An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

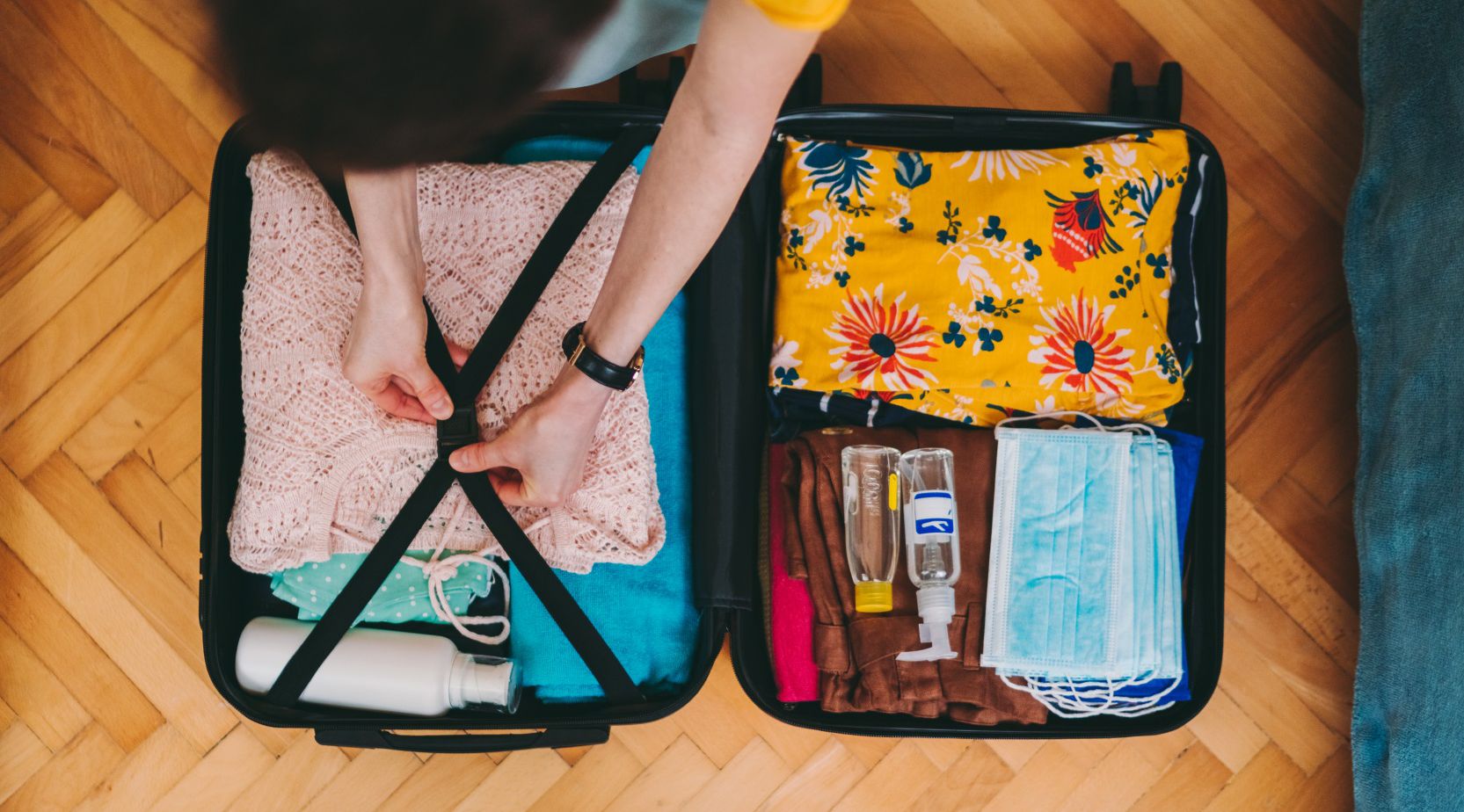
Vaccines for Travelers
Vaccines protect travelers from serious diseases. Depending on where you travel, you may come into contact with diseases that are rare in the United States, like yellow fever. Some vaccines may also be required for you to travel to certain places.
Getting vaccinated will help keep you safe and healthy while you’re traveling. It will also help make sure that you don’t bring any serious diseases home to your family, friends, and community.
On this page, you'll find answers to common questions about vaccines for travelers.
Which vaccines do I need before traveling?
The vaccines you need to get before traveling will depend on few things, including:
- Where you plan to travel . Some countries require proof of vaccination for certain diseases, like yellow fever or polio. And traveling in developing countries and rural areas may bring you into contact with more diseases, which means you might need more vaccines before you visit.
- Your health . If you’re pregnant or have an ongoing illness or weakened immune system, you may need additional vaccines.
- The vaccinations you’ve already had . It’s important to be up to date on your routine vaccinations. While diseases like measles are rare in the United States, they are more common in other countries. Learn more about routine vaccines for specific age groups .
How far in advance should I get vaccinated before traveling?
It’s important to get vaccinated at least 4 to 6 weeks before you travel. This will give the vaccines time to start working, so you’re protected while you’re traveling. It will also usually make sure there’s enough time for you to get vaccines that require more than 1 dose.
Where can I go to get travel vaccines?
Start by finding a:
- Travel clinic
- Health department
- Yellow fever vaccination clinic
Learn more about where you can get vaccines .
What resources can I use to prepare for my trip?
Here are some resources that may come in handy as you’re planning your trip:
- Visit CDC’s travel website to find out which vaccines you may need based on where you plan to travel, what you’ll be doing, and any health conditions you have.
- Download CDC's TravWell app to get recommended vaccines, a checklist to help prepare for travel, and a personalized packing list. You can also use it to store travel documents and keep a record of your medicines and vaccinations.
- Read the current travel notices to learn about any new disease outbreaks in or vaccine recommendations for the areas where you plan to travel.
- Visit the State Department’s website to learn about vaccinations, insurance, and medical emergencies while traveling.
Traveling with a child? Make sure they get the measles vaccine.
Measles is still common in some countries. Getting your child vaccinated will protect them from getting measles — and from bringing it back to the United States where it can spread to others. Learn more about the measles vaccine.
Find out which vaccines you need
CDC’s Adult Vaccine Quiz helps you create a list of vaccines you may need based on your age, health conditions, and more.
Take the quiz now !
Get Immunized
Getting immunized is easy. Vaccines and preventive antibodies are available at the doctor’s office or pharmacies — and are usually covered by insurance.
Find out how to get protected .
International Travel Restrictions by Country
Find out where you can travel and covid-19 policies.
Select origin country, search destination or select a country on the map to see travel restrictions.
The travel status of individual countries can change suddenly, and we know it can be hard to stay on top of it all. That's why we're getting you the information you need to consider when planning travel. Learn about country-specific entry requirements such as the border status, COVID-19 testing requirements, and quarantine requirements. Many countries are reopening their borders for international travel. Find out which countries are open to vaccinated travelers.
Just enter your departure country above - the map will update to reflect countries' opening status and any entry requirements for air travelers. Before you book, be sure to double check your country's official government site.
Destinations you can travel to now
Dominican republic, netherlands, philippines, puerto rico, switzerland, united arab emirates, united kingdom, know when to go.
Sign up for email alerts as countries begin to open - choose the destinations you're interested in so you're in the know.
Filter by region, status and more
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Albania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Algeria.
American Samoa
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter American Samoa.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Angola.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Anguilla.
Antigua And Barbuda
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Antigua And Barbuda.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Argentina.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Armenia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Aruba.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Australia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Austria.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Azerbaijan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bahrain.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bangladesh.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Barbados.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Belgium.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Belize.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Benin.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bermuda.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bhutan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bolivia.
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Botswana.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Brazil.
British Virgin Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the British Virgin Islands.
Brunei Darussalam
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Brunei Darussalam.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bulgaria.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Burundi.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Cambodia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Cameroon.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Canada.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Cape Verde.
Caribbean Netherlands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Caribbean Netherlands.
Cayman Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Cayman Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Chad.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Chile.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter China.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Colombia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Comoros.
Cook Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Cook Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Costa Rica.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Croatia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Curaçao.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Cyprus.
Czech Republic
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Czech Republic.
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Denmark.
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Djibouti without restrictions.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Dominica.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Dominican Republic.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, need to quarantine to enter East Timor.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ecuador.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Egypt.
El Salvador
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter El Salvador.
Equatorial Guinea
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Equatorial Guinea.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Eritrea.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Estonia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Eswatini.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ethiopia.
Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas)
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas).
Faroe Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Faroe Islands.
Federated States of Micronesia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Federated States of Micronesia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Fiji.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Finland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter France.
French Guiana
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter French Guiana.
French Polynesia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter French Polynesia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Gabon.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Gambia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Georgia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Germany.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ghana.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Gibraltar.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Greece.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Greenland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Grenada.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guadeloupe.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guam.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guatemala.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guinea.
Guinea-Bissau
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guinea-Bissau.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guyana.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Honduras.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Hong Kong.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Hungary.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Iceland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter India.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Indonesia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ireland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Italy.
Ivory Coast
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ivory Coast.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Jamaica.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Japan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Jersey.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Jordan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kazakhstan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kenya.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kiribati.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kosovo.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kuwait.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kyrgyzstan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Laos.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Latvia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Lesotho.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Liberia.
Liechtenstein
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Liechtenstein.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Lithuania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Luxembourg.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Macau.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Madagascar.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Malawi.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Malaysia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Maldives.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Malta.
Marshall Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Marshall Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Martinique.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mauritania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mauritius.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mayotte.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mexico.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Moldova.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mongolia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Montenegro.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Montserrat.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mozambique.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Namibia.
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Nauru without restrictions.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Nepal.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Netherlands.
New Caledonia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter New Caledonia.
New Zealand
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter New Zealand.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Nicaragua.
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Niger without restrictions.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Nigeria.
North Macedonia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter North Macedonia.
Northern Mariana Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Northern Mariana Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Norway.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Oman.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Pakistan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Palau.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Panama.
Papua New Guinea
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Papua New Guinea.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Paraguay.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Peru.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Philippines.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Poland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Portugal.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Puerto Rico.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Qatar.
Republic of the Congo
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Republic of the Congo without restrictions.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Réunion.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Romania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Rwanda.
Saint Barthélemy
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Barthélemy.
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Kitts and Nevis.
Saint Lucia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Lucia.
Saint Martin
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Martin.
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Samoa.
São Tomé and Príncipe
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter São Tomé and Príncipe.
Saudi Arabia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saudi Arabia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Senegal.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Serbia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Seychelles.
Sierra Leone
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Sierra Leone.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Singapore.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Slovakia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Slovenia.
Solomon Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Solomon Islands.
South Africa
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter South Africa.
South Korea
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter South Korea.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Spain.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Sri Lanka.
St. Maarten
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter St. Maarten.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Sudan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Suriname.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Sweden.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Switzerland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Taiwan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tajikistan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tanzania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Thailand.
The Bahamas
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter The Bahamas.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Togo.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tonga.
Trinidad and Tobago
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Trinidad and Tobago.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tunisia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Türkiye.
Turkmenistan
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, will not be allowed to enter Turkmenistan.
Turks and Caicos Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Turks and Caicos Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tuvalu.
U.S. Virgin Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the U.S. Virgin Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Uganda.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the United Arab Emirates.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the United Kingdom.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Uruguay.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Uzbekistan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Vanuatu.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Vietnam.
Wallis and Futuna
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Wallis and Futuna.
Western Sahara
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, will not be allowed to enter Western Sahara.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Zambia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Zimbabwe.

Get trip-ready with at-home COVID-19 tests
How often is the data on this page updated.
We check for travel restriction information from government authorities daily, and update the page any time we get new information. The following information regarding travel restrictions for each country is correct to the best of our knowledge at the time of publication.
How many countries are closed to visitors?
As of Sep 11, 2 countries have completely restricted entry to non-citizens and 5 are open but require quarantine and/or a negative COVID test.
Where can I travel without COVID restrictions?
Currently you can travel from the United States to 197 countries without restrictions. Please check our map to learn more.
Are there any other types of travel restrictions besides COVID-19 tests and quarantines?
These are the two main types of restrictions or requirements needed to travel into another country. However, the COVID-19 testing options are continually widening as new methods are developed. Different countries may accept results from different or multiple test types, so be sure to check the individual country's specific requirements.
What should I do if I get COVID-19 while in another country?
If you get COVID-19 while in another country, follow the local authority's recommendations. These may include hospitalization, self-isolating and testing in that country. Be sure to contact your travel insurance company and travel provider as well and inform them of your situation.
What should I do if the borders of the country I am visiting close?
Depending on your home country, you may need to change your departure date and return home as soon as possible. If that's the case, contact your travel provider to find the earliest departure.
Additional resources
- What you need to know
- Airline policies
- Hotel policies
- Car policies
- Tips for flying
- Tips for hotel
- Tips for vacation rental
If you're looking for personalized travel advice for your own travel plans like whether or not a restriction applies to your trip, we won't be able to answer any questions or offer advice. Please consult your local government's resources.
Travel vaccination advice
If you're planning to travel outside the UK, you may need to be vaccinated against some of the serious diseases found in other parts of the world.
Vaccinations are available to protect you against infections such as yellow fever , typhoid and hepatitis A .
In the UK, the NHS routine immunisation (vaccination) schedule protects you against a number of diseases, but does not cover all of the infectious diseases found overseas.

When should I start thinking about the vaccines I need?
If possible, see the GP or a private travel clinic at least 6 to 8 weeks before you're due to travel.
Some vaccines need to be given well in advance to allow your body to develop immunity.
And some vaccines involve a number of doses spread over several weeks or months.
You may be more at risk of some diseases, for example, if you're:
- travelling in rural areas
- backpacking
- staying in hostels or camping
- on a long trip rather than a package holiday
If you have a pre-existing health problem, this may make you more at risk of infection or complications from a travel-related illness.
Which travel vaccines do I need?
You can find out which vaccinations are necessary or recommended for the areas you'll be visiting on these websites:
- Travel Health Pro
- NHS Fit for Travel
Some countries require proof of vaccination (for example, for polio or yellow fever vaccination), which must be documented on an International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (ICVP) before you enter or when you leave a country.
Saudi Arabia requires proof of vaccination against certain types of meningitis for visitors arriving for the Hajj and Umrah pilgrimages.
Even if an ICVP is not required, it's still a good idea to take a record of the vaccinations you have had with you.
Find out more about the vaccines available for travellers abroad
Where do I get my travel vaccines?
First, phone or visit the GP practice or practice nurse to find out whether your existing UK vaccinations are up-to-date.
If you have any records of your vaccinations, let the GP know what you have had previously.
The GP or practice nurse may be able to give you general advice about travel vaccinations and travel health, such as protecting yourself from malaria.
They can give you any missing doses of your UK vaccines if you need them.
Not all travel vaccinations are available free on the NHS, even if they're recommended for travel to a certain area.
If the GP practice can give you the travel vaccines you need but they are not available on the NHS, ask for:
- written information on what vaccines are needed
- the cost of each dose or course
- any other charges you may have to pay, such as for some certificates of vaccination
You can also get travel vaccines from:
- private travel vaccination clinics
- pharmacies offering travel healthcare services
Which travel vaccines are free?
The following travel vaccines are available free on the NHS from your GP surgery:
- polio (given as a combined diphtheria/tetanus/polio jab )
- hepatitis A
These vaccines are free because they protect against diseases thought to represent the greatest risk to public health if they were brought into the country.
Which travel vaccines will I have to pay for?
You'll have to pay for travel vaccinations against:
- hepatitis B
- Japanese encephalitis
- tick-borne encephalitis
- tuberculosis (TB)
- yellow fever
Yellow fever vaccines are only available from designated centres .
The cost of travel vaccines that are not available on the NHS will vary, depending on the vaccine and number of doses you need.
It's worth considering this when budgeting for your trip.
Other things to consider
There are other things to consider when planning your travel vaccinations, including:
- your age and health – you may be more vulnerable to infection than others; some vaccines cannot be given to people with certain medical conditions
- working as an aid worker – you may come into contact with more diseases in a refugee camp or helping after a natural disaster
- working in a medical setting – a doctor, nurse or another healthcare worker may require additional vaccinations
- contact with animals – you may be more at risk of getting diseases spread by animals, such as rabies
If you're only travelling to countries in northern and central Europe, North America or Australia, you're unlikely to need any vaccinations.
But it's important to check that you're up-to-date with routine vaccinations available on the NHS.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Speak to a GP before having any vaccinations if:
- you're pregnant
- you think you might be pregnant
- you're breastfeeding
In many cases, it's unlikely a vaccine given while you're pregnant or breastfeeding will cause problems for the baby.
But the GP will be able to give you further advice about this.
People with immune deficiencies
For some people travelling overseas, vaccination against certain diseases may not be advised.
This may be the case if:
- you have a condition that affects your body's immune system, such as HIV or AIDS
- you're receiving treatment that affects your immune system, such as chemotherapy
- you have recently had a bone marrow or organ transplant
A GP can give you further advice about this.
Non-travel vaccines
As well as getting any travel vaccinations you need, it's also a good opportunity to make sure your other vaccinations are up-to-date and have booster vaccines if necessary.
Although many routine NHS vaccinations are given during childhood, you can have some of them (such as the MMR vaccine ) as an adult if you missed getting vaccinated as a child.
There are also some extra NHS vaccinations for people at higher risk of certain illnesses, such as the flu vaccine , the hepatitis B vaccine and the BCG vaccine for tuberculosis (TB) .
Your GP can advise you about any NHS vaccinations you might need.
Find out about NHS vaccinations and when to have them
Page last reviewed: 16 March 2023 Next review due: 16 March 2026
- Extra 15% off $30+ sitewide * with code JUNE15
- Clip your mystery deal!
- Up to 60% off clearance
- Your Account
- Walgreens Cash Rewards
- Prescription Refills & Status
- Vaccination Records
- Order Status & History
- Buy It Again
Select a store
Travel immunizations & resources.
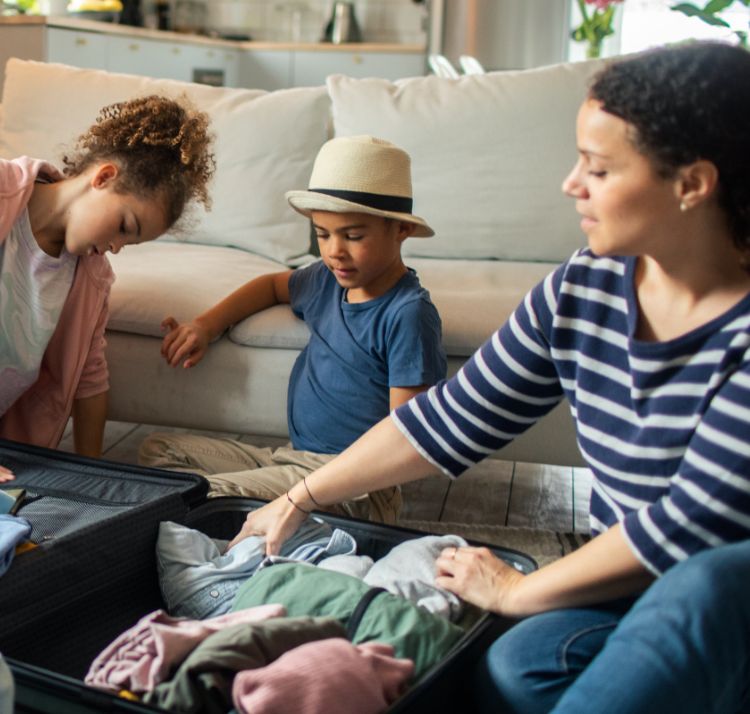

Because you shouldn’t stress about your health when you travel
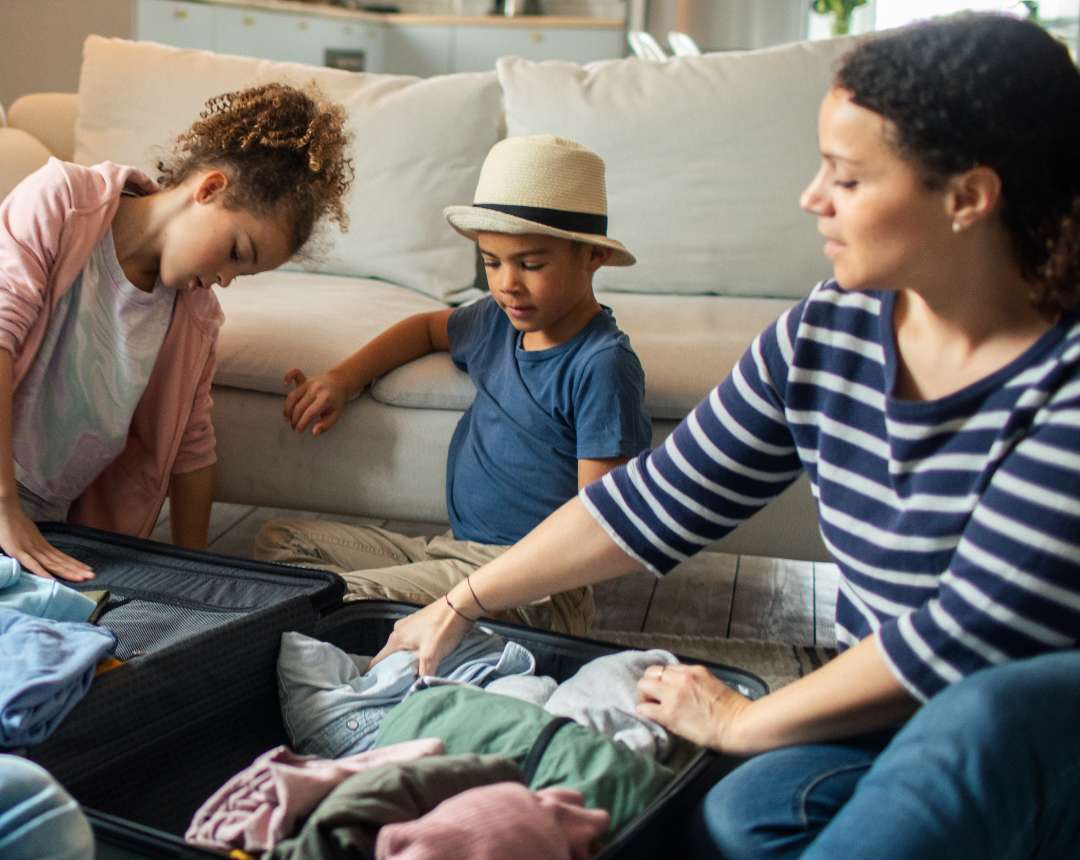

No one wants to get sick on vacation
Stick to your routine no matter where you are.

Making passport renewal easy
Need help with travel medical insurance?
Get up to date.
What vaccines do you need to travel?
The vaccines you need will depend on where you’re traveling and what you will be doing during your travels. Walgreens pharmacists are able to assist in helping you determine which vaccines you may need.
Which travel vaccines are available at Walgreens?
Travel vaccines Walgreens offers include: Yellow Fever, Meningitis, Polio, Typhoid, Japanese Encephalitis, Tick-Borne Encephalitis, Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B and Rabies*.
*Vaccines offered at Walgreens vary by state, age and health conditions. Talk to your local pharmacist about availability.
What other vaccines should I have before traveling?
It’s important to be up-to-date on routine vaccinations before traveling as well—like Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR), Tetanus, Flu and COVID-19.
You are leaving Walgreens.com Any information you provide will be subject to GeoBlue’s privacy and security policies.
Essentials you don’t want to be without


Search Smartraveller
Infectious diseases.

This page has information about the risk of infectious diseases for Australians overseas.
This page only gives general advice. Always talk to your healthcare providers for advice specific to you and your situation.
Read this page to learn about:
- infectious disease risks overseas
- vaccine-preventable diseases
- insect-borne diseases
- water or food-borne diseases
- contact, droplet or airborne diseases
- blood-borne diseases
- sexually transmissible infections (STIs)
- diseases spread by animals
- consular services and infectious diseases
Infectious disease risks overseas
Infectious diseases exist everywhere. But you have a higher risk of getting an infectious disease in some destinations. This can be due to:
- water and sanitation issues
- insects that carry diseases
- low vaccination rates.
Research the risks before you go. Then you can take preventive measures to reduce them.
- Read our travel advice for your destination . See if there are any health risks or suggested vaccines listed.
- Talk to your doctor or pharmacist. Tell them where you're going and ask their advice on prevention.
Vaccine-preventable diseases
Vaccination can prevent some diseases.
Get your travel vaccinations. Particularly if there's a travel warning for a vaccine-preventable disease where you're going. Ensuring you're vaccinated can protect you and those around you.
Talk to your doctor. Ask what travel vaccines they recommend. And find out if your standard vaccinations need boosting.
Get the vaccinations you need well before you go. Some take 6-8 weeks to work or need several doses.
Visit the Vaccine Hub to explore suggested vaccines for where you're going . Common travel vaccines include:
- chickenpox (varicella)
- hepatitis A and hepatitis B
- influenza (flu)
- Japanese encephalitis
- meningococcal
- tuberculosis (TB)
- yellow fever .
This list doesn't include everything. You may need to vaccinate against other diseases depending on your health and where you're going. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice.
Learn more about travel vaccinations .
Proof of vaccination
You may need proof of certain vaccinations when you're travelling.
Rules will vary between each country. Contact your destination's embassy or consulate in Australia for information.
Yellow fever
Some countries need you to show an international yellow fever vaccination certificate if you:
- arrive from a yellow fever-infected area
- transit through an infected area before arriving
- have been in an infected area within a number of days before arriving.
Your airline can stop you from boarding if you don't have one.
It's important to get your yellow fever vaccination at an approved clinic . You need it at least 10 days before you travel. The clinic will give you your certificate.
Read more about international yellow fever vaccination certificates .
Some countries may need you to show a COVID-19 vaccination certificate on entry or to access some services.
You can get your certificate through myGov or the Express Plus Medicare mobile app . If you can't use these options
- visit a Services Australia services centre
- contact the Australian Immunisation Register (AIR) at 1800 653 809 (in Australia) or +61 2 8633 3284 (from overseas).
Learn more about international COVID-19 vaccination certificates .
Insect-borne diseases
Insects can carry disease and spread it between people. They can also spread disease between animals and people.
You're more likely to get an insect-borne disease in tropical climates. This includes parts of
- Central America
- the Pacific.
You're also at risk in parts of Europe and the United States. Risks may differ depending on what you plan to do.
Some common insect-borne diseases are:
- chikungunya
- Lyme disease
- yellow fever
- Zika virus .
If you're pregnant or planning to get pregnant, your unborn child may face more risks from Zika virus. As a precaution, the Department of Health advises you to consider delaying travel to countries with Zika.
Reducing your risk of insect-borne diseases
You can get vaccinated against some insect-borne illnesses. For others, such as malaria, there's oral medicine you can take. Discuss options with your doctor or pharmacist.
Take steps to avoid insect bites.
- Cover exposed skin with light-coloured long-sleeved shirts and long pants.
- Use insect repellents with DEET or picaridin. If you use both sunscreen and insect repellent, apply the sunscreen first and then the repellent.
- Treat your clothing and gear with insecticides containing permethrin.
- Sleep in screened or air-conditioned rooms. Use bed nets if you can't keep mosquitoes from coming inside the room.
After walking through high grass or brush in tick-prone areas:
- brush off your clothes before getting in a car or going inside
- check yourself and others for ticks
- tumble dry your clothes hot for 20 minutes to kill ticks that may have hitched a ride.
Water- or food-borne diseases
Water- or food-borne diseases are common in many countries. You can catch them from:
- drinking or using tainted water
- drinking any drink with ice cubes made with tap water
- eating food washed with tap water
- brushing your teeth or washing your face with tap water
- eating tainted food, including meals prepared by people following poor hygiene practices
- taking part in activities in tainted water, such as swimming or water sports.
Some water- and food-borne diseases include:
- infections causing gastroenteritis (vomiting and diarrhoea )
- campylobacter
- hepatitis A
- leptospirosis
- polio (poliomyelitis)
- salmonella (including typhoid and paratyphoid )
- schistosomiasis
Cholera is less common, but it's very contagious and deadly.
Reduce your risk from water- or food-borne diseases
There are vaccines for some water and food-borne infectious diseases, including hepatitis A, typhoid and cholera.
You can do a lot to reduce your risk of infection where water and food-borne diseases are common.
- Wash your hands often and use hand sanitiser before you eat.
- Drink bottled water from a sealed bottle.
- Use water-sterilising tablets or filtration bottles to make tap water safe.
- Wash fresh produce thoroughly using bottled or sterilised water.
Try to avoid:
- drinking tap water or using it to clean your teeth
- drinks with ice cubes. Some restaurants may use water straight from the tap
- uncooked and undercooked food or food that has been left sitting for a while
- fresh salads and raw vegetables
- contact with water or soil that may be contaminated with sewerage
- in some places, swimming or wading in any fresh water.
For more information, see the Better Health Channel's advice on food safety while travelling .
Contact, droplet and airborne diseases
Some diseases can spread:
- through close contact with a person who is coughing, sneezing, or unwell
- through something an infected person touched after coughing, sneezing or blowing their nose.
These are called diseases spread by contact, droplets or through the air.
These include:
- chickenpox (varicella)
- coughs and colds
- influenza (flu)
- Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
Reducing your risk of contact, droplet and airborne diseases
Protect yourself from contact, droplet and airborne diseases.
- Stay up to date with your vaccinations for measles, rubella, diphtheria, pertussis, flu, COVID-19, and other vaccines recommended by your doctor.
- Wash your hands often or use hand sanitiser if soap and water aren't available.
- Avoid close contact with people who are sick or showing early symptoms.
- Avoid close contact with wild or domestic animals.
Blood-borne diseases
Some infectious diseases can be spread by blood. This can be:
- when an infected person's blood comes into direct contact with another person's blood, mouth or eyes
- when blood is on an object such as a needle or razor blade
- through bodily fluids (see also sexually transmissible infections )
Common blood-borne diseases overseas are:
- hepatitis B
- hepatitis C
Reduce your risk of blood-borne diseases
You can get vaccinated against some blood-borne diseases.
You can also reduce your risk of infection by being careful and making smart choices.
- Avoid contact with any objects that could be tainted with blood or body fluids.
- Never share needles, syringes, or other injecting tools.
- Choose tattoo, piercing and medical services that carefully sterilise their tools and surfaces. If you're not sure, ask for proof before they start.
- Practise safer sex.
- Cover wounds and cuts with a waterproof dressing.
- Don't share toothbrushes, razors and other personal items that may be tainted with blood.
- Use gloves and other relevant protection when giving first aid.
These diseases may not have symptoms in the early stages. If you think you've been exposed, seek medical advice early. There may be preventive treatment.
Sexually transmissible infections (STIs)
STIs are infections or diseases passed on during unprotected sex with an infected partner, including vaginal, anal and oral sex. Some STIs can spread through skin-to-skin contact with a person's infected genitals or mouth.
STIs include:
- genital herpes
- gonorrhoea
- human papillomavirus (HPV)
Other diseases can spread through sexual contact but are not called an STI. For example, water-borne diseases shigellosis and hepatitis A can also spread through sexual activity, including oral and anal sex.
Reducing your risk of STIs
Vaccines can prevent some STIs. But you must also take preventive measures to reduce your risk of infection.
Reduce your risk of infection by taking and using your own condoms from a brand you trust.
STIs may not have symptoms. If you think you've been exposed, seek medical advice.
If you're a victim of assault , including sexual assault , get medical care immediately to reduce the risk of infection.
For more information, see the Department of Health's information on STIs and HIV / AIDS .
Diseases spread by animals
Some animals can spread disease through close contact, scratches or bites. These diseases include:
- influenza A subtypes , including avian and swine influenza
- Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)
Reduce your risk of infection.
- Get vaccinated for rabies and influenza before you go, if recommended.
- Avoid contact with sick animals.
- Wash your hands well after contact with animals.
- Don't eat raw or undercooked meat or animal products.
If you have a pre-existing illness, you may need to avoid all contact with some animals. Seek medical advice.
If you're bitten, scratched or licked on an open wound by an animal:
- use first aid
- wash the wound out well with soap and water for at least 10 minutes
- use antiseptic solution
- get urgent medical advice about preventing rabies, tetanus, and bacterial infection.
Consular services and infectious diseases
You're responsible for protecting yourself against infectious diseases.
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas .
What we can do
- We can update our travel advice if we learn of a disease outbreak.
- We can give you a list of local English-speaking doctors and health services.
- We can help you get in contact with family and friends in Australia.
- We can provide emergency support if we declare a disease outbreak a crisis.
What we can't do
- We can't tell you every infectious disease in your destination.
- We can't give you medical advice.
- We can't tell you all the vaccines you may need.
- We can't tell you what to do or take to protect your health in your destination.
- We can't guarantee your health in any destination.
- We can't pay your medical costs if you get sick overseas.
- Read about travelling with medication and medical equipment .
- See our advice on travelling while pregnant .
- Learn about medical tourism .
- See our health advice for everyone .
- Read advice about travelling with children .
- See our advice on taking care of your mental health .
- See our advice for travellers with a disability .
- Read about health risks in all your destinations .
- Understand how and when consular services can help Australians overseas.
- Learn about infectious diseases and travel vaccinations (Department of Health).
- See a range of advice on international travel and health (World Health Organization).
- Read advice on food safety while travelling (Victorian Department of Health and Human Services).
- Learn about immunising your child (Department of Health).
- See information about insect-borne diseases (World Health Organisation).
Related content
Read our general advice for Australians planning to travel overseas with medications or medical equipment.
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
Official websites use .gov
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) Vaccination: What Everyone Should Know
CDC recommends that people get MMR vaccine to protect against measles, mumps, and rubella. Children should get two doses of MMR vaccine, starting with the first dose at 12 to 15 months of age, and the second dose at 4 through 6 years of age. Teens and adults should also be up to date on their MMR vaccination. Two MMR vaccines are available for use in the United States, M-M-R II and PRIORIX. M-M-R II and PRIORIX are fully interchangeable for all indications for which MMR vaccination is recommended. Children may also get MMRV vaccine , which protects against measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella (chickenpox). This vaccine is only licensed for use in children who are 12 months through 12 years of age.
- Who Should Get MMR Vaccine?
CDC recommends all children get two doses of MMR (measles-mumps-rubella) vaccine, starting with the first dose at 12 through 15 months of age, and the second dose at 4 through 6 years of age. Children can receive the second dose earlier as long as it is at least 28 days after the first dose.
Learn about MMRV vaccine , which protects against measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella (chickenpox). This vaccine is only licensed for use in children who are 12 months through 12 years of age.
Students at post-high school educational institutions
Students at post-high school educational institutions who do not have presumptive evidence of immunity need two doses of MMR vaccine, separated by at least 28 days.
Adults who do not have presumptive evidence of immunity should get at least one dose of MMR vaccine.
Certain adults may need 2 doses. Adults who are going to be in a setting that poses a high risk for measles or mumps transmission should make sure they have had two doses separated by at least 28 days. These adults include
- students at post-high school education institutions
- healthcare personnel
- international travelers
International travelers
People 6 months of age and older who will be traveling internationally should be protected against measles. Before any international travel—
- Infants 6 through 11 months of age should receive one dose of MMR vaccine. Infants who get one dose of MMR vaccine before their first birthday should get two more doses (one dose at 12 through 15 months of age and another dose separated by at least 28 days).
- Children 12 months of age and older should receive two doses of MMR vaccine, separated by at least 28 days.
- Teenagers and adults who do not have presumptive evidence of immunity against measles should get two doses of MMR vaccine separated by at least 28 days.
See also, Travel Information ( Measles | Mumps | Rubella )
Healthcare personnel
Healthcare personnel should have documented presumptive evidence of immunity , according to the recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices [48 pages] . Healthcare personnel without evidence of immunity should get two doses of MMR vaccine, separated by at least 28 days.
Who Should Not Get MMR Vaccine?
Who does not need mmr vaccine, how well does the mmr vaccine work, what is mmrv vaccine, should you get vaccinated after being exposed to measles, mumps, or rubella, what are the childcare and school requirements for mmr vaccine, how can parents pay for mmr vaccine, educational materials, for healthcare providers.
- Measles information for Healthcare Providers
- Measles Outbreak Communication Toolkits

Planning a trip outside the U.S.?
Find out if you need measles vaccine
Women of Childbearing Age
Women of childbearing age should check with their doctor to make sure they are vaccinated before they get pregnant. Women of childbearing age who are not pregnant and do not have presumptive evidence of immunity should get at least one dose of MMR vaccine.
It is safe for breastfeeding women to receive MMR vaccination. Breastfeeding does not interfere with the response to MMR vaccine, and the baby will not be affected by the vaccine through breast milk.
Groups at increased risk for mumps because of a mumps outbreak
During a mumps outbreak, public health authorities might recommend an additional dose of MMR vaccine for people who belong to groups at increased risk for getting mumps. These groups are usually those who are likely to have close contact, such as sharing sport equipment or drinks, kissing, or living in close quarters, with a person who has mumps. Your local public health authorities or institution will communicate to the groups at increased risk that they should receive this dose. If you already have two doses of MMR, it is not necessary to seek out vaccination unless you are part of this group.
Top of Page
Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) vaccine
Some people should not get MMR vaccine or should wait.
Tell your vaccine provider if the person getting the vaccine:
- Has any severe, life-threatening allergies. A person who has ever had a life-threatening allergic reaction after a dose of MMR vaccine, or has a severe allergy to any part of this vaccine, may be advised not to be vaccinated. Ask your health care provider if you want information about vaccine components.
- Is pregnant or thinks she might be pregnant. Pregnant women should wait to get MMR vaccine until after they are no longer pregnant. Women should avoid getting pregnant for at least 1 month after getting MMR vaccine.
- Has a weakened immune system due to disease (such as cancer or HIV/AIDS) or medical treatments (such as radiation, immunotherapy, steroids, or chemotherapy).
- Has a parent, brother, or sister with a history of immune system problems.
- Has ever had a condition that makes them bruise or bleed easily.
- Has recently had a blood transfusion or received other blood products. You might be advised to postpone MMR vaccination for 3 months or more.
- Has tuberculosis.
- Has gotten any other vaccines in the past 4 weeks. Live vaccines given too close together might not work as well.
- Is not feeling well. A mild illness, such as a cold, is usually not a reason to postpone a vaccination. Someone who is moderately or severely ill should probably wait. Your doctor can advise you.
This information was taken directly from the MMR (Measles, Mumps & Rubella) Vaccine information Statement (VIS) dated 2/12/2018.
Learn who should not get MMRV vaccine , which protects against measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella (chickenpox). This vaccine is only licensed for use in children who are 12 months through 12 years of age.
You do not need measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine if you meet any of these criteria for presumptive evidence of immunity*:
- at least one dose of a measles, mumps, and rubella virus-containing vaccine administered on or after the first birthday for preschool-age children and adults not at high risk for exposure and transmission
- two doses of measles and mumps virus-containing vaccine for school-age children and adults at high risk for exposure and transmission, including college students, healthcare personnel, international travelers, and groups at increased risk during outbreaks
- You have laboratory confirmation of past infection or had blood tests that show you are immune to measles, mumps, and rubella.
- You were born before 1957.**
If you do not have presumptive evidence of immunity against measles, mumps, and rubella, talk with your doctor about getting vaccinated. If you’re unsure whether you’ve been vaccinated, you should first try to find your vaccination records . If you do not have written documentation of MMR vaccine, you should get vaccinated. The MMR vaccine is safe, and there is no harm in getting another dose if you may already be immune to measles, mumps, or rubella.
If you received a measles vaccine in the 1960s, you may not need to be revaccinated. People who have documentation of receiving LIVE measles vaccine in the 1960s do not need to be revaccinated. People who were vaccinated prior to 1968 with either inactivated (killed) measles vaccine or measles vaccine of unknown type should be revaccinated with at least one dose of live attenuated measles vaccine. This recommendation is intended to protect those who may have received killed measles vaccine, which was available in 1963-1967 and was not effective.
*Except during a mumps outbreak. During a mumps outbreak public health authorities might recommend an additional dose of MMR vaccine for people who belong to groups at increased risk for getting mumps, regardless if they meet the criteria listed above.
**Birth before 1957 provides only presumptive evidence for measles, mumps, and rubella. Before vaccines were available, nearly everyone was infected with measles, mumps, and rubella viruses during childhood. The majority of people born before 1957 are likely to have been infected naturally and therefore are presumed to be protected against measles, mumps, and rubella. Healthcare personnel born before 1957 without laboratory evidence of immunity or disease should consider getting two doses of MMR vaccine.
MMR vaccine is very effective at protecting people against measles, mumps, and rubella, and preventing the complications caused by these diseases. People who receive MMR vaccination according to the U.S. vaccination schedule are usually considered protected for life against measles and rubella. While MMR provides effective protection against mumps for most people, immunity against mumps may decrease over time and some people may no longer be protected against mumps later in life. An additional dose may be needed if you are at risk because of a mumps outbreak.
One dose of MMR vaccine is 93% effective against measles, 78% effective against mumps, and 97% effective against rubella.
Two doses of MMR vaccine are 97% effective against measles and 88% effective against mumps.
MMR is an attenuated (weakened) live virus vaccine. This means that after injection, the viruses cause a harmless infection in the vaccinated person with very few, if any, symptoms before they are eliminated from the body. The person’s immune system fights the infection caused by these weakened viruses, and immunity (the body’s protection from the virus) develops.
Some people who get two doses of MMR vaccine may still get measles, mumps, or rubella if they are exposed to the viruses that cause these diseases. Experts aren’t sure why; it could be that their immune systems didn’t respond as well as they should have to the vaccine or their immune system’s ability to fight the infection decreased over time. However, disease symptoms are generally milder in vaccinated people.
- About 3 out of 100 people who get two doses of MMR vaccine will get measles if exposed to the virus. However, they are more likely to have a milder illness, and are also less likely to spread the disease to other people.
- Two doses of MMR vaccine are 88% (range 32% to 95%) effective at preventing mumps. Mumps outbreaks can still occur in highly vaccinated U.S. communities, particularly in settings where people have close, prolonged contact, such as universities and close-knit communities. During an outbreak, public health authorities may recommend an additional dose of MMR for people who belong to groups at increased risk for mumps. An additional dose can help improve protection against mumps disease and related complications.
- While there are not many studies available, most people who do not respond to the rubella component of the first MMR dose would be expected to respond to the second dose.
MMRV vaccine protects against four diseases: measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella (chickenpox). This vaccine is only licensed for use in children 12 months through 12 years of age.
CDC recommends that children get one dose of MMRV vaccine at 12 through 15 months of age, and the second dose at 4 through 6 years of age. Children can receive the second dose of MMRV vaccine earlier than 4 through 6 years. This second dose of MMRV vaccine can be given 3 months after the first dose. A doctor can help parents decide whether to use this vaccine or MMR vaccine.
MMRV is given by shot and may be given at the same time as other vaccines.
Please see the MMRV Vaccine Information Statement (VIS) for more information about who should not get MMRV vaccine or should wait.
For more information, see
- Factsheet: Two Options for Protecting Your Child Against Measles, Mumps, Rubella, and Varicella (MMRV)
- Measles, Mumps, Rubella, and Varicella (MMRV) Vaccine
- Frequently Asked Questions about Multiple Vaccinations and the Immune System
- Varicella (Chickenpox) Vaccination
If you do not have immunity against measles , mumps , and rubella and are exposed to someone with one of these diseases, talk with your doctor about getting MMR vaccine. It is not harmful to get MMR vaccine after being exposed to measles, mumps, or rubella, and doing so may possibly prevent later disease.
If you get MMR vaccine within 72 hours of initially being exposed to measles, you may get some protection against the disease, or have milder illness. In other cases, you may be given a medicine called immunoglobulin (IG) within six days of being exposed to measles, to provide some protection against the disease, or have milder illness.
Unlike with measles, MMR has not been shown to be effective at preventing mumps or rubella in people already infected with the virus (i.e., post-exposure vaccination is not recommended).
During outbreaks of measles or mumps, everyone without presumptive evidence of immunity should be brought up to date on their MMR vaccination. And some people who are already up to date on their MMR vaccination may be recommended to get an additional dose of MMR for added protection against disease.
All 50 states and the District of Columbia (DC) have state laws that require children entering childcare or public schools to have certain vaccinations. There is no federal law that requires this.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends that all states require children entering childcare, and students starting school, college, and other postsecondary educational institutions to be up to date on MMR vaccination:
- 1 dose is recommended for preschool-aged children 12 months or older
- 2 doses are recommended for school-aged children in kindergarten through grade 12 as well as students attending colleges or other post-high school educational institutions
For more information, see State Vaccination Requirements .
Most health insurance plans cover the cost of vaccines. But you may want to check with your health insurance provider before going to the doctor. Learn how to pay for vaccines.
If you don’t have insurance or if your insurance does not cover vaccines for your child, the Vaccines for Children (VFC) Program may be able to help. This program helps families of eligible children who might not otherwise have access to vaccines. To find out if your child is eligible, visit the VFC website or ask your child’s doctor. You can also contact your state VFC coordinator .
- Measles ( In English | En Español )
- Mumps (In English | En Español )
- Rubella (In English | En Español )
- Information on vaccines.gov ( Measles | Mumps | Rubella | Varicella )
- Measles: Vaccine for Measles
- Mumps: Be Sure Your Child Is Fully Immunized
- Rubella: Make Sure Your Child Gets Vaccinated
- What Would Happen If We Stopped Vaccinations?
- Questions and Answers, Immunization Action Coalition ( Measles [4 pages] | Mumps [4 pages] | Rubella [4 pages] )
- Measles, mumps, and rubella are serious diseases…Make sure your child is protected!, Immunization Action Coalition ( In English [1 page] | En Español [1 page] | по-русски [1 page] )
- MMR=measles, mumps, and rubella combination vaccine
- MMRV = measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella combination vaccine
- Measles=Rubeola
- Measles = ”10-day,” “hard” and “red” measles
- Rubella = also called “German” or “3-day” measles
- CRS = Congenital Rubella Syndrome
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
- Favorites & Watchlist Find a Cruise Cruise Deals Cruise Ships Destinations Manage My Cruise FAQ Perfect Day at CocoCay Weekend Cruises Crown & Anchor Society Cruising Guides Gift Cards Contact Us Royal Caribbean Group
- Back to Main Menu
- Search Cruises " id="rciHeaderSideNavSubmenu-2-1" class="headerSidenav__link" href="/cruises" target="_self"> Search Cruises
- Cruise Deals
- Weekend Cruises
- Last Minute Cruises
- Family Cruises
- 2024-2025 Cruises
- All Cruise Ships " id="rciHeaderSideNavSubmenu-4-1" class="headerSidenav__link" href="/cruise-ships" target="_self"> All Cruise Ships
- Cruise Dining
- Onboard Activities
- Cruise Rooms
- The Cruise Experience
- All Cruise Destinations " id="rciHeaderSideNavSubmenu-5-1" class="headerSidenav__link" href="/cruise-destinations" target="_self"> All Cruise Destinations
- Cruise Ports
- Shore Excursions
- Perfect Day at CocoCay
- Caribbean Cruises
- Bahamas Cruises
- Alaska Cruises
- European Cruises
- Mediterranean Cruises
- Royal Destinations
- Cruise Planner
- Make a Payment
- Check-In for My Cruise
- Beverage Packages
- Shore Excursions
- Update Guest Information
- Book a Flight
- Dining Packages
- Royal Gifts
- Required Travel Documents
- Transportation
- Book a Hotel
- Redeem Cruise Credit
- All FAQs " id="rciHeaderSideNavSubmenu-7-1" class="headerSidenav__link" href="/faq" target="_self"> All FAQs
- Boarding Requirements
- Future Cruise Credit
- Travel Documents
- Check-in & Boarding Pass
- Transportation
- Perfect Day at CocoCay
- Post-Cruise Inquiries
- Royal Caribbean
- Celebrity Cruises
Questions related to Boarding Requirements
Still need help contact us, get support by phone or email.
Email Your Questions
Locate a Travel Agent
Previewing: Promo Dashboard Campaigns
My Personas
Code: ∅.
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Travelers' Health Most Frequently Asked Questions
On this page, travel vaccines and medications, yellow fever vaccine.
CDC Travelers’ Health Branch provides health advice to international travelers, including advice about medications and vaccines. On this page, you’ll find some of our most frequently asked questions and responses.
1. What vaccines or medicines should I get before traveling to my destination?
A: It depends on where you are going and what you will be doing. Use our destination tool to find the vaccines and medications you need for your next trip, and schedule an appointment with your doctor or a travel medicine specialist at least a month before traveling to get recommended or required vaccines and medicines.
2. If I am going on a cruise that will stop in several countries, which vaccines should I get for each country?

A: You should be up-to-date on routine vaccines, such as measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), tetanus, and flu. Depending on where you’re going and what activities you plan, other vaccines may be recommended. More cruise information .
3. What is the difference between routine, recommended, and required vaccines?
A: Routine vaccines are those that are recommended for everyone in the United States based on their age, health condition, or other risk factors. You may think of these as the childhood vaccines you got before starting school, but some are routinely recommended for adults, like the adult pertussis booster Tdap, and some every year (like the flu vaccine) or every 10 years (like the tetanus booster for adults).
A required vaccine is one that travelers must have in order to enter a country, based on that country’s regulations. Yellow fever , meningococcal, and polio vaccines may be required by certain countries.
Recommended vaccines are those that CDC recommends travelers get to protect their health, even if they aren't required for entry by the government of the country you are visiting. They protect travelers from illnesses that are usually travel-related. For example, a typhoid vaccine can prevent typhoid , a serious disease spread by contaminated food and water, which is not usually found in the United States. The vaccines recommended for a traveler depend on several things, including age, health, and itinerary.
Find out more about travel vaccines . Clinicians: Use our 2-page Quick Guide to Travel Vaccination Recommendations .
4. What are the prices of vaccines needed for travel outside the United States?
A: Prices vary by provider and insurance coverage. You should be able to get routine vaccines from your primary health care provider, health clinic, or health department. Travel clinics and yellow fever vaccine clinics should be able to give you any vaccines that your health care provider cannot.
5. How long do travel vaccines last (when do I need to get a booster dose)?
A: How long travel vaccines last depends on the vaccine. If you're traveling outside the United States, you should see a health care provider who is familiar with travel medicine at least a month before your trip. They can give you advice about any vaccines and vaccine boosters based on where you are going and your previous vaccinations. Be sure to bring your vaccine records to your appointment!
6. Which medications can I travel with?
A: When packing for trips abroad, don’t forget there may be special considerations for bringing your prescriptions and other medicines with you. Some medicines that are commonly prescribed or available over-the-counter in the United States can be illegal in other countries. Check with the embassy or consulate in the country you will be visiting to make sure your medicines are permitted in that country.
See your health care provider at least a month before you go to get any needed or extra medications, and pack medications in your carry-on in case your luggage is lost.

7. Which countries require yellow fever vaccine for travel?
A: Some countries in South America and Africa require you to provide proof that you have been vaccinated against yellow fever by presenting an International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis when entering the country. However, there are other popular travel destinations where the threat of infection with yellow fever virus is very real, and there is no requirement for you to be vaccinated to enter the country.
If you only get the yellow fever vaccine before going to countries that require it, you could be putting your health at risk. Since yellow fever disease can be serious or even fatal, CDC recommends that individuals be vaccinated when traveling to any areas where there is a risk of acquiring infection with yellow fever virus. Use our destination tool to find out which vaccines the CDC recommends you have for anywhere you travel around the world and talk to a travel medicine provider for more details.
Yellow fever vaccine is only available at yellow fever vaccine clinic , so call ahead (well in advance of travel) and book your appointment.
Even if you get the yellow fever vaccine, you can still get other diseases from mosquito bites, like malaria, dengue, and Zika. The best ways to prevent mosquito-borne diseases are to use insect repellent while outdoors, wear long pants and long sleeves, and choose accommodations with air conditioning or mosquito nets. For travel to areas where malaria is a risk , taking medicine that can prevent malaria may also be advised.
8. How far in advance of my trip do I need to get the yellow fever vaccine?
A: For most people, it takes up to 10 days after the vaccine is given to be protected against the yellow fever virus . If your destination requires yellow fever vaccine, the proof of vaccination does not become valid until 10 days after the vaccine is given.
9. Where can I get a yellow fever vaccine in my area?
A: The nearest yellow fever vaccination clinic may be far away from where you live, and appointments may be limited. Be sure to contact the clinic ahead of time.
10. Who should not get the yellow fever vaccine?
A: Some people should not get the yellow fever vaccine : infants younger than 6 months, or people with a history of a bad reaction to the vaccine should not receive yellow fever vaccine. If you have a thymus disorder associated with abnormal immune cell function (such as a thymoma or myasthenia gravis) you should not receive yellow fever vaccine. If cancer, or the drugs or radiation used to treat cancer, has weakened your immune system, you should not receive yellow fever vaccine. If you received an organ transplant and take medicines to prevent rejection of that transplant, you should not receive yellow fever vaccine. Other conditions and medicines can also affect your immune system and could be a reason not to receive yellow fever vaccine. Check with your doctor to find out more.
If you are older than 60 years old, pregnant, or breastfeeding, talk to your doctor before getting a yellow fever vaccine. There are potential risks to your health from the vaccine. If you are infected with HIV, talk to your doctor; you may still be able to get yellow fever vaccine, depending on your CD4 cell count and immune function. Infants 6–8 months old can receive yellow fever vaccine, although it is less risky to postpone travel to areas with yellow fever until the baby is 9 months of age or older. After the age of 9 months, the health risks from the vaccine are considerably lower.
11. How can I contact the local US embassy?

A: 1. Enroll with the nearest US embassy or consulate through the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) . It’s a FREE service that allows US citizens traveling or living abroad to receive the latest security updates for their location. 2. If you need to contact a US embassy or consulate, call 1-888-407-4747 (from the US or Canada) OR 00-1-202-501-4444 (from other countries).
Travel healthy, from CDC’s Travelers’ Health!
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Language selection
- Français fr
Approved COVID-19 Vaccines
Information on COVID-19 vaccines including approved vaccines, types of vaccines and on-going safety monitoring
Most requested
- How to get vaccinated
- Canada’s vaccine supply and donation strategy
- Proof of vaccination
- Reported side effects following COVID-19 vaccination
- How vaccines and treatments are approved
- List of approved drugs, vaccines and expanded indications
- Number of people vaccinated
Approved vaccines
Moderna spikevax covid-19 vaccine.
About the vaccine, how it works, how it is given, ingredients, allergies, possible side effects, safety monitoring
Pfizer-BioNTech Comirnaty COVID-19 vaccine
Astrazeneca vaxzevria covid-19 vaccine, novavax nuvaxovid covid-19 vaccine, types of vaccines, mrna vaccines.
About mRNA vaccines, how they work, safety, effectiveness, monitoring
Viral vector-based vaccines
About viral vector-based vaccines, how they work, safety, effectiveness, monitoring
Protein subunit vaccines
About protein subunit vaccines, how they work, safety, effectiveness, monitoring
Plant-based vaccines
Did you find what you were looking for.
If not, tell us why:
You will not receive a reply. Telephone numbers and email addresses will be removed. Maximum 300 characters
Thank you for your feedback
Page details
Members save 10% or more on over 100,000 hotels worldwide when you’re signed in
Elektrostal travel guide, visit elektrostal, check elektrostal hotel availability, popular places to visit, electrostal history and art museum.
You can spend time studying the exhibits at Electrostal History and Art Museum in Elektrostal. Take in the museums while you're in the area.
- Cities near Elektrostal

- Places of interest
- Ramenskii History and Art Museum
- Malenky Puppet Theater
- Church of Our Lady of Kazan
- Pavlovsky Posad Museum of Art and History
- Church of Vladimir
- Likino Dulevo Museum of Local Lore
- Shirokov House
- Fairy Tale Children's Model Puppet Theater
- Fifth House Gallery
- Art Gallery of The City District
Likino-Dulyovo, Russia
Essential likino-dulyovo.

- Museum Dulevo Porcelain
- Museum Kudykinsk District. Smirnov
- Likino-Dulev Museum of Local Lore
- Church of the Holy Apostle and Evangelist John the Theologian
- Dulevskiy Palace of Culture
Plan Your Lyubertsy Holiday: Best of Lyubertsy

Explore Lyubertsy
Essential lyubertsy.

Lyubertsy Is Great For
Eat & drink.


COMMENTS
Find out which travel vaccines you may need to help you stay healthy on your trip. ... Check CDC's destination pages for travel health information. Check CDC's webpage for your destination to see what vaccines or medicines you may need and what diseases or health risks are a concern at your destination.
Vaccines for Travelers. Vaccines protect travelers from serious diseases. Depending on where you travel, you may come into contact with diseases that are rare in the United States, like yellow fever. Some vaccines may also be required for you to travel to certain places. Getting vaccinated will help keep you safe and healthy while you're ...
Before you embark on your journey, he suggests making sure you're up to date with routine vaccinations, including vaccines for: COVID-19. Flu. Hepatitis A. Hepatitis B. Tetanus. "People don ...
Vaccines. Vaccination is the administration of agent-specific, but safe, antigenic components that in vaccinated individuals can induce protective immunity against the corresponding infectious agent. Before departure, travelers should have a medical consultation to learn about the risk of disease in the country or countries they plan to visit ...
Dengue information for travelers. 23 November 2023 . Chikungunya information for travelers. 23 November 2023 . Zika information for travelers. 19 November 2022 ... Vaccination requirements and recommendations for international travellers; and malaria situation per country - 2022 edition. 18 November 2022 ...
NaTHNaC - Country List - TravelHealthPro COUNTRY INFORMATION is a webpage that provides comprehensive and up-to-date information on travel health risks and recommendations for over 200 countries. Whether you are travelling to Peru, Bali, Romania, Uganda or any other destination, you can find useful factsheets, vaccine advice, malaria prevention tips, outbreak alerts and more on this webpage.
The vaccines you should get depend on where you're going. No matter where you're going, check to make sure you're up to date on all routine vaccines: measles-mumps-rubella, diphtheria-tetanus ...
Many countries are reopening their borders for international travel. Find out which countries are open to vaccinated travelers. Just enter your departure country above - the map will update to reflect countries' opening status and any entry requirements for air travelers. Before you book, be sure to double check your country's official ...
The traveler's health section of the CDC web site has extensive information about which vaccines are recommended or required for each country, special travel alerts, a travel clinic locator, and ...
Dengue information for travelers. 23 November 2023 . Chikungunya information for travelers. 23 November 2023 . Zika information for travelers. 19 November 2022 ... Vaccination requirements and recommendations for international travellers; and malaria situation per country - 2021 edition. 26 May 2021 ...
Travel vaccination advice. If you're planning to travel outside the UK, you may need to be vaccinated against some of the serious diseases found in other parts of the world. Vaccinations are available to protect you against infections such as yellow fever, typhoid and hepatitis A. In the UK, the NHS routine immunisation (vaccination) schedule ...
Essentials you don't want to be without. We've got you covered. Travel safely with our TSA-approved items. At-home COVID-19 tests. Travel-sized toiletries. Shop all travel items. Walgreens can help you prepare for your next adventure. Talk to a pharmacist to find out what vaccines, prescriptions and OTC medicines you need for your trip.
Learn more about travel vaccinations. Proof of vaccination. You may need proof of certain vaccinations when you're travelling. Rules will vary between each country. Contact your destination's embassy or consulate in Australia for information. Yellow fever. Some countries need you to show an international yellow fever vaccination certificate if you:
The CDC's Order requiring proof of vaccination for non-U.S. citizen nonimmigrants to travel to the United States is still in effect. For more information see Requirement for Proof of COVID-19 Vaccination for Air Passengers. Check the CDC website for additional information and Frequently Asked Questions. Country-Specific Information:
Smartraveller, the Australian Government's travel advisory and consular information service, which provides up-to-date advice about health, safety and other risks of specific destinations for Australian travellers; The following resources have comprehensive technical advice on international travel and health, including vaccination: the latest ...
An additional dose may be needed if you are at risk because of a mumps outbreak. One dose of MMR vaccine is 93% effective against measles, 78% effective against mumps, and 97% effective against rubella. Two doses of MMR vaccine are 97% effective against measles and 88% effective against mumps. MMR is an attenuated (weakened) live virus vaccine.
Complete all fields of the health certificate, taking care to provide all information required in each field. Only provide required information in the health certificate. For example, if the destination country only requires a rabies vaccination, don't provide information on any other vaccinations administered to the pet.
What vaccines are required to travel on a Royal Caribbean cruise? All guests must ensure that they are medically and physically fit for travel. The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) provide guidelines as to which vaccinations are required in each country.
If you need to contact a US embassy or consulate, call 1-888-407-4747 (from the US or Canada) OR 00-1-202-501-4444 (from other countries). Travel healthy, from CDC's Travelers' Health! CDC Travelers' Health Branch provides health advice to international travelers, including advice about medications and vaccines.
Moderna Spikevax COVID-19 vaccine. About the vaccine, how it works, how it is given, ingredients, allergies, possible side effects, safety monitoring.
Elektrostal is linked by Elektrichka suburban electric trains to Moscow's Kursky Rail Terminal with a travel time of 1 hour and 20 minutes. Long distance buses link Elektrostal to Noginsk, Moscow and other nearby towns. Local public transport includes buses. Sports
Uncover Elektrostal's best with our Travel Guide for 2024. Expert tips & must see recommendations. Whether a tourist or local, plan your holiday today with this tourist guide!
Likino-Dulyovo Tourism: Tripadvisor has 61 reviews of Likino-Dulyovo Hotels, Attractions, and Restaurants making it your best Likino-Dulyovo resource.
Lyubertsy Tourism: Tripadvisor has 1,975 reviews of Lyubertsy Hotels, Attractions, and Restaurants making it your best Lyubertsy resource.