UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Global fdi greenfield investment trends in tourism, share this content.
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin

Tourism Investment Report 2020
In association with fdi intelligence from the financial times.
For the third year in a row, the UNWTO has partnered with the fDi intelligence from the Financial Times to develop a joint publication on Tourism Foreign Direct Investments (FDI) analyzing data on Greenfield investments trends. The relevance of this report is pivotal to governments and investors because it exposed data on flows of capital, and destinations for investments providing insight on market trends for the tourism recovery.
In times of uncertainty, expertise and trusted information is more important than ever. This report provides investment and market data that both investors and stakeholders will need to maximize their impact of the sector in terms of economic growth, job creation and sustainability. Especially when around 100-120 million direct tourism jobs are at risk, which threatens to roll back the progress we have made in establishing tourism as a driver towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). For this edition, the UNWTO’ Innovation, Digital Transformation and Investments department has developed an interactive report using data (2015-2019) from the fDi Intelligence on Tourism FDI.
The COVID-19 pandemic has hit the tourism sector hard; the data suggests that global FDI into tourism plummeted by 73.2% in the first half of 2020, compared with a year earlier. This put an end to the sector’s record high years. This data has a close relationship with the UNWTO’ scenarios for international tourist numbers decline, which could fall between 60 and 80% this year depending on the speed with which travel restrictions are lifted. This could translate into a loss of 850 million to 1.1 billion international tourist arrivals and a fall of $910 billion to $1.2 trillion in export revenues.
If you want to learn more, please register here
Although, the investment cycle remained strong throughout 2019, with tourism mobilizing $61.8bn in global FDI, which, in turn, created more than 135,000 jobs. The trend appeared particularly consistent in Latin America and the Caribbean, where FDI reached new record levels. For example it created more than 56.000 jobs in Mexico from 2015 – 2019. Tourism FDI was also strong in the Middle East and Africa, where it rose to the highest level in a decade. However, almost half of all tourism investments globally (46.51%) are made at top 10 countries. From which around 30% of projects are concentrated in five countries: United Kingdom, United States, Germany, China, and Spain. It is important to notice that more than 30% of projects and of capital investment announced in the tourism cluster between 2015 and 2019 occurred in 2019.
The major sub sector that has led tourism investments are consider traditional investments, with construction as the main driver for around 57% of total Greenfield investments from 2015 to 2019. As such, the trends in accommodation are around the sustainability where multinational companies are investing in green, and clean energy matrix of their operations. According to the fDi intelligence of the Financial Times, investors are paying increasing attention to the social and environmental footprint of the projects they assess in tourism. They seem willing to prioritize developments that lift communities and preserve ecosystems, as long as financial sustainability is also taken into account.
Finally, there is also an increasing number of non-traditional investments related to services around software technologies that include: Travel arrangement & reservation services, Internet publishing, web search among other, which represent around 32% of total investments considering investments between 2015 - 2019. This data invites to research more about investments in technology as a source of FDI in the tourism sector. The Travel Tech startups have been introducing innovations in the tourism ecosystem, and they are constantly changing business models attracting more investors.
The COVID-19 pandemic has made clear that sustainable tourism requires that sustainable investments are at the center of new solutions, and not just of traditional investments that promote and underpin economic growth and productivity. It has also highlighted the importance of non-traditional investments that enhance innovation through the creation and diffusion of new solutions to decarbonize the sector. To harness the advantages of investments, it is critical that governments promote policies as well as new investment vehicles to recover, retain and attract foreign direct investments. Only this way can we reimagine tourism and enhance the sector’s positive impact on people and planet as we accelerate the achievement of SDGs.
The UNWTO is developing a series of investment guidelines to understand and generate sustainable investments and promote innovations in the tourism ecosystem. If you are interested in the UNWTO’ reports and guidelines to understand, enable and mobilize tourism investments , we invite you to register to receive the our investment updates.
Please feel free to download the full report:

TOURISM INVESTMENT 2020

TOURISM INVESTMENT 2019

TOURISM INVESTMENT 2018
If you have questions about the report, or need more specific information about tourism investments white us an email to [email protected]
If you want to receive news about tourism investments please register in the bottom bellow.
- Open access
- Published: 05 January 2021
The relationship between tourism and economic growth among BRICS countries: a panel cointegration analysis
- Haroon Rasool ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0083-4553 1 ,
- Shafat Maqbool 2 &
- Md. Tarique 1
Future Business Journal volume 7 , Article number: 1 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
124k Accesses
104 Citations
13 Altmetric
Metrics details
Tourism has become the world’s third-largest export industry after fuels and chemicals, and ahead of food and automotive products. From last few years, there has been a great surge in international tourism, culminates to 7% share of World’s total exports in 2016. To this end, the study attempts to examine the relationship between inbound tourism, financial development and economic growth by using the panel data over the period 1995–2015 for five BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) countries. The results of panel ARDL cointegration test indicate that tourism, financial development and economic growth are cointegrated in the long run. Further, the Granger causality analysis demonstrates that the causality between inbound tourism and economic growth is bi-directional, thus validates the ‘feedback-hypothesis’ in BRICS countries. The study suggests that BRICS countries should promote favorable tourism policies to push up the economic growth and in turn economic growth will positively contribute to international tourism.
Introduction
World Tourism Day 2015 was celebrated around the theme ‘One Billion Tourists; One Billion Opportunities’ highlighting the transformative potential of one billion tourists. With more than one billion tourists traveling to an international destination every year, tourism has become a leading economic sector, contributing 9.8% of global GDP and represents 7% of the world’s total exports [ 59 ]. According to the World Tourism Organization, the year 2013 saw more than 1.087 billion Foreign Tourist Arrivals and US $1075 billion foreign tourism receipts. The contribution of travel and tourism to gross domestic product (GDP) is expected to reach 10.8% at the end of 2026 [ 61 ]. Representing more than just economic strength, these figures exemplify the vast potential of tourism, to address some of the world´s most pressing challenges, including socio-economic growth and inclusive development.
Developing countries are emerging as the important players, and increasingly aware of their economic potential. Once essentially excluded from the tourism industry, the developing world has now become its major growth area. These countries majorly rely on tourism for their foreign exchange reserves. For the world’s forty poorest countries, tourism is the second-most important source of foreign exchange after oil [ 37 ].
The BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) countries have emerged as a potential bloc in the developing countries which caters the major tourists from developed countries. Tourism becomes major focus at BRICS Xiamen Summit 2017 held in China. These countries have robust growth rate, and are focal destinations for global tourists. During 1990 to 2014, these countries stride from 11% of the world’s GDP to almost 30% [ 17 ]. Among BRICS countries, China is ranked as an important destination followed by Brazil, Russia, India and South Africa [ 60 ].
The importance of inbound tourism has grown exponentially, because of its growing contribution to the economic growth in the long run. It enhances economic growth by augmenting the foreign exchange reserves [ 38 ], stimulating investments in new infrastructure, human capital and increases competition [ 9 ], promoting industrial development [ 34 ], creates jobs and hence to increase income [ 34 ], inbound tourism also generates positive externalities [ 1 , 14 ] and finally, as economy grows, one can argue that growth in GDP could lead to further increase in international tourism [ 11 ].
The tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH) proposed by Balaguer and Cantavella-Jorda [ 3 ], states that expansion of international tourism activities exerts economic growth, hence offering a theoretical and empirical link between inbound tourism and economic growth. Theoretically, the TLGH was directly derived from the export-led growth hypothesis (ELGH) that postulates that economic growth can be generated not only by increasing the amount of labor and capital within the economy, but also by expanding exports.
The ‘new growth theory,’ developed by Balassa [ 4 ], suggests that export expansion can trigger economic growth, because it promotes specialization and raises factors productivity by increasing competition, creating positive externalities by advancing the dispersal of specialized information and abilities. Exports also enhance economic growth by increasing the level of investment. International tourism is considered as a non-standard type of export, as it indicates a source of receipts and consumption in situ. Given the difficulties in measuring tourism activity, the economic literature tends to focus on primary and manufactured product exports, hence neglecting this economic sector. Analogous to the ELGH, the TLGH analyses the possible temporal relationship between tourism and economic growth, both in the short and long run. The question is whether tourism activity leads to economic growth or, alternatively, economic expansion drives tourism growth, or indeed a bi-directional relationship exists between the two variables.
To further substantiate the nexus, the study will investigate the plausible linkages between economic growth and international tourism while considering the relative importance of financial development in the context of BRICS nations. Financial markets are considered a key factor in producing strong economic growth, because they contribute to economic efficiency by diverting financial funds from unproductive to productive uses. The origin of this role of financial development may is traced back to the seminal work of Schumpeter [ 50 ]. In his study, Schumpeter points out that the banking system is the crucial factor for economic growth due to its role in the allocation of savings, the encouragement of innovation, and the funding of productive investments. Early works, such as Goldsmith [ 18 ], McKinnon [ 39 ] and Shaw [ 51 ] put forward considerable evidence that financial development enhances growth performance of countries. The importance of financial development in BRICS economies is reflected by the establishment of the ‘New Development Bank’ aimed at financing infrastructure and sustainable development projects in these and other developing countries. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, no attempt has been made so far to investigate the long-run relationship Footnote 1 between tourism, financial development and economic growth in case of BRICS countries. Hence, the present study is an attempt to fill the gap in the existing literature.
Review of past studies
From last few decades there has been a surge in the research related to tourism-growth nexus. The importance of growth and development and its determinants has been studied extensively both in developed and developing countries. Extant literature has recognized tourism as an important determinant of economic growth. The importance of tourism has grown exponentially, courtesy to its manifold advantages in form of employment, foreign exchange production household income and government revenues through multiplier effects, improvements in the balance of payments and growth in the number of tourism-promoted government policies [ 21 , 41 , 53 ]. Empirical findings on tourism and economic development have produced mixed finding and sometimes conflicting results despite the common choice of time series techniques as a research methodology. On empirical grounds, four hypotheses have been explored to determine the link between tourism and economic growth [ 12 ]. The first two hypotheses present an account on the unidirectional causality between the two variables, either from tourism to economic growth (Tourism-led economic growth hypothesis-TLGH) or its reserve (economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis-EDTH). The other two hypotheses support the existence of bi-directional hypothesis, (bi-directional causality hypothesis-BC) or that there is no relationship at all (no causality hypothesis-NC), respectively. According to TLEG hypothesis, tourism creates an array of benefits which spillover though multiple routes to promote the economic growth [ 55 ]. In particular, it is believed that tourism (1) increases foreign exchange earnings, which in turn can be used to finance imports [ 38 ], (2) it encourages investment and drives local firms toward greater efficiency due to the increased competition [ 3 , 31 ], (3) it alleviates unemployment, since tourism activities are heavily based on human capital [ 10 ] and (4) it leads to positive economies of scale thus, decreasing production costs for local businesses [ 1 , 14 ]. Other recent studies which find evidence in favor of the TLGH hypothesis include [ 44 , 52 ]. Even though literature is dominated by TLGH, few studies produce a result in support of EDTH [ 40 , 41 , 45 ]. Payne and Mervar [ 45 ] posit that tourism growth of a country is mobilized by the stability of well-designed economic policies, governance structures and investments in both physical and human capital. This positive and vibrant environment creates a series of development activities which proliferate and flourish the tourism. Pertaining to the readily available information, bi-directional causality could also exist between tourism income and economic growth [ 34 , 49 ]. From a policy view, a reciprocal tourism–economic growth relationship implies that government agendas should cater for promoting both areas simultaneously. Finally, there are some studies that do not offer support to any of the aforementioned hypotheses, suggesting that the impact between tourism and economic growth is insignificant [ 25 , 47 , 57 ]. There is a vast literature examining the relationship between tourism and growth as a result, only a selective literature review will be presented here.
Banday and Ismail [ 5 ] used ARDL cointegration model to test the relationship between tourism revenue and economic growth in BRICS countries from the time period of (1995–2013). The study validates the tourism-led growth hypothesis for BRICS countries, which evinces that tourism has positive influence on economic growth.
Savaş et al. [ 54 ] evaluated the tourism-led growth hypothesis in the context of Turkey. The study employed gross domestic product, real exchange rate, real total expenditure and international tourism arrivals to sketch out the causality among variables. The result reveals a unidirectional relationship between tourism and real exchange rate. The findings suggest that tourism is the driving force for economic growth, which in turn helps turkey to culminate its current account deficit.
Dhungel [ 15 ] made an effort to investigate causality between tourism and economic growth, In Nepal for the period of (1974–2012), by using Johansen’s cointegration and Error correction model. The result states that unidirectional causality exists in the long run, while in short run no causality exists between two constructs. The study emphasized that strategies should be devised to attain causality running from tourism to economic growth.
Mallick et al. [ 36 ] analyzed the nexus between economic growth and tourism in 23 Indian states over a period of 14 years (1997–2011). Using panel autoregressive distributed lag model based on three alternative estimators such as mean group estimator, pooled mean group and dynamic fixed effects, Research found that tourism exerts positive influence on economic growth in the long run.
Belloumi [ 8 ] examines the causal relationship between international tourism receipts and economic growth in Tunisia by using annual time series data for the period 1970–2007. The study uses the Johansen’s cointegration methodology to analyze the long-run relationship among the concerned variables. Granger causality based Vector error correction mechanism approach indicates that the revenues generated from tourism have a positive impact on economic growth of Tunisia. Thus, the study supports the hypothesis of tourism-driven economic growth, which is specific to developing countries that base their foreign exchange earnings on the existence of a comparative advantage in certain sectors of the economy.
Tang et al. [ 58 ] explored the dynamic Inter-relationships among tourism, economic growth and energy consumption in India for the period 1971–2012. The study employed Bounds testing approach to cointegration and generalized variance decomposition methods to analyze the relationship. The bounds testing and the Gregory-Hansen test for cointegration with structural breaks consistently reveals that energy consumption, tourism and economic growth in India are cointegrated. The study demonstrated that tourism and economic growth have positive impact on energy consumption, while tourism and economic growth are interrelated; with tourism exert significant influence on economic growth. Consequently, this study validates the tourism-led growth hypothesis in the Indian context.
Kadir and Karim [ 24 ]) examined the causal nexus between tourism and economic growth in Malaysia by applying panel time series approach for the period 1998–2005. By applying Padroni’s panel cointegration test and panel Granger causality test, the result indicated both short and long-run relationship. Further, the panel causality shows unidirectional causality directing from tourism receipts to economic growth. The result provides evidence of the significant contribution of tourism industry to Malaysia’s economic growth, thereby justifying the necessity of public intervention in providing tourism infrastructure and facilities.
Antonakakis et al. [ 2 ] test the linkage between tourism and economic growth in Europe by using a newly introduced spillover index approach. Based on monthly data for 10 European countries over the period 1995–2012, the findings suggested that the tourism–economic growth relationship is not stable over time in terms of both magnitude and direction, indicating that the tourism-led economic growth (TLEG) and the economic-driven tourism growth (EDTG) hypotheses are time-dependent. Thus, the findings of the study suggest that the same country can experience tourism-led economic growth or economic-driven tourism growth at different economic events.
Oh [ 41 ] verifies the contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy by applying Engle and Granger two-stage approach and a bivariate Vector Autoregression model. He claimed that economic expansion lures tourists in the short run only, while there is no such long-run stable relationship between international tourism and economic development in Korea.
Empirical studies have pronouncedly focused on the literature that tourism promotes economic growth. To further substantiate the nexus, the study will investigate the plausible linkages between economic growth and international tourism while considering the relative importance of financial development in the context of BRICS nations. The inclusion of financial development in the examination of tourism-growth nexus is a unique feature of this study, which have an influencing role in economic growth as financial development has been theoretically and empirically recognized as source of comparative advantage [ 22 ].
This study employs panel ARDL cointegration approach to verify the existence of long-run association among the variables. Further, study estimated the long-run and short-run coefficients of the ARDL model. Subsequently, Dumitrescu and Hurlin [ 16 ] panel Granger causality test has been employed to check the direction of causality between tourism, financial development and economic growth among BRICS countries.
Database and methodology
Data and variables.
The study is analytical and empirical in nature, which intends to establish the relationship between economic growth and inbound tourism in BRICS countries. For the BRICS countries, limited studies have been conducted depicting the present scenario. Therefore, present study tries to verify the relevance of tourism in economic growth to further enhance the understanding of economic dynamics in BRICS countries. The data used in the study are annual figures for the period stretching from 1995 to 2015, consisting of one endogenous variable (GDP per capita, a proxy for economic growth) and two exogenous variables (international tourism receipts per capita and financial development). The variables employed in the study are based on the economic growth theory, proposed by Balassa [ 4 ], which states that export expansion has a relevant contribution in economic growth. Further, this study incorporates financial development in the model to reduce model misspecification as it is considered to have an influencing role in economic growth both theoretically and empirically [ 22 , 33 ].
The annual data for all the variables have been collected from the World Development Indicators (WDI, 2016) database. The variables used in the study includes gross domestic product per capita (GDP) in constant ($US2010) used as a proxy for economic growth (EG), international tourism receipts per capita (TR) in current US$ as it is widely accepted that the most adequate proxy of inbound tourism in a country is tourism expenditure normally expressed in terms of tourism receipts [ 32 ] and financial development (FD). In line with a recent study on the relationship between financial development and economic growth by Hassan et al. [ 19 ], financial development is surrogated by the ratio of the broad money (M3) to real GDP for all BRICS countries. Here we use the broadest definition of money (M3) as a proportion of GDP– to measure the liquid liabilities of the banking system in the economy. We use M3 as a financial depth indicator, because monetary aggregates, such as M2 or M1, may be a poor proxy in economies with underdeveloped financial systems, because they ‘are more related to the ability of the financial system to provide transaction services than to the ability to channel funds from savers to borrowers’ [ 26 ]. A higher liquidity ratio means higher intensity in the banking system. The assumption here is that the size of the financial sector is positively associated with financial services [ 29 ]. All the variables have been taken into log form.
Unit root test
To verify the long-run relationship between tourism and economic growth through Bounds testing approach, it is necessary to test for stationarity of the variables. The stationarity of all the variables can be assessed by different unit root tests. The study utilizes panel unit root test proposed by Levin et al. [ 35 ] henceforth LLC and Im et al. [ 23 ] henceforth IPS based on traditional augmented Dickey–Fuller (ADF) test. The LLC allows for heterogeneity of the intercepts across members of the panel under the null hypothesis of presence of unit root, while IPS allows for heterogeneity in intercepts as well as in the slope coefficients [ 48 ].
Panel ARDL approach to Cointegration
After checking the stationarity of the variables the study employs panel ARDL technique for Cointegration developed by Pesaran et al. [ 23 ]. Pesaran et al. [ 23 ] have introduced the pooled mean group (PMG) approach in the panel ARDL framework. According to Pesaran et al. [ 23 ], the homogeneity in the long-run relationship can be attributed to several factors such as arbitration condition, common technologies, or the institutional development which was covered by all groups. The panel ARDL bounds test [ 46 ] is more appropriate by comparing other cointegration techniques, because it is flexible regarding unit root properties of variables. This technique is more suitable when variables are integrated at different orders but not I (2). Haug [ 20 ] has argued that panel ARDL approach to cointegration provides better results for small sample data set such as in our case. The ARDL approach to cointegration estimates both long and short-run parameters and can be applied independently of variable order integration (independent of whether repressors are purely I (0), purely I(1) or combination of both. The ARDL bounds test approach used in this study is specified as follows:
where Δ is the first-difference operator, \(\alpha_{0}\) stands for constant, t is time element, \(\omega_{1} , \omega_{2} \;\;{\text{and}}\;\; \omega_{3}\) represent the short-run parameters of the model, \(\emptyset_{1} , \emptyset_{2} ,and \emptyset_{3}\) are long-run coefficients, while \(V_{it}\) is white noise error term and lastly, it represents country at a particular time period. In the ARDL model, the bounds test is applied to determine whether the variables are cointegrated or not.
This test is based on the joint significance of F -statistic and the χ 2 statistic of the Wald test. The null hypothesis of no cointegration among the variables under study is examined by testing the joint significance of the F -statistic of \(\omega_{1} , \omega_{2} ,\omega_{3}\) .
In case series variables are cointegrated, an error correction mechanism (ECM) can be developed as Eq. ( 2 ), to assess the short-run influence of international tourism and financial development on economic growth.
where ECT is the error correction term, and \(\varPhi\) is its coefficient which shows how fast the variables attain long-term equilibrium if there is any deviation in the short run. The error correction term further confirms the existence of a stable long-run relationship among the variables.
Panel granger causality test
To examine the direction of causality Dumitrescu and Hurlin [ 16 ] test is employed. Instead of pooled causality, Dumitrescu and Hurlin [ 16 ] proposed a causality based on the individual Wald statistic of Granger non-causality averaged across the cross section units. Dumitrescu and Hurlin [ 16 ] assert that traditional test allows for homogeneous analysis across all panel sets, thereby neglecting the specific causality across different units.
This approach allows heterogeneity in coefficients across cross section panels. The two statistics Wbar-statistics and Zbar-statistics provides standardized version of the statistics and is easier to compute. Wbar-statistic, takes an average of the test statistics, while the Zbar-statistic shows a standard (asymptotic) normal distribution.
They proposed an average Wald statistic that tests the null hypothesis of no causality in a panel subgroup against an alternative hypothesis of causality in at least one panel. Following equations will be used to check the direction of causality between the variables.
Estimation, results and Discussion
Descriptive statistics.
Table 1 presents descriptive statistics of variables selected for the period 1995–2015. The variable set includes GDP, FD and TR for all BRICS countries. Brazil tops the list with GDP per capita of 4.18, while India lagging behind all BRICS nations. In the recent economic survey by International Monetary Fund (IMF report 2016), India was ranked 126 for its per capita GDP. India’s GDP per capita went up to $7170 against all other BRICS countries which were placed in the above $10,000 bracket. China has the highest tourism receipts in comparison to other BRICS countries. China is a very popular country for foreign tourists, which ranks third after France and USA. In 2014, China invested $136.8 billion into its tourist infrastructure, a figure second only to the United States ($144.3 billion). Tourism, based on direct, indirect, and induced impact, accounted for near 10% in the GDP of China (WTTC report 2017).
Stationarity results
Primarily, we employed LLC and IPS unit root test to assess the integrated properties of the series. The results of IPS and PP tests are presented in Table 2 . Panel unit root test result evinces that FD and TR are stationary at level, while GDP per capita is integrated variable of order 1. The result exemplifies that GDP per capita, Tourism receipts and Financial Development are integrated at 1(0) and 1(1). Consequently, the panel ARDL approach to cointegration can be applied.
Cointegration test results
In view of the above results with a mixture of order integration, the panel ARDL approach to cointegration is the most appropriate technique to investigate whether there exists a long-run relationship among the variables [ 42 ]. Table 3 illustrates that the estimated value of F-statistics, which is higher than the lower and upper limit of the bound value, when InEG is used as a dependent variable. Hence, we reject the null hypothesis of no cointegration \(H_{0 } : \emptyset_{1} = \emptyset_{2} = \emptyset_{3} = 0\) of Eq. ( 1 ). Therefore, the result asserts that international tourism, financial development and economic growth are significantly cointegrated over the period (1995–2015).
Subsequently, the study investigates the long-run and short-run impact of international tourism and financial development on economic growth. Lag length is selected on the principle of minimum Bayesian information criterion (SBC) value, which is 2 in our case. The long-run coefficients of financial development and tourism receipts with respect to economic growth in Table 4 indicate that tourism growth and financial development exerts positive influence on economic growth in the long run. In other words, an increase in volume of tourism receipts per capita and financial depth spurs economic growth and both the coefficients are statistically significant in case of BRICS nations in the long run. The results are interpreted in detail as below:
The elasticity coefficient of economic growth with respect to tourism shows that 1% rise in international tourism receipts per capita would imply an estimated increase of almost 0.31% domestic real income in the long run, all else remaining the same. Thus, the earnings in the form of foreign exchange from international tourism affect growth performance of BRICS nations positively. This finding of our study is in consonance with the empirical results of Kreishan for Jordan [ 30 ], Balaguer and Cantavella-Jordá [ 3 ] for Spain and Ohlan [ 43 ] for India.
Further our finding lend support to the wide applicability of the new growth theory proposed by Balassa which states that export expansion promote growth performance of nations. Thus, validates TLGH coined by Balaguer and Cantavell-Jorda [ 3 ] which states that inbound tourism acts a long-run economic growth factor. The so called tourism-led growth hypothesis suggests that the development of a country’s tourism industry will eventually lead to higher economic growth and, by extension, further economic development via spillovers and other multiplier effects.
Likewise, financial development as expected is found to be positively associated with economic growth. The coefficient of financial development states that 1% improvement in financial development will push up economic growth by 0.22% in the long run, keeping all other variables constant. The empirical results are consistent with the finding of Hassan et al. [ 19 ] for a panel of South Asian countries. Well-regulated and properly functioning financial development enhances domestic production through savings, borrowings & investment activities and boosts economic growth. Further, it promotes economic growth by increasing efficiency [ 7 ]. Levine [ 33 ] believes that financial intermediaries enhance economic efficiency, and ultimately growth, by helping allocation of capital to its best use. Modern growth theory identifies two specific channels through which the financial sector might affect long-run growth; through its impact on capital accumulation and through its impact on the rate of technological progress. The sub-prime crisis which depressed the economic growth worldwide in 2007 further substantiates the growth-financial development nexus.
In the third and final step of the bounds testing procedure, we estimate short-run dynamics of variables by estimating an error correction model associated with long-run estimates. The empirical finding indicates that the coefficient of error correction term (ECT) with one period lag is negative as well as statistically significant. This finding further substantiates the earlier cointegration results between tourism, financial development and economic growth, and indicates the speed of adjustment from the short-run toward long-run equilibrium path. The coefficient of ECT reveals that the short-run divergences in economic growth from long-run equilibrium are adjusted by 43% every year following a short-run shock.
The short-run parameters in Table 5 demonstrates that tourism and financial development acts as an engine of economic growth in the short run as well. The coefficient of both tourism receipts per capita and financial development with one period lag is also found to be progressive and significant in the short run. These results highlight the role of earnings from international tourism and financial stability as an important driving force of economic growth in BRICS nations in the short run as well.
Further, a comparison between short-run and long-run elasticity coefficients evince that long-run responsiveness of economic growth with respect to tourism and financial development is higher than that of short run. It exemplifies that over time higher international tourism receipts and well-regulated financial system in BRICS nations give more boost to economic growth.
Analysis of causality
At this stage, we investigate the causality between tourism, financial development and economic growth presented in Table 6 . The result shows bi-directional causal relationship between tourism and economic growth, thereby validates ‘feedback hypothesis’ and consequently supported both the tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH) and its reciprocal, the economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis (EDTH). The bi-directional causality between inbound tourism and GDP, which directs the level of economic activity and tourism growth, mutually influences each other in that a high volume of tourism growth leads to a high level of economic development and reverse also holds true. These results replicate the findings of Banday and Ismail [ 5 ] in the context of BRICS countries, Yazdi et al. [ 27 ] for Iran and Kim et al. [ 28 ] for Taiwan. One of the channels through which tourism spurs economic growth is through the use of receipts earned in the form of foreign currency. Thus, growth in foreign earnings may allow the import of technologically advances goods that will favor economic growth and vice versa. Thus, results demonstrate that international tourism promotes growth and in turn economic expansion is necessary for tourism development in case of BRICS countries. With respect to policy context, this finding suggests that the BRICS nations should focus on economic policies to promote tourism as a potential source of economic growth which in turn will further promote tourism growth.
Similarly, in case of economic growth and financial development, the findings demonstrate the presence of bi-directional causality between two constructs. The findings validate thus both ‘demand following’ and supply leading’ hypothesis. The findings suggests that indeed financial development plays a crucial role in promoting economic activity and thus generating economic growth for these countries and reverse also holds. Our findings are in line with Pradhan [ 48 ] in case of BRICS countries and Hassan et al. [ 19 ] for low and middle-income countries. This suggests that finance development can be used as a policy variable to foster economic growth in the five BRICS countries and vice versa. The study emphasizes that the current economic policies should recognize the finance-growth nexus in BRICS in order to maintain sustainable economic development in the economy. The empirical results in this paper are in line with expectations, confirming that the emerging economies of the BRICS are benefiting from their finance sectors.
Finally, two-sided causal relationship is found between tourism receipts and financial development. That is, tourism might contribute to financial development and, in return, financial development may positively contribute to tourism. This means that financial depth and tourism in BRICS have a reinforcing interaction. The positive impact of tourism on financial development can be attributed to the fact that inflows of foreign exchange via international tourism not only increases income levels but also leads to rise in official reserves of central banks. This in turn enables central banks to adapt expansionary monetary policy. The positive contribution of financial sector to tourism is further characterized by supply leading hypothesis. Further, better financial and market conditions will attract tourism entrepreneurship, because firms will be able to use more capital instead of being forced to use leveraging [ 13 ]. Hence, any shocks in money supply could adversely affect tourism industry in these countries. Song and Lin [ 56 ] found that global financial crisis had a negative impact on both inbound and outbound tourism in Asia. This result is in consistent with Başarir and Çakir [ 6 ] for Turkey and four European countries.
Stability tests
In addition, to test the stability of parameters estimated and any structural break in the model CUSUM and CUSUMSQ tests are employed. Figs. 1 and 2 show blue line does not transcend red lines in both the tests, thus provides strong evidence that our estimated model is fit and valid policy implications can be drawn from the results.
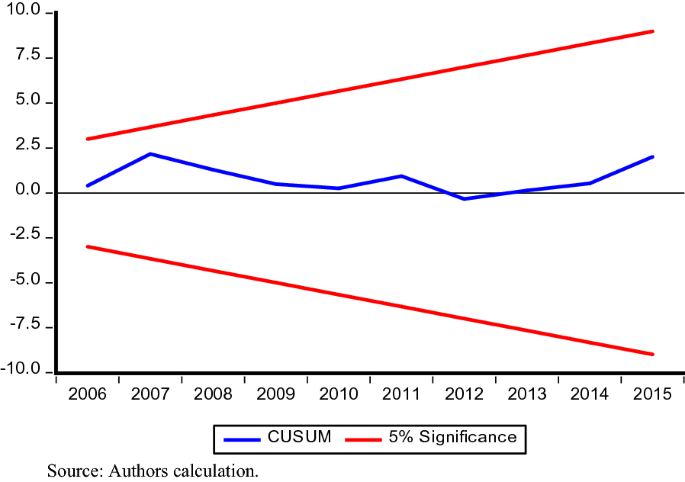
Plot of CUSUM
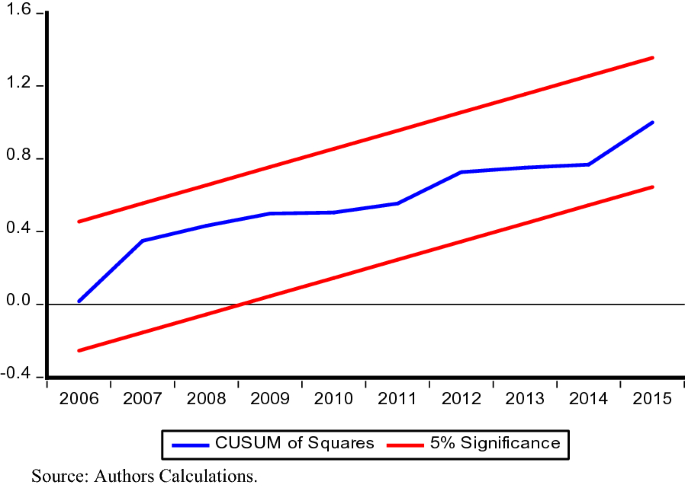
Plot of CUSUMQ
Summary and concluding remarks
A rigorous study of the relationship between tourism and economic growth, through the tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH) perspective has remained a debatable issue in the economic growth literature. This study aims to empirically investigate the relationship between inbound tourism, financial development and economic growth in BRICS countries by utilizing the panel data over the period 1995–2015. The study employs the panel ARDL approach to cointegration and Dumitrescu-Hurlin panel Granger causality test to detect the direction of causation.
To the best of authors’ knowledge, this is the first study which explored the relationship between economic growth and tourism while considering the relative importance of financial development in the context of BRICS nations. The empirical results of ARDL model posits that in BRICS countries inbound tourism, financial development and economic growth are significantly cointegrated, i.e., variables have stable long-run relationship. This methodology has allowed obtaining elasticities of economic growth with respect to tourism and financial development both in the long run and short run. The result reveals that international tourism growth and financial development positively affects economic growth both in the long run and short run. The coefficient of tourism indicates that with a 1% rise in tourism receipts per capita, GDP per capita of BRICS economies will go up by 0.31% in the long run. This finding lends support to TLGH coined by Balaguer and Cantavell-Jorda [ 3 ] which states that inbound tourism acts a long-run economic growth factor. The so called tourism-led growth hypothesis suggests that the development of a country’s tourism industry will eventually lead to higher economic growth and, by extension, further economic development via spillovers and other multiplier effects.
Likewise, 1% improvement in financial development, on average, will increase economic growth in BRICS countries by 0.22% in the long run. The result seems logical as modern growth theory identifies two channels through which the financial sector might affect long-run growth: first, through its impact on capital accumulation and secondly, through its impact on the rate of technological progress. The sub-prime crisis which hit the economic growth Worldwide in 2007 further substantiates the growth-financial development nexus.
The negative and statistically significant coefficient of lagged error correction term (ECT) further substantiates the long-run equilibrium relationship among variables. The negative coefficient of ECT also shows the speed of adjustment toward long-run equilibrium is 43% per annum if there is any short-run deviation. The estimates of parameters are found to be stable by applying CUSUM and CUSUMQ for the time period under consideration. Therefore, inbound tourism earnings and financial institutions can be used as a channel to increase economic growth in BRICS economies.
Further, Granger causality test result indicates the bi-directional causation in all cases. Hence, the causal relationship between international tourism and economic growth is bi-directional. And, consequently this empirical finding lends support to both the tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH) and its reciprocal, the economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis (EDTH). This means that tourism is not only an engine for economic growth, but the economic outcome on itself can play an important role in providing growth potential to tourism sector.
The Granger causality findings provide useful information to governments to examine their economic policy, to adjust priorities regarding economic investment, and boost their economic growth with the given limited resources. Thus, it is suggested that more resources should be allocated to tourism industry and tourism-related industries if the tourism-led growth hypothesis holds true. On the other side, if economic-driven tourism growth is supported then more resources should be diverted to leading industries rather than the travel and tourism sector, and the tourism industry will in turn benefit from the resulting overall economic growth. And, when bi-directional causality is detected, a balanced allocation of economic resources for the travel and tourism sector and other industries is important and necessary. The policy implication is that resource allocation supporting both the tourism and tourism-related industries could benefit both tourism development and economic growth.
To sum up, the major finding of this study lends support to wide applicability of the tourism-led growth hypothesis in case of BRICS countries. Thus, in the Policy context, significant impact of tourism on BRICS economy rationalizes the need of encouraging tourism. Tourism can spur economic prosperity in these countries and for this reason; policymakers should give serious consideration toward encouraging tourism industry or inbound tourism. BRICS countries should focus more on tourism infrastructure, such as, convenient transportation, alluring destinations, suitable tax incentives, viable hostels and proper security arrangements to attract the potential tourists. Most of these countries are devoid of rich facilities and popular tourist incentives, to get promoted as important destination and in the long-run promotes economic growth. Further, they need a staunch support from all sections of authorities, non-government organizations (NGOs), and private and allied industries, in the endeavor to attain sustainable growth in tourism. Both state and non-state actors must recognize this growing industry and its positive implication on economy.
For future research, we suggest that researchers should consider the nonlinear factor in the dynamic relationship of tourism and economic growth in case of BRICS countries. Further one can go for comparative study to examine the TLGH in BRICS countries.
Availability of data and materials
Data used in the study can be provided by the corresponding author on request.
There are no fixed definitions of short, medium and long run and generally in macroeconomics, short run can be viewed as 1 to 2 or 3 years, medium up to 5 years and long run from 5 years to 20 or 25 years.
Abbreviations
autoregressive distributed lag model
Brazil, Russia, India, China and South-Africa
United Nations World Tourism Organization
World Travel & Tourism Council
gross domestic product
world development indicators
tourism-led growth hypothesis
export-led growth hypothesis
economic-driven tourism hypothesis
augmented Dickey–Fuller test
error correction model
error correction term
Andriotis K (2002) Scale of hospitality firms and local economic development—evidence from Crete. Tourism Manag 23(4):333–341
Google Scholar
Antonakakis N, Dragouni M, Filis G (2015) How strong is the linkage between tourism and economic growth in Europe? Econ Modell 44:142–155
Balaguer J, Cantavella-Jorda M (2002) Tourism as a long-run economic growth factor: the Spanish case. Appl Econ 34(7):877–884
Balassa B (1978) Exports and economic growth: further evidence. J Dev Econ 5(2):181–189
Banday UJ, Ismail S (2017) Does tourism development lead positive or negative impact on economic growth and environment in BRICS countries? A panel data analysis. Econ Bull 37(1):553–567
Basarir C, Çakir YN (2015) Causal interactions between CO 2 emissions, financial development, energy and tourism. Asian Econ Financ Rev 5(11):1227
Bell C, Rousseau PL (2001) Post-independence India: a case of finance-led industrialization? J Dev Econ 65(1):153–175
Belloumi M (2010) The relationship between tourism receipts, real effective exchange rate and economic growth in Tunisia. Int J Tour Res 12(5):550–560
Blake A, Sinclair MT, Soria JAC (2006) Tourism productivity: evidence from the United Kingdom. Ann Tourism Res 33(4):1099–1120
Brida JG, Pulina M (2010) A literature review on the tourism-led-growth hypothesis. Working paper CRENoS201017. Centre for North South Economic Research, Sardinia
Brida JG, Cortes-Jimenez I, Pulina M (2016) Has the tourism-led growth hypothesis been validated? A literature review. Curr Issues Tourism 19(5):394–430
Chatziantoniou I, Filis G, Eeckels B, Apostolakis A (2013) Oil prices, tourism income and economic growth: a structural VAR approach for European Mediterranean countries. Tourism Manag 36:331–341
Chen M-H (2010) The economy, tourism growth and corporate performance in the Taiwanese hotel industry. Tourism Manag 31:665–675
Croes R (2006) A paradigm shift to a new strategy for small island economies: embracing demand side economics for value enhancement and long term economic stability. Tourism Manag 27:453–465
Dhungel KR (2015) An econometric analysis on the relationship between tourism and economic growth: empirical evidence from Nepal. Int J Econ Financ Manag 3(2):84–90
Dumitrescu EI, Hurlin C (2012) Testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Econ Modell 29(4):1450–1460
Daniel Mminele (2016) The role of BRICS in the global economy. Speech at the Bundesbank Regional Office in North Rhine-Westphalia, Düsseldorf, Germany. https://www.bis.org/review/r160720c.pdf
Goldsmith RW (1969) Financial structure and development (No. HG174 G57)
Hassan MK, Sanchez B, Yu JS (2011) Financial development and economic growth: new evidence from panel data. Quart Rev Econ Financ 51(1):88–104
Haug AA (2002) Temporal aggregation and the power of cointegration tests: A Monte Carlo study. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 64:399–412
Henry EW, Deane B (1997) The contribution of tourism to the economy of Ireland in 1990 and 1995. Tourism Manag 18(8):535–553
Hur J, Raj M, Riyanto YE (2006) Finance and trade: a cross-country empirical analysis on the impact of financial development and asset tangibility on international trade. World Dev 34(10):1728–1741
Im KS, Pesaran MH, Shin Y (2003) Testing for unit roots in heterogeneous panels. J Econ 115(1):53–74
Kadir N, Karim MZA (2012) Tourism and economic growth in Malaysia: evidence from tourist arrivals from Asean-S countries. Econ Res Ekonomska istraživanja 25(4):1089–1100
Katircioglu S (2009) Testing the tourism-led growth hypothesis: the case of Malta. Acta Oeconomica 59(3):331–343
Khan M, Senhadji A (2003) Financial development and economic growth: a review and new evidence. J Afr Econ 12:89–110
Khoshnevis Yazdi S, Homa Salehi K, Soheilzad M (2017) The relationship between tourism, foreign direct investment and economic growth: evidence from Iran. Curr Issues Tourism 20(1):15–26
Kim HJ, Chen MH (2006) Tourism expansion and economic development: the case of Taiwan. Tourism Manag 27(5):925–933
King R, Levine R (1993) Finance, entrepreneurship, and growth: theory and evidence. J Monet Econ 32:513–542
Kreishan FM (2010) Tourism and economic growth: the case of Jordan. Eur J Soc Sci 15:229–234
Krueger A (1980) Trade policy as an input to development. Am Econ Rev 70:188–292
Kumar RR (2014) Exploring the role of technology, tourism and financial development: an empirical study of Vietnam. Qual Quant 48(5):2881–2898
Levine R (1997) Financial development and economic growth: views and agenda. J Econ Lit 35(2):688–726
Lee CC, Chang CP (2008) Tourism development and economic growth: a closer look at panels. Tourism Manag 29(1):180–192
Levin A, Lin CF, Chu CSJ (2002) Unit root tests in panel data: asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J Econ 108(1):1–24
Mallick L, Mallesh U, Behera J (2016) Does tourism affect economic growth in Indian states? Evidence from panel ARDL model. Theor Appl Econ 23(1):183–194
Mastny L (2001) Treading lightly: new paths for international tourism. In: Peterson JA (ed) World Watch Paper 159. World Watch Institute
McKinnon RI (1964) Foreign exchange constraints in economic development and efficient aid allocation. Econ J 74(294):388–409
McKinnon RI (1973) Money and capital in economic development. The Brookings Institution, Washington
Narayan PK (2004) Economic impact of tourism on Fiji’s economy: empirical evidence from the computable general equilibrium model. Tourism Econ 10(4):419–433
Oh CO (2005) The contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy. Tourism Manag 26(1):39–44
Ohlan R (2015) The impact of population density, energy consumption, economic growth and trade openness on CO 2 emissions in India. Nat Hazards 79(2):1409–1428
Ohlan R (2017) The relationship between tourism, financial development and economic growth in India. Future Bus J 3(1):9–22
Parrilla JC, Font AR, Nadal JR (2007) Tourism and long-term growth a Spanish perspective. Ann Tourism Res 34(3):709–726
Payne JE, Mervar A (2010) Research note: the tourism-growth nexus in Croatia. Tourism Econ 16(4):1089–1094
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Econ 16(3):289–326
Po WC, Huang BN (2008) Tourism development and economic growth—a nonlinear approach. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 387(22):5535–5542
Pradhan RP, Dasgupta P, Bele S (2013) Finance, development and economic growth in BRICS: a panel data analysis. J Quant Econ 11(1–2):308–322
Ridderstaat J, Oduber M, Croes R, Nijkamp P, Martens P (2014) Impacts of seasonal patterns of climate on recurrent fluctuations in tourism demand: evidence from Aruba. Tourism Manag 41:245–256
Schumpeter JA (1911) The theory of economic development: an inquiry into profits, capital, credit, interest, and the business cycle. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, p 1934
Shaw ES (1973) Financial deepening in economic development. Oxford University Press, London
Sugiyarto G, Blake A, Sinclair MT (2003) Tourism and globalization: economic impact in Indonesia. Ann Tourism Res 30(3):683–701
Szivas E, Riley M (1999) Tourism employment during economic transition. Ann Tourism Res 26(4):747–771
Savaş B, Beşkaya A, Şamiloğlu F (2010) Analyzing the impact of international tourism on economic growth in Turkey. Uluslararası Yönetim İktisat ve İşletme Dergisi 6(12):121–136
Schubert SF, Brida JG, Risso WA (2011) The impacts of international tourism demand on economic growth of small economies dependent on tourism. Tourism Manag 32(2):377–385
Song H, Lin S (2010) Impacts of the financial and economic crisis on tourism in Asia. J Travel Res 49(1):16–30
Tang CF (2013) Temporal Granger causality and the dynamics relationship between real tourism receipts, real income and real exchange rates in Malaysia. Int J Tourism Res 15(3):272–284
Tang CF, Tiwari AK, Shahbaz M (2016) Dynamic inter-relationships among tourism, economic growth and energy consumption in India. Geosyst Eng 19(4):158–169
United Nations World Tourism Report (2014) Annual report 2014
World Travel & Tourism Council (2012) Travel & Tourism Economic Impact. World, London: World Travel & Tourism Council.
World Travel and Tourism Council (2016) Global travel and tourism economic impact update August 2016
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This research has received no specific funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Economics, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India
Haroon Rasool & Md. Tarique
Department of Commerce, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India
Shafat Maqbool
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
HR has written introduction, research methodology and results and discussion part. Review of literature and data analysis was done by SM. Conclusion was written jointly by HR and SM. MT has provided useful inputs and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Haroon Rasool .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
Authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Rasool, H., Maqbool, S. & Tarique, M. The relationship between tourism and economic growth among BRICS countries: a panel cointegration analysis. Futur Bus J 7 , 1 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-020-00048-3
Download citation
Received : 02 August 2019
Accepted : 30 November 2020
Published : 05 January 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-020-00048-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Economic growth
- Inbound tourism
- Financial development
- Cointegration
- Panel granger causality
JEL Classification
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 29 March 2024
Studying tourism development and its impact on carbon emissions
- Xiaochun Zhao 1 ,
- Taiwei Li 1 &
- Xin Duan 1
Scientific Reports volume 14 , Article number: 7463 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1206 Accesses
Metrics details
- Environmental impact
- Sustainability
Analyzing the influence of tourism on carbon emission has significant implications for promoting the sustainable development of tourism. Based on the panel data of 31 tourist cities in China from 2005 to 2022, this study utilizes a structural equation model to explore the carbon reduction effect of tourism development and its influencing mechanism. The results show that: (1) The overall carbon emission efficiency of tourism cities first decreased and then increased, rised to a peak of 0.923 in 2022. (2) Tourism development has a significant positive impact on carbon emission efficiency, and there are three influence paths: tourism → environmental regulation → carbon emission efficiency, tourism → environmental regulation → industrial structure → carbon emission efficiency, and tourism → industrial structure → carbon emission efficiency. (3) The influence of tourism development on carbon emission efficiency mainly depends on the direct effect, and the development of tourism also indirectly affect the industrial structure. Environmental regulation also mainly depends on the direct effect on carbon emission efficiency. (4) Foreign direct investment lead to the reduction of carbon emission efficiency in both direct and indirect aspects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Positive effects of COVID-19 lockdown on air quality of industrial cities (Ankleshwar and Vapi) of Western India

A unifying modelling of multiple land degradation pathways in Europe
The economic commitment of climate change
Introduction.
Global climate change has become one of the major challenges of humanity, bringing a series of harms, including an increase in extreme weather events such as heatwaves, droughts, floods, and hurricanes. According to the report of United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), by 2080, the average global temperature will increase by more than 1 °C 1 . Global warming is not merely a natural phenomenon, but also a result of human activity. In various sectors of the economy, the tourism industry has experienced rapid growth. According to data from the World Tourism Organization, the tourism industry accounts for 10.4% of the global Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and provides 313 million job opportunities 2 . However, the rapid development of the tourism industry has also resulted in intensified impacts on the environment. Tourism industry has become one of the main sources of global carbon dioxide emissions, accounting for 5% of the total global carbon emissions. China is one of the largest tourism markets in the world, and the tourism industry plays a vital role in China's economy. In China's 14th Five-Year Plan, the concept of green and low-carbon development is emphasized, highlighting the need for environmentally friendly tourism and carbon emission reduction. Balancing tourism industry development with carbon emission reduction is a major challenge for the tourism industry. Existing studies on tourism and carbon emissions mainly focus on the carbon emission efficiency of tourism development itself and the impact of tourism on carbon emissions. However, these studies fail to analyze the mechanism behind tourism's impact on carbon emission efficiency. While some studies have analyzed the impact mechanism of tourism development and carbon emissions 3 , they primarily focused on the impact of tourism on carbon emission intensity rather than carbon efficiency. Carbon intensity is typically measured as a ratio of carbon emissions to GDP. In contrast, carbon efficiency provides a more comprehensive assessment of a city's environmental performance and sustainability. Comprehensive analyzing the mechanism of the influence of tourism development on carbon emission efficiency is essential for formulating environmental protection policies to promote the green development of tourism. Therefore, this paper aims to study the influence mechanism of tourism on carbon emission efficiency s of tourism development. Using 31 tourist cities in China as research samples, the paper adopts the entropy weight method and the Slacks-Based Measure (SBM), introduces the Structural Equation Model (SEM), and uses panel data of 31 tourist cities to analyze the influence of tourism industry on carbon emission. The findings of this study are hoped to provide inspiration for the transformation of tourism cities.
The remainder of this study is divided into four sections. The first section is the literature review, which examines the carbon emission efficiency of the tourism industry itself and the impact of tourism development on carbon emission efficiency from a tourism research perspective. The second section is the research design, where the paper utilizes the entropy weight method and the super-efficiency SBM model to measure the development level of the tourism industry and carbon emission efficiency, respectively. This section also constructs a structural equation model to explore the mechanism of the impact of tourism development on carbon emission efficiency. The third section presents the research results and the last section concludes this study and provides suggestions based on research findings.
Literature review
Tourism plays a vital role in economic growth by creating jobs 4 . Scholars have conducted extensive research and achieved significant academic results. The current research on the tourism industry and carbon emission efficiency primarily revolves around two aspects.
Firstly, scholars focus on the carbon emission efficiency of the tourism industry. For example, Gössling et al. 5 analyzed the economic benefits and environmental effect of tourism, evaluating the ecological efficiency of the tourism industry by using carbon dioxide emissions and economic benefits. Osorio et al. 6 compared the carbon emission efficiency of the Spanish tourism industry before and after the pandemic of COVID-19, and found that the carbon emission efficiency in 2020 improved compared before COVID-19 pandemic. Ghaderi et al. 7 conducted research on the carbon emission efficiency of tourism industry in the Middle East and North Africa, this study indicated that tourist arrivals can reduce carbon emissions, while energy consumption and trade openness are contributors to carbon emissions.
Secondly, scholars focus on the impact of tourism on carbon emission. However, the consensus among scholars has not yet been reached on whether the tourism industry promotes carbon emission. Some scholars have analyzed the impact of tourism activities on carbon emissions in Mediterranean countries and concluded that tourism revenue does not have direct impact on carbon emissions 8 . Voumik et al. 9 studied tourism industry in 40 Asian countries and found that while tourism helps slow down the deterioration of environment, factors such as population growth, energy use, and economic development still contribute to increasing carbon emission, which is consistent with the conclusions of Guo et al. 10 . Erdoğan et al. 11 focused on the impact of international tourism on carbon emissions and found that international tourism leads to the increase of carbon emissions, but eco-friendly innovation in the transportation sector can mitigate the negative impact on the environment. Ahmad et al. 12 revealed an inverted U-shaped curve in the impact of international tourism development on carbon emissions in China, with the negative impact of technological innovation being strongest in highly developed provinces and weakest in moderately developed provinces. Ghosh et al. 13 found tourism industry can alleviate environmental degradation, policy direction that promote tourism, renewable energy, economic growth and urbanization have a significant effect on the environment, which is consistent with the conclusion of Zikirya et al. 14 . Rahman et al. 15 shifted their focus to Malaysia and found a positive correlation between the number of tourists and carbon emissions.
In summary, existing studies primarily focus on the carbon emission efficiency of tourism and the impact of tourism on carbon emission. However, there is a lack of focus on how tourism affects carbon emission efficiency. This study aims to address this gap by taking 31 tourist cities in China as research samples. This study constructs an indicator system to assess tourism industry and carbon emission efficiency. Furthermore, this study introduces a structural equation model to analyze the mechanisms about how tourism industry affects carbon emission efficiency, to provide inspiration for promoting the green development of tourism.
Research Design
Analyzing the influence mechanism of tourism on carbon emission.
The tourism industry is considered a smokeless and green industry, due to its significant advantages in resource utilization and environmental protection. The development of the tourism industry can not only promote the growth of employment rate in the destination, but also increase the income of tourist destinations. Compared with the secondary industry, the tourism industry is more environmentally friendly in terms of resource consumption and pollution emission. Especially in tourism cities, the proportion of tourism economy in GDP is larger, tourism has a bigger impact on the green development of the tourism city. Consequently, the influence mechanism of tourism on carbon emissions is analyzed as follows:
Firstly, a good natural ecological environment is a fundamental requirement for the development of the tourism industry. Tourism cities typically implement strict governance measures on the local environment and ecology. The development of tourism can incentive the local government to introduce more stringent environmental policies, thereby improving the ecological environment 16 . Additionally, stricter environmental regulations often impact carbon emission efficiency 17 , 18 . Simultaneously, intensified environmental regulations can limit the development space of heavily polluting industries and influence the industrial structure of the destination, ultimately affecting carbon emission efficiency 19 .
Secondly, the development of tourism also affects the industrial structure of cities 20 . The growth of tourism promotes the rise of related industries. Numerous supporting industries, such as hotels, catering, transportation, tour guides, and others, are needed to meet the demands of tourists and create numerous employment opportunities. Consequently, tourism development can attract individuals to switch from other industries to the tourism sector, which in turn impacts the industrial structure and has a significant effect on carbon emissions 21 .
Finally, foreign direct investment is an important factor that affects carbon emission efficiency 22 . This study draws on the conclusion of Bakhsh et al. 23 , which suggests that including foreign direct investment in analysis can improves the overall fit of the structural equation model. On one hand, foreign direct investment can bring advanced production technology, thereby directly improving carbon emission efficiency 24 . On the other hand, foreign investment also leads to pollution transfer, negatively impacting the environment and reducing carbon emission efficiency 25 . At the same time, foreign direct investment can indirectly affect carbon emission efficiency by influencing the local industrial structure. Moreover, the advanced technologies brought about by foreign direct investment also have an impact on technological innovation, thereby indirectly affecting carbon emissions.
Based on above analysis, this study builds a structural equation model about the influence of tourism on carbon emission (see Fig. 1 ).
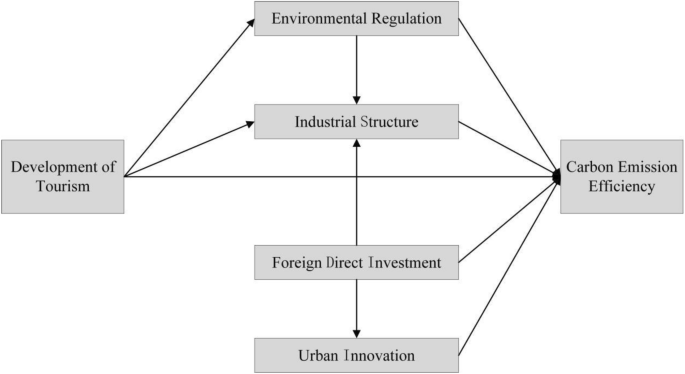
The influence mechanism of tourism on carbon emission.
Research method
- Structural equation model
The Structural Equation Model (SEM), first proposed by Jöreskog 26 , is used to study complex relationships among different variables, including multiple causal relationships. When examining the impact of tourism on carbon emissions, it is important to consider that this impact is not a single direct effect. Instead, there are complex internal mechanisms, including indirect effects and interactions among variables 27 . Therefore, this study chooses to employ SEM to analyze the internal mechanism of how tourism affects carbon emission efficiency.
Entropy weight method
In this study, the entropy weight method is utilized to calculate the Tourism Development (TD) level. The entropy weight method is a quantitative approach based on the concept of entropy in information theory. It helps determine the weight of indicators by calculating the entropy and difference coefficient of each index. This calculation process reflects the importance of each index in the overall assessment. By multiplying and summing the standardized index with the entropy weight, the assessment results can be obtained 28 . The specific calculation process is as follows:
Firstly, the raw data needs to be standardized, see formula ( 1 ) and formula ( 2 ) for details.
Positive indicator:
Negative indicator:
Among them, \({ }x_{ij} { }\) represents the data of the indicator, \(i{ }\) represents city. \(j{ }\) represents index, \(r_{ij}^{ + }\) and \(r_{ij}^{ - }\) represents standardized data.
Secondly, calculate the weight of \(j\) index by using formula ( 3 ).
Thirdly, calculate the entropy of \(j\) by using formula ( 4 ).
Fourthly, calculate information entropy redundancy by using formula ( 5 ).
Fifthly, calculate index weight by using formula ( 6 ).
Finally, calculate the assess results by using formula ( 7 ).
Non-expected output super efficiency SBM model
Tone 29 proposed a super-efficient model based on the traditional SBM model, which combines the advantages of both the traditional SBM model and the super efficiency model. This model not only considers the influence of unexpected output, but also solves the problem that the traditional SBM model cannot evaluate the Decision-Making Unit (DMU) with the efficiency value of 1 on the front plane. By recalculating the DMUs with an efficiency value of 1, the model enables the comparison of effective DMUs. The specific formulas are as follows:
Designing index system for tourism and carbon emission efficiency, variable explaining and data source
Designing index system and variable interpretation.
This study utilizing the entropy weight method to calculate the Tourism Development level(TD). To evaluate the development level of tourism, this paper designs the index system of tourism development (see Table 1 ). Firstly, the number of tourists is an important indicator that represents the development of tourism, as it reflects the scale of tourism and market demand 30 . Secondly, tourism income is a crucial index for measuring the economic benefit of tourism, as it represents the economic benefit and profit level of tourism. Tourism income directly impacts the sustainable development of tourism and related industries. Finally, the proportion of tourism revenue to GDP is an essential indicator for measuring the contribution and impact of tourism on the overall economy. On the basis of previous studies, this study constructs the evaluation index system of tourism development level.
The essence of Carbon Emission Efficiency (CEE) is the result of the joint action of capital, labor, energy, and other inputs and outputs in economic activities. Therefore, adopting a multi-input and multi-output perspective, this study uses MATLAB software to measure the carbon emission efficiency of 31 tourist cities. Acknowledging that efficiency values are influenced by both inputs and outputs, this study selects five indicators: labor input, capital input, energy input, expected output, and undesirable output to measure carbon emission efficiency (see Table 2 ). Firstly, the total number of employees in enterprises and public institutions reflects the economic scale of state-owned enterprises and public institutions, while the total number of urban private self-employed employees highlights the scale of the development of the private and individual economy 31 . Therefore, the sum of the total number of employees in enterprises and public institutions and the total number of private and individual employees in cities and towns is chosen as the representative of labor input, which fully reflects the employment scale and labor supply of a country or region. Secondly, electricity is widely used as an energy source in cities, and its consumption largely reflects a city's energy consumption 32 . The total electricity consumption of the city is selected to represent the energy input. Thirdly, investments in fixed assets reflects the investment of a country or region in capital goods such as production equipment and buildings over a certain period, and it is an important measure of capital formation 33 . The capital stock of the city is calculated based on the investment in fixed assets to represent the capital input. Fourthly, GDP is the sum of all the market value created by all the residents of a country or region in a certain period, and it is the most important macroeconomic indicator for measuring the overall economic performance of a country or region 34 . Fifthly, undesirable outputs usually denote by-products or negative effects that occur during the production process, which are not the desired outcomes of manufacturing activities. Carbon dioxide emissions are selected as the undesirable outputs. Finally, this paper takes 2005 as the base period to calculate the capital stock and GDP, to enhance the comparability of data between different years.
Variables involved in structural equation model
Based on the existing research and data availability, proxy variables for the structural equation model are set up (see Table 3 ). (1) Tourism, calculated by entropy weight method, reflects the development level of urban tourism; (2) Carbon emission efficiency, calculated by the non-expected output super efficiency SBM, reflects the carbon emission and resource utilization efficiency of the city; (3) Environmental regulation. Currently, there are three quantitative methods for environmental regulation, which are single index method 35 , scoring method 36 and comprehensive index method 37 . This paper uses the proportion of investment in environmental pollution control in GDP(Gross Domestic Product) as a proxy variable for environmental regulation. (4) Industrial structure, the proportion of the output value of the tertiary industry and the output value of the secondary industry are used as the proxy variable,(5) Foreign direct investment, some scholars believe that foreign direct investment has a negative impact on the environment, supporting the pollution paradise hypothesis, while other scholars believe that foreign direct investment has an improving effect on the environment, supporting the pollution halo hypothesis. Because of fact that the stock of foreign investment can more accurately reflect the impact of foreign investment on environmental pollution, this paper adopts the proportion of foreign direct investment in regional GDP as a proxy variable by referring to the practice of Afi et al. 38 . (6) Urban innovation, referring to the research of Cheng et al. 39 , China's urban innovation index is adopted as a proxy variable. The index is mainly based on two parts of data, namely patent data of the State Intellectual Property Office and enterprise registered capital data of the State Administration for Industry and Commerce, including innovation output and patent value.
Research sample and data source
This study selects Chinese tourism cities as research samples to explore the influence of tourism on carbon emission efficiency. This study refers to the research of Zhang et al. 40 and Huang et al. 41 , a total of 31 tourism cities were selected as research samples. These cities include Beijing, Tianjin, Shenyang, Dalian, Shanghai, Nanjing, Wuxi, Suzhou, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Xiamen, Jinan, Qingdao, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Zhuhai, Zhongshan, Guilin, Haikou, Wenzhou, Changchun, Harbin, Huangshan, Wuhan, Changsha, Luoyang, Zhangjiajie, Chongqing, Chengdu, Kunming and Xi 'an.
The study period was from 2005 to 2022. The data in this study were obtained from China Urban Statistical Yearbook (2006–2022), China Energy Statistical Yearbook (2006–2022), statistical yearbooks and statistical bulletins of provinces and cities.
Research results
Evaluation results of carbon emission efficiency and tourism development in tourist cities.
This study measured the carbon emission efficiency of 31 tourist cities from 2005 to 2022 and revealed its evolution characteristics. The calculation results are shown in Table 4 .
According to Table 4 , a clear upward trend is evident in the tourism development level of 31 tourist cities from 2005 to 2019, with the level increasing from 0.125 in 2005 to 0.499 in 2019, thereby reaching its peak. From 2020 to 2022, due to the impact of COVID-19, the number of tourists decreased, and the development level of tourism dropped significantly. From 2005 to 2022, the carbon emission efficiency of 31 tourism cities generally showed a fluctuating upward trend. The overall efficiency decreased year by year from 2005 to 2011, reaching its lowest at 0.707. But then it began to fluctuate and rise and reached a peak of 0.923 in 2022.
Analyzing the influence of tourism development on carbon emission efficiency and its influencing mechanism
Analysis the influence of tourism industry on carbon emission and its influencing mechanism based on all samples.
Based on the structural equation model, the required variables were introduced into the STATA software. The parameters of the constructed model were then estimated using the maximum likelihood estimation method, yielding the estimated results for standardized estimation coefficients, standard errors, Z-values, and P-values. The specific results are shown in Table 5 and Fig. 2 .
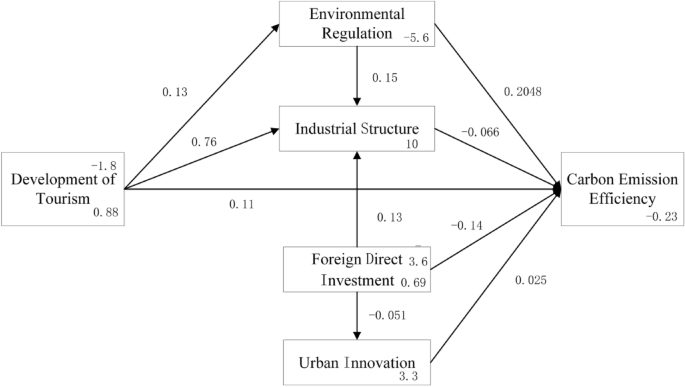
Structural equation model estimation results.
For all the tourist city samples, the structural equation model was estimated using the STATA software through the maximum likelihood estimation method. The estimated results included standardized estimation coefficients, standard errors, Z-values, and P-values. In terms of the overall fit of the model, the comparative fit index (CFI) is 0.902, slightly greater than 0.9, and the standardized residual root mean square (SRMR) is 0.07, slightly higher than 0.05 but less than 0.08 threshold, indicating that the overall fit of the model is good.
Logarithmic likelihood: − 8623.74;Likelihood ratio test of saturation model: chi-square(4) = 71.00, Prob > chi-square = 0.0000; The index of fit degree:RMSEA:0.109;AIC:14,115.030; BIC:16,023.930; CFI:0.902;SRMR: 0.070.
Table 5 and Fig. 2 demonstrate the mechanism of tourism's influence on carbon emission efficiency as follows: Firstly, a 1% increase in tourism development level leads to a direct increase of 0.1148% carbon emission efficiency, which passes the 1% significance level test. This indicates that the development of urban tourism significantly promotes the improvement in carbon emission efficiency. This indicates that tourism development can improve carbon emission efficiency, which is consistent with the study conducted by Si et al. 42 . On one hand, tourism stimulates local economic development,on the other hand, it consumes resources and emits less pollution compared to other industries. This implies that tourism development directly affects carbon emission efficiency and there is a mechanism of tourism → carbon emission efficiency. Secondly, the sustainable development of tourism imposes stricter demands on the ecological environment quality. As a result, the development of tourism prompts governments to introduce more rigorous environmental policies. The greater the intensity of urban environmental regulation, the more significant its impact on carbon emission efficiency. Each 1% increase in the level of tourism development would directly increase the intensity of environmental regulation by 0.1280%. There is a direct between environmental regulation and emission efficiency. Every 1% increase in environmental regulation, there is a corresponding 0.8% increase in carbon emission efficiency. This finding supports the conclusion that environmental regulation plays an effective role in reducing carbon emissions 43 . This finding also suggests that there is a mechanism of tourism → environmental regulation → carbon emission efficiency. Thirdly, empirical results reveal an influence effect of tourism → environmental regulation → industrial structure → carbon emission efficiency. Each 1% increase in environmental regulation would change the industrial structure by 0.1524%, and each 1% increase in industrial structure would increase carbon emission efficiency by 0.2048%. This suggests that the tourism industry impacts the local industrial structure by strengthening environmental regulations, thereby driving the improvement of carbon emission efficiency. Fourth, a 1% increase in tourism development level changes the industrial structure by 0.7597%, indicating that tourism development has a significant impact on the local industrial structure. Additionally, the estimated coefficient of industrial structure on carbon emission efficiency is 0.0664, meaning that the transformation of industrial structure promotes the improvement of carbon emission efficiency. In other words, tourism influences local carbon emission efficiency by influencing the industrial structure. There is a mechanism of tourism → industrial structure → carbon emission efficiency.
The mechanisms through which foreign direct investment influences carbon emission efficiency can be summarized in three aspects. Firstly, foreign direct investment has negative impacts on carbon emission efficiency. This indicates in tourist cities, FDI may intensify local energy consumption and production activities and becomes a refuge for heavily polluting enterprises. These findings are in line with the research conducted by Wang et al. 44 . Secondly, foreign direct investment significantly and positively affects the local industrial structure, indicating that the production technology brought by foreign direct investment has changed the industrial structure of the city. The results reveal an influence path of foreign direct investment → industrial structure. Empirical findings demonstrate that the industrial structure impacts carbon emission efficiency, resulting in a path of foreign direct investment → industrial structure → carbon emission efficiency. Thirdly, the impact of foreign direct investment on the innovation ability of cities did not pass the significance test (P = 0.603), indicating that there is no influence path of foreign direct investment → urban innovation → carbon emission efficiency.
Further analysis based on effect decomposition
Based on the above estimation results, this study further decomposed the direct, indirect, and total effects of each factor affecting carbon emission efficiency, the results are shown in Table 6 .
As shown in Table 6 , the total effect of tourism on carbon emission efficiency is 0.0624, with a direct effect of 0.1148, accounting for 54.36% of the total effect. The direct effect passed the significance test but the indirect effect failed. This indicates that the influence of tourism on carbon emission mainly stems from the direct impact of tourism development on carbon emission efficiency, rather than the indirect effect. This empirical result aligns with the current reality in China. Cities can achieve the goal of reducing carbon emissions by focusing on green tourism and low-carbon tourism, promoting the use of environmentally friendly transportation modes in tourism, and improving the energy efficiency of tourism facilities. Furthermore, the estimates results reveal other important factors and pathways influencing carbon efficiency. Firstly, a higher intensity of environmental regulations can directly improve carbon emission efficiency. Every 1% increase in environmental regulation intensity would directly increase carbon emission efficiency by 0.2048%. Secondly, the direct effect of foreign direct investment on carbon emission efficiency is − 0.1379, and the indirect effect is − 0.0098, indicating that foreign direct investment has a negative impact on carbon emission efficiency in both direct and indirect aspects. Foreign investors may transfer polluting enterprises to tourist cities, resulting in increased carbon emissions and decreased carbon emission efficiency. Finally, changes in industrial structure have a positively effect on carbon emission efficiency. Every 1% change in industrial structure will reduce carbon emission efficiency by 0.0664%.
Conclusion and discussion
Based on panel data from 31 tourist cities between 2005 and 2022, this study utilizes a structural equation model to analyze the influence of tourism on carbon emissions. The research findings indicate the following:
The carbon emission efficiency of tourism cities first decreased and then increased, reaching a peak of 0.923 in 2022. Second, tourism has a significant positive effect on carbon efficiency in the estimation of all samples. This influence can be summarized into three paths: tourism development → environmental regulation → carbon emission efficiency; Tourism development → environmental regulation → industrial structure → carbon emission efficiency; Tourism development → industrial structure → carbon emission efficiency. Thirdly, the influence of local tourism development on carbon emission efficiency mainly depends on the direct effect, which is consistent with the reality of China, and the development of tourism will also indirectly affect the local industrial structure. Environmental regulation also mainly depends on the direct effect on carbon emission efficiency, and foreign direct investment will lead to the reduction of carbon emission efficiency in both direct and indirect aspects.
Based on these research findings, this study proposes several suggestions: Firstly, tourism affects carbon emission efficiency through environmental regulation and industrial structure. To strengthen environmental regulation, local governments should increase supervision over enterprises, improve environmental standards, and take strict actions against environmental violations. These measures can enhance carbon emission efficiency and accelerate urban green transformation. Secondly, considering the negative impact of foreign direct investment on carbon emission efficiency, local governments should carefully evaluate potential environmental problems when dealing with foreign investments. Preferably, eco-friendly foreign direct investments should be prioritized. Thirdly, the influence of tourism on carbon emission efficiency mainly depends on the direct effect. Therefore, in the process of tourism development, the goal of improving carbon emission efficiency should be integrated to promote the development of tourism in the direction of eco-tourism and green tourism.
The content of this study is to analyze the influence of tourism on carbon efficiency, using 31 tourist cities as case studies. It introduces mechanism that explains how tourism development impacts carbon emission efficiency through considerations of environmental regulation and industrial structure. Nonetheless, it is important to acknowledge that this study also has certain limitations when compared to previous research. Firstly although this study considers the impact of environmental regulations on carbon emission efficiency, it did not conduct an in-depth analysis of different dimensions of environmental regulations. It is worth noting that the intensity and enforcement of environmental regulations may have significant differences in their impact on carbon emission efficiency as highlighted by Lin et al. 45 . Therefore, it is suggested that future studies incorporate the intensity and enforcement of environmental regulations into the model. By doing so, a more accurate assessment can be made regarding their impact on carbon efficiency. Secondly, this study suggests a pathway for tourism development to have an impact on carbon emission efficiency by influencing industrial structure. However, it does not delve deeply into the specific methods of adjusting industrial structure. Ahmad et al. 12 have demonstrated that tourism's alternative impact on traditional manufacturing and high-carbon industries is a crucial approach to reducing carbon emissions. Future studies can potentially further analyze the contribution of tourism to the low-carbon transformation of industrial structure. Thirdly, this study suggests that FDI has a negative impact on carbon emission efficiency, but it does not fully discuss its potential positive effects. Zhang et al. 47 have found that foreign direct investment can introduce advanced environmental protection technology and management experience, thereby improving the city's carbon emission efficiency. Therefore, future studies should how to achieve a positive impact on carbon emission efficiency through policy guidance and optimization of FDI structure.
Data availability
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Bunting, E. L., Fullman, T., Kiker, G. & Southworth, J. Utilization of the SAVANNA model to analyze future patterns of vegetation cover in Kruger National Park under changing climate. Ecol. Model. 342 , 147–160 (2016).
Article Google Scholar
Figini, P. & Patuelli, R. Estimating the economic impact of tourism in the European Union: Review and computation. J. Travel Res. 61 (6), 1409–1423 (2022).
Tong, Y., Zhang, R. & He, B. The carbon emission reduction effect of tourism economy and its formation mechanism: An empirical study of China’s 92 tourism-dependent cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19 (3), 1824 (2022).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Irfan, M., Ullah, S., Razzaq, A., Cai, J. & Adebayo, T. S. Unleashing the dynamic impact of tourism industry on energy consumption, economic output, and environmental quality in China: A way forward towards environmental sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 387 , 135778 (2023).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Gössling, S. et al. The eco-efficiency of tourism. Ecol. Econ. 54 (4), 417–434 (2005).
Osorio, P., Cadarso, M. Á., Tobarra, M. Á. & García-Alaminos, Á. Carbon footprint of tourism in Spain: Covid-19 impact and a look forward to recovery. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 65 , 303–318 (2023).
Ghaderi, Z., Saboori, B. & Khoshkam, M. Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in the MENA region: the roles of international tourist arrivals, energy consumption and trade openness. Sustainability 15 (3), 2553 (2023).
Yıldırım, D. Ç., Ektiren, B. & Erdoğan, F. The threshold effect of tourism, growth, and population interactions on environmental pollution in Mediterranean countries. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 47 , 101118 (2023).
Google Scholar
Voumik, L. C., Islam, M. A. & Nafi, S. M. Does tourism have an impact on carbon emissions in Asia? An application of fresh panel methodology. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 514 , 1–19 (2023).
Guo, Y., Zhao, L. & Zhang, C. Energy resources, tourism development and growth-emission nexus in developing countries. Resour. Policy 81 , 103407 (2023).
Erdoğan, S., Gedikli, A., Cevik, E. I. & Erdoğan, F. Eco-friendly technologies, international tourism and carbon emissions: Evidence from the most visited countries. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 180 , 121705 (2022).
Ahmad, M., Zhu, X. & Wu, Y. The criticality of international tourism and technological innovation for carbon neutrality across regional development levels. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 182 , 121848 (2022).
Ghosh, S., Balsalobre-Lorente, D., Doğan, B., Paiano, A. & Talbi, B. Modelling an empirical framework of the implications of tourism and economic complexity on environmental sustainability in G7 economies. J. Clean Prod. 376 , 134281 (2022).
Zikirya, B., Wang, J. & Zhou, C. The relationship between CO 2 emissions, air pollution, and tourism flows in China: A panel data analysis of Chinese Provinces. Sustainability 13 (20), 11408 (2021).
Rahman, A. R. A., Shaari, M. S., Masnan, F. & Esquivias, M. A. The impacts of energy use, tourism and foreign workers on CO 2 emissions in Malaysia. Sustainability 14 (4), 2461 (2022).
Sheppard, V. A. & Fennell, D. A. Progress in tourism public sector policy: Toward an ethic for non-human animals. Tour. Manag. 73 , 134–142 (2019).
Hashmi, R. & Alam, K. Dynamic relationship among environmental regulation, innovation, CO 2 emissions, population, and economic growth in OECD countries: A panel investigation. J. Clean. Prod. 231 , 1100–1109 (2019).
Zameer, H., Shahbaz, M. & Kontoleon, A. From Covid-19 to conflict: Does environmental regulation and green innovation improve industrial sector decarbonization efforts and environmental management?. J. Environ. Manag. 345 , 118567 (2023).
Ouyang, Y., Ye, F. & Tan, K. The effect of strategic synergy between local and neighborhood environmental regulations on green innovation efficiency: The perspective of industrial transfer. J. Clean. Prod. 380 , 134933 (2022).
Kronenberg, K. & Fuchs, M. Aligning tourism’s socio-economic impact with the United Nations’ sustainable development goals. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 39 , 100831 (2021).
Wang, S., Wang, H., Zhang, L. & Dang, J. Provincial carbon emissions efficiency and its influencing factors in China. Sustainability 11 (8), 2355 (2019).
Shaari, M. S., Lee, W. C., Ridzuan, A. R., Lau, E. & Masnan, F. The impacts of energy consumption by sector and foreign direct investment on CO 2 emissions in Malaysia. Sustainability 14 (23), 16028 (2022).
Bakhsh, K., Rose, S., Ali, M. F., Ahmad, N. & Shahbaz, M. Economic growth, CO 2 emissions, renewable waste and FDI relation in Pakistan: New evidences from 3SLS. J. Environ. Manag. 196 , 627–632 (2017).
Amara, D. B., Qiao, J. & Zada, M. How to reconcile the climate change issue with economic growth? Spatial dual mediating effects of carbon emissions and foreign investment. J. Clean. Prod. 411 , 137285 (2023).
Petrović, P. & Lobanov, M. M. Energy intensity and foreign direct investment nexus: Advanced panel data analysis. Appl. Energy 311 , 118669 (2022).
Jöreskog, K. G. A general method for estimating a linear structural equation system. ETS Res. Bull. Ser. 1970 (2), i–41 (1970).
Zyphur, M. J., Bonner, C. V. & Tay, L. Structural equation modeling in organizational research: The state of our science and some proposals for its future. Annu. Rev. Organ. Psychol. Organ. Behav. 10 , 495–517 (2023).
Wang, M., Su, M. M., Gan, C. & Yu, Z. A coordination analysis on tourism development and resident well-being in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. J. Clean Prod. 421 , 138361 (2023).
Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 130 (3), 498–509 (2001).
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Khan, N. U., Alim, W., Begum, A., Han, H. & Mohamed, A. Examining factors that influence the international tourism in pakistan and its nexus with economic growth: Evidence from ARDL approach. Sustainability. 14 (15), 9763 (2022).
Kou, J. & Xu, X. Does internet infrastructure improve or reduce carbon emission performance? A dual perspective based on local government intervention and market segmentation. J. Clean. Prod. 379 , 134789 (2022).
Chai, J., Tian, L. & Jia, R. New energy demonstration city, spatial spillover and carbon emission efficiency: Evidence from China’s quasi-natural experiment. Energy Policy 173 , 113389 (2023).
Gao, S., Sun, D. & Wang, S. Do development zones increase carbon emission performance of China’s cities?. Sci. Total Environ. 863 , 160784 (2023).
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Lan, B. et al. CO 2 emission reduction pathways of iron and steel industry in Shandong based on CO 2 emission equity and efficiency. Resour. Policy 81 , 103406 (2023).
Ahmed, Z., Ahmad, M., Rjoub, H., Kalugina, O. A. & Hussain, N. Economic growth, renewable energy consumption, and ecological footprint: Exploring the role of environmental regulations and democracy in sustainable development. Sustain. Dev. 30 (4), 595–605 (2022).
Albrizio, S., Kozluk, T. & Zipperer, V. Environmental policies and productivity growth: Evidence across industries and firms. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 81 , 209–226 (2017).
Dechezleprêtre, A. & Sato, M. The impacts of environmental regulations on competitiveness. Rev. Env. Econ. Policy 11 (2), 183–206 (2017).
Afi, H., Boubaker, S. & Omri, A. Do foreign investment and economic freedom matter for behavioral entrepreneurship? Comparing opportunity versus necessity entrepreneurs. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 181 , 121761 (2022).
Cheng, J. et al. Land marketization and urban innovation capability: Evidence from China. Habitat Int. 122 , 102540 (2022).
Zhang, J., Yu, Z., Miao, C., Li, Y. & Qiao, S. Cultural tourism weakens seasonality: Empirical analysis of Chinese tourism cities. Land. 11 (2), 308 (2022).
Huang, C. et al. Coupling relationship and interactive response between intensive land use and tourism industry development in China’s major tourist cities. Land 10 (7), 697 (2021).
Si, X. & Tang, Z. Assessment of low-carbon tourism development from multi-aspect analysis: A case study of the Yellow River Basin, China. Sci Rep. 14 (1), 4600 (2024).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wang, H. & Guo, J. Research on the impact mechanism of multiple environmental regulations on carbon emissions under the perspective of carbon peaking pressure: A case study of China’s coastal regions. Ocean Coast. Manag. 249 , 106985 (2024).
Wang, Q. & Zhang, Q. Foreign direct investment and carbon emission efficiency: The role of direct and indirect channels. Sustainability 14 (20), 13484 (2022).
Lin, B. & Zhang, A. Can government environmental regulation promote low-carbon development in heavy polluting industries? Evidence from China’s new environmental protection law. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 99 , 106991 (2023).
Ahmad, N. & Ma, X. How does tourism development affect environmental pollution?. Tour. Econ. 28 (6), 1453–1479 (2022).
Zhang, W., Li, G., Uddin, M. K. & Guo, S. Environmental regulation, foreign investment behavior, and carbon emissions for 30 provinces in China. J. Clean. Prod. 248 , 119208 (2020).
Download references
This research was supported by the Major Research Project of Philosophy and Social Sciences of Ministry of Education (23JZD019).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Management, Anhui University, Hefei, China
Xiaochun Zhao, Taiwei Li & Xin Duan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
X.Z. and T.L. drafted the manuscript. X.D. conceptualized and designed the study. X.Z. contributed to materials and analysis. X.Z. contributed to the theories and revised the manuscript. All authors read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Xin Duan .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Zhao, X., Li, T. & Duan, X. Studying tourism development and its impact on carbon emissions. Sci Rep 14 , 7463 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-58262-w
Download citation
Received : 09 January 2024
Accepted : 27 March 2024
Published : 29 March 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-58262-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Tourism industry
- Carbon emission efficiency
- Influence mechanism
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: Anthropocene newsletter — what matters in anthropocene research, free to your inbox weekly.

Should we be promoting tourism sector investment?
Kusi hornberger, hermione nevill.
When most people think of tourism, they think about a vacation to a new destination, an island retreat, a beautiful vineyard, or a hike in the mountains. They rarely think of tourism as a source of inclusive poverty reduction in the developing world.
Nkwichi Lodge in Mozambique is a good example. Investments to the projects created 75 jobs for locals supporting over 1,000 community members. It also established a community trust that built five local schools, a maternity clinic and a maize mill that provided nutrition and education to more than 350 farmers and their families. This is having a transformative impact on poverty reduction and improvements in the quality of life of some of the worlds poorest.
The potential of the tourism sector
The tourism sector is one of the priority sectors of the Investment Climate Advisory Services for investment generation and regulatory simplification. We and institutions like UNCTAD , as well as the World Economic Forum strongly believe this sector can boost competitiveness , expand economic opportunity and provide a pathway to prosperity in client countries. Unsurprisingly, developing economies like Haiti, Mozambique , the Solomon Islands, Yemen and Zambia recently prioritized tourism as a key target to produce economic growth.
But what makes the tourism sector so attractive?
While the answer is not 100 percent clear, it is clear that the tourism sector is growing and in particular in developing in transition countries. Its total contribution to global GDP has grown by 21 percent in the last decade to$5,992 billion in 2011 (Figure 1).
Source: World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) 2011
The tourism sector has strong links to economic growth.
Economic (GDP) growth is of principal concern for all countries, particularly those engaged in poverty reduction as a means to spread wealth across the population. Empirical studies in countries as diverse as Barbados, Croatia, India, Taiwan and Turkey have shown a causal relationship between tourism development and economic growth. A cross country study by the IMF showed that an increase of one standard deviation in the share of tourism in exports leads to about 0.5 percentage point in additional annual growth, everything else being constant. Thus many governments (particularly low income economies) should view investing in its tourism industry as a means to stimulate growth over the long term and enabling the poor to share in economic gains.
Tourism investments can benefit local people
Tourism is one of the only industries in the world where the ‘good’ or ‘service’ is consumed at the site of production. For this reason, local people are both at an advantage to reap the benefits associated with the sector, but also at risk from exclusion or even the negative impacts it can bring. A well planned, regulated and responsible tourism can be an excellent mechanism of channeling resources from rich to poor - even at the large scale. Commercial tourism activities provide an opportunity for local people to participate in direct employment, in providing goods and services to tourism businesses through the supply chain, but also in direct interaction with the tourist (for example: crafts, excursions, food and beverage). The generation of earnings amongst those local people directly involved with the industry in turn stimulates indirect spend (of wages) in the local economy.
Tourism provides opportunities for economic diversification and skills upgrading
Developing countries can leverage tourism to support local companies and entrepreneurs in developing new products and exports. The tourism sector provides a means by which local entrepreneurs can experiment with new products and test them on international markets in their home country before exporting. International tourists typically create demand for products and services which may not have already existed in the local market and also demand certain quality standards. Whilst these can be a challenge to meet in the short-term, tourism creates the market and the incentive to drive the process – leading to growth and improvement over time.
Sustainably protecting environmental and cultural assets
Many developing countries have rich natural or cultural heritage assets such as national parks, coral reefs, rare species, ancient cities or monuments that are under threat. Often, states do not have the financial resources to allocate to the preservation of these areas and more creative ways of funding their protection must be sought. The revenue generated from tourism is one such solution – provided it is regulated and managed in a responsible manner.
- Competitiveness
Investment Policy Officer

Join the Conversation
- Share on mail
- comments added
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Agriculture and the Environment
- Case Studies
- Chemistry and Toxicology
- Environment and Human Health
- Environmental Biology
- Environmental Economics
- Environmental Engineering
- Environmental Ethics and Philosophy
- Environmental History
- Environmental Issues and Problems
- Environmental Processes and Systems
- Environmental Sociology and Psychology
- Environments
- Framing Concepts in Environmental Science
- Management and Planning
- Policy, Governance, and Law
- Quantitative Analysis and Tools
- Sustainability and Solutions
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
The role of tourism in sustainable development.
- Robert B. Richardson Robert B. Richardson Community Sustainability, Michigan State University
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780199389414.013.387
- Published online: 25 March 2021
Sustainable development is the foundational principle for enhancing human and economic development while maintaining the functional integrity of ecological and social systems that support regional economies. Tourism has played a critical role in sustainable development in many countries and regions around the world. In developing countries, tourism development has been used as an important strategy for increasing economic growth, alleviating poverty, creating jobs, and improving food security. Many developing countries are in regions that are characterized by high levels of biological diversity, natural resources, and cultural heritage sites that attract international tourists whose local purchases generate income and support employment and economic development. Tourism has been associated with the principles of sustainable development because of its potential to support environmental protection and livelihoods. However, the relationship between tourism and the environment is multifaceted, as some types of tourism have been associated with negative environmental impacts, many of which are borne by host communities.
The concept of sustainable tourism development emerged in contrast to mass tourism, which involves the participation of large numbers of people, often in structured or packaged tours. Mass tourism has been associated with economic leakage and dependence, along with negative environmental and social impacts. Sustainable tourism development has been promoted in various ways as a framing concept in contrast to these economic, environmental, and social impacts. Some literature has acknowledged a vagueness of the concept of sustainable tourism, which has been used to advocate for fundamentally different strategies for tourism development that may exacerbate existing conflicts between conservation and development paradigms. Tourism has played an important role in sustainable development in some countries through the development of alternative tourism models, including ecotourism, community-based tourism, pro-poor tourism, slow tourism, green tourism, and heritage tourism, among others that aim to enhance livelihoods, increase local economic growth, and provide for environmental protection. Although these models have been given significant attention among researchers, the extent of their implementation in tourism planning initiatives has been limited, superficial, or incomplete in many contexts.
The sustainability of tourism as a global system is disputed among scholars. Tourism is dependent on travel, and nearly all forms of transportation require the use of non-renewable resources such as fossil fuels for energy. The burning of fossil fuels for transportation generates emissions of greenhouse gases that contribute to global climate change, which is fundamentally unsustainable. Tourism is also vulnerable to both localized and global shocks. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to localized shocks include the impacts of natural disasters, disease outbreaks, and civil unrest. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to global shocks include the impacts of climate change, economic crisis, global public health pandemics, oil price shocks, and acts of terrorism. It is clear that tourism has contributed significantly to economic development globally, but its role in sustainable development is uncertain, debatable, and potentially contradictory.
- conservation
- economic development
- environmental impacts
- sustainable development
- sustainable tourism
- tourism development
Introduction
Sustainable development is the guiding principle for advancing human and economic development while maintaining the integrity of ecosystems and social systems on which the economy depends. It is also the foundation of the leading global framework for international cooperation—the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) (United Nations, 2015 ). The concept of sustainable development is often associated with the publication of Our Common Future (World Commission on Environment and Development [WCED], 1987 , p. 29), which defined it as “paths of human progress that meet the needs and aspirations of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.” Concerns about the environmental implications of economic development in lower income countries had been central to debates about development studies since the 1970s (Adams, 2009 ). The principles of sustainable development have come to dominate the development discourse, and the concept has become the primary development paradigm since the 1990s.
Tourism has played an increasingly important role in sustainable development since the 1990s, both globally and in particular countries and regions. For decades, tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, non-extractive option for economic development, particularly for developing countries (Gössling, 2000 ). Many developing countries have managed to increase their participation in the global economy through development of international tourism. Tourism development is increasingly viewed as an important tool in increasing economic growth, alleviating poverty, and improving food security. Tourism enables communities that are poor in material wealth, but rich in history and cultural heritage, to leverage their unique assets for economic development (Honey & Gilpin, 2009 ). More importantly, tourism offers an alternative to large-scale development projects, such as construction of dams, and to extractive industries such as mining and forestry, all of which contribute to emissions of pollutants and threaten biodiversity and the cultural values of Indigenous Peoples.
Environmental quality in destination areas is inextricably linked with tourism, as visiting natural areas and sightseeing are often the primary purpose of many leisure travels. Some forms of tourism, such as ecotourism, can contribute to the conservation of biodiversity and the protection of ecosystem functions in destination areas (Fennell, 2020 ; Gössling, 1999 ). Butler ( 1991 ) suggests that there is a kind of mutual dependence between tourism and the environment that should generate mutual benefits. Many developing countries are in regions that are characterized by high levels of species diversity, natural resources, and protected areas. Such ideas imply that tourism may be well aligned with the tenets of sustainable development.
However, the relationship between tourism and the environment is complex, as some forms of tourism have been associated with negative environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions, freshwater use, land use, and food consumption (Butler, 1991 ; Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ; Hunter & Green, 1995 ; Vitousek et al., 1997 ). Assessments of the sustainability of tourism have highlighted several themes, including (a) parks, biodiversity, and conservation; (b) pollution and climate change; (c) prosperity, economic growth, and poverty alleviation; (d) peace, security, and safety; and (e) population stabilization and reduction (Buckley, 2012 ). From a global perspective, tourism contributes to (a) changes in land cover and land use; (b) energy use, (c) biotic exchange and extinction of wild species; (d) exchange and dispersion of diseases; and (e) changes in the perception and understanding of the environment (Gössling, 2002 ).
Research on tourism and the environment spans a wide range of social and natural science disciplines, and key contributions have been disseminated across many interdisciplinary fields, including biodiversity conservation, climate science, economics, and environmental science, among others (Buckley, 2011 ; Butler, 1991 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Given the global significance of the tourism sector and its environmental impacts, the role of tourism in sustainable development is an important topic of research in environmental science generally and in environmental economics and management specifically. Reviews of tourism research have highlighted future research priorities for sustainable development, including the role of tourism in the designation and expansion of protected areas; improvement in environmental accounting techniques that quantify environmental impacts; and the effects of individual perceptions of responsibility in addressing climate change (Buckley, 2012 ).
Tourism is one of the world’s largest industries, and it has linkages with many of the prime sectors of the global economy (Fennell, 2020 ). As a global economic sector, tourism represents one of the largest generators of wealth, and it is an important agent of economic growth and development (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ). Tourism is a critical industry in many local and national economies, and it represents a large and growing share of world trade (Hunter, 1995 ). Global tourism has had an average annual increase of 6.6% over the past half century, with international tourist arrivals rising sharply from 25.2 million in 1950 to more than 950 million in 2010 . In 2019 , the number of international tourists reached 1.5 billion, up 4% from 2018 (Fennell, 2020 ; United Nations World Tourism Organization [UNWTO], 2020 ). European countries are host to more than half of international tourists, but since 1990 , growth in international arrivals has risen faster than the global average, in both the Middle East and the Asia and Pacific region (UNWTO, 2020 ).
The growth in global tourism has been accompanied by an expansion of travel markets and a diversification of tourism destinations. In 1950 , the top five travel destinations were all countries in Europe and the Americas, and these destinations held 71% of the global travel market (Fennell, 2020 ). By 2002 , these countries represented only 35%, which underscores the emergence of newly accessible travel destinations in Africa, Asia, the Middle East, and the Pacific Rim, including numerous developing countries. Over the past 70 years, global tourism has grown significantly as an economic sector, and it has contributed to the economic development of dozens of nations.
Given the growth of international tourism and its emergence as one of the world’s largest export sectors, the question of its impact on economic growth for the host countries has been a topic of great interest in the tourism literature. Two hypotheses have emerged regarding the role of tourism in the economic growth process (Apergis & Payne, 2012 ). First, tourism-led growth hypothesis relies on the assumption that tourism is an engine of growth that generates spillovers and positive externalities through economic linkages that will impact the overall economy. Second, the economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis emphasizes policies oriented toward well-defined and enforceable property rights, stable political institutions, and adequate investment in both physical and human capital to facilitate the development of the tourism sector. Studies have concluded with support for both the tourism-led growth hypothesis (e.g., Durbarry, 2004 ; Katircioglu, 2010 ) and the economic-led growth hypothesis (e.g., Katircioglu, 2009 ; Oh, 2005 ), whereas other studies have found support for a bidirectional causality for tourism and economic growth (e.g., Apergis & Payne, 2012 ; Lee & Chang, 2008 ).
The growth of tourism has been marked by an increase in the competition for tourist expenditures, making it difficult for destinations to maintain their share of the international tourism market (Butler, 1991 ). Tourism development is cyclical and subject to short-term cycles and overconsumption of resources. Butler ( 1980 ) developed a tourist-area cycle of evolution that depicts the number of tourists rising sharply over time through periods of exploration, involvement, and development, before eventual consolidation and stagnation. When tourism growth exceeds the carrying capacity of the area, resource degradation can lead to the decline of tourism unless specific steps are taken to promote rejuvenation (Butler, 1980 , 1991 ).
The potential of tourism development as a tool to contribute to environmental conservation, economic growth, and poverty reduction is derived from several unique characteristics of the tourism system (UNWTO, 2002 ). First, tourism represents an opportunity for economic diversification, particularly in marginal areas with few other export options. Tourists are attracted to remote areas with high values of cultural, wildlife, and landscape assets. The cultural and natural heritage of developing countries is frequently based on such assets, and tourism represents an opportunity for income generation through the preservation of heritage values. Tourism is the only export sector where the consumer travels to the exporting country, which provides opportunities for lower-income households to become exporters through the sale of goods and services to foreign tourists. Tourism is also labor intensive; it provides small-scale employment opportunities, which also helps to promote gender equity. Finally, there are numerous indirect benefits of tourism for people living in poverty, including increased market access for remote areas through the development of roads, infrastructure, and communication networks. Nevertheless, travel is highly income elastic and carbon intensive, which has significant implications for the sustainability of the tourism sector (Lenzen et al., 2018 ).
Concerns about environmental issues appeared in tourism research just as global awareness of the environmental impacts of human activities was expanding. The United Nations Conference on the Human Environment was held in Stockholm in 1972 , the same year as the publication of The Limits to Growth (Meadows et al., 1972 ), which highlighted the concerns about the implications of exponential economic and population growth in a world of finite resources. This was the same year that the famous Blue Marble photograph of Earth was taken by the crew of the Apollo 17 spacecraft (Höhler, 2015 , p. 10), and the image captured the planet cloaked in the darkness of space and became a symbol of Earth’s fragility and vulnerability. As noted by Buckley ( 2012 ), tourism researchers turned their attention to social and environmental issues around the same time (Cohen, 1978 ; Farrell & McLellan, 1987 ; Turner & Ash, 1975 ; Young, 1973 ).
The notion of sustainable development is often associated with the publication of Our Common Future , the report of the World Commission on Environment and Development, also known as the Brundtland Commission (WCED, 1987 ). The report characterized sustainable development in terms of meeting “the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” (WCED, 1987 , p. 43). Four basic principles are fundamental to the concept of sustainability: (a) the idea of holistic planning and strategy making; (b) the importance of preserving essential ecological processes; (c) the need to protect both human heritage and biodiversity; and (d) the need to develop in such a way that productivity can be sustained over the long term for future generations (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ). In addition to achieving balance between economic growth and the conservation of natural resources, there should be a balance of fairness and opportunity between the nations of the world.
Although the modern concept of sustainable development emerged with the publication of Our Common Future , sustainable development has its roots in ideas about sustainable forest management that were developed in Europe during the 17th and 18th centuries (Blewitt, 2015 ; Grober, 2007 ). Sustainable forest management is concerned with the stewardship and use of forests in a way that maintains their biodiversity, productivity, and regeneration capacity as well as their potential to fulfill society’s demands for forest products and benefits. Building on these ideas, Daly ( 1990 ) offered two operational principles of sustainable development. First, sustainable development implies that harvest rates should be no greater than rates of regeneration; this concept is known as maximum sustainable yield. Second, waste emission rates should not exceed the natural assimilative capacities of the ecosystems into which the wastes are emitted. Regenerative and assimilative capacities are characterized as natural capital, and a failure to maintain these capacities is not sustainable.
Shortly after the emergence of the concept of sustainable development in academic and policy discourse, tourism researchers began referring to the notion of sustainable tourism (May, 1991 ; Nash & Butler, 1990 ), which soon became the dominant paradigm of tourism development. The concept of sustainable tourism, as with the role of tourism in sustainable development, has been interpreted in different ways, and there is a lack of consensus concerning its meaning, objectives, and indicators (Sharpley, 2000 ). Growing interest in the subject inspired the creation of a new academic journal, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , which was launched in 1993 and has become a leading tourism journal. It is described as “an international journal that publishes research on tourism and sustainable development, including economic, social, cultural and political aspects.”
The notion of sustainable tourism development emerged in contrast to mass tourism, which is characterized by the participation of large numbers of people, often provided as structured or packaged tours. Mass tourism has risen sharply in the last half century. International arrivals alone have increased by an average annual rate of more than 25% since 1950 , and many of those trips involved mass tourism activities (Fennell, 2020 ; UNWTO, 2020 ). Some examples of mass tourism include beach resorts, cruise ship tourism, gaming casinos, golf resorts, group tours, ski resorts, theme parks, and wildlife safari tourism, among others. Little data exist regarding the volume of domestic mass tourism, but nevertheless mass tourism activities dominate the global tourism sector. Mass tourism has been shown to generate benefits to host countries, such as income and employment generation, although it has also been associated with economic leakage (where revenue generated by tourism is lost to other countries’ economies) and economic dependency (where developing countries are dependent on wealthier countries for tourists, imports, and foreign investment) (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Khan, 1997 ; Peeters, 2012 ). Mass tourism has been associated with numerous negative environmental impacts and social impacts (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Fennell, 2020 ; Ghimire, 2013 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Liu, 2003 ; Peeters, 2012 ; Wheeller, 2007 ). Sustainable tourism development has been promoted in various ways as a framing concept in contrast to many of these economic, environmental, and social impacts.
Much of the early research on sustainable tourism focused on defining the concept, which has been the subject of vigorous debate (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Inskeep, 1991 ; Liu, 2003 ; Sharpley, 2000 ). Early definitions of sustainable tourism development seemed to fall in one of two categories (Sharpley, 2000 ). First, the “tourism-centric” paradigm of sustainable tourism development focuses on sustaining tourism as an economic activity (Hunter, 1995 ). Second, alternative paradigms have situated sustainable tourism in the context of wider sustainable development policies (Butler, 1991 ). One of the most comprehensive definitions of sustainable tourism echoes some of the language of the Brundtland Commission’s definition of sustainable development (WCED, 1987 ), emphasizing opportunities for the future while also integrating social and environmental concerns:
Sustainable tourism can be thought of as meeting the needs of present tourists and host regions while protecting and enhancing opportunity for the future. Sustainable tourism development is envisaged as leading to management of all resources in such a way that we can fulfill economic, social and aesthetic needs while maintaining cultural integrity, essential ecological processes, biological diversity and life support systems. (Inskeep, 1991 , p. 461)
Hunter argued that over the short and long terms, sustainable tourism development should
“meet the needs and wants of the local host community in terms of improved living standards and quality of life;
satisfy the demands of tourists and the tourism industry, and continue to attract them in order to meet the first aim; and
safeguard the environmental resource base for tourism, encompassing natural, built and cultural components, in order to achieve both of the preceding aims.” (Hunter, 1995 , p. 156)
Numerous other definitions have been documented, and the term itself has been subject to widespread critique (Buckley, 2012 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ). Nevertheless, there have been numerous calls to move beyond debate about a definition and to consider how it may best be implemented in practice (Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Liu, 2003 ). Cater ( 1993 ) identified three key criteria for sustainable tourism: (a) meeting the needs of the host population in terms of improved living standards both in the short and long terms; (b) satisfying the demands of a growing number of tourists; and (c) safeguarding the natural environment in order to achieve both of the preceding aims.
Some literature has acknowledged a vagueness of the concept of sustainable tourism, which has been used to advocate for fundamentally different strategies for tourism development that may exacerbate existing conflicts between conservation and development paradigms (Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ; McKercher, 1993b ). Similar criticisms have been leveled at the concept of sustainable development, which has been described as an oxymoron with a wide range of meanings (Adams, 2009 ; Daly, 1990 ) and “defined in such a way as to be either morally repugnant or logically redundant” (Beckerman, 1994 , p. 192). Sharpley ( 2000 ) suggests that in the tourism literature, there has been “a consistent and fundamental failure to build a theoretical link between sustainable tourism and its parental paradigm,” sustainable development (p. 2). Hunter ( 1995 ) suggests that practical measures designed to operationalize sustainable tourism fail to address many of the critical issues that are central to the concept of sustainable development generally and may even actually counteract the fundamental requirements of sustainable development. He suggests that mainstream sustainable tourism development is concerned with protecting the immediate resource base that will sustain tourism development while ignoring concerns for the status of the wider tourism resource base, such as potential problems associated with air pollution, congestion, introduction of invasive species, and declining oil reserves. The dominant paradigm of sustainable tourism development has been described as introverted, tourism-centric, and in competition with other sectors for scarce resources (McKercher, 1993a ). Hunter ( 1995 , p. 156) proposes an alternative, “extraparochial” paradigm where sustainable tourism development is reconceptualized in terms of its contribution to overall sustainable development. Such a paradigm would reconsider the scope, scale, and sectoral context of tourism-related resource utilization issues.
“Sustainability,” “sustainable tourism,” and “sustainable development” are all well-established terms that have often been used loosely and interchangeably in the tourism literature (Liu, 2003 ). Nevertheless, the subject of sustainable tourism has been given considerable attention and has been the focus of numerous academic compilations and textbooks (Coccossis & Nijkamp, 1995 ; Hall & Lew, 1998 ; Stabler, 1997 ; Swarbrooke, 1999 ), and it calls for new approaches to sustainable tourism development (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Sharpley, 2000 ). The notion of sustainable tourism has been reconceptualized in the literature by several authors who provided alternative frameworks for tourism development (Buckley, 2012 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ; McKercher, 1993b ; Sharpley, 2000 ).
Early research in sustainable tourism focused on the local environmental impacts of tourism, including energy use, water use, food consumption, and change in land use (Buckley, 2012 ; Butler, 1991 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Hunter & Green, 1995 ). Subsequent research has emphasized the global environmental impacts of tourism, such as greenhouse gas emissions and biodiversity losses (Gössling, 2002 ; Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ; Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Additional research has emphasized the impacts of environmental change on tourism itself, including the impacts of climate change on tourist behavior (Gössling et al., 2012 ; Richardson & Loomis, 2004 ; Scott et al., 2012 ; Viner, 2006 ). Countries that are dependent on tourism for economic growth may be particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change (Richardson & Witkoswki, 2010 ).
The early focus on environmental issues in sustainable tourism has been broadened to include economic, social, and cultural issues as well as questions of power and equity in society (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Sharpley, 2014 ), and some of these frameworks have integrated notions of social equity, prosperity, and cultural heritage values. Sustainable tourism is dependent on critical long-term considerations of the impacts; notions of equity; an appreciation of the importance of linkages (i.e., economic, social, and environmental); and the facilitation of cooperation and collaboration between different stakeholders (Elliott & Neirotti, 2008 ).
McKercher ( 1993b ) notes that tourism resources are typically part of the public domain or are intrinsically linked to the social fabric of the host community. As a result, many commonplace tourist activities such as sightseeing may be perceived as invasive by members of the host community. Many social impacts of tourism can be linked to the overuse of the resource base, increases in traffic congestion, rising land prices, urban sprawl, and changes in the social structure of host communities. Given the importance of tourist–resident interaction, sustainable tourism development depends in part on the support of the host community (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ).
Tourism planning involves the dual objectives of optimizing the well-being of local residents in host communities and minimizing the costs of tourism development (Sharpley, 2014 ). Tourism researchers have paid significant attention to examining the social impacts of tourism in general and to understanding host communities’ perceptions of tourism in particular. Studies of the social impacts of tourism development have examined the perceptions of local residents and the effects of tourism on social cohesion, traditional lifestyles, and the erosion of cultural heritage, particularly among Indigenous Peoples (Butler & Hinch, 2007 ; Deery et al., 2012 ; Mathieson & Wall, 1982 ; Sharpley, 2014 ; Whitford & Ruhanen, 2016 ).
Alternative Tourism and Sustainable Development
A wide body of published research is related to the role of tourism in sustainable development, and much of the literature involves case studies of particular types of tourism. Many such studies contrast types of alternative tourism with those of mass tourism, which has received sustained criticism for decades and is widely considered to be unsustainable (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Fennell, 2020 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Liu, 2003 ; Peeters, 2012 ; Zapata et al., 2011 ). Still, some tourism researchers have taken issue with the conclusion that mass tourism is inherently unsustainable (Sharpley, 2000 ; Weaver, 2007 ), and some have argued for developing pathways to “sustainable mass tourism” as “the desired and impending outcome for most destinations” (Weaver, 2012 , p. 1030). In integrating an ethical component to mass tourism development, Weaver ( 2014 , p. 131) suggests that the desirable outcome is “enlightened mass tourism.” Such suggestions have been contested in the literature and criticized for dubious assumptions about emergent norms of sustainability and support for growth, which are widely seen as contradictory (Peeters, 2012 ; Wheeller, 2007 ).
Models of responsible or alternative tourism development include ecotourism, community-based tourism, pro-poor tourism, slow tourism, green tourism, and heritage tourism, among others. Most models of alternative tourism development emphasize themes that aim to counteract the perceived negative impacts of conventional or mass tourism. As such, the objectives of these models of tourism development tend to focus on minimizing environmental impacts, supporting biodiversity conservation, empowering local communities, alleviating poverty, and engendering pleasant relationships between tourists and residents.
Approaches to alternative tourism development tend to overlap with themes of responsible tourism, and the two terms are frequently used interchangeably. Responsible tourism has been characterized in terms of numerous elements, including
ensuring that communities are involved in and benefit from tourism;
respecting local, natural, and cultural environments;
involving the local community in planning and decision-making;
using local resources sustainably;
behaving in ways that are sensitive to the host culture;
maintaining and encouraging natural, economic, and cultural diversity; and
assessing environmental, social, and economic impacts as a prerequisite to tourism development (Spenceley, 2012 ).
Hetzer ( 1965 ) identified four fundamental principles or perquisites for a more responsible form of tourism: (a) minimum environmental impact; (b) minimum impact on and maximum respect for host cultures; (c) maximum economic benefits to the host country; and (d) maximum leisure satisfaction to participating tourists.
The history of ecotourism is closely connected with the emergence of sustainable development, as it was born out of a concern for the conservation of biodiversity. Ecotourism is a form of tourism that aims to minimize local environmental impacts while bringing benefits to protected areas and the people living around those lands (Honey, 2008 ). Ecotourism represents a small segment of nature-based tourism, which is understood as tourism based on the natural attractions of an area, such as scenic areas and wildlife (Gössling, 1999 ). The ecotourism movement gained momentum in the 1990s, primarily in developing countries in Latin America and sub-Saharan Africa, and nearly all countries are now engaged in some form of ecotourism. In some communities, ecotourism is the primary economic activity and source of income and economic development.
The term “ecotourism” was coined by Hector Ceballos-Lascuráin and defined by him as “tourism that consists in travelling to relatively undisturbed or uncontaminated natural areas with the specific object of studying, admiring, and enjoying the scenery and its wild plants and animals” (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1987 , p. 13). In discussing ecotourism resources, he also made reference to “any existing cultural manifestations (both past and present) found in these areas” (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1987 , p. 14). The basic precepts of ecotourism had been discussed long before the actual use of the term. Twenty years earlier, Hetzer ( 1965 ) referred to a form of tourism “based principally upon natural and archaeological resources such as caves, fossil sites (and) archaeological sites.” Thus, both natural resources and cultural resources were integrated into ecotourism frameworks from the earliest manifestations.
Costa Rica is well known for having successfully integrated ecotourism in its overall strategy for sustainable development, and numerous case studies of ecotourism in Costa Rica appear in the literature (Chase et al., 1998 ; Fennell & Eagles, 1990 ; Gray & Campbell, 2007 ; Hearne & Salinas, 2002 ). Ecotourism in Costa Rica has been seen as having supported the economic development of the country while promoting biodiversity conservation in its extensive network of protected areas. Chase et al. ( 1998 ) estimated the demand for ecotourism in a study of differential pricing of entrance fees at national parks in Costa Rica. The authors estimated elasticities associated with the own-price, cross-price, and income variables and found that the elasticities of demand were significantly different between three different national park sites. The results reveal the heterogeneity characterizing tourist behavior and park attractions and amenities. Hearne and Salinas ( 2002 ) used choice experiments to examine the preferences of domestic and foreign tourists in Costa Rica in an ecotourism site. Both sets of tourists demonstrated a preference for improved infrastructure, more information, and lower entrance fees. Foreign tourists demonstrated relatively stronger preferences for the inclusion of restrictions in the access to some trails.
Ecotourism has also been studied extensively in Kenya (Southgate, 2006 ), Malaysia (Lian Chan & Baum, 2007 ), Nepal (Baral et al., 2008 ), Peru (Stronza, 2007 ), and Taiwan (Lai & Nepal, 2006 ), among many other countries. Numerous case studies have demonstrated the potential for ecotourism to contribute to sustainable development by providing support for biodiversity conservation, local livelihoods, and regional development.
Community-Based Tourism
Community-based tourism (CBT) is a model of tourism development that emphasizes the development of local communities and allows for local residents to have substantial control over its development and management, and a major proportion of the benefits remain within the community. CBT emerged during the 1970s as a response to the negative impacts of the international mass tourism development model (Cater, 1993 ; Hall & Lew, 2009 ; Turner & Ash, 1975 ; Zapata et al., 2011 ).
Community-based tourism has been examined for its potential to contribute to poverty reduction. In a study of the viability of the CBT model to support socioeconomic development and poverty alleviation in Nicaragua, tourism was perceived by participants in the study to have an impact on employment creation in their communities (Zapata et al., 2011 ). Tourism was seen to have had positive impacts on strengthening local knowledge and skills, particularly on the integration of women to new roles in the labor market. One of the main perceived gains regarding the environment was the process of raising awareness regarding the conservation of natural resources. The small scale of CBT operations and low capacity to accommodate visitors was seen as a limitation of the model.
Spenceley ( 2012 ) compiled case studies of community-based tourism in countries in southern Africa, including Botswana, Madagascar, Namibia, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. In this volume, authors characterize community-based and nature-based tourism development projects in the region and demonstrate how community participation in planning and decision-making has generated benefits for local residents and supported conservation initiatives. They contend that responsible tourism practices are of particular importance in the region because of the rich biological diversity, abundant charismatic wildlife, and the critical need for local economic development and livelihood strategies.
In Kenya, CBT enterprises were not perceived to have made a significant impact on poverty reduction at an individual household level, in part because the model relied heavily on donor funding, reinforcing dependency and poverty (Manyara & Jones, 2007 ). The study identified several critical success factors for CBT enterprises, namely, awareness and sensitization, community empowerment, effective leadership, and community capacity building, which can inform appropriate tourism policy formulation in Kenya. The impacts of CBT on economic development and poverty reduction would be greatly enhanced if tourism initiatives were able to emphasize independence, address local community priorities, enhance community empowerment and transparency, discourage elitism, promote effective community leadership, and develop community capacity to operate their own enterprises more efficiently.
Pro-Poor Tourism
Pro-poor tourism is a model of tourism development that brings net benefits to people living in poverty (Ashley et al., 2001 ; Harrison, 2008 ). Although its theoretical foundations and development objectives overlap to some degree with those of community-based tourism and other models of AT, the key distinctive feature of pro-poor tourism is that it places poor people and poverty at the top of the agenda. By focusing on a very simple and incontrovertibly moral idea, namely, the net benefits of tourism to impoverished people, the concept has broad appeal to donors and international aid agencies. Harnessing the economic benefits of tourism for pro-poor growth means capitalizing on the advantages while reducing negative impacts to people living in poverty (Ashley et al., 2001 ). Pro-poor approaches to tourism development include increasing access of impoverished people to economic benefits; addressing negative social and environmental impacts associated with tourism; and focusing on policies, processes, and partnerships that seek to remove barriers to participation by people living in poverty. At the local level, pro-poor tourism can play a very significant role in livelihood security and poverty reduction (Ashley & Roe, 2002 ).
Rogerson ( 2011 ) argues that the growth of pro-poor tourism initiatives in South Africa suggests that the country has become a laboratory for the testing and evolution of new approaches toward sustainable development planning that potentially will have relevance for other countries in the developing world. A study of pro-poor tourism development initiatives in Laos identified a number of favorable conditions for pro-poor tourism development, including the fact that local people are open to tourism and motivated to participate (Suntikul et al., 2009 ). The authors also noted a lack of development in the linkages that could optimize the fulfilment of the pro-poor agenda, such as training or facilitation of local people’s participation in pro-poor tourism development at the grassroots level.
Critics of the model have argued that pro-poor tourism is based on an acceptance of the status quo of existing capitalism, that it is morally indiscriminate and theoretically imprecise, and that its practitioners are academically and commercially marginal (Harrison, 2008 ). As Chok et al. ( 2007 ) indicate, the focus “on poor people in the South reflects a strong anthropocentric view . . . and . . . environmental benefits are secondary to poor peoples’” benefits (p. 153).
Harrison ( 2008 ) argues that pro-poor tourism is not a distinctive approach to tourism as a development tool and that it may be easier to discuss what pro-poor tourism is not than what it is. He concludes that it is neither anticapitalist nor inconsistent with mainstream tourism on which it relies; it is neither a theory nor a model and is not a niche form of tourism. Further, he argues that it has no distinctive method and is not only about people living in poverty.
Slow Tourism
The concept of slow tourism has emerged as a model of sustainable tourism development, and as such, it lacks an exact definition. The concept of slow tourism traces its origin back to some institutionalized social movements such as “slow food” and “slow cities” that began in Italy in the 1990s and spread rapidly around the world (Fullagar et al., 2012 ; Oh et al., 2016 , p. 205). Advocates of slow tourism tend to emphasize slowness in terms of speed, mobility, and modes of transportation that generate less environmental pollution. They propose niche marketing for alternative forms of tourism that focus on quality upgrading rather than merely increasing the quantity of visitors via the established mass-tourism infrastructure (Conway & Timms, 2010 ).
In the context of the Caribbean region, slow tourism has been promoted as more culturally sensitive and authentic, as compared to the dominant mass tourism development model that is based on all-inclusive beach resorts dependent on foreign investment (Conway & Timms, 2010 ). Recognizing its value as an alternative marketing strategy, Conway and Timms ( 2010 ) make the case for rebranding alternative tourism in the Caribbean as a means of revitalizing the sector for the changing demands of tourists in the 21st century . They suggest that slow tourism is the antithesis of mass tourism, which “relies on increasing the quantity of tourists who move through the system with little regard to either the quality of the tourists’ experience or the benefits that accrue to the localities the tourist visits” (Conway & Timms, 2010 , p. 332). The authors draw on cases from Barbados, the Grenadines, Jamaica, and Trinidad and Tobago to characterize models of slow tourism development in remote fishing villages and communities near nature preserves and sea turtle nesting sites.
Although there is a growing interest in the concept of slow tourism in the literature, there seems to be little agreement about the exact nature of slow tourism and whether it is a niche form of special interest tourism or whether it represents a more fundamental potential shift across the industry. Conway and Timms ( 2010 ) focus on the destination, advocating for slow tourism in terms of a promotional identity for an industry in need of rebranding. Caffyn ( 2012 , p. 77) discusses the implementation of slow tourism in terms of “encouraging visitors to make slower choices when planning and enjoying their holidays.” It is not clear whether slow tourism is a marketing strategy, a mindset, or a social movement, but the literature on slow tourism nearly always equates the term with sustainable tourism (Caffyn, 2012 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Oh et al., 2016 ). Caffyn ( 2012 , p. 80) suggests that slow tourism could offer a “win–win,” which she describes as “a more sustainable form of tourism; keeping more of the economic benefits within the local community and destination; and delivering a more meaningful and satisfying experience.” Research on slow tourism is nascent, and thus the contribution of slow tourism to sustainable development is not well understood.

Impacts of Tourism Development
The role of tourism in sustainable development can be examined through an understanding of the economic, environmental, and social impacts of tourism. Tourism is a global phenomenon that involves travel, recreation, the consumption of food, overnight accommodations, entertainment, sightseeing, and other activities that simultaneously intersect the lives of local residents, businesses, and communities. The impacts of tourism involve benefits and costs to all groups, and some of these impacts cannot easily be measured. Nevertheless, they have been studied extensively in the literature, which provides some context for how these benefits and costs are distributed.
Economic Impacts of Tourism
The travel and tourism sector is one of the largest components of the global economy, and global tourism has increased exponentially since the end of the Second World War (UNWTO, 2020 ). The direct, indirect, and induced economic impact of global travel accounted for 8.9 trillion U.S. dollars in contribution to the global gross domestic product (GDP), or 10.3% of global GDP. The global travel and tourism sector supports approximately 330 million jobs, or 1 in 10 jobs around the world. From an economic perspective, tourism plays a significant role in sustainable development. In many developing countries, tourism has the potential to play a unique role in income generation and distribution relative to many other industries, in part because of its high multiplier effect and consumption of local goods and services. However, research on the economic impacts of tourism has shown that this potential has rarely been fully realized (Liu, 2003 ).
Numerous studies have examined the impact of tourism expenditure on GDP, income, employment, and public sector revenue. Narayan ( 2004 ) used a computable general equilibrium model to estimate the economic impact of tourism growth on the economy of Fiji. Tourism is Fiji’s largest industry, with average annual growth of 10–12%; and as a middle-income country, tourism is critical to Fiji’s economic development. The findings indicate that an increase in tourism expenditures was associated with an increase in GDP, an improvement in the country’s balance of payments, and an increase in real consumption and national welfare. Evidence suggests that the benefits of tourism expansion outweigh any export effects caused by an appreciation of the exchange rate and an increase in domestic prices and wages.
Seetanah ( 2011 ) examined the potential contribution of tourism to economic growth and development using panel data of 19 island economies around the world from 1990 to 2007 and revealed that tourism development is an important factor in explaining economic performance in the selected island economies. The results have policy implications for improving economic growth by harnessing the contribution of the tourism sector. Pratt ( 2015 ) modeled the economic impact of tourism for seven small island developing states in the Pacific, the Caribbean, and the Indian Ocean. In most states, the transportation sector was found to have above-average linkages to other sectors of the economy. The results revealed some advantages of economies of scale for maximizing the economic contribution of tourism.
Apergis and Payne ( 2012 ) examined the causal relationship between tourism and economic growth for a panel of nine Caribbean countries. The panel of Caribbean countries includes Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Grenada, St. Kitts and Nevis, St. Lucia, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, and Trinidad and Tobago. The authors use a panel error correction model to reveal bidirectional causality between tourism and economic growth in both the short run and the long run. The presence of bidirectional causality reiterates the importance of the tourism sector in the generation of foreign exchange income and in financing the production of goods and services within these countries. Likewise, stable political institutions and adequate government policies to ensure the appropriate investment in physical and human capital will enhance economic growth. In turn, stable economic growth will provide the resources needed to develop the tourism infrastructure for the success of the countries’ tourism sector. Thus, policy makers should be cognizant of the interdependent relationship between tourism and economic growth in the design and implementation of economic policy. The mixed nature of these results suggest that the relationship between tourism and economic growth depends largely on the social and economic context as well as the role of tourism in the economy.
The economic benefits and costs of tourism are frequently distributed unevenly. An analysis of the impact of wildlife conservation policies in Zambia on household welfare found that households located near national parks earn higher levels of income from wage employment and self-employment than other rural households in the country, but they were also more likely to suffer crop losses related to wildlife conflicts (Richardson et al., 2012 ). The findings suggest that tourism development and wildlife conservation can contribute to pro-poor development, but they may be sustainable only if human–wildlife conflicts are minimized or compensated.
Environmental Impacts of Tourism
The environmental impacts of tourism are significant, ranging from local effects to contributions to global environmental change (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). Tourism is both dependent on water resources and a factor in global and local freshwater use. Tourists consume water for drinking, when showering and using the toilet, when participating in activities such as winter ski tourism (i.e., snowmaking), and when using swimming pools and spas. Fresh water is also needed to maintain hotel gardens and golf courses, and water use is embedded in tourism infrastructure development (e.g., accommodations, laundry, dining) and in food and fuel production. Direct water consumption in tourism is estimated to be approximately 350 liters (L) per guest night for accommodation; when indirect water use from food, energy, and transport are considered, total water use in tourism is estimated to be approximately 6,575 L per guest night, or 27,800 L per person per trip (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). In addition, tourism contributes to the pollution of oceans as well as lakes, rivers, and other freshwater systems (Gössling, 2002 ; Gössling et al., 2011 ).
The clearing and conversion of land is central for tourism development, and in many cases, the land used for tourism includes roads, airports, railways, accommodations, trails, pedestrian walks, shopping areas, parking areas, campgrounds, vacation homes, golf courses, marinas, ski resorts, and indirect land use for food production, disposal of solid wastes, and the treatment of wastewater (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). Global land use for accommodation is estimated to be approximately 42 m 2 per bed. Total global land use for tourism is estimated to be nearly 62,000 km 2 , or 11.7 m 2 per tourist; more than half of this estimate is represented by land use for traffic infrastructure.
Tourism and hospitality have direct and indirect links to nearly all aspects of food production, preparation, and consumption because of the quantities of food consumed in tourism contexts (Gössling et al., 2011 ). Food production has significant implications for sustainable development, given the growing global demand for food. The implications include land conversion, losses to biodiversity, changes in nutrient cycling, and contributions to greenhouse emissions that are associated with global climate change (Vitousek et al., 1997 ). Global food use for tourism is estimated to be approximately 39.4 megatons 1 (Mt), about 38% than the amount of food consumed at home. This equates to approximately 1,800 grams (g) of food consumed per tourist per day.
Although tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, nonextractive option for economic development, (Gössling, 2000 ), assessments reveal that such pursuits have a significant carbon footprint, as tourism is significantly more carbon intensive than other potential areas of economic development (Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Tourism is dependent on energy, and virtually all energy use in the tourism sector is derived from fossil fuels, which contribute to global greenhouse emissions that are associated with global climate change. Energy use for tourism has been estimated to be approximately 3,575 megajoules 2 (MJ) per trip, including energy for travel and accommodations (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). A previous estimate of global carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) emissions from tourism provided values of 1.12 gigatons 3 (Gt) of CO 2 , amounting to about 3% of global CO 2 -equivalent (CO 2 e) emissions (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). However, these analyses do not cover the supply chains underpinning tourism and do not therefore represent true carbon footprints. A more complete analysis of the emissions from energy consumption necessary to sustain the tourism sector would include food and beverages, infrastructure construction and maintenance, retail, and financial services. Between 2009 and 2013 , tourism’s global carbon footprint is estimated to have increased from 3.9 to 4.5 GtCO 2 e, four times more than previously estimated, accounting for about 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions (Lenzen et al., 2018 ). The majority of this footprint is exerted by and within high-income countries. The rising global demand for tourism is outstripping efforts at decarbonization of tourism operations and as a result is accelerating global carbon emissions.
Social Impacts of Tourism
The social impacts of tourism have been widely studied, with an emphasis on residents’ perceptions in the host community (Sharpley, 2014 ). Case studies include research conducted in Australia (Faulkner & Tideswell, 1997 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Tovar & Lockwood, 2008 ), Belize (Diedrich & Garcia-Buades, 2008 ), China (Gu & Ryan, 2008 ), Fiji (King et al., 1993 ), Greece (Haralambopoulos & Pizam, 1996 ; Tsartas, 1992 ), Hungary (Rátz, 2000 ), Thailand (Huttasin, 2008 ), Turkey (Kuvan & Akan, 2005 ), the United Kingdom (Brunt & Courtney, 1999 ; Haley et al., 2005 ), and the United States (Andereck et al., 2005 ; Milman & Pizam, 1988 ), among others. The social impacts of tourism are difficult to measure, and most published studies are mainly concerned with the social impacts on the host communities rather than the impacts on the tourists themselves.
Studies of residents’ perceptions of tourism are typically conducted using household surveys. In most cases, residents recognize the economic dependence on tourism for income, and there is substantial evidence to suggest that working in or owning a business in tourism or a related industry is associated with more positive perceptions of tourism (Andereck et al., 2007 ). The perceived nature of negative effects is complex and often conveys a dislike of crowding, traffic congestion, and higher prices for basic needs (Deery et al., 2012 ). When the number of tourists far exceeds that of the resident population, negative attitudes toward tourism may manifest (Diedrich & Garcia-Buades, 2008 ). However, residents who recognize negative impacts may not necessarily oppose tourism development (King et al., 1993 ).
In some regions, little is known about the social and cultural impacts of tourism despite its dominance as an economic sector. Tourism is a rapidly growing sector in Cuba, and it is projected to grow at rates that exceed the average projected growth rates for the Caribbean and the world overall (Salinas et al., 2018 ). Still, even though there has been rapid tourism development in Cuba, there has been little research related to the environmental and sociocultural impacts of this tourism growth (Rutty & Richardson, 2019 ).
In some international tourism contexts, studies have found that residents are generally resentful toward tourism because it fuels inequality and exacerbates racist attitudes and discrimination (Cabezas, 2004 ; Jamal & Camargo, 2014 ; Mbaiwa, 2005 ). Other studies revealed similar narratives and recorded statements of exclusion and socioeconomic stratification (Sanchez & Adams, 2008 ). Local residents often must navigate the gaps in the racialized, gendered, and sexualized structures imposed by the global tourism industry and host-country governments (Cabezas, 2004 ).
However, during times of economic crisis, residents may develop a more permissive view as their perceptions of the costs of tourism development decrease (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ). This increased positive attitude is not based on an increase in the perception of positive impacts of tourism, but rather on a decrease in the perception of the negative impacts.
There is a growing body of research on Indigenous and Aboriginal tourism that emphasizes justice issues such as human rights and self-empowerment, control, and participation of traditional owners in comanagement of destinations (Jamal & Camargo, 2014 ; Ryan & Huyton, 2000 ; Whyte, 2010 ).
Sustainability of Tourism
A process or system is said to be sustainable to the extent that it is robust, resilient, and adaptive (Anderies et al., 2013 ). By most measures, the global tourism system does not meet these criteria for sustainability. Tourism is not robust in that it cannot resist threats and perturbations, such as economic shocks, public health pandemics, war, and other disruptions. Tourism is not resilient in that it does not easily recover from failures, such as natural disasters or civil unrest. Furthermore, tourism is not adaptive in that it is often unable to change in response to external conditions. One example that underscores the failure to meet all three criteria is the dependence of tourism on fossil fuels for transportation and energy, which are key inputs for tourism development. This dependence itself is not sustainable (Wheeller, 2007 ), and thus the sustainability of tourism is questionable.
Liu ( 2003 ) notes that research related to the role of tourism in sustainable development has emphasized supply-side concepts such as sustaining tourism resources and ignored the demand side, which is particularly vulnerable to social and economic shocks. Tourism is vulnerable to both localized and global shocks. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to localized shocks include disaster vulnerability in coastal Thailand (Calgaro & Lloyd, 2008 ), bushfires in northeast Victoria in Australia (Cioccio & Michael, 2007 ), forest fires in British Columbia, Canada (Hystad & Keller, 2008 ); and outbreak of foot and mouth disease in the United Kingdom (Miller & Ritchie, 2003 ).
Like most other economic sectors, tourism is vulnerable to the impacts of earthquakes, particularly in areas where tourism infrastructure may not be resilient to such shocks. Numerous studies have examined the impacts of earthquake events on tourism, including studies of the aftermath of the 1997 earthquake in central Italy (Mazzocchi & Montini, 2001 ), the 1999 earthquake in Taiwan (Huan et al., 2004 ; Huang & Min, 2002 ), and the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake in western Sichuan, China (Yang et al., 2011 ), among others.
Tourism is vulnerable to extreme weather events. Regional economic strength has been found to be associated with lower vulnerability to natural disasters. Kim and Marcoullier ( 2015 ) examined the vulnerability and resilience of 10 tourism-based regional economies that included U.S. national parks or protected seashores situated on the Gulf of Mexico or Atlantic Ocean coastline that were affected by several hurricanes over a 26-year period. Regions with stronger economic characteristics prior to natural disasters were found to have lower disaster losses than regions with weaker economies.
Tourism is extremely sensitive to oil spills, whatever their origin, and the volume of oil released need not be large to generate significant economic losses (Cirer-Costa, 2015 ). Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to the localized shock of an oil spill include research on the impacts of oil spills in Alaska (Coddington, 2015 ), Brazil (Ribeiro et al., 2020 ), Spain (Castanedo et al., 2009 ), affected regions in the United States along the Gulf of Mexico (Pennington-Gray et al., 2011 ; Ritchie et al., 2013 ), and the Republic of Korea (Cheong, 2012 ), among others. Future research on the vulnerability of tourist destinations to oil spills should also incorporate freshwater environments, such as lakes, rivers, and streams, where the rupture of oil pipelines is more frequent.
Significant attention has been paid to assessing the vulnerability of tourist destinations to acts of terrorism and the impacts of terrorist attacks on regional tourist economies (Liu & Pratt, 2017 ). Such studies include analyses of the impacts of terrorist attacks on three European countries, Greece, Italy, and Austria (Enders et al., 1992 ); the impact of the 2001 terrorist attacks on the United States (Goodrich, 2002 ); terrorism and tourism in Nepal (Bhattarai et al., 2005 ); vulnerability of tourism livelihoods in Bali (Baker & Coulter, 2007 ); the impact of terrorism on tourist preferences for destinations in the Mediterranean and the Canary Islands (Arana & León, 2008 ); the 2011 massacres in Olso and Utøya, Norway (Wolff & Larsen, 2014 ); terrorism and political violence in Tunisia (Lanouar & Goaied, 2019 ); and the impact of terrorism on European tourism (Corbet et al., 2019 ), among others. Pizam and Fleischer ( 2002 ) studied the impact of acts of terrorism on tourism demand in Israel between May 1991 and May 2001 , and they confirmed that the frequency of acts of terrorism had caused a larger decline in international tourist arrivals than the severity of these acts. Most of these are ex post studies, and future assessments of the underlying conditions of destinations could reveal a deeper understanding of the vulnerability of tourism to terrorism.
Tourism is vulnerable to economic crisis, both local economic shocks (Okumus & Karamustafa, 2005 ; Stylidis & Terzidou, 2014 ) and global economic crisis (Papatheodorou et al., 2010 ; Smeral, 2010 ). Okumus and Karamustafa ( 2005 ) evaluated the impact of the February 2001 economic crisis in Turkey on tourism, and they found that the tourism industry was poorly prepared for the economic crisis despite having suffered previous impacts related to the Gulf War in the early 1990s, terrorism in Turkey in the 1990s, the civil war in former Yugoslavia in the early 1990s, an internal economic crisis in 1994 , and two earthquakes in the northwest region of Turkey in 1999 . In a study of the attitudes and perceptions of citizens of Greece, Stylidis and Terzidou ( 2014 ) found that economic crisis is associated with increased support for tourism development, particularly out of self-interest. Economic crisis diminishes residents’ concern for environmental issues. In a study of the behavior of European tourists amid an economic crisis, Eugenio-Martin and Campos-Soria ( 2014 ) found that the probability of households cutting back on travel expenditures depends largely on the climate and economic conditions of tourists’ home countries, and households that do reduce travel spending engage in tourism closer to home.
Becken and Lennox ( 2012 ) studied the implications of a long-term increase in oil prices for tourism in New Zealand, and they estimate that a doubling of oil prices is associated with a 1.7% decrease in real gross national disposable income and a 9% reduction in the real value of tourism exports. Chatziantoniou et al. ( 2013 ) investigated the relationship among oil price shocks, tourism variables, and economic indicators in four European Mediterranean countries and found that aggregate demand oil price shocks generated a lagged effect on tourism-generated income and economic growth. Kisswani et al. ( 2020 ) examined the asymmetric effect of oil prices on tourism receipts and the sensitive susceptibility of tourism to oil price changes using nonlinear analysis. The findings document a long-run asymmetrical effect for most countries, after incorporating the structural breaks, suggesting that governments and tourism businesses and organizations should interpret oil price fluctuations cautiously.
Finally, the sustainability of tourism has been shown to be vulnerable to the outbreak of infectious diseases, including the impact of the Ebola virus on tourism in sub-Saharan Africa (Maphanga & Henama, 2019 ; Novelli et al., 2018 ) and in the United States (Cahyanto et al., 2016 ). The literature also includes studies of the impact of swine flu on tourism demand in Brunei (Haque & Haque, 2018 ), Mexico (Monterrubio, 2010 ), and the United Kingdom (Page et al., 2012 ), among others. In addition, rapid assessments of the impacts of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 have documented severe disruptions and cessations of tourism because of unprecedented global travel restrictions and widespread restrictions on public gatherings (Gössling et al., 2020 ; Qiu et al., 2020 ; Sharma & Nicolau, 2020 ). Hotels, airlines, cruise lines, and car rentals have all experienced a significant decrease globally because of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the shock to the industry is significant enough to warrant concerns about the long-term outlook (Sharma & Nicolau, 2020 ). Qiu et al. ( 2020 ) estimated the social costs of the pandemic to tourism in three cities in China (Hong Kong, Guangzhou, and Wuhan), and they found that most respondents were willing to pay for risk reduction and action in responding to the pandemic crisis; there was no significant difference between residents’ willingness to pay in the three cities. Some research has emphasized how lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic can prepare global tourism for an economic transformation that is needed to mitigate the impacts of climate change (Brouder, 2020 ; Prideaux et al., 2020 ).
It is clear that tourism has contributed significantly to economic development globally, but its role in sustainable development is uncertain, contested, and potentially paradoxical. This is due, in part, to the contested nature of sustainable development itself. Tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, nonextractive option for economic development, particularly for developing countries (Gössling, 2000 ), and many countries have managed to increase their participation in the global economy through development of international tourism. Tourism development has been viewed as an important sector for investment to enhance economic growth, poverty alleviation, and food security, and the sector provides an alternative opportunity to large-scale development projects and extractive industries that contribute to emissions of pollutants and threaten biodiversity and cultural values. However, global evidence from research on the economic impacts of tourism has shown that this potential has rarely been realized (Liu, 2003 ).
The role of tourism in sustainable development has been studied extensively and with a variety of perspectives, including the conceptualization of alternative or responsible forms of tourism and the examination of economic, environmental, and social impacts of tourism development. The research has generally concluded that tourism development has contributed to sustainable development in some cases where it is demonstrated to have provided support for biodiversity conservation initiatives and livelihood development strategies. As an economic sector, tourism is considered to be labor intensive, providing opportunities for poor households to enhance their livelihood through the sale of goods and services to foreign tourists.
Nature-based tourism approaches such as ecotourism and community-based tourism have been successful at attracting tourists to parks and protected areas, and their spending provides financial support for biodiversity conservation, livelihoods, and economic growth in developing countries. Nevertheless, studies of the impacts of tourism development have documented negative environmental impacts locally in terms of land use, food and water consumption, and congestion, and globally in terms of the contribution of tourism to climate change through the emission of greenhouse gases related to transportation and other tourist activities. Studies of the social impacts of tourism have documented experiences of discrimination based on ethnicity, gender, race, sex, and national identity.
The sustainability of tourism as an economic sector has been examined in terms of its vulnerability to civil conflict, economic shocks, natural disasters, and public health pandemics. Most studies conclude that tourism may have positive impacts for regional development and environmental conservation, but there is evidence that tourism inherently generates negative environmental impacts, primarily through pollutions stemming from transportation. The regional benefits of tourism development must be considered alongside the global impacts of increased transportation and tourism participation. Global tourism has also been shown to be vulnerable to economic crises, oil price shocks, and global outbreaks of infectious diseases. Given that tourism is dependent on energy, the movement of people, and the consumption of resources, virtually all tourism activities have significant economic, environmental, and sustainable impacts. As such, the role of tourism in sustainable development is highly questionable. Future research on the role of tourism in sustainable development should focus on reducing the negative impacts of tourism development, both regionally and globally.
Further Reading
- Bramwell, B. , & Lane, B. (1993). Sustainable tourism: An evolving global approach. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 1 (1), 1–5.
- Buckley, R. (2012). Sustainable tourism: Research and reality. Annals of Tourism Research , 39 (2), 528–546.
- Butler, R. W. (1991). Tourism, environment, and sustainable development. Environmental Conservation , 18 (3), 201–209.
- Butler, R. W. (1999). Sustainable tourism: A state‐of‐the‐art review. Tourism Geographies , 1 (1), 7–25.
- Clarke, J. (1997). A framework of approaches to sustainable tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 5 (3), 224–233.
- Fennell, D. A. (2020). Ecotourism (5th ed.). Routledge.
- Gössling, S. (2002). Global environmental consequences of tourism. Global Environmental Change , 12 (4), 283–302.
- Honey, M. (2008). Ecotourism and sustainable development: Who owns paradise? (2nd ed.). Island Press.
- Inskeep, E. (1991). Tourism planning: An integrated and sustainable development approach . Routledge.
- Jamal, T. , & Camargo, B. A. (2014). Sustainable tourism, justice and an ethic of care: Toward the just destination. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 22 (1), 11–30.
- Liburd, J. J. , & Edwards, D. (Eds.). (2010). Understanding the sustainable development of tourism . Oxford.
- Liu, Z. (2003). Sustainable tourism development: A critique. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 11 (6), 459–475.
- Sharpley, R. (2020). Tourism, sustainable development and the theoretical divide: 20 years on. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 28 (11), 1932–1946.
- Adams, W. M. (2009). Green development: Environment and sustainability in a developing world (3rd ed.). Routledge.
- Andereck, K. L. , Valentine, K. M. , Knopf, R. A. , & Vogt, C. A. (2005). Residents’ perceptions of community tourism impacts. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (4), 1056–1076.
- Andereck, K. , Valentine, K. , Vogt, C. , & Knopf, R. (2007). A cross-cultural analysis of tourism and quality of life perceptions. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 483–502.
- Anderies, J. M. , Folke, C. , Walker, B. , & Ostrom, E. (2013). Aligning key concepts for global change policy: Robustness, resilience, and sustainability . Ecology and Society , 18 (2), 8.
- Apergis, N. , & Payne, J. E. (2012). Tourism and growth in the Caribbean–evidence from a panel error correction model. Tourism Economics , 18 (2), 449–456.
- Arana, J. E. , & León, C. J. (2008). The impact of terrorism on tourism demand. Annals of Tourism Research , 35 (2), 299–315.
- Ashley, C. , & Roe, D. (2002). Making tourism work for the poor: Strategies and challenges in southern Africa. Development Southern Africa , 19 (1), 61–82.
- Ashley, C. , Roe, D. , & Goodwin, H. (2001). Pro-poor tourism strategies: Making tourism work for the poor: A review of experience (No. 1). Overseas Development Institute.
- Baker, K. , & Coulter, A. (2007). Terrorism and tourism: The vulnerability of beach vendors’ livelihoods in Bali. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (3), 249–266.
- Baral, N. , Stern, M. J. , & Bhattarai, R. (2008). Contingent valuation of ecotourism in Annapurna conservation area, Nepal: Implications for sustainable park finance and local development. Ecological Economics , 66 (2–3), 218–227.
- Becken, S. , & Lennox, J. (2012). Implications of a long-term increase in oil prices for tourism. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 133–142.
- Beckerman, W. (1994). “Sustainable development”: Is it a useful concept? Environmental Values , 3 (3), 191–209.
- Bhattarai, K. , Conway, D. , & Shrestha, N. (2005). Tourism, terrorism and turmoil in Nepal. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (3), 669–688.
- Blewitt, J. (2015). Understanding sustainable development (2nd ed.). Routledge.
- Brouder, P. (2020). Reset redux: Possible evolutionary pathways towards the transformation of tourism in a COVID-19 world. Tourism Geographies , 22 (3), 484–490.
- Brunt, P. , & Courtney, P. (1999). Host perceptions of sociocultural impacts. Annals of Tourism Research , 26 (3), 493–515.
- Buckley, R. (2011). Tourism and environment. Annual Review of Environment and Resources , 36 , 397–416.
- Butler, R. W. (1980). The concept of a tourist area cycle of evolution: Implications for management of resources. Canadian Geographer/Le Géographe canadien , 24 (1), 5–12.
- Butler, R. , & Hinch, T. (Eds.). (2007). Tourism and indigenous peoples: Issues and implications . Routledge.
- Cabezas, A. L. (2004). Between love and money: Sex, tourism, and citizenship in Cuba and the Dominican Republic. Signs: Journal of Women in Culture and Society , 29 (4), 987–1015.
- Caffyn, A. (2012). Advocating and implementing slow tourism. Tourism Recreation Research , 37 (1), 77–80.
- Cahyanto, I. , Wiblishauser, M. , Pennington-Gray, L. , & Schroeder, A. (2016). The dynamics of travel avoidance: The case of Ebola in the US. Tourism Management Perspectives , 20 , 195–203.
- Calgaro, E. , & Lloyd, K. (2008). Sun, sea, sand and tsunami: Examining disaster vulnerability in the tourism community of Khao Lak, Thailand. Singapore Journal of Tropical Geography , 29 (3), 288–306.
- Castanedo, S. , Juanes, J. A. , Medina, R. , Puente, A. , Fernandez, F. , Olabarrieta, M. , & Pombo, C. (2009). Oil spill vulnerability assessment integrating physical, biological and socio-economical aspects: Application to the Cantabrian coast (Bay of Biscay, Spain). Journal of Environmental Management , 91 (1), 149–159.
- Cater, E. (1993). Ecotourism in the Third World: Problems for sustainable tourism development. Tourism Management , 14 (2), 85–90.
- Ceballos-Lascuráin, H. (1987, January). The future of “ecotourism.” Mexico Journal , 17 , 13–14.
- Chase, L. C. , Lee, D. R. , Schulze, W. D. , & Anderson, D. J. (1998). Ecotourism demand and differential pricing of national park access in Costa Rica. Land Economics , 74 (4), 466–482.
- Chatziantoniou, I. , Filis, G. , Eeckels, B. , & Apostolakis, A. (2013). Oil prices, tourism income and economic growth: A structural VAR approach for European Mediterranean countries. Tourism Management , 36 (C), 331–341.
- Cheong, S. M. (2012). Fishing and tourism impacts in the aftermath of the Hebei-Spirit oil spill. Journal of Coastal Research , 28 (6), 1648–1653.
- Chok, S. , Macbeth, J. , & Warren, C. (2007). Tourism as a tool for poverty alleviation: A critical analysis of “pro-poor tourism” and implications for sustainability. Current Issues in Tourism , 10 (2–3), 144–165.
- Cioccio, L. , & Michael, E. J. (2007). Hazard or disaster: Tourism management for the inevitable in Northeast Victoria. Tourism Management , 28 (1), 1–11.
- Cirer-Costa, J. C. (2015). Tourism and its hypersensitivity to oil spills. Marine Pollution Bulletin , 91 (1), 65–72.
- Coccossis, H. , & Nijkamp, P. (1995). Sustainable tourism development . Ashgate.
- Coddington, K. (2015). The “entrepreneurial spirit”: Exxon Valdez and nature tourism development in Seward, Alaska. Tourism Geographies , 17 (3), 482–497.
- Cohen, E. (1978). The impact of tourism on the physical environment. Annals of Tourism Research , 5 (2), 215–237.
- Conway, D. , & Timms, B. F. (2010). Re-branding alternative tourism in the Caribbean: The case for “slow tourism.” Tourism and Hospitality Research , 10 (4), 329–344.
- Corbet, S. , O’Connell, J. F. , Efthymiou, M. , Guiomard, C. , & Lucey, B. (2019). The impact of terrorism on European tourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 75 , 1–17.
- Daly, H. E. (1990). Toward some operational principles of sustainable development. Ecological Economics , 2 (1), 1–6.
- Deery, M. , Jago, L. , & Fredline, L. (2012). Rethinking social impacts of tourism research: A new research agenda. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 64–73.
- Diedrich, A. , & Garcia-Buades, E. (2008). Local perceptions of tourism as indicators of destination decline. Tourism Management , 41 , 623–632.
- Durbarry, R. (2004). Tourism and economic growth: The case of Mauritius. Tourism Economics , 10 , 389–401.
- Elliott, S. M. , & Neirotti, L. D. (2008). Challenges of tourism in a dynamic island destination: The case of Cuba. Tourism Geographies , 10 (4), 375–402.
- Enders, W. , Sandler, T. , & Parise, G. F. (1992). An econometric analysis of the impact of terrorism on tourism. Kyklos , 45 (4), 531–554.
- Eugenio-Martin, J. L. , & Campos-Soria, J. A. (2014). Economic crisis and tourism expenditure cutback decision. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 53–73.
- Farrell, B. , & McLellan, R. (1987). Tourism and physical environment research. Annals of Tourism Research , 14 (1), 1–16.
- Faulkner, B. , & Tideswell, C. (1997). A framework for monitoring community impacts of tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 5 (1), 3–28.
- Fennell, D. A. , & Eagles, P. F. (1990). Ecotourism in Costa Rica: A conceptual framework. Journal of Park and Recreation Administration , 8 (1), 23–34.
- Fullagar, S. , Markwell, K. , & Wilson, E. (Eds.). (2012). Slow tourism: Experiences and mobilities . Channel View.
- Garau-Vadell, J. B. , Gutierrez-Taño, D. , & Diaz-Armas, R. (2018). Economic crisis and residents’ perception of the impacts of tourism in mass tourism destinations. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management , 7 , 68–75.
- Garrod, B. , & Fyall, A. (1998). Beyond the rhetoric of sustainable tourism? Tourism Management , 19 (3), 199–212.
- Ghimire, K. B. (Ed.). (2013). The native tourist: Mass tourism within developing countries . Routledge.
- Goodrich, J. N. (2002). September 11, 2001 attack on America: A record of the immediate impacts and reactions in the USA travel and tourism industry. Tourism Management , 23 (6), 573–580.
- Gössling, S. (1999). Ecotourism: A means to safeguard biodiversity and ecosystem functions? Ecological Economics , 29 , 303–320.
- Gössling, S. (2000). Tourism–sustainable development option? Environmental Conservation , 27 (3), 223–224.
- Gössling, S. (2002). Global environmental consequences of tourism. Global Environmental Change , 12 , 283–302.
- Gössling, S. , & Peeters, P. (2015). Assessing tourism’s global environmental impact 1900–2050. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 23 (5), 639–659.
- Gössling, S. , Peeters, P. , Hall, C. M. , Ceron, J.‑P. , Dubois, G. , Lehman, L. V. , & Scott, D. (2011). Tourism and water use: Supply, demand and security, and international review. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 16–28.
- Gössling, S. , Scott, D. , & Hall, C. M. (2020). Pandemics, tourism and global change: A rapid assessment of COVID-19. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 29 (1), 1–20.
- Gössling, S. , Scott, D. , Hall, C. M. , Ceron, J. P. , & Dubois, G. (2012). Consumer behaviour and demand response of tourists to climate change. Annals of Tourism Research , 39 (1), 36–58.
- Gray, N. J. , & Campbell, L. M. (2007). A decommodified experience? Exploring aesthetic, economic and ethical values for volunteer ecotourism in Costa Rica. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 463–482.
- Grober, U. (2007). Deep roots—a conceptual history of “sustainable development” (Nachhaltigkeit) . Wissenschaftszentrum Berlin für Sozialforschung.
- Gu, H. , & Ryan, C. (2008). Place attachment, identity and community impacts of tourism—the case of a Beijing hutong. Tourism Management , 29 (4), 637–647.
- Gursoy, D. , Chi, C. G. , & Dyer, P. (2010). Locals’ attitudes toward mass and alternative tourism: The case of Sunshine Coast, Australia. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (3), 381–394.
- Haley, A. J. , Snaith, T. , & Miller, G. (2005). The social impacts of tourism a case study of Bath, UK. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (3), 647–668.
- Hall, C. M. , & Lew, A. A. (2009). Understanding and managing tourism impacts: An integrated approach . Routledge.
- Hall, C. M. , & Lew, A. A. (Eds.). (1998). Sustainable tourism: A geographical perspective . Longman.
- Haque, T. H. , & Haque, M. O. (2018). The swine flu and its impacts on tourism in Brunei. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management , 36 , 92–101.
- Haralambopoulos, N. , & Pizam, A. (1996). Perceived impacts of tourism: The case of Samos. Annals of Tourism Research , 23 (3), 503–526.
- Harrison, D. (2008). Pro-poor tourism: A critique. Third World Quarterly , 29 (5), 851–868.
- Hearne, R. R. , & Salinas, Z. M. (2002). The use of choice experiments in the analysis of tourist preferences for ecotourism development in Costa Rica. Journal of Environmental Management , 65 (2), 153–163.
- Hetzer, N. D. (1965). Environment, tourism, culture. Links , 1 (2), 1–3.
- Höhler, S. (2015). Spaceship earth in the environmental age, 1960–1990 . Routledge.
- Honey, M. , & Gilpin, R. (2009). Tourism in the developing world: Promoting peace and reducing poverty . United States Institute for Peace.
- Huan, T. C. , Beaman, J. , & Shelby, L. (2004). No-escape natural disaster: Mitigating impacts on tourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 31 (2), 255–273.
- Huang, J. H. , & Min, J. C. (2002). Earthquake devastation and recovery in tourism: The Taiwan case. Tourism Management , 23 (2), 145–154.
- Hunter, C. (1995). On the need to re-conceptualise sustainable tourism development. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 3 (3), 155–165.
- Hunter, C. , & Green, H. (1995). Tourism and the environment. A sustainable relationship? Routledge.
- Huttasin, N. (2008). Perceived social impacts of tourism by residents in the OTOP tourism village, Thailand. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research , 13 (2), 175–191.
- Hystad, P. W. , & Keller, P. C. (2008). Towards a destination tourism disaster management framework: Long-term lessons from a forest fire disaster. Tourism Management , 29 (1), 151–162.
- Katircioglu, S. (2009). Tourism, trade and growth: The case of Cyprus. Applied Economics , 41 (21), 2741–2750.
- Katircioglu, S. (2010). Testing the tourism-led growth hypothesis for Singapore: An empirical investigation from bounds test to cointegration and Granger causality tests. Tourism Economics , 16 (4), 1095–1101.
- Khan, M. M. (1997). Tourism development and dependency theory: Mass tourism vs. ecotourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 24 (4), 988–991.
- Kim, H. , & Marcouiller, D. W. (2015). Considering disaster vulnerability and resiliency: The case of hurricane effects on tourism-based economies. The Annals of Regional Science , 54 (3), 945–971.
- King, B. , Pizam, A. , & Milman, A. (1993). Social impacts of tourism: Host perceptions. Annals of Tourism Research , 20 (4), 650–665.
- Kisswani, K. M. , Zaitouni, M. , & Moufakkir, O. (2020). An examination of the asymmetric effect of oil prices on tourism receipts. Current Issues in Tourism , 23 (4), 500–522.
- Kuvan, Y. , & Akan, P. (2005). Residents’ attitudes toward general and forest-related impacts of tourism: The case of Belek, Antalya. Tourism Management , 26 (5), 691–706.
- Lai, P. H. , & Nepal, S. K. (2006). Local perspectives of ecotourism development in Tawushan Nature Reserve, Taiwan. Tourism Management , 27 (6), 1117–1129.
- Lanouar, C. , & Goaied, M. (2019). Tourism, terrorism and political violence in Tunisia: Evidence from Markov-switching models. Tourism Management , 70 , 404–418.
- Lee, C. C. , & Chang, C. P. (2008). Tourism development and economic growth: A closer look at panels. Tourism Management , 29 , 180–192.
- Lenzen, M. , Sun, Y. Y. , Faturay, F. , Ting, Y. P. , Geschke, A. , & Malik, A. (2018). The carbon footprint of global tourism. Nature Climate Change , 8 (6), 522–528.
- Lian Chan, J. K. , & Baum, T. (2007). Ecotourists’ perception of ecotourism experience in lower Kinabatangan, Sabah, Malaysia. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 574–590.
- Liu, A. , & Pratt, S. (2017). Tourism’s vulnerability and resilience to terrorism. Tourism Management , 60 , 404–417.
- Manyara, G. , & Jones, E. (2007). Community-based tourism enterprises development in Kenya: An exploration of their potential as avenues of poverty reduction. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (6), 628–644.
- Maphanga, P. M. , & Henama, U. S. (2019). The tourism impact of Ebola in Africa: Lessons on crisis management. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure , 8 (3), 1–13.
- Mathieson, A. , & Wall, G. (1982). Tourism, economic, physical and social impacts . Longman.
- May, V. (1991). Tourism, environment and development—values, sustainability and stewardship. Tourism Management , 12 (2), 112–124.
- Mazzocchi, M. , & Montini, A. (2001). Earthquake effects on tourism in central Italy. Annals of Tourism Research , 28 (4), 1031–1046.
- Mbaiwa, J. E. (2005). The socio-cultural impacts of tourism development in the Okavango Delta, Botswana. Journal of Tourism and Cultural Change , 2 (3), 163–185.
- McKercher, B. (1993a). Some fundamental truths about tourism: Understanding tourism’s social and environmental impacts, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 1 (1), 6–16.
- McKercher, B. (1993b). The unrecognized threat to tourism: Can tourism survive “sustainability”? Tourism Management , 14 (2), 131–136.
- Meadows, D. H. , Meadows, D. L. , Randers, J. , & Behrens, W. W. (1972). The limits to growth . Universe Books.
- Miller, G. A. , & Ritchie, B. W. (2003). A farming crisis or a tourism disaster? An analysis of the foot and mouth disease in the UK. Current Issues in Tourism , 6 (2), 150–171.
- Milman, A. , & Pizam, A. (1988). Social impacts of tourism on central Florida. Annals of Tourism Research , 15 (2), 191–204.
- Monterrubio, J. C. (2010). Short-term economic impacts of influenza A (H1N1) and government reaction on the Mexican tourism industry: An analysis of the media. International Journal of Tourism Policy , 3 (1), 1–15.
- Narayan, P. K. (2004). Economic impact of tourism on Fiji’s economy: Empirical evidence from the computable general equilibrium model. Tourism Economics , 10 (4), 419–433.
- Nash, D. , & Butler, R. (1990). Towards sustainable tourism. Tourism Management , 11 (3), 263–264.
- Novelli, M. , Burgess, L. G. , Jones, A. , & Ritchie, B. W. (2018). “No Ebola . . . still doomed”—the Ebola-induced tourism crisis. Annals of Tourism Research , 70 , 76–87.
- Oh, C. (2005). The contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy. Tourism Management , 26 , 39–44.
- Oh, H. , Assaf, A. G. , & Baloglu, S. (2016). Motivations and goals of slow tourism. Journal of Travel Research , 55 (2), 205–219.
- Okumus, F. , & Karamustafa, K. (2005). Impact of an economic crisis evidence from Turkey. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (4), 942–961.
- Page, S. , Song, H. , & Wu, D. C. (2012). Assessing the impacts of the global economic crisis and swine flu on inbound tourism demand in the United Kingdom. Journal of Travel Research , 51 (2), 142–153.
- Papatheodorou, A. , Rosselló, J. , & Xiao, H. (2010). Global economic crisis and tourism: Consequences and perspectives. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (1), 39–45.
- Peeters, P. (2012). A clear path towards sustainable mass tourism? Rejoinder to the paper “Organic, incremental and induced paths to sustainable mass tourism convergence” by David B. Weaver. Tourism Management , 33 (5), 1038–1041.
- Pennington-Gray, L. , London, B. , Cahyanto, I. , & Klages, W. (2011). Expanding the tourism crisis management planning framework to include social media: Lessons from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill 2010. International Journal of Tourism Anthropology , 1 (3–4), 239–253.
- Pizam, A. , & Fleischer, A. (2002). Severity versus frequency of acts of terrorism: Which has a larger impact on tourism demand? Journal of Travel Research , 40 (3), 337–339.
- Pratt, S. (2015). The economic impact of tourism in SIDS. Annals of Tourism Research , 52 , 148–160.
- Prideaux, B. , Thompson, M. , & Pabel, A. (2020). Lessons from COVID-19 can prepare global tourism for the economic transformation needed to combat climate change. Tourism Geographies , 22 (3), 667–678.
- Qiu, R. T. , Park, J. , Li, S. , & Song, H. (2020). Social costs of tourism during the COVID-19 pandemic . Annals of Tourism Research , 84 , 102994.
- Rátz, T. (2000). Residents’ perceptions of the socio-cultural impacts of tourism at Lake Balaton, Hungary. Tourism and Sustainable Community Development , 7 , 36.
- Ribeiro, L. C. D. S. , Souza, K. B. D. , Domingues, E. P. , & Magalhães, A. S. (2020). Blue water turns black: Economic impact of oil spill on tourism and fishing in Brazilian Northeast . Current Issues in Tourism , 1–6.
- Richardson, R. B. , Fernandez, A. , Tschirley, D. , & Tembo, G. (2012). Wildlife conservation in Zambia: Impacts on rural household welfare. World Development , 40 (5), 1068–1081.
- Richardson, R. B. , & Loomis, J. B. (2004). Adaptive recreation planning and climate change: A contingent visitation approach. Ecological Economics , 50 (1), 83–99.
- Richardson, R. B. , & Witkowski, K. (2010). Economic vulnerability to climate change for tourism-dependent nations. Tourism Analysis , 15 (3), 315–330.
- Ritchie, B. W. , Crotts, J. C. , Zehrer, A. , & Volsky, G. T. (2013). Understanding the effects of a tourism crisis: The impact of the BP oil spill on regional lodging demand. Journal of Travel Research , 53 (1), 12–25.
- Rogerson, C. M. (2011). Urban tourism and regional tourists: Shopping in Johannesburg, South Africa. Tijdschrift voor economische en sociale geografie , 102 (3), 316–330.
- Rutty, M. , & Richardson, R. (2019). Tourism research in Cuba: Gaps in knowledge and challenges for sustainable tourism. Sustainability , 11 (12), 3340–3346.
- Ryan, C. , & Huyton, J. (2000). Who is interested in Aboriginal tourism in the Northern Territory, Australia? A cluster analysis. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 8 (1), 53–88.
- Salinas, E. , Mundet, L. , & Salinas, E. (2018). Historical evolution and spatial development of tourism in Cuba, 1919–2017: What is next? Tourism Planning & Development , 15 (3), 216–238.
- Sanchez, P. M. , & Adams, K. M. (2008). The Janus-faced character of tourism in Cuba. Annals of Tourism Research , 35 , 27–46.
- Scott, D. , Hall, C. M. , & Gössling, S. (2012). Tourism and climate change: Impacts, adaptation and mitigation . Routledge.
- Seetanah, B. (2011). Assessing the dynamic economic impact of tourism for island economies. Annals of Tourism Research , 38 (1), 291–308.
- Sharma, A. , & Nicolau, J. L. (2020). An open market valuation of the effects of COVID-19 on the travel and tourism industry . Annals of Tourism Research , 83 , 102990.
- Sharpley, R. (2000). Tourism and sustainable development: Exploring the theoretical divide. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 8 (1), 1–19.
- Sharpley, R. (2014). Host perceptions of tourism: A review of the research. Tourism Management , 42 , 37–49.
- Smeral, E. (2010). Impacts of the world recession and economic crisis on tourism: Forecasts and potential risks. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (1), 31–38.
- Southgate, C. R. (2006). Ecotourism in Kenya: The vulnerability of communities. Journal of Ecotourism , 5 (1–2), 80–96.
- Spenceley, A. (Ed.). (2012). Responsible tourism: Critical issues for conservation and development . Routledge.
- Stabler, M. (Ed.). (1997). Tourism and sustainability: Principles to practice . Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International.
- Stronza, A. (2007). The economic promise of ecotourism for conservation. Journal of Ecotourism , 6 (3), 210–230.
- Stylidis, D. , & Terzidou, M. (2014). Tourism and the economic crisis in Kavala, Greece. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 210–226.
- Suntikul, W. , Bauer, T. , & Song, H. (2009). Pro-poor tourism development in Viengxay, Laos: Current state and future prospects. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research , 14 (2), 153–168.
- Swarbrooke, J. (1999). Sustainable tourism management . CABI.
- Tovar, C. , & Lockwood, M. (2008). Social impacts of tourism: An Australian regional case study. International Journal of Tourism Research , 10 (4), 365–378.
- Tsartas, P. (1992). Socioeconomic impacts of tourism on two Greek isles. Annals of Tourism Research , 19 (3), 516–533.
- Turner, L. , & Ash, J. (1975). The golden hordes: International tourism and the pleasure periphery . Constable.
- United Nations . (2015). Transforming our world: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development . Division for Sustainable Development Goals.
- United Nations World Tourism Organization . (2002). Tourism and poverty alleviation . United Nations World Tourism Organization.
- United Nations World Tourism Organization . (2020). UNWTO world tourism barometer . United Nations World Tourism Organization.
- Viner, D. (2006). Tourism and its interactions with climate change. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 14 (4), 317–322.
- Vitousek, P. M. , Mooney, H. A. , Lubchenco, J. , & Melillo, J. M. (1997). Human domination of Earth’s ecosystems. Science , 277 (5325), 494–499.
- World Commission on Environment and Development . (1987). Our common future . Oxford University Press.
- Weaver, D. (2007). Towards sustainable mass tourism: Paradigm shift or paradigm nudge? Tourism Recreation Research , 32 (3), 65–69.
- Weaver, D. B. (2012). Organic, incremental and induced paths to sustainable mass tourism convergence. Tourism Management , 33 (5), 1030–1037.
- Weaver, D. B. (2014). Asymmetrical dialectics of sustainable tourism: Toward enlightened mass tourism. Journal of Travel Research , 53 (2), 131–140.
- Wheeller, B. (2007). Sustainable mass tourism: More smudge than nudge the canard continues. Tourism Recreation Research , 32 (3), 73–75.
- Whitford, M. , & Ruhanen, L. (2016). Indigenous tourism research, past and present: Where to from here? Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 24 (8–9), 1080–1099.
- Whyte, K. P. (2010). An environmental justice framework for indigenous tourism. Environmental Philosophy , 7 (2), 75–92.
- Wolff, K. , & Larsen, S. (2014). Can terrorism make us feel safer? Risk perceptions and worries before and after the July 22nd attacks. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 200–209.
- Yang, W. , Wang, D. , & Chen, G. (2011). Reconstruction strategies after the Wenchuan earthquake in Sichuan, China. Tourism Management , 32 (4), 949–956.
- Young, G. (1973). Tourism—blessing or blight? Penguin.
- Zapata, M. J. , Hall, C. M. , Lindo, P. , & Vanderschaeghe, M. (2011). Can community-based tourism contribute to development and poverty alleviation? Lessons from Nicaragua. Current Issues in Tourism , 14 (8), 725–749.
1. One megatonne (Mt) is equal to 1 million (10 6 ) metric tons.
2. One megajoule (MJ) is equal to 1 million (10 6 ) joules, or approximately the kinetic energy of a 1-megagram (tonne) vehicle moving at 161 km/h.
3. One gigatonne (Gt) is equal to 1 billion (10 9 ) metric tons.
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Environmental Science. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 12 June 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|162.248.224.4]
- 162.248.224.4
Character limit 500 /500

- Scholarly Community Encyclopedia
- Log in/Sign up

Video Upload Options
- MDPI and ACS Style
- Chicago Style
Investment in tourism infrastructure includes investment in components such as transport and communications infrastructure, the hotel and restaurant industry, and recreation facilities... Investment in tourism infrastructure development to make destinations and services increasingly attractive is considered a key measure in developing a country’s tourist destinations. It has a strong and positive impact on visitor attraction.
1. Introduction
2. the role of transport infrastructure and communications infrastructure, 3. the role of the hotel and restaurant industry, 4. the role of recreation facilities, 5. the influence of uncertain factors.
- Sinclair, M. Thea. 1998. Tourism and economic development: A survey. Journal of Development Studies 34: 1–51.
- Boers, Bas, and Stuart Cottrell. 2007. Sustainable tourism infrastructure planning: A GIS-supported approach. Tourism Geographies 9: 1–21.
- Dujmovic, Mauro, and Aljoša Vitasovic. 2014. Tourism product and destination positioning. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences 5: 570–79.
- Matias, Alvaro, Peter Nijkamp, and Paulo Neto. 2007. Advances in Modern Tourism Research: Economic Perspectives. Heidelberg: Physica-Verlag.
- Tribe, John. 2004. Knowing about tourism: Epistemological issues. In Qualitative Research in Tourism, 1st ed. Oxfordshire: Routledge, ISBN 9780203642986.
- Naudé, Willem A., and Andrea Saayman. 2005. Determinants of tourist arrivals in Africa: A panel data regression analysis. Tourism Economics 11: 365–91.
- Seetanah, Boopen, Thanika Devi Juwaheer, Matthew John Lamport, Sawkut Rojid, Raja Vinesh Sannassee, and Ushad Subadar Agathee. 2011. Does infrastructure matter in Tourism Development? University of Mauritius Research Journal 17: 89–108.
- Mamirkulova, Gulnara, Jianing Mi, Jaffar Abbas, Shahid Mahmood, Riaqa Mubeen, and Arash Ziapour. 2020. New Silk Road Infrastructure Opportunities in Developing Tourism Environment for Residents Better Quality of Life. Global Ecology and Conservation 20: e01194.
- Prideaux, Bruce. 2000. The role of the transport system in destination development. Tourism Management 21: 53–63.
- Jovanović, Sonja, and Ivana Ilić. 2016. Infrastructure as important determinant of tourism development in the countries of Southeast Europe. Ecoforum Journal 5: 288–94.
- Yu, Min. 2016. Research on the impact of infrastructure construction on tourism industry: Evidence from the “Wuhan-Guangzhou high speed rail”. Open Journal of Social Sciences 4: 126–31.
- Suleiman, Najat Nassor, and Masoud Mohamed Albiman. 2014. Dynamic relationship between tourism, trade, infrastructure and economic growth: Empirical evidence from Malaysia. Journal of African Studies and Development 6: 49–55.
- Mandić, Ante, Željko Mrnjavac, and Lana Kordić. 2018. Tourism infrastructure, recreational facilities and tourism development. Tourism and Hospitality Management 24: 41–62.
- Khadaroo, Ahmad Jameel, and Boopen Seetanah. 2007a. Research Note: Does Transport Infrastructure Matter in Overall Tourism Development? Evidence from a Sample of Island Economies. Tourism Economics 13: 675–87.
- Khadaroo, Ahmad Jameel, and Boopen Seetanah. 2007b. Transport infrastructure and tourism development. Annals of Tourism Research 34: 1021–32.
- Khadaroo, Jameel, and Boopen Seetanah. 2008. The role of transport infrastructure in international tourism development: A gravity model approach. Tourism Management 29: 831–40.
- Seetanah, Boopen, and Jameel Khadaroo. 2009. An Analysis of the Relationship between Transport Capital and Tourism Development in a Dynamic Framework. Tourism Economics 15: 785–802.
- Ouariti, Ouafae Zerouali, and El Mehdi Jebrane. 2020. The impact of transport infrastructure on tourism destination attractiveness: A case study of Marrakesh City, Morocco. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure 9: 1–18.
- Lim, Christine, Liang Zhu, and Tay TR Koo. 2019. Urban redevelopment and tourism growth: Relationship between tourism infrastructure and international visitor flows. International Journal of Tourism Research 21: 187–96.
- Selvanathan, Saroja, E. Antony Selvanathan, and Brinda Viswanathan. 2012. Causality Between Foreign Direct Investment and Tourism: Empirical Evidence from India. Tourism Analysis 17: 91–98.
- Khoshnevis Yazidi, Soheila, Khadijeh Homa Salehi, and Mahshid Soheilzad. 2015. The relationship between tourism, foreign direct investment and economic growth: Evidence from Iran. Current Issues in Tourism 20: 15–26.
- Samimi, Ahmad Jafiri, Somaye Sadeghi, and Soraya Sadeghi. 2017. The Relationship between Foreign Direct Investment and Tourism Development: Evidence from Developing Countries. Institutions and Economies 5: 59–68. Available online: https://ijie.um.edu.my/article/view/4884 (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- Vietnam National Administration of Tourism. 2020. Vietnam Tourism Annual Report 2019. Hanoi: Labor Publishing House, ISBN 978-604-301-333-7.
- Kaul, Raghu Nath. 1985. Dynamics of Tourism: A Trilogy. Transportation and Marketing. New York: Sterling Publishers, vol. 3.
- Pearce, Philip L., and Mao-Ying Wu. 2015. Soft infrastructure at tourism sites: Identifying key issues for Asian tourism from case studies. Tourism Recreation Research 40: 120–32.
- Raina, Abhinav kamal. 2005. Ecology, Wildlife and Tourism Development: Principes, Practices and Strategies. Delhi: Sarup & Sons.
- Ghaderi, Zahed, Pezhman Hatamifar, and Jalayer Khalilzadeh. 2018. Analysis of tourist satisfaction in tourism supply chain management. An International Journal of Tourism and Hospitality Research 29: 433–44.
- Tang, Rui. 2020. Does trade facilitation promote the efficiency of inbound tourism?—The empirical test based on Japan. International Journal of Tourism Research 23: 39–55.
- Tourism and Transport Forum. 2012. Tourism Infrastructure Policy and Priorities. Available online: http://www.ttf.org.au/ (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- UNWTO. 2007. A Practical Guide to Tourism Destination Management. Available online: https://www.e-unwto.org/doi/book/10.18111/9789284412433 (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- Sharpley, Richard. 2009. Tourism Development and the Environment: Beyond Sustainability? Earthscan. Available online: http://www.istta.ir/upload/file/sustainableTourismBook2.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- Jafari, Jafar, and Honggen Xiao. 2016. Encyclopaedia of Tourism. New York: Springer.
- Vanegas Sr, Manuel, and Robertico R. Croes. 2000. Evaluation of demand: US tourist to Aruba. Annals of Tourism Research 27: 946–63.
- Lin, Vera Shanshan, Anyu Liu, and Haiyan Song. 2015. Modelling and Forecasting Chinese Outbound Tourism: An Econometric Approach. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing 32: 34–49.
- Greene, William H. 2008. Econometric Analysis. Harlow: Pearson Prentice Hall.
- Song, Haiyan, and Gang Li. 2008. Tourism demand modelling and forecasting: A review of recent research. Tourism Management 29: 203–20.

- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Advisory Board

Sustainable tourism
Related sdgs, promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable ....

Description
Publications.
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States (SIDS) and coastal least developed countries (LDCs) (see also: The Potential of the Blue Economy report as well as the Community of Ocean Action on sustainable blue economy).
The World Tourism Organization defines sustainable tourism as “tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment and host communities".
Based on General assembly resolution 70/193, 2017 was declared as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development.
In the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development SDG target 8.9, aims to “by 2030, devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism is also highlighted in SDG target 12.b. which aims to “develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”.
Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “by 2030, increase the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries” as comprised in SDG target 14.7.
In the Rio+20 outcome document The Future We want, sustainable tourism is defined by paragraph 130 as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities by supporting their local economies and the human and natural environment as a whole. ” In paragraph 130, Member States also “call for enhanced support for sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building in developing countries in order to contribute to the achievement of sustainable development”.
In paragraph 131, Member States “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small- and medium-sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”. In this regard, Member States also “underline the importance of establishing, where necessary, appropriate guidelines and regulations in accordance with national priorities and legislation for promoting and supporting sustainable tourism”.
In 2002, the World Summit on Sustainable Development in Johannesburg called for the promotion of sustainable tourism development, including non-consumptive and eco-tourism, in Chapter IV, paragraph 43 of the Johannesburg Plan of Implementation.
At the Johannesburg Summit, the launch of the “Sustainable Tourism – Eliminating Poverty (ST-EP) initiative was announced. The initiative was inaugurated by the World Tourism Organization, in collaboration with UNCTAD, in order to develop sustainable tourism as a force for poverty alleviation.
The UN Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD) last reviewed the issue of sustainable tourism in 2001, when it was acting as the Preparatory Committee for the Johannesburg Summit.
The importance of sustainable tourism was also mentioned in Agenda 21.
For more information and documents on this topic, please visit this link
UNWTO Annual Report 2016
In December 2015, the United Nations General Assembly declared 2017 as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development. This is a unique opportunity to devote a year to activities that promote the transformational power of tourism to help us reach a better future. This important cele...
UNWTO Annual Report 2015
2015 was a landmark year for the global community. In September, the 70th Session of the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a universal agenda for planet and people. Among the 17 SDGs and 169 associated targets, tourism is explicitly featured in Goa...
Emerging Issues for Small Island Developing States
The 2012 UNEP Foresight Process on Emerging Global Environmental Issues primarily identified emerging environmental issues and possible solutions on a global scale and perspective. In 2013, UNEP carried out a similar exercise to identify priority emerging environmental issues that are of concern to ...
Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
This Agenda is a plan of action for people, planet and prosperity. It also seeks to strengthen universal peace in larger freedom, We recognize that eradicating poverty in all its forms and dimensions, including extreme poverty, is the greatest global challenge and an indispensable requirement for su...
Towards Measuring the Economic Value of Wildlife Watching Tourism in Africa
Set against the backdrop of the ongoing poaching crisis driven by a dramatic increase in the illicit trade in wildlife products, this briefing paper intends to support the ongoing efforts of African governments and the broader international community in the fight against poaching. Specifically, this...
Status and Trends of Caribbean Coral Reefs: 1970-2012
Previous Caribbean assessments lumped data together into a single database regardless of geographic location, reef environment, depth, oceanographic conditions, etc. Data from shallow lagoons and back reef environments were combined with data from deep fore-reef environments and atolls. Geographic c...
15 Years of the UNWTO World Tourism Network on Child Protection: A Compilation of Good Practices
Although it is widely recognized that tourism is not the cause of child exploitation, it can aggravate the problem when parts of its infrastructure, such as transport networks and accommodation facilities, are exploited by child abusers for nefarious ends. Additionally, many other factors that contr...
Natural Resources Forum: Special Issue Tourism
The journal considers papers on all topics relevant to sustainable development. In addition, it dedicates series, issues and special sections to specific themes that are relevant to the current discussions of the United Nations Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD)....
Thailand: Supporting Sustainable Development in Thailand: A Geographic Clusters Approach
Market forces and government policies, including the Tenth National Development Plan (2007-2012), are moving Thailand toward a more geographically specialized economy. There is a growing consensus that Thailand’s comparative and competitive advantages lie in amenity services that have high reliance...
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal (NRF)
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal, seeks to address gaps in current knowledge and stimulate relevant policy discussions, leading to the implementation of the sustainable development agenda and the achievement of the Sustainable...
Road Map on Building a Green Economy for Sustainable Development in Carriacou and Petite Martinique, Grenada
This publication is the product of an international study led by the Division for Sustainable Development (DSD) of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA) in cooperation with the Ministry of Carriacou and Petite Martinique Affairs and the Ministry of Environment, Foreig...
UN Ocean Conference 2025
Our Ocean, Our Future, Our Responsibility “The ocean is fundamental to life on our planet and to our future. The ocean is an important source of the planet’s biodiversity and plays a vital role in the climate system and water cycle. The ocean provides a range of ecosystem services, supplies us with
UN Ocean Conference 2022
The UN Ocean Conference 2022, co-hosted by the Governments of Kenya and Portugal, came at a critical time as the world was strengthening its efforts to mobilize, create and drive solutions to realize the 17 Sustainable Development Goals by 2030.
58th Session of the Commission for Social Development – CSocD58
22nd general assembly of the united nations world tourism organization, world tourism day 2017 official celebration.
This year’s World Tourism Day, held on 27 September, will be focused on Sustainable Tourism – a Tool for Development. Celebrated in line with the 2017 International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development, the Day will be dedicated to exploring the contribution of tourism to the Sustainable Deve
World Tourism Day 2016 Official Celebration
Accessible Tourism for all is about the creation of environments that can cater for the needs of all of us, whether we are traveling or staying at home. May that be due to a disability, even temporary, families with small children, or the ageing population, at some point in our lives, sooner or late
4th Global Summit on City Tourism
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and the Regional Council for Tourism of Marrakesh with support of the Government of Morroco are organizing the 4th Global Summit on City Tourism in Marrakesh, Morroco (9-10 December 2015). International experts in city tourism, representatives of city DMOs, of
2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and Ulsan Metropolitan City with support of the Government of the Republic of Korea are organizing the 2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference, in Ulsan, Republic of Korea (14 - 16 October 2015). Under the title “Paving the Way for a Bright Future for Mounta
21st General Assembly of the United Nations World Tourism Organization
Unwto regional conference enhancing brand africa - fostering tourism development.
Tourism is one of the Africa’s most promising sectors in terms of development, and represents a major opportunity to foster inclusive development, increase the region’s participation in the global economy and generate revenues for investment in other activities, including environmental preservation.
- January 2017 International Year of Tourism In the context of the universal 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the International Year aims to support a change in policies, business practices and consumer behavior towards a more sustainable tourism sector that can contribute to the SDGs.
- January 2015 Targets 8.9, 12 b,14.7 The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development commits Member States, through Sustainable Development Goal Target 8.9 to “devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism, as a driver for jobs creation and the promotion of local culture and products, is also highlighted in Sustainable Development Goal target 12.b. Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “increase [by 2030] the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries”, through Sustainable Development Goals Target 14.7.
- January 2012 Future We Want (Para 130-131) Sustainable tourism is defined as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities” as well as to “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small and medium sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”.
- January 2009 Roadmap for Recovery UNWTO announced in March 2009 the elaboration of a Roadmap for Recovery to be finalized by UNWTO’s General Assembly, based on seven action points. The Roadmap includes a set of 15 recommendations based on three interlocking action areas: resilience, stimulus, green economy aimed at supporting the tourism sector and the global economy.
- January 2008 Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria The Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria represent the minimum requirements any tourism business should observe in order to ensure preservation and respect of the natural and cultural resources and make sure at the same time that tourism potential as tool for poverty alleviation is enforced. The Criteria are 41 and distributed into four different categories: 1) sustainability management, 2) social and economic 3) cultural 4) environmental.
- January 2003 1st Int. Conf. on Climate Change and Tourism The conference was organized in order to gather tourism authorities, organizations, businesses and scientists to discuss on the impact that climate change can have on the tourist sector. The event took place from 9 till 11 April 2003 in Djerba, Tunisia.
- January 2003 WTO becomes a UN specialized body By Resolution 453 (XV), the Assembly agreed on the transformation of the WTO into a United Nations specialized body. Such transformation was later ratified by the United Nations General Assembly with the adoption of Resolution A/RES/58/232.
- January 2002 World Ecotourism Summit Held in May 2002, in Quebec City, Canada, the Summit represented the most important event in the framework of the International Year of Ecosystem. The Summit identified as main themes: ecotourism policy and planning, regulation of ecotourism, product development, marketing and promotion of ecotourism and monitoring costs and benefits of ecotourism.
- January 1985 Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code At the World Tourism Organization Sixth Assembly held in Sofia in 1985, the Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code were adopted, setting out the rights and duties of tourists and host populations and formulating policies and action for implementation by states and the tourist industry.
- January 1982 Acapulco Document Adopted in 1982, the Acapulco Document acknowledges the new dimension and role of tourism as a positive instrument towards the improvement of the quality of life for all peoples, as well as a significant force for peace and international understanding. The Acapulco Document also urges Member States to elaborate their policies, plans and programmes on tourism, in accordance with their national priorities and within the framework of the programme of work of the World Tourism Organization.

10 Economic impacts of tourism + explanations + examples
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
There are many economic impacts of tourism, and it is important that we understand what they are and how we can maximise the positive economic impacts of tourism and minimise the negative economic impacts of tourism.
Many argue that the tourism industry is the largest industry in the world. While its actual value is difficult to accurately determine, the economic potential of the tourism industry is indisputable. In fact, it is because of the positive economic impacts that most destinations embark on their tourism journey.
There is, however, more than meets the eye in most cases. The positive economic impacts of tourism are often not as significant as anticipated. Furthermore, tourism activity tends to bring with it unwanted and often unexpected negative economic impacts of tourism.
In this article I will discuss the importance of understanding the economic impacts of tourism and what the economic impacts of tourism might be. A range of positive and negative impacts are discussed and case studies are provided.
At the end of the post I have provided some additional reading on the economic impacts of tourism for tourism stakeholders , students and those who are interested in learning more.
Foreign exchange earnings
Contribution to government revenues, employment generation, contribution to local economies, development of the private sector, infrastructure cost, increase in prices, economic dependence of the local community on tourism, foreign ownership and management, economic impacts of tourism: conclusion, further reading on the economic impacts of tourism, the economic impacts of tourism: why governments invest.
Tourism brings with it huge economic potential for a destination that wishes to develop their tourism industry. Employment, currency exchange, imports and taxes are just a few of the ways that tourism can bring money into a destination.
In recent years, tourism numbers have increased globally at exponential rates, as shown in the World Tourism Organisation data below.
There are a number of reasons for this growth including improvements in technology, increases in disposable income, the growth of budget airlines and consumer desires to travel further, to new destinations and more often.

Here are a few facts about the economic importance of the tourism industry globally:
- The tourism economy represents 5 percent of world GDP
- Tourism contributes to 6-7 percent of total employment
- International tourism ranks fourth (after fuels, chemicals and automotive products) in global exports
- The tourism industry is valued at US$1trillion a year
- Tourism accounts for 30 percent of the world’s exports of commercial services
- Tourism accounts for 6 percent of total exports
- 1.4billion international tourists were recorded in 2018 (UNWTO)
- In over 150 countries, tourism is one of five top export earners
- Tourism is the main source of foreign exchange for one-third of developing countries and one-half of less economically developed countries (LEDCs)
There is a wealth of data about the economic value of tourism worldwide, with lots of handy graphs and charts in the United Nations Economic Impact Report .
In short, tourism is an example of an economic policy pursued by governments because:
- it brings in foreign exchange
- it generates employment
- it creates economic activity
Building and developing a tourism industry, however, involves a lot of initial and ongoing expenditure. The airport may need expanding. The beaches need to be regularly cleaned. New roads may need to be built. All of this takes money, which is usually a financial outlay required by the Government.
For governments, decisions have to be made regarding their expenditure. They must ask questions such as:
How much money should be spent on the provision of social services such as health, education, housing?
How much should be spent on building new tourism facilities or maintaining existing ones?
If financial investment and resources are provided for tourism, the issue of opportunity costs arises.
By opportunity costs, I mean that by spending money on tourism, money will not be spent somewhere else. Think of it like this- we all have a specified amount of money and when it runs out, it runs out. If we decide to buy the new shoes instead of going out for dinner than we might look great, but have nowhere to go…!
In tourism, this means that the money and resources that are used for one purpose may not then be available to be used for other purposes. Some destinations have been known to spend more money on tourism than on providing education or healthcare for the people who live there, for example.
This can be said for other stakeholders of the tourism industry too.
There are a number of independent, franchised or multinational investors who play an important role in the industry. They may own hotels, roads or land amongst other aspects that are important players in the overall success of the tourism industry. Many businesses and individuals will take out loans to help fund their initial ventures.
So investing in tourism is big business, that much is clear. What what are the positive and negative impacts of this?

Positive economic impacts of tourism
So what are the positive economic impacts of tourism? As I explained, most destinations choose to invest their time and money into tourism because of the positive economic impacts that they hope to achieve. There are a range of possible positive economic impacts. I will explain the most common economic benefits of tourism below.

One of the biggest benefits of tourism is the ability to make money through foreign exchange earnings.
Tourism expenditures generate income to the host economy. The money that the country makes from tourism can then be reinvested in the economy. How a destination manages their finances differs around the world; some destinations may spend this money on growing their tourism industry further, some may spend this money on public services such as education or healthcare and some destinations suffer extreme corruption so nobody really knows where the money ends up!
Some currencies are worth more than others and so some countries will target tourists from particular areas. I remember when I visited Goa and somebody helped to carry my luggage at the airport. I wanted to give them a small tip and handed them some Rupees only to be told that the young man would prefer a British Pound!
Currencies that are strong are generally the most desirable currencies. This typically includes the British Pound, American, Australian and Singapore Dollar and the Euro .
Tourism is one of the top five export categories for as many as 83% of countries and is a main source of foreign exchange earnings for at least 38% of countries.
Tourism can help to raise money that it then invested elsewhere by the Government. There are two main ways that this money is accumulated.
Direct contributions are generated by taxes on incomes from tourism employment and tourism businesses and things such as departure taxes.
Taxes differ considerably between destinations. I will never forget the first time that I was asked to pay a departure tax (I had never heard of it before then), because I was on my way home from a six month backpacking trip and I was almost out of money!
Japan is known for its high departure taxes. Here is a video by a travel blogger explaining how it works.
According to the World Tourism Organisation, the direct contribution of Travel & Tourism to GDP in 2018 was $2,750.7billion (3.2% of GDP). This is forecast to rise by 3.6% to $2,849.2billion in 2019.
Indirect contributions come from goods and services supplied to tourists which are not directly related to the tourism industry.
Take food, for example. A tourist may buy food at a local supermarket. The supermarket is not directly associated with tourism, but if it wasn’t for tourism its revenues wouldn’t be as high because the tourists would not shop there.
There is also the income that is generated through induced contributions . This accounts for money spent by the people who are employed in the tourism industry. This might include costs for housing, food, clothing and leisure Activities amongst others. This will all contribute to an increase in economic activity in the area where tourism is being developed.
The rapid expansion of international tourism has led to significant employment creation. From hotel managers to theme park operatives to cleaners, tourism creates many employment opportunities. Tourism supports some 7% of the world’s workers.
There are two types of employment in the tourism industry: direct and indirect.
Direct employment includes jobs that are immediately associated with the tourism industry. This might include hotel staff, restaurant staff or taxi drivers, to name a few.
Indirect employment includes jobs which are not technically based in the tourism industry, but are related to the tourism industry. Take a fisherman, for example. He does not have any contact of dealings with tourists. BUT he does sell his fish to the hotel which serves tourists. So he is indirectly employed by the tourism industry, because without the tourists he would not be supplying the fish to the hotel.
It is because of these indirect relationships, that it is very difficult to accurately measure the economic value of tourism.
It is also difficult to say how many people are employed, directly and indirectly, within the tourism industry.
Furthermore, many informal employments may not be officially accounted for. Think tut tut driver in Cambodia or street seller in The Gambia – these people are not likely to be registered by the state and therefore their earnings are not declared.
It is for this reason that some suggest that the actual economic benefits of tourism may be as high as double that of the recorded figures!
All of the money raised, whether through formal or informal means, has the potential to contribute to the local economy.
If sustainable tourism is demonstrated, money will be directed to areas that will benefit the local community most.
There may be pro-poor tourism initiatives (tourism which is intended to help the poor) or volunteer tourism projects.
The government may reinvest money towards public services and money earned by tourism employees will be spent in the local community. This is known as the multiplier effect.
The multiplier effect relates to spending in one place creating economic benefits elsewhere. Tourism can do wonders for a destination in areas that may seem to be completely unrelated to tourism, but which are actually connected somewhere in the economic system.

Let me give you an example.
A tourist buys an omelet and a glass of orange juice for their breakfast in the restaurant of their hotel. This simple transaction actually has a significant multiplier effect. Below I have listed just a few of the effects of the tourist buying this breakfast.
The waiter is paid a salary- he spends his salary on schooling for his kids- the school has more money to spend on equipment- the standard of education at the school increases- the kids graduate with better qualifications- as adults, they secure better paying jobs- they can then spend more money in the local community…
The restaurant purchases eggs from a local farmer- the farmer uses that money to buy some more chickens- the chicken breeder uses that money to improve the standards of their cages, meaning that the chickens are healthier, live longer and lay more eggs- they can now sell the chickens for a higher price- the increased money made means that they can hire an extra employee- the employee spends his income in the local community…
The restaurant purchase the oranges from a local supplier- the supplier uses this money to pay the lorry driver who transports the oranges- the lorry driver pays road tax- the Government uses said road tax income to fix pot holes in the road- the improved roads make journeys quicker for the local community…
So as you can see, that breakfast that the tourist probably gave not another thought to after taking his last mouthful of egg, actually had the potential to have a significant economic impact on the local community!

The private sector has continuously developed within the tourism industry and owning a business within the private sector can be extremely profitable; making this a positive economic impact of tourism.
Whilst many businesses that you will come across are multinational, internationally-owned organisations (which contribute towards economic leakage ).
Many are also owned by the local community. This is the case even more so in recent years due to the rise in the popularity of the sharing economy and the likes of Airbnb and Uber, which encourage the growth of businesses within the local community.
Every destination is different with regards to how they manage the development of the private sector in tourism.
Some destinations do not allow multinational organisations for fear that they will steal business and thus profits away from local people. I have seen this myself in Italy when I was in search of a Starbucks mug for my collection , only to find that Italy has not allowed the company to open up any shops in their country because they are very proud of their individually-owned coffee shops.
Negative economic impacts of tourism
Unfortunately, the tourism industry doesn’t always smell of roses and there are also several negative economic impacts of tourism.
There are many hidden costs to tourism, which can have unfavourable economic effects on the host community.
Whilst such negative impacts are well documented in the tourism literature, many tourists are unaware of the negative effects that their actions may cause. Likewise, many destinations who are inexperienced or uneducated in tourism and economics may not be aware of the problems that can occur if tourism is not management properly.
Below, I will outline the most prominent negative economic impacts of tourism.

Economic leakage in tourism is one of the major negative economic impacts of tourism. This is when money spent does not remain in the country but ends up elsewhere; therefore limiting the economic benefits of tourism to the host destination.
The biggest culprits of economic leakage are multinational and internationally-owned corporations, all-inclusive holidays and enclave tourism.
I have written a detailed post on the concept of economic leakage in tourism, you can take a look here- Economic leakage in tourism explained .

Another one of the negative economic impacts of tourism is the cost of infrastructure. Tourism development can cost the local government and local taxpayers a great deal of money.
Tourism may require the government to improve the airport, roads and other infrastructure, which are costly. The development of the third runway at London Heathrow, for example, is estimated to cost £18.6billion!
Money spent in these areas may reduce government money needed in other critical areas such as education and health, as I outlined previously in my discussion on opportunity costs.

One of the most obvious economic impacts of tourism is that the very presence of tourism increases prices in the local area.
Have you ever tried to buy a can of Coke in the supermarket in your hotel? Or the bar on the beachfront? Walk five minutes down the road and try buying that same can in a local shop- I promise you, in the majority of cases you will see a BIG difference In cost! (For more travel hacks like this subscribe to my newsletter – I send out lots of tips, tricks and coupons!)
Increasing demand for basic services and goods from tourists will often cause price hikes that negatively impact local residents whose income does not increase proportionately.
Tourism development and the related rise in real estate demand may dramatically increase building costs and land values. This often means that local people will be forced to move away from the area that tourism is located, known as gentrification.
Taking measures to ensure that tourism is managed sustainably can help to mitigate this negative economic impact of tourism. Techniques such as employing only local people, limiting the number of all-inclusive hotels and encouraging the purchasing of local products and services can all help.
Another one of the major economic impacts of tourism is dependency. Many countries run the risk of becoming too dependant on tourism. The country sees $ signs and places all of its efforts in tourism. Whilst this can work out well, it is also risky business!
If for some reason tourism begins to lack in a destination, then it is important that the destination has alternative methods of making money. If they don’t, then they run the risk of being in severe financial difficulty if there is a decline in their tourism industry.
In The Gambia, for instance, 30% of the workforce depends directly or indirectly on tourism. In small island developing states, percentages can range from 83% in the Maldives to 21% in the Seychelles and 34% in Jamaica.
There are a number of reasons that tourism could decline in a destination.
The Gambia has experienced this just recently when they had a double hit on their tourism industry. The first hit was due to political instability in the country, which has put many tourists off visiting, and the second was when airline Monarch went bust, as they had a large market share in flights to The Gambia.
Other issues that could result in a decline in tourism includes economic recession, natural disasters and changing tourism patterns. Over-reliance on tourism carries risks to tourism-dependent economies, which can have devastating consequences.

The last of the negative economic impacts of tourism that I will discuss is that of foreign ownership and management.
As enterprise in the developed world becomes increasingly expensive, many businesses choose to go abroad. Whilst this may save the business money, it is usually not so beneficial for the economy of the host destination.
Foreign companies often bring with them their own staff, thus limiting the economic impact of increased employment. They will usually also export a large proportion of their income to the country where they are based. You can read more on this in my post on economic leakage in tourism .
As I have demonstrated in this post, tourism is a significant economic driver the world over. However, not all economic impacts of tourism are positive. In order to ensure that the economic impacts of tourism are maximised, careful management of the tourism industry is required.
If you enjoyed this article on the economic impacts of tourism I am sure that you will love these too-
- Environmental impacts of tourism
- The 3 types of travel and tourism organisations
- 150 types of tourism! The ultimate tourism glossary
- 50 fascinating facts about the travel and tourism industry
- 23 Types of Water Transport To Keep You Afloat
Liked this article? Click to share!
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, the impacts of tourism development on income inequality: how does tourism capital investment contribute to income distribution tourism agenda 2030.
Tourism Review
ISSN : 1660-5373
Article publication date: 12 January 2023
Issue publication date: 7 April 2023
This study aims to analyze tourism development's (TOD) role in demoting income inequality in South Asia from 1996 to 2020. To this end, this study explored the connection between TOD, tourism investment, economic growth (GDP), trade globalization (TGL) and income inequality.
Design/methodology/approach
This study used various techniques, including cross-sectional dependence, unit root, cointegration techniques, long-term elasticity estimators and short-term causality between the study variables. This study adopted Driscoll–Kraay standard errors and Dumitrescu Hurlin panel causality estimations.
This study’s results reveal that tourism has an inverted U-shaped association with income inequality in the long run, which supports the Kuznets Curve hypothesis. In contrast, capital investment in tourism (CIT) has a significant negative association with income inequality. At the same time, growth and TGL positively and significantly affect income inequality. Moreover, TOD has a bidirectional feedback causality of income inequality. These results also support tourism's “price effect” on income inequality. Hence, this study provides more practical implications regarding policymaking in tourism and income inequality in developing economies to target Agenda 2030.
Originality/value
This study is unique by considering the cross-sectional dependence in estimating the model that has been ignored in previous studies and provides new insights into the existing literature by investigating how TOD and CIT contribute to income inequality concentrating on the understudied South Asian economies from 1996 to 2020. As a result, this study has more practical implications for policymaking in the tourism industry and income inequality in emerging economies.
本研究分析了 1996 年至 2020 年旅游业发展在缓解南亚收入不平等方面的作用。为此, 该研究探讨了旅游业发展、旅游投资、经济增长、贸易全球化和收入不平等之间的联系。
本研究使用了多种技术, 包括横截面相关性 (CSD),单位根、协整技术、长期弹性估计量以及研究变量之间的短期因果关系。本研究采用 Driscoll-Kraay 标准误差和 Dumitrescu Hurlin 面板因果关系估计。
目前的研究结果表明, 从长远来看, 旅游业与收入不平等呈倒U型关联, 这支持了库兹涅茨曲线假说。相比之下, 旅游业的资本投资与收入不平等呈显著负相关。与此同时, 增长和贸易全球化对收入不平等产生了积极和显著的影响。此外, 旅游发展对收入不平等具有双向反馈因果关系。这些结果也支持旅游业对收入不平等的“价格效应”。因此, 本研究为发展中经济体的旅游业和收入不平等政策制定提供了更多实际意义, 以实现 2030 年议程。
本研究的独特之处在于考虑了估计模型的横截面相关性, 这在以前的研究中被忽略。重点关注1996年至2020年未被充分研究的南亚经济体, 通过调查旅游业发展和旅游业的资本投资如何导致收入不平等, 从而为现有文献提供新的见解。因此, 本研究对旅游业的政策制定和新兴经济体的收入不平等具有更实际的意义。
Este estudio analiza el papel del desarrollo turístico en la disminución de la desigualdad de ingresos en el sur de Asia entre 1996 y 2020. Para ello, el estudio explora la conexión entre el desarrollo del turismo, la inversión turística, el crecimiento económico, la globalización del comercio y la desigualdad de ingresos.
Diseño/metodología/enfoque
Este estudio utilizó diversas técnicas, como la dependencia transversal (DSC), la raíz unitaria, las técnicas de cointegración, los estimadores de la elasticidad a largo plazo y la causalidad a corto plazo entre las variables del estudio. Este estudio adoptó los errores estándar de Driscoll-Kraay y las estimaciones de causalidad de panel de Dumitrescu Hurlin.
Conclusiones
Los resultados del presente estudio revelan que el turismo tiene una asociación en forma de U invertida con la desigualdad de ingresos a largo plazo, lo que apoya la hipótesis de la curva de Kuznets. En cambio, la inversión de capital en turismo tiene una asociación negativa significativa con la desigualdad de ingresos. Al mismo tiempo, el crecimiento y la globalización del comercio afectan positiva y significativamente a la desigualdad de ingresos. Además, el desarrollo del turismo tiene una causalidad de retroalimentación bidireccional de la desigualdad de ingresos. Estos resultados también apoyan el “efecto precio” del turismo sobre la desigualdad de ingresos. Por lo tanto, este estudio proporciona más implicaciones prácticas con respecto a la formulación de políticas en materia de turismo y desigualdad de ingresos en las economías en desarrollo para apuntar a la Agenda 2030.
Originalidad/valor
El presente estudio es único al considerar la dependencia transversal en la estimación del modelo que ha sido ignorada en estudios anteriores y aporta nuevas perspectivas a la literatura existente al investigar cómo el desarrollo del turismo y la inversión de capital en turismo contribuyen a la desigualdad de ingresos. Este estudio se centra en las economías del sur de Asia que han sido poco estudiadas y se extiende desde 1996 hasta 2020. Como resultado, este trabajo tiene más implicaciones prácticas para la formulación de políticas en la industria turística y la desigualdad de ingresos en las economías emergentes.
- Tourism development
- Income inequality
- Tourism investment
- Economic growth
- Desarrollo turístico
- Desigualdad de ingresos
- Inversión turística
- Crecimiento económico
- Sur de Asia
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the National High-level Foreign Expert Project (No. QN2022125003L) and Tianjin Development Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship, partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (71971124, 71932005); and the One Hundred Talents Program of Nankai University (63213023).
Kumail, T. , Sadiq, M. , Ali, W. and Sadiq, F. (2023), "The impacts of tourism development on income inequality: how does tourism capital investment contribute to income distribution? Tourism Agenda 2030", Tourism Review , Vol. 78 No. 2, pp. 630-645. https://doi.org/10.1108/TR-08-2022-0378
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2022, Emerald Publishing Limited
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
Advertisement
Economic growth, foreign investment, tourism, and electricity production as determinants of environmental quality: empirical evidence from GCC region
- Research Article
- Published: 28 January 2023
- Volume 30 , pages 45768–45780, ( 2023 )
Cite this article

- Umar Farooq ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5772-5243 1 ,
- Mosab I. Tabash ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3688-7224 2 ,
- Suhaib Anagreh ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1751-7674 3 ,
- Mahmoud Al-Rdaydeh 4 &
- Samar Habib 5
658 Accesses
11 Citations
Explore all metrics
Each economic factor generates both positive and negative externalities regarding environmental quality. Owing to this, the current study aims to explore the impacts of various economic variables on the environmental quality of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) region. By sampling the 24 years (1996–2019) financial statistics of six GCC region countries, we investigate the impact of economic growth, foreign investment, trade volume, tourism investment and revenue, and electricity production on CO 2 emissions. The empirical analysis is based upon dynamic least square and fully modified ordinary least square model due to the existence of cointegration. Following the results, economic growth, foreign investment, tourism investment, electricity production, and population density have a positive impact, while trade volume and banking development have a negative impact on the volume of CO 2 emissions. The results support the pollution haven hypothesis in the GCC region and have many policies for environmental economists regarding the protection of the natural environment in the long run. In parallel to economic growth, the policy officials from the GCC region should focus on environmental sustainability. They should exert more effort for developing sustainable economic growth policies. The current analysis offers new insights regarding the dynamic role of various economic factors in establishing the CO 2 emission volume in the GCC region.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price excludes VAT (USA) Tax calculation will be finalised during checkout.
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

Similar content being viewed by others

Impact of green finance on economic development and environmental quality: a study based on provincial panel data from China

The relationship between CO2 emissions, economic growth, available energy, and employment in SEE countries
Evaluating the impact of GDP per capita on environmental degradation for G-20 economies: Does N-shaped environmental Kuznets curve exist?
Data availability.
Data that were used in the formal analysis do not require any formal consent and can be provided on demand..
Acaravci A, Ozturk I (2010) On the relationship between energy consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth in Europe. Energy 35(12). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2010.07.009
Acheampong AO (2019) Modelling for insight: does financial development improve environmental quality? Energy Econ 83(September):156–179
Google Scholar
Akadiri SS, Lasisi TT, Uzuner G, Akadiri AC (2018) Examining the causal impacts of tourism, globalization, economic growth and carbon emissions in tourism island territories: bootstrap panel Granger causality analysis. Curr Issue Tour: 1–15
AlKhars MA, Alwahaishi S, Fallatah MR, Kayal A (2022) A literature review of the environmental Kuznets curve in GCC for 2010–2020. Environ Sustain Indic 14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indic.2022.100181
Aller C, Ductor L, Grechyna D (2021) Robust determinants of CO2 emissions. Energy Econ 96(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105154
Al-mulali U, Tang CF (2013) Investigating the validity of pollution haven hypothesis in the gulf cooperation council (GCC) countries. Energy Policy 60:813–819
Alola AA, Bekun FV, Sarkodie SA (2019) Dynamic impact of trade policy, economic growth, fertility rate, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on ecological footprint in Europe. Sci Total Environ 685(1):702–709
CAS Google Scholar
Alsamara M, Mrabet Z, Saleh AS, Anwar S (2018) The environmental Kuznets curve relationship: a case study of the Gulf Cooperation Council region. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(33):33183–33195
Ameer A, Munir K (2020) Nonlinear effect of FDI, economic growth, and industrialization on environmental quality: evidence from Pakistan. Manag Environ Qual 31(1):223–234
Ansari MA, Ahmad MR, Siddique S, Mansoor K (2020a) An environment Kuznets curve for ecological footprint: evidence from GCC countries. Carbon Manage 11(4):355–368
Ansari MA, Haider S, Khan NA (2020b) Does trade openness affects global carbon dioxide emissions: evidence from the top CO2 emitters. Manag Environ Qual 31(1):32–53
Awodumi OB, Adewuyi AO (2020) The role of non-renewable energy consumption in economic growth and carbon emission: evidence from oil producing economies in Africa. Energy Strat Rev 27(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2019.100434
Azam M, Alam MM, Hafeez MH (2018) Effect of tourism on environmental pollution: further evidence from Malaysia, Singapore and Thailand. J Clean Prod 190(1):330–338
Babu TA, Kaechele H (2015) Dichotomy in carbon dioxide emissions–the case of India. Clim Dev 7(2):165–174
Bakay MS, Ağbulut Ü (2021) Electricity production based forecasting of greenhouse gas emissions in Turkey with deep learning, support vector machine and artificial neural network algorithms. J Clean Prod 285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125324
Bank TW (2022) World development indicators 2022, DC Washington: World Bank
Bélaïd F, Youssef M (2017) Environmental degradation, renewable and non-renewable electricity consumption, and economic growth: assessing the evidence from Algeria. Energy Policy 102(1):277–287
Charfeddine L, Kahia M (2019) Impact of renewable energy consumption and financial development on CO2 emissions and economic growth in the MENA region: a panel vector autoregressive (PVAR) analysis. Renew Energy 139(August):198–213
Charfeddine L, Al-Malk AY, Korbi K (2018) Is it possible to improve environmental quality without reducing economic growth: evidence from the Qatar economy. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 82(1):25–39
Chen L, Thapa B, Yan W (2018) The relationship between tourism, carbon dioxide emissions, and economic growth in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sustainability 10(1):1–20
Cole MA, Elliott RJR, Fredriksson PG (2006) Endogenous pollution havens: does FDI influence environmental regulations? Scand J Econ 108(1):157–178
Danish, Zhang B, Wang B, Wang Z (2017) Role of renewable energy and non-renewable energy consumption on EKC: evidence from Pakistan. J Clean Prod 156(855):864
Dinda S (2009) Climate change and human insecurity. Int J Glob Environ 9(1):103–109
Dogan E, Seker F, Bulbul S (2015) Investigating the impacts of energy consumption, real GDP, tourism and trade on CO2 emissions by accounting for cross-sectional dependence: a panel study of OECD countries. Curr Issue Tour 20(16):1–19
Essandoh OK, Islam M, Kakinaka M (2020) Linking international trade and foreign direct investment to CO2 emissions: any differences between developed and developing countries? Sci Total Environ 712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136437
Eyuboglu K, Uzar U (2020) The impact of tourism on CO2 emission in Turkey. Curr Issue Tour 23(13):1631–1645
Farooq U (2022) Foreign direct investment, foreign aid, and CO2 emissions in Asian economies: does governance matter? Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(5):7532–7547
Gao C et al (2021) Decoupling of provincial energy-related CO2 emissions from economic growth in China and its convergence from 1995 to 2017. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126627
Grimes P, Kentor J (2003) Exporting the greenhouse: foreign capital penetration and CO? Emissions 1980 1996. J World-Syst Res 9(1):261–275
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic growth and the environment. Q J Econ 110(2):353–377
Hayat F, Pirzada MDS, Khan AA (2018) The validation of Granger causality through formulation and use of finance-growth-energy indexes. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81(1):1859–1867
He J, Liu H, Salvo A (2019) Severe air pollution and labor productivity: evidence from industrial towns in China. Am Econ J: Appl Econ 11(1):173–201
Hossain MS (2011) Panel estimation for CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic growth, trade openness and urbanization of newly industrialized countries. Energy Policy 39(11):6991–6999
Huang Y et al (2022) The impacts of FDI inflows on carbon emissions: economic development and regulatory quality as moderators. Front Energy Res 9(1):1–11
IPCC (2015) Intergovernmental panel on climate change: the fifth assessment report. Gevena: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/syr/
Jalil A, Feridun M (2011) The impact of growth, energy and financial development on the environment in China: a cointegration analysis. Energy Econ 33(2). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2010.10.003
Jayanthakumaran K, Verma R, Liu Y (2012) CO2 emissions, energy consumption, trade and income: a comparative analysis of China and India. Energy Policy 42(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2011.12.010
Jensen AL (1996) Beverton and Holt life history invariants result from optimal trade off of reproduction and surviva. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 53(1):820–822
Jianguo D, Ali K, Alnori F, Ullah S (2022) The nexus of financial development, technological innovation, institutional quality, and environmental quality: evidence from OECD economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19763-1
Johansen S (1988) Statistical analysis of co-integrating vectors. J Econ Dyn Control 12(2–3):231–254
Jorgenson AK, Clark B (2010) Assessing the temporal stability of the population/environment relationship in comparative perspective: a cross-national panel study of carbon dioxide emissions, 1960–2005. Popul Environ 32(1):27–41
Koçak E, Ulucak R, Ulucak ZŞ (2020) The impact of tourism developments on CO2 emissions: an advanced panel data estimation. Tour Manag Perspect 33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2019.100611
Lamb WF et al (2014) Transitions in pathways of human development and carbon emissions. Environ Res Lett 9(1):1–10
Liddle B (2015) What are the carbon emissions elasticities for income and population? Bridging STIRPAT and EKC via robust heterogeneous panel estimates. Glob Environ Chang 31(1):62–73
Luo Y, Salman M, Lu Z (2021) Heterogeneous impacts of environmental regulations and foreign direct investment on green innovation across different regions in China. Sci Total Environ 759:1–11
Lv Z, Li S (2021) How financial development affects CO2 emissions: a spatial econometric analysis. J Environ Manag 277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111397
Mahadevan R, Sun Y (2020) Effects of foreign direct investment on carbon emissions: evidence from China and its belt and road countries. J Environ Manag 276(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111321
Mahmood H (2022) The spatial analyses of consumption-based CO2 emissions, exports, imports, and FDI nexus in GCC countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19303-x
Mikayilov JI, Galeotti M, Hasanov FJ (2018) The impact of economic growth on CO2 emissions in Azerbaijan. J Clean Prod 197(1):1558–1572
Odhiambo NM (2016) Coal consumption and economic growth in South Africa. Energy Environ 27(1):215–226
Ozturk I (2016) The relationships among tourism development, energy demand, and growth factors in developed and developing countries. Int J Sust Dev World 23(2):122–131
Ozturk I, Acaravci A (2013) The long-run and causal analysis of energy, growth, openness and financial development on carbon emissions in Turkey. Energy Econ 36(1):262–267
Ozturk I, Ullah S (2022) Does digital financial inclusion matter for economic growth and environmental sustainability in OBRI economies? An empirical analysis. Resour Conserv Recycl 185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106489
Ozturk I, Aslan A, Altinoz B (2021) Investigating the nexus between CO2 emissions, economic growth, energy consumption and pilgrimage tourism in Saudi Arabia. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja: 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2021.1985577
Panayotou T (1993) Empirical tests and policy analysis of environmental degradation at different stages of economic development. International Labour Organization, Geneva. p 1–42
Paramati SR, Alam MS, Lau CKM (2018) The effect of tourism investment on tourism development and CO2 emissions: empirical evidence from the EU nations. J Sustain Tour 26(9):1587–1607
Pesaran HM (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Economet 22(2):265–312
Phillips PC, Hansen BE (1990) Statistical inference in instrumental variable regression with I(1) processes. Rev Econ Stud 57(1):99–125
Rahman MM, Alam K (2021) Clean energy, population density, urbanization and environmental pollution nexus: evidence from Bangladesh. Renew Energy 172(July):1063–1072
Ravinthirakumaran K, Ravinthirakumaran N (2022) Examining the relationship between tourism and CO2 emissions: evidence from APEC region. Anatolia. https://doi.org/10.1080/13032917.2021.2021430 .
Raza SA, Sharif A, Wong WK, Karim MZA (2017) Tourism development and environmental degradation in the United States: evidence from wavelet-based analysis. Curr Issue Tour 20(16):1768–1790
Richmond AK, Kaufmann RK (2006) Is there a turning point in the relationship between income and energy use and/or carbon emissions? Ecol Econ 56(1):176–189
Sadorsky P (2010) The impact of financial development on energy consumption in emerging economies. Energy Policy 38(1):2528–2535
Sbai R, Shahbaz M, Hamdi H (2014) A contribution of foreign direct investment, clean energy, trade openness, carbon emissions and economic growth to energy demand in UAE. Econ Model 36(C):191–197
Shafiei S, Salim RA (2014) Non-renewable and renewable energy consumption and CO2 emissions in OECD countries: a comparative analysis. Energy Policy 66(March):547–556
Shahbaz M, Hye QMA, Tiwari AK, Leitão NC (2013a) Economic growth, energy consumption, financial development, international trade and CO2 emissions in Indonesia. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 25(September):109–121
Shahbaz M, Tiwari AK, Nasir M (2013b) The effects of financial development, economic growth, coal consumption and trade openness on CO2 emissions in South Africa. Energy Policy 61(1):1452–1459
Shakouri B, Yazdi SK, Ghorchebigi E (2017) Does tourism development promote CO2 emissions? Anatolia 28(3):444–452
Shi A (2003) The impact of population pressure on global carbon dioxide emissions, 1975–1996: evidence from pooled cross-country data. Ecol Econ 44(1):29–42
Shi H et al (2019) Global difference in the relationships between tourism, economic growth, CO2 emissions, and primary energy consumption. Curr Issue Tour 23(9):1–16
Tamazian A, Rao BB (2010) Do economic, financial and institutional developments matter for environmental degradation? Evidence from transitional economies. Energy Econ 32(1):137–145
United-Nations-General-Assembly-(UNGA) (2015) Sustainable development goals, New York
Zarco-Periñán PJ, Zarco-Soto IM, Zarco-Soto EJ (2021) Influence of population density on CO2 emissions eliminating the influence of climate. Atmosphere 12(19): https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091193
Zmami M, Ben-Salha O (2020) An empirical analysis of the determinants of CO2 emissions in GCC countries. Int J Sust Dev World 27(5):469–480
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Economics and Finance, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, People’s Republic of China
Umar Farooq
College of Business, Al Ain University, Al Ain, United Arab Emirates
Mosab I. Tabash
Higher Colleges of Technology, Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Suhaib Anagreh
Oman College of Management and Technology, Muscat, Oman
Mahmoud Al-Rdaydeh
American University in the Emirates, Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Samar Habib
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Umar Farooq: conceptualization, data curation, and writing—original draft preparation
Mosab I. Tabash: supervision, reviewing and editing, and methodology
Suhaib Anagreh: methodology, data handling, language, and spelling check
Mahmoud Al-Rdaydeh: literature review, proofreading, and discussion on results
Samar Habib: conclusion, policy implications, and comments handling
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Umar Farooq .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval.
I, Umar Farooq, hereby confirmed that the paper is solely submitted to this journal and not under the publication process in any other journal.
Consent to participate
In this research, no human being/animals is/are involved in direct research or observation. The analysis is purely based upon secondary data available on different data sites.
Consent for publication
We hereby grant the consent and acknowledge that the paper should be sent for peer review or any other publication process required by the journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Farooq, U., Tabash, M.I., Anagreh, S. et al. Economic growth, foreign investment, tourism, and electricity production as determinants of environmental quality: empirical evidence from GCC region. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30 , 45768–45780 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25545-0
Download citation
Received : 10 June 2022
Accepted : 20 January 2023
Published : 28 January 2023
Issue Date : April 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25545-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- CO 2 emissions
- Economic growth
- Pollution haven hypothesis
JEL Classification
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Although, the investment cycle remained strong throughout 2019, with tourism mobilizing $61.8bn in global FDI, which, in turn, created more than 135,000 jobs. The trend appeared particularly consistent in Latin America and the Caribbean, where FDI reached new record levels. For example it created more than 56.000 jobs in Mexico from 2015 - 2019.
Tourism has become the world's third-largest export industry after fuels and chemicals, and ahead of food and automotive products. From last few years, there has been a great surge in international tourism, culminates to 7% share of World's total exports in 2016. To this end, the study attempts to examine the relationship between inbound tourism, financial development and economic growth ...
into a recovery in tourism investment yet. As the data in this report, produced in partnership with the UN World Tourism Organization, suggest, foreign direct investment (FDI) into the tourism industry fell further in 2021, and remains on a downward trajectory in the first half of 2022.
This is the first volume to examine and shed significant light on the issues, challenges and prospects presented by foreign direct investment (FDI) in tourism - a topic of increasing relevance in light of the COVID-19 pandemic and economic consequences. This book addresses the need to examine the TFDI phenomenon considering resilient tourism ...
Investment in tourism infrastructure development to make destinations and services increasingly attractive is considered a key measure in developing a country's tourist destinations. This paper investigates the impact of investment in tourism infrastructure components on international visitor attraction using data from Vietnam for the period 1995-2019. The results of analyzing panel data ...
Balancing tourism industry development with carbon emission reduction is a major challenge for the tourism industry. ... considering the negative impact of foreign direct investment on carbon ...
overview of positive and negative impacts of tourism activities, and an introduction to FDI in the sector. Chapter 2 outlines the process of developing an investment promotion strategy for the tourism sector, while chapter 3 presents steps to be taken in the process of investor targeting. Chapter 4 contains the conclusions.
Abstract. This is the first volume to examine and shed significant light on the issues, challenges and prospects presented by foreign direct investment (FDI) in tourism - a topic of increasing ...
Tourism is becoming an important industry in global economy due to its contribution in the growth process of a country. Tourism helps to boost the economy by increasing its exports, creating employment opportunities, improving infrastructure, and increasing foreign exchange income of the country (Satrovic & Muslija, 2018).Specialization in tourism is a stimulator for economic development and ...
The first article highlights the importance of encounters in tourism and documents the threats of overtourism through mass tourism such as cruises. It offers solutions for managing host-tourist encounters more responsibly. The second article calls attention to the ways the tourism industry can give back.
The study's objective is to examine the impact of clean energy, foreign direct investment (FDI), education, and information and communication technology (ICT) on tourism development in Malaysia ...
The SARS coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic has had a protracted negative effect on all areas of economic activities across the world. Travel restrictions and closure of international borders severely impacted global travel and the tourism industry, with varying negative effects across countries (World Tourism Organization (WTO), 2020). Other ...
Today, international tourism is one of the most affected sectors of the economy due to the global COVID-19 pandemic. The main purpose of this article is to analyze current trends and identify prospects for the international tourism development in the context of increasing globalization risks in the world, using the example of Ukraine's integration into the global tourism industry, as Ukraine ...
Tourism investments can benefit local people . Tourism is one of the only industries in the world where the 'good' or 'service' is consumed at the site of production. For this reason, local people are both at an advantage to reap the benefits associated with the sector, but also at risk from exclusion or even the negative impacts it can ...
Moreover, the increase in capital investment for domestic tourism helps the industry to change the energy consumption patterns and limit the carbon emission of this sector. On the other side, to reduce the impact of globalization, policymakers need to consider both the economic and social aspects that enhance environmental issues.
The empirical research investigated the relationship between tourism development and environmental suitability to propose a framework for sustainable ecotourism. The framework suggested a balance between business and environmental interests in maintaining an ecological system with the moderating help of government support and policy interventions. The study population encompasses tourism ...
Background. Tourism is one of the world's largest industries, and it has linkages with many of the prime sectors of the global economy (Fennell, 2020).As a global economic sector, tourism represents one of the largest generators of wealth, and it is an important agent of economic growth and development (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018).Tourism is a critical industry in many local and national ...
Tourism plays a vital role in the economic growth of many countries, contributing to the development of related services and infrastructure. Thus, the development of tourism affects the progress and prosperity of the national economy (Sinclair 1998).International tourists bring foreign currencies to destination countries, increase residents' incomes, create jobs, improve living standards ...
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States ...
Contribution to government revenues. Employment generation. Contribution to local economies. Development of the Private Sector. Negative economic impacts of tourism. Leakage. Infrastructure cost. Increase in prices. Economic dependence of the local community on tourism.
However, tourism could also have a negative effect on the economy. Its boom may lead to a deindustrialization in other sectors (Copeland, 1991); this phenomenon is often called 'Dutch Disease effect'.Despite contractions of the manufacturing sector are not found in the long-run period, the authors warn that the danger of this effect could still be valid in either short or medium run (Song ...
1. Introduction. This study critically analyses and explores how hospitality and tourism (H&T) enterprises in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) can leverage funds from impact investing (i-investing or II) by examining the nature of II and its potential contribution to the development and growth of small and medium tourism firms (STFs).
In contrast, capital investment in tourism (CIT) has a significant negative association with income inequality. At the same time, growth and TGL positively and significantly affect income inequality. Moreover, TOD has a bidirectional feedback causality of income inequality. These results also support tourism's "price effect" on income ...
Following the results, economic growth, foreign investment, tourism investment, electricity production, and population density have a positive impact, while trade volume and banking development have a negative impact on the volume of CO 2 emissions. The results support the pollution haven hypothesis in the GCC region and have many policies for ...