- Where We Work

Tanzania Economic Update: How to Transform Tourism into a More Sustainable, Resilient and Inclusive Sector

Stone Town, Zanzibar
Photo credit: Christian Morgan/World Bank.
STORY HIGHLIGHTS
- The latest Tanzania Economic Update highlights the huge untapped potential of the tourism sector to drive the country’s development agenda
- The new analysis discusses long-standing issues facing tourism in Tanzania as well as new challenges brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic
- The report says that the pandemic offers an opportunity for policy actions for the sector to recover in the near term and become a sustainable engine of private-sector-driven growth, social and economic inclusion, and climate adaptation and mitigation over the long term
DAR ES SALAAM, July 29, 2021— Tourism offers Tanzania the long-term potential to create good jobs, generate foreign exchange earnings, provide revenue to support the preservation and maintenance of natural and cultural heritage, and expand the tax base to finance development expenditures and poverty-reduction efforts.
The latest World Bank Tanzania Economic Update, Transforming Tourism: Toward a Sustainable, Resilient, and Inclusive Sector highlights tourism as central to the country’s economy, livelihoods and poverty reduction, particularly for women, who make up 72% of all workers in the tourism sector.
“Without tourism, the situation would be bad,” said Rehema Gabriel, a hotel attendant in Dar es Salaam. “I have been working in the tourism industry for eight years now, so I do not know what it would be like without it.”
The economic system around tourism had grown in value over the years and in 2019 was the largest foreign exchange earner, the second largest contributor to the gross domestic product (GDP) and the third largest contributor to employment, the report says. On the semiautonomous Zanzibar archipelago, the sector has also experienced rapid growth, accounting for almost 30% of the island’s GDP and for an estimated 15,000 direct and 50,000 indirect jobs. However, the report notes, only a small fraction of Tanzania’s natural and cultural endowments has been put to economic use through tourism development.
“Tourism offers countries like Tanzania, with abundant natural and cultural endowments, access to many foreign markets,” said Shaun Mann, World Bank Senior Private Sector Development Specialist and co-author of the Tanzania Economic Update. “But the absence of tourism revenues, as we have seen during this pandemic, compromises the integrity and viability of not only endowments, but also the economic, environmental and social ecosystems built up around those endowments.”
Amid the ongoing COVID-19 (coronavirus) pandemic, the World Bank estimates that Tanzania’s GDP growth decelerated to 2.0% in 2020. Business slowed across a wide range of sectors and firms, especially export-oriented sectors such as tourism and manufacturing. The report highlights the impact of the crisis on tourism specifically, which has had consequences beyond just the industry, given the many other sectors that support, and are supported by, tourism. The 72% drop in the sector’s revenues in 2020 (from 2019 levels) closed businesses and caused layoffs.

Zanzibar’s economy was even more severely impacted with GDP growth slowing to an estimated 1.3%, driven by a collapse of the tourism industry. As the hospitality industry shut down between March and September 2020, occupancy rates dropped to close to zero. While the Zanzibar tourism sector started slowly rebounding in the last quarter of 2020, with tourist inflows in December 2020 reaching almost 80% of those in 2019, receipts from tourism fell by 38% for the year.
As the tourism sector transitions gradually into recovery mode with the rest of the world, the report urges authorities to look toward its future resilience by addressing long running challenges that could help position Tanzania on a higher and more inclusive growth trajectory. Areas of focus include destination planning and management, product and market diversification, more inclusive local value chains, an improved business and investment climate and new business models for investment that are built on partnership and shared value creation.

Tanzania is a globally recognized destination for nature-based tourism, a competitive market segment in eastern and southern Africa. Beyond attracting tourists, the country’s landscapes and seascapes produce a wide range of ecosystem services, including carbon sequestration and biodiversity co-benefits that are not efficiently priced and often generate little or no financial return. The global climate crisis has created significant demand for investment in these forms of natural capital, and Tanzania is well positioned to take advantage of nature-positive investment opportunities. The additional revenue derived from global climate programs could be an opportunity to ease the government’s fiscal constraints while also supporting the livelihoods of local communities.
“While restoring the trade and financial flows associated with tourism is an urgent priority, the disruption of the sector has created an opportunity to realign tourism development with economic, social, and environmental resilience,” said Marina Bakanova, World Bank Senior Economist, and co-author of the report. “The pandemic has created an opportunity to implement long-discussed structural reforms in the sector and use tourism as a leading example of improvement of the overall business climate for private investment.”
The authors suggest five priorities for a sustainable and inclusive recovery that lay the foundation for the long-term transformation of the tourism sector:
- Creating an efficient, reliable, and transparent business environment to reduce red tape and multiple distortions and inefficiencies, hindering decisions on private investments, domestic and foreign
- Establishing an information-management system that consolidates data from tourists and firms, enabling policymakers to improve sectoral planning and identify viable investment opportunities
- Ensuring that firms across the sector, as well as those in downstream value chains, have access to affordable transitional finance
- Consistently promoting, monitoring, and reporting on adherence to health and safety protocols.
- Developing co-investment and partnership arrangements to support nature-based landscape and seascape management
- Press Release: Tanzania has an Opportunity to Ignite Inclusive Economic Growth by Transforming its Tourism Sector
- Report: 16th Tanzania Economic Update: ‘Transforming Tourism: Toward a Sustainable, Resilient, and Inclusive Sector’
- Video: Launch event: 16th Tanzania Economic Update
- The World Bank in Tanzania
- The World Bank in Eastern and Southern Africa
- The World Bank in Africa
- Africa Collective
Business Insider Edition
- United States
- International
- Deutschland & Österreich
Tanzania eyes tourism growth to boost economy in 2024
Tanzania's tourism sector could potentially generate up to Sh3.38 trillion in additional revenue in the next financial year from Sh2.38 trillion in the current financial year, a senior official said on Tuesday.
Tanzania's tourism industry is making a remarkable comeback nearly four years after its revenues plummeted due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The tourism sector could potentially generate up to Sh3.38 trillion in additional revenue in the next financial year, according to a senior official.
- Enhancing the business climate and expanding projects are some of the factors that could greatly boost revenue collection.
Recommended articles
The Principal Secretary in the Ministry of State, Office of the President, Finance and Planning, Dr Juma Maliki Akili, disclosed this at the ‘2024/2025 Economy and Budget annual forum’ for stakeholders from local government and non-governmental organisations (NGOs).
While addressing the gathering at the Sheikh Idriss Abdulwakil Multipurpose Hall, Dr Akili explained that the revenue collection until the end of the current financial year, which ends in June this year, is projected to hit Sh2.38 trillion.
He added that the figure could significantly increase as a result of factors such as enhanced dedication from stakeholders in tax compliance and encouragement of voluntary tax contributions, intensified efforts by the Zanzibar Revenue Authority (ZRA) and Tanzania Revenue Authority (TRA), along with robust collaboration between the authorities and principal institutions.
“We predict to have economic growth of 7.2 per cent next year, and our revenue collection may increase to Sh3.38 trillion, while the number of tourists will increase to 829,000 next year from 638,000, ending the financial year,” Dr Akili said, according to Daily News .
Dr Akili expressed confidence that the target would be achieved, stating that in 2019, economic growth slowed down due to COVID-19 and that good planning has helped Zanzibar recover.
According to him, increasing knowledge about tax among ZRA and TRA staff, improving the business/investment environment, increasing projects, and increasing production from the blue economy are added advantages to an admirable bright future for Zanzibar.
Last year, data from the Bank of Tanzania revealed that tourism has staged an impressive recovery, contributing $2.99 billion to foreign exchange earnings in July 2023, compared to $1.95 billion in July 2022.
The bank also noted that this resurgence in tourism and increased earnings from gold have played a pivotal role in boosting Tanzania's service earnings to over $5 billion for the first time in its history.
FOLLOW BUSINESS INSIDER AFRICA
Thanks for signing up for our daily insight on the African economy. We bring you daily editor picks from the best Business Insider news content so you can stay updated on the latest topics and conversations on the African market, leaders, careers and lifestyle. Also join us across all of our other channels - we love to be connected!
Ethiopia moves to allow foreign banks to establish local subsidiaries
Nigeria's inflation rises for the 17th consecutive month in may, ex niger president now faced with the threat of persecution, the kenyan shilling may just be africa’s best-performing currency, the center for dialogue opens the door to a new relational paradigm shift in liberia, south africa re-elects cyril ramaphosa as president, exploring the best rtp (return to player) games on stake.com: a comprehensive guide, ghana resorts to load shedding due to gas supply shortfall from nigeria, top 5 countries nigeria imported from the most in q1 2024.
African countries ineligible for U.S. AGOA trade in 2024
Ethiopia and Russia's economic relationship discussed at BRICS meeting
Africa's richest man Dangote to venture into steel production

Dar es Salaam Stock Exchange Report – Week 24 of 2024: Turnover of Shares and Bond Activity See Massive Increase

STAMICO and Korea’s KOMIR Sign Agreement to Develop Strategic Minerals in Tanzania

Tanzania National Budget for 2024-2025: Key Highlights, Tax Breaks, and Implications

WFP to Purchase 60,000 Tons of Maize from Tanzanian Farmers for $22 Million

In 2023, tourist arrivals to Tanzania increased by 24.3% to a record-breaking 1,808,205, from 1,454,920 tourists in 2022, 922,692 in 2021, and 616,491 in 2020.
Tanzania’s tourism receipts reached a record-high USD 3,368.7 million in 2023, compared to USD 2,527.8 million in 2022 (USD 1,310.3 million in 2021). This increase is consistent with the rise in the number of tourist arrivals.
In 2020, revenues were down to USD 1 billion as it was severely affected by the Covid-19 pandemic and its impact on international travel, from a peak of USD 2.6 billion in revenues and 1.5 million arrivals in 2019.
The sector’s contribution to GDP fell from 10.6% in 2019 to 5.3% in 2020 and climbed to 5.7% in 2021.
However, given the ongoing fast recovery of the sector, the Tanzania National Business Council (TNBC) forecast that the share of tourism in the country’s GDP will reach 19.5% in 2025/26.
Europe traditionally accounts for the largest share of arrivals, followed by Asia and the Pacific, the Americas, Africa, and the Middle East.
Tanzania´s hotel occupancy rate was estimated at 53.8% in December 2019 compared to 44.9% in December 2018.
The increase in tourist arrivals in 2023 was attributed to the rebound of travel activity post-COVID. Additionally, it was driven by the continued efforts of the Tanzanian government to promote tourism attractions within and outside the country.
“The Royal Tour” Documentary
In April 2022 Tanzania’s President Samia Suluhu Hassan unveiled the “The Royal Tour” documentary while promoting FDIs during her official visit to the US.
Filmed throughout Tanzania in 2021, it features Emmy Award-winning journalist Peter Greenberg traveling to Tanzania with President Hassan.
She’s the ultimate guide for a week, exhibiting Tanzania’s history, culture, environment, food, and music, as well as telling the stories of Tanzania’s hidden jewels.
Source Markets
In 2022, the United States of America recorded the highest number of arrivals from the rest of the world at 100,600 followed by France (100,371), Germany (67,718), the United Kingdom (60,116) and Poland (46,431).
Meanwhile, arrivals from Africa were from Kenya (166,324) Burundi (100,851), Zambia (46,787), Malawi (44,438) and Rwanda (44,288).
Tourist arrivals from the top 10 countries out of 214 account for 53.2% of all arrivals.
Tanzania Tourism Offer
Tanzania’s incredibly rich natural tourism offer earned it the title of “Africa’s Leading Destination” in 2021.
The natural attractions fall into two main categories: wildlife and beach.
Tanzania Wildlife & Beaches
Tanzania’s wildlife resources are considered among the finest in the world. Tanzania is the only country, which has allocated more than 25% of its total area to wildlife national parks and protected areas.
There are 16 National Parks in Tanzania, 28 Game Reserves, 44 Game controlled areas, 1 conservation area, and 2 Marine Parks.
Tanzania boasts many of Africa’s most renewed destinations; in the north the Serengeti plains, the Ngorongoro Crater, Lake Manyara, and Mount Kilimanjaro, and in the south Mikumi and Ruaha National Parks and the Selous Game Reserve.
According to a survey conducted by SafariBookings.com, Tanzania’s Serengeti National Park was voted Africa’s best safari destination for 2020, followed by Mana Pools (Zimbabwe), Mala Mala (South Africa), Okavango Delta (Botswana), and Lower Zambezi (Zambia).
Mount Kilimanjaro was declared Africa’s leading tourist attraction in 2016 during the World Travel Awards Africa and the Indian Ocean Gala Ceremony in Zanzibar.
Other additional natural attractions include the white sandy beaches of the Zanzibar archipelago, those north and south of Dar es Salaam, and excellent deep-sea fishing at the Mafia and Pemba Islands.
Tanzania Hunting
Tanzania is prized for its superb trophy hunting (sport hunting or safari hunting).
Hunting in Tanzania is presently permitted and regulated by the Wildlife Conservation Act of 2009, and its subsidiary regulations.
The hunting industry has grown considerably in the last two decades and Tanzania is among the leading hunting destinations in the world.
Hunting and Forestry jointly contribute 2 to 3 % of the GDP of Tanzania. Given there is such commitment to the conservation and protection of wildlife, it may be surprising to note that, unlike neighboring Kenya, hunting still occurs in Tanzania.
However, there is no contradiction, as hunting in Tanzania is part of the wildlife conservation process, as it is done in a much-planned manner. Counts of wildlife are taken regularly and hunting licenses are issued accordingly.
Investments in the Tanzanian Tourism Sector
The Tanzanian Government is engaged in developing and promoting sustainable growth in the travel and tourism sector in Tanzania, to preserve its natural and cultural resources.
The Government, therefore, is focused on attracting high-income tourists who are less likely to spoil the culture and the natural environment.
Last Update: 23rd February 2024
Sources: Bank of Tanzania (BoT), Statista, Tanzania Immigration Department, Tanzania National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), World Bank (WB).

Zanzibar Second-Best Island Destination in The World in 2024
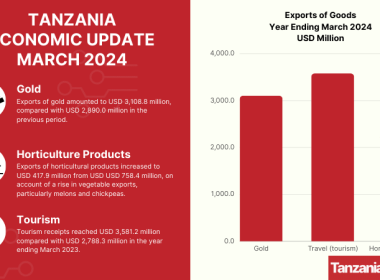
Tanzania Exports Up by 13% in The Year Ending March 2024, Tourism Receipts Up by 28%, Traditional Exports Up by 36%, and Horticultural Exports Up by 40%

Tanzania Tourist Arrivals Reached Record-Breaking 1.8 Million in 2023

Tanzania Economic Review November 2023: Tourist Arrivals Up by +27%

Tanzania Economic Review October 2023: Export of Traditional Goods Almost Doubled Driven by Coffee and Tobacco

Tanzania Parks Signs Carbon Credit Deal


Tanzania Economic Review, September 2023: Tourism and Transport Receipts Up by 30.5%

Tanzania Economic Review, August 2023: Strong Growth in Coal Exports and Resilient Tourism Sector

Serengeti Voted Africa’s Leading National Park For The 5th Time

Tanzania Coal Exports Triple, Diamond Sales Up By 60%, and Tourism Hits Record High in YE July 2023
Privacy overview.
This site uses cookies to optimize functionality and give you the best possible experience. If you continue to navigate this website beyond this page, cookies will be placed on your browser. To learn more about cookies, click here .
Rapid Growth Recorded in Tanzania's Tourism Sector as Economy Gains Momentum

"The current situation augurs well for tourism. The future looks promising," Hotel Association of Tanzania (HAT) chief executive Kennedy Edward told The Citizen. "This shift of culture is very good for tourism. Population growth also means that disposable incomes are increasing and there is growing awareness among Tanzanians."
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- tourism industry
- economic growth
- East Africa
- Terms of Use
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Privacy Feedback

Art in Tanzania Blog
Volunteer for africa, strategies to promote tourism development in tanzania: setting sights on europe.
By Romaisa Hussein – Art in Tanzania internship

African Tourism Development in Perspective
While the continent possesses a wealth of natural and cultural resources, tourism in Africa has largely performed below expectations, and its sometimes poorly managed expansion has had long-term detrimental implications for both people and the environment. To achieve long-term and sustainable forms of tourism that are respectful of Africa’s rich natural and cultural heritage, tourist industry executives and policymakers must take into account the broader historical and socioeconomic background in which tourism is introduced. It is quite wondrous that such a huge land mass lying between the Indian Ocean as well as the great lake Victoria and lake Tanganyika provide an exceptionally rich assortments of tourist sites, ranging from the snowy Mt. Kilimanjaro and open volcano craters to the boundless plains, and from the large tropical rain forests to the warm emerald ocean with white sandy beaches. Some of the world’s most beautiful wildlife regions are located in the northern hemisphere, while others are distributed throughout the country in national parks and game reserves that are densely populated with animals which set amid some of the world’s most breathtaking landscape. Exotic wildlife hunting, fishing, and scuba diving in the Indian Ocean including the friendliness and innate courtesy of the people appeals the visitors in this region from all around the world.
Tourism Master Plan in Tanzania
Tanzania has a plethora of natural, cultural, and man-made attractions in almost every region but many of these are overlooked from the aspect of sustainable tourism development. Although there is huge potential in the country, not all locations are said to develop any time soon in the foreseeable future due to poor access to resources, inadequate infrastructure, and a lack of utilities. Judging from the lack of infrastructure in remote areas of Tanzania, as well as a lack of utilities to put the plan into action, it summarizes that the last decade covered by the ten year Master plan in Tanzania, it is only proper to concentrate development efforts specifically in the parts of the country that lie between Mwanza and Mbeya. In accordance with the results of a poll conducted by the tour operators in Europe and US for the Master Plan, the majority believe that the condition, quantity, diversity and prospects of wildlife in Tanzania’s national parks surpasses to that of wildlife in rival destinations. Although the Northern Wildlife parts in Tanzania are becoming exceedingly packed with tourists, the majority of respondents stated that wildlife is not yet completely over crowded by tourists as it has the potential to compared to the competing destinations which also include hunting areas adjacent to the National Parks. The Ngorongoro Crater and the Serengeti Wildlife Migration are World Heritage Sites and deemed as “unique wildlife watching opportunities”. Participants noted that Tanzania also has the potential to fetch a higher price for its Wildlife Watching, but only if the conditions for the tourism development, as well as the quality of the housing and services are enhanced. Sport hunting may arguably be the ultimate enigma of sustainable tourism. Even though the majority involved in conservation and nature tourism go against hunting and consider it ethically iniquitous, many still acknowledge that, if supervised properly, trophy hunting helps to reduce poaching, causes less environmental degradation, and significantly generates more foreign revenue.
First Sustainable Tourism Management Meeting
In October 2012 in Arusha, the Government of Tanzania hosted the ‘First Pan-African Conference on Sustainable Tourism Management in National Parks and Protected Areas: Challenges and Opportunities’. The conference was organized by the Tanzanian Ministry of Tourism and Environment in which participants discussed “park tourism” to be crucial and a key component to overall national park management in Africa. The meeting was also directed towards having better understanding of the present difficulties in the areas of demand and supply chain management. Moreover, they discussed at length new collaborations and business models for park management structures, with the goal of maximizing the economic and social advantages to the surrounding communities.

Through 1.28 million visitor arrivals in 2016 in Sub-Saharan Africa, Tanzania has since gained popularity on a global scale with its most popular sites being the Serengeti National Park and Zanzibar. Tanzania has always been prime destination for travelers seeking adventure and at the same time has steered clear from mass-market overdevelopment by capitalizing on its natural and cultural assets. Such model is a goal for many developing countries to emulate in the future. With a aim of attracting three million visitors per year by 2022, the government is attempting to develop the first new national tourism strategy expected to focus on high-value infrastructure.
Europe as Potential Tourism Market
According to an official with Tanzania’s Tourist Board, the government is now focusing its tourism marketing efforts in Eastern Europe after experiencing vast success in Western Europe and North America. In an interview with the Tanzania Tourist Board (TTB), Willy Lyimo, the TTB’s northern zone manager stated that the new market will add to the country’s otherwise traditional markets like that of the United States, the United Kingdom, Germany, and France. After meeting with a delegation of travel agencies from Eastern Europe, Lyimo emphasized the importance of growth of new market in Tanzania’s tourism industry, stating that the country stands to gain significantly from it. “This is a distinctive opportunity to extend our base into rising markets.” He also highlighted the tourism potential in countries like Bulgaria and the Czech Republic. Tanzania’s Tourism Board official was also optimistic about the promotion of the country’s natural resources across international travel expos due to the attention indicated by foreign travel agencies and tourism operators to attract tourists in Tanzania.

A representative from Ukraine’s BCD Travel described Tanzania as a well-established safari destination for many Ukrainians and said that his firm will continue to bring more tourists from the country. Because of the “pristine heritage” of Tanzania as well as “plenty of natural resources,” he says, “Tanzania is the ideal gateway for tourists from Ukraine.” Voloshyn was encouraged by the introduction of direct flights from Ukraine’s capital Kiev to the spice island of Zanzibar and believed that this development would help to open up Tanzania to the rest of Eastern Europe. In 2019, Tanzania begun a six-day tourism roadshow in several European nations to promote the country’s tourist attractions. According to Francis Malugu, marketing officer for the Tanzania Tourist Board, ten Tanzanian tourist enterprises participated in roadshows between 3 rd June and 8 th June in London, Brussels, Paris, and Lyon. In terms of foreign exchange, tourism is one of Tanzania’s most important sources, delivering an average of 2 billion US dollars per year, which is comparable to 25 percent of total foreign exchange earnings, according to government statistics. According to CHL Consulting Groups, the most popular tour programs in the “European market demand profile” include Beach resort, Safari, Single destination /sightseeing, and Dual destination safari/sightseeing. In this market demand profile, Beach resort is the most popular tour program desired by Europe. Safaris are also significantly high in demand, and same goes for beach tourism. While just 15% of the market seeks a vacation that consists solely of beaches, more than one-third i.e. 35% seeks a vacation that includes both a beach and a safari. Tanzania’s most important export markets include the United Kingdom, Germany, France, Scandinavia and Italy.
Earnings from visitors at tourist attraction sites in Tanzania in 2020
According to the Tanzanian Tourism Development Authority, the number of visitors to Tanzania’s tourism attractions resulted in earnings of nearly 17.4 billion Tanzanian shillings (around $7.5 billion US) in the fourth quarter of 2020. In comparison to the fourth quarter of 2019, the value was dropped by about 75%. According to the source, the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic was to blame for the decline in the stock market. Furthermore, the Northern and Lake zones accounted for nearly 90 percent of the overall revenue generated by visitor arrivals in the country.
Prospects for Tourism Development in Tanzania

After a period of being negatively impacted by external challenges, Tanzania’s tourist sector is experiencing tremendous growth once more. Privatized investment in resorts and hotels as well as government investment in infrastructure are expanding new tourist destinations in remote parts of the country. Nevertheless, the tourism industry is still faced with obstacles, such as the application of VAT and the consequences of austerity on business demand. However, the government’s new sector strategy, which is now being developed, should give new impetus as well as a framework that will allow new markets to be explored. Tourism in Tanzania, as in other parts of Africa, should play a developmental role that is in line with the aspirations of the local population. According to Mwalimu Nyerere, “You cannot develop people until they grow themselves.” Even with the continuous development of tourism, it will never be enough to solve all of the difficulties facing the country. However, it can at the very least provide some jobs, help to diversify the local economy, and enhance the quality of life of the people. Tanzania should also take into consideration the establishment of a truly sustainable tourism development program. Such a program necessitates real collaboration across disciplines as well as across the numerous gaps that exist between academics, policymakers, business leaders, and other interested parties and stakeholders. To achieve sustainable tourism potential in the local livelihoods as well as biological conservation, one of the most important challenges is to empower the local people to take initiatives and exercise control over their economic activities and resources. In order to reach sustainable tourism in Tanzania, there is definitely a long road ahead.
Faria, J. (2021, May 5). Earnings from visitors at tourist attraction sites in Tanzania 2020, by zone . Retrieved from Statista: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1149350/earnings-from-visitors-at-tourist-attraction-sites-in-tanzania-by-zone/
Oxford Business Group. (2018). Tanzania to diversify tourism offerings and address growth challenges . Retrieved from Oxford Business Group: https://oxfordbusinessgroup.com/overview/achieving-potential-taking-steps-diversify-offerings-and-address-remaining-challenges-growth
Salazar, N. B. (2009). A troubled past, a challenging present, and a promising future? Tanzania’s tourism development in perspective. Tourism Review International , 259-273.
Tanzania Tourism Sector Survey. (2014). The 2012 International Visitor’s Exit Survey Report. Retrieved from https://www.bot.go.tz/Publications/Other/Tanzania%20Tourism%20Sector%20Survey%20Report/en/2020021122482624214.pdf
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA, MINISTRY OF NATURAL RESOURCES AND TOURISM. (2002). TOURISM MASTER PLAN: STRATEGY AND ACTIONS. CHL Consulting Group. Retrieved from http://www.tzonline.org/pdf/tourismmasterplan.pdf
Xinhua. (2018, May 6). Tanzania sets sights on Eastern Europe as potential tourism market . Retrieved from Xinhua.net: http://www.xinhuanet.com/english/2018-05/06/c_137159712.htm
Yan. (2019, June 7). Tanzania stages tourism roadshows in Europe: official . Retrieved from Xinhua.net: http://www.xinhuanet.com/english/2019-06/07/c_138122692.htm
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

The United Republic of Tanzania
Tanzania investment centre.

- Investment Opportunity Areas
- Indicative Return
Investment Timeframe
Market Size
Ticket Size
- Direct Impact SDG’s
Consumer Goods
- Extractives and Minerals Processing
Food and Beverage
Health Care
Infrastructure
- Renewable Resources and Alternative Energy
Resource Transformation
Technology and Communications
Transportation
- Success Stories
- Knowledge Repository
Indicative Return Describes the rate of growth an investment is expected to generate within the IOA.
Investment Timeframe Describes the time period in which the IOA will pay-back the invested resources.
Ticket Size Describes the USD amount for a typical investment required in the IOA.
Market Timeframe Describes the value of potential addressable market of the IOA.
Direct Impact SDG's Describes the primary SDG(s) the IOA addresses.
Regions Independent research and interviews with Government and private sector stakeholders.

Minerals Processing

Renewable Resources

Community-Based Tourism Products
Indicative Return:
Medium Term (5–10 years)
More than USD 1 billion
More than USD 10 million
Develop tourism products and associated services by utilizing the rich traditional cultures and diverse natural assets of rural communities to create eco-tourism experiences, such as tours of traditional ways of life, fishing, ziplining and parachuting. Through a community, public, private partnerships, the private sector invest in tourism assets, the public sector provides the supporting infrastructure and the community provides the land, labour, local expertise and cultural experiences.
Integrate inland and rural populations into the tourism industry and protect their biodiversity and wildlife.
Northern , Southern
Sector Services > Hospitality and Recreation
Sector Classification
Situate the investment opportunity within sustainability focused sector, subsector and industry classifications.
Development need: Tourism has the greatest employment generation potential in Tanzania. However, the country has performed at a fraction of its potential. The sector is poorly managed, underinvested, under-resourced, and lacks a coordinated all-of-government approach and vision. This has reduced its competitive advantage (1, 2, 3, 4).
Policy priority: Tanzania is committed to promoting diversified tourism products in order to increase its competitive advantage. The government seeks to promote tourism since it integrates more than one service, notably transport, accommodation and food, information and communication, offering significant socio-economic development potential (4, 5).
Gender inequalities and marginalization issues:Women face challenges participating in tourism activities in Tanzania. Most women in rural communities are excluded from tourism activities and some of them are exploited without commensurate returns. Taking full charge of responsibilities in their households gives women challenges that constrain their ability to perform in businesses, including in tourism (11).
Investment opportunities introduction: Opportunities in services include a broad range of diversified tourism activities, both regarding products and infrastructure, utilising community inputs, particularly in Tanzania’s Southern Circuit as a result of overcrowding and saturation in the Northern Circuit (9).
Key bottlenecks introduction: COVID-19 severely impacted Tanzania’s tourism activities due to the disruption of global travel, which resulted in a 72% drop in revenues with significant job losses and business closures. The poor performance in tourism adversely affects other sectors (8).
Development need: Community-based and sustainable tourism provides important opportunities to take advantage of the increasing demand for Tanzania’s eco-tourism products. It is strategically important to the national tourism industry, valued at approximately USD 725 million annually, in terms of diversifying tourism products, relieving pressure on over-crowded protected areas and offering the required infrastructure (6).
Policy priority: The government is committed empower rural communities and private land holders to manage natural resources, including wildlife, in a sustainable manner and for their own benefit. Developing co-investment and partnership arrangements to support nature-based landscape and seascape management is among the top priorities for the long-term transformation of Tanzania’s tourism activities (7, 8).
Business Case
Learn about the investment opportunity’s business metrics and market risks.
Tanzania’s tourism sector generated USD 2.6 billion in 2019 before COVID-19, and USD 1 billion in revenues in 2020 (14). Tanzania is first in Africa and 12th worldwide for the quality of its community- nature-based tourism resources, and 32nd in Africa and 112th in the world for its cultural resources (17).
Globally, nature tourism and ecotourism grew three times faster than the overall tourism industry, and investment is estimated to increase by 20% annually (29)
Significant tourism revenues accrue to local communities. For example, seven villages in Loliondo Division earn over USD 100,000 annually from several eco-tourism joint ventures carried out on their lands (14, 16).
According to local investors in Columbia, an expected holding period for investments in ecotourism models would be between 7 and 10 years (30)
Market – Volatile
Capital – CapEx Intensive
Impact Case
Read about impact metrics and social and environmental risks of the investment opportunity.
Tourism, which plays a prominent role in the Tanzanian economy, accounting for nearly 12% of GDP, has been the most severely affected sector from the COVID-19 pandemic due to travel restrictions (3, 8).
Despite the significance of the tourism sector, poverty is prevalent around touristic sites, indicating that strong linkages with local communities have yet to be established. Most tourist establishments source their supplies (e.g., vegetables) from large scale suppliers because of local communities inability to meet required quality standards (27, 28).
The growing industry has put pressure on people and the planet. Areas and adjacent lands to the ecotourism activities have been subjected to a number of emerging issues and challenge including failure of conservation (as a form of land use) to compete effectively with alternative land uses, habitat degradation and blockage of wildlife corridors, overexploitation and illegal resource extraction, wildfires, human population growth (30)
Community based tourism can accelerate rate of economic growth through the tourism sector which is estimated to have generated USD 2.6 billion in 2019 before COVID-19, and USD 1 billion in revenues in 2020 (14). Tanzania could utilize this potential to position itself in view of the competition in the region and utilize its competitive advantage of being the first in Africa and 12th worldwide for the quality of its community- nature-based tourism resources, and 32nd in Africa and 112th in the world for its cultural resources (17).
Community based tourism can promote rural development through employment of local community in the facilities, poor residents selling products and services directly to tourists, e.g., making and selling handicrafts, supplying various food products to the tourists’ facilities or provide guiding services or (31,32)
Sustainable community-based tourism can reduce pressure on people and the planet through effective conservation measures and sustainable exploitation. Total biodiversity can be conserved and supported by the added income generated by ecotourism (30).
Tourism can be an especially important vehicle for poverty reduction in rural areas, where the poverty rate among households with a member employed in the tourism sector (16 percent) is about half the overall poverty rate (31 percent). Households with a member employed in tourism are also more resilient to income shocks (8).
People: Communities with touristic products and activities, employees in the tourism industry, and local and foreign tourist benefit from diversified tourism offering.
Gender inequality and/or marginalization: Inland and rural populations benefit from the integration into the tourism industry, which brings about economic opportunities.
Planet: The environment benefits from sustainable tourism practices, biodiversity and the wildlife enjoys greater protection resultant from economic value generation.
Corporates: Tourism product and service providers enjoy greater demand, and tourism industry actors, such as hotels and tourism agencies, benefit from enhanced economic activity.
Public sector: Government enjoys economic growth, enhance environmental conservation and improve rural development through linkages promoted between tourism facilities and local communities
People: Rural populations benefit from increased economic activity and reduced environmental harm, supporting sustainable livelihoods.
Planet: The environment enjoys increased awareness on sustainable business practices in other industries.
Corporates: Suppliers of the tourism industry, such as agricultural businesses, benefit from new market demand.
Excessive levels of touristic interventions may cause damage to the environment and wildlife as well as disturb cultural and traditional practices of communities, if the number and activities of tourists is not well managed (8, 20).
Most local communities do not quite understand the best practices for environmental management and socially responsible tourism. These may therefore not be well implemented, risking the expected impact ((8, 10, 20).
If the communities’ interest and priorities are not take into account sufficiently, touristic activities may not experience a significant uptake and / or benefit the communities, which may limit the expected impact.
Impact Classification
B—Benefit Stakeholders
Community-based tourism products diversifies the tourism industry towards integration of inland and rural populations and sustainable practices.
Inland and rural communities, local and international tourists, the tourism industry, the environment, biodiversity and wildlife benefit from community-based tourism products.
While the model of community-based tourism is proven, environmentally and socially responsible practices as well as the communities’ interests and priorities require consideration.
Enabling Environment
Explore policy, regulatory and financial factors relevant for the investment opportunity.
Tanzania Tourism Policy, 2021: Outlines the government’s commitment to promote diversified tourism products and associated services including community and eco-tourism, historical and cultural heritage sites, conferencing and tourism supply chain (5).
Tanzania Tourism Master Plan, 2002: Emphasizes that the government is committed to promote diversified tourism sector in terms of geography (location), tourism products and associated services and activities. A renewed emphasis on targeting the Southern Circuit as a result of the saturation of the Northern Circuit (9).
Third National Five-Year Plan (FYDP 3), 2021: Outlines the government’s plan to promote tourism as one of the sub-sectors that integrates more than one services, notably local culture and natural endowments, transport, accommodation and food, information and communication (4).
The World Bank has offered a credit of USD 150 million to Tanzania to operationalize the REGROW project, which focuses on the promotion of alternative livelihoods for household around the protected areas of the Southern Circuit, including community-based tourism products. There is a special embedded package for identifying suitable joint economic opportunities between investors and communities (24).
Fiscal incentives: Tanzania offers import duty and VAT exemption on deemed capital goods, including building materials, utility vehicles and equipment. This applies to all types of tourism products including activity based tourism (25).
Tourism Act, 2008: Provides the institutional framework, administration, regulation, registration and licensing of tourism facilities and activities, and for related matters (21).
Wildlife Conservation Act, 2013: Makes provisions aimed at regulating sustainable utilization and management of wildlife resources and to provide for other related matters (23).
Case Studies
Discover case studies that are active in the investment opportunity.
Ololosokwan village In Loliondo District entered into an arrangement with a South African eco-tourism company to jointly operate a large commercial eco-tourism development project. Through the joint venture, the villages’ annual income increased from USD 25,000 in 1999 to USD 37,640 in 2003. It now constitutes more than 30% of the council’s income (12).
The Tanzip Zipline Adventure Park is located just outside of Mto wa Mbu village in Arusha. It is nestled at the base of the Great Rift Valley wall, offering stunning views of surrounding lakes, wetlands, maasai steppe, and the valley. The facility is run jointly with the village and provides a variety of tourism activities (13).
Discover public and private stakeholders that are active in the investment opportunity.
Private sector
Nomad Tours, Kudu safaris, Adventure Safaris, Kearsleys Travel & Tours, Takims Holidays, Widerange African Safaris, FCM Skylink Travel and Tours Ltd, Tanzania Mwangaza Tours & Safaris, The Sultan Tours, Gecko Adventure Tanzania Safaris etc
Ministry of Tourism and Natural Resources Management (MNRT), Tanzania Wildlife Authority(TAWA), Ministry of Economy and Finance, Ministry of Industry and Trade, Tanzania Tourism Board (TTB).
Multilaterals
World Tourism Organisation, Global Tourism Council, World Bank Group (WBG), African Development Bank (AfDB), World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC). World Tourism Forum Institute
Tanzania Wildlife Protection Fund, Wildlife Conservation Society of Tanzania, Community Wildlife Management Areas Consortium (CWMAC),Tanzania Association of Tour Operators, Hotels Association of Tanzania (HAT), Tanzania Natural Resource Forum (TNRF).
Public-Private Partnership
Chumbe Island Ecotourism A PPP between the government and a special purpose company, Chumbe Island Coral Park Ltd. (CICP) to restore the coral reef which was endangered by overfishing and unsustainable fishing practices, such as dynamiting the reef
See what sources were used to establish the investment opportunity’s data and find resources that could be consulted to explore more.
Sector & Subsector Sources
1) World Bank Group- Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA): Tanzania’s Investor Outreach Program 2005 2) De Chazal Du M(DCDM), Tourism in Tanzania : Investment in Tourism in Tanzania, 2011 3) Diagnostic Trade Integration Study (DTIS) for Tanzania, 2015 4) United Republic of Tanzania, Third National Five-Year Plan (FYDP 3), 2021 5) Tanzania Tourism Policy 2021 – Under review 6) Tanzania Natural Resource Forum (TNRF), Community-based Tourism in Northern Tanzania: Increasing Opportunities, Escalating Conflicts and an Uncertain Future, 2003 7) Resource Forum, Community-based Tourism in Northern Tanzania: Increasing Opportunities, Escalating Conflicts and an Uncertain Future, 2003 8) Word Bank Group, Tanzanian Economic |Update, Transforming Tourisms Sector, Toward a Sustainable, Resilient, and Inclusive Sector, 2021 9) United Republic of Tanzania, Tourism Master Plan, 2002 10) Journal of Ecotourism, A review of ecotourism in Tanzania: magnitude, challenges, and prospects for sustainability, 2015 11) ORSEA Journal Vol. 7 (2), 2017, Gender and Women Entrepreneurs’ Strategies in Tourism Markets: A Comparison between Tanzania and Sweden
IOA Sources
12) International Institute for Environment and Development, The evolution and impacts of community-based ecotourism in northern Tanzania, 2004 13) TanZip Adventures, www.bomaafrica.com 14) Tanzania Invest.com, https://www.tanzaniainvest.com/tourism 15) Jadian Company Limited, Feasibility Study Report, 2021 16) Tanzania Natural Resources Forum, Community-based Tourism in Northern Tanzania: Increasing Opportunities, Escalating Conflicts and an Uncertain Future, 2003
17) World Economic Forum, Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index Report, 2019 18) Development Southern Africa, Cultural community-based tourism in Tanzania: Lessons learned and way forward, 2015 19) Journal of Development Studies, Gender and Livelihood Diversification: Maasai Women’s Market Activities in Northern Tanzania, 2015 20) Research on Poverty Alleviation (REPOA), The Role of Tourism in Poverty Alleviation in Tanzania, 2003 21) URT, The Tourism Act, 2008 22) URT, Wildlife Conservation Act (No. 5 of 2009) 23) URT, The Wildlife Conservation Act 2013 24) The World Bank, New Opportunities for Development in Southern Tanzania Through Nature-Based Tourism, 2017 25) EAC Investment Guide, United Republic of Tanzania Standard Incentives for Investors 26) Ministry of Natural Resources and Tourism (MNRT), Tanzania Tourist Attractions: https://www.maliasili.go.tz/attractions/tanzania-tourist-attractions 27) World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC), 2020 28) World Bank Group, Tanzania Economic Update, 2015 29) Brink (2011) – The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity in National and International Policy Making. Accessed July 2nd 2020 30) Inversor Portafolio: Waya https://www.inversor.org.co/en/portafolio-2/waya-guajira/.
31) Happiness Kiami: Effects of Tourism Activities on The Livelihoods Of Local Communities In The Eastern Arc Mountains, 2018 32) The World Bank, Resilient Natural Resource Management for Growth (REGROW) Project, 2018 33) https://country-profiles.unstatshub.org/tza#goal-8 34) ADUMU Safaris, https://adumusafaris.com/destinations/tanzania-southern-circuit/
Tanzania: Govt Bullish About Growth Prospects

THE economy expanded by 5.1 per cent in 2023 despite the impacts of adverse global economic situation, and is projected to grow to 6 per cent this year, the government has said.
Presenting the state of the economy for 2023 in the National Assembly on Thursday, the Minister of State in the President's Office (Planning and Investments), Professor Kitila Mkumbo said the main drivers of growth were strategic investments in energy and transport infrastructure, tourism and mineral exports as the government undertook measures to cushion the economy from adverse impacts of global economic uncertainties.
However, despite stellar growth of the economy, it was slightly below 5.2 per cent target for 2023 mainly because of the rise in production costs in some sectors, and prolonged rains which affected agricultural production and damaged roads and bridges in some areas, he said.
The minister said the situation was also compounded by the impact of monetary policy tightening in advanced economies, which increased cost of borrowing from global financial markets, contributing to tight credit conditions, negatively affecting production.
ALSO READ: Tanzania's national debt reaches 91.7tri/-
Growth slowed to 4.7 per cent in 2022 from 4.9 per cent in 2021, due in part to the impact of the war in Ukraine that sent commodity prices, notably on food and energy, soaring.
The minister said in 2023 Tanzania's GDP value in current prices reached 188.588tri/- up from 171.3tri/- in 2022. With a population of about 61.7 million in 2023, GDP per capita increased by 7.1 per cent to 3,055,606/- (equivalent to 1,275.5 US dollars in 2022) up from 2,854,072/- in 2022 (equivalent to 1,233.1 US dollars) in 2022.
Agriculture accounted for 26.5 per cent for the total economy, followed by construction 13.2, minerals (9.0 per cent), trade and repairs (8.3 per cent).

Sign up for free AllAfrica Newsletters
Get the latest in African news delivered straight to your inbox
By submitting above, you agree to our privacy policy .
Almost finished...
We need to confirm your email address.
To complete the process, please follow the instructions in the email we just sent you.
There was a problem processing your submission. Please try again later.
In 2023, growth of agricultural activities that include cultivation of crops, livestock, forestry and fishing was 4.2 per cent up from 3.3 per cent in 2022, thanks to government's fertiliser subsidy programme that made the agricultural input more affordable to farmers as well as sufficient and timely rains in many areas.
Arts and entertainment sector led in growth of 17 per cent, followed by financial and insurance sector, (12.2 per cent), minerals (1.3 per cent), food and accommodation (8.3 per cent) and information and communication (7.6 per cent).
ALSO READ: Tanzania's economy grows by 5.4 percent
Despite leading in growth, arts and entertainment sector contributed little in economic growth as it has attracted a few people in various activities which include film, drama, music, sculpture, painting and tailoring.
The minister said in 2023 growth of mining activities reached 11.3 per cent up from 10.8 per cent due to increase in mineral production particularly coal, zinc, diamond, limestone and copper.
Contribution of the mining activities to the national economy was 9.0 per cent last year, unchanged from 2022.
Read the original article on Daily News .
Government Records Impressive 2023/24 Budget Execution
National Budget 2024/2025 - High Expectations
- East Africa
AllAfrica publishes around 500 reports a day from more than 100 news organizations and over 500 other institutions and individuals , representing a diversity of positions on every topic. We publish news and views ranging from vigorous opponents of governments to government publications and spokespersons. Publishers named above each report are responsible for their own content, which AllAfrica does not have the legal right to edit or correct.
Articles and commentaries that identify allAfrica.com as the publisher are produced or commissioned by AllAfrica . To address comments or complaints, please Contact us .
AllAfrica is a voice of, by and about Africa - aggregating, producing and distributing 500 news and information items daily from over 100 African news organizations and our own reporters to an African and global public. We operate from Cape Town, Dakar, Abuja, Johannesburg, Nairobi and Washington DC.
- Support our work
- Sign up for our newsletter
- For Advertisers

- © 2024 AllAfrica
- Privacy Policy
Tanzania’s tourism future looks increasingly bright

Tourists take a breather at one of Tanzania’s numerous tourist attractions. PHOTO | FILE
What you need to know:
That was announced during the World Travels Africa and Indian Gala in Zanzibar on April 9, boosting Tanzania’s image in continental tourism.
The mountain attracted 44,366 visitors during the 2015/16 financial year.
Dar es Salaam. Tanzania’s Mount Kilimanjaro has been declared the leading tourist attraction in Africa.
Humans' hazardously radioactive relationship behaviours

Dar Foto Festival giving Tanzanian photographers a unique stage

Mount Kilimanjaro is the highest in Africa, and rises about 4,900 metres (16,000 ft) from its base to 5,895 metres (19,341 ft) above sea level.
It is also the world’s highest freestanding mountain. Kilimanjaro has three volcanic cones-- Mawenzi, Shira and Kibo. Mawenzi and Shira are extinct but Kibo, the highest peak, is dormant and could erupt again. The most recent activity was about 200 years ago; the last major eruption was 360,000 years ago.
The Tanzania Tourist Board (TTB) believes that together with other initiatives, the country stands a chance of increasing the number of visitors.
It will also use Tanzanians in the diaspora to market Tanzania’s tourism.
The government has purchased two aircraft in an effort to revive Air Tanzania Company Limited (ATCL) and help attract visitors.
The country plans to attract 2 million tourists next year, up from the current 1.1 million.
TTB is cooperating with Ethiopia, South Africa and Qatar airlines to that effect.
It has also signed memoranda of understanding with some hotels, travel agents and the Tanzania National Parks.
Already, the number of international arrivals to the Ngorongoro Crater increased to 39,838 in July this year, up from 38,878 during the same period a year before.
Tourism promotion to the Southern circuit whose major attractions include Selous Game Reserve and Ruaha National Park will be enhanced.
However, TTB’s budget in the 2016/17 is Sh2.6 billion, down from Sh4.6 billion last financial year.
But out of Sh4.6 billion that was allocated to the board last year, only Sh655 million was disbursed.
During the period, the board was quoted by a section of local media as saying between Sh15 billion and Sh17 billion was needed for tourism marketing.
Natural Resources and Tourism minister Jumanne Maghembe early this year said the government would increase the budget to attract more tourists.
He said the aim was increase the sector’s contribution to the gross domestic product Sh8.8 trillion in the next two years.
However, the budget has been reduced. The government has promised to release the funds as budgeted.
TTB managing director Devota Mdachi is confident that the target of attracting 2 million tourists next year will be attained.
She has thanked the government for supporting the board in disbursing funds regularly, unlike in the last financial year. “With realistic market strategies, we are confident of reaching the target. We have categorised sources of tourists to make our marketing team easy to link up with its partners.”
The board targets the UK, US, Germany, China, the United Arab Emirates, Russia, Indi, and South Africa in marketing campaigns.
Recently, a government delegation visited Dubai to learn how tourism is marketed.
“Dubai is doing well in tourism, with the number of its annual international tourists averaging 14 million. We are also on the right track,” Ms Mdachi said.
Lessons drawn from Dubai’s tourism board include the use of social networks to market the sector. Adverts are translated into19 languages.
Dubai has a strong relationship with Emirates Airlines which transports tourists to various attractions.
A recent Bank of Tanzania economic review established that tourism is the country’s leading foreign exchange earner, generating $2.2 billion (about Sh4.4 trillion) annually.
The World Bank’s sixth Economic Update published in January last year said the sector could create more high-paying jobs and provide closer linkage with businesses and local communities if the government simplified its tax system.
In the headlines

Another 235 MW fed into Tanzania’s national grid from Julius Nyerere Hydropower Plant
The injected electricity from turbine eight brings the total power generated by JNHPP to 470 megawatts, thus resulting in the country’s power excess of 70 megawatts.

Experts urge reduced reliance on foreign aid
While Tanzania strives for economic resilience, reducing dependency on external funding remains crucial for long-term stability and growth.

Switzerland sink Hungary to make strong start at Euro 2024
Switzerland made a flying start at Euro 2024 as Kwadwo Duah and Michel Aebischer scored their first international goals in a 3-1 win against Hungary on Saturday.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Let's reimagine the future of Tourism in Tanzania. Tanzania's tourism sector is seeing a rebound after the Covid-19 pandemic—and the aspirations for its continued growth are high: by 2025, the country hopes to reach $6 billion in tourism revenue, which assumes the influx of five million tourists annually. To achieve such lofty goals will ...
Show plans. Dar es Salaam. Tanzania's tourism sector is seeing a rebound after the Covid-19 pandemic—and the aspirations for its continued growth are high: by 2025, the country hopes to reach $6 billion in tourism revenue, which assumes the influx of five million tourists annually. To achieve such lofty goals will require some important ...
Tanzania is a globally recognized destination for nature-based tourism, a competitive market segment in eastern and southern Africa. Beyond attracting tourists, the country's landscapes and seascapes produce a wide range of ecosystem services, including carbon sequestration and biodiversity co-benefits that are not efficiently priced and often generate little or no financial return.
Assuming the growth of 36 percent continues for the next two years, the receipts from tourist arrivals would reach USD 6. 3 billion by December 2025. In addition, if as a Country, we generated USD 3.4 billion with only 1.8 million tourist arrivals, one can argue that we do not need 5 million tourists to generate USD 6 billion.
Tanzania's tourism industry is making a remarkable comeback nearly four years after its revenues plummeted due to the COVID-19 pandemic. ADVERTISEMENT Last year, data from the Bank of Tanzania revealed that tourism has staged an impressive recovery, contributing $2.99 billion to foreign exchange earnings in July 2023, compared to $1.95 billion ...
Dar es Salaam. Tanzania has started 2024 with a notable surge in tourist arrivals, raising expectations for a continued industry upswing after full recovery from the Covid-19 pandemic's woes. The expectations are anchored on the arrival on Tuesday January 16 at the Dar es Salaam port of a ship carrying 2,340 passengers and more than 1,100 ...
Tanzania's Tourism Futures. Tanzania operates within a globally competitive tourism industry, including with competitors for wildlife tourism. Yet, Tanzania has reached an envi-able position as a high-value low-density (HVLD) tourist destination by restricting supply and targeting the high-end segment of the market that is largely unaffected by
With this fast-growing industry sending wealthy tourists, Tanzania had reached 1.5 million tourists in 2019. It was expecting to hit 2 million in 2020. Just the opposite has happened. There was a ...
2019 Tanzania's tourism sector contributed an estimated 17 percent of its GDP and directly employed over 850,000 workers,making it the country's second-largest component of GDP and third-largest source of employment. • Tourism had been Tanzania's largest foreign exchange earner since 2012, and in 2019 it
Tourism. In 2023, tourist arrivals to Tanzania increased by 24.3% to a record-breaking 1,808,205, from 1,454,920 tourists in 2022, 922,692 in 2021, and 616,491 in 2020. Tanzania's tourism receipts reached a record-high USD 3,368.7 million in 2023, compared to USD 2,527.8 million in 2022 (USD 1,310.3 million in 2021).
Tourism provides a robust stream of revenues for the country, with benefits that reverberate widely through the economy. The sector generates the bulk of exports for the . Tanzania's tourism futures : harnessing natural assets
In the wake of a steady economic recovery from the impact of Covid-19 pandemic that hit the global economy over the past few years, the tourism sector in Tanzania has experienced swift growth last year in both revenue and visitor numbers.Tourism receipts surged by 37.5% to $3.3 billion in the 12 months leading up to November 2023, while tourist arrivals rose by 27% to 1.797 million, according ...
With this fast-growing industry sending wealthy tourists, Tanzania had reached 1.5 million tourists in 2019. It was expecting to hit 2 million in 2020. Just the opposite has happened. There was a ...
Such model is a goal for many developing countries to emulate in the future. With a aim of attracting three million visitors per year by 2022, the government is attempting to develop the first new national tourism strategy expected to focus on high-value infrastructure. ... Prospects for Tourism Development in Tanzania. After a period of being ...
Council (WTTC), 2021. Travel and Tourism economic impacts reports - Tanzania. 4. Benson T et al., 2017. Prospects for the sectoral transformation of the rural economy in Tanzania: A review of the evidence. Feed the Future Innovation Lab for Food Security Research Paper No. 88. 5. Ntalwila J et al., 2017.
The US is still the biggest source of tourists visiting Tanzania, which is currently conducting a promotional drive to raise the number of arrivals to pre-pandemic levels. Latest National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) data shows that the number of tourist arrivals rose to 1,454,920 in 2022 from 922,692 in 2021, with the new figure falling short of ...
Tanzania has been a macro-economic success story for nearly two decades. The rate of economic growth increased from 3.5 pct. in the 1990s to 7 pct. in the 2000s. Despite the global financial crisis, growth rates have been remarkably stable over the last decade, and they are expected to continue or even increase in the foreseeable future.
Tanzania's tourism sector generated USD 2.6 billion in 2019 before COVID-19, and USD 1 billion in revenues in 2020 (14). Tanzania is first in Africa and 12th worldwide for the quality of its community- nature-based tourism resources, and 32nd in Africa and 112th in the world for its cultural resources (17).
The real GDP growth rate declined from 6.9% in 2019 to 4.8% in 2020 owing to regional trade disruptions and contraction in tourism and related sectors as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic ( NBS, 2019b ). Our study assesses the macroeconomic impact of COVID-19 on the tourism sector and the Tanzanian economy.
In the recent past, the concept of ecotourism has been promoted in Tanzania as an alternative, low-impact form of tourism that supports conservation of natural resources, preserves local culture, and provides economic benefits to the communities. Existing evidence shows that Tanzania has not utilised most of its ecotourism potential.
The United Republic of Tanzania is the 2nd largest country in the SADC Region and the 1st biggest in East Africa. It lies in the east coast of Africa between Latitudes 1 and 11 degrees South of the Equator. It covers 945,234 square Kilometres comprising Mainland and the islands of Zanzibar and Pemba. The estimated population of Tanzania for the ...
In the recent past, the concept of ecotourism has been promoted in Tanzania as an alternative, low-impact form of tourism that supports conservation of natural resources, preserves local culture, and provides economic benefits to the communities. Existing evidence shows that Tanzania has not utilised most of its ecotourism potential. The actual amount of ecotourism activity in the country is ...
Arusha. President Samia Suluhu Hassan said yesterday that the country's tourism sector was poised for accelerated growth. She said when addressing a global travel and tourism summit in Kigali that tourism would remain the key driver of the economy. "The sector, if well utilised, will reposition the country's export earnings for our ...
The minister said in 2023 Tanzania's GDP value in current prices reached 188.588tri/- up from 171.3tri/- in 2022. With a population of about 61.7 million in 2023, GDP per capita increased by 7.1 ...
As interest in sustainable tourism grows, community-based ecotourism has become a promising way to balance environmental conservation, cultural preservation, and local economic vitality [1,2,3,4].However, the success of ecolodge initiatives at the grassroots level is profoundly shaped by a complex interplay of place-based marketing and policy factors that remain underexplored in the literature ...
Mkumbo told parliament that the economy was projected to grow 5.4% this year from 5.1% in 2023, which was faster than the 4.7% a year earlier. Tanzania's economy largely relies on tourism ...
A recent Bank of Tanzania economic review established that tourism is the country's leading foreign exchange earner, generating $2.2 billion (about Sh4.4 trillion) annually. The World Bank's sixth Economic Update published in January last year said the sector could create more high-paying jobs and provide closer linkage with businesses and ...