear spot away from buildings and trees, and remember to drop, cover, and hold on
Tsunamis are colossal tidal waves triggered by earthquakes or seismic eruptions beneath ocean surfaces.
The most destructive tsunami in Haiti’s history occurred in 1842 , reaching a towering height of 16 feet (5m) and claiming 300 lives. The 7.0 earthquake in 2010 also generated a tsunami with 3.2-meter waves , resulting in three fatalities. In 2021, following the 7.2 earthquake, tsunami warnings were issued for some Haitian coasts, though fortunately, an official tsunami did not occur .
If you’re near the Haiti coast and experience a strong or prolonged earthquake, notice sea-level changes, or hear unusual oceanic noises, promptly move to higher ground as advised by local authorities.
Tsunamis can strike within minutes of seismic activity, but if you register on the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System , you’ll receive a timely alert if a tsunami is approaching. Don’t wait for official alarms, act swiftly. Once in a safe location, stay informed through local media.
Beware the Silent Threat: Carbon Monoxide Poisoning in Haiti
Hotels and motels face a genuine threat from carbon monoxide poisoning. In Mexico City , three AirBnB guests lost their lives to carbon monoxide, and another group faced a similar fate at a Sandals Resort in the Bahamas .
Haiti hasn’t experienced such incidents with tourists yet, but it doesn’t mean it’s impossible.
Carbon monoxide (CO) is an invisible and odorless toxic gas. For instance, if your hotel has a malfunctioning appliance, like a stove, water heater, or heating system, the gas can leak into your room, slowly poisoning you.
Many hotels use CO detectors to keep guests safe from dangerous gas—but not all of them. It’s best to purchase a portable CO detector , especially if the hotel doesn’t have one or it’s broken.
Remember, if you get headaches, throw up, or feel sick, that could be CO poisoning. Get medical care immediately. Longer exposure to CO may have tragic effects, like paralysis, brain damage, or fatal consequences.
Serenity by the Shore: The Safety of Haiti Beaches
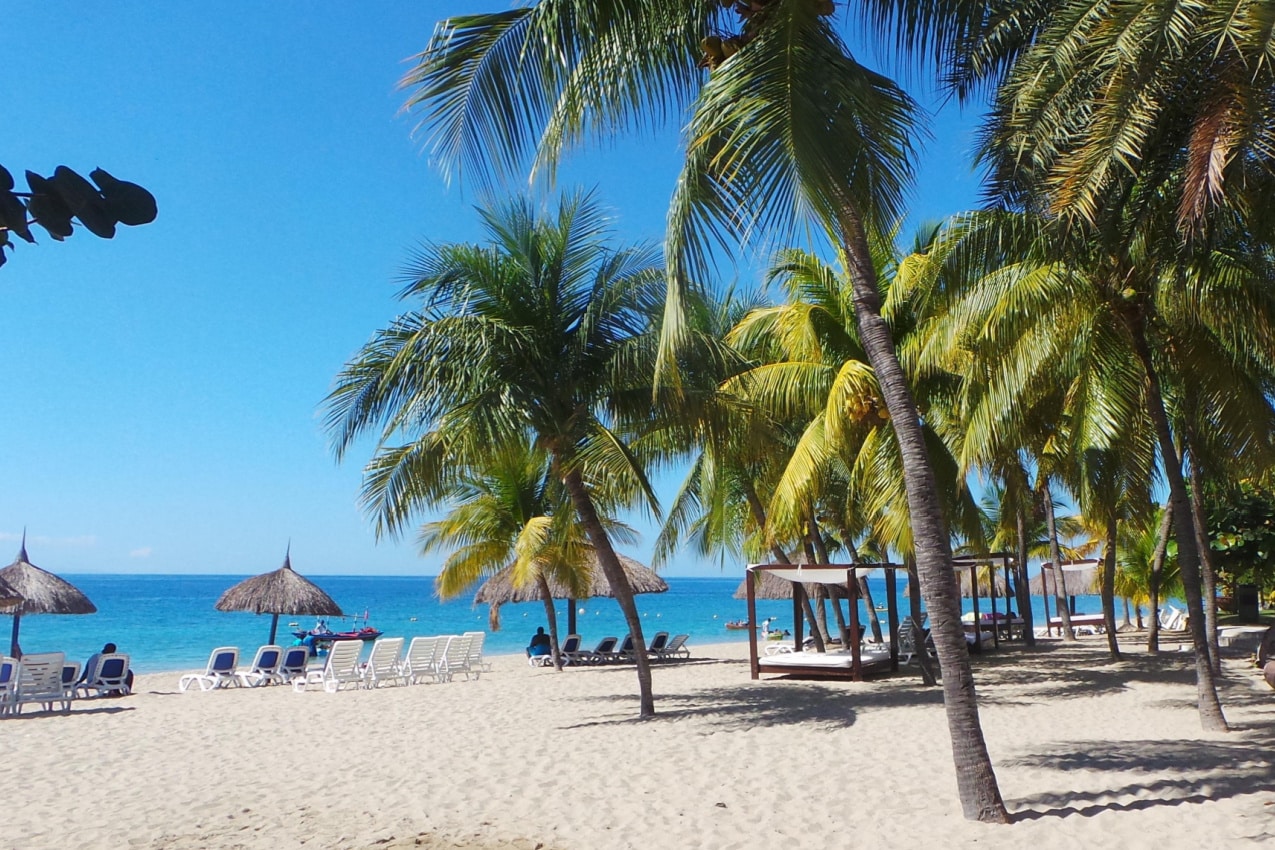

Considering the widespread violence in Haiti, some might think twice about visiting any of its beaches. However, if you decide to ignore the serious warnings, the safest beach to visit would be Labadee.
Labadee is a private beach resort on Haiti’s northern coast, owned by Royal Caribbean Cruise Lines and exclusively accessible to cruise ship passengers. The resort is well-protected, with trained security personnel ensuring the safety of tourists.
When hitting the beach, it’s a good idea to pay attention to warning flags:
- Red Flag: High surf, life-threatening currents – Don’t swim
- Yellow Flag: Potential high surf or risky currents – Swim with caution
- Green Flag: Safe to swim
- Purple Flag: Presence of dangerous marine life like sharks, jellyfish, or sea urchins – Swim with extreme caution
- Blue Flag: The beach is recognized for excellent water quality, environmental care, and safety
Not all beaches have these flags, so it’s advisable to talk to locals or resort staff about the safety situation before heading out for a swim. Once there, remember the basics: wear sunscreen and keep an eye on your stuff.
Haiti Weather Patterns: What to Expect
Haiti has a hot tropical climate year-round. The average temperatures range from the high 70s°F (about 25°C) in winter to the mid-80s°F (about 30°C) in summer.
The specific temperatures vary based on the elevation, with slightly higher temperatures in inland plains and on south-facing coasts, and slightly lower temperatures along north-facing coasts.
The sunny and dry season in Haiti starts in December and lasts until April. January is the sunniest month, with clear skies about 79% of the time and very little rain, averaging 0.4 inches (about 1 cm).
The cloudy and wet season spans from May to November. September is the cloudiest month, with overcast or mostly cloudy skies about 74% of the time. The wettest days occur in May, averaging 5.1 days with 2.1 inches of rainfall (about 13 cm).
Haiti gets quite windy from the end of June to mid-August, with average speeds exceeding 5.7 mph (about 9.2 km/h). June is the windiest month, with an average hourly speed of 6.4 mph (about 10.3 km/h). This aligns with the hurricane season from June to November, increasing the likelihood of hurricanes during the windy months.
Conversely, the calmer wind period spans 9.2 months, from the end of August to May. October is the calmest month, with an average hourly wind speed of 4.9 mph (about 7.9 km/h).
The water is warmest from July to November, with an average temperature above 84°F (about 28.9°C). September has the warmest water, with an average temperature of 85°F (about 29.4°C), while February sees the coolest water, averaging 81°F (about 27.2°C).
Monthly Average Temperatures in Haiti
Source : WeatherSpark , 2024 data

When Is the Best Time to Visit Haiti?
Currently, there’s no good time to book a trip to Haiti. However, if the safety situation improves, crime levels drop, and international travel advisories give it the green light, you might want to plan your trip during the dry season, from December to April .
The dry season has several perks: escape from the snow or cold of the northern hemisphere, balmy weather perfect for beach time, and calm seas that are great for activities like surfing, snorkeling, diving, and trekking.
However, there’s one downside: December to April is also peak tourist season, making it a bit tricky and sometimes expensive to find flights. The busiest months are December and January, with Haitians living abroad returning for end-of-year celebrations with friends and family.
If you do visit during peak tourist season, book well in advance and do a little digging to find the best hotel deal.
How to Stay Safe in Haiti
By now, it should be clear that traveling to Haiti involves serious risks. If you choose to travel there anyway, make sure to follow these safety guidelines :
- Sign up for the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program . It’s a free service that provides real-time security information and maintains a connection between you and your government.
- Consider booking a hotel room at the private beach resort Labadee . The resort is well-protected by trained security personnel.
- Get all recommended vaccinations (for diphtheria, tetanus, polio, hep A., typhoid, cholera) at least one month before your departure.
- Stay up-to-date on natural disasters . Monitor hurricanes at the National Hurricane Center , earthquakes on VolcanoDiscovery , and tsunamis on the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System .
- Have someone meet you at the airport or pre-book an airport transfer. Never use public transport.
- If you must drive, keep your fuel tank at least half-full , as the gas stations may often have limited supplies.
- Dress modestly and avoid flashy displays of wealth , as you don’t want any additional attention.
- Make and carry copies of important documents , such as your passport and driver’s license, in case of theft.
- People may not appreciate being photographed in poor or urban areas , so seek permission before taking pictures.
- Purchase a Digicel Haiti SIM card for reliable internet and cell service —you don’t want to be unable to contact emergency services (or your family abroad) while in Haiti.
- Exercise extreme caution when using banks . Use ATMs only in secure locations like malls or markets and never in public spaces.
- Avoid going out after sunset . If you’re hungry, consider using a food delivery app like Uber Eats , which operates in major cities in Haiti.
- Violent crimes are common . Be extremely vigilant and aware of your surroundings at all times. If someone tries to steal from you, don’t resist. Criminals are often armed, and resistance may lead to fatal injuries.
- Seek immediate medical help if you’re a victim of violent crime .
Emergency Numbers
- Ambulance: 116/ 3685-0717
- Police: 114/ 3805-8888/ 3838-1111
- Civil Protection: 4448-6571/ 3623-0303/ 4896-0564
- Electricity: 2212-2212
- Water Supply and Sanitation Directorate: 5959
- Fire department: 2945-1111
Leave Your Haiti Vacation for Better & Safer Times
Who would have guessed that such a stunning country could be so risky? Unfortunately, life-threatening dangers make visiting Haiti a rather bad idea at present.
So until the situation improves, we strongly recommend heeding international travel advisories and not visiting this country.
If you decide to go despite the warnings, take maximum precautions. Upon arrival, ensure that no one is following you, as criminals have been known to observe people arriving at the airport and then following them with malicious intent.
Stick to the secure resort areas, arrange organized transport, never venture into high-crime zones, and stay safely locked in at night.

Trinidad and Tobago Safety 2024: Trinidad and Tobago Safe to Visit

Cayman Safety 2024: Is Cayman Safe to Visit?

Dominican Republic Safety 2024: Is Dominican Republic Safe to Visit?

St. Lucia Safety 2024: Is St. Lucia Safe to Visit?
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
Bring photo ID to vote Check what photo ID you'll need to vote in person in the General Election on 4 July.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Warnings and insurance
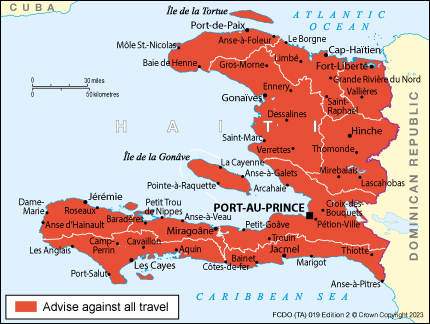
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office ( FCDO ) provides advice about risks of travel to help British nationals make informed decisions. Find out more about FCDO travel advice .
FCDO advises against all travel to Haiti
Your travel insurance could be invalidated if you travel against FCDO advice. Consular support is also severely limited where FCDO advises against travel.
FCDO advises against all travel to Haiti due to the volatile security situation. There are currently no British consular officials in Haiti and our ability to provide consular assistance is severely limited and cannot be delivered in person in Haiti.
British nationals may get consular services assistance at our diplomatic mission in the Dominican Republic .
If you choose to travel to or stay in Haiti against FCDO advice, try to avoid all crowds and public events, and take appropriate security precautions.
State of Emergency
There is a State of Emergency in Port-au-Prince until 8 June, which can include a curfew between 10pm-5am.
Before you travel
No travel can be guaranteed safe. Read all the advice in this guide and see support for British nationals abroad for information about specific travel topics.
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this advice is updated.
Travel insurance
If you choose to travel, research your destinations and get appropriate travel insurance . Insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities and expenses in an emergency.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .
Choose your language

Haiti up close
Is it really safe to travel to Haiti?
Boats at Ile-a-Vache, Haiti
Photo: Verdy Verna
One of America’s closest neighbours, Haiti has long been a source of fascination. American celebrities turned Haiti into one of the popular Caribbean holiday destinations in the 1960s and 70s, but this changed as Haiti suffered increasingly inept rule in the 70s and 80s. Decades of poverty, political instability and plain bad luck followed.
Is it safe to travel to Haiti?
Finally, after a decade of relatively peaceful democratic government, a tourism bounce-back has begun, and a new generation of tourists are discovering what makes Haiti so special. Haiti is becoming a sought-after experience for adventure-driven travelers, the culturally curious, and Millennials who’ve visited the Caribbean already and are seeking something different.
Since the 2010 earthquake, Haiti has been on the road to reconstruction. For several years, national icons lay in rubble and whole city squares cordoned off for repair, but the Caribbean nation is now recovering well. With tourism vital for continued prosperity, keeping visitors safe and satisfied is a priority for locals and government policy reflects this.
In fact, the 2019 Global Peace Index ranks Haiti at #87 out of the 163 countries on the list. According to the list, Haiti is more peaceful than many popular tourist destinations like Morocco, Brazil, Thailand, Kenya, the Philippines, Mexico, India and - interestingly - USA (#128).
Americans, Canadians and most Europeans can visit Haiti without a visa at all, making it a great alternative to Cuba . The Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index ranks Haiti very well when it comes to openness and value-for-money. Over the last ten years, tourism has doubled.
If you’re considering travel to Haiti, you probably still have some questions, so here are a few answers to help you before a first-time visit to the Caribbean island nation:
The current generation has grown up with images of Haiti suffering the effects of the 2010 earthquake , but the last decade has actually seen less political unrest, inequality and crime. Haiti remains poor, but it’s perfectly safe for visitors to walk around the cities on foot or travel across the country to see the many cultural icons and natural wonders , either alone or with a local guide.
As in any large city in the US, people visiting should take sensible precautions when in Port au Prince or Haiti’s other cities. But there’s no significant security threat, and it’s easy to find the parts of town safe for travellers to wander. It’s very common to see foreigners walking around unaccompanied in the streets of Port-au-Prince .
While political unrest can be a cause for worry, it should be noted that most of these events affect very specific politically active groups, not individual people going about their daily life, and certainly not foreigners.
Boat painter in Dame Marie
Photo: Mikkel Ulriksen
How to stay safe
Traffic in Haiti is fairly unregulated, so it serves to look both ways, twice , before crossing any street. As in any big city in the world, pickpockets are out there, so make sure that you keep your belongings close and out of your pockets – preferably in a small bag or pouch you can carry in your hand, or across your chest.
Current travel advisories: The US consulate currently has a Level 3 travel advisory for Haiti (issued 11 June 2019), and recommends that travellers stay safe by changing currency in advance (so you can avoid banks and ATMs), avoiding demonstrations, not attempting to go through roadblocks, and booking official, professional transport from the airport to your accommodation.
School girls, Corail
Photo: Franck Fontain
How to stay healthy
From a medical point of view, Haiti is generally safe as long as you're reasonably careful about what you eat and drink. Although tap water is considered generally safe for locals and long-term expats to drink, visitors who are in Haiti for only a short while are advised to avoid the risk of short-term stomach upsets by drinking bottled water. It’s cheap in the cities and not always available in small towns and on the road, so stock up before you venture out.
For more on what to eat, check out our guide to the delicious and distinctive street food of Haiti .
Get vaccinated before you go: Diphtheria, Hepatitis A and Tetanus shots are all recommended, but depending on your level of risk your doctor may recommend a few more.
Woman in Abricot
Photo: Kolektif 2 Dimansyon
Should you hire a local guide?
Yes. Your journey to all sights worth seeing - whether cultural icons like the World Heritage listed Citadelle , or natural wonders like Bassin Zim , or adventure destinations like Pic La Selle - will be improved if you go with a guide. Guides will ensure your safety, help you find the best routes, keep hawkers and hustlers at a distance and explain the local significance of the sights.
Even if you’re planning to stay in the city, it’s well worth a guided tour at the start to help you get your bearings and put you in a better position to enjoy the rest of your stay solo, without worrying about the local dos and don’ts.
Keep in mind that the two common languages in Haiti are Creole and French - if you don’t speak French, a tour guide is even more invaluable for helping you find your way around.
Is there internet?
Yes. Wifi is widely available in accommodation and restaurants.
Are there hotels up to an American standard?
One of the best things about Haiti as a travel destination is that it’s relatively free of juggernaut five-star resorts that dominate the landscape in other more well-trodden Caribbean destinations. In Haiti, you can ditch the noisy crowds and find much more down-to-earth experiences of beachside paradise.
That’s not to say you can't find luxury - there are several resorts and mid-size hotels dotted around the cities and exclusive beachfront destinations along the coast. Within the cities, there’s a good selection of boutique hotels to suit your budget and style.
Airbnb is gaining popularity too, with dozens of offerings across Haiti’s major cities from art-filled family homes to free-standing villas where you can sip rum sours in your own infinity pool.
What are the travel restrictions for visiting Haiti?
Americans, Canadians and most Europeans can visit Haiti without a visa at all, as long as you plan to stay for less than three months.
Upon your arrival to the island, you’ll be required to pay a USD $10 tourist fee, before you get in line to go through Customs.
Visa requirements:
The list of countries of which Haiti requires a Visa is very short: Syria, Libya, Iran, Vietnam, Yemen, and Chechnya. If you are visiting from the Dominican Republic , Panama, or Columbia, just make sure that you have a valid US, Canadian, or Schengen visa in your passport.
Haiti allows foreigners to stay for up to three months, after which they need to regularize their status. If you are planning to stay in Haiti for a long stretch of time, make sure that you keep this in mind and book your travel arrangements accordingly.
People relaxing, Pestel
Why visit Haiti?
Haiti is home to stunning beaches, unique Creole language and cuisine, a proud heritage of hard-won freedom and independence , and inspiring historical attractions.
Haiti is also home to the Caribbean’s premiere art scene, with an abundance of galleries and artist-owned initiatives showcasing distinctive Haitian styles. You’ll find thriving artist colonies in Grand Rue , Jacmel and Noailles.
Haiti’s most iconic historic site, the Citadelle fortress outside Cap Haïtien , houses the world’s biggest collection of 19th-century cannons and artillery. The island’s compelling past is expertly displayed at some of the Caribbean’s best museums, including the Museum of the Haitian National Pantheon on Champ-des-Mars .
The culturally curious can catch the Thursday-night Vodou rock show in downtown Port-au-Prince, or witness the whirlwind of costumes, music and performance during one of the many annual festivals.
Throughout a history of amazing achievements and heartbreaking disasters, the people of Haiti have demonstrated incredible resilience, creativity and determination.
Don’t miss your chance to soak up some of this spirit and sample what this unique culture has to offer. Visit Haiti.
Written by Kelly Paulemon .
Published November 2018
Top things to see in Haiti
Hike to historic fort jacques.
High in the dense mountains just outside Port-au-Prince, you'll find
Visit a museum dedicated to Vodou
A visit to the Bureau of Ethnology, a museum dedicated
How to Attend a Vodou Ceremony in Haiti
Skulls, sequins and gunpowder smoke - here’s a glimpse inside
Haitian Cuisine: A Culinary Map of Haiti
Come with us on a lip-smacking journey as we map
Your Ultimate Guide to Carnival in Haiti
Unleash your inner party spirit with our ultimate guide to
Explore Haitian Nature at Wynne Farm Ecological Reserve
Wynne Farm Ecological Reserve is a successful sustainability initiative where
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get more travel inspiration, tips and exclusive offers sent straight to your inbox
I would like to get VisitHaiti newsletters in my inbox
Paradise for Your Inbox

Subscribe to our newsletter for the best monthly stories and insider guides about Haiti!
I would like to get Visit Haiti newsletters in my inbox
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Haiti Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
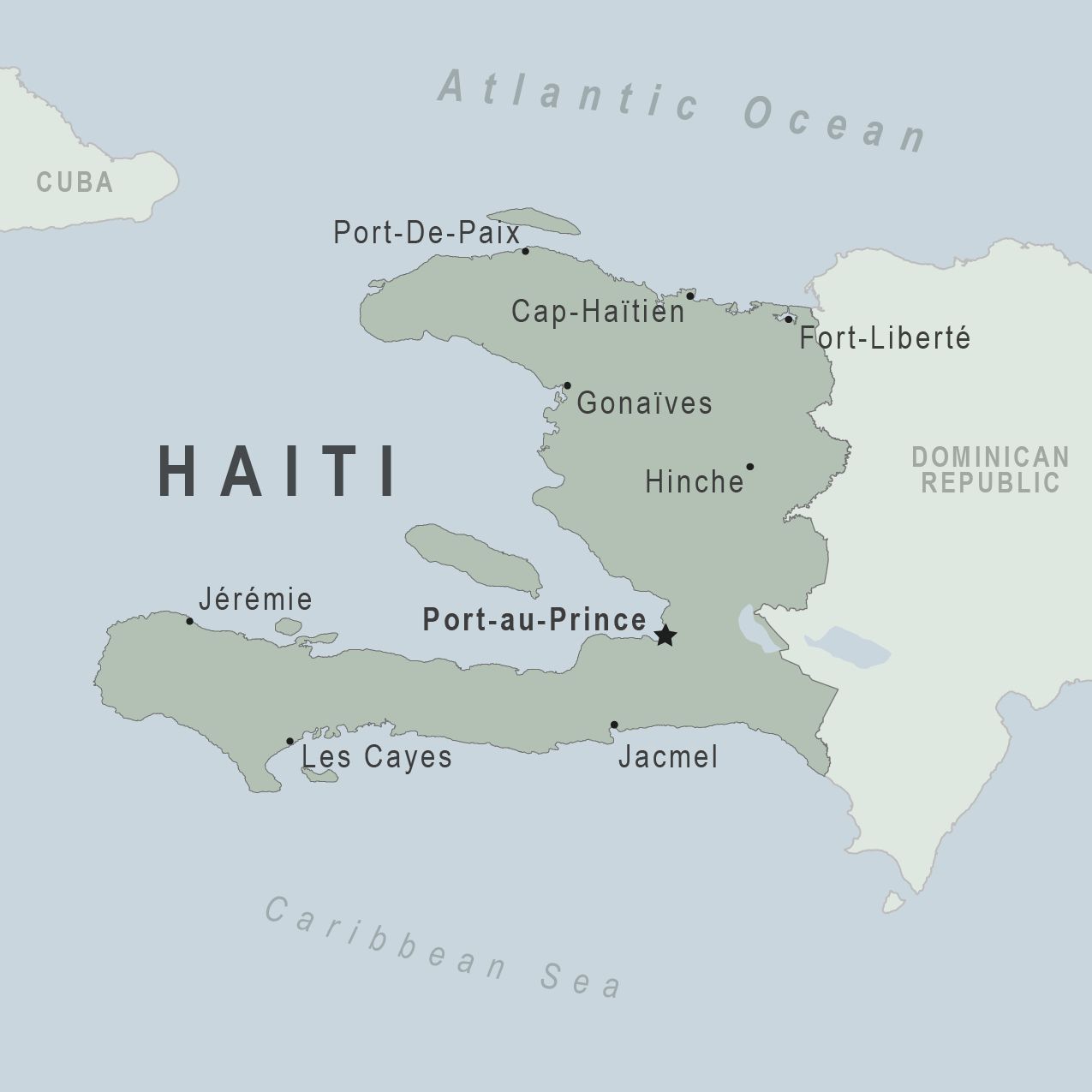
There are no notices currently in effect for Haiti.
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
Active cholera transmission is widespread in Haiti. Cholera is rare in travelers. Certain factors may increase the risk of getting cholera or having severe disease ( more information ). Avoiding unsafe food and water and washing your hands can also help prevent cholera.
Vaccination may be considered for children and adults who are traveling to areas of active cholera transmission.
Cholera - CDC Yellow Book
Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Haiti.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers younger than 60 years old traveling to Haiti. Unvaccinated travelers 60 years and older may get vaccinated before traveling to Haiti.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
CDC recommends that travelers going to Haiti take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for Haiti.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
Dogs infected with rabies are commonly found in Haiti.
Rabies is also present in some terrestrial wildlife species.
If rabies exposures occur while in Haiti, rabies vaccines may only be available in larger suburban/urban medical facilities.
Rabies pre-exposure vaccination considerations include whether travelers 1) will be performing occupational or recreational activities that increase risk for exposure to potentially rabid animals and 2) might have difficulty getting prompt access to safe post-exposure prophylaxis.
Please consult with a healthcare provider to determine whether you should receive pre-exposure vaccination before travel.
For more information, see country rabies status assessments .
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
Yellow Fever
Required for travelers ≥1 year old arriving from countries with risk for YF virus transmission. 1
Yellow Fever - CDC Yellow Book
Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
- Avoid floodwater
Clinical Guidance
Avoid bug bites.
- Mosquito bite
- Avoid Bug Bites
- An infected pregnant woman can spread it to her unborn baby
Airborne & droplet
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Haiti, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH)
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Haiti. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Haiti include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Leptospirosis, a bacterial infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Haiti. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Haiti’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in Haiti. Fill your malaria prescription before you leave and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Haiti may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Haiti, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
For information traffic safety and road conditions in Haiti, see Travel and Transportation on US Department of State's country-specific information for Haiti .
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Haiti for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.

Countries US Department of State travel advisories say NOT to go to as Haiti explodes in violence
A s tensions remain fraught in Haiti, with violent gangs joining forces in a bid to oust Prime Minister Ariel Henry, the US State Department has issued a travel advisory warning Americans not to travel to the Caribbean country.
In mid-October 2023, the U.S. Department of State 's Bureau of Consular Affairs issued a "Worldwide Caution," citing "increased tensions in various locations around the world." The warning included "the potential for terrorist attacks" and "demonstrations or violent actions against U.S citizens and interests" and told citizens to "exercise increased caution."
Violence remains rampant in Haiti , leading to near all-out war, with the violent gang boss 'Barbecue' threatening to take the country to civil war, saying he and other gang members will fight until the last drop of blood to remove Prime Minister Henry from office. Amidst the violence, the number of travel advisories issued by the US has increased, and the level of some has become more severe, in Haiti and elsewhere.
READ MORE: White House says 'too many innocent civilians have died in Gaza' amid Israel-Hamas war
Haiti has been on a Level 4 Travel Advisory — the highest, which is designated "Do not travel" — since July 2023, with the State Department writing in its advisory: "Do not travel to Haiti due to kidnapping, crime, civil unrest, and poor health care infrastructure."
The State Department ordered the departure of all family members of U.S. government employees in the country in late July and also all non-emergency personnel, with all other U.S. citizens in the country implored to depart as soon as possible by any means necessary. Of Haiti, the State Department wrote: "Kidnapping is widespread, and victims regularly include U.S. citizens.
"Kidnappers may use sophisticated planning or take advantage of unplanned opportunities, and even convoys have been attacked. Kidnapping cases often involve ransom negotiations and U.S. citizen victims have been physically harmed during kidnappings. Victim’s families have paid thousands of dollars to rescue their family members."
It added that violent crime is rampant in the country, with mob killings being on the rise since April 2023, and that hospitals are often out of supplies or are unequipped to care for patients, with police in the same boat. Haiti's prime minister recently fled to Puerto Rico , a U.S. territory, after the violence wrought by Barbecue and the 4,000 prisoners he released to incite a rebellion and take the country back. The U.S. Embassy in the country has been on lockdown a few times, too.
Join the Mirror's SMS news service to get the biggest breaking stories delivered straight to your phone. Click here to subscribe.
In addition to Haiti, here are the countries or regions at a Level 4 Threat Advisory (in alphabetical order):
- Afghanistan
- Burkina Faso
- Burma (Myanmar)
- Central African Republic
- Some Mexican states
- North Korea
- South Sudan
Click here to follow the Mirror US on Google News to stay up to date with all the latest news, sports and entertainment stories.
On a Level 3 Threat Advisory, or the second highest, which states "Reconsider travel," the following countries are on the list:
- Most Chinese territories
- Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC)
- El Salvador
- Guinea-Bissau
- Israel (and the West Bank)
- Papua New Guinea
- Saudi Arabia
- Trinidad and Tobago
Most of the advisories cite crime or terrorism as the reason for the advisory, with violent crime dominating certain areas or excessive risk of terrorism, against Americans specifically, warranting advisories.
In any case, the State Department recommends staying clear of the above-mentioned countries and regions, but if travel becomes a necessity, it warns first that help in emergency situations is likely impossible.
Travelers should, according to the State Department:
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP)
- Set up communication with loved ones while also sharing location
- Share important documents, logins or contacts with loved ones
- Draft a will and name insurance beneficiaries and a power of attorney that states what will happen if you die
- Make a personal security plan with your employer or host
- Identify the nearest U.S. Embassy or Consulate, FBI or State Department's Office of American Services
- Appoint a family member or loved one to serve as the point of contact if you are taken hostage or detained. That person should also have a proof of life protocol to follow
- Leave DNA samples with your medical provider for identification purposes, if necessary
- Erase any sensitive photos, comments or material from social media that could be controversial in your host country
- Leave expensive or sentimental belongings behind
In short, no matter where you're headed, the State Department recommends exercising as much caution as possible when traveling outside the country due to heightened levels of terrorism and threats worldwide. More information can be found on the department's website.
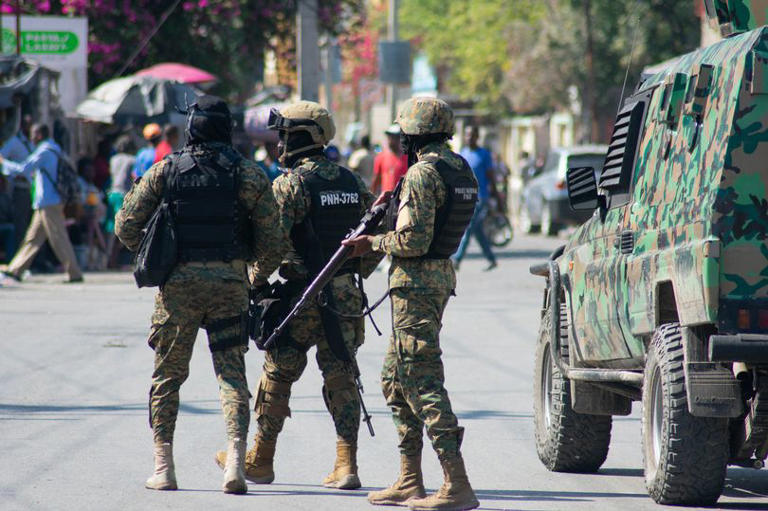

Haiti Travel Advisory
%201.webp)
Haiti – Level 4: Do Not Travel
Global Health Advisory: Do Not Travel. Avoid all international travel due to the global impact of COVID-19 .
Do not travel to Haiti due to crime , civil unrest, and kidnapping .
Country Summary: Violent crime, such as armed robbery and carjacking, is common. Kidnapping is widespread. Kidnappers may use sophisticated planning or take advantage of unplanned opportunities. Victims have included U.S. citizens.
Demonstrations, tire burning, and roadblocks are frequent, unpredictable, and can turn violent. Local police may lack the resources to respond effectively to serious criminal incidents. Emergency response, including ambulance service, is limited or non-existent.
Travelers are sometimes followed and violently attacked and robbed shortly after leaving the Port-au-Prince international airport. The U.S. Embassy requires its personnel to use official transportation to and from the airport. Robbers and carjackers have attacked private vehicles stuck in heavy traffic congestion and often target lone drivers, particularly women driving alone.
The U.S. government has limited ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in some areas of Haiti. U.S. government personnel are discouraged from walking in most neighborhoods. Only adult family members over the age of 18 are permitted to accompany U.S. government employees assigned to the U.S. Embassy in Port-au-Prince. U.S. government personnel in Haiti are prohibited from:
- Visiting establishments after dark without secure, on-site parking;
- Using any kind of public transportation or taxis;
- Visiting banks and using ATMs;
- Driving outside of Port-au-Prince at night;
- Traveling anywhere between 1:00 a.m. and 5:00 a.m.
- Visiting certain parts of the city at any time without prior approval and special security measures in place.
Read the Safety and Security section on the country information page .
If you decide to travel to Haiti:
- Avoid demonstrations and crowds. Do not attempt to drive through roadblocks.
- Arrange airport transfers and hotels in advance, or have your host meet you upon arrival.
- Do not provide personal information to unauthorized individuals (i.e. people without official uniforms or credentials) located in the immigration, customs, or other areas inside or near any airports.
- If you are being followed as you leave the airport, drive to the nearest police station immediately.
- Travel by vehicle to minimize walking in public.
- Travel in groups of at least two people.
- Always keep vehicle doors locked and windows closed when driving.
- Exercise caution and alertness, especially when driving through markets and other traffic-congested areas.
- Do not physically resist any robbery attempt.
- Purchase travel insurance and medical evacuation insurance ahead of time.
- Review information on Travel to High-Risk Areas .
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Overseas Security Advisory Council report on Haiti.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Last Update: Reissued with updates to the Travel Advisory Level and the Crime and Kidnapping risk indicators.
Original Source: https://travel.state.gov/content/travel/en/traveladvisories/traveladvisories/haiti-travel-advisory.html

Join Our Newsletter
Be a part of our mission and receive the latest news and updates from one of the leading Haiti organizations for children.


An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Press Releases
Secretary Mayorkas Announces Extension and Redesignation of Haiti for Temporary Protected Status
WASHINGTON —Secretary of Homeland Security Alejandro N. Mayorkas today announced the extension and redesignation of Haiti for Temporary Protected Status for 18 months, from Aug. 4, 2024, to Feb. 3, 2026, due to extraordinary and temporary conditions in Haiti. The corresponding Federal Register Notice provides information about registering for TPS as a new or current beneficiary under Haiti’s extension and redesignation.
After consultation with interagency partners, Secretary Mayorkas determined on June 3, 2024, that an 18-month extension and redesignation of Haiti for TPS is warranted because conditions that support Haiti’s designation are ongoing and that doing so was not contrary to the national interest of the United States. Several regions in Haiti continue to face violence or insecurity, and many have limited access to safety, health care, food, and water. Haiti is particularly prone to flooding and mudslides, and often experiences significant damage due to storms, flooding, and earthquakes. These overlapping humanitarian challenges have resulted in ongoing urgent humanitarian needs.
“We are providing this humanitarian relief to Haitians already present in the United States given the conditions that existed in their home country as of June 3, 2024,” said Secretary Mayorkas. “In doing so, we are realizing the core objective of the TPS law and our obligation to fulfill it.”
The redesignation of Haiti for TPS allows an estimated 309,000 additional Haitian nationals (or individuals having no nationality who last habitually resided in Haiti) to file initial applications for TPS, if they are otherwise eligible and if they established residence in the United States on or before June 3, 2024, and have continued to reside in the United States since then (“continuous residence”). Eligible individuals who do not have TPS may submit an initial Form I-821, Application for Temporary Protected Status , during the initial registration period that runs from July 1, 2024, through Feb. 3, 2026. Applicants also may apply for TPS-related Employment Authorization Documents and for travel authorization. Applicants can request an EAD by submitting a completed Form I-765, Application for Employment Authorization , with their Form I-821, or separately later.
Haitians who were not residing in the United States on or before June 3, 2024, are not eligible for such protection, and will face removal to Haiti if they do not establish a legal basis to stay.
The extension of TPS for Haiti allows current beneficiaries to retain TPS through Feb. 3, 2026, if they continue to meet TPS eligibility requirements. Current beneficiaries under TPS for Haiti must re-register in a timely manner during the 60-day re-registration period from July 1, 2024, through Aug. 30, 2024, to ensure they keep their TPS and employment authorization. Re-registration is limited to individuals who previously registered for and were granted TPS under Haiti’s initial designation.
DHS recognizes that not all re-registrants who apply for a new EAD may receive it before their current EAD expires and is automatically extending through Aug. 3, 2025, the validity of certain EADs previously issued under Haiti’s TPS designation. Details will be available on USCIS.gov.
If you have one of these EADs, to get an EAD that is valid after Aug. 3, 2025, you must re-register for TPS and file Form I-765, Application for Employment Authorization , following the instructions in the Federal Register notice extending and redesignating Haiti for TPS through Feb. 3, 2026. If U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services approves your newly filed Form I-765, USCIS will issue you an EAD valid through Feb. 3, 2026.
USCIS will continue to process pending applications filed under previous TPS designations for Haiti. Individuals with a pending Form I-821, Application for Temporary Protected Status , or a related Form I-765 as of July 1, 2024, do not need to file either application again. If USCIS approves a pending Form I-821 or Form I-765 filed under the previous designation of TPS for Haiti, USCIS will grant the individual TPS through Feb. 3, 2026, and issue an EAD valid through the same date.
The Federal Register Notice explains eligibility criteria, timelines, and procedures necessary for current beneficiaries to re-register and renew EADs, and for new applicants to submit an initial application under the redesignation and apply for an EAD.
This extension and redesignation does not apply for anyone who was not already in the United States on June 3, 2024, and consequences continue to be enforced on those attempting to cross unlawfully or without authorization into the United States. Since the Securing the Border Presidential Proclamation and Interim Final Rule was issued in early June, over 24,000 noncitizens have been removed or returned to more than 20 countries. All irregular migration journeys, especially maritime routes, are extremely dangerous, unforgiving, and often result in loss of life. DHS will continue to enforce U.S. laws and policy throughout the Florida Straits and the Caribbean region, as well as at the southwest border. U.S. policy is to return noncitizens who do not establish a legal basis to remain in the United States.
- Secretary of Homeland Security
- Secretary Alejandro Mayorkas
- Temporary Protected Status
Trending News

Related Practices & Jurisdictions
- Immigration
- Administrative Regulatory
- All Federal

The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) has extended and redesignated Temporary Protected Status (TPS) for Haiti until Feb. 3, 2026.
According to DHS Secretary Alejandro N. Mayorkas, the decision to renew and redesignate is based on the continued violence and insecurity in Haiti and limited access to safety, health care, food, and water in that country. In addition , Haiti is prone to flooding, mudslides, storm damage, and earthquakes that have resulted in ongoing humanitarian challenges.
The redesignation alone will allow approximately 309,000 Haitians who are otherwise eligible to make initial applications for TPS if they have continually resided in the United States on or before June 3, 2024. Initial TPS applications must be submitted from July 1, 2024, through Feb. 3, 2026.
Applications for TPS extensions and employment authorization document (EAD) renewals should be made during the 60-day re-registration period beginning on July 1, 2024, until Aug. 30, 2024. Individuals who have pending extensions and pending EAD renewals need not reapply. When their cases are adjudicated, the new documents will have Feb. 3, 2026, expiration dates. Applicants with the following EAD expiration dates will be eligible for automatic extensions of their EADs through Aug. 3, 2025, while they wait for their new EADs be approved:
2024: Aug. 3, June 30
2023: Feb. 3
2022: Dec. 31, Oct. 4, Jan. 4
2021: Oct. 4, Jan. 4
2020: Jan. 2
2019: July 22
2018: Jan. 22
2017: July 22
It is expected that special student relief for F-1 students from Haiti who are suffering severe economic hardship will also be extended.
Please see the official instructions that will be published in the Federal Register on July 1, 2024, for specific information.
Current Public Notices
Post Your Public Notice Today!
Current Legal Analysis
More from jackson lewis p.c., upcoming legal education events.

Sign Up for e-NewsBulletins
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Biden administration extends protected status for up to 309,000 migrants from Haiti

Sergio Martínez-Beltrán

Migrants eat a meal at the La Colaborativa day shelter in Chelsea, Massachusetts, on February 22, 2024. The shelter opened on February 20, and helps migrants, mainly from Haiti, build resumes, get work, receive health care. Joseph Prezioso/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
The Biden administration, on Friday, announced an 18 months extension —and redesignation- to temporary protected status for up to 309,000 unauthorized migrants from Haiti living in the country.
A temporary protected status, also known as TPS, is not a permanent legal status but protects against deportation, allows migrants to get a work permit, and sometimes travel authorization.
The TPS will apply for Haitians already under temporary protected status. And the redesignation will allow Haitians who have been in the U.S. since the beginning of the month to apply for an initial TPS.
The extension period starts on Aug. 4 and runs until Feb. 3, 2026. The Federal Register notice published Friday provides information about registering for the TPS.
In a statement, Homeland Security Secretary Alejandro Mayorkas said this extension is needed “due to extraordinary and temporary conditions in Haiti.”
“We are providing this humanitarian relief to Haitians already present in the United States given the conditions that existed in their home country as of June 3, 2024,” said secretary Mayorkas.
The TPS extension published today cites Haiti’s “simultaneous economic, security, political, and health crises,” as some of the reasons why the Biden Administration moved to extend this program.
NPR has reported that gangs have seized control of the streets , resulting in high levels of crime and violence.
The TPS proclamation also cites the effects of environmental disasters on the economy and political instability as reasons why people leave that country.
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
Haiti faces record displacement amid escalating gang violence

Facebook Twitter Print Email
Escalating gang violence and political instability in Haiti have forced a record 578,074 people from their homes this year, making it the country with the largest number of displacements due to crime-related violence, UN independent human rights experts said on Thursday.
“Violence, particularly in the capital Port-au-Prince, has reached alarming levels, with armed groups controlling large areas and complicating humanitarian access,” the experts, including the Special Rapporteur on the rights of internally displaced persons , said .
The clashes between gangs and the Haitian National Police have created a “pervasive environment of fear, restricting freedom of movement and access to basic services”, they added.
In the first quarter of 2024 alone, gang-related violence reportedly claimed the lives of or injured 2,500 Haitians, including 82 children.
Women and children have been the worst affected, amid heightened risk of sexual violence and exploitation.
Mass displacement
Many internally displaced persons (IDPs) are living in “overcrowded and inadequate conditions without basic hygiene and sanitation, facing severe shortages of food, water, shelter, and medical care, including a lack of safe and private spaces for psychological support,” the independent experts said.
According to the UN International Organization for Migration ( IOM ), nationally, 80 per cent of IDPs are living with host families while the remaining are sheltering in sites, many in gang-controlled or high-risk areas.
Nearly half of the country’s population is suffering from severe hunger, with 18 per cent at “emergency” level of food insecurity.
Impact on children and women
Children and women have been disproportionately impacted by the effects of the violence and instability in Haiti, with more than 310,000 women and girls, and 180,000 children among the displaced.
More than half a million children are living in neighbourhoods controlled by armed groups, at heightened risk of violence and child recruitment.
Furthermore, the growing number of unaccompanied displaced children makes them particularly vulnerable to exploitation, abuse and trafficking by gangs.
The violence and attacks on educational facilities have also forced the closure of nearly 900 schools, affecting almost 200,000 children, disrupting learning and putting children at increased risk.
Sexual violence against women and girls at IDP sites is also surging as gangs continue to use rape as a weapon of terror, the Human Rights Council -appointed independent experts said.
Call to action
Amidst the alarming situation, the experts called for greater female leadership and participation to ensure a successful political transition in Haiti.
They also urged greater efforts to address root causes of displacement to build sustainable solutions for the future.
“Durable solutions for IDPs, such as safe return, resettlement, or local integration, require addressing the root causes of displacement, including violence, political instability, and environmental degradation,” they said.
Independent experts
Appointed by the Geneva-based Human Rights Council and forming a part of its Special Procedures , Special Rapporteurs are mandated to monitor and assess the rights situation in certain thematic or country situations.
They work in their personal capacity, independent of the United Nations and national governments.
They are not UN staff and do not receive a salary.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Haiti - Level 4: Do Not Travel. O D K E N H U T C. Last Update: Updated to reflect the Ordered Departure of non-emergency U.S. government personnel and eligible family members for Embassy Port-au-Prince. Do not travel to Haiti due to kidnapping, crime, civil unrest, and poor health care infrastructure. On July 27, 2023, the Department of State ...
Haiti- Level 4: Do Not Travel. Updated to reflect the Ordered Departure of non-emergency U.S. government personnel and eligible family members for Embassy Port-au-Prince. Do not travel to Haiti due to kidnapping, crime, civil unrest, and poor health care infrastructure.
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories. Follow us on ...
Events: The U.S. State Department's Travel Advisory for Haiti remains at Level Four: Do not travel to Haiti. The current security situation in Haiti is unpredictable and dangerous. We are aware that there are few or no commercial options to depart Haiti safely at this time. As they become available, we urge U.S. citizens to take advantage of ...
While neither the warnings nor violence are entirely new - Haiti has been a Level 4: Do Not Travel destination in State Department travel advisories since before the 2021 assassination of ...
Travel Advisory. Do not travel to Haiti due to crime and civil unrest. There are currently widespread, violent, and unpredictable demonstrations in Port-au-Prince and elsewhere in Haiti. Due to these demonstrations, on February 14, 2019, the Department of State ordered the departure of all non-emergency U.S. personnel and their family members.
U.S. DEPARTMENT of STATE — BUREAU of CONSULAR AFFAIRS. Travel.State.Gov > Travel Advisories > Haiti Travel Advisory . Congressional Liaison; Special Issuance Agency; Legal Resources
Haiti - Avoid all travel. Avoid all travel to Haiti due to the threat posed by kidnappings, gang violence and the potential for civil unrest throughout the country. The security situation remains volatile in Haiti. You should consider leaving the country by commercial means if you can do so safely. Back to top.
Haiti - Level 4: Do Not Travel. KUC. Last Update: Updated to reflect changes to U.S. Embassy Port au Prince operational status. Do not travel to Haiti due to kidnapping, crime, and civil unrest. U.S. citizens should depart Haiti now in light of the current security and health situation and infrastructure challenges. U.S. citizens wishing to depart Port-au-Prince should monitor local news and ...
Travel Advisory for Haiti. Every international travel advisory echoes the same stark warning for Haiti—Do Not Travel. The United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand travel advisories all place Haiti in the highest risk category—Level Four—and strongly discourage travelers from visiting due to:
The last time the State Department issued a Level 4 Travel warning for Haiti was on Feb. 7, 2019 when civil unrest broke out and forced diplomats and Haitians to stay at home. At the time, the ...
FCDO travel advice for Haiti. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
Current travel advisories: The US consulate currently has a Level 3 travel advisory for Haiti (issued 11 June 2019), and recommends that travellers stay safe by changing currency in advance (so you can avoid banks and ATMs), avoiding demonstrations, not attempting to go through roadblocks, and booking official, professional transport from the ...
The country has been under a Level 4 "do not travel" travel advisory for a while now, but due to recent events, the US Embassy in Haiti is currently reiterating that it is strongly urging citizens ...
For travel to the United States on a temporary basis, including tourism, temporary employment, study and exchange. ... Security Alert: U.S. Embassy Port-au-Prince, Haiti (March 18, 2024) Message for U.S. Citizens: Upcoming Elections for Federal Office (November 8, 2023) ... Level 4: Last Update: Updated to reflect the Ordered Departure of non ...
U.S. Department of State Warns Against Travel to Haiti The dream vacation to Haiti might have to wait. The U.S. State Department issued a Level 4: Do Not Travel advisory for the Caribbean nation ...
If your travel plans in Haiti include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip. Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe. Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid ...
Haiti has been on a Level 4 Travel Advisory — the highest, which is designated "Do not travel" — since July 2023, with the State Department writing in its advisory: "Do not travel to Haiti due ...
Haiti - Level 4: Do Not Travel. KHUC. Global Health Advisory: Do Not Travel. Avoid all international travel due to the global impact of COVID-19. Do not travel to Haiti due to crime, civil unrest, and kidnapping. Country Summary: Violent crime, such as armed robbery and carjacking, is common. Kidnapping is widespread.
While Haiti has been under level four since July 2023 amid the rise of political gang violence, recent developments in the country have caused the government to reiterate its warning to travelers.
A US Department of State's Level 4 travel advisory ("do not travel," the highest warning level) for the Caribbean nation of Haiti was most recently updated on July 27, 2023, citing ...
WASHINGTON—Secretary of Homeland Security Alejandro N. Mayorkas today announced the extension and redesignation of Haiti for Temporary Protected Status for 18 months, from Aug. 4, 2024, to Feb. 3, 2026, due to extraordinary and temporary conditions in Haiti.The corresponding Federal Register Notice provides information about registering for TPS as a new or current beneficiary under Haiti's ...
The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) has extended and redesignated Temporary Protected Status (TPS) for Haiti until Feb. 3, 2026.
GENEVA (20 June 2024) - UN experts said today Haiti's escalating gang violence and political instability have forced a record 578,074 internal displacements in 2024 including over 310,000 women and girls and 180,000 children, more than double the figure from 2022, making it the country with the largest number of displacements globally due to crime-related violence.
For Immigrant or nonimmigrant visa cases, please contact the call center at 509-2819-2929 or by email at [email protected]. Call 1-888-407-4747 toll-free in the United States and Canada or 1-202-501-4444 from other countries from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m. Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
The Biden administration, on Friday, announced an 18 months extension —and redesignation- to temporary protected status for up to 309,000 unauthorized migrants from Haiti living in the country.
This replaces the previous Travel Advisory issued on July 17, 2018. The full text of the new Travel Advisory is as follows: Haiti - Level 3: Reconsider Travel. Reconsider travel to Haiti due to crime and civil unrest. Violent crime, such as armed robbery, is common. Protests, tire burning, and road blockages are frequent and often spontaneous.
Nearly half of the country's population is suffering from severe hunger, with 18 per cent at "emergency" level of food insecurity. ... Children and women have been disproportionately impacted by the effects of the violence and instability in Haiti, with more than 310,000 women and girls, and 180,000 children among the displaced. ...