WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION
Home | About WTO | News & events | Trade topics | WTO membership | Documents & resources | External relations
Contact us | Site map | A-Z | Search
español français
- trade topics
- sector-by-sector
- tourism and travel-related services
SERVICES: SECTOR BY SECTOR

Tourism and travel-related services
Tourism plays an important role for nearly all WTO members, especially in terms of its contribution to employment, GDP, and the generation of foreign exchange. Tourism-related services are typically labour-intensive, with numerous links to other major segments of the economy, such as transport, cultural and creative services, or financial and insurance services.
Tourism and travel-related services include services provided by hotels and restaurants (including catering), travel agencies and tour operator services, tourist guide services and other related services.
A crucial aspect of trade in tourism services is the cross-border movement of consumers (mode 2). This permits a variety of workers, including those in remote areas, to become services exporters — for instance, by guiding tourists, performing in local events, or working in tourist accommodation. While digitalisation offers great potential for many aspects of tourism services, the sector continues to depend highly on the cross-border movement of both customers and employees, and remains strongly linked to transport services.
Current commitments and exemptions
Tourism commitments have been undertaken by over 133 WTO members, more than in any other service sector. This indicates the desire of most members to expand their tourism sectors and to increase inward foreign direct investment (FDI) as part of their efforts to promote economic growth.
The level of commitments by sub-sector varies widely for tourism and travel-related services. Commitments on services provided by hotels and restaurants are the most frequent, with a significantly smaller number of WTO members making commitments on travel agencies and tour operator services. Only about half of members with commitments on tourism have included tourist guide services, and only a few members have made commitments for the “other” tourism services category.
- Schedules of WTO Members with Specific Commitments on Tourism Services
Treatment of the sector in negotiations
Tourism services, like other services covered by the General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS), were included in the services negotiations that began in 2000.
One of the earliest documents was a proposal for a GATS Annex on Tourism, originally sponsored by the Dominican Republic, El Salvador and Honduras ( S/C/W/127 and S/C/W/127/Corr.1 ). The proposal had two main aspects: more comprehensive treatment of the tourism sector (with respect to classification issues), and the prevention of anti-competitive practices. As part of the plurilateral process, a joint request was made by a group of developing countries, asking for improved tourism commitments for all modes of supply.
- Proposals and related negotiating documents on tourism services
Additional information
Search Documents Online These links open a new window: allow a moment for the results to appear.
- Secretariat background notes on tourism services (Document code S/C/W/* and keyword “tourism and Background Note”) > search > help
- Tourism services (Document code S/CSS/W/* or TN/S/W/* and Title Tourism) > search
You can perform more sophisticated searches from the Documents Online search facility by defining multiple search criteria such as document symbol (i.e. code number), full text search or document date.
Some useful links
- World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
- World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC)
- OECD Tourism Unit (Centre for Entrepreneurship, SMEs, Regions and Cities)
Problems viewing this page? If so, please contact [email protected] giving details of the operating system and web browser you are using.
The future of tourism: Bridging the labor gap, enhancing customer experience
As travel resumes and builds momentum, it’s becoming clear that tourism is resilient—there is an enduring desire to travel. Against all odds, international tourism rebounded in 2022: visitor numbers to Europe and the Middle East climbed to around 80 percent of 2019 levels, and the Americas recovered about 65 percent of prepandemic visitors 1 “Tourism set to return to pre-pandemic levels in some regions in 2023,” United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), January 17, 2023. —a number made more significant because it was reached without travelers from China, which had the world’s largest outbound travel market before the pandemic. 2 “ Outlook for China tourism 2023: Light at the end of the tunnel ,” McKinsey, May 9, 2023.
Recovery and growth are likely to continue. According to estimates from the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) for 2023, international tourist arrivals could reach 80 to 95 percent of prepandemic levels depending on the extent of the economic slowdown, travel recovery in Asia–Pacific, and geopolitical tensions, among other factors. 3 “Tourism set to return to pre-pandemic levels in some regions in 2023,” United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), January 17, 2023. Similarly, the World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC) forecasts that by the end of 2023, nearly half of the 185 countries in which the organization conducts research will have either recovered to prepandemic levels or be within 95 percent of full recovery. 4 “Global travel and tourism catapults into 2023 says WTTC,” World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC), April 26, 2023.
Longer-term forecasts also point to optimism for the decade ahead. Travel and tourism GDP is predicted to grow, on average, at 5.8 percent a year between 2022 and 2032, outpacing the growth of the overall economy at an expected 2.7 percent a year. 5 Travel & Tourism economic impact 2022 , WTTC, August 2022.
So, is it all systems go for travel and tourism? Not really. The industry continues to face a prolonged and widespread labor shortage. After losing 62 million travel and tourism jobs in 2020, labor supply and demand remain out of balance. 6 “WTTC research reveals Travel & Tourism’s slow recovery is hitting jobs and growth worldwide,” World Travel & Tourism Council, October 6, 2021. Today, in the European Union, 11 percent of tourism jobs are likely to go unfilled; in the United States, that figure is 7 percent. 7 Travel & Tourism economic impact 2022 : Staff shortages, WTTC, August 2022.
There has been an exodus of tourism staff, particularly from customer-facing roles, to other sectors, and there is no sign that the industry will be able to bring all these people back. 8 Travel & Tourism economic impact 2022 : Staff shortages, WTTC, August 2022. Hotels, restaurants, cruises, airports, and airlines face staff shortages that can translate into operational, reputational, and financial difficulties. If unaddressed, these shortages may constrain the industry’s growth trajectory.
The current labor shortage may have its roots in factors related to the nature of work in the industry. Chronic workplace challenges, coupled with the effects of COVID-19, have culminated in an industry struggling to rebuild its workforce. Generally, tourism-related jobs are largely informal, partly due to high seasonality and weak regulation. And conditions such as excessively long working hours, low wages, a high turnover rate, and a lack of social protection tend to be most pronounced in an informal economy. Additionally, shift work, night work, and temporary or part-time employment are common in tourism.
The industry may need to revisit some fundamentals to build a far more sustainable future: either make the industry more attractive to talent (and put conditions in place to retain staff for longer periods) or improve products, services, and processes so that they complement existing staffing needs or solve existing pain points.
One solution could be to build a workforce with the mix of digital and interpersonal skills needed to keep up with travelers’ fast-changing requirements. The industry could make the most of available technology to provide customers with a digitally enhanced experience, resolve staff shortages, and improve working conditions.
Would you like to learn more about our Travel, Logistics & Infrastructure Practice ?
Complementing concierges with chatbots.
The pace of technological change has redefined customer expectations. Technology-driven services are often at customers’ fingertips, with no queues or waiting times. By contrast, the airport and airline disruption widely reported in the press over the summer of 2022 points to customers not receiving this same level of digital innovation when traveling.
Imagine the following travel experience: it’s 2035 and you start your long-awaited honeymoon to a tropical island. A virtual tour operator and a destination travel specialist booked your trip for you; you connected via videoconference to make your plans. Your itinerary was chosen with the support of generative AI , which analyzed your preferences, recommended personalized travel packages, and made real-time adjustments based on your feedback.
Before leaving home, you check in online and QR code your luggage. You travel to the airport by self-driving cab. After dropping off your luggage at the self-service counter, you pass through security and the biometric check. You access the premier lounge with the QR code on the airline’s loyalty card and help yourself to a glass of wine and a sandwich. After your flight, a prebooked, self-driving cab takes you to the resort. No need to check in—that was completed online ahead of time (including picking your room and making sure that the hotel’s virtual concierge arranged for red roses and a bottle of champagne to be delivered).
While your luggage is brought to the room by a baggage robot, your personal digital concierge presents the honeymoon itinerary with all the requested bookings. For the romantic dinner on the first night, you order your food via the restaurant app on the table and settle the bill likewise. So far, you’ve had very little human interaction. But at dinner, the sommelier chats with you in person about the wine. The next day, your sightseeing is made easier by the hotel app and digital guide—and you don’t get lost! With the aid of holographic technology, the virtual tour guide brings historical figures to life and takes your sightseeing experience to a whole new level. Then, as arranged, a local citizen meets you and takes you to their home to enjoy a local family dinner. The trip is seamless, there are no holdups or snags.
This scenario features less human interaction than a traditional trip—but it flows smoothly due to the underlying technology. The human interactions that do take place are authentic, meaningful, and add a special touch to the experience. This may be a far-fetched example, but the essence of the scenario is clear: use technology to ease typical travel pain points such as queues, misunderstandings, or misinformation, and elevate the quality of human interaction.
Travel with less human interaction may be considered a disruptive idea, as many travelers rely on and enjoy the human connection, the “service with a smile.” This will always be the case, but perhaps the time is right to think about bringing a digital experience into the mix. The industry may not need to depend exclusively on human beings to serve its customers. Perhaps the future of travel is physical, but digitally enhanced (and with a smile!).
Digital solutions are on the rise and can help bridge the labor gap
Digital innovation is improving customer experience across multiple industries. Car-sharing apps have overcome service-counter waiting times and endless paperwork that travelers traditionally had to cope with when renting a car. The same applies to time-consuming hotel check-in, check-out, and payment processes that can annoy weary customers. These pain points can be removed. For instance, in China, the Huazhu Hotels Group installed self-check-in kiosks that enable guests to check in or out in under 30 seconds. 9 “Huazhu Group targets lifestyle market opportunities,” ChinaTravelNews, May 27, 2021.
Technology meets hospitality
In 2019, Alibaba opened its FlyZoo Hotel in Huangzhou, described as a “290-room ultra-modern boutique, where technology meets hospitality.” 1 “Chinese e-commerce giant Alibaba has a hotel run almost entirely by robots that can serve food and fetch toiletries—take a look inside,” Business Insider, October 21, 2019; “FlyZoo Hotel: The hotel of the future or just more technology hype?,” Hotel Technology News, March 2019. The hotel was the first of its kind that instead of relying on traditional check-in and key card processes, allowed guests to manage reservations and make payments entirely from a mobile app, to check-in using self-service kiosks, and enter their rooms using facial-recognition technology.
The hotel is run almost entirely by robots that serve food and fetch toiletries and other sundries as needed. Each guest room has a voice-activated smart assistant to help guests with a variety of tasks, from adjusting the temperature, lights, curtains, and the TV to playing music and answering simple questions about the hotel and surroundings.
The hotel was developed by the company’s online travel platform, Fliggy, in tandem with Alibaba’s AI Labs and Alibaba Cloud technology with the goal of “leveraging cutting-edge tech to help transform the hospitality industry, one that keeps the sector current with the digital era we’re living in,” according to the company.
Adoption of some digitally enhanced services was accelerated during the pandemic in the quest for safer, contactless solutions. During the Winter Olympics in Beijing, a restaurant designed to keep physical contact to a minimum used a track system on the ceiling to deliver meals directly from the kitchen to the table. 10 “This Beijing Winter Games restaurant uses ceiling-based tracks,” Trendhunter, January 26, 2022. Customers around the world have become familiar with restaurants using apps to display menus, take orders, and accept payment, as well as hotels using robots to deliver luggage and room service (see sidebar “Technology meets hospitality”). Similarly, theme parks, cinemas, stadiums, and concert halls are deploying digital solutions such as facial recognition to optimize entrance control. Shanghai Disneyland, for example, offers annual pass holders the option to choose facial recognition to facilitate park entry. 11 “Facial recognition park entry,” Shanghai Disney Resort website.
Automation and digitization can also free up staff from attending to repetitive functions that could be handled more efficiently via an app and instead reserve the human touch for roles where staff can add the most value. For instance, technology can help customer-facing staff to provide a more personalized service. By accessing data analytics, frontline staff can have guests’ details and preferences at their fingertips. A trainee can become an experienced concierge in a short time, with the help of technology.
Apps and in-room tech: Unused market potential
According to Skift Research calculations, total revenue generated by guest apps and in-room technology in 2019 was approximately $293 million, including proprietary apps by hotel brands as well as third-party vendors. 1 “Hotel tech benchmark: Guest-facing technology 2022,” Skift Research, November 2022. The relatively low market penetration rate of this kind of tech points to around $2.4 billion in untapped revenue potential (exhibit).
Even though guest-facing technology is available—the kind that can facilitate contactless interactions and offer travelers convenience and personalized service—the industry is only beginning to explore its potential. A report by Skift Research shows that the hotel industry, in particular, has not tapped into tech’s potential. Only 11 percent of hotels and 25 percent of hotel rooms worldwide are supported by a hotel app or use in-room technology, and only 3 percent of hotels offer keyless entry. 12 “Hotel tech benchmark: Guest-facing technology 2022,” Skift Research, November 2022. Of the five types of technology examined (guest apps and in-room tech; virtual concierge; guest messaging and chatbots; digital check-in and kiosks; and keyless entry), all have relatively low market-penetration rates (see sidebar “Apps and in-room tech: Unused market potential”).
While apps, digitization, and new technology may be the answer to offering better customer experience, there is also the possibility that tourism may face competition from technological advances, particularly virtual experiences. Museums, attractions, and historical sites can be made interactive and, in some cases, more lifelike, through AR/VR technology that can enhance the physical travel experience by reconstructing historical places or events.
Up until now, tourism, arguably, was one of a few sectors that could not easily be replaced by tech. It was not possible to replicate the physical experience of traveling to another place. With the emerging metaverse , this might change. Travelers could potentially enjoy an event or experience from their sofa without any logistical snags, and without the commitment to traveling to another country for any length of time. For example, Google offers virtual tours of the Pyramids of Meroë in Sudan via an immersive online experience available in a range of languages. 13 Mariam Khaled Dabboussi, “Step into the Meroë pyramids with Google,” Google, May 17, 2022. And a crypto banking group, The BCB Group, has created a metaverse city that includes representations of some of the most visited destinations in the world, such as the Great Wall of China and the Statue of Liberty. According to BCB, the total cost of flights, transfers, and entry for all these landmarks would come to $7,600—while a virtual trip would cost just over $2. 14 “What impact can the Metaverse have on the travel industry?,” Middle East Economy, July 29, 2022.
The metaverse holds potential for business travel, too—the meeting, incentives, conferences, and exhibitions (MICE) sector in particular. Participants could take part in activities in the same immersive space while connecting from anywhere, dramatically reducing travel, venue, catering, and other costs. 15 “ Tourism in the metaverse: Can travel go virtual? ,” McKinsey, May 4, 2023.
The allure and convenience of such digital experiences make offering seamless, customer-centric travel and tourism in the real world all the more pressing.

Three innovations to solve hotel staffing shortages
Is the future contactless.
Given the advances in technology, and the many digital innovations and applications that already exist, there is potential for businesses across the travel and tourism spectrum to cope with labor shortages while improving customer experience. Process automation and digitization can also add to process efficiency. Taken together, a combination of outsourcing, remote work, and digital solutions can help to retain existing staff and reduce dependency on roles that employers are struggling to fill (exhibit).
Depending on the customer service approach and direct contact need, we estimate that the travel and tourism industry would be able to cope with a structural labor shortage of around 10 to 15 percent in the long run by operating more flexibly and increasing digital and automated efficiency—while offering the remaining staff an improved total work package.
Outsourcing and remote work could also help resolve the labor shortage
While COVID-19 pushed organizations in a wide variety of sectors to embrace remote work, there are many hospitality roles that rely on direct physical services that cannot be performed remotely, such as laundry, cleaning, maintenance, and facility management. If faced with staff shortages, these roles could be outsourced to third-party professional service providers, and existing staff could be reskilled to take up new positions.
In McKinsey’s experience, the total service cost of this type of work in a typical hotel can make up 10 percent of total operating costs. Most often, these roles are not guest facing. A professional and digital-based solution might become an integrated part of a third-party service for hotels looking to outsource this type of work.
One of the lessons learned in the aftermath of COVID-19 is that many tourism employees moved to similar positions in other sectors because they were disillusioned by working conditions in the industry . Specialist multisector companies have been able to shuffle their staff away from tourism to other sectors that offer steady employment or more regular working hours compared with the long hours and seasonal nature of work in tourism.
The remaining travel and tourism staff may be looking for more flexibility or the option to work from home. This can be an effective solution for retaining employees. For example, a travel agent with specific destination expertise could work from home or be consulted on an needs basis.
In instances where remote work or outsourcing is not viable, there are other solutions that the hospitality industry can explore to improve operational effectiveness as well as employee satisfaction. A more agile staffing model can better match available labor with peaks and troughs in daily, or even hourly, demand. This could involve combining similar roles or cross-training staff so that they can switch roles. Redesigned roles could potentially improve employee satisfaction by empowering staff to explore new career paths within the hotel’s operations. Combined roles build skills across disciplines—for example, supporting a housekeeper to train and become proficient in other maintenance areas, or a front-desk associate to build managerial skills.
Where management or ownership is shared across properties, roles could be staffed to cover a network of sites, rather than individual hotels. By applying a combination of these approaches, hotels could reduce the number of staff hours needed to keep operations running at the same standard. 16 “ Three innovations to solve hotel staffing shortages ,” McKinsey, April 3, 2023.
Taken together, operational adjustments combined with greater use of technology could provide the tourism industry with a way of overcoming staffing challenges and giving customers the seamless digitally enhanced experiences they expect in other aspects of daily life.
In an industry facing a labor shortage, there are opportunities for tech innovations that can help travel and tourism businesses do more with less, while ensuring that remaining staff are engaged and motivated to stay in the industry. For travelers, this could mean fewer friendly faces, but more meaningful experiences and interactions.
Urs Binggeli is a senior expert in McKinsey’s Zurich office, Zi Chen is a capabilities and insights specialist in the Shanghai office, Steffen Köpke is a capabilities and insights expert in the Düsseldorf office, and Jackey Yu is a partner in the Hong Kong office.
Explore a career with us
- Understanding Poverty
- Competitiveness
Tourism and Competitiveness

- Publications
The tourism sector provides opportunities for developing countries to create productive and inclusive jobs, grow innovative firms, finance the conservation of natural and cultural assets, and increase economic empowerment, especially for women, who comprise the majority of the tourism sector’s workforce. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, tourism was the world’s largest service sector—providing one in ten jobs worldwide, almost seven percent of all international trade and 25 percent of the world’s service exports —a critical foreign exchange generator. In 2019 the sector was valued at more than US$9 trillion and accounted for 10.4 percent of global GDP.
Tourism offers opportunities for economic diversification and market-creation. When effectively managed, its deep local value chains can expand demand for existing and new products and services that directly and positively impact the poor and rural/isolated communities. The sector can also be a force for biodiversity conservation, heritage protection, and climate-friendly livelihoods, making up a key pillar of the blue/green economy. This potential is also associated with social and environmental risks, which need to be managed and mitigated to maximize the sector’s net-positive benefits.
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has been devastating for tourism service providers, with a loss of 20 percent of all tourism jobs (62 million), and US$1.3 trillion in export revenue, leading to a reduction of 50 percent of its contribution to GDP in 2020 alone. The collapse of demand has severely impacted the livelihoods of tourism-dependent communities, small businesses and women-run enterprises. It has also reduced government tax revenues and constrained the availability of resources for destination management and site conservation.

Naturalist local guide with group of tourist in Cuyabeno Wildlife Reserve Ecuador. Photo: Ammit Jack/Shutterstock
Tourism and Competitiveness Strategic Pillars

Our solutions are integrated across the following areas:
- Competitive and Productive Tourism Markets. We work with government and private sector stakeholders to foster competitive tourism markets that create productive jobs, improve visitor expenditure and impact, and are supportive of high-growth, innovative firms. To do so we offer guidance on firm and destination level recovery, policy and regulatory reforms, demand diversification, investment promotion and market access.
- Blue, Green and Resilient Tourism Economies. We support economic diversification to sustain natural capital and tourism assets, prepare for external and climate-related shocks, and be sustainably managed through strong policy, coordination, and governance improvements. To do so we offer support to align the tourism enabling and policy environment towards sustainability, while improving tourism destination and site planning, development, and management. We work with governments to enhance the sector’s resilience and to foster the development of innovative sustainable financing instruments.
- Inclusive Value Chains. We work with client governments and intermediaries to support Small and Medium sized Enterprises (SMEs), and strengthen value chains that provide equitable livelihoods for communities, women, youth, minorities, and local businesses.
The successful design and implementation of reforms in the tourism space requires the combined effort of diverse line ministries and agencies, and an understanding of the impact of digital technologies in the industry. Accordingly, our teams support cross-cutting issues of tourism governance and coordination, digital innovation and the use and application of data throughout the three focus areas of work.
Tourism and Competitiveness Theory of Change

Examples of our projects:
- In Indonesia , a US$955m loan is supporting the Government’s Integrated Infrastructure Development for National Tourism Strategic Areas Project. This project is designed to improve the quality of, and access to, tourism-relevant basic infrastructure and services, strengthen local economy linkages to tourism, and attract private investment in selected tourism destinations. In its initial phases, the project has supported detailed market and demand analyses needed to justify significant public investment, mobilized integrated tourism destination masterplans for each new destination and established essential coordination mechanisms at the national level and at all seventeen of the Project’s participating districts and cities.
- In Madagascar , a series of projects totaling US$450m in lending and IFC Technical Assistance have contributed to the sustainable growth of the tourism sector by enhancing access to enabling infrastructure and services in target regions. Activities under the project focused on providing support to SMEs, capacity building to institutions, and promoting investment and enabling environment reforms. They resulted in the creation of more than 10,000 jobs and the registration of more than 30,000 businesses. As a result of COVID-19, the project provided emergency support both to government institutions (i.e., Ministry of Tourism) and other organizations such as the National Tourism Promotion Board to plan, strategize and implement initiatives to address effects of the pandemic and support the sector’s gradual relaunch, as well as to directly support tourism companies and workers groups most affected by the crisis.
- In Sierra Leone , an Economic Diversification Project has a strong focus on sustainable tourism development. The project is contributing significantly to the COVID-19 recovery, with its focus on the creation of six new tourism destinations, attracting new private investment, and building the capacity of government ministries to successfully manage and market their tourism assets. This project aims to contribute to the development of more circular economy tourism business models, and support the growth of women- run tourism businesses.
- Through the Rebuilding Tourism Competitiveness: Tourism Response, Recovery and Resilience to the COVID-19 Crisis initiative and the Tourism for Development Learning Series , we held webinars, published insights and guidance notes as well as formed new partnerships with Organization of Eastern Caribbean States, United Nations Environment Program, United Nations World Tourism Organization, and World Travel and Tourism Council to exchange knowledge on managing tourism throughout the pandemic, planning for recovery and building back better. The initiative’s key Policy Note has been downloaded more than 20,000 times and has been used to inform recovery initiatives in over 30 countries across 6 regions.
- The Global Aviation Dashboard is a platform that visualizes real-time changes in global flight movements, allowing users to generate 2D & 3D visualizations, charts, graphs, and tables; and ranking animations for: flight volume, seat volume, and available seat kilometers. Data is available for domestic, intra-regional, and inter-regional routes across all regions, countries, airports, and airlines on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis from January 2020 until today. The dashboard has been used to track the status and recovery of global travel and inform policy and operational actions.

Traditional Samburu women in Kenya. Photo: hecke61/Shutterstock.
Featured Data
We-Fi WeTour Women in Tourism Enterprise Surveys (2019)
- Sierra Leone | Ghana
Featured Reports
- Destination Management Handbook: A Guide to the Planning and Implementation of Destination Management (2023)
- Blue Tourism in Islands and Small Tourism-Dependent Coastal States : Tools and Recovery Strategies (2022)
- Resilient Tourism: Competitiveness in the Face of Disasters (2020)
- Tourism and the Sharing Economy: Policy and Potential of Sustainable Peer-to-Peer Accommodation (2018)
- Supporting Sustainable Livelihoods through Wildlife Tourism (2018)
- The Voice of Travelers: Leveraging User-Generated Content for Tourism Development (2018)
- Women and Tourism: Designing for Inclusion (2017)
- Twenty Reasons Sustainable Tourism Counts for Development (2017)
- An introduction to tourism concessioning:14 characteristics of successful programs. The World Bank, 2016)
- Getting financed: 9 tips for community joint ventures in tourism . World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and World Bank, (2015)
- Global investment promotion best practices: Winning tourism investment” Investment Climate (2013)
Country-Specific
- COVID-19 and Tourism in South Asia: Opportunities for Sustainable Regional Outcomes (2020)
- Demand Analysis for Tourism in African Local Communities (2018)
- Tourism in Africa: Harnessing Tourism for Growth and Improved Livelihoods . Africa Development Forum (2014)
COVID-19 Response
- Expecting the Unexpected : Tools and Policy Considerations to Support the Recovery and Resilience of the Tourism Sector (2022)
- Rebuilding Tourism Competitiveness. Tourism response, recovery and resilience to the COVID-19 crisis (2020)
- COVID-19 and Tourism in South Asia Opportunities for Sustainable Regional Outcomes (2020)
- WBG support for tourism clients and destinations during the COVID-19 crisis (2020)
- Tourism for Development: Tourism Diagnostic Toolkit (2019)
- Tourism Theory of Change (2018)
Country -Specific
- COVID Impact Mitigation Survey Results (South Africa) (2020)
- COVID Preparedness for Reopening Survey Results (South Africa) (2020)
- COVID Study (Fiji) (2020) with IFC
Featured Blogs
- Louise Twining-Ward and Alba Suris , Bridging the Tourism Data Divide: New Tools for Policymaking
- Fiona Stewart, Samantha Power & Shaun Mann , Harnessing the power of capital markets to conserve and restore global biodiversity through “Natural Asset Companies” | October 12 th 2021
- Mari Elka Pangestu , Tourism in the post-COVID world: Three steps to build better forward | April 30 th 2021
- Hartwig Schafer , Regional collaboration can help South Asian nations rebuild and strengthen tourism industry | July 23 rd 2020
- Caroline Freund , We can’t travel, but we can take measures to preserve jobs in the tourism industry | March 20 th 2020
Featured Webinars
- Destination Management for Resilient Growth . This webinar looks at emerging destinations at the local level to examine the opportunities, examples, and best tools available. Destination Management Handbook
- Launch of the Future of Pacific Tourism. This webinar goes through the results of the new Future of Pacific Tourism report. It was launched by FCI Regional and Global Managers with Discussants from the Asian Development Bank and Intrepid Group.
- Circular Economy and Tourism . This webinar discusses how new and circular business models are needed to change the way tourism operates and enable businesses and destinations to be sustainable.
- Closing the Gap: Gender in Projects and Analytics . The purpose of this webinar is to raise awareness on integrating gender considerations into projects and provide guidelines for future project design in various sectoral areas.
- WTO Tourism Resilience: Building forward Better. High-level panelists from Sri Lanka, Costa Rica, Jordan and Kenya discuss how donors, governments and the private sector can work together most effectively to rebuild the tourism industry and improve its resilience for the future.
- Tourism Watch
- Tourism Factsheets
- [email protected]
Launch of Blue Tourism Resource Portal

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 7. Travel Services
7.3 Tourism Services
Many organizations can have a hand in tourism development. These include:
- Sector-specific associations
- Tourism and hospitality human resources organizations
- Training providers
- Educational institutions
- Government branches and ministries in land use, planning, development, environmental, transportation, consumer protection, and other related fields
- Economic development and city planning offices
Consultants
The rest of this section describes Canadian and BC-based examples of these.
Sector-Specific Associations
Numerous not-for-profit and arm’s-length organizations drive the growth of specific segments of our industry. Examples of these associations can be found throughout this textbook in the Spotlight On features, and include groups like:
- BC Hotel Association
- Sea Kayak Guides Alliance of BC
- Restaurants Canada
These can serve as regulatory bodies, advocacy agencies, certification providers, and information sources.
Tourism and Hospitality Human Resource Support
Tourism HR Canada — formally the Canadian Tourism Human Resource Council (CTHRC) — is a national sector council responsible for best practice research, training, and other professional development support on behalf of the 174,000 tourism businesses and the 1.75 million people employed in tourism-related occupations across the country. In BC, an organization called go2HR serves to educate employers on attracting, training, and retaining employees, as well as hosts a tourism job board to match prospective employees with job options in tourism around the province.
Training Providers
Throughout this textbook, you’ll see examples of not-for-profit industry associations that provide training and certification for industry professionals. For example, the Association of Canadian Travel Agents offers a full-time and distance program to train for the occupation of certified travel counsellor. Closer to home, an organization called WorldHost, a division of Destination BC, offers world-class customer service training.
You’ll learn more about training providers and tourism human resources development in Chapter 9 .
Educational Institutions
British Columbia is home to a number of high-quality public and private colleges and universities that offer tourism-related educational options. Training options at these colleges and universities include certificates, diplomas, degrees and masters-level programs in adventure tourism, outdoor recreation, hospitality management, and tourism management. For example, whether students are learning how to manage a restaurant at Camosun College, gaining mountain adventure skills at College of the Rockies, or exploring the world of outdoor recreation and tourism management at the University of Northern BC, tomorrow’s workforce is being prepared by skilled instructors with solid industry experience.
Spotlight On: Emerit
Emerit is Canada’s award winning training resource developed by Tourism HR Canada in collaboration with tourism industry professionals from across Canada. For more information on Emerit, visit the go2HR website .
Government Departments
At the time this chapter was written, there were at least eight distinct provincial government ministries that had influence on tourism and hospitality development in British Columbia. These are:
- Tourism, Arts, and Culture
- Advanced Education, Skills, and Training
- Transportation and Infrastructure
- Environment & Climate Change Strategy
- Forests, Lands, Natural Resource Operations & Rural Development
- Indigenous Relations & Reconciliation
- Jobs, Economic Development, & Competitiveness
- Public Safety & Solicitor General
Ministry names and responsibilities may change over time, but the functions performed by provincial ministries are critical to tourism operators and communities, as are the functions of similar departments at the federal level.
At the community level, tourism functions are often performed by planning officers, economic development officers, and chambers of commerce.
A final, hidden layer to the travel services sector is that of independent consultants and consulting firms. These people and companies offer services to the industry in a business-to-business format, and they vary from individuals to small-scale firms to international companies. In BC, tourism-based consulting firms include:
- IntraVISTAS: specializing in aviation and transportation logistics advising
- Chemistry Consulting: specializing in human relations and labour market development
- Beattie Tartan: a public-relations and reputation management firm
For many people trained in specific industry fields, consulting offers the opportunity to give back to the industry while maintaining workload flexibility.
Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC - 2nd Edition Copyright © 2015, 2020, 2021 by Morgan Westcott and Wendy Anderson, Eds is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Tourism: A Service Sector
- First Online: 23 November 2013
Cite this chapter

- Antonia Rosa Gurrieri 4 ,
- Marilene Lorizio 4 &
- Annamaria Stramaglia 4
Part of the book series: SpringerBriefs in Business ((BRIEFSBUSINESS))
841 Accesses
2 Citations
The tourism sector is a large and fast growing industry able to generate several potential benefits for the whole economy both at local and national level. In recent years new forms of tourism (labelled as alternative) have emerged. Among these, rural tourism plays an important role due to its influence on the development of local communities. Tourism is an economic sector in which a high degree of entrepreneurial involvement is required. Moreover in order to compete worldwide, both entrepreneurship and networking emerge as key features of successful tourism provision. The aim of this discussion is to highlight the role of these features with particular reference to their influence on achieving a robust and resilient performance of the tourism sector that is required in the present economic crisis.
This chapter is written by Annamaria Stramaglia
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Ateljevic I, Doorne S (2000) Staying with the fence: lifestyle entrepreneurship in tourism. J Sustain Tour 8(5):378–392. doi: 10.1080/09669580008667374
Article Google Scholar
Bruyat C, Julien PA (2000) Defining the field of research in entrepreneurship. J Bus Ventur 16:165–180. doi: 10.1016/S0883-9026(99)00043-9
Busby G, Rendle S (2000) The transition from tourism on farms to farm tourism. Tour Manag 21(8):635–642. doi: 10.1016/S0261-5177(00)00011-X
Cawley M, Gillmor DA (2008) Integrated rural tourism: concepts and practice. Ann Tour Res 35(2):316–337. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2007.07.011
Chuang ST (2013) Residents’ attitudes toward rural tourism in Taiwan: a comparative viewpoint. Int J Tour Res 15(2):152–170. doi: 10.1002/jtr.1861
Dernoi LA (1991) About rural and farm tourism. Tour Recreat Res 16(1):3–6
Google Scholar
Dimitrovski DD, Todorović AT, Valjarević AD (2012) Rural tourism and regional development: case study of development of rural tourism in the region of Gruţa, Serbia. Proc Environ Sci 14:288–297. doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2012.03.028
European Commission (1986) Action in the field of tourism. COM (86) 32 final, Brussels, 5 Feb 1986. http://aei.pitt.edu/5411/1/5411.pdf
European Commission (2006) A renewed EU tourism policy: towards a stronger partnership for European tourism. COM (2006) 134 final, Brussels, 17 Mar 2006. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=COM:2006:0134:FIN:en:PDF
European Commission (2007) Agenda for a sustainable and competitive European tourism. COM (2007) 621 final, Brussels, 19 Oct 2007. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=COM:2007:0621:FIN:EN:PDF
European Commission (2010) Europe, the world’s No. 1 tourist destination: a new political framework for tourism in Europe. COM (2010) 352 final, Brussels, 30 June 2010. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=COM:2010:0352:FIN:en:PDF
Eurostat (2013) Eurostat news releases, no. 59/2013. http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/cache/ITY_PUBLIC/4-15042013-BP/EN/4-15042013-BP-EN.PDF
Farmaki A (2012) An exploration of tourist motivation in rural setting. The case of Troodos, Cyprus. Tour Manag Perspect 2(3):72–78. doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2012.03.007
Fayos-Solá E (1996) Tourism policy: a midsummer night’s dream? Tour Manag 17(6):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0261-5177(96)00061-1
Frederick M (1992) Tourism as a rural development tool: an exploration of the literature, vol 22. US Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service, Washington, DC
Getz D, Carlson J (2000) Characteristics and goals of family and owner-operated businesses in rural tourism and hospitality sectors. Tour Manag 2(1):547–560. doi: 10.1016/S0261-5177(00)00004-2
Getz D, Petersen T (2005) Growth and profit-oriented entrepreneurship among family business owners in the tourism and hospitality industry. Int J Hosp Manag 24(2):219–242. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2004.06.007
Glosvik Ø (2003) Networks and learning in a rural development program. Paper presented at the reinventing regions in the global economy conference, Pisa, Italy 12–15 April 2003
Johns N, Mattsson J (2005) Destination development through entrepreneurship: a comparison of two cases. Tour Manag 26(4):605–616. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2004.02.017
Komppula R (2014) The role of individual entrepreneurs in the development of competitiveness for a rural tourism destination: a case study. Tour Manag 40:361–371. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2013.07.007
Lane B (1994) What is rural tourism? J Sustain Tour 2(1–2):7–21. doi: 10.1080/09669589409510680
Lashley C, Rowson B (2010) Lifestyle businesses: insights into Blackpool’s hotel sector. Int J Hosp Manag 29(3):511–519. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2009.10.027
Lerner M, Haber S (2001) Performance factors of small tourism ventures: the interface of tourism, entrepreneurship and the environment. J Bus Ventur 16(1):77–100. doi: 10.1016/S0883-9026(99)00038-5
McGehee NG, Kim K (2004) Motivation for agri-tourism entrepreneurship. J Travel Res 43(2):161–170. doi: 10.1177/0047287504268245
Medina-Muñoz D, Garcίa-Falcόn JM (2000) Successful relationships between hotels and agencies. Ann Tour Res 27(3):737–762. doi: 10.1016/S0160-7383(99)00104-8
Morrison A (2006) A contextualisation of entrepreneurship. Int J Entrep Behav Res 12(4):192–209. doi: 10.1108/13552550610679159
Morrison AJ, Baum T, Andrew R (2001) The lifestyle economics of small tourism businesses. J Travel Tour Res 1(1–2):16–25 ISSN 1302-8545
Morrison A, Lynch P, Johns N (2004) International tourism networks. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 16(3):198–204. doi: 10.1108/09596110410531195
Novelli M, Schmitz B, Spencer T (2006) Networks, clusters and innovation in tourism: a UK experience. Tour Manag 27:1141–1152. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2005.11.011
Oppermann M (1996) Rural tourism in southern Germany. Ann Tour Res 23(1):86–102. doi: 10.1016/0160-7383(95)00021-6
Park DB, Yoon YS (2009) Segmentation by motivation in rural tourism: a Korean case study. Tour Manag 30(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2008.03.011
Peters M, Frehse J, Buhalis D (2009) The importance of lifestyle entrepreneurship: a conceptual study of the tourism industry. Pasos 7(2):393–405 ISSN 1695-7121
Phillip S, Hunter C, Blackstock K (2010) A typology for defining agritourism. Tour Manag 31(6):754–758. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2009.08.001
Poon A (1993) Tourism, technology and competitive strategies. CAB, Wallingford
Ramayah T, Lee JWC, In JBC (2011) Network collaboration and performance in the tourism sector. Serv Bus 5(4):411–428. doi: 10.1007/s11628-011-0120-z
Roberts L, Hall D (2001) Rural tourism and recreation principles to practice. CABI, Wallingford
Book Google Scholar
Roberts L, Hall D (2004) Consuming the countryside: marketing for rural tourism. J Vacat Mark 10(3):253–263. doi: 10.1177/135676670401000305
Rosenfeld S (Sep 2001) Networks and clusters: the Yin and Yang of rural development proceedings: rural and agricultural conferences, pp 103–120
San Martin H, Herrero A (2012) Influence of user’s psychological factors on the online purchase intention in rural tourism. Tour Manag 33:341–350. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2011.04.003
Saxena G, Ilbery B (2008) Integrated rural tourism. A border case study. Ann Tour Res 35(1):233–254. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2007.07.010
Shane S, Venkataraman S (2000) The promise of entrepreneurship as a field of research. Acad Manag Rev 25(1):217–226. doi: 10.2307/259271
Sharpley R (2002) Rural tourism and the challenge of tourism diversification: the case of Cyprus. Tour Manag 23(3):233–244. doi: 10.1016/S0261-5177(01)00078-4
Tajeddini K (2010) Effect of customer orientation and entrepreneurial orientation on innovativeness: evidence from the hotel industry in Switzerland. Tour Manag 31(2):221–231. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2009.02.013
Tinsley R, Lynch PA (2001) Small tourism business networks and destination development. Int J Hosp Manag 20(4):367–378. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4319(01)00024-X
UNWTO—World Tourism Organization (2012) Tourism highlights, 2012 edn. http://mkt.unwto.org/sites/all/files/docpdf/unwtohighlights12enhr.pdf
Wagener S, Gorgievski M, Rijsdijk S (2010) Businessman or host? Individual differences between entrepreneurs and small business owners in the hospitality industry. Serv Ind J 30(9):1513–1527. doi: 10.1080/02642060802624324
Wang Y, Fesenmaier DR (2007) Collaborative destination marketing: a case study of Elkhart county, Indiana. Tour Manag 28(3):863–875. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2006.02.007
Wang Y, Krakover S (2008) Destination marketing: competition, cooperation or competition? Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 20(2):126–141. doi: 10.1108/09596110810852113
Williams AM, Shaw G, Greenwood J (1989) From tourist to tourism entrepreneur, from consumption to production: evidence from Cornwall, England. Environ Plann A 21(12):1639–1653. http://www.envplan.com/abstract.cgi?id=a211639
WTO—World Trade Organization (2013) Annual report 2013. http://www.wto.org/english/res_e/booksp_e/anrep_e/anrep13_e.pdf
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Foggia, Largo Giovanni Paolo II, 71100, Foggia, Italy
Antonia Rosa Gurrieri, Marilene Lorizio & Annamaria Stramaglia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Annamaria Stramaglia .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Gurrieri, A.R., Lorizio, M., Stramaglia, A. (2014). Tourism: A Service Sector. In: Entrepreneurship Networks in Italy. SpringerBriefs in Business. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-03428-7_3
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-03428-7_3
Published : 23 November 2013
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-03427-0
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-03428-7
eBook Packages : Business and Economics Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
What is customer service in travel and tourism? Quick-start guide

Global travel is booming — especially since COVID. The travel industry contributed $7.7 trillion U.S. dollars to global gross domestic product (GDP) in 2022 alone.
Travelling the world is an incredible experience. And the business opportunity within the travel industry is just as impressive. But, if you’re not offering great customer service, it can be a nightmare – both for the traveller and for the business.
If you want to ensure you reap the benefits of the growing travel industry, you need to know how to provide optimal customer service. In this guide, we’ll break down how to optimise your customer service in travel and tourism so you can grow your business.
What is customer service in travel and tourism
Travel is one of the most powerful industries in the world. With billions of dollars spent annually on tourism, there's an opportunity to capitalise on the industry for customer service that stands out. But, if your customer service is failing behind in travel, then your business will fall behind.
Travel and tourism is built on the foundation of great customer service. The reason it’s different from other industries?
Customer service in travel is incredibly timely. People are moving to and fro on set timelines and schedules and one hiccup or error could send their entire trip down the drain.
So service has to be fast in order to succeed in travel. On top of that, people expect superior customer service because there’s a lot more money on the line.
Customer expectations for the travel industry experience
The average household spends about $2,100 on travel each year . When people book trips for thousands of dollars, they expect great service. If something were to go wrong, it would be an incredible loss.
In travel, customer experience is arguably more important than advertising. This is because the customer experience fuels the entire operation. If a consumer has one bad travel experience, they’re telling everyone they know. That’s why poor travellers customer service experiences on airlines blow up on social media.
But, if you’re able to offer great service, customers will spread the good news themselves. Great customer service in travel impacts word-of-mouth marketing, which can lead to exponential growth or collapse in business.
The evolution of customer service in travel
20 years ago, if you wanted to book a trip across the world, there was only one way: travel agents. You would drive across town to your brick-and-mortar travel agent, and look at your options. Then, you’d book a trip, get your tickets, and wait until it was time to show up to the airport.
Your travel agent did it all for you. Nowadays, customer service in travel is much more self-service. You can do it all right from your smartphone – no matter where you are.
Customer service within travel for 2024
10 years ago, you had to call in or wait for a response from a customer service agent. But, as technology advanced, so did the speed at which customer service teams could help people.
Consumers can now book trips quicker, analyse prices easier, and get their questions answered in seconds without having to drive 20 minutes across town – or without having to wait 10-30 minutes to get through to someone on the phone.
Thanks to technology like AI and chatbots, consumers are able to get the help they need the moment they need it. Social media allowed for even quicker responses. But, there was one problem: with so many ways to get a hold of a company, it became incredibly challenging for travel companies to manage all the conversations on different platforms.
But now, with customer service platforms like Trengo , travel companies can serve their customers instantly without letting their inquiries slip through the cracks.
Because software like this will show every single conversation in one place: whether it’s coming from email, Instagram, Facebook messenger, or from your chatbot.
Key components of effective customer service
If you want to remain competitive with your travel business, you need to offer good customer service. But, if you want to grow as a business, you need to offer customer service that goes above and beyond.
Here’s how to improve customer service in travel agency and other tourism companies:
Speed and reliability
Quick responses are a given for any successful travel business today. You need to offer fast replies to inquiries in order to be seen as reliable.
Kind and courteous
Customers don’t just want fast responses with the right information. They want to feel that you’re empathetic towards them. They need travelers customer service teams to be kind, courteous, and understanding.
Looks matter
This doesn’t mean your team needs to be attractive. It means you need to have great branding – and it needs to be congruent with your service. Keep a professional website, and chatbot, and ensure your team is writing and speaking professionally with customers.
Personalisation
Modern customer service chatbots allow you to personalise the experience for your customers automatically . You can then take those conversations and let your human support members carry on with the personalised data to serve the customer (i.e. “Are you excited for your upcoming trip to Hawaii, John?”)
Multilingual support
Travel customer service isn’t just about your local travel agent anymore. It’s about global teams serving global customers. You need to ensure you have a diverse, multilingual team to help serve international customers.
Challenges in providing quality customer service
Good customer service isn’t a nice-to-have anymore. Consumers demand more than ever.
A Think with Google study found that great customer service is the number one factor of high-value travellers. Nearly 60% of them admit that customer service matters most to them when picking a company to travel with.
Technology has made it so service is back in the hands of the customer. If you aren’t providing great customer service, you’re going to get beaten out by the competition.
Here are a few challenges in providing quality customer service (and tips to overcome them).
Planning trips
The booking process has become much more technological. You need to offer fast responses to people who are comparing different travel companies. If you’re not fast, consumers will pick a competitor. Offer a chatbot that responds with personalised messages when your live support team is off the clock.
Help out exactly how consumers want it
Every customer is different. They want to be able to get the help they need how they want it. If you’re only offering one way to contact your team, you’re falling short. You need to offer multiple communication options (i.e. social media, phone number, email, live chat, etc.).
Lack of personalisation
Consumers expect more. This holds true with personalisation as well. You need to ensure you’re collecting first-party data like name, phone number, age, purchases, and booking information. Make sure you’re offering personalised advice and capturing and storing data digitally by using a platform like Trengo .
Technology’s role in enhancing customer service
Back in the day, you had to visit your local travel agency if you wanted to book a trip or ask a question about your booking. Then, you could phone in to call centres. Eventually, that moved to email. Now, technology has enabled fast-paced customer support.

In a 2023 Skift survey of travel and hospitality executives, 66% agreed that customer service was a high-priority digital investment in their business. Customer service beat out every single option, with customer engagement and retention at 60% and revenue optimisation at 55%.
If you want to provide stellar service in your travel or tourism business, then you need to leverage the right technology. Here are a few need-to-haves when it comes to customer service technology:
- Customer relationship management (CRM)
- Customer service software
By integrating all four of these technologies, you’ll have a proper foundation to offer great customer service to your travel customers quickly to keep them coming back for years to come.
Training and development for customer service teams
The right technology can be a major help in your customer service strategy. But, if you’re not providing adequate training to your support, it doesn’t matter how robust your technology is.
Here are some key tips to provide optimal training for your support team:
1. Effective communication
Customer service revolves around one core skill: communication. If your team isn’t able to communicate quickly and effectively, you’ll lose customers. You need to develop communication skills with your team, starting with empathetic listening and tone of voice.
2. Productivity
Offering service that goes above and beyond for a single customer is crucial.
But, if it’s taking all day to resolve a customer’s inquiry, there’s a problem. The reality is that your team needs to be able to handle high volumes of tickets and inquiries to be productive. Otherwise, your time to resolve tickets will slow down and you’ll need to pour more resources into your support strategy.
3. Foreign language training
You also need to ensure you’re training your teams on multiple languages to ensure you can serve a global audience.
For the most part, you should always ensure your team can speak your target audience’s native language. And, you should almost always include English language training as the top secondary language. Or when your team is not there yet, rely on automation, like chatbots, that'll service customers in their own language .
4. Problem-solving
Your customer service team isn’t just there to provide a friend for your customer. They’re working to solve customer problems. Your team needs to understand the fastest path to solve problems. This means having a service playbook at hand, templates to respond to customers, and an internal knowledge base that’s easy to access.
To go above and beyond, you should ensure your team has adequate knowledge of the places you’re offering travel experiences for (and can offer personalised tips).
Measuring the impact of customer service
Customer service is harder to measure than revenue. It’s not always black and white to determine how well a customer was helped.
But, it’s not impossible.
There are key metrics you can (and should) measure to determine the impact of your service:
Customer satisfaction score (CSAT): After an inquiry, ask every customer “How satisfied were you with [company] and [customer service representative]?” Give a scale of 1 to 5.
Net promoter score (NPS): This is one of the most common customer service metrics. Simply ask your customers, “How likely are you to refer us to a friend?” Then, give them a scale of 1 to 10.
Average resolution time (ART): This is simply the average amount of time it takes for your customer support team to fully resolve a customer’s inquiry. Software like Trengo can track this by individual representatives or by team.
Offer a travel experience that goes above and beyond
Travel is all about the experiences consumers have. Customer service is a major part of the travel experience – and it can make or break a trip.
If you aren’t offering great customer service as a travel or tourism company, your customers will quickly find a competitor to do business with.
By understanding the key concepts of great customer service, providing your team with the right development, and leveraging the right technology, you will be well on your way to providing exceptional service.
Deliver worldwide customer delight
Take your customer experience to the next level, and lean on the right customer service software. With Trengo, you can give your travel customers the best experience possible to ensure they keep coming back for years.
Learn more about how Trengo provides end-to-end travel experiences that lead to world-class holidays.

How to manage multiple WhatsApp Business accounts in one view
![services in tourism How to use WhatsApp Business with multiple users [Updated June 2024]](https://cdn.prod.website-files.com/65f4803d6dc2aecf0f7a1be2/666afcd28c2f5c82d0be5f27_SEO%20blog_WhatsApp%20multiple%20users_%2013-06-24_Image%20header.webp)
How to use WhatsApp Business with multiple users and multiple WhatsApp Business accounts

WhatsApp ticketing system: Track and handle customer conversations [June 2024]
Let's meet, self service.
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

U.S. Department of Commerce
- Fact Sheets
Was this page helpful?
Fact sheet: 2022 national travel and tourism strategy, office of public affairs.
The 2022 National Travel and Tourism Strategy was released on June 6, 2022, by U.S. Secretary of Commerce Gina M. Raimondo on behalf of the Tourism Policy Council (TPC). The new strategy focuses the full efforts of the federal government to promote the United States as a premier destination grounded in the breadth and diversity of our communities, and to foster a sector that drives economic growth, creates good jobs, and bolsters conservation and sustainability. Drawing on engagement and capabilities from across the federal government, the strategy aims to support broad-based economic growth in travel and tourism across the United States, its territories, and the District of Columbia.
The federal government will work to implement the strategy under the leadership of the TPC and in partnership with the private sector, aiming toward an ambitious five-year goal of increasing American jobs by attracting and welcoming 90 million international visitors, who we estimate will spend $279 billion, annually by 2027.
The new National Travel and Tourism Strategy supports growth and competitiveness for an industry that, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, generated $1.9 trillion in economic output and supported 9.5 million American jobs. Also, in 2019, nearly 80 million international travelers visited the United States and contributed nearly $240 billion to the U.S. economy, making the United States the global leader in revenue from international travel and tourism. As the top services export for the United States that year, travel and tourism generated a $53.4 billion trade surplus and supported 1 million jobs in the United States.
The strategy follows a four-point approach:
- Promoting the United States as a Travel Destination Goal : Leverage existing programs and assets to promote the United States to international visitors and broaden marketing efforts to encourage visitation to underserved communities.
- Facilitating Travel to and Within the United States Goal : Reduce barriers to trade in travel services and make it safer and more efficient for visitors to enter and travel within the United States.
- Ensuring Diverse, Inclusive, and Accessible Tourism Experiences Goal : Extend the benefits of travel and tourism by supporting the development of diverse tourism products, focusing on under-served communities and populations. Address the financial and workplace needs of travel and tourism businesses, supporting destination communities as they grow their tourism economies. Deliver world-class experiences and customer service at federal lands and waters that showcase the nation’s assets while protecting them for future generations.
- Fostering Resilient and Sustainable Travel and Tourism Goal : Reduce travel and tourism’s contributions to climate change and build a travel and tourism sector that is resilient to natural disasters, public health threats, and the impacts of climate change. Build a sustainable sector that integrates protecting natural resources, supporting the tourism economy, and ensuring equitable development.
Travel and Tourism Fast Facts
- The travel and tourism industry supported 9.5 million American jobs through $1.9 trillion of economic activity in 2019. In fact, 1 in every 20 jobs in the United States was either directly or indirectly supported by travel and tourism. These jobs can be found in industries like lodging, food services, arts, entertainment, recreation, transportation, and education.
- Travel and tourism was the top services export for the United States in 2019, generating a $53.4 billion trade surplus.
- The travel and tourism industry was one of the U.S. business sectors hardest hit by the COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent health and travel restrictions, with travel exports decreasing nearly 65% from 2019 to 2020.
- The decline in travel and tourism contributed heavily to unemployment; leisure and hospitality lost 8.2 million jobs between February and April 2020 alone, accounting for 37% of the decline in overall nonfarm employment during that time.
- By 2021, the rollout of vaccines and lifting of international and domestic restrictions allowed travel and tourism to begin its recovery. International arrivals to the United States grew to 22.1 million in 2021, up from 19.2 million in 2020. Spending by international visitors also grew, reaching $81.0 billion, or 34 percent of 2019’s total.
More about the Tourism Policy Council and the 2022 National Travel and Tourism Strategy
Created by Congress and chaired by Secretary Raimondo, the Tourism Policy Council (TPC) is the interagency council charged with coordinating national policies and programs relating to travel and tourism. At the direction of Secretary Raimondo, the TPC created a new five-year strategy to focus U.S. government efforts in support of the travel and tourism sector which has been deeply and disproportionately affected by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Read the full strategy here
Sustainable tourism
Related sdgs, promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable ....

Description
Publications.
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States (SIDS) and coastal least developed countries (LDCs) (see also: The Potential of the Blue Economy report as well as the Community of Ocean Action on sustainable blue economy).
The World Tourism Organization defines sustainable tourism as “tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment and host communities".
Based on General assembly resolution 70/193, 2017 was declared as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development.
In the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development SDG target 8.9, aims to “by 2030, devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism is also highlighted in SDG target 12.b. which aims to “develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”.
Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “by 2030, increase the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries” as comprised in SDG target 14.7.
In the Rio+20 outcome document The Future We want, sustainable tourism is defined by paragraph 130 as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities by supporting their local economies and the human and natural environment as a whole. ” In paragraph 130, Member States also “call for enhanced support for sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building in developing countries in order to contribute to the achievement of sustainable development”.
In paragraph 131, Member States “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small- and medium-sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”. In this regard, Member States also “underline the importance of establishing, where necessary, appropriate guidelines and regulations in accordance with national priorities and legislation for promoting and supporting sustainable tourism”.
In 2002, the World Summit on Sustainable Development in Johannesburg called for the promotion of sustainable tourism development, including non-consumptive and eco-tourism, in Chapter IV, paragraph 43 of the Johannesburg Plan of Implementation.
At the Johannesburg Summit, the launch of the “Sustainable Tourism – Eliminating Poverty (ST-EP) initiative was announced. The initiative was inaugurated by the World Tourism Organization, in collaboration with UNCTAD, in order to develop sustainable tourism as a force for poverty alleviation.
The UN Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD) last reviewed the issue of sustainable tourism in 2001, when it was acting as the Preparatory Committee for the Johannesburg Summit.
The importance of sustainable tourism was also mentioned in Agenda 21.
For more information and documents on this topic, please visit this link
UNWTO Annual Report 2016
In December 2015, the United Nations General Assembly declared 2017 as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development. This is a unique opportunity to devote a year to activities that promote the transformational power of tourism to help us reach a better future. This important cele...
UNWTO Annual Report 2015
2015 was a landmark year for the global community. In September, the 70th Session of the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a universal agenda for planet and people. Among the 17 SDGs and 169 associated targets, tourism is explicitly featured in Goa...
Emerging Issues for Small Island Developing States
The 2012 UNEP Foresight Process on Emerging Global Environmental Issues primarily identified emerging environmental issues and possible solutions on a global scale and perspective. In 2013, UNEP carried out a similar exercise to identify priority emerging environmental issues that are of concern to ...
Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
This Agenda is a plan of action for people, planet and prosperity. It also seeks to strengthen universal peace in larger freedom, We recognize that eradicating poverty in all its forms and dimensions, including extreme poverty, is the greatest global challenge and an indispensable requirement for su...
Towards Measuring the Economic Value of Wildlife Watching Tourism in Africa
Set against the backdrop of the ongoing poaching crisis driven by a dramatic increase in the illicit trade in wildlife products, this briefing paper intends to support the ongoing efforts of African governments and the broader international community in the fight against poaching. Specifically, this...
Status and Trends of Caribbean Coral Reefs: 1970-2012
Previous Caribbean assessments lumped data together into a single database regardless of geographic location, reef environment, depth, oceanographic conditions, etc. Data from shallow lagoons and back reef environments were combined with data from deep fore-reef environments and atolls. Geographic c...
15 Years of the UNWTO World Tourism Network on Child Protection: A Compilation of Good Practices
Although it is widely recognized that tourism is not the cause of child exploitation, it can aggravate the problem when parts of its infrastructure, such as transport networks and accommodation facilities, are exploited by child abusers for nefarious ends. Additionally, many other factors that contr...
Natural Resources Forum: Special Issue Tourism
The journal considers papers on all topics relevant to sustainable development. In addition, it dedicates series, issues and special sections to specific themes that are relevant to the current discussions of the United Nations Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD)....
Thailand: Supporting Sustainable Development in Thailand: A Geographic Clusters Approach
Market forces and government policies, including the Tenth National Development Plan (2007-2012), are moving Thailand toward a more geographically specialized economy. There is a growing consensus that Thailand’s comparative and competitive advantages lie in amenity services that have high reliance...
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal (NRF)
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal, seeks to address gaps in current knowledge and stimulate relevant policy discussions, leading to the implementation of the sustainable development agenda and the achievement of the Sustainable...
Road Map on Building a Green Economy for Sustainable Development in Carriacou and Petite Martinique, Grenada
This publication is the product of an international study led by the Division for Sustainable Development (DSD) of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA) in cooperation with the Ministry of Carriacou and Petite Martinique Affairs and the Ministry of Environment, Foreig...
UN Ocean Conference 2025
Our Ocean, Our Future, Our Responsibility “The ocean is fundamental to life on our planet and to our future. The ocean is an important source of the planet’s biodiversity and plays a vital role in the climate system and water cycle. The ocean provides a range of ecosystem services, supplies us with
UN Ocean Conference 2022
The UN Ocean Conference 2022, co-hosted by the Governments of Kenya and Portugal, came at a critical time as the world was strengthening its efforts to mobilize, create and drive solutions to realize the 17 Sustainable Development Goals by 2030.
58th Session of the Commission for Social Development – CSocD58
22nd general assembly of the united nations world tourism organization, world tourism day 2017 official celebration.
This year’s World Tourism Day, held on 27 September, will be focused on Sustainable Tourism – a Tool for Development. Celebrated in line with the 2017 International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development, the Day will be dedicated to exploring the contribution of tourism to the Sustainable Deve
World Tourism Day 2016 Official Celebration
Accessible Tourism for all is about the creation of environments that can cater for the needs of all of us, whether we are traveling or staying at home. May that be due to a disability, even temporary, families with small children, or the ageing population, at some point in our lives, sooner or late
4th Global Summit on City Tourism
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and the Regional Council for Tourism of Marrakesh with support of the Government of Morroco are organizing the 4th Global Summit on City Tourism in Marrakesh, Morroco (9-10 December 2015). International experts in city tourism, representatives of city DMOs, of
2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and Ulsan Metropolitan City with support of the Government of the Republic of Korea are organizing the 2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference, in Ulsan, Republic of Korea (14 - 16 October 2015). Under the title “Paving the Way for a Bright Future for Mounta
21st General Assembly of the United Nations World Tourism Organization
Unwto regional conference enhancing brand africa - fostering tourism development.
Tourism is one of the Africa’s most promising sectors in terms of development, and represents a major opportunity to foster inclusive development, increase the region’s participation in the global economy and generate revenues for investment in other activities, including environmental preservation.
- January 2017 International Year of Tourism In the context of the universal 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the International Year aims to support a change in policies, business practices and consumer behavior towards a more sustainable tourism sector that can contribute to the SDGs.
- January 2015 Targets 8.9, 12 b,14.7 The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development commits Member States, through Sustainable Development Goal Target 8.9 to “devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism, as a driver for jobs creation and the promotion of local culture and products, is also highlighted in Sustainable Development Goal target 12.b. Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “increase [by 2030] the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries”, through Sustainable Development Goals Target 14.7.
- January 2012 Future We Want (Para 130-131) Sustainable tourism is defined as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities” as well as to “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small and medium sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”.
- January 2009 Roadmap for Recovery UNWTO announced in March 2009 the elaboration of a Roadmap for Recovery to be finalized by UNWTO’s General Assembly, based on seven action points. The Roadmap includes a set of 15 recommendations based on three interlocking action areas: resilience, stimulus, green economy aimed at supporting the tourism sector and the global economy.
- January 2008 Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria The Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria represent the minimum requirements any tourism business should observe in order to ensure preservation and respect of the natural and cultural resources and make sure at the same time that tourism potential as tool for poverty alleviation is enforced. The Criteria are 41 and distributed into four different categories: 1) sustainability management, 2) social and economic 3) cultural 4) environmental.
- January 2003 1st Int. Conf. on Climate Change and Tourism The conference was organized in order to gather tourism authorities, organizations, businesses and scientists to discuss on the impact that climate change can have on the tourist sector. The event took place from 9 till 11 April 2003 in Djerba, Tunisia.
- January 2003 WTO becomes a UN specialized body By Resolution 453 (XV), the Assembly agreed on the transformation of the WTO into a United Nations specialized body. Such transformation was later ratified by the United Nations General Assembly with the adoption of Resolution A/RES/58/232.
- January 2002 World Ecotourism Summit Held in May 2002, in Quebec City, Canada, the Summit represented the most important event in the framework of the International Year of Ecosystem. The Summit identified as main themes: ecotourism policy and planning, regulation of ecotourism, product development, marketing and promotion of ecotourism and monitoring costs and benefits of ecotourism.
- January 1985 Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code At the World Tourism Organization Sixth Assembly held in Sofia in 1985, the Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code were adopted, setting out the rights and duties of tourists and host populations and formulating policies and action for implementation by states and the tourist industry.
- January 1982 Acapulco Document Adopted in 1982, the Acapulco Document acknowledges the new dimension and role of tourism as a positive instrument towards the improvement of the quality of life for all peoples, as well as a significant force for peace and international understanding. The Acapulco Document also urges Member States to elaborate their policies, plans and programmes on tourism, in accordance with their national priorities and within the framework of the programme of work of the World Tourism Organization.
- Discovery Platform
- Innovation Scouting
- Startup Scouting
- Technology Scouting
- Tech Supplier Scouting
- Venture Clienting
- Startup Program
- Trend Intelligence
- Business Intelligence
- All Industries
- Industry 4.0
- Manufacturing
- Case Studies
- Research & Development
- Corporate Strategy
- Corporate Innovation
- Open Innovation
- New Business Development
- Product Development
- Agriculture
- Construction
- Sustainability
- All Startups
- Circularity
- All Innovation
- Business Trends
- Emerging Tech
- Innovation Intelligence
- New Companies
- Scouting Trends
- Startup Programs
- Supplier Scouting
- Tech Scouting
- Top AI Tools
- Trend Tracking
- All Reports [PDF]
- Circular Economy
- Engineering
- Oil & Gas

Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)

Top 9 Travel Trends & Innovations in 2024
How are the latest trends in the travel industry reshaping trip planning and enhancing tourist experiences in 2024? Explore our in-depth industry research on the top 9 travel trends based on our analysis of 3500+ companies worldwide. These trends include AI, immersive tourism, IoT, contactless travel & more!
Technological advancements in the travel industry meet the growing demand for personalized experiences, safety, and sustainability. Post the COVID-19 pandemic, emerging travel trends mark a shift towards contactless travel through digital payments, self-check-ins, and more. Additionally, artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain are automating various hospitality and travel-related operations.
For instance, smart hotels make use of internet-connected devices to remotely control rooms. Further, businesses offer virtual tours by adopting extended reality (XR) technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). Travel companies also leverage data analytics to personalize marketing. At the same time, traveler assisting solutions like chatbots and voice technology aid them in booking accommodation and optimizing journeys. These travel trends improve the overall profitability of the tourism industry and enable it to make operations more sustainable and safe.
This article was published in July 2022 and updated in February 2024.
Innovation Map outlines the Top 9 Travel Trends & 18 Promising Startups
For this in-depth research on the Top 9 Trends & Startups, we analyzed a sample of 18 global startups and scaleups. The result of this research is data-driven innovation intelligence that improves strategic decision-making by giving you an overview of emerging technologies & startups in the travel industry. These insights are derived by working with our Big Data & Artificial Intelligence-powered StartUs Insights Discovery Platform , covering 2 500 000+ startups & scaleups globally. As the world’s largest resource for data on emerging companies, the SaaS platform enables you to identify relevant startups, emerging technologies & future industry trends quickly & exhaustively.
In the Innovation Map below, you get an overview of the Top 9 Travel Trends & Innovations that impact travel & tourism companies worldwide. Moreover, the Travel Innovation Map reveals 3 500+ hand-picked startups, all working on emerging technologies that advance their field.
Top 9 Travel Trends
- Artificial Intelligence
- Immersive Tourism
- Internet of Things
- Contactless Travel
- Big Data & Analytics
- Post-Pandemic Tourism
- Tour Premiumization
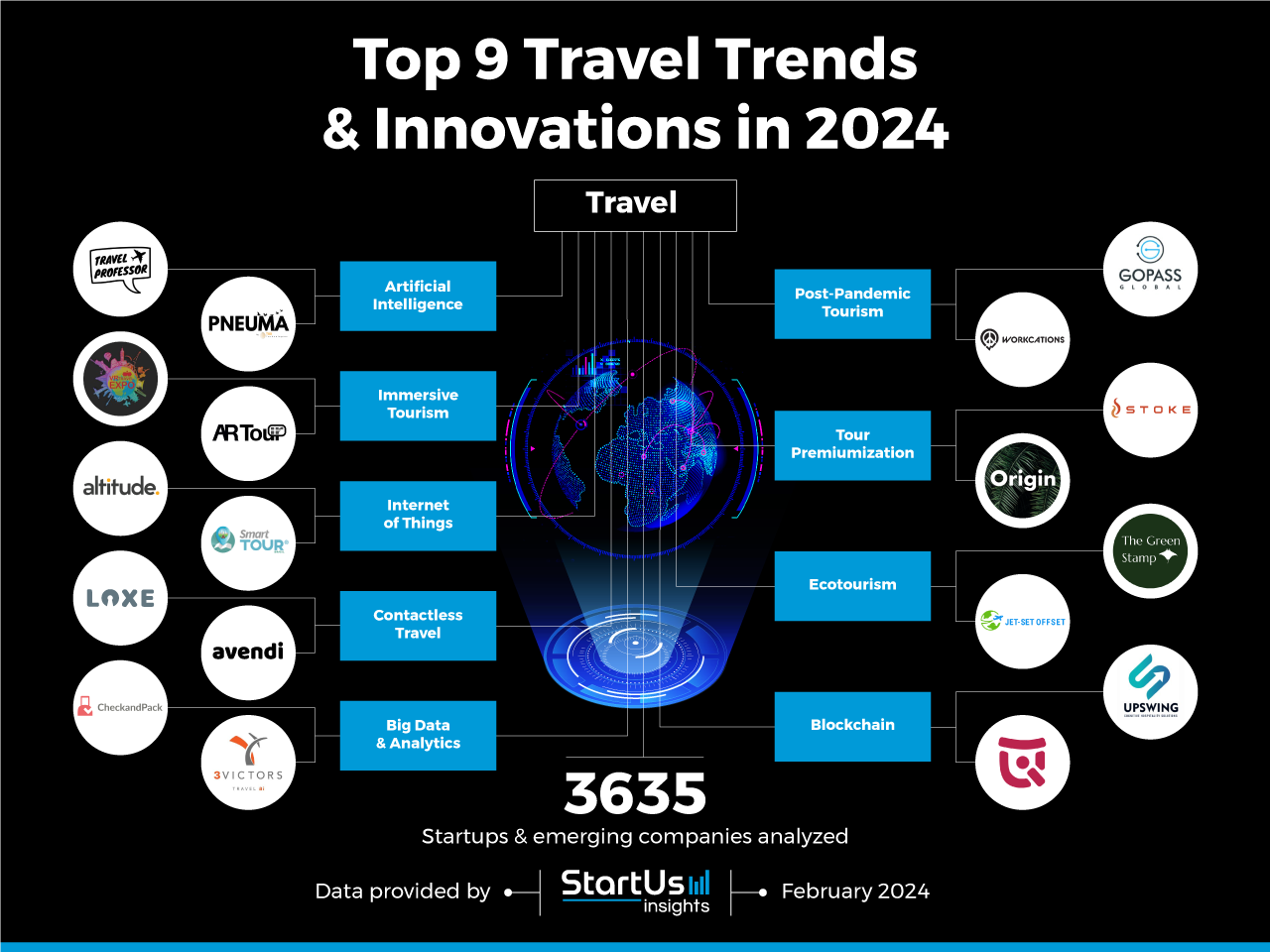
Click to download
Tree Map reveals the Impact of the Top 9 Travel Trends
Based on the Travel Innovation Map, the Tree Map below illustrates the impact of the Top 9 Travel Industry Trends in 2024. Startups and scaleups are enabling contactless travel using technologies like biometrics, radio-frequency identification (RFID), and near-field communication (NFC). This is due to increasing health and hygiene concerns post the pandemic. The use of AI in tourism ensures hassle-free trip planning while AR and VR allow tourists to virtually visit various locations and excursions. IoT increases visibility into tourism industry operations and allows passengers to track their luggage more efficiently. Further, the demand for personalized and luxurious travel is rising. Several startups enable recreational space travel as well as offer sustainable travel options to passengers.
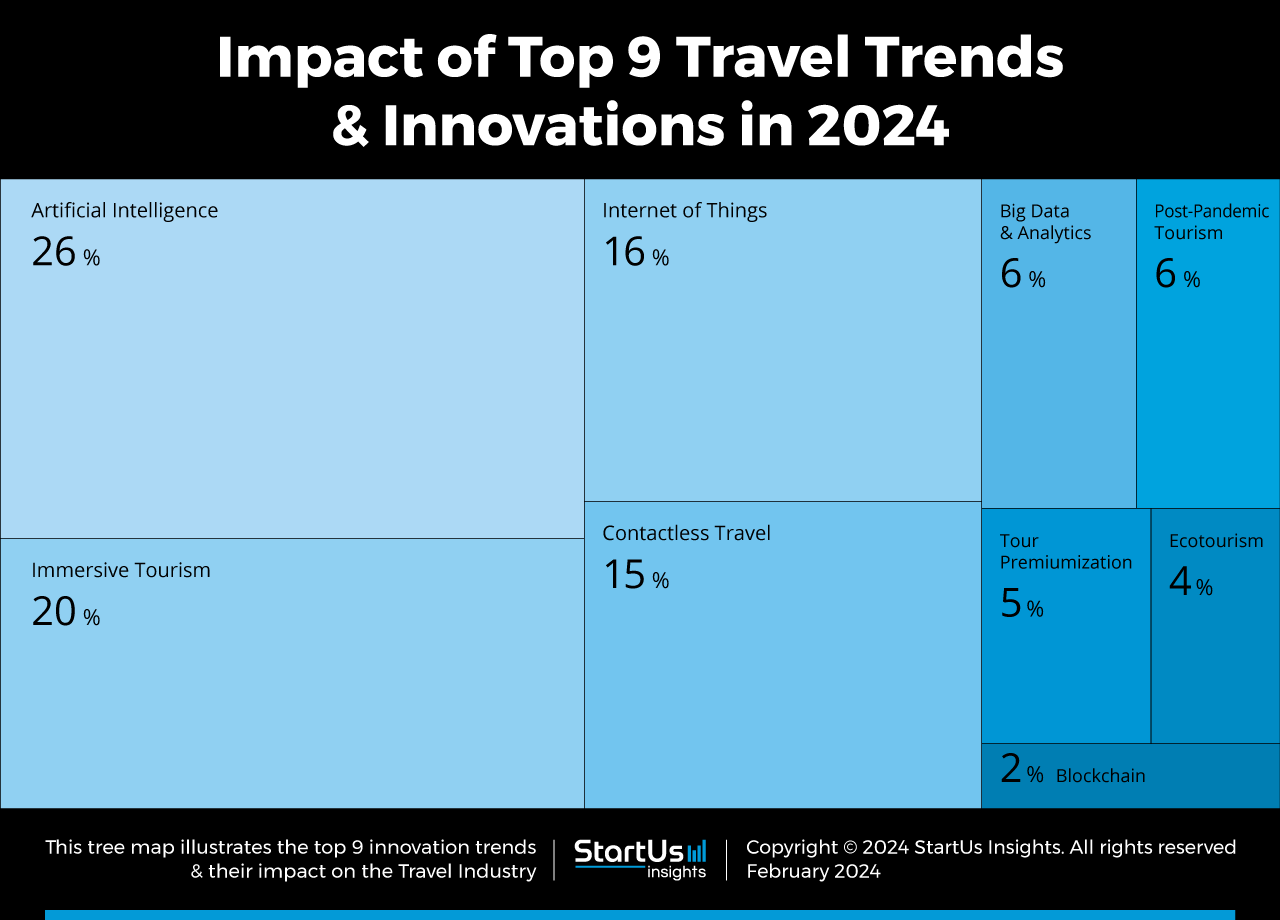
Global Startup Heat Map covers 3 635 Travel Startups & Scaleups
The Global Startup Heat Map below highlights the global distribution of the 3 635 exemplary startups & scaleups that we analyzed for this research. Created through the StartUs Insights Discovery Platform, the Heat Map reveals that the US, Europe, and India see the most activity.
Below, you get to meet 18 out of these 3 635 promising startups & scaleups as well as the solutions they develop. These 18 startups are hand-picked based on criteria such as founding year, location, funding raised, and more. Depending on your specific needs, your top picks might look entirely different.
Interested in exploring all 3500+ travel startups & scaleups?
Top 9 Travel Trends in 2024
1. artificial intelligence.
Hotels employ intelligent chatbots, powered by AI, to provide quick and personalized responses to traveler inquiries. These chatbots simplify the booking process and gather customer reviews, aiding potential travelers in making informed decisions. Moreover, AI-based robots enhance the customer experience by automating hotel disinfection and delivering room service.
At airports, these robots guide travelers and assist with luggage handling. Facial recognition technology, driven by AI, expedites identity verification at airports, enhancing security and offering a swift alternative to traditional methods. Startups are developing AI-powered trip planning solutions, optimizing journeys, and personalizing travel experiences.
Travel Professor develops a Travel Chatbot
UK-based startup Travel Professor offers an AI-enabled chatbot for travelers. The startup’s chat widget software monitors multiple flight deals and notifies users when their preferences match. It also provides travel destination recommendations and flight price alerts. This allows travelers to book economical flights and have a budget-friendly tourism experience.
Pneuma Travel facilitates Travel Planning
US startup Pneuma Travel develops a voice-assisted digital agent, Sarah , to streamline the process of travel planning. This assistant, powered by AI, excels in arranging flight and accommodation bookings and assists travelers in discovering a variety of activities. Sarah , available round the clock, provides continuous support for all travel-related inquiries.
Moreover, Sarah customizes travel options according to individual preferences and budgetary constraints. The agent further enhances the travel experience by providing insights into local attractions in unfamiliar cities. Importantly, Sarah enables real-time modifications to travel plans, in compliance with specific airline policies, thereby minimizing waiting times for users.
2. Immersive Tourism
Immersive tourism caters to the growing demand for meaningful experiences among travelers, leveraging AR, VR, and mixed reality (MR). VR simulates original locations through a computer-generated environment, allowing tourists to virtually explore destinations. It provides travelers with a comprehensive 360-degree tour of points of interest.
AR enhances the travel experience with interactive elements such as navigation maps and ads. Travel companies employ AR and VR-based gamification to heighten tourist attractions. Moreover, these technologies enable hotels and resorts to present amenities and rooms in an engaging, interactive manner.
VR Travel Expo offers VR-based Travel Plans
US startup VR Travel Expo develops a VR travel application to transform the way people research and book travel. The application enables users to plan their vacations more efficiently. It provides an engaging platform for users to explore and expand their knowledge of the world. Moreover, it employs 3D geospatial technology that creates real-time digital twins of the world. This further enhances the travel planning experience.
AR Tour makes AR Glasses
Italian startup AR Tour offers AR-powered tours. The startup’s AR glasses superimpose reconstructed images of archaeological ruins to show how the site originally was. Its tour informs the tourists about the site’s history and significance via an audio-visual package. Moreover, the startup designs lightweight AR glasses to prevent motion sickness among tourists, improving convenience.
3. Internet of Things
IoT generates ample data that tourism companies leverage to personalize services in their subsequent visits. Hotels use IoT sensors to enable smart rooms that automate room lighting, temperature, and ambiance control, enhancing guest comfort. These sensors adjust appliances in vacant rooms, conserving energy and reducing the building’s carbon footprint.
Startups harness IoT to deliver location-specific information to customers, including real-time luggage tracking via IoT tags, minimizing lost items. Airlines also incorporate IoT-based solutions into seats, monitoring passenger temperature and heart rate for proactive health management.
Altitude enables Smart Hotels
New Zealand-based startup Altitude creates an IoT-based hotel software and hardware to develop smart hotels. The startup makes self-service kiosks to automate reservations, room up-gradation, payments, as well as check-in and check-out. Its hotel management platform further enables contactless engagement with guests. Additionally, Altitude’s mobile keys allow guests to open doors using mobile phones, providing convenience and saving time for travelers.
Smart Tour provides Smart Itineraries
Brazilian startup Smart Tour offers smart itineraries using IoT and quick response (QR) codes. The startup recommends travel routes and destinations based on the user’s preference in real-time. This facilitates a seamless experience for travelers. Besides, the user-generated data enables tourism managers to better understand consumer behavior and indulge in proximity marketing. The startup also offers a contact tracing solution to monitor COVID-19 infected travelers and ensure public safety.
4. Contactless Travel
Travelers benefit from contactless recognition technologies like retina scanning, which replace traditional travel documents, speeding up passenger identification and reducing airport queues. QR codes offered by travel companies allow tourists to access relevant information on their mobile devices, enhancing engagement.
Hotels have introduced contactless self-check-ins, enabling visitors to arrange services before arrival. Additionally, contactless payment modes are available in hotels and restaurants for swift and secure transactions. Moreover, wearable devices are transforming the travel experience by providing real-time notifications and touch-free access to services and information.
Loxe designs Smart Hotel Keys
US-based startup Loxe makes smart mobile keys for hotels. The startup’s smartphone app replaces key cards with contactless mobile keys that allow users to unlock doors using smartphones. It also reduces operational costs incurred in the manufacturing of conventional keys or plastic cards. Moreover, the startup designs a Bluetooth retrofit module that converts normal door locks into mobile-ready door locks. This allows hotel owners to easily convert their existing locks into smart ones without additional expenses while improving guest safety and convenience.
Avendi provides Contactless Payment
Singaporean startup Avendi offers contactless and cashless payments for travelers. The startup allows tourists to accumulate expenses throughout their trip and pay at the end of the journey. Avendi’s app utilizes QR codes to add all the billed expenses and shown through its dashboard. The user settles the tab amount in the preferred currency, preventing the inconvenience of cash withdrawal or credit card payments.
5. Big Data & Analytics
Big data empowers travel companies with customer trends for strategic marketing. Analyzing traveler behavior, they offer tailored recommendations for hotel bookings, cab hires, flight reservations, and ticket purchases.
Predicting future demand is another advantage of big data and analytics, helping hotels and airlines identify peak periods to optimize revenue. Advanced analysis of transactional data aids in detecting cyber fraud, and safeguarding sensitive customer information such as credit card details and biometric data.
CheckandPack creates a Travel Platform
Dutch startup CheckandPack offers a big data travel platform. It runs marketing campaigns to gather traveler data and understand tourism trends. Based on these insights, the platform enables businesses to approach travelers with a customized appeal. It also provides travelers with holiday planning.
3Victors provides Travel Data Analytics
US-based startup 3Victors offers travel data analytics. The startup’s product, PriceEye Suite , proactively monitors the prices of numerous airlines to provide insights into competitor prices. It creates a dashboard to display travelers’ location of interest, allowing travel airlines to better manage their revenue and pricing strategy.

6. Post-Pandemic Tourism
Post-pandemic tourism focuses on safe, sustainable, and flexible travel options, responding to evolving traveler preferences and health guidelines. Enhanced health and safety protocols, including regular sanitization and contactless services, become standard in airlines and hotels, ensuring traveler confidence.
Destinations and operators emphasize outdoor and less crowded experiences, catering to a heightened demand for nature-based and wellness travel. Flexible booking policies and trip insurance gain prominence, offering peace of mind amid uncertainties. Sustainable travel gains traction, with tourists and businesses prioritizing environmental impact and community well-being.
GOPASS Global enables Pre-travel Risk Management
Singaporean startup GOPASS Global provides a travel risk analytics platform against COVID-19. It analyzes the biosecurity risk elements involved in a trip, such as border restrictions, quarantine requirements, airport type, and airline transit points or seating in real-time. This allows travelers to assess risk factors and plan their trips accordingly.
Moreover, the startup creates world maps displaying information regarding COVID-prone areas, testing areas, and vaccine coverage. This provides travelers with a preview of the current situation, allowing them to ensure safety during business and leisure travel.
Workcations enables Work from Anywhere
Indian startup Workcations provides properties at tourist destinations for remote-working individuals. It offers amenities like internet connectivity, food, and a quiet ambiance, allowing tourists to work in a peaceful environment without hindrance. This increases employee productivity, motivation, and retention.
7. Tour Premiumization
Hyper-personalization in travel experiences is on the rise, with tourists eager to immerse themselves in diverse cultures. Luxury travelers enjoy tailored experiences and intuitive services through tour premiumization. Health and wellness packages offered by travel startups help tourists unwind.
These retreats enhance health and offer detoxifying food options. Space tourism is another exciting development, offering leisure or research trips to space. Lastly, travel startups are fostering customer loyalty and building strong relationships through membership or subscription models.
STOKE provides Space Tour
US-based startup STOKE facilitates space travel using everyday-operable rockets. The startup’s rockets are reusable and deliver satellites to any desired orbit. This enables on-demand access to space, paving way for space tours for exploration, recreation, and research. The startup also emphasizes the economical and rapid development of its hardware for feasible spacecraft launches, advancing space tourism.
Origin offers Travel Personalization
Dutch startup Origin provides premium travel personalization to tourists. The startup utilizes machine learning and travel curators to plan creative vacations. It also arranges flights and accommodation for travelers. Further, the startup measures the carbon output of itineraries and offers sustainable tourism options.
8. Ecotourism
Traveling responsibly minimizes tourism’s environmental impact and supports local communities’ well-being. Ecotourists strive to reduce their carbon footprint during their journeys. Startups contribute by developing sustainable transport, ecolodges, and solar-powered resorts.
Airline passengers have the option to offset carbon emissions during flight bookings. Local tourism stimulates small businesses economically and creates job opportunities. It also emphasizes minimum littering, which lowers pollution and the time spent on cleanups.
Jet-Set Offset simplifies Flight Carbon Offset
US-based startup Jet-Set Offset creates a carbon-offsetting platform for air travel. The startup partners with non-profit organizations working against climate change and connects them with travelers. Each time travelers book flight tickets via the startup’s platform, Jet-Set Offset contributes a certain amount per mile for their journey to environmental organizations. This way, the passenger’s journey promotes mileage-based donations to offset carbon emissions.
The Green Stamp facilitates Ethical Wildlife Tour
Dutch startup The Green Stamp provides a platform to book ethical wildlife tours. It curates tours based on the tourists’ inclinations toward certain locations or wildlife. Exploration of these projects allows travelers to indirectly contribute to their cause as these wildlife projects donate to the welfare of local communities and the environment.
9. Blockchain
Blockchain provides the travel industry with operational transparency and security. Traceable payments, particularly for international travel, are a key application, that fosters trust among parties involved in transactions.
Automation and enforcement of agreements in travel insurance and supplier contracts are achieved through smart contracts. This strengthens reliability and cuts administrative costs. Travel firms establish customer loyalty programs where points are exchanged for cryptocurrency. Lastly, blockchain increases data storage security, reducing the risk of information leaks.
Upswing facilitates Guest Profiling
Indian startup Upswing creates AURA , a blockchain-powered platform for guest profiling. It provides a holistic view of guests, their preferences, and purchase patterns. The platform associates a score with each guest and suggests improvements in their service. This facilitates hotels to provide a personalized experience to their guests and, in turn, increase sales.
UIQ Travel develops a Solo Traveling App
US-based startup UIQ Travel develops a blockchain-based app to connect solo travelers. It discovers people with shared interests and suggests tours or attractions. Such hyper-personalized recommendations assist in experience discovery and also increase traveler engagement.
Discover all Travel Trends, Technologies & Startups
Tourism, although severely impacted by the pandemic, now continues to rapidly grow across the globe. Post-pandemic trends indicate an increasing emphasis on hygiene and safety during travel. The industry is witnessing the widespread adoption of disruptive technologies like AI, XR, IoT, and blockchain. The travel industry utilizes big data to understand traveler trends for targeted marketing. The transition to ecotourism is accelerating as businesses integrate zero-emission transit and carbon offset programs to reduce their carbon footprint.
The Travel Trends & Startups outlined in this report only scratch the surface of trends that we identified during our data-driven innovation and startup scouting process. Among others, personalization, decarbonization, and travel safety will transform the sector as we know it today. Identifying new opportunities and emerging technologies to implement into your business goes a long way in gaining a competitive advantage. Get in touch to easily and exhaustively scout startups, technologies & trends that matter to you!
Your Name Business Email Company
Get our free newsletter on technology and startups.
Protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Discover our Free Travel Report 21 pages
Book a call today!

Travel 21 pages report
Mobility 22 pages report, railway 22 pages report, cleantech 20 pages report.
Leverage our unparalleled data advantage to quickly and easily find hidden gems among 4.7M+ startups, scaleups. Access the world's most comprehensive innovation intelligence and stay ahead with AI-powered precision.
Get in touch
Your Name Business Email Company How can we support you? (optional)

Protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

- Tourism Management Tutorial
- Tourism Management - Home
- Tourism Basics
- Tourism Management - Introduction
- Tourism Management - Types
- Tourism Management - Terminology
- Tourism Management - Factors
- Tourism Management - Demand
- Tourism Mngmt - Motivation Factors
- Maslow's Pyramid of Motivation
- Consumer Behavior in Tourism
- Tourism Management - Plog's Model
- About Tourism Destinations
- Destination Awareness
- Tourism Management - Milieus
- Tourism Management Destination
- Tools for Destination Management
- Managing Tourism
- Tourism Management - Supply
- Tourism Functional Management
- Business Departments
- Market Segmentation
- Tourism Mngmt - Marketing Mix
- Tourism Mngmt - Products & Services
- Developing Product
- Product Development Phases
- Tourism Impacts, Trends, & Future
- Tourism Management - Impacts
- Tourism Mngmt - Trends & Future
- Tourism Management Resources
- Tourism Management - Quick Guide
- Tourism Management - Resources
- Tourism Management - Discussion
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
Products and Services
“Don’t give up and always keep on believing in your product. Because if you don’t, how can you make others believe in it?” − Niels Van Deuren, Founder, housinganywhere.com.
The tourism industry as a whole survives because of various tourism products and services. Tourism industry is flexible. The products of tourism cannot be easily standardized as they are created for the customers of varied interests and demands. As the tourism products are mainly the tourists’ experience, they can be stored only in the tourists’ memories.
Let us understand more about tourism products and services −
Types of Tourism Products
The tourism products are grouped into the following types −
Tourism Oriented Products (TOP)
These are the products and services created primarily for the tourists and also for the locals. These products need a great share of investments in private sector. A few of them are −
- Accommodations; For example, Taj, ITC Hotels.
- Transportation; For example, Owning taxis, luxury buses, and boats.
- Retail Travel Agents
- Tour Operators
- Shopping Centers such as malls
- Cinema Theatres such as PVR
- Restaurants for Food and Beverages
- Tourism Information Centers
- Souvenirs Outlets
- Museums, Temples, Gardens, and Theme parks
Residents Oriented Products (ROP)
Here, the products and services are created mainly for the local residents staying at a particular tourist destination. This category requires investment in public sectors more. Some of them are −
- Public Parks
- Banks and ATMs
- Petrol Pumps
- Postal Service
Intangible Products of Tourism
They include −
Bookings of accommodations, theatres, and at various sites.
Tourists’ experience by visiting a destination, eating at a restaurant, or performing an activity.
Tourists’ memory which is created by storing the details of events and experience on the tour. The high degree of satisfaction or dissatisfaction is often stored as a long term memory.
Transportation of tourists and their luggage from one place to another.
Tour Operator’s Products and Services
To realize the facilities and experience a tourism product offers, service is required by skilled and qualified staff. The tour operator provides the following typical products and services −
Accommodations
The tourist destinations are equipped with different types of accommodations. They cater for tourists’ stay at the destination.
Serviced − This type of accommodation is supported by skilled staff such as housekeepers, drivers, guides, and cooks.
Self-catering − This accommodation offers staying facilities but dining is required to be self-catered. It is equipped with cooking, fuel and facility, some basic supplies such as tea/coffee/sugar sachets, and a drinking water source.
Hotels − Budget rooms to 7* hotels with classy amenities. The hotels contribute a major share of imparting the experience to the tourists by providing best services and amenities.
Guest Houses − Owned by business or government organizations, which can be used by its staff and staff relatives.
Camping Sites − They are open sites often located in areas of lush greenery. They are equipped with clean place to pitch the personal tent, a water supply, and electric supply. Camp sites have common rest rooms.
Reservations
The tour operator is responsible for making reservations for special events or activities the tourists are interested in. At some places, the reservations are required to be done well in advance to avoid last minute hassles. The events or activities such as a music concert or a theatre show, visiting a theme park or a zoo, require people to secure seats or avail entry with prior reservations.
Guided Tours
The tour operators can arrange guided tours. Some qualified staff who can get access to the place, explain the importance of the place, support, and guide the participants through the entire visit. The guide is arranged to accompany the tour participants as a part of tour.
Transport Facilities
These facilities are for travelling from one place to another.
Surface Transport − It includes support of transport by road or water.
Air Transport − This is the support of transport by air, generally given for long distance travel. Many times the tours include a halt of a couple of hours at transit destinations. Today the airports are built and maintained as engaging tourist terminals by providing amenities such as spas, lounges, food joints, bars, and book shops, retail shops for selling authentic local food, clothes, and souvenirs.
Today the Airlines are no more backstage when it comes to caring for their customers. They offer loyalty programs to their customers under Frequent Flyer Program to encourage the customers to travel more and accumulate points and redeem them against travel or rewards.
Dining Facilities
The tour operators can book accommodation that provides dining facilities or it can tie up with the local restaurants which are ready to entertain groups. If the tour package is all inclusive, the tour operator pays for breakfast, lunch, and dinner. If not, the tourists need to pay from their own pocket.
To Continue Learning Please Login

What Are Ancillary Services in Tourism?
By Alice Nichols
If you’re planning a trip, you might have heard the term “ancillary services” in the tourism industry. But what exactly does it mean?
In simple terms, ancillary services refer to any additional products or services that a traveler may need during their trip. Let’s take a closer look at what these services include:
Transportation
One of the most common examples of ancillary services is transportation. This includes things like airport transfers, car rentals, and train tickets. These services are often offered by travel companies to make it easier for travelers to get around their destination.
Accommodation
Another important aspect of any trip is accommodation. Ancillary services in this category include things like hotel upgrades, room service, and spa treatments. These additional options can help make your stay more comfortable and enjoyable.
Tours and Activities
Many travelers want to experience everything their destination has to offer, which is where tours and activities come in. Ancillary services in this category may include guided tours, adventure activities like zip-lining or snorkeling, or even culinary experiences like cooking classes.
Travel Insurance
While no one wants to think about potential problems that could arise during their trip, it’s always better to be prepared. Travel insurance is an ancillary service that can provide peace of mind by covering things like lost luggage, medical emergencies, and trip cancellations.
10 Related Question Answers Found
What are ancillary services in tourism examples, what are the services in tourism, what are services in tourism, what are travel services in tourism, what are the services of tourism, what are the services in tourism industry, what are the services offered in the tourism industry, what is a service in tourism, what is a service in travel and tourism, what are consolidators in tourism, backpacking - budget travel - business travel - cruise ship - vacation - tourism - resort - cruise - road trip - destination wedding - tourist destination - best places, london - madrid - paris - prague - dubai - barcelona - rome.
© 2024 LuxuryTraveldiva
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Un standards for measuring tourism, share this content.
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
Glossary of tourism terms
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which involve tourism expenditure.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W Y Z
Activity/activities : In tourism statistics, the term activities represent the actions and behaviors of people in preparation for and during a trip in their capacity as consumers ( IRTS 2008, 1.2 ).
Activity (principal): The principal activity of a producer unit is the activity whose value added exceeds that of any other activity carried out within the same unit ( SNA 2008, 5.8 ).
Activity (productive): The (productive) activity carried out by a statistical unit is the type of production in which it engages. It has to be understood as a process, i.e. the combination of actions that result in a certain set of products. The classification of productive activities is determined by their principal output.
Administrative data : Administrative data is the set of units and data derived from an administrative source. This is a data holding information collected and maintained for the purpose of implementing one or more administrative regulations.
Adventure tourism : Adventure tourism is a type of tourism which usually takes place in destinations with specific geographic features and landscape and tends to be associated with a physical activity, cultural exchange, interaction and engagement with nature. This experience may involve some kind of real or perceived risk and may require significant physical and/or mental effort. Adventure tourism generally includes outdoor activities such as mountaineering, trekking, bungee jumping, rock climbing, rafting, canoeing, kayaking, canyoning, mountain biking, bush walking, scuba diving. Likewise, some indoor adventure tourism activities may also be practiced.
Aggregated data : The result of transforming unit level data into quantitative measures for a set of characteristics of a population.
Aggregation : A process that transforms microdata into aggregate-level information by using an aggregation function such as count, sum average, standard deviation, etc.
Analytical unit : Entity created by statisticians, by splitting or combining observation units with the help of estimations and imputations.
Balance of payments : The balance of payments is a statistical statement that summarizes transactions between residents and non-residents during a period. It consists of the goods and services account, the primary income account, the secondary income account, the capital account, and the financial account ( BPM6, 2.12 ).
Bias : An effect which deprives a statistical result of representativeness by systematically distorting it, as distinct from a random error which may distort on any one occasion but balances out on the average.
Business and professional purpose (of a tourism trip): The business and professional purpose of a tourism trip includes the activities of the self-employed and employees, as long as they do not correspond to an implicit or explicit employer-employee relationship with a resident producer in the country or place visited, those of investors, businessmen, etc. ( IRTS 2008, 3.17.2 ).
Business tourism : Business tourism is a type of tourism activity in which visitors travel for a specific professional and/or business purpose to a place outside their workplace and residence with the aim of attending a meeting, an activity or an event. The key components of business tourism are meetings, incentives, conventions and exhibitions. The term "meetings industry" within the context of business tourism recognizes the industrial nature of such activities. Business tourism can be combined with any other tourism type during the same trip.
Business visitor : A business visitor is a visitor whose main purpose for a tourism trip corresponds to the business and professional category of purpose ( IRTS 2008, 3.17.2 ).
Central Product Classification : The Central Product Classification (CPC) constitutes a complete product classification covering goods and services. It is intended to serve as an international standard for assembling and tabulating all kinds of data requiring product detail, including industrial production, national accounts, service industries, domestic and foreign commodity trade, international trade in services, balance of payments, consumption and price statistics. Other basic aims are to provide a framework for international comparison and promote harmonization of various types of statistics dealing with goods and services.
Census : A census is the complete enumeration of a population or groups at a point in time with respect to well defined characteristics: for example, Population, Production, Traffic on particular roads.
Coastal, maritime and inland water tourism : Coastal tourism refers to land-based tourism activities such as swimming, surfing, sunbathing and other coastal leisure, recreation and sports activities which take place on the shore of a sea, lake or river. Proximity to the coast is also a condition for services and facilities that support coastal tourism. Maritime tourism refers to sea-based activities such as cruising, yachting, boating and nautical sports and includes their respective land-based services and infrastructure. Inland water tourism refers to tourism activities such as cruising, yachting, boating and nautical sports which take place in aquatic- influenced environments located within land boundaries and include lakes, rivers, ponds, streams, groundwater, springs, cave waters and others traditionally grouped as inland wetlands.
Coherence : Adequacy of statistics to be combined in different ways and for various uses.
Competitiveness of a tourism destination : The competitiveness of a tourism destination is the ability of the destination to use its natural, cultural, human, man-made and capital resources efficiently to develop and deliver quality, innovative, ethical and attractive tourism products and services in order to achieve a sustainable growth within its overall vision and strategic goals, increase the added value of the tourism sector, improve and diversify its market components and optimize its attractiveness and benefits both for visitors and the local community in a sustainable perspective.
Consistency : Logical and numerical coherence.
Country of reference : The country of reference refers to the country for which the measurement is done. ( IRTS 2008, 2.15 ).
Country of residence : The country of residence of a household is determined according to the centre of predominant economic interest of its members. If a person resides (or intends to reside) for more than one year in a given country and has there his/her centre of economic interest (for example, where the predominant amount of time is spent), he/she is considered as a resident of this country.
Country-specific tourism characteristic products and activities : To be determined by each country by applying the criteria of IRTS 2008, 5.10 in their own context; for these products, the activities producing them will be considered as tourism characteristic, and the industries in which the principal activity is tourism-characteristic will be called tourism industries ( IRTS 2008, 5.16 ).
Cultural tourism : Cultural tourism is a type of tourism activity in which the visitor's essential motivation is to learn, discover, experience and consume the tangible and intangible cultural attractions/products in a tourism destination. These attractions/products relate to a set of distinctive material, intellectual, spiritual and emotional features of a society that encompasses arts and architecture, historical and cultural heritage, culinary heritage, literature, music, creative industries and the living cultures with their lifestyles, value systems, beliefs and traditions.
Data checking : Activity whereby the correctness conditions of the data are verified. It also includes the specification of the type of error or of the condition not met, and the qualification of the data and their division into "error-free data" and "erroneous data".
Data collection : Systematic process of gathering data for official statistics.
Data compilation : Operations performed on data to derive new information according to a given set of rules.
Data confrontation : The process of comparing data that has generally been derived from different surveys or other sources, especially those of different frequencies, in order to assess and possibly improve their coherency, and identify the reasons for any differences.
Data processing : Data processing is the operation performed on data by the organization, institute, agency, etc., responsible for undertaking the collection, tabulation, manipulation and preparation of data and metadata output.
Data reconciliation : The process of adjusting data derived from two different sources to remove, or at least reduce, the impact of differences identified.
Destination (main destination of a trip): The main destination of a tourism trip is defined as the place visited that is central to the decision to take the trip. See also purpose of a tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 2.31 ).
Destination management / marketing organization (DMO) : A destination management/marketing organization (DMO) is the leading organizational entity which may encompass the various authorities, stakeholders and professionals and facilitates tourism sector partnerships towards a collective destination vision. The governance structures of DMOs vary from a single public authority to a public/ private partnership model with the key role of initiating, coordinating and managing certain activities such as implementation of tourism policies, strategic planning, product development, promotion and marketing and convention bureau activities. The functions of the DMOs may vary from national to regional and local levels depending on the current and potential needs as well as on the decentralization level of public administration. Not every tourism destination has a DMO.
Documentation: Processes and procedures for imputation, weighting, confidentiality and suppression rules, outlier treatment and data capture should be fully documented by the survey provider. Such documentation should be made available to at least the body financing the survey.
Domestic tourism : Domestic tourism comprises the activities of a resident visitor within the country of reference, either as part of a domestic tourism trip or part of an outbound tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 2.39 ).
Domestic tourism consumption : Domestic tourism consumption is the tourism consumption of a resident visitor within the economy of reference ( TSA:RMF 2008, figure 2.1 ).
Domestic tourism expenditure : Domestic tourism expenditure is the tourism expenditure of a resident visitor within the economy of reference, (IRTS 2008, 4.15(a)).
Domestic tourism trip : A domestic tourism trip is one with a main destination within the country of residence of the visitor (IRTS 2008, 2.32).
Domestic visitor : As a visitor travels within his/her country of residence, he/she is a domestic visitor and his/her activities are part of domestic tourism.
Durable consumer goods : Durable consumer goods are goods that may be used repeatedly or continuously over a period of a year or more, assuming a normal or average rate of physical usage. When acquired by producers, these are considered to be capital goods used for production processes, as is the case of vehicles, computers, etc. When acquired by households, they are considered to be consumer durable goods ( TSA:RMF 2008, 2.39 ). This definition is identical to the definition of SNA 2008, 9.42 : A consumer durable is a goodthat may be used for purposes of consumption repeatedly or continuously over a period of a year or more.
Dwellings : Each household has a principal dwelling (sometimes also designated as main or primary home), usually defined with reference to time spent there, whose location defines the country of residence and place of usual residence of this household and of all its members. All other dwellings (owned or leased by the household) are considered secondary dwellings ( IRTS 2008, 2.26 ).
Ecotourism : Ecotourism is a type of nature-based tourism activity in which the visitor's essential motivation is to observe, learn, discover, experience and appreciate biological and cultural diversity with a responsible attitude to protect the integrity of the ecosystem and enhance the well-being of the local community. Ecotourism increases awareness towards the conservation of biodiversity, natural environment and cultural assets both among locals and the visitors and requires special management processes to minimize the negative impact on the ecosystem.
Economic analysis : Tourism generates directly and indirectly an increase in economic activity in the places visited (and beyond), mainly due to demand for goods and services thatneed to be produced and provided. In the economic analysis of tourism, one may distinguish between tourism's 'economic contribution' which refers to the direct effect of tourism and is measurable by means of the TSA, and tourism's 'economic impact' which is a much broader concept encapsulating the direct, indirect and induced effects of tourism and which must be estimated by applying models. Economic impact studies aim to quantify economic benefits, that is, the net increase in the wealth of residents resulting from tourism, measured in monetary terms, over and above the levels that would prevail in its absence.
Economic territory : The term "economic territory" is a geographical reference and points to the country for which the measurement is done (country of reference) ( IRTS 2008, 2.15 ).
Economically active population : The economically active population or labour force comprises all persons of either sex who furnish the supply of labour for the production of goods and services as defined by the system of national accounts during a specified time-reference period (ILO, Thirteenth ICLS, 6.18).
Economy (of reference): "Economy" (or "economy of reference") is an economic reference defined in the same way as in the balance of payments and in the system of national accounts: it refers to the economic agents that are resident in the country of reference ( IRTS 2008, 2.15 ).
Education tourism : Education tourism covers those types of tourism which have as a primary motivation the tourist's engagement and experience in learning, self-improvement, intellectual growth and skills development. Education Tourism represents a broad range of products and services related to academic studies, skill enhancement holidays, school trips, sports training, career development courses and language courses, among others.
Employees : Employees are all those workers who hold the type of job defined as "paid employment" (ILO, Fifteenth ICLS, pp. 20-22).
Employer-employee relationship : An employer-employee relationship exists when there is an agreement, which may be formal or informal, between an entity and an individual, normally entered into voluntarily by both parties, whereby the individual works for the entity in return for remuneration in cash or in kind ( BPM6, 11.11 ).
Employers : Employers are those workers who, working on their own account with one or more partners, hold the type of job defined as a "self-employment job" and, in this capacity, on a continuous basis (including the reference period) have engaged one or more persons to work for them in their business as "employee(s)" (ILO, Fifteenth ICLS, pp. 20-22).
Employment : Persons in employment are all persons above a specified age who, during a specified brief period, either one week or one day, were in paid employment or self-employment (OECD GST, p. 170).
Employment in tourism industries : Employment in tourism industries may be measured as a count of the persons employed in tourism industries in any of their jobs, as a count of the persons employed in tourism industries in their main job, or as a count of the jobs in tourism industries ( IRTS 2008, 7.9 ).
Enterprise : An enterprise is an institutional unit engaged in production of goods and/or services. It may be a corporation, a non-profit institution, or an unincorporated enterprise. Corporate enterprises and non-profit institutions are complete institutional units. An unincorporated enterprise, however, refers to an institutional unit —a household or government unit —only in its capacity as a producer of goods and services (OECD BD4, p. 232)
Establishment : An establishment is an enterprise, or part of an enterprise, that is situated in a single location and in which only a single productive activity is carried out or in which the principal productive activity accounts for most of the value added ( SNA 2008, 5.14 ).
Estimation : Estimation is concerned with inference about the numerical value of unknown population values from incomplete data such as a sample. If a single figure is calculated for each unknown parameter the process is called "point estimation". If an interval is calculated within which the parameter is likely, in some sense, to lie, the process is called "interval estimation".
Exports of goods and services : Exports of goods and services consist of sales, barter, or gifts or grants, of goods and services from residents to non-residents (OECD GST, p. 194)
Frame : A list, map or other specification of the units which define a population to be completely enumerated or sampled.
Forms of tourism : There are three basic forms of tourism: domestic tourism, inbound tourism, and outbound tourism. These can be combined in various ways to derive the following additional forms of tourism: internal tourism, national tourism and international tourism.
Gastronomy tourism : Gastronomy tourism is a type of tourism activity which is characterized by the visitor's experience linked with food and related products and activities while travelling. Along with authentic, traditional, and/or innovative culinary experiences, Gastronomy Tourism may also involve other related activities such as visiting the local producers, participating in food festivals and attending cooking classes. Eno-tourism (wine tourism), as a sub-type of gastronomy tourism, refers to tourism whose purpose is visiting vineyards, wineries, tasting, consuming and/or purchasing wine, often at or near the source.
Goods : Goods are physical, produced objects for which a demand exists, over which ownership rights can be established and whose ownership can be transferred from one institutional unit to another by engaging in transactions on markets ( SNA 2008, p. 623 ).
Gross fixed capital formation : Gross fixed capital formation is defined as the value of institutional units' acquisitions less disposals of fixed assets. Fixed assets are produced assets (such as machinery, equipment, buildings or other structures) that are used repeatedly or continuously in production over several accounting periods (more than one year) ( SNA 2008, 1.52 ).
Gross margin : The gross margin of a provider of reservation services is the difference between the value at which the intermediated service is sold and the value accrued to the provider of reservation services for this intermediated service.
Gross value added : Gross value added is the value of output less the value of intermediate consumption ( TSA:RMF 2008, 3.32 ).
Gross value added of tourism industries : Gross value added of tourism industries (GVATI) is the total gross value added of all establishments belonging to tourism industries, regardless of whether all their output is provided to visitors and the degree of specialization of their production process ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.86 ).
Grossing up : Activity aimed at transforming, based on statistical methodology, micro-data from samples into aggregate-level information representative of the target population.
Health tourism : Health tourism covers those types of tourism which have as a primary motivation, the contribution to physical, mental and/or spiritual health through medical and wellness-based activities which increase the capacity of individuals to satisfy their own needs and function better as individuals in their environment and society. Health tourism is the umbrella term for the subtypes wellness tourism and medical tourism.
Imputation : Procedure for entering a value for a specific data item where the response is missing or unusable.
Inbound tourism : Inbound tourism comprises the activities of a non-resident visitor within the country of reference on an inbound tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 2.39 ).
Inbound tourism consumption : Inbound tourism consumption is the tourism consumption of a non-resident visitor within the economy of reference ( TSA:RMF 2008, figure 2.1 ).
Inbound tourism expenditure : Inbound tourism expenditure is the tourism expenditure of a non-resident visitor within the economy of reference ( IRTS 2008, 4.15(b) ).
Innovation in tourism : Innovation in tourism is the introduction of a new or improved component which intends to bring tangible and intangible benefits to tourism stakeholders and the local community, improve the value of the tourism experience and the core competencies of the tourism sector and hence enhance tourism competitiveness and /or sustainability. Innovation in tourism may cover potential areas, such as tourism destinations, tourism products, technology, processes, organizations and business models, skills, architecture, services, tools and/or practices for management, marketing, communication, operation, quality assurance and pricing.
Institutional sector : An aggregation of institutional units on the basis of the type of producer and depending on their principal activity and function, which are considered to be indicative of their economic behaviour.
Institutional unit : The elementary economic decision-making centre characterised by uniformity of behaviour and decision-making autonomy in the exercise of its principal function.
Intermediate consumption : Intermediate consumption consists of the value of the goods and services consumed as inputs by a process of production, excluding fixed assets whose consumption is recorded as consumption of fixed capital ( SNA 2008, 6.213 ).
Internal tourism : Internal tourism comprises domestic tourism and inbound tourism, that is to say, the activities of resident and non-resident visitors within the country of reference as part of domestic or international tourism trips ( IRTS 2008, 2.40(a) ).
Internal tourism consumption : Internal tourism consumption is the tourism consumption of both resident and non-resident visitors within the economy of reference. It is the sum of domestic tourism consumption and inbound tourism consumption ( TSA:RMF 2008, figure 2.1 ).
Internal tourism expenditure : Internal tourism expenditure comprises all tourism expenditure of visitors, both resident and non-resident, within the economy of reference. It is the sum of domestic tourism expenditure and inbound tourism expenditure. It includes acquisition of goods and services imported into the country of reference and sold to visitors. This indicator provides the most comprehensive measurement of tourism expenditure in the economy of reference ( IRTS 2008, 4.20(a) ).
International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities : The International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities (ISIC) consists of a coherent and consistent classification structure of economic activities based on a set of internationally agreed concepts, definitions, principles and classification rules. It provides a comprehensive framework within which economic data can be collected and reported in a format that is designed for purposes of economic analysis, decision-taking and policymaking. The classification structure represents a standard format to organize detailed information about the state of an economy according to economic principles and perceptions (ISIC, Rev.4, 1).
International tourism : International tourism comprises inbound tourism and outbound tourism, that is to say, the activities of resident visitors outside the country of reference, either as part of domestic or outbound tourism trips and the activities of non-resident visitors within the country of reference on inbound tourism trips ( IRTS 2008, 2.40(c) ).
International visitor : An international traveller qualifies as an international visitor with respect to the country of reference if: (a) he/she is on a tourism trip and (b) he/she is a non-resident travelling in the country of reference or a resident travelling outside of it ( IRTS 2008, 2.42 ).
Job : The agreement between an employee and the employer defines a job and each self-employed person has a job ( SNA 2008, 19.30 ).
Measurement error : Error in reading, calculating or recording numerical value.
Medical tourism : Medical tourism is a type of tourism activity which involves the use of evidence-based medical healing resources and services (both invasive and non-invasive). This may include diagnosis, treatment, cure, prevention and rehabilitation.
Meetings industry : To highlight purposes relevant to the meetings industry, if a trip's main purpose is business/professional, it can be further subdivided into "attending meetings, conferences or congresses, trade fairs and exhibitions" and "other business and professional purposes". The term meetings industry is preferred by the International Congress and Convention Association (ICCA), Meeting Professionals International (MPI) and Reed Travel over the acronym MICE (Meetings, Incentives, Conferences and Exhibitions) which does not recognize the industrial nature of such activities.
Metadata : Data that defines and describes other data and processes.
MICE : See meetings industry.
Microdata : Non-aggregated observations, or measurements of characteristics of individual units.
Mirror statistics : Mirror statistics are used to conduct bilateral comparisons of two basic measures of a trade flow and are a traditional tool for detecting the causes of asymmetries in statistics (OECD GST, p. 335).
Mountain tourism : Mountain tourism is a type of tourism activity which takes place in a defined and limited geographical space such as hills or mountains with distinctive characteristics and attributes that are inherent to a specific landscape, topography, climate, biodiversity (flora and fauna) and local community. It encompasses a broad range of outdoor leisure and sports activities.
National tourism : National tourism comprises domestic tourism and outbound tourism, that is to say, the activities of resident visitors within and outside the country of reference, either as part of domestic or outbound tourism trips ( IRTS 2008, 2.40(b) ).
National tourism consumption : National tourism consumption is the tourism consumption of resident visitors, within and outside the economy of reference. It is the sum of domestic tourism consumption and outbound tourism consumption ( TSA:RMF 2008, figure 2.1 ).
National tourism expenditure : National tourism expenditure comprises all tourism expenditure of resident visitors within and outside the economy of reference. It is the sum of domestic tourism expenditure and outbound tourism expenditure ( IRTS 2008, 4.20(b) ).
Nationality : The concept of "country of residence" of a traveller is different from that of his/her nationality or citizenship ( IRTS 2008, 2.19 ).
Non-monetary indicators : Data measured in physical or other non-monetary units should not be considered a secondary part of a satellite account. They are essential components, both for the information they provide directly and in order to analyse the monetary data adequately ( SNA 2008, 29.84 ).
Observation unit : entity on which information is received and statistics are compiled.
Outbound tourism : Outbound tourism comprises the activities of a resident visitor outside the country of reference, either as part of an outbound tourism trip or as part of a domestic tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 2.39(c) ).
Outbound tourism consumption : Outbound tourism consumption is the tourism consumption of a resident visitor outside the economy of reference ( TSA:RMF 2008, figure 2.1 ).
Outbound tourism expenditure : Outbound tourism expenditure is the tourism expenditure of a resident visitor outside the economy of reference ( IRTS 2008, 4.15(c) ).
Output : Output is defined as the goods and services produced by an establishment, a) excluding the value of any goods and services used in an activity for which the establishment does not assume the risk of using the products in production, and b) excluding the value of goods and services consumed by the same establishment except for goods and services used for capital formation (fixed capital or changes in inventories) or own final consumption ( SNA 2008, 6.89 ).
Output (main): The main output of a (productive) activity should be determined by reference to the value added of the goods sold or services rendered (ISIC rev.4, 114).
Pilot survey : The aim of a pilot survey is to test the questionnaire (pertinence of the questions, understanding of questions by those being interviewed, duration of the interview) and to check various potential sources for sampling and non-sampling errors: for instance, the place in which the surveys are carried out and the method used, the identification of any omitted answers and the reason for the omission, problems of communicating in various languages, translation, the mechanics of data collection, the organization of field work, etc.
Place of usual residence : The place of usual residence is the geographical place where the enumerated person usually resides, and is defined by the location of his/her principal dwelling (Principles and recommendations for population and housing censuses of the United Nations, 2.20 to 2.24).
Probability sample : A sample selected by a method based on the theory of probability (random process), that is, by a method involving knowledge of the likelihood of any unit being selected.
Production account : The production account records the activity of producing goods and services as defined within the SNA. Its balancing item, gross value added, is defined as the value of output less the value of intermediate consumption and is a measure of the contribution to GDP made by an individual producer, industry or sector. Gross value added is the source from which the primary incomes of the SNA are generated and is therefore carried forward into the primary distribution of income account. Value added and GDP may also be measured net by deducting consumption of fixed capital, a figure representing the decline in value during the period of the fixed capital used in a production process ( SNA 2008, 1.17 ).
Production : Economic production may be defined as an activity carried out under the control and responsibility of an institutional unit that uses inputs of labour, capital, and goods and services to produce outputs of goods or services ( SNA 2008, 6.24. ).
Purpose of a tourism trip (main): The main purpose of a tourism trip is defined as the purpose in the absence of which the trip would not have taken place ( IRTS 2008, 3.10. ). Classification of tourism trips according to the main purpose refers to nine categories: this typology allows the identification of different subsets of visitors (business visitors, transit visitors, etc.) See also destination of a tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 3.14 ).
Quality of a tourism destination : Quality of a tourism destination is the result of a process which implies the satisfaction of all tourism product and service needs, requirements and expectations of the consumer at an acceptable price, in conformity with mutually accepted contractual conditions and the implicit underlying factors such as safety and security, hygiene, accessibility, communication, infrastructure and public amenities and services. It also involves aspects of ethics, transparency and respect towards the human, natural and cultural environment. Quality, as one of the key drivers of tourism competitiveness, is also a professional tool for organizational, operational and perception purposes for tourism suppliers.
Questionnaire and Questionnaire design : Questionnaire is a group or sequence of questions designed to elicit information on a subject, or sequence of subjects, from a reporting unit or from another producer of official statistics. Questionnaire design is the design (text, order, and conditions for skipping) of the questions used to obtain the data needed for the survey.
Reference period : The period of time or point in time to which the measured observation is intended to refer.
Relevance : The degree to which statistics meet current and potential users' needs.
Reliability : Closeness of the initial estimated value to the subsequent estimated value.
Reporting unit : Unit that supplies the data for a given survey instance, like a questionnaire or interview. Reporting units may, or may not, be the same as the observation unit.
Residents/non-residents : The residents of a country are individuals whose centre of predominant economic interest is located in its economic territory. For a country, the non-residents are individuals whose centre of predominant economic interest is located outside its economic territory.
Response and non-response : Response and non-response to various elements of a survey entail potential errors.
Response error : Response errors may be defined as those arising from the interviewing process. Such errors may be due to a number of circumstances, such as inadequate concepts or questions; inadequate training; interviewer failures; respondent failures.
Rural tourism : Rural tourism is a type of tourism activity in which the visitor's experience is related to a wide range of products generally linked to nature-based activities, agriculture, rural lifestyle / culture, angling and sightseeing. Rural tourism activities take place in non-urban (rural) areas with the following characteristics:
- Low population density;
- Landscape and land-use dominated by agriculture and forestry; and
- Traditional social structure and lifestyle
Same-day visitor (or excursionist): A visitor (domestic, inbound or outbound) is classified as a tourist (or overnight visitor), if his/her trip includes an overnight stay, or as a same-day visitor (or excursionist) otherwise ( IRTS 2008, 2.13 ).
Sample : A subset of a frame where elements are selected based on a process with a known probability of selection.
Sample survey : A survey which is carried out using a sampling method.
Sampling error : That part of the difference between a population value and an estimate thereof, derived from a random sample, which is due to the fact that only a subset of the population is enumerated.
Satellite accounts : There are two types of satellite accounts, serving two different functions. The first type, sometimes called an internal satellite, takes the full set of accounting rules and conventions of the SNA but focuses on a particular aspect of interest by moving away from the standard classifications and hierarchies. Examples are tourism, coffee production and environmental protection expenditure. The second type, called an external satellite, may add non-economic data or vary some of the accounting conventions or both. It is a particularly suitable way to explore new areas in a research context. An example may be the role of volunteer labour in the economy ( SNA 2008, 29.85 ).
SDMX, Statistical Data and Metadata Exchange : Set of technical standards and content-oriented guidelines, together with an IT architecture and tools, to be used for the efficient exchange and sharing of statistical data and metadata (SDMX).
Seasonal adjustment : Seasonal adjustment is a statistical technique to remove the effects of seasonal calendar influences on a series. Seasonal effects usually reflect the influence of the seasons themselves, either directly or through production series related to them, or social conventions. Other types of calendar variation occur as a result of influences such as number of days in the calendar period, the accounting or recording practices adopted or the incidence of moving holidays.
Self-employment job : Self-employment jobs are those jobs where remuneration is directly dependent upon the profits (or the potential of profits) derived from the goods or services produced.
Self-employed with paid employees : Self-employed with paid employees are classified as employers.
Self-employed without employees : Self-employed without employees are classified as own-account workers.
Services : Services are the result of a production activity that changes the conditions of the consuming units, or facilitates the exchange of products or financial assets. They cannot be traded separately from their production. By the time their production is completed, they must have been provided to the consumers ( SNA 2008, 6.17 ).
Social transfers in kind : A special case of transfers in kind is that of social transfers in kind. These consist of goods and services provided by general government and non-profit institutions serving households (NPISHs) that are delivered to individual households. Health and education services are the prime examples. Rather than provide a specified amount of money to be used to purchase medical and educational services, the services are often provided in kind to make sure that the need for the services is met. (Sometimes the recipient purchases the service and is reimbursed by the insurance or assistance scheme. Such a transaction is still treated as being in kind because the recipient is merely acting as the agent of the insurance scheme) (SNA 2008, 3.83).
Sports tourism : Sports tourism is a type of tourism activity which refers to the travel experience of the tourist who either observes as a spectator or actively participates in a sporting event generally involving commercial and non-commercial activities of a competitive nature.
Standard classification : Classifications that follow prescribed rules and are generally recommended and accepted.
Statistical error : The unknown difference between the retained value and the true value.
Statistical indicator : A data element that represents statistical data for a specified time, place, and other characteristics, and is corrected for at least one dimension (usually size) to allow for meaningful comparisons.
Statistical metadata : Data about statistical data.
Statistical unit : Entity about which information is sought and about which statistics are compiled. Statistical units may be identifiable legal or physical entities or statistical constructs.
Survey : An investigation about the characteristics of a given population by means of collecting data from a sample of that population and estimating their characteristics through the systematic use of statistical methodology.
System of National Accounts : The System of National Accounts (SNA) is the internationally agreed standard set of recommendations on how to compile measures of economic activity in accordance with strict accounting conventions based on economic principles. The recommendations are expressed in terms of a set of concepts, definitions, classifications and accounting rules that comprise the internationally agreed standard for measuring indicators of economic performance. The accounting framework of the SNA allows economic data to be compiled and presented in a format that is designed for purposes of economic analysis, decision-taking and policymaking ( SNA 2008, 1.1 ).
Total tourism internal demand : Total tourism internal demand, is the sum of internal tourism consumption, tourism gross fixed capital formation and tourism collective consumption ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.114 ). It does not include outbound tourism consumption.
Tourism : Tourism refers to the activity of visitors ( IRTS 2008, 2.9 ).
Tourism characteristic activities : Tourism characteristic activities are the activities that typically produce tourism characteristic products. As the industrial origin of a product (the ISIC industry that produces it) is not a criterion for the aggregation of products within a similar CPC category, there is no strict one-to-one relationship between products and the industries producing them as their principal outputs ( IRTS 2008, 5.11 ).
Tourism characteristic products : Tourism characteristic products are those that satisfy one or both of the following criteria: a) Tourism expenditure on the product should represent a significant share total tourism expenditure (share-of-expenditure/demand condition); b) Tourism expenditure on the product should represent a significant share of the supply of the product in the economy (share-of-supply condition). This criterion implies that the supply of a tourism characteristic product would cease to exist in meaningful quantity in the absence of visitors ( IRTS 2008, 5.10 ).
Tourism connected products : Their significance within tourism analysis for the economy of reference is recognized although their link to tourism is very limited worldwide. Consequently, lists of such products will be country-specific ( IRTS 2008, 5.12 ).
Tourism consumption : Tourism consumption has the same formal definition as tourism expenditure. Nevertheless, the concept of tourism consumption used in the Tourism Satellite Account goes beyond that of tourism expenditure. Besides the amount paid for the acquisition of consumption goods and services, as well as valuables for own use or to give away, for and during tourism trips, which corresponds to monetary transactions (the focus of tourism expenditure), it also includes services associated with vacation accommodation on own account, tourism social transfers in kind and other imputed consumption. These transactions need to be estimated using sources different from information collected directly from the visitors, such as reports on home exchanges, estimations of rents associated with vacation homes, calculations of financial intermediation services indirectly measured (FISIM), etc. ( TSA:RMF 2008, 2.25 ).
Tourism destination : A tourism destination is a physical space with or without administrative and/or analytical boundaries in which a visitor can spend an overnight. It is the cluster (co-location) of products and services, and of activities and experiences along the tourism value chain and a basic unit of analysis of tourism. A destination incorporates various stakeholders and can network to form larger destinations. It is also intangible with its image and identity which may influence its market competitiveness.
Tourism direct gross domestic product : Tourism direct gross domestic product (TDGDP) is the sum of the part of gross value added (at basic prices) generated by all industries in response to internal tourism consumption plus the amount of net taxes on products and imports included within the value of this expenditure at purchasers' prices ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.96 ).
Tourism direct gross value added : Tourism direct gross value added (TDGVA) is the part of gross value added generated by tourism industries and other industries of the economy that directly serve visitors in response to internal tourism consumption ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.88 ).
Tourism expenditure : Tourism expenditure refers to the amount paid for the acquisition of consumption goods and services, as well as valuables, for own use or to give away, for and during tourism trips. It includes expenditures by visitors themselves, as well as expenses that are paid for or reimbursed by others ( IRTS 2008, 4.2 ).
Tourism industries : The tourism industries comprise all establishments for which the principal activity is a tourism characteristic activity. Tourism industries (also referred to as tourism activities) are the activities that typically producetourism characteristic products. The term tourism industries is equivalent to tourism characteristic activities and the two terms are sometimes used synonymously in the IRTS 2008, 5.10, 5.11 and figure 5.1 .
Tourism product : A tourism product is a combination of tangible and intangible elements, such as natural, cultural and man-made resources, attractions, facilities, services and activities around a specific center of interest which represents the core of the destination marketing mix and creates an overall visitor experience including emotional aspects for the potential customers. A tourism product is priced and sold through distribution channels and it has a life-cycle.
Tourism ratio : For each variable of supply in the Tourism Satellite Account, the tourism ratiois the ratio between the total value of tourism share and total value of the corresponding variable in the Tourism Satellite Account expressed in percentage form ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.56 ). (See also Tourism share).
Tourism Satellite Account : The Tourism Satellite Account is the second international standard on tourism statistics (Tourism Satellite Account: Recommended Methodological Framework 2008 –TSA:RMF 2008) that has been developed in order to present economic data relative to tourism within a framework of internal and external consistency with the rest of the statistical system through its link to the System of National Accounts. It is the basic reconciliation framework of tourism statistics. As a statistical tool for the economic accounting of tourism, the TSA can be seen as a set of 10 summary tables, each with their underlying data and representing a different aspect of the economic data relative to tourism: inbound, domestic tourism and outbound tourism expenditure, internal tourism expenditure, production accounts of tourism industries, the Gross Value Added (GVA) and Gross Domestic Product (GDP) attributable to tourism demand, employment, investment, government consumption, and non-monetary indicators.
Tourism Satellite Account aggregates : The compilation of the following aggregates, which represent a set of relevant indicators of the size of tourism in an economy is recommended ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.81 ):
- Internal tourism expenditure;
- Internal tourism consumption;
- Gross value added of tourism industries (GVATI);
- Tourism direct gross value added (TDGVA);
- Tourism direct gross domestic product (TDGDP).
Tourism sector : The tourism sector, as contemplated in the TSA, is the cluster of production units in different industries that provide consumption goods and services demanded by visitors. Such industries are called tourism industries because visitor acquisition represents such a significant share of their supply that, in the absence of visitors, their production of these would cease to exist in meaningful quantity.
Tourism share : Tourism share is the share of the corresponding fraction of internal tourism consumption in each component of supply ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.51 ). For each industry, the tourism share of output (in value), is the sum of the tourism share corresponding to each product component of its output ( TSA:RMF 2008, 4.55 ). (See also Tourism ratio ).
Tourism single-purpose consumer durable goods : Tourism single-purpose consumer durables is a specific category of consumer durable goods that include durable goods that are used exclusively, or almost exclusively, by individuals while on tourism trips ( TSA:RMF 2008 , 2.41 and Annex 5 ).
Tourism trip : Trips taken by visitors are tourism trips ( IRTS 2008, 2.29 ).
Tourist (or overnight visitor): A visitor (domestic, inbound or outbound) is classified as a tourist (or overnight visitor), if his/her trip includes an overnight stay, or as a same-day visitor (or excursionist) otherwise ( IRTS 2008, 2.13 ).
Tourism value chain : The tourism value chain is the sequence of primary and support activities which are strategically fundamental for the performance of the tourism sector. Linked processes such as policy making and integrated planning, product development and packaging, promotion and marketing, distribution and sales and destination operations and services are the key primary activities of the tourism value chain. Support activities involve transport and infrastructure, human resource development, technology and systems development and other complementary goods and services which may not be related to core tourism businesses but have a high impact on the value of tourism.
Travel / traveller : Travel refers to the activity of travellers. A traveller is someone who moves between different geographic locations, for any purpose and any duration ( IRTS 2008, 2.4 ). The visitor is a particular type of traveller and consequently tourism is a subset of travel.
Travel group : A travel group is made up of individuals or travel parties travelling together: examples are people travelling on the same package tour or youngsters attending a summer camp ( IRTS 2008, 3.5 ).
Travel item (in balance of payments): Travel is an item of the goods and services account of the balance of payments: travel credits cover goods and services for own use or to give away acquired from an economy by non-residents during visits to that economy. Travel debits cover goods and services for own use or to give away acquired from other economies by residents during visits to other economies ( BPM6, 10.86 ).
Travel party : A travel party is defined as visitors travelling together on a trip and whose expenditures are pooled ( IRTS 2008, 3.2 ).
Trip : A trip refers to the travel by a person from the time of departure from his/her usual residence until he/she returns: it thus refers to a round trip. Trips taken by visitors are tourism trips.
Urban/city tourism : Urban/city tourism is a type of tourism activity which takes place in an urban space with its inherent attributes characterized by non-agricultural based economy such as administration, manufacturing, trade and services and by being nodal points of transport. Urban/city destinations offer a broad and heterogeneous range of cultural, architectural, technological, social and natural experiences and products for leisure and business.
Usual environment: The usual environment of an individual, a key concept in tourism, is defined as the geographical area (though not necessarily a contiguous one) within which an individual conducts his/her regular life routines ( IRTS 2008, 2.21 ).
Usual residence : The place of usual residence is the geographical place where the enumerated person usually resides (Principles and recommendations for population and housing censuses of the United Nations, 2.16 to 2.18).
Vacation home : A vacation home (sometimes also designated as a holiday home) is a secondary dwelling that is visited by the members of the household mostly for purposes of recreation, vacation or any other form of leisure ( IRTS 2008, 2.27 ).
Valuables : Valuables are produced goods of considerable value that are not used primarily for purposes of production or consumption but are held as stores of value over time ( SNA 2008, 10.13 ).
Visit : A trip is made up of visits to different places.The term "tourism visit" refers to a stay in a place visited during a tourism trip ( IRTS 2008, 2.7 and 2.33 ).
Visitor : A visitor is a traveller taking a trip to a main destination outside his/her usual environment, for less than a year, for any main purpose (business, leisure or other personal purpose) other than to be employed by a resident entity in the country or place visited ( IRTS 2008, 2.9 ). A visitor (domestic, inbound or outbound) is classified as a tourist (or overnight visitor), if his/her trip includes an overnight stay, or as a same-day visitor (or excursionist) otherwise ( IRTS 2008, 2.13 ).
Wellness tourism : Wellness tourism is a type of tourism activity which aims to improve and balance all of the main domains of human life including physical, mental, emotional, occupational, intellectual and spiritual. The primary motivation for the wellness tourist is to engage in preventive, proactive, lifestyle-enhancing activities such as fitness, healthy eating, relaxation, pampering and healing treatments.
It’s been a record-setting year for global travel – here’s how we make tourism inclusive and sustainable

Inclusive and sustainable travel and tourism includes supporting micro-, small- and medium-sized businesses. Image: Unsplash/Michael Barón
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Nicola Villa

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved .chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
- The global travel sector is experiencing a robust recovery, with tourists increasingly spending more on travel.
- Despite the overall positive outlook, some destinations struggle with operational challenges, including workforce issues and resource management amid rising tourist numbers and environmental concerns.
- The travel and tourism sector’s potential for advancing socio-economic prosperity is particularly impactful through the support of micro-, small-, and medium-sized enterprises.
The global travel sector forecast is in and it's sunny skies ahead. Through March 2024, consumer spending on travel remains strong, and passenger traffic has soared. Empowered by a strong labour market worldwide, tourists will be on the roads, air and seas once again, with more of people’s budgets on travel.
The latest report from the Mastercard Economics Institute, Travel Trends 2024: Breaking Boundaries , reveals that 2024 has already witnessed multiple record-setting days as consumer spending on leisure travel remains strong. The data shows that post-pandemic travellers continue to seek unique experiences rooted in local cultures while increasingly prioritizing spending on memorable events across sports, music and festivals.
The Mastercard Economics Institute’s analysis reveals that travellers also seek opportunities to extend their stays, prioritizing leisure for longer. For the first 12 months between March 2019 and February 2020, a trip’s average length of stay was about four days. As of March 2024, the average length of a leisure trip has edged closer to five days, which translates into an economic boost for the destinations and communities hosting them.
Have you read?
These are the top 10 countries for travel and tourism, what is travel and tourism’s role in future global prosperity, travel & tourism development index 2024, tackling tourism’s challenges.
Yet, while the overall outlook for travellers looks bright, that’s not the case for all destinations. Some tourism hotspots and lesser-known locales are facing growing challenges around operating conditions. The World Economic Forum’s Travel & Tourism Development Index (TTDI) 2024 highlights the ongoing constraints facing the global travel and tourism sector – including the lack of investment in skilled and resilient workforces and issues around resource management – cultural and natural – as destinations grapple with higher tourist visitor numbers and rising environmental concerns.
The report offers travel and tourism decision-makers recommendations around how the sector can take a more active role in tackling social challenges across socio-economic prosperity, peace and cultural exchange. As the industry accounts for approximately one-tenth of global gross domestic product and employment , the public and private sectors must work together to ensure future tourism development is, first and foremost, inclusive and sustainable.
Supporting the backbone of travel and tourism
As the TTDI 2024 notes, one area where the sector’s potential in advancing socio-economic prosperity can be particularly impactful is in the economic empowerment of micro-, small- and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs). According to the World Travel & Tourism Council, more than 80% of travel and tourism businesses fall under this category.
Policies and investments promoting the adoption of digital solutions and enhancing digital skills development while improving access to credit can provide a major boost to tourism-focused MSMEs.
In Costa Rica, the Instituto Costariccense de Turismo, a member of Mastercard’s Tourism Innovation Hub , is championing such an approach to ensure increased tourist traffic results in better opportunities for MSMEs. Last year, the institute launched Tico Treasures , a platform facilitating tourist connections with Costa Rica’s Crafts with Identity programme, a group of 17 artisan collectives across the country. The platform allows visitors to discover local Costa Rican products, learn about artisan communities and then purchase and ship the goods back to their home country – all through one experience.
The programme is an example of public-private collaboration, including backing from Correos de Costa Rica, Banco de Costa Rica and the Instituto Costariccense de Turismo. Its objectives are multifold: delivering more authentic experiences for tourists, expanding citizens’ access to the digital economy and contributing to MSME resilience.
Protecting future environments
There are also novel approaches to solving destinations’ sustainability challenges underway. A key role of the Travel Foundation , a global non-government organization, is to facilitate innovative public-private collaborations in tourism that accelerate and scale sustainable solutions. One notable example is in Scotland, where the national tourism organization VisitScotland is partnering with the Travel Corporation, a global tour operator, to help decarbonize the destination supply chain. Both organizations are pooling their insights, data and expertise to support local businesses, develop new ideas for reducing carbon footprints and identify barriers to a green transition.
The learnings from this and other projects led by the Travel Foundation will be shared to influence future policy, investment and product development decisions at national and global levels. By combining public sector resources and capabilities with private sector technological expertise, travel and tourism decision-makers can enact policies and programmes that balance tourism growth with environmental protection, providing a nuanced approach that works for unique destinations.
It’s an important time for the sector – to leverage travel and tourism’s robust recovery and advance socio-economic prosperity, fuelling a more inclusive future for our treasured destinations. By accelerating collaboration between governments, destination management organizations and technology companies, we can ensure destinations, the communities that power them and the environments they inhabit are at the heart of all future tourism development.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
The Agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Trade and Investment .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

How an affordable cross-border delivery service will unlock the promise of millions of SMEs in Southeast Asia
Pete Chareonwongsak
June 17, 2024

IDEA: Investing in the Digital Economy of Azerbaijan

Digitalization is disrupting global trade – here's how AI can help customs and businesses to respond
Sebastian Klotz, Steve Barr and Jimena Sotelo
June 6, 2024

TradeTech is revolutionizing global trade
June 5, 2024

US hikes tariffs on Chinese imports, and other global trade stories to read this month
Guillaume Dabré
May 24, 2024

Are these five trends disrupting or driving logistics growth?
Ali Alwaleed Al-Thani and Sheikh Mohammed bin Hamad bin Faisal Al-Thani
- Have any questions ?
- +971 552272114
- [email protected]

- Links with the Industry
- Our Partners
- Online Executive MBA - CMU
- MBA – Strategic Management & Leadership - CMU
- MBA International - CCCU
- MBA International (Top- up)
- MBA - University of Gloucestershire (GLOS)
- MBA with Global Business Administration (GLOS)
- MBA with Global Business Administration with Marketing Intelligence and Big Data (GLOS)
- MBA with Global Business Administration with Cyber Governance and Digital Transformation (GLOS)
- MBA with Global Business Administration with Financial Services Management (GLOS)
- MBA with Global Business Administration with Applied Entrepreneurship, Design Thinking and Innovation (GLOS)
- MBA in Global Business Administration with International Tourism and Hospitality Management (GLOS)
- MBA with Supply Chain Management - Abertay University
- MBA with Healthcare Management - Abertay University
- MBA with HR and Organizational Psychology - Abertay University
- MBA with Finance and Risk Management - Abertay University
- MBA with Engineering Management - Abertay University
- MBA with Information Technology - Abertay University
- MBA with Educational Leadership - Abertay University
- MBA with Health and Safety Leadership - Abertay University
- MBA with Management of Public Health
- MBA with Cyber Governance and Law - Abertay University
- MBA with Entrepreneurship & Innovation - Abertay University
- MBA with Business Analytics - Abertay University
- MBA with Operations and Project Management - Abertay University
- MBA with Marketing Intelligence & Big data - Abertay University
- MBA with Sales and Marketing - Abertay University
- Executive MBA in HR Management and Analytics - UCAM
- Executive MBA in Business Operations
- Executive MBA in Logistics and Supply Chain Leadership - UCAM
- Executive MBA in Global Business Management - UCAM
- Executive MBA in Engineering Management - UCAM
- Executive MBA in Healthcare Leadership - UCAM
- Executive MBA in Information Technology Leadership - UCAM
- MBA with Sales & Marketing - UCAM
- MBA with Specialization - Girne American University
- CMI L7 Strategic Management and Leadership Practice
- MSc Digital Marketing and e-Business
- MSc Accounting and Finance (CIMA Gateway)
- MSc. Construction and Project Management
- Masters in Data Science and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- BSc (Hons) Business with International Business Management (LJMU)
- BSc (Hons) Business with Finance (LJMU)
- BSc (Hons) Business with Digital Marketing (LJMU)
- BSc (Hons) Computer Science - LJMU
- BSc (Hons) Business Psychology with Human Resource Management - LJMU
- BA (Hons) in Fashion: Design and Communication - LJMU
- BA (Hons) Media, Culture and Communication - LJMU
- BA (Hons) Sports Business - LJMU
- BSc (Hons) Business Management - CCCU
- BA (Hons) Accounting and Finance - GLOS
- BA (Hons ) Business Management - ABERTAY
- BA (Hons) Business Management with Business Analytics - ABERTAY
- BA (Hons) in Business with Digital Marketing - Abertay University
- BA (Hons) in Business with Finance - Abertay University

- Doctorate of Business Administration
- Postgraduate Diploma in Procurement & Contract Management
- Postgraduate Diploma in Sales & Marketing Management
- Postgraduate Diploma in Supply Chain Management and Logistics
- Postgraduate Diploma in Healthcare Management and Leadership
- Postgraduate Diploma in Tourism and Hospitality Management
- Postgraduate Diploma in Human Resource Management | HRM
- Postgraduate Diploma in Finance & Risk Management
- Postgraduate Diploma in Engineering Management
- Postgraduate Diploma in Project Management
- Certificate in Strategic Management and Leadership Practice
- CMI Programs
- Diploma in Business Psychology
- Diploma in Fashion Illustration
- Diploma in Supply Chain and Logistics Management
- Diploma in Business Analytics
- Diploma in Information Technology
- Diploma in Finance and Risk Management
- Diploma in Business Management
- Diploma in Fashion Design
- Diploma in Healthcare Management and Leadership
- Diploma in Business Finance
- Diploma in Digital Marketing
- Diploma in Operations and Project Management
- Diploma in Engineering Management
- Diploma in Human Resources & Organizational Culture
- Diploma in Computing
- Diploma in Film and Media
- Diploma in Sports Management
- ACCA – Association Chartered Certified Accountants
- Higher National Diploma in Art and Design (Fashion)
- Higher National Diploma in Computing
- HND in Counselling and Applied Psychology
- Higher National Diploma In Business
- Higher National Diploma in Sport
- BTEC Level 3 National Foundation Diploma in Business
- Master of Arts in Leadership in Education
- Master of Arts in Education
- Postgraduate Certificate in Education (International) - LJMU

- Postgraduate Certificate in Education International (PGCEi)
- Notable Westford Alumni
- Student Interview
- DBA Candidates
- Research Journals
- Humans Of Westford
- MBA Decoded
- Mentorship program
- International Immersion Program
- Toastmaster Club
- Accommodation Partner- Nest
- International Faculty Research Conference (IFRC)
- Student Recruitment Drive
- Westford for Business
- April 30, 2016
- Management Articles
- < 1 minute
Different Service Levels in Tourism Industry
Agencies dealing with travel offers consumer different levels of service according to the preferences in transportation, accommodation, food and other facilities. As there are many levels of services in tourism industry the services offered vary in a wide range. However, there are certain standards with respect to the service levels offered in the travel industry.
Basic Levels of Servicing The basic service levels offer tourists amenities like conveyance booking from starting to a destination through various points during the travel. Accommodation facilities generally include basic services in this level of services. Shared Rooms and Bathrooms are usually available in such levels of services. In some cases, the ground travel will not be included in the travel services list. These type of travel packages are meant for travellers on a low budget.
Standard Level of Service In the standard level of services, more facilities will be included than the basic level of services. This can sometimes include basic flight packages, rooms with privacy and higher classroom services like private cooking areas. car Rentals and basic transportation and food are available in standard packages.
Luxury Level of Service This often includes premium services offered to clients. First Class Air travel is offered in such cases and point to point transportation facilities will be provided. In this kind of services, multiple bedrooms and private bathrooms can be accessed with catered meals for all members. some luxury travel servicing offers personalised beauty and health care packages included with it.
get in touch
Phone Number
Latest Blogs

Transformative Power of Internships during your bachelor’s Program

Transforming Decision-Making Through Big Data

Uniting Communities Through Compassion and Service – A Westford WeCares Initiative!

Mastering Soft Skills: Why Communication, Leadership, and Critical Thinking Matter in Bachelor Programs

Westford Continues To Empower Women With Over 3 Million Dirhams In Accelerather Scholarships
Established in 2009, The Westford University College is the most trusted executive educational institution in UAE, providing flexible learning and affordable programs for regular students and working professionals (Perfect ‘Work-Life-Study’ Balance). We provide top rated MBA Programs, Bachelors Courses, Professional Programs and corporate training. 13300+ students, 80+ Courses, 130+ Nationalities, 20+ Academic Partners, 14+ years in the market.
Our Student Base
Mba programs.
- Cardiff Met MBA (Advanced Entry)
- MBA – Cardiff Metropolitan University
- MBA – Healthcare Management
- MBA – Supply Chain and Logistics Management
- MBA – Engineering Management
- MBA – Information Technology
- MBA – HR & Organizational Psychology
- MBA – Project Management
- MBA – International
- MBA - University of Gloucestershire
- MBA with Specialization - GAU
- MBA – Education Leadership
- UCAM MBA Executive
Bachelors Programs
- BSc (Hons) in Business with Finance
- BSc (Hons) in Business with Digital Marketing
- BSc (Hons) in Business with International Business
- BA (Hons) in Media, Culture and Communication
- BSc (Hons) in Business Psychology with Human Resource Management
Diploma Coures
- Diploma in Business Finance
- Diploma in Human Resources & Organizational Culture
- PG Diploma in Engineering Management
- PG Diploma in Retail Management
- PG Diploma in Sales & Marketing Management
- HND in Art and Design
- HND in Computing
Other Programs
- Teacher Training
Ready to get started ? Talk to us today
Al Taawun Campus Tejara 3, Al Taawun, Sharjah, UAE
Westford University College | Masters Degree | Under Graduate Degree | Diploma Courses | Certificate Courses | Corporate Training | Management Programs
- Privacy Policy
- Anti-Bribery & Corruption Policy
- Data Protection Policy
- Equality & Diversity Policy
- Environmental Policy
- Refund Policy

Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution, update may 10, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents, tourism & visit.
Study & Exchange
Other Visa Categories
U.S. Visa: Reciprocity and Civil Documents by Country
Share this page:
Visitor Visa
Visa Waiver Program
Travel Without a Visa
Citizens of Canada and Bermuda
Tourism & Visit

A foreign national traveling to the United States for tourism needs a visitor visa (B-2 or combined B1/B2) unless qualifying for entry under the Visa Waiver Program.
Travel for pleasure or tourism may include a short visit for vacation, visiting family and friends, or for medical treatment.
Visitor Visa for Tourism (B-2 or B1/B2 visa)
For vacation, seeing family and friends, or medical treatment.
- How to Apply
- Required Documentation
Visa Waiver Program VWP
Most citizens of participating countries (see NOTE below)* may travel to the United States for short visits without a visa though the Visa Waiver Program .
Travel to the United States under the Visa Waiver Program Requires ESTA Approval
Canadian & Bermudian Citizens
Citizens of Canada and Bermuda generally do not need nonimmigrant visas for tourism.
Traveling to the United States for another reason?
SEE ALL VISA CATEGORIES
* With respect to a "country" or "countries" participating in VWP, it should be noted that the Taiwan Relations Act of 1979, Pub. L. No. 96-8, Section 4(b)(1), provides that “[w]henever the laws of the United States refer or relate to foreign countries, nations, states, governments, or similar entities, such terms shall include and such laws shall apply with respect to Taiwan.” 22 U.S.C. § 3303(b)(1). Accordingly, all references to “country” or “countries” in the Visa Waiver Program authorizing legislation, Section 217 of the Immigration and Nationality Act, 8 U.S.C. 1187, are read to include Taiwan. This is consistent with the one-China policy of the United States, under which the United States has maintained unofficial relations with Taiwan since 1979.
More Information
A-Z Index Legal Rights & Protections Lost/Stolen Travel Documents Denials Ineligibilities & Waivers Citizens of Canada & Bermuda Find a U.S. Embassy or Consulate Straight Facts on U.S. Visas Customer Service Statement U.S. Tax Information
In the United States
Visit The USA U.S. Tax Information
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tourism and travel-related services include services provided by hotels and restaurants (including catering), travel agencies and tour operator services, tourist guide services and other related services. A crucial aspect of trade in tourism services is the cross-border movement of consumers (mode 2). This permits a variety of workers ...
As travel resumes and builds momentum, it's becoming clear that tourism is resilient—there is an enduring desire to travel. Against all odds, international tourism rebounded in 2022: visitor numbers to Europe and the Middle East climbed to around 80 percent of 2019 levels, and the Americas recovered about 65 percent of prepandemic visitors 1 "Tourism set to return to pre-pandemic levels ...
A service in tourism is an action that is provided in respect to the regulations of a country and its industry structure. These include but are not limited to services in catering and the hotel sectors, services of travel agencies and tour guides, tourist representatives in a destination, and the rental of vehicles, boats, or equipment for sports and recreation.
Travel Agencies. Figure 7.2 A travel agency in the United Kingdom. A travel agency is a business that operates as the intermediary between the travel industry (supplier) and the traveller (purchaser). Part of the role of the travel agency is to market prepackaged travel tours and holidays to potential travellers.
The concept of Tourism as a Service (TaaS) takes inspiration from Mobility as a Service (MaaS), that is, the integration of various transport services into a standalone service the users can plan, book and pay for. MaaS provides a convenient way for more sustainable travel, helping to battle the congestion of road networks (Giesecke et al. 2016).
Before we move on, let's explore the term travel services a little more. As detailed in Chapter 1, Canada, the United States, and Mexico have used the NAICS guidelines, which define the tourism industry as consisting of transportation, accommodation, food and beverage, recreation and entertainment, and travel services (Tourism HR Canada, 2020 ...
tourism, the act and process of spending time away from home in pursuit of recreation, relaxation, and pleasure, while making use of the commercial provision of services.As such, tourism is a product of modern social arrangements, beginning in western Europe in the 17th century, although it has antecedents in Classical antiquity.. Tourism is distinguished from exploration in that tourists ...
Examples of our projects: In Indonesia, a US$955m loan is supporting the Government's Integrated Infrastructure Development for National Tourism Strategic Areas Project.This project is designed to improve the quality of, and access to, tourism-relevant basic infrastructure and services, strengthen local economy linkages to tourism, and attract private investment in selected tourism destinations.
Tourism HR Canada — formally the Canadian Tourism Human Resource Council (CTHRC) — is a national sector council responsible for best practice research, training, and other professional development support on behalf of the 174,000 tourism businesses and the 1.75 million people employed in tourism-related occupations across the country.
UN Tourism. As society progresses, the tourism sector, much like many other sectors, needs to transform to serve as a catalyst for prosperity at a universal scale. Enhancing the well-being of individuals, safeguarding the natural environment, stimulating economic advancement, and fostering international harmony are key goals that are the ...
Tourism can generate jobs directly through its various activities, and indirectly through the supply of goods and services needed by tourism related businesses. Moreover, it is important to stimulate development in local communities from a social point of view through their participation in tourism related events, but also in the reduction of ...
In a 2023 Skift survey of travel and hospitality executives, 66% agreed that customer service was a high-priority digital investment in their business. Customer service beat out every single option, with customer engagement and retention at 60% and revenue optimisation at 55%. If you want to provide stellar service in your travel or tourism ...
Italy - Services, Tourism, Culture: The service sector is one of the most important in Italy in terms of the number of people employed. If the definition extends to cover tourism, the hotel industry, restaurants, the service trades, transport and communications, domestic workers, financial services, and public administration, well over half of the workforce operates in the sector.
Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, in 2019, international visitors spent $233.5 billion experiencing the United States; injecting nearly $640 million a day into the U.S. economy. The U.S. travel and tourism industry generated $1.9 trillion in economic output; supporting 9.5 million American jobs and accounted for 2.9% of U.S. GDP.
Travel and tourism was the top services export for the United States in 2019, generating a $53.4 billion trade surplus. The travel and tourism industry was one of the U.S. business sectors hardest hit by the COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent health and travel restrictions, with travel exports decreasing nearly 65% from 2019 to 2020. ...
Conclusion: The tourism industry is a vast field that offers various services to travelers. Transportation, accommodation, food, entertainment, and tour guide services are some of the essential services offered in this sector. These services provide travelers with an opportunity to explore different parts of the world and have a memorable ...
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States ...
6. Post-Pandemic Tourism. Post-pandemic tourism focuses on safe, sustainable, and flexible travel options, responding to evolving traveler preferences and health guidelines. Enhanced health and safety protocols, including regular sanitization and contactless services, become standard in airlines and hotels, ensuring traveler confidence.
Services research in tourism: Advocating the integration. of the supplier side. Anita Zehrer. Management Center Innsbruck (MCI), Austria. Birgit Muskat and Matthias Muskat. University of Canberra ...
The tourism industry as a whole survives because of various tourism products and services. Tourism industry is flexible. The products of tourism cannot be easily standardized as they are created for the customers of varied interests and demands. As the tourism products are mainly the tourists' experience, they can be stored only in the ...
Tourism is a rapidly growing industry that provides travelers with an array of services to enhance their travel experiences. Services in tourism are the range of products or facilities provided by hotels, resorts, airlines, tour operators, and other organizations involved in the tourism industry.
Competitiveness of a tourism destination: The competitiveness of a tourism destination is the ability of the destination to use its natural, cultural, human, man-made and capital resources efficiently to develop and deliver quality, innovative, ethical and attractive tourism products and services in order to achieve a sustainable growth within ...
The travel and tourism sector's potential for advancing socio-economic prosperity is particularly impactful through the support of micro-, small-, and medium-sized enterprises. The global travel sector forecast is in and it's sunny skies ahead. Through March 2024, consumer spending on travel remains strong, and passenger traffic has soared.
Agencies dealing with travel offers consumer different levels of service according to the preferences in transportation, accommodation, food and other facilities. As there are many levels of services in tourism industry the services offered vary in a wide range. However, there are certain standards with respect to the service levels offered in the travel industry. […]
Travel for pleasure or tourism may include a short visit for vacation, visiting family and friends, or for medical treatment. Visitor Visa for Tourism (B-2 or B1/B2 visa) ... the products or services it provides, or the accuracy of information contained therein. The order in which names appear has no significance, and the listings or links may ...
Praytell lands US PR & influencer duties for the Cayman Islands Department of Tourism.The agency is tasked with overseeing media relations, CIDOT's visiting journalist program, influencer ...
MidCoast Council is a finalist in the 2024 North Coast Tourism Awards in the category 'Excellence in Tourism Services' for its destination brand Barrington Coast. This award recognises the innovative practices of the Barrington Coast Visitor Information Centres as they showcase the region, as well as offering an exceptional visitor experience.
MSN
TAI'AN, China, June 19, 2024 /PRNewswire/ -- This is a report from the Shandong Office of Hong Kong Business Daily. In early June, the 2024 Tai 'an City Cultural and Tourism Industry High Quality ...
Court Appointed Special Advocate (CASA) Children's Intervention Services - $10,000 - To protect and serve the county's abused, neglected and abandoned children; and to provide a voice for these children in court proceedings. ... The Prince William County Department of Economic Development and the Office of Tourism Looking for Feedback ...