- Chapter List
- Testimonials
- Join Luke Unfiltered
- Enter Luke Unfiltered
- Members Area
- Live Call-In Show
- Luke Unfiltered Forum
- Members Only Store
- Apocalypse Survival Training
- Travel & Escape Hacking
- Change Media University
- Member Support
- Edit Your Profile
Select Page

U.S. Supreme Court Says No License Necessary To Drive Automobile On Public Roads
Posted by Jeffrey Phillips | Jul 21, 2015 |

U.S. SUPREME COURT AND OTHER HIGH COURT CITATIONS PROVING THAT NO LICENSE IS NECESSARY FOR NORMAL USE OF AN AUTOMOBILE ON COMMON WAYS
“The right of a citizen to travel upon the public highways and to transport his property thereon, by horsedrawn carriage, wagon, or automobile, is not a mere privilege which may be permitted or prohibited at will, but a common right which he has under his right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. Under this constitutional guaranty one may, therefore, under normal conditions, travel at his inclination along the public highways or in public places, and while conducting himself in an orderly and decent manner, neither interfering with nor disturbing another’s rights, he will be protected, not only in his person, but in his safe conduct.”
Thompson v.Smith, 154 SE 579, 11 American Jurisprudence, Constitutional Law, section 329, page 1135 “The right of the Citizen to travel upon the public highways and to transport his property thereon, in the ordinary course of life and business, is a common right which he has under the right to enjoy life and liberty, to acquire and possess property, and to pursue happiness and safety. It includes the right, in so doing, to use the ordinary and usual conveyances of the day, and under the existing modes of travel, includes the right to drive a horse drawn carriage or wagon thereon or to operate an automobile thereon, for the usual and ordinary purpose of life and business.” –
Thompson vs. Smith, supra.; Teche Lines vs. Danforth, Miss., 12 S.2d 784 “… the right of the citizen to drive on a public street with freedom from police interference… is a fundamental constitutional right” -White, 97 Cal.App.3d.141, 158 Cal.Rptr. 562, 566-67 (1979) “citizens have a right to drive upon the public streets of the District of Columbia or any other city absent a constitutionally sound reason for limiting their access.”
Caneisha Mills v. D.C. 2009 “The use of the automobile as a necessary adjunct to the earning of a livelihood in modern life requires us in the interest of realism to conclude that the RIGHT to use an automobile on the public highways partakes of the nature of a liberty within the meaning of the Constitutional guarantees. . .”
Berberian v. Lussier (1958) 139 A2d 869, 872, See also: Schecter v. Killingsworth, 380 P.2d 136, 140; 93 Ariz. 273 (1963). “The right to operate a motor vehicle [an automobile] upon the public streets and highways is not a mere privilege. It is a right of liberty, the enjoyment of which is protected by the guarantees of the federal and state constitutions.”
Adams v. City of Pocatello, 416 P.2d 46, 48; 91 Idaho 99 (1966). “A traveler has an equal right to employ an automobile as a means of transportation and to occupy the public highways with other vehicles in common use.”
Campbell v. Walker, 78 Atl. 601, 603, 2 Boyce (Del.) 41. “The owner of an automobile has the same right as the owner of other vehicles to use the highway,* * * A traveler on foot has the same right to the use of the public highways as an automobile or any other vehicle.”
Simeone v. Lindsay, 65 Atl. 778, 779; Hannigan v. Wright, 63 Atl. 234, 236. “The RIGHT of the citizen to DRIVE on the public street with freedom from police interference, unless he is engaged in suspicious conduct associated in some manner with criminality is a FUNDAMENTAL CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHT which must be protected by the courts.” People v. Horton 14 Cal. App. 3rd 667 (1971) “The right to make use of an automobile as a vehicle of travel long the highways of the state, is no longer an open question. The owners thereof have the same rights in the roads and streets as the drivers of horses or those riding a bicycle or traveling in some other vehicle.”
House v. Cramer, 112 N.W. 3; 134 Iowa 374; Farnsworth v. Tampa Electric Co. 57 So. 233, 237, 62 Fla. 166. “The automobile may be used with safety to others users of the highway, and in its proper use upon the highways there is an equal right with the users of other vehicles properly upon the highways. The law recognizes such right of use upon general principles.
Brinkman v Pacholike, 84 N.E. 762, 764, 41 Ind. App. 662, 666. “The law does not denounce motor carriages, as such, on public ways. They have an equal right with other vehicles in common use to occupy the streets and roads. It is improper to say that the driver of the horse has rights in the roads superior to the driver of the automobile. Both have the right to use the easement.”
Indiana Springs Co. v. Brown, 165 Ind. 465, 468. U.S. Supreme Court says No License Necessary To Drive Automobile On Public Highways/Streets No License Is Necessary Copy and Share Freely YHVH.name 2 2 “A highway is a public way open and free to any one who has occasion to pass along it on foot or with any kind of vehicle.” Schlesinger v. City of Atlanta, 129 S.E. 861, 867, 161 Ga. 148, 159;
Holland v. Shackelford, 137 S.E. 2d 298, 304, 220 Ga. 104; Stavola v. Palmer, 73 A.2d 831, 838, 136 Conn. 670 “There can be no question of the right of automobile owners to occupy and use the public streets of cities, or highways in the rural districts.” Liebrecht v. Crandall, 126 N.W. 69, 110 Minn. 454, 456 “The word ‘automobile’ connotes a pleasure vehicle designed for the transportation of persons on highways.”
-American Mutual Liability Ins. Co., vs. Chaput, 60 A.2d 118, 120; 95 NH 200 Motor Vehicle: 18 USC Part 1 Chapter 2 section 31 definitions: “(6) Motor vehicle. – The term “motor vehicle” means every description of carriage or other contrivance propelled or drawn by mechanical power and used for commercial purposes on the highways…” 10) The term “used for commercial purposes” means the carriage of persons or property for any fare, fee, rate, charge or other consideration, or directly or indirectly in connection with any business, or other undertaking intended for profit. “A motor vehicle or automobile for hire is a motor vehicle, other than an automobile stage, used for the transportation of persons for which remuneration is received.”
-International Motor Transit Co. vs. Seattle, 251 P. 120 The term ‘motor vehicle’ is different and broader than the word ‘automobile.’”
-City of Dayton vs. DeBrosse, 23 NE.2d 647, 650; 62 Ohio App. 232 “Thus self-driven vehicles are classified according to the use to which they are put rather than according to the means by which they are propelled” – Ex Parte Hoffert, 148 NW 20 ”
The Supreme Court, in Arthur v. Morgan, 112 U.S. 495, 5 S.Ct. 241, 28 L.Ed. 825, held that carriages were properly classified as household effects, and we see no reason that automobiles should not be similarly disposed of.”
Hillhouse v United States, 152 F. 163, 164 (2nd Cir. 1907). “…a citizen has the right to travel upon the public highways and to transport his property thereon…” State vs. Johnson, 243 P. 1073; Cummins vs. Homes, 155 P. 171; Packard vs. Banton, 44 S.Ct. 256; Hadfield vs. Lundin, 98 Wash 516, Willis vs. Buck, 263 P. l 982;
Barney vs. Board of Railroad Commissioners, 17 P.2d 82 “The use of the highways for the purpose of travel and transportation is not a mere privilege, but a common and fundamental Right of which the public and the individual cannot be rightfully deprived.”
Chicago Motor Coach vs. Chicago, 169 NE 22; Ligare vs. Chicago, 28 NE 934; Boon vs. Clark, 214 SSW 607; 25 Am.Jur. (1st) Highways Sect.163 “the right of the Citizen to travel upon the highway and to transport his property thereon in the ordinary course of life and business… is the usual and ordinary right of the Citizen, a right common to all.” –
Ex Parte Dickey, (Dickey vs. Davis), 85 SE 781 “Every Citizen has an unalienable RIGHT to make use of the public highways of the state; every Citizen has full freedom to travel from place to place in the enjoyment of life and liberty.” People v. Nothaus, 147 Colo. 210. “No State government entity has the power to allow or deny passage on the highways, byways, nor waterways… transporting his vehicles and personal property for either recreation or business, but by being subject only to local regulation i.e., safety, caution, traffic lights, speed limits, etc. Travel is not a privilege requiring licensing, vehicle registration, or forced insurances.”
Chicago Coach Co. v. City of Chicago, 337 Ill. 200, 169 N.E. 22. “Traffic infractions are not a crime.” People v. Battle “Persons faced with an unconstitutional licensing law which purports to require a license as a prerequisite to exercise of right… may ignore the law and engage with impunity in exercise of such right.”
Shuttlesworth v. Birmingham 394 U.S. 147 (1969). U.S. Supreme Court says No License Necessary To Drive Automobile On Public Highways/Streets No License Is Necessary Copy and Share Freely YHVH.name 3 “The word ‘operator’ shall not include any person who solely transports his own property and who transports no persons or property for hire or compensation.”
Statutes at Large California Chapter 412 p.83 “Highways are for the use of the traveling public, and all have the right to use them in a reasonable and proper manner; the use thereof is an inalienable right of every citizen.” Escobedo v. State 35 C2d 870 in 8 Cal Jur 3d p.27 “RIGHT — A legal RIGHT, a constitutional RIGHT means a RIGHT protected by the law, by the constitution, but government does not create the idea of RIGHT or original RIGHTS; it acknowledges them. . . “ Bouvier’s Law Dictionary, 1914, p. 2961. “Those who have the right to do something cannot be licensed for what they already have right to do as such license would be meaningless.”
City of Chicago v Collins 51 NE 907, 910. “A license means leave to do a thing which the licensor could prevent.” Blatz Brewing Co. v. Collins, 160 P.2d 37, 39; 69 Cal. A. 2d 639. “The object of a license is to confer a right or power, which does not exist without it.”
Payne v. Massey (19__) 196 SW 2nd 493, 145 Tex 273. “The court makes it clear that a license relates to qualifications to engage in profession, business, trade or calling; thus, when merely traveling without compensation or profit, outside of business enterprise or adventure with the corporate state, no license is required of the natural individual traveling for personal business, pleasure and transportation.”
Wingfield v. Fielder 2d Ca. 3d 213 (1972). “If [state] officials construe a vague statute unconstitutionally, the citizen may take them at their word, and act on the assumption that the statute is void.” –
Shuttlesworth v. Birmingham 394 U.S. 147 (1969). “With regard particularly to the U.S. Constitution, it is elementary that a Right secured or protected by that document cannot be overthrown or impaired by any state police authority.” Donnolly vs. Union Sewer Pipe Co., 184 US 540; Lafarier vs. Grand Trunk R.R. Co., 24 A. 848; O’Neil vs. Providence Amusement Co., 108 A. 887. “The right to travel (called the right of free ingress to other states, and egress from them) is so fundamental that it appears in the Articles of Confederation, which governed our society before the Constitution.”
(Paul v. Virginia). “[T]he right to travel freely from State to State … is a right broadly assertable against private interference as well as governmental action. Like the right of association, it is a virtually unconditional personal right, guaranteed by the Constitution to us all.” (U.S. Supreme Court,
Shapiro v. Thompson). EDGERTON, Chief Judge: “Iron curtains have no place in a free world. …’Undoubtedly the right of locomotion, the right to remove from one place to another according to inclination, is an attribute of personal liberty, and the right, ordinarily, of free transit from or through the territory of any State is a right secured by the Constitution.’
Williams v. Fears, 179 U.S. 270, 274, 21 S.Ct. 128, 45 L.Ed. 186. “Our nation has thrived on the principle that, outside areas of plainly harmful conduct, every American is left to shape his own life as he thinks best, do what he pleases, go where he pleases.” Id., at 197.
Kent vs. Dulles see Vestal, Freedom of Movement, 41 Iowa L.Rev. 6, 13—14. “The validity of restrictions on the freedom of movement of particular individuals, both substantively and procedurally, is precisely the sort of matter that is the peculiar domain of the courts.” Comment, 61 Yale L.J. at page 187. “a person detained for an investigatory stop can be questioned but is “not obliged to answer, answers may not be compelled, and refusal to answer furnishes no basis for an arrest.”Justice White, Hiibel “Automobiles have the right to use the highways of the State on an equal footing with other vehicles.”
Cumberland Telephone. & Telegraph Co. v Yeiser 141 Kentucy 15. “Each citizen has the absolute right to choose for himself the mode of conveyance he desires, whether it be by wagon or carriage, by horse, motor or electric car, or by bicycle, or astride of a horse, subject to the sole condition that he will observe all those requirements that are known as the law of the road.”
Swift v City of Topeka, 43 U.S. Supreme Court says No License Necessary To Drive Automobile On Public Highways/Streets No License Is Necessary Copy and Share Freely YHVH.name 4 Kansas 671, 674. The Supreme Court said in U.S. v Mersky (1960) 361 U.S. 431: An administrative regulation, of course, is not a “statute.” A traveler on foot has the same right to use of the public highway as an automobile or any other vehicle.
Cecchi v. Lindsay, 75 Atl. 376, 377, 1 Boyce (Del.) 185. Automotive vehicles are lawful means of conveyance and have equal rights upon the streets with horses and carriages.
Chicago Coach Co. v. City of Chicago, 337 Ill. 200, 205; See also: Christy v. Elliot, 216 Ill. 31; Ward v. Meredith, 202 Ill. 66; Shinkle v. McCullough, 116 Ky. 960; Butler v. Cabe, 116 Ark. 26, 28-29. …automobiles are lawful vehicles and have equal rights on the highways with horses and carriages. Daily v. Maxwell, 133 S.W. 351, 354.
Matson v. Dawson, 178 N.W. 2d 588, 591. A farmer has the same right to the use of the highways of the state, whether on foot or in a motor vehicle, as any other citizen.
Draffin v. Massey, 92 S.E.2d 38, 42. Persons may lawfully ride in automobiles, as they may lawfully ride on bicycles. Doherty v. Ayer, 83 N.E. 677, 197 Mass. 241, 246;
Molway v. City of Chicago, 88 N.E. 485, 486, 239 Ill. 486; Smiley v. East St. Louis Ry. Co., 100 N.E. 157, 158. “A soldier’s personal automobile is part of his ‘household goods[.]’
U.S. v Bomar, C.A.5(Tex.), 8 F.3d 226, 235” 19A Words and Phrases – Permanent Edition (West) pocket part 94. “[I]t is a jury question whether … an automobile … is a motor vehicle[.]”
United States v Johnson, 718 F.2d 1317, 1324 (5th Cir. 1983). Other right to use an automobile cases: –
EDWARDS VS. CALIFORNIA, 314 U.S. 160 –
TWINING VS NEW JERSEY, 211 U.S. 78 – WILLIAMS VS. FEARS, 179 U.S. 270, AT 274 – CRANDALL VS. NEVADA, 6 WALL. 35, AT 43-44 – THE PASSENGER CASES, 7 HOWARD 287, AT 492 – U.S. VS. GUEST, 383 U.S. 745, AT 757-758 (1966) –
GRIFFIN VS. BRECKENRIDGE, 403 U.S. 88, AT 105-106 (1971) – CALIFANO VS. TORRES, 435 U.S. 1, AT 4, note 6 –
SHAPIRO VS. THOMPSON, 394 U.S. 618 (1969) – CALIFANO VS. AZNAVORIAN, 439 U.S. 170, AT 176 (1978) Look the above citations up in American Jurisprudence. Some citations may be paraphrased.
This article first appeared on SomeNextLevelShit.com and was authored by Jeffrey Phillips.
Sign up on lukeunfiltered.com or to check out our store on thebestpoliticalshirts.com .
About The Author
Jeffrey Phillips
Join we are change.
- Facebook 572.5k Followers
- X 466k Followers
- YouTube 870k Followers
- Instagrm 130k Followers

You have Successfully Subscribed!
Do You Need a Driver's License to Legally Operate a Car on Public Roads?
Despite what you may read on social media, you still need a driver's license to legally drive a car, and the u.s. supreme court hasn't ruled otherwise., kim lacapria, david mikkelson, published july 24, 2015.

About this rating
For years now, impressive-looking texts and documents have been circulated online under titles such as "U.S. Supreme Court Says No License Necessary to Drive Automobile on Public Highways/Streets," implying that some recent judicial decision has struck down the requirement that motorists possess state-issued driver's licenses in order to legally operate vehicles on public roads.
One example of this claim opens with an out-of-context quote before launching into a potpourri of case excerpts from the Supreme Court and lower courts:
"The right of a citizen to travel upon the public highway and to transport his property thereon, by horsedrawn carriage, wagon, or automobile, is not a mere privilege which may be permitted or prohibited at will, but a common right which he has under his right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. Under this constitutional guaranty one may, therefore, under normal conditions, travel at his inclination along the public highways or in public places, and while conducting himself in an orderly and decent manner, neither interfering with nor disturbing another's rights, he will be protected, not only in his person, but in his safe conduct."
However, a full reading of the referenced case, Thompson v. Smith , 155 Va. 367 — Va: Supreme Court 1930 (available via Google Scholar ) presents that inaugural quote in an entirely different context:
The right of a citizen to travel upon the public highways and to transport his property thereon in the ordinary course of life and business is a common right which he has under his right to enjoy life and liberty, to acquire and possess property, and to pursue happiness and safety. It includes the right in so doing to use the ordinary and usual conveyances of the day; and under the existing modes of travel includes the right to drive a horse-drawn carriage or wagon thereon, or to operate an automobile thereon, for the usual and ordinary purposes of life and business. It is not a mere privilege, like the privilege of moving a house in the street, operating a business stand in the street, or transporting persons or property for hire along the street, which a city may permit or prohibit at will. The exercise of such a common right the city may, under its police power, regulate in the interest of the public safety and welfare ; but it may not arbitrarily or unreasonably prohibit or restrict it, nor may it permit one to exercise it and refuse to permit another of like qualifications, under like conditions and circumstances, to exercise it. The regulation of the exercise of the right to drive a private automobile on the streets of the city may be accomplished in part by the city by granting, refusing, and revoking, under rules of general application, permits to drive an automobile on its streets ; but such permits may not be arbitrarily refused or revoked, or permitted to be held by some and refused to other of like qualifications, under like circumstances and conditions.
In other words, the court held that although the use of public roads is a right which citizens enjoy, local authorities may nonetheless regulate such use (including imposing a requirement that motor vehicle operators obtain licenses) so long as such regulations are reasonable, not arbitrary, and apply equally to everyone.
Another bit of context elided from the example article is the fact that in when the referenced decision was handed down by the Supreme Court of Virginia in 1930 , several of the 48 states did not yet require motorists to possess driver's licenses to operate motor vehicles on public roads. Moreover, fewer than one in five Americans owned a car in the 1930s (a demographic that saw little upswing until after the end of World War II). Therefore, regulatory issues stemming from broader vehicle ownership and more modern vehicle operating conditions were still decades in the future at the time the ruling was issued.
No recent Supreme Court ruling has in any way challenged the legality of a requirement for driver's licenses. Driver's licenses are issued state by state (with varying requirements), not at the federal level or according to federal requirements. And driving without a license is indeed illegal in all 50 states.
By Kim LaCapria
Kim LaCapria is a former writer for Snopes.
By David Mikkelson
David Mikkelson founded the site now known as snopes.com back in 1994.
Article Tags
Debunking sovereign citizens, freemen-on-the-land and other pseudo-legal theories.
Is there a right to travel without a driver's license in the united states.

Right to Travel vs. Freedom of Movement
The phrase "right to travel" should be clarified because it's commonly confused.
Many cases, documents, etc. using the phrase "right to travel" are in fact about Freedom of Movement , which is the Constitutional right to travel between States at will. If anyone speaks of a "Constitutional right to travel" Freedom of Movement is the only valid thing they could be referring to, as we'll show.
In pseudo-legal circles, "right to travel" means the supposed right to "travel freely in your private property / automobile / conveyance on the public roads / highways without a driver's license, insurance or registration and exempt from regulation or interruption provided one does not engage in commerce / earn profit or cause harm to people or property."
Absolute freedom! Could it be true? How does the law work?
Tenth Amendment, State Codes
Traffic regulation isn't mentioned in the Constitution, the supreme law of the land , therefore the power generally falls to the States pursuant to the 10th Amendment :
The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the states, are reserved to the states respectively, or to the people.
States are free to enact whatever traffic regulations they want provided they do not violate federal law, as determined by the federal courts, pursuant to their police power .
All 50+ States, through their legislatures consisting of the people's elected representatives, have seen fit to devise and enact their own traffic codes and police them.
Was it always this way?
There wasn't always legislation displacing the common law. Automobile regulation began in the early 1900's. Here is an excellent paper that thoroughly explores the transitional period when decisions could go either way: The Orphaned Right: The Right to Travel by Automobile, 1890-1950 .
Bicycles were regulated decades before automobiles were invented and activists of the day faced many of the same questions and challenges modern right to travel proponents do. An analysis of that period can be found in this publication: The Impact of the Sport of Bicycle Riding on Safety Law .
Constitutionality
The States have all enacted traffic regulations, but do they violate federal law or the Constitution?
Judging constitutionality is ultimately up to the Supreme Court pursuant to Article 3:
The judicial power of the United States, shall be vested in one Supreme Court, and in such inferior courts as the Congress may from time to time ordain and establish.
Appeals are more-often-than-not declined by the Supreme Court so adjudication may stop at the federal United States Courts of Appeals (circuit courts) or District Courts and those are a good place to look for precedent, too. We prefer citations from these federal courts to avoid presumptions of bias that might arise by the State judging its own regulations and because federal decisions are superior to State decisions pursuant to the Supremacy Clause .
Federal Court Decisions
Let's have a look at some federal cases on the right of States to regulate traffic.
Hendrick v. Maryland 235 US 610 (1915)
The movement of motor vehicles over the highways is attended by constant and serious dangers to the public, and is also abnormally destructive to the ways themselves . . . In the absence of national legislation covering the subject a State may rightfully prescribe uniform regulations necessary for public safety and order in respect to the operation upon its highways of all motor vehicles — those moving in interstate commerce as well as others. And to this end it may require the registration of such vehicles and the licensing of their drivers . . . This is but an exercise of the police power uniformly recognized as belonging to the States and essential to the preservation of the health, safety and comfort of their citizens.
Hess v. Pawloski 274 US 352 (1927)
Motor vehicles are dangerous machines; and, even when skillfully and carefully operated, their use is attended by serious dangers to persons and property. In the public interest the State may make and enforce regulations reasonably calculated to promote care on the part of all, residents and non-residents alike, who use its highways.
Reitz v. Mealey 314 US 33 (1941)
The use of the public highways by motor vehicles, with its consequent dangers, renders the reasonableness and necessity of regulation apparent. The universal practice is to register ownership of automobiles and to license their drivers. Any appropriate means adopted by the states to insure competence and care on the part of its licensees and to protect others using the highway is consonant with due process.
There we have three solid federal Supreme Court decisions that set nationwide precedent that cannot be ignored. The Supreme Court is the final arbiter of law in the United States. Unless "right to travel" proponents can come up with a later Supreme Court ruling that states otherwise, their claims are busted.
And we have one less-impressive but telling quote from a lower federal district court:
Wells v. Malloy 402 F. Supp. 856 (1975)
Although a driver's license is an important property right in this age of the automobile, it does not follow that the right to drive is fundamental in the constitutional sense.
A few of the above cases were found in a somewhat inflammatory and dated but comprehensive publication, Idiot Legal Arguments . We picked out the relevant federal cases, but many more high-level State cases can be found there, too, if you're interested.
There actually isn't a whole lot at the federal level because appeals beyond State courts are often denied as it has long been accepted by the federal government that traffic regulation is a proper exercise of State police power. Federal courts uphold the ability of States to regulate road traffic provided it is done so with equality, reasonableness and for public safety and doesn't violate any federal laws or rights.
But I don't "drive" or use a "motor vehicle"! Those are legal terms used to enslave me and I'm smarter than that!
I'm afraid the State and its courts dictate how things are viewed under its law. You don't get to decide what's considered driving or a motor vehicle, they do. You can't simply switch out a few words to avoid responsibility. If you're in territory controlled by the US and/or a State then its laws may be applied to you and you have no lawful recourse (see Law Basics ).
I've heard of people being ignored or let go by police, even without a license or insurance!
Police have discretion . The world is a very dynamic place. There are any number of reasons why you might be passed by or allowed to proceed at any given time. The cop might be a scared rookie, not care, not want to fight, have a date, have to pee, be on lunch break, be at the end of their shift and going home – think about it – they're human, not machines. The priorities of police and prosecuting attorneys vary. The law is what it is, though, and when you understand it you know in the long run you're looking for trouble if you don't obey it.
I don't like traffic regulations. What can I do?
Your lawful remedy is to convince the majority of people in your State to put pressure on your elected representatives in the State legislature to change the law. That or you could move to another State or country where there are less regulations (and perhaps more fatalities ).
Study hard, verify claims, think for yourself, question this, comment.
- Right to Travel
- United States
- Find a Lawyer
- Ask a Lawyer
- Research the Law
- Law Schools
- Laws & Regs
- Newsletters
- Justia Connect
- Pro Membership
- Basic Membership
- Justia Lawyer Directory
- Platinum Placements
- Gold Placements
- Justia Elevate
- Justia Amplify
- PPC Management
- Google Business Profile
- Social Media
- Justia Onward Blog
Kent v. Dulles, 357 U.S. 116 (1958)
U.S. Supreme Court
Kent v. Dulles
Argued April 10, 1958
Decided June 16, 1958
357 U.S. 116
At a time when an Act of Congress required a passport for foreign travel by citizens if a state of national emergency had been declared by the President, and when the Proclamation necessary to make the Act effective had been made, the Secretary of State denied passports to petitioners because of their alleged Communistic beliefs and associations and their refusal to file affidavits concerning present or past membership in the Communist Party.
Held: The Secretary was not authorized to deny the passports for these reasons under the Act of July 3, 1926, 22 U.S.C. § 211a, or § 215 of the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1952, 8 U.S.C. § 1185. Pp. 357 U. S. 117 -130.
(a) The right to travel is a part of the "liberty" of which a citizen cannot be deprived without due process of law under the Fifth Amendment. Pp. 357 U. S. 125 -127.
(b) The broad power of the Secretary under 22 U.S.C. § 211a to issue passports, which has long been considered "discretionary," has been construed generally to authorize the refusal of a passport only when the applicant (1) is not a citizen or a person owing allegiance to the United States, or (2) was engaging in criminal or unlawful conduct. Pp. 357 U. S. 124 -125, 357 U. S. 127 -128.
(c) This Court hesitates to impute to Congress, when, in 1952, it made a passport necessary for foreign travel and left its issuance to the discretion of the Secretary of State, a purpose to give him unbridled discretion to withhold a passport from a citizen for any substantive reason he may choose. P. 357 U. S. 128 .
(d) No question concerning the exercise of the war power is involved in this case. P. 357 U. S. 128 .
(e) If a citizen's liberty to travel is to be regulated, it must be pursuant to the lawmaking functions of Congress, any delegation of the power must be subject to adequate standards, and such delegated authority will be narrowly construed. P. 357 U. S. 129 .
(f) The Act of July 3, 1926, 22 U.S.C. § 211a, and § 215 of the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1952, 8 U.S.C. § 1185, do not delegate to the Secretary authority to withhold passports to
Page 357 U. S. 117
citizens because of their beliefs or associations, and any Act of Congress purporting to do so would raise grave constitutional questions. Pp. 357 U. S. 129 -130.
(g) The only Act of Congress expressly curtailing the movement of Communists across our borders, §§ 2 and 6 of the Internal Security Act of 1950, has not yet become effective, because the Communist Party has not registered under that Act, and there is not in effect a final order of the Board requiring it to do so. P. 357 U. S. 121 , n. 3, p. 357 U. S. 130 .
101 U.S.App.D.C. 278, 239, 248 F.2d 600, 561, reversed.
- Opinions & Dissents
- Oral Arguments
- Copy Citation
Get free summaries of new US Supreme Court opinions delivered to your inbox!
- Bankruptcy Lawyers
- Business Lawyers
- Criminal Lawyers
- Employment Lawyers
- Estate Planning Lawyers
- Family Lawyers
- Personal Injury Lawyers
- Estate Planning
- Personal Injury
- Business Formation
- Business Operations
- Intellectual Property
- International Trade
- Real Estate
- Financial Aid
- Course Outlines
- Law Journals
- US Constitution
- Regulations
- Supreme Court
- Circuit Courts
- District Courts
- Dockets & Filings
- State Constitutions
- State Codes
- State Case Law
- Legal Blogs
- Business Forms
- Product Recalls
- Justia Connect Membership
- Justia Premium Placements
- Justia Elevate (SEO, Websites)
- Justia Amplify (PPC, GBP)
- Testimonials
Some case metadata and case summaries were written with the help of AI, which can produce inaccuracies. You should read the full case before relying on it for legal research purposes.
Right to Travel
Fourteenth Amendment , Section 1:
All persons born or naturalized in the United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, are citizens of the United States and of the State wherein they reside. No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws.
The doctrine of the “right to travel” actually encompasses three separate rights, of which two have been notable for the uncertainty of their textual support. The first is the right of a citizen to move freely between states, a right venerable for its longevity, but still lacking a clear doctrinal basis. 1 Footnote Saenz v. Roe, 526 U.S. 489 (1999) . “For the purposes of this case, we need not identify the source of [the right to travel] in the text of the Constitution. The right of ‘free ingress and regress to and from’ neighboring states which was expressly mentioned in the text of the Article of Confederation, may simply have been ‘conceived from the beginning to be a necessary concomitant of the stronger Union the Constitution created.’” Id. at 501 (citations omitted). The second, expressly addressed by the first sentence of Article IV, provides a citizen of one state who is temporarily visiting another state the “Privileges and Immunities” of a citizen of the latter state. 2 Footnote Paul v. Virginia, 75 U.S. (8 Wall.) 168 (1869) ( “without some provision . . . removing from citizens of each State the disabilities of alienage in other States, and giving them equality of privilege with citizens of those States, the Republic would have constituted little more than a league of States; it would not have constituted the Union which now exists.” ). The third is the right of a new arrival to a state, who establishes citizenship in that state, to enjoy the same rights and benefits as other state citizens. This right is most often invoked in challenges to durational residency requirements, which require that persons reside in a state for a specified period of time before taking advantage of the benefits of that state’s citizenship.
Durational Residency Requirements
Challenges to durational residency requirements have traditionally been made under the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment . In 1999, however, the Court approved a doctrinal shift, so that state laws that distinguished between their own citizens, based on how long they had been in the state, would be evaluated instead under the Privileges or Immunities Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment . 3 Footnote Saenz v. Roe, 526 U.S. 489, 502–03 (1999) . The Court did not, however, question the continuing efficacy of the earlier cases.
A durational residency requirement creates two classes of persons: those who have been within the state for the prescribed period and those who have not. 4 Footnote Dunn v. Blumstein, 405 U.S. 330, 334 (1972) . Because the right to travel is implicated by state distinctions between residents and nonresidents, the relevant constitutional provision is the Privileges and Immunities Clause, Article IV, § 2, cl. 1. But persons who have moved recently, at least from state to state, 5 Footnote Intrastate travel is protected to the extent that the classification fails to meet equal protection standards in some respect. Compare Hadnott v. Amos , 320 F. Supp. 107 (M.D. Ala. 1970) (three-judge court), aff’d. per curiam , 405 U.S. 1035 (1972) , with Arlington County Bd. v. Richards, 434 U.S. 5 (1977) . The same principle applies in the commerce clause cases, in which discrimination may run against in-state as well as out-of-state concerns. Cf. Dean Milk Co. v. City of Madison, 340 U.S. 349 (1951) . have exercised a right protected by the Constitution, and the durational residency classification either deters the exercise of that right or penalizes those who have exercised it. 6 Footnote Shapiro v. Thompson, 394 U.S. 618, 629–31, 638 (1969) ; Dunn v. Blumstein, 405 U.S. 330, 338–42 (1972) ; Memorial Hospital v. Maricopa County, 415 U.S. 250 (1974) ; Jones v. Helms, 452 U.S. 412, 420–21 (1981) . See also Oregon v. Mitchell, 400 U.S. 112, 236–39 (1970) (Justices Brennan, White, and Marshall), and id. at 285–92 (Justices Stewart and Blackmun and Chief Justice Burger). Any such classification is invalid “unless shown to be necessary to promote a compelling governmental interest.” 7 Footnote Shapiro v. Thompson, 394 U.S. 618, 634 (1969) (emphasis by Court); Graham v. Richardson, 403 U.S. 365, 375–76 (1971) . The constitutional right to travel has long been recognized, 8 Footnote Crandall v. Nevada, 73 U.S. (6 Wall.) 35 (1868) ; Edwards v. California, 314 U.S. 160 (1941) (both cases in context of direct restrictions on travel). The source of the right to travel and the reasons for reliance on the Equal Protection Clause are questions puzzled over and unresolved by the Court. United States v. Guest, 383 U.S. 745, 758, 759 (1966) , and id. at 763–64 (Justice Harlan concurring and dissenting), id. at 777 n.3 (Justice Brennan concurring and dissenting); Shapiro v. Thompson, 394 U.S. 618, 629–31 (1969) , and id. at 671 (Justice Harlan dissenting); San Antonio School Dist. v. Rodriguez, 411 U.S. 1, 31–32 (1973) ; Jones v. Helms, 452 U.S. 412, 417–19 (1981) ; Zobel v. Williams, 457 U.S. 55, 60 & n.6 (1982) , and id. at 66–68 (Justice Brennan concurring), 78-81 (Justice O’Connor concurring). but it is only relatively recently that the strict standard of equal protection review has been applied to nullify durational residency requirements.
Thus, in Shapiro v. Thompson , 9 Footnote 394 U.S. 618 (1969) . durational residency requirements conditioning eligibility for welfare assistance on one year’s residence in the state 10 Footnote The durational residency provision established by Congress for the District of Columbia was also voided. 394 U.S. at 641–42 . were voided. If the purpose of the requirements was to inhibit migration by needy persons into the state or to bar the entry of those who came from low-paying states to higher-paying ones in order to collect greater benefits, the Court said, the purpose was impermissible. 11 Footnote 394 U.S. at 627–33 . Gaddis v. Wyman , 304 F. Supp. 717 (N.D.N.Y. 1969) , aff’d sub nom. Wyman v. Bowens, 397 U.S. 49 (1970) , struck down a provision construed so as to bar only persons who came into the state solely to obtain welfare assistance. If, on the other hand, the purpose was to serve certain administrative and related governmental objectives—the facilitation of the planning of budgets, the provision of an objective test of residency, minimization of opportunity for fraud, and encouragement of early entry of new residents into the labor force—then the requirements were rationally related to the purpose but they were not compelling enough to justify a classification that infringed a fundamental interest. 12 Footnote 394 U.S. at 633–38 . Shapiro was reaffirmed in Graham v. Richardson, 403 U.S. 365 (1971) (striking down durational residency requirements for aliens applying for welfare assistance), and in Memorial Hospital v. Maricopa County, 415 U.S. 250 (1974) (voiding requirement of one year’s residency in county as condition to indigent’s receiving nonemergency hospitalization or medical care at county’s expense). When Connecticut and New York reinstituted the requirements, pleading a financial emergency as the compelling state interest, they were summarily rebuffed. Rivera v. Dunn , 329 F. Supp. 554 (D. Conn. 1971) , aff’d per curiam , 404 U.S. 1054 (1972) ; Lopez v. Wyman , Civ. No. 1971-308 (W.D.N.Y. 1971) , aff’d per curiam , 404 U.S. 1055 (1972) . The source of the funds, state or federal, is irrelevant to application of the principle. Pease v. Hansen, 404 U.S. 70 (1971) . In Dunn v. Blumstein , 13 Footnote 405 U.S. 330 (1972) . But see Marston v. Lewis, 410 U.S. 679 (1973) , and Burns v. Fortson, 410 U.S. 686 (1973) . Durational residency requirements of five and seven years respectively for candidates for elective office were sustained in Kanapaux v. Ellisor , 419 U.S. 891 (1974) , and Sununu v. Stark , 420 U.S. 958 (1975) . where the durational residency requirements denied the franchise to newcomers, such administrative justifications were found constitutionally insufficient to justify the classification. 14 Footnote For additional discussion of durational residence as a qualification to vote, see Voter Qualifications, supra . The Privileges or Immunities Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment was the basis for striking down a California law that limited welfare benefits for California citizens who had resided in the state for less than a year to the level of benefits that they would have received in the state of their prior residence. 15 Footnote Saenz v. Roe, 526 U.S. 489, 505 (1999) .
However, a state one-year durational residency requirement for the initiation of a divorce proceeding was sustained in Sosna v. Iowa . 16 Footnote 419 U.S. 393 (1975) . Justices Marshall and Brennan dissented on the merits. Id. at 418 . Although it is not clear what the precise basis of the ruling is, it appears that the Court found that the state’s interest in requiring that those who seek a divorce from its courts be genuinely attached to the state and its desire to insulate divorce decrees from the likelihood of collateral attack justified the requirement. 17 Footnote 419 U.S. at 409 . But the Court also indicated that the plaintiff was not absolutely barred from the state courts, but merely required to wait for access (which was true in the prior cases as well and there held immaterial), and that possibly the state interests in marriage and divorce were more exclusive and thus more immune from federal constitutional attack than were the matters at issue in the previous cases. The Court also did not indicate whether it was using strict or traditional scrutiny. Similarly, durational residency requirements for lower in-state tuition at public colleges have been held constitutionally justifiable, again, however, without a clear statement of reason. 18 Footnote Starns v. Malkerson , 326 F. Supp. 234 (D. Minn. 1970) , aff’d per curiam , 401 U.S. 985 (1971) . Cf. Vlandis v. Kline, 412 U.S. 441, 452 & n.9 (1973) , and id. at 456, 464, 467 (dicta). In Memorial Hospital v. Maricopa County, 415 U.S. 250, 256 (1974) , the Court, noting the results, stated that “some waiting periods . . . may not be penalties” and thus would be valid. More recently, the Court has attempted to clarify these cases by distinguishing situations where a state citizen is likely to “consume” benefits within a state’s borders (such as the provision of welfare) from those where citizens of other states are likely to establish residency just long enough to acquire some portable benefit, and then return to their original domicile to enjoy them (such as obtaining a divorce decree or paying the in-state tuition rate for a college education). 19 Footnote Saenz v. Roe , 526 U.S. at 505 .
A state scheme for returning to its residents a portion of the income earned from the vast oil deposits discovered within Alaska foundered upon the formula for allocating the dividends; that is, each adult resident received one unit of return for each year of residency subsequent to 1959, the first year of Alaska’s statehood. The law thus created fixed, permanent distinctions between an ever-increasing number of classes of bona fide residents based on how long they had been in the state. The differences between the durational residency cases previously decided did not alter the bearing of the right to travel principle upon the distribution scheme, but the Court’s decision went off on the absence of any permissible purpose underlying the apportionment classification and it thus failed even the rational basis test. 20 Footnote Zobel v. Williams, 457 U.S. 55 (1982) . Somewhat similar was the Court’s invalidation on equal protection grounds of a veterans preference for state employment limited to persons who were state residents when they entered military service; four Justices also thought the preference penalized the right to travel. Attorney General of New York v. Soto-Lopez, 476 U.S. 898 (1986) .
Still unresolved are issues such as durational residency requirements for occupational licenses and other purposes. 21 Footnote La Tourette v. McMaster, 248 U.S. 465 (1919) , upholding a two-year residence requirement to become an insurance broker, must be considered of questionable validity. Durational periods for admission to the practice of law or medicine or other professions have evoked differing responses by lower courts. But this line of cases does not apply to state residency requirements themselves, as distinguished from durational provisions, 22 Footnote E.g. , McCarthy v. Philadelphia Civil Service Comm’n, 424 U.S. 645 (1976) (ordinance requiring city employees to be and to remain city residents upheld). See Memorial Hospital v. Maricopa County, 415 U.S. 250, 255 (1974) . See also Martinez v. Bynum, 461 U.S. 321 (1983) (bona fide residency requirement for free tuition to public schools). and the cases do not inhibit the states when, having reasons for doing so, they bar travel by certain persons. 23 Footnote Jones v. Helms, 452 U.S. 412 (1981) (statute made it a misdemeanor to abandon a dependent child but a felony to commit the offense and then leave the state).


Pulse of Pride
Only Legal in America: 21 Things You CAN’T Do in the Rest of the World
Posted: June 4, 2024 | Last updated: June 4, 2024

The U.S. dances to its own beat, especially when it comes to laws that make the rest of the world do a double-take. Here’s a lineup of things that scream “Only in America,” sticking strictly to what’s written in the law books. Ready for a tour through the American legal landscape that’ll leave you wondering if freedom might just be a bit too free?

1. Advertisements for Prescription Drugs
Turn on the TV, and there’s a good chance you’ll see an ad for some medication, side effects and all. Elsewhere, this direct-to-consumer advertising is a big no-no.

2. Owning Exotic Pets
Want a lion in Louisiana or a bear in Montana? Certain states say, “Sure, why not?” Meanwhile, the rest of the world tightens the leash on exotic pet ownership.

3. The Right to Repair
The U.S. is pioneering “Right to Repair” laws, allowing consumers to fix their own electronics and machinery without voiding warranties—a battle against the tide of proprietary repairs and closed systems favored by manufacturers. While some might argue it’s a push for consumer freedom, it’s an area where American legislation is actually ahead, pushing back against global tech giants’ grip on how and who repairs what you own.

4. Child Labor Laws in Agriculture
The U.S. has some surprisingly lax child labor laws when it comes to farming. Kids as young as 12 can work long hours in the fields, a practice that’s stricter elsewhere.

5. Corporal Punishment in Schools
Spanking in school might sound like a relic from the past, but it’s still on the books in 19 states. In contrast, many countries have banned corporal punishment outright.
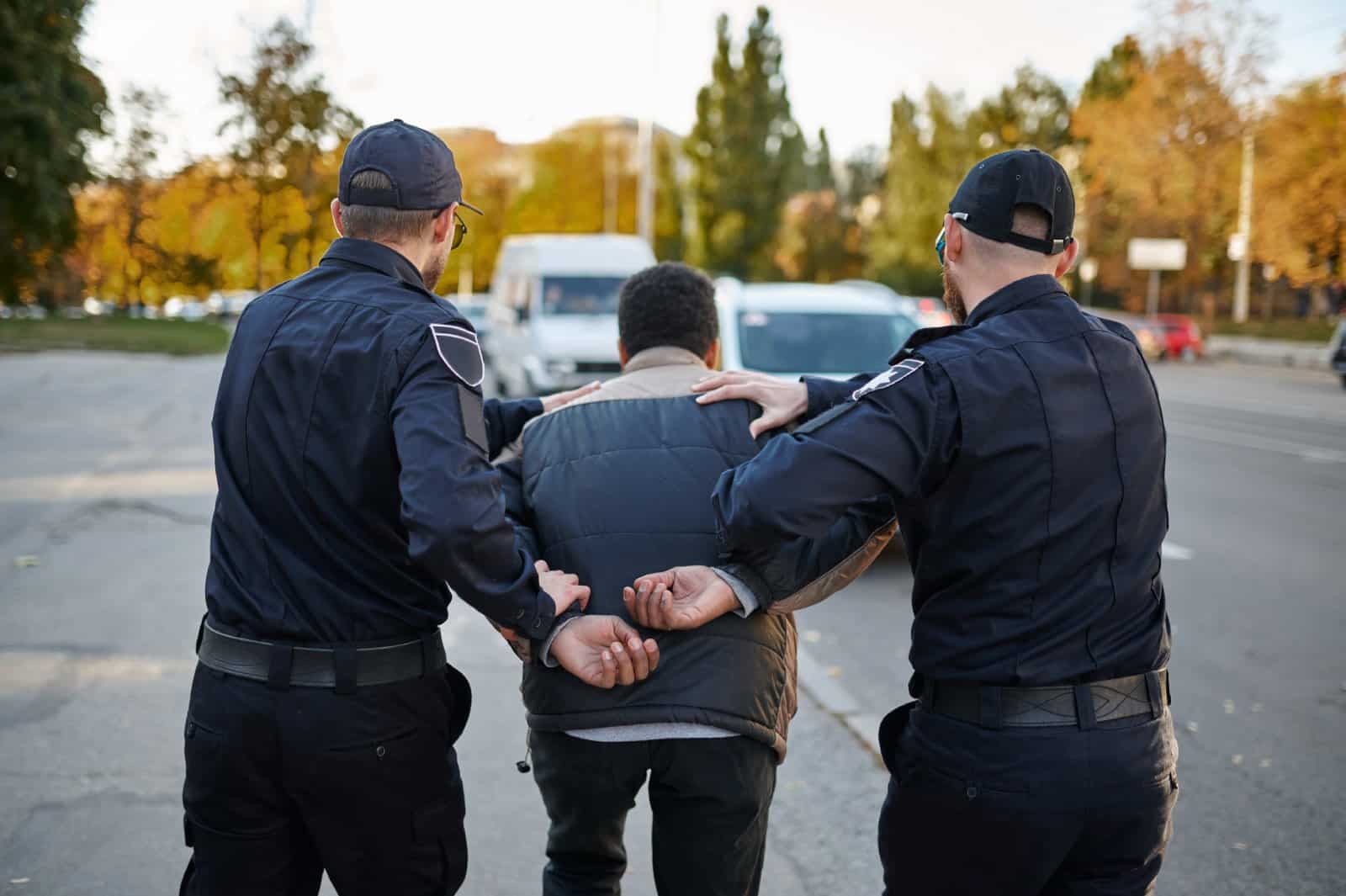

6. Carrying Concealed Weapons
In many states, carrying a concealed weapon is as American as apple pie. Try packing heat in public in most other places, and you’re looking at serious jail time.

7. Flamethrowers for Recreational Use
Yes, you read that right. In most of the U.S., you can own a flamethrower with fewer restrictions than a driving license. Because, freedom?

8. Drive-Thru Liquor Stores
In the land where convenience is king, the U.S. takes the crown with drive-thru liquor stores. Yes, you can order a bottle of your favorite spirit without leaving your car, a concept that might make more traditionally-minded countries spit out their wine. It blurs the line between convenience and responsibility, offering a uniquely American solution to the age-old problem of how to replenish your liquor cabinet in the most effortless way possible.

9. Creationism Taught in Schools
While much of the world sticks to evolution in science class, several U.S. states endorse teaching creationism alongside or instead of evolution.

10. Firing an Employee for No Reason
Welcome to “at-will” employment, where, in most states, employers can say “you’re fired” without giving a reason. Worker protections? Not so much.

11. Jail Time for Debt
Though rare, some U.S. states still allow debtors to be jailed if they can’t pay up—a throwback to Dickensian times that’s largely outlawed elsewhere.

12. Castle Doctrine and Stand Your Ground Laws
Defend your turf with lethal force if you feel threatened? In many U.S. states, it’s your right. Other countries prefer you retreat before resorting to violence.

13. Food Dyes Galore
Those bright, artificial colors in your cereal and candy? Banned or regulated in much of the world, but in the U.S., it’s a rainbow of chemical possibilities.


14. Bounty Hunting
Skip bail in the U.S., and a bounty hunter might just come knocking. This Wild West profession is unique to the American justice system.

15. Unlimited Political Campaign Spending
Thanks to certain rulings, there’s virtually no cap on what you can spend to support your favorite (or least favorite) politician. Other democracies keep a tighter wallet on elections.

16. Civil Forfeiture Without Conviction
The police can seize your property suspected of being involved in a crime, even if you’re never convicted. It’s a controversial practice that’s rare outside the U.S.

17. Making Moonshine
While strictly regulated and illegal in some states, distilling your own spirits can be done with the right permits. Elsewhere, homemade hooch is often a no-go.

18. Mega Churches and Tax Exemptions
Religious organizations in the U.S. enjoy significant tax exemptions, even for mega-churches with millionaire pastors. Other countries are less generous to their gods.

19. Patenting Life Forms
In the U.S., you can patent genetically modified organisms, from seeds to lab animals. The ethics and legality of this practice are hotly debated elsewhere.

20. Private Prisons for Profit
The idea of making money off incarceration is a uniquely American experiment, with private companies running prisons for profit—a concept that many find morally dubious.

21. Cloning Your Pet
Miss your furry friend? In the U.S., you can clone your pet for a price. This futuristic form of animal companionship hasn’t caught on in most other places.

The Land of Too Much Freedom?
From the quirky to the contentious, these laws and practices set the U.S. apart on the global stage. Whether they make you proud or puzzled, they’re all part of the grand, sometimes baffling, experiment in freedom and democracy that is the United States.
The post Only in the USA! 21 Things You Can’t Do Anywhere Else first appeared on Pulse of Pride .
Featured Image Credit: Pexels / Ivan Samkov.
For transparency, this content was partly developed with AI assistance and carefully curated by an experienced editor to be informative and ensure accuracy.
More for You
Stephen Hawking once gave a simple answer as to whether there was a God
Mechanic shares photo of unexpected object that punctured vehicle's tire: 'This will be increasingly common'
Hear retired US general’s response to Ukrainian soldiers who say US-issued tanks are underperforming
7 Actors Who Have Played Hercule Poirot, Ranked (Photos)
6 Reasons Netflix's New Thriller Eric Needs To Be Your Next Binge-Watch
Byron Donalds Corrected Live On-Air About Donald Trump
Who Makes The Duramax V8 Engine & What Kind Of Horsepower Does It Produce?
Map shows states affected by recalled cucumbers potentially contaminated with salmonella
Citizen shares frustrations with before-and-after photos after city expands roadways: 'How do urban planners and city designers not understand this'
American Idol star Mandisa’s cause of death disclosed
Why you’re always forgetting things, according to a memory scientist
12 Social Isolation Red Flags for Those Living Alone
Here's What Happens if You Claim Social Security at 62
'Exodus' of Russian Ships From Black Sea Fleet's Reserve Base Sparks Rumors
Mae West's Iconic Fashion Through the Years, Photos
You Should Really Think Twice Before Killing That Earwig
Here's What Happens If You Never Change Your Transmission Fluid
A look back at D-Day: Why the World War II invasion remains important on its 80th anniversary
I'm Nobody's Guest, Thank You Very Much
25 Exceptional Spy Films Beyond 'James Bond' and 'Mission: Impossible'
Money blog: New Jaffa Cake flavour launches - and makers admit it might divide people
Disfrutar in Barcelona has been named the world's best restaurant; there's a new cola-flavoured Jaffa Cake launching; our psychology of shopping series concludes with the tricks shops use to get us to spend. Read these and the rest of today's consumer news in the Money blog.
Thursday 6 June 2024 12:45, UK
- There's a new best restaurant in the world - this is how much it costs to eat there
- McVitie's launches first ever non-fruit flavoured Jaffa Cake
- Now is the time to lock some of your cash away - here's why
- Asda goes from cheapest to most expensive supermarket for petrol
- Ian King : Why European rates decision could impact global economy - and your holiday money
Essential reads
- How brands get you to buy more, more, more
- Top chef shares his take on an Italian classic - and Warwickshire Cheap Eats
- Ed Conway : Claim of £2k tax rise under Labour is over four years - same maths suggests Tories have raised taxes by £13k in last four years
- How much are student loans, when do you start paying back and what is the interest?
- Your rights when deliveries or returns don't arrive - and why leaving instructions could jeopardise them
- Best of the Money blog - an archive
Ask a question or make a comment
McVitie's is selling a new flavour of Jaffa Cake - and it marks the first ever non-fruit flavour since the treat launched in 1927.
Shelves across the country will soon be stocked cola bottle flavoured cakes.
The new flavour will launch in Asda stores from 10 June and be available in other UK supermarkets - including Tesco, Sainsbury's, Morrisons, Iceland and Co-op - in the coming weeks.
Adam Woolf, marketing director at McVitie's, said: "Jaffa Cakes Cola Bottle is certainly one of our more unexpected product launches – stepping away from fruit flavours for the very first time.
"Jaffa Cakes have always stood out from the crowd (and the biscuit aisle), but we really wanted to try something new with this one. It's no doubt going to cause some debate among our Jaffanatics, and we can't wait to hear what they think."
By Sarah Taaffe-Maguire , business reporter
Are we entering an era of interest rate cuts? Probably not. Or at least, not yet.
But the European Central Bank (ECB) which controls the euro currency does look set to make their first cut in four years this afternoon.
And Canada yesterday became the first country in the club of G7 industrialised nations to bring down borrowing costs by lowering their benchmark interest rate.
The UK, however, isn't currently expected by markets to make a cut until September.
Elsewhere, oil prices remain below $80 but are slightly more expensive than earlier this week. A barrel of the benchmark Brent crude oil costs $79.10.
The good news for people going on holidays to countries using the euro continues - the pound is still doing well against the currency with £1 equal to €1.1757.
That could go even higher after the ECB decision at 1.15pm. A pound also can buy $1.2783.
Like in the US, the UK's most valuable companies have become more valuable as the FTSE (Financial Times Stock Exchange) 100 and 250 indices are up 0.33% and 0.41% respectively.
Every Thursday Savings Champion founder Anna Bowes gives an insight into the savings market and how to make the most of your money...
Can you believe we are almost halfway through 2024?
Although the rate rises that we have seen this year have slowed compared with the previous couple of years, and we have even seen some falls, savers are now able to find hundreds of savings accounts that pay an interest rate higher than inflation.
The latest data from the Office for National Statistics showed inflation was still higher than predicted, however - which means the anticipated base rate cut is likely to be pushed back again – into the second half of this year.
While bad news for borrowers, this is great news for savers.
Incredibly, the latest statistics from the Bank of England show there is over £253bn sitting in current accounts and savings accounts earning no interest at all.
With top rates available paying 5% or even a bit more, that is potentially £12.65bn of gross interest that is not being claimed by savers.
So now really is the time to move your money if you have cash languishing, earning less than inflation, especially if you can lock some away with a fixed rate, as a base rate cut will happen at some stage, we just don't know when.
Easy access
If you think you'll need access to your money, an easy access account is a wise choice.
The base rate cuts that we have been waiting for are yet to start, so the top rates on offer are still paying almost as much as they were at the beginning of the year.
Fixed-term bonds
There is a strange phenomenon with fixed-term bond rates at the moment: the longer you tie up your cash, the lower the interest rates on offer.
Normally, you'd expect to be rewarded for tying up your cash over the longer term - but base rate forecasts have flipped this.
Fixed-term cash ISAs
A frequent complaint that I hear from savers is that the tax-free rates on ISAs are usually lower than the pre-tax rates on the equivalent non-ISA accounts – and this is particularly true with fixed-term accounts.
As many more savers are paying tax on their interest once again, cash ISAs are more popular than ever, as the tax-free rate of the ISA can still be considerably more than the interest earned after tax has been deducted on the non-ISA bond equivalents.
The renowned "50 Best" list of the world's best restaurants was revealed in Las Vegas last night - with a new restaurant taking top spot.
Disfrutar in Barcelona took the crown from Central in Lima, Peru (previous winners are ineligible and instead join a Best of the Best list).
Eating the standard menu costs £247 (€290) - with an extra £136 (€160) if you want the wine pairing.
To be fair, you do get around 30 courses.
They also offer a unique menu for your table for between €1,050 and €390 per person - the more people, the less it costs.
The 50 Best list says: "The combination of brilliantly imaginative dishes, unsurpassed technical mastery and playful presentation results in the dining experience of a lifetime, as full of surprises as it is memories."
Dishes include:
- Caviar-filled Panchino doughnut
- Frozen gazpacho sandwich
- Thai-style cuttlefish with coconut multi-spherical
- Squab with kombu spaghetti, almond and grape
Two UK restaurants made the top 50 but the UK was eclipsed by countries from across South America as well as Thailand, Italy, France and Spain.
London's Kol moved up slightly to 17, while Ikoyi, which we reported on a few weeks ago following a link-up with Uber Eats, came it at 42.
Three whiskies created by Aldi have been named among the best in the world.
The budget supermarket took home three golds at the International Spirits Challenge awards for:
- Glen Marnoch Highland Single Scotch Whisky (£18.49, 70cl)
- Highland Earl Blended Scotch Whisky (£16.89, 1L)
- Samuel Joe’s Straight Kentucky Bourbon (£14.99, 70cl)
In the single malt category, Aldi's submission beat the likes of M&S as well as premium brand Lochlea Distillery, which costs around £45 a bottle.
Other gold winners included Johnnie Walker, Jameson and Glenfiddich.
Aldi was also given three silver medals for its Highland Black Blended Scotch Whisky, Glen Marnoch Speyside Single Malt Whisky and Glen Marnoch Islay Single Malt Whisky.
"This industry recognition helps to prove that great quality doesn't have to come with a luxury price tag and customers can be confident they're saving money with us, whilst getting the best whisky taste and experience," said Julie Ashfield, managing director of buying at Aldi UK.
As we've previously discussed in the Money blog, holidaying Brits can avoid costly roaming charges by using their own travel eSim - and there's now another mainstream option to choose from courtesy of Uswitch.
UK travellers who want to use their phones abroad usually rely on their roaming plans and data passes or sign up for a local SIM at their destination, which can often require time-consuming ID checks and additional documentation.
That can be costly.
Since Brexit, the UK no longer benefits from several EU-mandated rules, including a worldwide data roaming cap of £45.
Roaming costs, especially in countries outside the EU, can now be as high as £9 for every 1MB of roaming data - equivalent to streaming Netflix for 14.4 seconds.
The savings with eSims are potentially massive, as our cost of living specialist Megan Harwood-Baynes outlined here last month...
USwitch product
Using 10GB of data in Morocco on a UK Pay As You Go network with uncapped fees would cost on average of £56,166, compared to just £17 with a USwitch eSim.
eSims are available online and are entirely digital - meaning customers don't need to visit a phone network store or wait for a physical SIM card to arrive in the post.
Most new smartphones are already compatible with eSim technology, including every iPhone released from 2018 onwards and most Samsung devices released from 2020 onwards.
"eSIMs offer them a newfound freedom that's cheaper than traditional data roaming and with none of the hassle of finding a local SIM card provider when you arrive," said CEO and co-founder of (USwitch's partner in this project) eSIM Go Zacchary Couldrick.
Asda has gone from selling the cheapest petrol out of the supermarket chains to now costing the most, according to the latest fuel price figures.
RAC says Asda's big rivals, Morrisons, Sainsbury's and Tesco, all sold a litre of unleaded petrol for 2.1p less on average at the end of May.
Diesel was also coming out costlier at Asda, with the supermarket 2.5p per litre more expensive than the rest of its supermarket competition.
Drivers are being urged - by the RAC - to change their refuelling habits to find the best prices.
What makes up the cost of a litre of petrol?
The price you pay for fuel at the pumps is governed by wholesale fuel prices, which are affected by several factors.
These include the global price of crude oil, which itself is governed by supply and demand and oil refinery production and capacity.
Distribution costs, fuel duty (currently 52.95p a litre in the UK), VAT (currently at 20%) and profit margins dictated by fuel retailers all come into account when working out why prices of fuel rise and fall.
Fuel duty rate and VAT largely stay the same, though oil prices and the strength of the pound to the US dollar (refined fuel is sold in dollars per metric tonne) can cause prices to be extremely volatile.
How have UK petrol prices changed in the 21st century
Unleaded fuel in 2000 had an average cost of 80.35p, while the average cost of diesel in the same year was 81.73p.
The lowest average cost for unleaded petrol in the last 24 years came in 2002, where the average was 73.5p. Diesel also had its cheapest average cost in this year at 75.6p.
Unsurprisingly, the most expensive average prices for fuel have fallen in recent years. In 2022, the average cost of unleaded fuel was 165.06p and the average cost of diesel was 178.13p.
By Emily Mee , news reporter
We've all been there. You have a bad day and you need a little pick-me-up - so you head straight to your favourite website to buy something new.
That hit of dopamine you get when buying something is what many businesses rely on - and no one seems to understand it better than fast fashion brands.
But not only is this hurting our wallets, it's also harming the planet.
In the final part of our psychology of shopping series, we spoke to fair fashion campaigner Venetia La Manna ( @venetialamanna ) - who advocates for a more sustainable approach to clothing - about the little tricks fast fashion companies use to get people to spend, spend, spend...
Always in a rush - and slippery floors
Many of the techniques fashion companies use involve ensuring people feel rushed to make purchasing decisions.
Ms La Manna says websites and social media pages are set up to make them look "very immediate" so we "always feel like we have to buy something before it's gone" - meaning you're not able to sit with a purchase and think about whether you need it.
Fast fashion companies also keep an eye on trends and push out products as soon as possible to make sure people are "buying very, very quickly without necessarily much thought".
And the sense of urgency is not just limited to online stores.
Ms La Manna says physical clothes shops will make sure their floors are slippery "so you can almost whizz around with more ease".
Often they will also have loud music to encourage "shopping in a frenzy".
They know what you want
Fashion sites use "highly advanced" search engine optimisation to find out what kind of products their customers are searching for and push these items to them, Ms La Manna says.
They also work with popular online influencers and get them to post affiliate links - meaning if you want to look like your favourite influencer or celebrity, you can buy what they're wearing "in just a few clicks".
Ultimately, they are making things "very easy to buy" and often have shopfronts on popular social media sites like Instagram and TikTok.
Plus, there is the issue of affordability.
Many are driving their prices down so low that "it makes you feel like 'hey, why not' when it's cheaper than a sandwich or a coffee", Ms La Manna says.
Heaters at the entrance
Physical shops use other techniques to entice customers to buy.
For example, Ms La Manna says the heat changes when you go into the shop so you're "invited into a warmer environment".
Shops are also set out in a specific way, often placing cheaper items near checkouts and easy outfit formulas near each other.
The dopamine hit
With lots going on in the world, we may be more susceptible to falling into the spending trap than ever.
"The world is really heavy and people are struggling. Buying fast fashion or buying stuff gives us a momentary hit of dopamine, and of course we need that - when we're suffering, when we're feeling low, [shopping] is an easy one to reach for," Ms La Manna says.
Despite practising "slow fashion" - trying to buy less and more consciously - for years, Ms La Manna says she still has moments where she feels that buying something would make her feel better.
But she says it's possible to get much-needed dopamine hits from elsewhere - including by being active in your community, or by taking your time to find something you really, really want (ideally secondhand!).
Why does it matter?
Aside from being bad for your wallet, Ms La Manna says overconsumption is also bad for the planet and for the garment workers making your clothes.
She says many big fashion companies don't pay their garment workers a fair living wage - with many unable to provide food for their families, living in poverty and lacking paid time off.
The overproduction of clothing is also harming communities in the global south who are left to deal with vast piles of unwanted items, she says.
The majority of clothes taken to charity shops or recycling bins don't end up being resold - instead they are shipped off largely to places in the global south, where communities are "left to deal with a problem that's not theirs".
For more information on slow fashion, Ms La Manna suggests checking out The Or Foundation, Remake and the Clean Clothes Campaign.
P Diddy has sold off his stake in the media company he founded more than a decade ago.
The rapper, whose real name is Sean Combs, released his shares of Revolt with the company saying the have been fully redeemed and retired.
Revolt has not disclosed how much Combs was paid for his stake in the hip-hop news and entertainment company, which he founded in 2013.
It also announced a new ownership structure that will give its employees an equity stake in the company.
The move comes after several lawsuits were filed against Combs , accusing him of sexual assault and rape.
In November, he was sued by R&B singer Cassie, who said he subjected her to a years-long abusive relationship that included beatings and rape.
Combs settled the lawsuit with Cassie, whose full name is Casandra Ventura, a few days after it was filed.
Three in five secondary school teachers and nearly 80% of primary school teachers are spending their own money on supporting students, according to new research.
A report by the National Foundation for Educational Research, based on a survey of 1,282 teachers and senior leaders, found a quarter of teachers had already spent £100 of their own cash on their pupils or school this academic year.
Some 79% of primary school teachers and 62% of secondary school educators reported spending their own money at some point.
And nearly one in five primary and 17% of secondary teachers said they were spending money on meeting pastoral needs such as providing food or clothes.
Jude Hillary, the NFER's co-head of UK policy and practice, said the report "clearly highlights the high level of need among young people".
She said teachers were "going above and beyond to meet pupils' pastoral needs using their personal funds" and the "unrecognised" support was coming at a time when staff themselves are facing their own cost pressures.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


american history
- the constitutionally repugnant reconstruction acts imposed the 14th amendment via martial law powers in time of peace
- free at last
- america - some assembly required
- understanding the new world order
- quick start guide
- There is No "Fourteenth Amendment"!
three constitutions
- three constitutions (this article in development)
correct your status
- correcting your political status
- a call to action that can no longer wait
- 1779 vs. 928s
- Declaration of Political Status
- the truth about the irs
- global sovereign's handbook
driving and traveling
Right to travel without a license.
- the twelve presumptions of court
- judicial notice / demand for rights
- 18 U.S. Code § 241 - conspiracy against rights
- 18 U.S. Code § 242 - deprivation of rights under color of law
reconstruction
- who and what is the state assembly
- who controls whom
- structure of the original government to be reconstructed
- the american government
- the jural assembly handbook
corporate documents
- Hospitals and Physicians Handbook on Birth Registration and Fetal Death Reporting
the academy
Correct your status: 101.
- Articles coming soon
reconstruction: 101
- CRACKING THE CODE
state enactments
Florida state enactments, 3.4 out of 5 stars, u.s. supreme court says no license necessary to drive automobile on public roads.
“The right of a citizen to travel upon the public highways and to transport his property thereon, by horsedrawn carriage, wagon, or automobile, is not a mere privilege which may be permitted or prohibited at will, but a common right which he has under his right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. Under this constitutional guaranty one may, therefore, under normal conditions, travel at his inclination along the public highways or in public places, and while conducting himself in an orderly and decent manner, neither interfering with nor disturbing another’s rights, he will be protected, not only in his person, but in his safe conduct.”
Thompson v.Smith, 154 SE 579, 11 American Jurisprudence, Constitutional Law, section 329, page 1135 “The right of the Citizen to travel upon the public highways and to transport his property thereon, in the ordinary course of life and business, is a common right which he has under the right to enjoy life and liberty, to acquire and possess property, and to pursue happiness and safety. It includes the right, in so doing, to use the ordinary and usual conveyances of the day, and under the existing modes of travel, includes the right to drive a horse drawn carriage or wagon thereon or to operate an automobile thereon, for the usual and ordinary purpose of life and business.” –
Thompson vs. Smith, supra.; Teche Lines vs. Danforth, Miss., 12 S.2d 784 “… the right of the citizen to drive on a public street with freedom from police interference… is a fundamental constitutional right” -White, 97 Cal.App.3d.141, 158 Cal.Rptr. 562, 566-67 (1979) “citizens have a right to drive upon the public streets of the District of Columbia or any other city absent a constitutionally sound reason for limiting their access.”
Caneisha Mills v. D.C. 2009 “The use of the automobile as a necessary adjunct to the earning of a livelihood in modern life requires us in the interest of realism to conclude that the RIGHT to use an automobile on the public highways partakes of the nature of a liberty within the meaning of the Constitutional guarantees. . .”
Berberian v. Lussier (1958) 139 A2d 869, 872, See also: Schecter v. Killingsworth, 380 P.2d 136, 140; 93 Ariz. 273 (1963). “The right to operate a motor vehicle [an automobile] upon the public streets and highways is not a mere privilege. It is a right of liberty, the enjoyment of which is protected by the guarantees of the federal and state constitutions.”
Adams v. City of Pocatello, 416 P.2d 46, 48; 91 Idaho 99 (1966). “A traveler has an equal right to employ an automobile as a means of transportation and to occupy the public highways with other vehicles in common use.”
Campbell v. Walker, 78 Atl. 601, 603, 2 Boyce (Del.) 41. “The owner of an automobile has the same right as the owner of other vehicles to use the highway,* * * A traveler on foot has the same right to the use of the public highways as an automobile or any other vehicle.”
Simeone v. Lindsay, 65 Atl. 778, 779; Hannigan v. Wright, 63 Atl. 234, 236. “The RIGHT of the citizen to DRIVE on the public street with freedom from police interference, unless he is engaged in suspicious conduct associated in some manner with criminality is a FUNDAMENTAL CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHT which must be protected by the courts.” People v. Horton 14 Cal. App. 3rd 667 (1971) “The right to make use of an automobile as a vehicle of travel long the highways of the state, is no longer an open question. The owners thereof have the same rights in the roads and streets as the drivers of horses or those riding a bicycle or traveling in some other vehicle.”
House v. Cramer, 112 N.W. 3; 134 Iowa 374; Farnsworth v. Tampa Electric Co. 57 So. 233, 237, 62 Fla. 166. “The automobile may be used with safety to others users of the highway, and in its proper use upon the highways there is an equal right with the users of other vehicles properly upon the highways. The law recognizes such right of use upon general principles.
Brinkman v Pacholike, 84 N.E. 762, 764, 41 Ind. App. 662, 666. “The law does not denounce motor carriages, as such, on public ways. They have an equal right with other vehicles in common use to occupy the streets and roads. It is improper to say that the driver of the horse has rights in the roads superior to the driver of the automobile. Both have the right to use the easement.”
Indiana Springs Co. v. Brown, 165 Ind. 465, 468. U.S. Supreme Court says No License Necessary To Drive Automobile On Public Highways/Streets No License Is Necessary Copy and Share Freely YHVH.name 2 2 “A highway is a public way open and free to any one who has occasion to pass along it on foot or with any kind of vehicle.” Schlesinger v. City of Atlanta, 129 S.E. 861, 867, 161 Ga. 148, 159;
Holland v. Shackelford, 137 S.E. 2d 298, 304, 220 Ga. 104; Stavola v. Palmer, 73 A.2d 831, 838, 136 Conn. 670 “There can be no question of the right of automobile owners to occupy and use the public streets of cities, or highways in the rural districts.” Liebrecht v. Crandall, 126 N.W. 69, 110 Minn. 454, 456 “The word ‘automobile’ connotes a pleasure vehicle designed for the transportation of persons on highways.”
-American Mutual Liability Ins. Co., vs. Chaput, 60 A.2d 118, 120; 95 NH 200 Motor Vehicle: 18 USC Part 1 Chapter 2 section 31 definitions: “(6) Motor vehicle. – The term “motor vehicle” means every description of carriage or other contrivance propelled or drawn by mechanical power and used for commercial purposes on the highways…” 10) The term “used for commercial purposes” means the carriage of persons or property for any fare, fee, rate, charge or other consideration, or directly or indirectly in connection with any business, or other undertaking intended for profit. “A motor vehicle or automobile for hire is a motor vehicle, other than an automobile stage, used for the transportation of persons for which remuneration is received.”
-International Motor Transit Co. vs. Seattle, 251 P. 120 The term ‘motor vehicle’ is different and broader than the word ‘automobile.’”
-City of Dayton vs. DeBrosse, 23 NE.2d 647, 650; 62 Ohio App. 232 “Thus self-driven vehicles are classified according to the use to which they are put rather than according to the means by which they are propelled” – Ex Parte Hoffert, 148 NW 20 ”
The Supreme Court, in Arthur v. Morgan, 112 U.S. 495, 5 S.Ct. 241, 28 L.Ed. 825, held that carriages were properly classified as household effects, and we see no reason that automobiles should not be similarly disposed of.”
Hillhouse v United States, 152 F. 163, 164 (2nd Cir. 1907). “…a citizen has the right to travel upon the public highways and to transport his property thereon…” State vs. Johnson, 243 P. 1073; Cummins vs. Homes, 155 P. 171; Packard vs. Banton, 44 S.Ct. 256; Hadfield vs. Lundin, 98 Wash 516, Willis vs. Buck, 263 P. l 982;
Barney vs. Board of Railroad Commissioners, 17 P.2d 82 “The use of the highways for the purpose of travel and transportation is not a mere privilege, but a common and fundamental Right of which the public and the individual cannot be rightfully deprived.”
Chicago Motor Coach vs. Chicago, 169 NE 22; Ligare vs. Chicago, 28 NE 934; Boon vs. Clark, 214 SSW 607; 25 Am.Jur. (1st) Highways Sect.163 “the right of the Citizen to travel upon the highway and to transport his property thereon in the ordinary course of life and business… is the usual and ordinary right of the Citizen, a right common to all.” –
Ex Parte Dickey, (Dickey vs. Davis), 85 SE 781 “Every Citizen has an unalienable RIGHT to make use of the public highways of the state; every Citizen has full freedom to travel from place to place in the enjoyment of life and liberty.” People v. Nothaus, 147 Colo. 210. “No State government entity has the power to allow or deny passage on the highways, byways, nor waterways… transporting his vehicles and personal property for either recreation or business, but by being subject only to local regulation i.e., safety, caution, traffic lights, speed limits, etc. Travel is not a privilege requiring licensing, vehicle registration, or forced insurances.”
Chicago Coach Co. v. City of Chicago, 337 Ill. 200, 169 N.E. 22. “Traffic infractions are not a crime.” People v. Battle “Persons faced with an unconstitutional licensing law which purports to require a license as a prerequisite to exercise of right… may ignore the law and engage with impunity in exercise of such right.”
Shuttlesworth v. Birmingham 394 U.S. 147 (1969). U.S. Supreme Court says No License Necessary To Drive Automobile On Public Highways/Streets No License Is Necessary Copy and Share Freely YHVH.name 3 “The word ‘operator’ shall not include any person who solely transports his own property and who transports no persons or property for hire or compensation.”
Statutes at Large California Chapter 412 p.83 “Highways are for the use of the traveling public, and all have the right to use them in a reasonable and proper manner; the use thereof is an inalienable right of every citizen.” Escobedo v. State 35 C2d 870 in 8 Cal Jur 3d p.27 “RIGHT — A legal RIGHT, a constitutional RIGHT means a RIGHT protected by the law, by the constitution, but government does not create the idea of RIGHT or original RIGHTS; it acknowledges them. . . “ Bouvier’s Law Dictionary, 1914, p. 2961. “Those who have the right to do something cannot be licensed for what they already have right to do as such license would be meaningless.”
City of Chicago v Collins 51 NE 907, 910. “A license means leave to do a thing which the licensor could prevent.” Blatz Brewing Co. v. Collins, 160 P.2d 37, 39; 69 Cal. A. 2d 639. “The object of a license is to confer a right or power, which does not exist without it.”
Payne v. Massey (19__) 196 SW 2nd 493, 145 Tex 273. “The court makes it clear that a license relates to qualifications to engage in profession, business, trade or calling; thus, when merely traveling without compensation or profit, outside of business enterprise or adventure with the corporate state, no license is required of the natural individual traveling for personal business, pleasure and transportation.”
Wingfield v. Fielder 2d Ca. 3d 213 (1972). “If [state] officials construe a vague statute unconstitutionally, the citizen may take them at their word, and act on the assumption that the statute is void.” –
Shuttlesworth v. Birmingham 394 U.S. 147 (1969). “With regard particularly to the U.S. Constitution, it is elementary that a Right secured or protected by that document cannot be overthrown or impaired by any state police authority.” Donnolly vs. Union Sewer Pipe Co., 184 US 540; Lafarier vs. Grand Trunk R.R. Co., 24 A. 848; O’Neil vs. Providence Amusement Co., 108 A. 887. “The right to travel (called the right of free ingress to other states, and egress from them) is so fundamental that it appears in the Articles of Confederation, which governed our society before the Constitution.”
(Paul v. Virginia). “[T]he right to travel freely from State to State … is a right broadly assertable against private interference as well as governmental action. Like the right of association, it is a virtually unconditional personal right, guaranteed by the Constitution to us all.” (U.S. Supreme Court,
Shapiro v. Thompson). EDGERTON, Chief Judge: “Iron curtains have no place in a free world. …’Undoubtedly the right of locomotion, the right to remove from one place to another according to inclination, is an attribute of personal liberty, and the right, ordinarily, of free transit from or through the territory of any State is a right secured by the Constitution.’
Williams v. Fears, 179 U.S. 270, 274, 21 S.Ct. 128, 45 L.Ed. 186. “Our nation has thrived on the principle that, outside areas of plainly harmful conduct, every American is left to shape his own life as he thinks best, do what he pleases, go where he pleases.” Id., at 197.
Kent vs. Dulles see Vestal, Freedom of Movement, 41 Iowa L.Rev. 6, 13—14. “The validity of restrictions on the freedom of movement of particular individuals, both substantively and procedurally, is precisely the sort of matter that is the peculiar domain of the courts.” Comment, 61 Yale L.J. at page 187. “a person detained for an investigatory stop can be questioned but is “not obliged to answer, answers may not be compelled, and refusal to answer furnishes no basis for an arrest.”Justice White, Hiibel “Automobiles have the right to use the highways of the State on an equal footing with other vehicles.”
Cumberland Telephone. & Telegraph Co. v Yeiser 141 Kentucy 15. “Each citizen has the absolute right to choose for himself the mode of conveyance he desires, whether it be by wagon or carriage, by horse, motor or electric car, or by bicycle, or astride of a horse, subject to the sole condition that he will observe all those requirements that are known as the law of the road.”
Swift v City of Topeka, 43 U.S. Supreme Court says No License Necessary To Drive Automobile On Public Highways/Streets No License Is Necessary Copy and Share Freely YHVH.name 4 Kansas 671, 674. The Supreme Court said in U.S. v Mersky (1960) 361 U.S. 431: An administrative regulation, of course, is not a “statute.” A traveler on foot has the same right to use of the public highway as an automobile or any other vehicle.
Cecchi v. Lindsay, 75 Atl. 376, 377, 1 Boyce (Del.) 185. Automotive vehicles are lawful means of conveyance and have equal rights upon the streets with horses and carriages.
Chicago Coach Co. v. City of Chicago, 337 Ill. 200, 205; See also: Christy v. Elliot, 216 Ill. 31; Ward v. Meredith, 202 Ill. 66; Shinkle v. McCullough, 116 Ky. 960; Butler v. Cabe, 116 Ark. 26, 28-29. …automobiles are lawful vehicles and have equal rights on the highways with horses and carriages. Daily v. Maxwell, 133 S.W. 351, 354.
Matson v. Dawson, 178 N.W. 2d 588, 591. A farmer has the same right to the use of the highways of the state, whether on foot or in a motor vehicle, as any other citizen.
Draffin v. Massey, 92 S.E.2d 38, 42. Persons may lawfully ride in automobiles, as they may lawfully ride on bicycles. Doherty v. Ayer, 83 N.E. 677, 197 Mass. 241, 246;
Molway v. City of Chicago, 88 N.E. 485, 486, 239 Ill. 486; Smiley v. East St. Louis Ry. Co., 100 N.E. 157, 158. “A soldier’s personal automobile is part of his ‘household goods[.]’
U.S. v Bomar, C.A.5(Tex.), 8 F.3d 226, 235” 19A Words and Phrases – Permanent Edition (West) pocket part 94. “[I]t is a jury question whether … an automobile … is a motor vehicle[.]”
United States v Johnson, 718 F.2d 1317, 1324 (5th Cir. 1983). Other right to use an automobile cases: –
EDWARDS VS. CALIFORNIA, 314 U.S. 160 –
TWINING VS NEW JERSEY, 211 U.S. 78 – WILLIAMS VS. FEARS, 179 U.S. 270, AT 274 – CRANDALL VS. NEVADA, 6 WALL. 35, AT 43-44 – THE PASSENGER CASES, 7 HOWARD 287, AT 492 – U.S. VS. GUEST, 383 U.S. 745, AT 757-758 (1966) –
GRIFFIN VS. BRECKENRIDGE, 403 U.S. 88, AT 105-106 (1971) – CALIFANO VS. TORRES, 435 U.S. 1, AT 4, note 6 –
SHAPIRO VS. THOMPSON, 394 U.S. 618 (1969) – CALIFANO VS. AZNAVORIAN, 439 U.S. 170, AT 176 (1978)
Look the above citations up in American Jurisprudence. Some citations may be paraphrased.
How can we improve this article?
Please submit the reason for your vote so that we can improve the article..
File : Flag of Golovachevskoe (Moscow oblast) (02-2007).svg
File history, file usage on commons, file usage on other wikis.
Original file (SVG file, nominally 1,200 × 800 pixels, file size: 736 bytes)
Structured data
Items portrayed in this file, 22 march 2007.
- SVG flags of cities and villages of Moscow Oblast
- Valid SVG created with Other tools:Flags
- PD-RU-exempt (flags)
Navigation menu
Advertisement
What Penalties Does Trump Face Now That He Has Been Convicted?
Each of the 34 counts carries the possibility of up to four years in prison, but incarceration is not a given: Justice Juan M. Merchan could opt to impose a sentence of probation, with no prison time.
- Share full article

By Kate Christobek
- Published May 29, 2024 Updated May 30, 2024
Now that a New York jury has convicted Donald J. Trump of all 34 felony counts against him, it will be up to Justice Juan M. Merchan to decide whether his punishment will include prison time.
Mr. Trump was charged with 34 counts of falsifying business records related to the coverup of a $130,000 hush money payment that was made to the porn star Stormy Daniels in the days leading up to the 2016 election. All the charges are class E felonies, the least serious, in New York State.
Mr. Trump was released on his own recognizance until his sentencing, which was scheduled for July 11. Each count carries the possibility of up to four years in prison. If Justice Merchan were to opt for prison time, he would likely impose the punishment concurrently, meaning he would have Mr. Trump serve the sentence for each count simultaneously.
Incarceration is not a given: Justice Merchan could instead opt to impose a sentence of probation, with no prison time. Mr. Trump would then be required to regularly report to New York City’s Probation Department. He could also be jailed immediately if he committed additional crimes.
Mr. Trump, who is again the presumptive Republican presidential nominee, will undoubtedly appeal any conviction, a lengthy process that could take months or longer and would likely not be resolved before Election Day.
There has been no indication yet of what Justice Merchan could decide, though he has made it known that he takes white-collar crime seriously. Mr. Trump has continually attacked and denounced him as “biased” and “corrupt.”
Kate Christobek is a reporter covering the civil and criminal cases against former president Donald J. Trump for The Times. More about Kate Christobek
Our Coverage of the Trump Hush-Money Trial
Guilty Verdict : Donald Trump was convicted on all 34 counts of falsifying records to cover up a sex scandal that threatened his bid for the White House in 2016, making him the first American president to be declared a felon .
What Happens Next: Trump’s sentencing hearing on July 11 will trigger a long and winding appeals process , though he has few ways to overturn the decision .
Reactions: Trump’s conviction reverberated quickly across the country and around the world . Here’s what voters , New Yorkers , Republicans , Trump supporters and President Biden had to say.
The Presidential Race : The political fallout of Trump’s conviction is far from certain , but the verdict will test America’s traditions, legal institutions and ability to hold an election under historic partisan tension .
Making the Case: Over six weeks and the testimony of 20 witnesses, the Manhattan district attorney’s office wove a sprawling story of election interference and falsified business records.
Legal Luck Runs Out: The four criminal cases that threatened Trump’s freedom had been stumbling along, pleasing his advisers. Then his good fortune expired .
- Yekaterinburg
- Novosibirsk
- Vladivostok
- Tours to Russia
- Practicalities
- Russia in Lists
Rusmania • Deep into Russia
Out of the Centre
Savvino-storozhevsky monastery and museum.

Zvenigorod's most famous sight is the Savvino-Storozhevsky Monastery, which was founded in 1398 by the monk Savva from the Troitse-Sergieva Lavra, at the invitation and with the support of Prince Yury Dmitrievich of Zvenigorod. Savva was later canonised as St Sabbas (Savva) of Storozhev. The monastery late flourished under the reign of Tsar Alexis, who chose the monastery as his family church and often went on pilgrimage there and made lots of donations to it. Most of the monastery’s buildings date from this time. The monastery is heavily fortified with thick walls and six towers, the most impressive of which is the Krasny Tower which also serves as the eastern entrance. The monastery was closed in 1918 and only reopened in 1995. In 1998 Patriarch Alexius II took part in a service to return the relics of St Sabbas to the monastery. Today the monastery has the status of a stauropegic monastery, which is second in status to a lavra. In addition to being a working monastery, it also holds the Zvenigorod Historical, Architectural and Art Museum.
Belfry and Neighbouring Churches

Located near the main entrance is the monastery's belfry which is perhaps the calling card of the monastery due to its uniqueness. It was built in the 1650s and the St Sergius of Radonezh’s Church was opened on the middle tier in the mid-17th century, although it was originally dedicated to the Trinity. The belfry's 35-tonne Great Bladgovestny Bell fell in 1941 and was only restored and returned in 2003. Attached to the belfry is a large refectory and the Transfiguration Church, both of which were built on the orders of Tsar Alexis in the 1650s.

To the left of the belfry is another, smaller, refectory which is attached to the Trinity Gate-Church, which was also constructed in the 1650s on the orders of Tsar Alexis who made it his own family church. The church is elaborately decorated with colourful trims and underneath the archway is a beautiful 19th century fresco.
Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral

The Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral is the oldest building in the monastery and among the oldest buildings in the Moscow Region. It was built between 1404 and 1405 during the lifetime of St Sabbas and using the funds of Prince Yury of Zvenigorod. The white-stone cathedral is a standard four-pillar design with a single golden dome. After the death of St Sabbas he was interred in the cathedral and a new altar dedicated to him was added.

Under the reign of Tsar Alexis the cathedral was decorated with frescoes by Stepan Ryazanets, some of which remain today. Tsar Alexis also presented the cathedral with a five-tier iconostasis, the top row of icons have been preserved.
Tsaritsa's Chambers

The Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral is located between the Tsaritsa's Chambers of the left and the Palace of Tsar Alexis on the right. The Tsaritsa's Chambers were built in the mid-17th century for the wife of Tsar Alexey - Tsaritsa Maria Ilinichna Miloskavskaya. The design of the building is influenced by the ancient Russian architectural style. Is prettier than the Tsar's chambers opposite, being red in colour with elaborately decorated window frames and entrance.

At present the Tsaritsa's Chambers houses the Zvenigorod Historical, Architectural and Art Museum. Among its displays is an accurate recreation of the interior of a noble lady's chambers including furniture, decorations and a decorated tiled oven, and an exhibition on the history of Zvenigorod and the monastery.
Palace of Tsar Alexis

The Palace of Tsar Alexis was built in the 1650s and is now one of the best surviving examples of non-religious architecture of that era. It was built especially for Tsar Alexis who often visited the monastery on religious pilgrimages. Its most striking feature is its pretty row of nine chimney spouts which resemble towers.

Plan your next trip to Russia
Ready-to-book tours.
Your holiday in Russia starts here. Choose and book your tour to Russia.
REQUEST A CUSTOMISED TRIP
Looking for something unique? Create the trip of your dreams with the help of our experts.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Thompson v.Smith, 154 SE 579, 11 American Jurisprudence, Constitutional Law, section 329, page 1135 "The right of the Citizen to travel upon the public highways and to transport his property thereon, in the ordinary course of life and business, is a common right which he has under the right to enjoy life and liberty, to acquire and possess ...
II Am. Jur. (1st) Constitutional Law, Sec. 329, p. 1135 P. 3 "The right of a citizen to travel upon the public highways and to transport his property thereon, by horsedrawn carriage, wagon, or automobile, is not a mere privilege which may be permitted or prohibited at will, but a common right which he has under his right to life, liberty
The right to travel doesn't mean you can drive without a valid driver's license and proper vehicle registration. Public safety can override individual freedoms in some contexts, like driving. Roads and highways are public infrastructure. Dangerous driving has the potential to harm others and their property. Travel is a right, but driving is a ...
All have agreed that the right exists.). For example, the Court held that a state could not constitutionally limit access to medical care to its own residents, and deny access to nonresidents, without interfering with the right to travel. 3 Footnote Doe v. Bolton, 410 U.S. 179, 200 (1973), abrogated on other grounds by Dobbs v. Jackson Women ...
31. There is no basis for the view that requiring a driver's license is unconstitutional. First, it's critical to realize that a right to travel has nothing whatsoever to do with licensing drivers. A right to travel does not in any way mean there's a right to travel in a particular way. Likewise, using a car does not mean you're traveling.
The U.S. Supreme Court has ruled that motorists need not have licenses to drive vehicles on public roads. For years now, impressive-looking texts and documents have been circulated online under ...
If anyone speaks of a "Constitutional right to travel" Freedom of Movement is the only valid thing they could be referring to, as we'll show. In pseudo-legal circles, "right to travel" means the supposed right to "travel freely in your private property / automobile / conveyance on the public roads / highways without a driver's license ...
All have agreed that the right exists." ). For example, the Court held that a state could not constitutionally limit access to medical care to its own residents, and deny access to nonresidents, without interfering with the right to travel.3 Footnote Doe v. Bolton, 410 U.S. 179, 200 (1973), abrogated on other grounds by Dobbs v. Jackson Women ...
No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws. The doctrine of the right to travel actually ...
Blumstein, 405 U.S. 330, 334 (1972). Because the right to travel is implicated by state distinctions between residents and nonresidents, the relevant constitutional provision is the Privileges and Immunities Clause, Article IV, § 2, cl. 1. Intrastate travel is protected to the extent that the classification fails to meet equal protection ...
The forgotten legal maxim is that free people have a right to travel on the roads which are provided by their servants for that purpose, using ordinary transportation of the day. Licensing cannot be required of free people, because taking on the restrictions of a license requires the surrender of a right.
The right to travel is a part of the "liberty" of which the citizen cannot be deprived without due process of law under the Fifth Amendment. So much is conceded by the Solicitor General. In Anglo-Saxon law, that right was emerging at least as early as the Magna Carta. [Footnote 12] Chafee, Page 357 U. S. 126
In Paul v. Virginia, 75 U.S. 168 (1869), the court defined freedom of movement as "right of free ingress into other States, and egress from them." [1] However, the Supreme Court did not invest the federal government with the authority to protect freedom of movement. Under the "privileges and immunities" clause, this authority was given to the ...
Shown Here: Introduced in House (06/28/2022) This resolution expresses the sense that every person has the right to travel freely within the United States and that no one should be held criminally or civilly liable for seeking, providing, or assisting with out-of-state health care services that are legal in the jurisdiction in which they are delivered.
relied on common law traditions that protected the right of every person to travel upon public roadways without a license. Courts repeatedly wrote of an individual's "right to travel" by automobile and struck down regulations aimed at limiting the liberties of automobile drivers on constitutional grounds. With the passage of time,
CASE #3: "The right to travel is a part of the liberty of which the citizen cannot be deprived without due process of law under the Fifth Amendment." Kent v. Dulles, 357 US 116, 125. CASE #4: "The right to travel is a well-established common right that does not owe its existence to the federal government. It is recognized by the courts as a ...
i expressly RESERVE ALL RIGHTS WITHOUT PREJUDICE or RECOURSE HEREIN AND HEREAFTER. This AFFIDAVIT becomes constructive filing, administrative Notice and an evidentiary document submitted upon request or demand of a "Driver License", registration, or proof of insurance, and as part of the Official Record of ANY ensuing action. THIS AFFIDAVIT
But under Florida law, the state's Clemency Board "will not consider requests for firearm authority from individuals convicted in federal or out-of-state courts," according to the state.
The doctrine of the "right to travel" actually encompasses three separate rights, of which two have been notable for the uncertainty of their textual support. The first is the right of a citizen to move freely between states, a right venerable for its longevity, but still lacking a clear doctrinal basis. 1.
Image Credit: Shutterstock / Pixel-Shot . The U.S. is pioneering "Right to Repair" laws, allowing consumers to fix their own electronics and machinery without voiding warranties—a battle ...
I grant anyone the right to use this work for any purpose, without any conditions, unless such conditions are required by law. Captions. English. Add a one-line explanation of what this file represents. Items portrayed in this file depicts. creator. some value.
Subway is following in the steps of some of its fast-food rivals with the introduction of self-service kiosks and its own dedicated app. Read this and the rest of today's consumer and personal ...
A version of this story appears in CNN's What Matters newsletter. To get it in your inbox, sign up for free here. The US Constitution lays out just three requirements for presidential candidates ...
Law #130/2004-OZ of October 25, 2004 On the Status and the Border of Elektrostal Urban Okrug, as amended by the Law #82/2010-OZ of July 1, 2010 On Amending the Law of Moscow Oblast "On the Status and the Border of Elektrostal Urban Okrug" and the Law of Moscow Oblast "On the Status and Borders of Noginsky Municipal District and the Newly ...
The renowned "50 Best" list of restaurants was revealed in Las Vegas last night - with a new restaurant taking top spot. Disfrutar in Barcelona took the crown from Central in Lima, Peru (previous ...
Thompson v.Smith, 154 SE 579, 11 American Jurisprudence, Constitutional Law, section 329, page 1135 "The right of the Citizen to travel upon the public highways and to transport his property thereon, in the ordinary course of life and business, is a common right which he has under the right to enjoy life and liberty, to acquire and possess ...
Original file (SVG file, nominally 1,200 × 800 pixels, file size: 736 bytes)
Each of the 34 counts carries the possibility of up to four years in prison, but incarceration is not a given: Justice Juan M. Merchan could opt to impose a sentence of probation, with no prison time.
Zvenigorod's most famous sight is the Savvino-Storozhevsky Monastery, which was founded in 1398 by the monk Savva from the Troitse-Sergieva Lavra, at the invitation and with the support of Prince Yury Dmitrievich of Zvenigorod. Savva was later canonised as St Sabbas (Savva) of Storozhev. The monastery late flourished under the reign of Tsar ...