

Is Time Travel Possible?
We all travel in time! We travel one year in time between birthdays, for example. And we are all traveling in time at approximately the same speed: 1 second per second.
We typically experience time at one second per second. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
NASA's space telescopes also give us a way to look back in time. Telescopes help us see stars and galaxies that are very far away . It takes a long time for the light from faraway galaxies to reach us. So, when we look into the sky with a telescope, we are seeing what those stars and galaxies looked like a very long time ago.
However, when we think of the phrase "time travel," we are usually thinking of traveling faster than 1 second per second. That kind of time travel sounds like something you'd only see in movies or science fiction books. Could it be real? Science says yes!
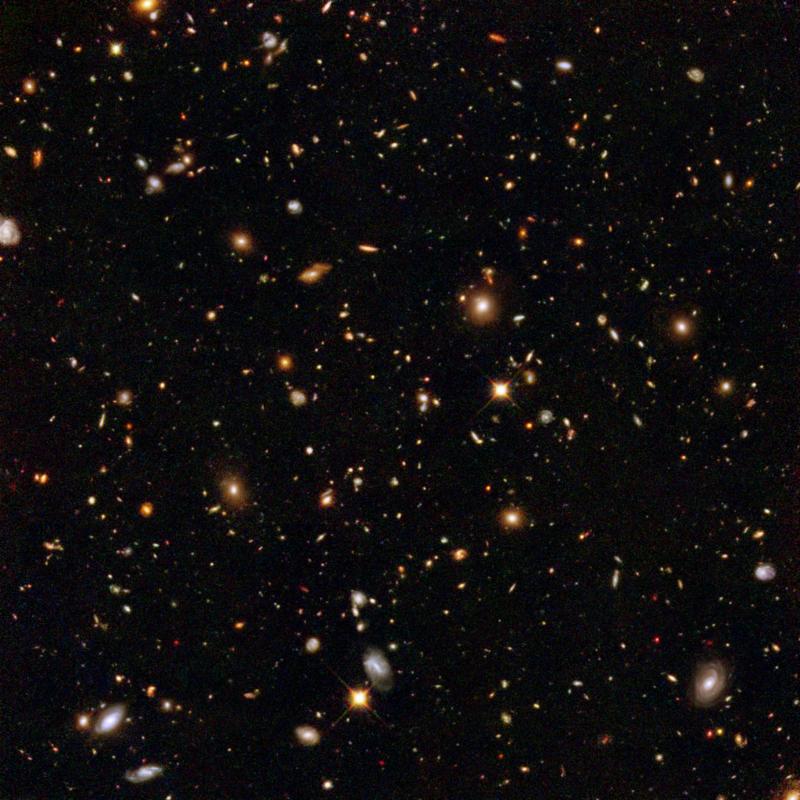

This image from the Hubble Space Telescope shows galaxies that are very far away as they existed a very long time ago. Credit: NASA, ESA and R. Thompson (Univ. Arizona)
How do we know that time travel is possible?
More than 100 years ago, a famous scientist named Albert Einstein came up with an idea about how time works. He called it relativity. This theory says that time and space are linked together. Einstein also said our universe has a speed limit: nothing can travel faster than the speed of light (186,000 miles per second).
Einstein's theory of relativity says that space and time are linked together. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
What does this mean for time travel? Well, according to this theory, the faster you travel, the slower you experience time. Scientists have done some experiments to show that this is true.
For example, there was an experiment that used two clocks set to the exact same time. One clock stayed on Earth, while the other flew in an airplane (going in the same direction Earth rotates).
After the airplane flew around the world, scientists compared the two clocks. The clock on the fast-moving airplane was slightly behind the clock on the ground. So, the clock on the airplane was traveling slightly slower in time than 1 second per second.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Can we use time travel in everyday life?
We can't use a time machine to travel hundreds of years into the past or future. That kind of time travel only happens in books and movies. But the math of time travel does affect the things we use every day.
For example, we use GPS satellites to help us figure out how to get to new places. (Check out our video about how GPS satellites work .) NASA scientists also use a high-accuracy version of GPS to keep track of where satellites are in space. But did you know that GPS relies on time-travel calculations to help you get around town?
GPS satellites orbit around Earth very quickly at about 8,700 miles (14,000 kilometers) per hour. This slows down GPS satellite clocks by a small fraction of a second (similar to the airplane example above).
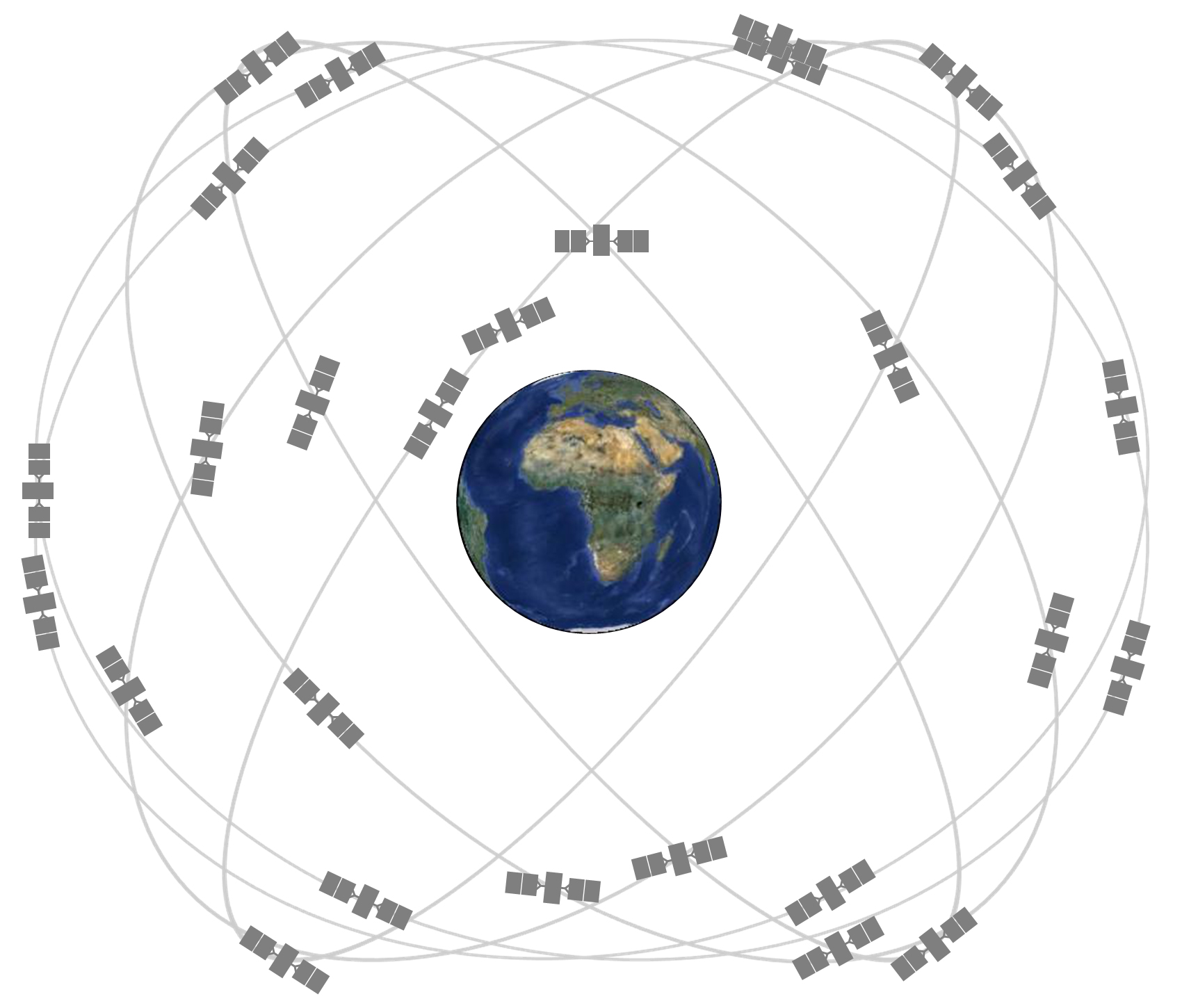
GPS satellites orbit around Earth at about 8,700 miles (14,000 kilometers) per hour. Credit: GPS.gov
However, the satellites are also orbiting Earth about 12,550 miles (20,200 km) above the surface. This actually speeds up GPS satellite clocks by a slighter larger fraction of a second.
Here's how: Einstein's theory also says that gravity curves space and time, causing the passage of time to slow down. High up where the satellites orbit, Earth's gravity is much weaker. This causes the clocks on GPS satellites to run faster than clocks on the ground.
The combined result is that the clocks on GPS satellites experience time at a rate slightly faster than 1 second per second. Luckily, scientists can use math to correct these differences in time.
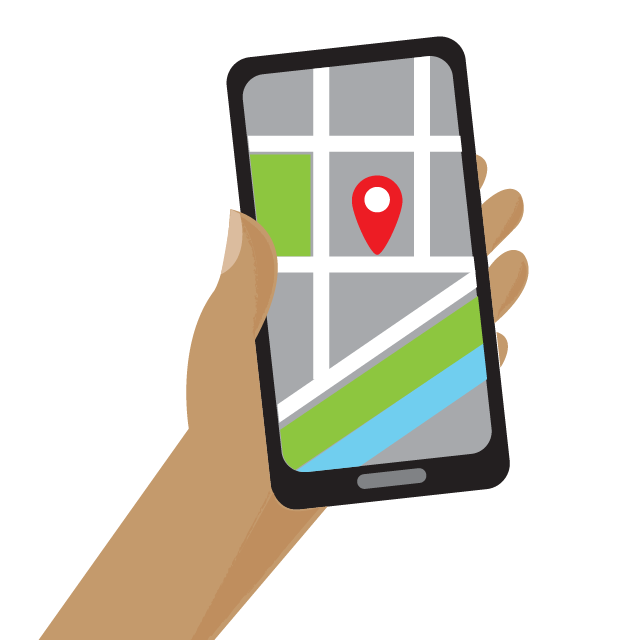
If scientists didn't correct the GPS clocks, there would be big problems. GPS satellites wouldn't be able to correctly calculate their position or yours. The errors would add up to a few miles each day, which is a big deal. GPS maps might think your home is nowhere near where it actually is!
In Summary:
Yes, time travel is indeed a real thing. But it's not quite what you've probably seen in the movies. Under certain conditions, it is possible to experience time passing at a different rate than 1 second per second. And there are important reasons why we need to understand this real-world form of time travel.
If you liked this, you may like:
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

- LISTEN & FOLLOW
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
- Amazon Music
- Amazon Alexa
Your support helps make our show possible and unlocks access to our sponsor-free feed.
Paradox-Free Time Travel Is Theoretically Possible, Researchers Say

Matthew S. Schwartz

A dog dressed as Marty McFly from Back to the Future attends the Tompkins Square Halloween Dog Parade in 2015. New research says time travel might be possible without the problems McFly encountered. Timothy A. Clary/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
A dog dressed as Marty McFly from Back to the Future attends the Tompkins Square Halloween Dog Parade in 2015. New research says time travel might be possible without the problems McFly encountered.
"The past is obdurate," Stephen King wrote in his book about a man who goes back in time to prevent the Kennedy assassination. "It doesn't want to be changed."
Turns out, King might have been on to something.
Countless science fiction tales have explored the paradox of what would happen if you went back in time and did something in the past that endangered the future. Perhaps one of the most famous pop culture examples is in Back to the Future , when Marty McFly goes back in time and accidentally stops his parents from meeting, putting his own existence in jeopardy.
But maybe McFly wasn't in much danger after all. According a new paper from researchers at the University of Queensland, even if time travel were possible, the paradox couldn't actually exist.
Researchers ran the numbers and determined that even if you made a change in the past, the timeline would essentially self-correct, ensuring that whatever happened to send you back in time would still happen.
"Say you traveled in time in an attempt to stop COVID-19's patient zero from being exposed to the virus," University of Queensland scientist Fabio Costa told the university's news service .
"However, if you stopped that individual from becoming infected, that would eliminate the motivation for you to go back and stop the pandemic in the first place," said Costa, who co-authored the paper with honors undergraduate student Germain Tobar.
"This is a paradox — an inconsistency that often leads people to think that time travel cannot occur in our universe."
A variation is known as the "grandfather paradox" — in which a time traveler kills their own grandfather, in the process preventing the time traveler's birth.
The logical paradox has given researchers a headache, in part because according to Einstein's theory of general relativity, "closed timelike curves" are possible, theoretically allowing an observer to travel back in time and interact with their past self — potentially endangering their own existence.
But these researchers say that such a paradox wouldn't necessarily exist, because events would adjust themselves.
Take the coronavirus patient zero example. "You might try and stop patient zero from becoming infected, but in doing so, you would catch the virus and become patient zero, or someone else would," Tobar told the university's news service.
In other words, a time traveler could make changes, but the original outcome would still find a way to happen — maybe not the same way it happened in the first timeline but close enough so that the time traveler would still exist and would still be motivated to go back in time.
"No matter what you did, the salient events would just recalibrate around you," Tobar said.
The paper, "Reversible dynamics with closed time-like curves and freedom of choice," was published last week in the peer-reviewed journal Classical and Quantum Gravity . The findings seem consistent with another time travel study published this summer in the peer-reviewed journal Physical Review Letters. That study found that changes made in the past won't drastically alter the future.
Bestselling science fiction author Blake Crouch, who has written extensively about time travel, said the new study seems to support what certain time travel tropes have posited all along.
"The universe is deterministic and attempts to alter Past Event X are destined to be the forces which bring Past Event X into being," Crouch told NPR via email. "So the future can affect the past. Or maybe time is just an illusion. But I guess it's cool that the math checks out."
- time travel
- grandfather paradox
share this!
April 25, 2022
Time travel could be possible, but only with parallel timelines
by Barak Shoshany, The Conversation

Have you ever made a mistake that you wish you could undo? Correcting past mistakes is one of the reasons we find the concept of time travel so fascinating. As often portrayed in science fiction, with a time machine, nothing is permanent anymore—you can always go back and change it. But is time travel really possible in our universe , or is it just science fiction?
Our modern understanding of time and causality comes from general relativity . Theoretical physicist Albert Einstein's theory combines space and time into a single entity—"spacetime"—and provides a remarkably intricate explanation of how they both work, at a level unmatched by any other established theory. This theory has existed for more than 100 years, and has been experimentally verified to extremely high precision, so physicists are fairly certain it provides an accurate description of the causal structure of our universe.
For decades, physicists have been trying to use general relativity to figure out if time travel is possible . It turns out that you can write down equations that describe time travel and are fully compatible and consistent with relativity. But physics is not mathematics, and equations are meaningless if they do not correspond to anything in reality.
Arguments against time travel
There are two main issues which make us think these equations may be unrealistic. The first issue is a practical one: building a time machine seems to require exotic matter , which is matter with negative energy. All the matter we see in our daily lives has positive energy—matter with negative energy is not something you can just find lying around. From quantum mechanics , we know that such matter can theoretically be created, but in too small quantities and for too short times .
However, there is no proof that it is impossible to create exotic matter in sufficient quantities. Furthermore, other equations may be discovered that allow time travel without requiring exotic matter . Therefore, this issue may just be a limitation of our current technology or understanding of quantum mechanics.
The other main issue is less practical, but more significant: it is the observation that time travel seems to contradict logic, in the form of time travel paradoxes . There are several types of such paradoxes, but the most problematic are consistency paradoxes .
A popular trope in science fiction, consistency paradoxes happen whenever there is a certain event that leads to changing the past, but the change itself prevents this event from happening in the first place.
For example, consider a scenario where I enter my time machine, use it to go back in time five minutes, and destroy the machine as soon as I get to the past. Now that I destroyed the time machine, it would be impossible for me to use it five minutes later.
But if I cannot use the time machine, then I cannot go back in time and destroy it. Therefore, it is not destroyed, so I can go back in time and destroy it. In other words, the time machine is destroyed if and only if it is not destroyed. Since it cannot be both destroyed and not destroyed simultaneously, this scenario is inconsistent and paradoxical.
Eliminating the paradoxes
There's a common misconception in science fiction that paradoxes can be "created." Time travelers are usually warned not to make significant changes to the past and to avoid meeting their past selves for this exact reason. Examples of this may be found in many time travel movies, such as the "Back to the Future" trilogy.
But in physics, a paradox is not an event that can actually happen—it is a purely theoretical concept that points towards an inconsistency in the theory itself. In other words, consistency paradoxes don't merely imply time travel is a dangerous endeavor, they imply it simply cannot be possible.
This was one of the motivations for theoretical physicist Stephen Hawking to formulate his chronology protection conjecture , which states that time travel should be impossible. However, this conjecture so far remains unproven. Furthermore, the universe would be a much more interesting place if instead of eliminating time travel due to paradoxes, we could just eliminate the paradoxes themselves.
One attempt at resolving time travel paradoxes is theoretical physicist Igor Dmitriyevich Novikov's self-consistency conjecture , which essentially states that you can travel to the past, but you cannot change it.
According to Novikov, if I tried to destroy my time machine five minutes in the past, I would find that it is impossible to do so. The laws of physics would somehow conspire to preserve consistency.
Introducing multiple histories
But what's the point of going back in time if you cannot change the past? My recent work, together with my students Jacob Hauser and Jared Wogan, shows that there are time travel paradoxes that Novikov's conjecture cannot resolve. This takes us back to square one, since if even just one paradox cannot be eliminated, time travel remains logically impossible.
So, is this the final nail in the coffin of time travel? Not quite. We showed that allowing for multiple histories (or in more familiar terms, parallel timelines) can resolve the paradoxes that Novikov's conjecture cannot. In fact, it can resolve any paradox you throw at it.
The idea is very simple. When I exit the time machine, I exit into a different timeline. In that timeline, I can do whatever I want, including destroying the time machine, without changing anything in the original timeline I came from. Since I cannot destroy the time machine in the original timeline, which is the one I actually used to travel back in time, there is no paradox.
After working on time travel paradoxes for the last three years , I have become increasingly convinced that time travel could be possible, but only if our universe can allow multiple histories to coexist. So, can it?
Quantum mechanics certainly seems to imply so, at least if you subscribe to Everett's "many-worlds" interpretation , where one history can "split" into multiple histories, one for each possible measurement outcome—for example, whether Schrödinger's cat is alive or dead, or whether or not I arrived in the past.
But these are just speculations. My students and I are currently working on finding a concrete theory of time travel with multiple histories that is fully compatible with general relativity . Of course, even if we manage to find such a theory, this would not be sufficient to prove that time travel is possible, but it would at least mean that time travel is not ruled out by consistency paradoxes.
Time travel and parallel timelines almost always go hand-in-hand in science fiction , but now we have proof that they must go hand-in-hand in real science as well. General relativity and quantum mechanics tell us that time travel might be possible, but if it is, then multiple histories must also be possible.
Provided by The Conversation
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Look to women for sustainable livestock farming bordering the Amazon rainforest, says study
7 minutes ago
New study finds at least 1 in 4 US residential yards exceeds new EPA lead soil level guideline
19 minutes ago

Biologists take closer look at stress response in cells

City sprawl is now large enough to sway global warming over land

New theory broadens phase transition exploration
2 hours ago

Physicists combine multiple Higgs boson pair studies and discover clues about the stability of the universe
3 hours ago

Anti-Asian rhetoric during the pandemic negatively impacted employment and earnings, new research finds
4 hours ago

New method enhances X-ray microscopy for detecting tiny defects

New technique achieves visualization of instantaneous states of materials in high-speed devices
Team of biologists discover fluorescence in 27 marine creatures
Relevant physicsforums posts, gravity & organic matter.
6 hours ago
Researchers find experimental evidence for a graviton-like particle
Jun 13, 2024
How to Calculate electron temperature of Arc Plasma?
Jun 11, 2024
Could you use the Moon to reflect sunlight onto a solar sail?
Jun 10, 2024
List of Verdet Constants?
May 31, 2024
Discussion about least squares method
May 29, 2024
More from Other Physics Topics
Related Stories

Time travel is possible – but only if you have an object with infinite mass
Dec 13, 2018

Young physicist 'squares the numbers' on time travel
Sep 24, 2020

Video: Can wormholes act like time machines?
Apr 30, 2020

Stephen Hawking's final book suggests time travel may one day be possible – here's what to make of it
Nov 9, 2018

Avengers: Endgame exploits time travel and quantum mechanics as it tries to restore the universe
Apr 25, 2019

Warp drives: Physicists give chances of faster-than-light space travel a boost
Apr 26, 2021
Recommended for you

Physicists find a new way to represent π
7 hours ago

Scientists develop 3D printed vacuum system that aims to trap dark matter
Jun 17, 2024
Quantum entangled photons react to Earth's spin
Jun 14, 2024
Quantum data assimilation offers new approach to weather prediction
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
April 26, 2023
Is Time Travel Possible?
The laws of physics allow time travel. So why haven’t people become chronological hoppers?
By Sarah Scoles
yuanyuan yan/Getty Images
In the movies, time travelers typically step inside a machine and—poof—disappear. They then reappear instantaneously among cowboys, knights or dinosaurs. What these films show is basically time teleportation .
Scientists don’t think this conception is likely in the real world, but they also don’t relegate time travel to the crackpot realm. In fact, the laws of physics might allow chronological hopping, but the devil is in the details.
Time traveling to the near future is easy: you’re doing it right now at a rate of one second per second, and physicists say that rate can change. According to Einstein’s special theory of relativity, time’s flow depends on how fast you’re moving. The quicker you travel, the slower seconds pass. And according to Einstein’s general theory of relativity , gravity also affects clocks: the more forceful the gravity nearby, the slower time goes.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
“Near massive bodies—near the surface of neutron stars or even at the surface of the Earth, although it’s a tiny effect—time runs slower than it does far away,” says Dave Goldberg, a cosmologist at Drexel University.
If a person were to hang out near the edge of a black hole , where gravity is prodigious, Goldberg says, only a few hours might pass for them while 1,000 years went by for someone on Earth. If the person who was near the black hole returned to this planet, they would have effectively traveled to the future. “That is a real effect,” he says. “That is completely uncontroversial.”
Going backward in time gets thorny, though (thornier than getting ripped to shreds inside a black hole). Scientists have come up with a few ways it might be possible, and they have been aware of time travel paradoxes in general relativity for decades. Fabio Costa, a physicist at the Nordic Institute for Theoretical Physics, notes that an early solution with time travel began with a scenario written in the 1920s. That idea involved massive long cylinder that spun fast in the manner of straw rolled between your palms and that twisted spacetime along with it. The understanding that this object could act as a time machine allowing one to travel to the past only happened in the 1970s, a few decades after scientists had discovered a phenomenon called “closed timelike curves.”
“A closed timelike curve describes the trajectory of a hypothetical observer that, while always traveling forward in time from their own perspective, at some point finds themselves at the same place and time where they started, creating a loop,” Costa says. “This is possible in a region of spacetime that, warped by gravity, loops into itself.”
“Einstein read [about closed timelike curves] and was very disturbed by this idea,” he adds. The phenomenon nevertheless spurred later research.
Science began to take time travel seriously in the 1980s. In 1990, for instance, Russian physicist Igor Novikov and American physicist Kip Thorne collaborated on a research paper about closed time-like curves. “They started to study not only how one could try to build a time machine but also how it would work,” Costa says.
Just as importantly, though, they investigated the problems with time travel. What if, for instance, you tossed a billiard ball into a time machine, and it traveled to the past and then collided with its past self in a way that meant its present self could never enter the time machine? “That looks like a paradox,” Costa says.
Since the 1990s, he says, there’s been on-and-off interest in the topic yet no big breakthrough. The field isn’t very active today, in part because every proposed model of a time machine has problems. “It has some attractive features, possibly some potential, but then when one starts to sort of unravel the details, there ends up being some kind of a roadblock,” says Gaurav Khanna of the University of Rhode Island.
For instance, most time travel models require negative mass —and hence negative energy because, as Albert Einstein revealed when he discovered E = mc 2 , mass and energy are one and the same. In theory, at least, just as an electric charge can be positive or negative, so can mass—though no one’s ever found an example of negative mass. Why does time travel depend on such exotic matter? In many cases, it is needed to hold open a wormhole—a tunnel in spacetime predicted by general relativity that connects one point in the cosmos to another.
Without negative mass, gravity would cause this tunnel to collapse. “You can think of it as counteracting the positive mass or energy that wants to traverse the wormhole,” Goldberg says.
Khanna and Goldberg concur that it’s unlikely matter with negative mass even exists, although Khanna notes that some quantum phenomena show promise, for instance, for negative energy on very small scales. But that would be “nowhere close to the scale that would be needed” for a realistic time machine, he says.
These challenges explain why Khanna initially discouraged Caroline Mallary, then his graduate student at the University of Massachusetts Dartmouth, from doing a time travel project. Mallary and Khanna went forward anyway and came up with a theoretical time machine that didn’t require negative mass. In its simplistic form, Mallary’s idea involves two parallel cars, each made of regular matter. If you leave one parked and zoom the other with extreme acceleration, a closed timelike curve will form between them.
Easy, right? But while Mallary’s model gets rid of the need for negative matter, it adds another hurdle: it requires infinite density inside the cars for them to affect spacetime in a way that would be useful for time travel. Infinite density can be found inside a black hole, where gravity is so intense that it squishes matter into a mind-bogglingly small space called a singularity. In the model, each of the cars needs to contain such a singularity. “One of the reasons that there's not a lot of active research on this sort of thing is because of these constraints,” Mallary says.
Other researchers have created models of time travel that involve a wormhole, or a tunnel in spacetime from one point in the cosmos to another. “It's sort of a shortcut through the universe,” Goldberg says. Imagine accelerating one end of the wormhole to near the speed of light and then sending it back to where it came from. “Those two sides are no longer synced,” he says. “One is in the past; one is in the future.” Walk between them, and you’re time traveling.
You could accomplish something similar by moving one end of the wormhole near a big gravitational field—such as a black hole—while keeping the other end near a smaller gravitational force. In that way, time would slow down on the big gravity side, essentially allowing a particle or some other chunk of mass to reside in the past relative to the other side of the wormhole.
Making a wormhole requires pesky negative mass and energy, however. A wormhole created from normal mass would collapse because of gravity. “Most designs tend to have some similar sorts of issues,” Goldberg says. They’re theoretically possible, but there’s currently no feasible way to make them, kind of like a good-tasting pizza with no calories.
And maybe the problem is not just that we don’t know how to make time travel machines but also that it’s not possible to do so except on microscopic scales—a belief held by the late physicist Stephen Hawking. He proposed the chronology protection conjecture: The universe doesn’t allow time travel because it doesn’t allow alterations to the past. “It seems there is a chronology protection agency, which prevents the appearance of closed timelike curves and so makes the universe safe for historians,” Hawking wrote in a 1992 paper in Physical Review D .
Part of his reasoning involved the paradoxes time travel would create such as the aforementioned situation with a billiard ball and its more famous counterpart, the grandfather paradox : If you go back in time and kill your grandfather before he has children, you can’t be born, and therefore you can’t time travel, and therefore you couldn’t have killed your grandfather. And yet there you are.
Those complications are what interests Massachusetts Institute of Technology philosopher Agustin Rayo, however, because the paradoxes don’t just call causality and chronology into question. They also make free will seem suspect. If physics says you can go back in time, then why can’t you kill your grandfather? “What stops you?” he says. Are you not free?
Rayo suspects that time travel is consistent with free will, though. “What’s past is past,” he says. “So if, in fact, my grandfather survived long enough to have children, traveling back in time isn’t going to change that. Why will I fail if I try? I don’t know because I don’t have enough information about the past. What I do know is that I’ll fail somehow.”
If you went to kill your grandfather, in other words, you’d perhaps slip on a banana en route or miss the bus. “It's not like you would find some special force compelling you not to do it,” Costa says. “You would fail to do it for perfectly mundane reasons.”
In 2020 Costa worked with Germain Tobar, then his undergraduate student at the University of Queensland in Australia, on the math that would underlie a similar idea: that time travel is possible without paradoxes and with freedom of choice.
Goldberg agrees with them in a way. “I definitely fall into the category of [thinking that] if there is time travel, it will be constructed in such a way that it produces one self-consistent view of history,” he says. “Because that seems to be the way that all the rest of our physical laws are constructed.”
No one knows what the future of time travel to the past will hold. And so far, no time travelers have come to tell us about it.
Time travel is theoretically possible, calculations show. But that doesn't mean you could change the past.
- Time travel is possible based on the laws of physics, according to researchers.
- But time-travelers wouldn't be able to alter the past in a measurable way, they say.
- And the future would essentially stay the same, according to the reseachers.

Imagine you could hop into a time machine, press a button, and journey back to 2019, before the novel coronavirus made the leap from animals to humans.
What if you could find and isolate patient zero? Theoretically, the COVID-19 pandemic wouldn't happen, right?
Not quite, because then future-you wouldn't have decided to time travel in the first place.
For decades, physicists have been studying and debating versions of this paradox: If we could travel back in time and change the past, what would happen to the future?
A 2020 study offered a potential answer: Nothing.
"Events readjust around anything that could cause a paradox, so the paradox does not happen," Germain Tobar, the study's author previously told IFLScience .
Tobar's work, published in the peer-reviewed journal Classical and Quantum Gravity in September 2020, suggests that according to the rules of theoretical physics, anything you tried to change in the past would be corrected by subsequent events.
Related stories
Put simply: It's theoretically possible to go back in time, but you couldn't change history.
The grandfather paradox
Physicists have considered time travel to be theoretically possible since Albert Einstein came up with his theory of relativity. Einstein's calculations suggest it's possible for an object in our universe to travel through space and time in a circular direction, eventually ending up at a point on its journey where it's been before – a path called a closed time-like curve.
Still, physicists continue to struggle with scenarios like the coronavirus example above, in which time-travelers alter events that already happened. The most famous example is known as the grandfather paradox: Say a time-traveler goes back to the past and kills a younger version of his or her grandfather. The grandfather then wouldn't have any children, erasing the time-traveler's parents and, of course, the time-traveler, too. But then who would kill Grandpa?
A take on this paradox appears in the movie "Back to the Future," when Marty McFly almost stops his parents from meeting in the past – potentially causing himself to disappear.
To address the paradox, Tobar and his supervisor, Dr. Fabio Costa, used the "billiard-ball model," which imagines cause and effect as a series of colliding billiard balls, and a circular pool table as a closed time-like curve.
Imagine a bunch of billiard balls laid out across that circular table. If you push one ball from position X, it bangs around the table, hitting others in a particular pattern.
The researchers calculated that even if you mess with the ball's pattern at some point in its journey, future interactions with other balls can correct its path, leading it to come back to the same position and speed that it would have had you not interfered.
"Regardless of the choice, the ball will fall into the same place," Dr Yasunori Nomura, a theoretical physicist at UC Berkeley, previously told Insider.
Tobar's model, in other words, says you could travel back in time, but you couldn't change how events unfolded significantly enough to alter the future, Nomura said. Applied to the grandfather paradox, then, this would mean that something would always get in the way of your attempt to kill your grandfather. Or at least by the time he did die, your grandmother would already be pregnant with your mother.
Back to the coronavirus example. Let's say you were to travel back to 2019 and intervene in patient zero's life. According to Tobar's line of thinking, the pandemic would still happen somehow.
"You might try and stop patient zero from becoming infected, but in doing so you would catch the virus and become patient zero, or someone else would," Tobar said, according to Australia's University of Queensland , where Tobar graduated from.
Nomura said that although the model is too simple to represent the full range of cause and effect in our universe, it's a good starting point for future physicists.
Watch: There are 2 types of time travel and physicists agree that one of them is possible
- Main content
Advertisement
Mathematics
The mathematician who worked out how to time travel.
Mathematics suggested that time travel is physically possible – and Kurt Gödel proved it. Mathematician Karl Sigmund explains how the polymath did it
By Karl Sigmund
5 April 2024

Gödel proved that, mathematically speaking, time travel is physically possible
Quality Stock / Alamy
The following is an extract from our Lost in Space-Time newsletter. Each month, we hand over the keyboard to a physicist or mathematician to tell you about fascinating ideas from their corner of the universe. You can sign up for Lost in Space-Time for free here .
There may be no better way to get truly lost in space-time than to travel to the past and fiddle around with causality. Polymath Kurt Gödel suggested that you could, for instance, land near your younger self and…
Sign up to our weekly newsletter
Receive a weekly dose of discovery in your inbox! We'll also keep you up to date with New Scientist events and special offers.
To continue reading, subscribe today with our introductory offers
No commitment, cancel anytime*
Offer ends 2nd of July 2024.
*Cancel anytime within 14 days of payment to receive a refund on unserved issues.
Inclusive of applicable taxes (VAT)
Existing subscribers
More from New Scientist
Explore the latest news, articles and features

How to wrap your mind around the real multiverse
Subscriber-only

How materials that rewind light can test physics' most extreme ideas

Time may be an illusion created by quantum entanglement

The Monty Hall problem shows how tricky judging the odds can be
Popular articles.
Trending New Scientist articles
An Extraordinary Particle Could Travel Back in Time, Scientists Say
The potential is tantalizing.

- Scientists like Albert Einstein have believed a class of particles could travel faster than light.
- If these particles existed, what would it mean for our understanding of time travel?
The tachyon particle has an almost mythical air about it in the scientific community, mostly because we don’t know if it actually exists. But if it does, the tachyon has some tantalizing connections to time travel.
The concept of the speed of light, and a particle that may travel faster than the speed of light, started gaining pace with Albert Einstein in 1905. Physicist Gerald Feinberg termed this potential particles a “tachyon” in 1967. We’ve long been intrigued by the promise of the tachyon and now, thanks to a recent Discover Magazine article , the perplexing particle is once again back in the mainstream.
Here’s the gist: Right now, we don’t know of anything that’s faster than the speed of light. Light has no mass, so it doesn’t gain size as it speeds up. Meanwhile, an object with mass gain s mass as it speeds up, which means it doesn’t have enough energy to keep pace with the speed of light. So, with everything in our world traveling slower than the speed of light, every cause that occurs within our known universe happens within the speed of light’s time parameters.
A tachyon, though, is a particle that travels faster than the speed of light—in theory, at least. Somehow, the tachyon has to achieve a constant speed faster than the speed of light, meaning it can never go slower. For now, that’s a pretty tall task.
But here’s where time travel comes in: If you can travel faster than the speed of light, you could hypothetically send messages at speeds exceeding time, which means you can send a message backward. That message can then reach you before you even thought to send the original message. It’s a bit of a mind-bender.
As posited in the Discover story , the big question is if the time travel component of the tachyon is simply an unproven one or an impossible one. Not only do we need to figure out the whole faster-than-the-speed-of-light conundrum, but the other little fact that makes this thorny is that our universe doesn’t offer up a way to travel in any direction other than the future ... yet.
We just need to figure out both of those scenarios to make the hypothetical tachyon not only faster than the speed of light, but capable of traveling back in time. Better get to trying.
Tim Newcomb is a journalist based in the Pacific Northwest. He covers stadiums, sneakers, gear, infrastructure, and more for a variety of publications, including Popular Mechanics. His favorite interviews have included sit-downs with Roger Federer in Switzerland, Kobe Bryant in Los Angeles, and Tinker Hatfield in Portland.

.css-cuqpxl:before{padding-right:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;} Science .css-xtujxj:before{padding-left:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;}

Time May Actually Be One Big Illusion

Squeezing IR Light Farther Than Ever Before

This Plasma Escape Plan Could Be a Big Fusion Boon
Want a Better Laser? Quantum Entanglement Can Help

Archeological Find May Become Modern Housing

Nanorobots To Take Over Human Function

Study Offers Upside-Down Look on 'First Chordate'

Olmec ‘Portal to the Underworld’ Returns to Mexico

The Third Form of Life's Energy-Making Secret

Jet Missing in U.S. Since 1971 Found in Lake

The CIA’s Plan to Deploy an Army of Super Spies
To revisit this article, visit My Profile, then View saved stories .
- Backchannel
- Newsletters
- WIRED Insider
- WIRED Consulting
Justin Smith-Ruiu
A New Time-Travel App, Reviewed

We all know by now that the time-reversal invariance governing statistical mechanics at the microlevel maps by a simple equation onto the macroworld, making “time travel” a wholly unsurprising possibility … but damn! The first time you go back there’s just nothing like it.
I know all these first-person accounts of ChronoSwooping have become a cliché here on Substack, where, let’s face it, anyone can write pretty much whatever they want no matter how self-indulgent and derivative. Nonetheless I think I have some unusual insights to share, which derive from my own experience but which may offer some general lessons as to the nature and significance of time travel, both the original and long-prohibited “body-transit” method as well as the newer and more streamlined ChronoSwoop.
This is not only because I spent some years in the archives of the Stadzbybliotiēka of the Margravate of East K****, poring over the notebooks in which Quast first landed on the Quast equation, while in parallel jotting down sundry philosophical reflexions about the nature of Divine Tempus—as he called it—that have largely been neglected by other researchers. It is also because I have used the ChronoSwoop app in ways that are expressly prohibited by its makers, and indeed by the federal government. In light of this, while I am writing this product review for Substack and in the emerging “Substack style,” until the law changes or I depart permanently from the chronological present, I will be posting this piece only on the Hinternet-based Substack oglinda (Romanian for “looking-glass,” a hacking neologism supposedly coined by Guccifer 3.0), which I’m told is undetectable, remaining entirely unknown even to the original company’s founders. Fingers crossed.
Perhaps some readers on this oglinda will appreciate a brief summary of what’s been happening in the world of time travel since Quast first came up with his equation in 1962. I don’t know what sort of information has been circulating down here, and I don’t want anyone to feel left behind.
The early 1960s witnessed great leaps forward not just in time-travel technology, but in the technology of teletransportation as well—which is to say dematerialization of the body, and its rematerialization elsewhere, but without any measurable “metachrony.” By late 1966 poorly regulated teletransporters had begun to pop up on the state fair circuit, tempting daredevils into ever more foolish stunts. But this practice was curtailed already the following year, when, expecting to reappear kneeling before his sweetheart Deb at the stables with a ring in his hand, Roy Bouwsma, aka “the Omaha Kid,” got rematerialized instead with the stable door cutting directly through the center of his body from groin to skull—one half of him flopping down at Deb’s feet, the other half falling, like some neat bodily cross section carefully made for students of anatomy, into the stable with Deb’s confused horse Clem.
But while this atrocious moment, broadcast live on KMTV, nipped the new craze in the bud, the technology underlying it had already been adapted for use in what was then called “Tempus-Gliding,” which had the merely apparent advantage of concealing from those in the present any potential accident in the rematerialization of the voyager to the past. Of course, accidents continued to happen, and news of them eventually made its way back from past to present, bringing about all sorts of familiar paradoxes in the spacetime continuum. Tempus-Gliding, like any metachronic technology relying on body-transit, was a door thrown wide open to all the crazy scenarios we know from the time-travel tropes in science fiction going back at least to H. G. Wells: adults returning to the past and meeting themselves as children, meeting their parents before they were even born, causing themselves never to have been born and so suddenly to vanish, and so on. By the end of the 1960s people, and sometimes entire families, entire lineages, were vanishing as a daily occurrence (just recall the 1969 Harris family reunion in Provo!). You could almost never say exactly why, since the traveler to the past who would unwittingly wipe out all his descendants often had yet, in the present, ever to even try Tempus-Gliding.

By Kim Zetter

By Mark Harris

By Chris Baraniuk

By Amanda Hoover
A campaign to end the practice quickly gained speed. By 1973 the “Don’t Mess With Spacetime” bumper stickers were everywhere, and by the following year Tempus-Gliding was outlawed—which is to say, as is always the case in such matters, that only outlaws continued to Tempus-Glide. Scattered disappearances continued, public outcry against illicit Tempus-Gliding became more widespread. In 1983 Nancy Reagan made an unforgettable guest appearance on Diff’rent Strokes to help get out the message about the dangers of illegal body-transit. (“More than 40,000 young lives are lost each year to illegal Metachron gangs.” “What you talkin’ ’bout Mrs. Reagan?”) By the late 1980s a combination of tough-on-crime measures and transformations in youth culture largely ended the practice, and time travel would likely have remained as dormant as moon-travel if it had not in the last decade been so smoothly integrated into our new mobile technologies, and in a way that overcomes the paradoxes and inconveniences of Tempus-Gliding. It does so, namely, by taking the body out of the trip altogether.
This is the mode of time travel, of course, that has shaped a significant subcurrent of science fiction scenarios, notably Chris Marker’s La Jetée (1962), later adapted into the better known Bruce Willis vehicle 12 Monkeys (1995). While these films might seem exceptional, they also share something important with the great majority of what may be called time-travel tales avant la lettre, in which, typically, a man such as Rip Van Winkle goes to sleep for a very long time and wakes up in “the future.” The “zero form” of time travel, we are reminded, is simply to live, which is to say to travel forward in time at a slow and steady rate that only appears to be sped up or “warped” through deep sleep.
Be that as it may, when the new app-based time-travel technologies began to emerge in the late 2010s—relying as they did on a loophole in the 1974 law against time travel that defined it strictly as “metachronic body-transit”—they were all confronted by the hard limit on innovation already predicted by Quast, who remained committed until the end to the impossibility in principle of future-directed time-travel. “If you want to get to the future, you’re just going to have to wait,” Quast wrote in an entry in his Hefte dated 6 October, 1959 (SB-1omk 21.237). “To live in time is already to travel in time. So be patient” [ In der Zeit zu leben, das ist schon in der Zeit zu reisen. Hab also Geduld ]. Rumors of future-transit apps downloadable from ultra-sketchy oglindas have been circulating for years, but I’ve never seen any, and having studied Quast’s work I have come to believe that they are a theoretical impossibility.
The earliest apps, popping up mostly from anonymous sources, were mostly perceived as too dangerous and illicit to gain widespread appeal. “We’ve got that legal cannabis here in California now,” Whoopi Goldberg said on an episode of The View in September 2019. “If I want to take a little trip, I’m sorry but there’s edibles for that. I’m not messing with spacetime [ audience laughter ].” In an echo of the panic leading to the prohibition of Tempus-Gliding in the early 1970s, the government began to issue PSAs sensitizing the public to the serious psychological trauma that a return to our own pasts can trigger. “This is not lighthearted fun,” the messaging went. “Metachronism can ruin your life.”
The campaign against these new technologies would probably have killed them, or at least pushed them so far down into the oglindas as to occlude them from the public’s consciousness, if in 2021, at the worst moment of the pandemic, the ChronoSwoop company had not appeared as if out of nowhere and dropped its addictive new app with its signature “Swoop left/Swoop right” functions. Key to ChronoSwoop’s success was the discovery that users will draw significantly more pleasure from being cast into random moments in the past (Swoop left) than from being permitted to choose particular moments they have deemed significant in the post-hoc construction of their autobiographical self-narrative. And if you find yourself thrown back into an unpleasant or dull moment, then a single swift Swoop right will bring you immediately back into the present. You can of course go into your settings and laboriously reconfigure the app to permit you to choose your precise dates, but the great miracle of ChronoSwoop’s success is that almost no one bothers to do this. The people want their time travel to come with streamlined, easy interfaces. They want to move through the past like they move through their feeds: going nowhere in particular, with no clear purpose.
Quast had remained agnostic as to the possibility of body-less time travel, though he always insisted that, if it turns out to be possible, this will amount to an empirical proof of body-soul dualism. If the “self” can easily be inserted into the body it possessed at an earlier stage of life, while retaining all the memories of experiences from after that stage, this means, he believed, that the memories, as well as consciousness itself, cannot be dependent on the physical substrate of the brain that supposedly hosts them. When people first started ChronoSwooping, there were rumors of “headaches,” which were supposed to have resulted from the transit back in time of the more fully developed neurological structure of the time traveler—essentially cramming, say, a 38-year-old’s brain into the cranium of his 10-year-old past self. But of course no such thing occurs, for what travels back, as Quast predicted, is the immaterial self alone, and the fact that this is possible does indeed demonstrate, whether the scientific establishment is ready to admit it or not, that we do not need to remain anchored to any parcel of matter at all in order to exist as conscious beings.
ChronoSwoop beat out its early competitors (remember TimeDig? 😂) not only by getting rid of the date-choosing option, but also by adding sensorimotor control to the package. The earliest apps only planted your consciousness into the body of your past self and permitted you to “ride along,” to see and feel everything your former self saw and felt, but not to exercise any control over any of this. Quast predicted that only such passive riding would ever be possible, in part because any will-driven intervention in the sequence of past events, such as ChronoSwooping now makes possible, seems to generate at least as many paradoxes for the spacetime continuum as old-fashioned body-transit.
It’s not clear how ChronoSwoop managed to pull it off, but we can at least affirm what the emerging scientific consensus says about this new option, namely that it demonstrates the truth of the so-called “Many Worlds” interpretation of quantum mechanics, where each new timeline created by a different course of action initiated by a time traveler through the vehicle of that traveler’s own former self simply places that self on a different timeline of a different world, of which there are in any case infinitely many. These worlds are all self-contained and non-interacting, unless you can call ChronoSwooping itself a form of interaction, so that, however strange it all is, we at least avoid the more awkward conundra of body-transit, as when, for the millionth time, some idiot gets it into his head to “kill baby Hitler,” which of course means that more or less everyone in the world from roughly 1933 on, being affected by different events of the world, also ends up having sex at different times, different spermatozoa end up fecundating different eggs, and virtually all of us children of the 20th century disappear, until someone else arranges to kill the idiot who killed baby Hitler and set us back on our course again.
As an early adopter, I first ChronoSwooped in November 2021. The particular experience might seem unremarkable when I describe it, but for me, beyond being an occasion to see my deceased father again, it was my initiation into a world from which I have not really returned. I ended up, at random, back in December 2003. It’s Christmastime, and I’m visiting with my dad in Little Rock, where, I quickly recall, he has recently relocated after some career difficulties in the wake of the dotcom crash. “Have you seen this guy called Crazy Frog?” he’s asking me, as we stand in front of his desktop. “He’s kind of dumb but he makes me laugh.” I look at the animated amphibian with the aviator glasses, singing his ringtone melody over a techno remix of Herbie Hancock’s “Rockit.” I had forgotten all about this. How many other fragments of lost culture, I wonder, lie dormant in me at every moment? Crazy Frog jumps on an invisible motorcycle and revs it along a Möbius-strip highway. “I like it,” my dad says, smiling childlike. I am filled suddenly with infinite love for him. I can’t bear it, and I Swoop right.
I go back again and ChronoSwoop tells me it’s June 21, 1998. I’m sitting on a barstool in a place I seem to remember, but only vaguely. I can tell immediately that it’s very late at night, and that the version of me I have just Swooped into was feeling considerable stress just seconds before. I don’t share his precise memories, or, rather, what happened for him just a moment ago is at a 24-year remove for me, but his cortisol levels are mine now too, and I can tell something’s wrong. After a minute or so my ex-girlfriend S**** bursts out of the men’s room, followed by some miserable low-life wearing a T-shirt with a dumb neon alien’s head on it. He wanders off and she comes sheepishly to me. “We were only doing lines, I swear.” She sniffs and rubs her nose. I am suddenly filled with rage. What a miserable time of my life this was, I think, and again I Swoop right.
I took a break for the next three days, believing I had already had enough. I found myself not quite traumatized, but far more melancholic than I usually am, and largely convinced that what the PSAs were saying was true. This is not lighthearted fun. And yet, for some reason, I went back. I landed this time on February 11, 1979. It’s morning, and I’m on the playground of my Montessori school with Jeremy. He’s wearing an Oakland Raiders windbreaker and has mushroom hair like Nicholas from Eight Is Enough. He’s holding his thumb up to his mouth like it’s a microphone and his hand over his ear as if he has a headset. “This is Howard Cosell,” he says in a funny voice—a “Howard Cosell” voice. I am staring at him confusedly. He sees that I’m not laughing at his imitation. Something in my face frightens him, and he begins to cry. I Swoop right.
What was that all about? Jeremy was always a crybaby, but not like this. What did he see in my face that frightened him so? I drink a Nespresso and I think about what to do next. Maybe I’ve had enough already? No, I Swoop left, and it’s August 18, 1975. I’ve just had a shower and I’m in my long red nightshirt. It’s a summer evening in Rio Linda, the windows are open, and the frogs and bugs are croaking and chirping. I’m lying on the couch, and Mom’s cutting my toenails. I have the strong sense that this entire composition and every being involved in it—the frogs, the bugs, Mom, the sun—is in fact only one being; or more precisely, that it is only one being, and that being is me . This is what life used to be like! Before what? Before things came apart. That’s what it is to grow up: to see the world come apart. It’s too much for me. I Swoop right.
I resolve to end my explorations here, and a good two weeks go by before I find myself quite unconsciously, lying on my back on the couch, moving through the well-hidden settings in my app. I click on “Set Target Date” and immediately I am taken to a screen requiring me to upload a scan of a state-issued ID, which will then confirm my date of birth and prevent me from choosing any target date preceding that all-important threshold. Once this formality has been handled, I aim it back to November 19, 1972, and I set the visit duration for just 30 seconds. (I presume that if I am not yet four months old, even if I have some sensorimotor control over my body as well as my usual 49-year old consciousness about me, I still might simply lack the coordination to Swoop right.) It’s hard to say what I experience when I arrive. It’s warm, it’s light, and all is one. I’m lying there next to a funny man who’s watching something on TV, but I don’t know it’s a TV, and the sound of laughter is coming out of it. “PB&J with pickles,” the man says, repeating what he has heard, laughing. Somehow I don’t understand what this means, but I’m thrilled that he finds it so funny. “Did you hear that one? PB&J with pickles !” he shouts to someone who is not in the room with us, but whose presence I can feel. Such joy. Such love. I disappear.
The block on pre-birth travel is ostensibly to prevent the risk of “ditching,” where someone gets permanently stuck in the past. But as long as we are able to preset the duration of the visit, this concern seems ill-placed, and we can only imagine that the real reason is the one that Quast foresaw: “If it ever becomes possible experimentally to prove the immateriality of the soul,” he wrote, “they will do everything in their power to prevent us from finding out about it” (SB-1omk 24.785).
I’m not the sort of person to break the law casually, but what I experienced in the autumn of 1972 was simply too powerful, and I wanted more. I went to the Pakistani mobile-phone shop down at the corner, and sure enough, what they always say about these places is true. Just as the agile shopkeeper will happily oblige any request to repair your touchscreen or to unblock some old battered phone, no questions asked, neither will he look surprised when you ask him, as the parlance has it, to “take away your birthday.”
When I got back home I drank a Diet Dr. Pepper and I pondered different dates and durations until one came to me as if in a message: 1 minute, July 30, 1971—exactly a year before my birth. I Swooped left. I cannot tell you how or why this is so, but I can tell you that exactly a year before I was born, I was floating in warm liquid, and although I had no eyes to see it, I can tell you that there was light. This scene too was charged up with love.
It was also, somehow, charged up with knowledge. Though I did not “know” anything—about PB&J sandwiches, for example, or about parents, or Howard Cosell, or Crazy Frog—it seemed to me after my return that this is only because I knew everything, and I knew it from a vantage where the sharp differentiation between these sundry things seemed a far greater error than their combination. Seeing them all as one, it seemed to me now, felt unmistakably like what is imagined under the idea of heaven. St. Augustine writes that in death the soul returns to regionem suae originis —to the region of its origin, and here he is adapting within a Christian context the broadly Platonic vision of a pre-life life spent in direct communion with the eternal and unchanging Forms. Is that what I was seeing in 1971? If so, then why was everything so wet? No Platonic philosopher, Christian or heathen, ever conceived “baby heaven” in precisely this way.
You probably have some idea of what I did next. I scrolled back to the earliest transit date possible—January 1, 1900. I would have gone back far earlier, to 500 BCE, to 50 million ybp, to God knows when, but the drop-down calendar made its cutoff the beginning of the 20th century. So that’s where I went; nor did I set a duration for the visit.
I can’t tell you what happened after that, or whether I’m still there, or what is even happening anymore. If you think I’ve been spending my days watching mustachioed men on velocipedes going to the beach and changing there into comical striped one-piece bathing suits to play beach-croquet with ladies in bloomers, you really haven’t understood what pre-birth ChronoSwooping is like. I set the thing for 1900, but the human calendar doesn’t mean very much when you’ve shed your body, and your senses, and any trace of your connection to the world of particulars.
I would not recommend doing what I have done. It is not a question of being able “to handle it”; we “handle” whatever comes our way, even or perhaps especially the most impossible things. Unlike the world I saw in 1971, here it’s not even wet or light, but neither is it dry or dark. I know everything, if by “everything” we mean the timeless and universal truths, but as for individuals, facts, things that come and go, contingent beings and the ever-vanishing traces of events, I just can’t make anything out anymore.
“God made time to prevent everything from happening at once,” the diminutive Billy ponders, while looking up at the bright North Star like some junior magus in a Family Circus cartoon circa 1988 that somehow remains vivid to me in its particularity, like the answer to a riddle I never meant to pose, even as almost all other particulars recede from my consciousness. This too is a cliché, of course. Albert Einstein said something similar; so did many other people in fact, and they were all drawing broadly on a theory of temporal idealism that runs through many philosophical systems, including, on at least one understanding, that of Augustine. But no matter, it’s Bil Keane’s cartoon version that sticks with me. I love the Sunday funnies: so stupid; so comforting; so warm. I love TV. I love memes. They’re kind of dumb but I love them.
On these and other such small things was I trained up, like some innocent AI that knows no temporal flow at all, so that the dim outlines of them still move across memory’s stage even after I have used my app against the rules and withdrawn from Time altogether—before Time was yet able to withdraw from me.
You Might Also Like …
Navigate election season with our WIRED Politics Lab newsletter and podcast
Don’t think breakdancing is an Olympic sport ? The world champ agrees (kinda)
How researchers cracked an 11-year-old password to a $3M crypto wallet
The uncanny rise of the world’s first AI beauty pageant
Give your back a break: Here are the best office chairs we’ve tested

Joel Khalili

Megan Farokhmanesh

Angela Watercutter

Eric Ravenscraft

Jennifer M. Wood

Marah Eakin
Time Travel Tuesday: NewsChannel 7 of yesterday
PANAMA CITY, Fla. (WJHG/WECP) -Political moves, dealership debates, and a look at our past! Historian Bill Hudson joins us for another Time Travel Tuesday.
If you are looking to chat about local history, you can contact Bill Hudson at (850) 785-3364.
Copyright 2024 WJHG. All rights reserved.

Panama City Beach Police Chief Talamantez placed on administrative leave pending investigation

Plastic surgeon charged with manslaughter after wife’s post-surgery death, officials say

Suspect arrested after barricading himself, threatening deputies to “bash their heads in”

JCSO: Deputies find stolen vehicle being driven by missing person


Boat overturns with five people on it in St. Andrews
Latest news.

Morning Extra: Top stories from Tuesday June 18

Biden approves disaster declaration for Florida after severe weather

Thousands of dollars raised so far through purple ribbons for shark attack victim

Do you believe in time travel? I’m a skeptic myself — but if these people’s stories about time travel are to be believed, then I am apparently wrong. Who knows? Maybe one day I’ll have to eat my words. In all honesty, that might not be so bad — because the tradeoff for being wrong in that case would be that time travel is real . That would be pretty rad if it were true.
Technically speaking time travel does exist right now — just not in the sci fi kind of way you’re probably thinking. According to a TED-Ed video by Colin Stuart, Russian cosmonaut Sergei Krikalev actually traveled 0.02 seconds into his own future due to time dilation during the time he spent on the International Space Station. For the curious, Krikalev has spent a total of 803 days, nine hours, and 39 minutes in space over the course of his career.
That said, though, many are convinced that time dilation isn’t the only kind of time travel that’s possible; some folks do also believe in time travel as depicted by everything from H. G. Wells’ The Time Machine to Back to the Future . It’s difficult to find stories online that are actual accounts from real people — many of them are either urban legends ( hi there, Philadelphia Experiment ) or stories that center around people that I’ve been unable to verify actually exist — but if you dig hard enough, sincere accounts can be found.
Are the stories true? Are they false? Are they examples of people who believe with all their heart that they’re true, even if they might not actually be? You be the judge. These seven tales are all excellent yarns, at any rate.
The Moberly–Jourdain Incident
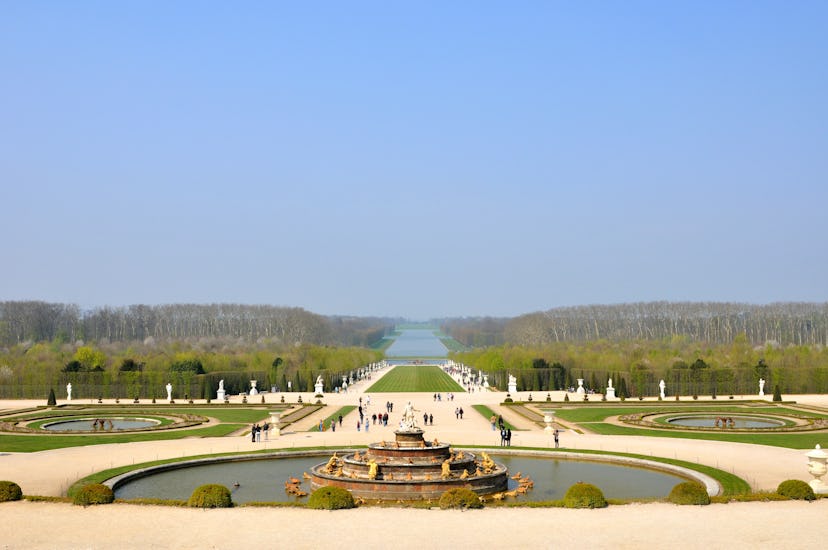

In 1901, two Englishwomen, Anne Moberly and Eleanor Jourdain , took a vacation to France. While they were there, they visited the Palace of Versailles (because, y’know, that’s what one does when one visits France ). And while they were at Versailles, they visited what’s known as the Petit Trianon — a little chateau on the palace grounds that Louis XVI gave to Marie Antoinette as a private space for her to hang out and do whatever it was that a teenaged queen did when she was relaxing back then.
But while they were there, they claimed, they saw some… odd occurrences. They said they spotted people wearing anachronistic clothing, heard mysterious voices, and saw buildings and other structures that were no longer present — and, indeed, hadn’t existed since the late 1700s. Finally, they said, they caught sight of Marie Antoinette herself , drawing in a sketchbook.
They claimed to have fallen into a “time slip” and been briefly transported back more than 100 years before being jolted back to the present by a tour guide.
Did they really travel back in time? Probably not; various explanations include everything from a folie a deux (basically a joint delusion) to a simple misinterpretation of what they actually saw. But for what it’s worth, in 1911 — roughly 10 years after what they said they had experienced occurred — the two women published a book about the whole thing under the names Elizabeth Morison and Frances Lamont simply called An Adventure. These days, it’s available as The Ghosts of Trianon ; check it out, if you like.
The Mystery Of John Titor

John Titor is perhaps the most famous person who claims he’s time traveled; trouble is, no one has heard from him for almost 17 years. Also, he claimed he came from the future.
The story is long and involved, but the short version is this: In a thread begun in the fall of 2000 about time travel paradoxes on the online forum the Time Travel Institute — now known as Curious Cosmos — a user responded to a comment about how a time machine could theoretically be built with the following message:
“Wow! Paul is right on the money. I was just about to give up hope on anyone knowing who Tipler or Kerr was on this worldline.
“By the way, #2 is the correct answer and the basics for time travel start at CERN in about a year and end in 2034 with the first ‘time machine’ built by GE. Too bad we can’t post pictures or I’d show it to you.”
The implication, of course, was that the user, who was going by the name TimeTravel_0, came from a point in the future during which such a machine had already been invented.
Over the course of many messages spanning from that first thread all the way through the early spring of 2001, the user, who became known as John Titor, told his story. He said that he had been sent back to 1975 in order to bring an IBM 5100 computer to his own time; he was just stopping in 2000 for a brief rest on his way back home. The computer, he said, was needed to debug “various legacy computer programs in 2036” in order to combat a known problem similar to Y2K called the Year 2038 Problem . (John didn’t refer to it as such, but he said that UNIX was going to have an issue in 2038 — which is what we thought was going to happen back when the calendar ticked over from 1999 to 2000.)
Opinions are divided on whether John Titor was real ; some folks think he was the only real example of time travel we’ve ever seen, while others think it’s one of the most enduring hoaxes we’ve ever seen. I fall on the side of hoax, but that’s just me.
Project Pegasus And The Chrononauts

In 2011, Andrew D. Basiago and William Stillings stepped forward, claiming that they were former “chrononauts” who had worked with an alleged DARPA program called Project Pegasus. Project Pegasus, they said, had been developed in the 1970s; in 1980, they were taking a “Mars training class” at a community college in California (the college presumably functioning as a cover for the alleged program) when they were picked to go to Mars. The mode of transport? Teleportation.
It gets better, too. Basiago and Stillings also said that the then- 19-year-old Barack Obama , whom they claimed was going by the name “Barry Soetero” at the time, was also one of the students chosen to go to Mars. They said the teleportation occurred via something called a “jump room.”
The White House has denied that Obama has ever been to Mars . “Only if you count watching Marvin the Martian,” Tommy Vietor, then the spokesman for the National Security Council, told Wired’s Danger Room in 2012.
Victor Goddard’s Airfield Time Slip

Like Anne Moberly and Eleanor Jourdain, senior Royal Air Force commander Sir Robert Victor Goddard — widely known as Victor Goddard — claimed to have experienced a time slip.
In 1935, Goddard flew over what had been the RAF station Drem in Scotland on his way from Edinburgh to Andover, England. The Drem station was no longer in use; after demobilization efforts following WWI, it had mostly been left to its own devices. And, indeed, that’s what Goddard said he saw as he flew over it: A largely abandoned airfield.
On his return trip, though, things got… weird. He followed the same route he had on the way there, but during the flight, he got waylaid by a storm. As he struggled to regain control of his plane, however, he spotted the Drem airfield through a break in the clouds — and when he got closer to it, the bad weather suddenly dissipated. But the airfield… wasn’t abandoned this time. It was busy, with several planes on the runway and mechanics scurrying about.
Within seconds, though, the storm reappeared, and Goddard had to fight to keep his plane aloft again. He made it home just fine, and went on to live another 50 years — but the incident stuck with him; indeed, in 1975, he wrote a book called Flight Towards Reality which included discussion of the whole thing.
Here’s the really weird bit: In 1939, the Drem airfield was brought back to life. Did Goddard see a peek into the airfield's future via a time slip back in 1935? Who knows.
Space Barbie

I’ll be honest: I’m not totally sure what to do with thisone — but I’ll present it to you here, and then you can decide for yourself what you think about it. Here it is:
Valeria Lukyanova has made a name for herself as a “human Barbie doll” (who also has kind of scary opinions about some things ) — but a 2012 short documentary for Vice’s My Life Online series also posits that she believes she’s a time traveling space alien whose purpose on Earth is to aid us in moving “from the role of the ‘human consumer’ to the role of ‘human demi-god.’”
What I can’t quite figure out is whether this whole time traveling space alien thing is, like a piece of performance art created specifically for this Vice doc, or whether it’s what she actually thinks. I don’t believe she’s referenced it in many (or maybe even any) other interviews she’s given; the items I’ve found discussing Lukyanova and time travel specifically all point back to this video.
But, well… do with it all as you will. That’s the documentary up there; give it a watch and see what you think.
The Hipster Time Traveler

In the early 2010s, a photograph depicting the 1941 reopening of the South Fork Bridge in Gold Bridge, British Columbia in Canada went viral for seemingly depicting a man that looked… just a bit too modern to have been photographed in 1941. He looks, in fact, like a time traveling hipster : Graphic t-shirt, textured sweater, sunglasses, the works. The photo hadn’t been manipulated; the original can be seen here . So what the heck was going on?
Well, Snopes has plenty of reasonable explanations for the man’s appearance; each item he’s wearing, for example, could very easily have been acquired in 1941. Others have also backed up those facts. But the bottom line is that it’s never been definitively debunked, so the idea that this photograph could depict a man from our time who had traveled back to 1941 persists. What do you think?
Father Ernetti’s Chronovisor

According to two at least two books — Catholic priest Father Francois Brune’s 2002 book Le nouveau mystère du Vatican (in English, The Vatican’s New Mystery ) and Peter Krassa’s 2000 book Father Ernetti's Chronovisor : The Creation and Disappearance of the World's First Time Machine — Father Pellegrino Ernetti, who was a Catholic priest like Brune, invented a machine called a “chronovisor” that allowed him to view the past. Ernetti was real; however, the existence of the machine, or even whether he actually claimed to have invented it, has never been proven. Alas, he died in 1994, so we can’t ask him, either. I mean, if we were ever able to find his chronovisor, maybe we could… but at that point, wouldn’t we already have the information we need?
(I’m extremely skeptical of this story, by the way, but both Brune’s and Krassa’s books swear up, down, left, and right that it’s true, so…you be the judge.)
Although I'm fairly certain that these accounts and stories are either misinterpreted information or straight-up falsehoods, they're still entertaining to read about; after all, if you had access to a time machine, wouldn't you at least want to take it for a spin? Here's hoping that one day, science takes the idea from theory to reality. It's a big ol' universe out there.

Time travel could be possible, but only with parallel timelines
Assistant Professor, Physics, Brock University
Disclosure statement
Barak Shoshany does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Brock University provides funding as a member of The Conversation CA-FR.
Brock University provides funding as a member of The Conversation CA.
View all partners
Have you ever made a mistake that you wish you could undo? Correcting past mistakes is one of the reasons we find the concept of time travel so fascinating. As often portrayed in science fiction, with a time machine, nothing is permanent anymore — you can always go back and change it. But is time travel really possible in our universe , or is it just science fiction?
Read more: Curious Kids: is time travel possible for humans?
Our modern understanding of time and causality comes from general relativity . Theoretical physicist Albert Einstein’s theory combines space and time into a single entity — “spacetime” — and provides a remarkably intricate explanation of how they both work, at a level unmatched by any other established theory. This theory has existed for more than 100 years, and has been experimentally verified to extremely high precision, so physicists are fairly certain it provides an accurate description of the causal structure of our universe.
For decades, physicists have been trying to use general relativity to figure out if time travel is possible . It turns out that you can write down equations that describe time travel and are fully compatible and consistent with relativity. But physics is not mathematics, and equations are meaningless if they do not correspond to anything in reality.
Arguments against time travel
There are two main issues which make us think these equations may be unrealistic. The first issue is a practical one: building a time machine seems to require exotic matter , which is matter with negative energy. All the matter we see in our daily lives has positive energy — matter with negative energy is not something you can just find lying around. From quantum mechanics, we know that such matter can theoretically be created, but in too small quantities and for too short times .
However, there is no proof that it is impossible to create exotic matter in sufficient quantities. Furthermore, other equations may be discovered that allow time travel without requiring exotic matter. Therefore, this issue may just be a limitation of our current technology or understanding of quantum mechanics.

The other main issue is less practical, but more significant: it is the observation that time travel seems to contradict logic, in the form of time travel paradoxes . There are several types of such paradoxes, but the most problematic are consistency paradoxes .
A popular trope in science fiction, consistency paradoxes happen whenever there is a certain event that leads to changing the past, but the change itself prevents this event from happening in the first place.
For example, consider a scenario where I enter my time machine, use it to go back in time five minutes, and destroy the machine as soon as I get to the past. Now that I destroyed the time machine, it would be impossible for me to use it five minutes later.
But if I cannot use the time machine, then I cannot go back in time and destroy it. Therefore, it is not destroyed, so I can go back in time and destroy it. In other words, the time machine is destroyed if and only if it is not destroyed. Since it cannot be both destroyed and not destroyed simultaneously, this scenario is inconsistent and paradoxical.
Eliminating the paradoxes
There’s a common misconception in science fiction that paradoxes can be “created.” Time travellers are usually warned not to make significant changes to the past and to avoid meeting their past selves for this exact reason. Examples of this may be found in many time travel movies, such as the Back to the Future trilogy.
But in physics, a paradox is not an event that can actually happen — it is a purely theoretical concept that points towards an inconsistency in the theory itself. In other words, consistency paradoxes don’t merely imply time travel is a dangerous endeavour, they imply it simply cannot be possible.
This was one of the motivations for theoretical physicist Stephen Hawking to formulate his chronology protection conjecture , which states that time travel should be impossible. However, this conjecture so far remains unproven. Furthermore, the universe would be a much more interesting place if instead of eliminating time travel due to paradoxes, we could just eliminate the paradoxes themselves.
One attempt at resolving time travel paradoxes is theoretical physicist Igor Dmitriyevich Novikov’s self-consistency conjecture , which essentially states that you can travel to the past, but you cannot change it.
According to Novikov, if I tried to destroy my time machine five minutes in the past, I would find that it is impossible to do so. The laws of physics would somehow conspire to preserve consistency.
Introducing multiple histories
But what’s the point of going back in time if you cannot change the past? My recent work, together with my students Jacob Hauser and Jared Wogan, shows that there are time travel paradoxes that Novikov’s conjecture cannot resolve. This takes us back to square one, since if even just one paradox cannot be eliminated, time travel remains logically impossible.
So, is this the final nail in the coffin of time travel? Not quite. We showed that allowing for multiple histories (or in more familiar terms, parallel timelines) can resolve the paradoxes that Novikov’s conjecture cannot. In fact, it can resolve any paradox you throw at it.
The idea is very simple. When I exit the time machine, I exit into a different timeline. In that timeline, I can do whatever I want, including destroying the time machine, without changing anything in the original timeline I came from. Since I cannot destroy the time machine in the original timeline, which is the one I actually used to travel back in time, there is no paradox.
After working on time travel paradoxes for the last three years , I have become increasingly convinced that time travel could be possible, but only if our universe can allow multiple histories to coexist. So, can it?
Quantum mechanics certainly seems to imply so, at least if you subscribe to Everett’s “many-worlds” interpretation , where one history can “split” into multiple histories, one for each possible measurement outcome – for example, whether Schrödinger’s cat is alive or dead, or whether or not I arrived in the past.
But these are just speculations. My students and I are currently working on finding a concrete theory of time travel with multiple histories that is fully compatible with general relativity. Of course, even if we manage to find such a theory, this would not be sufficient to prove that time travel is possible, but it would at least mean that time travel is not ruled out by consistency paradoxes.
Time travel and parallel timelines almost always go hand-in-hand in science fiction, but now we have proof that they must go hand-in-hand in real science as well. General relativity and quantum mechanics tell us that time travel might be possible, but if it is, then multiple histories must also be possible.
- Time travel
- Theoretical physics
- Time machine
- Albert Einstein
- Listen to this article
- Time travel paradox

Social Media Producer

Student & Academic Services Officer

Dean (Head of School), Indigenous Knowledges

Senior Research Fellow - Curtin Institute for Energy Transition (CIET)

Laboratory Head - RNA Biology

Cruise Ship Diverts to Bahamas to Avoid Seizure in U.S.

Here Are the Most 'Attractive' Global Cities

There's a Travel Ban on Dogs, and You Can Blame COVID-19

U.S. Lawmaker Wants to Ban Booze ‘To Go’ at Airports

Biden Reinstates International Travel Restrictions
The latest ban would prevent most non-u.s. citizens from entry if they have recently been in south africa, where a new strain of the virus has been identified.

Passenger on Cruise to Nowhere Tests Positive for COVID-19
Royal caribbean international and genting cruise lines have been running cruises to nowhere as singapore aims to bolster its tourism sector.

America's Travel Guru Rick Steves Talks About Staying in One Place, What America Is Getting Wrong, and Dreaming of Escargots
This summer, i traveled. there were sun-soaked italian hill towns; a sleepy portuguese fishing village; a musty, centuries-old timber church in romania. i saw it all from my couch, or sometimes the faded hammock on....

Europe Hopes Summer Tourism Will Boost Economy
Europe's recovery from covid-19 depends on the return of summer vacations.

It's Definitely Worth Following Gary the Cat for Travel Inspiration. Despite His Instagram Fame, He's Still 'Just a Cat.'
The traveling cat’s instagram feed is inspiring.

Cruise Sailing for Mexico After Being Denied Entry Over Coronavirus Fears
Msc meraviglia has received “formal and final authorization” to call in cozumel, mexico.
Why It May Be Impossible to Stop Every Traveler With Coronavirus
Experts say its difficult to screen for covid-19 because of its long incubation period and mild symptoms.

'Diamond Princess' Crew Begin Second Quarantine
As passengers started leaving the diamond princess wednesday following a quarantine that saw them largely confined to their rooms for two weeks, another quarantine is about to begin.the 1,000-some crew members still left on the....

Inside Life Below Decks on the Stricken Cruise Ship
At least 454 cases of covid-19 have been confirmed on the diamond princess, where over 1,000 crew members continue to serve passengers on board.

U.S. Cruise Ship Passenger Now Has Coronavirus
An 83-year-old american woman tested positive for covid-19 after disembarking.

Cruise Passengers Back in U.S.
There were around 400 americans on the quarantined diamond princess, of which 44 had tested positive for covid-19.

This Cruise Ship Has the Highest Infection Rate in the World
Passengers on the diamond princess cruise ship, docked at japan's yokohama bay, are halfway through their 14-day quarantine.

Stranded U.S. Cruise Ship Docks in Cambodia
The ship docked in cambodia after rejections from thailand, japan, guam, the philippines and taiwan over coronavirus fears.

Fly From Hong Kong to New York for Just $193 — If You’re Willing to Stop in Wuhan
The coronavirus, which originated in wuhan, china, has killed more than 200 and it's not clear how long the crisis will last.

Hong Kong Wants Disney Land for Affordable Housing
The city is home to some of the most unaffordable housing in the world.

Japan Airlines Is Giving Away 50,000 Free Flights to Tourists
Tourists flying to japan with japan airlines this summer can win free tickets to a surprise destination in the country.

Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
Readout of President Joe Biden’s Meeting with Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg of NATO
President Joseph R. Biden, Jr. met today with Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) ahead of NATO’s 75th Anniversary Summit in Washington, DC next month, which the President will host. The President welcomed steps NATO Allies are taking to support Ukraine and to deepen partnerships, including in the Indo-Pacific. President Biden and Secretary General Stoltenberg also discussed significant progress on defense spending, including that a record 23 Allies will reach NATO’s two percent spending threshold, a more than two-fold increase since President Biden took office.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.
Watch CBS News
Passports can now be renewed online. Here's how to apply.
By Khristopher J. Brooks
Edited By Anne Marie Lee
June 13, 2024 / 11:24 AM EDT / CBS News
U.S. travelers can now renew their passport online under a pilot program the U.S. Department of State launched on Thursday.
The State Department's new online system will allow U.S. passport holders to start a renewal application for a short window of time every day, closing once the system has reached a designated number of new applications, officials said in a statement . The agency is preparing a full launch of the renewal system at some point after testing, but didn't provide an exact date.
If successful, an online renewal system could shorten the sometimes monthslong process travelers experience when trying to update their passport.
"During the next several months, we plan to continue to limit the number of applications accepted each day so we can monitor the system's performance in real time," the department said. "If you are unable to start your application, try again on another day."
Processing passports has become a growing problem for the State Department ever since COVID-19 travel restrictions were lifted, with the agency bombarded with an overwhelming number of applications each week. The passport application backlog grew so heavy last year that federal lawmakers from California, Colorado and Oklahoma introduced separate proposals to the Senate to speed up the application process.
Republican Sen. James Lankford of Oklahoma proposed legislation that would improve the online tracking of passport applications and allow the State Department to hire more staff. Democratic Reps. Adam Schiff and Ted Lieu of California introduced the PASSPORT Act to streamline the passport application and renewal process.
The number of Americans holding valid U.S. passports has grown at roughly 10% faster than the population over the past three decades, said Jay Zagorsky, an economist at Boston University. Just 5% of Americans had a passport in 1990, according to the State Department. That number grew to 48% in December.
The State Department issued a record setting 24 million passports in 2023. Wait times for passport applications and renewals returned to their normal 6-8 week time frame in December , the State Department said .
Renewing your passport online involves a six-step process:
- Create a free MyTravelGov online account.
- After the account is created, log in and start a renewal application by clicking on the "Renew Your Passport" button.
- On the form that appears, fill in all the boxes with the information currently printed on your passport.
- Enter your plans to travel internationally if your departure is within the next eight weeks.
- Upload a jpeg photo of yourself. No selfies.
- Pay the passport renewal fee and digitally sign the application.
Visit the State Department's online renewal website for more details.
Khristopher J. Brooks is a reporter for CBS MoneyWatch. He previously worked as a reporter for the Omaha World-Herald, Newsday and the Florida Times-Union. His reporting primarily focuses on the U.S. housing market, the business of sports and bankruptcy.
More from CBS News

Nationwide to drop about 100,000 pet insurance policies

Vladimir Putin to visit Kim Jong Un in North Korea

McDonald's ends AI drive-thru orders — for now

Amazon's bestselling window air conditioner is on sale now
San Jose Sharks | Should the Sharks claim one-time playoff hero?
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
Today's e-Edition
- Earthquakes
- High School
- Pac-12 Hotline
- Dieter Kurtenbach
Breaking News
San jose sharks | map: air advisory for bay area goes out as smoke from point, sites fires sends haze, san jose sharks, one-time san jose sharks playoff hero barclay goodrow was placed on waivers tuesday by the new york rangers.

NHL teams now have until 11 a.m. (PDT) on Wednesday to claim the 31-year-old Goodrow, who started his professional career in San Jose in 2014. If he goes unclaimed, Goodrow would remain with the Rangers, although it’s quite possible that the rest of his contract would soon be bought out by the team.
Goodrow has three years left on a six-year, $21.85 million contract he signed with the Rangers as a free agent in 2021. The deal carries a cap hit of just over $3.64 million, a steep price considering Goodrow had 12 points in 80 games and averaged just 12:34 in ice time per game this past season.
Goodrow, though, did have six goals and eight points in this year’s playoffs as the Rangers advanced to the Eastern Conference final.
The NHL’s first buyout window begins 48 hours after the conclusion of the playoffs. The Florida Panthers lead the Edmonton Oilers three games to one in the best-of-seven Stanley Cup Final and have a chance to clinch in Tuesday’s Game 5.
A buyout would spread two-thirds of Goodrow’s remaining salary over six years and save the Rangers approximately $5.5 million under the cap over the next two seasons. The Rangers, as of Tuesday, have roughly $9.2 million in cap space for next season with 19 players under contract, per CapFriendly.
Goodrow, an Aurora, Ontario native, was signed by the Sharks as an undrafted free agent in 2014. He played most of his first three pro seasons in the AHL with the Barracuda before becoming a full-time NHL player during the 2017-2018 season.
Goodrow won over Sharks fans and was a popular teammate in San Jose with his versatility, no-nonsense style, and willingness to stick up for teammates. In 2019, he cemented his spot in Sharks lore as he scored one of the most famous goals in team history.
In overtime of Game 7 of San Jose’s first-round series with the Vegas Golden Knights, Goodrow took a pass from Erik Karlsson inside the blue line, skated toward the Vegas net, and scored around goalie Marc-Andre Fleury to give the Sharks a series-clinching 5-4 win.
Goodrow was traded to the Tampa Bay Lightning at the 2020 trade deadline for a first-round draft pick used on forward Ozzy Wiesblatt. Goodrow won the Stanley Cup with the Lightning in 2020 and 2021, adding 12 points in 43 playoff games.
The rebuilding Sharks will have a young team next season and might be in the market for players of Goodrow’s ilk this summer as they aim to insulate their rookies and become a harder team to play against. They would have the first crack at claiming Goodrow off waivers since they finished last in the NHL’s overall standings this past season.
The Sharks have enough cap space to absorb Goodrow’s cap hit as a waiver claim. But if they are interested, they could also acquire Goodrow via trade, with the Rangers retaining some salary. Or, assuming there’s a buyout, they could wait and try to sign him as a free agent once the market opens up on July 1, although Goodrow, considering his playoff pedigree, could have other suitors more ready to compete for a playoff spot.
For his NHL career, Goodrow has 169 points in 572 regular-season games and 24 points in 97 playoff games.
- Report an error
- Policies and Standards
More in San Jose Sharks

San Jose Sharks | Sharks president eyes new arena lease, has questions about BART extension

San Jose Sharks | Sharks’ Grier not interested in trading Logan Couture. Here’s why

San Jose Sharks | Warsofsky, a disciple of Penguins’ Sullivan, ready to lead Sharks

Local News | ‘Inside Out 2’ viewers should listen for Sharks broadcaster Randy Hahn’s voice
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Frugal Traveler
Where to Get the Most Bang for Your Buck
American travelers going abroad this summer will find their money buys more in some unexpected countries, including Japan and Australia.

By Elaine Glusac
Elaine Glusac is the Frugal Traveler columnist, focusing on budget-friendly tips and journeys.
It’s the backpacker’s call to India, the sunseeker’s attraction to Mexico, and the digital nomad’s drive to get to Thailand: Go where the dollar buys more.
The evergreen budget travel strategy is getting a boost this summer: The dollar has surged against a number of foreign currencies, including the Japanese yen, thanks to high interest rates offered by the Federal Reserve — attracting foreign investment, which bolsters the dollar.
“A destination’s weaker currency spells greater value for U.S. tourists,” said Erina Pindar, the chief operating officer and managing partner at SmartFlyer , a global travel agency based in New York City.
“This economic advantage could make far-flung bucket list destinations in Asia, such as Indonesia, Vietnam and Japan, or in South America, like Peru, Argentina and Chile, more accessible than ever before,” she added.
Distant destinations are usually more expensive to fly to, which, along with the physical toll of jet lag, helps make the case for the country’s North American neighbors, Canada and Mexico , where the exchange rates have long favored the dollar’s buying power.
But this year there are some new contenders with attractive exchange rates to consider, including the following destinations.
Currently, the U.S. dollar is worth about 1.50 Australian dollars, up about 16 percent over the last three years.
The hurdle, of course, is the long flight, which can easily run over $1,000 round trip. But the travel search engine Kayak lists some attractive summer round-trip fares between the West Coast and Sydney starting at $770, with the best availability in August.
Getting around Australia by air isn’t cheap either, especially since the recent collapse of the low-cost carrier Bonza. Jetstar offers lower fares, including, recently, $50 one-way tickets between Melbourne and Adelaide.
Camper vans can be an affordable way to take an Australian road trip, with companies like Jucy , Britz and Apollo offering vehicles that include beds and cooking facilities. Jucy recently priced a two-person van rented for a week in July at about $53 a night.
The Northern Hemisphere summer is Australia’s winter. If you’re planning a ski vacation in the Australian Alps, Tourism Australia suggests avoiding mid-July when schools are on break and many families head to the slopes.
Australia does not have a culture of tipping, potentially saving travelers 20 percent on restaurant meals, according to Craig Bradbery, the chief operating officer of Baillie Lodges, which includes the newly rebuilt Southern Ocean Lodge , a luxury property on Kangaroo Island.
Bali, Indonesia
Many destinations in Southeast Asia, including Thailand, Vietnam and Cambodia, offer compelling exchange rates. In Indonesia, the rupiah is at a four-year low against the dollar.
“I would send clients to Bali, Indonesia,” said Rob Huie, the owner of Luxury Travel Services by Rob , based in Millsboro, Del., noting that the cost of living is low on the island. “The caveat is a higher upfront cost to fly there, but once you’re there you are able to stay at three- and four-star hotels at very affordable rates, have meals for $10 to $25 per day and massages for $10 to $30.”
Travelers with Marriott loyalty points can cash them in at the Four Points by Sheraton Bali, Kuta (rooms from $57 a night). IGH Reward members can spend or earn points at Hotel Indigo Bali Seminyak Beach (from $138).
Tripadvisor’s list of the top budget hotels in the central highlands around Ubud includes options under $100.
Bali is a good place to look for a vacation rental, according to the home rental platform HomeToGo . Its data shows the median per-night price for a rental property on Bali this summer is $86, compared to the median price of a rental in the United States at $388.
“Despite the strength of the U.S. dollar on a global scale, prices across the states continue to rise, prompting travelers to look to international destinations where their dollar can stretch further,” said Eleanor Moody, a travel expert at HomeToGo, who added that searches for rentals in Indonesia have more than doubled in the past year.
South America — including Argentina where inflation has spiraled, and Peru where the sol has softened against the dollar — is another place to look for value.
“Stop going to Europe,” said Cecile Blot, the owner of the travel agency Boundless Travels in Washington, D.C., praising “destination dupes” in South America. “Many of the countries on the southern continent offer the entire package — history, culture, nature, culinary delights, world-class accommodation — at a fraction of the price.”
One of these is Colombia , where the dollar recently equaled about 3,935 pesos, a gain of roughly 20 percent over the past five years.
“Colombia has something for everyone,” said Stefanie Pichonnat, the owner of AAV Travel , based in Terre Haute, Ind., citing Cartagena on the Caribbean as a budget-friendly substitute for a European capital, and coastal Tayrona National Natural Park as a cheaper alternative to Costa Rica.
“Coffee aficionados can spend days touring the coffee fincas, passionate hikers can challenge themselves with a trek to the páramo desert and bird watchers will find an abundance of options to explore,” she added.
Air service is frequent and affordable. A recent search for round-trip fares from the New York area turned up summer departures starting from about $290 to the capital of Bogotá and $320 to coastal Cartagena.
From Bogotá, visitors can reach Chingaza National Natural Park in the eastern Andes or spend a few days in the laid-back colonial city of Villa de Leyva . But Colombia’s mountainous terrain and perilous roads often require travelers to fly domestically to see other areas.
Among tour operators that do the planning for you, Responsible Travel , based in England, offers a customizable 12-day trip to Colombia that visits Bogotá, Medellín and the central coffee country, including the lush Cocora Valley with its nearly 200-foot-tall wax palm trees (from $2,990 a person).
The U.S. dollar is currently worth about 156 Japanese yen, a gain of more than 11 percent over the past year.
Demand for Japan was already booming when the economic picture improved. BWH Hotels , which includes Best Western Hotels & Resorts, said occupancy and rates have grown steadily for the past two years because of demand and a shortage of employees, especially in popular destinations like Tokyo, Osaka, Kyoto and Hokkaido.
But with careful planning, Americans can still exploit the exchange rate. IHG Hotels & Resorts , which operates hotel brands in the country from the design-focused Voco to the high-end InterContinental, suggested traveling by early July for the best rates (an overnight at the Voco Osaka Central starts at $135).
The Japanese-owned Hoshino Resorts tend to be upscale, but their OMO line offers more entry-level accommodations, from capsule hotels to full-service locations. The OMO5 Kyoto Gion , for example, offers rooms that sleep up to six people and include kitchens, starting at 24,000 yen, or about $153. Staff guides offer free tours to temples in the area.
While many temples, parks and shrines are free, travelers in the capital can get the Tokyo Museum Grutto Pass for 2,500 yen (about $16) that includes admission to more than 100 museums and attractions around town.
Among its tips for budget travelers, the tourism office of Japan recommends making lunch your big meal as many restaurants offer midday specials.
There are a number of cost-conscious ways to get around Japan, including trains (a Japan Rail Pass starts at 50,000 yen, or about $320, for seven days), low-cost airlines like Peach and Zipair and overnight buses .
Or consider walking the Kumano Kodo pilgrimage route that connects sacred shrines in the Kii Mountains. Walk Japan has a self-guided seven-day trip, including accommodations and most meals, starting at 224,000 yen.
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram and sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to get expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation. Dreaming up a future getaway or just armchair traveling? Check out our 52 Places to Go in 2024 .
Open Up Your World
Considering a trip, or just some armchair traveling here are some ideas..
52 Places: Why do we travel? For food, culture, adventure, natural beauty? Our 2024 list has all those elements, and more .
Port Antonio, Jamaica: The Grammy-nominated D.J. and music producer Diplo recommends spots in a city he loves on Jamaica’s northeast coast. A dance party makes the cut.
New Mexico: The Gila Wilderness, home to wolves, mountain lions and other wildlife, marks a century as a “land lab,” where nature thrives as far as the eye can see.
Greece: Is Serifos the perfect Greek island? A writer’s checklist included ferry service, great beaches and good local restaurants.
Brooklyn: This 36-hour itinerary skips the most touristy and overdeveloped areas, including Williamsburg and Dumbo, and requires no restaurant reservations or advance planning.
Costa Rica: Travelers are signing up for phone-free tours to try to escape technology’s tether on daily life. But would it make for a better experience ?
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Mallett was aged 10 when his father died suddenly, of a heart attack, an event that the scientist says changed the track of his life forever. "For me, the sun rose and set on him, he was just ...
Gödel found that if you follow a particular path in this rotating universe you can end up in your own past. You would have to travel incredibly far, billions of light years long, to do it, but it ...
In Summary: Yes, time travel is indeed a real thing. But it's not quite what you've probably seen in the movies. Under certain conditions, it is possible to experience time passing at a different rate than 1 second per second. And there are important reasons why we need to understand this real-world form of time travel.
"Say you traveled in time in an attempt to stop COVID-19's patient zero from being exposed to the virus," University of Queensland scientist Fabio Costa told the university's news service.
Who used the this time machine, called the TARDIS, to travel through space and time on the BBC television show Dr. Who. Babbel1996 / Wikimedia Commons January 28, 2019
News tagged with time travel. Date. 6 hours 12 hours 1 day 3 days all. Rank. Last day 1 week 1 month all. LiveRank. Last day 1 week 1 month all. Popular. Last day 1 week 1 month all.
Find the latest Time Travel news from WIRED. See related science and technology articles, photos, slideshows and videos.
Time travel and parallel timelines almost always go hand-in-hand in science fiction, but now we have proof that they must go hand-in-hand in real science as well. General relativity and quantum ...
Scientists are trying to figure out if time travel is even theoretically possible. If it is, it looks like it would take a whole lot more knowledge and resources than humans have now to do it.
A collection of "Time Travel" columns published in The New York Times.
Time traveling to the near future is easy: you're doing it right now at a rate of one second per second, and physicists say that rate can change. According to Einstein's special theory of ...
Time travel is possible based on the laws of physics, according to researchers. But time-travelers wouldn't be able to alter the past in a measurable way, they say. And the future would ...
A Student Just Proved Paradox-Free Time Travel Is Possible. Now we can all go back to 2019. Time travel is deterministic and locally free, a paper says —resolving an age-old paradox. This ...
Just Scott and Mark Kelly - twin brothers born six minutes apart back in 1964. In 2016, Scott, an astronaut, returned to Earth after 340 days zipping around in the International Space Station ...
I resent that I won't ever get back the hours of my life that Richard Linklater stole with "Boyhood" — his two-and-three-quarter-hour film, shot over a 12-year period in which time is the ...
Mathematics suggested that time travel is physically possible - and Kurt Gödel proved it. Mathematician Karl Sigmund explains how the polymath did it. By Karl Sigmund. 5 April 2024. Gödel ...
A Student Just Proved Time Travel Is Possible; As posited in the Discover story, the big question is if the time travel component of the tachyon is simply an unproven one or an impossible one. Not ...
"To live in time is already to travel in time. So be patient" [In der Zeit zu leben, das ist schon in der Zeit zu reisen. Hab also Geduld]. Rumors of future-transit apps downloadable from ...
PANAMA CITY, Fla. (WJHG/WECP) -Political moves, dealership debates, and a look at our past! Historian Bill Hudson joins us for another Time Travel Tuesday. If you are looking to chat about local ...
According to a TED-Ed video by Colin Stuart, Russian cosmonaut Sergei Krikalev actually traveled 0.02 seconds into his own future due to time dilation during the time he spent on the International ...
Time travel appears to contradict logic. (Shutterstock) The other main issue is less practical, but more significant: it is the observation that time travel seems to contradict logic, in the form ...
Read the latest stories about Travel on Time. Biden Reinstates International Travel Restrictions The latest ban would prevent most non-U.S. citizens from entry if they have recently been in South ...
The latest travel news, deals, guides and tips from the travel experts at USA TODAY. All the travel insights you need to plan your dream vacation.
President Joseph R. Biden, Jr. met today with Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) ahead of NATO's 75th Anniversary Summit in Washington, DC next ...
Tips and tricks for summer travel season 03:33. U.S. travelers can now renew their passport online under a pilot program the U.S. Department of State launched on Thursday.. The State Department's ...
The deal carries a cap hit of just over $3.64 million, a steep price considering Goodrow had 12 points in 80 games and averaged just 12:34 in ice time per game this past season.
Two new overnight routes connecting the city with Beijing and Shanghai entered into service on June 15. Both trains depart Hong Kong West Kowloon Station in the evening and arrive in Beijing at 6. ...
June 10, 2024. It's the backpacker's call to India, the sunseeker's attraction to Mexico, and the digital nomad's drive to get to Thailand: Go where the dollar buys more. The evergreen ...
June 14, 2024 at 1:07 AM PDT. Listen. 2:57. Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis said the time has come to place restrictions on cruise ships visiting Greece's most popular islands, the government ...