- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"

Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Indonesia travel advice
Latest updates: Editorial change
Last updated: June 5, 2024 06:24 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, indonesia - exercise a high degree of caution.
Exercise a high degree of caution in Indonesia due to political and social tensions and the threat of terrorism throughout the country.
Indonesian Papua - Avoid non-essential travel
Avoid non-essential travel to all the provinces of Indonesia Papua due to the regular occurrence of violent incidents, threats made against foreigners by militant groups and risk of kidnapping.
Back to top
- Indonesian Papua
Political tension and regular violent incidents continue to occur in Indonesian Papua.
In February 2023, militant groups threatened to attack and take hostages, specifically referencing foreigners. You may also face increased threats of violence or kidnapping if you travel to Indonesian Papua.
Labour disputes at the Freeport-McMoRan mine near Timika have led to demonstrations, public transportation disruptions and violence.
Fatal attacks have occurred on roads near the mine. Foreigners have been targeted by local militants.
There is a heightened police and military presence in this area.
There is a threat of terrorism in Indonesia.
While effective counterterrorism measures by Indonesian authorities are in place, terrorist cells are active and have the capacity to carry out attacks throughout the country.
Attacks have targeted:
- military and government facilities
- tourist attractions and popular public places
- nightclubs and entertainment venues
- public transportation
Further attacks are likely, and terrorists may also target:
- crowded places
- places with high pedestrian traffic and where foreigners may gather
- commercial establishments
- local government offices
- public transit stations
- busy streets
- long lineups at tourist attractions
- places of worship
Stay at hotels that have robust security measures, including metal detectors, guards and security cameras. Keep in mind, however, that even the most secure locations cannot be considered completely free of risk.
Be particularly vigilant during religious holidays and other public celebrations, as terrorists have used such occasions to mount attacks.
- Always be aware of your surroundings when in public places and identify ways to leave the area in case of emergency
- Monitor local media
- Follow the instructions of the local authorities
Violent crime
Violent crime, such as armed robberies, occurs regularly. Be particularly cautious on the road from Banda Aceh to Medan, where armed robberies have occurred.
Foreigners travelling alone and those travelling at night are at particular risk.
Standards of police services differ considerably from those in Canada.
- Avoid showing signs of affluence
- Ensure that your personal belongings, including your passport and other travel documents, are secure at all times
- If you’re travelling by car, keep valuable belongings out of sight, windows closed and doors locked
Petty crime
Petty crime, such as pickpocketing and purse snatching, occurs throughout Indonesia, specifically in tourist areas, such as Bali and Lombok. Criminals sometimes force people to withdraw cash from ATMs.
Merchants don’t always honour pricing agreements. Use good judgment in engaging services of tourist guides, especially in places that tourists rarely visit.
There is a threat of kidnapping, particularly in the provinces of Indonesian Papua and Aceh province. Foreign travellers have been kidnapped and killed. Terrorist groups have also kidnapped tourists in East and West Kalimantan.
- Be extra vigilant if travelling in these areas
- Avoid travelling alone and after dusk
- Use varied routes and schedules when moving from one place to another
Women's safety
Women travelling alone may face some forms of harassment and verbal abuse.
Advice for women travellers
Demonstrations
Demonstrations take place from time to time. Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. They can also lead to disruptions to traffic and public transportation.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Political and social tension
There are long-standing sectarian and social tensions throughout Indonesia, particularly in the provinces of:
- Central Sulawesi, in Palu, Poso and Tentena
- Maluku, especially in Ambon
Sectarian violence targeting civilians has occurred. The potential for violence remains, despite ongoing security operations efforts from local authorities. Be aware of your surroundings.
There is a very high rate of credit and debit card fraud in Indonesia, including online fraud.
When using debit or credit cards:
- pay careful attention if other people are handling your cards
- use ATMs located in public areas or inside a bank or business
- avoid using card readers with an irregular or unusual feature
- cover the keypad with one hand when entering your PIN
- check for any unauthorized transactions on your account statements
Romance scams
If you’re travelling to Indonesia to meet someone you’ve only met online, keep it mind that you may be the victim of a scam. Be wary of unsolicited emails or requests for a wire transfer.
Don’t send money to someone you have never met in person.
Overseas fraud
Spiked food and drinks
Even if the wrapping or container appears intact, snacks, beverages, gum and cigarettes may contain drugs that could put you at risk of sexual assault and robbery.
- Be wary of accepting these items from new acquaintances
- Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers
People have died after drinking methanol-adulterated alcohol. Counterfeits of well-known alcohol brands often contain dangerous amounts of methanol. Poisoning incidents have happened at hotels, bars, and shops in tourist areas like Bali, Lombok, the Gili Islands and Sumatra.
- Be cautious if you choose to drink alcohol
- Be wary of lesser-known or illegal brands
- Avoid buying alcohol from individuals
- Seek medical assistance if you begin to feel sick
Alcohol, drugs and travel
Road safety
Road conditions and road safety vary greatly throughout the country. Driving conditions may be hazardous during the rainy season.
Road travel in Indonesia can be very challenging due to:
- reckless driving
- perilous road conditions
- inadequate lighting
- poor signage
- high traffic congestion
If you plan to rent a car, consider hiring a driver.
Avoid driving after dark outside of major cities or major roads as some drivers do not use lights.
You may face mob anger if you are involved in an accident that causes serious injury. In such cases, remain in your vehicle and wait for a police officer to arrive.
Motorcycles and scooters
Motorcycle and scooter accidents are the main cause of death and serious injury among foreigners visiting many parts of Indonesia, including Bali.
Rental motorcycles are also often targeted and stolen. In such cases, you may have to pay the replacement cost for a new motorcycle.
Public transport
Public transport can be crowded and safety standards are poor. Many remote parts of Indonesia have poor transportation networks.
Crashes involving overcrowded buses are common. Large buses are generally available only on Java. Minibuses are available elsewhere.
If you choose to travel by bus,
- keep in mind that minibus drivers may try to overcharge foreigners
- keep your belongings secure due to pickpocketing
The condition of taxis varies. Foreign travellers using taxis have been victims of armed robbery, either by the driver or other passengers.
- Pre-arrange transportation with a safe and reliable taxi company
- Only use a taxi company whose vehicles are equipped with a meter
- Never enter a cab if it already has one or more passengers
- Don’t hail taxis off the street and avoid using unmarked taxi services
Reliable taxis are available from Bluebird, Thunderbird and Express. Be careful of “lookalike” taxis from competitors.
Ferry accidents are common and are often caused by poor safety practices or extreme weather conditions.
If you choose to travel by ferry:
- make sure the vessel you are boarding is carrying appropriate safety equipment and that life jackets are provided for all passengers and accessible at all times
- don’t board vessels that appear overloaded or unseaworthy
- verify the safety standards of ferries with your tour operator
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Indonesian authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date of entry into Indonesia and must contain at least one blank page for the placement of the Indonesian visa or entry stamp.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: required Business visa: required Social-cultural visit visa: required
Indonesia strictly enforces its immigration and visa requirements. Foreign travellers have been detained in immigration detention centres for visa violations or overstays. Those in violation may be subject to substantial fines and deportation.
A round-trip or onward airline ticket is required to obtain all types of visas.
Tourist visa
If you are travelling for tourism with a regular Canadian passport, you may obtain a visa in advance or on arrival at select points of entry.
Business and social-cultural visas
If you are travelling to Indonesia for business or social-cultural purposes (e.g. volunteer work), you must obtain a visa prior to your arrival. You must provide a letter from both the sponsoring organization in Indonesia and the sending organization in Canada to obtain your visa.
A business or social-cultural single-entry visa is extendable from within Indonesia.
Aid workers
Aid workers must have a sponsor in Indonesia to obtain a visa. Those going to Aceh also require prior authorization from the Directorate General of Immigration in Aceh or Jakarta.
Journalists
Journalists visiting Indonesia for reporting and filming purposes must obtain authorization from the Directorate General of Immigration in Jakarta before applying for a visa.
Directorate General of Immigration – Ministry of Law and Human Rights of Indonesia
Restricted areas
You must obtain a permit to travel to Indonesian Papua.
Entry regulations and permission to remain in Indonesian Papua may change at any time.
Other entry requirements
Starting February 14, 2024, tourists entering Bali will be subject to a new tax, the Love Bali Tourist Levy. This fee will be in addition to the visa fees paid to enter Indonesia.
If your are travelling to Bali, you must pay directly though the Provincial Government of Bali website.
Levy for Foreign Tourists – Provincial Government of Bali
Customs officials may ask you to show them a return or onward ticket and proof of sufficient funds to cover your stay.
- Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- Zika virus: Advice for travellers - 31 August, 2023
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
- Polio: Advice for travellers - 6 May, 2024
- Dengue: Advice for travellers - 6 May, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is no risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is required if you are coming from a country where yellow fever occurs.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is not recommended.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre
* It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Japanese encephalitis is a viral infection that can cause swelling of the brain. It is spread to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito. Risk is very low for most travellers. Travellers at relatively higher risk may want to consider vaccination for JE prior to travelling.
Travellers are at higher risk if they will be:
- travelling long term (e.g. more than 30 days)
- making multiple trips to endemic areas
- staying for extended periods in rural areas
- visiting an area suffering a JE outbreak
- engaging in activities involving high contact with mosquitos (e.g., entomologists)
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes. There is a risk of malaria in certain areas and/or during a certain time of year in this destination.
Antimalarial medication may be recommended depending on your itinerary and the time of year you are travelling. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times: • Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin. • Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows. • Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area. • Wear permethrin-treated clothing. If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
In this destination, rabies is commonly carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. In this destination, rabies treatment may be limited or may not be available, therefore you may need to return to Canada for treatment.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Polio (poliomyelitis) is an infectious disease that can be prevented by vaccination. It is caused by poliovirus type 1, 2 or 3. Circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus 2 (cVDPV2) is present in this country. Polio is spread from person to person and through contaminated food and water. Infection with the polio virus can cause paralysis and death in individuals of any age who are not immune.
Recommendations:
- Be sure that your polio vaccinations are up to date before travelling. Polio is part of the routine vaccine schedule for children in Canada.
- One booster dose of the polio vaccine is recommended as an adult .
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
There is a risk of schistosomiasis in this destination. Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by tiny worms (blood flukes) which can be found in freshwater (lakes, rivers, ponds, and wetlands). The worms can break the skin, and their eggs can cause stomach pain, diarrhea, flu-like symptoms, or urinary problems. Schistosomiasis mostly affects underdeveloped and r ural communities, particularly agricultural and fishing communities.
Most travellers are at low risk. Travellers should avoid contact with untreated freshwater such as lakes, rivers, and ponds (e.g., swimming, bathing, wading, ingesting). There is no vaccine or medication available to prevent infection.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
Lymphatic filariasis , also known as elephantiasis, is caused by filariae (tiny worms) spread to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can cause a range of illnesses. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from mosquito bites. There is no vaccine available for lymphatic filariasis although drug treatments exist.
- In this country, dengue is a risk to travellers. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue.
Zika virus is a risk in this country.
Zika virus is primarily spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can also be sexually transmitted. Zika virus can cause serious birth defects.
During your trip:
- Prevent mosquito bites at all times.
- Use condoms correctly or avoid sexual contact, particularly if you are pregnant.
If you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy, you should discuss the potential risks of travelling to this destination with your health care provider. You may choose to avoid or postpone travel.
For more information, see Zika virus: Pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Human cases of avian influenza have been reported in this destination. Avian influenza is a viral infection that can spread quickly and easily among birds and in rare cases it can infect mammals, including people. The risk is low for most travellers.
Avoid contact with birds, including wild, farm, and backyard birds (alive or dead) and surfaces that may have bird droppings on them. Ensure all poultry dishes, including eggs and wild game, are properly cooked.
Travellers with a higher risk of exposure include those:
- visiting live bird/animal markets or poultry farms
- working with poultry (such as chickens, turkeys, domestic ducks)
- hunting, de-feathering, field dressing and butchering wild birds and wild mammals
- working with wild birds for activities such as research, conservation, or rehabilitation
- working with wild mammals, especially those that eat wild birds (e.g., foxes)
All eligible people are encouraged to get the seasonal influenza shot, which will protect them against human influenza viruses. While the seasonal influenza shot does not prevent infection with avian influenza, it can reduce the chance of getting sick with human and avian influenza viruses at the same time.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Tuberculosis is an infection caused by bacteria and usually affects the lungs.
For most travellers the risk of tuberculosis is low.
Travellers who may be at high risk while travelling in regions with risk of tuberculosis should discuss pre- and post-travel options with a health care professional.
High-risk travellers include those visiting or working in prisons, refugee camps, homeless shelters, or hospitals, or travellers visiting friends and relatives.
Medical services and facilities
Heath care is inadequate.
Most medical staff don’t speak English or French. You may have to pay in advance, in cash, to obtain medical services.
Medical evacuation can be very expensive and you may need it in case of serious illness or injury.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Overview of the criminal law system in Indonesia
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe. Convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences. They can also be detained for long periods, without the possibility of release on bail, while police conduct investigations prior to prosecution.
Police have arrested tourists after random drug testing throughout the country.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
Some prescription and over-the-counter medications that are legal in Canada, such as those containing morphine and codeine, are classified as controlled substances in Indonesia. It’s illegal to bring them into the country, even in small quantities, without prior permission from the Indonesian Ministry of Health and the required documentation.
If you attempt to bring banned pharmaceuticals into Indonesia without prior authorization and proper documentation, Indonesian authorities may confiscate them. You may also be subject to fines and imprisonment.
In some areas, Islamic practices and beliefs closely adhere to local customs, laws and regulations.
Religious police enforce sharia law in Aceh. Specific applications of sharia may differ by region and apply to non-Muslims as well.
Be aware of the relevant provisions specifically related to the region, regardless of your religion.
Dress and behaviour
To avoid offending local sensitivities:
- dress conservatively
- behave discreetly
- respect religious and social traditions
In 2025, the lunar month of Ramadan is expected to begin on or around February 28.
In public, between sunrise and sunset, be discreet when:
2SLGBTQI+ travellers
Indonesian national law doesn’t criminalize sexual acts or relationships between persons of the same sex. However, they are prohibited and punishable under local laws in some provinces.
In Aceh, Sharia law is enforced and sexual acts between Muslim individuals of the same sex is punished by caning. They could also face arrest under charges related to immoral behaviour, prostitution or social ills.
2SLGBTQI+ travellers could be discriminated against based on their sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression or sex characteristics.
2SLGBTQI+ individuals should carefully consider the risks of travelling to Indonesia.
Travel and your sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is not legally recognized in Indonesia.
If local authorities consider you a citizen of Indonesia, they may refuse to grant you access to Canadian consular services. This will prevent us from providing you with those services.
Indonesia allows minors to carry dual citizenship until the age of 18. After this time, they must choose between their Indonesian citizenship and foreign citizenship.
General information for travellers with dual citizenship
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and Indonesia.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Indonesia by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Indonesia to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children's Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country's judicial affairs.
- International Child Abductions: A guide for affected parents
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Request emergency assistance
Imports and exports
Local customs authorities may enforce strict regulations concerning temporary import or export of items such as audiovisual material.
Gambling is illegal in Indonesia.
Identification
You must carry adequate identification, such as your passport and your stay permit, at all times.
You may be detained and fined if you don’t have the original on you.
Traffic drives on the left.
You must carry an International Driving Permit along with your Canadian driver’s licence.
If you got your International Driving Permit outside of Indonesia, local authorities may ask to approve it.
If you’re involved in an accident, you must stop and exchange information with and provide assistance to other drivers.
- International Driving Permit registration – Traffic Police, Government of Indonesia (in Indonesian)
- More about the International Driving Permit
The currency is the rupiah (IDR).
Credit cards are not widely accepted outside of large urban centres and tourist areas.
Carry cash when visiting remote areas.
Climate change is affecting Indonesia. Extreme and unusual weather events are becoming more frequent. Indonesia is located in a very active seismic zone and is prone to natural disasters such as:
- earthquakes
- volcanic eruptions
Monitor local news to stay informed on the current situation.
Earthquakes and tsunamis
Each year, Indonesia experiences thousands of earthquakes. Some trigger tsunamis and cause significant damage. Deaths and injuries occasionally occur.
A tsunami can occur within minutes of a nearby earthquake. However, the risk of tsunami can remain for several hours following the first tremor. If you're staying on the coast, familiarize yourself with the region's evacuation plans in the event of a tsunami warning.
- Earthquakes - What to Do?
- Tsunami alerts - U.S. Tsunami Warning System
Indonesia has 129 active volcanoes and periodically experiences major volcanic events that can be dangerous, even life-threatening. Ash clouds can disrupt air travel, including on the island of Bali, and cause or worsen respiratory problems.
Active volcanoes are monitored to provide residents with an early warning should unusual activity occur. Local authorities can raise alert levels and order evacuations on short notice.
If you are near active volcanoes:
- take official warnings seriously and respect exclusion zones
- monitor local media to stay up-to-date on latest developments
- follow the advice of local authorities, including evacuation orders
- be prepared to modify your travel arrangements or even evacuate the area on short notice
- National Disaster Management Authority
- Map of active volcanoes in Indonesia – MAGMA Indonesia
Rainy season
The rainy season extends from November to March, but heavy rains are common throughout the year. Flooding and landslides can occur with little warning, especially in remote areas where extensive deforestation is common, but also in major cities, including Jakarta. Such incidents have led to fatalities and destruction of property.
Seasonal flooding can hamper overland travel and reduce the provision of essential services. Roads may become impassable and bridges damaged.
- Be aware of health risks associated with flood waters
- Keep informed of regional weather forecasts as well as road closures or detours
- Avoid disaster areas
- Follow the advice of local authorities
Tornadoes, cyclones, hurricanes, typhoons and monsoons
Air pollution
Unrestricted burning in Sumatra and Kalimantan sometimes causes air pollution to rise to unhealthy levels, especially from June to October.
Monitor air pollution levels closely, as they change quickly.
During periods of high pollution:
- limit your activities outdoors
- monitor local media
- follow the instructions of local authorities
Local services
In case of emergency, dial 110 for police.
Research and carry contact information for local medical facilities.
Consular assistance
Timor-Leste
There is no Canadian government office in Bali. You can obtain consular assistance from the Australian Consulate General of Australia, in Bali, under the Canada-Australia Consular Services Sharing Agreement.
Sign up to receive email updates from the Australian government on situations and events that could affect your safety while in Bali.
Smartraveller - Australian travel advice
For emergency consular assistance, call the Embassy of Canada to Indonesia, in Jakarta, and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.
Travel vaccination advice
If you're planning to travel outside the UK, you may need to be vaccinated against some of the serious diseases found in other parts of the world.
Vaccinations are available to protect you against infections such as yellow fever , typhoid and hepatitis A .
In the UK, the NHS routine immunisation (vaccination) schedule protects you against a number of diseases, but does not cover all of the infectious diseases found overseas.
When should I start thinking about the vaccines I need?
If possible, see the GP or a private travel clinic at least 6 to 8 weeks before you're due to travel.
Some vaccines need to be given well in advance to allow your body to develop immunity.
And some vaccines involve a number of doses spread over several weeks or months.
You may be more at risk of some diseases, for example, if you're:
- travelling in rural areas
- backpacking
- staying in hostels or camping
- on a long trip rather than a package holiday
If you have a pre-existing health problem, this may make you more at risk of infection or complications from a travel-related illness.
Which travel vaccines do I need?
You can find out which vaccinations are necessary or recommended for the areas you'll be visiting on these websites:
- Travel Health Pro
- NHS Fit for Travel
Some countries require proof of vaccination (for example, for polio or yellow fever vaccination), which must be documented on an International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (ICVP) before you enter or when you leave a country.
Saudi Arabia requires proof of vaccination against certain types of meningitis for visitors arriving for the Hajj and Umrah pilgrimages.
Even if an ICVP is not required, it's still a good idea to take a record of the vaccinations you have had with you.
Find out more about the vaccines available for travellers abroad
Where do I get my travel vaccines?
First, phone or visit the GP practice or practice nurse to find out whether your existing UK vaccinations are up-to-date.
If you have any records of your vaccinations, let the GP know what you have had previously.
The GP or practice nurse may be able to give you general advice about travel vaccinations and travel health, such as protecting yourself from malaria.
They can give you any missing doses of your UK vaccines if you need them.
Not all travel vaccinations are available free on the NHS, even if they're recommended for travel to a certain area.
If the GP practice can give you the travel vaccines you need but they are not available on the NHS, ask for:
- written information on what vaccines are needed
- the cost of each dose or course
- any other charges you may have to pay, such as for some certificates of vaccination
You can also get travel vaccines from:
- private travel vaccination clinics
- pharmacies offering travel healthcare services
Which travel vaccines are free?
The following travel vaccines are available free on the NHS from your GP surgery:
- polio (given as a combined diphtheria/tetanus/polio jab )
- hepatitis A
These vaccines are free because they protect against diseases thought to represent the greatest risk to public health if they were brought into the country.
Which travel vaccines will I have to pay for?
You'll have to pay for travel vaccinations against:
- hepatitis B
- Japanese encephalitis
- tick-borne encephalitis
- tuberculosis (TB)
- yellow fever
Yellow fever vaccines are only available from designated centres .
The cost of travel vaccines that are not available on the NHS will vary, depending on the vaccine and number of doses you need.
It's worth considering this when budgeting for your trip.
Other things to consider
There are other things to consider when planning your travel vaccinations, including:
- your age and health – you may be more vulnerable to infection than others; some vaccines cannot be given to people with certain medical conditions
- working as an aid worker – you may come into contact with more diseases in a refugee camp or helping after a natural disaster
- working in a medical setting – a doctor, nurse or another healthcare worker may require additional vaccinations
- contact with animals – you may be more at risk of getting diseases spread by animals, such as rabies
If you're only travelling to countries in northern and central Europe, North America or Australia, you're unlikely to need any vaccinations.
But it's important to check that you're up-to-date with routine vaccinations available on the NHS.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Speak to a GP before having any vaccinations if:
- you're pregnant
- you think you might be pregnant
- you're breastfeeding
In many cases, it's unlikely a vaccine given while you're pregnant or breastfeeding will cause problems for the baby.
But the GP will be able to give you further advice about this.
People with immune deficiencies
For some people travelling overseas, vaccination against certain diseases may not be advised.
This may be the case if:
- you have a condition that affects your body's immune system, such as HIV or AIDS
- you're receiving treatment that affects your immune system, such as chemotherapy
- you have recently had a bone marrow or organ transplant
A GP can give you further advice about this.
Non-travel vaccines
As well as getting any travel vaccinations you need, it's also a good opportunity to make sure your other vaccinations are up-to-date and have booster vaccines if necessary.
Although many routine NHS vaccinations are given during childhood, you can have some of them (such as the MMR vaccine ) as an adult if you missed getting vaccinated as a child.
There are also some extra NHS vaccinations for people at higher risk of certain illnesses, such as the flu vaccine , the hepatitis B vaccine and the BCG vaccine for tuberculosis (TB) .
Your GP can advise you about any NHS vaccinations you might need.
Find out about NHS vaccinations and when to have them
Page last reviewed: 16 March 2023 Next review due: 16 March 2026
Vaccinations for Indonesia
- What Travel Vaccines Do I Need?
- Vaccinations for Asia
Information on this page is only intended as a guide to the travel vaccinations recommended for this country
Indonesia is a country in Asia whose borders are shared with Malaysia and Papua New Guinea . One of Indonesia’s most popular islands with travellers is Bali.
For most travellers the recommended vaccinations vaccinations for Indonesia include: Diphtheria , Hepatitis A & Tetanus
For people trekking in the countryside, staying for longer periods or for those at higher risk, recommended vaccinations for India might include: Cholera , Hepatitis B , Japanese Encephalitis , Measles Mumps & Rubella , Rabies , Typhoid & Yellow Fever
There is a risk of Malaria in Indonesia, see below for advice
There is no risk of Yellow Fever in Indonesia, but there are Yellow Fever certificate entry requirements. See below for advice.
Vaccines Recommended to All Travellers to Indonesia
All travellers to all areas of this country are advised to have these vaccinations along with staying up to date with the routine vaccination schedule for the UK. Book a consultation for a full travel health risk assessment.
Diphtheria is a bacterial disease spread through close contact with infected persons. Vaccination against Diphtheria may be recommended
1 dose of Diphtheria is required Given any time before travel
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is a virus spread through food, water or contact with an infected person that affects the liver. Vaccination against Hepatitis A is recommended, as well as adequate food & water hygiene.
1 dose of Hepatitis A is required Given a minimum of 2 weeks before travel
Tetanus is a disease caused by bacteria present in soil everywhere in the world. Tetanus causes painful muscle spasms and can lead to death. Vaccination against Tetanus is recommended to all travellers.
1 dose of Tetanus is required Given any time before travel
Vaccines Recommended to Some Travellers to Indonesia
These vaccinations may be advised depending on the specific areas you are travelling to, your medical history and your itinary. Book a consultation for expert guidance on whether these vaccines are recommended for you.
Cholera is caused by bacteria spread through food and water. Vaccination against Cholera may be recommended, along with adequate food & water hygiene.
2 doses of Cholera are required Doses administered 1-6 weeks apart Given any time before travel
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is viral disease that is spread through blood and bodily fluids. Vaccination against Hepatitis B may be recommended
3-4 doses of Hepatitis B are required 21 days apart with a further dose 1 year later for full protection Given any time before travel
Japanese Encephalitis
Japanese Encephalitis is a disease spread through the bite of an infected mosquito, which can cause inflammation of the brain. Japanese Encephalitis is most common in parts of Asia. Vaccination against Japanese Encephalitis may be recommended
2 doses of Japanese Encephalitis are required Doses administered 28 days apart Given any time before travel
Measles, Mumps & Rubella
Measles, Mumps & Rubella (MMR) are viral illnesses spread by the respiratory route; coughing, sneezing etc. They are present globally in all countries of the world and are therefore MMR is a risk to all travellers.
2 doses of MMR are required Doses administered 1 month apart Given any time before travel
Rabies is endemic throughout most of the world. The Rabies virus is carried in the saliva of infected mammals. Rabies affects the nervous system and, once symptoms develop, death is inevitable – even with good medical care.
3 doses of Rabies are required Doses administered 21-28 days apart Given any time before travel
Typhoid is spread through contaminated food and water. Typhoid is common in areas with poor standards in food hygiene & preparation, and where suitable treatment of sewage is lacking. There are several types of Typhoid vaccination available.
1-3 doses of Typhoid are required Doses administered once or over 4 days Given 7-14 days before travel
Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever is endemic in parts of Sub-Saharan Africa and South America. Yellow Fever is spread by infected mosquitoes normally most active from sunrise to sunset. Many countries, where the disease is not endemic, require a valid certificate of vaccination against Yellow Fever before you can enter as a traveller.
1 dose of Yellow Fever is required Given any time before travel Yellow Fever certificate of vaccination is valid for life
Malaria Risk in Indonesia
Malaria is present in Indonesia.
There is no vaccination against Malaria , you may need to take Antimalarial tablets there are some high risk areas. We recommend you have a consultation with an expert Nomad nurse to talk through your malaria tablet recommendations.
For a detailed map of the Malaria risk in this country, click here (Source: fitfortravel)
Yellow Fever in Indonesia
There is no risk of Yellow Fever in Indonesia.
Yellow fever vaccination certificate is required for travellers over 9 months of age arriving from countries with risk of yellow fever transmission.
For details on Yellow Fever risk areas, click here (Source: fitfortravel)
Other Health Risks
Chikungunya in Indonesia
There is a risk of Chikungunya virus in this country. Spread by mosquitos, Chikungunya virus is widespread across Africa, South-East Asia, the Indian sub-continent and the Philippines. Occasionally, the virus can be found in other countries where the mosquito that spreads Chikungunya can also be found. There is no vaccination against Chikungunya, it is important to protect yourself with bite avoidance products like DEET. For more information – click here.
High Altitude in Indonesia
There are some high altitude areas. Travellers should take care to avoid Acute Mountain Sickness (AMS) by taking time to acclimatise properly. AMS can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, level of fitness or training. At high altitude, extra precautions should be taken against the harsh conditions, which can cause damaging ultraviolet and cold exposure. All Nomad Travel Health Nurses are trained to advise on AMS, and it may be appropriate for you to take certain medications that may help with acclimatisation. Book an appointment to discuss health issues related to altitude, based on your specific itinerary. For more information – click here.
Dengue Fever in Indonesia
There is a risk of Dengue Fever. It is spread by a species of mosquito called Aedes aegypti, otherwise known as the ‘tiger mosquito’ which mainly bites during the day. The illness is widespread throughout the tropics and subtropics, affecting over 100 countries with approximately 50 million cases globally a year. Currently most infections occur in SE Asia, South and Central America, Mexico, Africa, Indian sub-continent, Hawaii and the Pacific. There is currently no vaccination against Dengue Fever, it is therefore important to protect yourself during the day with bite avoidance products like DEET. For more information – click here.

Zika Virus in Indonesia
Zika is a viral infection transmitted by daytime biting mosquitoes. These mosquitoes bite an infected person and then spread the infection to others when they bite again. Pregnant women are advised not to travel into Zika regions, and male partners must use condoms for 6 months after travel into affected areas to prevent sexual transmission of the disease to a pregnant partner. If planning pregnancy, female travellers should avoid getting pregnant for at least 8 weeks after being in a Zika region. Whereas men must avoid getting a woman pregnant for at least 6 months following travel into a Zika region as the virus can survive in sperm for much longer and can be sexually transmitted. For more information – click here.
Recommended Kit for Indonesia

Ultimate Medical Kit

Worldwide Diarrhoea Kit
Indonesia Travel Blogs

Staying Healthy When Travelling Solo

What Travel First Aid Should I Pack?

Respecting Local Cultures When Travelling

Bali Bucket List: Top Things to do in Bali

How to Keep Your Belongings Safe When Backpacking

Malaria Tablets for Children

How to Make Friends While Travelling Solo

Safely Buy Malaria Tablets Online

Which malaria tablets should I take?
Malarone vs Atovquone/Proguanil: Whats the Difference?
We recommend you book a consultation with one of our specialist Travel Health Nurses to determine the exact vaccinations recommended for you based on a bespoke risk assessment that will take into account your itinerary, medical history, activities and length of travel, which are all risk factors affecting your immunisation recommendations. If you would like to book with us please call 01341 555 061 or click here. For the most up to date information, visit Fit For Travel and search for the countries you are travelling to.
- Afghanistan
- Philippines
- Saudi Arabia
- South Korea
- Turkmenistan
BECOME A NOMAD - SUBSCRIBE TODAY
Join the Nomad community for updates and expert insight
Search for...
- Book Appointment
- Find a Travel Clinic
- Find a Travel Store
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
Register to vote Register by 18 June to vote in the General Election on 4 July.
COVID-19: guidance for people whose immune system means they are at higher risk
- Department of Health & Social Care
- UK Health Security Agency
Updated 21 May 2024
Applies to England

© Crown copyright 2024
This publication is licensed under the terms of the Open Government Licence v3.0 except where otherwise stated. To view this licence, visit nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3 or write to the Information Policy Team, The National Archives, Kew, London TW9 4DU, or email: [email protected] .
Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned.
This publication is available at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/covid-19-guidance-for-people-whose-immune-system-means-they-are-at-higher-risk/covid-19-guidance-for-people-whose-immune-system-means-they-are-at-higher-risk
This guidance only applies to people living in England. There is separate guidance available for people living in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
Introduction
The success of the COVID-19 vaccination programme has meant that the requirement for shielding and identifying people as clinically extremely vulnerable ( CEV ) is no longer necessary.
Most people who were part of this CEV patient cohort are no longer at substantially greater risk than the general population and are advised to follow the same guidance as everyone else on staying safe and preventing the spread of COVID-19 and other respiratory infections, as well as any further advice received from their healthcare professional.
However, there remains a smaller number of people whose weakened immune system means they may be at higher risk of serious illness from COVID-19, despite vaccination.
Enhanced protection measures, such as those offered by specific treatments or additional vaccinations alongside other protective behaviours, may benefit these individuals. This guidance is for those individuals who remain at higher risk.
This page contains information on:
- who this guidance is for
- keeping yourself safe
COVID-19 vaccines
Covid-19 treatments, covid-19 testing.
- what to do if you test positive for COVID-19
- what to do if you test negative for COVID-19 and still feel unwell
Who this guidance is for
Immunosuppression means you have a weakened immune system due to a particular health condition or because you are on medication or treatment that suppresses your immune system. People who are immunosuppressed, or who have specific other medical conditions, may have a reduced ability to fight infections and other diseases, including COVID-19.
Most people with immunosuppression will be under the care of a hospital specialist and/or known to their GP. As a result of this they will usually be eligible for either or both of:
additional vaccines including COVID-19 boosters
Further information on who is included in these groups of people is included in the sections on vaccination and treatments below. If you are in one of these groups, consider following the guidance below on keeping yourself safe.
Keeping yourself safe
The following advice on ‘keeping yourself safe’ is aimed at adults. Children and young people are recommended to continue to attend education, unless they are advised otherwise by their clinician. Attending education is hugely important for children and young people’s health and their future.
If you have been advised by the NHS that you are in one of these groups, you are advised to:
- ensure you have had all of the vaccines you are eligible to receive
- continue to follow any condition-specific advice you may have been given by your specialist
You are advised to try to avoid contact with people who have symptoms of COVID-19 or other respiratory infections. A detailed description of COVID-19 symptoms can be found in guidance for people with symptoms of a respiratory infection including COVID-19 .
If you have visitors to your home, consider ventilating your rooms by opening windows and doors to let fresh air in. More advice on ventilating your home can be found on GOV.UK.
Consider asking visitors to your home to take additional precautions, such as keeping their distance. COVID-19 tests are no longer free for the general public, but you may wish to ask visitors to take a lateral flow device ( LFD ) test before visiting. You might also consider asking them to wear a face covering and you may want to wear a face covering yourself.
If it feels right for you, work from home if you can. If you cannot work from home, speak to your employer about what arrangements they can make to reduce your risk. It may be that you are entitled to a Reasonable Adjustment under the Equality Act . See Public health principles for reducing the spread of COVID-19 and other respiratory infections in the workplace
If you are too ill to work, you may be eligible for Statutory Sick Pay .
When out and about, you may want to try to keep your distance from others if that feels right for you, and consider reducing the time you spend in crowded spaces or anywhere that is enclosed or poorly ventilated. Wash your hands regularly and avoid touching your face.
Consider wearing a well-fitting face covering in crowded public spaces. Although face coverings are primarily worn to protect others, because they cover the nose and mouth, which are the main routes of transmission of the virus that causes COVID-19 infection, they may also provide some limited protection to the wearer.
Further advice about face coverings can be found in guidance on living safely with respiratory infections including COVID-19 .
If you have a weakened immune system due to a health condition or medical treatment, and you are aged 6 months or over, you are eligible for a COVID-19 vaccination this spring if it has been at least 3 months since your last vaccination.
This is to help improve any protection you may have built from previous vaccination or infection.
By having a further dose of vaccine, you may reduce your chance of catching the COVID-19 infection. If you do catch COVID-19, the symptoms may be less severe and the illness shorter than if you had not had the extra vaccination.
Further information, including about those who may need an extra dose this spring, is available . You should receive a letter inviting you to book. If not, check with your GP or specialist whether you are eligible.
You should be offered an appointment between April and June, with those at highest risk being called in first.
How to book
If you are eligible for a vaccine, you can book a COVID-19 vaccine:
- on the national booking system
- by going to a walk-in COVID-19 vaccination site
- on the NHS app
- by talking to a local NHS service, such as a GP surgery
- by talking to your care home
It will help to take the vaccination invite letter, an NHS letter describing your condition or treatment, or a repeat prescription slip with you, or you can show your health record or prescription history in the NHS App.
You can book or manage a COVID-19 vaccination online through the NHS website.
If you can’t book online, phone 119 free of charge, 9am to 5:30pm Monday to Friday. You can ask someone else to do this for you. Please ensure you have your NHS number at hand. If you have difficulties communicating or hearing, or are a British Sign Language ( BSL ) user, you can use textphone 18001 119 or the NHS BSL interpreter service .
The NHS strongly encourages those with a weakened immune system to take up their offer for the spring 2024 COVID-19 vaccination as soon as possible to ensure they have the highest possible level of protection.
Further information on COVID-19 vaccinations is available on NHS.UK.
The NHS is offering treatments to those people with COVID-19 who are at highest risk of becoming seriously ill and who are aged 12 years or above. Not all treatments are suitable for people aged 12 to 17 years.
The list of eligible people who are offered these treatments is regularly reviewed and is available on the NHSE and GOV.UK websites. The list currently includes some people who have:
- Down’s syndrome, or another chromosomal disorder that affects their immune system
- certain types of cancer or have received treatment for certain types of cancer
- sickle cell disease
- certain conditions affecting their blood
- chronic kidney disease ( CKD ) stage 4 or 5
- severe liver disease
- had an organ transplant
- certain autoimmune or inflammatory conditions (such as rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease)
- HIV or AIDS and have a weakened immune system
- a condition affecting their immune system
- a condition affecting the brain or nervous system, such as multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, motor neurone disease, myasthenia gravis, Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease or certain types of dementia
- certain lung conditions or treatments for lung conditions
This list is a summary and does not cover everything.
If you were identified as being eligible for assessment for COVID-19 treatments before 27 June 2023, you will have been contacted by the NHS to make you aware of this.
If you have become eligible for assessment for COVID-19 treatments since June 2023 (or become eligible), you will have been told about this (or will be told about this) by your doctor or specialist at the point that you were diagnosed with a qualifying condition or began a qualifying treatment.
If you are unsure whether you are eligible, speak to your doctor or hospital specialist who can advise you.
Treatments for COVID-19 are most effective if they are started early (ideally within 5 days of you first developing symptoms). It is therefore important that you take a COVID-19 test as soon as possible if you develop symptoms so that you can access treatments early if you test positive for COVID-19.
A broader group of patients (currently those aged 18 years and over, and with underlying health conditions) may also be able to take part in the PANORAMIC clinical study if they test positive for COVID-19 and are symptomatic.
In England, patients eligible for COVID-19 treatments can access free LFD tests.
If you are eligible for COVID-19 treatments, please make sure you have a supply of LFD tests at home so that you can test yourself quickly if you develop symptoms of COVID-19. You can now obtain free LFD tests from your local pharmacy. You can also use tests you’ve paid for, for example, a test you’ve bought from a supermarket or pharmacy. Further information is available on NHS: Treatments for COVID-19 .
Symptoms of COVID-19, flu and other respiratory infections include, among others:
- a high temperature
- unexplained tiredness or lack of energy
- shortness of breath
- a loss of, or change to, your normal sense of smell or taste
Test kits contain instructions and links to support those who need assistance in testing.
If you test positive
If you test positive, you should try to stay at home and avoid contact with other people. Further advice about staying at home can be found in guidance for people with symptoms of a respiratory infection including COVID-19 .
If you are eligible for treatment, it’s important to start as soon as you can. To be effective, treatments for COVID-19 need to be given quickly after your symptoms start.
If your COVID-19 test result is positive, follow the information for accessing treatments in your area on the NHS COVID-19 treatments page.
If you test negative and you still feel unwell
If your test is negative but you still have symptoms, you should take another test on each of the next 2 days (3 tests in total over 3 days).
If you continue to feel unwell, you should seek healthcare advice via your GP or NHS 111. If it is an emergency, you should call 999.
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .
Traveling to Indonesia? Here are 9 Points You Need to Know
In order to tighten the health protocols in Indonesia, the Air Task Force in Handling Covid-19 and PT Angkasa Pura established 9 essential procedures for both local and foreign passengers arriving from international flights. These implementations include filling passengers' data on the Hore (Hotel Reservation) V2 app to having their identity information and quarantine location collected by the airport authority. The procedures have been implemented since May 2021 at the Soekarno–Hatta International Airport.
All passengers arriving from international flights must go through the following 9 checkpoints:
- Fill in passenger's data on Hore V2 application
- Go through the health document checkpoint by the Port Health Office (KKP Kemenkes)
- Data collection regarding passenger's quarantine locations
- Go through the immigration process
- Collect baggage(s) at the baggage claim area
- Go through the customs process
- Register at the Help Desk Hotel
- Passenger's identity information and quarantine location are collected by the airport authorities
- Passengers will be picked up by bus to the quarantine location
Besides these 9 procedures, all travelers from abroad must comply with health protocols, such as providing Covid-19 test results and going through the quarantine process. International passengers are obligated to conduct a 5 x 24 hours quarantine upon arrival. They must also take another RT-PCR test when quarantine is completed. This is in accordance with Circular Letter Number 8 of 2021 on International Travel Health Protocols during the Covid-19 Pandemic and Number 9 of 2021 concerning Health Protocols for International Travels during the Covid-19 Pandemic.
The new procedures are hoped to ease the quarantine process to allocate local and international travelers to Wisma Atlet Pademangan or quarantine hotels.
For more information on this, visit the official website of the Directorate General of Immigration here .
Suggested for you

Bali: 1,006 CARE-Certified Tourism Businesses
Bali's 2M Vaccinated for Tourism Revival by July 2021

10 Best Escapes You can Enjoy in Beautiful Lombok

1,861 Tourism Stakeholders in Bali are Targeted to Receive InDOnesia CARE Certification by the End of 2021

Find Your Perfect Destination in Bali According to Your Zodiac
Bali Speeding up to Vaccinate 3 Million for Tourism Recovery Plan

Visit our other website
This is the official website of the Ministry of Tourism, Republic of Indonesia. The contents listed on this website are intended for informational purposes rather than commercial. Any displayed sale is meant as a token of partnership and will always redirect you to our partners' sites.
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Learn more

Information on how to stay safe and healthy abroad. About us.
Travel health advice.
- Before You Travel
- Yellow Fever
Current popular advice pages:
- Staying Healthy if Travelling Abroad this Summer
- Travelling Abroad to Attend Festivals and Other Gatherings
- Mosquito Bite Avoidance
- Food and Water Precautions
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Indonesia Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
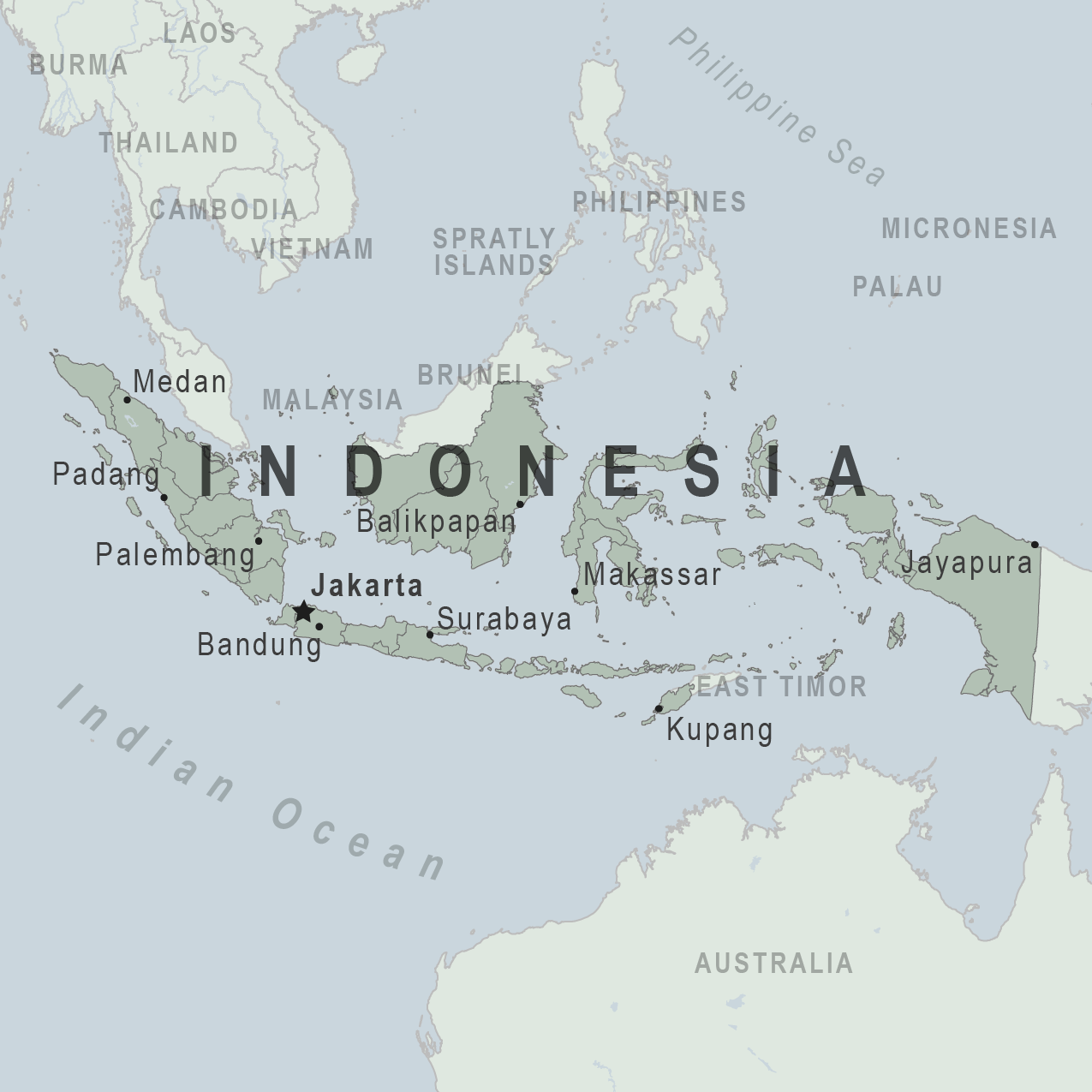
Be aware of current health issues in Indonesia. Learn how to protect yourself.
Level 2 Practice Enhanced Precautions
- Global Polio May 23, 2024 Some international destinations have circulating poliovirus. Before any international travel, make sure you are up to date on your polio vaccines. Destination List: Afghanistan, Algeria, Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Guinea, Indonesia, Kenya, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Pakistan, Republic of the Congo, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, Sudan, Tanzania, including Zanzibar, Yemen, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Level 1 Practice Usual Precautions
- Updated Global Measles May 28, 2024 Many international destinations are reporting increased numbers of cases of measles. Destination List: Afghanistan, Angola, Armenia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, India, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Lebanon, Liberia, Libya, Malaysia, Mauritania, Nepal, Niger, Nigeria, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Republic of South Sudan, Republic of the Congo, Romania, Russia, Senegal, Somalia, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Syria, Tajikistan, Togo, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Yemen, Zambia
- Dengue in Asia and the Pacific Islands May 16, 2024 Dengue is a risk in many parts of Asia and the Pacific Islands. Some countries are reporting increased numbers of cases of the disease. Travelers to Asia and the Pacific Islands can protect themselves by preventing mosquito bites. Destination List: Cambodia, Fiji, Indonesia, Laos, Samoa, Singapore, Sri Lanka
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
Chikungunya
There has been evidence of chikungunya virus transmission in Indonesia within the last 5 years. Chikungunya vaccination may be considered for the following travelers:
- People aged 65 years or older, especially those with underlying medical conditions, who may spend at least 2 weeks (cumulative time) in indoor or outdoor areas where mosquitoes are present in Indonesia, OR
- People planning to stay in Indonesia for a cumulative period of 6 months or more
Chikungunya - CDC Yellow Book
Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Indonesia.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers of all ages traveling to Indonesia.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
Japanese Encephalitis
Recommended for travelers who
- Are moving to an area with Japanese encephalitis to live
- Spend long periods of time, such as a month or more, in areas with Japanese encephalitis
- Frequently travel to areas with Japanese encephalitis
Consider vaccination for travelers
- Spending less than a month in areas with Japanese encephalitis but will be doing activities that increase risk of infection, such as visiting rural areas, hiking or camping, or staying in places without air conditioning, screens, or bed nets
- Going to areas with Japanese encephalitis who are uncertain of their activities or how long they will be there
Not recommended for travelers planning short-term travel to urban areas or travel to areas with no clear Japanese encephalitis season.
Japanese encephalitis - CDC Yellow Book
Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine for US Children
CDC recommends that travelers going to certain areas of Indonesia take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for Indonesia.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
In Indonesia poliovirus has been identified in the past year.
Travelers to Indonesia are at increased risk of exposure to poliovirus.
Vaccine recommendations : Adults traveling to Indonesia who received a complete polio vaccination series as children may receive a single lifetime booster dose of inactivated polio vaccine; travelers who are unvaccinated or not fully vaccinated should receive a complete polio vaccination series before travel. Children who are not fully vaccinated will be considered for an accelerated vaccination schedule .
Polio - CDC Yellow Book
Polio: For Travelers
Dogs infected with rabies are commonly found in Indonesia.
If rabies exposures occur while in Indonesia, rabies vaccines are typically available throughout most of the country.
Rabies pre-exposure vaccination considerations include whether travelers 1) will be performing occupational or recreational activities that increase risk for exposure to potentially rabid animals and 2) might have difficulty getting prompt access to safe post-exposure prophylaxis.
Please consult with a healthcare provider to determine whether you should receive pre-exposure vaccination before travel.
For more information, see country rabies status assessments .
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
Yellow Fever
Required for travelers ≥9 months old arriving from countries with risk for YF virus transmission. 1
Yellow Fever - CDC Yellow Book
- Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
- Avoid floodwater
Clinical Guidance
Schistosomiasis
- Wading, swimming, bathing, or washing in contaminated freshwater streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, or untreated pools.
Avoid bug bites
- Mosquito bite
- Avoid Bug Bites
- Mosquito bite
- An infected pregnant woman can spread it to her unborn baby
Airborne & droplet
Avian/bird flu.
- Being around, touching, or working with infected poultry, such as visiting poultry farms or live-animal markets
- Avoid domestic and wild poultry
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Indonesia, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH)
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Indonesia. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Indonesia include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Schistosomiasis, a parasitic infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Indonesia. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Indonesia’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in some parts of Indonesia. If you are going to a risk area, fill your malaria prescription before you leave, and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Indonesia may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Indonesia, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
For information traffic safety and road conditions in Indonesia, see Travel and Transportation on US Department of State's country-specific information for Indonesia .
Traffic flows on the left side of the road in Indonesia.
- Always pay close attention to the flow of traffic, especially when crossing the street.
- LOOK RIGHT for approaching traffic.
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Indonesia for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Election latest: Sunak not taking questions amid talk of Tory battle to succeed him - as Dragon joins Starmer at brewery
A poll has found Reform's Nigel Farage would be the favourite to take over as Tory leader if Rishi Sunak loses the election. Labour says the Conservatives are already battling over the succession. Earlier, the transport secretary denied that the PM's D-Day blunder had lost the election.
Saturday 8 June 2024 13:46, UK
- General Election 2024
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
Election news
- PM not taking questions as D-Day row rumbles on
- Sir Keir joined by Dragons to launch small businesses plan
- Farage should take over from Sunak as leader of Tories, poll finds
- Tories will scrap ULEZ expansion in 'backing drivers bill'
- Sunak vows to axe stamp duty for first-time buyers
- Electoral Dysfunction: What could be in the party manifestos?
- Live reporting by Josephine Franks
Expert analysis
- Rob Powell: It beggars belief someone didn't sound the alarm about PM leaving D-Day events early
- Tamara Cohen: Labour can't believe their luck
Election essentials
- Battle For No 10: PM and Starmer taking part in Sky News special
- Campaign Heritage: Memorable moments from elections gone by
- Trackers: Who's leading polls? | Is PM keeping promises?
- Follow Sky's politics podcasts: Electoral Dysfunction | Politics At Jack And Sam's
- Read more: Who is standing down? | Key seats to watch | How to register to vote | What counts as voter ID? | Check if your constituency is changing | Your essential guide to election lingo | Sky's election night plans
61% of people quizzed in an exclusive Sky News poll think the NHS is in a "poor state", with parts of it "broken".
Reducing NHS waiting times is the issue voters want the next government to prioritise, with 39% of people saying it was their top issue.
The same Sky News poll asked voters who they trust most to run the NHS. The majority - 32% - said Labour, while only 9% thought the Conservatives.
But a quarter of those polled didn't think any party could be trusted with the NHS.
With waiting times on voters' minds, Sky's people and politics correspondent Nick Martin spoke to Jasmine, one of the millions waiting months, sometimes years, for treatment.
At 23, she has spent the last 11 years battling endometriosis and lives with what feels like "a ball of acid in the middle of my torso".
Read more of her story here:
The latest Sky News poll tracker has the Conservatives on the same level of support - just 22.8% - as the day Liz Truss left office.
Labour has 43.6% of the share, while Reform UK is on 13.1%, Lib Dems on 9.6%, Greens on 5.7% and SN p on 3%.
The live poll tracker collates the results of opinion surveys carried out by all the main polling organisations - and allows you to see how the political parties are performing in the run-up to the general election.
Read more here:
Rishi Sunak took up a watering can and was encouraged to apply for an allotment garden by volunteers while on the campaign trail in County Durham.
An opportunity for the media to ask questions of Rishi Sunak did not take place as was originally planned, likely following the fallout on Friday of his early return from D-Day commemorations.
Members of the public could be seen gathered on a hillside above the garden to try to catch a glimpse of the prime minister.
At the garden, Mr Sunak spoke with volunteers Margaret Lambert and Hilary Bellwood and watered plants with Jane MacBean, Conservative candidate for Bishop Auckland.
Sir Keir Starmer has promised to overhaul the business rates system, saying there's "not a level playing field between businesses that are online and those that are ... bricks and mortar".
The Labour leader was joined by Dragons' Den star Deborah Meaden at 3 Locks Brewery in Camden, London, to launch the party's plan for small businesses.
"We want small businesses to thrive because they are the backbone of our economy and they need that stability in our economy, and they need to know that their energy bills are actually going to be lower and stable," he said.
Labour launched its plans for Great British Energy policy a week ago - a new, publicly owned company that would generate homegrown green energy across the country.
Meaden voiced her support for the plans: "Businesses don't like being out of control of costs and energy is one of those costs that simply fluctuates beyond your control," she said.
Sir Keir pulled the first pint of the day at 10.55am and was heard saying "if all else fails", he will be back at the brewery on 5 July.
John Swinney says Rishi Sunak "completely destroyed" his credibility as prime minister by leaving D-Day commemorations early.
Speaking to journalists on the campaign trail in Livingston, the Scottish First Minister said: "I think Rishi Sunak's credibility is completely destroyed by his departure from D-Day early and the insult he delivered to the veterans who had travelled to Normandy for that solemn occasion.
"It also, frankly, was a desertion of the international responsibilities of the prime minister.
"The prime minister and especially the Conservative election campaign is now utterly in tatters."
Mr Sunak was forced to apologise for leaving France before an international ceremony attended by world leaders, saying it had been a mistake - but he said it was important not to "politicise" the decision.
The Tory battle bus has rolled into County Durham, with Rishi Sunak heading to two locations in the North East today - but don't expect him to be answering questions.
The PM is not doing any interviews with national or broadcast media today and a possible huddle - when he takes questions from reporters off-camera - has been cancelled.
He may, however, do some interviews with regional media.
While the PM may not be speaking for himself today, much has been said this morning about his decision to bow out of D-Day commemorations early.
Shadow business secretary Jonathan Reynolds called it "inexplicable" while Sir Ed Davey said it made him "pretty cross" and Transport Secretary Mark Harper labelled it a "mistake" - but said it wouldn't cost the Tories the election.
The Lib Dem leader says he's "pretty cross" about Rishi Sunak's decision to leave D-Day commemorations early and has called on him to make a donation to a veterans' charity to make amends.
Sir Ed Davey urged the Conservatives to give some of the cash donated to the party by Frank Hester, a businessman who was embroiled in a racism row, to charity.
"I think the Conservative Party should give £5m of that donation to a veterans' charity. I think if they did that, then people might be able to draw the line.
"But it's such a letdown for our whole country and our history, particularly for our brave veterans."
The Liberal Democrats have pledged to create three new national parks in England.
This manifesto commitment would bring the number of national parks in England up to 13, with the party saying it would spend £50m a year maintaining them.
The Chilterns in Hertfordshire and Buckinghamshire are possible locations for the new parks, along with the Mendips, Cotswolds and Quantocks.
Other proposed areas include the Surrey Hills, Northumberland coast and Dorset.
Liberal Democrat leader Sir Ed Davey accused the Tories of having "broken too many promises to protect our countryside".
"It is hard to overstate the difference things like National Parks can make to entire communities," he said.
Reform UK and the Conservatives are neck-and-neck in a new poll of Welsh voters with each party taking an 18% share of those surveyed.
But both trail Labour, which is far ahead on 45%, according to the survey by Redfield & Wilton.
The poll of 960 Welsh voters put Plaid Cymru on 11%, Liberal Democrats on 5% and Greens on 4%.
Only 39% of those who voted for the Conservatives in Wales in 2019 will vote Conservative again, the poll showed - with 32% of past Conservative voters saying they would defect to Reform UK.
It comes after the latest YouGov poll of UK voters for Sky News showed Reform had pulled to within two points of the Conservatives.
Sky News has been tracking locations visited by party leaders in the first two weeks of the general election campaign to decipher what their choices tell us about the parties' election strategies.
Of the 650 seats, 54 have now been visited during the campaign by Rishi Sunak, Sir Keir Starmer or Ed Davey.
The South East seems to be garnering the most attention with 12 visits overall - highlighting the importance of the region for all of the English parties.
Read more from Sky News elections analyst Dr Hannah Bunting and data journalist Joely Santa Cruz here:
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Latest FCDO travel advice for Indonesia including on entry requirements, ... The NHS has information on whether you can take your medicine abroad. Healthcare facilities in Indonesia.
Advice for All Destinations COVID-19. Read the information on the COVID-19: Health Considerations for Travel page for advice on travelling during the COVID-19 pandemic.. Vaccinations and malaria risk. Review both the Vaccination and Malaria sections on this page to find out if you may need vaccines and/or a malaria risk assessment before you travel to this country.
Read this travel advice and carry out your own research before deciding whether to travel. Emergency services in Indonesia. Ambulance: 118. Fire: 112. Police: 110. Contact your travel provider and ...
Website : Contact Center : +628118956767. Hotline : 112 and 119. Indonesia Covid-19 Information (Government) : The Ministry of Tourism and Creative Economy introduced InDOnesia CARE, a symbol of support for Indonesia's strong effort in implementing the cleanliness, health, and safety protocols across the tourism industry as mandatory precautions.
Your search for indonesia returned 9 results. Indonesia. Travel health and immunisation advice for Indonesia, including Bali, Java, Sumatra and West Papua. Borneo. Travel health and immunisation advice for Borneo, which is comprised of Brunei, Indonesia and Malaysia. Indonesia Malaria Map. East Indonesia Malaria Map.
23 May 2024 - Advice on Dengue Fever if Travelling Abroad. 40 additional items in the news archive for this country. back to top. Travel health and immunisation advice for Borneo, which is comprised of Brunei, Indonesia and Malaysia.
Typhoid. There is a high risk of typhoid infection in Indonesia, so: ensure that travellers to Indonesia are offered typhoid immunisation and advice on prevention of enteric fever. remember ...
Due to the increase in the spread of the new SARS-CoV-2 virus variants (Alpha, Beta, Delta, and Gamma) in various countries in the world, including Indonesia, Head of the COVID-19 Task Force, Ganip Warsito, issued an Addendum to the Circular of the COVID-19 Handling Task Force Number 8 of 2021 regarding International Travel Health Protocols During the Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19 ...
You can contact these numbers below for an update on Covid-19 from The Ministry of Health: Hotline Emerging Operation Center ( EOC ): 021-5210411 and 081212123119. Depok: 112 and 119. Majalengka District: 112. Sukabumi District: 08001000119 / 0266-6243816. Bandung District: 082118219287. Garut District: 0262-2802800 and 119.
For tailored advice for your individual situation, we recommend you make an appointment with a travel health professional. To make an appointment for a travel health risk assessment: In Scotland, you should contact the NHS health board where you live. In England, Wales and Northern Ireland you should contact your NHS GP.
Indonesia: Travel Advice Please note Briefing Maps are not to be taken as necessarily representing the views of the UK government on boundaries or political status. This map has been designed for briefing purposes only and should not be used for determining the precise location of places or features, or considered an authority on the ...
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations. Routine vaccines Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Philip Beale, from our supplier, Pioneer Expeditions, shares his Indonesia travel advice: "You could argue that the Komodo National Park it is a tourist hotspot, but that takes nothing away from how incredible seeing Komodo dragons is; it has to be slightly controlled and managed because Komodo dragons are amazing, but they're not cute, they're killers.
30 November 2023. New International Travel Regulations to Enter Indonesia as of 1 February 2022. As an immediate follow-up to prevent the spread of SARS-COV-2 B.1.1.529 from South Africa and some other countries in the world, COVID-19 Task Force issued the Circular of the Head of the COVID-19 Handling Task Force Number 4 of 2022 regarding International Travel Health Protocol during the Corona ...
Current travel vaccine advice and how to prevent infections when travelling to Indonesia. The recommendations and advice on this page can never replace a medical consultation. To get the best effect from the vaccines, you should begin vaccination well before departure.
Travel vaccination advice. If you're planning to travel outside the UK, you may need to be vaccinated against some of the serious diseases found in other parts of the world. Vaccinations are available to protect you against infections such as yellow fever, typhoid and hepatitis A. In the UK, the NHS routine immunisation (vaccination) schedule ...
For most travellers the recommended vaccinations vaccinations for Indonesia include: Diphtheria , Hepatitis A & Tetanus. For people trekking in the countryside, staying for longer periods or for those at higher risk, recommended vaccinations for India might include: Cholera, Hepatitis B , Japanese Encephalitis , Measles Mumps & Rubella , Rabies ...
You can use the NHS COVID Pass to demonstrate your vaccination record when entering Indonesia. You will need to present both soft and hard copies of your NHS vaccination certificates at various stages of your journey. ... Entry requirements - Indonesia travel advice - GOV.UK (www.gov.uk) About Us ; Our Team ; Reviews; Careers; 4.6/5 Independent ...
COVID-19 treatments. The NHS is offering treatments to those people with COVID-19 who are at highest risk of becoming seriously ill and who are aged 12 years or above. Not all treatments are ...
Go through the immigration process. Collect baggage (s) at the baggage claim area. Go through the customs process. Register at the Help Desk Hotel. Passenger's identity information and quarantine location are collected by the airport authorities. Passengers will be picked up by bus to the quarantine location.
fitfortravel is a public access website provided by the NHS (Scotland). It gives travel health information for people travelling abroad from the UK. Remember that you should always discuss your particular needs with your own GP or Practice Nurse. The website is compiled by the Travel and International Health Team at Health Protection Scotland (HPS).
The latest updates from the general election campaign, as Rishi Sunak is heckled by a GP and Nigel Farage gets stuck in during a televised debate. Snap findings from a More in Common poll of more ...
People planning to stay in Indonesia for a cumulative period of 6 months or more. Chikungunya - CDC Yellow Book. Hepatitis A. Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Indonesia. Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A.
A poll has found Reform's Nigel Farage would be the favourite to take over as Tory leader if Rishi Sunak loses the election. Labour says the Conservatives are already battling over the succession.