Bolivia Travel Restrictions
Traveler's COVID-19 vaccination status

Traveling from the United States to Bolivia
Open for vaccinated visitors
COVID-19 testing
Not required
Not required for vaccinated visitors
Restaurants
Not required in public spaces and public transportation.
Bolivia entry details and exceptions
Ready to travel, find flights to bolivia, find stays in bolivia, explore more countries on travel restrictions map, destinations you can travel to now, dominican republic, netherlands, philippines, puerto rico, switzerland, united arab emirates, united kingdom, know when to go.
Sign up for email alerts as countries begin to open - choose the destinations you're interested in so you're in the know.
Can I travel to Bolivia from the United States?
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bolivia.
Can I travel to Bolivia if I am vaccinated?
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Bolivia without restrictions.
Can I travel to Bolivia without being vaccinated?
Unvaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Bolivia without restrictions.
Do I need a COVID test to enter Bolivia?
Visitors from the United States are not required to present a negative COVID-19 PCR test or antigen result upon entering Bolivia.
Can I travel to Bolivia without quarantine?
Travelers from the United States are not required to quarantine.
Do I need to wear a mask in Bolivia?
Mask usage in Bolivia is not required in public spaces and public transportation.
Are the restaurants and bars open in Bolivia?
Restaurants in Bolivia are open. Bars in Bolivia are .
- My View My View
- Following Following
- Saved Saved
U.S. CDC to shrink COVID-19 int'l travel avoidance list
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by David Shepardson in Berkeley, California; Editing by Leslie Adler and David Gregorio
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

World Chevron

EU Election 2024 Results Live: Macron calls election as exit polls show far right gains
Results are due to begin coming in from four days of elections for the EU parliament across the 27 EU member states and will be closely watched for the rising popularity of right wing parties.


Yellow Fever
- Requirements: Required if traveling from a country with risk of YF virus transmission and ≥1 year of age. 1
- Recommendations:
- Recommended for all travelers ≥9 months of age traveling to the following areas <2,300 m (7,546 ft) in elevation and east of the Andes Mountains: the entire departments of Beni, Pando, Santa Cruz, and designated areas (Map 2-2 ) of Chuquisaca, Cochabamba, La Paz, and Tarija departments.
- Not recommended for travelers whose itineraries are limited to areas >2,300 m (7,546 ft) in elevation and all areas not listed above, including the cities of La Paz and Sucre.
- Areas with malaria: All areas <2,500 m (8,202 ft). None in the city of La Paz (Map 2-3 ).
- Drug resistance 3 : Chloroquine.
- Malaria species: P. vivax 93%, P. falciparum 7%.
- Recommended chemoprophylaxis: Atovaquone-proguanil, doxycycline, mefloquine, primaquine 4 , or tafenoquine. 4
1. Download the Relief Central app by Unbound Medicine
2. Select Try/Buy and follow instructions to begin your free 30-day trial

Want to regain access to Relief Central?
Renew my subscription
Not now - I'd like more time to decide
Log in to Relief Central
Forgot your password, forgot your username, contact support.
- unboundmedicine.com/support
- [email protected]
- 610-627-9090 (Monday - Friday, 9 AM - 5 PM EST.)
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Bolivia travel advice
Latest updates: Editorial change
Last updated: June 7, 2024 13:58 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, bolivia - exercise a high degree of caution.
Exercise a high degree of caution in Bolivia due to the continuing political and social tensions resulting in frequent roadblocks throughout the country.
Back to top
Roadblocks are common throughout the country. They can lead to significant disruptions to traffic and public transportation. Roadblocks can also restrict the flow of goods and services throughout the country. The following are particularly vulnerable to blockades:
- main roads leading to large cities
- main arteries in cities
- roads leading to airports
Before making your way to the airport, check with your airline to determine if there are delays or changes in flight schedules caused by roadblocks
If you plan to take a road trip:
- review your travel plans to determine if they will be affected by roadblocks
- take personal security measures
- monitor local media
Once a roadblock is in place, local authorities, officials, and vendors will not be able to enter or exit the city to provide supplies to stranded travellers. As a precaution, you should take extra:
- warm clothing
Don’t cross roadblocks, even if they appear unattended. This may aggravate the situation and lead to physical harm. Instead, consider:
- taking an alternative safer route
- returning to your place of departure
Road closures and blockages – Bolivian Highway Administrator (in Spanish)
Demonstrations
Demonstrations and labour strikes occur frequently, often with little or no notice. Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. They can also lead to disruptions to traffic and public transportation. Protesters may also use dynamite during protests. The police often respond with tear gas to disperse crowds.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Petty crime
Petty crime, such as pickpocketing and purse snatching, is common in large cities, including La Paz and Santa Cruz. Thieves target tourist areas and public transport. Theft also occurs in unofficial taxis.
- Only use a reputable taxi company or a trusted ride-sharing app
- Avoid hailing taxis on the street
Criminals often operate in organized groups. They will distract victims while an accomplice steals from them. Strategies include:
- staging a fight
- starting a conversation or offering help
- blocking a sidewalk
- throwing an object or liquid on the victims, then offering to help clean up
- posing as a victim of crime
- posing as a law enforcement officer
- using a young child to lure a tourist to a separate location
To avoid becoming a victim of theft:
- ensure that your belongings, including your passport and other travel documents, are secure at all times
- don’t travel alone, especially at night
- be cautious of strangers approaching you
- remain alert to your surroundings at all times
- avoid showing signs of affluence
- avoid carrying large sums of money
- keep cellphones, cameras and other electronic equipment out of sight
Violent and drug-related crime
Violent crime against tourists is uncommon but does occur. Foreigners have been victims of armed robberies and assaults at tourist destinations.
Violent crime, carjacking and civil unrest, mainly associated with drug trafficking, pose risks in:
- the Chapare region between Santa Cruz and Cochabamba
- the Yungas region, northeast of La Paz
- border areas with Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Paraguay and Peru
Fraudulent police officers
Criminals often pose as police officers and ask to examine the traveller’s belongings or ask the traveller to accompany them to a bogus police station, sometimes in collusion with a criminal posing as a taxi driver or as another traveller.
Under Bolivian law, there’s no obligation to go with an officer to a police station unless they have a formal written request from a judge with your name on it. Any search or seizure must occur at a genuine police station in the prosecutor's presence.
If you’re stopped while travelling by someone claiming to be a local authority, ask to see their official identification.
Overseas fraud
Credit card and ATM fraud
Credit card and ATM fraud occurs. When using debit or credit cards:
- pay careful attention when others are handling your cards
- use ATMs located in well-lit public areas or inside a bank or business
- avoid using card readers with an irregular or unusual feature
- cover the keypad with one hand when entering your PIN
- check for any unauthorized transactions on your account statements
Vehicle and auto-parts theft, as well as theft from vehicles, are common throughout Bolivia.
- Keep valuables in the trunk, and only when necessary
- Park your car in a supervised lot
- Keep car windows and doors locked at all times
Express kidnapping
There is a risk of express kidnappings. Criminals ask for small, immediate ransoms. They usually force their victims to withdraw funds from an ATM or to arrange for family or friends to pay the ransom. This ploy is often used by criminal taxi drivers, who pick up the victim and then stop to pick up associates. These kidnappings are committed by organized gangs and occur throughout the country.
- Use only reputable taxi companies or ride-sharing apps
- If armed criminals threaten you, cooperate and don’t resist
Women's safety
Women travelling alone may be subject to some forms of harassment or verbal abuse.
Incidents of sexual assault against women travellers have occurred, including on guided tours.
- Do not accept offers of transportation from strangers
- Keep your hotel doors and windows locked
Advice for women travellers
Spiked food and drinks
There are reports of criminals adding drugs into items that could put you at risk of sexual assault or robbery. Items include food and drinks.
Incidents are most likely to occur:
- in nightclubs
- in bars and restaurants
- on public transportation, including taxis on the street
While you’re in Bolivia:
- be wary of accepting these items from new acquaintances
- never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers
- ask for drinks coming from sealed bottles or cans instead of in plastic cups
Adventure tourism
There are no official minimum safety standards for tour operators, and reputable tour operators are limited.
Only participate in tours with well-established companies for adventure tourist activities, including:
- Salar de Uyuni
- jungle expeditions
- mountain biking, including old Yungas Road (commonly known as “Death Road”)
- Potosi mine tours
Be vigilant when hiking or trekking as criminals have targeted these tourist areas:
- in the areas surrounding La Paz, such as the Muela del Diablo
- near Rurrenabaque
- the Bolivian Andes
- in the Yungas region
- on the Inca trail
If you intend to participate in adventure tourism activities:
- stay on marked trails and consider hiring an experienced guide from a reputable company
- obtain detailed information on your activity and on the environment in which you will be setting out
- buy travel insurance that covers incidents related to this type of recreational activity
- ensure that your physical condition is good enough to tackle the challenges of your activity
- ensure that you have proper equipment and bring sufficient water
- monitor weather conditions and other possible hazards;
- share your itinerary with a friend or family member if hiking alone
- know the symptoms of acute altitude sickness, dehydration and heatstroke, which can be fatal
- stay away from stray dogs, which can be aggressive and carry rabies.
Useful links:
- National registration of tourist services – Government of Bolivia (in Spanish)
- Certified mountain guides - Bolivian mountain guides association (in Spanish)
Spiritual cleansing ceremonies
Spiritual cleansing ceremonies involving hallucinogenic substances (ayahuasca, peyote, San Pedro, etc.) have led to serious illness, injury, physical and sexual assault and even the deaths of several tourists.
Ceremonies involve consuming substances that can cause medical complications and severely impair cognitive and physical abilities. They often take place in remote areas with no access to medical or mental health facilities or resources. Often, there is no access to communications with local authorities. Facilities generally lack basic first aid or emergency plans to help those suffering from physical or psychological illness during these ceremonies.
Spiritual cleansing ceremonies are not regulated and individuals offering them are not licensed. There is no way to assess the safety of any of the services or the operators.
Avoid participating in spiritual cleansing ceremonies using hallucinogenic substances.
Road safety
Road safety is poor throughout the country. Accidents and fatalities are common.
Road conditions
Road conditions are poor throughout the country.
Although improved highways connect Cochabamba, La Paz, Santa Cruz and Sucre, many roads in Bolivia are unpaved. The old Yungas Road (commonly known as “Death Road”) is considered one of the world’s most dangerous roads.
Driving can also be dangerous due to:
- narrow, winding and mountainous roads
- lack of guardrails
- insufficient lighting
- lack of traffic signs
- poorly marked construction sites
- unpaved roads
- torrential rain and landslides
- poorly maintained vehicles
Four-wheel-drive vehicles are necessary outside major cities, especially in mountainous areas and during the rainy season.
Driving habits
Drinking and driving is common.
Drivers do not always respect traffic laws. Drivers can be aggressive and reckless and often speed.
Water activities
Lifeguard services do not always meet Canadian standards. Most lakes do not have warning flags to alert of unsafe conditions.
- Consult residents and tour operators for information on possible hazards and safe swimming areas
If you take a boat tour:
- make sure the boat you are boarding is carrying appropriate safety equipment, including life jackets accessible for all passengers at all times
- don’t board boats that appear overloaded or unsafe
- verify the safety standards of boats with your tour operator
- if you have any doubts about the safety of the equipment, do not use it.
Water safety abroad
Public transportation
Crime is high in public transportation and at transportation hubs. Accidents are common due to:
- poor maintenance of vehicles
- lack of safety standards
- poor road conditions
Buses and coaches
Road accidents involving local/interurban buses are frequent, especially with overnight buses.
If you choose to travel by intercity bus, exercise caution in:
- La Paz bus terminals due to petty crime, including:
- the main bus terminal on Peru Avenue in Zona Norte
- the terminal near the La Paz cemetery, and the Minasa terminal in Zona Villa Fatima
- the Santa Cruz bus/train terminal, where violent crimes against foreigners have occurred
- Coronilla Hill, adjacent to the main bus terminal in Cochabamba, due to assaults
Accidents involving poorly maintained coaches have caused death and injuries among tourists.
Only use tour buses operated by well-known, reputable companies. If you have any doubt about the safety of a bus or its driver, use another company.
Many taxis are poorly maintained and do not have functional seatbelts.
You can call registered radio taxi companies from a landline or from a hotel. Radio taxis are identifiable by the telephone number and name of the taxi company on the vehicle’s roof.
- Avoid hailing taxis on the street and taking motorcycle taxis
- Note the driver’s name on his or her photo identification card and license number
- Exercise caution when taking cabs to and from airports, especially in Santa Cruz and La Paz, where tourists have been the victims of robberies
- Decline transportation from people offering cheaper fares
- Never share a taxi with strangers
- Confirm the fare in advance , as taxis are not equipped with meters
Ridesharing services
Ride-sharing services are not available in many cities.
If you use a ride-sharing app:
- confirm the driver’s identity and license plate before getting in the car
- use the security features in rideshare apps
Train service is limited and irregular.
You can cross Lake Titicaca by ferry.
If you choose to travel by ferry:
- make sure the ferry you are boarding is carrying appropriate safety equipment
- make sure that life jackets are provided for all passengers and accessible at all times
- avoid boarding ferries that appear overloaded
- verify the safety standards of ferries with your tour operator
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Bolivian authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months from the date you arrive in Bolivia.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: not required for stays up to 30 days Business visa: required Student visa: required Volunteer work visa: required
Registration
All foreign residents and tourists must complete the web-based registration process (SIGEMIG) prior to arriving in Bolivia. Registration must include lodging information for the entire stay.
If you have not completed the electronic registration prior to arriving in Bolivia, immigration agents at the port of entry will register you and give you further instructions. If you fail to comply, you will be subject to fines upon leaving the country.
Address registration – General Directorate of Migration (in Spanish)
Extensions of tourist visa
Applications for tourist visa extensions must be submitted to the General Directorate of Migration before the end of the 30-day period. A 30-day extension can be obtained twice, at no extra cost and to a maximum of 90 days during one calendar year.
If you overstay the 90-day period without proper authorization, you may be fined upon departure.
Other entry and exit requirements
Customs officials may ask you to show them a return or onward ticket and proof of sufficient funds to cover your stay.
When arriving by land, ensure your passport is stamped upon exiting the country you’re leaving and upon entering Bolivia. If you fail to do so, you’ll be fined upon departure. Avoid travelling at night when border officials and police may not be present.
Luggage screening
Bolivia employs strict luggage screening measures at its international airports. You must complete an online declaration form prior to luggage screening and show an electronic or printed version of the QR code to authorities. All luggage is routinely X-rayed upon arrival.
- Children and travel
Bolivia has strict requirements for the entry and exit of persons under the age of 18, including special documentation.
Parents of children travelling alone, with one parent or with another individual are strongly encouraged to contact the nearest Bolivian embassy or consulate before departure to ensure that the latest entry and exit requirements, which may change without notice, are met.
Travelling with children
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- Zika virus: Advice for travellers - 31 August, 2023
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
- Dengue: Advice for travellers - 6 May, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is a risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is required if you are coming from a country where yellow fever occurs.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is recommended depending on your itinerary.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites .
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada * It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes. There is a risk of malaria in certain areas and/or during a certain time of year in this destination.
Antimalarial medication may be recommended depending on your itinerary and the time of year you are travelling. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times: • Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin. • Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows. • Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area. • Wear permethrin-treated clothing. If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
In this destination, rabies is commonly carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. In this destination, rabies treatment may be limited or may not be available, therefore you may need to return to Canada for treatment.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
Cutaneous and mucosal leishmaniasis causes skin sores and ulcers. It is caused by a parasite spread through the bite of a female sandfly.
Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from sandfly bites, which typically occur after sunset in rural and forested areas and in some urban centres. There is no vaccine or medication to protect against leishmaniasis.
- In this country, dengue is a risk to travellers. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue.
Zika virus is a risk in this country.
Zika virus is primarily spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can also be sexually transmitted. Zika virus can cause serious birth defects.
During your trip:
- Prevent mosquito bites at all times.
- Use condoms correctly or avoid sexual contact, particularly if you are pregnant.
If you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy, you should discuss the potential risks of travelling to this destination with your health care provider. You may choose to avoid or postpone travel.
For more information, see Zika virus: Pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
American trypanosomiasis (Chagas disease) is a risk in this country. It is caused by a parasite spread by infected triatomine bugs. The infection can be inactive for decades, but humans can eventually develop complications causing disability and even death.
Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from triatomine bugs, which are active at night, by using mosquito nets if staying in poorly-constructed housing. There is no vaccine available for Chagas disease.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Tuberculosis is an infection caused by bacteria and usually affects the lungs.
For most travellers the risk of tuberculosis is low.
Travellers who may be at high risk while travelling in regions with risk of tuberculosis should discuss pre- and post-travel options with a health care professional.
High-risk travellers include those visiting or working in prisons, refugee camps, homeless shelters, or hospitals, or travellers visiting friends and relatives.
Medical services and facilities
The quality of health care varies greatly throughout the country. Good health care is available only in private hospitals in larger cities.
Public medical services and facilities have limited resources and don’t meet Canadian standards. There’s limited access to healthcare facilities and medical assistance in rural areas, including tourist areas. It can take days to receive medical services in remote areas.
Ambulance services are limited throughout Bolivia.
If you have doubts about the medical services you are being provided, contact the Embassy of Canada.
Evacuation by air ambulance can be difficult. Some air ambulance providers are unable to fly into locations at higher altitudes, such as La Paz. You may need it in case of serious illness or injury.
Most healthcare providers speak only Spanish.
Many clinics and hospitals accept cash only. They may require upfront payment or proof of medical insurance before providing medical services, even in an emergency.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
Altitude sickness
You’re at risk of altitude sickness if you travel 2500 metres above sea level or more.
In some departments, you may experience health problems due to high altitudes including in:
- La Paz (3,640 metres above sea level)
- Uyuni (3,656 metres above sea level)
- Oruro (3,735 metres above sea level)
- Potosi (4,090 metres above sea level)
You're more at risk if you:
- ascend quickly
- exercise or drink alcohol before you get used to the altitude
Altitude sickness can be fatal. You may require immediate medical evacuation, which is less accessible in remote areas. Seek medical attention at a lower altitude if you develop symptoms.
Well on Your Way - A Canadian’s Guide to Healthy Travel Abroad
Certain prescription and over-the-counter medications legally available in Canada are classified as controlled substances in Bolivia. Consult the list of controlled substances to avoid trouble.
If you attempt to bring banned medication into Bolivia, you may be subject to:
- confiscation of medication
- heavy fines
- jail sentences
If you take prescription medications, it’s your responsibility to determine their legality in Bolivia. If you decide to bring medication to Bolivia:
- always keep them in the original container
- pack them in your carry-on luggage
- carry a copy of your prescriptions
Bolivia’s list of controlled substances – Vice Ministry of Social Defence and Controlled Substances (in Spanish)
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .

Transfer to a Canadian prison
No transfer of offender’s treaty exists between Canada and Bolivia. If you’re convicted of a serious crime, you must serve your jail sentence in Bolivia. You may also have to remain in the country for a parole period after your release.
Detention conditions may be below the standards of Canadian prisons.
Bolivian drug laws include a zero-tolerance policy. Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe. Convicted offenders can expect lengthy prison sentences and heavy fines.
Travellers have fallen victim to scams in which illegal drugs are hidden inside objects or luggage that an acquaintance has asked them to bring to or take away from Bolivia. Dating websites are a source of such scams.
- Pack your own luggage
- Never transport luggage or packages on behalf of another person
Unlicensed bars
Unlicensed bars in Bolivia are illegal. They are known to sell drugs. Police may detain and question you if they raid the establishment, even if you’re not consuming any illegal substances.
Avoid unlicensed bars.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
It’s illegal to export any item that the Bolivian government considers a national treasure (Patrimonio cultural) without formal written permission from the Ministry of Culture, including:
- pre-Columbian artifacts
- historical paintings
- items of Spanish colonial architecture and history
- native textiles
- flora, fauna and fossils
Any type of excavation for fossils or collection of fossils without prior written authorization is illegal.
Coca leaves
It’s illegal to import coca leaves and related products into Canada.
Controlled drugs and substances act – Government of Canada
Identification
Police and immigration officials occasionally conduct identification checks. You may have to present your passport upon check-in at hotels and other commercial accommodation providers.
- Carry copies of your passport and Bolivian entry stamp pages of your passport
- Never leave your passport or any other identity document with anyone
Photography
Locals may find the presence of photographers intrusive, particularly in remote areas.
- Be careful when travelling with cameras and communications devices
- Befort taking someone’s photo, ask for permission
2SLGBTQI+ travellers
Bolivian law does not prohibit sexual acts between individuals of the same sex.
Homosexuality is increasingly socially accepted, but much of Bolivian society remains conservative. 2SLGBTQI+ travellers could be discriminated against based on their sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression or sex characteristics.
Travel and your sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is legally recognized in Bolivia.
If you are a Canadian citizen, but also a citizen of Bolivia, our ability to offer you consular services may be limited while you're there. You may also be subject to different entry/exit requirements .
Travellers with dual citizenship
Military service
Military service is compulsory in Bolivia. Males aged 18 or over who are dual citizens must undertake military service upon arrival in the country.
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and Bolivia.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Bolivia by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Bolivia to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children's Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country's judicial affairs.
- International Child Abductions: A guide for affected parents
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Request emergency assistance
You must carry an international driving permit to rent or drive a vehicle.
The legal blood alcohol limit is 0.00%. If the police suspect you of drinking and driving, they could confiscate your driver’s licence on the spot and apply heavy fines and jail sentences.
If you’re involved in a traffic accident, remain at the scene until local police arrive. Attempting to leave the scene violates Bolivian law.
International Driving Permit
The currency in Bolivia is the boliviano (BOB).
Credit and debit cards are not widely accepted outside urban centres. Carry small bank notes to facilitate daily transactions such as:
- street food
It’s difficult to exchange Canadian dollars in Bolivia. Bring U.S. dollars if you need to exchange cash.
Bolivia is subject to various natural disasters such as:
- earthquakes
- torrential rains
Climate change
Climate change is affecting Bolivia. Extreme and unusual weather events are becoming more frequent and may affect your travel plans. Monitor local news to stay informed on the current situation.
Rainy season
The rainy season extends from November to March.
Seasonal flooding occurs throughout the country, mainly as a result of heavy rains and overloaded sewage systems. Seasonal flooding can hamper overland travel and reduce the provision of essential services. Roads may become impassable and bridges damaged. Heavy rains may contribute to dangerous landslides. In particular, the Uyuni Salt Flats become dangerous to visit in the rainy season.
If you decide to travel to Bolivia during the rainy season:
- be prepared to change your travel plans on short notice, including cutting short or cancelling your trip
- stay informed of the latest regional weather forecasts
- carry emergency contact information for your airline or tour operator
- follow the advice and instructions of local authorities
Weather alerts – National Meteorological and Hydrological Service (in Spanish)
Forest fires are at risk during the dry season, from July to October. Heavy smoke may deteriorate the air quality in areas near active fires.
In case of a significant fire:
- stay away from affected areas, particularly if you suffer from respiratory ailments
- monitor local media for up-to-date information on the situation
- follow the advice of local authorities
Latest alerts – Vice Ministry of Civil Defence (in Spanish)
Earthquakes
Bolivia is in an active seismic zone and is prone to earthquakes in the centre and southwest areas.
Dangerous landslides can also occur, even after minor earthquakes.
In the event of an earthquake:
- monitor local news to stay informed on the evolving situation
- follow the instructions of local authorities, including evacuation orders
- Earthquake monitoring – San Calixto Observatory (in Spanish)
- Latest earthquakes – U.S. Geological Survey
- Prepare for earthquakes
Local services
In case of emergency, dial:
- police: 110
- firefighters: 119
- gender-based violence: 800-14-0348
- ambulance service in La Paz: 165
- tourist police in La Paz: +591-2-222-5016
Consular assistance
For emergency consular assistance, call the Embassy of Canada to Bolivia (Program Office), in La Paz, and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.

- High contrast
Search UNICEF
- Bolivia receives first of COVID-19 vaccines through COVAX Mechanism
- News and stories

- Available in:
El Alto, Bolivia, 21 March 2021 (OPS/OMS/UNICEF) - Bolivia received today 228 thousand doses of COVID-19 vaccines through the COVAX Mechanism, a global effort between the Coalition for Promoting Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization (Gavi), the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
This arrival is a historic step towards our goal of ensuring equitable distribution of COVID-19 vaccines globally, in what will be the largest vaccine procurement and supply operation in history. The delivery is part of a first phase of doses to be received by Bolivia and more vaccines are planned to arrive successively during 2021. Until May, the country is expected to continue receiving doses until the vaccines allocated to Bolivia are reached: 672,000 from AstraZeneca and 92,430 from Pfizer-BioNtech, according to the first round of COVAX allocation.
PAHO's Revolving Fund, in charge of procuring COVID-19 vaccines for the countries of the Americas under the COVAX Mechanism, shipped 228,000 doses of the AstraZeneca/Oxford vaccine, manufactured by the Serum Institute of India (SII), from Mumbai. The vaccines arrived today at the Air Task Force “Diablos Negros” airport in the city of El Alto by Bolivian Air Transport TAB, flight 751 from Miami, to Santa Cruz and then transferred to a Bolivian Air Force (FAB) Hercules aircraft. The aircraft arrived in El Alto, final destination, at around 16:00.
On the occasion, the PAHO/WHO Representative, Dr. Alma Morales Salinas, said: “For me it is a privilege to participate in this arrival of anti-COVID-19 vaccines meaning that more people will be able to be protected against COVID-19.” She added, “We will continue to work with the country to support vaccination and all known public health measures that together can stop the spread of COVID-19, protect health services and most importantly save lives.
The arrival of these first vaccines will serve to protect priority groups most at risk of developing severe cases of COVID-19, such as healthcare workers and the elderly. Bolivia is one of ten countries in the Americas that are receiving vaccines at no cost through the COVAX Advance Market Commitment (AMC).
“Today we reaffirm our commitment to vaccine equity and fulfill our promise to leave no one behind,” said Rafael Ramirez, UNICEF Representative in Bolivia.
Bolivian National Vaccination Plan
The National Vaccination Plan for the introduction of the anti-COVID-19 vaccine prepared by the Ministry of Health and Sports, through the National Expanded Program of Immunization (PAI) was designed according to international recommendations and requirements to access the COVAX Mechanism. Thus, it is a plan that has received the satisfactory approval of the main international COVAX experts.
Evaluation of the Bolivian immunization plan with the COVID-19 vaccine was key to the country being one of the four countries chosen to receive the first COVAX vaccines. The plan establishes as principles a universal, free and voluntary vaccination against COVID-19 for all Bolivians aged 18 years and older, with a defined schedule by age.
Since the first case of COVID-19 was reported in the territory, in March 2020, Bolivia recorded 262,941 cumulative cases and 12,028 deaths as a result of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
“Due to the fact that COVID-19 is one of the main causes of illness and death, because of its transcendence in families and in the community, its attention has become a priority in our country’s health policies,” reads one of the objectives of the country’s vaccination plan.
To address this, the national government determined to guarantee that vaccines for vaccination against COVID-19 will be available throughout the national territory, free of charge, equitably and equally, and to achieve this goal, not only did they acquire batches of vaccines bilaterally, but they also accessed the COVAX Mechanism to obtain safe and effective vaccines that comply with international standards and those of the National Regulatory Authority.
The efforts of the country and its cooperating partners such as PAHO/WHO and UNICEF are contributing to all components of the vaccination plan, including the development of a contextualized communication strategy with messages for the different Bolivian populations, with emphasis on indigenous and rural communities, street people, migrants, prisoners, in addition to the priority and most at-risk population to be vaccinated.
Equitable distribution
COVAX seeks to provide vaccines for at least 20 per cent of the population in each participating country globally during 2021. In this first round of vaccine allocation, all COVAX participating countries will receive doses to vaccinate between 2.2 per cent and 2.6 per cent of their population. The only exceptions are small island developing states, which because of their size will receive between 16 per cent and 20 per cent of their population, due to the high logistical cost of delivering small quantities of vaccine.
Until vaccination is widespread in the population, basic public health measures remain the foundation of the pandemic response. For public health authorities, this means continuing diagnostic testing, contact tracing, isolation, assisted quarantine and quality care. And for individuals, it means continuing to practice physical distancing, hand hygiene, use of masks, space ventilation, and crowd avoidance.
COVAX, the vaccine pillar of the COVID-19 Access to Tools Accelerator (ATA), is co-led by the the Coalition for Promoting Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization (Gavi), and the World Health Organization (WHO), working in partnership with UNICEF, as well as civil society organizations, vaccine manufacturers, the World Bank and others.
In the Americas, the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) Revolving Fund is the recognized procurement agent to the COVAX mechanism for countries in the region.
PAHO’s Revolving Fund: https://www.paho.org/es/fondorotatorio
COVAX publishes the first round of allocations: https://www.gavi.org/news/media-room/covax-publishes-first-round-allocations
PAHO web page on CODID-19: www.paho.org/coronavirus
COVAX: https://www.who.int/es/initiatives/act-accelerator/covax
Media contacts
About unicef.
UNICEF works in some of the world's toughest places, to reach the world's most disadvantaged children. Across more than 190 countries and territories, we work for every child, everywhere, to build a better world for everyone.
For more information about UNICEF and its work for children, visit www.unicef.org/lac .
Follow UNICEF on Twitter and Facebook
Related topics
More to explore.
Global immunization efforts have saved at least 154 million lives over the past 50 years
Reaching children who missed out on vaccines in Brazil
Discover how community health workers navigate rural rivers and bustling cities to reach those who need vaccines most
Childhood vaccination in Latin America and the Caribbean shows signs of recovery but still lags dangerously behind
Volunteers keep watch over children’s immunization
Maria Ortencia Catucuago is one of 500 volunteers helping to promote family health in communities in Ecuador.
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
Register to vote Register by 18 June to vote in the General Election on 4 July.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Before you travel check that:
- your destination can provide the healthcare you may need
- you have appropriate travel insurance for local treatment or unexpected medical evacuation
This is particularly important if you have a health condition or are pregnant.
Emergency medical number
Call 118 and ask for an ambulance.
Contact your insurance company quickly if you’re referred to a medical facility for treatment.
Vaccinations and health risks
At least 8 weeks before your trip check:
- the latest information on vaccinations and health risks in TravelHealthPro’s Bolivia guide
- where to get vaccines and whether you have to pay on the NHS travel vaccinations page
Altitude sickness is a risk in parts of Bolivia, including in La Paz and the Salar de Uyuni salt flats. Read more about altitude sickness on TravelHealthPro .
The legal status and regulation of some medicines prescribed or bought in the UK can be different in other countries.
Read best practice when travelling with medicines on TravelHealthPro .
The NHS has information on whether you can take your medicine abroad .
Healthcare facilities in Bolivia
The public healthcare system does not meet the same standards as the UK, and you may not be able to access the public health system as it is already overstretched. There are private clinics in all main cities that work with international insurance. It is very important to have travel insurance and access to funds, as you will need to pay up front to receive treatment.
FCDO has a list of English-speaking doctors in Bolivia .
There is also guidance on healthcare if you’re living in Bolivia .
Travel and mental health
Read FCDO guidance on travel and mental health . There is also mental health guidance on TravelHealthPro .
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .
Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution, update may 10, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Dominican Republic
Travel Advisory June 6, 2023
Dominican republic - level 2: exercise increased caution.
Reissued with updates to health information.
Exercise increased caution in the Dominican Republic due to crime.
Country Summary: Violent crime, including armed robbery, homicide and sexual assault is a concern throughout the Dominican Republic. The development of a professional tourist police corps, institution of a 911 system in many parts of the country, and a concentration of resources in resort areas means these tend to be better policed than urban areas like Santo Domingo. The wide availability of weapons, the use and trade of illicit drugs, and a weak criminal justice system contribute to the high level of criminality on the broader scale.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to the Dominican Republic.
If you decide to travel to the Dominican Republic:
- Be aware of your surroundings.
- Do not physically resist any robbery attempt.
- Do not display signs of wealth, such as wearing expensive watches or jewelry.
- Follow the advice of resort and tour operators regarding local safety and security concerns.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for the Dominican Republic.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
Passports must be valid for the period of stay in the Dominican Republic.
1 page required for entry stamp
Not required for visits shorter than 30 days
None required if arriving from the United States
$10,000 and over or its equivalent must be declared
Embassies and Consulates
U.s. embassy santo domingo.
Av. República de Colombia #57 Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic Telephone: +(809) 567-7775 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(809) 567-7775, dial zero (0) ask for Duty Officer Email: [email protected] Hours: Monday through Friday from 7:00 AM to 4:00 PM except U.S. and Dominican holidays
Consular Agencies
U.S. Consular Agent - Puerto Plata Plaza el Doral, carretera Luperón KM 3 1/2 Puerto Plata, Dominican Republic Telephone: +(809) 586-4204, +(809) 586-8023 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: (809) 567-7775, dial zero (0) ask for Duty Officer Email: [email protected] Hours: Monday through Friday from 8:00 AM to 5:00 PM except U.S. and Dominican holidays
U.S. Consular Agent - Bavaro/Punta Cana Palma Real Shopping Center Business Center 2nd Floor Bavaro, La Altagracia, Dominican Republic Telephone: (809) 552-8990 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(809) 567-7775, dial zero (0) ask for Duty Officer Email: [email protected] Hours: Monday through Friday from 8:00 AM to 5:00 PM except U.S. and Dominican holidays
Destination Description
Learn about the U.S. relationship to countries around the world.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
Visas are not required for visits shorter than 30 days. Visit the Embassy of the Dominican Republic website for current visa information.
All visitors to the Dominican Republic are charged a $10 tourist card fee that is incorporated into airline charges. Cruise passengers must obtain a tourist card if they are disembarking for longer than 24 hours. Once used, the card allows for stays up to 30 days but can be extended at the General Directorate of Migration in Santo Domingo.
Contact the Migration Department in Santo Domingo for visa extension requests. Failure to request an extension will result in a fine at the airport upon departure. The fines range from approximately $55 USD for one month to as high as $1,555 USD for overstays of 10 years or more.
All passengers are required to fill out an E-Ticket or paper form when entering or exiting the Dominican Republic. If using E-Ticket, a new form is required for each entry and exit and the code generated upon form completion can be presented at the airport on a digital device.
Visitors must have a ticket entering and leaving the country, the financial means to pay for their stay, and an address in the Dominican Republic where they will be staying.
Exit Requirements for Children: Minors (children under 18) who are citizens (including dual citizens) or legal residents of the Dominican Republic, if not accompanied by both parents or legal guardian(s), are required to present official proof of parental consent to travel. Please see the Dominican Migration Department's website for detailed instructions on the required documents.
HIV/AIDS Restrictions: Some HIV/AIDS entry restrictions exist for visitors to and foreign residents of the Dominican Republic. The Dominican Republic has restrictions on granting residency to people with HIV/AIDS. Please verify information with the Dominican Republic’s Migration Department before you travel.
Yellow Fever Vaccine: Proof of vaccination against yellow fever is required for travelers entering the Dominican Republic from Brazil. Similar requirements may apply to those traveling from other countries with yellow fever risk .
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction , and customs regulations on our websites.
Safety and Security
Crime: Crime is a threat throughout the Dominican Republic. Tourist destinations are generally more policed than metropolitan areas.
- If robbed, hand over your personal belongings without resisting.
- Do not carry or wear valuable items that will attract attention.
- Be wary of strangers.
- Travel with a partner or group if possible.
International Financial Scams: See the Department of State and the FBI pages for information.
Dating App Robberies: Several U.S. citizen travelers in the Dominican Republic have reported that they were robbed by people they met through popular online dating applications. If meeting with strangers, you should strongly consider meeting only in public places and avoiding isolated locations where crimes are most likely to occur.
Demonstrations: Avoid areas of demonstrations and exercise caution if you are in the vicinity of large gatherings or protests.
Victims of Crime: Report crimes to the local tourist police (POLITUR) at 809-222-2026 or 911 and contact the U.S. Embassy at 809-567-7775. 911 is operational throughout the country apart from some areas located near the Haitian border. Remember that local authorities are responsible for investigating and prosecuting crime.
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
- Help you find appropriate medical care.
- Assist you in reporting a crime to the police.
- Contact relatives or friends with your written consent.
- Provide general information regarding the victim’s role during the local investigation and following its conclusion.
- Provide a list of local attorneys.
- Provide our information on victim’s compensation programs in the U.S.
- Provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical support in cases of destitution.
- Replace a stolen or lost passport.
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence are encouraged to contact POLITUR (809-222-2026), the National Police ( 809-682-2151), and the U.S. Embassy for assistance.
Sexual Assault: Rape and sexual assault has been reported throughout the Dominican Republic, including at major resorts and hotels.
Notes for your safety:
- U.S. citizens have been targeted with date rape drugs.
- Sexual assault victims in the Dominican Republic should not expect the totality of assistance offered in the United States. Rape kits are often not available until the following morning and must be administered by Dominican authorities.
- Victims often have to request medication to avoid transmission of STDs and reduce the chances of pregnancy.
- Prosecution of a rape case moves forward very slowly. Dominican law may require the victim to return to the Dominican Republic at some stages of the judicial process.
- Security outside of the resort area, including beach areas, is unpredictable, especially at night.
Best Practices:
- Contact the police/hotel management if resort staff demonstrate unwanted attention.
- Victims of sexual/other assault should contact the police and the Embassy. Insist that hotel management take immediate action by contacting the police.
- In a resort, avoid secluded places. Always be accompanied by someone you know, even going to the restroom.
- Do not consume alcoholic beverages alone or with new acquaintances. Do not leave drinks unattended. Know your limits and help your friends/travelling companions to remain safe.
- Shout for help immediately if threatened or made uncomfortable.
- Report suspicious activity, including excessive friendliness by hotel employees, to hotel management, the U.S. Embassy, and local police.
- Do not swim alone due to life-threatening undertows.
Tourism: The tourism industry is unevenly regulated, and safety inspections for equipment and facilities may not commonly occur in all parts of the country. Hazardous areas and activities are not always identified with appropriate signage, and staff may not be trained or certified either by the host government or by recognized authorities in the field. In the event of an injury, appropriate medical treatment is typically available only in or near major cities or major tourist zones. First responders may be unable to access areas outside of major cities or major tourist zones. The ability to provide urgent medical treatment may be limited. U.S. citizens are encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage .
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to local laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Individuals establishing a business or practicing a profession that requires additional permits or licensing should seek information from the competent local authorities, prior to practicing or operating a business.
Furthermore, some laws are also prosecutable in the United States, regardless of local law. For examples, see our website on crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking illegal drugs in the Dominican Republic are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. Arrest Notification: If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy immediately. See our webpage and general information on legal assistance for further information.
Counterfeit and Pirated Goods: Although counterfeit and pirated goods are prevalent in many countries, their possession they may still be illegal according to local laws. You may also pay fines or have to give them up if you bring them back to the United States. See the U.S. Department of Justice website for more information.
Faith-Based Travelers: See the following webpages for details:
- Faith-Based Travel Information
- International Religious Freedom Report – see country reports
- Human Rights Report – see country reports
- Hajj Fact Sheet for Travelers
- Best Practices for Volunteering Abroad
LGBTI Travelers: There are no legal restrictions on same-sex sexual relations or the organization of LGBTI events in the Dominican Republic.
See our LGBTI Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Travelers with Disabilities: The law in the Dominican Republic prohibits discrimination against persons with physical, sensory, intellectual or mental disabilities, but the law is not enforced consistently. Social acceptance of persons with disabilities in public is not as prevalent as in the United States. Accessible facilities, information, communication/access to services and ease of movement is limited in most parts of the country. Large resorts and Santo Domingo may have some generally accessible infrastructure, but travelers should not expect the level available in the United States.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
Disaster Preparedness: Register with the Embassy on or before your arrival through our travel registration website . In the event of a natural disaster or emergency, this will keep you informed. Additional information on natural disasters and disaster preparedness can be found on our website. Real Estate: Property rights are irregularly enforced, and investors often encounter problems in receiving clear title to land. Consult a reputable attorney before signing documents or closing on any real estate transactions. Real estate investments by U.S. citizens have been subject to legal and physical takeover attempts. Absentee landlords and absentee owners of undeveloped land are particularly vulnerable. Consider purchasing title insurance. Scams: Scammers often target elderly people by pretending to be a law enforcement official, an attorney, or a U.S. Embassy official, claiming that a loved one has been arrested overseas. The caller instructs the victim to wire money. Scammers sometimes impersonate family members, such as a scared grandchild. Contact the U.S. Embassy before wiring money to the Dominican Republic. When in doubt, try to contact your loved one directly.
For emergency services in the Dominican Republic, dial 911 or 809-202-2026 .
Ambulance services:
- The training and availability of emergency responders may be below U.S. standards.
- Ambulances are not present or reliable in most areas of the country. They are more reliable and available in Santo Domingo, Santiago, Punta Cana, and Puerto Plata.
We do not pay medical bills. Be aware that U.S. Medicare/Medicaid does not apply overseas. Most hospitals and doctors overseas do not accept U.S. health insurance.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept cash payments. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage. Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information on type of insurance you should consider before you travel overseas.
We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation.
Always carry your prescription medication in original packaging, along with your doctor’s prescription. Check with the Ministry for Public Health to ensure the medication is legal in the Dominican Republic.
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Further health information:
- World Health Organization
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Air Quality: Visit AirNow Department of State for information on air quality at U.S. Embassies and Consulates.
The U.S. Embassy maintains a list of doctors and hospitals . We do not endorse or recommend any specific medical provider or clinic.
Health facilities in general:
- Public medical clinics lack basic resources and supplies.
- Hospitals and doctors require payment “up front” prior to service or admission.
- Private hospitals usually require advance payment or proof of adequate insurance before admitting a patient.
- Be aware that some hotels, resorts, etc. have exclusive agreements with medical providers, which have costs associated and may limit your choices in seeking emergency medical attention.
- Medical staff may speak little or no English.
- Generally, in public hospitals only minimal staff is available overnight in non-emergency wards. Consider hiring a private nurse or having family spend the night with the patient, especially a minor child.
- Patients bear all costs for transfer to or between hospitals.
- Psychological and psychiatric services are limited, even in the larger cities, with hospital-based care only available through government institutions
Medical Tourism and Elective Surgery
U.S. citizens have suffered serious complications or died during or after having cosmetic or other elective surgery.
If you are considering travel to the Dominican Republic for cosmetic surgery, be mindful of the following:
- Have a medical evaluation from a U.S. doctor to determine if you are a good candidate for surgery.
- Before travel, carefully research the doctor (e.g. qualifications, experience performing the surgery, complication rate) and credentials of the recovery facility you plan to use.
- Share all health information (e.g. medical conditions, medications, allergies) with your doctor before your surgery.
- Obtain international travel insurance that covers medical evacuation back to the United States and repatriation of remains. For more information, see: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/page/insurance .
- See a travel medicine professional in the United States at least 4–6 weeks before your trip to discuss healthy travel and to learn about specific risks related to your surgery and travel. For more information on the risks of medical tourism, see: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/page/medical-tourism .
- Your legal options in case of malpractice are very limited in the Dominican Republic.
Tap Water: Tap water is unsafe to drink. Bottled water and beverages are considered safe. Please note that many restaurants use tap water for ice.
Adventure Travel
- Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information about Adventure Travel .
General Health
The following diseases are prevalent:
- Tuberculosis
- Chikungunya
Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information about Resources for Travelers regarding specific issues in the Dominican Republic .
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety: Driving conditions vary across the country. Drive defensively and with extreme caution.
Consider hiring a professional driver instead of driving yourself. You can hire licensed drivers who are familiar with local roads through local car rental agencies. In case of accidents, normally only the driver will be taken into custody. In 2019 six people died per day due to traffic accidents in the Dominican Republic.
Frequent hazards include:
- other drivers not using headlights and/or taillights after dark
- animals in the road
- missing manhole covers and large potholes
- uneven road surfaces
- scooters and motorcycles driving erratically and splitting lanes
- driving on sidewalks or against traffic
- intersections without stop signs
- unregulated and congested traffic patterns
- speeding or the running of stoplights
- heavy urban traffic
Traffic Laws: Traffic laws are not enforced consistently. After an accident causing serious injury or death, authorities will often take the driver into custody, even if the driver is insured and appears to have not been at fault. Detentions frequently last until a judicial decision has been reached or until a waiver has been signed by the injured party.
Seat belts, and helmets for motorcyclists, are required by law. Violators may be fined. There are no child car seat laws. Police stop drivers using cell phones without a hands-free device.
Public Transportation: Public transportation includes a metro and public bus system as well as shared bus or van taxis known as “guaguas” (converted vans or microbuses, often without doors). Guaguas run regular routes within urban areas and between towns in the countryside. Public buses and guaguas operating in the capital do not meet U.S. safety standards. Avoid unregulated taxis, which also often lack basic safety features. Use a reputable taxi service, either one recommended by your hotel or a well-known, vetted company. Rideshare services such as Uber are available in many parts of the country. Private bus lines travel between large cities and to popular tourist destinations.
See our Road Safety page for more information. Visit the website of the Dominican Republic’s Ministry of Tourism and INTRANT (Instituto Nacional de Transito y Transporte Terrestre) the national authority responsible for road safety.
Aviation Safety Oversight: The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed the government’s Civil Aviation Authority as being in compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of the Dominican Republic’s air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA’s website. FAA’s safety assessment page .
Maritime Travel: The U.S. Coast Guard has concerns about the security practices in the ports of the Dominican Republic. Until those concerns can be addressed, the Coast Guard advises that Mariners and passengers on commercial vessels traveling through the ports of the Dominican Republic should exercise caution.
Mariners planning travel to the Dominican Republic should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts . Information may also be posted to the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website , and the NGA broadcast warnings .
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Dominican Republic . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, dominican republic map, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Make two copies of all of your travel documents in case of emergency, and leave one with a trusted friend or relative.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
- Section 2 - Interactions Between Travel Vaccines & Drugs
- Section 2 - Travelers’ Diarrhea
Yellow Fever Vaccine & Malaria Prevention Information, by Country
Cdc yellow book 2024.
Author(s): Mark Gershman, Rhett Stoney (Yellow Fever) Holly Biggs, Kathrine Tan (Malaria)
The following pages present country-specific information on yellow fever (YF) vaccine requirements and recommendations, and malaria transmission information and prevention recommendations. Country-specific maps are included to aid in interpreting the information. The information in this chapter was accurate at the time of publication; however, it is subject to change at any time due to changes in disease transmission or, in the case of YF, changing entry requirements for travelers. Updated information reflecting changes since publication can be found in the online version of this book and on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Travelers’ Health website. Recommendations for prevention of other travel-associated illnesses can also be found on the CDC Travelers’ Health website .
Yellow Fever Vaccine
Entry requirements.
Entry requirements for proof of YF vaccination under the International Health Regulations (IHR) differ from CDC’s YF vaccination recommendations. Under the IHR, countries are permitted to establish YF vaccine entry requirements to prevent the importation and transmission of YF virus within their boundaries. Certain countries require proof of vaccination from travelers arriving from all countries ( Table 5-25 ); some countries require proof of vaccination only for travelers above a certain age coming from countries with risk for YF virus transmission. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines areas with risk for YF virus transmission as countries or areas where YF virus activity has been reported currently or in the past, and where vectors and animal reservoirs exist.
Unless issued a medical waiver by a yellow fever vaccine provider, travelers must comply with entry requirements for proof of vaccination against YF.
WHO publishes a list of YF vaccine country entry requirements and recommendations for international travelers approximately annually. But because entry requirements are subject to change at any time, health care professionals and travelers should refer to the online version of this book and the CDC Travelers’ Health website for any updates before departure.
CDC Recommendations
CDC’s YF vaccine recommendations are guidance intended to protect travelers from acquiring YF virus infections during international travel. These recommendations are based on a classification system for destination-specific risk for YF virus transmission: endemic, transitional, low potential for exposure, and no risk ( Table 2-08 ). CDC recommends YF vaccination for travel to areas classified as having endemic or transitional risk (Maps 5-10 and 5-11 ). Because of changes in YF virus circulation, however, recommendations can change; therefore, before departure, travelers and clinicians should check CDC’s destination pages for up-to-date YF vaccine information.
Duration of Protection
In 2015, the US Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices published a recommendation that 1 dose of YF vaccine provides long-lasting protection and is adequate for most travelers. The recommendation also identifies specific groups of travelers who should receive additional doses, and others for whom additional doses should be considered (see Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 26, Yellow Fever ). In July 2016, WHO officially amended the IHR to stipulate that a completed International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis is valid for the lifetime of the vaccinee, and YF vaccine booster doses are not necessary. Moreover, countries cannot require proof of revaccination (booster) against YF as a condition of entry, even if the traveler’s last vaccination was >10 years ago.
Ultimately, when deciding whether to vaccinate travelers, clinicians should take into account destination-specific risks for YF virus infection, and individual risk factors (e.g., age, immune status) for serious YF vaccine–associated adverse events, in the context of the entry requirements. See Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 26, Yellow Fever , for a full discussion of YF disease and vaccination guidance.
Table 2-08 Yellow fever (YF) vaccine recommendation categories 1
Malaria prevention.
The following recommendations to protect travelers from malaria were developed using the best available data from multiple sources. Countries are not required to submit malaria surveillance data to CDC. On an ongoing basis, CDC actively solicits data from multiple sources, including WHO (main and regional offices); national malaria control programs; international organizations; CDC overseas offices; US military; academic, research, and aid organizations; and the published scientific literature. The reliability and accuracy of those data are also assessed.
If the information is available, trends in malaria incidence and other data are considered in the context of malaria control activities within a given country or other mitigating factors (e.g., natural disasters, wars, the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic) that can affect the ability to control malaria or accurately count and report it. Factors such as the volume of travel to that country and the number of acquired cases reported in the US surveillance system are also examined. In developing its recommendations, CDC considers areas within countries where malaria transmission occurs, substantial occurrences of antimalarial drug resistance, the proportions of species present, and the available malaria prophylaxis options.
Clinicians should use these recommendations in conjunction with an individual risk assessment and consider not only the destination but also the detailed itinerary, including specific cities, types of accommodations, season, and style of travel, as well as special health conditions (e.g., pregnancy). Several medications are available for malaria prophylaxis. When deciding which drug to use, consider the itinerary and length of trip, travelers’ previous adverse reactions to antimalarials, drug allergies, medical history, and drug costs. For a thorough discussion of malaria and guidance for prophylaxis, see Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 16, Malaria .
Entry requirements : Required for travelers ≥1 year old arriving from countries with risk for YF virus transmission. 1
CDC recommendations : Recommended for travelers ≥9 months old going to areas <2,300 m (≈7,550 ft) elevation, east of the Andes Mountains: the entire departments of Beni, Pando, Santa Cruz, and designated areas in the departments of Chuquisaca, Cochabamba, La Paz, and Tarija. Not recommended for travel limited to areas >2,300 m (≈7,550 ft) elevation and any areas not listed above, including the cities of La Paz (administrative capital) and Sucre (constitutional [legislative and judicial] capital).
- All areas <2,500 m (≈8,200 ft) elevation
- No malaria transmission in La Paz (administrative capital)
- Chloroquine
- P. vivax (99%)
- P. falciparum (1%)
- Atovaquone-proguanil, doxycycline, mefloquine, primaquine 5 , tafenoquine 3
Related Maps
Map 2-02. Yellow fever vaccine recommendations for Bolivia & neighboring countries
Other Vaccines to Consider
See Health Information for Travelers to Bolivia
Map 2-02 Yellow fever vaccine recommendations for Bolivia & neighboring countries 1
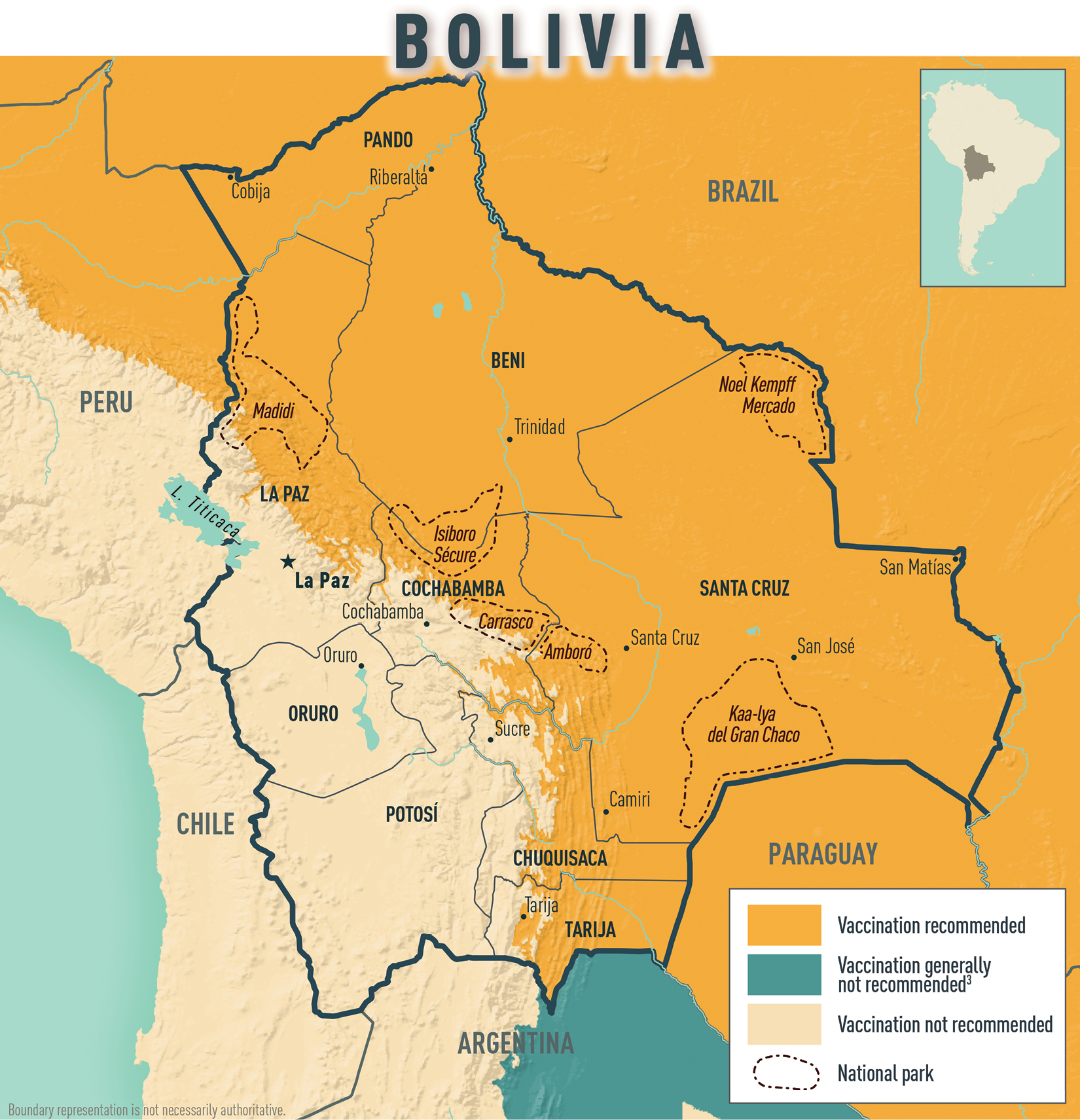
View Larger
1 Current as of November 2022. This is an update of the 2010 map created by the Informal WHO Working Group on the Geographic Risk of Yellow Fever.
2 Refers to Plasmodium falciparum malaria, unless otherwise noted.
3 Tafenoquine can cause potentially life-threatening hemolysis in people with glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency. Rule out G6PD deficiency with a quantitative laboratory test before prescribing tafenoquine to patients.
4 Mosquito avoidance includes applying topical mosquito repellant, sleeping under an insecticide-treated mosquito net, and wearing protective clothing (e.g., long pants and socks, long-sleeve shirt). For additional details on insect bite precautions, see Sec. 4, Ch. 6, Mosquitoes, Ticks & Other Arthropods.
5 Primaquine can cause potentially life-threatening hemolysis in people with G6PD deficiency. Rule out G6PD deficiency with a quantitative laboratory test before prescribing primaquine to patients.
6 P. knowlesi is a malaria species with a simian (macaque) host. Human cases have been reported from most countries in Southwest Asia and are associated with activities in forest or forest-fringe areas. P. knowlesi has no known resistance to antimalarials.
Yellow Fever Maps
2 In 2017, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) expanded its YF vaccination recommendations for travelers going to Brazil because of a large YF outbreak in multiple states in that country. Please refer to the CDC Travelers’ Health website for more information and updated recommendations.
3 YF vaccination is generally not recommended for travel to areas where the potential for YF virus exposure is low. Vaccination might be considered, however, for a small subset of travelers going to these areas who are at increased risk for exposure to YF virus due to prolonged travel, heavy exposure to mosquitoes, or inability to avoid mosquito bites. Factors to consider when deciding whether to vaccinate a traveler include destination-specific and travel-associated risks for YF virus infection; individual, underlying risk factors for having a serious YF vaccine–associated adverse event; and destination entry requirements.
The following authors contributed to the previous version of this chapter: Mark D. Gershman, Emily S. Jentes, Rhett J. Stoney (Yellow Fever) Kathrine R. Tan, Paul M. Arguin (Malaria)
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6-11 months, according to CDC's measles vaccination recommendations for international travel. Dogs infected with rabies are commonly found in Bolivia.
Bolivia - Level 2: Exercise Increased Caution. U C. Reissued after annual review. Exercise increased caution in Bolivia due to civil unrest. Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory. Do not travel to: Chapare region due to crime. Country Summary : Demonstrations, strikes, and roadblocks can occur at any time in Bolivia.
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Bolivia. If you decide to travel to Bolivia: Read the Department of State's COVID-19 page before planning any international travel, and read the Embassy COVID-19 page for country-specific COVID-19 information. Monitor local media for breaking events and be prepared to ...
Level 1: COVID-19 Low. All travelers should wear a mask, avoid crowds, stay at least 6 feet from people who are not traveling with you, wash your hands often or use hand sanitizer, and watch your health for signs of illness. American Samoa Anguilla Australia British Virgin Islands Brunei Cayman Islands China Faroe Islands Falkland Islands Fiji ...
Find continuously updated travel restrictions for Bolivia such as border, vaccination, COVID-19 testing, and quarantine requirements.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has moved Bolivia and Peru in South America, Lebanon in the Middle East and Tunisia in North Africa to its "high" risk category for travel.
The CDC in recent weeks has been dropping a number of countries from the "Level 4" rating including Saudi Arabia, Myanmar, Peru, Ecuador, Columbia, Bolivia, Botswana, and Haiti.
The US Department of State currently recommends US citizens exercise increased caution in Bolivia due to civil unrest. ... The CDC and WHO recommend the following vaccinations for Bolivia: hepatitis A, hepatitis B, typhoid, ... US State Dept Travel Information - Overall information about foreign travel for US citizens.
Bolivia answers are found in the CDC Yellow Book powered by Unbound Medicine. Available for iPhone, iPad, Android, and Web. ... Recommended for all travelers ≥9 months of age traveling to the following areas <2,300 m (7,546 ft) in elevation and east of the Andes Mountains: ...
Visit the Embassy of Bolivia website for the most current visa information. Entry requirements: Valid U.S. passport with at least 6 months validity remaining. International Certificate of Yellow Fever Vaccination. With a visitor visa, you may stay 30 days per trip, not to exceed 90 days per year. A Bolivian visitor visa costs $160 US and can be ...
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country's entry rules. Regular Canadian passport. Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months from the date you arrive in Bolivia. Passport for official travel. Different entry rules may apply.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website. Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
El Alto, Bolivia, 21 March 2021 (OPS/OMS/UNICEF) - Bolivia received today 228 thousand doses of COVID-19 vaccines through the COVAX Mechanism, a global effort between the Coalition for Promoting Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization (Gavi), the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) and the ...
Homepage - U.S. Embassy in Bolivia. Emergency Information for American Citizens. U.S. Deputy Assistant Secretary for Western Hemisphere Affairs Visits…. Alert: There have been reports of H-2A and H-2B visa…. VOTING IN 2024 U.S. FEDERAL ELECTIONS. NOTICE OF FUNDING OPPORTUNITY for: ALUMNI…. The United States donates 640,800 Pfizer….
At least 8 weeks before your trip check: the latest information on vaccinations and health risks in TravelHealthPro's Bolivia guide. where to get vaccines and whether you have to pay on the NHS ...
El Alto, Bolivia, 21 March 2021 (PAHO/WHO/UNICEF) - Bolivia today received 228,000 doses of COVID-19 vaccines through the COVAX Facility, a global effort involving the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization (Gavi), the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), and the World Health ...
Best Covid Travel Insurance Policies. Travel Insured - Worldwide Trip Protector. WorldTrips - Atlas Journey Premier/Atlas Journey Preferred. Seven Corners - Trip Protection Choice/Trip ...
CNN —. Bolivia doesn't seem like an obvious foodie destination. But the big, landlocked South American country is making waves in the culinary world via top-notch restaurants and transforming ...
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
CDC Yellow Book 2024. Preparing International Travelers. Author (s): Mark Gershman, Rhett Stoney (Yellow Fever) Holly Biggs, Kathrine Tan (Malaria) The following pages present country-specific information on yellow fever (YF) vaccine requirements and recommendations, and malaria transmission information and prevention recommendations.