- svg]:fill-accent-900"> 826K
- svg]:fill-accent-900"> 622K
- svg]:fill-accent-900"> 246K
- svg]:fill-accent-900"> 45K

Why Is My Circuit Breaker Tripping? 4 Potential Problems and Solutions
By Glenda Taylor , Bob Vila , Evelyn Auer
Updated on Dec 15, 2023 4:16 AM EST
We may earn revenue from the products available on this page and participate in affiliate programs. Learn More ›
What You Need to Know
- A tripping circuit breaker could be a sign of an overloaded circuit, a short circuit, a ground fault, or a worn-out breaker.
- Homeowners will want to hire an electrician to determine the cause of the frequently tripping circuit breaker.
- Electricians may recommend replacing the circuit breaker, installing GFCI outlets, or rewiring part or all of the home.
Q: Every few hours—sometimes minutes!—my living room and one side of my kitchen lose electrical power. I’ll check the breaker panel and, sure enough, a circuit breaker has tripped…again. Should I call an electrician, or is there a simple DIY fix I can try first?
A: While it’s frustrating when a circuit breaker keeps tripping, they are important safety mechanisms. Designed to shut off the electrical current when something goes wrong, circuit breakers are one of the best ways of protecting a home from an electrical fire. “When a circuit breaker trips, typically it is because we use too much electricity, which causes it to overload and turn off,” says Christopher Haas, expert electrician and owner of Haas & Sons Electric in Millersville, Maryland. For those who need an electrical panels 101 refresher course or aren’t sure how to reset circuit breakers, each breaker has an on/off switch and controls a separate electrical circuit in the home. When a breaker trips, its switch automatically flips “off,” and it must be manually turned back on to restore electricity to the circuit. For those wondering, “Is it dangerous if a circuit breaker keeps tripping?” the answer is that it can be, depending on the source of the problem. An electrician can ultimately deal with the root issue, but a little sleuthing will reveal whether it’s something that’s easily remedied.
In many cases, the cause of a circuit breaking tripping is an overloaded circuit.
A circuit overloads when more electrical current is being drawn through the wires than they can handle, tripping the circuit breaker. If this happens, there may be a few additional signs:
- Buzzing noises coming from outlets
- Devices charging slowly
- Electrical outlets not working
- Flickering lights
- Scorch marks on outlets and light switches
If a circuit breaker keeps tripping in one room, homeowners can test for circuit overload by turning off all the switches in the affected area and unplugging all appliances and devices. After the breaker is flipped back on, the devices can be turned back on one at a time, with homeowners waiting a few minutes in between to see if the circuit remains on. If the breaker trips before all the appliances are turned on, the experiment can be repeated, this time turning them on in a different order. It may be necessary to do this several times to find out how many appliances can be operated at once before the circuit overloads.
“As a short-term solution, you can unplug unnecessary appliances to prevent tripping circuit breakers. You may still get some trips, but you can limit them by unplugging devices that you don’t need to use,” advises Dan Mock, vice president of operations at Mister Sparky , an electrical company with 90 locations in the U.S. The best long-term solution, however, is to pay an electrician for the cost to rewire the house and add additional circuits. The cost to replace an electrical panel is about $1,274 on average.

Other times, the issue may be caused by a short circuit.
A “short” circuit means that two wires that should not be coming into contact are inadvertently touching, triggering a sudden surge of electricity through the wires. A short can occur in an outlet, a switch, or within an appliance if wires are loose or have been chewed through by mice or pets. Some signs of a short circuit include:
- Popping sounds
- Discolored outlets or switches
- Burning smells
Testing to see if an appliance has a short is similar to testing for an overloaded circuit. When an appliance that has a short in its wiring is turned on, it will immediately trip the circuit. Homeowners can also try plugging it into an outlet in a different room. If the breaker for that room trips, there’s a short in the appliance (if it’s unclear what breaker goes to what room, the breaker can be identified with one of the best circuit breaker finders ). Electrical shorts can be a major fire hazard, so it’s a good idea to call a licensed electrician for this circuit breaker repair. It’s wise to stop using the outlet or appliance until a pro takes care of the problem.
Another potential cause of a circuit breaker tripping is a ground fault.
A ground fault occurs when the electricity running through a home’s wiring diverts from the wiring loop and travels to the ground, usually due to faulty wiring or water infiltration in an outlet or switch box. Water is a conductor, which is why walking through puddles is often listed as something not to do in a power outage in case of downed power lines. Once water makes contact with wires, electricity can jump from the wiring loop and follow the water trail. This creates a surge in electricity leading to a tripped circuit breaker. If a person comes in contact with the electricity that is on its way to the ground, this can result in electrocution. Homeowners may notice a few signs of a ground fault, including:
- Tripped GFCI (ground fault circuit interrupter) outlets;
- A burning smell coming from an outlet; and
- Lights flickering.
Newer electrical breakers have features designed to protect against the danger of ground faults. According to Haas, “Ground fault breakers sense electricity going to earth as opposed to going through the wires of the circuit. You’ll find [these] for bathrooms, kitchens, garages, exteriors, and basements.” GFCI outlets are another safety feature that shut off the electric current within a fraction of a second of sensing a ground fault.
If a ground fault is the problem, the cause of the errant water must be discovered and repaired, and any damaged wiring must also be replaced. It’s also a good idea to install GFCI outlets in rooms where water is commonly used. A GFCI outlet costs $210 on average.
Sometimes a bad or worn-out circuit breaker can be the culprit.
In some cases, the circuit breaker itself may be faulty. Breakers that are old, damaged, or were installed incorrectly may trip frequently for no apparent reason. Alternatively, faulty breakers may not trip when they are supposed to, leaving the home at risk of electrical fire. Some signs of a bad circuit breaker include:
- The circuit breaker getting hot and tripping frequently;
- The circuit breaker won’t reset;
- It has been over 10 years since the breaker was last serviced; and
- The breaker has scorch marks.
An important electrical safety tip to keep in mind is that resetting a breaker over and over again can cause what is called an arc flash, which is a small electrical explosion that can be deadly. If resetting the breaker once does not remedy the issue, it’s a good idea for the homeowner to hire an electrician near them who knows how to replace a circuit breaker safely. Mock warns, “Don’t take any chances with circuit breakers. Instead, call a licensed electrician who knows the safe ways to replace breaker boxes, upgrade circuits, and diagnose potential electrical problems in your home.” Wiring a breaker box is a job to leave to an experienced electrician.
A professional electrician can help determine the specific cause of a frequently tripping circuit breaker.
Most circuit breaker problems—aside from those explained in the sections above—will need to be inspected and addressed by a licensed electrician. According to the Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI) , each year “thousands of people in the United States are critically injured and electrocuted as a result of electrical fires, accidents, [or] electrocution in their own homes.” While homeowners may be tempted to save on electrician costs by attempting circuit breaker replacement or repair themselves, electrical work is not suitable for casual DIYers. “Yes, you have to pay, but you can save many hours of head-scratching by hiring an electrician. Electricians will also have all the right tools for diagnosing and repairing the circuit,” Haas adds. “Lastly, they will come with a warranty/guarantee should something arise, and they will typically return at no additional cost.”
- Account Settings
Home Services
- Home Security
- Pest Control
- Living Room
- Other Rooms
Home Improvement
- Cost Guides
- Floor Plans
- Housekeeping
- Cleaning Tips
- Organization
- Popular Brands
- Sizes & Dimensions
Smart Living
- Dangerous Areas
- Safest Areas
- Most Affordable Areas
Top stories

Breaker Tripping With Nothing Plugged In (Why & How to Fix)

When we think of a circuit breaker that keeps tripping, common wisdom would be that you’re dealing with a home that’s using up too much energy. So, if it’s happening to you, you might unplug some stuff. But, sometimes, the breaker just will keep tripping regardless of how much stuff you unplug. Clearly, it’s not energy consumption anymore. So, what gives?
A circuit breaker can trip when there is nothing plugged in if there is a ground fault or the circuit breaker is outdated. Damaged wires within the circuit breaker can cause it to keep tripping for no reason. The average circuit breaker lasts for 35 years, and they can trip with nothing plugged in when they are over 30 years old.
Circuit breakers are necessary to prevent electrical problems, expensive damage, and most importantly fires. It can be alarming when your circuit breaker keeps tripping when there is nothing plugged in. Follow along as we explore what it means when your circuit breaker trips for no apparent reason.
Do You Need to Hire an Electrician?
Get free, zero-commitment quotes from pro contractors near you.

Why Would A Circuit Breaker Trip Without Anything Plugged In?
A breaker is meant to break electrical currents due to an overload, so it really shouldn’t be breaking without anything plugged in. This means that you might be dealing with an electrical issue regarding the breaker. This can be potentially dangerous, so it’s important to troubleshoot this as soon as possible, and call an electrician to fix it.
Troubleshooting Your Circuit Breaker
So, you already know that you’ve got a breaker that’s not doing what it’s supposed to do. What should you do now? The answer, clearly, is that you are gonna have to troubleshoot your circuit breaker . Here’s how to do it:
- Before anything else, check to see that you don’t have anything that could be causing the breaker to trip. If your breaker’s tripping is related to two rooms, check to see that it’s not your DJ equipment or extra-large entertainment set up in the next room that’s causing it.
- Check the input wires for damage. If you notice that they’re frayed or have reason to believe that their movement is causing the breaks, call an electrician. You need to get the input wires replaced or fixed.
- Reset the breaker. Remove all connected items in your room from their plugs and reset your breaker. If it breaks again, then there is an issue that you have to fix.
- Keep an eye out for signs of a short circuit, fuse issue, or ground fault. When you’re dealing with a short circuit, you might notice a burn mark or a smell near an outlet. With a ground fault break or fuse issue, you may have a problem with wiring overheating or being exposed to water. If you believe you have an issue with this, give an electrician a call.
- If all else fails, you have a faulty breaker. Even circuit breakers will eventually need to be replaced. They will eventually go bad. If you can’t find anything else wrong, it’s time to get a new circuit breaker. If you’ve had your circuit breaker for a very long time, it’s possible that your breaker just ran its course and needs to be replaced.
However, there are several problems that range from a ground fault to an outdated circuit breaker that you need to consider. Let’s take a look a the most common reasons that your circuit breaker keeps tripping when nothing is plugged in.
Ground Fault
A ground fault, or earth fault, is when an active wire touches the earth . Ground faults occur when a wire and the ground interact and overload the circuit breaker with the current. There is no resistance or restrictions with the earth, so an unrestricted flow of current goes through the wire and to the circuit breaker.
A ground fault is similar to a short circuit because the current bypasses the circuit wiring . The reaction from a ground fault is immediate, and the circuit will immediately flow uncontrollably. Between the lack of resistance and increased current flow, a ground fault can trip your circuit breaker and potentially damage it permanently.
Electricians treat a ground fault differently than a short circuit, but both problems require a fix. Ground faults are dangerous to fix or come into contact with, and there is potential for electrical shock.
Outdated Circuit Breaker
Circuit breakers have a lifespan just like any other key electrical fixture in your home. The average circuit breaker lasts for 35 years , but they can last for up to 40 years. You can generally tell that your circuit breaker is outdated when it acts up, and old breakers often trip when nothing is plugged in.
Worn breakers are less conductive and reliable, and they are often difficult or impossible to reset . Old circuit breakers produce a distinct burning smell that can be alarming. The voltage and current strength on an outdated circuit breaker are unpredictable and fluctuate wildly.
If your circuit breaker is nearly 30 years old and often feels hot, it is likely outdated . Replace your old circuit breaker if it frequently trips with nothing plugged in after you reset it
Old homes have different wiring configurations than modern homes, and that can affect your circuit breaker. Generally, old homes have circuit breakers that work via a single circuit. A single circuit is not enough to keep up with the electrical demands of modern homes .
Homes that are 40-50 years old or older likely have single circuit units that affect multiple outlets and even rooms. Your circuit breaker can trip even if there is nothing plugged in if you have an old home with outdated wiring and an underpowered single circuit system. The only solution, in this case, is to replace your circuit breaker and update your wiring.
Short Circuit
Similar to a ground fault, a short circuit occurs when the electrical flow goes through a short path that it wasn’t supposed to . A short circuit can easily occur if the insulation on a wire is damaged and leaves them exposed. The most common cause for a short circuit is when multiple wires become exposed and touch each other.
The current essentially takes a shortcut instead of going through the circuit wiring. Short circuits cause a massive spike in current flow that overloads the circuit breaker and causes it to trip. It is good that your circuit breaker trips during a short circuit because that can prevent expensive and harmful damage.
Lamps, electric space heaters, and plug-in appliances commonly cause short circuits. Luckily, modern devices generally have well-insulated wires to prevent short circuits. However, a short circuit can happen when nothing is plugged in because the breaker’s wires themselves can cause a short.
Damaged Wires
The wires inside of and connected to a circuit breaker are well-protected, but they can still succumb to damage. Wires are covered with insulation that can melt over time and leave them vulnerable to damage. You should be concerned if you have a damaged input wire because that can be dangerous to touch or work with .
A damaged wire can cause a current leak and your circuit breaker will trip when it recognizes it. This is a safety precaution and prevents the current from going where it shouldn’t and causing a bigger problem. It is ideal to hire a professional electrician to repair damaged wires in your circuit breaker because it is complicated and potentially dangerous.
How Much Does It Cost To Replace a Circuit Breaker?
It costs an average of $1,250 to replace an entire circuit breaker box . However, you can expect to pay $1,800 or more for an upgraded circuit breaker box, but it may be worth the added safety. Replacing single switches on a circuit breaker is much cheaper and that generally costs $45 per switch .
You can spend as little as $205 to replace an AFCI circuit breaker in some cases, but it can cost $280 or more. It is worth the cost to replace a circuit breaker because it is difficult and dangerous to replace one without professional help. However, you need to refer to local building codes if you replace your circuit breaker as a DIY project to save money.
Can You Replace A Circuit Breaker On Your Own?
Technically, most people would agree that this could be a DIY job. However, I’m a little skeptical. With electricity, working on it without much knowledge of what you’re doing is a lot like trying to shoot an arrow up in the air and hope that it won’t hit anything. You might be fine, but you might not be.
If you choose to go the DIY way, just make sure that your local building codes allow you to do this. Many cities now require all electrical work to be done through the use of a certified electrician. So, if you aren’t sure, check with your local municipal office to find out whether DIY is an option.
Related Questions
How long do circuit breakers last.
Circuit breakers last for an average of 35 years , but they can last for up to 40 years. You can tell that you need to replace your circuit breaker if it won’t hold a reset or you notice a burning smell coming from it. Generally, circuit breakers become less conductive when they are old and trip more often.
Why does the circuit breaker trip when lightning strikes
A circuit breaker can trip when lightning strikes because it detects the thousands of amps that come from it . The current from a lightning strike is overwhelming and would overload your home’s electrical grid. It can trip even if the lighting doesn’t touch your house because a circuit breaker can detect the current in the earth or air.

Ossiana Tepfenhart is an expert writer, focusing on interior design and general home tips. Writing is her life, and it's what she does best. Her interests include art and real estate investments.
More by Ossiana Tepfenhart

How To Set Up A Cheap Home Gym
Popular articles.

Why Do My Berries Get Moldy So Fast (And How To Fix)

The Ugly Truth About Binge-Watching HGTV

Eight Tips To Help Your Hammock Last Longer

End-Of-Season Pool Maintenance Checklist

How Often Should I Wash My Bath Towels?
You may also be interested in.

How To Update A 1970's Stone Fireplace

Smooth Vs. Textured Walls: Which Is Better to Refinish Walls?

How to Hang Double Curtains Without A Double Rod

Toilet Flapper Closes Too Soon? (We Have Ways to Fix It)

How Long is Cream Cheese (Open and Unopened) Good For?

15+ Different Types of Ceilings (with Photos)

How To Reset A Kenmore Elite Dishwasher 665 (Do This!)

17 Places to Get 55-Gallon Drum For Free (Near You)

Sprinkler Zone Won't Turn Off? (Here's How To Fix It)

How To Unclog A Refrigerator Drain Tube (Quickly & Easily!)

How to Clear the Schedule on Your Honeywell Thermostat (Fast & Easy)

Baby Grand Piano Dimensions (with Drawings)

8 Types of Outdoor Faucets (for Residential Use)

Why is My Milwaukee Charger Blinking Red and Green?

10 Types Of House Moths (With Photos)

How to Stabilize Pea Gravel Walkways (In a Few Easy Steps)

Honeywell Thermostat Blinking "Cool On"? (Here's Why!)
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Home and Garden
- Home Maintenance
- Electrical Maintenance
Reasons Your Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping (Plus, What to Do)
Last Updated: March 11, 2024 Fact Checked
- Causes for a Tripped Breaker
- Fixing a Tripped Breaker
Is it dangerous for a breaker to trip?
This article was co-authored by Jesse Kuhlman and by wikiHow staff writer, Mason Martinez, BA . Jesse Kuhlman is a Master Electrician and the Owner of Kuhlman Electric based in Massachusetts. Jesse specializes in all aspects of home and residential wiring, troubleshooting, generator installation, and WiFi thermostats. Jesse is also the author of four eBooks on home wiring including "Residential Electrical Troubleshooting" which covers basic electrical troubleshooting in residential homes. There are 16 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 4,420 times.
You may be familiar with tripping a breaker because of too many plugged-in appliances, but what about when there's nothing plugged in? Well, it's unlikely that nothing is plugged in unless you're living off the grid. So, before you get ready to peel back some wires, double-check inside and outside your house for any forgotten appliances. Then, grab this guide to learn more about the common causes of a tripped breaker!
What causes a breaker to trip if nothing is plugged in?
When electrical demand is high, a circuit breaker can overheat and trip. Wire damage can also cause tripping, so check for signs of burning, cracking, or sparking when you plug a device in, as this can mean wire damage. Damaged wires or GFCIs may also cause trips when they touch another live wire or outlet box.
Why does my breaker keep tripping?

- For a 20-amp circuit, you can put a maximum of 16 outlets on it. Meanwhile, a 15-amp circuit can handle 12 outlets. [2] X Research source
- Unplug unused electronics or avoid using two demanding appliances at once if you don't know how to wire a circuit breaker to redistribute appliances or add new circuits.
- If your circuit breaker frequently trips, this may be a sign that it's time to replace your breaker.
- Cost: $200 to $600 to replace a main breaker or $150 to $1,000 for rewiring. [3] X Research source

- If you're an experienced electrician, locate the short circuit within the wiring system and make a new wire to replace the damaged one. Remove insulation from the ends of the new wire and solder them in place. [5] X Research source
- If you're unfamiliar with wiring, it's best to call an electrician for assistance as soon as possible to avoid an electrical fire!
- Cost: Fixing a short circuit can cost $75 to $200. [6] X Research source

- GFCIs are often installed in wet environments, like bathrooms or kitchens. Any lingering water can create a new path for electricity to flow. Be sure the outlet is dry before inspecting it.
- Unplug all the appliances from the circuit and press the reset button on the GFCI. Plug in your electronics one by one to determine the cause of the trip. If it continues to trip, call an electrician. [8] X Research source
- Cost: A replacement can cost between $100 to $400. [9] X Research source

- Cost: If your home lacks power surge protection, a whole house installation can cost between $70 to $700. [11] X Research source

- You can also use an electronic circuit breaker finder to map out which outlets are connected to which breakers. [13] X Research source
How to Fix a Tripped Breaker

- If the circuit breaker continues to flip and you can't identify which appliance is causing it, call a licensed electrical contractor to find the source of the problem.

Expert Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.homelectrical.com/understanding-capacity-your-circuit-breaker.6.html
- ↑ https://todayshomeowner.com/electrical/guides/how-many-outlets-on-a-15-amp-circuit/
- ↑ https://homeguide.com/costs/cost-to-replace-a-circuit-breaker-switch
- ↑ https://www.rowse.co.uk/blog/post/what-causes-circuit-breakers-to-trip
- ↑ https://www.thelocalelectrician.com.au/how-to-fix-short-circuits/
- ↑ https://www.fixr.com/costs/electrical-outlet-repair
- ↑ https://gopaschal.com/why-does-my-circuit-breaker-keep-tripping/
- ↑ https://www.mistersparky.com/denver/about-us/blog/2023/february/fix-a-gfci-outlet-that-keeps-tripping/
- ↑ https://www.angi.com/articles/how-much-should-it-cost-electrician-replace-combination-gfci-switch-and-receptacle.htm
- ↑ https://www.sunpower-uk.com/glossary/what-is-a-power-surge/
- ↑ https://www.bobvila.com/articles/whole-house-surge-protector-cost/
- ↑ https://kolbelectric.com/blog/5-reasons-circuit-breaker-tripping/
- ↑ https://youtu.be/niJtOOPfMXg?t=161
- ↑ https://www.johnmooreservices.com/how-to-safely-reset-a-tripped-breaker/
- ↑ https://energized.edison.com/stories/a-step-by-step-guide-to-safely-resetting-your-breakers
- ↑ https://www.tingfire.com/home-safety/what-every-homeowner-should-know-about-resetting-circuit-breakers/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
5+ Reasons Why Your Breaker Keeps Tripping – And How to Fix It
Your breaker may trip due to circuit overload, short circuits, ground faults, outdated wiring, or a faulty breaker. Follow tips to fix each issue and ensure safety.

Your circuit breaker will trip once in a while if it detects an electrical fault. After all, that’s what it’s designed to do. Without the breaker, you could be putting yourself, loved ones, and property at risk of electrocutions and fires. But what if the breaker keeps tripping and leaves you in pitch darkness?
Before you call an electrician, consider implementing the tips below. You’ll discover the root causes and what to do if your breaker keeps tripping.
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases. Thanks!
Why Does My Breaker Keep Tripping?
If your breaker frequently trips, examine your electric power system to determine if the issue results from one of the following causes.
Hey hey! Don’t forget to subscribe to get our best content 🙂
Type your email…
Circuit Overload
Have you checked whether you’re dealing with an overloaded circuit? A circuit overload occurs when the wires receive more electrical current than they can handle.
Each circuit has a maximum current it can handle. The breaker will trip if it detects that the current exceeds the circuit’s capacity.
Often, a circuit overload happens if you’ve plugged multiple appliances, including high-power devices, into the circuit. You might notice that power goes out in your kitchen or living room when the breaker trips. That’s a telltale that a single circuit in either of the rooms is powering multiple appliances.
- Disconnect all the devices and reset the breaker.
- Before connecting an appliance, allow your electric power system to rest for a few minutes. Plug in your devices one at a time.
- If it trips again as you plug in the devices, relocate the appliances to other outlets.
- If the breaker continues to trip, call an electrician to troubleshoot the problem.
Short Circuit
A short circuit might be another reason why your breaker keeps tripping. Unlike circuit overloads, short circuits have more potential to cause fires.
A short circuit happens when a live or “hot” wire touches a neutral wire. When the two wires touch, they cause a sudden surge of current through the wires. This surge leads to a circuit overload, which causes the breaker to trip. If your circuit breaker fails to trip, it can put your property at risk of fire.
To know whether the culprit is a short circuit, you can look for sparks, smoke, burning smells, or popping sounds. A short circuit will occur in a switch, outlet, or within the circuit breaker due to the following reasons:
- Slipped wires
- Damaged wires
- Loose connections
Do you know what to do if your breaker keeps tripping? Unless you have professional experience, avoid trying to fix a short circuit in your electric power system. The affected cables can instigate fire and further damage. You may also get electrocuted. Call your electrician to fix the problem.
Ground Faults
When it comes to ground faults, a live or “hot” wire touches a ground wire or the breaker’s outer casing. This contact causes a sudden surge of current passing through the breaker. The breaker will trip if it detects more electricity than it can handle.
Ground faults occur when water enters the appliance or an outlet. If it touches the hot wire, the current changes its route and follows the water path. This might cause electrocution if you touch the water with bare hands or feet.
Thankfully, the National Electrical Code (NEC) requires buildings to install Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlets . These outlets can detect ground faults and cut off the current.

- Find where the water is coming from and fix it. If it’s damaged roofing directing rainwater into the box, call a roofer to fix it.
- Replace damaged wiring. Call your electrician to replace the damaged wiring to avoid causing further damage.
- If you’ve not installed GFCI outlets, call a licensed electrician to install them for you.
Outdated Wiring
Outdated wiring is prevalent in older homes. If you live in an old house, you’re likely to have a breaker that keeps tripping. The electric power system in that home can only handle low-power devices. If you plug in modern appliances, you might experience frequent breaker trips due to circuit overload.
Old aluminum wires might melt when the circuit overloads. The melting cables might burn the plastic casing, causing a fire.
If you check the insulation in one of your outdated wires, you might find it deteriorating. When this insulation touches a conductor, it can cause a ground fault.
According to the National Fire Prevention Association (NFPA), faulty wiring leading to electrical failure is one of the main causes of fires in residential areas. The wiring can be outdated if you live in a house over 40 years old. Outdated and faulty wiring will likely cause a fire during overloads or short circuits.
The only way to fix outdated wiring is to have it replaced. Find a professional who’ll inspect the wiring and upgrade it.
A Bad Circuit Breaker
If your breaker doesn’t stop tripping even after fixing some or all of the above causes, then your breaker might be faulty. Sometimes, a breaker will trip even when it’s newly installed. This might be due to an undersized breaker, manufacturer’s defect, or loss of efficiency. If one of these is the case, your breaker will trip even if there are no overloading, short circuits, or ground faults.
When inspecting your old wiring, check whether you’re working with an old breaker. It may no longer produce electricity for your modern appliances if it’s old. You should also check whether the breaker is tripping due to a lack of maintenance.
Avoid tampering with your faulty breaker, especially if you don’t have the necessary skills. Call a certified electrician to diagnose the problem and fix it. If your breaker is old or beyond repair, they can replace it.
How To Reset a Tripped Breaker
If your breaker won’t stop tripping, resetting it is the first thing you might consider. Resetting the circuit breaker is a great way to determine what causes the tripping.
To reset your breaker:
- Locate the appliance’s handle or switch and move it to the “OFF” position.
- Before this, ensure you’ve unplugged all the devices.
- Move the switch to the “ON” position.
When turning the switch on, the breaker might produce sparks that might cause a fire or electrocution. To be safe, avoid standing near and directly facing the panel. You can stand at the side or a few steps back. After resetting, allow the breaker to rest for a few minutes before plugging in your devices. Now you know what to do if your breaker keeps tripping.
The following are some of the most common questions people have asked about circuit breakers.
How can you tell if your circuit breaker has gone bad?
The following symptoms should help you know that your circuit breaker has gone bad:
- Frequent tripping
- Unable to reset
- Burnt smell
- Scorch marks on its box
- Visibly damaged breaker
- Worn-out breaker
- Hot circuit breaker
What causes the breaker not to reset?
A breaker might fail to reset if it has gone bad. The breaker won’t reset if you’ve plugged in too many devices that consume a lot of power.
What is the average life of a circuit breaker?
The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) states that the lifespan of breakers is between 30-40 years . Factors such as fluctuating voltages and poor power ratings can affect the life of your breaker.

Jeff (pen name for privacy) is our primary contributor. Previously, he has worked at 84 Lumber as a manager trainee and contractor sales rep. Before that, he worked for a local plumbing firm doing everything from rough-ins to septic repair and more.
Similar Posts

What Is a Fish Tape & What Is It Used For?

5 Key Differences: Battery Maintainer vs Trickle Charger

10 Essential Electrical Wire Pulling Tools for Electricians

9 Key Costs of Running Electricity to Your Property

What Is a 24V Power Supply & What Is It Used For?

9 Essential Tips for Electrical Outlet Safety at Home

Circuit Breaker Tripping: Troubleshooting Guide
Hubert Miles | Licensed Home Inspector, CMI, CPI
Updated on January 5, 2024
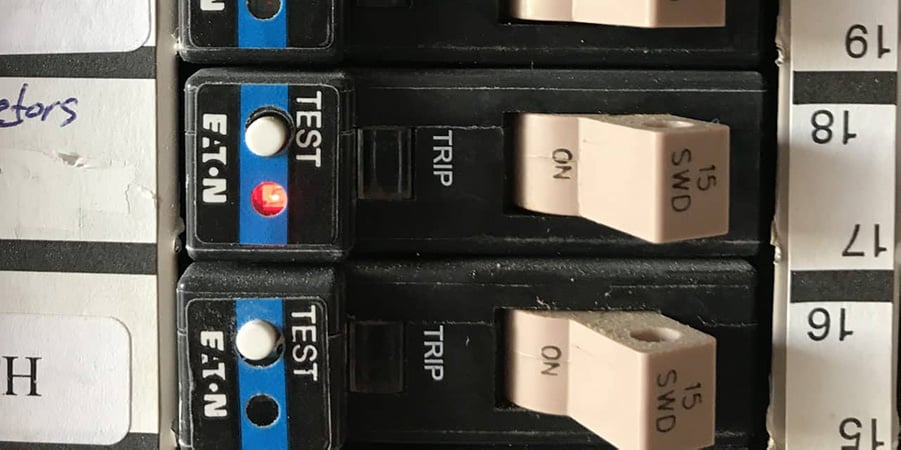

A circuit breaker tripping results from short circuits, overloaded circuits, and ground faults. In each case, an unintended excessive flow of current triggers the trip. You must reset the circuit breaker by flipping it back on to restore power.
Circuit breakers trip because they cannot handle the amount of current running through them. Tripping the circuit breaker interrupts the flow of electricity and protects your devices or appliances from damage.

Get FREE estimates from licensed electricians in your area today. Whether you need to replace an outlet, hang a ceiling fan, a new electrical panel, or repair wiring, We Can Help!
Without electrical circuit breakers , the possibility of electrical fires would be much higher.
This guide looks at what causes circuit breakers to trip, what you can do, and how to identify a bad breaker.
What Would Cause a Circuit Breaker to Trip
There are three leading causes of circuit breaker trips:
- circuit overload
- electrical faults (i.e., ground faults and arc faults)
- short circuits
Below are factors that can cause circuit breaker trips.
Circuit Overload
A circuit overload happens when the flow of electric current running through the circuit exceeds the amperage of the devices it serves.
For example, if your microwave is a 12.5 amp appliance, you can run it on a 15 amp circuit. That means your microwave is safe as long as the amperage running through the circuit is 15 amps .
However, if the circuit receives an excessive electrical load over 15 amps , it will automatically trip to protect your device from damage. If the circuit doesn’t trip, the excess current will fry the circuit in your microwave.
Also, if you operate too many appliances and devices on one circuit, its internal mechanism heats up, causing the breaker to trip.
Circuit overload is the most common reason for breakers tripping.
Ground Faults
A ground fault occurs when the active wire comes into contact with a ground wire made of bare copper. Sometimes, this fault may happen when the hot wire touches the metal box connected to the ground wire.
Excessive current flows once the active wire touches the ground wire, flowing into the earth. If you step on the affected area, ground faults can cause shock and even electrocution. The uncontrolled flow of electricity will cause the circuit breaker to trip.
Arc Faults
An arc fault happens when exposed faulty wiring touches, causing the electric current to arc at the meeting point. As a result, sparks occur, which can ignite an electric fire.
A corroded or loose connection is the main culprit for arc faults. Circuit overloads, ground faults, or short circuits trip an AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter) circuit breaker.
Arc faults result from damaged, loose, or corroded terminals and wires. The arc fault builds up over time as the heat due to the cable damage and terminals build up to the point of ignition.
Short Circuits
A short circuit occurs when an active wire touches a neutral wire, and the electrical current takes an unintended path of least resistance.
The common cause of short circuits is frayed wires coming into contact when the wires touch. The electrical current flow increases significantly, causing the circuit breaker to trip to stop the electricity from damaging appliances.
It is a short circuit because the current bypasses the proper circuit wiring channels and flows through a shorter, unplanned pathway.
Short circuits occur
- When insulation melts and wires are exposed
- Within appliances with damaged internal wiring
- Due to damaged and frayed extension or appliance cords
How do You Fix a Breaker that Keeps Tripping?
A dedicated circuit breaker tripping indicates too much current flowing through the wiring or connection to the outlet.
Here is a step-by-step guide to follow when you notice the first trip:
- Begin by turning off all the appliances and unplug electrical devices from the outlet. Also, switch off light fixtures and unplug those that you can. This prevents any appliances from damaged when the breaker is reset and a sudden surge of power comes through.
- Open the circuit panel or box and locate the on and off buttons of the circuit breaker. You may notice an orange or red color on the breaker when it is off.
- Flip the switch from off to on to reset the circuit breaker. Once the breaker is reset, you can switch and test the appliances to see if the electrical power is flowing.
- Keep safe as you reset the breaker by working from the side of the electrical box instead of the front. That way, you will avoid any sparks (should there be any) when you switch the breaker back on.
- Some people prefer to switch the main electrical switch when working on the circuit breaker for added safety.
Types of Circuit Breakers
Standard circuit breaker.
Standard circuit breakers monitor the modulation of the electric current coming into your devices and appliances.
This circuit breaker stops the current from flowing when it detects the excessive flow of electricity.
Standard circuit breakers come in two forms:
- Single-pole circuit breakers
- Double pole circuit breakers
Single-Pole Circuit Breakers
Single-pole circuit breakers are the most common breakers in homes and buildings. They monitor the electric current’s flow in one wire and trip if that wire experiences a very high influx of electricity.
These breakers deliver only 120 volts and work well for 15 to 30 amp circuits. Single-pole circuit breakers come with one switch in the back.
Double-Pole Circuit Breakers
The double-pole circuit breakers monitor the current in two wires simultaneously. You will notice two switches on the back of these breakers.
The double-pole circuit breakers will trip even if only one of the wires receives too much current. They can accommodate between 15 to 200 amps while delivering 240 volts.
Single-pole breakers are a good fit for lighting fixtures and other standard home outlets. On the other hand, double-pole breakers work for larger appliances like dryers and washing machines.
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI)
The GFCI circuit breaker interrupts the line due to ground faults. They trip when the current starts to follow an uncharted path into the ground. These ground fault surges occur when a foreign conductor, like water, comes in contact with a receptacle .
At the same time, they offer protection against circuit overloads and short circuits.
GFCI circuit breakers come built into specialized outlets required for wet areas in the home, including :
- Outdoor areas like the balcony, patio, porches, and decks
- Laundry rooms
- Swimming pools
- Six feet from a sink
- Six feet from the bathroom
These breakers help prevent shock or electrocution should the electrical outlet contact water.
Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI)
The AFCI circuit breaker detects normal and abnormal arc faults, so it will trip when it detects a dangerous arc fault that can cause a fire.
The AFCI circuit breaker doesn’t work to protect devices and appliances plugged into an outlet. It works to prevent electrical fires due to faulty connections and wiring. The internal sensing mechanism in the circuit breaker senses the conditions of an electric arc, and the circuit trips to avoid an electric fire.
AFCI protection can also be built into an outlet. The National Electrical Code (NEC) requires these types of breakers to feature in :
- Common rooms
- Laundry areas
AFCI and GFCI circuit breakers can co-exist and complement each other for the best protection.
Combination All Fault Circuit Interrupter (CAFCI)
The CAFCI breaker senses and reacts to any electrical fault, including ground and arc faults.
CAFCI is a relatively new technology that meets new NEC requirements for circuits requiring arc and ground fault protection.
Do Circuit Breakers Get Weak?
A circuit breaker can wear out and become weak. If a breaker trips frequently, the thermal or magnetic element can lose calibration, causing it to trip at lower amp loads than intended. A breaker constantly under thermal stress caused by overloading the circuit will eventually trip more frequently.
Let’s not forget breakers are not impervious to damage. As the internal mechanical parts wear out, they become very sensitive and may not hold under normal load amperage and temperatures.
Electricians refer to this as a bad breaker .
Will a Bad Breaker Keep Tripping
By definition, bad breaker malfunctions, so it will keep tripping until it is either replaced or rectified .
A licensed electrician performs this simple test to see if a breaker will keep tripping and determine if it can be repaired or replaced in the following steps.
- The electrician will switch off all the fixtures and appliances in the house. Also, unplug everything.
- Find the malfunctioning circuit breaker . The electrician will go to the electrical box and locate the breaker lighting orange or red or the one with the switch off.
- They will ascertain that it is the correct circuit breaker. After that, the electrician puts the breaker off.
- With the switch on, the breaker is back on as well. The electrician will plug the appliances into the outlet with the problem circuit breaker. Now, they will turn the devices and appliances on.
If the breaker trips, the electrician will investigate the circuit’s current amount. The breaker is bad if the current is according to the appliance’s rating.
How You know if a Circuit Breaker is Bad
Breakers do wear out after a while. It has a problem if the breaker doesn’t stay on after resetting it.
Since the circuit breaker controls the electric flow in the house, it is essential to monitor it and catch signs that it has gone bad early.
Here are key signs that denote a bad circuit breaker :
It Frequently Trips
Frequent tripping could be because of a bad breaker. After tripping and resetting, your circuit breaker should stay on unless it detects high current flow.
To ensure that the issue is not the electricity but the circuit breaker, call an electrician to examine your electricity’s flow and determine whether it is the cause of the constant tripping.
If it is not, then the circuit breaker is the problem.
The Breaker Overheats
Electrical systems will heat up when active. Typically a breaker can heat to about 60°C (140°F) before problems arise.
Terminations for standard rated breakers: UL 489 Paragraph 7.1.4.2.2 says the temperature rise on a wiring terminal at a point to which the insulation of a wire is brought up as in actual service shall not exceed 50°C (122°F). Terminations for 100% rated breakers: UL489 Paragraph 7.1.4.3.3 says the temperature rise on the termination shall not exceed 60°C (140°F). Handles, knobs, and other user surfaces: UL489 Paragraph 7.1.4.1.6 says the maximum temperature on handles, knobs, and other surfaces subject to user contact during normal operation shall not exceed 60°C (140°F) on metallic and 85°C (185°F) on nonmetallic surfaces. Source: https://www.clipsal.com/faq/fa173839
Call an electrician immediately if the breaker becomes too hot.
There are Scorch Marks
Scorch marks around receptacles, appliances, and the electrical box should tell you your circuit breaker has gone bad.
The burn marks indicate that wiring insulation has melted off and the circuit wires are now sparking and emanating heat or fire. That means that the circuit breaker did not interrupt the excess current and reached the wires and burned them.
You may see melted wire sheathing on the wire where it connects to the breaker.
Professional electricians can use a thermal imaging infrared camera to locate the heat source. The infrared camera allows them to pinpoint the problem area through the walls and other construction material.
A Burning Smell
Sometimes you may smell the insulation burning, but no scorch marks are present to denote which outlet is the problem.
With the help of the infrared camera, an electrician can help locate electrical issues.
If you encounter a burning odor, shut off the main power and call for emergency service from an electrician.
The electrical wires burn because power surges through the circuit, melting the wire insulation.
What is Nuisance Tripping
Nuisance tripping is when a breaker trips without a fault to warrant the interruption to the electric current flow.
Nuisance tripping occurs due to several reasons:
Stringent Protection on Circuits
Sometimes the circuit is protected by stringent conditions that detect any variance as a fault and cause a trip.
Such stringent conditions can be tuned to accommodate the home’s or building’s electric needs.
A Highly Sensitive Circuit Breaker
In some cases, the circuit breaker has been set to susceptible settings so that they can detect even the slightest fault, even a minor average variance.
For example, the manufacturer can set an AFCI circuit breaker to sensitive standards to detect another circuit’s arc. This common issue may occur in a daisy chain where the circuit breakers connect in a linear series. There may be a faulty electrical outlet you are unaware of on the circuit. It is common for multiple rooms to share a breaker in older houses.
The Breaker Encounters Power Under Different Conditions
The variation in the current is normal, but the breaker responds to it by tripping because the flow is outside the breaker’s regular operation.
Your circuit breaker is tripping because the voltage it is encountering is not within the standard operation. You will need to adjust the circuit breaker or the voltage to eliminate nuisance tripping.
The Breaker Trips with Nothing Plugged in
A breaker tripping with nothing plugged in occurs when a hot, neutral wire is touching somewhere in the circuit. The common causes include frayed or damaged electrical wires, loose connections, faulty electrical receptacles, light switches , or dimmers.
Electrical wire damage happens when:
- wiring is chewed by animals such as rats, squirrels , raccoons, etc
- wire sheathing and insulation ages and become frayed
- wires rub against sharp edges such as punch-outs with missing grommets or wire clamps
Loose connections often occur when electrical wire nuts come loose or electrical tape wears out causing wires to touch.
Defective wiring can be anywhere along the circuit, so it’s best to contact a licensed electrician to troubleshoot why the breaker is tripping.
Replacing a Bad Circuit Breaker
- Check the electrical panel to see the compatible approved circuit breaker brands. Also, make a note of the brand of the electric panel . This is to help you determine if there are upgrades they could recommend for the hardware.
- Order online or go to the hardware store and purchase the breaker of the same voltage as the one you are replacing.
- Go and open the electrical box and switch off the bad breaker. Loosen the terminals and remove the wires using a pair of needle-nosed pliers. Ensure the pliers have rubber insulated handles to avoid shock or electrocution since you will use the pliers to grab the live wires from the terminal. That is a safety measure.
- Remove the bad breaker. Replace it with the new breaker and slip its clips into place. Remember to switch off the replacement breaker.
- Next, using the pliers, hold the wiring and tighten the screws on the terminal. It is crucial to ensure that the wires and screws in the terminals are in the right place.
- Turn the breaker on and replace the electrical panel cover.
Can a Breaker Fail Without Tipping
If you have a newer electrical panel , it’s not likely for a breaker to fail and not trip. However, in older breaker boxes like Federal Pacific , the breaker failing to trip is common.
The main reason Federal Pacific was investigated by the Consumer Products Safety Commission (CPSC) was widespread structure fires involving breakers failing to trip when an electrical overload was present. They found that the circuit breaker contacts would fuse to the bus bar.
Modern breakers will trip when a failure occurs as an added layer of safety. Most older breakers did not have these safeguards.
With AFCI breakers, if the Internal sensing mechanism fails, the breaker reverts to a standard breaker. The AFCI sensor mechanism will no longer work, but the breaker would still trip from overcurrent protection. Therefore, you should test the AFCI breaker regularly.
Conclusion
Listen to your circuit breaker . It’s alerting you of a problem when it trips. That communication could be a problem with the breaker itself, the circuit, or the amount of electric current coming into your home.
Hubert Miles is a licensed home inspector (RBI# 2556) with more than two decades of experience in inspection and construction. Since 2008, he has been serving South Carolina through his company, Patriot Home Inspections LLC. As a Certified Master Inspector, Hubert is dedicated to providing his expertise in home inspections, repairs, maintenance, and DIY projects.
Continue Reading

Watts to Amps Calculator: DC/AC Wattage to Amps Conversion

70 Amp Wire Size: Breaker & Wiring Gauge Guide

80 Amp Wire Size: Breaker & Wiring Gauge Guide

200 Amp Wire Size: Service Length & Wiring Gauge Guide

10/2 or 10/3 Wire for Mini Split: A Professional Guide

GFI vs GFCI: Understanding the Key Differences

Founded by Hubert Miles, Certified Master Inspector
Home Inspectors
Calculators
Privacy Policy
Terms of Service
©2024 Home Inspection Insider 898 Whispering Pines Rd, Johnsonville, SC 29555 843-250-1882
WhatsApp Our Local Electrician To Get a Fast Response & Quote For Your Electrical Needs.

What Causes Circuit Breakers To Trip?
- September 1, 2024
If you notice that your circuit breakers are often tripping, don’t worry. It’s a typical issue. Below, you’ll find reasons why this occurs and tips to avoid it moving forward. Get a handle on your circuit breaker problems!
Table of Contents
Understanding Circuit Breaker Tripping

Circuit breakers are protection devices for electrical circuits. When too much current passes, the breaker trips, stopping the flow of electricity and preventing damage. This can be caused by faulty wiring, too many appliances on one circuit, or a ground fault.
Overloading can cause tripping. This happens when too many devices are connected to a single circuit. Heat builds up in the wires, which can start fires or cause damage. To prevent this, distribute loads across multiple circuits and don’t connect too many appliances to one outlet.
Short circuits also lead to tripping. This happens when two wires with opposite charges come in contact or when a wire touches something grounded. This causes an immediate surge in current that triggers the breaker. Check for exposed wires or insulation damage, and call an electrician if you spot any signs of trouble.
Ground faults can also cause tripping. This happens when there’s an unintentional connection between a live wire and a conductive surface. Install GFCIs to avoid this.
In short, know what causes circuit breakers to trip. Identify potential hazards like overloading, short circuits, and ground faults. Take steps to prevent accidents and ensure your electrical equipment is safe. If you’re unsure how to handle electrical problems, call a licensed electrician.
Overloading Causes
Circuit breakers trip to stop overheating, electrical fires, and damage to electrical parts. Plugging in too many devices can cause the circuit to become overloaded, so the breaker trips to cut off the power.
Short circuits are like a blind date gone wrong. They can be explosive, and often end in disaster. This happens when a hot wire comes into contact with a neutral or insulation/water. This throws off the electric balance, causing danger and tripping.
Short Circuit Causes
A short circuit happens when a low-resistance path appears between two points in the circuit that aren’t usually connected. This can cause too much current to flow, making a circuit breaker trip. Insulation or wiring damage, faulty appliances, and circuit overload are the most common reasons for a short circuit. It’s critical to identify and fix the root cause quickly to avoid electrical fires and other dangers .
When too much power passes through a circuit, the circuit breaker will automatically turn off. It’s designed to protect wiring and guard against electrical accidents . But if the breaker trips regularly, there may be underlying issues that need investigation and repair. Often times, this means upgrading or replacing components.
Sometimes short circuits are caused by human error or wear and tear. But they may also come from design or installation problems. Planning and upkeep from local electricians can keep electrical systems running safely and appropriately for a long time. If your circuit breaker is tripping a lot, get an experienced technician to review your system and suggest solutions that match your needs and budget .
Overheating Causes
Circuit breakers are essential safety features. They stop electrical fires and protect your appliances. When overloaded, too much current flows, producing heat. This causes the breaker to trip!
Other factors can cause overheating. Damaged insulation on wires increases resistance. Loose connections add resistance and heat. High temperatures and poor ventilation worsen the situation.
It’s important to maintain and service the electrical system. Checks of all components will make sure they work efficiently. To avoid tripping, prevent overheating. This will reduce energy consumption and safeguard equipment. So, let’s learn about circuit breakers and how they deal with overloads!
Circuit Breaker Types
Circuit breakers are essential for any electrical system. They prevent overloaded and faulted circuits . There are different types of circuit breakers suitable for specific electrical loads.
See the table below for the different types of circuit breakers and their functions:
It is crucial to select the right type of breaker. Each one has its own advantages in specific situations. For instance, thermal circuit breakers are perfect for small appliances like hair dryers or irons . Meanwhile, magnetic circuit breakers are great for bigger loads such as air conditioners or refrigerators .
Remember, circuit breakers are like Beyoncé – they can handle a lot, but have their limits.
Circuit Breaker Ratings and Specifications
Circuit breakers are designed to protect electrical circuits from overloads. To ensure that circuits and appliances are safe, the ratings and specifications of circuit breakers need to be understood.
If a circuit breaker trips often, it may mean there’s an issue. It’s best to get professional help in these cases. Time to go on a hunt for your electrical wiring!
Troubleshooting Circuit Breaker Tripping
Circuit breakers can flip out for multiple reasons, like overloads , short circuits , and ground faults .
Overloads happen when too much electricity passes through the circuit, creating too much heat and tripping the breaker. Short circuits are when two or more wires touch, resulting in extra current. Ground faults occur when the power takes an unexpected route, like through a person’s body.
To figure out why your circuit breaker is tripping, it’s important to figure out what is going on and act accordingly. Inspections and maintenance can also help avoid future tripping.
Stop your circuit breaker from misbehaving with these prevention tips!
Preventing Circuit Breaker Tripping
A circuit breaker tripping can be prevented with understanding. When circuits are overloaded, breakers trip to avoid overheating and potential fires. Here are 3 steps that can help you prevent circuit breakers tripping:
- Know the electrical load – work out how many appliances & devices are connected to one circuit. Don’t overload them by spreading high-energy equipment across multiple circuits .
- Look after your appliances – ensure all your appliances & devices are in good condition, with no damaged cords or frayed wires.
- Upgrade your system – if you’re tripping breakers often you may need to upgrade the electrical system with higher capacity breakers or more circuits.
Plus, investing in surge protectors can also assist in preventing circuit overload and subsequent tripping of breakers. By following these steps you can make sure your home’s electricity runs safely and without interruption due to circuit breakers tripping.
Remember: these precautions will keep you from tripping more than just your circuit breakers!
Safety Precautions
Safety must be taken seriously when dealing with circuit breakers . Always switch off the main power supply before beginning work. Wear protective gear such as insulated gloves and boots to stay safe from electrocution. Never touch wires or components inside the box without proper training. Keep the area around the breaker box free from any flammable substances. Inspect breakers for damage or wear regularly .
Label each circuit breaker correctly . Test them frequently for functionality. This will help identify circuits quickly in case of an emergency. These precautions and practices ensure safety while dealing with circuit breakers. When in doubt, blame it on the circuit breaker – it’s always a good scapegoat for electrical woes!
Circuit breakers are essential components of any electrical system. They stop too much current flowing and thus, protect against potential fires . The most common cause for tripping is overload. But, other causes like short circuits and ground faults can also cause the breaker to trip. When it trips, there is something wrong that needs to be fixed right away.
Short circuits occur when two wires touch each other. This creates a low resistance path which allows a lot of current to flow with no load. Ground faults occur when the hot wire touches something incorrectly wired or with a damaged cord.
To prevent tripping, regular maintenance of the electrical system is needed. Keeping appliances in good condition, replacing worn-out cords and fixtures, and periodically checking for loose wires all help reduce the chances of tripping. In summary, understanding why the breaker trips and taking precautionary measures will keep you safe and save you repair costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what causes a circuit breaker to trip.
There are several possible causes, including overheating due to circuit overload, short circuits, ground faults, and age-related wear and tear.
2. How can I prevent my circuit breaker from tripping?
You can avoid overloading your circuit by keeping the number of electrical appliances used on one circuit to a minimum, regularly checking wires for signs of wear and tear, and not using too many extension cords.
3. What should I do if my circuit breaker keeps tripping?
If your circuit breaker is constantly tripping, it is important to identify and fix the underlying issue. Contact an electrician to inspect and repair any faulty wiring or electrical devices.
4. Can a circuit breaker trip without an overload?
Yes, a circuit breaker can trip due to a short circuit or a ground fault, which may occur without an overload.
5. How do I reset a tripped circuit breaker?
To reset a tripped circuit breaker, turn it off and then back on again. Make sure to identify and correct the underlying issue that caused the trip before restoring power.
6. What is the lifespan of a circuit breaker?
The lifespan of a circuit breaker can vary depending on usage and other factors. However, most circuit breakers last between 10 and 30 years.
Related posts:
- Common Electrical Issues in Kuala Lumpur Restaurant Kitchens
- The Top Electrical Problems Caused During Storms
- Difference between Handyman and Electrician
- How Many Outlets Can Be In A Commercial Circuit?

- Circuit Breakers
- Connecticut Electric
- Crouse-Hinds Cooper
- Eaton Cutler Hammer
- Federal Pacific
- Thomas Betts
- Westinghouse
Motor Controls
- Allen Bradley
- Appleton Electric
- Cutler Hammer
- E.M. & Wiegmann
- Joslyn Clark
- Killark Electric
- Moeller Electric
- NSI Industries
Transformers
- Dongan Electric
- Hammond Power

6 Reasons Your Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping with Nothing Plugged In
- 07 Feb, 2018
- Posted by: Circuit Breaker Wholesale

No one likes dealing with a tripped circuit breaker, but usually, it’s just a mild annoyance.
The solution is simple.
You unplug the responsible device(s) and reset the breaker.
Then, everything goes back to normal.
However, if your circuit breaker keeps tripping with nothing plugged in , it can be tough to keep your cool.
Fortunately, the reality of the situation is fairly straightforward.
Once you understand it, you’ll have an easy time restoring your circuit breaker to normal operation.
Why Does My Breaker Keep Tripping with Nothing Plugged In?
Electrical circuit breakers are essential for maintaining the safety and functionality of our electrical systems.
Their purpose is to interrupt the flow of electricity when there is an overload or fault in the circuit. However, it can be baffling and frustrating when a circuit breaker repeatedly trips without any apparent cause, even when no appliances or devices are connected.
Let's discuss potential reasons behind a circuit breaker tripping with nothing plugged in and provide potential solutions.
Here’s the truth: it’s very unlikely that your circuit breaker keeps tripping with nothing plugged in. Unless your building or home has had the electricity completely cut off from it, there is always some amount of load on your breaker.
Troubleshooting a Circuit Breaker that Keeps Tripping with Nothing Plugged In
Let’s look at some possibilities that could be behind your circuit breaker tripping even though nothing is plugged in.
1. Overloaded Circuit
One possible explanation for a circuit breaker repeatedly tripping despite no devices being connected is an overloaded circuit.
Each circuit has a specific capacity, measured in amps, that it can handle. If the combined power demand of all the devices on a circuit exceeds its capacity, the circuit breaker will trip as a protective measure.
To address this issue, it is crucial to assess the number and types of appliances sharing the circuit and redistribute the load accordingly.
2. Something Actually Is Plugged In
While you’ve probably already checked for this a million times, make sure that nothing could be tripping the breaker that you haven’t considered.
You might have a device plugged in outside or in the garage where you’ve forgotten all about it. Maybe there’s a device in another room that you don’t think is on the same breaker.
One way to check for this is to use an electronic circuit breaker finder to map out which outlets are connected to which breakers.
If you don’t want to make that kind of investment, just do a quick check and consider unplugging some devices in the surrounding area just to see if they were actually connected to the breaker in question.
3. A Damaged Input Wire or Faulty Wire
Another potential cause of a circuit breaker tripping without any devices plugged in is faulty wiring.
If you’re sure you’ve checked that first box, the next suspect is a damaged input wire or faulty wire that is causing current leakage . This problem could be dangerous if it wasn’t for your trusty circuit breaker constantly tripping to keep you safe.
Over time, electrical wiring can deteriorate due to wear and tear or other factors. Loose connections, damaged insulation, or short circuits can generate excess heat, increasing the likelihood of tripping the circuit breaker.
Of course, that doesn’t make it any less annoying.
You’ll need an electrician to come out and chase down the source of the leakage in order to fix it. This isn’t the type of weekend project most people are equipped for in terms of both the expertise and equipment required.
4. Ground Faults
Ground faults occur when the hot wire in an electrical circuit comes into contact with a grounded surface, such as a metal conduit or the grounding wire itself.
Ground faults can cause a circuit breaker to trip, even in the absence of connected devices.
To troubleshoot this issue, it is important to check for damaged wiring, faulty outlets, or improper grounding.
If a ground fault is suspected, consulting an electrician for a thorough examination and appropriate repairs is advisable.
5. Circuit Breaker Malfunction
Finally, you may need to replace your circuit breaker .
In certain instances, the problem may lie with the circuit breaker itself.
Over time, circuit breakers can wear out or become defective, resulting in false trips.
Factors like dust accumulation, excessive heat, or internal component failures can contribute to circuit breaker malfunction.
If there are suspicions of a faulty breaker, seeking guidance from a professional electrician to test, replace, or upgrade the circuit breaker is recommended.

6. Other Factors
Additional factors may contribute to circuit breaker trips, even when no devices are plugged in.
These factors could include:
- power surges
- external environmental conditions (e.g., lightning strikes)
- faulty appliances connected to other circuits in the same electrical panel
In such situations, further investigation is necessary, and the assistance of an electrician should be sought to diagnose and address the underlying issue.
Fixing Your Circuit Breaker So It Quits Tripping with Nothing Pugged In
Encountering a circuit breaker that keeps tripping with nothing plugged in can be perplexing and inconvenient. However, by considering potential causes such as overloaded circuits, faulty wiring, ground faults, circuit breaker malfunctions, or external factors, you can initiate troubleshooting and resolve the problem.
Provided you checked for devices that could be responsible, hopefully, you now have a better understanding of why your circuit breaker keeps tripping with nothing plugged in.
Always remember that electrical work can be hazardous, so it is best to consult a professional electrician to ensure the safety and integrity of your electrical system.
At least by troubleshooting first, you won’t be paying them for nothing. It also shouldn’t take them too long to root out the source of the constant tripping and fix it.

1335 Martin Luther King Jr Ave
Dunedin, fl 34698, (727) 648-6101.

1335 Martin Luther King Jr Ave, Dunedin, FL 34698
CALL US: (727) 648-6101

5 Reasons Your Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping and What You Can Do About It
Keep losing power, and aren't sure why here are five of the most common reasons why a circuit breaker keeps tripping, and what you can do to fix the problem..

1. Ground Fault
2. short circuit, 3. circuit overload, 4. arc fault, 5. damaged breakers, circuit breaker keeps tripping.
Newer Post >
Buell Electric's Blog

Electrical Safety Tips for Hurricane Season in Tampa

Protect Your Business with Professional Commercial Electrical Services

Shedding Light on Your Home: Finding the Right Electrician in Tampa

How Electricians Keep Up with Changing Technology in the Industry

The Importance of Regular Electrical Maintenance For Your Business

Marine Electrical Standards and Regulations You Need to Know

The Benefits of Installing a Smart Home System
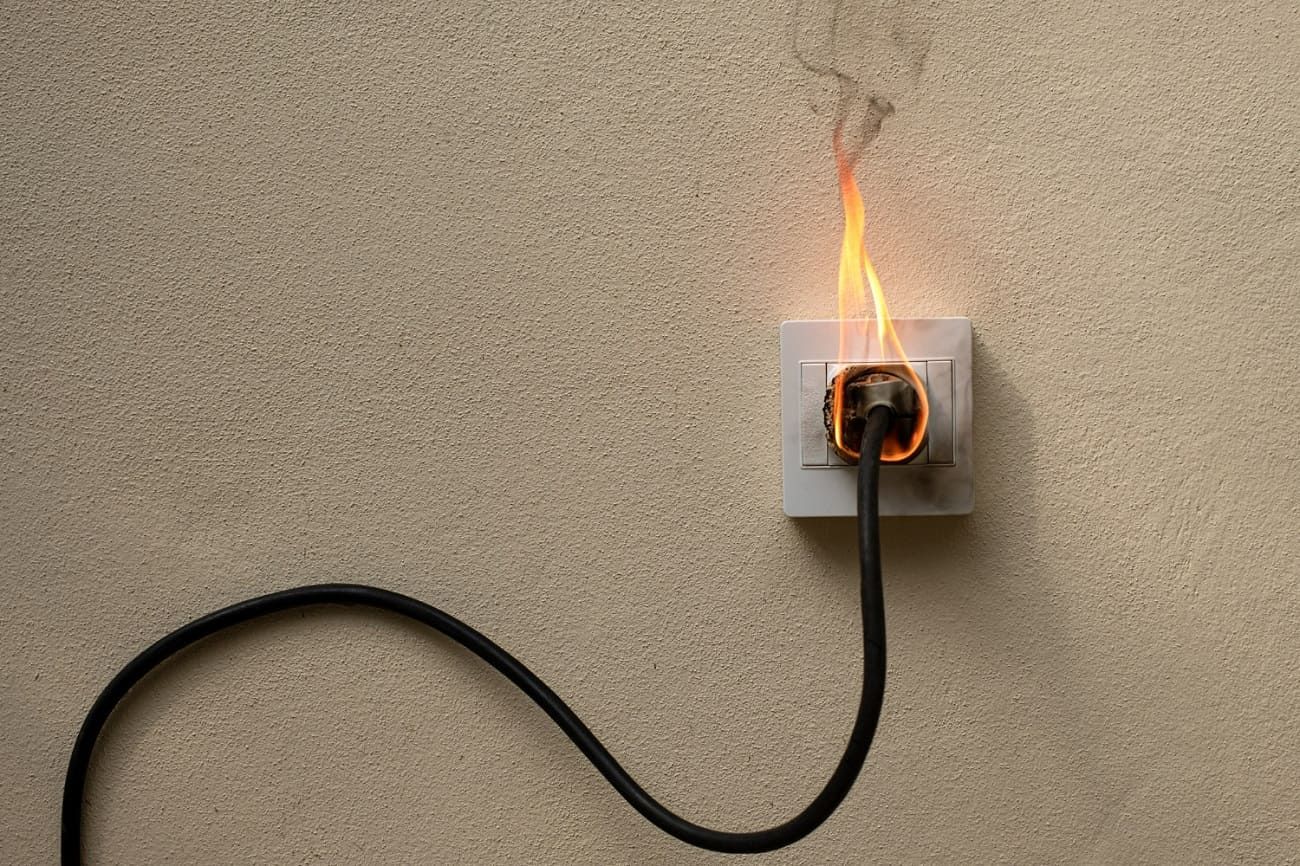

How to Prepare Your Home for an Electrical Emergency

5 Reasons Your Ceiling Fan Installation Should be Left to the Pros

5 Tips for Hiring Residential Electrical Services
[email protected]
Mon-fri 9:00 am - 5:00 pm sat-sun 10:00 am - 5:00 pm privacy page, connect with us:.

Mon-Fri 9:00 AM - 5:00 PM Sat-Sun 10:00 AM - 5:00 PM
All Rights Reserved | Buell Electric, Inc.

10 Steps to Take When Your Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping

What is a Circuit Breaker?
Take these 10 steps if your circuit breaker keeps tripping..
- Step 1: Identify the cause
- Step 2: Unplug appliances and devices
- Step 3: Reset the circuit breaker
- Step 4: Observe for immediate re-tripping
- Step 5: Determine the load
- Step 6: Assess the electrical load
- Step 7: Divide the load
- Step 8: Address wiring issues
- Step 9: Consider professional assistance
- Step 10: Maintain regular electrical inspections
Who should I call for an electrical repair service?

As the seasons unfurl their vibrant tapestry, it's time to infuse your living spaces with the artistry of light. Welcome to our guide on "Spring and Summer Ligh...

Three main features Our technicians are knowledgeable and they have up-to-date information about AC technology. For us, customers always come first. You can c...

Even though double ovens have been out for a little over 50 years, curiosity can still bring up the question “is this for me?”. Maytag double ovens have become ...

Galvin Power is reader-supported. When you buy via our links, we may earn a commission at no cost to you. Learn more
Why Does My Breaker Keep Tripping with Nothing Plugged In? (A Common Household Problem)
Written by Edwin Jones / Fact checked by Andrew Wright

Does your circuit breaker leave you puzzled and annoyed whenever it trips without a particular load responsible? It is essential to list down the possible reasons to the question – why does my breaker keep tripping with nothing plugged in.
Before contacting your electrician and paying for the service you can do it yourself; a little troubleshooting won’t harm you. The reasons for this issue could be a short circuit, overcurrent, ground fault, or defective circuit breaker.

Table of Contents
How to Identify a Tripped Circuit Breaker
1. short circuit, 2. overcurrent, 3. ground fault, 4. defective circuit breaker, how to troubleshoot your circuit breaker, can you replace the circuit breaker yourself, prioritize safety.

If there’s an overall power interruption inside the house, the first thing we think of is a power cut-off from the main supply. However, it’s a tripped breaker if only a specific part of the building experiences a blackout.
Primarily, you will look at the power indicator (on or off) of the breaker to understand the situation. However, you should also check the breaker’s interior if it is the type that stays “on” even though the circuit trips already.
Why Does Breaker Keep Tripping with Nothing Plugged In
A circuit breaker tripping without load repeatedly is a rare case of an electrical malfunction. First, however, we will tackle the probable reasons to check and give a corresponding action later on.

A short circuit causes a breaker to trip due to a large amount of current flow through the wires, leading to overloading of the outlet. This malfunction happens when a neutral wire touches an active or hot wire.
This issue results from a wiring problem somewhere around the house, such as wires damaged or chewed by animals, unsecured connections, or defective electrical switches and appliances.
A short circuit can give rise to a fire hazard situation if not attended to early. Aside from how hot it makes the wirings, the tripping breaker may also spark when it blows a fuse. You will notice it is already dangerous when smoke is already coming out from the fuse box.
Whenever a current surpasses the intended load or amperage capacity of an electrical circuit in a short period, overcurrent occurs. This kind of incident happens when an electrical device like appliances connects through those circuits.
The value of an electrical current in the normal state exceeds a hundred times much significant, so typically, the thermal point also rises. Then the breaker, which has a bi-metallic rod, makes it super-hot, making it trip.
Faulty wirings, arc fault, ground fault, or overload may cause this phenomenon.
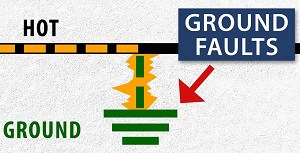
A ground fault happens when there’s an interaction between an active or hot wire and the ground. The vast amount of electric discharge from the grounded area of an electrical device directs back to the circuit breaker with more current than it can handle, causing it to trip.
National Electric Code (NEC) requires Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI) to prevent electric and fire hazards. On the other hand, whenever a ground fault occurs, an appliance or the GFCI itself is defective or broken.
If your tripped breaker problem is not from any of the possible issues listed above, you may be experiencing a fault in the circuit breaker itself. You can tell that your breaker has gone wrong if it frequently trips, incapable of resetting, burnt smell, and scorch marks in the electrical box.
When a breaker’s parts get old and won’t conduct electricity well anymore, that’s when you know it reached the peak of its lifespan. Likewise, it is likely to be worn out and get dull when a panel hasn’t been maintained or checked by a professional for quite some time.

Now that you know what the problem is, your next step is to solve it. The breaker tripping scenario will need a logical and systematic approach to deal with the issues above.
1. Double Check Plugged in Electrical Devices
You might say that an overload does not cause it, but in the end, there’s just a neglected electrical stove in the kitchen. It’s best to keep in check with the appliances we use around the house and know how much watts they consume.
There are tendencies where you’ll forget that a piece of equipment was in the socket of the same breaker that tripped. So apply the possibilities that not all of your electrical devices are out of the plugs.
If you’re willing to invest in an electrical circuit breaker finder , it is better to do so. A product like Klein Tools ET310 Circuit Breaker Finder can provide the accurate location of a particular outlet into its correct breaker.
2. Check the Input Wires
Input wires that went through wear and tear are also culprits of a tripped breaker. These wires tend to have a current leakage when busted, resulting in a short circuit and the tripping of the breaker.
Searching for the source of the electrical leak should be handed to the professionals. Electricians have the experience and equipment needed for a project like this.
3. Reset the Circuit Breaker
If there’s an absolute zero load and no input wire issues found, try resetting the main panel where the responsible circuit breaker lies. Wait for a moment, and if it trips again, there might be a problem with the circuit breaker, or it’s already defective.
4. Replace the Circuit Breaker

If all the troubleshooting methods fail, your last resort is to change the circuit breaker. When changing the old ones, consider the type, size, and brand of your new breaker. The type and size should be compatible, or else it won’t fit well inside your electrical panel.
In terms of brand, the quality is best if it passed all the NEC requirements. Good circuit breakers you can find are Siemens Q115 15-amp Circuit Breaker for a single-pole type and Siemens Q230 30-amp for a double-pole variety.
However, I highly advise using a circuit breaker from the same manufacturer as your main breaker panel . Although some brand new breakers look identical to those you used to have, their differences may lead to severe electrical complications if you insist on using them.
Many would agree that this is a Do-It-Yourself project, but you should also take responsibility for knowing what the building codes are. Rental homes, for example, prohibit replacing a breaker by yourself to ensure the safety of your neighbors.
Replacement can be pretty laborious, especially if you try to change multiple circuit breakers or the main panel box. Unfortunately, there are too many complexities to look out for, so it’s best to contact your electrician. They’re the best in this field anyway.
Since we’re talking about electrical matters, safety should be the number one priority. So as you inspect your circuit breaker, input wires, and electrical devices, you should wear safety gear, a goggle, for instance, to protect yourself.
When checking the breaker, you should not directly stand in front, for it may spark and give you electrical burns or, worse, get electrocuted. Also, if you’re working on an area that doesn’t give you enough visuals, use a flashlight so you can determine what you touch.
Lastly, if your breaker issue is beyond your skills, don’t go further and hand it to the professionals. Trust me. It’s better to pay the labor of an electrician than your hospital bills.
Why does my breaker keep tripping with nothing plugged in – To find out the answer, listing out the possible problems and troubleshooting is the best immediate action. However, a rushed solution is not safe and practical, leading to a waste of money or an unexpected injury.
Take note that the circuit breaker is the primary concern. If ever you need to change one, ensure its compatibility with the panel. Good breakers like Siemens Q115 15-amp are best to pair with a Siemens breaker panel, plus it’s cheap.

I am Edwin Jones, in charge of designing content for Galvinpower. I aspire to use my experiences in marketing to create reliable and necessary information to help our readers. It has been fun to work with Andrew and apply his incredible knowledge to our content.
Home » circuit breaker » circuit breaker tripping
Why Does my Breaker Keep Tripping With Nothing plugged In?

A circuit breaker can trip, but when it keeps tripping with nothing plugged in, it may be a sign of short circuit , ground fault , or a bad breaker.
This article will guide you on why a circuit breaker trips with nothing plugged in and how to fix it.
Table of Contents
why does my circuit breaker keeps tripping with nothing plugged in
Circuit breakers trip for four major reasons, and they include:
Circuit overload
Circuit overload is when you plug too many devices into a circuit than it can carry. Whenever there is more load on a circuit than rated, the circuit breaker trips to prevent electrical hazards .
Short circuit
A short circuit is one of the factors that can turn OFF your breaker . It occurs when a hot wire and neutral wire bridges.
This contact causes high current flow along the line, generating more heat than what the circuit can handle.
When such happens, the safety switch shuts off the current to avert damage to electrical appliances.
Short circuits may occur for several reasons, such as loose connections, damaged electrical insulators, faulty switches and appliances.
Grounds fault
Ground faults occur when a hot wire comes into contact with the earth wire. The contact pushes more current to the circuit than it can handle, causing your circuit breaker to switch off.
Ground faults can lead to electrical shock if left unchecked.
Faulty circuit breaker
If none of the above is causing your circuit breaker trip, it may mean that your breaker/outlet has gone bad. A bad circuit breaker can cause your lights to go off unexpectedly. If your power failure is because of a bad outlet, replace it with a new circuit breaker.
Consult an electrician to fix the issue for you.
You can buy a new breaker here on Amazon .
How to troubleshoot and fix a circuit breaker that keeps tripping without load.
To troubleshoot and fix a breaker that is tripping without load, follow these steps:
1. Check for overloaded circuits
If your breaker continues to trip, it may be that you plug too many appliances on the circuit.
- Start by unplugging all the devices on the circuit
- Reset the breaker
- Plug those devices one by one and watch the circuit. If it goes off again, you then know it’s a circuit overload problem.
- You can fix an overload problem by reducing the number of devices you plug into the circuit or by or by installing a new dedicated circuit for the load.
Related article: how many outlets on a 20 amp circuit?
2. Check for short circuits
Wires that have been severally exposed to high voltage are bound to have tears and wear and may be the reason your circuit breaker is tripping.
Troubleshooting a short circuit requires the use of your sensory organ (the nose and your eyes) to trace the area with a damaged insulator or burning smell usually left in the affected area. I suggest you look for a qualified electrician for the repair, as doing it yourself may cause electric shock.
Test for ground faults
GFCI stands for ground fault circuit interrupters . If your GFCI keeps tripping , it may be that you have a ground fault.
You can test for ground fault with a multimeter by inserting the red probe in the brass port of the outlet, and the black probe into the silver port.
If the voltage reading is zero, there is no ground fault, but if it’s otherwise, there is ground fault.
This will require the service of an electrician to replace it.
Related article: What are the differences between circuit breakers and GFCIs?
4. Replace the circuit breaker.
If all the troubleshooting fails and the receptacle still trips with no load, replace it, it has gone bad.
When replacing an old breaker, always consider the make, type, and size of your new breaker. The type and size should be compatible with the old one, else it won’t fit into your electrical panel.
Also, make sure the breaker passes all the NEC requirements else. It will not serve you well.
Some good circuit breakers you can find are Square D 20 amp breakers for a single pole and 30 amp breakers for double poles.
However, it is advisable to use a circuit breaker from the manufacturer of the main breaker panel to avoid sizing and fitting problems.
For more details on replacing a bad breaker, read our guide on how to replace a bad circuit breaker .
Need an electrician? Contact us for inspection.
If the breaker trips every time even with nothing plugged in and you are not confident enough to find the cause, call us to help you fix the issue.
Frequently Asked Questions
My light went off, but the circuit breaker did not trip. why.
Some circuit breakers work like that; they are called trip-free circuit breakers. Trip-free circuit breakers shut off the lights even when the switch is ON.
They work best on circuits that do not withstand over-currents. If you experience a free trip, call your electrician for troubleshooting.
How do you know if a circuit breaker has tripped?
If your lights have gone off in a certain part of the house rather than the entire building, you suspect a tripped breaker.
You can also see that by looking at the breaker’s switch to see if it is ON or OFF. Some types of circuit breakers (the trip free) remain ON when there is no light. However, using either of the two methods can help you detect if your circuit protector is off.
How do I reset a tripped circuit breaker
To reset the tripped breaker, turn it off and unplug all the appliances connected to it, and then ON it again. For safety reasons, we recommend that you stand by the side of the breaker’s panel should it spark a light while resetting.
You should wear goggles and also make use of torchlight to illuminate the area if there is no light.
After the reset, wait for some time before plugging back your appliances to make sure you do not overload the circuit.
Related articles
- What Wire Size Do I Need for my 60 Amp Breaker?
- What is a 15-amp Circuit Breaker Used for?
- Square D Circuit Breaker Types and Uses
- What is an Oil Circuit Breaker?
- Overview of Square D BDL36100 Powerpact Molded Case Circuit Breaker
- Eaton Cutler Hammer Breakers
- What is a Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)?
- Causes of Power Surge and How to Prevent it.
- What is a Motor Protection Circuit Breaker?
- GFCI Won’t reset, 7 Causes and How to Fix it.
About mariaelectricals
Hi, I am Emmanuel Nwankwo, a commercial electrician and the founder of mariaelectricals.com . I established this blog to share my decades of work experience in electrical installations and repairs.
- (317) 834-1922

Dealing with a Tripping Circuit Breaker: Troubleshooting and Solutions
A tripping circuit breaker can be a frustrating and inconvenient issue in your electrical system. Circuit breakers are designed to protect your home or building from electrical overloads and short circuits. When a breaker repeatedly trips, it indicates a problem that needs to be addressed. Let’s talk through the steps to troubleshoot and resolve a tripping circuit breaker.
Understand Circuit Breaker Tripping
Circuit breakers are designed to automatically shut off power when there is an excessive current flow through a circuit. This action protects the circuit and prevents electrical hazards such as overheating, fires, or electrical shock.
Identify Potential Causes
A tripping circuit breaker can occur for a multitude of reasons, and it’s best to know the potential causes for this issue. Here are several reasons your circuit breaker may be tripping consistently:
Overloaded Circuit
One of the common causes of a tripping breaker is an overloaded circuit. This occurs when the total electrical load on the circuit exceeds its capacity. It can happen if you are running too many high-power devices simultaneously on the same circuit.
Short Circuit
A short circuit occurs when a hot wire encounters a neutral wire or a ground wire, resulting in a sudden surge of electrical current. This can cause the breaker to trip instantly.
Ground Fault
Like a short circuit, a ground fault occurs when a hot wire meets a ground wire or a conductive surface. It can also lead to a tripped breaker.
Faulty Appliance or Wiring
A malfunctioning appliance or faulty wiring in the circuit can cause the breaker to trip. Identifying the specific device or wiring that is causing the issue is crucial for troubleshooting.
Reset the Circuit Breaker
When a circuit breaker trips, the first step is to locate the breaker panel and identify the tripped breaker. It will be in the “off” position or between the “on” and “off” positions. To reset it, push the breaker handle firmly to the “off” position and then to the “on” position. If it immediately trips again, proceed to the next steps.
Determine the Load
To troubleshoot the circuit, unplug or turn off all devices connected to it, then reset the breaker. Gradually reconnect or turn on one device at a time and observe if the breaker trips after each reconnection. If it trips immediately after connecting a specific device, it may be faulty and require repair or replacement.
Inspect for Wiring Issues
Inspect the circuit’s outlets and switches for signs of damage, loose connections, or exposed wires. If any abnormalities are noticed, consult a local licensed electrician to inspect and repair the wiring.
Address Overloaded Circuits
To ensure the safe operation of the circuit, first determine its electrical load capacity, typically marked on the breaker or panel. Then, distribute the load among multiple circuits by connecting devices to different outlets.
Consult a Professional
If the tripping issue persists or you are unsure about any aspect of troubleshooting the breaker, it is advisable to contact a qualified electrician. They have the expertise to diagnose and address complex electrical problems safely.
Put Your Circuit Breaker Issues Behind You
A tripping circuit breaker should not be ignored, as it indicates an underlying issue that needs attention. By understanding the potential causes, resetting the breaker, identifying the load, inspecting for wiring issues, addressing overload situations, and seeking help from a local licensed electrician, you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve a tripping breaker.
Make sure you contact Grounded Solutions to inspect your home’s electrical system. We’re here to help you with any and all maintenance, installation, or general electrical needs!

Grounded Solutions is licensed, bonded, and insured. We’re headquartered in Indianapolis, but we service the entire state of Indiana and beyond.
- Bargersville
- Beech Grove
- Indianapolis
- Martinsville
- McCordsville
- Mooresville
- Noblesville
- Shelbyville
- Whiteland (And New Whiteland)

- 450 E Mahalasville Dr Martinsville, IN 46151
Need excavation, drainage or concrete work?

- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Get Service TODAY: (415)-559-3333
- Commercial Electrical
- Industrial Electrical
- Facility Services
- Emergency Power
- Design Build
- Fire-Life-Safety
- Data Telecom
- Electrical Contractors
- Electrical Lighting
- Electrical Outlet
- Electrical Switches
- Electrical Service Upgrade
- Fire Safety Systems
- Health/Air Quality Systems
- Child Safety Systems
- Electrical Distribution Safety Systems
- Home Grounding Safety Systems
- Home Surge Protection Systems
- Security Safety Systems
- Home Lighting and Automation
- Motorized Window Treatments
- Tesla EV Charger
- JuiceBox Pro 40
- ChargePoint Home Flex
- Features Of Energy Backup
- Home Batteries
- Heat-Pumps & Mini-Splits
- Areas We Serve
Circuit Breaker Not Tripped but No Power: Understanding Symptoms and Solutions
- by Momentum Electrical Team
- September 25, 2024

Introduction
Discovering that your home has lost power despite the circuit breaker remaining untripped can be puzzling and frustrating. In this article, we will delve into the common causes of power outages without a tripped breaker and explore troubleshooting steps to diagnose and resolve the issue. From inadequate power supply to damaged wires and faulty circuit breakers, we will provide expert insights and real-world examples to help you understand and address electrical issues effectively.
Whether you’re a homeowner or an aspiring electrician, this article is a valuable resource for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of power outages and ensure the safety and functionality of their electrical systems.
Common Causes of No Power Without a Tripped Breaker
Realizing that your home has lost electricity despite the circuit breaker remaining untripped can be puzzling and frustrating. It’s essential to delve into the common culprits behind such occurrences to diagnose and resolve the issue. One scenario might involve insufficient energy supply due to a surge in demand, similar to a plastic products producer who faced low pressure incidents after adding new machinery, leading to the mistaken belief that a capacity increase required an additional compressor. In another situation, a blackout could compel residents to find refuge, as encountered by Durham citizens who depended on emergency shelters during a loss of electricity. Troubleshooting can also be complicated by the lack of clear guidance, such as when vehicle owners struggle to identify relevant relays in the absence of an owner’s manual or when fuse covers do not clearly indicate relay functions.
Loss of electrical supply, whether brief brownouts or full-fledged blackouts, can be triggered by various factors, including extreme weather events that damage electrical lines or affect electricity generation. For example, blackouts in western North America have been attributed to a combination of hotter summers, decreased hydroelectric reservoir levels, and increased electricity demand. Furthermore, residences with obsolete power systems may not be prepared to manage the contemporary energy usage requirements, resulting in possible blackouts. Ensuring that portable generators are correctly installed and used is crucial for safety, as improper use can endanger both residents and utility crews.
Comprehending your home’s power supply and amperage is crucial; it determines the maximum amount of energy accessible to your household. This knowledge is particularly important as we transition to a more electrified home environment, aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. The capacity of your home’s system, which can range from 30 to 400 amps, serves as a limit to how much you can safely electrify. In preparing for outages, being financially ready and knowing your insurance coverage can alleviate stress during these disruptions, ensuring that you can cover temporary expenses if needed.
Checking for Simple Issues
When dealing with issues related to electricity, it’s advantageous to begin with the fundamentals before progressing to more complex problem-solving. First, determine whether the electricity disruption is confined to one specific area or appliance by examining other devices in the vicinity for functionality. Confirm that the circuit breaker switch corresponding to the affected area is indeed switched to the ON position. This initial inspection can frequently uncover straightforward resolutions to electrical interruptions, as not all interruptions in electricity result from intricate issues. For example, during a significant interruption that affected the MBTA Green Line in Kenmore, it was initially unclear what caused the disruption. However, it was determined that an electrical problem was the culprit, emphasizing the significance of checking for simple issues first.
Residents in Monroe, Ontario, and Livingston counties took similar proactive measures as they prepared for a planned interruption of electricity by setting up warming stations in anticipation. This preparation highlights the significance of taking into account simple, yet crucial factors such as ensuring power switches are on before delving into deeper diagnostics related to electricity. These real-world examples serve as reminders that while larger-scale outages often require professional intervention, individual homeowners can address many common power-related issues by starting with the basics.
Understanding GFCI Outlets and Their Role
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlets are crucial for ensuring the safety of a home’s power system. These specialized outlets are designed to monitor the flow of electricity and can detect even slight imbalances in the current. If a discrepancy is observed, the GFCI outlet swiftly interrupts the circuit, effectively preventing shock or the potential for a fire. Knowing the locations of GFCI outlets in your home is crucial for effectively addressing electric problems. Consider them as indispensable safeguards; for example, in the event of a lightning strike that delivers over a million volts of electricity, capable of inflicting extensive damage to a property’s electronic systems, a GFCI can serve as a first line of defense against potential hazards. With the frequency of fires caused by electrical problems , highlighted by over 22,000 fire department responses annually, the proper function of these outlets becomes a cornerstone of home safety measures.

Identifying and Fixing Damaged Wires
Faulty wiring is a common cause behind outages that occur without a tripped circuit breaker. Various factors can lead to wire degradation, such as aging infrastructure, animal interference, and environmental damage. It’s essential to examine the circuit’s wiring for any apparent wear and tear or damage. Encountering such issues necessitates intervention by a qualified electrician to ensure repairs are performed safely and correctly.
For instance, an air compressor in a metal processing plant suffered from a fire that damaged its VSD controlled machine. Despite being disconnected from the main source, undocumented alterations had introduced an external energy supply into the compressor’s panel, posing a significant risk to service technicians. In another instance, the illicit practice of electricity theft through ‘kunda’ connections in Pakistan has led to a network of entangled and exposed wires. This not only poses a significant safety hazard causing many accidents and fatalities but also undermines the dependability of the electricity supply, leading to enforced load shedding by companies to minimize revenue losses.
Furthermore, unforeseen events such as the fire at a substation in Chennai, which resulted in a considerable blackout, highlight the susceptibility of systems to equipment malfunctions. This situation demonstrates the importance of maintaining and updating electrical infrastructure, as outdated systems can lead to outages with large-scale implications.
The electricity network, mainly constructed in the 1960s and 1970s, is now under pressure due to contemporary demands. With 70 percent of transmission lines over 25 years old, the risk of power disruptions is exacerbated. The recent declaration by the Department of Energy (DOE) to invest $3.5 billion in enhancing the resilience of the power grid throughout the United States is proof of the urgent requirement for modernized infrastructure capable of meeting current energy demands and protecting communities from power failure.
Power outages, influenced by factors like extreme weather conditions, can leave communities without essential services such as heat, water, and communication channels. The significance of dependable wiring and power systems cannot be emphasized enough, as they are the lifelines that keep our society functioning. With the growing support for the right to repair movement, consumers and independent repair businesses are equipped with the necessary resources to tackle such technical problems, guaranteeing safety, dependability, and uninterrupted functioning in our everyday existence.

Troubleshooting Electrical Outlets
When examining electrical concerns in your residence, electrical outlets are frequently the initial suspects. For example, imagine you’re trying to charge your laptop, but despite being plugged in, the battery isn’t charging, and nearby, a desk lamp remains unlit. This situation indicates that the outlet may not be delivering electricity. To confirm, you could observe the laptop’s functioning on battery operation, but its inability to charge indicates a problem with the outlet itself.
George Tucker, with over three decades of experience in the AV industry, explains that the internal contacts within the outlet can become loose over time. This loosening typically results from general wear and tear or improper use. The metal contacts, designed to hold the plug’s blades securely and establish a connection, can lose their tension, resulting in intermittent or failed power delivery.
To properly diagnose and address these issues, it’s imperative to disconnect any devices and inspect the outlet for damage or loose wiring. If any problems are identified, they should be rectified by a professional electrician. This method not only guarantees safety but also prevents the potential danger of fires, which can have serious consequences for the safety of your home and loved ones. Furthermore, staying informed about how to respond during blackouts and the dangers posed by carbon monoxide during such times is crucial for maintaining a safe and functional living environment.

Can a Circuit Breaker Fail Without Tripping?
Circuit breakers are crucial components in systems, offering protection by tripping to interrupt flow during an overload. However, there are instances where circuit breakers may malfunction and fail to trip, sometimes due to a faulty breaker or complications within the wiring itself. For instance, a case study at a metal processing plant uncovered how a compressor’s panel posed a noteworthy safety risk. Despite being disconnected from electricity, previous undocumented alterations introduced an unknown electrical supply into the panel, which could have severe consequences for service personnel.
In another incident reported in Chennai, a fire incident at a Manali substation led to widespread power outages. The issue was not attributed to overload, as the demand was lower than usual, but rather to an equipment malfunction, highlighting the importance of regular inspections and maintenance.
These examples underscore the necessity for vigilance and proactive measures. When suspicions arise concerning a circuit breaker’s performance, the best course of action is to consult a licensed electrician to inspect the system. If a faulty circuit breaker is identified, replacement by a professional is imperative to ensure ongoing safety and reliability of the electrical system. In addition to immediate safety concerns, such preventative measures can avert potential cascading failures that could impact broader systems and services.
Steps to Troubleshoot the Problem
In the event of an outage where the circuit breaker hasn’t tripped, it’s critical to systematically identify the problem. Start by examining which circuits are impacted and rule out any simple problems, such as disconnected devices or turned-off power strips. Examine the wiring and outlets for any damage that’s visible to the naked eye. If everything appears normal, yet the problem persists, it’s time to call in a professional. A certified electrician can perform a thorough assessment and fix any underlying electrical problems securely and effectively. It’s crucial to bear in mind that trying to solve problems with electricity without the right knowledge can be risky and may worsen the problem.

When to Call a Licensed Electrician
When power problems arise, homeowners may be tempted to address them independently, but there are critical moments when the expertise of a licensed electrician is indispensable. For example, if identifying the main reason for a power outage proves difficult, or there are visible indications of wiring damage, or simply a lack of familiarity with power systems, professional intervention is recommended. Electricians not only come equipped with the necessary tools but also possess an in-depth understanding of power systems, which is crucial for ensuring safety and functionality in residential settings. The complex nature of power work is evident in the case of an air compressor at a metal processing plant, which, after being modified unsafely following a fire, became a latent hazard. Similarly, during an inspection of a Tesla Wall Connector at a residence, multiple underlying issues were uncovered, including improperly torqued connections, which could have led to catastrophic failures. These examples underscore the importance of meticulous attention to detail and adherence to safety standards, qualities embodied by seasoned electricians. With the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics citing an average salary of $60,240 annually for electricians, the field not only promises a stable career but also provides an essential service to homeowners and the community at large. The variety of environments in which electricians work—from residential to industrial—further emphasizes the comprehensive training they undergo to handle a range of maintenance tasks and complex fittings, ensuring that every power system they touch adheres to the highest standards of safety and efficiency.

Replacing a Faulty Circuit Breaker
When a circuit breaker fails, one might consider replacing it as a last resort after all troubleshooting steps have proven ineffective. However, this task is not for the untrained. A cautionary tale comes from a metal processing plant where an air compressor suffered fire damage. An improperly installed Variable Speed Drive (VSD) led to a hazardous panel with undocumented changes, posing a serious risk to service technicians. It’s such risks that underscore why only a licensed electrician should undertake the replacement of circuit breakers. They have the expertise to ensure compatibility with the existing power system and adherence to safety protocols. Unlicensed work, like that of Oscar Lewis who was fined $25,000 for operating without a license, not only breaches legal requirements but also puts people and property at risk. Certified electricians are trained to comprehend the intricacies of systems found in various environments, from homes to commercial buildings and industrial settings, where the stakes are high and the infrastructure is intricate. Their role is critical in maintaining the safety and functionality of electrical features, a responsibility that should not be taken lightly.

In conclusion, power outages without a tripped circuit breaker can be caused by factors like inadequate power supply, damaged wires, faulty circuit breakers, extreme weather events, and outdated electrical systems. Troubleshooting these issues requires starting with simple checks, such as ensuring power switches are on and examining other devices for functionality. Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlets play a crucial role in home safety by detecting imbalances in electrical currents.
Damaged wires are a common culprit behind power outages without a tripped breaker, and it is important to have a qualified electrician inspect and repair any damage. While circuit breakers are designed to trip during an overload, malfunctions can occur, and it is necessary to consult a licensed electrician for replacement. When troubleshooting power outages, it is important to check affected circuits, inspect wiring and outlets, and seek professional help if needed.
Replacing a faulty circuit breaker should only be done by a licensed electrician to ensure compatibility and safety. Understanding the causes of power outages without a tripped breaker and knowing when to seek professional help are essential for maintaining the safety and functionality of electrical systems. By following proper troubleshooting steps and relying on licensed electricians when necessary, homeowners can effectively address these issues and ensure the continuous operation of their electrical systems.
Contact Momentum Electrical Contractors today for professional help and ensure the safety and functionality of your electrical systems.
What Our Clients Say
They were fabulous with their work and communication. We used them on a commercial project for our electronic lockers and it went very smoothly. Thanks so much!
I am very impressed with Tom and his crew. They’re responsive, reliable, and do top quality work.
We hired Momentum to help with installing an electric wall oven. These guys are remarkably professional; and they take customer satisfaction very seriously.
Momentum offered a reasonable price, accommodated our tight timing and executed the project seamlessly. The project had many unexpected issues and they solved all of them in a short period of time.
Momentum’s work was done efficiently and professionally at a reasonable price. Will definitely use them for future projects if anything comes up.
Highly recommend!! Exceptional service and price. Tom was very helpful, a really nice straight forward guy who definitely cares about his clients.

- Electrical , How To & Guides
Why Does My Breaker Keep Tripping With Nothing Plugged In?
- August 20, 2024
- By Leela Prasad
In most cases, we blame a tripped circuit breaker on high-power-usage appliances like air conditioners, hair dryers, curling irons, and blenders. But suppose the circuit breaker trips, and no such devices are plugged in. Since nothing is plugged in, it is reasonable to question why the breaker keeps tripping.
Faulty electrical systems can cause fires, so it’s understandable if you’re worried about the potential danger to your home.
Is it frustrating and perplexing when your circuit breaker trips for no apparent reason? Why does my breaker constantly trip when there is nothing plugged into it? It is a question we must answer, and you must compile a list of potential causes.
Trying a few troubleshooting steps before calling an electrician and potentially wasting money on work you can complete on your own is a good idea. Possible causes of this problem include a faulty circuit breaker, overcurrent, ground fault, or short circuit.
Explain What A Circuit Breaker Is?
Circuit breakers stop energy from flowing through a circuit if the current is too high. Electrical fires, shocks, and other injuries would be more common without circuit breakers.
Understand electricity before learning how a circuit breaker works. Electricity is electrical charge transfer between atoms. Electricity comes from natural gas, coal, or solar. Voltage, current, and resistance define electricity.
Voltage is the pressure needed to carry electric charge through a conductor. When current meets the conductor, resistance occurs. Some materials transmit electricity better than others because conductors have different resistances.
Hot, neutral, and ground cables make up your home’s wiring. Hot and neutral wires rarely touch, like ships at night. A high-resistance appliance maintains voltage safe by passing a current through it.
Sometimes the hot and neutral wires touch. It reduces current resistance, causing dangerous voltage and current levels and even fires—circuit breakers trip when voltage and current are too high. The trip disables the circuit until the problem is fixed.
When Does A Circuit Breaker Trip?
A tripped circuit breaker typically cuts power to a single room rather than the entire home. Several power outlets in a single room, possibly a USB power outlet, may suddenly stop functioning.
To determine why your circuit breaker keeps tripping, inspect your home’s electrical panel or fuse box. Keep any furniture, boxes, books, and shelves well away from the electrical panel or fuse box’s opening and familiarize yourself with its location.
Take the time to learn the relationship between each switch or fuse and the component it controls if your circuit breaker and fuse box aren’t easily accessible or well-labeled. If a circuit or fuse trips or blows, you’ll be able to pinpoint which one it is. When working with many circuit breakers or fuses in a single room, such as the kitchen, clearly denote which appliances each switch controls. Doing so will save time and effort trying to fix a faulty circuit breaker.
When an overcurrent condition causes a circuit breaker to trip , the switch’s handle will be halfway between the “on” and “off” positions. A red region could appear if the circuit breaker has been tripped. Of course, that’s subject to your home’s electrical system capabilities. Suppose the handle of the panel barely moved at all when tripped. In that case, you’ll need to examine the switches thoroughly to determine which one has malfunctioned.
Why Your Circuit Breaker Trips “Without Load”?
You must first understand why your circuit breaker continues tripping without load.
- Because there exists a load
- Unless your home or building has no electricity, the breaker is constantly working
- Capacitors are in your TV. Diodes, transistors, and others conduct
- Relatively modest quantities of current even when the TV is off
Therefore, it’s not tripping without a load
Then, what’s the issue?
The wiring is likely the issue assuming there isn’t a mechanical issue with the circuit breaker.
3 Common Causes Of A Tripping Circuit Breaker
Before we run through a possible list of wiring issues that could be to blame, please double-check that no appliance is still plugged in and turned on that you had forgotten about.
It’s common for homeowners to forget about electronics left in the garage or plugged in outside.
If that isn’t happening, here are three electrical issues to think about.
1. The Current Overflow
One possible cause is the current leaking from one or more of the input wires. If that’s the case, the difficulty you encounter ultimately benefits you. It’s for your protection.
2. Torn Wires
It’s not simply the input wires that it could harm. Perhaps insects or rodents got to them and chewed significant holes in them. This issue can trigger a breaker trip even with very light loads.
3. An Electrical Outlet with a Loose Wire
This electrical issue can be frustrating. A loose wire in one of your outlets trips your circuit breaker and will continue until you have it fixed. It frequently occurs if the outlet is not GFCI (Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupter).
Check Wires Properly Now
If your circuit breaker continues tripping without load, follow the preceding recommendations.
Power surges can cause this once.
Why Does Breaker Still Trip With Nothing Plugged In?
A circuit breaker frequently tripping without load is rare. First, we’ll discuss possible reasons to check and then take action.
1. Something Is Plugged In
Make sure everything has stayed on the breaker that you have examined.
You may need to remember an item plugged in outside or in the garage. A device in another room is on a different breaker.
Have used an electronic circuit breaker finder to determine which outlets are connected to which breakers.
Whether you don’t want to spend that much, perform a fast check and unplug any nearby gadgets to see if they’re linked to the breaker.
2. Wires and Outlets Cause Short Circuits
Your house has wiring issues if the circuit breaker repeatedly trips without appliances. Damaged cables, electrical connections, switches, and devices can cause short circuits.
Short circuits overheat and overload wires. A circuit breaker trips to protect your appliances.
If this happens without additional energy-consuming appliances, inspect your electrical outlets and wiring to find the cause and fix it.
3. Ground Fault
If a hot wire meets a ground wire, metal wall box, or metal frame members, it causes a “ground-fault” short circuit. Kitchens, baths, and outdoor areas with high moisture levels are especially vulnerable to ground faults. Electrical shock can result from ground faults.
You can diagnose and rectify a ground fault, but you should also prevent them. When ground or water contact is probable, NEC laws may require GFCIs on outlets (ground-fault circuit interrupters).
Ground faults reduce resistance and improve electrical flow instantly, like hard shorts. The circuit breaker’s internal mechanism heats up and trips. If there is a ground fault, the circuit breaker may trip again after being reset.
4. Overcurrent
Overcurrent occurs when current exceeds load quickly. It commonly happens when electrical items like home appliances connect through circuits. The thermal bridge grows as expected because the normal electric flow is worth many times more. The clad metal in the breaker gets quite hot, tripping it.
5. Arc Fault
Most local electrical regulations are based on the National Electrical Code, which has gradually increased arc-fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) requirements (AFCI).
AFCI breakers detect power fluctuations caused by wire connection sparking (“arcing”) in addition to overloads, short circuits, and ground faults. Loose switch or outlet screw terminal connections can cause arcing.
These breakers detect wiring issues before they cause short circuits or ground faults. Neither fuses nor circuit breakers protect against arc failures. Arc fault protection prevents arcing-related fires.
Regular breakers reset AFCI breakers. Loose wire connections in the circuit cause recurrent tripping and arcing.
6. Overuse Of Home Appliances
An amp meter is used to measure electrical current, and each circuit breaker is rated to provide a specific amount of that current.
When the circuit breaker’s maximum amp load is reached, the breaker will likely trip.
It is a common occurrence after purchasing a high-power device for the home, such as a plasma TV, which necessitates the use of a dedicated circuit or the maximum available current.
7. Troubleshooting The Circuit-Breaker Issue
If none of those causes your circuit breaker to trip, the problem may be a malfunctioning breaker. Something needs to be fixed if your breaker keeps tripping, won’t reset, has a scorched smell, and leaves markings in the electrical box.
A breaker has reached the end of its useful life when its components no longer conduct electricity efficiently. Similarly, suppose a panel has yet to be maintained or checked by a professional. In that case, it’s likely to be worn out and dull.
What Signs Indicate a Bad Breaker?
A breaker is terrible if it sparks when turning on, the breaker trips quickly, and the breaker is making a popping sound or clicking sound. If your breakers are flashing, you need to change them immediately. If the breakers are tripping quickly, they also need to be changed.
If it hums, replace it.
How to Fix a Breaker That Tripped With Nothing Plugged in?
Step 1: turn off light switches.
Start by turning off all the lights and unplugging all the electronics and appliances in the powerless rooms. Check for connections. This step is vital To avoid overload. I’m sure you’ve tried turning on your breaker a million times with all those appliances off. Check for overloading one last time.
You may have plugged anything in the garage and need to remember it. An electronic circuit breaker locator can assist you in locating the breaker’s related areas to rule out overloading.
Step 2: Identification Of Tripped Circuit Breaker
Open your circuit breaker box and find the tripping breaker . Circuit boxes are typically placed outdoors, away from elements and impediments. Most boxes are locked with a tiny metal plate.
Overloaded circuit breakers hum before turning off. The breaker is off if there is no sound after unplugging all devices.
Step 3: Check Your Circuit Breaker
For proper diagnosis, you must learn your breaker’s behavior while all appliances and lights are off.
Test your circuit breaker and turn on the lights without the appliances.
Check two things:
1.The lights return but the breaker trips after a few seconds.
2.The breaker trips promptly, flickering the lights “ON” and “OFF.”
Your observation may indicate wiring, circuit damage, or overloading (yes, you got that right). Your circuit breaker may overload if the lights are switched on but shut off. Check your checklist for breaker overloads.
If the breaker trips when you turn it “ON,” it may be a malfunctioning wire or breaker. Call an expert to inspect and fix the wiring.
Step 4: Turn Off Appliances And Lights Once
Start by shutting everything off and checking what might be generating the overload. Overloaded breakers rarely turn off immediately. Instead, they power all switches and outlets until they’re exhausted.
Before resetting the breaker, turn off all appliances. To locate the perpetrator, turn on each gadget many times.
Step 5: If The Problem Persists, Recheck The Input Wires
As with the output wires, the input wires will eventually wear out and could be the root cause of your breaker’s frequent trips. When these wires are broken, the current might seep out, causing a short circuit and the circuit breaker to trigger.
If you have poor wiring, you may experience frequent breaker trips, which, if left unchecked, could result in electrical shock if you use certain appliances. If you have yet to experience working with electricity, it is best to have a pro handle the wiring.
Step 6: Turn Off The Circuit Breaker And Turn It Back On
Resetting the breaker will ensure the problem is permanently resolved once the broken wire has been located and repaired. Simply cycling the switch between “OFF” and “ON” will reset the breaker. When the lights come on, it’s because it’s resetting. Once the status light stops blinking, you know everything has finished processing. Another option is to press the test button to see if the circuit breaker is functioning correctly. Because of this, the breaker will close by itself. If it does not trip, it must be replaced immediately.
Step 7: Changing The Breaker
If you have exhausted all other troubleshooting steps and the breaker still won’t work, you will need to replace it. Although the method is straightforward, working with the panel is risky due to the high energy levels of the hot bus bars. If you insist on replacing the breaker on your own, do so only if you have a flashlight handy before shutting off the main power supply switch.
Now that you’re ready to go, here are the necessary measures:
- Carefully pry off the cover plate of the circuit breakers with the screwdriver. Then, locate the tripped circuit breaker and switch it to the “OFF” position.
- Keeping in mind that you don’t want to tangle any other wires, slowly extend the wire from the breaker out of the panel.
- Pull the old breaker out of the panel by grabbing the edge and turning it to the side. The circuit breaker must break loose from the control board.
- Unscrew the terminal and pull the wire to disconnect the black circuit.
- Install the replacement circuit breaker by sliding the bare end of the black circuit wire beneath the screw terminal. Commonly known as the LOAD symbol.
- Hook the replacement breaker’s back into the holding clip at the back, then slide it forward into its proper spot. As you install the breaker, ensure it is in a position parallel to the bus bar.
- The extra wire should be folded up and tucked below the panel. Once again, avoid touching any other cables or metal components.
- You should swap out the panel cover and its screws. To prevent a surge in electricity demand and possible power outage, you should switch the main breaker off first.
- To activate everything, flip the main switch to the “ON” position.
If the Circuit Breaker Trips, Don’t Ignore It
Pay attention to a constantly tripping circuit breaker. One of your circuits is probably being routinely overloaded if this keeps happening. There is a maximum voltage that your circuits can safely take. If you go above that voltage, an electrical fire could occur. Because of this, the circuit breaker has tripped, cutting off power to your home.
It’s terrible when a tripped circuit breaker causes a power outage. Nonetheless, keep in mind that the circuit breaker plays a crucial function. Overheating of wires due to excessive current is avoided by using a circuit breaker. Overheated wires provide a fire hazard. We recommend that you contact one of our electricians immediately if your circuit breaker keeps tripping. Now is the time to call!
Reasons To Change Your Service Panel
Built before 1960, they may have used a fuse box instead of a panel in the home’s electrical system, which may need help to handle the current needs of modern appliances. Furthermore, if your service panel is quite old, it will need to be repaired frequently and at great expense.
Skilled and reliable professionals will evaluate your panel system thoroughly and provide you with their honest recommendations so you can make the best possible choice for your home.
3 Key Reasons To Consider While Replacing Your Service Panel
Expand your circuit’s capacity first: Consider adding new circuits to your electrical system when you make significant changes to your home’s layout or install new or larger appliances. But your electrical panel needs more circuits. In that case, you’ll need to update it to finish your renovation.
Extra safeguards:
- Thanks to updated service panels, electrical shock and arcing are no longer a concern. With the option to combine AFCI and GFCI breakers, they provide a comprehensive indoor/outdoor solution that is code compliant.
- Increase the worth of your home by doing these three upgrades:
- Have a professional electrician install a new service panel to quickly and easily increase your home’s resale value.
- Double Tapped Breaker – How To Fix?
- Shunt Trip Breaker Explained: What It Is And How It Works
- Circuit Breakers vs. Fuse Boxes
- How To Troubleshoot And Fix AC Breaker Tripping Issues?
The Bottom Line
Even if no appliances are turned on, the breaker can repeatedly trip if there are other issues. These problems, such as broken input wires or an overloaded circuit, should be investigated further. Since the procedure has been laid out for you, more testing is unnecessary.
If a breaker keeps tripping, it may be time to call in the specialists. Short circuits, overloaded circuits, and ground faults can all be safely repaired by an electrician. If any of the breakers on your electrical panel are undersized, broken, old, or otherwise on the verge of failing, it is best to have a professional come and service the panel.
Related Posts:
- Water Heater Tripping Breaker
- What Size Breaker For Dryer?
- What Causes a Circuit Breaker To Trip
- Why does GFCI Keeps Tripping? How to Fix it?
- Single Pole vs Double Pole Breaker | Which Has…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Get our Latest Newletters
Get great content that you love. No ads or spams, we promise.

How To Guides
Android Apple Windows Email YouTube Instagram SnapChat Gaming Discord Cloud Storage Google Sheets
Product Reviews
Home & Security Camera Motherboard PC & PC Accessories Laptops Speakers Car Accessories Air Conditioner Lawn & Garden Software Modem & Router
For Students
Electronics Projects Arduino Projects Embedded Free Circuits Mini Projects Robotics Sensor Cables & Wires RV Systems Solar
Interesting
Insights Tutorials Upcoming Sales Usernames Symbols Calculators Courses Deals Our Story
- Affiliate Disclosure
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Electronicshub.org

Reasons Why Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping Without Load

Circuit breakers play an essential role in your home’s electrical system as they monitor the flow of electricity.
Occasional breaker trips are nothing to worry about, but if your circuit breaker keeps tripping, keep reading to find out how to fix it.
The breakers can cause a power outage in your home if they are triggered for some reason. Sometimes, a circuit breaker can stop working even when no load is present.
It’s a common misconception that no load means no current is passing from the breaker.
Circuit breakers are designed to automatically cut the electricity flow as a safety measure.
Standard circuit breakers present in most homes are two types: Single Pole Breakers and Double Pole Breakers.
Reasons it Keeps Tripping:
- Damaged Wires
- Loose Wires
- Current Leakage
- Ground Fault Surges
- Short Circuits
Some load is connected to the circuit breaker unless the electricity supply to your home is cut off completely. In simple terms, it’s a misnomer to say that circuit breakers can trip without load.
6 Causes of Circuit Breaker Trips
Six major causes can cause circuit breakers to trip repeatedly. Knowing about the causes in detail will make it easier to fix circuit tripping for good.
1. Overloads

Overload is a situation that describes the connection of too many devices with an electrical circuit. Circuit breakers are designed to handle a certain amount of current.
Putting additional load on a circuit can cause the wires to heat up. Excessive heat causes the wires to burn, which can lead to a fire incident.
When the heat in wires is to a certain level, the circuit breaker will open the circuit and cut the electricity supply. Overloads might cause frequent tripping of circuit breakers.
2. Damaged Wires

Pests, wear and tear, resistance, and poor fitting can damage wires. Physical damage to wires can disturb the flow of current through wires and increase resistance.
An imbalance of resistances will heat the wire and trigger the circuit breaker to trip.
3. Loose Wires

The wires in electrical circuits can get loose over time. Physical damage or pull can cause the wires to loosen up and disturb the electricity supply.
The circuit breaker will keep tripping if a loose keeps getting disconnected.
4. Current Leakage
Leakage of current can cause the circuit breaker to trip. Current leakage can be caused if the wires are not grounded properly.
The faulty fabrication of electrical components can also cause it. Current leakage will cause the current to flow through conductors other than the ones identified in the circuit.
Improper flow of current will heat the wires. The circuit breaker will open the circuit to stop the flow of current.
5. Ground Fault Surges
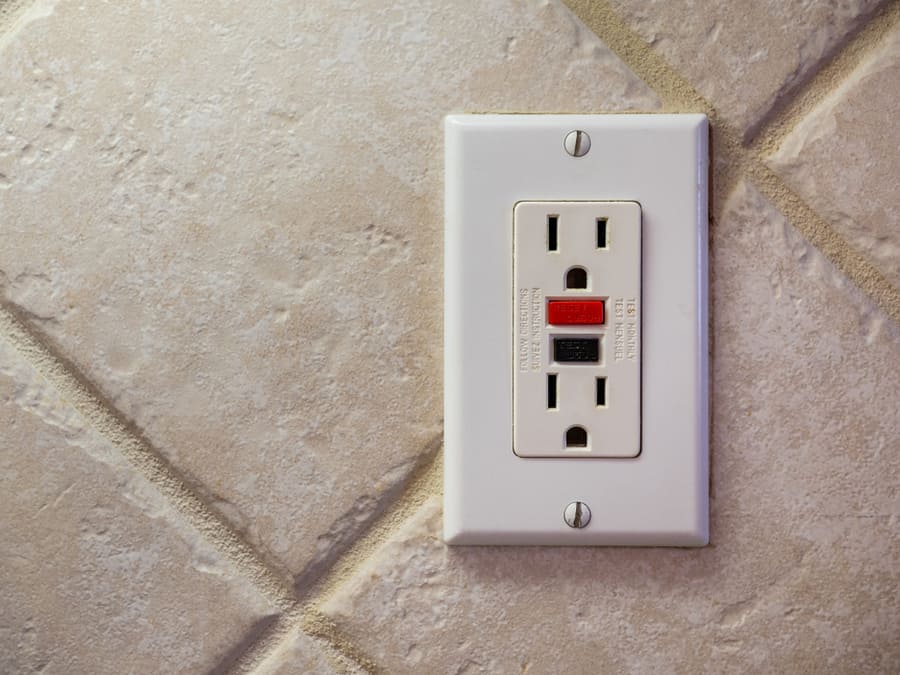

Ground fault surges are also a type of current leakage. These surges are highly dangerous as they can cause the current to flow through materials people can touch accidentally.
Ground fault surges occur when a live wire contacts any component inside or outside that circuit that cannot allow the current passage.
Proper grounding is done to stop ground fault surges. The circuit breaker can trip if it senses a ground fault surge in the electricity system.
6. Short Circuits
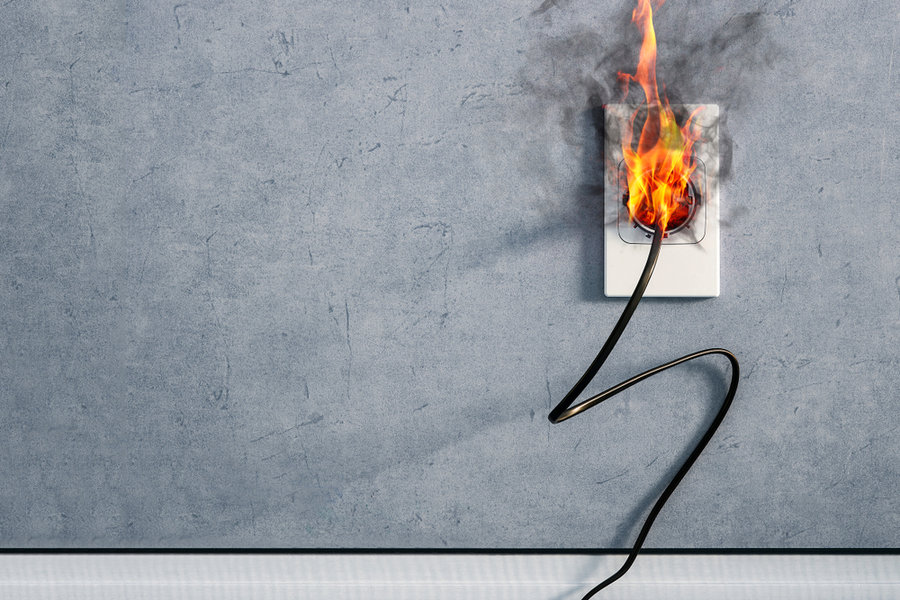

Short circuits are more dangerous compared to overloads.
A short circuit occurs when a live wire in your electrical circuit gets connected to a neutral wire. This contact of live and neutral wire can cause an accident.
A loose connection can also cause a short circuit and trigger the circuit breaker to trip. Faulty wiring of an appliance can lead to a short circuit as well.
In a short circuit, the current is forced to pass through the circuit in huge amounts. This phenomenon overrides the normal electrical resistance of the wires.
Excessive resistance can cause the wires to burn. The circuit breaker will trip to cut the electricity supply and prevent a fire incident.
Fixing the Circuit Breaker Trips
Trying to reset the circuit breaker repeatedly won’t help you stop it from tripping. Here are three actionable tips that can get the circuit breaker to function properly:
1. Identify Overload
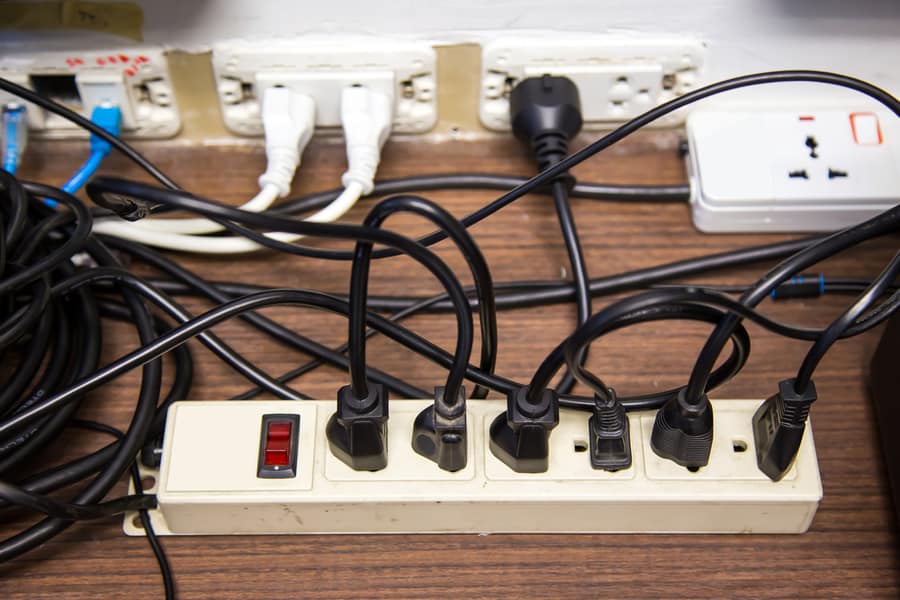

You need to identify the circuit breaker that is repeatedly tripping. Identify the part of your home connected to the circuit breaker that keeps tripping.
Turn off the circuit breaker for that part, and then unplug everything in that area. Now go back and turn on the circuit breaker.
If the breaker goes off immediately, even when no appliance is plugged in, the tripping might be caused by a tripping circuit instead of an overload.
But if the circuit breaker doesn’t trip, head back to that area and start plugging devices in one after another. You can redistribute the load to keep the circuit breaker from tripping.
2. Check Your Appliances

An appliance with a short circuit can cause the circuit breaker to keep tripping. During your inspection of overload, if you find an appliance that trips the circuit breaker even after redistributing the load, the device might be faulty.
Unplug that device, and don’t use it until you get it repaired.
3. Call an Electrician
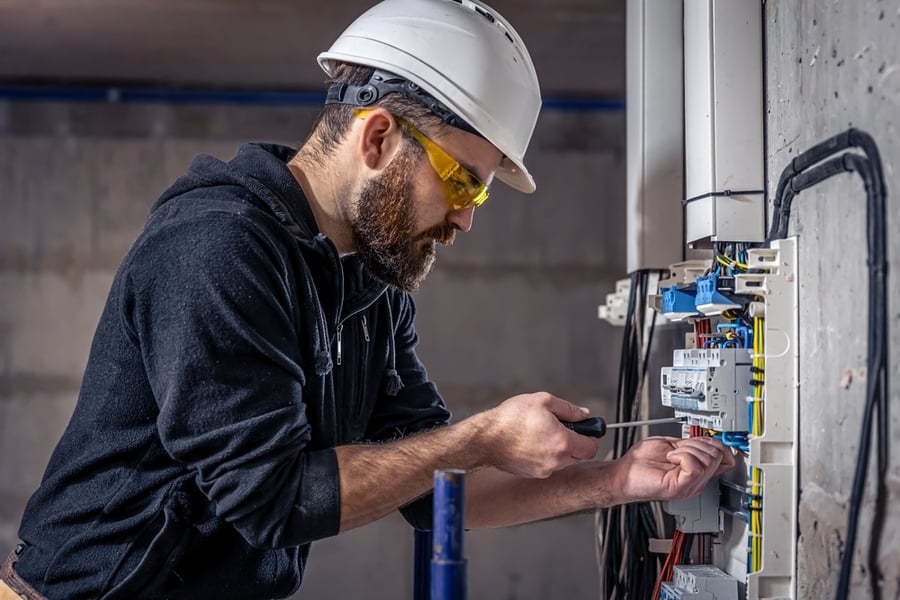

Checking for overload or inspecting your appliances one by one can be risky and time-consuming.
Hiring a skilled electrician who can check the circuit thoroughly and fix the problem by following the best safety practices is better.
The Bottom Line
The tripping of a circuit breatrippingomething you shouldn’t ignore. Try inspecting the issues and following the above fixes to keep your circuit breaker from tripping.
Avoid getting close to the circuit board if it’s flooded or you don’t have proper knowledge of handling circuits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can i replace the circuit breakers myself.
You can replace circuit breakers if you can identify circuit breakers to buy new ones and have a toolkit at your home.
But you should avoid doing so if you are not experienced and don’t know about proper safety practices.
When Should I Call an Electrician?
It’s better to call an electrician if you cannot identify overload/faulty appliances or if there’s sparking in the circuit.
Can Add More Circuit Breakers Stop Tripping?
You should avoid adding circuit breakers even if there’s a place in the board to install more. If the tips mentioned above don’t stop the circuit breaker from tripping, the best option is to call an electrician.
Related Posts

Washing Machine Capacity and Load Size Guide

Why Isn’t My Toaster Oven Heating Up?

Why Should You Cover an Air Conditioner?

How To Make Dishwasher Drain Hose Connections

What Gauge Wire for a Dryer Heating Element?

What Is Metal Cooling in a Refrigerator?
About the author, stanley gilmore, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Stanley is an appliance repairman with 10 years of experience. He has seen it all when it comes to broken home appliances and decided to share his knowledge by writing for ApplianceTeacher.

How Hot Does a Commercial Dishwasher Get?

How To Repair a Washing Machine PCB Board

Where Is the Temperature Control on a Whirlpool Refrigerator?

How To Set Auto Mode in LG AC

Where Is the Charcoal Filter on a GE Microwave?

How To Disable the Child Lock on a Samsung Dishwasher

What to Do if Your Microwave Keeps Tripping the Breaker
Is your microwave constantly tripping the breaker? Learn the common causes and step-by-step troubleshooting tips to safely fix this issue. Protect your home from electrical hazards and get your microwave working again!
Common Causes
Troubleshooting steps, 1. identify the affected circuit, 2. reset the breaker, 3. identify a different circuit for testing, 4. test the microwave.
A microwave that consistently trips the circuit breaker in your electrical panel is more than just a minor inconvenience-it's a red flag signaling potential electrical hazards lurking within your home. Ignoring this issue can lead to serious consequences, from appliance damage and electrical fires to potential electrocution. Underlying electrical problems, such as faulty wiring or overloaded circuits, demand immediate attention to safeguard your home and family.
This guide will help you diagnose why your microwave keeps tripping the breaker. We'll cover common problems, offer step-by-step troubleshooting instructions, and provide essential safety precautions to make sure your electrical system remains safe and functional. Whether you're a DIY enthusiast or prefer professional help, this article will empower you to address this issue effectively and confidently.
Safety First
Electrical repairs can be dangerous. Always turn off the power at the breaker before working on any electrical components. Don't attempt DIY electrical repairs unless you're qualified. If in doubt, hire a licensed electrician.
Before troubleshooting, let's look at the typical reasons a microwave trips the breaker. Understanding these will help you narrow down the problem and find the most likely solution.
- Overloaded circuit. Plugging too many power-hungry appliances into the same circuit can overwhelm its capacity, causing the breaker to trip as a safety measure.
- Faulty microwave. A malfunctioning microwave with internal issues like a short circuit or worn-out components can draw excessive power and trigger the breaker.
- Wiring issues. Outdated or damaged wiring in your walls or the microwave's power cord can create electrical faults that lead to breaker trips.
- Breaker problems. A worn-out or defective breaker might trip even with a normal electrical load, and will need to be replaced.
Now, let's figure out which of these issues is causing the problem.
Identifying the specific cause requires a systematic approach. Here's a step-by-step guide:
First locate the tripped breaker. Open your electrical panel and look for a breaker that's in the "Off" position or in a middle position between "On" and "Off." Some breakers may also have a red or orange indicator light to signal that they've tripped.
Once you've identified the tripped breaker, switch it fully to the "Off" position, then firmly flip it back to the "On" position. If the breaker trips again when you try using your microwave, it indicates a problem with either the microwave, the circuit's wiring, or an overloaded circuit. This is a potential safety hazard-stop using the appliance until the issue is fixed. Proceed to the next troubleshooting steps or consult a licensed electrician for assistance.
If a microwave is built-in, you'll need to use a heavy-duty extension cord to test it by plugging it into a working receptacle. If it isn't built-in, you can move the whole microwave to another working receptacle, and you won't need a heavy-duty extension cord.
Find an outlet that still has power even when the microwave's breaker has tripped. This means that it's on a different circuit. Make sure that the new outlet is on a circuit that can handle the microwave's amperage. You can usually find this information in your electrical panel or on the appliance itself. If unsure, consult an electrician.
Pro Tip: A typical microwave (700 to 1200 watts) usually needs a 15 or 20 amp breaker because most draw 6 to 10 amps. However, check your microwave's specific amperage requirements -some may need a dedicated 20-amp circuit. You can usually find this on a label on the back or inside the door of the microwave, or in the owner's manual.
Plug the microwave into the new working outlet and try using it.
If the breaker on this circuit doesn't trip, the problem is likely with the original circuit, its wiring, or-more likely-the circuit is overloaded. Identify other appliances connected to the same circuit as the microwave-especially heating appliances like coffee makers and toasters. Unplug some to reduce the load and see if the breaker still trips when using the microwave.
If the breaker trips even on a different circuit, the problem is likely with the microwave itself. Unplug the microwave and carefully check the power cord for damage, fraying, or exposed wires. If you find any damage, replace the power cord or have it repaired by a qualified appliance repair person. If the problem isn't the cord, ask an appliance repair person if it's worth fixing the microwave or if you should replace it.
By following these steps, you can systematically eliminate potential causes and find the root of the problem. Remember, safety is paramount when dealing with electrical issues. If you're unsure about any step or encounter complex wiring problems, consult a licensed electrician.
The post What to Do if Your Microwave Keeps Tripping the Breaker appeared first on HomeTips .

- Circuit Breakers
- Molded Case Circuit Breakers
Record Plus™ Thermal Magnetic Trip

View Larger
Representative Image
Catalog No. : FBV26TE025R
Description: 25A MCCB 2P 600Y347
UPC: 783164335330
Email page to others
- Email Address
Email Address (For your convenience, you can send the page to up to three e-mail addresses at a time. Your e-mail address will be shown in the forwarded message.)
Note: ABB will only use the e-mail addresses you provide to forward this page. ABB will not distribute or use the email addresses to contact your colleagues again.
Message Sent
Your message has been sent successfully.
We're sorry
Your e-mail can not be sent at this time. Please try again later.
Specifications
- Publications
Descriptors
Classifications, record plus types fc&fb - peak let through current.
Publication No.: DES-030
Publication Type: Time Current Curves
Record Plus Types FC&FB - 25A
Publication No.: DES-015C
Record Plus Types FC&FB - Let Through Energy Curves
Publication No.: DES-031
JavaScript appears to be disabled in your browser. Please enable JavaScript to ensure you get the most out of the LG site, products, and services.
We use cookies, including cookies from third parties, to enhance your user experience and the effectiveness of our marketing activities. These cookies are performance, analytics and advertising cookies, please see our Privacy and Cookie policy for further information. If you agree to all of our cookies select “Accept all” or select “Cookie Settings” to see which cookies we use and choose which ones you would like to accept.
{notificationMessage} {buttonName}
- Register a Product
- Member Benefits
- Sign In / Join Us
- Cart 1 */ -->
- Cart 5 */ -->
- Open Menu Close Menu
Share This Content.
You Can Share The Items You Like With Your Friends
Article feedback
0 / 500 Characters
Product Register
Product Registration Failed
Select Ctrl+V to paste.
- Product registration
- Product support
- Share Your Feedback
The URL has been copied to the clipboard.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Find out the cost to replace an electrical panel. On every breaker, there will be an "On" and "Off" position. On a tripped breaker, the handle will be in the middle, neither On nor Off. To reset, flip the handle to Off first, then to On. Stand to the side of the panel and turn your face away when flipping breakers.
Devices charging slowly. Electrical outlets not working. Flickering lights. Scorch marks on outlets and light switches. If a circuit breaker keeps tripping in one room, homeowners can test for ...
A circuit breaker can trip when there is nothing plugged in if there is a ground fault or the circuit breaker is outdated. Damaged wires within the circuit breaker can cause it to keep tripping for no reason. The average circuit breaker lasts for 35 years, and they can trip with nothing plugged in when they are over 30 years old.
When electrical demand is high, a circuit breaker can overheat and trip. Wire damage can also cause tripping, so check for signs of burning, cracking, or sparking when you plug a device in, as this can mean wire damage. Damaged wires or GFCIs may also cause trips when they touch another live wire or outlet box.
Step 2: Identify the Tripped Circuit Breaker. Go to your circuit breaker box, open it, and locate the tripped circuit breaker switch. In my experience, circuit boxes are typically positioned in an open area away from elements and obstructions. Most circuit boxes are enclosed in a small metal plate with a simple lock.
Disconnect all the devices and reset the breaker. Before connecting an appliance, allow your electric power system to rest for a few minutes. Plug in your devices one at a time. If it trips again as you plug in the devices, relocate the appliances to other outlets. If the breaker continues to trip, call an electrician to troubleshoot the problem.
This can create a situation where a circuit breaker keeps tripping without a load. Damage or deterioration to wires or cords also causes arcing faults and will trip the circuit. To prevent this, avoid pushing furniture against plugs in an outlet. Usually, unplugging electrical and electronic devices solves the problem.
Updated on January 5, 2024. A circuit breaker tripping results from short circuits, overloaded circuits, and ground faults. In each case, an unintended excessive flow of current triggers the trip. You must reset the circuit breaker by flipping it back on to restore power. Circuit breakers trip because they cannot handle the amount of current ...
Highlights. There are three reasons why a circuit breaker trips: a ground fault surge, a short circuit, or an overloaded circuit. A hot wire crossing with or touching a neutral wire triggers a short circuit, tripping your circuit breaker. If resetting the breaker doesn't solve the problem, consult a licensed electrician.
Preventing Circuit Breaker Tripping. A circuit breaker tripping can be prevented with understanding. When circuits are overloaded, breakers trip to avoid overheating and potential fires. Here are 3 steps that can help you prevent circuit breakers tripping: Know the electrical load - work out how many appliances & devices are connected to one ...
Let's look at some possibilities that could be behind your circuit breaker tripping even though nothing is plugged in. 1. Overloaded Circuit. One possible explanation for a circuit breaker repeatedly tripping despite no devices being connected is an overloaded circuit. Each circuit has a specific capacity, measured in amps, that it can handle.
Before the circuit reset, disarm the situation by disconnecting or turning off all devices tied to the affected circuit. This precautionary measure prevents potential overload when the circuit is reinstated. 3. Resetting the Circuit Breaker. With a gentle touch, nudge the tripped breaker switch from "off" to "on."
A circuit breaker may trip due to three primary reasons: overloads, short circuits, and ground fault surges. Overloads occur when a circuit draws more power than it can handle, usually due to too many appliances operating on the same circuit. Short circuits and ground fault surges happen when a hot wire comes into contact with a neutral wire or ...
Here are five reasons your circuit breaker keeps tripping, as well as some ways you can diagnose the cause. 1. Ground Fault. Environmental factors may sometimes create an unintended path to the ground. If a hot circuit brushes up against a conductive surface, the electricity will follow this path rather than the wire.
To reset it, switch the breaker all the way to the "off" position first, and then firmly switch it back to the "on" position. This reset process restores power to the circuit and allows you to test if the breaker continues to trip or if the issue has been resolved. Step 4: Observe for immediate re-tripping.
I have a 20A 240V GFCI breaker in my main breaker box going to a conduit to another breaker box outside. All worked well last summer. Now, when I put any load (weed-eater, light, etc.) on an outlet connected to the outside breaker box, the indoor breaker immediately trips.
Reset the Circuit Breaker. If there's an absolute zero load and no input wire issues found, try resetting the main panel where the responsible circuit breaker lies. Wait for a moment, and if it trips again, there might be a problem with the circuit breaker, or it's already defective. 4. Replace the Circuit Breaker.
To troubleshoot and fix a breaker that is tripping without load, follow these steps: 1. Check for overloaded circuits. If your breaker continues to trip, it may be that you plug too many appliances on the circuit. Start by unplugging all the devices on the circuit. Reset the breaker.
1. I installed a 20A GFCI breaker on a circuit of 6 wall & counter outlets in kitchen and it trips instantly. I unplugged everything from the outlets and still trips. Then disconnected load and neutral from the GFCI breaker leaving only the neutral pigtail connected to the neutral bar and it trips instantly as well.
Unplug Appliances: If the tripping occurs when a specific appliance is used, unplug that appliance and try resetting the circuit breaker. If the breaker does not trip, the appliance might be faulty and cause an overload. Check for Overloading: Assess whether the circuit is overloaded by connecting too many high-powered devices to the same circuit. Try redistributing the load by connecting ...
Determine the Load. To troubleshoot the circuit, unplug or turn off all devices connected to it, then reset the breaker. Gradually reconnect or turn on one device at a time and observe if the breaker trips after each reconnection. If it trips immediately after connecting a specific device, it may be faulty and require repair or replacement.
Circuit breakers are crucial components in systems, offering protection by tripping to interrupt flow during an overload. However, there are instances where circuit breakers may malfunction and fail to trip, sometimes due to a faulty breaker or complications within the wiring itself.
Test your circuit breaker and turn on the lights without the appliances. Check two things: 1.The lights return but the breaker trips after a few seconds. 2.The breaker trips promptly, flickering the lights "ON" and "OFF.". Your observation may indicate wiring, circuit damage, or overloading (yes, you got that right).
Physical damage or pull can cause the wires to loosen up and disturb the electricity supply. The circuit breaker will keep tripping if a loose keeps getting disconnected. 4. Current Leakage. Leakage of current can cause the circuit breaker to trip. Current leakage can be caused if the wires are not grounded properly.
Unplug some to reduce the load and see if the breaker still trips when using the microwave. If the breaker trips even on a different circuit, the problem is likely with the microwave itself.
FB 100 circuit breakers are supplied with factory installed non-user interchangeable thermal-magnetic trip units and ca n be supplie d with o r wit hout l ugs. FB breakers are available in 1-, 2- and 3-pole versions. ... An R1 suffix indicates that the breaker is supplied with line and load lugs, R2 indicates load lugs, and R3 indicates line ...
Help library: LG Front Load Washer - Why the circuit breaker is tripped while using the machine? Learn how to use, update, maintain and troubleshoot your LG devices and appliances.