Not a member?
Find out what The Global Health Network can do for you. Register now.

Member Sites A network of members around the world. Join now.
- 1000 Challenge
- ODIN Wastewater Surveillance Project
- Global Health Research Management
- UK Overseas Territories Public Health Network
- Global Malaria Research
- Coronavirus
- Sub-Saharan Congenital Anomalies Network
- Global Health Data Science
- AI for Global Health Research
- MRC Clinical Trials Unit at UCL
- Virtual Biorepository
- Epidemic Preparedness Innovations
- Rapid Support Team
- The Global Health Network Africa
- The Global Health Network Asia
- The Global Health Network LAC
- Global Health Bioethics
- Global Pandemic Planning
- EPIDEMIC ETHICS
- Global Vector Hub
- Global Health Economics
- LactaHub – Breastfeeding Knowledge
- Global Birth Defects
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
- Human Infection Studies
- EDCTP Knowledge Hub
- CHAIN Network
- Brain Infections Global
- Research Capacity Network
- Global Research Nurses
- ZIKAlliance
- TDR Fellows
- Global Health Coordinators
- Global Health Laboratories
- Global Health Methodology Research
- Global Health Social Science
- Global Health Trials
- Zika Infection
- Global Musculoskeletal
- Global Pharmacovigilance
- Global Pregnancy CoLab
- INTERGROWTH-21ˢᵗ
- East African Consortium for Clinical Research
- Women in Global Health Research
- Global Pathogen Variants
Research Tools Resources designed to help you.
- Site Finder
- Process Map
- Global Health Training Centre
- Resources Gateway
- Global Health Research Process Map
- About This Site
Downloadable Templates and Tools for Clinical Research
Welcome to global health trials' tools and templates library. please note that this page has been updated for 2015 following a quality check and review of the templates, and many new ones have been added. please click on the orange text to download each template., the templates below have been shared by other groups, and are free to use and adapt for your researchstudies. please ensure that you read and adapt them carefully for your own setting, and that you reference global health trials and the global health network when you use them. to share your own templates and sops, or comment on these, please email [email protected]. we look forward to hearing from you.
These templates and tools are ordered by category, so please scroll down to find what you need.
To share your own templates and SOPs, or comment on these, please email [email protected]. We look forward to hearing from you!
- Webinar on community engagement in clinical research involving pregnant women
- Free Webinar: Science, technology and innovation for upskilling knowledge-based economies in Africa
- Open Public Consultation on “Strengthened cooperation against vaccine preventable diseases”
Trial Operations Trial Management Ethics and Informed Consent Resources Trial Design Data Management and Statistics
training
This is Degena Bahrey Tadesse from Tigray, Ethiopia. I am new for this web I am assistant professor in Adult Health Nursing Could you share me the sample/templet research proposal for Global Research Nurses Pump-priming Grants 2023: Research Project Award
I have learned lot..Thanks..
i was wondering why there is no SOP on laboratory procedures ?
Hi, Can you provide me the SOP for electronic signatures in Clinical trial
Do you have an "SOP for Telephonic site selection visit". Kindly Share on my registered mail ID
Thank you for sharing the resources. It is very kind of you.
Hi These tolls are very useful! Thank you
Do you have a task and responsability matrix template for clinical trial managment ? Best
I am very much happy to find myself here as a clinician
Dear Getrude
We have a free 14-module course on research ethics on our training centre; you'll receive a certificate if you complete all the modules and quizzes. You can take it in your own time. Just visit 'Training centre' in the tabs above, then 'short courses'.
Kind regards The Editorial Team
need modules on free online gcp course on research ethics
Estimados: me parece excelente el aporte que han hecho dado que aporta. por un lado a mejorar la transparencia del trabajo como a facilitar el seguimiento y supervisión de los mismos. Muchas gracias por ello
We also have an up to date list of global health events available here: https://globalhealthtrials.tghn.org/community/training-events/
Dear Nazish
Thank you, I am glad you found the seminars and the training courses useful. We list many training events (all relevant to Global Health, and as many of them as possible are either free or subsidised) on the 'community' web pages above. Keep an eye on those for events and activities which you can get involved with. Also, if you post an 'introduction' on the introduction group stating where you are from and your research interests, we can keep you updated of relevant local events.
Thanks so much. These are very helpful seminars. Please let me know any other websites/links that provide free or inexpensive lectures on clinical Research. Appreciate your help.
Hi Nazish, and welcome to the Network. The items here are downloadable templates for you to use; it sounds like you may be seeking lectures and eLearning courses? If so - no problem! You can find free seminars with sound and slides here: https://globalhealthtrainingcentre.tghn.org/webinars/ , and you can find free, certified eLearning courses here: https://globalhealthtrials.tghn.org/elearning . Certificates are awarded for the eLearning courses for those scoring over 80% in the quiz at the end of each course. If you need anything else, do ask! Kind regards The Editorial Team
Hi, I am new to this website and also to the Clinical Research Industry for that matter I only am able to see the PDF of these courses, just wanted to know are these audio lectures and also happen to have audio clips that go with the pdf?
This site is impeccable and very useful for my job!!!!
Thank you for your kind comments.
Fantastic resources
I am delighted you found this website. I earlier introduced it to you because of your prolific interest in health care information and resource sharing....
Please Sign in (or Register ) to view further.
Useful Resources
Related articles.
- PRISMA for Abstracts: Reporting Systematic Reviews in Journal and Conference Abstracts BY Jai K Das
- 5 ways statistics can fool you—Tips for practicing clinicians BY Jai K Das
- How to prepare for a job interview and predict the questions you’ll be asked BY The Editorial Team
- Preparing for and Executing a Randomised Controlled Trial of Podoconiosis Treatment in Northern Ethiopia BY Henok Negussie, Thomas Addissie, Adamu Addissie, Gail Davey
- Dengue: Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention and Control BY WHO/ TDR
Most popular tags
- Archive (303)
- archive (104)
- data sharing (70)
- sharing (63)
- training (49)
- malaria (30)
- ACT consortium (25)
- informed consent (7)
- data management (6)
- trial management (6)
- careers (5)
- guidelines (5)
- monitoring (5)
- workshop (5)
- administration (4)
- clinical research (4)

Clinical Trial Monitoring Reports and How to Write Them
Among the most important aspects of study is observation. Overseeing the advancement of any stage, measure, process, and procedure in real time is essential to the accurate conclusion of any clinical trial undertaking. Normal monitoring actions are needed to guarantee caliber, efficiency, compliance within predefined and regulations fundamentals. In addition, it guarantees comprehensiveness, and precision within clinical investigation. Such actions also ensure that the trial isn't just conducted in compliance with Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). They must also function to validate it is correctly reported and recorded. Consider enrolling in the Clinical Research Coordinator course or the CRA training provided by CCRPS.
There demands something vital as a part in the execution of trials. And this thing is known as trial development reports.
Such a report ought to be carefully prepared and it must summarize the means that a study is done. It also ought to point out recruiting progress and procedures; should emphasize and clarify adjustments to the analysis, and ought to point security issues. If you're involved in such reporting or need an in-depth understanding of the procedures, the Advanced Clinical Research Project Manager Certification might be of interest.
Aside from the ethics committee, researchers could also need to present yearly improvement reports of an investigation (such as any applicable alterations or dangers) to spouses, encouraging associations, and/or organizations, along with other interested parties if needed. To understand more about these requirements and get certified, the ICH-GCP course is an excellent resource.
If you're thinking about getting important skills on GCP or you also would like to upgrade your own know-how, subscribe to our comprehensive Good Clinical Practice class here .
In summary, tracking and reporting processes is an incredibly significant function in clinical trials. The right conduct of these procedures ensure compliance with legislation, regulations, and predetermined conditions. In addition, they make certain that the study doesn't pose any dangers to wellbeing. Progress reports, subsequently, empower practitioners, specialists, researchers, ethics committees, as well as others involved to keep a tab on the trial and its own advancement. Clinical professionals need to signal any alterations or risks to react to them timely, correctly, and efficiently. For further training, consider the Pharmacovigilance Certification to deepen your knowledge in monitoring drug safety.
The objective of progress reports would be to accumulate and outline upgrades, key facets, along with summaries of a continuing trial. It's very crucial to be aware that progress reports must be filed to institutional evaluation board/independent integrity questionnaire (IRB/IEC), following a trial that has obtained positive opinion.
One other important issue to mention is there are many different forms and when it comes to submitting progress reports that researchers must take into consideration before proceeding.
Precisely, these kinds are:
Printing name and date of entry ought to be composed also. A digital copy is also needed to be delivered to the interested websites and committees inside a 30-day interval following the reporting procedure was completed.
The period of time whereby an advance report ought to be filed is at least one time in a year. Nevertheless, based upon the situation as well as the RECs' needs, these reports might be passed in more often, although the analysis is still going and till its official conclusion date.
Take courses from CCRPS and learn more on how to become a clinical research professional. For detailed guidance on submission requirements and processes, the Medical Monitor Certification and Advanced Principal Investigator Physician Certification can provide extensive knowledge.
Discover more from Clinical Trials Assistant Training | Clinical Research Training | Certified Clinical Research Professionals Course to further your career in clinical research management.
CRA Exam Questions
2018 clinical research associate (cra) salaries estimated from 1,850 american employees.
- ITHS SharePoint
Search the Site
Connect with us, need help have a question.
Contact the Research Navigator
ITHS Email Updates

Pre-Study Preparation
The key decisions involved with the pre-study preparation of industry-sponsored clinical trials include the following:
Confirm Research Support Services/Facilities
Based on your final budget and contract, contact the supporting departments who will be involved with the trial to let them know you are ready to begin. This might include:
ITHS CLINICAL RESEARCH CENTER
ITHS RESEARCH COORDINATION CENTER
INVESTIGATIONAL DRUG SERVICE PHARMACY Harborview Medical Center (206) 744-5448 | [email protected] UW Medical Center (206) 598-6054 | [email protected] Website
UWMC LABORATORY MEDICINE Administration (206) 598-6131 | [email protected]
RESEARCH TESTING SERVICE (206) 616-8979 | [email protected]
UW DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY NWBioSpecimen
UW DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY RESEARCH PROGRAM
Site Initiation Visit
Many industry sponsors/Clinical Research Organizations conduct a Site Initiation Visit (SIV) to prepare and set up a research site, conduct protocol training, and ensure the Principal Investigator (PI) fully understands all trial responsibilities. The visit usually occurs after the site has completed all regulatory requirements, including Institutional Review Board approval, but prior to recruiting participants. The sponsor/Clinical Research Organization will want to meet with the PI and as many members of the research team as possible. The sponsor/Clinical Research Organization may ask to meet with representatives from supporting departments (e.g., pharmacy, radiology, lab medicine).
Topics of discussion during the site initiation visit include:
- PI responsibilities
- PI and research team qualifications
- Study objectives, eligibility criteria, recruitment, and procedures
- Space requirements, availability of a secure area to store investigational drug or devices, availability of required equipment
- Lab manual, specimen processing, and shipping
- Regulations and Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines, informed consent requirements, Institutional Review Board obligations, adverse event reporting, drug accountability, source documentation, and records retention (regulatory documents and study file organization)
- Data forms review (Case Report Forms, or CRFs), including electronic data entry
If it is a large multi-site trial, a sponsor/Clinical Research Organization may choose to hold an Investigator Meeting in lieu of conducting site initiation visits. In this case, the meeting is held sometime after the Site Qualification Visit (link to Site Qualification Visit ) and prior to recruiting participants. The Investigator Meeting is usually only attended by the PI. However, if the PI is unable to attend, the sponsor/Clinical Research Organization may allow a co-investigator or research coordinator to attend. Travel to this meeting is coordinated and paid for by the sponsor/Clinical Research Organization.
Access to UW Electronic Medical Records
To use the University of Washington’s electronic medical record systems (ORCA and Epic) to identify eligible patients or capture clinical data about participants, you will need to request ORCA and Epic access for necessary research staff from User Access Administration .
If you have questions about ORCA access privileges or how to complete the form, contact: [email protected] .
If you access PHI for research purposes under an Institutional Review Board-approved HIPAA waiver, you must record and submit records of the dates and purposes of these disclosures to UW Medicine Compliance via the UW Medicine Disclosure Accounting online database.
UW MEDICINE COMPLIANCE (206) 543-3098 | [email protected] Accounting of Disclosures Use & Disclosure of Protected Health Information for Research Accounting of Disclosures of Protected Health Information
Pre-Screening to Identify Participants
To identify possible subjects for research, you may need to access Epic or ORCA to look at healthcare records. Even if you are involved in the clinical care of the possible subjects, you will need Institutional Review Board approval of a Waiver of HIPAA Authorization (and if the UW is the Institutional Review Board reviewing the project, a Waiver of Informed Consent and Confidentiality Agreement as well).
Members of your research team may need to complete Epic Training, which is described in the “Training/Credentialing” section below.
Clinical Research Billing for Research Procedures
There are complex federal and private payer rules that govern the conditions under which clinical services, items and tests associated with a research study can be billed to study sponsors, study subjects and/or their insurers. Research teams are required to use Epic to accurately bill for research procedures. Accurate research billing depends on planning and collaboration between the research team and a wide variety of individuals and offices before, during and after the study is initiated.
EPIC REVENUE CYCLE OPERATIONS EDUCATION [email protected] Research Billing Compliance Policies Research Participant Association in Epic Epic Billing Tools
Laboratory Medicine and Research Testing Services
If results of testing performed by University of Washington Lab Medicine will be part of data capture, you must maintain copies of lab normal ranges along with CLIA and CAP certifications.
Licenses & Accreditation
Lab Medicine is also the home department for Research Testing Services, which coordinates and provides research-related phlebotomy, CLIA-licensed testing, research-only testing, processing, and limited specimen storage.
UW LABORATORY MEDICINE Research Testing Service (206) 616‑8979 | [email protected]
Research Instrument Validation and Calibration
Scientific Instruments supports more than 18,000 pieces of patient care, laboratory, and research equipment spread across the greater Seattle area including UW Medical Center, Harborview Medical Center, Northwest Hospital & Medical Center, Seattle Cancer Care Alliance, UW Physician’s Neighborhood Clinics and a variety of other University, state, federal and other publicly funded agencies. Their records can be used to document compliance with TJC, CAP, CLEA, AABB, Food and Drug Administration, CMS, or other accrediting agencies’ requirements for equipment maintenance.
UW HEALTH SCIENCES SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS Machine Shop (206) 616-5074 | [email protected]
Arranging Compensation for Research Participants
Trials often offer compensation to research participants to encourage and appreciate the time and effort involved in participation. Payments or travel/parking reimbursements to research subjects must be approved by the IRB as part of the research activities. You may need to work with your department to identify specific procedures for compensation of research participants.
UW HUMAN SUBJECTS DIVISION (206) 543-0098 | [email protected]
UW PROCUREMENT SERVICES (206) 543-4500 | [email protected]
UW TRANSPORTATION SERVICES 206-221-3701 | [email protected]
Register Study on Participate in Research
Researchers can post their trials to www.ParticipateInResearch.org , and potential volunteers can search for studies that apply to them. This website was developed by the Institute of Translational Health Sciences in partnership with the UW School of Medicine’s Office of Research and Graduate Education to connect research teams with members of the community.
Set Up the Study Binder
Regulatory binders help research teams organize their files, maintain regulatory compliance, and adhere to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) standards for record keeping practices for research involving human subjects. Most sponsors/Clinical Research Organizations will provide the organizational forms and supplies they require you to maintain throughout the trial.
Helpful background can be found in Section 8, “Essential Documents for the Conduct of a Clinical Trial,” of the Food and Drug Administration’s guidance document E6, Good Clinical Practice: Consolidated Guidance.
Do a Walk Through
To make sure you are prepared to conduct the trial, do a walk-through of the research procedures before you schedule the first visit:
- Confirm pre-screening steps in Epic and ORCA
- Create visit packets that contain your recruitment, consent, and data collection resources you will use when approaching participants
- Role play a recruitment conversation using the recruitment script
- Pretend to schedule a study visit
- Role play an informed consent discussion
- Walk from the place where you’ll meet the participant to the visit location(s)
- Make sure you have everything you need at the visit location(s): lab kits, MD orders, pharmacy communication, lab requisition slips, data collection forms, laptop to access eCRFs/regulatory docs, equipment calibrated and in working order, mailing/shipping containers
- Review data collection forms (CRFs) and confirm access to electronic data entry system
Training/Credentialing
Human subjects protections training.
There is no institutional-wide requirement for human subjects training at the University of Washington. However, many sponsors, funding agencies, UW departments, and collaborating institutions require that all members of the research team have completed a standard training course on the protecting human subjects in research. The Collaborative Institutional Training Initiative (CITI) web-based training meets the requirements of most industry sponsors. To take a course on the CITI website, you must register for an account and then affiliate yourself with the UW.
UW HUMAN SUBJECTS DIVISION TRAINING (206) 543-0098 | [email protected] Human Subjects Division website
Clinical Trial Policy Training
University of Washington’s Clinical Research Budget & Billing (CRBB) support office provides Clinical Trial Policy Training to ensure that all UW Medicine faculty have a uniform knowledge of the regulations governing clinical research and that they understand the internal processes that have been implemented in order to maintain compliance in clinical research billing.
Your research support staff may also need to complete the CRBB modules within the UW Medicine Clinical Research Staff Training Program (CRB1, CRB2, CRB3) .
HIPAA Training
UW employees who are involved with research conducted with UW Medicine facilities must complete “HIPAA Online Training” and sign the “UW Medicine Privacy, Confidentiality and Information Security Agreement” within the first 30 days of the individual’s first day as a member of the research team.
UW MEDICINE COMPLIANCE (206) 543-3098 | [email protected] HIPAA Privacy and Information Security Training
Epic Training
For trials that utilize UW Medicine clinical facilities, investigators (or their designees) are required to use Epic scheduling software to enter research subject enrollment status information and to forward study-related admission notifications to the UW Clinical Research Budget and Billing office. To do this work, members of the research team need to complete Epic training and obtain access to Epic.
Register for the Epic classroom training course, RES110: Epic Research Participant Enrollment.
EPIC REVENUE CYCLE OPERATIONS EDUCATION [email protected] UW Medicine Account Activation Request Form
Bloodborne Pathogens Training
Principal investigators are responsible for assessing research activities to determine if members of the research team have a potential for exposure to human blood and its components, human tissue, all human cell lines, human source materials, as well as medications derived from blood (e.g., immune globulins, albumin) and other potentially infectious materials. If your research activities involve human blood and its components, you and your research team are required to comply with the UW’s Bloodborne Pathogens Program, which includes a training requirement.
UW ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH AND SAFETY Training Administration (206) 543-7201 | [email protected] Bloodborne Pathogens Program
Radiation Safety Training
Members of your research team may need to complete radiation safety training or review “Radiation Safety Training for Ancillary Personnel.”
UW ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH AND SAFETY Training Administration (206) 543-7201 | [email protected] Radiation Safety Training for Ancillary Personnel Radiation Safety Training
Shipping Biohazards Certification
If your research team will package and ship specimens via land, air, or sea, all team members must be trained and certified to ship hazardous materials. There are prescriptive requirements for packaging and labeling of hazardous materials and for the associated documentation used in the event of an emergency. There are fines for lack of certification and improper packaging and, worse, a chance for loss of life and property.
UW ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH AND SAFETY Training Administration (206) 543-7201 | [email protected] Shipping Hazardous Materials
UW Medical Center Credentialing
The UW Medical Center credentialing process ensures that individuals other than physicians, Nurse Practitioners, and Physician’s Assistants who interact with patients at UW Medical Center are competent to practice in their role and have current immunizations to ensure the safety of the patients. Members of your research team interacting with UW Medical Center patients must have current credentialing.
UW MEDICAL CENTER CREDENTIALING [email protected] Credentialing

Clinical Pre-Study Site Visit Report Form
$ 11.99
A form template to report pre-study site visit activities.
- Description
- Reviews (0)
This template package includes:
- Pre-Study Site Visit Report Form
There are no reviews yet.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Your review *
Name *
Email *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related products

Clinical Study Monitoring Log
Clinical protocol review checklist, clinical study device accountability log, sponsor audit checklist.
- No products in the cart.
Clinical Trial Templates to Start Your Clinical Research
By Kate Eby | May 13, 2019
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, you will find everything you need to start your clinical research trials, with easy-to-understand guidance and terminology, 26 adaptable templates, and project plans in Microsoft Word, Excel, Project, and SharePoint formats.
Included on this page, you'll find details on what a research protocol is, project management for clinical trials , research compliance templates , and post-clinical study research documentation and templates
What Is the Research Protocol?
All clinical research starts with the research protocol , a document that details all aspects of the trial: its background, rationale, objectives, design, methodology, statistical analysis plan, and organization. With the protocol, you can make sure you protect the participants and collect the data. Using protocol templates, you can start thinking through what you need to meet compliance standards with the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and clinical study best practices.
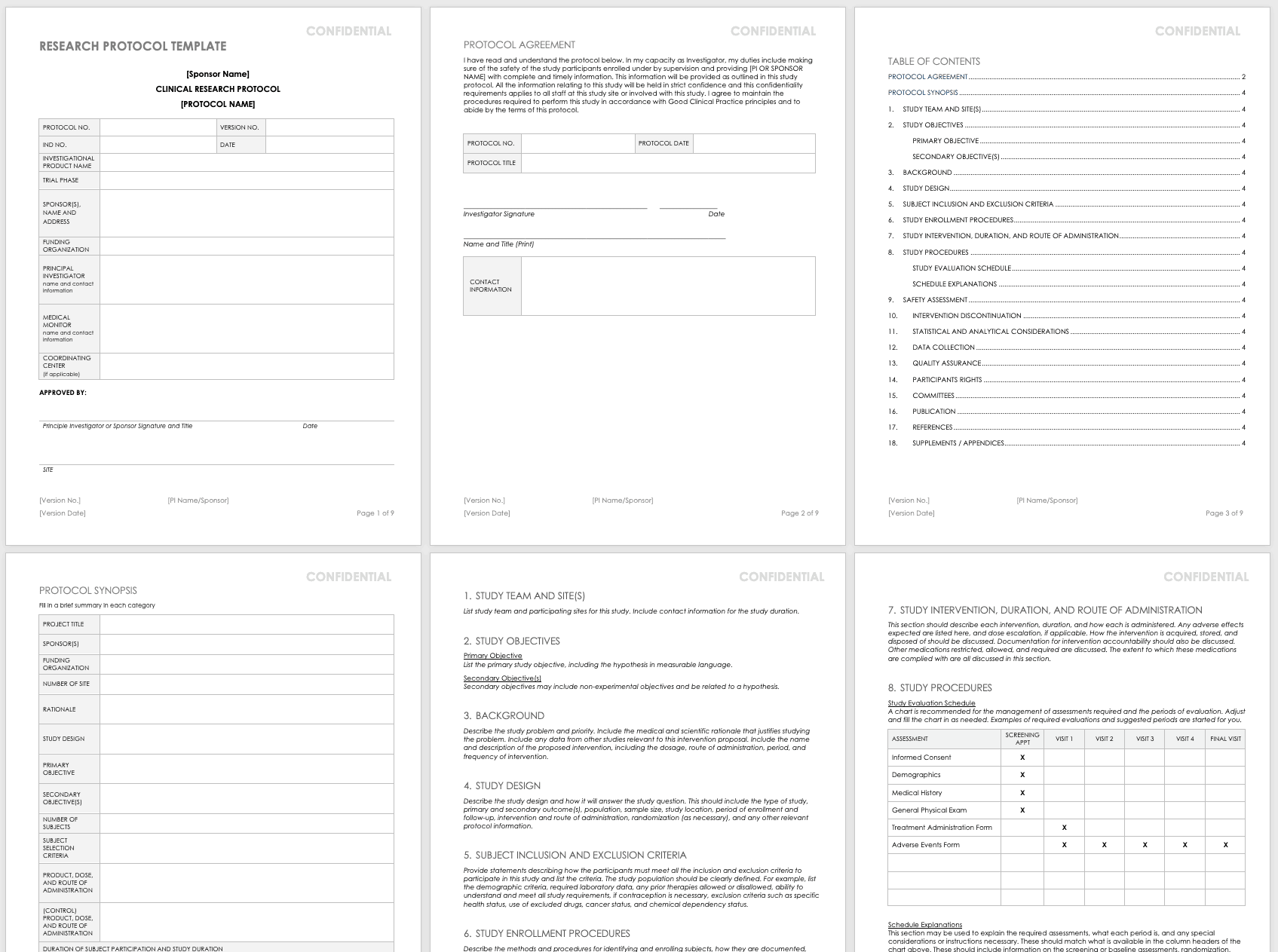
Download Research Protocol Template - Word
The full research protocol includes the following sections and topics:
- Title Pages: These pages provide general information about the protocol, including name, number, version number and date, trial phase, investigational product name, investigational new drug (IND) number, sponsor (or principal investigator in academia), funding organization, medical monitor, and coordinating center. The pages include the principal investigator’s signature (or sponsor), as well as site-specific information, such as the agreement, and protocol details. They also detail the study team and site, particularly in the case of multiple teams and sites.
- Objectives: List the study’s primary and secondary objectives.
- Background Information: Describe the problem under study and priority. Include the medical and scientific rationale that justifies researching the problem. Include data from other studies relevant to this proposed research. Include the name and description of the proposed intervention, including the dosage, route of administration, period, and frequency of intervention.
- Study Design: Describe the methodology and how it will answer the study question. This should include the type of study, primary and secondary outcome(s), population, sample size, study location, period of enrollment and follow-up, intervention and route of administration, randomization (as necessary), and any other relevant protocol information.
- Selection and Exclusion of Subjects: Provide statements describing how the participants must meet all the inclusion and exclusion criteria, and list the criteria. Clearly define the study population. For example, list the demographic criteria, required laboratory data, any prior therapies allowed or disallowed, ability to understand and meet all study requirements, if contraception is necessary, exclusion criteria such as specific health status, use of excluded drugs, cancer status, and chemical dependency status.
- Study Enrollment Procedures: Describe the methods and procedures for identifying and enrolling subjects, how they are documented, how consent is obtained, and any randomization procedures.
- Study Intervention, Duration, and Route of Administration: This section should describe each intervention and duration, as well as how each is administered. List expected adverse effects and dose escalation, if applicable. Discuss how the intervention is acquired, stored, and disposed of, as well as documentation for intervention accountability. In addition, note the medications restricted, allowed, and required, along with the extent to which these medications are tracked and documented.
- Study Procedures: This section includes a study evaluation schedule (presented as a chart) and explanations of the required assessments, what each period is, and any special considerations or instructions necessary. These should match what is available in the column headers of the chart above, and they should include information on the screening or baseline assessments, randomization, blinding, follow-up visits, and final assessments.
- Safety Assessment: List any expected adverse events, and how these could be managed. Mention any toxicities seen in earlier IND studies here. Also, include safety measures as identified in laboratory findings, methods and timing for safety parameters based on the risk profile, definitions for adverse events (AE) and serious adverse events (SAE) and laboratory values used to identify their possibility, timeframes for reporting and collecting information on AEs and SAEs, the reporting system, how you will follow up on AEs, and the specific guidelines for independent monitoring.
- Intervention Discontinuation: List criteria for intervention discontinuation and how you could meet them. Also list possible reasons for discontinuation, any modifications to the schedule should it be discontinued, duration of follow-up, any temporary discontinuation criteria, or any evaluations should participants be temporarily or permanently discontinued from the study.
- Statistical and Analytical Considerations: Include primary and secondary statistical hypotheses, why you chose the study design, the primary and secondary outcome measures, and the validity and reliability of these measures. Also discuss sample size and randomization, treatment assignment procedures, how you define the population, any interim analyses, primary and secondary outcome analyses, the statistical methods you use to consider any necessary intervention effect between groups, and if necessary, the expected positive within group correlations among different study arms.
- Data Collection: Detail how you will gather the data, the required forms, how to keep these forms confidential, and what source data to expect. Note site responsibility for data collection and management, and (if necessary) the responsibilities of the coordinating center.
- Quality Assurance: Describe training for study staff, whether there is a control committee and their required practices, any quality control metrics, how you will identify and document protocol deviations, how you will assure protocol compliance, and the schedule for reviews. If you have a manual of procedures (MOP), reference it here.
- Participants Rights: Include references to the Institutional Review Board (IRB) requirements, informed consent documents, procedures for participant confidentiality, and study discontinuation requirements.
- Committees: List any committees associated with the study, along with their roles.
- Publication: Outline the requirements and procedures for publication.
- References: List any citations referenced in this protocol.
- Supplements/Appendices: Include any additional documentation.
To track every aspect of the proposed research for each participant, create a case report form (CRF) that you can use in both paper and electronic formats. With CRFs, you can collect and analyze data for analysis, and then generate a conclusion for your study. For more information on the distinct phases of clinical trials, see “ Understanding the Phases of Clinical Trials .”
Concept Protocol Template
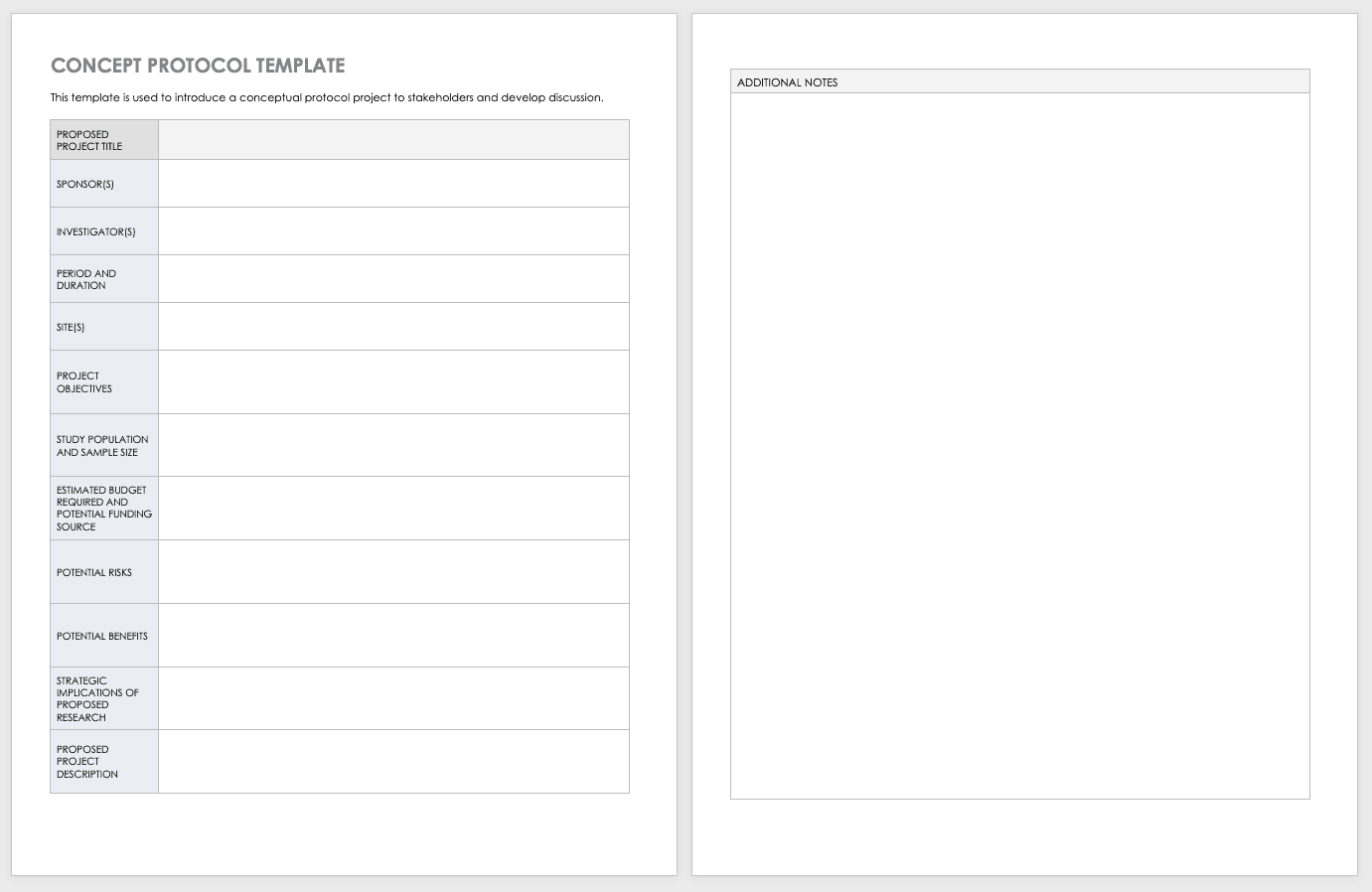
Before you start your full protocol, consider putting together a concept protocol. A concept protocol helps you introduce an abstract project to stakeholders and encourage discussion around the proposed project.
Download Concept Protocol Template for Clinical Research
Phase 1 Clinical Trial Protocol Template

For nonclinical research or clinical trials that are Phase 0 or Phase 1, use this free template. Phase 1 or nonclinical trials do not require the same amount of detail as a full study protocol.
Download Phase 1 Clinical Trial Protocol Template - Word
Research Compliance Templates
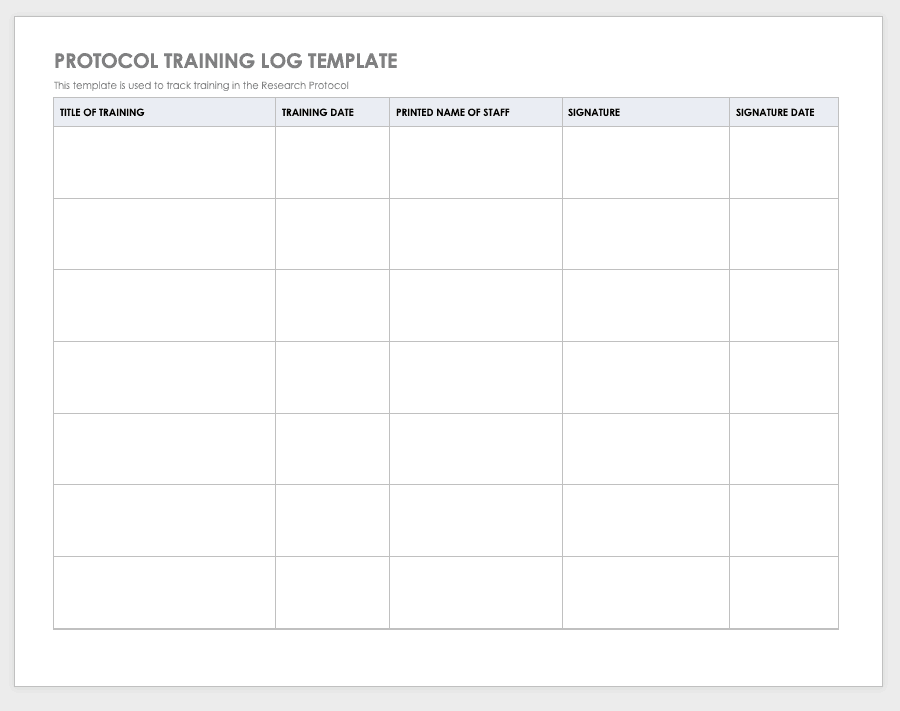
By training staff members on the research protocol, you’ll help them meet compliance standards and understand the purpose and details of the study. Use a training log to record all training that the site study staff completes, signing the log entry for verification.
Download Protocol Training Log Template
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Protocol Deviation Template
Protocol deviations are inadvertent or unplanned changes or noncompliance with the research protocol. These events do not increase risk or decrease benefit, nor do they impinge on participants’ safety or rights. They do not compromise study data, but you should capture the deviation for reference.
Download Protocol Deviation Log Template
Excel | Word | PDF
Delegation of Authority Log Template
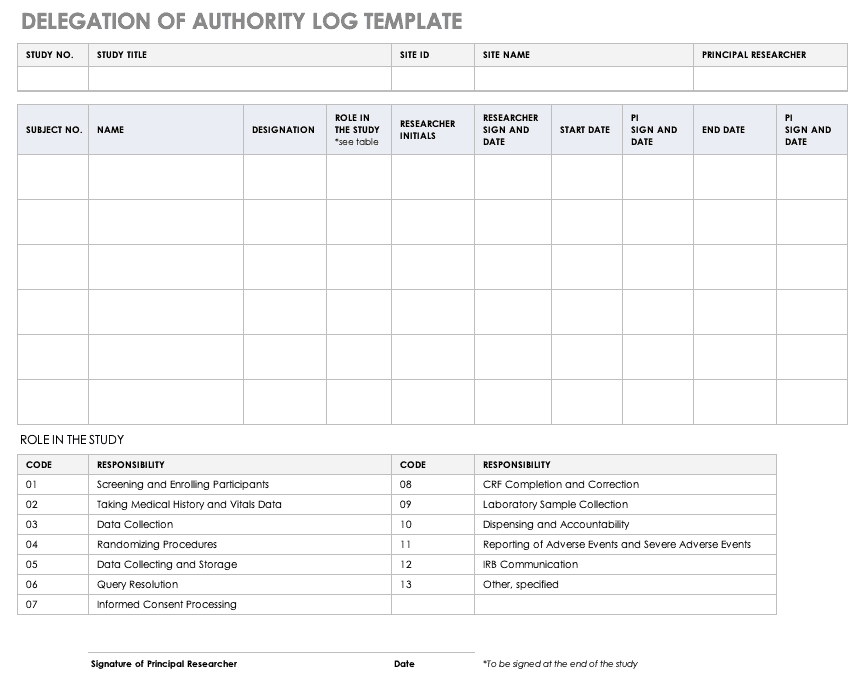
Once you’ve trained your staff and figured out their roles and responsibilities, the principal investigator must delegate authority. The delegation of authority log should be filled out and signed prior to the study’s start.
Download Delegation of Authority Log Template
Site Selection Visit Form Template
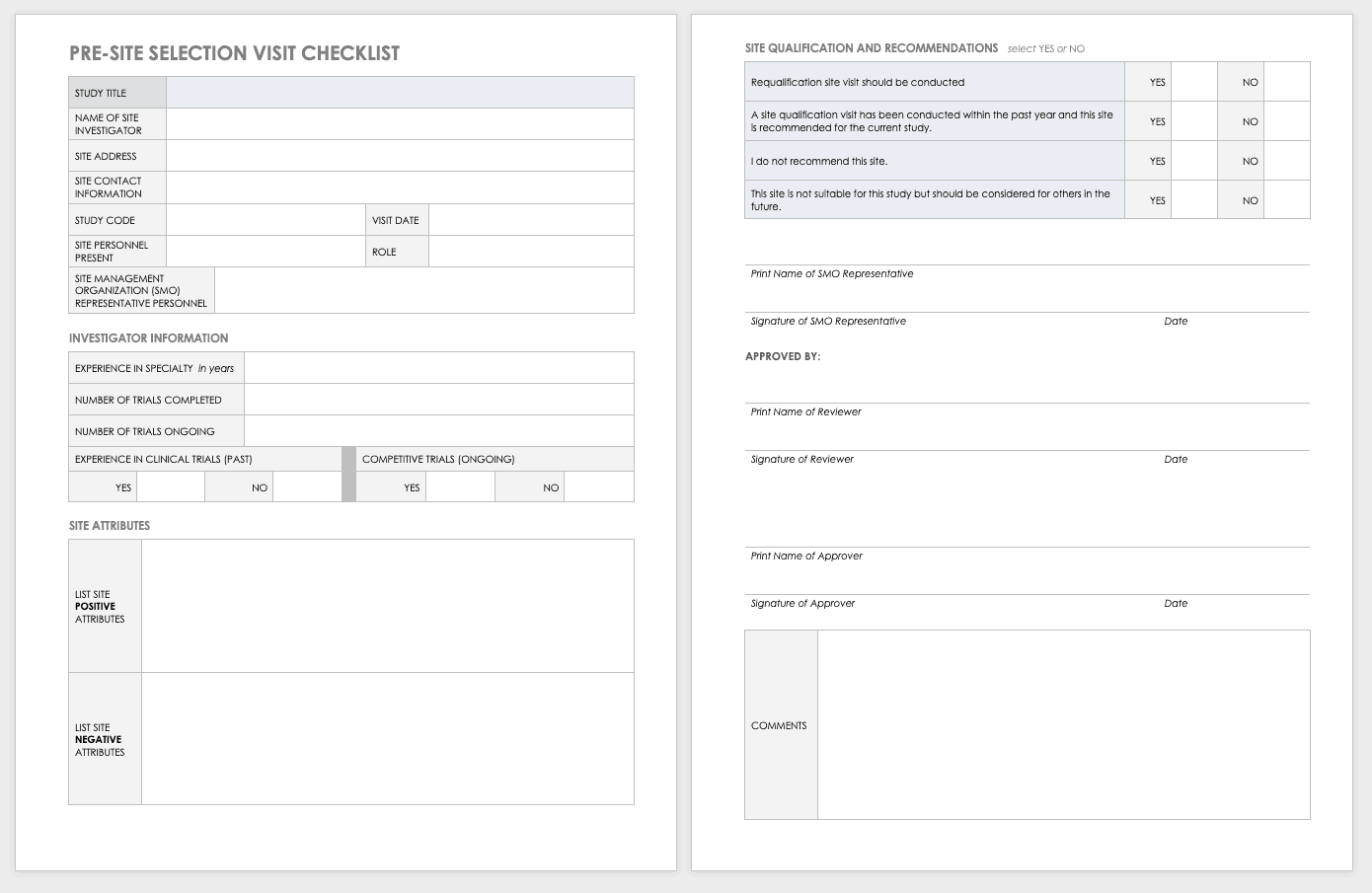
The sponsor must perform a site visit to determine its suitability as part of a multisite study. This means taking a tour to determine whether the site has the capabilities to meet the sponsor’s goals.
Download Site Selection Visit Form Template
Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Study Site Initiation Checklist
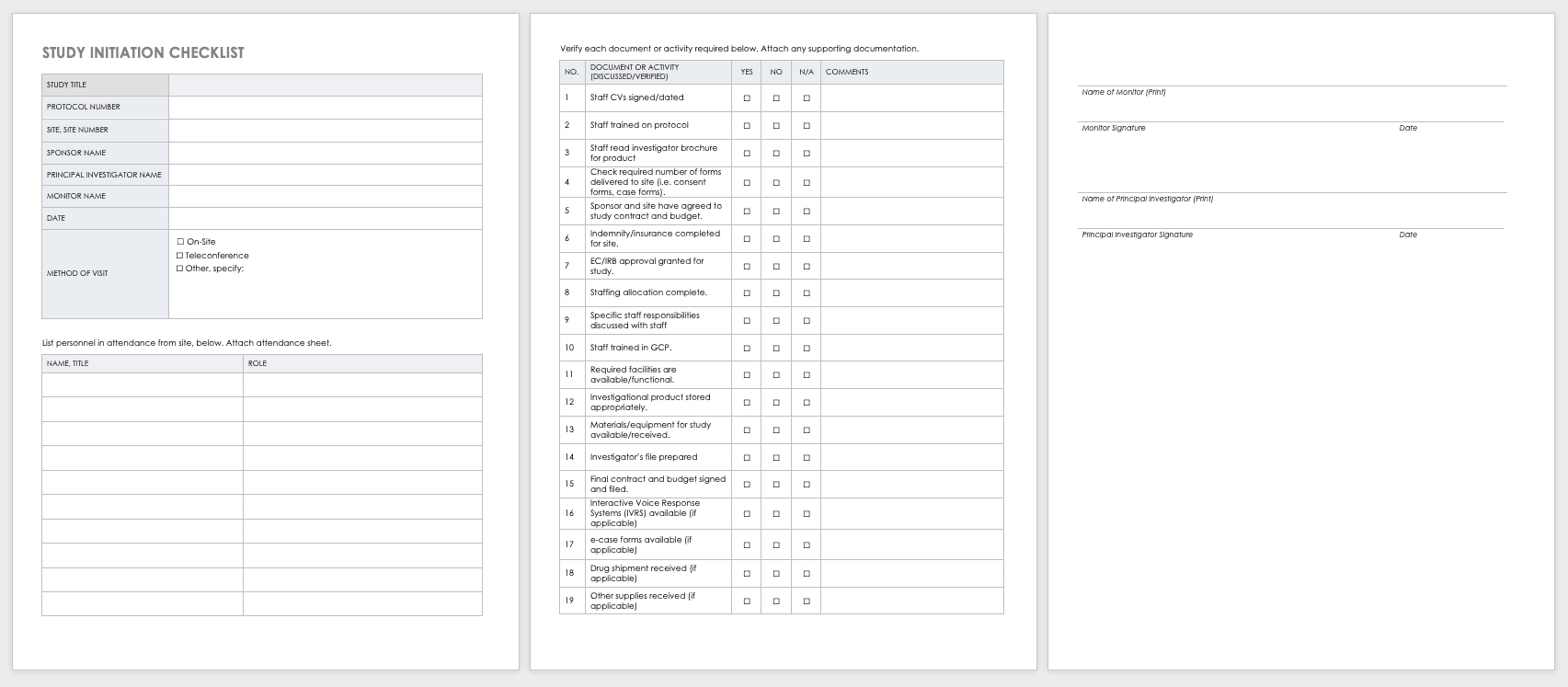
Teams must also perform an inspection to determine if a site has the appropriate staff, training, equipment, and supplies to be part of a multisite trial.
Download Study Site Initiation Checklist
Project Management for Clinical Trials, Practices, Templates, and Documents
Clinical trials are big projects. If the organization is not used to planning and wants to conduct clinical research, it must hire a project manager and work with senior leadership to introduce planning into the organization.
Together, they should develop the main goals and define their limits and the terms of success. They should set out a strategy for which tasks and sets of tasks to perform and in what manner. Test any planning tools or software before the trials start. When possible, use templates to ensure consistency and best practices.
Once the trial starts, evaluate your systems with standardized metrics. The project manager can track study deviations and apply corrective actions. Use the lessons learned from past and current projects to help guide future projects. Employing consistent tools gives you the opportunity to draw from a reservoir of data.
Clinical research can cost billions of dollars and years of time, resources, and effort. As
such, project management best practices and methodologies are critical to the success of a clinical trial, according to experts .
Many software systems are available to manage clinical trials. When very specialized, these are referred to as clinical trial management systems (CTMSs). However, other platforms can also manage clinical trials and may already be embedded with your information technology. Regardless of the platform you use, you should have full project management functionality, such as planning and reporting modules, as well as the ability to track participant contact information, deadlines, and milestones.
You may want to consider the following project management documents for your clinical research.
Project Management Plan (PMP) for Clinical Trials
A PMP delineates and acts as an agreed-upon document of scope, responsibilities, and guidance. You can use it throughout the project to help stay on track. Every clinical trial has difficult milestones, but a good project management plan can help you sidestep some of the regular issues.
You have many PMP software platforms to choose from, but regardless of your ultimate decision, your PMP must focus on protocol adherence, subject care, and service quality, along with how to achieve each standard. Here are the sections you should include in your PMP for a clinical trial:
- Project Objectives: This is an outline of the research objectives for the study, your quantifying standards, and your goals.
- Background and Strategic Context: By documenting background and context, you establish a foundation for decisions and discussion to follow.
- Study Governance: The governance covers the roles and responsibilities in the project, encouraging open communication, sharing, and accountability.
- Stakeholder Management Plan: This plan details how the staff and investigators will collaborate and effectively communication with stakeholders. This could include (as per the roles and responsibilities) regular emails, newsletters, consultation, oversight, training, and documentation.
- Scope: This document delineates assumptions, constraints, and deliverables (and their expected dates).
- Project Risk Assessment: This document helps you prepare for risks and decide on the risk profile.
Clinical Research Project Activity List
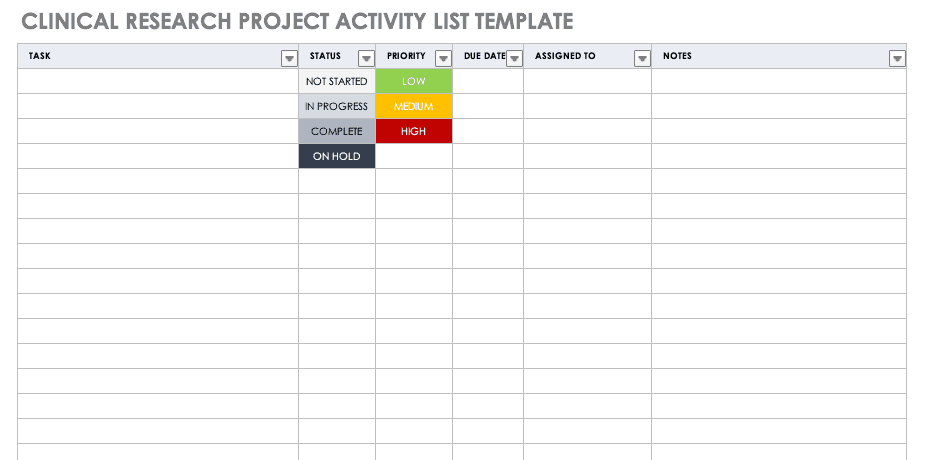
A project activity list is an itemized documentation of all the activities scheduled as part of the project. This list should be very detailed, including the status and priority of the task, when it is due, and to whom it is assigned.
Download Clinical Research Project Activity List Template
Excel | Smartsheet
Clinical Trial Timeline Template
A timeline enables you and your staff to track each major portion or milestone of your clinical trial. Your timeline should include these steps:
- Choose Research Questions and Study Design: Research always begins with questions. Your research question will determine how you design your study.
- Choose Outcomes: The outcomes for any trial are dependent on many factors, including scope, health conditions under study, target population, type of intervention. One resource to help develop outcomes is Core Outcome Measures in Effectiveness Trials (COMET) . This database details core outcome sets for comparison in clinical trials.
- Prospectively Register the Trial: Whether you are working through the FDA, World Health Organization (WHO), or another national agency, study transparency is critical. Prospective registration of trials is recommended. One resource for registration is the ISRCTN registry .
- Obtain Ethics Approval: Any trial involving human participants must go through an ethics review to safeguard the subjects’ rights, safety, well-being, and dignity. There are many options for institutional review, including through a university or a private or governmental organization. Without this step, research cannot commence.
- Prospectively Publish Protocol and Analysis Plan: Before a clinical trial, you must complete some pilot research. When you publish the research leading up to a clinical trial, along with the protocol and analysis for the trial itself, you increase transparency and accountability of the research.
- Planning for the Trial and Data Management: Many clinical research professionals recommend including patients in the planning phase of clinical trials, at least as stakeholders to review the plan. By completing the plan early and allowing potential participants to review it, you help improve recruitment and retention during the trial.
- Recruitment and Retention: Recruitment is getting the right people to take part in your trial, and retention is about keeping their interest and trust. A source of unending frustration for researchers, recruitment and retention can make or break a trial.
- Identify and Manage Trial Sites and Staff: This process is not as straightforward as it is often thought to be. Study coordinators must use feasibility checklists to choose sites and figure out how to get bring on staff who have the bandwidth to recruit for the study.
- Data Collection: The methods for collecting data are critical to any study. Advance planning and structure help you stay organized, comprehensive, and transparent so that your study can have a seamless analysis and solid conclusions.
- Data analysis: Flaws in analysis can generate poor, biased, or erroneous outcomes. In advance, researchers should consider patient blinding, randomization procedures, and sequence generation.
- Findings dissemination: Some researchers recommend threading all research on a trial topic. One resource for this is CrossRef , a database that links similar research. Regardless, the point of research is to capitalize on scientific progress and move it along. By having a plan to disseminate your results, you ensure that others capitalize on your research and move the knowledge forward.
Use this free template to develop your own clinical trial timeline. Add your own steps, milestones, and dates for a comprehensive, expansive view.
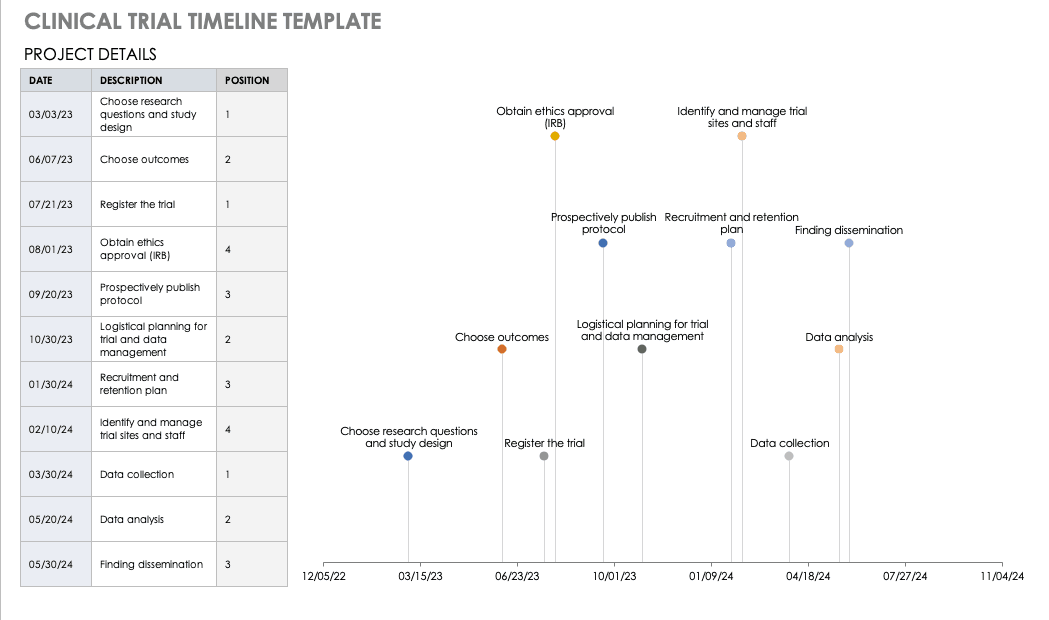
Download Clinical Trial Timeline Template
For a different perspective, add your project details to this free template so you can view your timeline visually.
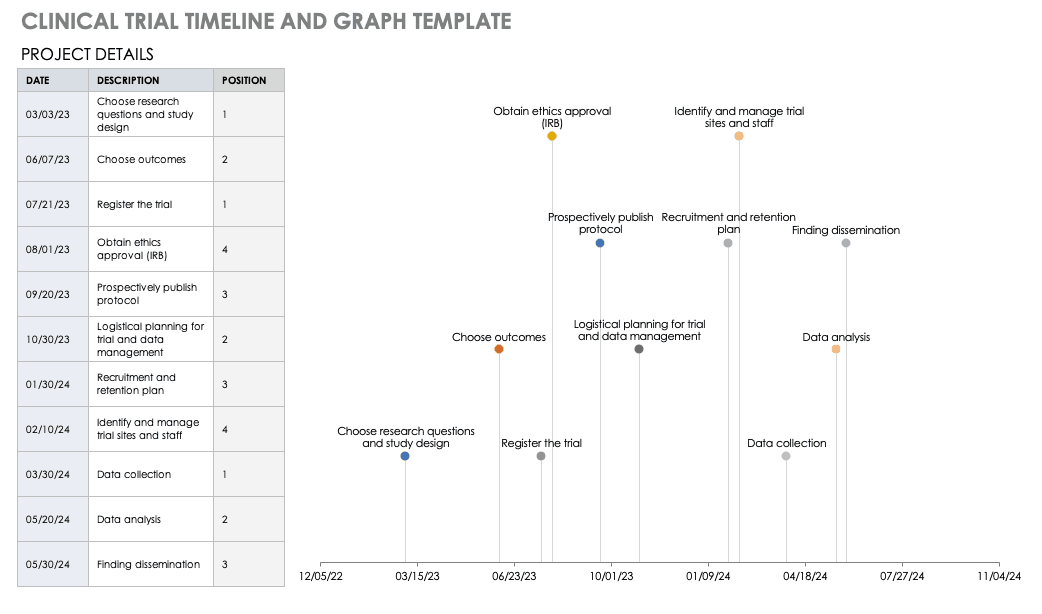
Download Trial Timeline and Graph Template
Microsoft Project Management for Clinical Trials
First released in 1985, Project is a well-respected Microsoft product for project management. Microsoft Project was not traditionally available as a part of Office Suites, a package of programs for professionals and professional organizations. However, Microsoft recently included it as a part of the Windows 2016 suite.
Microsoft Project Management has the following features:
- Built-in templates
- Project portfolio management
- IT management
- Presentations
- Out-of-the-box reports
- Multiple timelines
- Real-time reporting
- Dependency management
- Priority assignment
- Lean management
- Gantt charts/project mapping
- Calendar views
- Setting baselines/KPIs
- Project budgeting
- Issue tracking
- Task creation
- Resource management
- Cloud access
Microsoft Project has built-in templates that you can apply to clinical trial management.
Microsoft SharePoint for Clinical Trials
SharePoint is a collaboration platform that is integrated with Microsoft Office. SharePoint manages and stores documents , and it enables multiple users to access the documents via their own site or a standardized Microsoft site. A subscription to Microsoft Office 365’s SharePoint does not require a server, but customization options are limited; the flexible authentication and authorization systems are built in.
SharePoint Server, available in Standard or Enterprise versions, can be developed as either
virtual or hosted services in a business’s IT department. SharePoint Server enables the organization to control the SharePoint features available to staff, and you can scale it to meet different numbers of users.
Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 is a Microsoft-hosted version that comes with Microsoft Office. Microsoft provides a template in SharePoint for Clinical Trials: Clinical Trial Initiation and Management application template for Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 . You can download and add this template to your SharePoint Services, which enables you to create the following:
- Clinical Trial Protocols: This includes the objectives, study design, project plan, subject selection, and budget.
- Protocol Documents: This includes additional documents relative to your study.
- Calendar: Track milestones in the project.
- Threaded Document Discussions: Team members can start and track discussions within documents.
- Task Creation and Assignment: You can create and assign tasks to users, who receive email notifications.
- Archiving: You can move documents or groups of documents to archive status, keeping them but not making them visible.
The clinical trial template has site lists of libraries for clinical trial protocols, protocol documents, announcements, calendars, issues, tasks, and document discussions. These can be further customized with different versions of SharePoint. To download this template, you will need access to SharePoint Server 3.0.
Clinical Research Budget Plan Template
In many instances, you set the clinical trial budget after much negotiation with a sponsor. Other times, you need to build a budget before the sponsor is even on board, as a way to convince them of the project’s feasibility. The key cost drivers for any clinical research project are the following:
- Patient Grants: These include the costs for screening failures, baseline patient measurements, and procedural costs.
- Site Costs: This covers any expenses associated with the site, such as start-up fees, IRB fees, storage fees, and site management costs.
- Non-Patient Costs: This includes consultation fees, monitoring board fees, and any medical device costs.
- Labor Costs: You must account for all the staff required for the project and their full-time equivalency (FTE).
- Site Management: These costs include pre-study visits, initiation fees, monitoring, and close-out fees.
- Miscellaneous: These include investigator meetings, any technology needs, and ad hoc travel.
- Unexpected Costs: These are costs resulting from protocol amendments, value added tax (VAT), delays, and inflation.
Before you start putting together your research budget, you must gather the following:
- Schedule of assessments from the protocol
- Standard institutional fees from your institution, if applicable
- Evaluation and procedural costs
- Staff allocation and their hourly rates
- Indirect cost rate
- Subject compensation costs
- Data storage fee estimate
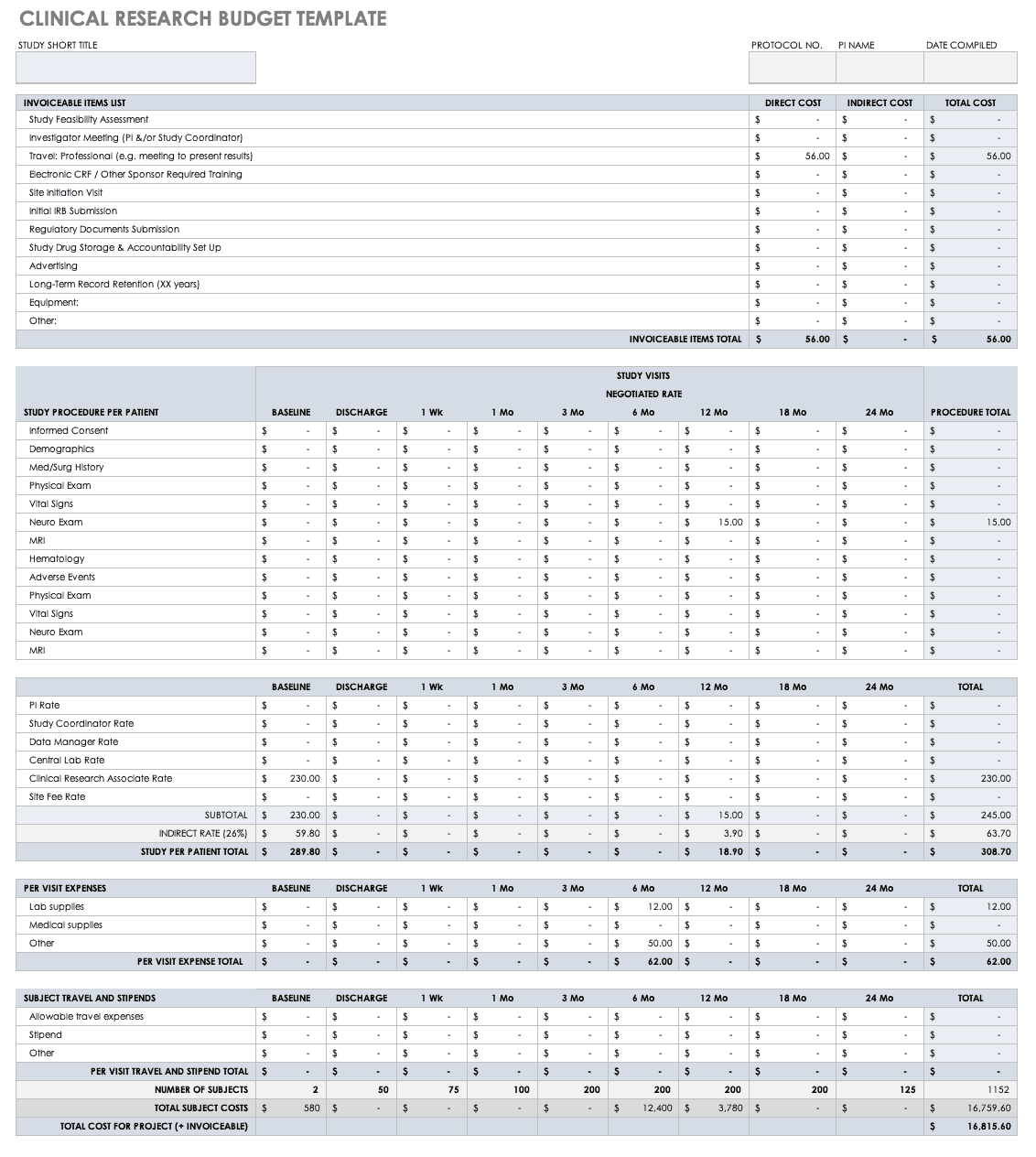
Put together your own clinical trial budget with this free clinical research budget template.
Download Clinical Research Budget Template - Excel
Clinical Research Tracking Log Templates
Clinical research requires scrupulous planning, a well-developed team, regulatory adherence, and above all, excellent documentation. It is therefore critical for clinical trial project managers to have a completed scope of work and to develop all the forms and templates before the trial begins. Some of these documents are for planning, and some, like those included below, are for operational purposes.
Regulatory Binder Checklist

Strong clinical practice thrives with a regulatory binder checklist. This checklist keeps track of all paper versions of essential regulatory study documents. Each document should also include any electronic locations. This document should be regularly updated, customized for unique studies, and stored in reverse chronological order.
Download Regulatory Binder Checklist
Clinical Study Document Tracking Log
It is important to not only track all paperwork related to a clinical trial, but also be able to locate it easily between various staff and sites. A clinical trial document tracking log can help you keep a written trail of the documents and when they were submitted and approved. You should also keep copies of the documents with the log. Use this free template to develop your own clinical study document tracking log. You can also adapt the log for specific correspondence, such as documents relating to FDA or IRB submissions, but it should not be mixed with regulatory documentation.
Download Clinical Study Document Tracking Log
Data and Safety Monitoring Plan (DSMP) Template
Before you can undertake a study, you must develop a DSMP for how to keep participants safe and how to secure data and ensure accuracy. The DSMP has several sections:
- The study purpose
- An adherence statement
- Any protocol amendments
- Multisite agreements
- A plan for subject privacy
- Confidentiality during adverse event reporting
- Expected risks
- Adverse events, unanticipated problems, and serious adverse events: how they are defined, their relation to the study, expectations, severity grading, and reporting procedures in single-site and multisite trials, and whether they are IND or non-IND studies
- Events of special interest
- Pregnancy reporting
- Rules to halt the study for participants
- Quality control and quality assurance
- Subject accrual and compliance
- Sample size justification
- Stoppage rules
- Monitoring committee designation
- Safety review plan
- Study report plan for independent monitors
- Plan to submit reports from onsite monitoring and audits
- Data handling and record keeping
- Informed consent
- Reporting changes in study status

Create your own data and safety monitoring plan using this free template. It lays out each section so you can specify them for your research. The principal investigator should sign and date this document once it is complete so that it may be filed.
Download Data and Safety Monitoring Plan Template - Word
Research Communication Plan Template
A communication plan should describe how you will converse with internal and external stakeholders during your project. Your communication plan should include a brief overview of your project and a breakdown of the messages you need to get out. You should adapt the messages for different audiences and define who will deliver these messages. The messages should include the following:
- The purpose and benefits of the research
- The known effectiveness of the intervention, or (if the intervention is under study) the disclosure that the effectiveness is unknown
- How participants will be protected
- The risks and benefits of participating

Develop your own communication plan using this free clinical trial communication plan template. This template also includes a section for situation analysis and risk analysis that asks for inputs on strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Download Clinical Trial Communication Plan Template - Word
Participant Management in Clinical Trials Using Templates
A few main documents help ensure that your participants are tracked and well-cared for before and during your research study.
Enrollment Log for Clinical Trials Template
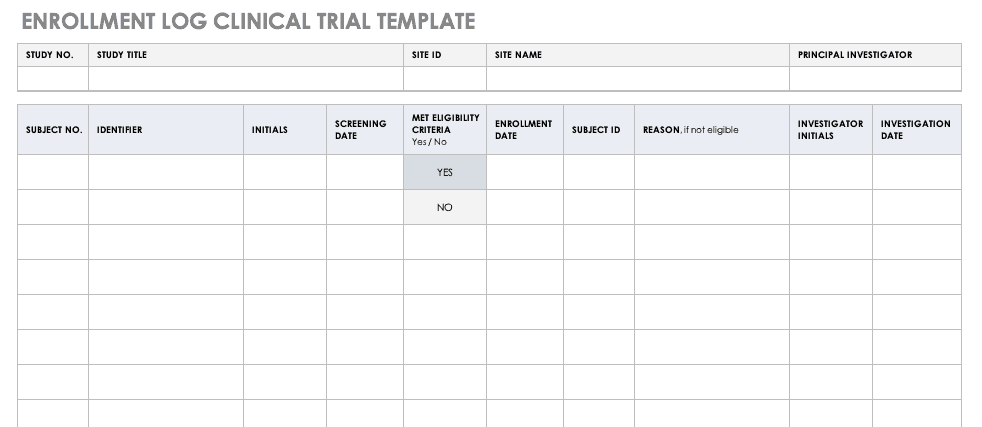
This log keeps track of everyone that has been enrolled for participation in your study. This does not mean that they have met the eligibility requirements or have been otherwise screened, but it is a record that they have signed up to be admitted.
Download Enrollment Log for Clinical Trials Template
Informed Consent Form Templates
Informed consent is the central tenet of ethical research with human subjects. The consent process typically involves a researcher delineating what is involved in the study, its risks and benefits, what a participant’s duties entail, and answering any questions they have. Before you perform any research, make sure the informed consent document is signed and the participant receives a copy, unless the informed consent document has been waived by an institutional review board (IRB). Federal regulations 45 CFR 46.116 govern what you must provide in the informed consent process in the United States.
To prepare informed consent documentation, researchers must do the following:
- Use plain, easily understandable language no higher than an 8th-grade reading level.
- Tailor documents to the potential population.
- Avoid technical jargon.
- Use the second or third person (you/he/she) to present study details.
- Include a statement of agreement.
- Ensure that the consent document is consistent with information in the IRB application.
These templates assist the principal investigator in the design of their informed consent forms (ICFs). You can adapt them to accommodate the details of any study and include both the information sheet and the consent form. Modify each section with the appropriate description described in italics. Use the general template for any type of research.
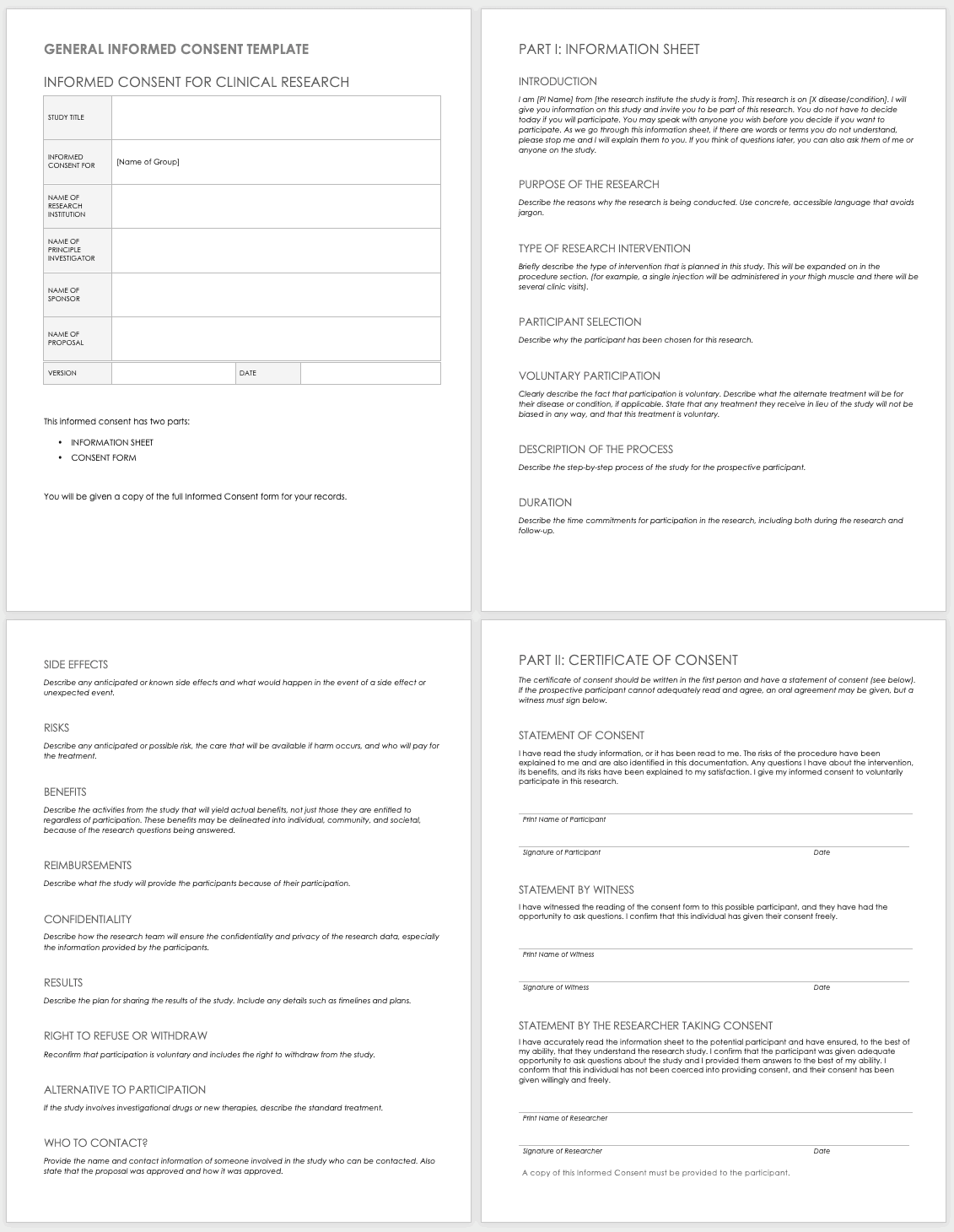
Download General Informed Consent Template - Word
Use the clinical trial template for medical research.

Download Informed Consent for Clinical Trials Template - Word

Eligibility Criteria (Inclusion/Exclusion) Checklist
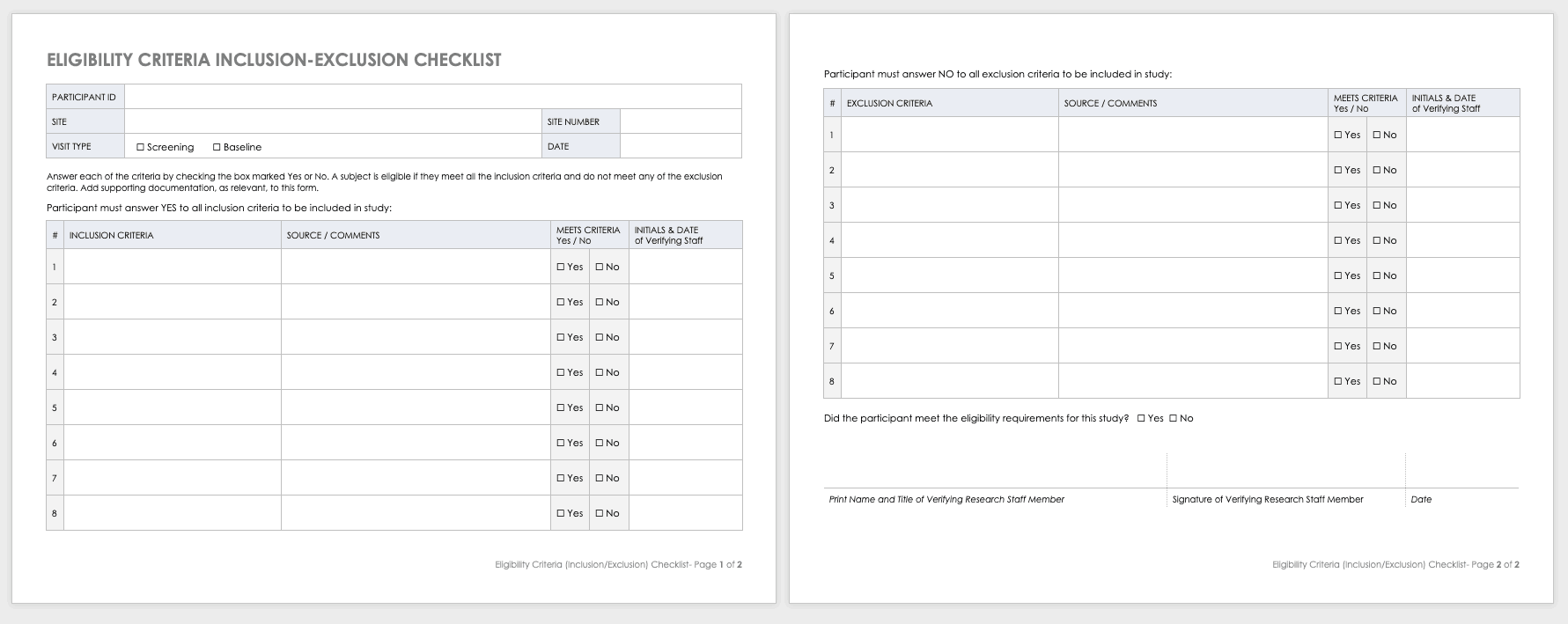
Eligibility criteria are an essential part of clinical trials. They define the population under investigation.
Inclusion criteria are the standards that participants must meet to enroll in the study. For example, in a study on a new diabetes medication, you would likely want participants who have already been diagnosed with diabetes.
Exclusion criteria specify the characteristics that disqualify participants from taking part in the research. For example, in the diabetes study above, the proposed diabetes drug may target a specific age demographic. One exclusion criterion could be a participant whose age falls outside of the range.
Download Eligibility Checklist Inclusion-Exclusion Template
Concomitant Medication Log Template
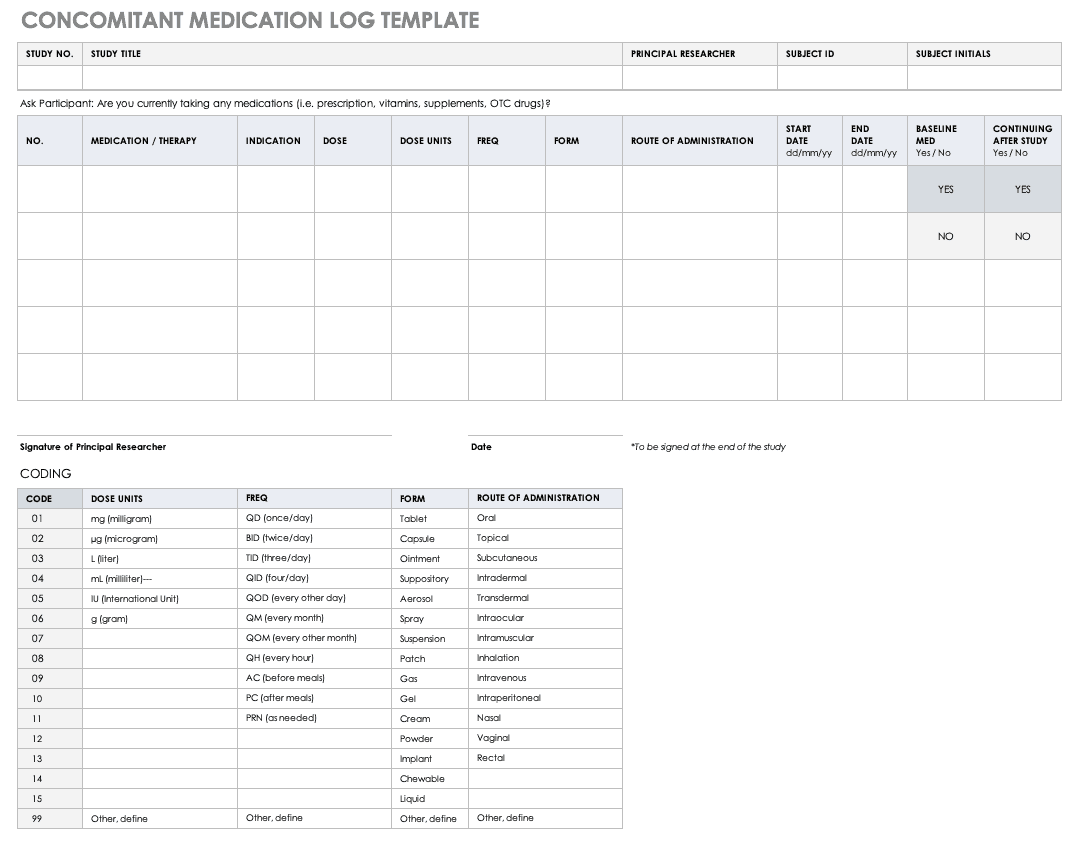
Properly documenting any medications that participants are taking is imperative to understanding the reactions occurring in their bodies, as well as what could spur adverse and severe adverse events during the study. Fill out a concomitant medication log for every participant and account for everything participants take, even seemingly innocuous items like multivitamins.
Download Concomitant Medication Log Template
Excel | Word | PDF
Adverse Event Form
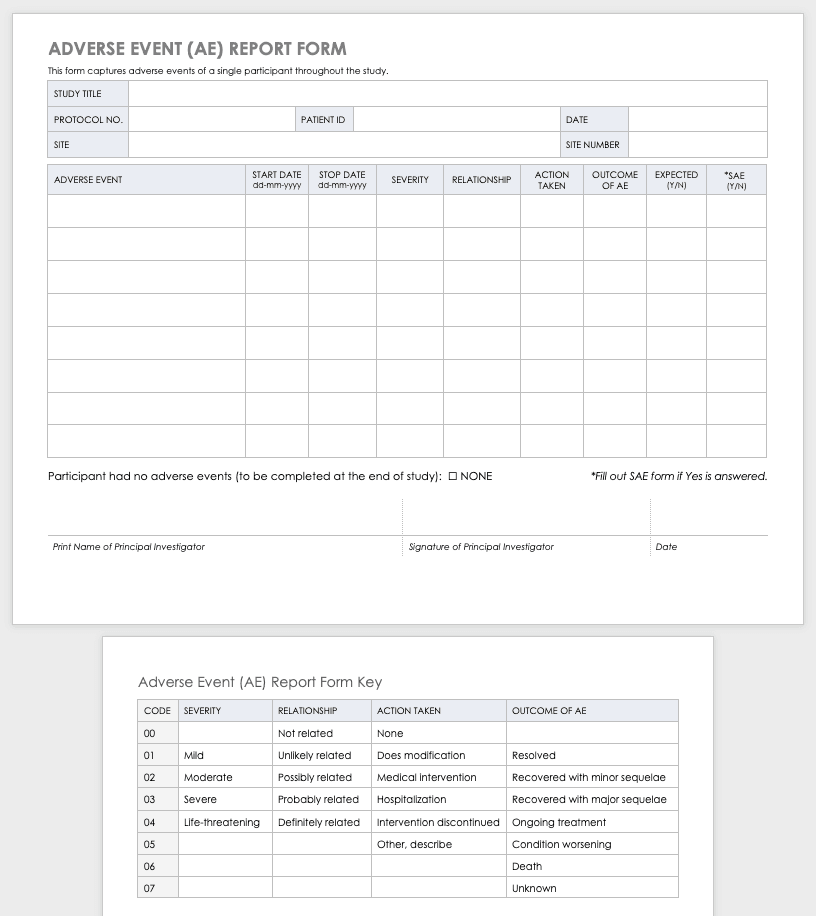
Clinical research can result in complications for the participants and trigger an adverse or severe adverse event. An adverse or severe adverse event is when participants in a clinical trial have negative medical symptoms that can be shown in laboratory or physical testing. Each participant in a clinical trial should have an adverse event log that tracks any adverse events through the duration of the study.
Download Adverse Event Form Template
Severe Adverse Event Form
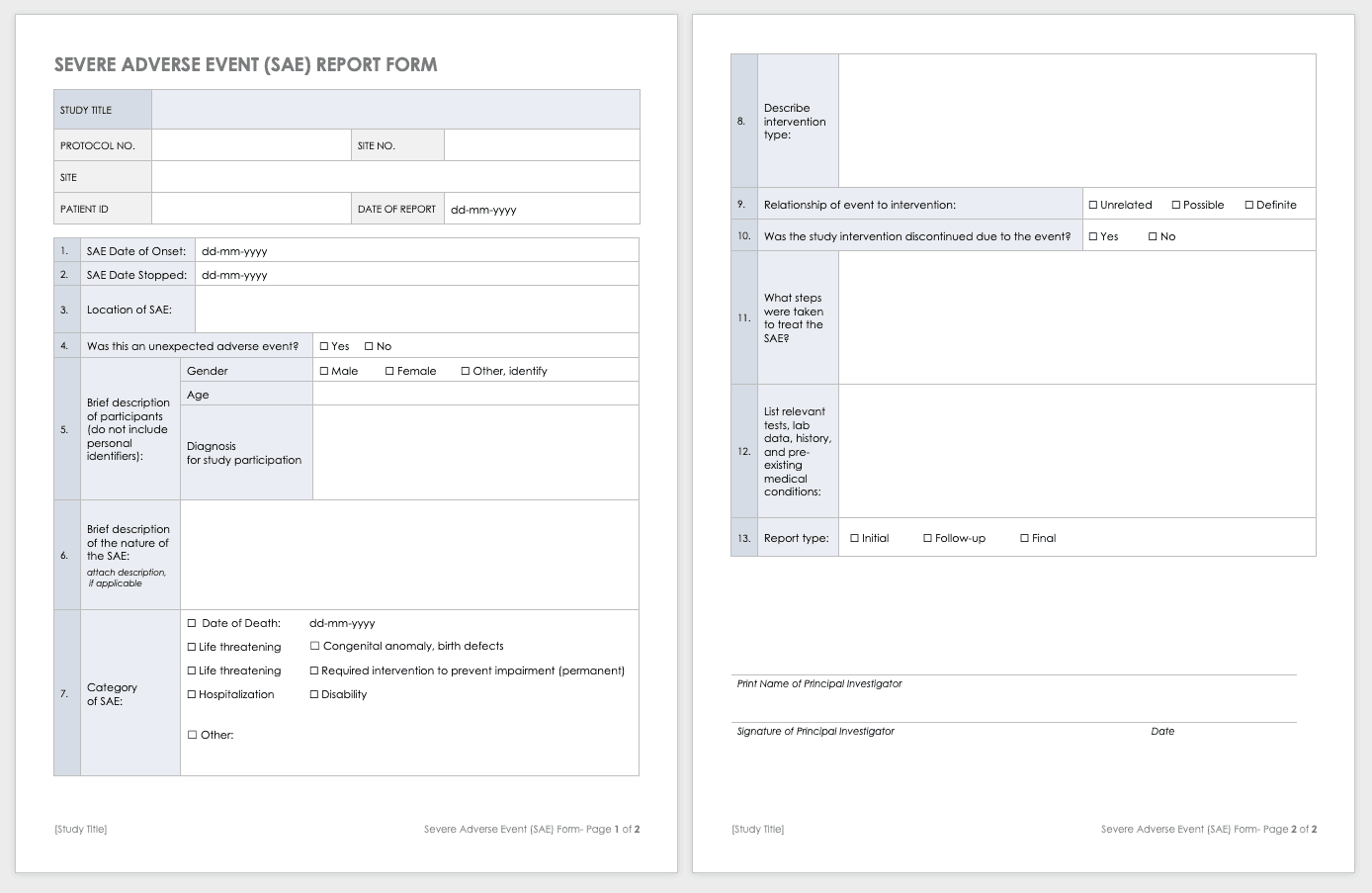
A severe adverse event (SAE) is a special case of an adverse event in which the outcomes are acute. Examples of SAEs include death, life-threatening complications, or anything leading to immediate hospitalization, physical disability, or congenital abnormalities. Log SAEs in the AE form, but fill out an additional SAE form.
Download Severe Adverse Event Form Template
Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Post-Clinical Study Research Documentation and Templates
After you complete or terminate a clinical trial, you should prepare several additional documents. Here are some examples of this documentation:
- Investigational Product Accountability Log: You generally provide an accountability log to the authorities that tracks drug products to show product disposition and accountability per participant. It also helps you track the drug product stock and any imbalance at the end of the study.
- Investigational Product Destruction: Due to regulations governing the proper disposition of investigational products in clinical research, you must properly dispose of products left at the end of a study (as evidenced by the product accountability log). This form describes and ensures that you have properly handled any leftover products.
- Close-out Checklist/Report: A study close-out checklist and report helps ensure that you complete all closing procedures, archive the paperwork, and resolve electronic data.
Clinical Study Summary Report Template
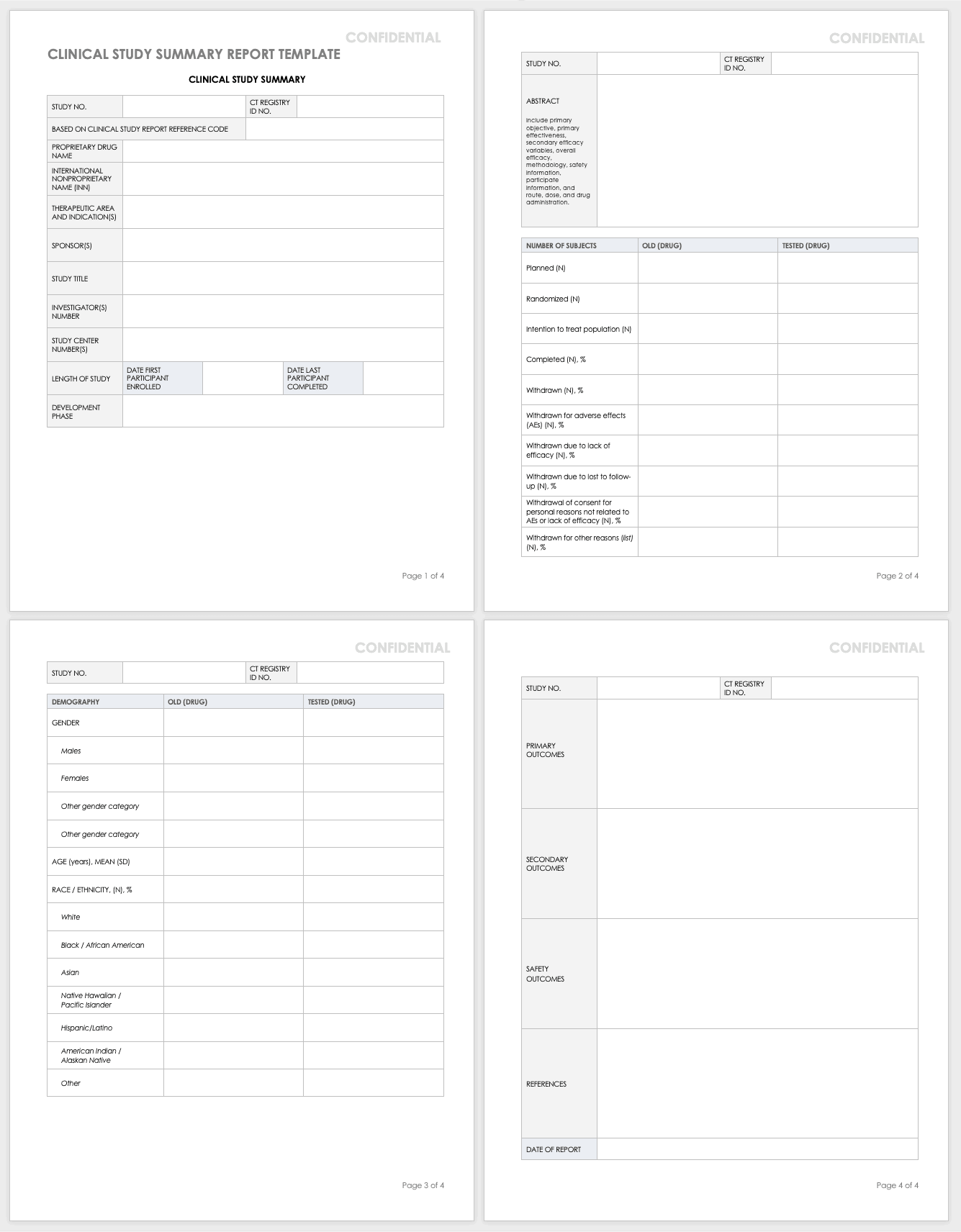
Assemble the summary report at the end of a study to get results into the sponsor’s or public’s hands while you complete the full report. A summary report is typically about 2-3 page-long document that encompasses the highlights from the trial.
Download Study Summary Report Template - Word
Clinical Study Report (Full) Template

The full clinical study report (CSR) encompasses all aspects and details of the research you’ve conducted. It is not a sales or marketing tool; instead, it is a scientific report details the methodology and shows scientific rigor.
Download Clinical Study Report Template - Word
Public Links and Resources for Clinical Trials
The following are publicly available resources, tools, and links for clinical trial practitioners and principal investigators:
- PROMIS : Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) software gives clinicians health status patient measures that are physical, mental, and social patient-reported metrics. Funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), PROMIS can be used in clinical trials as measures of conditions and disease and as a comparison to the general population. The measures in PROMIS are free to administer on paper, by computer (computer adaptive tests), or with an app. The computer adaptive tests may be conducted on REDCap , Assessment Center , or Epic .
- REDCap: REDCap (Research Electronic Data Capture) is an electronic data capture system that works on browsers to develop research databases. It was developed at Vanderbilt University to support clinical research data collection and is a free resource to nonprofit organizations. It is limited to organizations joining the REDCap consortium and is not open-source or available for commercial use.
- Good Clinical Practice (GCP) Training: GCP is an international quality standard designed for use by staff involved in clinical trials. The guidelines for this are from the International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH). These regulate the ethical guidelines, documentation, record keeping, training, facilities, technology, and inspections. The purpose of these guidelines is to keep clinical trials scientifically rigorous and to delineate the roles and responsibilities of research staff. The National Institutes of Health administers training for GCP.
- Quality Management Study-wide Review Tool: Developed by the NIH, this review tool is for PIs and study teams to manage their quality reviews, and may be customized for unique studies.
- Quality Management Subject Review Tool: Also developed by the NIH, this review tool provides study teams the structure for review of participant data, and may be customized for the unique study. This should be developed in concert with the DSMP.
- AccrualNet: AccrualNet is sponsored by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), and offers advice and training to staff on how to recruit study participants.
- Regulatory Education for Industry (REdI): The FDA offers a Clinical Investigator Training Course for researchers conducting investigational new drug (IND) or device exemption (IDE) studies.
- ResearchMatch: Available to volunteers and researchers affiliated with the NIH Clinical and Translational Science Award (CTSA) program, this site helps match prospective participants with specific studies.
- Grant Policies and Guidance: The NIH and National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH) offer links to many resources that are policy- and grant-specific to the NIH and NCCIH, updated regularly.
- Protocol Amendments: The NIH and NCCIH offer regularly updated guidance for NIH policy and protocol changes.
- Clinical Terms of Award for Human Subjects Research: The NIH and NCCIH offer guidance for clinical trial grant awardees for compliance.
- NIH Single IRB (sIRB) Policy for Multisite Research: The NIH offers a FAQ page for multisite research that includes policy, contract and application information, responsibilities, exceptions, and costs.
- Dictionary of Cancer Terms: The National Cancer Institute (NCI) offers a dictionary of cancer terms for researchers and laypersons. You can add this dictionary to your website as a widget.
- Informed Consent FAQs: The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and the Office for Human Research Protections (OHRP) offer a FAQ page about informed consent for researchers and lay persons.\Informed Consent Language (ICL) Database: The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) offers a database to help write informed consents. This database is specific to medical conditions and different risk language.
Improve Clinical Trial Research with Smartsheet for Healthcare
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Screening and Preparing for a Study Visit
There are several steps that must be taken prior to conducing a study visit..
Many human subject protocols require participants to be scheduled for specific research visits. The number and length of time required for a research appointment to occur is highly dependent on the specifics of the study design. The specifics of the appointment are highly dependent on the location of the appointment. Appointments can occur in inpatient units, outpatient clinics, lab draw locations, diagnostic testing locations, research labs, Clinical Research Center (CRC), at the participant’s home or a neutral site convenient for the participant. The visits where the study will occur must be listed with the IRB.
It is important to set the expectations of each visit for the participant. For example, where the visit will take place, how long the visit will take, tasks to be completed at the visit, what tasks are clinical vs. what is research related, special instructions the participant must follow prior to the visit, directions and parking information, whether or not compensation for time or parking will take place and who will be involved in the visit. This should all be included in a confirmation letter.
Access Screening Letter
Access Confirmation Letter
Access Confirmation Letter 2
Once the visit is scheduled, follow-up contact within a week prior to the visit by a phone call to the participant. It is essential to reinforce the requirements of the study and ensure there has not been any changes since the last time you spoke (broke a leg, new infection, changed medication). Some of these changes might make the patient ineligible and would be better to catch ahead of time.
It is important to be understanding of the participant’s personal schedule and to help identify research visit times that are convenient for the individual to commit to without sacrificing protocol compliance. If the study lasts a while and you know the study visit windows, it is good to provide it to the subject to help them plan ahead of when you might want them to come back for visits.
Access Schedule Template
Access Subject Schedule by Enrollment
Prior to each study visit, the research team must be prepared for all known and unknown tasks that may need to be completed per protocol. If applicable, physician orders need to be completed and authorized for lab draws, study medication and additional testing; research lab kits should be prepared and available to the appropriate clinical team drawing the samples; participant questionnaires should be prepared; flowsheets required for research documentation should be made available to the appropriate team members; and any end of study visit items should be readily available if the participant decides to withdraw from the study or is removed from the study due to adverse events or investigator discretion, etc.
Access Checklist Screening
Access Checklist Follow-up
Obtaining a Medical Record Number
A medical record number (MRN) needs to be assigned to a research participant if they will be admitted to the hospital in the outpatient or inpatient setting or if they will undergo any medical tests that need to be processed by a hospital lab. When first scheduling the participant, research staff can check whether a medical record number already exists for the individual by checking IHIS. If they have a medical record number, that number will be used to identify them for any hospital-related admissions or tests. If they do not have a medical record number you are able to create a new patient in IHIS. Talk with your clinical research manager about how your department wants the new MRN to be created.
Clinic Visits
Many studies at Ohio State recruit research participants from patients that are already scheduled for healthcare visits in the medical center or cancer center. If the study design is such that these visits can serve the dual purpose of study visit and doctor visits, then scheduling is relatively straightforward and involves coordinating with the clinical treatment team. Clinic and diagnostic testing appointments are scheduled in IHIS, the provider scheduling database. The research team can review the electronic medical record, for specific information on the visits scheduled. It is important to review the participant visits often, as they could be altered or canceled by someone else which may result in protocol compliance concerns or impact the anticipated activities for that day.
For research appointments that need to be scheduled in the Ohio State hospital or clinics, independent of the patient’s medical appointments, most of the scheduling is done by the hospital schedulers or you might have a point person to ensure you have the correct staffing needed for the research visit. However, it is still the responsibility of the research staff to communicate the specifics of the protocol visit, including the timing of the visits scheduled, how long visits are expected to take, complete any paperwork necessary, obtain physician order for lab or special testing that needs to be performed at a given visit.
Research Appointments
Many studies require that research visits take place in a location that is specifically equipped to carry out the research protocol. Space may be designed to administer specific computer questionnaires, to conduct interviews in a private setting, to be proximal to labs for obtaining and processing blood or other biological specimen or to medical equipment like research CT scans or MRI equipment that cannot be moved. Sometimes certain controlled environment or conditional experiences are part of the research visit. These visits will be arranged with the key research staff involved in the research visit and may not be formally scheduled in the medical center scheduling system. This can cause patients to get reminder calls about a research procedure that happens later in the day and it is separate from the time/location you had discussed for the consent procedure visit to take place. It is essential to send a research confirmation letter that lists the procedures to help clarify to the who, what when and where for the entire study visit.
Scheduling Off-Site Research Visits
There are research studies that allow the visits to take place in the participant’s home or another neutral location, more convenient for the individual. Off-site study visits pose some additional challenges to the research staff in the form of feasibility and safety.
Before scheduling a home visit, the research staff must assess if the visit tasks can be accomplished in the specific location. For example, is there a workspace sufficient to carry out lab draws and physical examinations, are there electrical outlets for medical equipment or laptop computers, etc.
The distance away from the study center needs to be taken into consideration as many studies have a travel limit for outreach research staff. Distance can also cause some feasibility issues such as timeframe that blood specimens must be processed to maintain the integrity of the sample. Other things to consider include how the data will be transported to and from the home or off-site study visit. If laptops are used to transport data, they need to be encrypted to ensure HIPAA compliance.
Safety is also a necessary consideration when conducting home visits. When a member of the research team goes to an unfamiliar area to conduct a study visit, at least one other coworker should know that the appointment is occurring. The researcher should communicate with the research team immediately before and after the study visit occurs. The safety of the research staff should always be the primary consideration over the completion of a study visit outside the research study center and appropriate judgment should be utilized.
Lab Result Reviews
When you receive lab reports your investigator will need to document that they have been reviewed. On any abnormal lab value the investigator must document if it is clinically significant. If it is documented as clinically significant then you will need to create an Adverse Event form. Sometimes the lab is related to other areas of the patient’s medical history so if it is abnormality, it can be documented as such. Great investigator write on the first batch of labs what the abnormal lab value correlates with in subject’s medical history (ie elevated glucose=subject is diabetic) so that reviewers can see that they reviewed all abnormalities seriously.
Below is a link to a sticker you can attach to printed reports that quickly documents that the investigator has reviewed the labs and then have your investigator sign off on it.
Abnormal Lab Result Sticker
If you have a disability and experience difficulty accessing this content, please submit an email to [email protected] for assistance.

- What is the UNC Scientific Review Committee (SRC)?
- The SRC Mission and Scope
- How Does the SRC Review Process Work?
- When is SRC Review Required?
- Protocol Development Tips and Resources
- Committee Members
- Required Costs
- Budget Development Tools
- Clinical Trial Registration Overview and UNC Policy Statement
- Registering an Investigator-Initiated Clinical Trial Overview
- Trial Registration Highlights
- ICMJE Data Sharing Statement Guidance
- ClinicalTrials.gov Protocol Registration and Results System
- Ongoing Record Maintenance Requirements
- Informed Consent Posting Requirements
- Additional Resources
- How Do I Request a Coverage Analysis?
- How Can I Find Research Costs For A Grant Proposal?
- Linking Subjects in Epic
- Quality Assurance Reviews
- FDA Inspections
- Sponsor Audits
- Monitoring Letter Review
- Clinical Research Updates April 2021
- CITI Training
- Conflict of Interest Training
- LMS: CRMS & BCA Training
- Network of Research Professionals 🡥
- Forms & Templates
- Billing Coverage Analysis Resources
- Compliance Checks for PS Proj ID Setup
- Research Participant Reimbursement Information
- Protocol Builder
- Subject Injury Language for Informed Consent Forms
Forms & Templates
Clinical trials quality assurance (ctqa) regulatory templates.
- Adverse Event Log
- Close-out Checklist
- Concomitant Medication/Therapies Worksheet
- Delegation of Responsibility Log
- Deviation Log
- Device Accountability Log
- Eligibility Checklist Template
- Enrollment Log
- FDA Part 11 Certification
- Feasibility Assessment
- Good Clinical Practices Checklist
- Guidance for Completing a Supervisory Plan for Clinical Research
- Informed Consent Process and HIPAA Authorization Documentation
- Inventory List for Study Storage Documents
- Master Subject ID Log
- Comprehensive Monitoring Plan Template
- Concise Monitoring Plan Template
- Monitoring Visit Log
- Participant Enrollment Documentation
- PI Supervisory Plan for Clinical Research
- Protocol/Amendment Tracking Log
- Data Managment
- Informed Consent Process
- Investigational Product (IP) Accountability Standard Operating Procedure and Work Instructions
- Management and Reporting Adverse Events
- Study Start-Up Checklist
- Training Log
- Transfer of Subject Checklist
- About the Clinical Operations - EDC Connection
- Configuring the Clinical Operations - EDC Connection
- CTMS Overview
- Blinded & Unblinded Content Administration (CTMS)
- Creating Blinded & Unblinded Content (CTMS)
- Clinical CRM
- Configuring Clinical CRM
- Configuring Risk Based Study Management (CTMS)
- Configuring Yuzu Clinical Trial Notifications in CTMS
- Defining Subject Visits in CTMS
- Issue Management Administration in CTMS
- Issue Management in CTMS
- Managing Subject & Enrollment Metrics Jobs (CTMS)
- Monitoring Schedules (CTMS)
- Risk Based Study Management (RBSM) in CTMS
- Subject & Enrollment Metrics in CTMS
- Subject Recruitment Planning in CTMS
- Trip Report Administration in CTMS
- Using the CRA Homepage in CTMS
- Using the EDC Connection in CTMS
- Using the Study Manager Homepage in CTMS
- Working with Trip Reports in CTMS
- Japanese Clinical Trial Notifications in CTMS
- eTMF Overview
- About the Model & Artifact Objects (eTMF & CTMS)
- Archiving Studies in eTMF
- Auto-Filing Documents in TMF Binders
- Bulk Creating Study Binders (eTMF)
- Configuring for Study Archival in eTMF
- Configuring the TMF Homepage
- Configuring the TMF Viewer
- Configuring Quality Issues (eTMF & Study Startup)
- Managing Locations
- Managing Studies with Lifecycles in eTMF
- Managing the TMF Index
- Setting Up CRF Import in eTMF
- Setting up TMF Transfer
- TMF Homepage
- TMF Transfer
- Using CRF Import in eTMF
- Working with EDLs
- Configuring EDLs (Clinical Operations)
- Evaluating TMF Bot Auto-classification Models
- TMF Bot FAQ (eTMF)
- Training Auto-classification Models for TMF Bot (eTMF)
- Using the TMF Bot (eTMF)
- Evaluating Metadata Extraction Models
- Testing Metadata Extraction Models
- Using TMF Bot Document Quality Control
- Vault Payments Overview
- Configuring for Study Budget Tracking
- Configuring Vault Payments
- Setting Up Studies for Site Payments
- Study Budget Tracking with Vault Payments
- Study Startup Overview
- About the Model & Artifact Objects (Study Startup)
- Auto-Filing Documents in Study Startup Binders
- Clinical Application Management
- Configuring Surveys for External Respondents
- Setting Up Site Activation Progress View
- Site Feasibility in Study Startup
- Using Site Activation Progress View (Study Startup)
- Using the Study Startup Specialist Homepage
- Working with Surveys for External Respondents
- Veeva Site Connect Overview
- Configuring Document Reconciliation (Veeva Site Connect)
- Configuring Safety Distributions
- Configuring Veeva Site Connect
- Distributing Safety Documents with Veeva Site Connect
- Document Reconciliation (Veeva Site Connect)
- Document Transfer Behavior with Veeva Site Connect
- Sending Documents & Document Requests (Veeva Site Connect)
- Setting Up Study Site Agreements for Veeva Site Connect
- SiteVault Inviter
- Veeva eConsent Overview
- Configuring Veeva eConsent Authoring (Clinical Operations)
- Veeva eConsent Authoring (Clinical Operations)
- Using the Veeva eConsent Editor
- Veeva ePRO Overview
- Using MyVeeva Studio
- Using a Collection
- Using Survey Libraries
- Configuring Surveys
- Configuring Conditions
- Configuring Scores
- Managing Groups
- Managing Events
- Configuring Schedules and Notifications
- Managing Languages and Translations
- Performing User Acceptance Testing (UAT) on a Collection
- Approving, Upversioning, and Deleting a Collection
- Connecting a SiteVault to Your Collection
- Exporting Survey, Adherence, and Audit Trail Data
- Changing Survey Data
- Sample JSON Survey, Schedule, and Notification Templates
Working with Milestones (Clinical Operations)
Vault Milestones specify important points in time at the study, study country, and study site levels. During the course of a study, you accumulate documents of various types. By associating milestones with documents, you can measure milestone completeness by reporting on the status of the study’s documents and those documents’ milestones.
Note : This feature is only available on Clinical Operations Vaults.
How to Create Milestones
Milestone object records define your individual milestones. You can modify these in the same way as other object data records .
Even if you created milestones from a template , you can still add individual milestones.
Each milestone object record includes the Study , Study Country , or Study Site to which the milestone applies. The object record also specifies the planned and actual start and finish dates, the milestone type, and other milestones that share dependencies.
When creating or editing Milestone object records, you’ll need to fill the following object fields:
Note : Depending on your Vault’s version, application, and configuration, you may have different field labels on Milestone and its related objects.
Milestones & Monitoring Events (CTMS)
In CTMS, Monitoring Event records have a Milestone object reference field. You can select a Milestone from this field to associate that milestone to the monitoring event. If you don’t select a Milestone , Vault creates a Milestone record of the correct type automatically after you save your Monitoring Event record. Depending on the object type of your Monitoring Event record, Vault creates different types of Milestones . For example, if you create a Pre Study Visit monitoring event, Vault creates a Pre Study Monitoring Visit milestone. Keep in mind that Vault only creates Milestones for the following standard monitoring event types: Interim Monitoring Event , Pre Study Visit , Site Close Out Visit , and Site initiation Visit .
Vault auto-populates the Study , Study Country , and Study Site fields on the new Milestone record. If your Vault has additional required fields on the Milestone object, the Milestone record creation fails. Vault sends you a notification for the failure. Note that Vault still creates the Monitoring Event record even if the Milestone record creation fails.
About Milestones from Templates
You can create Milestones in bulk using milestone templates . Template Milestones , Milestone Dependency Templates , and Template Tasks are grouped in a single Template Milestone Set object record, similar to ELDs. Once an Admin creates a Template Milestone Set , you can use it to create milestones in bulk at any level. You can create milestones from a template at the start of your study using the Create Milestone from Template action. When your study is in progress, and you require additional milestones to represent ad hoc events, such as a protocol amendment, your Vault may have Story Events configured to create milestones.
How to Create Milestones from Templates
- Select Create Milestones from Template from the Study , Study Country , or Study Site’s Actions menu. The Create Milestones from Template dialog opens.
- Click Continue .
Vault creates Milestones from the template at the Study level and adds the associated Milestones to the Study Country and Study Site levels. After Vault creates Milestones , it checks to see if the associated Study has an EDL Template record associated with it. If it does, Vault will use that EDL Template when creating EDL Item records.
If the milestone template has its own EDL Template associated to it, Vault ignores it and uses the EDL Template at the Study level.
- After the asynchronous job completes, you’ll receive a notification.
Milestones & Story Events
Depending on your Vault’s configuration, you can create milestones and EDLs for ad hoc events in your study using Story Events . Story Events represent different points in time during your Study , such as Site Selection or Protocol Amendment . They include templated milestones, milestone dependencies, and EDL items.
- Select Apply Milestone Template from the Study , Study Country , or Study Site ’s Actions menu.
- Select a Story Event to use for milestone and EDL creation.
- Vault creates milestones and EDLs from templates related to the Story Event at the Study level, and adds the associated milestones and EDLs to the Study Country and Study Site levels.
You can use the Apply Milestone Template action during any lifecycle states it is configured for. This way, you can create any necessary milestones or EDL items for ad hoc events, as well as planned events.
Note that your Vault may have the Apply Milestone Template entry action configured in addition to or instead of the user action. With this configuration, Vault automatically creates the appropriate records when a Study , Study Country , or Study Site enters a certain lifecycle state.
Milestones & Task Templates
Depending on your Vault’s configuration, Admins can define the creation of templated Clinical User Tasks associated with a Template Milestone Set .
When you create milestones from a Template Milestone Set , either as part of planned activities or an ad hoc event, Vault creates individual Clinical User Tasks from the associated Template Tasks , sets their due dates, category, requiredness, and task priority, and populates the Study , Study Country , and Study Site based on the context in which they were created. Vault relates the Clinical User Task to the appropriate Milestone , based on the Template Milestone selected on the Template Task record. Vault creates Clinical User Tasks as Study Tasks, Study Country Tasks, or Study Site Tasks, based on the level of the Template Milestone Set . Vault sends a notification about task creation, and the newly-created user tasks appear in the task assignee’s My Tasks tab. You can complete and work with these tasks as you would for any user task .
Note that your Vault may have the Apply Milestone Template entry action configured in addition to or instead of a user action. With this configuration, Vault automatically creates the appropriate Clinical User Task records when an associated Study , Study Country , or Study Site enters a certain lifecycle state.
About Milestone Autocompletion
An Admin can configure your milestones to autocomplete. When the Autocomplete field is set to All Dependencies or Any Dependencies , Vault moves the milestone to the Completed lifecycle state and populates the Actual Finish Date field once dependent milestones are complete, EDL items have matched, and required Clinical User Tasks are complete. Vault uses the most recent date on previous milestones, matched documents, and required tasks for the milestone’s Actual Finish Date .
Vault does not recalculate % Complete , or any of the metric fields on which it is based, on completed milestones.
Note : Vault automatically calculates completeness metrics and autocompletion after a five-minute delay to ensure that the calculations account for related activities.
Admins can also set up milestone autocompletion on your existing Milestone object records.
Automated Enrollment Milestones (CTMS)
An Admin can configure your CTMS Vault to automatically populate the Actual Finish Dates of first and last subject-related milestones based on the corresponding dates on Subject records at the site level and for a study arm or the study as a whole. For example, if the earliest Screened Date of the Subjects at a site is 10/27/2020, Vault automatically populates the Actual Finish Date of the First Subject Screened milestone for the site with 10/27/2020.
To utilize this feature, you must set the Metric Calculation field to Date-Based on the Study record. If the Metric Calculation field is set to Status Snapshot , Vault will not automatically populate the Actual Finish Dates of milestones for the study.
Note that subject-related milestones without study arms evaluate all subjects at the site, including subjects with study arms.
First Subject Milestones
The Actual Finish Dates of first-subject related milestones are populated as follows:
Last Subject Milestones
The Actual Finish Date fields on last subject-related milestones are populated when you set the No New Subjects checkbox for the Study Site record and all subjects at the site meet the milestone criteria. Clearing the No New Subjects checkbox on the Study Site record clears dates from all related Milestone records.
The Actual Finish Dates of last-subject related milestones are populated as follows:
No Subjects Enrolled
The No Subjects Enrolled field identifies any non-enrolling sites when you set the No New Subjects checkbox for the Study Site record. In your configuration, you can use this field to set a site’s milestones and determine which milestones dependencies to inactivate. This ensures proper roll-up of milestone dates. Clearing the No New Subjects checkbox on the Study Site record clears dates from all related Milestone records and sets No Subjects Enrolled to False/No .
How to Add Milestones to Documents
In order to use milestones, an Admin must first add the Milestone object document field to documents. When the Milestone document field is active and a Milestone object record exists, a user with Edit Document permission can update the field by choosing from existing milestones. An Admin can also configure a Vault to populate the Milestone field by EDL Item .
Viewing Expected Documents
You can view all Expected Document records associated with a Milestone record using EDL Hierarchical View .
About Milestone Types
The Milestone Type picklist field ( milestone_type__v ) is defined on the Milestone object ( milestone__v ) and as a document field. Vault allows an Admin to define custom milestone types based on the level of detail needed when tracking study startup or TMF completeness. Vaults using Study Startup and the associated milestone template set have milestones types pre-configured.
Your organization may expand milestone types to include higher levels of detail. This is common in large organizations who want to leverage milestone data coming from a CTMS or other project management source.
About Global Milestone Types
If you use Study Startup, your Admin can map standard milestone types and offset types to custom milestone types to enable Vault to automatically calculate cycle times for completed milestones.
Note : Note that your Admin must configure Global Milestone Mapping for Vault to calculate cycle times.
About Cycle Times
Vaults with Study Startup automatically calculate cycle times when an Admin has mapped Global Milestone Types to custom Milestone Types . Vault uses a system-managed job to calculate cycle times based on the actual offset times between milestones in your Vault. When active, the job calculates Cycle Times for milestones that meet one of the following conditions:
- A new milestone record was created and has an Actual Finish Date
- The Actual Finish Date field was populated or was modified since the job ran the day prior
- Milestone Type
- Study Country
The job applies existing Cycle Time records to milestones, creates new records if needed, and deletes records that no longer apply.
How Vault populates new Cycle Time records for Finish to Finish offset types:
About Milestone Object Types
If you use Study Startup, you may have default object types on the Milestone object. Milestone object types specify different fields and page layouts to differentiate types of milestones, like those related to submissions or study startup. You can select a Milestone object type when creating a new milestone record or by editing the Milestone Object Type field.
About Milestone Dependencies
Each Milestone Dependency object record represents pre-conditions for a Milestone ’s status. You can configure the order of milestones and the dependencies involved in milestone completion. When related to Milestone Dependency records, Milestone records can have many-to-many relationships . For example, one milestone may depend on the completion of three other milestones. Milestone dependencies follow the Study , Study Country , and Study Site hierarchy.
As of V16, milestone dependencies replaced “Up” and “Previous” milestone fields. ( “Up” and “Previous” fields are still available .)
Example: Protocol Approval & Study Greenlight
For example, for a study to enter the Protocol Approval milestone, the milestone Study Greenlight must be in Completed status. This can be ensured using a “Finish to Finish” milestone dependency. An Admin can enforce the order of milestones by using a lifecycle and entry criteria .
Example: Site Initiation
For example, a “rollup” type dependency can automatically fill the Actual Finish Date field on the Country First Site Initiated milestone with the earliest Actual Finish Date from all of the Site Initiated milestones associated with that Study Country . In this example, the Country First Site Initiated milestone has multiple Milestone Dependencies . These “rollup” type dependencies all use Country First Site Initiated as the Next Milestone field, and each Site Initiated milestone is the Previous Milestone for each dependency.
Milestone Dependency Types
A milestone dependency’s type determines how it functions:
Enabling Milestone Rollups introduces behavior for two (2) other milestone dependency types. You can also enable Milestone Rollup Enhancements, which adds additional checks and can provide more accurate rollup behavior in some scenarios.
Note : Your Vault may have customizations that modify the Standard Behavior listed here.
If needed, an Admin can configure additional milestone dependency types .
Note : When a milestone dependency involves updating any date values, the audit logs record it as a System Action. The action is not dependent on the permissions of the user changing the date values on the previous milestone.
How to Create a Milestone Dependency
You can create milestone dependencies individually or from milestone templates using the Create Milestones from Template action. If you created milestones individually, you must also configure milestone dependencies individually:
- Open the Milestone Dependency object in Admin > Business Admin or in a custom tab.
- Click Create .
- Fill the required fields and relate the Milestone Dependency record to the correct Milestone records.
- For Finish to Finish type dependencies, enter a number of days in the Date Offset field. This number of days (true days) represents the number of days Vault adds to dependent milestones with the Apply Updated Dependencies workflow step .
- Click Save .
Updating Dependent Milestones
You can update Baseline and Planned dates of your milestone records, and then choose to have Vault propagate those changes to all downstream milestone records. Note that this is only available for milestones connected by Finish to Finish type milestone dependencies.
- Update a Milestone record’s Baseline or Planned date.
- Select the Apply updates to dependent milestones verdict to update dependent milestones.
- Vault initiates the Apply Updated Dependencies system action to update your dependent milestones based on the Date Offset field. Vault also reevaluates all existing rollups affected by the date changes.
- Vault sends a notification after updating all dependent milestones.
Choosing Dismiss closes the workflow task window and does not update any dependent milestones. Vault still saves your update to the Milestone record.
Set the Block Automatic Updates field to Yes to prevent the Update Dependencies workflow from updating the baseline and planned date fields on the next Milestone record. This setting supports top-down planning for the study.
Note : Vault cannot initiate the Update Dependencies workflow when a Milestone record is involved with a different object workflow. Wait until the active workflow ends before updating dependent milestones.
Milestone Hovercards
When you hover over a Milestone , Vault displays a hovercard for the record that allows you to quickly view a summary of the Milestone ’s completeness. This hovercard includes:
- Milestone name
- % Complete ; see details below for how Vault calculates this value
- Status indicator icon, representing the milestone’s Completeness value
- List of Milestone Dependencies with each record’s Completeness , Name , Planned Finish Date , and Actual Finish Date
- List of expected documents with the number of Expected , Actual , and Approved documents related to the Milestone
- List of matched documents with each document’s Name , Status , and Version
- Counts of clinical user tasks, with the number of Total , Complete , Required , and Complete Required clinical user tasks
Click a document or object record link in the hovercard to navigate to that document or record detail page. If you click a View All link, Vault navigates you to a list view, for example, a list of all Milestone Dependencies .
Note that Milestone hovercards must be enabled by an Admin .
Milestone Completeness
Vault calculates the % Complete for a milestone by adding Completed Previous Milestones ( completed_previous_milestones__v ), Completed EDL Item Records ( completed_edl_item_records__v ) and Total Complete Required Tasks ( count_of_complete_required_tasks__v ), and dividing that total by the sum of Total Previous Milestones ( total_previous_milestones__v ), Total EDL Item Records ( total_edl_item_records__v ), and Total Required Tasks ( count_of_required_tasks__v ).
Vault takes these values from EDL Item object records. Note that the # Expected value of the EDL Item record is not considered when calculating completeness.
In the Completeness field, Vault references a milestone’s % Complete and displays the value as a status indicator icon. If a milestone has an Actual Finish Date , the % Complete displays 100%, even if your Vault allows a milestone to complete before all expected documents are approved.
Vault does not recalculate % Complete , or any of the metric fields on which it is based, on completed milestones. It will only recalculate those fields if the value in Actual Finish Date is removed.
Related Permissions
You can complete all steps in this article with the standard Business Admin, System Admin or Vault Owner profile.
If your Vault uses custom security profiles, your profile must grant the following permissions :
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Weekend Edition Sunday
- Latest Show
Sunday Puzzle
- Corrections
Listen to the lead story from this episode.
Politics chat: White House Correspondent's dinner, control of Congress
by Ayesha Rascoe , Susan Davis
Byte-Dance was told to sell TikTok or face a ban. There are legal complications
by Ayesha Rascoe
Middle East
An independent review finds no evidence for israel's claims about unrwa and hamas.
by Ayesha Rascoe , Jackie Northam
Arkansas and Tennessee challenge federal rule adding abortion to pregnancy protections
by Maggie Ryan
Startups want to cool Earth by reflecting sunlight. There are few rules and big risks
by Julia Simon
Southern California gets ready to fight mosquito season — by releasing more mosquitoes

Sunday Puzzle NPR hide caption
Sunday Puzzle: Rearrange and match the clues
by Will Shortz
Utah hockey fans will pick the name of its new NHL team — March Madness-style
Minhal baig's 'we grown now' follows two chicago kids in the early 1990s, do students and faculty facing arrest at protests have first amendment rights, cult leader charged with murder in kenya, south carolina rep. nancy mace on trump's trial and what it means for the election, fact-check: south carolina rep. nancy mace's statements on the trump trials, why 911 emergency systems in 3 states went dead earlier this month, as israel threatens to move into rafah, hamas releases video of two hostages.
by Michele Kelemen
NPR Investigations: Off The Mark
A historical marker in alabama unearths a long-forgotten cold case.
by Laura Sullivan
Music Interviews
George brown of kool & the gang on party music, his memoir and the band's new album, george brown of kool & the gang on party music, his memoir and the band's new album.
Searching for a song you heard between stories? We've retired music buttons on these pages. Learn more here.

COMMENTS
Provide a summary of the results, if applicable, in comment section. y Obtain copy of any FDA 483s, Warning Letters or other reports / correspondence and any response letter(s) from the site to FDA. Please complete all questions. For documents, answer YES only if the document is present and correct.
Effective Date: 01-JUL-2017 Site Qualification Visit Page 1 of 4 . SOP-05: Site Qualification Visit . 1. Objective To ensure that the Principal Investigator (PI) and all research team members assisting in the conduct of clinical research are informed about their obligations and responsibilities as they pertain to Good Clinical Practices
Initial (first)monitoring visit. If you were recently hired for a CRA position in a new pharmaceutical company, you would need to do the next steps prior to scheduling the first monitoring visit: - Familiarize with the company's general SOPs and Sponsor's study-specific SOPs (if applicable) relating to the clinical study initiation ...
Study Participant Visit Checklist. This template helps track a research participant's study visit to ensure that protocol-designated procedures for each visit are completed. Access this template. Study Participant Telephone Call Log. This template can be used to document study-specific conversations with or about a study participant.
Each monitoring visit is an integral part of the clinical research process. In conclusion, the different types of monitoring visits, PSVs, SIVs, IMVs, and COVs, are designed to ensure that the study is being conducted in a way that the subjects are safe and the data is valid. The CRA must ensure that sites are performing the study in compliance ...
Requalification site visit should be conducted YES NO A site qualification visit has been conducted within the past year and this site is recommended for the current study. YES NO I do not recommend this site. YES NO This site is not suitable for this study but should be consi dered for others in the future. YES NO
SOP-05 describes the process for conducting a site qualification visit, also known as a pre-study site visit. Attachment templates include: A: Site Qualification Visit Agenda B: Checklist for a Site Qualification Visit C: Site Qualification Visit Summary Responsibility Ochsner Research develops, implements, and maintains SOPs.
Regular site monitor visits can be broken down into four types: pre-study visits, initiation visits, periodic monitoring visits, and close-out visits. Study sites may also be monitored or audited by the FDA, Clinical Research Organizations (CROs), IRBs and sponsors. For more information on site audits by outside entities please visit the training documents on Quality Management: Audits.
Site Preparation Checklist (Pre-Study Visit) - Research - Washington University in St. Louis. Animal Care and Use Award Management Conflicts of Interest Contracts and Subawards Controlled Substances Environmental Health and Safety Export Control HIPAA Human Stem Cell Research Human Subjects Research.
Sample Visit Flow and Schedule (MS Word, 25K) - The visit schedule tracks an individual participant's progress through the study and helps to ensure that visits take place during the protocol-specified timeframe. The visit flow provides an overview of the activities that take place at each study visit, and may be customized for each study site.
Pre-study Qualification Visit • Purpose: Determine the site's ability to conduct the clinical trial prior to commencement of the investigation. often place new trials at sites with a good track record of success • Goal of the pre-study qualification visit: • Visit the site • Meet with study staff • Inspect the facilities
Clinical study report template : Finances Management : Budget Monitoring tool : ... Subject visit log vaccine trial. Pre and post admission study team meetings SOP. Subject visit log any trial. ... CRF tracking template : Study and Site Management : Trial contacts sheet. Investigator site file (Master File) set up and maintenance SOP ...
A. Agenda for Pre-study Site Visit (PSSV) B. Checklist of Activities Associated with the Pre-study Site Visit C. Pre-study Site Visit Follow-up 6. RESPONSIBILITY This SOP applies to Georgia CORE staff members and others involved in arranging, managing, or participating in the pre-study site visit. This may include one or more of the following:
Clinical Trial Monitoring Reports and How to Write Them. Oct 31. Among the most important aspects of study is observation. Overseeing the advancement of any stage, measure, process, and procedure in real time is essential to the accurate conclusion of any clinical trial undertaking. Normal monitoring actions are needed to guarantee caliber ...
Access to UW Electronic Medical Records. To use the University of Washington's electronic medical record systems (ORCA and Epic) to identify eligible patients or capture clinical data about participants, you will need to request ORCA and Epic access for necessary research staff from User Access Administration.. If you have questions about ORCA access privileges or how to complete the form ...
Checklist of Activities for Pre-Study Qualification Visit Page 1 of 3 SOP # 1101- B Effective Date 10/01/2010 Supersedes 10/01/2009 This checklist should be used as a tool to assist you with a Pre-study/Site Qualification Visit . 1. Before the visit . Request from the sponsor several potential meeting dates and times to accommodate as ...
A form template to report pre-study site visit activities. Skip to content. Home; About; Templates; Services; Contact; Shop $ 0.00 Cart. Home / Quality Forms / Clinical Pre-Study Site Visit Report Form Clinical Pre-Study Site Visit Report Form $ 11.99.
The clinical trial template has site lists of libraries for clinical trial protocols, protocol documents, announcements, calendars, issues, tasks, and document discussions. These can be further customized with different versions of SharePoint. To download this template, you will need access to SharePoint Server 3.0.
SOP-05 describes the process for conducting a site qualification visit, also known as a pre -study site visit. Attachment templates include: A: Site Qualification Visit Agenda ... PI will identify key research personnel who will be involved in the conduct of the clinical research study. In preparation of the visit, a Site Qualification Visit ...
Pre-study report. A good start of your project! Helps you to define - in your own words and in more detail - what you are going to do, how and when. Should be completed within first two weeks: Draft within one week - circulated and discussed with your supervisor(s) Final within two weeks.
Prior to each study visit, the research team must be prepared for all known and unknown tasks that may need to be completed per protocol. If applicable, physician orders need to be completed and authorized for lab draws, study medication and additional testing; research lab kits should be prepared and available to the appropriate clinical team ...
Informed Consent Process and HIPAA Authorization Documentation. Inventory List for Study Storage Documents. Master Subject ID Log. Monitoring Plans. Comprehensive Monitoring Plan Template. Concise Monitoring Plan Template. Monitoring Visit Log. Participant Enrollment Documentation. PI Supervisory Plan for Clinical Research.
How to Create Milestones. Milestone object records define your individual milestones. You can modify these in the same way as other object data records.. Even if you created milestones from a template, you can still add individual milestones.. Each milestone object record includes the Study, Study Country, or Study Site to which the milestone applies. The object record also specifies the ...
Hear the Weekend Edition Sunday program for April 28, 2024