

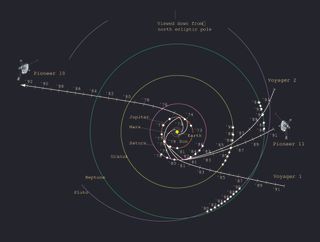
Voyager 1 and Voyager 2
Where are they now.
Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have reached "interstellar space" and each continue their unique journey deeper into the cosmos. In NASA's Eyes on the Solar System app, you can see the actual spacecraft trajectories of the Voyagers updated every five minutes.
Mission Status
Instrument status.
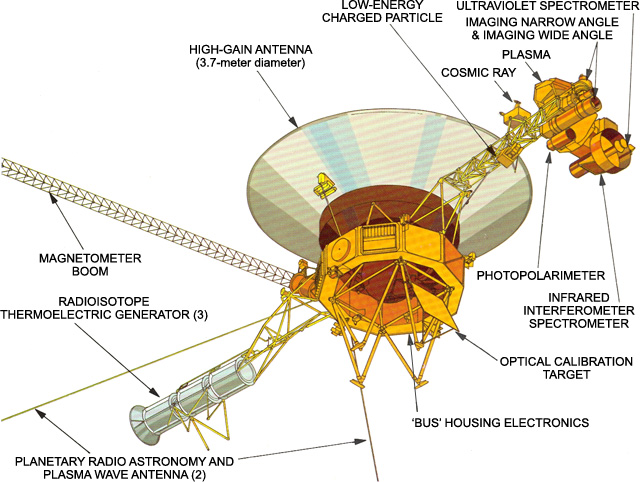
Voyager 1 Present Position
Voyager 2 present position, voyager's grand tour: 1977 - today.
share this!
August 18, 2022
Voyager, NASA's longest-lived mission, logs 45 years in space
by Jet Propulsion Laboratory

NASA's twin Voyager probes have become, in some ways, time capsules of their era: They each carry an eight-track tape player for recording data, they have about 3 million times less memory than modern cellphones, and they transmit data about 38,000 times slower than a 5G internet connection.
Yet the Voyagers remain on the cutting edge of space exploration. Managed and operated by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, they are the only probes to ever explore interstellar space—the galactic ocean that our sun and its planets travel through.
The sun and the planets reside in the heliosphere, a protective bubble created by the sun's magnetic field and the outward flow of solar wind (charged particles from the sun). Researchers—some of them younger than the two distant spacecraft—are combining Voyager's observations with data from newer missions to get a more complete picture of our sun and how the heliosphere interacts with interstellar space.
"The heliophysics mission fleet provides invaluable insights into our sun, from understanding the corona or the outermost part of the sun's atmosphere, to examining the sun's impacts throughout the solar system, including here on Earth, in our atmosphere, and on into interstellar space," said Nicola Fox, director of the Heliophysics Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington. "Over the last 45 years, the Voyager missions have been integral in providing this knowledge and have helped change our understanding of the sun and its influence in ways no other spacecraft can."

The Voyagers are also ambassadors, each carrying a golden record containing images of life on Earth, diagrams of basic scientific principles, and audio that includes sounds from nature, greetings in multiple languages, and music. The gold-coated records serve as a cosmic "message in a bottle" for anyone who might encounter the space probes. At the rate gold decays in space and is eroded by cosmic radiation, the records will last more than a billion years.
Beyond expectations
Voyager 2 launched on Aug. 20, 1977, quickly followed by Voyager 1 on Sept. 5. Both probes traveled to Jupiter and Saturn, with Voyager 1 moving faster and reaching them first. Together, the probes unveiled much about the solar system's two largest planets and their moons. Voyager 2 also became the first and only spacecraft to fly close to Uranus (in 1986) and Neptune (in 1989), offering humanity remarkable views of—and insights into—these distant worlds.
While Voyager 2 was conducting these flybys, Voyager 1 headed toward the boundary of the heliosphere. Upon exiting it in 2012, Voyager 1 discovered that the heliosphere blocks 70% of cosmic rays, or energetic particles created by exploding stars. Voyager 2, after completing its planetary explorations, continued to the heliosphere boundary, exiting in 2018. The twin spacecraft's combined data from this region has challenged previous theories about the exact shape of the heliosphere.
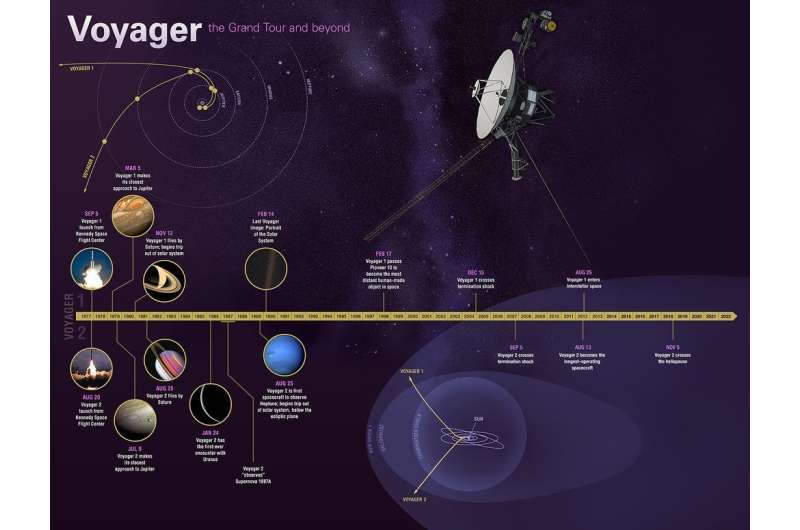
"Today, as both Voyagers explore interstellar space, they are providing humanity with observations of uncharted territory," said Linda Spilker, Voyager's deputy project scientist at JPL. "This is the first time we've been able to directly study how a star, our sun, interacts with the particles and magnetic fields outside our heliosphere , helping scientists understand the local neighborhood between the stars , upending some of the theories about this region, and providing key information for future missions."
The long journey
Over the years, the Voyager team has grown accustomed to surmounting challenges that come with operating such mature spacecraft, sometimes calling upon retired colleagues for their expertise or digging through documents written decades ago.
Each Voyager is powered by a radioisotope thermoelectric generator containing plutonium , which gives off heat that is converted to electricity. As the plutonium decays, the heat output decreases and the Voyagers lose electricity. To compensate, the team turned off all nonessential systems and some once considered essential, including heaters that protect the still-operating instruments from the frigid temperatures of space. All five of the instruments that have had their heaters turned off since 2019 are still working, despite being well below the lowest temperatures they were ever tested at.
Recently, Voyager 1 began experiencing an issue that caused status information about one of its onboard systems to become garbled. Despite this, the system and spacecraft otherwise continue to operate normally, suggesting the problem is with the production of the status data, not the system itself. The probe is still sending back science observations while the engineering team tries to fix the problem or find a way to work around it.
"The Voyagers have continued to make amazing discoveries, inspiring a new generation of scientists and engineers," said Suzanne Dodd, project manager for Voyager at JPL. "We don't know how long the mission will continue, but we can be sure that the spacecraft will provide even more scientific surprises as they travel farther away from the Earth."
Provided by Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Saturday Citations: Bulking tips for black holes; microbes influence drinking; new dinosaur just dropped
Jun 22, 2024

China, France launch satellite to better understand the universe

Key mechanism in nuclear reaction dynamics promises advances in nuclear physics
Jun 21, 2024

Study challenges popular idea that Easter islanders committed 'ecocide'

New AI-driven tool improves root image segmentation

Many more bacteria produce greenhouse gases than previously thought, study finds

Stacking three layers of graphene with a twist speeds up electrochemical reactions

A black hole of inexplicable mass: JWST observations reveal a mature quasar at cosmic dawn

Beyond CRISPR: seekRNA delivers a new pathway for accurate gene editing

Transforming drug discovery with AI: New program transforms 3D information into data that typical models can use
Relevant physicsforums posts, why is the cno cycle considered catalytic.
2 hours ago
Is the Universe older than we think?
15 hours ago
Will we ever communicate with extraterrestial life in a reasonable time frame?
Jun 19, 2024
Solar Activity and Space Weather Update thread
Jun 18, 2024
Very bright geo satellite in my night sky?
The james webb space telescope.
More from Astronomy and Astrophysics
Related Stories

NASA Voyager 2 could be nearing interstellar space
Oct 5, 2018

Engineers investigating NASA's Voyager 1 telemetry data
May 18, 2022

Voyager 2 illuminates boundary of interstellar space
Nov 5, 2019

NASA's Voyager 2 probe enters interstellar space
Dec 10, 2018

Probing deep space with Interstellar
Apr 26, 2021

A new plan for keeping NASA's oldest explorers going
Jul 9, 2019
Recommended for you

Drone racing prepares neural-network AI for space
Jun 20, 2024

Researchers investigate the impacts of space travel on astronauts' eye health

Would astronauts' kidneys survive a roundtrip to Mars?
Jun 11, 2024

Human bodies mostly recover from space, tourist mission shows

Researchers explore how the immune system goes awry during space travel and the implications for human aging on Earth
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
5.1.1 Lost in the Delta Quadrant
5.1.2 Starting points
While Voyager's journey through the Delta Quadrant was considerably better documented than for instance the subdivision of the Galaxy or the structure of the Federation at the beginning, and was more simple and logical than many other parts of the Star Trek Cartography, in the meantime this journey have rather complicated due to numerous continuity problems, contradictions, but also new basis information. The latter fact has lead to the problem that concerning Voyager's journey, one cannot simply use 1000 ly/year regularly travel distance per year plus the leaps made in the course of the seven year journey any longer. How Rick Sternbach, the "keeper" of the official route of Voyager (that we unfortunately will not know exactly until the ST:VOY TM is published) recently remarked correctly, the distance of Sol to the Galactic core, the initial distance of Voyager from Earth and her bearing are decisive for a depiction of Voyager's journey. A further cornerstone of the Voyager cartography is also Voyager's average speed which has been officially fixed recently. However, the problem arises that all these "fixed values" aren't that fixed in the end. This even applies to the distance of Earth from the center of the Galaxy. Yet, I tried to use the most recent and least contradictious values.
5.1.3 Overview of the journey
5.1.4 Calculation of the momentary distance
While the above table of course only shows Voyager's distance to Earth for selected key events, it is also possible to determine a precise distance at any time by not deducting the yearly covered distance abruptly at the end of each year, but distributing it equally over the whole year. We then get the momentary distance by deducting the already travelled percentage of the yearly covered distance from the appropriate table distance before the given stardate
For the calculation of Voyager's distance to Earth at a particular time (and therefore the distance of the regions of space crossed and the planets visited at this time etc.), you can use the following step-by-step instructions.
1. Look up the stardate of the episode, e.g. in the ST:VOY Guide .
Example: For [VOY] Message in a Bottle Stardate 51461.5
2. Choose a reference distance to Earth from the above table by comparing the stardate with the table stardates. Important: You have to ignore all yearly covered distances (Stardate xx0000-xx999)!
Example: Stardate 51461.5 is bigger than 51268 in 6., but smaller than 51978 in 8.; the reference distance to Earth is therefore 62134 ly.
3. Beside the now following normal deduction of the percentage of the yearly covered distance (1), 2 special cases have to be considered: (2) in the first year (stardate 48317-48999), Voyager only travelled 300 ly, therefore the yearly distance being accordingly smaller, and (3) between stardate 51008 and 52619, a Borg correction factor has to bee added to the distance, because during this period of time, Voyager's journey became 2 years longer because of avoiding Borg space.
Example: Stardate 51461.5 is between 51008 and 52619, thus variant (2) has to be used. Enter the stardate and reference distance 62134 ly at (2) and click on the button to calculate the momentary distance of Voyager from Earth at this time.
With the locations of Voyager's journey and a possibility to calculate her exact positions, we also know the positions of all planets visited by Voyager and the territories crossed by the ship. Consequently, the "official" Delta Quadrant is paradoxically much better known than the Alpha or Beta quadrants. Therefore, the following passages deal with the significant locations of the journey of the USS Voyager. Finally, at the end of the chapter a short prospect for the further course of the still continuing journey will be given.
5.1.5 The first year
Since the USS Voyager was taken to the Delta Quadrant by the Caretaker not before stardate 48317 (that is in April 2371), the first "year" of Voyager's journey covers only 683 stardate units or 249 days. Consequently, at an average speed of warp 6.2 (438c), Voyager can only travel 300 ly out of the usual 438 ly in 2371. With such a short annual distance, the galactic surroundings has to remain the same to a large extent during this first year - and indeed, Voyager stays the entire year in the sphere of influence of the Kazon-Ogla, Vidiians and Talaxians, who they contacted already in the first weeks in the Delta Quadrant.
5.1.6 The second year
During the second year of her journey, Voyager seems to get on as slowly as in the first year, still passing colonies of the Talaxians, Vidiians and Kazons (mainly Ogla and Nistrim, but also other sects). The reason for this congruence are the diverse delays and course deviations due to the fights with the Kazons, which make a lower speed than the average warp 6.2 and therefore a annual distance of less than 438 ly plausible. However, there were further events in this year that delayed the voyage home, what is proven by the following example
Involuntary "shore leave"
Only after six weeks, during which Voyager kept on flying with normal speed and, according to Tuvok, covered 70 ly in this time, what corresponds to an average speed of warp 6.8 , Voyager has the opportunity to get a cure from the Vidiians. Although Tuvok set a speed of warp 6 after they escaped the Vidiian trap, it is unlikely that Voyager stayed at that speed for the whole time of the flight back to the planet, because then they would have needed a longer time than for the outward flight. Therefore, we can assume that it took Voyager between 3 weeks (at warp 8) and 5 weeks (at warp 7) to travel back to "New Earth". Using the first, more optimistic figure, the crew therefore loses 80 d all in all, what corresponds to a annual distance shortened by 95.998 ly at an average speed of warp 6.2. At the end of the episode, Captain Janeway resumed the course home at warp 8 in order to make up the lost time, but is this possible at all? Day 24 of the involuntary "shore leave" (probably counted without the 17d stasis) corresponds to stardate 49690.1 according to the episode, what places the resumption of the voyage home on stardate 49892.7 . In the remaining 107.3 stardate units or 39.1645d, Voyager could have indeed make up the lost distance of 95.998 ly with an average speed of nearly warp 8 ( warp 7.684 ) , and with an average speed of somewhat more than warp 8 ( Warp 8.66 ), she could additionally travelled the rest of the annual distance of 46.9974 ly that has still to be managed in the remaining time.
During her journey without captain and first officer, the crew has contact to the Vidiians for the last time, therefore Voyager definitely leaves the sphere of influence of this species. Provided that Voyager made first contact with the Vidiians on stardate 48532.4, their territory seems to cover at least 535 ly , although a large extension "above" Voyager's position at the time of first contact is not impossible.
5.1.7 The third year
Despite no large leaps and the usual annual distance of 438 ly, the third year is a year of changes for Voyager's journey. After two years, she finally leaves the known space populated by the Kazons and Vidiians and ventures to new, unknown regions of the Delta Quadrant.
Leaving Kazon space
Already just at the beginning of the year, on stardate 50032.7, the crew of Voyager has the last contact with the Kazon, what seems to imply that they finally leave their "territory" (better called the space dominated by the - nomadic - Kazon sects). It is unknown how far Kazon space extends "above" the Ocampa homeworld, where first contact were made by the crew of Voyager on stardate 48317. However, this planets seems to be located in the border zone rather than in the center of their space, which is dominated by more powerful sects than the Kazon-Ogla, for instance the Kazon-Nistrim. Regarding the space crossed by Voyager within the last 2 years (since the arrival in the Delta Quadrant on stardate 48317), this leads to a diameter of about 750 ly , what can be considerably less (using a lower annual average speed of Voyager in the first year) or more (based on the assumption that Kazon space extends over several hundred light years above the Ocampa homeworld. A diameter of this magnitude seems to be plausible in view of the fact that the Kazon, being nomadic living traders and conquerors, must naturally populate a larger region of space, what necessarily means that every single planet within this territory must be in their hands, but that the region can have larger "gaps". At any rate, these extensions of the influence spheres of the Vidiians and Kazons support the low annual average speed of 6.2, since based on the maximum cruising speed of Voyager (warp 8 = 1000c), the territories of this rather insignificant species would cover 1500-2000 ly.
The Barzan Wormhole
The territory of the Swarm
The Nekrit Expanse
The Nekrit Expanse is described as an extensive, not surveyed, instable region of space which is full of interstellar dust clouds and plasma storms, but contains only few planets. The expanse has a width of several thousand light years , but seems to be not very deep since Voyager can cross the region in relatively short time. She enters the Nekrit Expanse in "Fair Trade" and apparently already leaves it sometime between "Unity" and "The Darkling", because in the first episode, the expanse is explicitly mentioned (and shown), while in the latter one, with the arrival at the Mikhal outpost Voyager enters a completely new, unknown region of space, and the expanse does not play any part in the following episodes. Consequently, Voyager was definitely inside the Nekrit Expanse between stardate 50443 and 50654 - what results in a total time of 211 stardate units or 77d . If Voyager travelled only at an average speed of warp 6.2 during this two and a half months, then the expanse has a depth of 92.398 ly . However, it is more likely that Voyager travelled at a considerably faster speed during that time. In "Fair Trade", it was mentioned that there are only few planets within the expanse and Voyager loads all necessary supplies for the journey in this episode so that regular stops aren't necessary in the end. This assumption is confirmed by the small number of missions while they travelled through the expanse (visit of four planets). Therefore using the maximum cruising speed of Voyager - warp 8, we get a depth of 216.017 ly for the Nekrit Expanse, a figure, that is considerably more plausible in view of the large width and the ignorance of the people in the regions explored by the USS Voyager about the space behind the expanse. Based on a constant cruising speed of warp 8 and the stardates of the single episodes we can now calculate the distances of the visited planets and crossed regions within the Nekrit Expanse from the border of the expanse:
5.1.8 The forth year
The Mutara class nebula
Note : Because of the incorrect stardate calculation (2.7 days / unit instead of the correct 2.7 units / day) this episode overlaps with the next one, [VOY] Hope and Fear.
5.11 Conclusions
Summarizing, most episodes seem to confirm the calculated route of Voyager. However, there are countless possible variants that would roughly match with the distances given in the episodes. Surely the ST:VOY Technical Manual - should it ever be published - will show a completely other picture of the journey, but until then, the depicted table is as exact and "canon" as possible in view of the many variables that have to be taken into consideration and the many discrepancies and errors in the show itself. Concluding, the following table lists some of the congruences as well as the discrepancies of the calculated route and the actual distances mentioned in the series.
In the end, the last leap on stardate 53329 and the distance Voyager has bridge since then results in a distance of 30067 ly to Earth in the middle of season 7 (by stardate 54500), if the already covered part of the annual distance (219 of 438 ly) is included in the calculations. Consequently, at this time Voyager is only 1944 ly away from the border of the Delta Quadrant, using the revised distance of Earth from the Galactic core (25,800 ly). Hence, she will probably never reach the Beta Quadrant, which is inexplicably a taboo in Star Trek: Voyager, but will surely directly travel back to Earth (by slipstream, transwarp or whatever propulsion technology or powerful being) by the end of season 7, if the "policy of small leaps" of the recent episodes is kept up.
� 1999-2001 by Star Trek Dimension / Webmaster . Last update: February 14th, 2001

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.
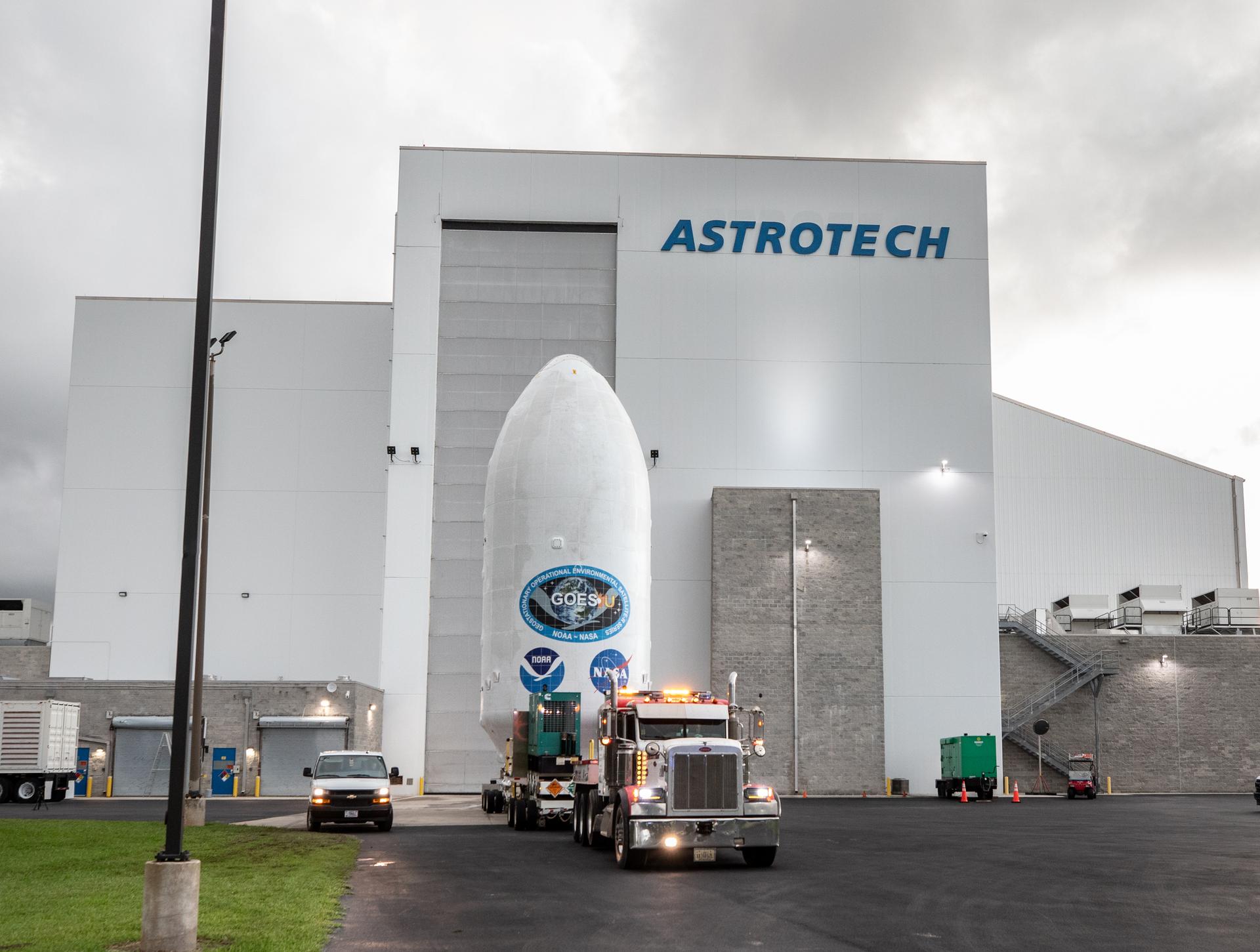

NASA Invites Public to Share Excitement of NOAA GOES-U Launch
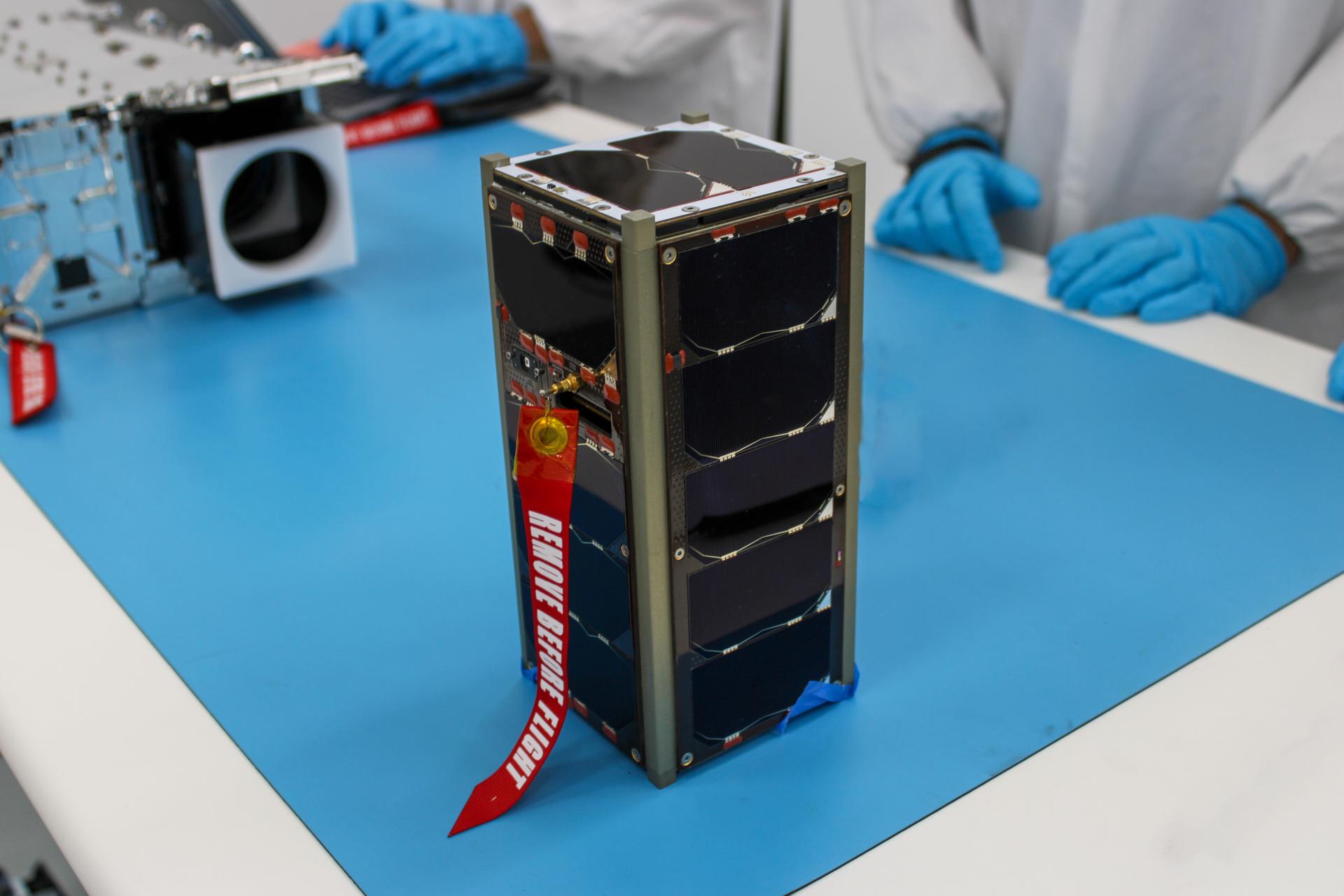

NASA’s ELaNa 43 Prepares for Firefly Aerospace Launch
Why scientists are intrigued by air in nasa’s mars sample tubes.
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia


Amendment 22: Heliophysics Flight Opportunities in Research and Technology Final Text and Due Date

Mercury Resources

Former Astronaut Charles M. Duke, Jr.

Lakita Lowe: Leading Space Commercialization Innovations and Fostering STEM Engagement

Former Astronaut Russell L. “Rusty” Schweickart
The Ocean and Climate Change

NASA Satellites Find Snow Didn’t Offset Southwest US Groundwater Loss

NASA-Led Mission to Map Air Pollution Over Both U.S. Coasts

Perseverance Finds Popcorn on Planet Mars

Hubble Captures Infant Stars Transforming a Nebula

First of Its Kind Detection Made in Striking New Webb Image

NASA Releases Hubble Image Taken in New Pointing Mode

Hypersonic Technology Project

NASA Engineer Honored as Girl Scouts ‘Woman of Distinction’

NASA, MagniX Altitude Tests Lay Groundwork for Hybrid Electric Planes

Augmented Reality Speeds Spacecraft Construction at NASA Goddard

Giant Batteries Deliver Renewable Energy When It’s Needed
Slow Your Student’s ‘Summer Slide’ and Beat Boredom With NASA STEM
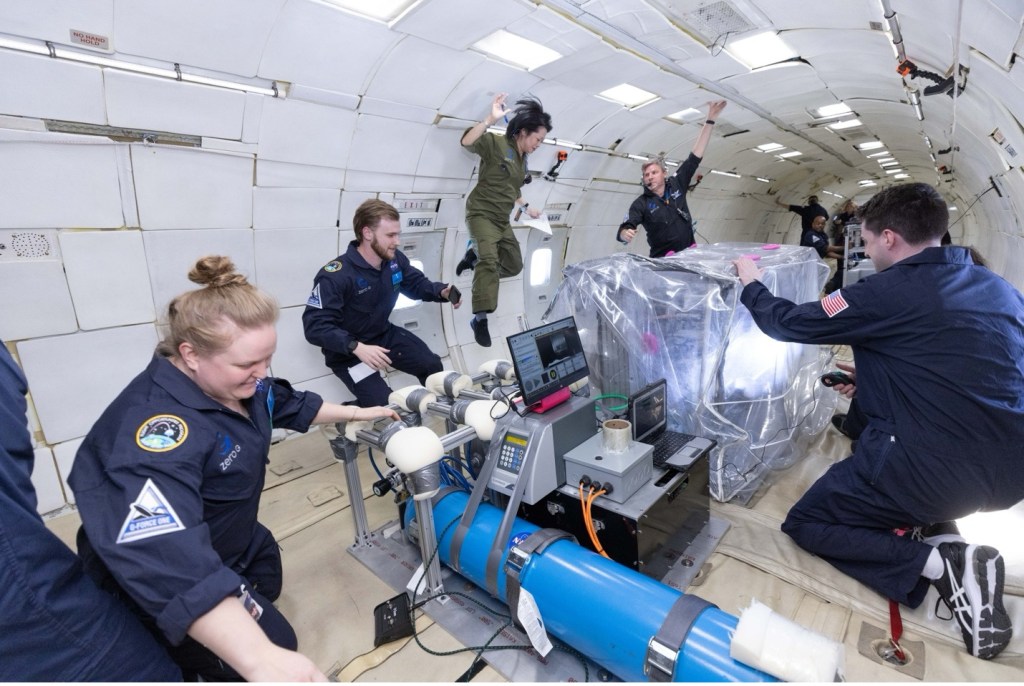

Next Generation NASA Technologies Tested in Flight

Astronauta de la NASA Frank Rubio

Diez maneras en que los estudiantes pueden prepararse para ser astronautas

Astronauta de la NASA Marcos Berríos
45 years ago: voyager 1 begins its epic journey to the outer planets and beyond, johnson space center.
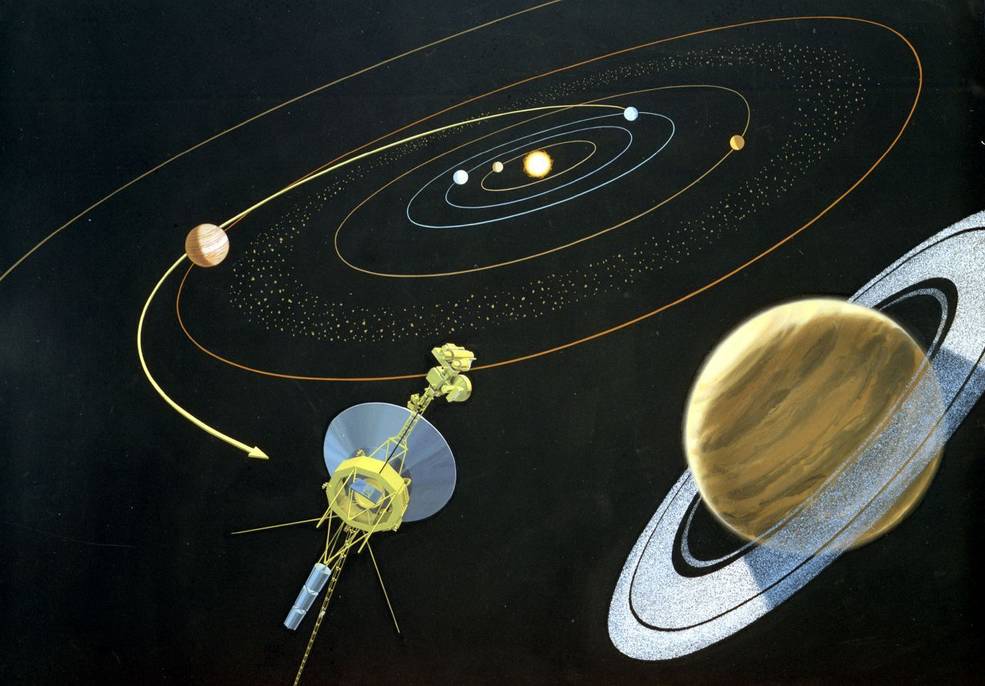
Forty-five years ago, the Voyager 1 spacecraft began an epic journey that continues to this day. The second of a pair of spacecraft, Voyager 1 lifted off on Sept. 5, 1977, 16 days after its twin left on a similar voyage. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, managed the two spacecraft on their missions to explore the outer planets. Taking advantage of a rare planetary alignment to use the gravity of one planet to redirect the spacecraft to the next, the Voyagers planned to use Jupiter’s gravity to send them on to explore Saturn and its large moon Titan. They carried sophisticated instruments to conduct their in-depth explorations of the giant planets. Both spacecraft continue to return data as they make their way out of our solar system and enter interstellar space.
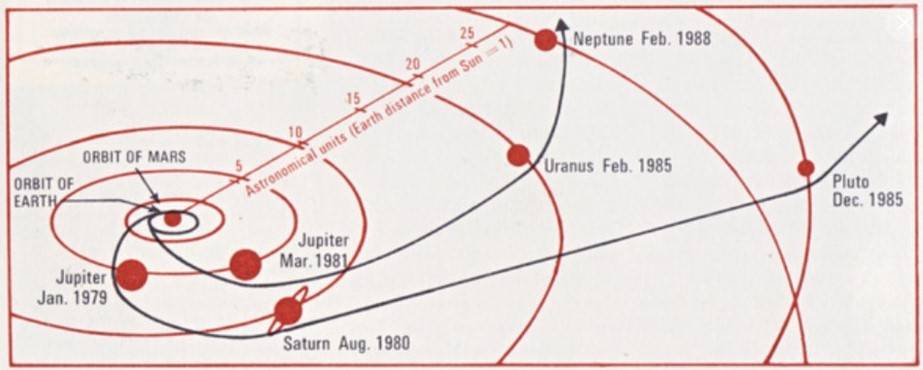
In the 1960s, mission designers at JPL noted that the next occurrence of a once-every-175-year alignment of the outer planets would happen in the late 1970s. A spacecraft could take advantage of this opportunity to fly by Jupiter and use its gravity to bend its trajectory to visit Saturn, and repeat the process to also visit Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. Launching several missions to visit each planet individually would take much longer and cost much more. The original plan to send two pairs of Thermoelectric Outer Planet Spacecraft on these Grand Tours proved too costly leading to its cancellation in 1971. The next year, NASA approved a scaled-down version of the project to send a pair of Mariner-class spacecraft in 1977 to explore just Jupiter and Saturn, with an expected five-year operational life. On March 7, 1977, NASA Administrator James C. Fletcher announced the renaming of these Mariner Jupiter/Saturn 1977 spacecraft as Voyager 1 and 2. Scientists held out hope that one of them could ultimately visit Uranus and Neptune, thereby fulfilling most of the original Grand Tour’s objectives – Pluto would have to wait several decades for its first visit.
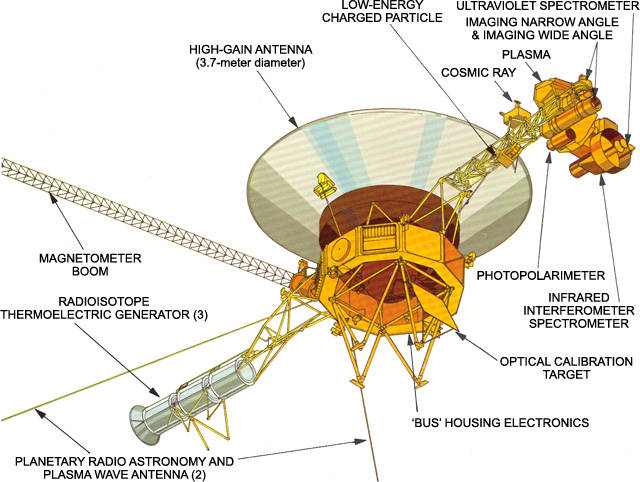
Each Voyager carried a suite of 11 instruments to study the planets during each encounter and to learn more about interplanetary space in the outer reaches of the solar system, including:
- An imaging science system consisting of narrow-angle and wide-angle cameras to photograph the planet and its satellites.
- A radio science system to determine the planet’s physical properties.
- An infrared interferometer spectrometer to investigate local and global energy balance and atmospheric composition.
- An ultraviolet spectrometer to measure atmospheric properties.
- A magnetometer to analyze the planet’s magnetic field and interaction with the solar wind.
- A plasma spectrometer to investigate microscopic properties of plasma ions.
- A low-energy charged particle device to measure fluxes and distributions of ions.
- A cosmic ray detection system to determine the origin and behavior of cosmic radiation.
- A planetary radio astronomy investigation to study radio emissions from Jupiter.
- A photopolarimeter to measure the planet’s surface composition.
- A plasma wave system to study the planet’s magnetosphere.
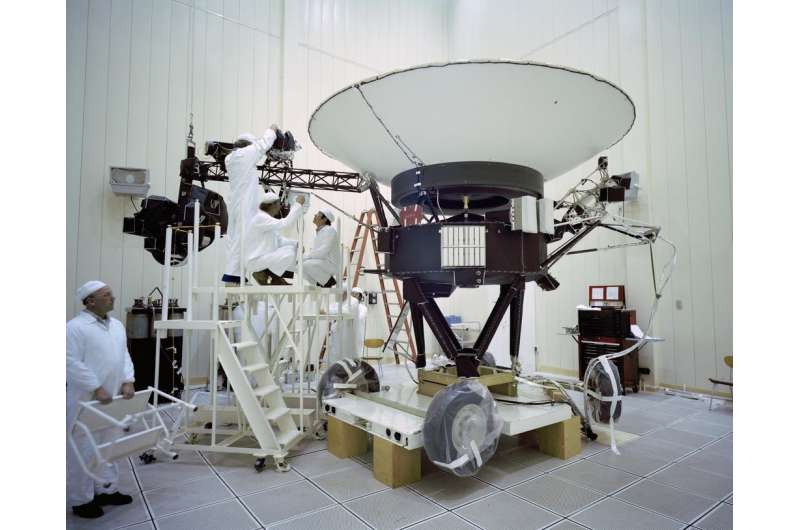
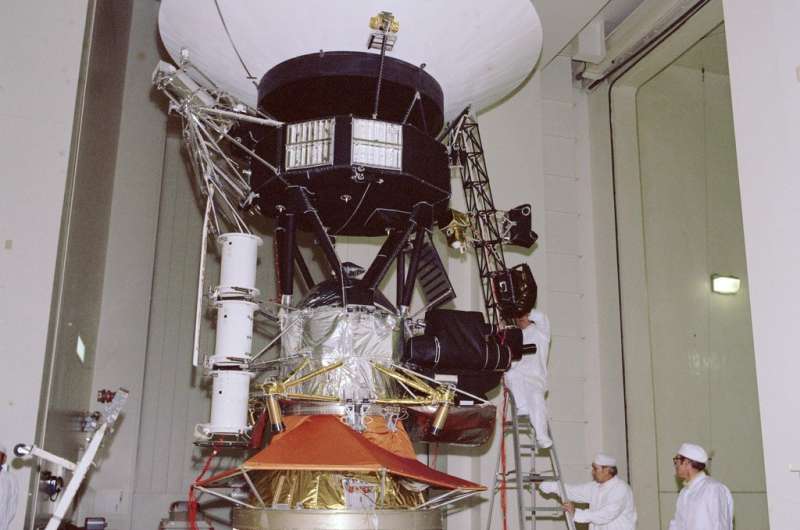
Voyager 1 lifted off on Sept. 5, 1977, atop a Titan IIIE-Centaur rocket from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, now Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, in Florida. Two weeks after its launch, from a distance of 7.25 million miles, Voyager 1 turned its camera back toward its home planet and took the first single-frame image of the Earth-Moon system. The spacecraft successfully crossed the asteroid belt between Dec. 10, 1977, and Sept. 8, 1978.

Although Voyager 1 launched two weeks after its twin, it traveled on a faster trajectory and arrived at Jupiter four months earlier. Voyager 1 conducted its observations of Jupiter between Jan. 6 and April 13, 1979, making its closest approach of 216,837 miles from the planet’s center on March 5. The spacecraft returned 19,000 images of the giant planet, many of Jupiter’s satellites, and confirmed the presence of a thin ring encircling it. Its other instruments returned information about Jupiter’s atmosphere and magnetic field. Jupiter’s massive gravity field bent the spacecraft’s trajectory and accelerated it toward Saturn.
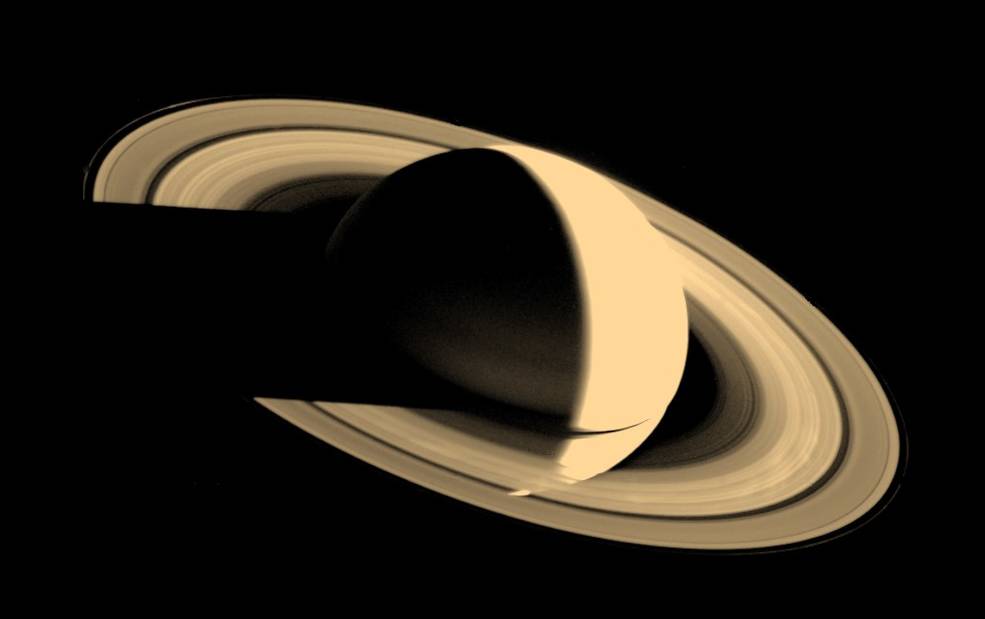

Voyager 1 began its long-range observations of Saturn on Aug. 22, 1980, passed within 114,500 miles of the planet’s center on Nov. 12, and concluded its studies on Dec. 14. Because of its interest to scientists, mission planners chose the spacecraft’s trajectory to make a close flyby of Saturn’s largest moon Titan – the only planetary satellite with a dense atmosphere – just before the closest approach to the planet itself. This trajectory, passing over Saturn’s south pole and bending north over the plane of the ecliptic, precluded Voyager 1 from making any additional planetary encounters. The spacecraft flew 4,033 miles from Titan’s center, returning images of its unbroken orange atmosphere and high-altitude blue haze layer. During the encounter, Voyager 1 returned 16,000 photographs, imaging Saturn, its rings, many of its known satellites and discovering several new ones, while its instruments returned data about Saturn’s atmosphere and magnetic field.
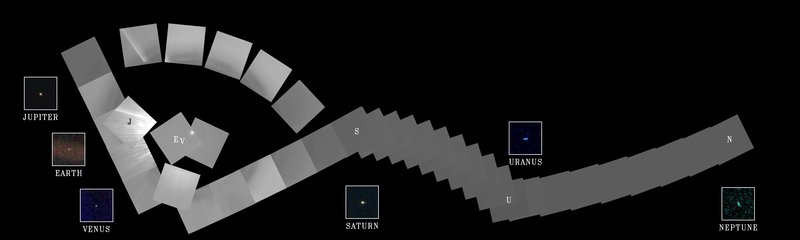
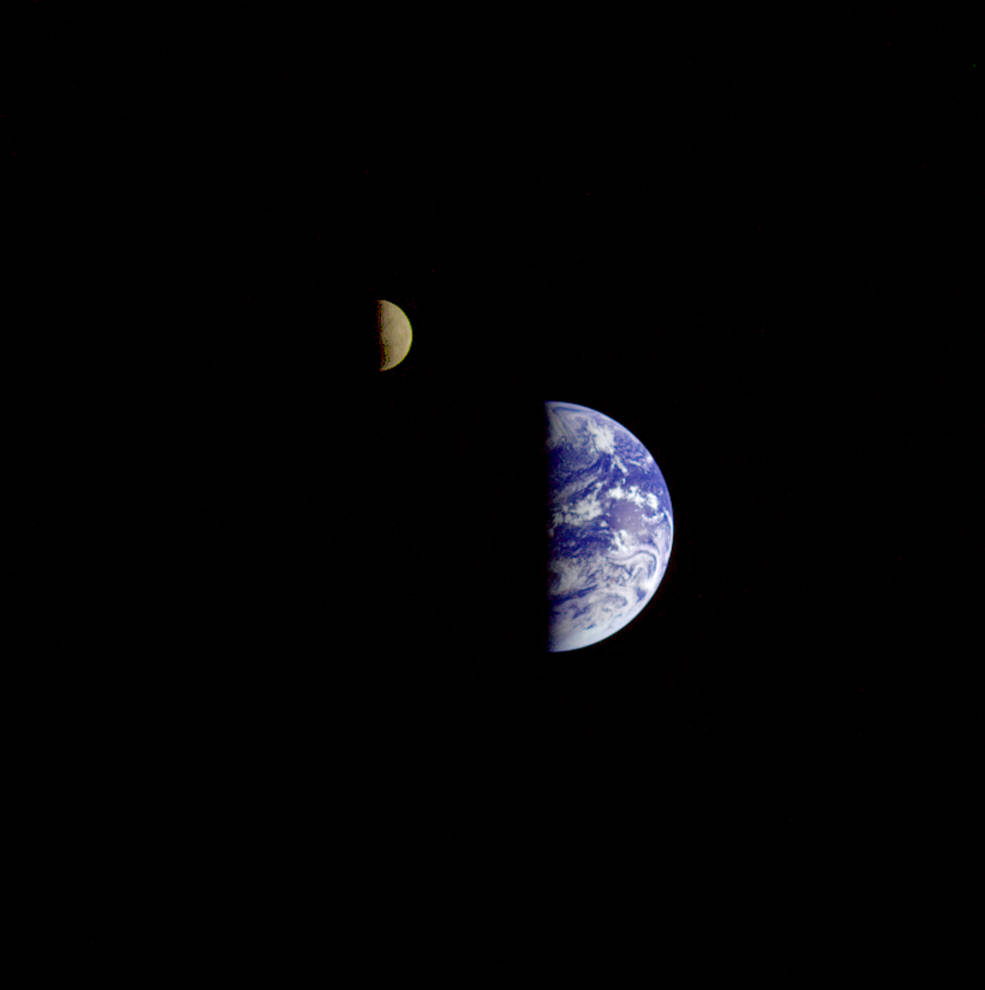
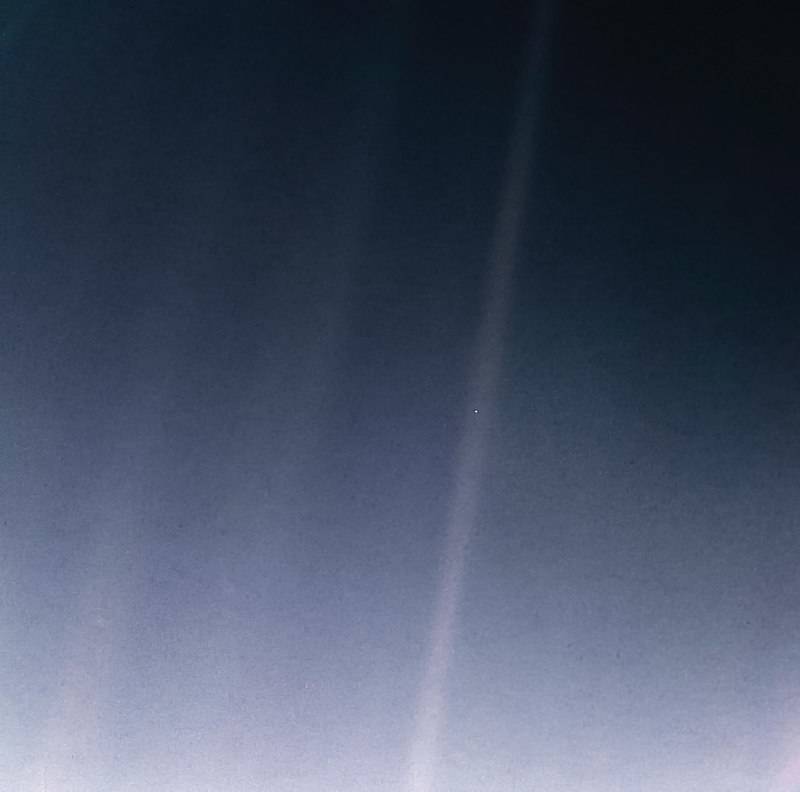
On Feb. 14, 1990, more than 12 years after it began its journey from Earth and shortly before controllers permanently turned off its cameras to conserve power, Voyager 1 spun around and pointed them back into the solar system. In a mosaic of 60 images, it captured a “family portrait” of six of the solar system’s planets, including a pale blue dot called Earth more than 3.7 billion miles away. Fittingly, these were the last pictures returned from either Voyager spacecraft. On Feb. 17, 1998, Voyager 1 became the most distant human-made object, overtaking the Pioneer 10 spacecraft on their way out of the solar system. In February 2020, to commemorate the photograph’s 30th anniversary, NASA released a remastered version of the image of Earth as Pale Blue Dot Revisited .

On New Year’s Day 1990, both spacecraft officially began the Voyager Interstellar Mission as they inexorably made their escape from our solar system. On Aug. 25, 2012, Voyager 1 passed beyond the heliopause, the boundary between the heliosphere, the bubble-like region of space created by the Sun, and the interstellar medium. Its twin followed suit six years later. Today , 45 years after its launch and 14.6 billion miles from Earth, four of Voyager 1’s 11 instruments continue to return useful data, having now spent 10 years in interstellar space. Signals from the spacecraft take nearly 22 hours to reach Earth, and 22 hours for Earth-based signals to reach the spacecraft. Engineers expect that the spacecraft will continue to return data from interstellar space until about 2025 when it will no longer be able to power its systems. And just in case an alien intelligence finds it one day, Voyager 1 like its twin carries a gold-plated record that contains information about its home planet, including recordings of terrestrial sounds, music, and greetings in 55 languages. Engineers at NASA thoughtfully included Instructions on how to play the record.

The voyage continues…
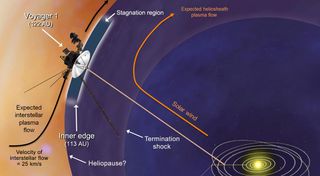
How Do We Know When Voyager Reaches Interstellar Space?

Why the debate about if and when Voyager 1 reached interstellar space is so complicated.
"We have been cautious because we're dealing with one of the most important milestones in the history of exploration," said Voyager Project Scientist Ed Stone of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. "Only now do we have the data -- and the analysis -- we needed."
Basically, the team needed more data on plasma, which is ionized gas, the densest and slowest moving of charged particles in space. (The glow of neon in a storefront sign is an example of plasma.) Plasma is the most important marker that distinguishes whether Voyager 1 is inside the solar bubble, known as the heliosphere, which is inflated by plasma that streams outward from our sun, or in interstellar space and surrounded by material ejected by the explosion of nearby giant stars millions of years ago. Adding to the challenge: they didn't know how they'd be able to detect it.
"We looked for the signs predicted by the models that use the best available data, but until now we had no measurements of the plasma from Voyager 1," said Stone. Scientific debates can take years, even decades to settle, especially when more data are needed. It took decades, for instance, for scientists to understand the idea of plate tectonics, the theory that explains the shape of Earth's continents and the structure of its sea floors. First introduced in the 1910s, continental drift and related ideas were controversial for years. A mature theory of plate tectonics didn't emerge until the 1950s and 1960s. Only after scientists gathered data showing that sea floors slowly spread out from mid-ocean ridges did they finally start accepting the theory. Most active geophysicists accepted plate tectonics by the late 1960s, though some never did. Voyager 1 is exploring an even more unfamiliar place than our Earth's sea floors -- a place more than 11 billion miles (17 billion kilometers) away from our sun. It has been sending back so much unexpected data that the science team has been grappling with the question of how to explain all the information. None of the handful of models the Voyager team uses as blueprints have accounted for the observations about the transition between our heliosphere and the interstellar medium in detail. The team has known it might take months, or longer, to understand the data fully and draw their conclusions. "No one has been to interstellar space before, and it's like traveling with guidebooks that are incomplete," said Stone. "Still, uncertainty is part of exploration. We wouldn't go exploring if we knew exactly what we'd find." The two Voyager spacecraft were launched in 1977 and, between them, had visited Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune by 1989. Voyager 1's plasma instrument, which measures the density, temperature and speed of plasma, stopped working in 1980, right after its last planetary flyby. When Voyager 1 detected the pressure of interstellar space on our heliosphere in 2004, the science team didn't have the instrument that would provide the most direct measurements of plasma. Instead, they focused on the direction of the magnetic field as a proxy for source of the plasma. Since solar plasma carries the magnetic field lines emanating from the sun and interstellar plasma carries interstellar magnetic field lines, the directions of the solar and interstellar magnetic fields were expected to differ. Most models told the Voyager science team to expect an abrupt change in the magnetic field direction as Voyager switched from the solar magnetic field lines inside our solar bubble to those in interstellar space. The models also said to expect the levels of charged particles originating from inside the heliosphere to drop and the levels of galactic cosmic rays, which originate outside the heliosphere, to jump. In May 2012, the number of galactic cosmic rays made its first significant jump, while some of the inside particles made their first significant dip. The pace of change quickened dramatically on July 28, 2012. After five days, the intensities returned to what they had been. This was the first taste of a new region, and at the time Voyager scientists thought the spacecraft might have briefly touched the edge of interstellar space. By Aug. 25, when, as we now know, Voyager 1 entered this new region for good, all the lower-energy particles from inside zipped away. Some inside particles dropped by more than a factor of 1,000 compared to 2004. The levels of galactic cosmic rays jumped to the highest of the entire mission. These would be the expected changes if Voyager 1 had crossed the heliopause, which is the boundary between the heliosphere and interstellar space. However, subsequent analysis of the magnetic field data revealed that even though the magnetic field strength jumped by 60 percent at the boundary, the direction changed less than 2 degrees. This suggested that Voyager 1 had not left the solar magnetic field and had only entered a new region, still inside our solar bubble, that had been depleted of inside particles. Then, in April 2013, scientists got another piece of the puzzle by chance. For the first eight years of exploring the heliosheath, which is the outer layer of the heliosphere, Voyager's plasma wave instrument had heard nothing. But the plasma wave science team, led by Don Gurnett and Bill Kurth at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, had observed bursts of radio waves in 1983 to 1984 and again in 1992 to 1993. They deduced these bursts were produced by the interstellar plasma when a large outburst of solar material would plow into it and cause it to oscillate. It took about 400 days for such solar outbursts to reach interstellar space, leading to an estimated distance of 117 to 177 AU (117 to 177 times the distance from the sun to the Earth) to the heliopause. They knew, though, that they would be able to observe plasma oscillations directly once Voyager 1 was surrounded by interstellar plasma. Then on April 9, 2013, it happened: Voyager 1's plasma wave instrument picked up local plasma oscillations. Scientists think they probably stemmed from a burst of solar activity from a year before, a burst that has become known as the St. Patrick's Day Solar Storms. The oscillations increased in pitch through May 22 and indicated that Voyager was moving into an increasingly dense region of plasma. This plasma had the signatures of interstellar plasma, with a density more than 40 times that observed by Voyager 2 in the heliosheath. Gurnett and Kurth began going through the recent data and found a fainter, lower-frequency set of oscillations from Oct. 23 to Nov. 27, 2012. When they extrapolated back, they deduced that Voyager had first encountered this dense interstellar plasma in August 2012, consistent with the sharp boundaries in the charged particle and magnetic field data on August 25. Stone called three meetings of the Voyager team. They had to decide how to define the boundary between our solar bubble and interstellar space and how to interpret all the data Voyager 1 had been sending back. There was general agreement Voyager 1 was seeing interstellar plasma, based on the results from Gurnett and Kurth, but the sun still had influence. One persisting sign of solar influence, for example, was the detection of outside particles hitting Voyager from some directions more than others. In interstellar space, these particles would be expected to hit Voyager uniformly from all directions. "Now that we had actual measurements of the plasma environment - by way of an unexpected outburst from the sun - we had to reconsider why there was still solar influence on the magnetic field and plasma in interstellar space," Stone said. "The path to interstellar space has been a lot more complicated than we imagined." Stone discussed with the Voyager science group whether they thought Voyager 1 had crossed the heliopause. What should they call the region were Voyager 1 is? "In the end, there was general agreement that Voyager 1 was indeed outside in interstellar space," Stone said. "But that location comes with some disclaimers - we're in a mixed, transitional region of interstellar space. We don't know when we'll reach interstellar space free from the influence of our solar bubble." So, would the team say Voyager 1 has left the solar system? Not exactly - and that's part of the confusion. Since the 1960s, most scientists have defined our solar system as going out to the Oort Cloud, where the comets that swing by our sun on long timescales originate. That area is where the gravity of other stars begins to dominate that of the sun. It will take about 300 years for Voyager 1 to reach the inner edge of the Oort Cloud and possibly about 30,000 years to fly beyond it. Informally, of course, "solar system" typically means the planetary neighborhood around our sun. Because of this ambiguity, the Voyager team has lately favored talking about interstellar space, which is specifically the space between each star's realm of plasma influence. "What we can say is Voyager 1 is bathed in matter from other stars," Stone said. "What we can't say is what exact discoveries await Voyager's continued journey. No one was able to predict all of the details that Voyager 1 has seen. So we expect more surprises." Voyager 1, which is working with a finite power supply, has enough electrical power to keep operating the fields and particles science instruments through at least 2020, which will mark 43 years of continual operation. At that point, mission managers will have to start turning off these instruments one by one to conserve power, with the last one turning off around 2025. Voyager 1 will continue sending engineering data for a few more years after the last science instrument is turned off, but after that it will be sailing on as a silent ambassador. In about 40,000 years, it will be closer to the star AC +79 3888 than our own sun. (AC +79 3888 is traveling toward us faster than we are traveling towards it, so while Alpha Centauri is the next closest star now, it won't be in 40,000 years.) And for the rest of time, Voyager 1 will continue orbiting around the heart of the Milky Way galaxy, with our sun but a tiny point of light among many. The Voyager spacecraft were built and continue to be operated by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in Pasadena, Calif. Caltech manages JPL for NASA. The Voyager missions are a part of NASA's Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. For more information about Voyager, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/voyager and http://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov .
News Media Contact
Jia-Rui Cook
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
818-354-0724
After Months of Glitches and Gradual Fixes, Voyager 1 Is Fully Operational Once Again
Currently 15 billion miles away from Earth, one of NASA’s longest-tenured spacecraft is back from the brink after a technical failure last year put its future in question
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/ChristianThorsberg_Headshot.png)
Christian Thorsberg
Daily Correspondent
:focal(4096x2321:4097x2322)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/c1/85/c185108a-791f-4610-9084-98dcb2c0a49a/voyager2.jpg)
After a technical malfunction late last year rendered all of its subsequent readings as useless , NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft—which has spent nearly a half-century in space—has been brought back online and is once again fully functioning.
“The spacecraft has resumed gathering information about interstellar space,” NASA said in a press release .
Launched in 1977 and drifting some 15 billion miles away from Earth, on the outer reaches of our solar system, the satellite is both one of the world’s oldest-tenured crafts and currently the most distant—making its recovery from what was once presumed a dismal prognosis nothing short of miraculous.
Last November, the satellite began transmitting unintelligible strings of data, as opposed to the binary code it is supposed to send, back to NASA’s scientists. Initial efforts to diagnose and fix the problem were tedious. New commands took nearly a full day, 22.5 hours, to reach Voyager 1, and responses took an equal amount of time.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/4a/b3/4ab36e30-501d-4e86-98cb-8d2d039b7917/voyager4.jpg)
“Finding solutions to challenges the probes encounter often entails consulting original, decades-old documents written by engineers who didn’t anticipate the issues that are arising today,” Miles Hatfield wrote in a December NASA press release . “As a result, it takes time for the team to understand how a new command will affect the spacecraft’s operations in order to avoid unintended consequences.”
Waiting 45 hours between individual troubleshooting efforts was tedious. But incremental gains were made, and after five months of steady trial and error, the team found that Voyager 1’s problem lay in its flight data subsystem (FDS), which packages earthbound data. They pinpointed one faulty chip in particular, and were able to engineer a work-around.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/04/33/043302ae-8e02-4bbe-ae32-31b8dada23b9/voyager6.jpg)
In April, they enjoyed a breakthrough: a health and status report that indicated the satellite was still capable of lucid communication.
“Today was a great day for Voyager 1,” Linda Spilker, a Voyager project scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), said in a statement from that weekend, CNN’s Ashley Strickland reported. “We’re back in communication with the spacecraft. And we look forward to getting science data back.”
The team didn’t need to wait long. In late May, two of the spacecraft’s four scientific instruments began sending usable scientific data once again: the “bunny-eared” plasma wave subsystem , which protrudes 30 feet off the spacecraft and measures electron density, and the magnetometer instrument , which measures and analyzes the magnetic fields of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/22/4d/224dbde8-e9c0-4115-93ae-e92f94ef3892/voyager5.jpg)
“NASA has previously estimated that the nuclear-powered generators on Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 were likely to die around 2025,” the New York Times’ Orlando Mayorquín reports.
But, if they can survive until 2027, both spacecraft will reach their 50th anniversary.
Voyagers 1 and 2 are NASA’s only spacecraft to have explored outside of the sun’s heliosphere. Over the decades, they have explored the solar system’s gas giant planets and 48 moons . They also carry the Voyager Golden Records , intended to share sounds and images of Earth with alien civilizations.
“That's here. That's home. That's us. On it everyone you love, everyone you know, everyone you ever heard of, every human being who ever was, lived out their lives,” astronomer Carl Sagan famously said in 1990 on the day Voyager 1 took the iconic “pale blue dot” image of Earth at a distance of 3.7 billion miles from the sun.
Get the latest stories in your inbox every weekday.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/ChristianThorsberg_Headshot.png)
Christian Thorsberg | READ MORE
Christian Thorsberg is an environmental writer and photographer from Chicago. His work, which often centers on freshwater issues, climate change and subsistence, has appeared in Circle of Blue , Sierra magazine, Discover magazine and Alaska Sporting Journal .
Voyager 1 Spacecraft's Road to Interstellar Space: A Photo Timeline
Nasa's voyager 1 spacecraft.

NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft launched in 1977 and reached interstellar space 35 years later. Take a look at Voyager 1's bold journey into a new space frontier with this SPACE.com timeline. [ See SPACE.com's Compete Coverage: Voyager 1 In Interstellar Space ]
Sept. 5, 1977: Voyager 1 Launch

This photo shows NASA's Voyager 2's launch on Aug. 20, 1977. Voyager 1 launched on Sept. 5 of the same year. [ See SPACE.com's Compete Coverage: Voyager 1 In Interstellar Space ]
Sept. 5, 1977: Voyager 1 Snaps Photo of Earth and Moon

This image of the Earth and moon in a single frame, the first of its kind ever taken by a spacecraft, was recorded on Sept. 18, 1977, by Voyager 1 when it was 7.25 million miles from Earth. The moon is at the top of the picture and beyond the Earth as viewed by Voyager. [ See SPACE.com's Compete Coverage: Voyager 1 In Interstellar Space ]
March 5, 1979: Voyager 1 Makes Jupiter Flyby

Voyager 1 took photos of Jupiter and two of its satellites (Io, left, and Europa). The new study says that moons orbiting a gas giant planet greater than 8 Jupiter masses could help astronomers detect a rogue planet. [ See SPACE.com's Compete Coverage: Voyager 1 In Interstellar Space ]
Nov. 12, 1980: Voyager 1 Flies By Saturn

NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft revealed the kinks in one of Saturn's narrowest rings. The Voyager 1 image (left) was released on Nov. 12, 1980. The closer view of the F ring (right) was obtained by NASA's Cassini spacecraft on April 13, 2005. The moon Pandora is to the left (exterior) of the ring and the moon Prometheus is to the right (interior) of the ring. [ See SPACE.com's Compete Coverage: Voyager 1 In Interstellar Space ]
1982: NASA Upgrades Deep Space Network Antennas

In 1982, NASA upgraded its Deep Space Network of antennas which it uses to control and receive messages from Voyager 1 and its twin Voyager 2. [ See SPACE.com's Compete Coverage: Voyager 1 In Interstellar Space ]
Jan. 1, 1990: Voyager Begins Extended' Interstellar Mission '
This artist's concept shows plasma flows around NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft as it gets close to entering interstellar space. The orange arrow shows the direction of the solar wind. Image released Dec. 3, 2012. [ See SPACE.com's Compete Coverage: Voyager 1 In Interstellar Space ]
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Feb. 14, 1990: Voyager Takes Final Solar System Portrait

This narrow-angle color image of the Earth s a part of the first ever "portrait" of the solar system taken by Voyager 1. The spacecraft acquired a total of 60 frames for a mosaic of the solar system from a distance of more than 4 billion miles from Earth and about 32 degrees above the ecliptic. Image released Feb. 14, 1990. [ See SPACE.com's Compete Coverage: Voyager 1 In Interstellar Space ]
Feb. 17, 1998: Voyager 1 passes Pioneer 10
On Feb. 17, 1998, Voyager 1 became the farthest manmade object in space when it passed Pioneer 10 on the way out of the solar system. [ See SPACE.com's Compete Coverage: Voyager 1 In Interstellar Space ]
Voyager Signal Spotted By Earth Radio Telescopes
In 1990, Voyager 1 took the famous "Pale Blue Dot" picture looking back at Earth. In 2013, the Very Long Baseline Array got the reverse-angle shot — this radio telescope image showing the signal of the spacecraft as a similar point of light. Image released Sept. 12, 2013. [ See SPACE.com's Compete Coverage: Voyager 1 In Interstellar Space ]
August 2012: Voyager Enters Interstellar Space

This artist's concept depicts NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft entering interstellar space, or the space between stars. Interstellar space is dominated by the plasma, or ionized gas, that was ejected by the death of nearby giant stars millions of years ago. The environment inside our solar bubble is dominated by the plasma exhausted by our sun, known as the solar wind. The interstellar plasma is shown with an orange glow similar to the color seen in visible-light images from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope that show stars in the Orion nebula traveling through interstellar space. Image released Sept. 12, 2013. [ See SPACE.com's Compete Coverage: Voyager 1 In Interstellar Space ]
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].
Current page: Page 1
Tariq is the Editor-in-Chief of Space.com and joined the team in 2001, first as an intern and staff writer, and later as an editor. He covers human spaceflight, exploration and space science, as well as skywatching and entertainment. He became Space.com's Managing Editor in 2009 and Editor-in-Chief in 2019. Before joining Space.com, Tariq was a staff reporter for The Los Angeles Times covering education and city beats in La Habra, Fullerton and Huntington Beach. In October 2022, Tariq received the Harry Kolcum Award for excellence in space reporting from the National Space Club Florida Committee. He is also an Eagle Scout (yes, he has the Space Exploration merit badge) and went to Space Camp four times as a kid and a fifth time as an adult. He has journalism degrees from the University of Southern California and New York University. You can find Tariq at Space.com and as the co-host to the This Week In Space podcast with space historian Rod Pyle on the TWiT network . To see his latest project, you can follow Tariq on Twitter @tariqjmalik .
SpaceX launches 20 Starlink satellites from California
NASA, Boeing delay Starliner astronaut landing to June 26 amid thruster issues
Why smaller planets are better at building large moons
Most Popular
- 2 Strawberry Solstice Moon of June 2024 shines tonight for summer stargazers (video)
- 3 Pentagon picks SpaceX, Blue Origin and ULA for $5.6 billion launch deal
- 4 Saturn's planet-wide storms driven by seasonal heating, Cassini probe reveals
- 5 How neutron stars 'playing it cool' could unlock exotic physics
Where is Voyager 1 now? Repairs bring space probe back online as journey nears 50 years
After many months of extremely long-distance repairs, NASA’s Voyager 1 space probe is fully operational once again.
“The spacecraft has resumed gathering information about interstellar space,” the agency announced last Thursday, and has resumed its normal operations.
The spacecraft , now travelling through interstellar space more than 15 billion miles from Earth, began sending back corrupted science and engineering data last November.
Over the ensuing months, engineers worked to troubleshoot the problem, a tedious and complicated process given the vast distance between Earth and Voyager 1. Each message took 22.5 hours to transmit, meaning each communication between engineers and the spacecraft was a nearly two day long process.
By April, NASA engineers had traced to root of the problem to a single chip in Voyager 1’s Flight Data System, allowing them to begin rearranging lines of computer code so that the spacecraft could continue transmitting data. Last month, NASA announced that it had restored functionality to two of the spacecraft’s science instruments, followed by the announcement last week that Voyager 1 had been fully restored to normal operations.
Voyager 1: Still traveling 1 million miles per day
Launched in 1977 along with its sister craft Voyager 2, the twin craft are robotic space probes that are now the longest operating spacecraft in history. Their initial mission was to study the outer planets of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune, but they have continued their long journey in the ensuing decades, travelling farther and wider than any other man-made object in history.
In 1990, Voyager 1 transmitted the famous “ Pale Blue Dot ” photograph of Earth, taken when the spacecraft was 3.7 billion miles from the Sun.
By 2012, Voyager 1 became the first spacecraft to enter interstellar space, where they have continued transmit data on plasma waves, magnetic fields and particles in the heliosphere – the outermost region of space directly influenced by the Sun.
As part of their one-way mission, both Voyager spacecraft also carry copies of the “ Golden Records ,” gold plated copper discs containing sounds and images from Earth that were curated by the astronomer Carl Sagan.
Currently travelling roughly one million miles per day, Voyager 1 will continue it journey until at least early next year, when NASA estimates that diminishing power levels may “ prevent further operation .”
MayflowerHistory.com
Voyage of the mayflower.

The Mayflower was hired in London, and sailed from London to Southampton in July 1620 to begin loading food and supplies for the voyage--much of which was purchased at Southampton. The Pilgrims were mostly still living in the city of Leiden, in the Netherlands. They hired a ship called the Speedwell to take them from Delfshaven, the Netherlands, to Southampton, England, to meet up with the Mayflower . The two ships planned to sail together to Northern Virginia. The Speedwell departed Delfthaven on July 22, and arrived at Southampton, where they found the Mayflower waiting for them. The Speedwell had been leaking on her voyage from the Netherlands to England, though, so they spent the next week patching her up.
On August 5, the two ships finally set sail for America. But the Speedwell began leaking again, so they pulled into the town of Dartmouth for repairs, arriving there about August 12. The Speedwell was patched up again, and the two ships again set sail for America about August 21. After the two ships had sailed about 300 miles out to sea, the Speedwell again began to leak. Frustrated with the enormous amount of time lost, and their inability to fix the Speedwell so that it could be sea-worthy, they returned to Plymouth, England, and made the decision to leave the Speedwell behind. The Mayflower would go to America alone. The cargo on the Speedwell was transferred over to the Mayflower ; some of the passengers were so tired and disappointed with all the problems that they quit and went home. Others crammed themselves onto the already very crowded Mayflower .

Finally, on September 6, the Mayflower departed from Plymouth, England, and headed for America. By the time the Pilgrims had left England, they had already been living onboard the ships for nearly a month and a half. The voyage itself across the Atlantic Ocean took 66 days, from their departure on September 6, until Cape Cod was sighted on 9 November 1620. The first half of the voyage went fairly smoothly, the only major problem was sea-sickness. But by October, they began encountering a number of Atlantic storms that made the voyage treacherous. Several times, the wind was so strong they had to just drift where the weather took them, it was not safe to use the ship's sails. The Pilgrims intended to land in Northern Virginia, which at the time included the region as far north as the Hudson River in the modern State of New York. The Hudson River, in fact, was their originally intended destination. They had received good reports on this region while in the Netherlands. All things considered, the Mayflower was almost right on target, missing the Hudson River by just a few degrees.
As the Mayflower approached land, the crew spotted Cape Cod just as the sun rose on November 9. The Pilgrims decided to head south, to the mouth of the Hudson River in New York, where they intended to make their plantation. However, as the Mayflower headed south, it encountered some very rough seas, and nearly shipwrecked. The Pilgrims then decided, rather than risk another attempt to go south, they would just stay and explore Cape Cod. They turned back north, rounded the tip, and anchored in what is now Provincetown Harbor. The Pilgrims would spend the next month and a half exploring Cape Cod, trying to decide where they would build their plantation. On December 25, 1620, they had finally decided upon Plymouth, and began construction of their first buildings.
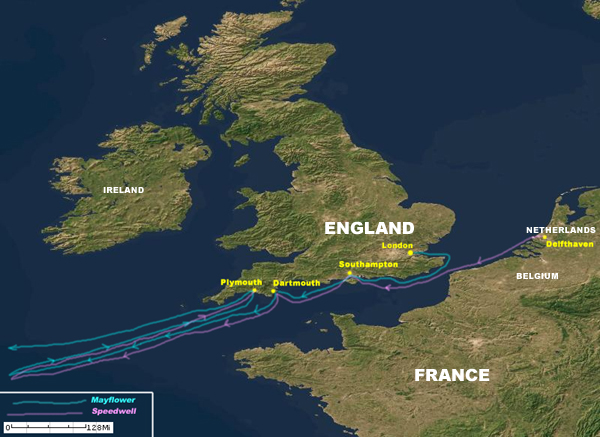
The Mayflower attempted to depart England on three occasions, once from Southampton on 5 August 1620; once from Darthmouth on 21 August 1620; and finally from Plymouth, England, on 6 September 1620.
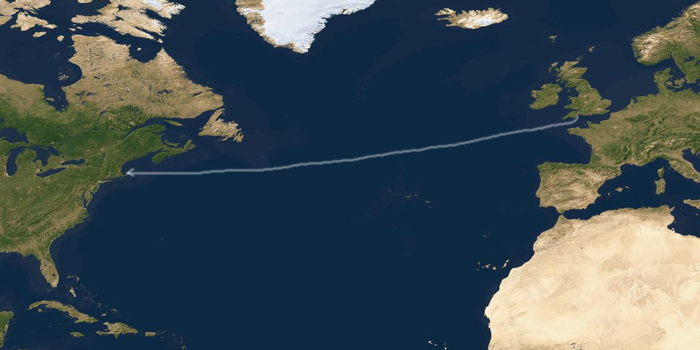
The Mayflower departed Plymouth, England, on 6 September 1620 and arrived at Cape Cod on 9 November 1620, after a 66 day voyage.
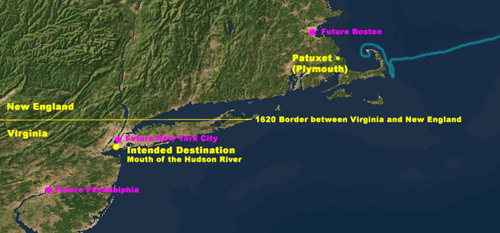
After sighting Cape Cod, the Mayflower heads south hoping to reach the mouth of the Hudson River in modern-day New York (then a part of Northern Virginia), but were forced back to Provincetown Harbor in Cape Cod after encountering treacherous seas.

The Ship In Which A Famous British-Irish Explorer Of Antarctica Made His Final Voyage Was Discovered On The Seafloor Off The Coast Of Canada
T he wreck of the ship on which Ernest Shackleton made his final voyage was recently discovered on the seafloor off the coast of the Labrador Sea in Canada.
Shackleton was a famous British-Irish explorer of Antarctica. He suffered a heart attack on board in 1922 while trying to reach the Antarctic. The ship continued to be used for Arctic research until it sank in 1962 during a whaling trip.
The vessel, called Quest , was found by the Royal Canadian Geographical Society. A team of researchers used sonar scans to locate the ship under thousands of feet of frigid water.
The Quest was found sitting upright on its keel. Its main mast was splintered and hung over the port side. The mast likely broke off when the vessel struck ice.
The Quest has great historical significance. Shackleton was revered for his travels to the Antarctic because very few people had been able to venture into the frozen landscape at that time. His death marked the end of what is known as the “heroic age” of Antarctic exploration.
The adventurer led three expeditions to the Antarctic. He died of a heart attack at the age of 47 during a fourth journey. The ship had been just off South Georgia, east of the Falkan Islands located in the South Atlantic.
Shackleton had originally bought the schooner-rigged steamship to travel to Canada’s High Arctic. But, he ended up changing his mind and set sail for the Antarctic once again.
The ship was built in Norway and measured about 124 feet in length. Its remains were in excellent condition, even though it experienced damage from ice.
Researchers don’t have plans to haul the wreckage to the surface, as it would be too costly. Instead, they will conduct a series of dives in the near future to study and document the details of the vessel further.
Sign up for Chip Chick’s newsletter and get stories like this delivered to your inbox.
“Right now, we don’t intend to touch the wreck. It actually lies in an already protected area for wildlife, so nobody should be touching it,” said associate search director Antoine Normandin. “But we do hope to go back and photograph it with a remotely operated vehicle to really understand its state.”
In 2022, researchers identified another one of Shackleton’s ships. They found the Endurance in about 10,000 feet of icy water about a century after its sinking.
A team of experts used an icebreaker ship and underwater drones to detect the wreck at the bottom of the Wendell Sea near the Antarctica Peninsula.
Ernest Shackleton will continue to live on as one of the greatest explorers of all time. He made groundbreaking achievements in exploration and was known for looking after his crew. Every year, hundreds of people still visit his grave to pay their respects.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Voyager 1 flew within 64,200 kilometers (40,000 miles) of the cloud tops, while Voyager 2 came within 41,000 kilometers (26,000 miles). Saturn is the second largest planet in the solar system. It takes 29.5 Earth years to complete one orbit of the Sun, and its day was clocked at 10 hours, 39 minutes.
Present Status. As of April 2020, Voyager 1 is at a distance of 22.3 billion kilometers (149.0 AU) from the Sun. Voyager 2 was at a distance of 18.5 billion kilometers (123.6 AU). Voyager 1 is escaping the solar system at a speed of about 3.6 AU per year. Voyager 2 is escaping the solar system at a speed of about 3.3 AU per year.
Mission Overview. The twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before. Continuing on their more-than-40-year journey since their 1977 launches, they each are much farther away from Earth and the sun than Pluto. In August 2012, Voyager 1 made the historic entry into interstellar space, the region between ...
A poster of the planets and moons visited during the Voyager program. The Voyager program is an American scientific program that employs two interstellar ... (7.9 in) focal length wide-angle lens with an aperture of f/3 (the wide-angle camera), while the other uses a higher resolution 1,500 mm (59 in) narrow-angle f/8.5 lens (the narrow-angle ...
The twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before. Continuing on their more-than-45-year journey since their 1977 launches, they each are much farther away from Earth and the Sun than Pluto.
Beyond Expectations. Voyager 2 launched on Aug. 20, 1977, quickly followed by Voyager 1 on Sept. 5. Both probes traveled to Jupiter and Saturn, with Voyager 1 moving faster and reaching them first. Together, the probes unveiled much about the solar system's two largest planets and their moons.
Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have reached "interstellar space" and each continue their unique journey deeper into the cosmos. In NASA's Eyes on the Solar System app, you can see the actual spacecraft trajectories of the Voyagers updated every five minutes.
Voyager 1 is the first spacecraft to travel beyond the solar system and reach interstellar space . The probe launched on Sept. 5, 1977 — about two weeks after its twin Voyager 2 — and as of ...
Voyager 2 launched on Aug. 20, 1977, quickly followed by Voyager 1 on Sept. 5. Both probes traveled to Jupiter and Saturn, with Voyager 1 moving faster and reaching them first.
4. Voyager's average speed Surprisingly, concerning Voyager's normal cruising speed some considerable changes were made recently, although both fans and official sources presupposed for years that Voyager covers, based on a journey of 75 years and the revised distance of 75000 ly, 1000 ly per year, what corresponds to warp 7.9.
Forty-five years ago, the Voyager 1 spacecraft began an epic journey that continues to this day. The second of a pair of spacecraft, Voyager 1 lifted off on Sept. 5, 1977, 16 days after its twin left on a similar voyage. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, managed the two spacecraft on their missions to explore the outer planets.
This was the first taste of a new region, and at the time Voyager scientists thought the spacecraft might have briefly touched the edge of interstellar space. By Aug. 25, when, as we now know, Voyager 1 entered this new region for good, all the lower-energy particles from inside zipped away. Some inside particles dropped by more than a factor ...
Voyager 1 is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and the interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. ... Both Voyagers measured the rotation of Saturn (the length of a day) at 10 hours, 39 minutes, 24 seconds.
Explore the farthest reaches of the solar system with Voyager, NASA's longest-running and most iconic mission. Learn about the spacecraft, the discoveries, and the interstellar journey.
NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is fully operational for the first time since November 2023, with all four science instruments returning usable data to Earth. ... Continuing its journey away from ...
New commands took nearly a full day, 22.5 hours, to reach Voyager 1, and responses took an equal amount of time. A photo of Jupiter's Great Red Spot, taken by Voyager 1 on March 1, 1979.
NASA . NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft launched in 1977 and reached interstellar space 35 years later. Take a look at Voyager 1's bold journey into a new space frontier with this SPACE.com timeline.
Voyager 2 is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, as a part of the Voyager program. ... The length of a day on Uranus as measured by Voyager 2 is 17 hours, 14 minutes. Uranus was shown to have a magnetic field that was misaligned with its rotational axis, ...
In 1977, The Voyager program sent two spacecraft to explore the solar system and travel to interstellar space. In this video from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, learn how Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 are now the farthest any spacecraft has traveled from the Sun, and are still making discoveries in the outer reaches of the solar system. As they continue outward beyond the heliosphere, they will ...
Voyager 1: Still traveling 1 million miles per day. Launched in 1977 along with its sister craft Voyager 2, the twin craft are robotic space probes that are now the longest operating spacecraft in ...
Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have reached "Interstellar space" and each continue their unique journey through the Universe. In the NASA Eyes on the Solar System app, you can see the real spacecraft trajectories of the Voyagers, which are updated every five minutes. Distance and velocities are updated in real-time.
The voyage itself across the Atlantic Ocean took 66 days, from their departure on September 6, until Cape Cod was sighted on 9 November 1620. The first half of the voyage went fairly smoothly, the only major problem was sea-sickness. But by October, they began encountering a number of Atlantic storms that made the voyage treacherous. ...
Starliner's journey to this historic crewed test mission began in 2014 when NASA tapped both Boeing and SpaceX to develop a spacecraft capable of carrying astronauts to the International Space ...
The Project Begins. "Mariner Jupiter/Saturn 1977," the name of the mission before it became Voyager, is approved by NASA, with day-to-day management by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The original plans commit only to flybys of Jupiter and Saturn and build upon the heritage of earlier Mariner spacecraft that flew by ...
The wreck of the ship on which Ernest Shackleton made his final voyage was recently discovered on the seafloor off the coast of the Labrador Sea in Canada. Shackleton was a famous British-Irish ...