- 0 Shopping Cart


What is the impact of tourism?
Benefits and problems of tourism Tourism can bring both benefits and problems to an area.
Positive effects of tourism include:
- Creates employment opportunities for local people
- Promotes cultural awareness and can help preserve local culture and traditions e.g. Masai Mara in Kenya
- Income from tourists can be used to develop local infrastructure and services e.g. new roads and airports. In LEDCs money can be spent on developing access to education, clean water and sanitation
- Foreign currency can help local people
- Natural features that attract tourists in the first place can be protected using income from tourism
The negative effects of tourism include:
- Tourism can have a negative environmental impact . This is at a range of scales. The increase in air travel has contributed towards increased carbon dioxide emissions. On a local level natural features that attract tourists are themselves under threat due to human actions
- often local people are employed in low skill, poorly paid work in unsatisfactory working conditions
- travel agents, airline companies and hoteliers benefit more than local companies when holidays are booked to destinations in LEDCs companies based in MEDCs set up luxury hotels in LEDCs. The profits usually return to MEDCs. They also create more competition for locally run guest houses
- destroys local culture and traditions as areas becomes more westernised
Latest Blog Entries
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.
Previous Topic Page
Topic home, next topic page, share this:.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Please Support Internet Geography
If you've found the resources on this site useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Search Internet Geography
Top posts and pages.
Pin It on Pinterest
- Click to share
- Print Friendly

Full unit of work for tourism. All lesson are suitable for 50 minutes to 1 hour of teaching time. Includes supporting worksheets for lessons - no additional resources are required. Homework's integrated into lessons where appropriate. Most suitable for KS3 geography. All lessons have a starter and lesson objectives. All PowerPoints in the same style. Lesson sequence: 1 - What is tourism? 2 - The growth of tourism 3 - What attracts tourists to different destination? 4 - British tourism 5 - What are the impacts of tourism in National Parks? 6 - Declining tourism in Britain 7 - History and tourism 8 - The impact of tourism 9 - Jobs in the tourist industry 10 - Ski resorts 11 - Tourism in Kenya 12 - Sustainable tourism 13 - Sustainable tourism in Peru 14 - Does tourism cause conflict?
This unit of work was featured in the TES Geography newsletter
Use the code thisisKS3 at checkout and get 1 x KS3 resource free when you purchase 2 units or more
You Might Also Like

Get news and updates
We respect your privacy

- About & Contact
- Sample Lessons IGCSE/IBDP
- Site Testimonials
- Snow & Mountains
- Qatar World Cup 2022
- Famous Refugees
- Over the Horizon
- Classroom Display
- Hurricane Matthew Display
- Nepal Earthquake 2015
- Don't Panic - The Truth About Population
- Israel & Palestine Group 3
- Global Village + Maths
- IB Sample Lesson 2017
- Theme 1 Population & Settlement.
- Theme 2 - Natural Environment
- Theme 3 - Economic Development
- IGCSE Berlin Fieldwork
- IGCSE Rivers France
- IGCSE Barcelona Fieldwork
- IGCSE Exam Revision
- G6 Factfulness
- Introducing Tectonics
- Earthquakes
- The New Silk Road
- The Ice Man
- 2016 Efforts
- End of Year Exam
- Parent Information
- G7 Factfulness
- 8850 Top of the World
- Geography of My Stuff
- Another Shopping Centre?
- Carcassonne Connection
- Renaissance Day
- G8 Factfulness
- Global Development
- Global Biomes
- Climate & Rainforest
- Palm Oil Assessment
- Introducing Waterfalls
- Tourism Blessing or Curse?
- Niagara Redeveloped DME
- IGCSE Options
Our Shrinking World & Tourism Growth

The Impacts Of Tourism - Case Study: Benidorm

Tourism in Wales
Tourism is a very important part of the Welsh Economy. This is because:
Tourists spend over £8 million a day in Wales - this adds up to around £3 billion a year!
About 100,000 people in Wales are employed in the tourism industry. This accounts for nearly ten per cent of the workforce.
Over one million tourists come to Wales every year. The most popular origins of overseas visitors are from the Republic of Ireland, USA and Germany.
What tourists do in Wales:
The most popular activities for tourists visiting Wales include: walking, swimming and visiting historical attractions such as castles, museums and galleries.
The most popular attraction in Wales is the Museum of Welsh Life which attracts over 600,000 visitors per year.
There are over 80,000 bed spaces available in Wales.
So tourism is really important, but what is it about Wales that makes it such a tourist attraction?
To answer this question we need to know about the different types of tourist attractions. We can classify tourism as being due to either physical or human reasons.
Physical reasons for tourism
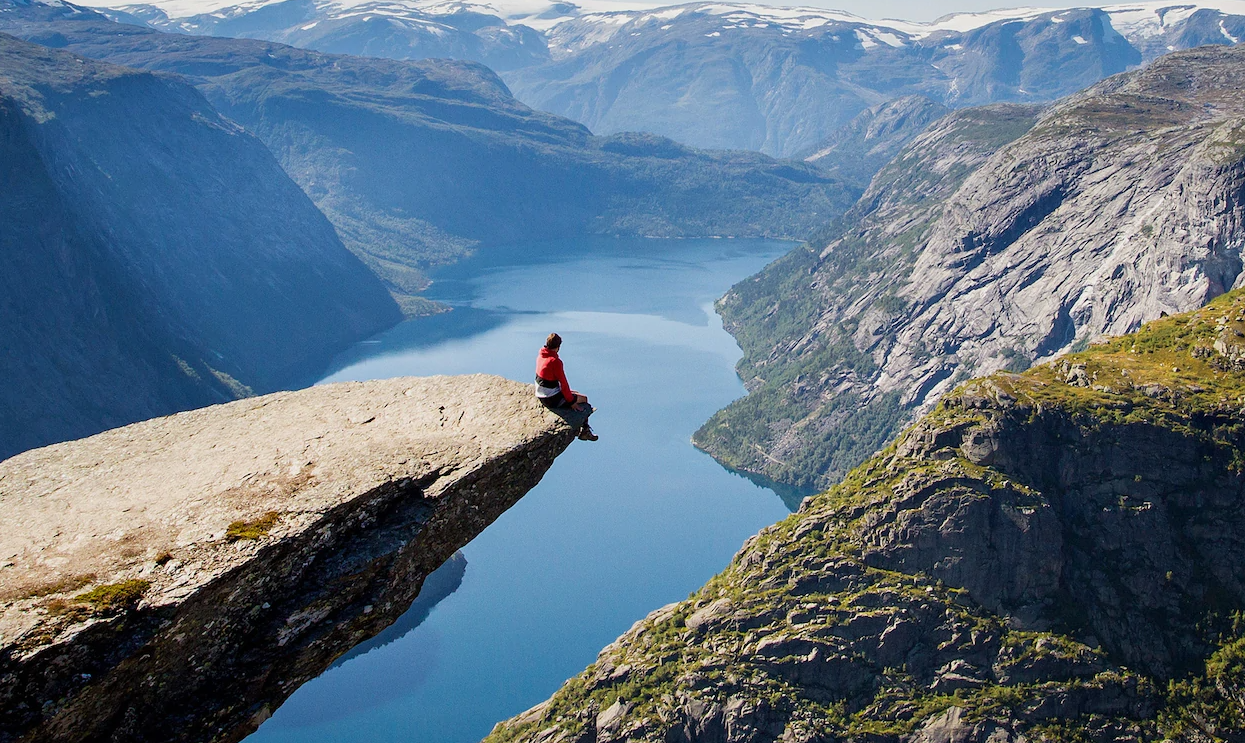
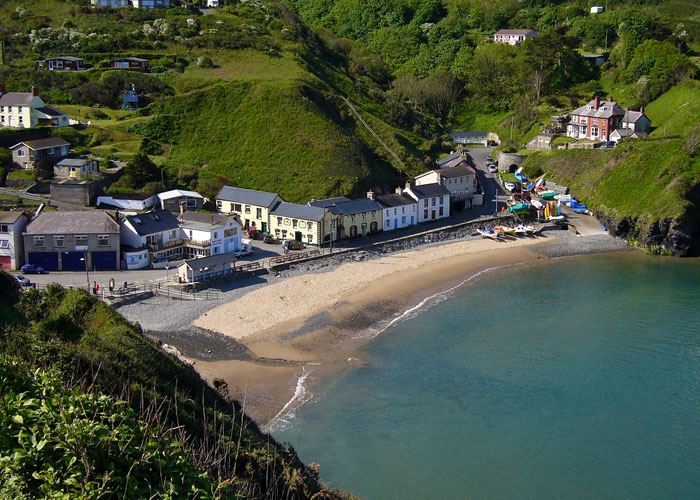
Physical geography means things to do with the natural world. Wales has some beautiful beaches such as this one in Llangrannog in West Wales (Llangrannog is also a human tourist attraction).

Other physical attractions include Mount Snowdon in North Wales. People travel thousands of miles just to see these views.
The three most outstanding places of beauty in Wales have been made National Parks. Other physical attractions include the clean rivers, countryside and even cave systems which extend for miles in underground caverns beneath much of South West Wales.
Did you know?

National Parks are areas of outstanding natural beauty that have been given legal protection by an act of parliament. In Wales there are three National Parks:
The Snowdonia National Park in North Wales
The Pembrokeshire Coast National Park in West Wales
The Brecon Beacons National Park in South Wales
Human reasons for tourism
Human geography means things to do with people in Wales. This can include cultural, historical or even sporting events. Cultural includes things to do with language and art. Llangrannog attracts tourists not just because of its beach but because it has a residential centre owned by Urdd Gobaith Cymru (Wales's League of Youth). This is where people go to learn and improve their Welsh language skills.
Other major cultural attractions include Eisteddfods such as the Llangollen International Music Eisteddfod which this year will be attracting thousands of tourists to North Wales between 5th – 11th July.

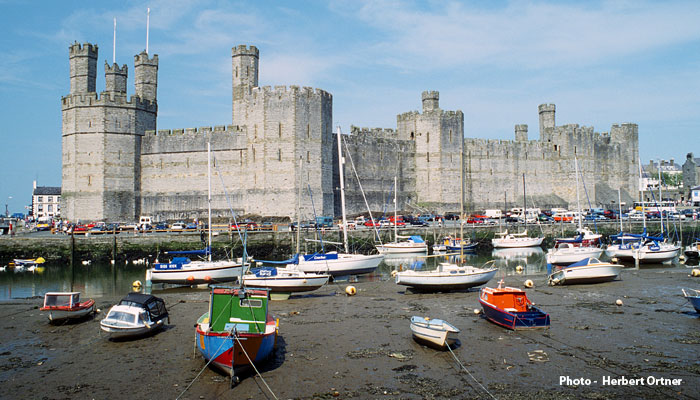
A major category is historical and includes sites like the magnificent castles of North Wales such as this one here in Caernarvon. Other historical attractions include industrial sites such as the National Slate Museum in Llanberis in North Wales or the Big Pit mining museum in Blaenavon in South Wales.

Sporting activities also attract large numbers of visitors to Wales either as spectators or as participants. Big spectator events include the rugby internationals, the Wales Rally G.B. and in October 2010 the Ryder Cup will be be help in Wales.

The benefits of tourism
The most obvious benefit of tourism to an area is that tourists spend money and this provides jobs. Nearly ten per cent of jobs in Wales depend directly on tourism and many more depend on the money that these jobs earn. However, there are other benefits like improved facilities such as swimming pools or cinemas to accommodate tourists.
The disadvantages of tourism
It is not all good news! Tourists bring problems: walkers leave open farm gates or drop litter causing farmers many problems (tourists don't always follow the countryside code).

Respect - Protect - Enjoy
Be Safe - plan ahead and follow any signs.
Leave gates and property as you find them.
Protect plants and animals, and take your litter home.
Keep dogs under close control.
Consider other people.
Popular tourist spots are sometimes called honeypot sites – a sweet honeypot left in the garden on a warm summer's day soon attracts a lot of wasps and starts to become something nasty! When too many tourists visit a place they spoil it. This includes pollution from cars, crowds of people and far too often traffic jams on motorways during the tourism season.
These disadvantages sometimes leads to Conflict. Conflict doesn't mean fighting but road rage has led to more than one bout of fisticuffs! It means that different people want different things. For example, a tourist wants to visit an area to go walking; this is great for a hotel owner and local pub landlord. But this is bad news for farmer who has a sheep killed on a road because the walker left a field gate open!
Choose a tourist attraction that you have visited in Wales:
What are the physical and human features that attract tourists?
What are the benefits of tourism to that location?
What are the disadvantages of tourism to that location?
What kinds of conflicts might this create?
Related Articles...

Tectonic Mayhem

The Ryder Cup

- AI Lesson Planner
- Search Resources
- Become a Seller
- Your Account
- Education Blog
- Login/Register
Free and Premium Teaching Resources & Worksheets
Geography tourism scheme of work.
£1.00
- Item Details
This resource is a scheme of work on Tourism for KS3 Geography. It includes: Growth of tourism Positive and negative impacts of tourism National Parks in the UK Tourism in Bath Tourism in Antarctica Advertising
All worksheets can be adapted.

Write a Review
Review Title *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Leave a Reply
Related items may you also like.

Social Media
Quick marking feedback sheets for English Literature...
Item Information
- geography tourism questions worksheet
- Issue: * Copyright Infringement Spam Invalid Contents Broken Links
- Your Name: *
- Your Email: *
Join Free and Premium Teaching Resources & Worksheets | Lesson Planned
Login to free and premium teaching resources & worksheets | lesson planned.
Global tourism Case study: Lake District
Tourism develops due to natural and man-made factors. It is a global issue with positive and negative effects. Responsible management can minimise the impact of tourism in the 21st century.
Part of Geography Global issues
Case study: Lake District
Sustainability in the lake district.

Measures that have been adopted to help maintain the Lake District for future generations close future generations People who will be alive in many years to come. .
The National Trust close National Trust A charity responsible for ensuring the protection and preservation of historic places and spaces for public enjoyment. and other conservation groups have undertaken footpath maintenance. Some paths have been rebuilt or access restricted to reduce the effects on paths and vegetation close vegetation Trees and plants. .
Public transport has been improved and subsidised, for example the Langdale Rambler bus service. Visitors are encouraged to use the buses instead of bringing their cars into the national park.
Restricted parking zones have been set up in some villages, for example in Elterwater. The car park on the edge of the village has been expanded and parking on grass verges and near houses has been restricted.
Raising awareness of conservation issues for visitors with posters and leaflets at tourist information and visitor centres.
A 10 mph speed limit was introduced on Windermere in March 2005. The lake had become congested with powerboats and water-skiers, and noise from the speedboats was spoiling the lake for other users such as swimmers and canoeists.
There was also concern that the wake from powerboats had caused shore erosion and that boats had contributed to pollution and the disappearance of reed beds in the lake.
Conservationists welcomed the new speed limit, but speedboat owners, water-skiers and boat companies around the lake objected to the change. Businesses have been affected and boat users have had to find alternative lakes.
More guides on this topic
- Climate change
- Natural regions
- Environmental hazards
- Trade and globalisation
- Classroom Videos
Related links
- BBC Weather
- BBC News: Science, Environment
- BBC Two: Landward
- SQA National 5 Geography
- Planet Diary
- Scotland's Environment
- Royal Geographical Society
The Growth of Tourism
Growth of tourism.
Tourism has grown since the 1500s. Innovations in transport has had huge impacts on tourism.

Beginnings of tourism
- Tourism started with public baths that people relaxed in. Middle and upper class people would travel to these baths from the 1700s.
- The Colosseum (Rome) and the Acropolis (Athens) were frequently visited, as well as the capital cities of Vienna and Paris (Austria and France), which were seen as the home of the arts and culture.
- These holidays would usually have to last months or years because of the limited means of transport.
- Journeys would be taken by horse and carriage along dirt tracks.

Package deals
- The first one in the UK was for a religious seminar on avoiding alcohol in 1841, encouraging travel by train between Leicester and Loughborough.

- In the UK, tourism grew through railways.
- This opened up opportunities to go to holiday parks like Butlins and seaside resorts like Blackpool.

Transport 2
- Post-1945, the invention of the jet engine made air travel much more attractive for larger numbers of people.
- Many UK locations could not compete with the sunshine in Spain and France, especially because it had become so quick to go abroad.
- Budget airlines like Easyjet were created in the 1990s, which made going abroad cheaper by being more basic a service.
- This made travel more affordable so it became more normal to go abroad.

- TV and the internet make other parts of the world visible and encourages people to visit more isolated locations to do some exploring, e.g. Antarctica or St Helena island.

Which attractions are popular?
- Some attractions are popular because they are interesting physical landscapes, like the the Grand Canyon, Niagara Falls and Victoria Falls.
- e.g. cityscapes like Manhattan (Empire State building, Chrysler building, Grand Central station).
- London is also an example of a cityscape (Houses of Parliament, the Shard, the London Eye, the Tower of London).
- These attract millions of visitors a year.
1 Geography Skills
1.1 Mapping
1.1.1 Map Making
1.1.2 OS Maps
1.1.3 Grid References
1.1.4 Contour Lines
1.1.5 Symbols, Scale and Distance
1.1.6 Directions on Maps
1.1.7 Describing Routes
1.1.8 Map Projections
1.1.9 Aerial & Satellite Images
1.1.10 Using Maps to Make Decisions
1.2 Geographical Information Systems
1.2.1 Geographical Information Systems
1.2.2 How do Geographical Information Systems Work?
1.2.3 Using Geographical Information Systems
1.2.4 End of Topic Test - Geography Skills
2 Geology of the UK
2.1 The UK's Rocks
2.1.1 The UK's Main Rock Types
2.1.2 The UK's Landscape
2.1.3 Using Rocks
2.1.4 Weathering
2.2 Case Study: The Peak District
2.2.1 The Peak District
2.2.2 Limestone Landforms
2.2.3 Quarrying
3 Geography of the World
3.1 Geography of America & Europe
3.1.1 North America
3.1.2 South America
3.1.3 Europe
3.1.4 The European Union
3.1.5 The Continents
3.1.6 The Oceans
3.1.7 Longitude
3.1.8 Latitude
3.1.9 End of Topic Test - Geography of the World
4 Development
4.1 Development
4.1.1 Classifying Development
4.1.3 Evaluation of GDP
4.1.4 The Human Development Index
4.1.5 Population Structure
4.1.6 Developing Countries
4.1.7 Emerging Countries
4.1.8 Developed Countries
4.1.9 Comparing Development
4.2 Uneven Development
4.2.1 Consequences of Uneven Development
4.2.2 Physical Factors Affecting Development
4.2.3 Historic Factors Affecting Development
4.2.4 Human & Social Factors Affecting Development
4.2.5 Breaking Out of the Poverty Cycle
4.3 Case Study: Democratic Republic of Congo
4.3.1 The DRC: An Overview
4.3.2 Political & Social Factors Affecting Development
4.3.3 Environmental Factors Affecting the DRC
4.3.4 The DRC: Aid
4.3.5 The Pros & Cons of Aid in DRC
4.3.6 Top-Down vs Bottom-Up in DRC
4.3.7 The DRC: Comparison with the UK
4.3.8 The DRC: Against Malaria Foundation
4.4 Case Study: Nigeria
4.4.1 The Importance & Development of Nigeria
4.4.2 Nigeria's Relationships with the Rest of the World
4.4.3 Urban Growth in Lagos
4.4.4 Population Growth in Lagos
4.4.5 Factors influencing Nigeria's Growth
4.4.6 Nigeria: Comparison with the UK
5 Weather & Climate
5.1 Weather
5.1.1 Weather & Climate
5.1.2 Components of Weather
5.1.3 Temperature
5.1.4 Sunshine, Humidity & Air Pressure
5.1.5 Cloud Cover
5.1.6 Precipitation
5.1.7 Convectional Precipitation
5.1.8 Frontal Precipitation
5.1.9 Relief or Orographic Precipitation
5.1.10 Wind
5.1.11 Extreme Wind
5.1.12 Recording the Weather
5.1.13 Extreme Weather
5.2 Climate
5.2.1 Climate of the British Isles
5.2.2 Comparing Weather & Climate London
5.2.3 Climate of the Tropical Rainforest
5.2.4 End of Topic Test - Weather & Climate
5.3 Tropical Storms
5.3.1 Formation of Tropical Storms
5.3.2 Features of Tropical Storms
5.3.3 The Structure of Tropical Storms
5.3.4 Tropical Storms Case Study: Katrina Effects
5.3.5 Tropical Storms Case Study: Katrina Responses
6 The World of Work
6.1 Tourism
6.1.1 Landscapes
6.1.2 The Growth of Tourism
6.1.3 Benefits of Tourism
6.1.4 Economic Costs of Tourism
6.1.5 Social, Cultural & Environmental Costs of Tourism
6.1.6 Tourism Case Study: Blackpool
6.1.7 Ecotourism
6.1.8 Tourism Case Study: Kenya
7 Natural Resources
7.1.1 What are Rocks?
7.1.2 Types of Rock
7.1.4 The Rock Cycle - Weathering
7.1.5 The Rock Cycle - Erosion
7.1.6 What is Soil?
7.1.7 Soil Profiles
7.1.8 Water
7.1.9 Global Water Demand
7.2 Fossil Fuels
7.2.1 Introduction to Fossil Fuels
7.2.2 Fossil Fuels
7.2.3 The Global Energy Supply
7.2.5 What is Peak Oil?
7.2.6 End of Topic Test - Natural Resources
8.1 River Processes & Landforms
8.1.1 Overview of Rivers
8.1.2 The Bradshaw Model
8.1.3 Erosion
8.1.4 Sediment Transport
8.1.5 River Deposition
8.1.6 River Profiles: Long Profiles
8.1.7 River Profiles: Cross Profiles
8.1.8 Waterfalls & Gorges
8.1.9 Interlocking Spurs
8.1.10 Meanders
8.1.11 Floodplains
8.1.12 Levees
8.1.13 Case Study: River Tees
8.2 Rivers & Flooding
8.2.1 Flood Risk Factors
8.2.2 Flood Management: Hard Engineering
8.2.3 Flood Management: Soft Engineering
8.2.4 Flooding Case Study: Boscastle
8.2.5 Flooding Case Study: Consequences of Boscastle
8.2.6 Flooding Case Study: Responses to Boscastle
8.2.7 Flooding Case Study: Bangladesh
8.2.8 End of Topic Test - Rivers
8.2.9 Rivers Case Study: The Nile
8.2.10 Rivers Case Study: The Mississippi
9.1 Formation of Coastal Landforms
9.1.1 Weathering
9.1.2 Erosion
9.1.3 Headlands & Bays
9.1.4 Caves, Arches & Stacks
9.1.5 Wave-Cut Platforms & Cliffs
9.1.6 Waves
9.1.7 Longshore Drift
9.1.8 Coastal Deposition
9.1.9 Spits, Bars & Sand Dunes
9.2 Coast Management
9.2.1 Management Strategies for Coastal Erosion
9.2.2 Case Study: The Holderness Coast
9.2.3 Case Study: Lyme Regis
9.2.4 End of Topic Test - Coasts
10 Glaciers
10.1 Overview of Glaciers & How They Work
10.1.1 Distribution of Glaciers
10.1.2 Types of Glaciers
10.1.3 The Last Ice Age
10.1.4 Formation & Movement of Glaciers
10.1.5 Shaping of Landscapes by Glaciers
10.1.6 Glacial Landforms Created by Erosion
10.1.7 Glacial Till & Outwash Plain
10.1.8 Moraines
10.1.9 Drumlins & Erratics
10.1.10 End of Topic Tests - Glaciers
10.1.11 Tourism in Glacial Landscapes
10.1.12 Strategies for Coping with Tourists
10.1.13 Case Study - Lake District: Tourism
10.1.14 Case Study - Lake District: Management
11 Tectonics
11.1 Continental Drift & Plate Tectonics
11.1.1 The Theory of Plate Tectonics
11.1.2 The Structure of the Earth
11.1.3 Tectonic Plates
11.1.4 Plate Margins
11.2 Volcanoes
11.2.1 Volcanoes & Their Products
11.2.2 The Development of Volcanoes
11.2.3 Living Near Volcanoes
11.3 Earthquakes
11.3.1 Overview of Earthquakes
11.3.2 Consequences of Earthquakes
11.3.3 Case Study: Christchurch, New Zealand Earthquake
11.4 Tsunamis
11.4.1 Formation of Tsunamis
11.4.2 Case Study: Japan 2010 Tsunami
11.5 Managing the Risk of Volcanoes & Earthquakes
11.5.1 Coping With Earthquakes & Volcanoes
11.5.2 End of Topic Test - Tectonics
12 Climate Change
12.1 The Causes & Consequences of Climate Change
12.1.1 Evidence for Climate Change
12.1.2 Natural Causes of Climate Change
12.1.3 Human Causes of Climate Change
12.1.4 The Greenhouse Effect
12.1.5 Effects of Climate Change on the Environment
12.1.6 Effects of Climate Change on People
12.1.7 Climate Change Predictions
12.1.8 Uncertainty About Future Climate Change
12.1.9 Mitigating Against Climate Change
12.1.10 Adapting to Climate Change
12.1.11 Case Study: Bangladesh
13 Global Population & Inequality
13.1 Global Populations
13.1.1 World Population
13.1.2 Population Structure
13.1.3 Ageing Populations
13.1.4 Youthful Populations
13.1.5 Population Control
13.1.6 Mexico to USA Migration
13.1.7 End of Topic Test - Development & Population
14 Urbanisation
14.1 Urbanisation
14.1.1 Rural Characterisitcs
14.1.2 Urban Characteristics
14.1.3 Urbanisation Growth
14.1.4 The Land Use Model
14.1.5 Rural-Urban Pull Factors
14.1.6 Rural-Urban Push Factors
14.1.7 The Impacts of Migration
14.1.8 Challenges of Urban Areas in Developed Countries
14.1.9 Challenges of Urban Areas in Developing Countries
14.1.10 Urban Sustainability
14.1.11 Case Study: China's Urbanisation
14.1.12 Major UK Cities
14.1.13 Urbanisation in the UK
14.1.14 End of Topic Test- Urbanisation
14.1.15 End of Topic Test - Urban Issues
15 Ecosystems
15.1 The Major Biomes
15.1.1 Distribution of Major Biomes
15.1.2 What Affects the Distribution of Biomes?
15.1.3 Biome Features: Tropical Forests
15.1.4 Biome Features: Temperate Forests
15.1.5 Biome Features: Tundra
15.1.6 Biome Features: Deserts
15.1.7 Biome Features: Tropical Grasslands
15.1.8 Biome Features: Temperate Grasslands
15.2 Case Study: The Amazon Rainforest
15.2.1 Interdependence of Rainforest Ecosystems
15.2.2 Nutrient Cycling in Tropical Rainforests
15.2.3 Deforestation in the Amazon
15.2.4 Impacts of Deforestation in the Amazon
15.2.5 Protecting the Amazon
15.2.6 Adaptations of Plants to Rainforests
15.2.7 Adaptations of Animals to Rainforests
16 Life in an Emerging Country
16.1 Case Studies
16.1.1 Mumbai: Opportunities
16.1.2 Mumbai: Challenges
17 Analysis of Africa
17.1 Africa
17.1.1 Desert Biomes in Africa
17.1.2 The Semi-Desert Biome
17.1.3 The Savanna Biome
17.1.4 Overview of Tropical Rainforests
17.1.5 Colonisation History
17.1.6 Population Distribution in Africa
17.1.7 Economic Resources in Africa
17.1.8 Urbanisation in Africa
17.1.9 Africa's Location
17.1.10 Physical Geography of Africa
17.1.11 Desertification in Africa
17.1.12 Reducing the Risk of Desertification
17.1.13 Case Study: The Sahara Desert - Opportunities
17.1.14 Case Study: The Sahara Desert - Development
18 Analysis of India
18.1 India - Physical Geography
18.1.1 Geographical Location of India
18.1.2 Physical Geography of India
18.1.3 India's Climate
18.1.4 Natural Disasters in India
18.1.5 Case Study: The Thar Desert
18.1.6 Case Study: The Thar Desert - Challenges
18.2 India - Human Geography
18.2.1 Population Distribution in India
18.2.2 Urabinsation in India
18.2.3 The History of India
18.2.4 Economic Resources in India
19 Analysis of the Middle East
19.1 The Middle East
19.1.1 Physical Geography of the Middle East
19.1.2 Human Geography of the Middle East
19.1.3 Climate Zones in the Middle East
19.1.4 Climate Comparison with the UK
19.1.5 Oil & Natural Gas in the Middle East
19.1.6 Water in the Middle East
19.1.7 Population of the Middle East
19.1.8 Development Case Studies: The UAE
19.1.9 Development Case Studies: Yemen
19.1.10 Supporting Development in Yemen
19.1.11 Connection to the UK
19.1.12 Importance of Oil
19.1.13 Oil & Tourism in the UAE
20 Analysis of Bangladesh
20.1 Bangladesh Physical Geography
20.1.1 Location of Bangladesh
20.1.2 Climate of Bangladesh
20.1.3 Rivers in Bangladesh
20.1.4 Flooding in Bangladesh
20.2 Bangladesh Human Geography
20.2.1 Population Structure in Bangladesh
20.2.2 Urbanisation in Bangladesh
20.2.3 Bangladesh's Economy
20.2.4 Energy & Sustainability in Bangladesh
21 Analysis of Russia
21.1 Russia's Physical Geography
21.1.1 Russia's Climate
21.1.2 Russia's Landscape
21.2 Russia's Human Geography
21.2.1 Population of Russia
21.2.2 Russia's Economy
21.2.3 Energy & Sustainability in Russia
Jump to other topics

Unlock your full potential with GoStudent tutoring
Affordable 1:1 tutoring from the comfort of your home
Tutors are matched to your specific learning needs
30+ school subjects covered
Benefits of Tourism
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

KS3 Tourism - Impacts of tourism in Iceland
Subject: Geography
Age range: 11-14
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
15 July 2017
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Get this resource as part of a bundle and save up to 64%
A bundle is a package of resources grouped together to teach a particular topic, or a series of lessons, in one place.
KS3 GEOGRAPHY SOW - Tourism BUNDLE
My entire half-terms work for KS3 Tourism. Taught in the order of: 1\. The different types of tourism. 2\. UK tourism choropleth map. 3\. Why do tourists go to Blackpool? 4\. Mass Tourism. 5\. Positives and negatives of tourism in Blackpool. 6\. Improving Blackpool 7\. Tourism in an LIC: Kenya. 8\. Negative factors affecting tourism. 9\. Impacts of tourism in Iceland. 10\. Managing tourism in the Lake District (Potential for double lesson) No assessment for this work, but plenty of content available to create a short assessment if need be.
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
Resources you can trust
Impacts of Tourism

All reviews
Have you used this resource?
Resources you might like

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn about the positive and negative impacts of tourism and how it can be managed. KS3 Geography Tourism learning resources for adults, children, parents and teachers.
protected using income from tourism. The negative effects of tourism include: Tourism can have a negative environmental impact. This is at a range. of scales. The increase in air travel has contributed towards. increased carbon dioxide emissions. On a local level natural features. that attract tourists are themselves under threat due to human.
5 - What are the impacts of tourism in National Parks? 6 - Declining tourism in Britain 7 - History and tourism 8 - The impact of tourism 9 - Jobs in the tourist industry ... KS3 Human Geography - Tourism, Population & Settlement. 39 lessons for 3 core KS3 human geography topics. All lesson are suitable for 50 minutes to 1 hour of teaching time.
File. 21.35 KB. Download. File. 83.14 KB. Free download. This KS3 geography resource looks at the growth in tourism and the impacts this has had. Students represent the growth of world tourism using their graphical skills and then complete a categorising task identifying the benefits and problems of tourism.
Most suitable for KS3 geography. All lessons have a starter and lesson objectives. All PowerPoints in the same style. ... The impact of tourism 9 - Jobs in the tourist industry 10 - Ski resorts 11 - Tourism in Kenya 12 - Sustainable tourism 13 - Sustainable tourism in Peru 14 - Does tourism cause conflict? This unit of work was featured in the ...
Tourism can have positive economic effects on the receiving area. The receiving area is the place tourists go to on holiday (the destination, resort, city etc. that they stay at while away on holiday/vacation). ... KS3. KS3 Science Revision KS3 Maths Revision KS3 Geography Revision KS3 History Revision. GCSE. GCSE Biology Revision; GCSE ...
pptx, 1.32 MB. A clear and engaging lesson that introduces mass tourism and explores the impacts this can have on host countries. Lesson includes: A picture starter and discussion of the meaning of mass tourism. A brainstorm activity on why people might travel to Kenya. A statement-coding activity on the positive/negative impacts, and also the ...
Task 2 - Impacts of Tourism. Open the evidence board below. This shows you a global tourism growth graph from the year 1950 to the year 2020 (predicted and of course not considering Covid-19). You will see that tourism numbers can be calculated by global region. Be careful when you are reading it through as it is a cumulative graph and simply ...
pptx, 14.42 MB. pptx, 6.86 MB. Updated May 2024. This is a KS3 unit on leisure and tourism. It covers one half-term of lessons. Topics included: Introduction. Changing patterns. Growth factors.
A useful worksheet to help students identify and categorise the social, economic and environmental effects of tourism. Twinkl KS3 / KS4 Geography KS3 Geography - Full Collection Human Geography KS3 Tourism. travel and tourism tourism impact of tourism tourism geography economic activities ecotourism.
Tourism in Wales. KS 2 KS 3. Tourism is a very important part of the Welsh Economy. This is because: Tourists spend over £8 million a day in Wales - this adds up to around £3 billion a year! About 100,000 people in Wales are employed in the tourism industry. This accounts for nearly ten per cent of the workforce.
This resource is a scheme of work on Tourism for KS3 Geography. It includes: Growth of tourism Positive and negative impacts of tourism National Parks in the UK Tourism in Bath Tourism in Antarctica Advertising. All worksheets can be adapted. £1.00 - Download Complete Download. Write a Review ...
Tourism develops due to natural and man-made factors. It is a global issue with positive and negative effects. Responsible management can minimise the impact of tourism in the 21st century.
Introduction to tourism. This lesson was designed to introduce the tourism unit to year 8 students. It will help students to define tourism and explain why people go on holiday, with reference to culture, natural resources and entertainment. A complete lesson to define and introduce tourism, exploring why different people go on holiday.
A useful worksheet to help students identify and categorize the social, economic and environmental effects of tourism. Twinkl KS3 / KS4 Geography KS3 Geography - Full Collection Human Geography KS3 Tourism. tourism impact of tourism travel and tourism tourism geography sustainable tourism travel. ecotourism impacts of tourism interconnections ...
Innovations in transport has had huge impacts on tourism. Beginnings of tourism Tourism started with public baths that people relaxed in. Middle and upper class people would travel to these baths from the 1700s.
A lesson for the topic of Tourism. Ideal for years 7 to 9. Previously taught in a 1hr lesson. This lesson explores the HIC case of Iceland in Northern Europe. The lesson starter involves the pupils deciding on whether the image presented to them is either Greenland or Iceland. Later in the lesson the pupils will be dividing impacts of tourism ...
Tourism is influencing millions of peoples lives every day. What are the positive and negative impacts of tourism?#tourism #tourismindustry #travel #travelin...
They should then choose their top two advantages and disadvantages and give reasoned justifications. This KS3-4 geography resource helps students identify the positives and negatives of tourism on the host country. Students complete a sorting activity to help categorise them into social, economic and environmental impacts.