Animal Corner
Discover the many amazing animals that live on our planet.

Brazilian Wandering Spider
The Brazilian Wandering Spider (Phoneutria fera) is an aggressive and highly venomous spider . It was first discovered in Brazil hence its name. However, this genus is known to exist elsewhere in South and Central America .
The Brazilian Wandering spider is a member of the Ctenidae family of wandering spiders.
The Brazilian Wandering spider appeared in the Guinness Book of World Records 2007 for being the most venomous animal .
In this particular genus, there are five known similar species whose members are also highly venomous. They include some of the relatively few species of spiders that present a threat to human beings.
Brazilian Wandering Spider Characteristics
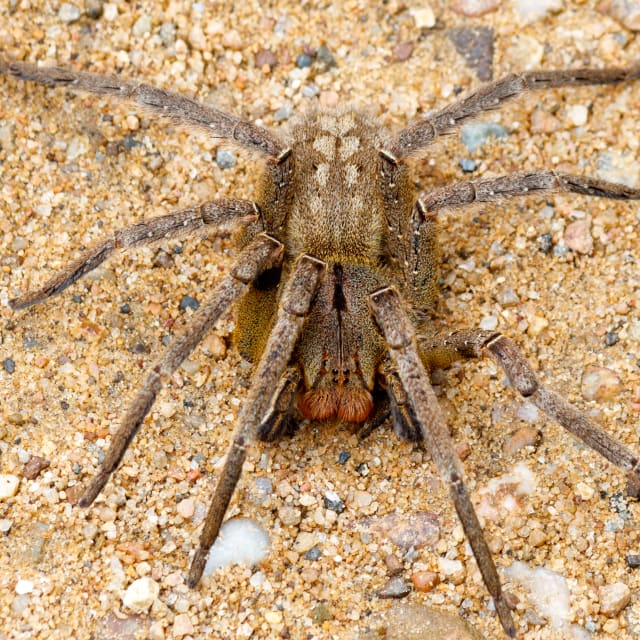
The Brazilian wandering spider can grow to have a leg span of up to 4 – 5 inches. They are large hairy spindly-looking spiders who have eight eyes, two of which are large. Brazilian wandering spiders are fast-moving spiders, their legs are strong and spiny and they have distinctive red jaws which they display when angered.
The Brazilian wandering spider is not a Tarantula . Brazilian wandering spiders are not even in the same family group. Tarantulas are harmless to humans and are mostly ambush killers who wait for prey to come to them. Brazilian wandering spiders are active hunters. Brazilian wandering spiders and Tarantulas do have one thing in common, however, they do not eat bananas.
Brazilian Wandering Spider Habitat and Spider Webs
The Brazilian Wandering spider is so-called because it wanders the jungle floor, rather than residing in a lair or maintaining a web. This is another reason it is considered so dangerous. In densely populated areas, the Brazilian Wandering spider will usually search for cover and dark places to hide during daytime, leading it to hide within houses, clothes, cars, boots, boxes and log piles. This usually causes accidents when people disturb them.
The Brazilian Wandering spider is also called the ‘banana spider’ as it is occasionally found within shipments of bananas. As a result, any large spider appearing in a bunch of bananas should be treated with due care.
Brazilian Wandering Spider Diet
Adult Brazilian Wandering spiders eat crickets, other large insects, small lizards and mice. Spiderlings of this species eat flightless fruit flies and pinhead crickets.
Brazilian Wandering Spider Reproduction
All spiders produce silk, a thin, strong protein strand extruded by the spider from spinnerets most commonly found on the end of the abdomen. Many species use it to trap insects in webs, although there are many species that hunt freely such as the Brazilian Wandering spider. Silk can be used to aid in climbing, form smooth walls for burrows, build egg sacs, wrap prey and temporarily hold sperm, among other applications.
Brazilian Wandering spiders reproduce by means of eggs, which are packed into silk bundles called egg sacs. The male spider must (in most cases) make a timely departure after mating to escape before the females normal predatory instincts return.
Mature male spiders have swollen bulbs on the end of their palps for this purpose and this is a useful way to identify whether the spider is male or female. Once the sperm is inside the female spider, she stores it in a chamber and only uses it during the egg-laying process, when the eggs come into contact with the male sperm for the first time and are fertilized. The Brazilian Wandering spiders life cycle is 1 – 2 years.
Brazilian Wandering Spider Venom
Bites from the Brazilian Wandering spider may result in only a couple of painful pinpricks to full-blown envenomed. In either case, people bitten by this spider or any Ctenid should seek immediate emergency treatment as the venom is possibly life threatening.
The Phoneutria fera and Phoneutria nigriventer (two species of wandering spider) are the two most commonly implicated as the most vicious and deadly of the Phoneutria spiders.
The Phoneutria not only has a potent neurotoxin, but is reported to have one of the most excruciatingly painful envenoms of all spiders due to its high concentration of serotonin. They have the most active venom of any living spiders.
One of their members, the Brazilian Huntsman, is thought to be the most venomous spider in the world. Brazilian wandering spiders are certainly dangerous and bite more people than any other spiders.
Check out more animals that begin with the letter B
More Fascinating Animals to Learn About
About joanne spencer.
I've always been passionate about animals which led me to a career in training and behaviour. As an animal professional I'm committed to improving relationships between people and animals to bring them more happiness.

Understanding the Wandering Spider: Quick Essential Facts
Wandering spiders are a group of venomous arachnids found primarily in South America.
Among these, the Brazilian wandering spider is particularly known for its potent venom and unique behavior. They are often referred to as “banana spiders” due to their frequent encounters with humans in banana plantations.
As a reader, you might be interested in learning more about these fascinating creatures, including their habitat, hunting techniques, and the effects of their venom.
In this article, we will delve into the world of wandering spiders and provide you with all the essential information to satisfy your curiosity.

Scientific Classification and Naming
The wandering spider belongs to the genus Phoneutria , which is a part of the Ctenidae family.
These spiders are known for their potent venom and aggressive behavior. Here is the scientific classification of the wandering spider:
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Subphylum: Chelicerata
- Class: Arachnida
- Order: Araneae
- Family: Ctenidae
- Genus: Phoneutria
Within the genus Phoneutria, two species are particularly noteworthy: Phoneutria fera and Phoneutria nigriventer, also known as P. nigriventer . These spiders are primarily found in South America and other tropical regions.
Phoneutria fera and P. nigriventer differ in some aspects. Let’s compare their features using a table:
Some key characteristics of the wandering spiders in the genus Phoneutria include:
- Potent venom that can be dangerous to humans
- Nocturnal hunters and are active at night
- Equipped with long, spiny legs for capturing prey
- Aggressive defenders of their territory
By understanding the scientific classification and differences between Phoneutria species, you can better appreciate the diversity and fascinating biology of these wandering spiders.
Identification and Appearance
Color and size.
The wandering spider, also known as the banana spider, has a distinctive appearance that can help you easily identify it in the wild.
They usually have a combination of hairy brown and black colors on their body. Their size can vary, but they are generally considered large spiders. Their size can range from 1 to 2 inches in body length.

When it comes to wandering spider’s leg span, these creatures can have an impressive reach. Their leg span can extend up to 5-6 inches.
Some key characteristics of a wandering spider’s legs include:
Habitat and Distribution
Wandering Spiders are known to inhabit various environments, including rainforests and tropical forests.
These spiders can adapt to different habitats based on their needs and availability of food sources. They prefer warm and humid places, as these conditions suit their growth and reproduction.
Geographical Coverage
Wandering spiders are found in Central and South America .
They live in forests from Costa Rica to Argentina, including Colombia, Venezuela, The Guianas, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay, and Northern Argentina.
They may also be present in some parts of the United States, particularly in the northern part of southern America.
However, they don’t inhabit countries like Australia. In summary, the Wandering Spider is mostly prevalent in the following areas:
- South America
- Central America
- Southern parts of the United States
Types of Wandering Spiders
Here’s a brief description of the major types of wandering spiders.
Brazilian wandering spiders
Also known as armed or banana spiders, these spiders are nocturnal and don’t make webs.
They are known to have been transported outside of South America in banana shipments.
Phoneutria nigriventer
These spiders contain neurotoxins that can cause cerebral changes and breakdown of the blood-brain barrier .
Their venom is medically significant and has been used in manufacturing drugs. Their bites may be fatal to children.
Ctenus captiosus
Also known as the Florida false wolf spider or tropical wolf spider, this species is found in the United States.
Some species of these spiders are large and scary-looking, but they’re only mildly venomous. Their venom is comparable to a bee sting.
Other types of wandering spiders include: Acantheis, Acanthoctenus, Africactenus, and Afroneutria.

Behavior and Diet
Aggression level.
Wandering spiders, as their name suggests, are known for their aggressive behavior .
While they won’t attack without provocation, if they feel threatened, they will not hesitate to defend themselves.
This is especially true during mating season.
Prey and Predators
In their natural habitat, wandering spiders primarily feed on insects and small vertebrates, such as:
- Insects like ants and moths
- Small amphibians
This diverse diet allows them to thrive in various ecosystems.
However, they are not top predators, as their natural predators include larger birds, mammals, and other spiders.
Nocturnal Activities
Wandering spiders are nocturnal creatures , which means they are active during the night.
During the day, they remain hidden in their retreats, often made from rolled-up leaves or small crevices.
At night, they leave their hiding spots to search for prey using their strong hunting skills.

Venom and Its Effects
Composition of venom.
The venom of the wandering spider is a complex mixture containing several toxic components.
Its main component is a potent neurotoxin, which can have severe effects on your nervous system 1 . Here’s a brief overview of its composition:
- Neurotoxins
Symptoms and Severity
A wandering spider’s venomous bite can cause a wide range of symptoms, depending on the severity of envenomation. These symptoms may include 2 :
- Mild to moderate pain
- Redness and swelling at the bite site
- Irregular heartbeat
- Difficulty breathing
- Blurred vision
- High blood pressure
Some severe cases may result in life-threatening complications, such as respiratory failure or even death 2 .
Medical Treatment and Antivenom
If bitten by a wandering spider, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Treatment often involves the following steps:
- Cleaning and immobilizing the affected area
- Monitoring and managing the symptoms
- Administering antivenom if it’s available and appropriate, depending on the severity of envenomation 3
Antivenom is specific to the venom of the wandering spider and can help neutralize its effects.
However, the availability of antivenom may be limited in some regions 3 .
Always remember that prevention is better than cure: learning how to identify and avoid wandering spiders is the best way to stay safe.

Reproduction and Mating
Mating ritual.
When it’s time for reproduction, the wandering spider undergoes an intriguing mating ritual.
The male spider performs a dance to attract the female by displaying his brightly colored legs and vibrating his body.
During the process, the male also produces a sperm web and transfers his sperm to the female’s reproductive organs using his pedipalps.
Egg Sacs and Offspring
After the mating process, the female wandering spider will create an egg sac to protect her eggs.
The sac consists of silk and can hold hundreds of eggs. She then attaches it to a safe hiding place, usually against a protective surface or within a secure web.
The female often guards the egg sac to ensure the protection of her offspring until they hatch.
Once the spiderlings hatch, they are known to be highly independent.
They disperse quickly and start their own journey, fending for themselves soon after emerging from the egg sac.
As they grow, they’ll go through a series of molts before reaching adulthood and beginning their own reproductive cycle.
Danger and Defense Mechanisms
The Wandering Spider is known to be one of the most dangerous spiders in the world.
Although they can potentially kill humans, fatalities are rare due to their reluctance to bite.
Oddly enough, their venom can cause an involuntary erection in men, alongside other painful symptoms.
Here are some ways the Wandering Spider protects itself and displays its dangerous nature:
- Fangs : These spiders are equipped with strong, sharp fangs that can easily pierce human skin, allowing them to inject their venom with ease.
- Venom : Their venom is potent and can cause severe pain, inflammation, and other adverse effects. In rare cases, it can even lead to death.
While interacting with Wandering Spiders, be cautious and observe them from a safe distance.
Knowing their defense mechanisms will help you respect their space and avoid any unpleasant encounters.
Remember, it’s essential to be informed and aware when dealing with these fascinating, yet dangerous creatures.

Comparison with Other Dangerous Spiders
Comparison to black widow.
The black widow spider is notorious for its potent venom, but the wandering spider has a stronger venom overall.
Both spiders are capable of causing severe symptoms, but the black widow’s venom is primarily neurotoxic, affecting your nervous system.
In contrast, the wandering spider’s venom can cause both neurotoxic and cytotoxic effects, potentially damaging your nerves and cells.
- Potent neurotoxic venom
- Red hourglass marking
- Stronger venom (neurotoxic and cytotoxic)
- No distinct marking
Comparison to Brown Recluse
The brown recluse spider is known for its necrotic venom that can lead to tissue damage and sometimes requires medical intervention.
While both the brown recluse and wandering spider can produce venomous bites, wandering spiders are considered more dangerous due to the potency of their venom and the severity of their bite symptoms.
- Necrotic venom
- Dark violin-shaped marking
Comparison to Wolf Spider
Wolf spiders are frequently mistaken for more dangerous spiders due to their size and appearance.
Although they can bite, their venom is not particularly potent and generally only causes mild itching, redness, and swelling.
In comparison, the wandering spider’s venom is far more dangerous, and its bite can result in serious symptoms, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Large and hairy
- Smoother appearance
Comparison to Sydney Funnel-Web Spider
The Sydney funnel-web spider is another highly venomous spider known for its potentially lethal bites.
While both spiders possess powerful venom, the wandering spider has a broader range of symptoms due to the combination of neurotoxic and cytotoxic effects.
In conclusion, wandering spiders are more dangerous than wolf spiders but their venom’s effects are more varied compared to black widows, brown recluses, and Sydney funnel-web spiders.
Be cautious around these spiders and seek medical help if bitten.
Interesting Facts and Guinness World Records
The Wandering Spider, also known as the Brazilian Wandering Spider, is a fascinating creature that has caught the attention of many.
They belong to the genus Phoneutria , which means “murderess” in Greek, giving you an idea of their potency. Let’s explore some interesting facts about this spider and its place in the Guinness World Records.

First, you might be curious about their venom. The Wandering Spider is known for having one of the most potent venoms among spiders.
In fact, it holds the Guinness World Record for the most venomous spider. Their venom contains a potent neurotoxin that can cause severe symptoms, including difficulty breathing, high blood pressure, and intense pain.
Apart from their venom, their behavior is also quite intriguing. These spiders are called “wandering” because they are known for actively hunting their prey rather than spinning webs to catch them.
They are mostly nocturnal creatures and, during the day, can be found hiding in logs or dark crevices.
Here are a few more notable characteristics of the Wandering Spider:
- Females are larger than males, with a body length of up to 1.6 inches (4 cm).
- They have eight eyes, arranged in two rows, which help them in hunting.
- The Wandering Spider is primarily found in Central and South America, particularly in Brazil.
- They are known to show aggression when threatened.
While the Wandering Spider is a marvel of the arachnid world, it’s essential to keep a safe distance from them due to their venomous nature.
However, their unique characteristics and record-breaking venom potency make them a fascinating subject for those interested in the natural world.
Prevention and Safety Measures
To protect yourself from wandering spiders, there are some simple safety measures you can take.
Firstly, be cautious in areas where these spiders may live, such as dark and warm spaces. For example, avoid reaching into crevices or lifting piles of wood without inspecting them first.
Always wear appropriate shoes when outdoors, particularly in wooded or grassy areas. This can help prevent bites on your feet or ankles.
Reduce the risk of wandering spiders entering your home by sealing gaps and cracks. This minimizes the chance of the spiders finding a way inside.
Regularly clean your living spaces, paying special attention to dark and hidden areas. By maintaining a clean environment, you’ll discourage wandering spiders from making themselves at home.
When out in nature, avoid disturbing spider habitats like webs or egg sacs. This can prevent agitating wandering spiders, reducing your chance of accidental encounters.
Remember, wandering spiders can be dangerous, but by taking these precautions, you can significantly reduce your risk of encountering them or being bitten. Stay safe and always be aware of your surroundings.
In summary, wandering spiders, particularly those in the genus Phoneutria, are a group of venomous arachnids predominantly found in Central, South America and parts of Southern United States.
These spiders, including the Brazilian wandering spider, are known for their potent venom, nocturnal hunting habits, and aggressive defense mechanisms.
Their venom, containing neurotoxins and other components, can cause severe symptoms in humans, making them one of the most dangerous spider species.
Despite their fearsome reputation, fatalities are rare, and they play a vital role in their ecosystems.
It’s important to respect their space and take preventive measures to avoid encounters. Understanding these spiders’ behavior, habitat, and characteristics can help in appreciating their role in nature while ensuring safety.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2857337/ ↩
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3851068/ ↩ ↩ 2
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6560916/ ↩ ↩ 2
Reader Emails
Over the years, our website, whatsthatbug.com has received hundreds of letters and some interesting images asking us about wandering spiders. Scroll down to have a look at some of them.
Letter 1 – Wandering Spider from Ecuador

Hi Michele, There is a resemblance to the Dolomedes Fishing Spiders, and finding it near a river lends credence to that possibility. Eric Eaton noticed this posting and has this to say: ” Ok, the spiders from Ecuador and Costa Rica: They are most likely NOT wolf spiders, but wandering spiders, either in the family Ctenidae or Sparassidae. They tend to be more common, and even larger than, wolf spiders in the tropics. At least one species, Phoneutria fera, is extremely aggressive, with potentially deadly venom. Do not mess with large spiders in Central and South America! The venomous types are very difficult to distinguish from harmless species, and in any event, a bite is going to be really painful. These spiders sometimes stow away in bananas, houseplants, and other exported goods, so they can show up in odd places. Be careful where you put your hands.”
Update: May 14, 2013 We now have a confirmation that this is a Wandering Spider, Phoneutria fera , and it is a dangerous species. See Encyclopedia Britannica and Animal Corner .
Letter 2 – Brazilian Wandering Spider: Most Venomous Animal

Hi Martin, We are happy you were able to write to us after your encounter with this Brazilian Wandering Spider and are thrilled to be able to post your story and photos to our site. We started to research, and our first hit has a different species name. Phoneutria fera is described as: “The Brazilian Wandering Spider is not for the ‘pet keeper’. Brazilian Wandering Spiders are extremely fast, extremely venomous, and extremely aggressive. These large and dangerous true spiders are ranked among the most venomous spiders known to man. In fact, the Brazilian Wandering Spider is the most venomous spider in the New World! In South America, these true spiders are commonly encountered in peoples’ homes, supposedly hiding in peoples’ shoes, hats, and other clothes. The Brazilian Wandering Spider does not remain on a web, rather, it wanders the forest floor, hence the name.” Our favorite information on Wikipedia is that Phoneutria is Greek for “murderess”. Here is one final tidbit about the effect of the bite of the Brazilian Wandering Spider on the human male .
Letter 3 – Possibly Wandering Spider from Ecuador

Dear Mike, This is really an interesting Spider, but other than to say it appears to be a hunting spider that does not build a web to entrap prey, we aren’t sure about its identity. Many hunting spiders can jump quite well. It looks very much like the spider in a posting in our archives, also from Ecuador, that we identified as possibly a Wandering Spider in the genus Phoneutria, a venomous and potentially dangerous genus . The spotted legs on your individual look like the spotted legs on an individual in an image on Wikipedia of a Wandering Spider in the genus Phoneutria . There are many images of Brazilian Wandering Spiders on Primal Shutter and we believe that might be a correct identification for your individual.
Thank you for the information. After reading more about the spider, I’m glad it didn’t jump! Mike
Letter 4 – Possibly Wandering Spider from Ecuador

Dear Carl, We believe, though we are not certain, that this might be a Wandering Spider in the genus Phoneutria, and you may read more about Wandering Spiders on the Museum für Naturkunde Karlsruhe website where it states: “There is no doubt that the venom of some of the species is quite potent for mammals, including humans.” We eagerly welcome additional opinions on this identification. Perhaps Cesar Crash of Insetologia can provide something. In the future, please submit a single species per submission form as it makes it extremely difficult for us to categorize postings with multiple species.
Letter 5 – Wandering Spider from Belize

Hi Karl, Thanks for allowing us to post your excellent image of a Wandering Spider, Cupiennius salei . The species is pictured on iNaturalist .
Bugman aka Daniel Marlos has been identifying bugs since 1999. whatsthatbug.com is his passion project and it has helped millions of readers identify the bug that has been bugging them for over two decades. You can reach out to him through our Contact Page .

Piyushi is a nature lover, blogger and traveler at heart. She lives in beautiful Canada with her family. Piyushi is an animal lover and loves to write about all creatures.
8 thoughts on “Understanding the Wandering Spider: Quick Essential Facts”
Hi Michele, I am an Ecuadorian scientist and specialized on spiders, I would like to find one like yours, I can say that, almost without doubt, you found the Phoneutria itself, it is the Phoneutria fera, look at this picture: http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://4.bp.blogspot.com/-bFH9qzT0F7U/T_2sZuk6xAI/AAAAAAAAAGY/8jnMVcPOcNI/s1600/phoneutria_fera2.jpg&imgrefurl=http://rangerbaiano.blogspot.com/2012/07/animais-peconhentos-e-venenosos.html&usg=__iCWEz7S86xub6RAyvXTER6HBaco=&h=864&w=834&sz=215&hl=es-419&start=6&zoom=1&tbnid=jjOROVO9h-vKXM:&tbnh=145&tbnw=140&ei=99eRUY6xKo2K9QTLvYCoDQ&prev=/search%3Fq%3Dphoneutria%2Bfera%26sa%3DN%26hl%3Des-US%26sout%3D1%26tbm%3Disch%26prmd%3Divns&itbs=1&sa=X&ved=0CDYQrQMwBQ Can you see the similarities?, unfortunately the spider might be in a better life today 🙂 Another thing, when you want identifications you should take a picture in front, the under part, and the upper part, as well as some characteristics about behaviour like how they react when you approach. The Phoneutria is a very agressive one.. best wishes, bye.
Hi Miguel, Thanks so much for the comment. This is a seven year old posting and we did not have the ability to post comments when it was originally posted online. We have made an update on What’s That Bug? and your comment is greatly appreciated.
Ah, there is also needed the size and the picture of its face so we can see the eye arrangement, depending on that it could also be pisauridae, but I stay in Ctenidae..
This is a female Cupiennius sp. wandering spider.
Perhaps surprisingly, this ubiquitous large spider of the Mindo area appears to be undescribed to species level.
Although one is indeed best advised to exercise caution in the presence of large ctenids, members of the genus Cupiennius are not known to be dangerously venomous (Barth, 2002). By way of confirmation, my girlfriend, Shannon Bowley, managed to be bitten by a mature female of this Mindo species in 2013 – she felt only mild effects, equivalent to a bee sting.
Thanks for this valuable information.
I’m planning a trip to Ecuador and I’m fearing these spiders. Do they get in houses? Any tips to keep them out, so I can sleep at night?
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of followup comments via e-mail. You can also subscribe without commenting.

Fact Animal
Facts About Animals
Brazilian Wandering Spider Facts
Brazilian wandering spider profile.
There are more than 50,000 species of spider, and the vast majority are less dangerous than a honeybee. Almost none are aggressive, and of those with medically significant venom, only a small percentage are capable of causing death. So, on the whole, arachnophobes are just being a bit silly.
But there’s one spider that vindicates all of these fears, and few animals are as globally renowned to be a serious threat to human lives as the Brazilian Wandering Spider .
Brazilian Wandering Spiders are actually 9 species of spider in the same genus ‘Phoneutria’, one of which is found in Central America, with the rest in South America.
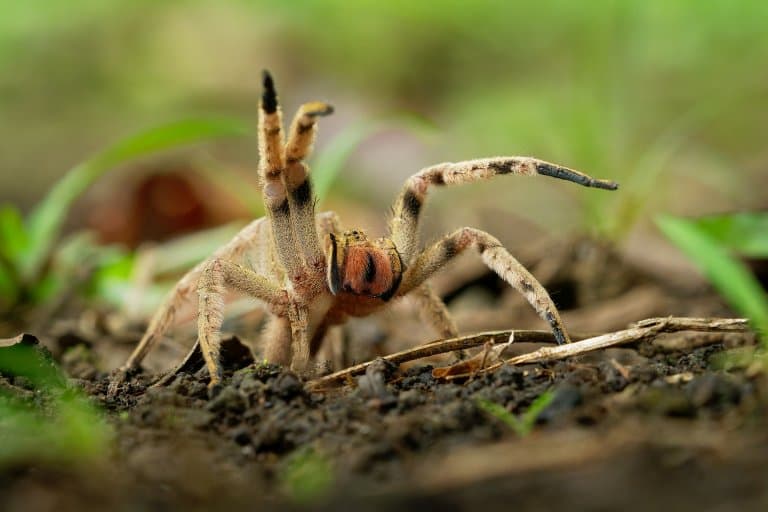

Brazilian Wandering Spider Facts Overview
These spiders are called wandering spiders because of instead of spinning a web to wait for food, or occupying a lair, they spend their night wandering in the leaf litter of the jungle floor for prey.
The sensitive hairs on its body help detect vibrations of passing prey, and it will feed on insects, lizards, frogs and any animals as large as itself.
During the day they will hide under logs, rocks, or inside termite mounds and banana plants. They will also sometimes wander into urban areas and homes, where they can come into contact with humans.
Brazilian wandering spiders are aggressive , dangerous and frightening. For once, this is an animal you should be wary of.
The females are larger, around 50% heavier than males, and produce more venom, and this might be a clue as to why their Greek name translates to “ Mudress” . These spiders will often stand and fight and have an intimidating threat display.
The potency of their venom is one of the reasons they’re so dangerous, and their ability to hide away in fruit and shoes explains why most bites are on extremities.
Interesting Brazilian Wandering Spider Facts
1. armed spiders.
In Brazilian, these are sometimes known as armed spiders, on account of their elongated front legs.
They can convey quite a bit of information with these legs, and as wandering spiders, use them to get about the forest, looking for food.
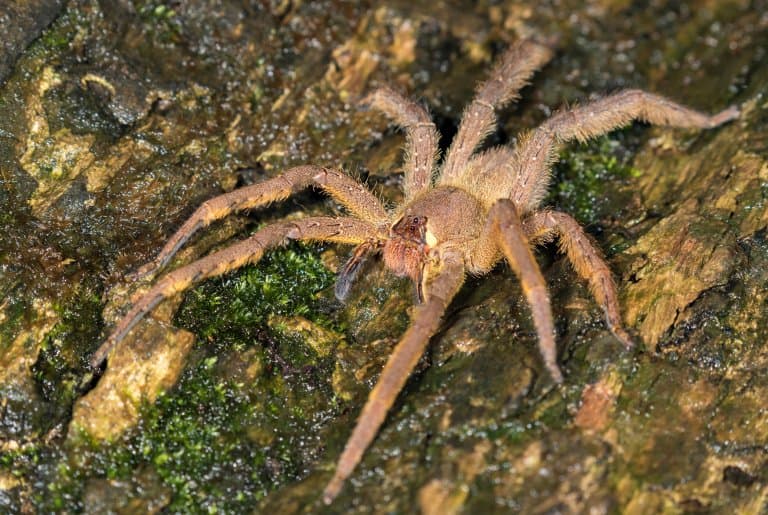

2. Banana Spiders
They’re also sometimes called ‘banana spiders’ on account of their status as a stowaway on popular fruit imported from the tropics.
This is becoming less common as stricter regulations ensure there’s less contamination of fruits, but there’s always a chance your next bunch of bananas will have a family of these spiders living inside it.
3. They have the largest venom glands of any spider
Females produce more venom than males, but both sexes have enormous venom glands. These glands are even more impressive when you consider the size of the spider is significantly less than the largest around.
The venom glands of the Brazilian Wandering Spider are over a centimetre long, and this is all housed inside the bright red chelicerae (mouth parts) which they are quick to display whenever they get upset. 1
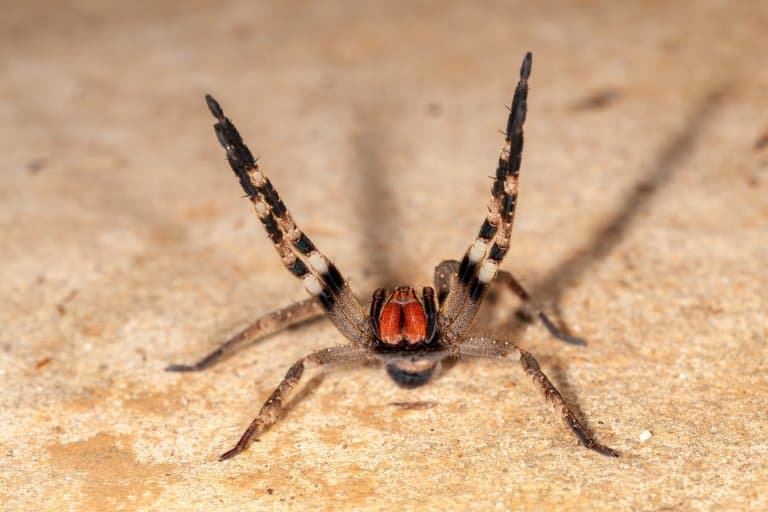
4. They’re aggressive
These spiders can grow quite large and have long, brightly-coloured legs. Unlike most spiders, they’re known to stand their ground when threatened and are far quicker to bite than many other species.
They’ll still try to scurry away where possible, and they’re not out to get anybody.
But where most other species will flee, the wandering spiders’ aggression does make it more likely to be involved in incidents.
Most bites are on fingers and toes, a sign that they’re being stepped on or grabbed inadvertently. When the spider feels cornered, it’ll rear up on its back legs and waves its colourful arms around as a warning.
Then it’ll sway side to side, beckoning you to have a go. Anything foolhardy enough to call this bluff gets a wealth of envenomation effects. 2 3

5. They give some men erections
There are ways to accomplish this with fewer side effects, but a bit from a Brazilian wandering spider does come with a certain Viagral quality.
This isn’t as fun as it might sound. Prolonged erections in this manner are likely to harm and destroy muscles and blood vessels in the penis and could cause irreparable damage.
Besides this, the assault on the central nervous system that comes with envenomation by this spider doesn’t sound worth it. 4
6. And some people die
This assault brings with it a whole host of unpleasant symptoms. Seizures, foaming at the mouth, inability to speak, collapse, and a host of other miserable experiences.
Paralysis is possible, as is cardiac shock. Blood vessels can burst in the brain, or anywhere else, and in many cases, this can be enough to kill a person.
This spider has one of the most potent venoms of all, and there are multiple legitimate records of death as a result of bites.
7. But they’re rarely fatal
While the Brazilian wandering spider is potentially one of the most dangerous spiders in the world, there is some evidence to suggest it gives a dry bite, defensively.
This means that despite exceptionally toxic venom, the amount actually injected is less than some of the other contenders, and this is what makes it typically less lethal than the Australian funnel webs.
These spiders are classified as Dangerous Wild Animals and would therefore require a special permit to keep. Bites from wandering spiders are common in South America, but antivenom is often readily available, and they rarely result in death.
In most cases, lethal bites are cases of a very young or very old victim, and few people of healthy age are killed. 5
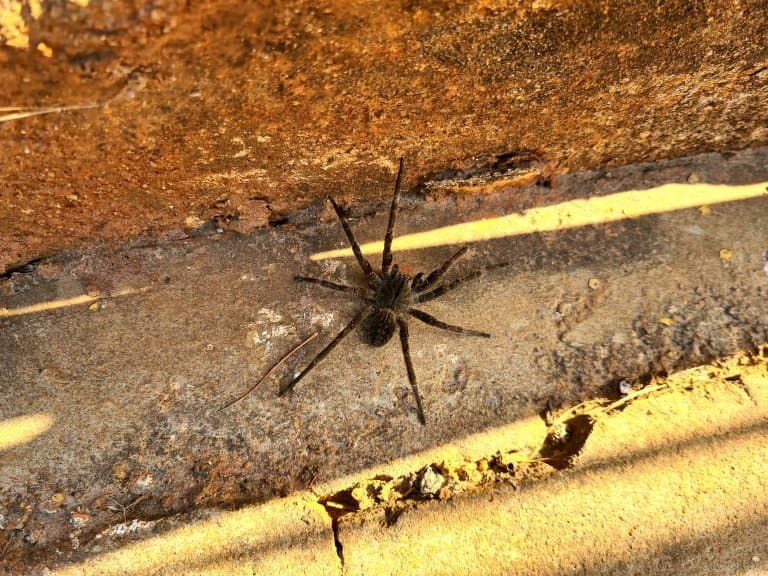

8. They do invade the UK sometimes
These unquestionably scary spiders show up in supermarkets in the UK on occasion, having hitched a ride on banana shipments.
On more than one occasion they’ve made their way into shoppers’ homes, but it doesn’t appear that there are any cases of them biting people as a result.
These spiders aren’t suited for temperate climates and don’t survive Winter, so there’s no risk of them multiplying.
Brazilian Wandering Spider Fact-File Summary
Scientific classification, fact sources & references.
- PeerJ. (2017), “ Dimensions of venom gland of largest venom glands in all spiders ”, Bio Numbers.
- Dave Clarke (2010), “ Venomous spider found in Waitrose shopping ‘beautiful but aggressive’” , The Guardian.
- “ Phoneutria Perty (Arachnida: Araneae: Ctenidae) ”, UF-IFAS University of Florida
- Kátia R.M. Leite (2012), “ Phoneutria nigriventer spider toxin Tx2-6 causes priapism and death: A histopathological investigation in mice ”, Science Direct.
- “ Brazilian wandering spiders: Bites & other facts ”, Live Science.

Wellcome to SpiderZoon
- Spider Facts
Brazilian Wandering Spider: Size, Bite, Diet and Other Facts
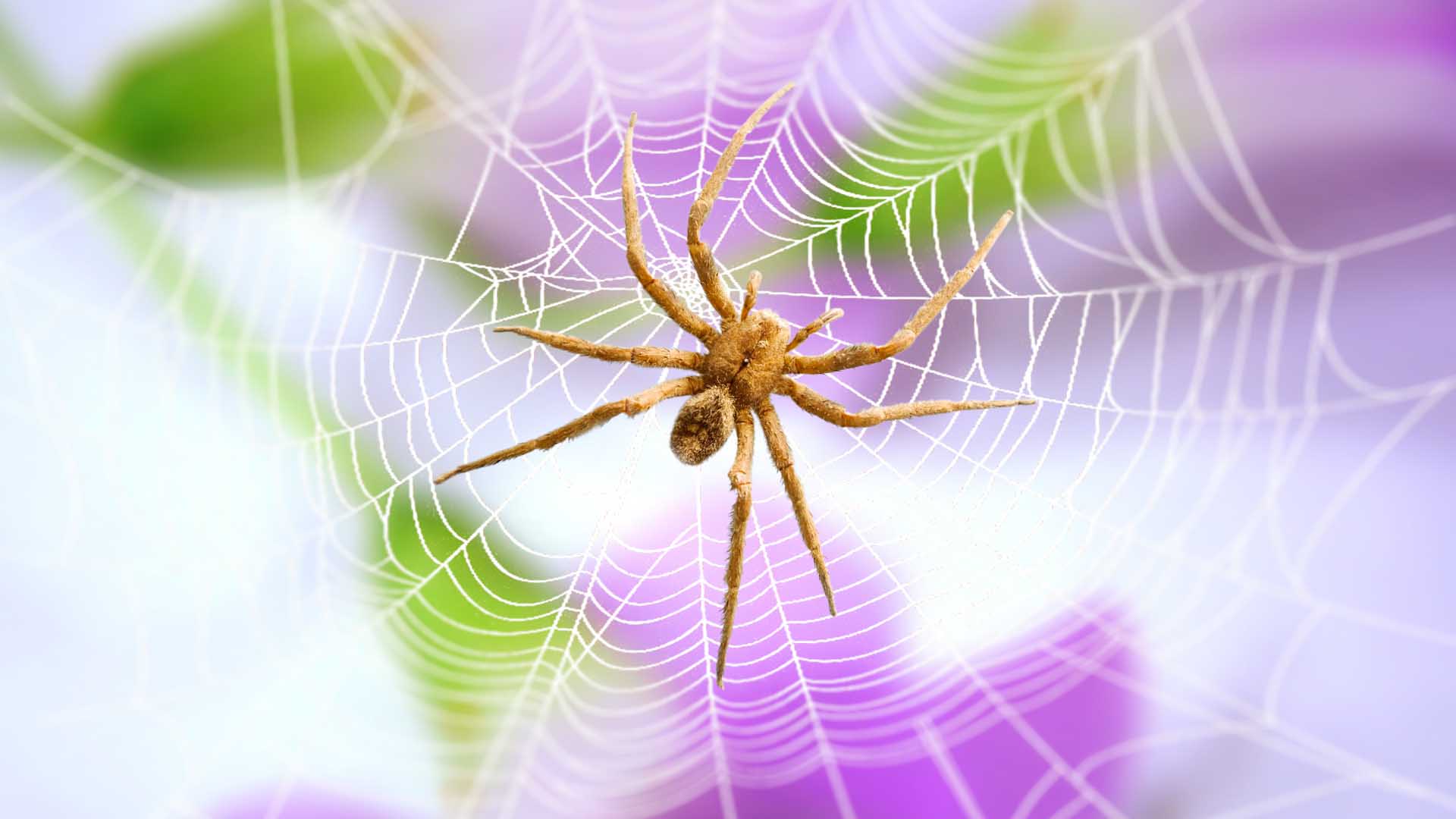

The Brazilian Wandering Spider is a venomous arachnid with a fearsome reputation. This South American rainforest dweller packs a powerful punch, but don’t let its nickname “banana spider” fool you – they’re active hunters, not web-spinners. Despite their size and venom, bites are uncommon as they’re typically shy.
The Brazilian Wandering Spider has garnered significant attention due to its potent venom, which makes it one of the world’s most venomous spiders. Understanding its biology and behavior is crucial for both scientific research and public safety.
Scientific classification
The Brazilian Wandering Spider belongs to the family Ctenidae within the order Araneae. Its scientific classification is as follows:
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Arachnida
- Order: Araneae
- Family: Ctenidae
- Genus: Phoneutria
The Brazilian Wandering Spider goes by various common names, including “armed spider,” “banana spider,” and “wandering spider.” Synonyms for this species may include Ctenus , which was formerly used for some Phoneutria species.
Distribution and habitat
Distribution:
- South American: Found throughout most of South America east of the Andes mountains, including countries like Brazil (their namesake), Argentina, Paraguay, and up into northern regions.
- Central American Touch: A few species even reach southern Central America.
- Rainforest Dwellers: Primarily found in the lush rainforests of South America.
- Not Picky Places: They can also adapt to other habitats like the Atlantic Forest and even some urban areas.
- Daytime Hideouts: While they wander at night, they seek shelter during the day in places like termite mounds, under rocks, or even (unintentionally) in bananas!
Physical Characteristics
size and weight.
The Brazilian wandering spider is a creepy crawly giant. Their bodies can grow up to 2 inches (5 centimeters) long, but that’s not the scary part. Their legs can span a whopping 7 inches (18 cm), making them look even bigger. They are one of the biggest true spiders by body weight and size.
Despite their impressive leg span, Brazilian wandering spiders are relatively light. They only weigh around 6 grams, which is about the same as two pennies. While they might look imposing, they’re not the heaviest arachnids around.
Coloration and markings
These spiders exhibit a range of colors, including brown, black, and sometimes reddish hues. They often have distinctive markings on their bodies, which can vary between species. These markings may include stripes or patterns that serve as a key identification feature.
Notable features
One of the most notable features of the Brazilian Wandering Spider is its elongated, robust body and long, agile legs. They have sharp fangs, which they use to inject venom into their prey or in self-defense.
Sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is evident in this species. Females are larger and bulkier than males, while males have longer, more slender legs. Additionally, males possess specialized structures known as pedipalps, which are used during mating.
In the following sections of this article, we will delve deeper into the behavior, venom, and ecological role of the Brazilian Wandering Spider, shedding light on why this species has both fascinated and instilled fear in those who encounter it.
Behavior and Ecology
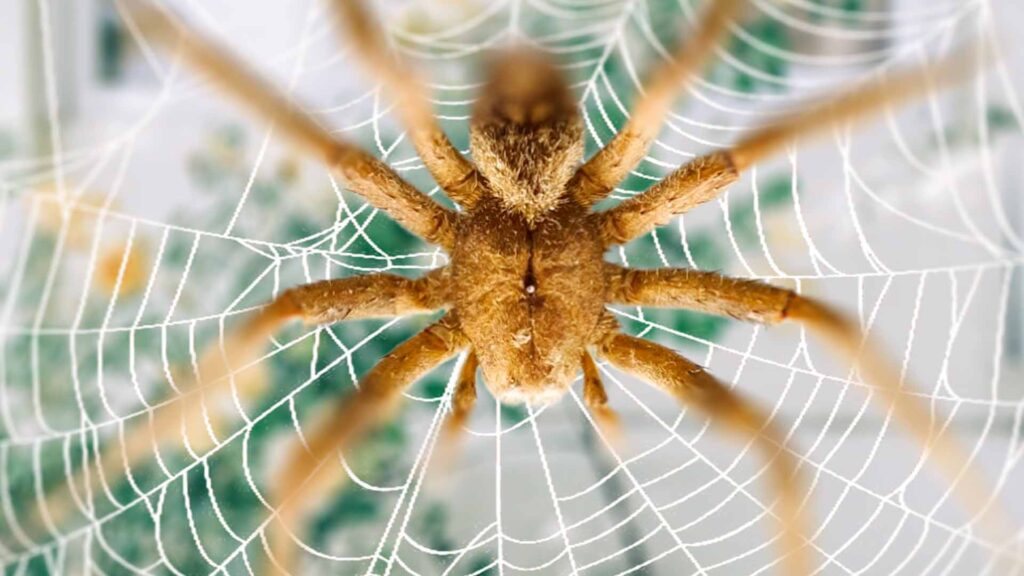

Nocturnal habits
Brazilian Wandering Spiders are primarily nocturnal creatures. They are most active during the night, venturing out of their daytime hiding places to hunt for prey and engage in mating activities. Their nighttime activity allows them to avoid predators and reduce the risk of desiccation in the hot tropical sun.
Hunting and feeding behavior
These spiders are agile hunters and primarily feed on insects, small vertebrates, and other arachnids. They do not build webs to capture prey but instead rely on their excellent senses, including acute vision and touch, to locate and stalk their victims. They often wander in search of food and are known for their swift and lethal strikes. Once they subdue their prey, they inject venom to immobilize it before feeding.
Brazilian Wandering Spiders (Phoneutria) are active hunters and have distinctive feeding behaviors. Here’s an overview of their feeding habits:
- Active Predators: Brazilian Wandering Spiders are not web-builders like many other spider species. Instead, they are active predators. They actively roam their environment in search of prey rather than waiting for insects to stumble into a web.
- Hunting Strategy: When hunting, these spiders use their excellent senses, including acute vision and touch, to locate potential prey. They are known for their agility and speed, which they use to stalk and capture their victims. They have sharp fangs, which they use to deliver a venomous bite to immobilize their prey.
- Diet: Their diet consists primarily of insects and other arthropods, but they are opportunistic feeders and may consume a variety of small creatures, including small vertebrates such as frogs and lizards when the opportunity arises.
- Venom Use: Brazilian Wandering Spiders inject venom into their prey to immobilize and partially digest it. Their venom contains neurotoxins that affect the nervous system of their victims. Once the prey is incapacitated, the spider can feed on it at its leisure.
- Feeding Process: After subduing their prey with a venomous bite, the spider uses its chelicerae (fangs) to break down the prey’s tissues. The venom also helps in predigestion, turning the prey’s insides into a semi-liquid form that the spider can ingest. They can consume both the internal fluids and solid parts of their prey.
- Frequency of Feeding: The frequency of feeding can vary depending on factors such as the availability of prey and the spider’s size. Generally, they need to feed periodically to sustain their energy and growth. Spiderlings may require more frequent meals to support their rapid growth, while adults can go longer periods between meals.
Overall, the Brazilian Wandering Spider’s feeding strategy is well-suited for their active and wandering lifestyle, allowing them to efficiently capture and consume a variety of prey in their natural habitat.
Role in the ecosystem
The Brazilian Wandering Spider plays a vital role in controlling insect populations within its habitat. By preying on a variety of insects and other small creatures, they help maintain ecological balance. Additionally, their presence in the rainforest ecosystem contributes to the overall biodiversity and food web.
Mating and reproduction
Mating in Brazilian Wandering Spiders is a complex and potentially dangerous process. Male spiders must carefully approach and court a receptive female to avoid being mistaken for prey. They use specialized pedipalps to transfer sperm to the female’s reproductive organs. After successful mating, females lay egg sacs containing hundreds of eggs. They guard these sacs and ensure the survival of their offspring until they hatch.
Lifespan and growth
The lifespan of Brazilian Wandering Spiders varies between males and females. Males generally have a shorter lifespan, typically living for a few months to a year after reaching maturity. Females, on the other hand, can live for several years. The growth of these spiders involves a series of molts, during which they shed their exoskeletons to accommodate their increasing size. Molting is a vulnerable period in their lives as their new exoskeleton is initially soft and requires time to harden.
Venom and Envenomation
Composition of venom.
The venom of Brazilian Wandering Spiders is a complex mixture of neurotoxins, cytotoxins, and other enzymes. One of the most significant components is a neurotoxin called PhTx3, which targets the nervous system of their prey.
Toxicity and effects on humans
The venom of these spiders is highly potent and can be lethal to their prey. In humans, envenomation can cause a range of symptoms, including intense pain, muscle cramps, fever, nausea, and in severe cases, paralysis and death. It’s important to note that while their venom is potent, actual fatalities from Brazilian Wandering Spider bites are rare due to the availability of medical treatment.
First aid and medical treatment
In the event of a Brazilian Wandering Spider bite, immediate medical attention is crucial. First aid measures may include cleaning the wound and applying ice to reduce pain and swelling. However, the primary treatment involves antivenom, which can counteract the effects of the spider’s venom.
Cases of envenomation and fatalities
Although fatalities from Brazilian Wandering Spider bites are uncommon, there have been documented cases of severe envenomation, especially in regions where medical treatment is not readily available. These spiders are generally non-aggressive and will bite humans only in self-defense when provoked, or if they feel cornered.
Understanding the behavior, ecology, and venomous nature of the Brazilian Wandering Spider is crucial for both scientific research and public awareness, helping to minimize the risk of envenomation and promote coexistence with this remarkable but potentially dangerous arachnid.
Brazilian wandering spider life cycle
The Brazilian wandering spider has a fascinating life cycle that revolves around hunting and motherhood. Here’s a breakdown:
- Egg Haven: After mating, the female lays hundreds, sometimes even a thousand, eggs in a silken sac. This becomes their protected nursery.
- Tiny Terrors: Hatching from the eggs emerge translucent spiderlings called larvae.
- Nymph Stage: The larvae molt a few times, transforming into nymphs. Think of them as mini-adults but without the ability to reproduce yet.
- Shedding for Size: As nymphs grow, they undergo multiple molts, shedding their outer shell to accommodate their larger bodies.
- Ready to Roam: After the final molt, the spider emerges as a full-fledged adult, complete with reproductive organs. Now, they can join the wandering lifestyle and continue the cycle.
The life cycle begins when a female Brazilian Wandering Spider lays her eggs. She typically creates an egg sac made of silk and deposits it in a concealed location, such as a tree hollow or leaf litter. Inside the sac, she may lay hundreds of eggs. The female guards the egg sac and ensures its protection until the spiderlings hatch. The duration of the egg stage varies depending on environmental conditions but generally lasts for a few weeks.
Spiderling Stage
After the incubation period, spiderlings (young spiders) emerge from the egg sac. They are extremely vulnerable at this stage and rely on their mother’s protection and guidance. Spiderlings are miniature versions of adult spiders but lack the full coloration and size. They disperse from the nest once they have molted and are capable of hunting on their own. During this stage, they grow rapidly by molting, shedding their exoskeletons to accommodate their increasing size.
Juvenile Stage
As spiderlings continue to molt and grow, they progress into the juvenile stage. During this phase, their coloration becomes more distinct, and they start to develop the characteristic features of adult Brazilian Wandering Spiders. They become increasingly independent and begin to exhibit hunting behaviors. The duration of the juvenile stage can vary but often lasts several months.
Sub-Adult Stage
The sub-adult stage is an intermediate phase between juvenile and adult. At this point, the spiders are closer in size and appearance to adults but have not yet reached sexual maturity. They continue to molt, with the frequency of molting gradually decreasing as they approach adulthood. Sub-adult spiders may exhibit more territorial behaviors as they compete for resources and prepare for eventual mating.
Adult Stage
Upon reaching sexual maturity, Brazilian Wandering Spiders enter the adult stage. This is when they are fully developed and capable of reproduction. Females are larger and bulkier than males, and males possess specialized structures called pedipalps, which they use during mating. Adult spiders engage in mating activities, and females lay eggs to continue the life cycle. Adult Brazilian Wandering Spiders can live for several years, with females typically having longer lifespans than males.
Understanding the life cycle of these spiders is essential for studying their behavior, reproductive biology, and population dynamics. It also provides insights into their adaptation strategies in the complex ecosystems of South and Central America.
Brazilian Wandering Spider Bite
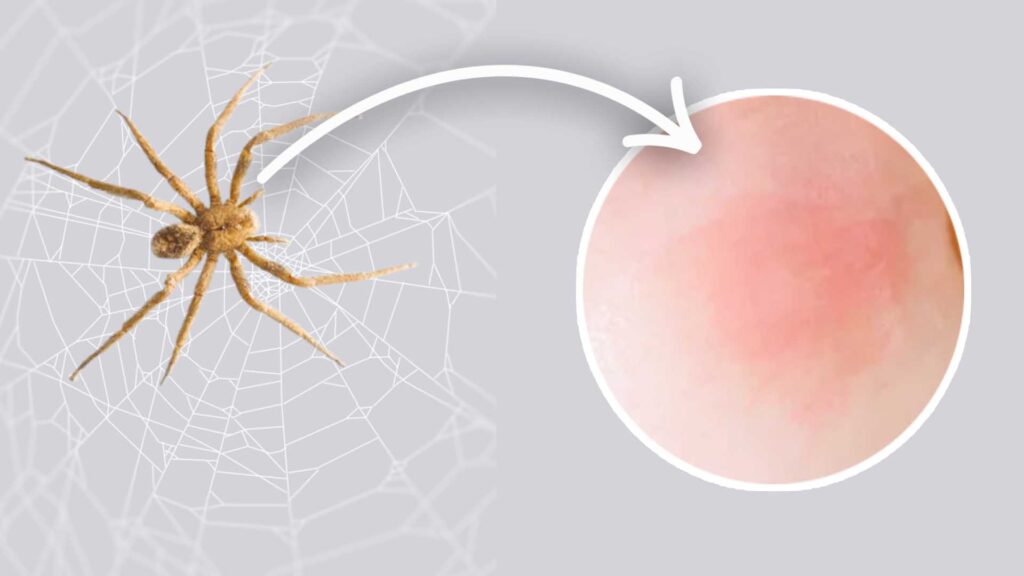
Brazilian Wandering Spiders are known for their potent venom and, occasionally, their bites on humans. While bites are relatively rare due to the spider’s non-aggressive nature, understanding the consequences of a bite is crucial for public safety.
Studying Brazilian Wandering Spider bites is of great interest for several reasons. It helps healthcare professionals provide appropriate medical treatment, raises awareness among communities in spider habitats, and contributes to our understanding of venomous arachnid envenomations.
The venom of Brazilian Wandering Spiders is a complex mixture of neurotoxins, cytotoxins, and enzymes. It contains various components, including PhTx3, which is a potent neurotoxin affecting the nervous system.
Brazilian Wandering Spider bites can have a range of effects on the human body, including intense pain, muscle cramps, fever, nausea, and in severe cases, paralysis. The severity of the symptoms depends on factors such as the amount of venom injected and the individual’s sensitivity to the venom. There are several types of spider bites .
Symptoms of a Brazilian Wandering Spider Bite
Local symptoms
- Intense pain
- Itching or burning sensation
- Formation of blisters or lesions
Systemic symptoms
- Muscle cramps and spasms
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Elevated heart rate
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Respiratory distress
Severity and variations
The severity of Brazilian Wandering Spider bite symptoms can vary widely. In some cases, symptoms may be mild and resolve on their own, while in severe envenomations, life-threatening complications can occur. Individual reactions to the venom can also vary, making it challenging to predict the exact outcome of a bite.
First Aid and Immediate Response
Steps to take after a bite
Immediate response to a Brazilian Wandering Spider bite should include:
- – Washing the bite area with soap and water.
- – Applying a clean, cool compress to reduce pain and swelling.
- – Immobilizing the affected limb or area.
- – Keeping the bite victim calm to prevent an elevated heart rate.
Do’s and don’ts in case of a bite
- – Seek medical attention promptly.
- – Take note of the spider’s appearance (if possible) to aid identification.
- – Keep the bite victim still and calm to reduce the spread of venom.
- – Do not try to suck out venom or make incisions at the bite site.
- – Avoid applying tourniquets.
- – Don’t use ice directly on the skin as it can worsen tissue damage.
Seeking medical attention
Medical attention is essential after a Brazilian Wandering Spider bite, even if symptoms appear mild initially. Antivenom is available and can be administered to counteract the effects of the venom. Medical professionals can also manage symptoms and monitor for potential complications.
Complications and Long-Term Effects
Potential complications
Complications from Brazilian Wandering Spider bites can include:
- – Severe muscle spasms
- – Respiratory distress
- – Cardiovascular issues
- – Kidney failure (rare)
- – Allergic reactions to antivenom
Long-term consequences
Long-term consequences of a bite can vary depending on the severity and medical treatment received. Some individuals may experience lingering pain, muscle weakness, or psychological trauma following a severe envenomation.
Recovery and rehabilitation
Recovery from a Brazilian Wandering Spider bite typically involves medical treatment, rehabilitation for muscle and nerve damage, and psychological support for individuals affected by the experience. Rehabilitation may include physical therapy to regain muscle strength and function. Prompt medical attention and appropriate care are crucial for minimizing long-term effects and complications.
Facts of Brazilian Wanding Spider
Here are 10 creepy crawly facts about the Brazilian Wandering Spider:
- Big and Hairy: These spiders are giants! Their bodies can grow up to 2 inches (5 centimeters) long, with a leg span of up to 7 inches (18 cm). They are covered in hairs, making them appear even bigger.
- Wanderlust: They are aptly named – Brazilian wandering spiders don’t spin webs. Instead, they wander the forest floor at night in search of prey.
- Venomous Bite: Their venom is considered one of the most potent among spiders. A bite can cause severe pain, swelling, sweating, nausea, and even priapism in males. Thankfully, bites are rare as they are typically shy and defensive.
- Not So Fond of Bananas: While sometimes called ‘banana spiders,’ they are not typically found in bananas. They might, however, take shelter in them during transport, which is how they might end up in a faraway land.
- Rainforest Resident: These spiders are native to the rainforests of South America, particularly in Brazil.
- Fearsome Feasters: They’re active hunters and will eat almost anything they can overpower, including insects, lizards, frogs, and even small rodents.
- Mom’s the Word: Female Brazilian wandering spiders are dedicated mothers. They lay hundreds of eggs in a silken sac and fiercely guard them until they hatch.
- Multiple Molts: Like all spiders, Brazilian wandering spiders grow through molting. They shed their exoskeleton multiple times as they grow into adults.
- Mating Dance: Male Brazilian wandering spiders perform a elaborate mating dance to attract a female.
- Medicinal Potential: Despite their scary reputation, the venom of the Brazilian wandering spider is being studied for its potential use in treating erectile dysfunction.
What happens if a Brazilian Wandering Spider bites a man?
A Brazilian Wandering Spider bite on a man can cause a range of symptoms, some severe:
- Pain: The bite is known for causing intense, localized pain at the site.
- Autonomic effects: Sweating, nausea, and increased heart rate are common.
- Priapism: In some cases, males may experience a prolonged and painful erection (priapism). This is due to a component in the venom.
- Muscle paralysis: Severe bites can lead to muscle paralysis, which can affect breathing in rare cases.
However, it’s important to remember:
- Bites are uncommon as these spiders are typically shy and defensive.
- Antivenom is available and effective in treating bites.
If bitten, seek medical attention immediately. Early treatment can help prevent complications and ensure a full recovery.
How poisonous is a Brazilian Wandering Spider?
Brazilian Wandering Spider packs a nasty venomous punch, considered one of the strongest among spiders. Bites are rare though, as they’re shy and prefer to escape trouble.
What is the world’s deadliest spider?
The term “deadliest” can be subjective and depends on how one defines it (e.g., based on venom potency or human fatalities). However, the Brazilian Wandering Spider (Phoneutria) is often considered one of the most venomous spiders in the world. Another spider often mentioned in discussions of venom toxicity is the Sydney Funnel-web Spider (Atrax robustus and Atrax formosus), found in Australia. These spiders are known for their potent venom and have caused fatalities in the past.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Article

Can a Daddy Long Legs Bite Kill You (You Need to Know)
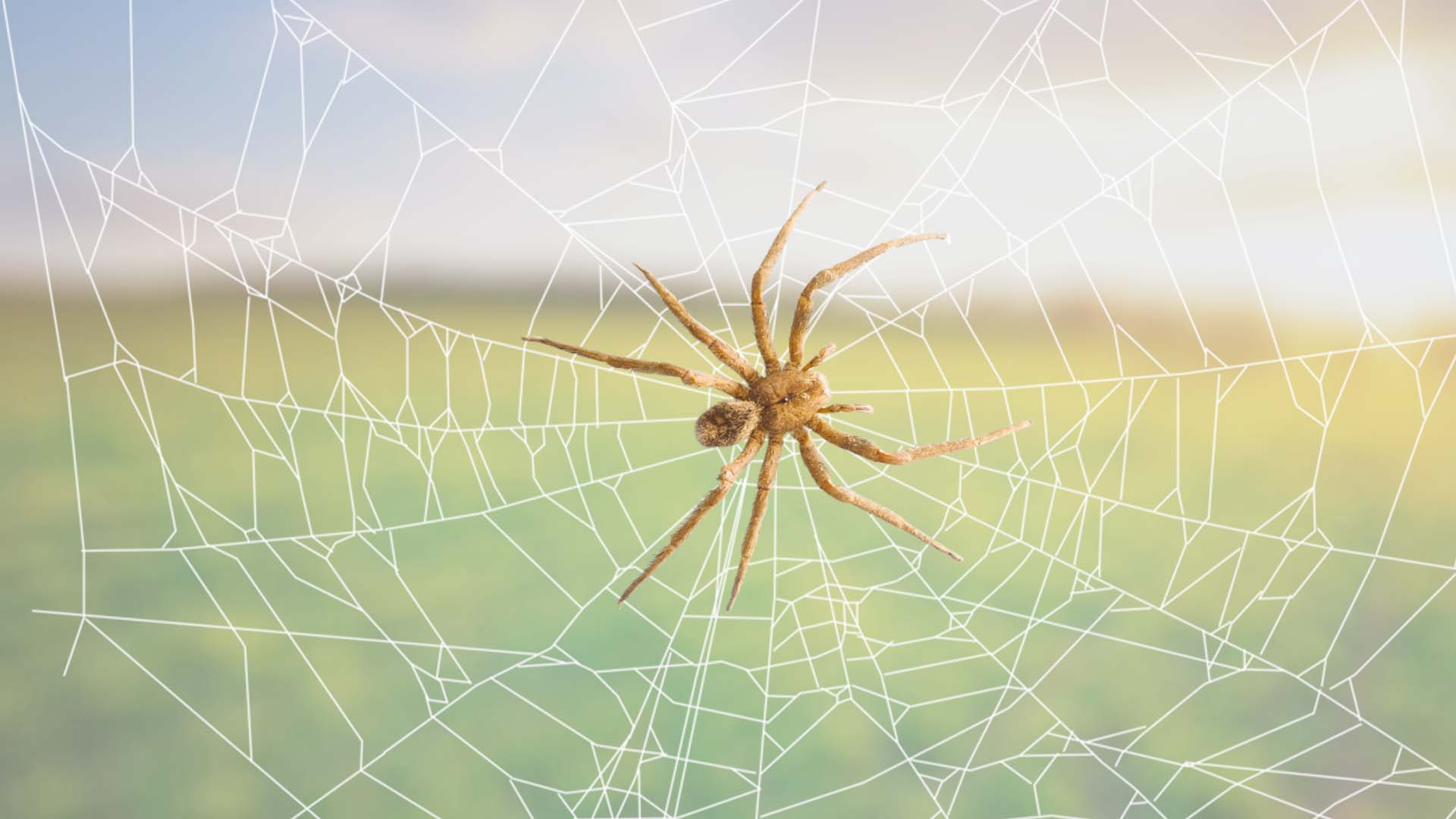

7 Facts About The Brazilian Wandering Spider
Are Wolf Spiders Poisonous for Humans, Cats or Dogs? (Explained)
When To Worry About A Spider Bite? (Need to Know)

Brazilian Wandering Spider
The Brazilian Wandering Spider (Phoneutria fera) is a teardrop-shaped arachnid with a brown coloration. Known for its potent venom, it thrives in both the lush rainforests and human dwellings of Brazil. Its notorious wandering behavior makes it a significant presence in its habitats.

Fascinating Facts about Brazilian Wandering Spider
Here are 3 interesting facts about Brazilian Wandering Spider:
- The Brazilian Wandering Spider is considered the world's most venomous spider by the Guinness World Records.
- They are known as 'wandering' spiders because they roam the jungle floor at night instead of residing in a lair or web.
- Despite their notorious reputation, their bites rarely cause death in humans due to the small amount of venom they inject.
Taxonomy and Classification
Here is the scientific categorization of Brazilian Wandering Spider, providing a glimpse of their position in the biological hierarchy:
Lifecycle and Growth
Brazilian Wandering Spider's life is a journey of transformation - an adventure marked by the following captivating stages:
Egg → Spiderling → Adult
The Brazilian Wandering Spider, primarily found in the rainforest, exhibits a lifecycle that spans both wilderness and human habitats. From egg to adult, it navigates a complex path through dense foliage and human dwellings, adapting to these contrasting environments.
Brazilian Wandering Spider Behaviour and Adaptations
Brazilian Wandering Spiders are known for their nomadic behavior. Instead of building webs to catch prey, they actively hunt at night, using their highly developed senses, particularly vision, to locate and stalk their prey.
These arachnids have adapted to a wide range of habitats, from forests to urban areas. Their potent neurotoxic venom, one of the most powerful among spiders, allows them to incapacitate and consume a variety of prey.
Brazilian Wandering Spider Interaction with the Ecosystem
Now, let's look at how they help maintain the balance in the ecosystem:
- Brazilian Wandering Spiders play a crucial role in controlling the population of their prey, which includes insects and small mammals.
- They serve as a food source for larger animals, contributing to the food chain in their ecosystem.
- Their venom, although dangerous to humans, is studied for medicinal purposes including treatments for erectile dysfunction and pain relief.
Threats to Brazilian Wandering Spider
Despite their popularity and predator status, Brazilian Wandering Spider encounter several threats as well:
- Destruction of natural habitat due to deforestation
- Increased usage of pesticides affecting their food chain
- Climate change potentially disrupting their breeding patterns
Also Check:
If you're interested in learning about at some more interesting insects, here are two suggestions for you, below 👇
Do Brazilian Wandering Spider Bite?
Learn if Brazilian Wandering Spider bite, what you should do if you get bitten by them, and other interesting information.
Other Bug Profiles
Check other interesting bugs:
- Lone Star Tick
- Brown Dog Tick
What do Brazilian Wandering Spider Eat?
Learn what food Brazilian Wandering Spider eat, and also information about how they eat and drink.

AnimalBehaviorCorner

Brazilian Wandering Spider
Brazilian Wandering Spider , scientifically known as Phoneutria, emerges as a captivating enigma in the realm of arachnids.
Renowned for its formidable reputation as one of the world’s most venomous spiders , Phoneutria embodies a plethora of intriguing traits that have captured the curiosity of enthusiasts and researchers alike.
From its distinctive appearance and neurotoxic venom to its nomadic hunting strategies and unique mating behaviors , this remarkable spider species holds a wealth of fascinating secrets waiting to be unraveled.
Join us as we embark on a journey to explore the captivating world of the Brazilian Wandering Spider, shedding light on its captivating characteristics and dispelling myths that have shrouded its true nature.
1. Taxonomy and Distribution of the Brazilian Wandering Spider
A. scientific classification of phoneutria.
The Brazilian Wandering Spider, scientifically referred to as Phoneutria, occupies a distinct place within the arachnid taxonomy.

Belonging to the family Ctenidae, this spider genus is further categorized into several species, each boasting unique traits and behaviors .
Phoneutria’s taxonomic position not only distinguishes it from its arachnid counterparts but also underscores its intriguing evolutionary journey.
B. Native Habitat in South and Central America
Endemic to the lush landscapes of South and Central America, the Brazilian Wandering Spider finds its natural haven within these diverse regions.
From the rainforests of the Amazon to the tropical stretches of the Caribbean, Phoneutria has adapted to a range of environments over the course of its evolution.
The spider’s ancestral ties to these regions are tightly woven into their behaviors , anatomy, and survival strategies.
C. Preference for Tropical Rainforests and Urban Areas
Within its native territories, the Brazilian Wandering Spider exhibits remarkable versatility in its chosen habitats.
While it thrives amidst the vibrant biodiversity of tropical rainforests, it has also displayed a propensity for urban locales.

Phoneutria’s adaptability has led it to establish a presence in urban areas, where it often finds shelter in crevices, gardens, and even human dwellings.
This adaptability to both wild and urban spaces further showcases the spider’s resilience and capacity to thrive in varying conditions.
2. Physical Characteristics of the Brazilian Wandering Spider
A. size, coloration, and distinctive markings.
The Brazilian Wandering Spider , a creature of remarkable visual intrigue, boasts an array of captivating physical attributes.
Ranging in size from a few centimeters to several inches, Phoneutria showcases a size diversity that reflects the breadth of its genus.
Its coloration varies across species, encompassing shades of brown, black, and gray, often accompanied by intricate patterns and markings that adorn its exoskeleton.
These unique markings serve not only as a visual spectacle but also as essential components of its survival toolkit.
B. Camouflage and Defense Mechanisms
The Brazilian Wandering Spider’s appearance is a masterpiece of evolution, meticulously crafted to ensure both survival and predation .

Its coloration and markings are tailor-made for blending seamlessly into its surroundings, granting it a potent advantage in ambushing prey and evading predators . Moreover, these markings also play a role in its defense mechanisms.
When threatened, Phoneutria adopts a defensive posture, raising its front legs and revealing its striking markings, a visual warning to potential threats. This dual-purpose camouflage and defense strategy exemplify nature’s ingenuity at its finest.
C. Sexual Dimorphism: Unveiling Gender Differences
A fascinating facet of the Brazilian Wandering Spider lies in the realm of sexual dimorphism , where gender-based variations manifest in pronounced ways.
Females tend to be larger and more robust than their male counterparts, showcasing a size disparity that has evolved in tandem with their roles in reproduction and hunting .
Beyond size, other characteristics, such as leg structure and coloration, also exhibit subtle differences between male and female Phoneutria specimens.
This divergence in physical traits adds depth to our understanding of the species’ intricate biology and behavior .
In exploring the physical characteristics of the Brazilian Wandering Spider , we uncover a canvas painted with size diversity, intricate coloration, and unique markings.
These features, finely tuned by evolution, contribute to its prowess in camouflage and defense, while the fascinating interplay of sexual dimorphism further enriches our perception of this captivating arachnid species .
3. Venomous Nature of the Brazilian Wandering Spider
A. potent neurotoxic venom: a silent lethal weapon.
The Brazilian Wandering Spider, known scientifically as Phoneutria, harbors a venomous arsenal that stands as a testament to nature’s intricate design.

This spider’s venom contains a potent concoction of neurotoxic compounds, tailored by evolution to incapacitate its prey swiftly and efficiently.
The neurotoxins interfere with nerve cell communication, leading to paralysis and ensuring that Phoneutria’s quarry is rendered immobile and defenseless, setting the stage for a successful meal.
B. Effects on Prey and Human Hazard
When a victim succumbs to the Brazilian Wandering Spider’s venom , the effects are a symphony of paralysis and predation .
The venom’s impact on the prey’s nervous system results in swift immobilization, offering the spider a decisive advantage in subduing its catch.
While this venomous efficiency is well-adapted for predation, it also underscores the potential danger to humans.
A bite from Phoneutria can lead to a series of neurotoxic reactions, with varying degrees of severity depending on factors such as the individual’s age and overall health.
While human envenomations are relatively rare, they can result in a range of symptoms, from localized pain and swelling to more severe neurological effects.
C. Recorded Cases of Envenomations: Unraveling the Symptoms
Throughout history, documented cases of Phoneutria envenomations have offered insights into the spider’s potential threat to humans .

Symptoms typically include intense pain at the bite site, accompanied by swelling and redness . In some instances, victims have reported systemic reactions, such as muscle cramps, elevated heart rate, and even breathing difficulties.
Swift medical attention and the administration of antivenom have proven effective in mitigating the severity of these symptoms.
These cases serve as a reminder of the delicate balance between the Brazilian Wandering Spider’s potent venom and the potential risks it poses to those who unwittingly encounter it.
4. Hunting and Diet of the Brazilian Wandering Spider
A. hunting techniques and wandering behavior.
The Brazilian Wandering Spider, scientifically known as Phoneutria, unveils a mesmerizing repertoire of hunting techniques that set it apart as a master predator .
Displaying an agile and nomadic behavior , Phoneutria does not confine itself to the confines of a web. Instead, it actively prowls its surroundings, tirelessly searching for potential prey.
This dynamic wandering behavior ensures that its chances of encountering a variety of food sources are maximized, showcasing a strategic approach to sustenance.
B. Active Hunting Triumphs Over Web-Building
Unlike its web-weaving counterparts, the Brazilian Wandering Spider relies on a more hands-on approach to securing its next meal.
While weaving webs might seem an efficient method, Phoneutria’s active hunting strategy offers a distinct advantage in versatility.
By forgoing the constraints of a stationary web, it can tailor its approach to suit different environments and prey types, adapting its tactics on the fly.
This adaptability demonstrates the spider’s remarkable ability to adjust its methods for optimal results.
C. Diverse Prey Spectrum: Insects to Small Vertebrates
Phoneutria’s diet is a testament to its prowess as an opportunistic predator . Its menu spans a diverse range of creatures, from insects like crickets and cockroaches to small vertebrates such as lizards and frogs , and even small rodents.

This wide-ranging palate highlights its ecological significance in controlling various populations within its habitat.
By consuming creatures both large and small, Phoneutria ensures a balanced ecosystem, playing a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity and ecological equilibrium.
5. Mating and Reproduction of the Brazilian Wandering Spider
A. courtship rituals and behaviors: a complex affair.
The Brazilian Wandering Spider, scientifically referred to as Phoneutria, reveals a captivating array of courtship rituals and behaviors that form the cornerstone of its reproductive cycle.
Courtship among these arachnids is a complex affair, involving intricate dances and displays that serve as both communication and assessment.
Male Phoneutria employs a combination of visual cues, vibrations, and tactile interactions to court potential mates.
This elaborate courtship process highlights the significance of precise communication in the delicate dance of reproduction .
B. Cannibalistic Tendencies: A Post-Mating Phenomenon
An aspect that sets Phoneutria’s mating process apart is the notorious cannibalistic tendency exhibited by females after mating.
Following successful mating, females may exhibit an inclination to consume their partners. This seemingly counterintuitive behavior has evolutionary underpinnings.
It is believed that this cannibalistic act not only provides the female with a much-needed nutritional boost but also eliminates potential competitors and safeguards the male’s investment in the next generation.
This intriguing behavior sheds light on the complexities of reproductive strategies within the species.
C. The Unique Mating Plug Phenomenon: A Puzzling Enigma
A distinctive feature in Phoneutria’s reproductive saga is the enigmatic mating plug phenomenon. After mating, male Phoneutria deposit a specialized substance that forms a plug within the female’s reproductive tract.
This plug is believed to serve multiple purposes. It may prevent other males from mating with the female, thus ensuring the successful transmission of the mating male’s genetic material.
Additionally, it might aid in sealing off the female’s reproductive tract, potentially protecting her from external pathogens.
This phenomenon underscores the intricate interplay of biological strategies that contribute to the species’ reproductive success.
6. Human Interaction and Urban Legends of the Brazilian Wandering Spider
A. occasional presence in urban areas: nature in our midst.
The Brazilian Wandering Spider, scientifically known as Phoneutria, has carved a niche for itself not only in the wild but also in the fabric of urban environments.

While its primary habitats are the lush landscapes of South and Central America, Phoneutria occasionally ventures into human -inhabited spaces. Its adaptability allows it to find shelter in gardens, crevices, and even within homes.
This coexistence with humans adds an intriguing dimension to our encounters with this enigmatic arachnid .
B. Debunking Misconceptions: Separating Fact from Fiction
The presence of the Brazilian Wandering Spider has sparked a plethora of misconceptions and exaggerated tales, contributing to the creation of urban legends.
Stories of spiders leaping from banana bunches or hiding under toilet seats have become part of modern folklore, often fueled by sensationalism.
It’s crucial to sift through these tales and recognize that while Phoneutria’s venom is potent, the likelihood of encountering a dangerous encounter is relatively low.
Separating fact from fiction empowers individuals to approach these creatures with accurate knowledge.
C. Importance of Proper Education: Identifying Friend from Foe
Education plays a pivotal role in fostering a harmonious coexistence between humans and the Brazilian Wandering Spider .
Learning to identify and understand the behaviors of Phoneutria species enhances safety for both humans and the spiders themselves.
Instead of succumbing to unwarranted fear, individuals can take steps to reduce the chances of accidental encounters and, if necessary, engage in responsible removal methods.
By arming themselves with knowledge, individuals can navigate encounters with urban-dwelling Phoneutria specimens with confidence and respect.
7. Brazilian Wandering Spider Conservation and Misunderstanding
A. significance of phoneutria in ecosystem dynamics.
The Brazilian Wandering Spider , scientifically termed Phoneutria, assumes a pivotal role within its ecosystem, contributing to a delicate balance of populations and interactions.

As a top-tier predator , it plays a crucial part in controlling insect and small vertebrate populations, preventing unchecked growth that could disrupt the ecosystem’s equilibrium.
By maintaining these population dynamics, Phoneutria ensures the health and stability of its habitat, highlighting its significance beyond its ominous reputation.

B. Impact of Fear and Misunderstanding: Hindrances to Conservation
Despite its ecological contributions, the Brazilian Wandering Spider often falls victim to fear-driven misconceptions that negatively impact conservation efforts.
Misunderstandings surrounding its behavior and potential danger can lead to unwarranted extermination campaigns and habitat destruction.
Fear-driven reactions not only disrupt the natural balance but also hinder opportunities to study and appreciate the species for its ecological significance.
Addressing these misconceptions is crucial to ensuring the spider’s survival and maintaining the health of its ecosystems.
C. Efforts to Dispel Myths and Promote Coexistence
Efforts to conserve the Brazilian Wandering Spider are interwoven with endeavors to educate and dispel myths.
By providing accurate information and dispelling exaggerated tales, conservationists aim to reshape public perception.
Collaborative initiatives emphasize coexistence, highlighting the importance of responsible behavior when encountering Phoneutria.
Educating communities about the spider’s role, behavior, and conservation status fosters an environment where fear gives way to appreciation, and where balanced cohabitation becomes a reality.
8. Research and Medical Significance of the Brazilian Wandering Spider
A. ongoing scientific research on phoneutria venom.
The Brazilian Wandering Spider , Phoneutria, has garnered significant attention from the scientific community due to the unique properties of its venom.
Ongoing research delves into the intricate composition of the venom, aiming to unlock its mysteries and potential applications in various fields.
The diverse array of compounds within the venom, particularly its neurotoxic components, has attracted interest for their potential medical and therapeutic implications.
B. Antivenom Development and Therapeutic Prospects
One of the most promising areas of research surrounding Phoneutria lies in the development of antivenoms and therapeutic agents.

The venom’s potent neurotoxic effects on the nervous system have spurred efforts to create targeted treatments for conditions such as chronic pain and neurological disorders .
Additionally, the potential for antivenoms holds promise in mitigating the effects of envenomations, offering a lifeline for individuals who encounter these spiders .
This focus on harnessing the venom’s properties for positive medical outcomes highlights the transformative potential within this enigmatic arachnid .
C. Balanced Perspectives: Navigating Ethical and Scientific Endeavors
While research on the Brazilian Wandering Spider’s venom offers tremendous potential, it necessitates a balanced perspective.
As researchers probe the venom’s properties, ethical considerations arise, including the well-being of the spiders and their ecosystems.
A holistic approach acknowledges the value of understanding Phoneutria’s natural behaviors and conserving its habitats.
This balanced perspective extends to utilizing the venom’s potential responsibly, ensuring that breakthroughs are achieved while respecting the complex interplay of science and nature.
9. Frequently Asked Questions about the Brazilian Wandering Spider
What is the brazilian wandering spider.
The Brazilian Wandering Spider , scientifically known as Phoneutria, is a venomous arachnid found in South and Central America. It’s notorious for its potent venom and is considered one of the most venomous spiders in the world.
Is the Brazilian Wandering Spider dangerous to humans?
Yes, the Brazilian Wandering Spider’s venom contains potent neurotoxins that can cause a range of symptoms in humans , from localized pain and swelling to more severe reactions. While bites are relatively rare, it’s advisable to exercise caution when encountering these spiders.
What is the spider’s habitat?
The Brazilian Wandering Spider is native to tropical rainforests of South and Central America. However, it’s adaptable and can also be found in urban areas, such as gardens and houses.
How does the Brazilian Wandering Spider hunt?
Unlike many spiders that build webs, Phoneutria is an active hunter. It roams its environment in search of prey, relying on its keen senses to detect vibrations and movements.
Are Brazilian Wandering Spiders aggressive toward humans?
Brazilian Wandering Spiders are not naturally aggressive towards humans and will typically only bite in self-defense. However, caution is advised, especially in areas where these spiders are known to inhabit.
Can the Brazilian Wandering Spider’s venom be used for medical purposes?
Yes, research is ongoing into the potential medical applications of Phoneutria’s venom. Its neurotoxic properties have sparked interest in pain management and neurological treatments.
Is the spider’s reputation for crawling into banana shipments true?
While there have been stories of Brazilian Wandering Spiders being found in shipments of bananas, these occurrences are extremely rare. Spiders are unlikely to survive the conditions of shipping and storage.
How can I stay safe around Brazilian Wandering Spiders?
To stay safe, it’s important to be cautious when encountering spiders in their natural habitat. Avoid provoking or handling them, especially if you’re unsure of their identity. If you suspect you’ve been bitten, seek medical attention promptly.
Are there any efforts to conserve the Brazilian Wandering Spider?
Conservation efforts for the Brazilian Wandering Spider are intertwined with public education and dispelling myths. Recognizing its role in ecosystems and promoting coexistence are essential steps in preserving this unique species.
What can I do if I find a Brazilian Wandering Spider in my home?
If you encounter a Brazilian Wandering Spider in your home, it’s advisable to contact local pest control professionals who can safely remove the spider without causing harm.
In the intricate tapestry of nature, the Brazilian Wandering Spider , Phoneutria, emerges as a creature of both fascination and caution.
Its venomous nature and captivating behaviors have earned it a place among the most enigmatic arachnids .
As we continue to explore its world, debunk myths, and understand its vital role in ecosystems, we find a delicate balance between awe and respect.
Armed with knowledge, we navigate the realm of Phoneutria, appreciating its complexity while fostering coexistence, a testament to the intricate dance between humans and the natural world.
Share this:
Similar posts.

Gerbil Behavior
Gerbil behavior offers a captivating glimpse into the world of these small rodents, known for their energetic and social nature. Gerbils are popular pets for families and individuals alike, cherished for their endearing antics and charming personalities. In this article, we’ll explore the intricate aspects of gerbil behavior, shedding light on their habitat, diet, social…

Sahara Desert Animals
Sahara Desert animals inhabit one of the largest and most inhospitable deserts on Earth. This vast expanse of arid land is home to a remarkable variety of resilient species that have adapted to survive in the harsh desert environment. In this article, we will take a closer look at the captivating world of Sahara Desert…

Penguins Facts
Looking for some fascinating penguin facts? Look no further! Penguins are a unique and beloved species of birds that have captured the hearts of people around the world. Not only are they adorable and entertaining to watch, but they also play a vital role in the ecosystem as both predators and prey. In this article,…

Hippo Behavior
Hippo Behavior is a fascinating subject that sheds light on the intriguing ways in which these massive, semi-aquatic mammals interact with their environment and one another. Understanding the intricacies of Hippo Behavior is not only a matter of scientific curiosity but also a crucial element in the realm of wildlife conservation and management. From their…

Angel Sharks
Angel sharks, also known as Squatina, are a unique species of sharks that are classified under the family Squatinidae. They are known for their flattened bodies and broad pectoral fins, which give them a distinct angelic appearance. These sharks can be found in various locations around the world, from the coasts of the Mediterranean Sea…

Harrier Birds
Harrier Birds, with their remarkable hunting skills and graceful flight, hold a special place in the avian world. These birds of prey, belonging to the genus Circus, are known for their agility, adaptability, and vital role in maintaining ecological balance. In this article, we delve into the captivating world of Harrier Birds, exploring their taxonomy,…


The Brazilian Wandering Spider
The Brazilian Wandering Spider, also known as the armed spider or banana spider, is a venomous arachnid found in Central and South America. It is considered one of the most dangerous spiders in the world. The spider is medium to large in size, with a leg span of up to 6 inches. It has a hairy body, long and slender legs, and displays a variety of colors and patterns, including a distinctive red or orange mark on its abdomen. Unlike most spiders, it does not build a web; instead, it wanders the forest floor or hides in crevices during the day, making it particularly dangerous to humans.

Brazilian Wandering Spider Matchups
We use AI to simulate matchups between the Brazilian Wandering Spider and other animals. Our simulation considers size, strength, and natural predatory behaviors to determine the most likely outcome.

Brazilian Wandering Spider vs Brown Recluse Spider

Brazilian Wandering Spider vs Deathstalker Scorpion
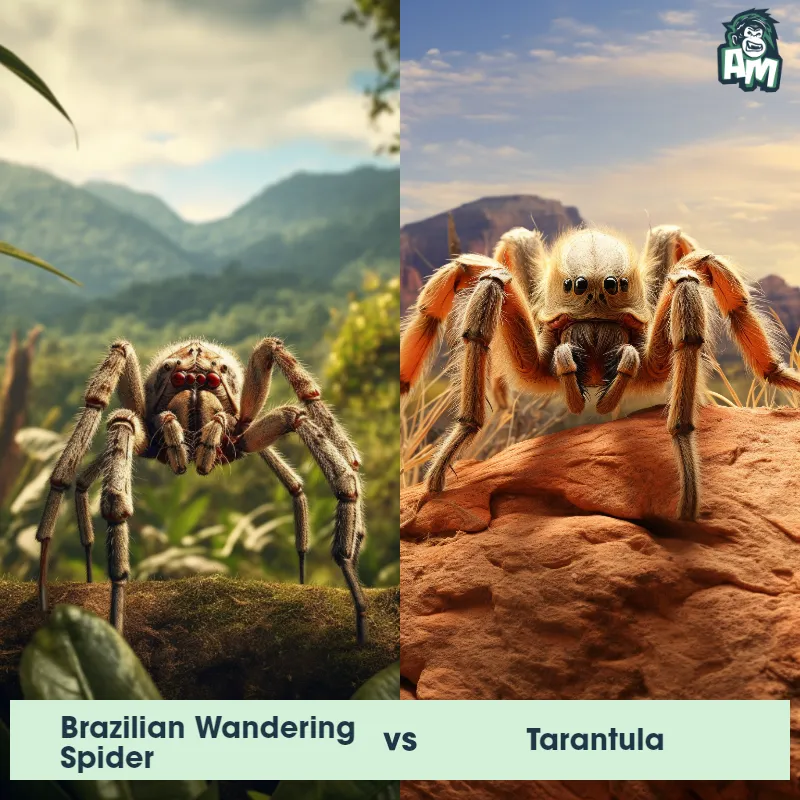

Brazilian Wandering Spider vs Tarantula

Can't find the Matchup you want?
Brazilian wandering spider : diet, predators, aggression, and defensive behaviors, what do brazilian wandering spiders eat.
Brazilian Wandering Spiders are carnivorous predators, feeding primarily on insects like crickets, cockroaches, and beetles. They are also known to hunt small vertebrates such as lizards, frogs, and mice. These spiders may also catch other spiders or even small snakes as prey. Their venom helps to immobilize and digest their food.
Do Brazilian Wandering Spiders have any predators?
While Brazilian Wandering Spiders are apex predators in their ecosystems, they do have some predators. Birds like owls and hawks have been observed preying on these spiders. Additionally, snakes and certain types of wasps are known to feed on these spiders. However, due to their venomous bite and agile movements, Brazilian Wandering Spiders are not an easy meal for most predators.
Are Brazilian Wandering Spiders aggressive?
Brazilian Wandering Spiders are known to be highly aggressive when threatened or provoked. They will not hesitate to bite if they feel cornered or in danger. However, they will typically give warning signs such as rearing up on their hind legs and exposing their fangs before attacking. It is important to exercise caution and avoid provoking these spiders in their natural habitat.
Do Brazilian Wandering Spiders fight with other species?
Brazilian Wandering Spiders are solitary creatures and will generally avoid confrontation with other spiders or animals, unless it is for hunting or self-defense. They are more likely to engage in combat with prey or potential threats than with members of their own species. However, if two male Brazilian Wandering Spiders encounter each other during mating season, they may engage in a territorial dispute.
How do Brazilian Wandering Spiders defend themselves?
When faced with a threat, Brazilian Wandering Spiders have several defense mechanisms at their disposal. They may exhibit aggressive behavior, raising their front legs and exposing their fangs as a warning. If this does not deter the threat, they are capable of delivering a venomous bite that can cause severe pain and potentially be fatal to humans. Additionally, these spiders are agile and quick, enabling them to evade predators or escape dangerous situations.
What is the biggest weakness of Brazilian Wandering Spiders in a fight?
Despite their potent venom and aggressive nature, Brazilian Wandering Spiders have a vulnerability in their soft exoskeleton. Their bodies are not as robust as some other arachnid species, making them more susceptible to physical damage in a fight. Predators that can overpower them with sheer strength, like large birds or snakes, may pose a serious threat to these spiders. Additionally, injuries sustained in combat can hinder their ability to hunt and survive in their environment.
Fun Fact : This spider has been listed in the Guinness World Records as the world's most venomous spider, as its venom can cause severe pain, swelling, and even paralysis or death in humans if untreated.
Fun Fact : Male Brazilian Wandering Spiders often exhibit a unique and fascinating courtship ritual, which involves drumming or tapping their legs on the leaves to attract females, showcasing their agility and fitness in the process.
Explore More Animals

Invertebrates


Brazilian wandering spider | bite,Size, Habitat, & Facts
Brazilian wandering spider.
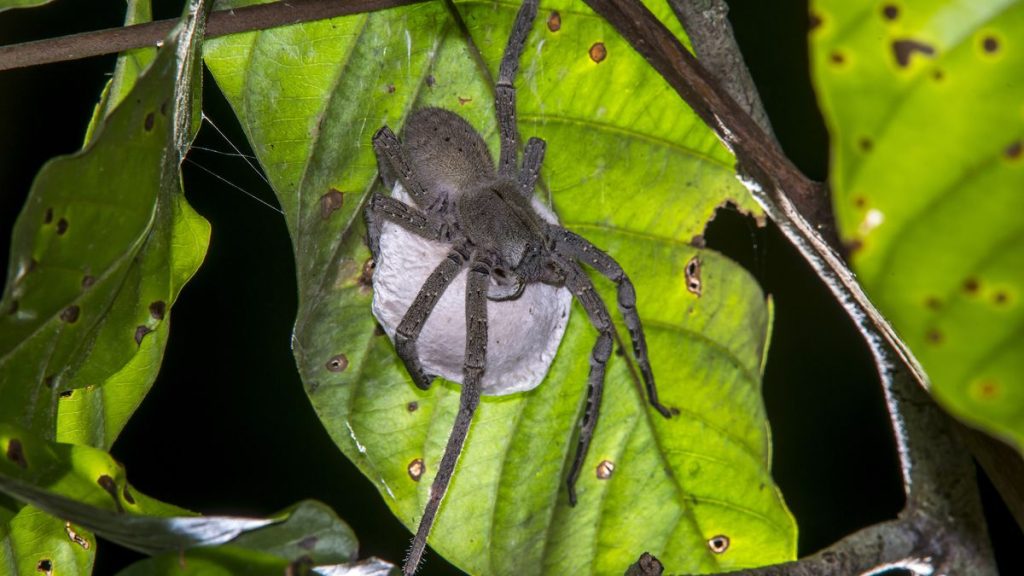

brazilian wandering spider size
Their body length ranges from 17 to 48 mm (43⁄64 to 1+57⁄64 in). Phoneutria are impressive spiders reaching body sizes up to 3.5 centimeters and leg spans up to 15 centimeters. They are nocturnal, hunting at night, and hiding in dark places during the day.
Wandering spider bite
Along with other members of the genus, they are often referred to as Brazilian wandering spiders. Its bite can cause severe symptoms, including increased pulse, blood pressure, and respiratory rate; extraordinary pain; penile erection that lasts for several hours; and, in several documented cases, death.
Phoneutria spp. is actually a genus with five known similar species whose members are highly venomous. They include some of the relatively few species of spiders that present a threat to human beings. The Brazilian Wandering Spider (Phoneutria fera) can grow to have a leg span of up to 4-5 inches.
Wandering spider, (family Ctenidae), any member of the family Ctenidae (order Araneida), a small group of large spiders of mainly tropical and subtropical regions, commonly found on foliage and on the ground.
The Brazilian wandering spiders, Phoneutria fera and P. nigriventer, are sometimes also referred to as banana spiders because they are frequently found on banana leaves. They have an aggressive defense posture, in which they raise their front legs straight up into the air. Phoneutria are venomous, and their venom is toxic to the nervous system, causing symptoms such as salivation, irregular heartbeat, and prolonged painful erections (priapism) in men. Scientists are investigating the venom of P. nigriventer as a possible treatment for erectile dysfunction.
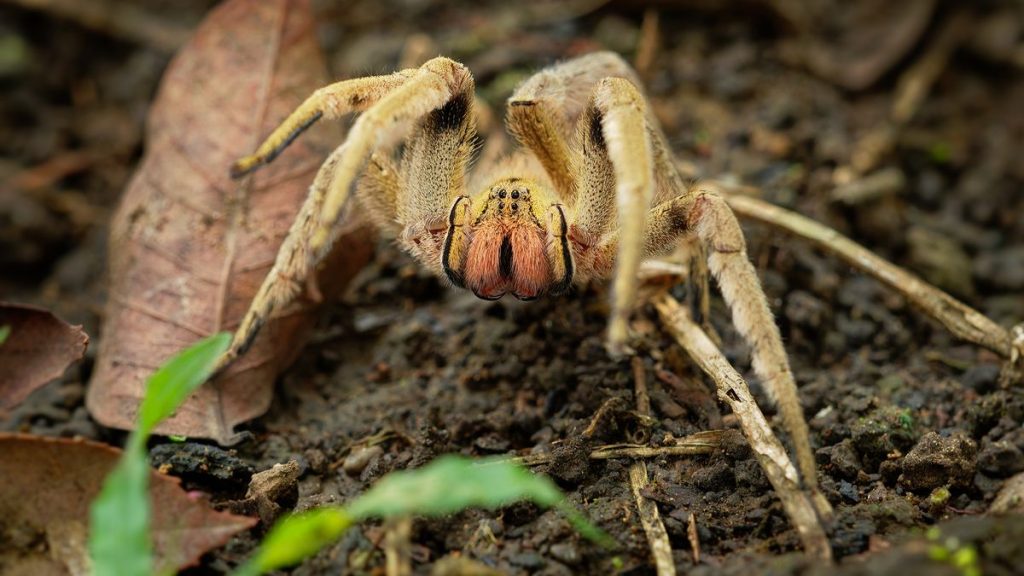

These spiders are notorious both due to their toxic venom, and because they are not reluctant to attack people who appear threatening.
Of the five species known, P. nigriventer and P. fera most frequently receive mention in mass-media publications. P.nigriventer species are responsible for most cases of venom intoxication in Brazil because this species is commonly found in highly populated areas of Brazil, namely the South-eastern states: São Paulo, Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro and Espírito Santo.The P. fera is native to the northern portion of South America, especially the Brazilian Amazônia, Venezuela and French Guiana.

Brazilian wandering spider BITES AND VENOMB
razilian wandering spiders’ venom is a complex cocktail of toxins, proteins and peptides, according to the Natural History Museum in Karlsruhe, Germany. The venom affects ion channels and chemical receptors in victims’ neuromuscular systems.
After a human is bitten by one of these spiders, he or she may experience initial symptoms such as severe burning pain at the site of the bite, sweating and goosebumps, Sewlal said. Within 30 minutes, symptoms become systemic and include high or low blood pressure, fast or a slow heart rate, nausea, abdominal cramping, hypothermia, vertigo, blurred vision, convulsions and excessive sweating associated with shock. People who are bitten by a Brazilian wandering spider should seek medical attention immediately.
Recent studies suggest that these spiders only inject venom in approximately one-third of their bites and may only inject a small amount in another third. However, research in this area is hindered by the difficulty of identifying particular subspecies. Thus the effects of the bites from these spiders are hard to predict when based on sketchy information or if the spider has not been identified definitively.
Bites from these spiders may result in only a couple of painful pinpricks to full-blown envenomation. In either case, people bitten by a Phoneutria or any Ctenid should seek immediate emergency treatment as the venom is possibly life threatening.
he Phoneutria fera and nigriventer are the two most commonly implicated as the most virulent of the Phoneutria spiders. The Phoneutria not only has a potent neurotoxin, but is reported to have one of the most excruciatingly painful envenomations of all spiders due to its high concentration of serotonin.
Brazilian Wandering Spiders are extremely fast, extremely venomous, and extremely aggressive and are ranked among the most venomous spiders known to man. In fact, the Brazilian Wandering Spider is the most venomous spider in the New World! In South America, these true spiders are commonly encountered in peoples’ homes, supposedly hiding in peoples’ shoes, hats, and other clothes. It does not remain on a web, rather, it wanders the forest floor, which is how it got its name.
The Brazilian Wandering Spider has another name – the Banana Spider and it was given this name because there have been cases where these spiders unintentionally appeared on banana boats heading for the United States.
Brazilian Wandering Spider: One Of The World’s Most Venomous Spiders May Be Lurking In Your Bananas
Meet the Brazilian wandering spiders in the genus Phoneutria, also referred to as the armed spiders or the banana spiders. The members of this group have one of the most dangerous bites of any spider species on Earth and they have been classified as the world’s most venomous spider many times.

What Are The Effects Of A Brazilian Wandering Spider Bite?
Brazilian wandering spiders often make the news because of the unusual symptoms caused to humans after being bitten by one.
A 2023 study in Frontiers In Molecular Biosciences suggested there were around 4,000 cases of people being bitten by Phoneutria nigriventer in Brazil each year. Their venom affects the nervous system, causing double vision, salvation, irregular heartbeat – and even prolonged painful erections, known as priapism. In fact, because of this, their venom is being explored as a possible treatment for erectile dysfunction conditions.
Can A Brazilian Wandering Spider Bite Kill You?
The neurotoxin PhTx3 is to blame for these symptoms, and according to the Independent, a wandering spider bite can reportedly be fatal in as little as 60 minutes. However, an effective anti-venom is usually enough to save those affected. A study into Phoneutria boliviensis in 2019 suggested that the species had adapted its venom to catch vertebrates as opposed to lizards and amphibians, which might explain why the venom is so toxic to humans.
black and yellow garden spider
Brown recluse spider bite stages pictures.

Brazilian Wandering Spider: Care, Food, Habitat & Preventions
Mike Wallace
Have you ever heard of or do you know what a Brazilian wandering spider is ? It is a big venomous spider from places like Central and South America, and people sometimes call it the banana spider . Why? Well, we are about to find out!
Table of Contents
These wandering spiders are aggressive hunters who go out on the hunt at night. Their meals include both invertebrates (like insects) and vertebrates (creatures with a backbone, like small animals).
These spiders are super dangerous because their venom is like a powerful potion that can make people really sick or even worse. They usually hang out in tropical rainforests and even in cities, hiding in banana plants.
So, let’s get more information about the world of this sneaky spider to learn the details about its looks, eating habits, where it lives, the venom it carries, and find out if it is genuinely risky. Ready to explore? Keep reading!
Brazilian Wandering Spider Description:
Scientific name and family:.
In Brazil, they are sometimes known as “ armed spiders ” (armadeiras), and they share the name “ banana spiders ” with a few other spiders. They have different names, but they are all talking about the same interesting spider!
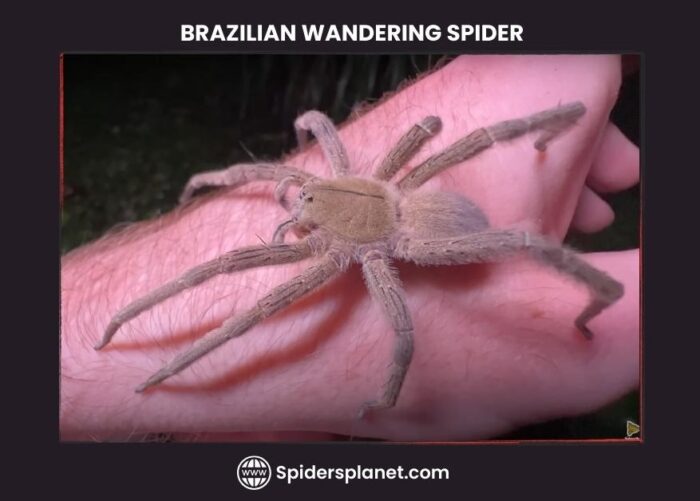

The Brazilian wandering spider, scientifically known as Phoneutria , Maximilian Perty kickstarted the Phoneutria genus in 1833. The name comes from the Greek word φονεύτρια , which means “murderess” and falls under the Animalia kingdom, Arthropoda phylum, and Arachnida class.
Within Arachnida, it is classified in the order Araneae, infraorder Araneomorphae, and Ctenidae family. The genus Phoneutria, described by Perty in 1833, includes the type species Phoneutria fera .
This classification helps us understand where these spiders fit into the larger picture of living organisms.
The following 9 species are accepted by The World Spider Catalog :
- Phoneutria bahiensis
- Phoneutria boliviensis
- Phoneutria eickstedtae
- Phoneutria fera
- Phoneutria keyserlingi
- Phoneutria nigriventer
- Phoneutria pertyi
- Phoneutria reidyi
- Phoneutria depilata
What do Brazilian Wandering Spider look like?
Size range:.
The spiders in the Phoneutria group can get pretty big in size. Their legs can stretch out to be 13 to 18 centimeters (5 to 7 inches) wide, and their bodies can have a range between 17 to 48 millimeters (a little more than half an inch to almost 2 inches) long.
The female Brazilian spiders can get pretty big, reaching up to 15 centimeters (5.9 inches) in length. On the other hand, the males are smaller, usually measuring around 7 centimeters (2.8 inches). They usually weigh up to 0.21 ounces.
They have long, slender legs, and even though some other spiders with different names might have longer legs, the Phoneutria spiders are champions when it comes to having the longest bodies and being the heaviest in their spider gang.
The spider’s body has two main parts. The first is the prosoma, kind of like its “head,” where you will find all eight legs, eyes, fangs (chelicera), and little multitasking arms (pedipalps).
The second part is the opisthosoma, holding the spinnerets for making silk, the back end opening (anal opening), “the lungs,” the heart, and the important bits for making baby spiders (reproductive organs).
So, the prosoma is like the front control center, and the opisthosoma is like the back office, handling things like silk-making and baby-making.
Brazilian spiders come in different colors, with most being hairy and shades of brown and gray. Some species may have lightly colored spots on their abdomen.
A distinctive feature of many species is the presence of bands of black and yellow or white on the underside of their two front legs.
Identification:
To identify a spider from the Phoneutria group, look for a dense brush of fine hairs on their leg parts. They might seem like other spiders, especially Cupiennius , but here is how you can differentiate:
- Phoneutria often have a dark line on the front of their palps and a thin black line on top of their head.
- Check underneath, too; their legs usually have dark parts and light joints. Sometimes, the belly has black dots or is reddish.
- Usually it has been observed that when they are upset, they do a cool defensive move like lifting their front legs high with a distinctive pattern. So, if you see a spider doing that dance, it is probably a Phoneutria!
Brazilian Wandering Spiders live all over the Americas, from Costa Rica to northern Argentina. They are like the residents of the jungle, chilling in forests east of the Andes in countries like Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay, and the Guianas.
Some, like P. reidyi, P. boliviensis, and P. fera, love the Amazon rainforest, while others prefer the Atlantic Forest in Argentina, Paraguay, and Brazil.
They have also made themselves at home in the Cerrado savanna. But if you head to northeastern Brazil, they are not around. These spiders have even taken trips to Chile and Uruguay.
Why are they called Banana Spiders?
These spiders are linked with bananas. Richard S. Vetter, a researcher at the University of California, found that these powerful spiders sometimes end up in North America and Europe by accident, hitching a ride in banana shipments.
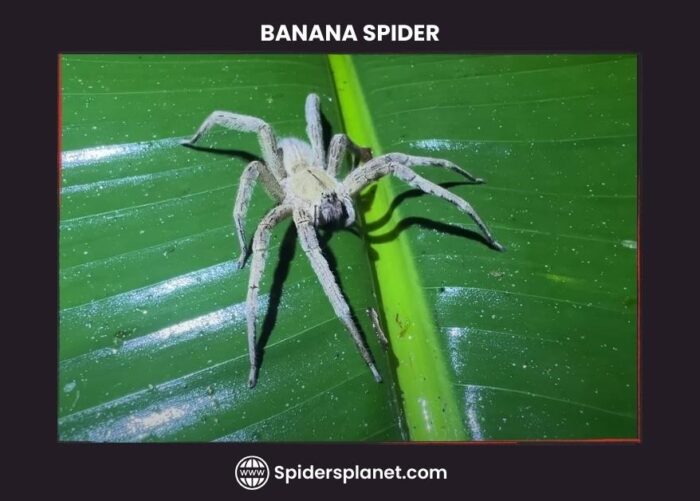

But it is often a case of mistaken identity. Only a few Phoneutria species have been found in banana shipments, and sometimes, other spiders get the blame due to misidentification.
What They Like to Eat or Hunt?
Their food includes flies, beetles, butterflies, moths, grasshoppers, locusts, and crickets. Occasionally, they might even feast on small creatures like amphibians, reptiles, or mice. All these diet or food findings tell us about how diversified eating habits these fascinating spiders have.
Mating and Lifecycle:
Like most spiders, the female spiders are bigger than the males. When the male spider wants to be friends, they do a little dance (vibrating his pedipalps and specialized sensory appendages) to signal his intentions to impress the female, but it is a cautious approach.
The behavior of the female can be choosy, and she might say no to a few before picking the right one.
After the dance, sometimes, the females decide to attack them, or if she is interested, she can store the male’s baby-making material in a special place until she is ready to use it.
Then, she lays a bunch of eggs, up to 1,000 at a time, and keeps them safe in a silk egg sac. Sadly, after laying her eggs, the mom spider says goodbye. It is her way of making sure the new spiders are ready to explore the world on their own.
The lifespan of the banana spider (Phoneutria nigriventer) differs for males and females. Females usually live for 6 to 8 weeks after reaching maturity, while males have a shorter lifespan of 2 to 3 weeks after their last molt.
Certain mammals, like coatis (Procyonidae, which includes raccoons) and other small insectivores, birds are potential predators of large wandering spiders.
These spiders got their name as wandering spiders because of the fact that they are not into web building. Instead, they stroll around the forest floor at night(nocturnal), searching for dinner.
Brazilian Wandering Spiders are active hunters and use both ambush tactics and direct attacks to catch their prey. During the day, they prefer cozy spots like under logs or in crevices, only emerging at night for their hunting adventures. These spiders do not build nests like other spider species.
While wandering spiders are not naturally aggressive towards humans, they won’t hesitate to bite if they feel cornered or threatened. Most bites happen when a spider accidentally gets trapped in clothing or bedding.
Bite and Venom:
The bite of the armed spider is the most dangerous in the world as the venom it carries can be harmful to humans.
The danger is not just about how strong the venom is; it is also about factors like the spider’s likelihood to bite and how close it is to where people live.
These spiders often hide in houses, clothes, and other dark places during the day, making accidental bites more likely.
While their fangs are adapted for small prey, some experts think they might give a “dry” bite in defense to save venom. Studies suggest that not all bites inject venom, and serious cases requiring antivenom are rare.
However, there have been confirmed cases of death, with symptoms appearing quickly, including:
- Severe pain
- Breathing difficulties
- Increased heart rate and blood pressure
- In severe cases, paralysis and death
The severity can depend on the spider’s sex, with females generally more dangerous. The spiders produce less venom in colder months, and a small amount can be potent enough to harm.
Fortunately, bites from Brazilian spiders are rare, and when they do occur, the exposure to the toxins is generally mild, as explained by Vetter.
Also Read: What is a Huntsman Spider? (Heteropodidae) – The Ultimate Guide
Banana Spider’s Facts:
Below are essential details about Brazilian wandering spiders:
- They hold the title for the world’s largest spiders , boasting leg spans reaching up to 15 centimeters (6 inches).
- Their venom packs a powerful punch, capable of inducing severe pain, paralysis, and, in extreme cases, fatal outcomes for humans.
- Despite their intimidating reputation, they are generally non-aggressive and resort to biting only when provoked.
- These spiders inhabit tropical rainforests and urban areas across Central and South America.
- In case someone has been bitten by this spider, he/she needs quick medical treatment to control the effects timely.
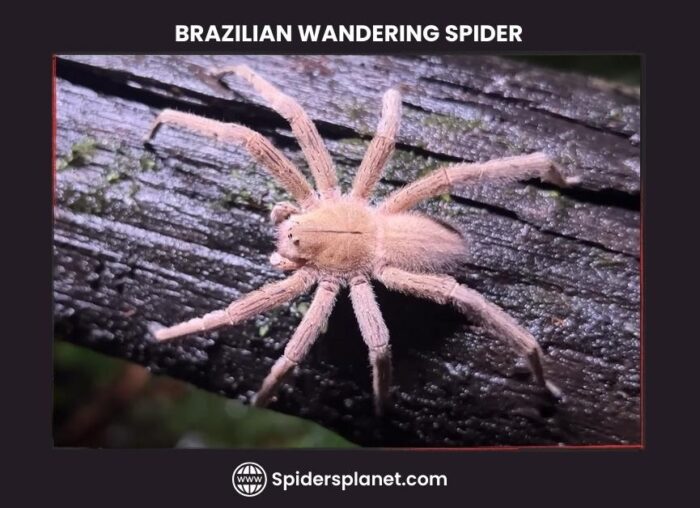

Treatment and Preventive Measures:
If bitten by a wandering spider or armed spiders, prompt medical attention is crucial. There is an antivenom for the spider’s venom, but its effectiveness is highest when administered within a few hours of the bite.
To prevent a bite:
- Wear protective clothing, use shoes and long pants when in areas where these spiders are found.
- Before wearing your clothes and shoes, make sure to check them to ensure no spiders are hiding.
- Maintain cleanliness and avoid leaving food or garbage exposed, as this can attract spiders.
These preventive measures are essential for minimizing the risk of encountering and getting bitten by Banana spiders.
Can Brazilian spiders kill humans?
Brazilian wandering spiders (Phoneutria nigriventer) are venomous and can potentially kill a human with a single bite. Their venom contains a potent neurotoxin that can cause severe pain, paralysis, and even death.
Are Brazilian spiders poisonous?
Yes the venom of this spider is poisonous, that can cause death. While Brazilian wandering spiders are potentially dangerous, actual bites are relatively rare.
By adopting preventive measures and promptly seeking medical attention if bitten, the risk of serious complications can be significantly reduced.
Can you keep Brazilian spiders as pets?
It is strongly advised against keeping wandering spiders as pets due to their venomous nature and the potential risk to human safety.
Managing these spiders in captivity demands specialized knowledge and handling procedures to minimize the risk of bites.
Final Thoughts:
The Brazilian wandering spider, banana spider, or armed spider is a large and venomous arachnid found in Central and South America. While their potent venom can be harmful to humans, encounters are rare.
These nocturnal hunters have adopted various habitats, from rainforests to urban areas, and are associated with banana shipments. Understanding their appearance, behavior, and habitat is crucial for minimizing risks.
Seeking immediate medical attention after a bite is essential, as antivenom is available but most effective when administered promptly. Despite their fearsome reputation, the Brazilian spider remains a captivating and potentially dangerous species.
About the author
Spiders Planet is the ultimate source of information about spiders! All the articles on this site will provide you with the most accurate and up-to-date information written by me and a group of writers, that is well-researched and fact-checked before it’s published.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Latest posts

Do Spiders Eat Fruit? Unveiling the Secrets
The connection between animals and fruits showcases a captivating example of mutualism, a win-win relationship where both parties benefit. Animals gain access to…

Are Woodlouse Spiders Venomous?
The Woodlouse spider (Dysdera crocata) is a spider species that mainly hunts and feeds on woodlice and is mostly found in Africa, Asia,…

What Does Wolf Spiders Eat?
Wolf spiders are excellent hunters of small insects. Unlike spiders that weave intricate webs, these predators rely on sharp vision and stealthy moves…
- MORE Rabbits & Furry Friends Fish Horses Other Pets Random Article
- Rabbits & Furry Friends
How to Identify a Brazilian Wandering Spider
Last Updated: February 12, 2021 Approved
This article was co-authored by wikiHow Staff . Our trained team of editors and researchers validate articles for accuracy and comprehensiveness. wikiHow's Content Management Team carefully monitors the work from our editorial staff to ensure that each article is backed by trusted research and meets our high quality standards. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 93% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 133,533 times.
The Brazilian wandering spider is a large, hairy spider that lives in South and Central America. It’s considered the most venomous spider in the world. Since these spiders sometimes wander right into towns, cities, and shipments of fruit, it’s important to be able to recognize this spider and know its habitat. If you happen to be bitten, you should get immediate medical attention. Don’t panic, however! These bites can almost always be treated.
Recognizing a Brazilian Wandering Spider

- Some spiders may be more yellowish than brown. Others may appear to have black legs, or black bands on brown legs. [3] X Research source

- Do not try to trap this spider. Call animal control professionals if you think you have one in your home or outdoor buildings, and leave those buildings while you wait for help.
Being Aware of Their Habitats

- Small, unlit closets or nooks in homes
- Outdoor sheds and garages
- Unused clothes, shoes, or gloves
- Boxes of food in pantries
- Boxes in attics or garages

Avoiding a Bite

- If a spider falls out, don’t panic. Back away slowly and leave the area.

- You can also spray bug and spider repellant around doors and windows to ward off creepy crawlies.

Treating a Bite

- In men, these bites can also cause a long and painful erection.

Community Q&A
- Keep in mind that these spiders prefer to wander along the ground. Always wear sturdy shoes if you are in an area where these spiders are known to live. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- These spiders are highly dangerous and should not be approached or provoked unless you are an expert such as an entomologist. They are recognized as one of the most dangerous spiders in the world and are the most venomous so they should always be treated with care and respect. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- Children are more susceptible than adults to the venom of a Brazilian wandering spider, and you should ensure that any child who’s bitten gets medical attention as quickly as possible. Thanks Helpful 6 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.livescience.com/41591-brazilian-wandering-spiders.html
- ↑ http://www.wandering-spiders.net/phoneutria/gallery/
- ↑ https://animalcorner.co.uk/animals/brazilian-wandering-spider/
- ↑ http://bioweb.uwlax.edu/bio203/s2013/johnson_jor4/habitat.htm
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/spider-bites/manage/ptc-20204189
- ↑ https://www.livescience.com/37974-he-surprising-cause-of-most-spider-bites.html
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-spider-bites/basics/art-20056618
- ↑ http://www.webmd.com/first-aid/snakebite-treatment
About this article

To identify a Brazilian wandering spider, look for a spider with a long leg span of about 6 inches and a brown, hairy body. Also, carefully examine the spider from afar to see if it has large red fangs, which are common in Brazilian wandering spiders. Keep in mind that Brazilian wandering spiders only live in South and Central America. If you encounter one, move away slowly since Brazilian wandering spiders are aggressive and very poisonous. To learn how to avoid getting bitten by a Brazilian wandering spider, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
Reader Success Stories
Xhulia Xhaferri
Apr 5, 2016
Did this article help you?
Meradydd Scott
Apr 25, 2018

- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info

A home for Tarantula, Spider, Scorpion and Arachnid Enthusiasts.

Brazilian Wandering Spider size: how big do they get?
As an avid arachnid enthusiast, my fascination with these eight-legged creatures knows no bounds. There’s something utterly captivating about their intricate web-weaving capabilities, their exceptional survival strategies, and of course, their range of sizes and appearances. But amongst this vast collection of species, one has particularly piqued my interest – the Brazilian Wandering Spider.
Arguably one of the most notorious names in the world of arachnids, the Brazilian Wandering Spider, holds a firm position at the pinnacle of spider folklore. Their reputation extends far beyond their native tropical South American rainforests, captivating the minds of arachnologists and laymen alike around the globe.
What sets this spider apart in the arachnid world? It’s not just its venomous nature – it’s also its astonishing size. The dimensions of the Brazilian Wandering Spider are a spectacle in themselves.
How big are Brazilian Wandering Spiders?
Picture this: a spider so large that it could comfortably cover an average dinner plate. That’s right – the Brazilian Wandering Spider can grow to an impressive leg span of up to 7 inches , or approximately 18 cm, with females tending to be larger than the males.
To put this into perspective, that’s around half the size of an average adult human’s face! The body length of these spiders can reach up to 2 inches, or around 5 cm. This considerable size, coupled with their highly potent venom, makes them a formidable presence in their habitats.
But as an arachnid hobbyist, the allure of the Brazilian Wandering Spider’s size lies not in its potential threat, but in the fascinating evolutionary adaptations that have allowed it to grow to such an impressive scale.
The advantage of large size for a cursorial hunter
From an evolutionary standpoint, the Brazilian Wandering Spider’s significant size offers multiple advantages. For starters, their considerable size allows them to subdue and consume a larger variety of prey, including insects, other spiders, and sometimes even small amphibians and reptiles. This dietary diversity is a testament to their adaptability and survival prowess.
However, the size of these spiders is not solely an indicator of their hunting prowess. It also reveals a fascinating aspect of their biology. The Brazilian Wandering Spider, unlike some smaller spider species, does not weave a web to capture its prey. Instead, as their name suggests, they wander in search of food, relying on their size and strength to overpower their prey. This is called cursorial hunting .
Their size also plays a crucial role in their mating rituals. Male Brazilian Wandering Spiders, despite being smaller than their female counterparts, engage in a daring dance of danger during mating. They utilize their size and strength to lift the larger female’s body to prevent her from eating him – a gruesome but prevalent behavior known as sexual cannibalism in the arachnid world.
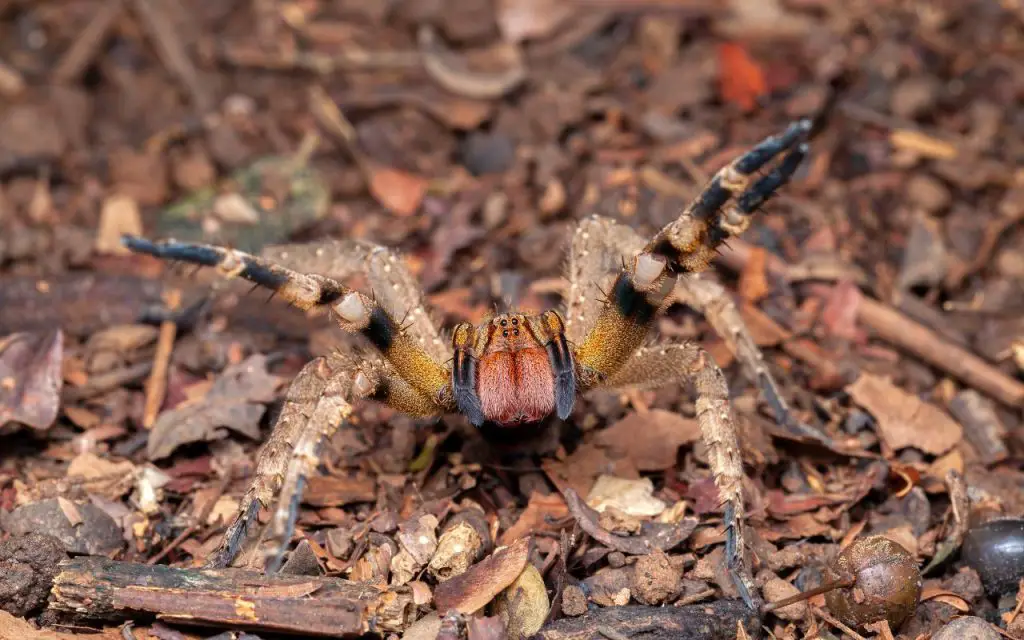

Size relates to the biology of the Wandering Spider
The Brazilian Wandering Spider’s size, therefore, is much more than just an intimidating factor. It’s a key to understanding their hunting methods, their mating rituals, and their overall survival strategy. Each inch adds to the mystique of these extraordinary creatures and deepens our understanding of the diverse world of arachnids.
The Brazilian Wandering Spider is undeniably a creature of fascination. From its substantial size to its potent venom, it’s a spider that demands respect. Whether you’re an arachnid hobbyist like me, or just someone intrigued by the wonders of the natural world, the Brazilian Wandering Spider offers a fascinating insight into the awe-inspiring world of arachnids.
Final thoughts…
In conclusion, the world of spiders is as vast and varied as the creatures themselves. The Brazilian Wandering Spider, with its impressive size, offers a fascinating window into this world. It’s a testament to the incredible diversity of life on Earth and a reminder of the intricate balance that governs our ecosystems.
My fascination with spiders continues to grow, much like the impressive size of the Brazilian Wandering Spider. And while their size may be a source of fear for some, for me, it only fuels my passion and curiosity about these fascinating creatures. After all, understanding is the first step to appreciation, and these giant spiders deserve nothing less.
Whether you’re a fellow arachnid enthusiast or just passing by, I hope this deep-dive into the size of the Brazilian Wandering Spider has sparked your curiosity. So the next time you hear about this giant spider, remember, there’s more to its size than meets the eye!
If you’d like to learn more about these spiders, check out my article on Brazilian Wandering Spider facts .
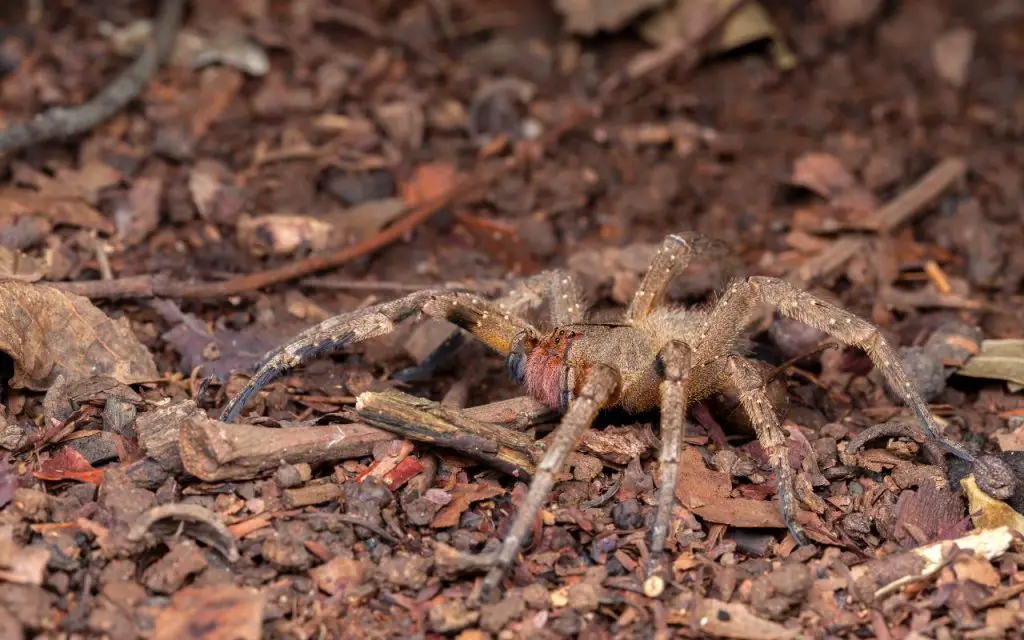

FAQ related to Brazilian Wandering Spider Size
How bad is a brazilian wandering spider bite.
A Brazilian Wandering Spider bite is considered a medical emergency. If you have a suspected or confirmed bite, your first move should be to contact the emergency services. Upon reaching you, they will determine whether to administer antivenom, and how to proceed with treatment. Fortunately, deaths are very rare, and the antivenom is widely available in South America.
Is a banana spider the same as a Brazilian wandering spider?
The common name of “Banana Spider” is used for a few species, not just the Brazilian Wandering Spider. For example, the Golden Silk Orb Weaver is often referred to as a banana spider, despite being completely unrelated. If you wish to find out if a spider is venomous, always rely on its scientific, or binomial name, rather than common names.
Where do Brazilian wandering spiders hide?
Brazilian Wandering Spiders are nocturnal hunters, and generally prefer to shy away from daylight. This means they often hide in the shadiest places they can find, either indoors or outdoors. For example, under a log or in leaf litter would be a perfect place outdoors. Indoors, they will try to hid behind or under furniture, or in dark corners.
What is the world’s biggest Brazilian wandering spider?
There are around 40 species of Wandering Spider, but the largest, and most infamous are those that we call the Brazilian Wandering Spider. This name is in fact commonly ascribed to two species: Phoneutria nigriventer and Phoneutria fera. Both of these spiders can reach at least 6 inches (15cm) in legspan.
Related Posts:

Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


- Orb Weavers
- Jumping Spiders
- Cobweb Spiders
- Huntsman Spiders
- Wolf Spiders
- Sicariidae Spiders
- Funnel Weaver Spiders
- Crab Spiders
- Nursery Web Spiders
- Spiders in US
- Parts of a Spider
- Life Cycle of a Spider
- Where do Spiders Live
- What do Spiders Eat
- How long do Spiders Live
- Where do Spiders go in Winter
- Spider Ballooning
- Spider Molting
- Spider Eyes
- Spider Predators

Wandering Spiders
Wandering spiders is the name given to the species of the Ctenidae family having about 50 genera. The most popular species of this group is the Brazilian Wandering spider.
Spiders Belonging To This Family
- Afroneutria
- Chococtenus
- Wiedenmeyeria
- Brazilian Wandering
- Southeastern Wandering
- Phoneutria keyserlingi
- Cupiennius chiapanensis
- Phoneutria fera
- Cupiennius salei
- Ctenus villasboasi
- Ctenus hibernalis
- Phoneutria pertyi
- Phoneutria nigriventer
Physical Description & Identification
Size: They have a moderately small body, being about 5 cm (2 inches) long.
Color: Most spiders of this family have a brown body.
Other characteristics: The upper part of the oval carapace of this species possess a longitudinal groove.
They are small in size and enclosed in a white sac.
Spiderlings
The spiderlings stay with the mother for a short span until maturity.
Though not much detail is available, most members of this family like the Brazilian Wandering spider do not build webs. They search for their pray by roaming around the jungle floor.
Are Species of the Wandering Spider Family Poisonous and Do They Bite
The members of the wandering spider family are venomous, though those belonging to the Phoneutria genus tops the list and are known to have hazardous effects on humans.
Quick Facts
Did you know.
- They have a defensive strategy, being highly notorious as hunters.
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
UK Edition Change
- UK Politics
- News Videos
- Paris 2024 Olympics
- Rugby Union
- Sport Videos
- John Rentoul
- Mary Dejevsky
- Andrew Grice
- Sean O’Grady
- Photography
- Theatre & Dance
- Culture Videos
- Fitness & Wellbeing
- Food & Drink
- Health & Families
- Royal Family
- Electric Vehicles
- Car Insurance Deals
- Lifestyle Videos
- UK Hotel Reviews
- News & Advice
- Simon Calder
- Australia & New Zealand
- South America
- C. America & Caribbean
- Middle East
- Politics Explained
- News Analysis
- Today’s Edition
- Home & Garden
- Broadband deals
- Fashion & Beauty
- Travel & Outdoors
- Sports & Fitness
- Sustainable Living
- Climate Videos
- Solar Panels
- Behind The Headlines
- On The Ground
- Decomplicated
- You Ask The Questions
- Binge Watch
- Travel Smart
- Watch on your TV
- Crosswords & Puzzles
- Most Commented
- Newsletters
- Ask Me Anything
- Virtual Events
- Betting Sites
- Online Casinos
- Wine Offers
Thank you for registering
Please refresh the page or navigate to another page on the site to be automatically logged in Please refresh your browser to be logged in
Brazilian wandering spider: Where are they from and how deadly are they?
One was found in a bunch of supermarket bananas in london, article bookmarked.
Find your bookmarks in your Independent Premium section, under my profile
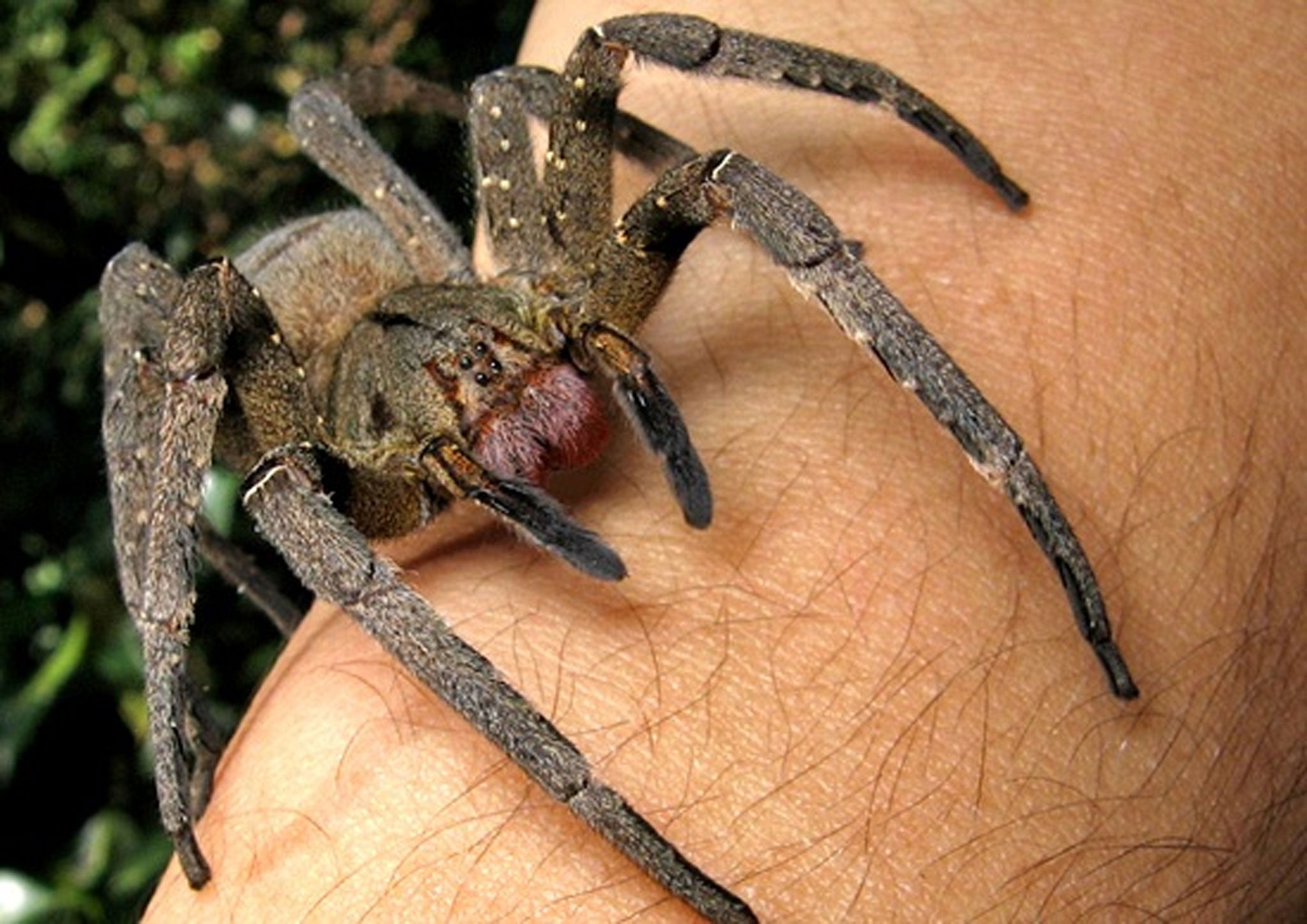

Sign up to the Independent Climate email for the latest advice on saving the planet
Get our free climate email, thanks for signing up to the independent climate email.
The world’s most venomous spider has been delivered to a south London home in a bunch of bananas.
Specialists were called in to trap the Brazilian wandering spider, which ripped its leg off in a bid to escape and left an egg sac full of thousands of baby spiders behind.
The family who received the deadly arachnid in their Waitrose online shop told the Mail on Sunday they were “too traumatised to remain in the house”, while the supermarket apologised for the “distressing” incident.
It was not the first time a Brazilian wandering spider made the long journey to the UK.
In 2005, a chef in Somerset was bitten by a stowaway that had been hiding in bananas delivered to his pub.
He was saved by anti-venom administered after a nearby zoo identified the arachnid from a picture he took on his phone before passing out.
The spiders and their eggs have also been found in bananas from a Tesco in Essex and One Stop in Staffordshire.
Where are they from?
Fortunately, it is very rare to find Brazilian wandering spiders in the UK or anywhere outside their natural habitat in South America.
They live in the forests of Costa Rica, Columbia, Peru, Brazil, and Paraguay and gain their name from the habit of moving across jungle floors at night in search of food.
In the day, they like hiding in places that are dark and moist and are known to favour piles of wood, garages, cupboards, shoes and even heaps of clothes.
The apparent tendency to hide in banana bunches – like in the latest incident – has given them the nickname “banana spider”.
Their scientific name translates as “murderess” in Greek and they are also known as the “armed spider”, because of their unusual attacking stance, and “horse stinger”.
How deadly is it?
The Guinness Book of World Records has named it the most venomous spider in the world for possessing the most active neurotoxic venom of any living spider.
The toxin PhTx3 causes extreme pain, swelling, paralysis, skin cell destruction, fatal breathing complications, heart attacks and painful erections (priapism) in men lasting up to four-hours.
Victims of a Brazilian wandering spider bite can reportedly be killed in an hour.
But few deaths occur because an effective anti-venom is available in Brazil and Guinness claims that people are killed, it is usually in children under the age of seven.
Scientists have reportedly considered investigating the use of the deadly venom as a possible ingredient for drugs treating erectile dysfunction.
What do Brazilian wandering spiders look like?
There are eight known species, with the most dangerous being the Phoneutria fera and the Phoneutria nigriventer.
All vary slightly in appearance but are known for their size, with a leg span of up to 15 cm (6 ins) and body length of up to 5 cm (2 ins).
They are covered with hair and usually dark brown in colour, with some displaying bright red hairs on their venom glands.
When Brazilian wandering spiders feel threatened, they adopt a distinctive “attacking” stance with their front legs in the air, swaying from side to side.
How do they attack?
The spiders use bites as their main form of attack but do not always deliver venom, using it only in an estimated third of bites.
They eat insects and small mammals, including other spiders, amphibians, reptiles and mice, hunting them on the ground and killing with an ambush or direct attack.

Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Subscribe to Independent Premium to bookmark this article
Want to bookmark your favourite articles and stories to read or reference later? Start your Independent Premium subscription today.
New to The Independent?
Or if you would prefer:
Want an ad-free experience?
Hi {{indy.fullName}}
- My Independent Premium
- Account details
- Help centre
- Check availability
- Book online
- Posada Amazonas
- Refugio Amazonas
- Tambopata Research Center
- Jungle Lodge Comparison Chart
- What to bring
- All You Need To Know About Travel To Tambopata
- Tambopata National Reserve
- The Wildlife
- Amazon Tours
- Accessible Amazon – Virtual Experiences
- Canopy Tower
- AmazonCam Tambopata – Citizen science
- Chuncho Macaw Clay Lick
- Discovering New Species
- See All Activities
- Travel offers
- Wired Amazon Program
- Ese Eja Native Community of Infierno
- Traveling sustainable

FACTS ABOUT Wandering spider
Brazilian wandering spider
Phoneutria genus.
BACK TO ALL WILDLIFE
Did you know? Our Rainforest Expeditions guests find the relatives of these shy, eight-legged creatures on night hikes!
Brazilian wandering spider fun facts.
- Most toxic spider venom is known : The venom of at least one species of Phoneutria is much more toxic than the Black Widow Spider and can easily kill mice with one bite. Human fatalities in Brazil are an extremely rare occurrence.
- No web : Unlike many other spiders, the wandering spiders don’t build webs but actively search for their prey.
- The banana spider : Wandering spiders occasionally turn up in shipments of bananas! One such stowaway actually bit a man in England in 2005. He survived but spent a week in the hospital!
- Understory predator : These spiders are active, aggressive predators that feed on large insects, small lizards, mice, and frogs.
How to plan your Amazon jungle travel to see Brazilian Wandering Spiders and other jungle wildlife
- Go on a night hike: These large spiders are most active at night. We have nightly hikes in the rainforest with trained guides so you can see wandering spiders and other nocturnal jungle animals.
- Make science happen with AmazonCam: even if Amazon Travel is not in your short-term plans, you can connect with Amazon wildlife!
- And of course, if you´re thinking (or even dreaming) of Amazon jungle Travel, drop by to chat with the Amazon Travel experts . We will help you get there.
OTHER EXPLORERS HAS ALSO CHECKED
- SCARLET MACAW (Ara Macao) SCARLET MACAW (Ara Macao) Height 90.70 cm Weight 1 kg Lodge Tambopata Research Center
- CANDIRU (Vandellia Cirrhosa) CANDIRU (Vandellia Cirrhosa) Height 17 cm Weight no information available Lodge Posada Amazonas, Refugio Amazonas, Tambopata Research Center
- COCOI (WHITE-NECKED) HERON (Ardea cocoi) COCOI (WHITE-NECKED) HERON (Ardea cocoi) Height 95-120 cm Weight 1.9 kg Lodge Tambopata Research Center, Refugio Amazonas
- POTOO BIRD (Nyctibius griseus) POTOO BIRD (Nyctibius griseus) Height 21 - 58 cm in length Weight 250 gr Lodge Posada Amazonas
{$MOD_TEXTOINTRO_01$}
{$MOD_GRILLAWILDLIFE$}
What our guest say
- Valuation Excellent
Jacob Shama May 2024
Yaacov may 2024, secaboulder may 2024, cecilia d may 2024, andrea breanna apr 2024, a user apr 2024, niko dietsch apr 2024, yuting c apr 2024, yuting chen apr 2024, víctor moscoso apr 2024, ari s march 2024, dreamer627120 march 2024.

The lodge is located in the middle of the forest accessible only by boat. The experience was very unique and exciting. S ervice is great, and the fun part are the nature activities and tours the hotel offers for free. We had an amazing tour guide that had a lot of knowledge and was fun to spend time with. The rooms are totally open to the forest which is really cool the struggle is the there is no privacy at all in between the rooms, also food was pretty basic. All together a very unique experience. Read all
Read all
This hotel is the perfect blend of comfort and hospitality, with the natural experience. The hotel is reached by a hour� ��s boat ride from Puerto Maldonado, expertly organized and accomplished. Most staff are members of the local Esa Ejja community. The food is good and plentiful. Hot water is always available and lovely bedding features mosquito nets. There is of course no air conditioning (one side wall is open in rach room) and the electricity is off for a few hours at night affecting overhead fans, so I was glad to have brought a small battery powered fan for sleeping. But the best of the experience is the wildlife. Our expert guide Oscar Mishaja introduced us to nearly 100 bird species, along with caimans, river otters, poison dart frogs and capybara. A trip of a lifetime. Read all
Excellent experience overall— really kind and welcoming staff at every point of the journey. All transfers were well o rganized and smooth. Excellent and educational excursions all around the rainforest. Delicious food for every meal. We had wonderful guides- Freet and Alvaro. Enjoyed our time here! Read all
Unbelievable.... Magical Everything I have dreamed of since I was 8 years old but MORE Read all
We had a surreal experience at Refugio Amazonas. From the well organized transportation to the warm welcome, hospitality and the experience of living in nature - we loved it all. Huge shout out to our guide Boris who went out of his way to ensure we had a good experience and got to watch all kinds of wild life. The meals and cocktails were delicious. And even though this place is smack in the middle of the jungle there was super fast WiFi available. We made unforgettable memories. Read all
We had an amazing time in TRC. From the guide, tours, lounge staff, food and room, everything has exceeded our expectati on and like an amazing dream came true. We highly recommend to directly book with the lounge website, so that you got a private guide for your group. Special thanks to our guide Saul, who made this experience extra special! We were so impressed by his knowledge about all the animals and the rainforest. Read all
We had an amazing time in TRC. From the guide, tours, lounge staff, food and room, everything has exceeded our expectati on and like an amazing dream came true. This is the only lounge available in Tambopata national park, and this eco lounge takes environment seriously. We highly recommend to directly book with the lounge website, so that you got a private guide for your group. Special thanks to our guide Saul, who made this experience extra special! We were so impressed by his knowledge about all the animals and the rainforest. If you are a natural lover, you can’t miss this place Read all
Excellent and luxurious place, wonderful experience and our guide Boris was first class, he had a unique patience with m y 8 year old son. An experience in the tropical rainforest that marks the life of its visitors. In addition to the scientific research that takes place in the place: a whole research center. Rooms: Very comfortable and luxuriou Read all
El mejor hotel para visitar la Amazonia peruana. Hotel eco turístico metido en medio de la selva, equipado para visitar y vivir la selva, su flora y fauna, en todas sus facetas. Todo incluido, con guías preparados y amables, resultó una experiencia increíble para mi familia. Dentro de las opciones no se debe perder el Canopy de 45 metros de altura para observar y escuchar la selva, así como el lago de las tres Chimbadas, lugar único para ver caimanes, nutrias gigantes, monos y aves exóticas. Recomiendo mínimo dos noches!!! Read all
Wunderbare lodge mit freundlichen Menschen. sehr persönliche guides, tolle Tourangebote und super kulinarische Verpfleg ung ! Wir wurden herzlichst von Caesar empfangen und unser guide JuanJo hat uns phantastische Dinge gezeigt. Wir können die lodge nur wärmstens empfehlen! Read all
Join To Our Newsletter

Southeastern Wandering Spider (Anahita punctulata )
Detailing the physical features, habits, territorial reach and other identifying qualities of the southeastern wandering spider.
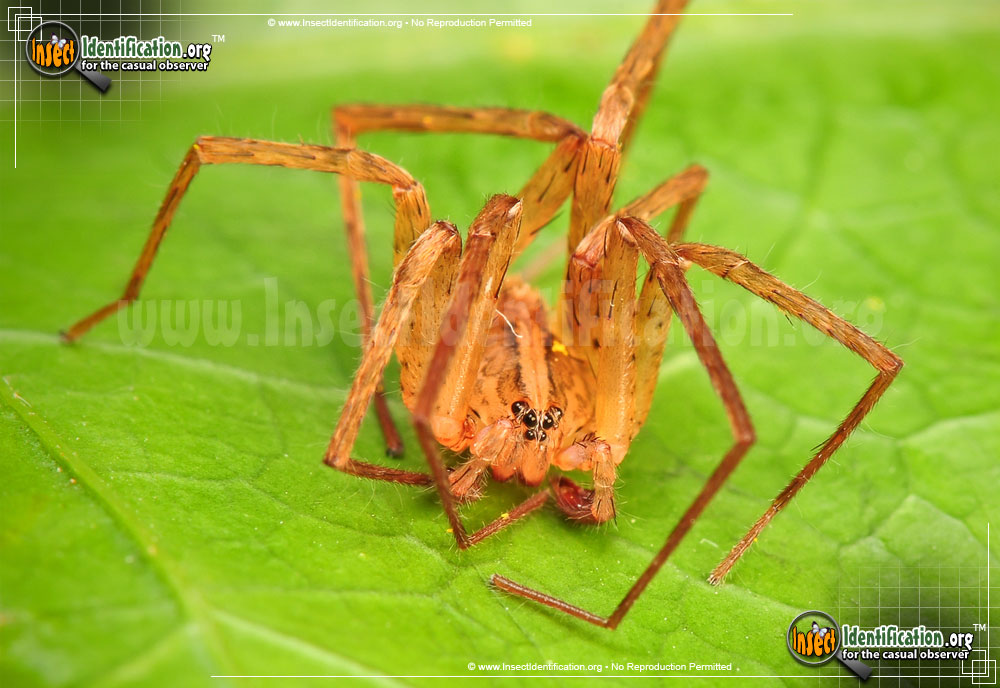

The tropical Southeastern Wandering Spider is an active hunter, making the most of a warm climate teeming with insect prey.
General characteristics.

Taxonomic Hierarchy
Identifying information.
Relative Size Comparison
Territorial Reach (A-to-Z)

Territorial Map*

11 deadliest spiders
From the funnel web spider to the brown recluse, here are some of the deadliest spiders on Earth.
Spiders are some of the most successful arthropods on the planet, having colonized every continent except Antarctica. Not all of these eight-legged arachnids are venomous, but some can be deadly to humans . From the notorious black widow to the ultra-deadly funnel web spider, here are some of the deadliest spiders on Earth.
Brown recluse spider

As their name suggests, brown recluse spiders ( Loxosceles reclusa ) have a shy nature and tend to hide away in dark, sheltered places. However, the brown recluse spider will bite if they feel threatened, and their bites can be deadly. They are usually found in the south and central United States, spanning southeastern Nebraska to southwestern Ohio, south to northwestern Georgia and into Texas.
The brown recluse spider can be dangerous to people because their venom contains a toxin that can cause skin necrosis (rotting). For the most part, symptoms, such as burning and itching at the bite site, as well as fever and nausea, develop a few hours after a bite. In extreme cases, the venom can lead to serious reactions or even death, especially to more vulnerable groups such as young children and the elderly.
Hobo spider

Part of the family of spiders known as the funnel web spiders, the hobo spider ( Eratigena agrestis , formerly Tegenaria agrestis ) can be recognized by it's light to medium brown coloring and the multiple chevron patterns (v-shaped) on its abdomen pointing toward their head. They are often confused with the brown recluse spider (and vice versa), but the brown recluse is much more dangerous to humans. While hobo spiders have been known to bite if they feel threatened, there is much debate about how venomous they actually are. So much so that the Center for Disease Control and Prevention has removed them from their venomous spiders list. However, it's still wise to be cautious as hobo spider bites result in swelling and redness around the area, and can have more severe effects in young children.
Hobo spiders are not great climbers, so you'll find their funnel-shaped webs at ground level. Geographically, they can be found in western North America, in the Pacific Northwest and Great Basin, as well as distributed throughout Europe to Central Asia.
Black widow spider

In the genus Latrodectus , the black widow is one of the most venomous spiders and is found on every continent except Antarctica. In North America, they're commonly found in southern Canada and in the northeastern United States. You can identify the female black widow spider by its shiny black body and distinct red hourglass-shape on the underside of the abdomen. The male black widow is smaller in size, brown or gray in color with small red sports and does not have the hourglass marking.
While both male and female black widows are venomous, only the female is dangerous to humans. The venom of a black widow is reported to be 15 times stronger than that of a rattlesnake, although they don’t deliver as much venom in their bite, so fatalities are rare. That’s not to say a black widow bite isn’t painful! Those unlucky enough to be bitten by a black widow will experience nausea, fever, sweating, restlessness, muscle cramps and labored breathing, and these symptoms may last for several days.
Brazilian wandering spider

Commonly referred to as armed spiders or banana spiders (as they tend to be found hiding within shipments of bananas), the Brazilian wandering spider is one that you'll definitely want to avoid. They belong to the genus Phoneutria , Greek for "murderess," which is quite apt as they are one of the most venomous spiders on Earth.
This arachnid is aggressive, and rather than camping out, the Brazilian wandering spider actively hunts its prey, searching the jungle floor at night. If you ever find yourself in Central and South America, such as Costa Rica or Argentina, watch out! Their neurotoxic venom is extremely painful and affects the nervous system, causing increased sweating and drooling, loss of muscle control, breathing problems, and, in some cases, unwanted prolonged erections.
Yellow sac spider

The yellow sac spiders ( Cheiracanthium) are in the family Cheiracanthiidae and they probably account for more human bites that any other type of spider. These arachnids are distributed all over the globe, from America to Northern Europe, South Africa to India, and even Australia and Japan. They’re nocturnal predators and during the day they hide in small white web cocoons.
Mildly venomous to humans, the yellow sac spider bite can be painful and sometimes misdiagnosed as brown recluse bites. Their venom can cause necrotic legions, as well as redness, swelling and sores around the bite site.
Brown widow spider

Latrodectus geometricus is the scientific name for the brown widow spider. It looks similar to its infamous " cousin " the black widow, right down to the hourglass-shaped marking on its abdomen, but there are some key differences. The brown widow’s marking is orange and yellow rather than red, and as their name suggests, they predominantly have tan and brown mottling and a spiky, rather than smooth, appearance. Believed to originate in South America, the brown widow spider is found all around the world.
The brown widow's venom is less toxic than that of its black cousin. However, it can still be deadly. Although they don't deliver as much venom as a black widow, the brown widow's bite can still cause latrodectism due to its neurotoxic venom. Symptoms of lactrodectism include pain, perspiration, muscle rigidity and vomiting.
Red widow spider

Living mostly in sand dunes in Central and Southern Florida, the red widow spider ( Latrodectus bishop) is another member of the notorious "widow" family. Their venom is just as lethal as brown and black widows, but as they live so far from human contact there has been no recorded bite in medical literature. The female red widow spider's venom is a neurotoxin which is thought to cause prolonged muscle spasms.
The red widow spider has a red-orange head and legs and a black abdomen with yellow rings around red dots. Rather than an hourglass marking like its "cousins," the red widow usually has one or two red marks.
Redback spider

Due to its strikingly similar appearance, the redback spider ( Latrodectus hasselti ) was once thought to be a sub species of the black widow spider, but it is a distinct species. Also known as the Australian black widow, you can find this creepy crawly throughout Australia, Southeast Asia and New Zealand. The redback spider has even been found in Japan, the United Arab Emirates and Belgium due to inadvertent introductions.
Highly venomous, the bite from the female redback spider can be life-threatening. Using its fangs, it injects a complex venom that causes intense pain at the bite area, in addition to sweating and goosebumps. As time goes on, these symptoms worsen and there may also be redness and swelling, as well as nausea, muscle twitching, headache and fever. Respiratory failure may occur in severe cases. Thankfully, in 1956 scientists released a redback spider antivenom which is very effective, even when used several weeks after the initial bite. No deaths have been reported since.
Funnel-web spiders

Normally in the world of spiders it is the female that is more deadly, but for funnel-web spiders ( Atrax ) the male has the more toxic bite. Any attack must be treated quickly with antivenom, especially if a child has been bitten. There have been several recorded fatalities due to the venomous bites of the funnel-web spider, with death occurring within the hour after being bitten. However, since the development of the antivenom in 1981, there haven’t been any more recorded deaths. Predominantly located in southeast Australia (Sydney), funnel-web spiders are also found in New Zealand, Chile and Europe.
Interestingly, animals such as cats and dogs can actually survive a funnel web bite – it takes about 30 minutes for their body to neutralize the toxin – it's just humans who have such a severe reaction. This venom effects the nervous system and causes symptoms such as an elevated heart rate, numbness/tingling of the mouth and difficulty breathing.
Six-eyed sand spider

Found in deserts in southern Africa, the six-eyed sand spider ( Hexophthalma hahni ) buries itself in the sand to ambush unsuspecting prey. The small, stiff hairs that cover the spider helps to hold sand particles in place, adding to its camouflage. It's otherwise known as the six-eyed crab spider due to its crab-like legs.
Another arachnid that produces venom with necrotic effects, the six-eyed sand spider is the most venomous of any of its arachnid relatives, toxicology studies reveal. Scientists have found that there are proteins within their venom that can cause tissue destruction, blood vessel leakage, and thinning of the blood. No antivenom currently exists.
Mouse spider

Black in color with stocky, thick legs and a distinctively bulbous head and jaw regions, the mouse spider ( Missulena ) looks a lot more frightening than its name sounds. One species is located in Chile, another in South America and the rest distributed throughout Australia. They live in soil-covered burrows, popping out the hinged trapdoor top to attack prey.
Their hard, large fangs can cause a deep and very painful bite. However, while scientists believe that the venom of the mouse spider is very toxic, it is rarely injected. As so few cases have been reported, it is thought that mouse spiders don't use a lot of venom or may even "dry bite." Fortunately, funnel-web spider antivenom has proven effective in cases of mouse spider bite.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Christina is a freelancer writer and editor from the UK. She has a degree in English Language and Literature with geography from the University of Keele, and a Masters in Publishing from Anglia Ruskin University. She covers everything from Lego sets and science kits through to laptops for students. If it helps you learn, she'll help you find it for cheaper.
Giant, invasive Joro spiders with 6-foot webs could be poised to take over US cities, scientists warn
Diving bell spider: The only aquatic arachnid that creates a web underwater to live in
28 'carefully placed' horses in ancient burial in France may have been part of a sacrificial ritual
Most Popular
- 2 James Webb telescope sees 'birth' of 3 of the universe's earliest galaxies in world-1st observations
- 3 Space photo of the week: NASA sees a 'Platypus' move on Jupiter's moon Europa
- 4 Things are finally looking up for the Voyager 1 interstellar spacecraft
- 5 Double cicada bloom 2024: Google Doodle celebrates once-in-221-year event with band of bugs
- 2 How people without 'inner voices' could help reveal the mysteries of consciousness
- 3 Secrets of radioactive 'promethium' — a rare earth element with mysterious applications — uncovered after 80-year search
- 4 Auroras could paint Earth's skies again in early June. Here are the key nights to watch for.
- 5 World's 1st carved horse: The 35,000-year-old ivory figurine from Vogelherd cave
Screen Rant
What spider-man 2099 injects himself with in across the spider-verse (does it make his powers).

Your changes have been saved
Email Is sent
Please verify your email address.
You’ve reached your account maximum for followed topics.
Greta Gerwig's Chronicles Of Narnia Reboot Must Overcome One Harsh Reality Of The Series
10 times hollywood gave up on movie series, denzel washington's most underrated movie is a $46 million flop from 26 years ago.
WARNING: This article contains SPOILERS for Spider-Man: Across The Spider-Verse. What Spider-Man 2099 injects himself with in Spider-Man: Across the Spider-Verse traces back to Miguel O’Hara’s comic book origins and may help explain his powers. Across the Spider-Verse finally paid off Spider-Man: Into the Spider-Verse ’s ending by bringing Miguel O’Hara, Spider-Man 2099, into the story. Spider-Man 2099 may have been one of Across the Spider-Verse ’s main characters, but Across the Spider-Verse 's ending left a few questions unanswered when it comes to the futuristic Spider-Man.
Across the Spider-Verse jumped right into the action as Spider-Woman and Spider-Man 2099 crashed into Spider-Gwen’s universe to capture the Renaissance Vulture . The Into the Spider-Verse sequel moved arguably faster than the first film, introducing several new characters and universes. One of the mysteries associated with Spider-Man 2099 was the substance Miguel injected himself with, which ties into the character’s origin story.
Spider-Man 2099's Injections Link To His Comic Backstory
Spider-Man: Across the Spider-Verse did not offer too much context on Spider-Man 2009’s injections, yet they link to Miguel O’Hara’s comic book backstory. In Marvel Comics, before he turns into Spider-Man, Miguel becomes addicted to an extremely powerful drug known as Rapture. Rapture, which binds to the user’s DNA, was the reason why Miguel performed a genetic experiment on himself – he wanted to break free of the Rapture addiction. Miguel’s experiment went wrong, and while the Rapture addiction was resolved, he became “half spider” on a molecular level. There are no Spider-Man 2099 injections in the comics, but those could be Across the Spider-Verse ’s version of Rapture.
Another option is that Across the Spider-Verse is combining the Rapture addiction storyline with the serum used in the experiment that transformed Miguel into Spider-Man. Perhaps Spider-Man 2099 is still addicted to Rapture in this particular Across The Spider-Verse universe . Another possibility is that the serum that gave Spider-Man 2099 his powers, which in the comics is sort of a Super Soldier serum variation based on Peter Parker's physiology, has now become addictive to Miguel.
Do Spider-Man 2099's Injections Give Him His Powers?
If Across the Spider-Verse ’s Spider-Man 2099 powers have the same origin story as his comic book counterpart, then the injections do not give him special abilities. In the comics, Miguel’s powers come from a failed experiment. While a serum was involved, Spider-Man 2099’s origin has nothing to do with injections. That said, Across the Spider-Verse ’s Spider-Man 2099 is different from Marvel Comics in a few ways, including parts of his backstory. Therefore, it would be no surprise if Miguel’s transformation into a literal Spider-Man is linked to the injections. Should that be the case, Across the Spider-Verse 's Spider-Man 2099 injections might be what give him powers after all.
It is also possible that Spider-Man 2099’s injections help keep Miguel’s DNA stable, thus preventing him from becoming “50% spider.” Miguel O Hara’s spider-like traits, including the fangs and the red eyes, were kept for Across the Spider-Verse . Miguel was even compared to a vampire in Across the Spider-Verse , as he uses his fangs as a weapon quite often. Regardless of the full context behind Spider-Man 2099’s injections, that small Spider-Man: Across the Spider-Verse Easter egg perfectly ties the film's Miguel O’Hara to his Marvel Comics counterpart.
- Spider-Man: Across the Spider-Verse (2023)
- Spider-Man: Into the Spider-Verse (2018)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
wandering spider, (family Ctenidae), any member of the family Ctenidae (order Araneida), a small group of large spiders of mainly tropical and subtropical regions, commonly found on foliage and on the ground. Their first two legs are armed with strong bristles on the lower side. Cupiennius salei, found in rainforests in Central and South ...
Bites and venom. Brazilian wandering spiders' venom is a complex cocktail of toxins, proteins and peptides, according to the Natural History Museum in Karlsruhe, Germany. The venom affects ion ...
Learn about the Brazilian Wandering Spider, a highly venomous and aggressive spider that wanders the jungle floor and hides in dark places. Find out how it hunts, reproduces, and what to do if bitten by this spider.
Wandering spiders (Ctenidae) are a family of spiders that includes the Brazilian wandering spiders.These spiders have a distinctive longitudinal groove on the top-rear of their oval carapace similar to those of the Amaurobiidae. They are highly defensive and venomous nocturnal hunters. Wandering spiders are known to hunt large prey, for example hylid species Dendropsophus branneri.
Here are a few more notable characteristics of the Wandering Spider: Females are larger than males, with a body length of up to 1.6 inches (4 cm). They have eight eyes, arranged in two rows, which help them in hunting. The Wandering Spider is primarily found in Central and South America, particularly in Brazil.
The venom glands of the Brazilian Wandering Spider are over a centimetre long, and this is all housed inside the bright red chelicerae (mouth parts) which they are quick to display whenever they get upset. 1. 4. They're aggressive. These spiders can grow quite large and have long, brightly-coloured legs.
Brazilian Wandering Spider Size. Being quite large and impressive compared to most arachnids, adult Brazilian Wandering Spiders can reach a leg span of up to 7 inches (18 cm). The body size excluding the legs can be up to 2 inches (5 cm). Their size contributes to their intimidating presence.
The Brazilian wandering spider is a creepy crawly giant. Their bodies can grow up to 2 inches (5 centimeters) long, but that's not the scary part. Their legs can span a whopping 7 inches (18 cm), making them look even bigger. They are one of the biggest true spiders by body weight and size.
Phoneutria nigriventer is a species of medically significant spider in the family Ctenidae, found in the Southern Cone of South America (Brazil, Uruguay, Paraguay, and Argentina). Along with other members of the genus, they are often referred to as Brazilian wandering spiders.. Its bite can cause severe symptoms, including increased pulse, blood pressure, and respiratory rate; extraordinary ...
The Brazilian Wandering Spider (Phoneutria fera) is a teardrop-shaped arachnid with a brown coloration. Known for its potent venom, it thrives in both the lush rainforests and human dwellings of Brazil. Its notorious wandering behavior makes it a significant presence in its habitats. Characteristic. Details.
The Brazilian Wandering Spider, known scientifically as Phoneutria, harbors a venomous arsenal that stands as a testament to nature's intricate design. This spider's venom contains a potent concoction of neurotoxic compounds, tailored by evolution to incapacitate its prey swiftly and efficiently. The neurotoxins interfere with nerve cell ...
Phoneutria is a genus of spiders in the family Ctenidae.They are mainly found in northern South America, with one species in Central America. Members of the genus are commonly referred to as Brazilian wandering spiders. Other English names include armed spiders (armadeiras in Brazilian Portuguese) and banana spiders (a name shared with several others).
How do Brazilian Wandering Spiders defend themselves? When faced with a threat, Brazilian Wandering Spiders have several defense mechanisms at their disposal. They may exhibit aggressive behavior, raising their front legs and exposing their fangs as a warning. If this does not deter the threat, they are capable of delivering a venomous bite ...
Brazilian wandering spider brazilian wandering spider size Their body length ranges from 17 to 48 mm (43⁄64 to 1+57⁄64 in).Phoneutria are impressive spiders reaching body sizes up to 3.5 centimeters and leg spans up to 15 centimeters. They are nocturnal, hunting at night, and hiding in dark places during the…
Size: They are large in size, with their body being 17- 48mm (.67 - 1.89 inches) long and they also have a leg span of 130 - 150 mm (5.1-5.9 inches). Color: The color may vary from one species to the other, though most of them have a brown hairy body, with black spots on their stomach. Some have bright, red hairs on their mouthparts or ...
The Brazilian wandering spider, scientifically known as Phoneutria, Maximilian Perty kickstarted the Phoneutria genus in 1833. The name comes from the Greek word φονεύτρια, which means "murderess" and falls under the Animalia kingdom, Arthropoda phylum, and Arachnida class. Within Arachnida, it is classified in the order Araneae ...
Recognizing a Brazilian Wandering Spider. 1. Watch out for 6-inch (15 cm) long spiders with leg span. Adult Brazilian wandering spiders have a body that's about 2 inches (5 cm) large. Their leg span, which may be easier to recognize, is about 6 inches (15 cm) in length.
The body length of these spiders can reach up to 2 inches, or around 5 cm. This considerable size, coupled with their highly potent venom, makes them a formidable presence in their habitats. But as an arachnid hobbyist, the allure of the Brazilian Wandering Spider's size lies not in its potential threat, but in the fascinating evolutionary ...
Wandering spiders are venomous spiders that roam around the jungle floor in search of prey. They belong to the Ctenidae family and have about 50 genera, with the Brazilian Wandering spider being the most famous one.
Victims of a Brazilian wandering spider bite can reportedly be killed in an hour. But few deaths occur because an effective anti-venom is available in Brazil and Guinness claims that people are ...
The Brazilian Wandering Spider is the name of many spider species in thePhoneutria genus. They are large, intimidating, and infamous for being the most toxic spider venom in the world. These spiders actually occur in many areas outside of Brazil, from Costa Rica to Argentina. Nevertheless, the Brazilian Wandering Spider (Phoneutria nigriventer ...
Wandering spiders are active hunters though, not web-spinners, much like Wolf Spiders, and they attack their prey by ambushing them. They live in burrows on the ground or on plants. They are primarily found in warmer, tropical climates. Most Wandering Spiders found in North America were imported on tropical fruits, like bananas.
The brown recluse spider is one of the deadliest in the world. (Image credit: Rick Vetter) As their name suggests, brown recluse spiders ( Loxosceles reclusa) have a shy nature and tend to hide ...
It is also possible that Spider-Man 2099's injections help keep Miguel's DNA stable, thus preventing him from becoming "50% spider.". Miguel O Hara's spider-like traits, including the fangs and the red eyes, were kept for Across the Spider-Verse. Miguel was even compared to a vampire in Across the Spider-Verse, as he uses his fangs as ...