An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.


COVID-19 international travel advisories
Visitors to the U.S. do not need to be tested or vaccinated for COVID-19. U.S. citizens going abroad, check Department of State travel advisories for the country you will visit.
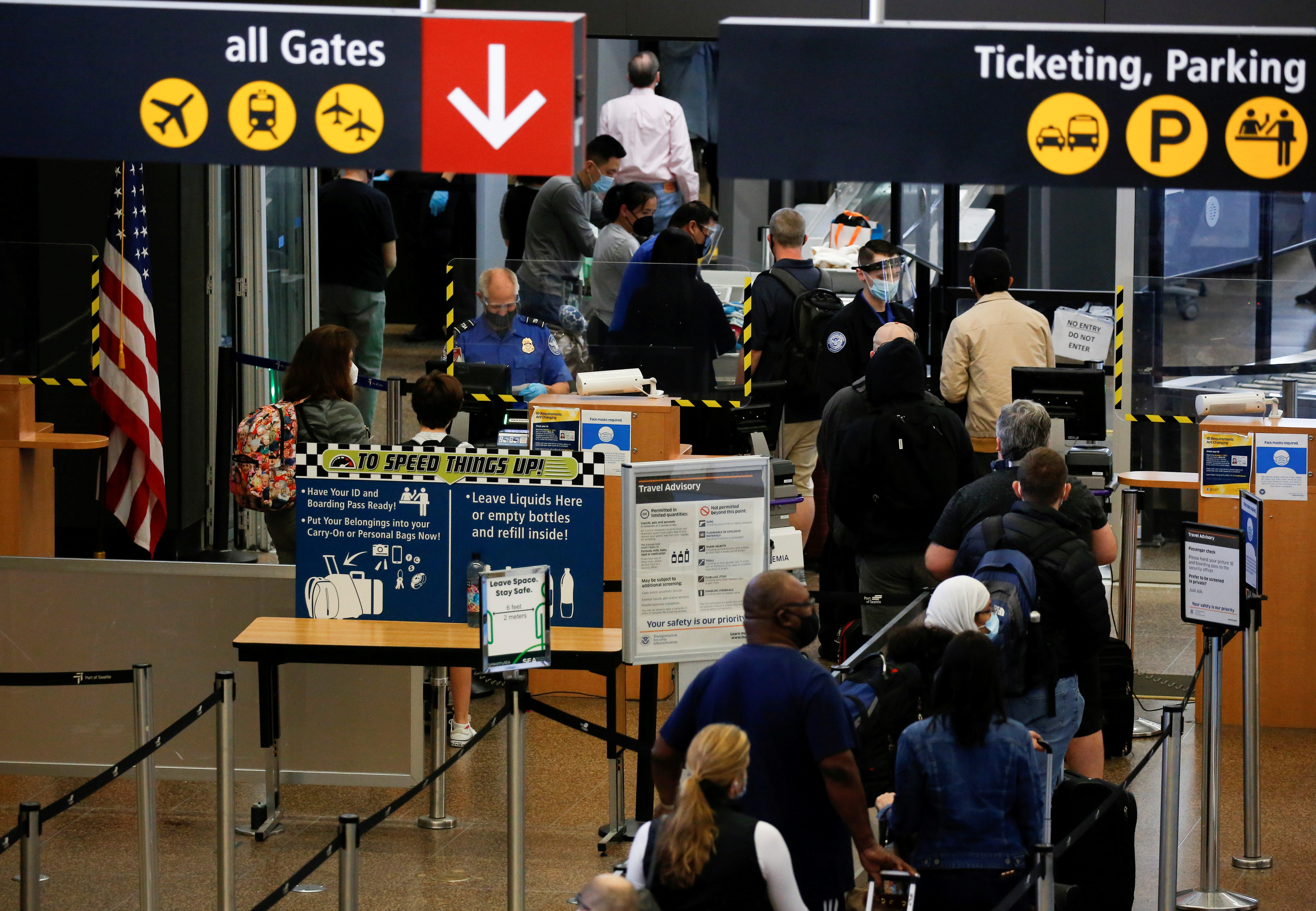
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S.
You do not need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19 or take a COVID-19 test to enter the U.S. This applies to U.S. citizens and non-citizens.
U.S. citizens traveling to a country outside the U.S.
Find country-specific travel advisories, including COVID-19 restrictions, from the Department of State.
See the CDC's COVID-19 guidance for safer international travel to learn:
- If you can travel if you recently had COVID-19
- What you can do to help prevent COVID-19
LAST UPDATED: May 31, 2024
Have a question?
Ask a real person any government-related question for free. They will get you the answer or let you know where to find it.
U.S. to lift restrictions Nov 8 for vaccinated foreign travelers
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by David Shepardson; additional reporting by Tyler Clifford; Editing by Jonathan Oatis;
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

World Chevron

No progress in Gaza ceasefire talks with Israel, says Hamas official
A senior official of the militant Islamist group Hamas, Osama Hamdan, said on Saturday there has been no progress in ceasefire talks with Israel over the Gaza war.
Map: Coronavirus travel restrictions by state
Guidance on traveling and travel restrictions varies across the United States as the country faces new surges in Covid-19 cases .
The patchwork of restrictions between regions highlights the ability of states to take different approaches while dealing with the coronavirus pandemic.
While all of the Northeast and most of the mid-Atlantic states have implemented statewide travel restrictions, more than half the states, including two of the biggest, Texas and Florida, have no such restrictions.
States hit the hardest when the epidemic began in the United States last spring, such as New York, New Jersey and Connecticut, have some of the most stringent travel restrictions.
Instead of opting for statewide restrictions, some local officials have imposed restrictions on travel to the most populous cities.
Check the interactive map below to see the latest guidance on travel and possible travel restrictions. This map will be updated weekly.
See NBC News’ coverage of the coronavirus , and see a map of coronavirus cases around the world or charts showing the day-by-day number of infections in the U.S. and worldwide .
CORRECTION (Dec. 18, 2020, 5:30 p.m.): A previous version of this map used the wrong colors for states with recommended travel restrictions and those with city-level travel restrictions. The colors were flipped: Recommendations should be orange (not yellow), and city-level restrictions should be yellow (not orange). The map has been fixed.
Matt Marshall is an associate producer for NBC News Now's "Top Story with Tom Llamas."
Kanwal Syed is a researcher for the Plan Your Vaccine interactive tool on NBCNews.com.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
I’m a U.S. Citizen. Where in the World Can I Go?
For Americans eager to resume international travel, here are the countries that currently allow U.S. citizens to enter, though there may be restrictions, including vaccine requirements.

By Paige McClanahan
This list is no longer being updated. Find the latest coronavirus updates here .
Most of the world’s countries are open to travelers from the United States, and many nations are easing their requirements for visitors to test or quarantine. Some countries that had fully closed to foreign tourists — including Israel, Morocco, Bhutan, Australia and New Zealand — have now reopened to U.S. visitors, although they may continue to impose testing, vaccination or quarantine requirements.
In Europe, a growing number of nations — including Germany, Greece, Italy, Ireland, Switzerland and the United Kingdom, among many others — have eliminated their Covid-related travel restrictions for the summer travel season. Meanwhile, several Southeast Asian nations that had closed their borders to tourists have now reopened. Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar and Cambodia are once again welcoming American visitors, although vaccine or testing requirements are in force in most cases.
For its part, the United States has lifted the requirement that inbound passengers, including returning Americans, provide a negative test result taken within one day of departure. The decision to lift the test requirement will be re-evaluated in September; the rule could be reinstated if authorities deem it necessary.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, meanwhile, continues advising Americans not to travel internationally until they are fully inoculated against Covid-19.
Those wanting to learn about the coronavirus risk in a specific country can visit the C.D.C. website where a four-tier ranking system provides guidance. The agency reserves the highest “Level 4” ranking for countries with “special circumstances” that include spiking case numbers, the emergence of worrying variants, or threats to the viability of health care infrastructure. (Levels 1 to 3 are still based primarily on Covid-19 case counts.) At the moment, no countries are classified at Level 4; those at Level 3, which have a “high” incidence of Covid-19, are indicated in the list below. For information on entry requirements like testing and quarantine, as well as curfews and movement restrictions, the State Department’s website offers detailed information by country.
What follows is a list of countries that are open to tourists from the United States. Many require visitors to complete a health form, provide proof of vaccination, and present a recent negative Covid-19 test result. To qualify as fully vaccinated in places such as France, Spain and the Netherlands, a visitor must have received either a booster shot or a second dose within a specified period.
As of May 1, visitors are no longer required to provide a negative test result or proof of vaccination. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Travel to Andorra is over land from Spain or France, so check the entry requirements for those countries first. There are no limits on movement between Spain and Andorra, nor for travelers entering Andorra from France. Travelers 12 and over departing Andorra for France must provide proof of full vaccination, a certificate of recent recovery, or a negative antigen test result from the previous 24 hours. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Visitors must complete a registration form before travel. They must also present a negative result from an R.T.-P.C.R. test administered no more than 72 hours before departure and pay about $20 on arrival to undergo a rapid antigen test at the airport. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Angola.
All adult visitors must be vaccinated. Arriving passengers must also carry a negative result from a Covid-19 test. The result may be either from a rapid test taken within two days of arrival, or from an R.T.-P.C.R. test, N.A.A.T. test, or other molecular test administered within three days of arrival. Visitors who completed their primary course of vaccination more than six months previously and who have not received a booster are also required to test on arrival, at their own expense. Guests staying for more than eight days may undergo a free test on day 4 of their visit. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
ANTIGUA and BARBUDA
Vaccinated travelers are no longer required to test before travel, provided they are asymptomatic. Unvaccinated visitors must present either a negative result from a P.C.R. test conducted no more than three days before arrival, or a negative result from an antigen test from the previous 24 hours; they must also be without symptoms. On arrival, they must submit to an R.T.-P.C.R. test at their own expense and self-quarantine for 14 days. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Americans may now enter Argentina without testing. Visitors must complete an electronic sworn statement within 48 hours of traveling and provide proof of medical insurance that covers Covid-19 treatment and quarantine. The government recommends that all visitors age 6 and over undergo a Covid-19 test within 24 hours of arrival, regardless of their vaccination status. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
The country has lifted its pandemic-related travel restrictions.
The country is open to visitors from the United States who have finished a primary course of vaccination (two doses of an mRNA vaccine or one dose of Johnson & Johnson). All passengers arriving by air must submit the Digital Passenger Declaration within 72 hours of their departure for Australia; they are no longer required to test before travel. Depending on their final destination within Australia, visitors may have to quarantine on arrival, even if they are vaccinated. Travelers should check the rules of the state or territory they are visiting to find the relevant quarantine requirements. Prospective visitors who are not fully vaccinated must qualify for an exemption . The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
The country lifted all pandemic-related travel restrictions on May 16. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Visitors age 18 and over must present proof of vaccination or a certificate of recovery from Covid-19 infection.
THE BAHAMAS
All travelers age 18 and older must apply for a Bahamas Travel Health Visa; the cost of the visa includes insurance coverage and varies with the length of stay and vaccination status of the traveler. Health visa applications can take up to 24 hours to process; travelers must present their visa confirmation before departure to the Bahamas. Travelers with valid proof of vaccination may now enter without a negative test result. Unvaccinated travelers age 2 and over must present a negative result from a rapid antigen or R.T.-P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of travel. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
According to the U.S. Embassy, visitors must download the “ BeAware Bahrain ” app before travel. Arriving passengers are no longer required to test or show proof of vaccination. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Visitors must complete a health declaration form within three days of arrival. Vaccinated travelers may enter without a pretest. (A booster is not required to qualify.) Unvaccinated travelers age 12 and older must provide a negative result from an R.T.-P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of departure. Symptomatic passengers may be subject to testing on arrival.
Vaccinated travelers may now enter without testing. Before departure, visitors should download the BIMSafe app and complete an online immigration and customs form . Vaccinated visitors may enter without quarantine, although they may be randomly selected for testing on arrival. Unvaccinated travelers age 5 and above must obtain a negative result from an R.T.-P.C.R. test taken within three days of arrival, or from a rapid test taken within one day of entry; they must also undergo a rapid test on arrival. Children under 18 who aren’t vaccinated must follow the guidelines of their accompanying adult. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
U.S. visitors may now enter without testing or proof of vaccination. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Travelers with proof of vaccination may enter without a negative test result. Unvaccinated visitors age 5 and over must show a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of arrival, or from a rapid test taken within 48 hours of arrival. Alternatively, testing is available on arrival at the airport for $50; only cash payments are accepted. All foreign tourists must show proof of having purchased Belize travel insurance ($18 for 21 days). The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
All visitors to Benin must apply online for an eVisa before departure. Predeparture testing is no longer required.
Arriving passengers must show proof of vaccination (booster shots are not required) as well as a negative result from a rapid antigen test taken no more than two days before arrival, or a negative result from a P.C.R., N.A.A.T, T.M.A., or L.A.M.P. test taken within four days of arrival. Children under 2 are exempt from the pretest requirement, while children under 12 are exempt from the vaccination requirement. Visitors must pay $40 to apply for a travel authorization , which they can do up to one month before departure. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Vaccinated travelers must quarantine for five days after arrival; unvaccinated travelers must quarantine for ten days. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Bhutan.
Arriving passengers must present either proof of vaccination or a valid negative result from a Covid-19 test. The test result may be from an R.T.-P.C.R. test taken no more than 72 hours before boarding, or from a rapid antigen test taken no more than 48 hours before boarding. Children under 5 are exempt from the requirements.
BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA
The country lifted its pandemic-related travel restrictions on May 26; travelers may now enter without a negative test result or proof of vaccination.
Visitors must have completed at least a primary course of vaccination; they are not required to test. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
U.S. tourists age 12 and older must present proof of vaccination, even if they have recovered from Covid-19; they no longer need to test before travel. Unvaccinated children under 12 who are traveling with vaccinated adults may also enter without testing. Unvaccinated adults must qualify for an exemption to be allowed entry. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
BRITISH VIRGIN ISLANDS
Regardless of their vaccination status, all visitors over age 5 must present a negative result from a Covid-19 test (either rapid antigen or R.T.-P.C.R.) taken within 48 hours of arrival. Travelers who have recovered from Covid-19 in the previous 90 days may present proof of recovery in lieu of a negative test result. Anyone arriving without a valid test result or proof of recovery must pay $50 to undergo testing on arrival. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
As of May 1, Bulgaria has removed all pandemic-related travel restrictions. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
BURKINA FASO
Arriving passengers must present proof of full vaccination or a negative result from a P.C.R. or rapid test taken in the previous five days. Travelers who arrive without proof of vaccination or a valid negative test result will be required to pay roughly $45 to undergo a rapid antigen test on arrival. To exit the country by air, travelers must present either proof of vaccination or a negative P.C.R. test dated within three days of their departing flight. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Burkina Faso.
Arriving passengers must present a negative result from a P.C.R. test administered no more than 72 hours before boarding their flight to Burundi. According to the U.S. Embassy, travelers must also pay $100 for an on-arrival test and self-isolate at an accommodation of their choice until they receive a negative result, usually within 24 hours. A negative P.C.R. result is also required to exit the country. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Burundi.
Arriving passengers must present either proof of vaccination or a negative Covid-19 test result. The result may be from a P.C.R. test taken no more than 72 hours before departure, or from a rapid antigen test taken no more than 48 hours before departure. Visitors must also register , pay an airport fee, and complete a health questionnaire before travel. Arriving passengers are subject to a temperature check. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Visitors may now enter without testing. Fully vaccinated travelers are not required to quarantine. Those who are unvaccinated must quarantine for seven days at a designated facility at their own expense; they must also undergo a rapid test on the final day before being released. The government encourages all travelers to purchase Covid-19 travel health insurance. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Cambodia.
Visitors from the United States who hold a valid tourist visa may enter Cameroon. Passengers age 5 and above must present a negative result from a P.C.R. test administered no more than 72 hours before arrival; the result must include a QR code.
Vaccinated U.S. citizens and residents may enter Canada for nonessential reasons, including tourism, without providing a negative test result. (A booster is not required to qualify.) All travelers must use the ArriveCAN system to enter their proof of vaccination and other traveler information within 72 hours of entry into Canada. Unvaccinated and partially vaccinated children under 12 are no longer required to test before travel if they are accompanied by a vaccinated adult. Unvaccinated and partially vaccinated minors ages 12 to 17 are subject to testing requirements and a 14-day quarantine. Unvaccinated adults must qualify for an exemption; if approved for entry, they are also subject to testing and quarantine requirements. The current rules are expected to remain in force until at least September 30 . The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
CAYMAN ISLANDS
As of June 30, vaccinated travelers may enter without testing. Unvaccinated visitors age 12 and over will not be allowed entry unless they can prove that they have a close tie to the country. Visitors are encouraged to test themselves daily during their first week in the country. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
THE CENTRAL AFRICAN REPUBLIC
A negative P.C.R. test from the previous 72 hours is required for both entry and departure. According to the U.S. Embassy, tourists from the United States must quarantine for 14 days after arrival; employees of international and humanitarian organizations may end their quarantine early if they receive a negative result from a post-arrival P.C.R. test at the local Pasteur Institute. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Travelers with proof of vaccination may enter without a pretest. Unvaccinated travelers 12 and older must present a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken within 96 hours of arrival.
Arriving passengers must complete a traveler’s affidavit within 48 hours of boarding and provide proof of travel medical insurance that covers a minimum of $30,000 worth of Covid-19 medical expenses in Chile; they may now enter without testing. Visitors are no longer required to obtain a mobility pass (which requires proof of vaccination) to enter the country, but they may be required to present the pass to enter restaurants, participate in group tours, and attend concerts and sports events. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Arriving passengers age 18 and older must present either proof of vaccination or a valid negative result from a Covid-19 test. The result may be from a P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of travel or from an antigen test taken in the 48 hours before travel. Incoming passengers must also complete an online form within 72 hours of boarding their flight.
Visitors may enter with a negative result from a P.C.R. test conducted in the 72 hours before travel. A negative P.C.R. result that is no more than 72 hours old is also required to leave the country. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Comoros.
The country has lifted its pandemic-related entry requirements. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
COTE D’IVOIRE
Fully vaccinated travelers may now enter without a negative test result. (A booster is required to qualify if the primary course of vaccination was completed more than nine months previously.) Unvaccinated travelers must carry a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of arrival in Abidjan. All passengers will have their temperatures checked and must undergo rapid antigen testing on arrival. Departing passengers who are unvaccinated must present a negative P.C.R. test from no more than 72 hours before travel, regardless of the testing requirements of their destination. Land and maritime borders remain closed to U.S. citizens.
Croatia has removed its Covid-related border rules; U.S. visitors may now enter as before the pandemic. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
General tourism is not permitted, but Americans are allowed to visit to see family and under certain professional and humanitarian circumstances. All incoming passengers must complete an online sworn statement before they depart for Cuba. Visitors are no longer required to present proof of vaccination or a negative Covid-19 test result. Health authorities will randomly select passengers for Covid-19 screening on arrival.
As of June 1, visitors are no longer required to present proof of vaccination or a negative Covid-19 test result. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
CZECH REPUBLIC
The country has removed all pandemic-related travel restrictions. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF CONGO
Before traveling, visitors should register at INRBCOVID.com . All travelers age 11 and older must present a negative result from a Covid-19 test taken within three days of departure. Unvaccinated travelers must undergo another test on arrival at their own expense and self-quarantine until they receive a negative result, generally within 24 hours. Visitors should also have proof of health and medical evacuation insurance and a certificate of yellow fever vaccination. To exit the country, travelers age 11 and over must present a negative result from a Covid-19 test taken at a government-approved lab within three days of departure. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to the D.R.C.
Denmark has lifted all pandemic-related travel restrictions. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Potential visitors must apply online for an eVisa before travel. All arriving passengers 11 and older must provide proof of vaccination as well as a negative result from a Covid-19 test taken within 72 hours of boarding their flight, and not more than 120 hours before their arrival in the country. Upon landing, travelers are given another test at a cost of $30. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Djibouti.
As of April 4, arriving passengers are no longer required to complete a health questionnaire before entry. Vaccinated travelers may enter without a pretest, though they may be tested on arrival if they display symptoms. Unvaccinated travelers must present a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of arrival or from an antigen test taken within 48 hours of arrival. Children aged 12 and under assume the status of their accompanying parent or guardian. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
Visitors may now enter without testing or providing proof of vaccination. Passengers age 7 and over may be selected for random testing on arrival; those who can present a valid vaccination certificate will be exempt from the random test. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
DUTCH CARIBBEAN
Aruba allows visitors to enter without a negative test result or proof of vaccination. Arriving passengers are required to purchase Aruba Visitors Insurance and to complete an Embarkation/Disembarkation card before arrival. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Bonaire has lifted its pandemic-related travel restrictions. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Curaçao has lifted its pandemic-related travel restrictions. However, visitors must complete a digital immigration card before travel. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Saba has removed its pandemic-related travel restrictions.
Sint Eustatius has removed its pandemic-related travel restrictions.
Sint Maarten , which is Dutch, and French St. Martin are primarily entered through Princess Juliana Airport on the Dutch side. Visitors must register online at least 12 hours before travel. Vaccinated travelers, those who have proof of recovery from Covid-19 in the previous nine months, and children under 5 are not required to test before entry. Unvaccinated travelers 5 and over must present a negative P.C.R. result from the previous 48 hours or a negative antigen result from the previous 24 hours. Before travel, all visitors must submit a health authorization form , the completion of which includes the purchase of mandatory Covid-19 insurance. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
The country no longer requires a negative test result for entry; however, the U.S. Embassy notes that airlines may impose their own requirements. Passengers who display symptoms on arrival may be subject to testing. The Embassy advises potential visitors to confirm the latest entry rules with the Timorese Embassy in Washington before travel.
All arriving passengers age 3 and over must provide either proof of vaccination or a negative result from an R.T.-P.C.R. test taken no more than 72 hours before boarding their flight to Ecuador. They must also complete a declaration of traveler health . Visitors may be subject to random antigen testing on arrival. Those traveling to the Galápagos must provide proof of vaccination or a negative R.T.-P.C.R. test result from the previous 72 hours; they must also obtain a transit control card from the government of Ecuador. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
EL SALVADOR
Visitors may now enter without testing or proof of vaccination.
EQUATORIAL GUINEA
All arriving passengers must present a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken within 48 hours of travel; travelers age 18 and over must also present proof of vaccination. Visitors must quarantine for three days after arrival at an accommodation of their choosing and obtain a negative test result before being released. A negative P.C.R. test result is also required to exit the country.
Visitors must present a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of entry and submit to an antigen test on arrival. Unvaccinated travelers must quarantine for five days, then obtain a negative test result before exiting quarantine. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Eritrea.
Arriving passengers must complete an online form in the 72 hours before entering the country. Visitors from the United States who are vaccinated or who have recovered from Covid-19 in the previous 180 days may enter without testing. (Travelers who have received two doses of vaccine are considered fully vaccinated for nine months after completing their primary course of vaccination; a booster dose extends the period of validity for one year.) Unvaccinated and unrecovered visitors may enter with a negative result from an R.T.-P.C.R. or antigen test taken in the 48 hours before arrival. Children under 12 are exempt from the requirements. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Vaccinated visitors and those who have a certificate of Covid-19 recovery from the previous 90 days are no longer required to test before travel. (A booster is not required to qualify.) Unvaccinated visitors over age 12 must carry a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of departure, or a negative result from an antigen test taken within 24 hours of arrival.
All visitors must provide proof of vaccination, proof of travel insurance, and confirmation that they have pre-booked a rapid test to be taken after arrival. (Children under 12 are exempt from the in-country test requirement; children under 16 are exempt from the vaccination requirement.)
The country lifted its pandemic-related travel restrictions on June 30. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Fully vaccinated visitors no longer need to test before arrival. (To qualify as fully vaccinated, arriving passengers must have received their second dose of vaccine within the past nine months; those who have also received a booster dose are not subject to a time limit.) Unvaccinated travelers from the U.S. must present a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of departure or a negative result from an antigen test from the previous 48 hours. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
FRENCH POLYNESIA
The country is open to fully vaccinated tourists from the United States. Those who have received only two doses of vaccine qualify as “fully vaccinated” for nine months following the date of their second dose; those who have also received a booster face no time limit. Arriving passengers aged 12 or older who are flying to French Polynesia directly from the United States are required to present a negative result from an R.T.-P.C.R. taken within 72 hours of boarding or a negative result from an antigen test administered within 48 hours of boarding. Those who are unvaccinated must provide a compelling reason for their visit to French Polynesia. If permitted entry, unvaccinated travelers must test before travel and quarantine for seven days after arrival. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to French Polynesia.
FRENCH WEST INDIES
(Most islands consider two weeks after the second injection as full vaccination, and four weeks for Johnson & Johnson.)
St. Barts is open to fully vaccinated travelers without a test requirement. Unvaccinated visitors must present a negative result either from a P.C.R. test conducted no more than 72 hours before departure, or from an antigen test from the previous 48 hours. All visitors must present a sworn statement that they have no symptoms and that they are not aware of Covid-19 exposure in the previous 14 days. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
St. Martin : See Sint Maarten under Dutch Caribbean.
Guadeloupe and Martinique are open to vaccinated travelers, but those 12 and older who are coming from the United States need a negative result from a P.C.R. or antigen test taken in the 24 hours before departure. They may also be subject to testing on arrival. Unvaccinated visitors must show proof of a compelling reason to travel. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
The country has lifted its pandemic-related restrictions. Visitors may now enter without a negative test result.
Fully vaccinated travelers do not need a pretest, but they may be subject to rapid testing on arrival if they display symptoms. Unvaccinated travelers must present a negative result from a P.C.R. test administered no more than 72 hours before departure.
The country has lifted its pandemic-related travel restrictions. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
The country has suspended its pandemic-related travel restrictions until the end of August. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Non-citizen and non-resident visitors who are 18 or older must show proof of vaccination in order to qualify for an entry visa (a booster is not required). Arriving passengers no longer need to provide a negative test result. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Ghana.
As of May 1, visitors may enter without providing proof of vaccination or recovery or a negative Covid-19 test result. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
The country has removed its pandemic-related travel requirements. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Greenland.
Travelers must present either proof of vaccination (a booster is not required) or a negative result from a P.C.R. or antigen test conducted no more than three days before check-in at the airport or arrival at a land border. Children under 10 are exempt.
The government of Guinea no longer requires pre-departure testing, but the U.S. Embassy recommends that travelers confirm the latest rules with their airline before departure. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; if you are unvaccinated, the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Guinea.
GUINEA-BISSAU
Visitors may enter with a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken in the previous 48 hours. Travelers must also obtain a negative P.C.R. result within 72 hours of their departure from the country; tests can be obtained in the capital city of Bissau for about $45.
Arriving passengers must show proof of full vaccination and carry a negative result from a Covid-19 test administered within 72 hours of arrival. Anyone arriving with an expired test result must pay about $85 to undergo testing at the airport and quarantine until they receive a negative result. Unvaccinated travelers over the age of 12 will not be allowed entry. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Visitors to Haiti must present a negative result from either a P.C.R. or antigen test administered no more than 72 hours before travel. Passengers who have had Covid-19 may present their positive test as well as documentation from their doctor confirming recovery.
Fully vaccinated tourists are not required to pretest, but others must have a negative result from a Covid-19 test taken in the previous 72 hours. Visitors must also complete an online pre-check form before travel.
Hungary has lifted all pandemic-related travel restrictions. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
The country lifted all Covid-related border restrictions on Feb. 25. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Passengers arriving from the United States must submit either proof of vaccination (with or without a booster) or a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of departure. Travelers should upload the relevant documentation to the Air Suvidha portal before departure. Two percent of arriving passengers are randomly selected to undergo testing on arrival. Children under 5 are exempt from testing unless they develop Covid-19 symptoms. All travelers are asked to monitor their health for 14 days after arrival and self-isolate if they develop Covid-19 symptoms.
U.S. travelers are eligible for a visa on arrival if they can show proof of vaccination (with or without a booster; children under 12 are exempt). They must also download the PeduliLindungi app before departure; submit to a temperature screening on arrival; provide proof of health insurance that covers at least $25,000 worth of medical treatment in Indonesia; pay a visa fee of approximately $35; carry a passport with a validity of at least six months; and be able to present either a return ticket or a ticket for onward travel to another country. Covid-19 testing is no longer required. The U.S. Embassy recommends that travelers consult the Indonesian Embassy in the United States for the latest entry rules.
Visitors must apply for a tourist visa , which can be done online. Arriving passengers must present proof of vaccination as well as a negative result from a P.C.R. test conducted within 72 hours of arrival.
Arriving passengers must present either proof of vaccination or a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken in the previous 72 hours. The U.S. Embassy advises that all arriving passengers should be prepared to pay in cash for on-arrival testing at the airport, although this requirement is unevenly enforced. Visitors to the Iraqi Kurdistan Region require a negative P.C.R. result from the previous 48 hours; anyone without a negative test result must test on arrival. Visitors must also pledge to self-isolate for 14 days.
Ireland has removed all pandemic-related travel restrictions. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Visitors must provide a completed incoming passenger form and show proof of insurance covering Covid-19 treatment. Testing is no longer required. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Italy lifted its pandemic-related travel restrictions on June 1. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Jamaica has removed all pandemic-related travel restrictions. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Japan has reopened to U.S. visitors who are pre-booked on package tours. After applying for their visa, visitors must obtain a negative result from a Covid-19 test taken within 72 hours of departure; install the MySOS app and complete the app’s questionnaire; register their information on Visit Japan Web , which will generate a required QR code; and purchase health insurance to cover Covid-19 treatment in Japan. Visitors are required to wear masks in the country. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Visitors age 5 and over must complete an online declaration and present the resulting QR code when boarding. Testing is no longer required. According to the U.S. Embassy, non-Jordanians must present proof of health insurance.
According to Air Astana, the country’s biggest airline, passengers arriving in Kazakhstan are no longer required to present a negative test result or proof of vaccination. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Kazakhstan.
Fully vaccinated visitors may enter without a pretest. Unvaccinated travelers age 5 and above must present a negative P.C.R. result from up to 72 hours before departure; they must also pay $30 to undergo rapid testing on arrival. Visitors should upload their proof of vaccination or negative test result to the Global Haven platform before departure. They must also complete a health surveillance form and present the resulting QR code when traveling.
The country has removed its pandemic-related entry requirements.
The country has lifted its pandemic-related travel requirements. U.S. visitors must apply online for an eVisa before departure. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
KYRGYZ REPUBLIC
The country has lifted its pandemic-related travel requirements. However, the U.S. Embassy notes that the rules may change with little or no advance notice and that airline requirements may differ from those of the government.
Visitors with proof of vaccination may enter without restriction; C.D.C. cards are accepted. Unvaccinated travelers age 12 and over must obtain a negative result from a Covid-19 test within 48 hours of their departure for Laos; rapid tests are accepted. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
As of April 1, visitors may enter without proof of vaccination or a negative test result, provided that their point of departure is not on Latvia’s list of “high-risk countries” (at the moment, no countries are on this list). The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Fully vaccinated travelers may enter without a negative test result. (Visitors who completed their primary course of vaccination more than six months previously must have also received a booster dose to qualify as vaccinated.) Unvaccinated travelers age 12 and over must present a negative result from a P.C.R. or antigen test taken with 48 hours of departure. They must also undergo a P.C.R. test on arrival and avoid public places until they receive a negative result, usually within 24 hours.
Travelers must present a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken in the 72 hours before departure. All passengers are screened on arrival; those presenting Covid-19 symptoms may be denied entry. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Travelers age 18 and over must show proof of vaccination and complete a health screening form via the Lib Travel app . In addition, all travelers age 5 and over must present a negative result from a P.C.R. or rapid antigen test taken in the 72 hours before departure.
U.S. citizens may enter with a negative result from a P.C.R. test administered no more than 48 hours before travel. According to the U.S. Embassy, visitors from the United States may be required to quarantine; it recommends that travelers confirm the latest rules with the Libyan Embassy in Washington, D.C. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Libya.
LIECHTENSTEIN
See Switzerland.
As of May 1, U.S. visitors are no longer required to provide proof of vaccination or a negative test result on entry; the requirement to complete an arrival form has also been removed. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
U.S. tourists may enter with proof of vaccination or recovery. Travelers are considered vaccinated for nine months following the completion of their primary course of vaccination; a booster extends the validity of their vaccination certificate indefinitely. Recovery certificates are valid for 180 days. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Arriving passengers must present a negative result from an R.T.-P.C.R. test administered no more than 72 hours before boarding. A second test is required on arrival, at a cost of $20. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Madagascar.
Arriving passengers must present a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of departure; children under the age of 1 are exempt. A negative result from the previous 72 hours is also required to exit Malawi, regardless of the requirements of the destination country.
Fully vaccinated travelers and children age 12 and under may enter without testing. Visitors who were vaccinated outside of Malaysia must upload their proof of vaccination via the MySejahtera app before departure. Unvaccinated adult visitors must obtain a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken within two days of departure; they must also submit to a test within 24 hours of arrival and quarantine for five days. Additional travel restrictions apply for travel to the states of Sabah and Sarawak . The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Arriving passengers no longer need to present a negative test result, but they must complete a Traveler Health Declaration form within 72 hours of departure. They must also carry proof of a booking at a registered tourist accommodation. No quarantine is required for travelers who do not exhibit symptoms. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to the Maldives.
Arriving passengers must present either proof of vaccination or a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken in the previous 72 hours. The same rule applies to those departing the country.
Arriving passengers must present one of the following: proof of vaccination, a certificate of recovery, or a valid negative test result. U.S. travelers should verify their C.D.C. vaccination cards through the VeriFLY app . To qualify as fully vaccinated , travelers aged 18 and over who have undergone only a primary course of vaccination must have received the final dose in the previous 270 days; those who have also received a booster dose are considered vaccinated indefinitely. (Minors are considered vaccinated indefinitely following a primary course of vaccination.) Recovery certificates are valid for 180 days. Negative test results are valid for 24 hours (if from an antigen test) or 72 hours (if from a P.C.R. test). Children under 12 are exempt from the requirements. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Visitors must present proof of vaccination or a negative result from a P.C.R. test conducted within three days of entry. Passengers are subject to a temperature check on arrival. The U.S. Embassy notes that some visitors have reported that their airlines have demanded a negative test result in addition to their proof of vaccination.
Visitors must complete a travel form . Vaccinated travelers do not need to test before departure but must undergo testing on arrival. In addition to the travel form and on-arrival test, unvaccinated travelers age 18 and over must also self-isolate for seven days after arrival in an accommodation of their choice. They must test on day 7 and, if the result is negative, are free to move around the island on day 8. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
U.S. travelers may enter Mexico without testing or quarantine, though they may be subject to health screenings on arrival. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Moldova has lifted all Covid-related entry requirements.
The United States is on the list of “green zone” countries, which means that travelers 16 and over may enter Monaco by presenting one of the following: proof of full vaccination against Covid-19; proof of recovery in the past six months; or a negative result from a P.C.R. or antigen test conducted within the previous 24 hours. To qualify as fully vaccinated, everyone 18 or over must have received a booster dose of an mRNA vaccine no later than nine months following the completion of their first course of vaccination. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
The country has removed its Covid-related entry requirements. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Arriving passengers are no longer required to present proof of vaccination or a negative test result. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Arriving passengers must present a completed health form . They must also provide either proof of vaccination or a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken in the 72 hours before travel. Children under 12 are exempt from the requirements.
Vaccinated visitors as well as children age 11 and younger may now enter without testing. Unvaccinated travelers over the age of 11 must present a negative result from a P.C.R. test administered within 72 hours of their departure for Mozambique; alternatively, they may choose to pay to undergo a rapid test on arrival. The U.S. Embassy encourages U.S. travelers to obtain their visa before departure via the Mozambican Embassy in Washington, D.C. or the Mozambican consulate in New York.
Visitors must carry a valid tourist visa. They must also present either proof of vaccination or a negative result from a P.C.R. test within 72 hours of departure. (Children under 6 are exempt.) In addition, they must carry Covid-19 insurance, complete a health declaration, and pay to undergo rapid testing on arrival.
Passengers who present proof of vaccination may enter without testing. Unvaccinated visitors age 5 and over must provide a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of travel. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Visitors age 5 and over arriving by air must present either proof of vaccination or a negative result from a Covid-19 test (R.T.-P.C.R., N.A.A.T., or Gene Xpert) taken within 72 hours of departure. Travelers who display symptoms may be subject to testing on arrival.
NETHERLANDS
Vaccinated visitors from the United States may now enter without a negative test result. (A booster dose is required if more than 270 days have passed since the traveler completed his or her primary course of vaccination.) Unvaccinated travelers 18 and over are not allowed entry unless they qualify for an exemption . The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
NEW CALEDONIA
U.S. tourists age 12 and over must present one of the following: proof of vaccination, a certificate of recovery from the previous six months; a negative result from an R.T.-P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of boarding; or a negative result from a rapid antigen test taken in the previous 48 hours. At the time of boarding, they must also present a sworn statement in which they commit to undergo testing within two days of arrival. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to New Caledonia. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
NEW ZEALAND
New Zealand is now open to vaccinated visitors from the United States and other “visa waiver” countries. Arriving passengers must complete an online declaration ; provide a negative test result before departure; and self-test on arrival and on day 5 or 6 in the country. Children under 2 are exempt from the pre-departure test requirement; babies under 6 months are exempt from the post-arrival test requirement. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Travelers who can provide proof of vaccination may now enter without testing. Unvaccinated travelers must present a negative result from an R.T.-P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of entry. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Nicaragua.
Travelers must obtain a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken no more than 72 hours before departure and register the result online. A negative test result from the previous 72 hours is also required to exit the country.
Arriving passengers must register online before travel. Fully vaccinated travelers may now enter without testing (a booster is not required to qualify). Unvaccinated travelers must upload a negative result from a P.C.R. test administered within 48 hours of departure; they must also pre-pay for tests on days 2 and 7 and isolate after arrival until they receive a negative result from the second test. Children under 18 are exempt from the requirements. Travelers leaving Nigeria must present either proof of vaccination or a negative result from a P.C.R. test conducted within 48 hours of departure.
NORTH MACEDONIA
Visitors are no longer required to provide a negative test result or proof of vaccination. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Norway has lifted all pandemic-related travel restrictions. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Vaccinated travelers may enter without a pretest. Unvaccinated travelers over the age of 12 must present a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of boarding. All passengers should download the Pass Track App before travel and should be aware that they may be subject to rapid testing on arrival.
Palau is open to fully vaccinated visitors. Arriving passengers must provide a negative result from a P.C.R., N.A.A.T., R.T.-P.C.R. or other approved molecular test taken within three days of their departure. Alternatively, they may present a negative result from an antigen test taken no more than one day before departure, or documentation of recovery from Covid, including proof of a recent positive viral test and a letter from a health care provider or a public health official clearing the person to travel. All travelers will also undergo testing after arrival in Palau.
Travelers are required to submit a completed health affidavit to their airline before boarding. Vaccinated travelers can enter Panama without a pretest (a booster is not required to qualify). Unvaccinated travelers must present a negative result from a P.C.R. or antigen test. If the test result is more than 72 hours old at the time of the traveler’s arrival in Panama, a rapid Covid-19 test will be performed at the airport, at a cost of $50. Accompanied children under 17 are exempt from the requirements. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
PAPUA NEW GUINEA
U.S. visitors must apply for a tourist visa before travel. Visitors age 18 and over must show proof of vaccination; testing is no longer required. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Foreign visitors with proof of vaccination are no longer required to test before travel. Unvaccinated travelers must present a negative result from an R.T.-P.C.R., L.A.M.P., or N.A.A.T. test taken no more than 72 hours before departure; children under 12 are exempt.
Visitors must present either proof of full vaccination or a negative result from a molecular test taken within 48 hours of departure; they must also complete an affidavit of health . Children under 12 are exempt from the testing and vaccination requirements but must be without Covid-19 symptoms at the time of boarding.
PHILIPPINES
Visitors from the United States are allowed entry provided they carry the following documents: proof of vaccination; passports that are valid for at least six months beyond their date of arrival; and a ticket for outbound travel within 30 days of arrival. Visitors must also complete a health declaration card ; they are no longer required to test before entry. Unvaccinated visitors over age 12 will not be allowed entry.
Visitors may now enter without testing, quarantine or proof of vaccination.
Arriving passengers age 12 and over must present a negative result from an R.T.-P.C.R. or N.A.A.T. test conducted no more than 72 hours before boarding, or from a rapid test from the previous 24 hours. Travelers who carry an E.U. Digital Covid Certificate or proof of vaccination issued in one of several approved countries may enter without a negative pretest. The United States is not among the approved countries; however, some travelers have reported that their airlines have told them that their C.D.C. vaccination cards will be accepted in lieu of a negative test result. There is no official guidance on this point, so the U.S. Embassy “ strongly recommends ” that travelers carrying C.D.C. vaccination cards arrive with a valid negative test result. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Visitors must register online before travel. Fully vaccinated and recovered travelers from the United States and other countries that do not appear on Qatar’s red list may enter with a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken within 48 hours of departure. In addition to the pretest, unvaccinated travelers from the United States must also quarantine for five days after arrival and undergo a P.C.R. test on arrival and a rapid test on day 5. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
REPUBLIC OF CONGO
Those planning to travel to the Republic of Congo must complete an online form , pre-pay roughly $68 for a Covid-19 test to be administered on arrival, and print the receipt for that payment to carry with them while traveling. Anyone who tests positive on arrival must isolate until they receive a negative result. Departing travelers must present a negative result from a virus test conducted no more than 72 hours before their scheduled departure.
Romania has lifted all pandemic-related travel restrictions.
Before traveling to Rwanda, visitors must complete a passenger locator form and obtain a negative result from an antigen test conducted no more than 72 hours before their flight departure. Visitors must also pay $5 to undergo an additional rapid test on arrival. Travelers leaving Rwanda must obtain a negative Covid-19 test result within 72 hours of their departing flight. Children under 5 are exempt from testing. Tourists to the national parks may face additional requirements.
ST. KITTS AND NEVIS
All visitors 18 and over must be fully vaccinated, while unvaccinated minors may enter with their accompanying vaccinated adults and follow the same regulations. In addition to their proof of vaccination, arriving passengers must present either a negative result from an R.T.-P.C.R. or N.A.A.T. test taken within three days of arrival, or a negative result from a rapid antigen test taken within one day of arrival. Each visitor must also complete an embarkation form no later than 24 hours before departure. Travelers who have recovered from Covid-19 are not exempt from the pretest requirement. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Visitors must complete a health screening form before departure. As of April 2, fully vaccinated travelers are no longer required to test before travel. Unvaccinated travelers 5 and over must present a negative result from a P.C.R. test conducted in the five days before arrival. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
ST. VINCENT AND THE GRENADINES
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States no longer need to test before travel; they must complete a health form on landing and may be subject to testing. Unvaccinated travelers must arrive with one of the following: a negative result from a P.C.R. test conducted in the previous 72 hours, or a negative antigen result from the previous 24 hours. They may be subject to testing on arrival; they must quarantine for 5 days and undergo an additional test on day 3 or 4 of quarantine. Minors follow the protocol of their parents or guardians. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
See Italy. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
SÃO TOMÉ AND PRÍNCIPE
The government has lifted all pandemic-related travel restrictions.
SAUDI ARABIA
Visitors must apply for a tourist visa before travel. According to the U.S. Embassy, they must also show proof of insurance that covers illness related to Covid-19.
Arriving passengers must present either proof of vaccination or a negative result from a P.C.R. or R.T.-P.C.R. test taken in the 72 hours before arrival. Children under 2 are exempt.
The country has removed its pandemic-related travel restrictions. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Visitors must apply for travel authorization up to 72 hours before departure. Most applications are processed within 12 hours of submission; expedited processing is available for an additional fee. In applying for authorization, unvaccinated visitors must upload a negative result from an R.T.-P.C.R. test administered no more than 72 hours before departure or a negative result from a rapid antigen test from within 24 hours of departure. Vaccinated travelers do not need to provide a negative test result. (Travelers age 18 and over who completed their primary course of vaccination more than six months previously must also have received a booster dose to qualify as vaccinated.) Visitors must also submit their accommodation bookings as well as proof of travel insurance with full medical coverage valid for the duration of their stay. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
SIERRA LEONE
Visitors must register online before departure. Vaccinated travelers may enter without testing. Unvaccinated travelers do not need a pre-departure test, but they must pay in advance to undergo both a rapid test and a P.C.R. test on arrival. All passengers are subject to a health screening at the airport. To exit the country, all travelers, regardless of their vaccination status, must obtain a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken between 48 and hours before departure. Children under 5 are exempt from the test requirements.
All visitors must complete an arrival card within three days of entry and install the TraceTogether app. Vaccinated travelers as well as unvaccinated children born in or after 2010 may now enter without testing or quarantine. Unvaccinated travelers born in or before 2009 must apply for permission to enter. If approved, they must obtain a negative result from either a P.C.R. test or an antigen test administered within two days of departure. (Unvaccinated travelers who have a positive test result dated between 14 and 90 days before their departure for Singapore may be exempt from the pre-departure test.) Unvaccinated travelers must also quarantine for seven days after arrival. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Slovakia has eliminated all pandemic-related travel restrictions. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Visitors arriving from the United States are no longer required to test or show proof of vaccination. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Visitors must present a negative result from a Covid-19 test conducted within 72 hours of arrival and submit to a health screening on entry. Travelers to Somaliland may avoid a 14-day quarantine by presenting a negative result from a Covid-19 test taken in the previous 96 hours. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
SOUTH AFRICA
South korea.
Visitors should register their information on the Q-Code website before departure. Arriving passengers must present proof of full vaccination (including a booster shot if more than 180 days have passed since the completion of the traveler’s first vaccine series). Travelers must also complete a health questionnaire and travel record declaration. In addition, visitors must provide a negative result from a supervised rapid antigen test taken within 24 hours of departure, or a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken in the previous 48 hours. In addition, all travelers must undergo a P.C.R. test within three days of entry. Travelers who display symptoms on arrival may be subject to testing at the airport. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
SOUTH SUDAN
Both inbound and outbound passengers must present proof of vaccination and a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken in the previous 72 hours. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
U.S. visitors may enter Spain with one of the following: proof of vaccination; a certificate of recovery from the previous 180 days; a negative result from an N.A.A.T. test performed within 72 hours of departure; or a negative result from a rapid antigen test performed within 24 hours of departure. To qualify as vaccinated, visitors who have completed only a primary course of vaccination must have received their final dose within the past nine months; those who have also received a booster dose face no time restriction. Children under 12 are exempt from the requirements. Before departure, all visitors must complete a health control form , which will generate a QR code that must be presented at the time of boarding and upon entry in Spain. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Fully vaccinated visitors as well as children under 12 may enter Sri Lanka without testing. Unvaccinated travelers age 12 and over must present a negative result from P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of departure, or a negative result from a rapid antigen test conducted within 48 hours of departure. All visitors must purchase Covid-19 insurance at a cost of $12 per month.
Visitors age 8 and over arriving from the United States must present either a certificate of vaccination or a negative result from a P.C.R. test administered no more than 96 hours before arrival. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Sudan.
Travelers who are vaccinated or who can document their recovery from Covid-19 in the previous six months are no longer required to test before entry. Unvaccinated visitors age 12 and over must carry a negative result from a P.C.R. test conducted within 48 hours of travel or from an antigen test from the previous 24 hours. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Sweden has lifted all pandemic-related entry restrictions.
SWITZERLAND
As of May 2, U.S. visitors may enter without testing or providing proof of vaccination. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
All travelers age 3 and over must show either proof of vaccination or a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of their arrival in the country. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Tajikistan.
Visitors to Tanzania must complete a health surveillance form within 24 hours of arrival. (Those traveling directly to Zanzibar should complete this form instead.) Travelers who present a vaccination card that includes a QR code may enter without testing. (The U.S. Embassy advises travelers to look here for information on how to obtain a QR code for a C.D.C. vaccination card.) Unvaccinated travelers must present a negative result from an R.T.-P.C.R. or N.A.A.T. test administered within 72 hours of travel; the test result must include a QR code. Children 5 and under are exempt from the test requirement.
Fully vaccinated and recovered international visitors may now enter Thailand without quarantine or testing. Travelers must apply for a Thailand Pass before departure and provide proof of health insurance to cover at least $10,000 in medical expenses. Unvaccinated travelers must provide a negative result from an R.T.-P.C.R. test conducted within 72 hours of departure. They must also apply for a Thailand Pass and provide proof of insurance. Unvaccinated travelers who arrive without a valid negative test result must follow the instructions of the public health officer they meet on arrival. All passengers undergo health screening on arrival, including a temperature check. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
All visitors must complete a travel form and upload a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken no more than three days before their departure for Togo. Visitors must also pay in advance for a second P.C.R. test, to be administered upon their arrival at Lomé Airport; proof of payment for the test must be shown before boarding. Arriving passengers must self-isolate until they receive a negative result from their on-arrival test, usually within 24 hours. Visitors are required to download the Togo Safe app; those who refuse may have to quarantine in a state facility for at least two weeks. Exit testing at the traveler’s expense is required no more than 72 hours before their departing flight.
TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO
As of July 1, visitors will no longer be required to test before entry. They also no longer need to show proof of vaccination or apply for a travel pass. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Arriving passengers must complete an online questionnaire . Travelers who are fully vaccinated do not need to test before travel. Unvaccinated travelers 6 and over must present either a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken no more than 48 hours before departure or a negative result from an antigen test that is no more than 24 hours old. Travelers may be subject to random testing on arrival.
TURKS AND CAICOS
Fully vaccinated visitors may now enter without testing (a booster is not required to qualify). Unvaccinated travelers age 18 and over are not allowed entry. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Fully vaccinated travelers and children age 5 and under may enter without testing. Unvaccinated and partially vaccinated travelers must present a negative result from a P.C.R. test conducted no more than 72 hours before boarding.
UNITED ARAB EMIRATES
Vaccinated visitors to Abu Dhabi are no longer required to test before travel. Unvaccinated travelers age 16 and over must present either a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken in the previous 48 hours, or a Covid-19 recovery certificate dated within 30 days of departure; the certificate must have a QR code. Visitors must be fully vaccinated to enter most public places in Abu Dhabi.
Fully vaccinated visitors to Dubai no longer need to test before travel; their proof of vaccination must include a QR code. Unvaccinated travelers age 12 and over must present a negative result from a P.C.R. test from the previous 48 hours; alternatively, they may present proof of recovery from Covid-19 in the previous month. The U.S. Embassy advises travelers to check with their airlines for the latest information on testing requirements. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
UNITED KINGDOM
The United Kingdom has lifted all pandemic-related travel restrictions. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Visitors must complete a health declaration form before departure and carry proof of travel insurance. Vaccinated travelers and those who have recovered from Covid-19 in the previous 90 days may now enter without testing. Unvaccinated and unrecovered travelers age 6 and over must present a negative result from a P.C.R. or antigen test conducted in the 72 hours before departure; in addition, they must either quarantine for 14 days or undergo a P.C.R. test on day 7. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Travelers may now enter without testing or proof of vaccination; they must complete a health screening form on arrival and may be subject to testing if they display symptoms. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Uzbekistan.
Arriving passengers must present either proof of vaccination or a negative result from an R.T.-P.C.R. test taken within 72 hours of entry. (A booster dose is required to qualify as vaccinated if more than 270 days have passed since the completion of the first vaccine series.) The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is “Level Unknown”; the agency recommends that those who are unvaccinated avoid travel to Venezuela.
Foreign visitors must present proof of travel insurance worth at least $10,000 and download and use the PC-COVID app while in the country. Travelers are not required to test or provide proof of vaccination, but they are asked to monitor their health for 10 days and inform authorities if they develop any Covid-19 symptoms. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
Vaccinated travelers may now enter without testing (a booster is not required to qualify). Unvaccinated travelers must carry a negative result from a P.C.R. test taken in the 72 hours before departure; children under 12 are exempt. All passengers undergo health screening on arrival; symptomatic travelers must isolate for 14 days and may be required to undergo testing.
Vaccinated visitors may now enter without testing. Unvaccinated visitors must present a negative result from a P.C.R. test administered no more than 48 hours before travel.
Heather Murphy, Ceylan Yeginsu, Concepción de León and Karen Schwartz contributed reporting.
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram , Twitter and Facebook . And sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to receive expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation. Dreaming up a future getaway or just armchair traveling? Check out our 52 Places for a Changed World for 2022.
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
A Proclamation on Advancing the Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID- 19 Pandemic
The continued spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a global threat to our health and safety. COVID-19 has resulted in more than 733,000 deaths in the United States and more than 4,932,000 deaths worldwide. New variants of SARS-CoV-2 have also emerged globally, and variants that are more transmissible or cause more severe disease than the original virus strain are identified by the United States Government SARS-CoV-2 Interagency Group as variants of concern. Globally, as of October 20, 2021, 166 countries have reported cases of the B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant, a variant of concern that spreads more easily than previously discovered variants of SARS-CoV-2. The potential emergence of a variant of high consequence — one that significantly reduces the effectiveness of prevention measures or medical countermeasures — is also a primary public health concern.
It is the policy of my Administration to implement science-based public health measures, across all areas of the Federal Government, to prevent further introduction, transmission, and spread of COVID-19 into and throughout the United States, including from international air travelers. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) within the Department of Health and Human Services has determined that the best way to slow the spread of COVID-19, including preventing infection by the Delta variant, is for individuals to get vaccinated. According to the CDC, vaccinated individuals are 5 times less likely to be infected and 10 times less likely to experience hospitalization or death due to COVID-19 than unvaccinated individuals. Other mitigation measures are also critical to slowing the spread of COVID-19. These measures include testing and mask-wearing, which are particularly important strategies to limit the spread of COVID-19 from asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic individuals, as well as self-quarantining and self-isolating. But vaccination is the most important measure for reducing the risk of COVID-19 transmission and for avoiding severe illness, hospitalization, and death.
Substantial efforts are being made to increase vaccination rates across the globe. The availability of COVID-19 vaccines is rising, and over 6 billion doses have been administered globally. As of October 24, 2021, 29 countries have a COVID-19 vaccination rate higher than 70 percent, many countries are making efforts to encourage COVID-19 vaccination for their populations, and some countries are considering or adding proof of vaccination requirements as conditions for entry. Many low-income countries continue to have limited vaccine availability, but the United States is leading a global effort to donate hundreds of millions of vaccine doses where they are needed the most.
In light of these facts and circumstances, I have determined that it is in the interests of the United States to move away from the country-by-country restrictions previously applied during the COVID-19 pandemic and to adopt an air travel policy that relies primarily on vaccination to advance the safe resumption of international air travel to the United States. This proclamation governs the entry into the United States of noncitizen nonimmigrants — that is, noncitizens who are visiting the United States or otherwise being admitted temporarily — traveling to the United States by air. It suspends the entry of unvaccinated noncitizen nonimmigrants, except in limited circumstances, and it ensures that the entry of unvaccinated noncitizen nonimmigrants is consistent with applicable health and safety determinations made by the Director of the CDC, including a requirement that, where appropriate, such individuals agree and arrange to become fully vaccinated against COVID-19 upon their arrival. My Administration has also taken action, apart from this proclamation, to ensure that noncitizen immigrants are vaccinated prior to air travel to the United States. Together, these policies aim to limit the risk that COVID-19, including variants of the virus that causes COVID-19, is introduced, transmitted, and spread into and throughout the United States, potentially overwhelming United States healthcare and public health resources, endangering the health and safety of the American people, and threatening the security of our civil aviation system. Given the resumption of air travel as worldwide restrictions due to the COVID-19 pandemic begin to ease, these policies will, consistent with the measures required by Executive Order 13998 of January 21, 2021 (Promoting COVID-19 Safety in Domestic and International Travel), advance the safety and security of the air traveling public, the government personnel responsible for ensuring the security of air travel, and the millions of individuals employed by the United States air travel industry, as well as their families and communities, while also allowing the domestic and global economy to continue its recovery from the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic.
NOW, THEREFORE, I, JOSEPH R. BIDEN JR., President of the United States, by the authority vested in me by the Constitution and the laws of the United States of America, including sections 1182(f) and 1185(a) of title 8, United States Code, and section 301 of title 3, United States Code, hereby find that it is in the interests of the United States to advance the resumption of international travel to the United States, provided necessary health and safety protocols are in place to protect against the further introduction, transmission, and spread of COVID-19 into and throughout the United States. I further find that vaccination requirements are essential to advance the safe resumption of international travel to the United States and that the unrestricted entry of persons described in section 2 of this proclamation would, except as provided for in section 3(a) of this proclamation, be detrimental to the interests of the United States, and that their entry should be subject to certain restrictions, limitations, and exceptions. I therefore hereby proclaim the following:
Section 1. Revocation of Country-Specific Suspensions and Limitations on Entry. Proclamation 9984 of January 31, 2020 (Suspension of Entry as Immigrants and Nonimmigrants of Persons Who Pose a Risk of Transmitting 2019 Novel Coronavirus and Other Appropriate Measures To Address This Risk), Proclamation 9992 of February 29, 2020 (Suspension of Entry as Immigrants and Nonimmigrants of Certain Additional Persons Who Pose a Risk of Transmitting 2019 Novel Coronavirus), Proclamation 10143 of January 25, 2021 (Suspension of Entry as Immigrants and Nonimmigrants of Certain Additional Persons Who Pose a Risk of Transmitting Coronavirus Disease 2019), and Proclamation 10199 of April 30, 2021 (Suspension of Entry as Nonimmigrants of Certain Additional Persons Who Pose a Risk of Transmitting Coronavirus Disease 2019), are revoked.
Sec. 2. Global Suspension and Limitation on Entry of Certain Individuals Who Are Not Fully Vaccinated Against COVID-19. (a) The entry into the United States by air travel of noncitizens who are nonimmigrants and who are not fully vaccinated against COVID-19 is suspended and limited, except as provided in section 3 of this proclamation. This suspension and limitation on entry applies only to air travelers to the United States and does not affect visa issuance. (b) Any noncitizen who is a nonimmigrant, who is not fully vaccinated against COVID-19, and who, notwithstanding section 2(a) of this proclamation, is permitted to enter the United States by air travel pursuant to section 3(b) of this proclamation must agree to comply with applicable public health precautions established by the Director of the CDC to protect against the public health risk posed by travelers entering into the United States. Such precautions may be related to vaccination, testing, mask-wearing, self-quarantine, and self-isolation, as determined by the Director of the CDC, and may include requirements that individuals: (i) provide proof of pre-departure testing for COVID-19, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (ii) take precautions during air travel to protect against the further introduction, transmission, and spread of COVID-19, including by wearing a face mask, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (iii) provide proof of having arranged for post-arrival testing for COVID-19, as determined by the Director of the CDC; and (iv) provide proof of having arranged to self-quarantine or self-isolate after arriving in the United States, as determined by the Director of the CDC. (c) Any noncitizen who is a nonimmigrant, who is not fully vaccinated against COVID-19, and who, notwithstanding section 2(a) of this proclamation, is permitted to enter the United States by air travel pursuant to section 3(b) of this proclamation must agree to become fully vaccinated against COVID-19 within 60 days of arriving in the United States, within some other timeframe as determined by the Director of the CDC, or as soon as medically appropriate as determined by the Director of the CDC, and must provide proof of having arranged to become fully vaccinated against COVID-19 after arriving in the United States, unless: (i) the noncitizen’s intended stay is sufficiently brief, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (ii) the noncitizen is one for whom, given their age, requiring vaccination would be inappropriate, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (iii) the noncitizen has participated or is participating in certain clinical trials for COVID-19 vaccination, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (iv) COVID-19 vaccination is medically contraindicated for the noncitizen, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (v) the noncitizen is described in section 3(b)(i) or 3(b)(ii) of this proclamation and has previously received a COVID-19 vaccine that is authorized or approved by the noncitizen’s country of nationality, as determined by the Director of the CDC, in consultation with the Secretary of State; or (vi) the Director of the CDC otherwise determines that COVID-19 vaccination is not warranted for the noncitizen.
Sec. 3. Scope of Suspension and Limitation on Entry. (a) The suspension and limitations on entry in section 2 of this proclamation shall not apply to any noncitizen seeking entry as a crew member of an airline or other aircraft operator if such crew member or operator adheres to all industry standard protocols for the prevention of COVID-19, as set forth in relevant guidance for crew member health issued by the CDC or by the Federal Aviation Administration in coordination with the CDC. (b) The suspension and limitations on entry in section 2(a) of this proclamation shall not apply to: (i) any noncitizen seeking entry into or transiting the United States pursuant to one of the following nonimmigrant visa classifications: A-1, A-2, C-2, C-3 (as a foreign government official or immediate family member of an official), E-1 (as an employee of TECRO or TECO or the employee’s immediate family members), G-1, G-2, G-3, G-4, NATO-1 through NATO-4, or NATO-6 (or seeking to enter as a nonimmigrant in one of those NATO classifications); (ii) any noncitizen whose travel falls within the scope of section 11 of the United Nations Headquarters Agreement or who is traveling pursuant to United States legal obligation (as evidenced by a letter of invitation from the United Nations or other documentation showing the purpose of such travel); (iii) any noncitizen for whom, given their age, requiring vaccination would be inappropriate, as determined by the Director of the CDC, taking into account global vaccine availability for individuals in that age group; (iv) any noncitizen who has participated or is participating in certain clinical trials for COVID-19 vaccination, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (v) any noncitizen for whom accepted COVID-19 vaccination is medically contraindicated, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (vi) any noncitizen who has been granted an exception by the Director of the CDC for humanitarian or emergency reasons, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (vii) any noncitizen who is a citizen of a foreign country where the availability of COVID-19 vaccination is limited, as identified pursuant to section 4(a)(v) of this proclamation, and who seeks to enter the United States pursuant to a nonimmigrant visa, except for a B-1 or B-2 visa; (viii) any noncitizen who is a member of the United States Armed Forces or who is a spouse or child of a member of the United States Armed Forces; (xi) any noncitizen seeking entry as a sea crew member traveling pursuant to a C-1 and D nonimmigrant visa, if such crew member adheres to all industry standard protocols for the prevention of COVID-19, as set forth in relevant guidance for crew member health by the CDC; or(x) any noncitizen or group of noncitizens whose entry would be in the national interest, as determined by the Secretary of State, the Secretary of Transportation, the Secretary of Homeland Security, or their designees.
Sec. 4. Implementation and Enforcement. (a) The Secretary of Health and Human Services, through the Director of the CDC, shall implement this proclamation as it applies to the public health through such procedures as may be established, and consistent with the CDC’s independent public health judgment, including by: (i) defining and specifying accepted COVID-19 vaccines or combinations of accepted COVID-19 vaccines, and medical contraindications to accepted COVID-19 vaccines or combinations of accepted COVID-19 vaccines, for purposes of this proclamation; (ii) defining whether an individual is fully vaccinated against COVID-19, and specifying acceptable methods of proving that an individual is fully vaccinated against COVID-19, for purposes of this proclamation; (iii) specifying acceptable methods of proving that an individual has arranged to comply with applicable public health requirements and protocols to protect against the further introduction, transmission, and spread of COVID-19 into and throughout the United States, including pre-departure testing, post-arrival testing, post-arrival self-quarantine or self-isolation, and post-arrival vaccination against COVID-19, for purposes of this proclamation; (iv) determining whether certain persons qualify as participants in certain clinical trials for COVID-19 vaccination, for purposes of this proclamation; (v) maintaining a list of countries where the availability of COVID-19 vaccination is limited, with such countries defined as those where less than 10 percent of the country’s total population has been fully vaccinated with any available COVID-19 vaccine or are otherwise determined by the Director of the CDC to qualify as countries where the availability of COVID-19 vaccination is limited; and (vi) establishing other public health measures consistent with this proclamation to protect against the further introduction, transmission, and spread of COVID-19 into and throughout the United States by persons described in section 2 of this proclamation. (b) The Secretary of Transportation and the Secretary of Homeland Security shall take steps to ensure that airlines do not permit noncitizens barred from entry pursuant to this proclamation to board an aircraft traveling to the United States, to the extent permitted by law. (c) Executive departments and agencies shall implement this proclamation, as appropriate and consistent with applicable law, in accordance with such procedures as they may establish. (d) The Secretary of State, the Secretary of Transportation, and the Secretary of Homeland Security shall review any regulations, orders, guidance documents, policies, and any other similar agency actions developed pursuant to Proclamations 9984, 9992, 10143, and 10199 and, as appropriate, shall consider revising or revoking these agency actions consistent with the policy set forth in this proclamation. (e) Nothing in this proclamation shall be construed to affect any individual’s eligibility for asylum, withholding of removal, or protection under the regulations issued pursuant to the legislation implementing the Convention Against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment, consistent with the laws and regulations of the United States. (f) Nothing in this proclamation shall be construed to limit the CDC’s authority to impose public health requirements and protocols, including on individuals who are fully vaccinated against COVID-19, individuals covered by this proclamation, or individuals not covered by this proclamation, such as United States citizens, lawful permanent residents, or noncitizens traveling on immigrant visas.
Sec. 5. Termination. This proclamation shall remain in effect until terminated by the President. The Secretary of Health and Human Services shall, as circumstances warrant and no more than 60 days after the date of this proclamation and by the final day of each calendar month thereafter, recommend whether the President should continue, modify, or terminate this proclamation.
Sec. 6. Effective Date. This proclamation is effective at 12:01 a.m. eastern standard time on November 8, 2021. This proclamation does not apply to persons aboard a flight scheduled to arrive in the United States that departed prior to 12:01 a.m. eastern standard time on November 8, 2021.
Sec. 7. Severability. It is the policy of the United States to enforce this proclamation to the maximum extent possible to advance the national security, public safety, and foreign policy interests of the United States. Accordingly, if any provision of this proclamation, or the application of any provision to any person or circumstance, is held to be invalid, the remainder of this proclamation and the application of its provisions to any other persons or circumstances shall not be affected thereby.
Sec. 8. General Provisions. (a) Nothing in this proclamation shall be construed to impair or otherwise affect: (i) the authority granted by law to an executive department or agency, or the head thereof; or (ii) the functions of the Director of the Office of Management and Budget relating to budgetary, administrative, or legislative proposals. (b) This proclamation shall be implemented consistent with applicable law and subject to the availability of appropriations. (c) This proclamation is not intended to, and does not, create any right or benefit, substantive or procedural, enforceable at law or in equity by any party against the United States, its departments, agencies, or entities, its officers, employees, or agents, or any other person.
IN WITNESS WHEREOF, I have hereunto set my hand this twenty-fifth day of October, in the year of our Lord two thousand twenty-one, and of the Independence of the United States of America the two hundred and forty-sixth.
JOSEPH R. BIDEN JR.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.
International Travel Restrictions by Country
Find out where you can travel and covid-19 policies.
Select origin country, search destination or select a country on the map to see travel restrictions.
The travel status of individual countries can change suddenly, and we know it can be hard to stay on top of it all. That's why we're getting you the information you need to consider when planning travel. Learn about country-specific entry requirements such as the border status, COVID-19 testing requirements, and quarantine requirements. Many countries are reopening their borders for international travel. Find out which countries are open to vaccinated travelers.
Just enter your departure country above - the map will update to reflect countries' opening status and any entry requirements for air travelers. Before you book, be sure to double check your country's official government site.
Destinations you can travel to now
Dominican republic, netherlands, philippines, puerto rico, switzerland, united arab emirates, united kingdom, know when to go.
Sign up for email alerts as countries begin to open - choose the destinations you're interested in so you're in the know.
Filter by region, status and more
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Albania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Algeria.
American Samoa
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter American Samoa.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Angola.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Anguilla.
Antigua And Barbuda
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Antigua And Barbuda.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Argentina.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Armenia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Aruba.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Australia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Austria.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Azerbaijan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bahrain.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bangladesh.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Barbados.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Belgium.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Belize.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Benin.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bermuda.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bhutan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bolivia.
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Botswana.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Brazil.
British Virgin Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the British Virgin Islands.
Brunei Darussalam
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Brunei Darussalam.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bulgaria.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Burundi.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Cambodia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Cameroon.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Canada.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Cape Verde.
Caribbean Netherlands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Caribbean Netherlands.
Cayman Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Cayman Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Chad.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Chile.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter China.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Colombia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Comoros.
Cook Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Cook Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Costa Rica.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Croatia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Curaçao.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Cyprus.
Czech Republic
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Czech Republic.
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Denmark.
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Djibouti without restrictions.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Dominica.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Dominican Republic.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, need to quarantine to enter East Timor.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ecuador.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Egypt.
El Salvador
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter El Salvador.
Equatorial Guinea
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Equatorial Guinea.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Eritrea.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Estonia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Eswatini.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ethiopia.
Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas)
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas).
Faroe Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Faroe Islands.
Federated States of Micronesia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Federated States of Micronesia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Fiji.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Finland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter France.
French Guiana
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter French Guiana.
French Polynesia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter French Polynesia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Gabon.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Gambia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Georgia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Germany.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ghana.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Gibraltar.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Greece.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Greenland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Grenada.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guadeloupe.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guam.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guatemala.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guinea.
Guinea-Bissau
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guinea-Bissau.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guyana.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Honduras.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Hong Kong.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Hungary.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Iceland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter India.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Indonesia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ireland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Italy.
Ivory Coast
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ivory Coast.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Jamaica.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Japan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Jersey.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Jordan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kazakhstan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kenya.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kiribati.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kosovo.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kuwait.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kyrgyzstan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Laos.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Latvia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Lesotho.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Liberia.
Liechtenstein
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Liechtenstein.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Lithuania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Luxembourg.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Macau.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Madagascar.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Malawi.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Malaysia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Maldives.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Malta.
Marshall Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Marshall Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Martinique.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mauritania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mauritius.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mayotte.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mexico.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Moldova.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mongolia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Montenegro.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Montserrat.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mozambique.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Namibia.
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Nauru without restrictions.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Nepal.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Netherlands.
New Caledonia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter New Caledonia.
New Zealand
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter New Zealand.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Nicaragua.
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Niger without restrictions.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Nigeria.
North Macedonia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter North Macedonia.
Northern Mariana Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Northern Mariana Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Norway.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Oman.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Pakistan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Palau.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Panama.
Papua New Guinea
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Papua New Guinea.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Paraguay.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Peru.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Philippines.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Poland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Portugal.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Puerto Rico.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Qatar.
Republic of the Congo
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Republic of the Congo without restrictions.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Réunion.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Romania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Rwanda.

Saint Barthélemy
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Barthélemy.
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Kitts and Nevis.
Saint Lucia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Lucia.
Saint Martin
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Martin.
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Samoa.
São Tomé and Príncipe
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter São Tomé and Príncipe.
Saudi Arabia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saudi Arabia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Senegal.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Serbia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Seychelles.
Sierra Leone
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Sierra Leone.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Singapore.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Slovakia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Slovenia.
Solomon Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Solomon Islands.
South Africa
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter South Africa.
South Korea
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter South Korea.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Spain.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Sri Lanka.
St. Maarten
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter St. Maarten.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Sudan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Suriname.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Sweden.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Switzerland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Taiwan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tajikistan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tanzania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Thailand.
The Bahamas
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter The Bahamas.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Togo.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tonga.
Trinidad and Tobago
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Trinidad and Tobago.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tunisia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Türkiye.
Turkmenistan
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, will not be allowed to enter Turkmenistan.
Turks and Caicos Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Turks and Caicos Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tuvalu.
U.S. Virgin Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the U.S. Virgin Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Uganda.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the United Arab Emirates.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the United Kingdom.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Uruguay.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Uzbekistan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Vanuatu.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Vietnam.
Wallis and Futuna
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Wallis and Futuna.
Western Sahara
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, will not be allowed to enter Western Sahara.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Zambia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Zimbabwe.

Get trip-ready with at-home COVID-19 tests
How often is the data on this page updated.
We check for travel restriction information from government authorities daily, and update the page any time we get new information. The following information regarding travel restrictions for each country is correct to the best of our knowledge at the time of publication.
How many countries are closed to visitors?
As of Sep 11, 2 countries have completely restricted entry to non-citizens and 5 are open but require quarantine and/or a negative COVID test.
Where can I travel without COVID restrictions?
Currently you can travel from the United States to 197 countries without restrictions. Please check our map to learn more.
Are there any other types of travel restrictions besides COVID-19 tests and quarantines?
These are the two main types of restrictions or requirements needed to travel into another country. However, the COVID-19 testing options are continually widening as new methods are developed. Different countries may accept results from different or multiple test types, so be sure to check the individual country's specific requirements.
What should I do if I get COVID-19 while in another country?
If you get COVID-19 while in another country, follow the local authority's recommendations. These may include hospitalization, self-isolating and testing in that country. Be sure to contact your travel insurance company and travel provider as well and inform them of your situation.
What should I do if the borders of the country I am visiting close?
Depending on your home country, you may need to change your departure date and return home as soon as possible. If that's the case, contact your travel provider to find the earliest departure.
Additional resources
- What you need to know
- Airline policies
- Hotel policies
- Car policies
- Tips for flying
- Tips for hotel
- Tips for vacation rental
If you're looking for personalized travel advice for your own travel plans like whether or not a restriction applies to your trip, we won't be able to answer any questions or offer advice. Please consult your local government's resources.
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Covid-19 related travel restrictions, share this content.
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
Travel Restrictions

The end of COVID-19 travel restrictions: Summary of findings from the COVID-19 related travel restrictions reports
Following the decision of WHO to determine the end of the public health emergency phase for COVID-19, UNWTO has released an in-depth analysis of the travel restrictions introduced in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.

Report: Travel Restrictions 11 th
One out of five destinations continue to have their borders completely closed as new surges of COVID-19 impact the restart of international tourism. The latest research shows that still 98% of all destinations have some kind of travel restrictions in place.

Report: Travel Restrictions 10 th
The global vaccination rollout and increased adoption of digital solutions for safe travel should lead to a rise in international mobility over the weeks and months ahead,the latest data from the UNWTO indicates.

Report: Travel Restrictions 9 th
The emergence of new variants of the COVID-19 virus has prompted many governments to reverse efforts to ease restrictions on travel, with total closures to tourists most prevalent in Asia and the Pacific and Europe.

Report: Travel Restrictions 8 th
According to the eighth edition of the UNWTO Travel Restrictions Report, 70% of all global destinations have eased restrictions on travel introduced in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.

Report: Travel Restrictions 7 th
Though many remain cautious in view of the development of the pandemic, the seventh edition of the UNWTO “COVID-19 Related Travel Restrictions: A Global Review for Tourism” confirms the ongoing trend towards the gradual restart of tourism.

Report: Travel Restrictions 6 th
87 destinations that have now eased travel restrictions, just four have completely lifted all restrictions, while 83 have eased them while keeping some measures such as the partial closure of borders in place.

Report: Travel Restrictions 5 th
According to UNWTO, as of 15 June, 22% of all destinations (48 destinations) have now eased restrictions on travel, up from just 3% (7 destinations) on 18 May.

Report: Travel Restrictions 4 th
The report notes that 100% of all destinations worldwide continue to have some form of COVID-19-related travel restrictions in place. Furthermore, as of 18 May 75% continued to have their borders completely closed for international tourism.

Report: Travel Restrictions 3 rd
UNWTO has found that 83% of destinations in Europe have introduced complete closure of borders for international tourism. In the Americas, this proportion stands at 80%, in Asia and the Pacific it is 70%, in the Middle East it is 62% and in Africa it is 57%.

Report: Travel Restrictions 2 nd
The COVID-19 pandemic has prompted all destinations worldwide to introduce restrictions on travel, research by the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) has found.

Report: Travel Restrictions 1 st
Almost all global destinations have imposed restrictions on travel since January 2020, including complete bans on all travel as they work to contain the pandemic.
Lockdowns and travel bans: which countries have COVID-19 restrictions

Mar 30, 2020 • 17 min read

Travel bans, lockdowns and partial shutdowns are being implemented as countries work to contain the spread of the coronavirus COVID-19 pandemic . The situation is rapidly evolving, and checking the most up-to-date government sources is always advised, but here is a list of how countries are dealing with the outbreak.

Ethiopia's state-carrier Ehiopian Airlines suspended flights to 30 countries with high numbers of reported COVID-19 cases on 20 March. From 23 March, all travellers arriving into the country are subject to a mandatory 14-day quarantine. See here for more information.
On 17 March, Ghana banned entry to foreign visitors who have been in the worst affected countries (those with 200 cases and more) in the last 14 days. Ghanian citizens and permanent residents are exempt. There is a mandatory self-quarantine for anyone entering the country. From 30 March, it imposed a lockdown on the capital Accra, and the cities of Kumasi and Tema. See here for more information.
On Sunday, 15 March Kenya announced its denying entry to non-citizens or permanent residents. Anyone arriving into the country in the last 14 days must self-isolate. On 28 March, it introduced a 7pm to 5am curfew. See here for more information.
On Friday, 20 March, Madagascar banned all commercial passenger flights to and from Europe for 30 days. All passengers arriving into the country must self-isolate for 14 days. See here for more information.
Mali has suspended commercial passenger flights from affected countries from 19 March. See here for more information.
Effective 15 March 15, all commercial international flights have been suspended, as well as passenger ferry services. Morocco also closed its land borders with Ceuta and Melilla. See here for more information.
Nigeria had banned entry to citizens of 13 countries who have all reported more than 1000 cases, including the US, UK, Italy, Spain, Germany, Norway and the Netherlands. On Saturday, 21 March, it took the measure further by closing its airports to all international travel for one month. A lockdown has been imposed on its two main cities, Lagos and Abuja. See here for more information.
Rwanda has enforced a lockdown, banning all unnecessary movements outside the home for two weeks as of midnight on Sunday, 22 March. See here for more information.
Somalia has banned all international flights. See here for more information.
South Africa
On Sunday, 15 March, South Africa declared a "state of disaster" and announced that it will close its borders to all foreign visitors from high-risk countries. On 28 March, it imposed a three-week nationwide lockdown. See here for more information.
Uganda has closed its borders to all travel and commercial traffic, except for cargo. See here for more information.
On 16 March, Tunisia closed public buildings, land borders and suspended international flights. A curfew from 6pm to 6am was introduced on 18 March. See here for more information.
Read more: What to do when you can’t get home due to travel restrictions
As of 16 March, Argentina closed its borders for 15 days to non-residents. A mandatory quarantine was introduced on 20 March to last until mid-April. See here for more information.
As of 17 March, Bolivia has closed its borders to all non-residents and suspended all international flights. The measures are in place until 31 March. See here for more information.
On Monday, 16 March, Canada's prime minister Justin Trudeau announced it is closing its borders to non-citizens and non-residents. As of 18 March, that has been extended to its land border with the US in a mutual agreement between the two countries. See here for more information.
Chile closed its borders on Wednesday, 18 March. See here for more information.
Colombia has banned the entry of foreign visitors from Monday, 16 March. Returning Colombian citizens and residents returning must self-isolate for two weeks. Schools and universities are also closed. See here for more information.
Costa Rica will close its borders to all international visitors from 18 March. Costa Rican citizens and residents will be subject to a mandatory 14-day quarantine. See here for more information.
On Saturday, 14 March, Ecuador announced it will close its borders to all foreign visitors. Ecuadorean citizens and permanent residents have been advised to return to the country before Monday. Restrictions will apply thereafter. See here for more information.
El Salvador
El Salvador declared a state of emergency on Sunday, 15 March, despite having no confirmed cases at present. Restrictions on entry to and exit from the country are in place, as well as curbs on public gatherings. See here for more information.
On Friday, 12 March, Guatemala announced a ban on citizens from Europe, Iran, China, South and North Korea from entering the country. On Saturday that ban was extended to cover the US and Canada. See here for more information.
Honduras has closed its borders for one week, effective 16 March. See here for more information.
Panama is one of the hardest-hit countries in Central America. As of 16 March, it has banned the entry of non-residents. All non-essential businesses have been shut. On 24 March, it introduced a 5pm to 5am curfew and announced it would issue fines of up to US$100,000 for any confirmed cases breaking self-quarantine. See here for more information.
As of 17 March, residents have been ordered to stay at home in mandatory self-isolation, and Peru's borders are closed for 15 days. See here for more information.
From 13 March, Uruguay has required that all passengers arriving from China, South Korea, Japan, Singapore, Iran, Spain, Italy, France and Germany go into mandatory self-quarantine for 14 days. See here for more information.
The US has imposed a travel ban for all of Europe, and the border between Canada and the US is closed to non-essential traffic as of 18 March. On March 19, the US State Department issued a level-4 global travel advisory , recommending that all Americans abroad either return home or stay in place.
Domestically, as of Monday, 16 March, Americans have been asked to avoid social gatherings of more than 10 people and to limit non-essential travel within the United States. For a full breakdown of state-by-state restrictions see here .
On 15 March, Venezuela ordered a mandatory quarantine on those living in nine states, including the capital Caracas. See here for more information.
Read more: How each US state and territory is handling coronavirus closures and restrictions
On 14 March, Cambodia issued a 30-day ban on entry to visitors from the US, France, Germany, Italy and Spain from 17 March. See here for more information.
China introduced strict containment measures, which have managed to slow down the number of new COVID-19 cases. Those measures include a lockdown of nearly 60 million people in Hubei province (the source of the outbreak) and mandatory quarantine instructions, which have started to ease in recent days. On 28 March the Chinese government introduced a temporary ban on all foreign visitors to push back on imported cases. See here for more information.
From 25 March, all foreign arrivals into the country are banned, with some exceptions including the immediate family of Hong Kong residents and those returning from China, Macau and Taiwan ,though they must self-quarantine for 14 days. See here for more information.
On 24 March, India announced it would tighten its containment measures by introducing a nationwide 21-day lockdown, effective from midnight on 25 March. The prime minister Narenda Modi announced on a television address that "nobody is allowed to leave their homes" during this time. As of 13 March, the Indian government suspended most travel and tourism visas until 15 April. See here for more information.
Japan has banned entry to passengers who have been in affected regions of China, South Korea or Italy within the last 14 days. Japanese nationals and their immediate families are exempt. Major attractions like Tokyo Disney Resort have been closed for a number of weeks, while the country is under partial shutdown. As of 29 March, Japan expanded its entry ban to include citizens from the US and most of Europe. See here for more information.
On 16 March, the Malaysian government announced a nationwide lockdown, effective 18 March until the end of the month. See here for more information.
Philippines
Travel in and out of the capital Manila is prohibited until 14 April and some areas are under a curfew from 8pm until 5am. From 22 March, foreign visitors are barred from entry. See here for more information.
From 23 March, Singapore banned all international travellers except for those working in healthcare or essential services. All arrivals must present health certificates. Large gatherings have been banned but schools and workplaces remain open. See here for more information.
South Korea
Visitors who have been in China's Hubei Province in the past 14 days, and citizens from that region are not permitted to enter South Korea. See here for more information.
On 17 March, Sri Lanka announced it would ban all incoming flights for two weeks from Wednesday, 18 March. No cruise passengers and crew are allowed to enter. See here for more information.
As of 15 March, there is a ban on entry on foreign nationals who have visited China, Hong Kong and Macau in the last 14 days. See here for more information.
On 13 March, Thailand said it would suspend its visa exemption policies for travellers from Hong Kong, South Korea and Italy, while visa on arrival would be stopped for 18 countries: Bulgaria, Bhutan, Cyprus, Ethiopia, Fiji, Georgia, India, Kazakhstan, Malta, Mexico, Nauru, Papua New Guinea, Romania, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Uzbekistan, Vanuatu and China. On 23 March, Bangkok went into lockdown and borders have been tightened. See here for more information.
From 22 March, there is a ban on all foreign entry until further notice. See here for more information.

Australia and New Zealand
Australia will close its borders to foreign visitors from Friday, 20 March. Only Australian citizens, their immediate family and permanent residents will be allowed to enter. On Monday, 23 March, the government announced that most public places will temporarily close, including beaches, cafes, restaurants, places of worship, bars and casinos in a further set of restrictions on businesses and individual behaviours. See here for more information.
New Zealand
New Zealand's prime minister Jacinda Arden announced on 14 March that "New Zealand will have the widest-ranging and toughest border restrictions of anyone in the world." All international passengers, including returning citizens, were subject to self-isolation for 14 days; cruise ships are not permitted to dock in New Zealand's ports until at least 30 June and residents have been advised to avoid all non-essential travel for now. From 25 March, those measures were extended to a month-long nationwide lockdown with the country progressing to a 'level 4' alert, which means people must stay in their homes unless they are working in essential services. See here for more information.
British Virgin Islands
On 14 March, the Government of the Virgin Islands announced a 30-day ban on entry to cruise ships calling into the British Virgin Islands. Mass gatherings and festivals have also been postponed or cancelled. See here for more information.
Dominican Republic
From 19 March, the Dominican Republic will suspend all commercial flights and ships, as well as close schools and entertainment centres for 15 days. The government is making arrangements to evacuate tourists over the coming days. See here for more information.
Haiti has closed its land border with the Dominican Republic. See here for more information.
On Sunday, 15 March, Jamaica declared a state of disaster. All public events have been postponed for the month of March, until further notice. Jamaica has also banned entry to visitors from the UK - except for Jamaican citizens and their immediate family, and residents of Jamaica travelling from the UK. See here for more information.
Puerto Rico
On 16 March, Puerto Rico imposed a nationwide curfew from 9pm until 5am to last until 29 March. During the day, people can only leave their home to buy food, medicine or gasoline. See here for more information.
Trinidad and Tobago
On 17 March, Trinidad and Tobago closed its borders to international visitors for 14 days. All arrivals must self-isolate for 14 days. See here for more information.

On 17 March, EU leaders issued a 30-day travel non-essential ban on those travelling from outside the EU. The 26 member states of the EU are: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain and Sweden.
Austrians are being asked to self-isolate as major restrictions on movement were imposed on Sunday, 15 March. All non-essential shops are closed from Monday, and restaurants from Tuesday. People are advised to only leave their homes when necessary and gatherings of more than five people are banned. The government has banned entry to people travelling from the UK, the Netherlands, Russia and Ukraine without a medical certificate. All rail and flight connections from Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Spain and France to Austria are also suspended. See here for more information.
All schools and universities will be closed from Monday, 16 March until 3 April. All recreational and sporting events have been cancelled or postponed. Cafes, pubs and restaurants have closed, while shops have been advised to shut at weekends. Pharmacies and supermarkets remain unaffected. See here for more information.
Czech Republic
On Thursday, 12 March, the Czech Republic declared a 30-day state of emergency. Schools, universities and cultural institutions are closed; gatherings of more than 30 people are banned and restaurants and pubs must close between 8pm and 6am. On Saturday morning it extended its measures to close all retail businesses, including shopping centres, for at least 10 days, and announced a shutdown of its borders to foreign visitors. See here for more information.
Denmark announced it is closing its borders to all international visitors from midday on Saturday, 14 March until 13 April, only returning Danish citizens and documented residents will be allowed into the country. People have been asked to restrict their movements and only leave home when it's necessary. See here for more information.
France imposed a lockdown on the evening of Monday, 16 March, to last for 15 days. Citizens can only leave their homes to go to the supermarket, pharmacy or work. President Emmanuel Macron said borders would be closed from Tuesday, although French citizens and residents would be allowed to return home. On 23 March, restrictions were tightened with citizens instructed they could only exercise alone or with their children once a day and for no more than an hour, staying within one kilometre of their home. See here for more information.
Nationwide all schools, universities and non-essential shops are closed. German Chancellor Angela Merkel has also called for a ban on gatherings with more than two people. Germany has also temporarily closed its borders Switzerland, Austria, Denmark and Luxembourg. See here for more information.
On 16 March, Greece announced all international arrivals must undergo a 14-day quarantine. It also closed its borders with Albania and North Macedonia. See here for more information.
Passengers arriving from China, Italy, Iran, Israel or South Korea must self-quarantine for 14 days. Cultural and sporting activities are prohibited; restaurants and bars are closed; shops likely to be open at limited hours; health screenings on arrival likely. See here for more information.
Italy introduced nationwide quarantine measures that are in place until 3 April 2020. The country is under lockdown and all shops – except for supermarkets and pharmacies –are closed. Citizens can only leave their homes with a form that provides a justified reason for doing so, such as buying food, medical supplies, or assisting those in need. The form can be accessed here . On 22 March, restrictions were tightened in Lombardy with outdoor sports and other physical activities banned. See here for more information.
On Thursday, 12 March, Ireland entered a period of partial shutdown with schools, universities and cultural institutions closed. Bars and restaurants closed on 15 March and large public gatherings were banned. Restrictions on movement have gradually been introduced since. As of 29 March, all non-essential businesses have been shut. People have been advised to stay at home unless shopping for food or medicine and they can only engage in outdoor exercise within 2km of their homes. See here for more information.
Netherlands
All schools, cafes, restaurants and sports clubs were ordered to be closed on Sunday, 14 March. Public places such as museums, concert venues, theatres and sports clubs are also closed. See here for more information.
International travellers arriving in Norway from outside the Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden, plus Greenland, the Faroe Islands and the Åland Islands) are subject to 14-day self-isolation. See here for more information.
Poland is banning all foreign visitors from entering the country from Sunday, 15 March and is imposing a 14-day quarantine on returning citizens. On 26 March, the government announced a ban on public gatherings of more than two people, with the exception for families and religious gatherings. See here for more information.
On 21 March, Romania introduced a ban on foreign visitors from entering the country; exceptions will be made for those transiting through Romania. See here for more information.
Russia has banned the entry of foreign visitors from 18 March until 1 May. Returning Russian citizens and permanent residents are exempt. Moscow has closed restaurants, bars, parks and non-essential retail outlets. See here for more information.
Serbia closed its airports, road and rail borders on 19 March and suspended all internal transport. See here for more information.
Slovakia is stopping all international travel to and from the country and introducing border checks. Schools, leisure centres and some cultural attractions are closed. See here for more information.
From midnight on Sunday, 15 March all shops, other than supermarkets, newsstands, petrol stations, pharmacies, banks and agricultural shops, were ordered to close. Schools are also closed and public transport has been halted. Special travel advisories are in place for Italy, Serbia, Spain, Iran, South Korea, the US and China. See here for more information.
Spain is the second-hardest hit country in Europe, after Italy. In order to contain the spread of infection, Spain's prime minister Pedro Sánchez announced a 15-day partial lockdown on 14 March. On 22 March, it was announced the ban could be in place for a further 15 days. All non-essential shops have been shut and citizens can only leave their homes when necessary, such as when buying food, going to work, seeking healthcare and assisting those in need. Citizens can be fined if they're found outside without justified reasons. Schools, restaurants, entertainment facilities and bars are closed. See here for more information.
Switzerland
Switzerland has closed schools, banned public gatherings of more than 100 people, and limited access to restaurants, bars and clubs to a maximum of 50 people. Numerous ski resorts have also temporarily shut. At the borders, additional screening procedures have been implemented, and a number of borders between Italy and Switzerland have closed. See here for more information.
On Tuesday, 17 March, the UK government advised people to avoid non-essential travel, to avoid social gatherings and to work from home where possible. On Monday, 23 March, the government announced a plan to further reduce coronavirus transmission by only allowing people to leave their homes to shop for basic necessities, go to doctor appointments and to travel to work only when absolutely necessary. See here for more information.
Read more: What's it like living in lockdown? Three people in Italy share their stories
Middle East
As of 23 March, Azerbaijan closed its borders to all foreign visitors except for those with work permits. See here for more information.
From Thursday, 18 March, Egypt will suspend all incoming and outbound flights for two weeks. See here for more information.
Israel initially banned citizens or visitors of Germany, France, Spain, Switzerland, Austria, Andorra and San Marino unless they have proof they have to a place to self-isolate for 14 days. On 9 March that was extended to a 14-day quarantine on all visitors and returning citizens. The country has also entered into a partial shutdown with non-essential public places closed. On 17 March, Israel went one step closer to total lockdown by instructing people to stay at home unless absolutely necessary and avoid public transportation. See here for more information.
As of March 17, Jordan has closed its land and sea borders and suspended all international flights. See here for more information.
As of 15 March, Oman suspended tourist visas for all foreign visitors for one month. See here for more information.
As of 17 March, the UAE suspended issuing foreign visitors, except diplomatic visas. To facilitate a deep clean campaign, an 8pm to 6am curfew was introduced on 26 March, to last until 5 April. See here for more information.
This article was first published on 13 March and updated on 30 March, 2020.
The novel coronavirus (Covid-19) is now a global pandemic. Find out what this means for travellers .
This article was first published Mar 13, 2020 and updated Mar 30, 2020.
Explore related stories

Jun 29, 2024 • 8 min read
Planning a trip to Central America? Read up on our picks of the can’t-miss places to visit in the region, from coral reefs to Mayan ruins and beyond.

Jun 28, 2024 • 5 min read

Jun 28, 2024 • 9 min read

Jun 28, 2024 • 7 min read

Jun 27, 2024 • 11 min read

Jun 27, 2024 • 9 min read

Jun 27, 2024 • 7 min read

Jun 26, 2024 • 6 min read

Jun 26, 2024 • 9 min read
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
What is COVID-19?
Who can get covid-19, can i travel if i recently had covid-19, what can travelers do to prevent covid-19, more information.
CDC Respiratory Virus Guidance has been updated. The content of this page will be updated soon.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a respiratory illness caused by the virus SARS-CoV-2. The virus spreads mainly from person to person through respiratory droplets and small particles produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. The virus spreads easily in crowded or poorly ventilated indoor settings.
People with COVID-19 have reported a wide range of symptoms – ranging from no or mild symptoms to severe illness. Symptoms may appear 2–14 days after exposure to the virus. Possible symptoms include fever, chills, cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, muscle aches, headache, new loss of taste and smell, sore throat, runny nose, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Anyone can get COVID-19. However, some people are more likely than others to get very sick if they get COVID-19. These include people who are older, are immunocompromised , or have certain disabilities , or have underlying health conditions . Vaccination, past infection, and timely access to testing and treatment can help protect you from getting very sick from COVID-19.
Yes, you can travel once you have ended isolation . Check CDC guidance for additional precautions, including testing and wearing a mask around others. If you recently had COVID-19 and are recommended to wear a mask, do not travel on public transportation such as airplanes, buses, and trains if you are unable to wear a mask whenever around others.
Get up to date with your COVID-19 vaccines before you travel and take steps to protect yourself and others . Consider wearing a mask in crowded or poorly ventilated indoor areas, including on public transportation and in transportation hubs. Take additional precautions if you were recently exposed to a person with COVID-19. Don’t travel while sick.
If you have a weakened immune system or are at increased risk for severe disease talk to a healthcare professional before you decide to travel. If you travel, take multiple prevention steps to provide additional layers of protection from COVID-19, even if you are up to date with your COVID-19 vaccines. These include improving ventilation and spending more time outdoors, avoiding sick people, getting tested for COVID-19 if you develop symptoms, staying home if you have or think you have COVID-19, and seeking treatment if you have COVID-19.
Consider getting travel insurance in case you need medical care abroad .
Consider getting a COVID-19 test if you:
- Develop COVID-19 symptoms before, during, or after travel.
- Will be traveling to visit someone who is at higher risk of getting very sick from COVID-19.
- Were in a situation with a greater risk of exposure during travel (e.g., in an indoor, crowded space like an airport terminal while not wearing a mask).
If you traveled and feel sick, particularly if you have a fever, talk to a healthcare professional, and tell them about your recent travel.
- Masking During Travel
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Coronavirus Updates
As omicron spreads, studies suggest that travel bans alone don't do much good.

Deepa Shivaram

Emma Bowman

Jaclyn Diaz

People line up to get on the Air France flight to Paris at OR Tambo's airport in Johannesburg, South Africa, on Friday. The United States, Israel and other European nations have already imposed travel restrictions on South Africa and other nations in the region. Jerome Delay/AP hide caption
People line up to get on the Air France flight to Paris at OR Tambo's airport in Johannesburg, South Africa, on Friday. The United States, Israel and other European nations have already imposed travel restrictions on South Africa and other nations in the region.
When the omicron variant of COVID-19 was first identified in South Africa, the country's scientists were quick to inform global health leaders of the new mutations they had found.
Though scientists have little information about the new variant and aren't certain where it originated, several countries, including the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom and the European Union announced almost immediate travel bans from South Africa and other southern African nations.
As the week began, Japan followed suit with far more restrictive measures.
Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida announced Monday the decision to reestablish entry rules for foreign travelers to limit any potential spread of the omicron variant. This comes just weeks after the country reopened its borders on Nov. 8.
Kishida told reporters this step is a "temporary measure until information about the omicron variant becomes clear."
Israel also implemented a blanket ban to all foreigners Sunday night after initially establishing restrictions on travelers just from southern African countries. According to The Jerusalem Post , under this new policy anyone returning from any country — vaccinated Israelis included — will need to isolate for three days once in the country.
The restrictive measures around the world sparked outcry from some health officials and experts who caution that the bans are premature and could set a harmful precedent .
"There is very little utility of these kinds of bans," Saad Omer, director of the Yale Institute of Global Health, told NPR.
"Unfortunately, from what we know about the epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 and the epidemiology of this variant, the horse has probably left the barn," Omer said, noting the high transmissibility of this coronavirus and its variants.
And even though the omicron variant has been reported in several other countries in Europe, Asia and North America, travel bans are largely being imposed on southern African countries.
One of the identified cases of the omicron variant in Belgium had no contact or travel with any nations in southern Africa, suggesting community spread could already be taking place.
"If the question is to prevent the variant from coming in, it really doesn't make sense to exempt countries where it has been identified and that has even more direct flights than southern Africa," Omer said.
Studies show travel bans are ineffective at curbing the spread of disease
Travel bans from the start of the COVID-19 pandemic resulted in economic and other consequences we're still seeing today.
A recent study from the journal Science shows that restricting international travel in the beginning stages of the COVID-19 pandemic did have some effect on delaying spread, but the researchers said restricting travel is only truly effective when paired with curbing the spread of infection through hand-washing, isolation and early detection.
Another study , in the Journal of Emergency Management , concluded that little evidence exists to prove that international travel bans are effective in controlling the spread of infectious disease, and such measures should only be taken if recommended by the World Health Organization. With the omicron variant, the WHO has already cautioned against imposing travel bans.
Dr. Margaret Harris, a public health doctor and a spokesperson for the World Health Organization, told NPR's Morning Edition that the restrictions do give countries some "breathing space" in their early responses to omicron.
She urged governments to "make the most of that time. Build up your hospital capacity, build up your tracking and tracing, build up your surveillance, prepare."
However, introducing a travel ban can give a false sense that the virus is being contained, researchers said, adding that such policies can also make it difficult to transport health care workers and other resources.
Additionally, the stigma of travel bans can exacerbate racism and xenophobia, according to Nicole Errett of the University of Washington, who was the lead author on the Journal of Emergency Management study.
Travel bans could lead to less scientific transparency
Omer, of the Yale Institute of Global Health, has another concern about implementing travel bans during a public health crisis: It can dampen the commitment to scientific transparency.
When countries that are proactive about disclosing the circulation of a virus are hit with travel restrictions, he said, that undercuts the case for health officials to be forthcoming about what's happening in their countries.
"You don't want a situation where, a month from now, a country health minister ... gets a result of sequenced virus and they say, 'OK, if it is that widespread, it's going to come out anyways from some other country, why be the first one?' And that cycle starts," said Omer.
Addressing vaccine inequity around the world is the best way to stop these new variants from emerging, Omer said.
"If there are more transmission events going on with every hour, with every day, with every week, the likelihood of a variant emerging goes up," he said.
And one of the most effective ways to address inequity, Omer said, is to allow for all regions, low-income countries in particular, to produce their own vaccines.
It's too early to tell whether the omicron variant in particular will become a serious public health threat, Omer added, "but that doesn't mean that we are not playing with fire by by letting vaccine inequity continue."
- South Africa
Traveling Abroad: Coronavirus Restrictions
- Last updated Jun 25, 2024
- Difficulty Intemediate
- Category Travel

The COVID-19 pandemic has had a massive impact on travel, with countries imposing sweeping travel bans and advisories to stem the spread of the virus. Initially, countries imposed restrictions on travellers from mainland China, the epicentre of the outbreak, but as the virus spread globally, travel advisories and bans were extended to other countries as well. The US, for instance, advised its citizens to avoid all international travel and return to the country immediately if they intended to stay indefinitely. The UK also advised against all non-essential international travel for 30 days.
The pandemic has led to chaos at airports, with flights being drastically reduced and borders being closed. Many countries have imposed lockdowns and stay-at-home orders, making travel difficult, if not impossible. Travel insurance companies have also seen an increase in claims and cancellations related to the coronavirus.
For those who still need to travel, it is important to take precautions such as frequent handwashing, using hand sanitisers, and avoiding contact with sick people. It is also recommended to clean your hands after touching surfaces in airports and on planes.
What You'll Learn
Travel bans and advisories, flight cancellations and airline policies, cruise line suspensions, vacation rental and hotel booking waivers, screening and precautions at airports.

A study in Science found that travel restrictions could delay the arrival of COVID-19 in a country, but that they had only a modest overall effect unless combined with infection prevention and control measures to considerably reduce transmissions. Travel bans may be most effective for isolated locations, such as small island nations, and at the start and end of a pandemic.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, many countries implemented global or non-global travel restrictions. For example, Algeria suspended all international flights, while Peru reopened its borders to tourists from a select few South American countries. Some countries, such as the United Arab Emirates, had different quarantine requirements depending on the country of origin.
The United States, from the beginning of the pandemic and into 2021, closed its northern and southern borders to non-essential travel. Inbound travel from China, Europe, and other countries was suspended, and American citizens travelling from China were monitored by local health departments.
The European Union also debated and eventually implemented travel restrictions within the bloc and to external countries. The European Council agreed to ban incoming travel from outside the EU, EEA, Switzerland, and the UK, with some exceptions, for 30 days starting on 17 March 2020. This restriction was later repeatedly prolonged until 30 June.
The Difference Between Known Traveler Number and Redress Number
You may want to see also
Industry-Wide Policies
Basic economy fares cannot be changed or cancelled for free on any airline. Basic fares are normally non-refundable, so it is important to keep cancellation policies in mind when booking. "Free" cancellations do not always mean a refund; they often result in a voucher or credit with an expiry date. Fare differences also apply to changes, with last-minute changes incurring higher costs.
Airline-Specific Policies
Each airline has its own policies, and passengers should always check the latest travel advice from their airline. Some airlines, such as Allegiant, American Airlines, Delta, and United, have eliminated change fees for many types of tickets. Others, such as Air Canada, Air France, Alaska Airlines, and British Airways, are offering flexible rebooking options. Some budget airlines, like Frontier and Spirit, do not offer free changes or cancellations unless done well in advance.
Passenger Rights
If a flight is cancelled due to coronavirus, passengers are entitled to a full refund or an alternative flight. This is because coronavirus is considered an extraordinary circumstance outside the scope of an airline's control. However, passengers are not entitled to compensation for missed flights due to coronavirus. If stranded at the airport due to a coronavirus-related cancellation, passengers may be entitled to care from their airline, including access to communication and hotel accommodation.
Convenience on the Go: Where to Find Travel Size Items for Your Adventures
The cruise industry was possibly the hardest hit by the COVID-19 pandemic. The pandemic led to the voluntary suspension of worldwide cruising in March 2020.
More than 50 cruise lines suspended operations to and from US ports for 30 days due to the coronavirus pandemic. This included major cruise lines such as Disney, Carnival, Princess, Norwegian and Royal Caribbean. The suspension was announced by the Cruise Lines International Association (CLIA).
The CLIA statement said cruise lines were working on the return of ships at sea that were affected by the suspension. The cruise industry supports more than 421,000 jobs in the US and contributes nearly $53 billion to the economy annually, according to the CLIA.
The suspension of cruise operations had a significant economic impact, resulting in financial losses of $50 billion and 334,000 job losses worldwide from mid-March 2020 to the end of September 2020.
In response to the pandemic, cruise lines offered flexible cancellation and rebooking policies, as well as future cruise credits for affected passengers. Some cruise lines also implemented restricted passenger capacity and COVID-19 vaccination requirements.
As of May 2021, cruise lines such as Norwegian, Carnival, Celebrity, Disney, Holland America, MSC, Princess and Royal Caribbean had resumed operations with limited capacity and COVID-19 safety measures in place.
Gift Ideas for Someone Who Loves to Travel
The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted travel plans across the world, with many countries imposing travel bans and restrictions to curb the spread of the virus. As a result, travellers have had to reconsider their plans, leading to a rise in cancellations and a decline in demand for international travel.
In such uncertain times, it is important for travellers to be aware of their options when it comes to cancellations and refunds. While some companies offer full refunds or the option to rebook at a later date, others may have more stringent policies in place. Understanding the terms and conditions of your bookings is crucial to avoid financial loss.
When it comes to vacation rentals and hotel bookings, one option to consider is a waiver. A waiver is an agreement between two parties, where one party gives up the right to hold the other party legally responsible for any issues that may arise. In the context of vacation rentals and hotel bookings, waivers are typically used to protect the property owner or manager from potential claims.
Types of Waivers:
- Damage Waiver: This type of waiver covers minor, accidental damage that may occur during a guest's stay. It is usually included in the overall cost of the rental and is non-refundable. Damage waivers typically cover incidents such as scratches, stains, and broken items. However, it's important to note that they do not cover intentional damage, theft, or loss of personal items.
- Liability Waiver: This type of waiver protects the property owner or manager from legal claims related to bodily injury or property damage. By signing a liability waiver, guests acknowledge their awareness of any risks associated with their stay and agree to take full responsibility for any injuries or accidents that occur.
Pros and Cons of Waivers:
Damage Waiver Pros:
- Peace of mind for guests: Guests can relax during their stay, knowing that minor accidental damage will be covered.
- Protection for hosts: Hosts are protected from financial loss due to accidental damage caused by guests.
Damage Waiver Cons:
- Limited coverage: Damage waivers typically have low coverage amounts, usually under $3,000.
- Non-refundable: Guests may be reluctant to pay a non-refundable fee, especially if they do not cause any damage during their stay.
- Complicated claims process: Claiming reimbursement for damage may involve a complicated process, and guests must report any damage before leaving the property.
Liability Waiver Pros:
Protection from legal claims: Liability waivers shield property owners and managers from potential lawsuits arising from injuries or accidents during a guest's stay.
Liability Waiver Cons:
- Increased risk: Liability waivers shift the burden of responsibility to the property owner or manager, who may have to navigate court proceedings and bear unexpected costs.
- Varying enforceability: The enforceability of liability waivers can vary across states and countries, making court proceedings lengthy and complicated.
Alternatives to Waivers:
- Security Deposit: Instead of a damage waiver, hosts can charge a refundable security deposit to cover any accidental or intentional damage caused by guests. This option may be more appealing to guests as it is refundable if no damage occurs.
- Short-Term Rental Insurance: This type of insurance is designed specifically for vacation rental properties and offers comprehensive coverage for both accidental and intentional damage, theft, and loss of guest items. It also covers bodily injury and provides clear-cut protection without the need for legal proceedings.
In conclusion, while waivers can offer some protection for both guests and property owners, it is important to carefully consider the specific needs and risks associated with your vacation rental or hotel booking. Alternatives such as security deposits and short-term rental insurance may provide more comprehensive coverage and peace of mind for all parties involved.
Amazon's Policy on Reimbursing Interview Travel Expenses
In January 2020, several airports around the world began announcing preventive safety measures against the spread of coronavirus. These included temperature checks for incoming travellers, which were implemented in countries including the US, Canada, the UK, Russia, Germany, France, Japan, India, South Korea, Hong Kong, Macau, Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia, Turkey, Australia, New Zealand, Trinidad and Tobago, and Taiwan.
Thermal screening at airports has long been controversial. It was widely implemented during the 2003 SARS epidemic and later during the 2009 bird flu epidemic. The idea is to detect anyone with an elevated body temperature and, therefore, a possible infectious disease. However, thermal screening isn't always effective at detecting early signs of infection. It may flag up passengers who have a different type of infection, while missing those who are incubating the virus but haven't started to show symptoms yet.
According to a study from the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, out of every 100 infected travellers taking a 12-hour flight, 42 would pass through both entry and exit screening undetected. This is mostly due to the virus's incubation period, which can be as long as 14 days. Some cases are mild and may not show symptoms at all.
In the US, 20 airports instituted screenings for citizens coming from China, where the virus originated. Passengers filled out documentation of their travel history and were checked for fever. Any passengers with symptoms that could match coronavirus infection were treated at an airport Quarantine Station, staffed by medical personnel from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Similar measures were taken in other countries.
However, health experts say that screenings will likely not be the deciding factor in whether the virus continues to spread globally. The global spread of the coronavirus complicates efforts to screen for the disease. As more cases appear in different countries, it becomes less clear that only travellers to Wuhan are potential carriers.
The Current Status of European Travel to America: What You Need to Know
Frequently asked questions.
This depends on where you are travelling from and to. Many countries imposed travel bans and advisories to stop the spread of coronavirus. For example, the US advised citizens to avoid all international travel and the UK advised against all nonessential international travel for 30 days. If you are travelling, make sure that your destination has not restricted your arrival.
The best protections you can take are the same as those for avoiding the flu, common cold and other viruses: wash your hands frequently and use hand sanitiser. On planes, open the air vents and aim them at your face to breathe in filtered air.
Check with your airline, as many offered flexible rebooking policies during the pandemic. For example, some airlines offered full refunds, the option to travel at a later date or to travel to a different destination.

- Karisa Garcia Author Reviewer Traveller

- Elani Piper Author Editor Reviewer
It is awesome. Thank you for your feedback!
We are sorry. Plesae let us know what went wrong?
We will update our content. Thank you for your feedback!
Leave a comment
Travel photos, related posts.

Don't Marry for Money, Collect Memories and Travel: Inspiring Quotes to Keep in Mind
- May 12, 2024

Exploring the World: Can I Travel with an F1 Visa?
- Apr 01, 2024

Unlocking Memories and Experiences: Why Investing in Travel Is More Fulfilling than Material Possessions
- May 13, 2024

Understanding the Redress Number for Travelers: A Complete Guide
- May 31, 2024

Discovering the Mysteries of Traveling to the Poles
- May 28, 2024

The Journey of the Age-Old Travel Visa: A Cultural Odyssey through Time
- Apr 28, 2024
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
Here Are the Rules for Flying When You're Pregnant
Whether you're newly pregnant or planning a babymoon right before welcoming your baby, here's what parents-to-be need to know about airline travel during each trimester.
GETTY IMAGES
Expectant parents need to know: Can you fly when pregnant?
While it's mostly OK to travel until the last few weeks of pregnancy, there are some precautions to take depending on when you decide to book a trip and how high risk your pregnancy is. Here's what you need to know before your next vacation.
Pregnancy and Flying: Your Trimester by Trimester Guide
As a general rule of thumb, most airlines will allow pregnant people to fly right up until week 36 of pregnancy, but you should absolutely do your research before booking your flight to check restrictions. You'll also want to consult with your OB-GYN or midwife before traveling—especially if you're at a higher risk for complications during pregnancy.
Before you travel
While you may be accustomed to planning a vacation on a whim or only packing your usual necessities, there's one extra thing you should consider doing before booking a flight during your pregnancy: Opt for travel insurance.
Should travel restrictions change, your health care provider recommends you stay home, or if you experience any concerning symptoms —like bleeding, abdominal pain, swelling, headaches, vision changes, or decreased fetal movement—you'll want to postpone or cancel your plans and see your doctor as soon as possible.
According to the ACOG, travel is not recommended for pregnant people with certain complications like preeclampsia, premature rupture of membranes (PROM), or who are at risk of preterm labor.
First trimester
Flying earlier on in pregnancy is actually considered pretty safe. And, no, metal detectors won't harm your fetus.
"Pregnant women can observe the same basic precautions for air travel as the general public," Raul Artal, M.D., former vice chairman of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) Committee on Obstetric Practice, previously told Parents .
One thing pregnant air travelers should take extra precautions to avoid at any trimester? Blood clots, which pregnant people are 7 times more likely to develop—especially during long flights. To help minimize your risk, you can book an aisle seat, walk around every so often, and wiggle your legs and toes while seated.
And since morning sickness and fatigue might be your biggest first trimester complaints, you may want to check with your health care provider about bringing anti-nausea medicine with you.
Second trimester
According to the ACOG, "The best time to travel is mid-pregnancy (14 to 28 weeks). During these weeks, your energy has returned, morning sickness is improved or gone, and you are still able to get around easily. After 28 weeks , it may be harder to move around or sit for a long time."
If you're flying during your second trimester, it's a good idea to stay hydrated, think about wearing support stockings to reduce edema and clot risk, and make sure you've done your research on hospitals located near your destination should an emergency arise.
Carrying twins or more? Your health care provider might recommend you stop traveling earlier due to the higher risk of complications.
Third trimester
How late in pregnancy can you fly? If you're relatively healthy—and not at risk of complications like preterm labor, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, or placenta previa—then you're usually OK to travel up until 36 weeks, though some OB-GYNs may prefer you stay closer to your home near the end should you encounter any complications or in case your baby comes sooner than expected.
High-risk patients—and especially those with pregnancy-induced hypertension, diabetes, and sickle-cell disease—may be advised not to fly after 24 weeks—or not at all.
Check with your doctor before traveling at the end of your pregnancy.
Related Articles

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Fact Sheets
FACT SHEET: President Biden’s Presidential Proclamation and Joint DHS-DOJ Interim Final Rule Cut Encounters at Southwest Border by Over 40 Percent in First Three Weeks
The Presidential Proclamation issued by President Biden to temporarily suspend the entry of certain noncitizens across the Southern border and the complementary joint interim final rule (IFR) issued by DHS and DOJ have now been in effect for three weeks, resulting in a significant reduction in the number of encounters at our Southwest Border. Under the IFR, asylum eligibility is generally limited for those who cross the southern border unlawfully or without authorization during times of high encounters. While it is still early, the Border Patrol’s 7-day encounter average has decreased more than 40 percent to under 2,400 encounters per day.
These executive actions are no substitute for Congressional action. Twice now, Congress has failed to pass the bipartisan border security agreement negotiated in the U.S. Senate, which would have provided the critical personnel and funding needed to further secure our Southern border. The agreement would have added 1,500 U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) Agents and Officers, added 1,200 U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) personnel, invested in technology to catch illegal fentanyl, and delivered sweeping reforms to the asylum system. Congress must still act.
Enhanced Enforcement and Consequences
Noncitizens who are subject to the rule’s limitation on asylum eligibility and who do not establish a legal basis to remain in the United States are being promptly removed. Those removed are subject to at least a five-year bar to reentry and potential criminal prosecution.
DHS personnel at CBP, ICE, and U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) have quickly operationalized and implemented the Proclamation and IFR over the past three weeks, with notable impacts including:
- Average daily encounters by Border Patrol at the Southwest Border are below 2,400 per day, the lowest level of encounters since January 17, 2021, but still above the level that would lift the suspension under the Proclamation and IFR.
- DHS has removed and returned more than 24,000 individuals to more than 20 countries, including by operating more than 100 international repatriation flights.
- DHS has doubled the percentage of noncitizens removed or returned directly from Border Patrol custody.
- DHS has doubled the share of encounters processed through Expedited Removal while in USBP or ICE custody. Expedited Removal processing was already at record levels prior to the Declaration.
- DHS has decreased the number of people released pending their removal proceedings by over 65 percent.
- We continue to implement recently announced measures to increase the overall capacity of enforcement resources — including repatriation flights and detention capacity. ICE is optimizing air charter contracts to ensure the maximum amount of repatriation flights can be effectuated weekly. Over the past year, ICE averaged 29 repatriation flights per week. Record numbers of flights have been enabled by continued diplomatic efforts to significantly expand the number of countries to which ICE is able to regularly remove individuals.
- Over the last year, the agency has conducted removal flights to a range of South American and Eastern Hemisphere countries, including Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Egypt, Mauritania, Senegal, Uzbekistan, and India. Efforts to expand the number of removal flights continue with the expectation of additional flights added to the schedule in the coming weeks.
- ICE ERO is adjusting existing detention facility contracts to expand the number of beds in its detention network.
Public Safety
The Presidential Proclamation and IFR have enhanced DHS’s capacity for enforcement against individuals who pose a public safety or national security threat, such as gang members attempting to enter the country unlawfully or without authorization, because the IFR renders those individuals ineligible for asylum and enables their quick removal. With the 1,500 Border Patrol Agents and CBP Officers that the bipartisan border security agreement would add, DHS would be able to enhance enforcement even further.
- DHS has returned more Border Patrol agents to the field to undertake front line border security operations, enhancing DHS efforts to interdict individuals who pose a threat to public safety.
- These efforts continue to expand and maximize DHS enforcement against individuals who pose a threat to our communities , including the announcement on May 9 of a Proposed Rule to apply statutory bars to asylum for individuals who pose a public safety concern earlier in the process, during the credible fear screening.
- To identify individuals of concern, DHS uses a range of resources and information, including information shared by partners worldwide, to inform screening and vetting and to target such individuals attempting to come to United States. DHS works tirelessly to expand access to additional foreign records systems through new international agreements.
- Along with law enforcement partners worldwide, DHS is constantly monitoring new and emerging threats, including the threat posed by criminal organizations that could present a concern to public safety. The Department conducts thorough screening and vetting for any individual that we encounter on the southern border who could be affiliated with these organizations.
- For example, DHS has implemented enhanced screening measures at the border to identify known or suspected gang members, including members of the Venezuelan gang Tren de Aragua. Individuals confirmed to be gang members are required to be referred for criminal prosecution or placed into Expedited Removal and detained.
How it Works
The Presidential Proclamation suspends the entry of noncitizens across the southern U.S. border, which includes the Southwest land and the southern coastal borders, with certain exceptions. The rule, issued consistent with the Proclamation, restricts asylum eligibility for those who cross the southern U.S. border unlawfully or without authorization. That means that noncitizens who have crossed unlawfully or without authorization since June 5, 2024, are considered ineligible for asylum, with certain exceptions.
- The limitation on asylum eligibility will be discontinued when encounters fall below certain levels but will come back into effect if encounters rise again. For additional details on the Proclamation and IFR, see the DHS fact sheet available at the following link:
- Fact Sheet: Presidential Proclamation to Suspend and Limit Entry and Joint DHS-DOJ Interim Final Rule to Restrict Asylum During High Encounters at the Southern Border | Homeland Security
Individuals in Mexico may continue to use the CBP One ™ mobile app’s appointment scheduling function. Currently, CBP makes 1,450 appointments available per day at eight land ports of entry via this functionality. Use of the app requires those seeking an appointment to submit vital information in advance, improving DHS’s ability to conduct screening and vetting.
Building on Significant Actions to Enforce our Laws and Expand Access to Lawful Pathways and Processes
- A majority of all southwest border encounters during the past three fiscal years resulted in a removal, return, or expulsion. DHS removed or returned over 740,000 individuals in the 12 months after the end of the Title 42 public health Order, more than any year since 2010. This has included more removals to countries other than Mexico than in any prior year ever.
- DHS has significantly expanded its capacity to conduct credible fear interviews. Since May 12, 2023, DHS has conducted more than 152,000 credible fear interviews. The Proclamation and IFR follow a series of steps that the Administration has taken over the past three years as it prepared for the end of the Title 42 public health Order, and after it was lifted last year, including surging personnel, infrastructure, and technology to the border, issuing the Circumvention of Lawful Pathways Rule, and referring record numbers of noncitizens into expedited removal.
For additional information on the actions taken over the past three years, see our fact sheet at the link below:
- Fact Sheet: DHS Continues to Strengthen Border Security, Reduce Irregular Migration, and Mobilize International Partnerships | Homeland Security
This Administration has also carried out the largest expansion of lawful pathways and orderly processes in decades. The Presidential Proclamation and corresponding rule are already enabling DHS to quickly remove those without a lawful basis to remain, strengthening enforcement and freeing up the asylum system for those with legitimate claims.
- Through the CHNV processes, nationals of Cuba, Haiti, Nicaragua, and Venezuela who have a supporter and who clear background checks, may receive advanced travel authorization to travel to the United States lawfully, without going through dangerous and costly irregular migration routes. Through the end of May, more than 462,100 CHNV nationals have arrived lawfully through the process.
- Through the Safe Mobility initiative, U.S. government and international non-governmental organizations are working with several countries to establish centers where individuals can find information and screening for potential access to processes, including the U.S. Refugee Admissions Program, and information on other pathways and orderly processes to the United States as well as other countries, such as Canada and Spain. More than 10,000 refugees have arrived in the United States through this initiative thus far.
Still, it is important to underscore that these actions cannot achieve the same results as Congressional action. DHS needs additional personnel and funding in order to quickly impose consequences on all noncitizens who cross irregularly and do not have a legal basis to remain in the United States.
- Border Security
- Immigration and Customs Enforcement
- Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
- Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE)
- Enforcement and Removal Operations (ERO)

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Starting Monday, the U.S. begins accepting fully vaccinated travelers at airports and land borders, doing away with a COVID-19 restriction that dates back to the Trump administration.
March was by far the busiest month for COVID-19-related travel restrictions. After the World Health Organization (WHO) declared COVID-19 a pandemic on March 11, the Trump administration issued a travel ban on non-Americans who visited more than two dozen European countries within 14 days of coming to the United States. On March 17, the United States and Canada mutually agreed to close their ...
U.S. citizens traveling to a country outside the U.S. Find country-specific travel advisories, including COVID-19 restrictions, from the Department of State. See the CDC's COVID-19 guidance for safer international travel to learn: If you can travel if you recently had COVID-19. What you can do to help prevent COVID-19.
What to Know: U.S. Travel Restrictions. The hope is with these longstanding bans being lifted, the U.S. tourism industry will start to recover. The halt on travel caused a loss of nearly $300 ...
A COVID-19 testing centre for travellers at Heathrow Airport. During the COVID-19 pandemic, many countries and territories imposed quarantines, entry bans, or other travel restrictions for citizens of or recent travelers to the most affected areas. [1] Some countries and territories imposed global restrictions that apply to all foreign ...
Leslie Josephs @lesliejosephs. Key Points. The U.S. on Monday will lift a pandemic travel ban on international visitors from more than 30 countries after 19 months. New rules will replace the ban ...
The White House on Friday will lift COVID-19 travel restrictions for fully vaccinated international visitors starting Nov. 8, ending historic restrictions that had barred much of the world from ...
Find which ones across the United States have implemented travel restrictions to curb the spread of COVID-19. Print Aug. 7, 2020, 4:27 PM UTC / Updated Dec. 17, 2020, 10:28 PM UTC
Section 1. Policy. Science-based public health measures are critical to preventing the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) by travelers within the United States and those who enter the ...
Today, the Administration is releasing the following documents to implement these requirements: 1) a Presidential Proclamation to Advance the Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID-19 ...
Before travel, all visitors must submit a health authorization form, the completion of which includes the purchase of mandatory Covid-19 insurance. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level ...
Andrzej Formaniak greets his wife Eva Eggar after she arrives at Logan International Airport as the U.S. reopens air and land borders to vaccinated travellers for the first time since coronavirus ...
The continued spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a global threat to our health and safety. COVID-19 has resulted in more than 733,000 deaths in the ...
Planning a trip within the United States during the pandemic? Check CNN Travel's state-by-state guide with any remaining restrictions plus links to Covid safety guidance and mandates.
Many countries are reopening their borders for international travel. Find out which countries are open to vaccinated travelers. Just enter your departure country above - the map will update to reflect countries' opening status and any entry requirements for air travelers. Before you book, be sure to double check your country's official ...
According to UNWTO, as of 15 June, 22% of all destinations (48 destinations) have now eased restrictions on travel, up from just 3% (7 destinations) on 18 May. The report notes that 100% of all destinations worldwide continue to have some form of COVID-19-related travel restrictions in place. Furthermore, as of 18 May 75% continued to have ...
Have the travel bans on arrivals from southern Africa been lifted? Yes, as of 12:01 a.m. ET on December 31, the travel bans are lifted. ... UK during Covid-19: What you need to know.
Outbound travel to high-risk countries is also banned. The ban applies to visitors from China, South Korea, Iran, Italy, Spain, Austria, Germany, Switzerland, Sweden, UK, Norway, Denmark and ...
Travel bans, lockdowns and partial shutdowns are being implemented as countries work to contain the spread of the coronavirus COVID-19 pandemic. The situation is rapidly evolving, and checking the most up-to-date government sources is always advised, but here is a list of how countries are dealing with the outbreak. Africa.
Consider getting a COVID-19 test if you: Develop COVID-19 symptoms before, during, or after travel. Will be traveling to visit someone who is at higher risk of getting very sick from COVID-19. Were in a situation with a greater risk of exposure during travel (e.g., in an indoor, crowded space like an airport terminal while not wearing a mask).
During the COVID-19 pandemic, WHO has largely reinforced its historic antipathy to travel restrictions. And as in many past emergencies, governments widely disregarded WHO's advice.
Travel bans from the start of the COVID-19 pandemic resulted in economic and other consequences we're still ... has another concern about implementing travel bans during a public health crisis: It ...
Travel bans and advisories. ... During the COVID-19 pandemic, many countries implemented global or non-global travel restrictions. For example, Algeria suspended all international flights, while Peru reopened its borders to tourists from a select few South American countries. Some countries, such as the United Arab Emirates, had different ...
What can I do to decrease my chances of getting COVID-19 while I'm traveling this summer? It's important to remember that COVID-19 is not a winter-only virus and can still spread during the summer.If you're taking a flight or any other public transportation, don't forget to pack masks and practice good hand hygiene. Masks protect you from COVID-19 and other respiratory viruses, and ...
Pregnancy and Flying: Your Trimester by Trimester Guide . As a general rule of thumb, most airlines will allow pregnant people to fly right up until week 36 of pregnancy, but you should absolutely ...
A majority of all southwest border encounters during the past three fiscal years resulted in a removal, return, or expulsion. ... may receive advanced travel authorization to travel to the United States lawfully, without going through dangerous and costly irregular migration routes. Through the end of May, more than 462,100 CHNV nationals have ...