5 of the Best Ground Zero & 9/11 Memorial Tours
A solemn tour of the harrowing Ground Zero site is an essential way to pay your respects to those who tragically lost their lives on 9/11.

(Photo: Viator.com)
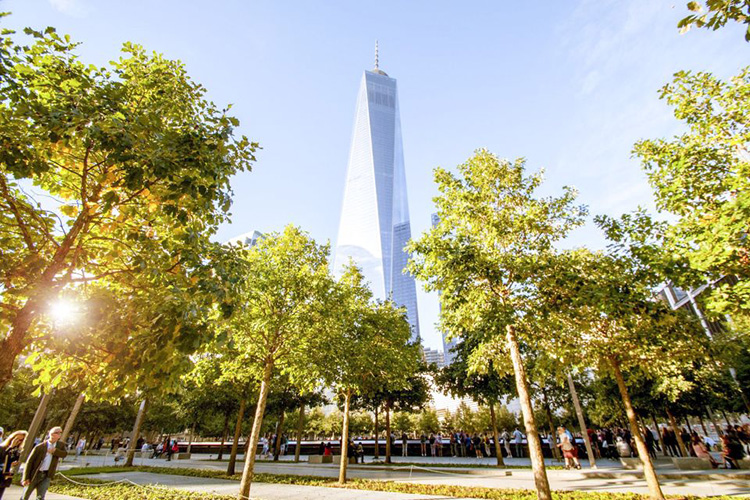
The 9/11 Memorial and Museum is a deeply moving and fitting tribute to the pain and suffering caused by the terrorist attacks on the World Trade Center. The site is located exactly where the Twin Towers once stood, the foundations now replaced with square reflecting pools amid clusters of swamp white oak trees and one Callery pear tree, known as the Survivor Tree; the only one to emerge from the rubble alive. Tours of the 9/11 Memorial and Ground Zero are often led by survivors, whose stories offer unparalleled insight and perspective.
NYC 9/11 Memorial & Museum Timed-Entry Ticket
The best low-cost way to explore Ground Zero is via this self-guided option, which includes a timed entry ticket to the 9/11 Museum. Here you can learn the story of that fateful day in depth alongside thousands of 9/11 artifacts ranged over three exhibitions, which include a timeline of events not just in New York, but at the Pentagon and on Flight 93, also. The Memorial Exhibition is a testament to the lives lost on that day, as well as those killed on February 26th, 1993 in that separate attack on the World Trade Center. From $18 per person.
Book at Getyourguide.com

(Photo: Getyourguide.com)
World Trade Center 911 and Ground Zero Walking Tour
If you’d prefer to explore Ground Zero with a local guide instead, there are a number of options available. There’s something far more profound and poignant about seeing this space through the eyes of those who lived through the events of 9/11. During this two-hour walk, you’ll discover the main sights, including the Reflecting Pools, One World Trade Center, and the Oculus, while hearing the stories of bravery and endurance. This tour runs Weds to Mon throughout the year. From $35 per person.
Book at Viator.com
Ground Zero 9/11 Memorial Tour
This walking tour is all about seeking the small landmarks around Ground Zero that tell the biggest stories. You’ll learn about the heroics of the emergency services at the Firefighter’s 9/11 Memorial and stop by St Paul’s Chapel, which was repurposed as a rescue center at the time. New Yorkers lead the tours and bring a passion and base of personal knowledge that would be missed by anybody who were to visit this site on their own. Tours run twice daily, usually at 10:30am and 1pm. From $39 per person.

Lower Manhattan Tour Wall Street & 9/11 Memorial
It’s possible to incorporate a visit to the 9/11 Memorial at Ground Zero into a broader walking tour of Lower Manhattan. This popular two-hour walking tour visits the 9/11 sites and Wall Street, exposing how this little region of the city played (and still plays) a significant role in world history. Other landmarks visited on this tour include the New York Stock Exchange, the Charging Bull and the final resting place of Alexander Hamilton at Trinity Church. This is a daily excursion and for $250, a private tour option is also available. From $39 per person.
9/11 Ground Zero Tour & Museum Preferred Access
If you are keen to experience Ground Zero as thoroughly as possible, then why not combine a guided walking tour of the 9/11 Memorial site with a timed entry ticket to the 9/11 Memorial Museum? Learn about lesser known facets of the rescue operation, for example Operation Aegis, in which 500,000 people were evacuated from Lower Manhattan by boat. Then skip the museum’s queues to explore the three exhibitions and the Foundation Hall, where the remaining column of the Twin Towers remains. From $79 per person.

Latest Articles
- A Comparison of Luxury & Boutique Hotels in Charlottesville September 6, 2024
- 5 of the Best Tours from Prague to Budapest September 6, 2024
- 7 Unique Things to Do in & around Soho September 6, 2024
- 7 Exhibitions to Visit in Washington DC this Fall September 5, 2024
- 5 Unique Day Tours from Helsinki September 5, 2024
National Geographic content straight to your inbox—sign up for our popular newsletters here

Dark tourism: when tragedy meets tourism
The likes of Auschwitz, Ground Zero and Chernobyl are seeing increasing numbers of visitors, sparking the term 'dark tourism'. But is it voyeuristic or educational?
Days after 71 people died in a London tower block fire last June, something strange started to happen in the streets around it. Posters, hastily drawn by members of the grieving community of Grenfell Tower, appeared on fences and lamp posts in view of the building's blackened husk.
'Grenfell: A Tragedy Not A Tourist Attraction,' one read, adding — sarcastically — a hashtag and the word 'selfies'. As families still searched for missing inhabitants of the 24-storey block, and the political shock waves were being felt through the capital, people had started to arrive in North Kensington to take photos. Some were posing in selfie mode.
"It's not the Eiffel Tower," one resident told the BBC after the posters attracted the attention of the press. "You don't take a picture." Weeks later, local people were dismayed when a coachload of Chinese tourists pulled up nearby so that its occupants could get out and take photos.
Grenfell Tower, which still dominates the surrounding skyline (it's due to be demolished in late 2018), had become a site for 'dark tourism', a loose label for any sort of tourism that involves visiting places that owe their notoriety to death, disaster, an atrocity or what can also loosely be termed 'difficult heritage'.
It's a phenomenon that's on the rise as established sites such as Auschwitz and the September 11 museum in Manhattan enjoy record visitor numbers. Meanwhile, demand is rising among those more intrepid dark tourists who want to venture to the fallout zones of Chernobyl and Fukushima, as well as North Korea and Rwanda. In Sulawesi, Indonesia, Western tourists wielding GoPros pay to watch elaborate funeral ceremonies in the Toraja region, swapping notes afterwards on TripAdvisor.
Along the increasingly crowded dark-tourist trail, academics, tour operators and the residents of many destinations are asking searching questions about the ethics of modern tourism in an age of the selfie and the Instagram hashtag. When Pompeii, a dark tourist site long before the phrase existed, found itself on the Grand Tour of young European nobility in the 18th century, dozens of visitors scratched their names into its excavated walls. Now we leave our mark in different ways, but where should we draw the boundaries?
Questions like these have become the life's work of Dr Philip Stone , perhaps the world's leading academic expert on dark tourism. He has a background in business and marketing, and once managed a holiday camp in Scotland. But a fascination with societal attitudes to mortality led to a PhD in thanatology, the study of death, and a focus on tourism.
"I'm not even a person who enjoys going to these places," Stone says from the University of Central Lancashire, where he runs the Institute for Dark Tourism Research. "But what I am interested in is the way people face their own mortality by looking at other deaths of significance. Because we've become quite divorced from death yet we have this kind of packaging up of mortality in the visit economy which combines business, sociology, psychology under the banner of dark tourism. It's really fascinating to shine a light on that."
Historical roots
The term 'dark tourism' is far newer than the practice, which long predates Pompeii's emergence as a morbid attraction. Stone considers the Roman Colosseum to be one of the first dark tourist sites, where people travelled long distances to watch death as sport. Later, until the late 18th century, the appeal was starker still in central London, where people paid money to sit in grandstands to watch mass executions. Hawkers would sell pies at the site, which was roughly where Marble Arch stands today.
It was only in 1996 that 'dark tourism' entered the scholarly lexicon when two academics in Glasgow applied it while looking at sites associated with the assassination of JFK. Those who study dark tourism identify plenty of reasons for the growing phenomenon, including raised awareness of it as an identifiable thing. Access to sites has also improved with the advent of cheap air travel. It's hard to imagine that the Auschwitz-Birkenau memorial and museum would now welcome more than two million visitors a year (an average of almost 5,500 a day, more than two-thirds of whom travel to the Polish site from other countries in Europe) were it not for its proximity to Krakow's international airport.
Peter Hohenhaus, a widely travelled dark tourist based in Vienna, also points to the broader rise in off-the-beaten track tourism, beyond the territory of popular guidebooks and TripAdvisor rankings. "A lot of people don't want mainstream tourism and that often means engaging with places that have a more recent history than, say, a Roman ruin," he says. "You go to Sarajevo and most people remember the war being in the news so it feels closer to one's own biography."
Hohenhaus is also a fan of 'beauty in decay', the contemporary cultural movement in which urban ruins have become subject matter for expensive coffee-table books and a thousand Instagram accounts. The crossover with death is clear. "I've always been drawn to derelict things," the 54-year-old says. As a child in Hamburg, he would wonder at the destruction of war still visible around the city's harbour.
That childhood interest has developed into an obsession; Hohenhaus has visited 650 dark tourist sites in 90 countries, logging them all and more besides on his website . He has plans to put together the first dark tourism guidebook. His favourite holiday destination today is Chernobyl and its 'photogenic' ghost town. "You get to time travel back into the Soviet era but also into an apocalyptic future," he says. He also enjoys being emotionally challenged by these places. "I went to Treblinka in 2008 and heard the story of a teacher at an orphanage in Warsaw who was offered a chance to escape but refused and went with his children to the gas chambers. Stories like that are not everyday, you mull over them. Would you have done that?"
But while, like any tourism, dark tourism at its best is thought-provoking and educational, the example of Grenfell Tower hints at the unease felt at some sites about what can look like macabre voyeurism. "I remember the Lonely Planet Bluelist book had a chapter about dark tourism a while ago and one of the rules was 'don't go back too early'," Hohenhaus says. "But that's easier said than calculated. You have to be very aware of reactions and be discreet when you're not in a place with an entrance fee and a booklet." Hohenhaus said he had already thought about Grenfell Tower and admits he would be interested to see it up close. "It's big, it's dramatic, it's black and it's a story you've followed in the news," he says. "I can see the attraction. But I would not stand in the street taking a selfie."
A mirror to mortality
An urge to see and feel a place that has been reduced to disaster shorthand by months of media coverage is perhaps understandable, but Stone is most interested in the draw — conscious or otherwise — of destinations that hold up a mirror to our own mortality. "When we touch the memory of people who've gone what we're looking at is ourselves," he says. "That could have been us in that bombing or atrocity. We make relevant our own mortality." That process looks different across cultures — and generations — and Stone says we should take this into account before despairing of selfie takers at Grenfell Tower or Auschwitz.
"I've heard residents at Grenfell welcoming visitors because it keeps the disaster in the public realm, but they didn't like people taking photos because it's a visual reminder that you're a tourist and therefore somehow defunct of morality," he explains. "We're starting to look at selfies now. Are they selfish?" Stone argues that the language of social media means we no longer say "I was here", but "I am here — see me". He adds: "We live in a secular society where morality guidelines are increasingly blurred. It's easy for us to say that's right or wrong, but for many people it's not as simple as that."
"Travel itself is innately voyeuristic," argues Simon Cockerel, the general manager of Koryo Tours , a North Korea specialist based in Beijing. Cockerel, who has lived in China for 17 years and joined Koryo in 2002, says demand has grown dramatically for trips to Pyongyang and beyond, from 200 people a year in the mid 1990s, when the company started, to more than 5,000 more recently. He has visited the country more than 165 times and says some clients join his tours simply to bag another country, and some for bragging rights. But the majority have a genuine interest in discovering a country — and a people — beyond the headlines.
"I've found everyone who goes there to be sensitive and aware of the issues," he says. "The restrictions do create a framework for it to be a bit like a theme park visit but we work hard to blur those boundaries. More than 25 million people live in North Korea, and 24.99 million of them have nothing to do with what we read in the news and deserve to be seen as people not as zoo animals or lazy caricatures."
More challenging recently has been the US ban on its citizens going to North Korea, imposed last summer after the mysterious death of Otto Warmbier. The American student had been arrested in Pyongyang after being accused of trying to steal a propaganda poster. Americans made up about 20% of Koryo's business, but Cockerel argues the greater loss is to mutual perception in the countries. "The North Korean government represent Americans as literal wolves with sharpened nails," he says. "At least a few hundred Americans going there was a kind of bridgehead against that. Now that's gone."
At Grenfell Tower, responsible tourism may yet serve to keep alive the memory of the disaster, just as it does, after a dignified moratorium, at Auschwitz and the former Ground Zero. Hohenhaus says he will resist the urge to go until some sort of memorial is placed at the site of the tower. At around the time of a commemorative service at St Paul's Cathedral six months after the fire, there were calls for the site eventually to be turned into a memorial garden. The extent to which Hohenhaus and other dark tourists are welcomed will be decided by the people still living there.
Five of the world's dark tourism sites
1. North Korea Opened to visitors in the late 1980s, North Korea now attracts thousands of tourists each year for a peek behind the headlines.
2. Auschwitz-Birkenau The former Nazi death camp became a memorial in 1947 and a museum in 1955. It's grown since and in 2016 attracted a record two million visitors.
3. 9/11 Memorial and Museum Built in the crater left by the twin towers of the World Trade Center, the museum, opened in 2014, has won plaudits for its portrayal of a disaster and its impact.
4. Rwanda Visitor numbers to genocide memorials have grown in Cambodia and Bosnia as well as in Rwanda, where there are several sites dedicated to the 1994 massacre of up to a million people. The skulls of victims are displayed.
5. Chernobyl & Pripyat, Ukraine Several tour companies exist to send visitors to the exclusion zone and ghost town left otherwise empty after the nuclear accident in 1986. All are scanned for radiation as they leave.
Published in the March 2018 issue of National Geographic Traveller (UK)
Find us on social media
Facebook | Instagram | Twitter
Related Topics
- EDUCATIONAL TRAVEL
- CULTURAL TOURISM
- HISTORY AND CIVILIZATION
You May Also Like

An insider's guide to Denver, Colorado's wildly creative capital

They inspire us and teach us about the world: Meet our 2024 Travelers of the Year
Become a subscriber and support our award-winning editorial features, videos, photography, and much more..
For as little as $2/mo.

10 reasons to visit the East Coast in 2024

An architectural tour of the Georgian capital, Tbilisi

7 of the UK's best gallery cafes

A long weekend in Orkney

How to plan a walking tour of Glasgow in the footsteps of Charles Rennie Mackintosh
- Environment
- Paid Content
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
- Church of Wisdom and Healing: Aya Sophia
- Glamorous Harem: Topkapi Palace
- Live the real Crocodile Dundee in Kakadu Park
- Hammam Turkish Bath – The Art of Relaxation
- The Larapinta Trail

Ground Zero & the phenomena of ‘Dark Tourism
History facts.
Where: Manhattan, New York, USA When: 2001 History: Site of the former World Trade Center, destroyed in a terrorist attack, now attracting twice as many visitors as a memorial space in construction
Born from a ‘Day of Terror’
In 2002, the ruins of the World Trade Center in New York attracted 3.6 million visitors; the observation deck from the intact towers used to pull in an average of 1.8 million tourists per year. ‘Ground Zero’ as the site became known in the aftermath of the terrorist attacks on September 11 2001 appears to be the newest, most unlikely tourist attraction in the Big Apple.
Within months of the attacks the area became the latest home of sightseers and hawkers; around the site’s perimeter all manner of souvenirs, from Ground Zero NYC T-shirts and baseball caps to ‘Day of Terror’ commemorative books and DVD montages of the disaster are available. There’s even a big line in Osama bin Laden printed toilet paper feeding into people’s anger against the supposed terrorist mastermind. Tour guides lead groups around the site, pointing out places like the spot where fire fighters erected the American flag in rubble.

Photo of the 9/11 memorial taken from the World Financial Center, as it appeared in June 2012, photo by Cadiomals
Other ‘dark tourism’ sites
But is this really such a surprising phenomenon? Across the world there are lots of sites of human depravity which attract visitors. Auschwitz in Poland was listed a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1979; it’s mandatory for all German schoolchildren to visit during their education and it’s virtually an Israeli right-of-passage to visit this Nazi extermination camp. The Killing Fields of Pol Pot’s genocidal regime in Cambodia are drawing more and more tourists and Hiroshima in Japan (where the Allies dropped the atomic bomb that ended World War II in the east) is also on the tourist trail.
Within the United States itself there are already several tourist destinations defined by tragedy. The Sixth Floor Museum in Dallas’ former Texas Book Repository is one such place. It opened 26 years after gunman Lee Harvey Oswald shot President Kennedy from a sixth-floor window there – it has since become the city’s biggest attraction, with 450,000 people a year. Ford’s Theater , where President Lincoln was assassinated, the museum in the Lorraine Motel in Memphis where Dr Martin Luther King was shot and Pearl Harbour are all historic memorial sites.
Therapy or morbid obsession?
Because of the cataclysmic effect 9/11 had on the American psyche and the shockwaves it had across the world, this latest manifestation of disaster tourism has brought the whole issue into sharp relief. Papers in the States have been full of articles debating its moral validity and the New York tourist board has found it hard to approach its newest attraction, conscious of the need not to appear to be capitalising on the tragedy. Opinions differ radically; for some it’s like slowing down to look at a crash site – like September’s Mission (a victims’ families advocacy group) who called the vendors near the site and their customers ‘unbelievably sick’. Residents near the site, finding it hard to recover from the trauma anyway, feel that the throngs of tourists are intruding on their community. Others however, see it as a legitimate part of the national grieving process – a form of therapy. Others still, see it as the ultimate example of the American habit of commodification at work – like the authors of ‘Dark Tourism’ who suggest that it’s a typically westernised response to horror.
The question of its legitimacy are tied up in questions of memory, trauma and politics. In fact, it’s something that hasn’t really been seriously addressed until now. What is certain is that ‘dark tourism’ isn’t a new phenomenon – the violent death of the British Archbishop of Canterbury in the town’s cathedral in the twelfth century attracted throngs of people to the site. Perhaps they were pilgrims or perhaps it was morbid curiosity. With such a long history, it’s safe to say, whether you like it or not, dark tourism is here to stay.
MORE INFORMATION
Enter Ground Zero A dedication to the men and women at World Trade Center ground zero.
By Kate Griffiths
- Globe Trekker turns 25…. and is still travelling!
- Kalash Festival of Choimus
You May Also Like

The Most Spectacular Show on Earth: Masai Mara

World’s Deadliest Plagues

The Medieval Cave City of Vardzia, Georgia

- Social Justice
9/11 Memorial: Ground Zero as Dark Tourist Site
New York’s ground zero, where the World Trade Center’s Twin Towers once stood, is a place of what was and what will be. Ten years after terrorists flew planes into the buildings, the memories of what had been are fading into the dust of time and new construction.
Chaos mixes with normality, pilings are driven into the ground, steel clatters as new structures rise. Bicyclists whiz past briefcase-toting commuters, both groups oblivious to curious onlookers straining to see through slits in the construction fences. These are the ground zero pilgrims, numbering daily in the thousands, many never having seen the towers when they existed.
As a New Yorker, I have my own memories of the towers and their destruction — from my sister having the good fortune of running late for work that morning at the World Financial Center across the street, to four days later, photographing and working on a ground zero cleanup crew with my then-brother-in-law, a New Jersey police officer. This was my first time — and last, I hope — digging for dead bodies in rubble, in what was in essence a war zone within my own city.
The experience vastly altered the direction of my travel writing — inspiring me to cover culture and tourism within the war zones the U.S. found itself in soon after — Afghanistan and Iraq — along with other countries in and out of conflict across the globe. Virtually every Sept. 11, I return to ground zero and photograph crowds. Last year, tension over the planned construction of Park51 , the nearby Muslim community center, offered engaging photographic opportunities, demonstrating how ground zero remains a volatile touchpoint for many Americans.
Still, while the location and its associations have long pulled me back, I had never given much thought to how tourists visit ground zero and learn the stories of Sept. 11.
To visit New York’s ground zero is clearly a different experience from Times Square or Central Park. It is what is called “thanatourism,” or “death” or “dark” tourism — the visiting of sites associated with death. It’s a relatively new field of tourism research, but the idea has long been with us. Perhaps the most famous dark tourism site is Poland’s Auschwitz , where the Nazis murdered hundreds of thousands of Jews and others. In the United States, they include now deceptively tranquil battlefields, such as Gettysburg , or the wave-lapped U.S.S. Arizona Memorial in Pearl Harbor.

Dark tourism, says New York University professor Brigitte Sion , is “about going to a place where something terrible happened, usually mass death.”
While the idea of hallowing ground where many people or particularly important people have perished is ancient, formal academic study of dark tourism began with British researchers John Lennon and Malcolm Foley , who published the 2000 book Dark Tourism . In April 2010, the Dark Tourism conference was held at NYU, organized by Sion and sponsored by Transitions, A Center for International Research in the Humanities and Social Sciences . Sept. 11 was an important focus at the conference, which drew academics from a variety of fields. Sion explained, “Dark tourism is important for academia because it offers interdisciplinary analysis — not only for scholars of tourism, hospitality or hotel management, but to sociologists, anthropologists, art historians, historians, media analysts, memory experts and many others.”
Conference attendees lectured on sites in Argentina, Chile, Vietnam, the United States, Europe and other locations. As an adjunct professor at NYU, I presented on Halabja in Kurdish Iraq, the site of a memorial museum commemorating the nearly 5,000 people who died in a 1988 chemical bombing ordered by Saddam Hussein. Survivors serve as guides, and the structure reminds young Kurds what the older generation endured before the creation of the no-fly zone after the first Gulf War. The memorial also has a political purpose: It’s an indirect plea to the global community explaining that Kurds, the world’s largest ethnic group without a homeland, have suffered vast indignities and deserve independence.
Multiple meanings for monuments associated with death are common. Sion, who is writing her own dark tourism book, says such sites face issues from becoming centers for political celebration, as happened at ground zero with Osama bin Laden’s death , to sanitizing events. “One of the big issues that the 9/11 memorial is facing is the fear that the museum displays might traumatize or re-traumatize visitors,” she says.
Because of this, she explains, “the architecture of absence is now the model” for most dark tourism sites.
Absence is clearly an overriding draw of ground zero, the emptiness representing the physical destruction of two 110-story structures, once the world’s most recognizable skyscrapers.
The National September 11 Memorial and Museum , with its two separate but linked features, marks this absence and gives visitors an idea of what has been lost.
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
Seven stories underground, in what had been the foundation of the Twin Towers, I’m standing with Clifford Chanin , senior program adviser and acting director of education for the 9/11 memorial. Sporting hard hats with the museum’s logos, we’ll see granite-encased steel beams resembling ancient castle ruins, the concrete slurry wall that once held back the Hudson, even the rusted steel squares that anchored the buildings into Manhattan’s ancient bedrock.
Chanin looks at the dust-filled space surrounding us, the din of the equipment above muffled by the endless concrete. “The museum architecture is going to be the unexpected discovery of the visit. I don’t think people will realize until they get here how the volume of the towers is encompassed.”
When the museum opens on Sept. 11, 2012, it will hold 120,000 square feet of exhibition space under the eight acres once occupied by the Twin Towers and their plaza. Some 1,500 visitors an hour are expected once it’s in operation. The memorial — two black squares in the footprints of the towers — is expected to open this Sept. 11.
Those black squares are reverse fountains — water flowing down into the ground, edges marked with the names of the nearly 3,000 killed.
Chanin gestures beyond my shoulder to an enormous square jutting from the ceiling. It’s still unfinished, wiring and other construction bits still hanging from it. These are the continuations of the pools above us.
“The intent is to create this hovering presence of the towers in the museum,” Chanin says, asking me to look around two corners. They seem to go on forever in the dim underground lighting, a rippling sheen from metal framework marking its dimensions. “That is essentially the length of the Twin Towers,” he says, his arms outstretched. It tugs at my memory, but I recall not the building’s exterior but the vast lobby — a modern, brilliantly lit space covered in white stone, metal and glass, a 1970s Space Odyssey cathedral.
Chanin continues, “This will give some sense of what it is, what was lost .” Here, underground, more than in the daylight at the black pools, I feel the buildings. Near where we are standing, Chanin tells me a quote from Virgil’s Aeneid will be posted: “No day shall erase you from the memory of time.”
Perhaps nothing brings the Twin Towers and their destruction more to life than a visit with those who once worked in them.
On a warm Saturday before Father’s Day, I join 20 visitors for a ground zero tour with Chris Hardej . A jolly, 51-year-old Brooklyn native with a thick accent, he’s palpably excited. We’ve all met at the Tribute WTC Visitor Center , also a mix of memorial and museum, this one started on the fifth anniversary of 9/11 by the families of those who were killed. So far, it’s been seen by more than 2.2 million visitors.
“People went around the site and needed information,” Hardej tells us. “There are people with direct connections to 9/11, whether they be retired firefighters, somebody who lives in the neighborhood, somebody who was a volunteer, or even someone who survived 9/11. And what the Tribute Center does is it brings both of us together, such that it keeps the memory of 9/11 alive.”
Our group is largely from the South; a few are children. “How many people actually saw the Twin Towers prior to Sept. 11?” Hardej asks. Just a few raise their hands.
Hardej brings working at the towers to life, even joking about the sway of toilet water in the bathrooms of Tower 1’s 82nd floor, where he worked for the New York Metropolitan Transportation Council . He talks about the underground shopping complex and the lobby’s airline ticket counters, prompting my own flood of memories.
He pauses. “You really don’t know what you’re missing until obviously you don’t have that place to work anymore.” Here he begins to tell us about that day — the feel of the planes hitting the towers, the expressions of the firefighters as they move up the emergency stairwells while Hardej and his co-workers move down. He talks about a woman burned, “coming down like a mummy,” and how his boss grabbed her, making her scream in pain.
It’s here that the audience begins to understand. They are mesmerized, ground zero in view behind Hardej through an enormous glass window of the World Financial Center. Hardej’s neck and face redden, his voice stumbling, as he says, “We saw a sight that you really don’t see: one tower,” and then, how it falls. “That’s the last I saw of the towers … I was the last from my office to make it out of the complex,” and then he breaks down. One visitor is in tears.
Hardej hands us to Mia Robello , his co-tour guide, a Manhattan native who slightly resembles the late actress Suzanne Pleshette , both in looks and voice. A schoolteacher, she volunteered with the Salvation Army for eight-and-a-half months. Her recollection of her final day, when the last supporting beam was removed from ground zero, soothes the visitors, giving a sense of closure.
Hardej and I walk back together to the Tribute WTC Center. “I was always willing to share my story,” he tells me. It’s a form of therapy, true, but he also doesn’t want Sept. 11 “pushed into the background, and I am afraid of that. That’s why I do these tours — to keep the memory alive.” He worries the museum will displace the experience tourists have with survivors.
Until the museum opens, the Tribute WTC Center offers the most immediate connection to that day. It is a project of the September 11th Families’ Association , an organization begun in November 2001. Lee Ielpi , who lost a son on 9/11 (and looks like he could be former Mayor Rudolph Giuliani ‘s little brother), is president of the association’s board of directors and co-founder of the Tribute WTC Visitor Center.
Ielpi guides me, helping me understand the center.
The explanatory panels are 22 inches wide, like the Twin Tower windows. A wall within the center is a beautiful sky blue, evoking the morning of Sept. 11. As patrons walk along, the wall becomes obscured by hundreds of missing-person posters. Display cases are quite visceral: One features a debris-encrusted stuffed bunny and patches from firemen’s turnouts. Ielpi’s son Jonathan was a firefighter who died in the collapse of the towers, and his recovered jacket has its own case. Lee, a retired FDNY firefighter, helped recover remains at the site for nine months, including the body of his son . Next to Jonathan’s jacket is a piece of twisted steel, a beam isolated within a photographic background of the debris.
I tell Ielpi it gives the impression of standing in the rubble. He grasps the beam for several seconds, silently looking forward. “People like to put their hands here. Notice how smooth it is here,” he finally says. It’s a way for visitors to make real what happened, to physically touch a piece of the Twin Towers.
Soon we reach an inner sanctum at the Tribute WTC Center — what Ielpi calls the Family Room, where photographs and other objects have been donated by family members. It reminds me of a space planned within the Memorial Museum. The concepts are similar: photos and objects; a one-minute bio at the museum; a name briefly held on screen here. Ielpi tells me this area is the most emotional for visitors, pointing to a young woman crying. We talk about the problems of tourists becoming immune to emotion as time passes, but it is not something he fears. He tells me that when he poses with tourists, “they start to smile because that is what we do in photographs, but then they remember where they are.”
Jan Seidler Ramirez , chief curator and director of collections for the September 11 Memorial Museum, gave an idea of the challenges of formalizing the presentation and impact of that day’s events.
“It’s a really tough line we’re trying to navigate here. We don’t want to intentionally traumatize people. We don’t want to also create a situation where they shut down because they are in compassion overload,” she says. One way to show more difficult aspects of the day is through separated alcoves, where Ramirez explains, “you can make a choice: You can walk in if you like, or you can walk past it.”
One alcove will be used for a more controversial display: photographs of people jumping from windows . Ramirez explains the presentation will be a “quiet, solemn space,” adding, “A lot of the experience in this alcove actually would be reading the quotes, the incredible way that people who were on the streets processed what they were seeing that day.” In this way, she says, “it moves the story from the people that jumped to the people that witnessed it.”
Ramirez says that her own first taste of dark tourism came as a child visiting Deerfield, Mass . She was fascinated by hatchet marks meant to represent the Deerfield Massacre of 1704 , when 56 English settlers were killed by French and Indian forces. Even then, she says, she understood it “is these sites of dark tourism that provide this necessary jolt to make us look and think more deeply about our capacity for harm and for hurting one another.”
For this reason, Ramirez does not believe the events of Sept. 11 should be sanitized for visitors. The events are a “complex story that I hope is not being artificially tidied up and wrapped with a nice bow for them. We wanted to provoke and stimulate thought.”
After 10 years, Ramirez believes, “people have forgotten already. Everyone has heard of Sept. 11; they don’t have the sense of it.” Moreover, she says for many visitors coming to ground zero now, Sept. 11 is “just a bumper-sticker word to them, and that’s pretty scary.
“There will be more terrorists in the world; that is one thing we know,” Ramirez adds. A goal of the museum is that, by focusing on the victims, visitors will be reminded “that most people are charitable, decent, courageous, kind, ingenuous, brilliant, all told over time. And it’s borne out in many of the stories of 9/11 and the legacy of 9/11.”
Memory as people, then, not objects or buildings.
Sion tells me these notions are at the heart of why academics study such places. Dark tourism sites stand “at the nexus of history,” she says, and their memorials combine “death, architecture and design, mass media, education, politics, leisure and economy.” Ultimately, once both the September 11 memorial and its adjacent museum have opened, she explains they will speak “to human emotions about war, death, remembrance, spectacle and others.”
The memorial and the museum, along with the Tribute WTC Center, will be ways for us to remember and to honor the events of that day – and in some ways, perhaps, to fold them back into the past as we subconsciously move on with each passing anniversary, the day itself fading as a living memory.
Sign up for the free Miller-McCune.com e-newsletter.
“Like” Miller-McCune on Facebook.
Follow Miller-McCune on Twitter.
Add Miller-McCune.com news to your site.

- Magazine Feature Story
- September-October 2011
Related Posts
The new york times and a mistaken infant mortality trend.

Does a Nation’s Wealth Fuel Terrorism?
The 30 top thinkers under 30: jared aldwin crooks.
- Attractions
- Restaurants
- Sample Sales
- Things to Do
- Trip Reports
- Print NYC Guide
- NYC Coupons
- NYC on a Budget
- Free in NYC
- Events & Holidays
- + Add Event
- +Get Listed
9-11 Memorial and Museum
9/11 memorial.
- Insider Tips
- Tours and Discount Passes
- 9/11 Memorial Museum
- Photo Gallery
Visiting the Ground Zero 9/11 Memorial
- As of May 2014, the 9-11 Memorial no longer requires a visitor pass or reservation. More: 911memorial.org
- If you are visiting the 9/11 Memorial Museum , a ticket is required.
- Print your maps in advance telling you the location of names (first responders, flight victims, WTC workers, etc).
- Allow 1.5 to 2 hours for a complete visit.
- Be prepared to show your identification and go through a security screening.
- Plan to spend at least an hour at the Memorial. Even if you’re not a "typical tourist," there is so much to absorb and process.
- Consider a guided 9-11 Memorial Tour , if you are interested in a personal guided tour or want to combine a 9-11 Memorial visit with other downtown sightseeing options, such as Wall Street and the Statue of Liberty.
Visiting 9/11 Memorial and Museum Quick Facts
- The 9/11 Memorial was dedicated on the 10th anniversary of 9-11 (September 11, 2011) and opened to the public on 9-12-11
- The Preview Site, at 20 Vesey Street (2 blocks from the Memorial) provides visitors with information about the 9/11 Memorial, the National September 11 Memorial & Museum and World Trade Center redevelopment.
- The 9/11 Memorial Museum opened May 21, 2014
- The New World Trade Center Towers include One World Trade Center (formerly the Freedom Tower), and WTC 2 through 7
About the 9/11 Ground Zero Memorial
Birthday remembrance at the 9-11 memorial, 9/11 memorial photo gallery, 9-11 memorial downtown nyc tours and nyc passes, boutique downtown hotels new york.
- Frederick Hotel - one of NYC's best lesser know hidden gems
- Moxy NYC Downtown - 30 stories, local coffee program, arcade games, DJ and a basketball court
- The Artezen Hotel - high-tech suites, yoga & fitness center + HIDE, a swanky, two-story sky lounge (photo)
The 9/11 Memorial Museum (May 2014)
The 9/11 tribute museum, directions to the 9-11 memorial and wtc.
- A, C, 1, 2, 3 to Chambers Street
- A, C, J, Z, 2, 3, 4, or 5 trains to Fulton Street
- 2 or 3 trains to Park Place
- E train to World Trade Center
- R to Cortland Street or Rector St
- 1 to Rector St
About the New World Trade Center Towers
9-11 museum store, anniversary of 9-11-01 special events, 9-11 memorial more info.
- Address: 80 Greenwich St, New York, NY 10006
- 9-11 Memorial Tours
- Nearby: Wall Street , Financial District , One World Observatory NYC , Statue of Liberty , Battery Park City , City Hall, South Street Seaport
Most Popular Ticketed Tourist Attractions
- Empire State Building
- Statue of Liberty Museum
- Broadway Shows
- Madame Tussauds
- Circle Line Cruise
- One World Observatory
- Top of the Rock
- 9-11 Museum
Free NYC Tourist Attractions
- Central Park
- Grand Central Terminal
- Statue of Liberty Island
- Times Square
- Rockefeller Center
- Bryant Park
- Lincoln Center
- The Highline
- Brooklyn Bridge
- St. Patrick's Cathedral
- Wall Street/Charging Bull
- NYC Museums FREE Days and Times
New York City Museum Guides
- All NYC Museum Guides
- NYC Museums FREE Days Download Chart
- Metropolitan Museum of Art
- 9-11 Memorial & Museum
- Museum of Natural History
- Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum
- Museum at Eldridge Street
- Whitney Museum of American Art
Museum Sleepovers NYC
- Itinerary: Art Lovers Tour of NYC Museums
- NYC Tourist Attractions
- 9-11 Memorial
RELATED ARTICLES
Visiting the bronx zoo, nyc attractions pass discounts.
looking for walking map of 9/11
Hi Rosemary – if you are referring to the maps that show the locations of names (first responders, flight victims, WTC workers, etc), please see the 9-11 Memorial Site.
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of followup comments via e-mail. You can also subscribe without commenting.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Site Sponsors
The escape game manhattan, nyc group transportation – taking the stress out, group transportation in nyc with national charter bus, site sponsorship, recent posts, annual african american day parade – nyc events september, september new york city concerts and shows, celebs on broadway | r. downey jr, idina, j. parsons, g..., annual bushwick film festival october, the escape game | manhattan escape room, solve puzzles, hotel deals, cheap hotels in midtown west nyc, july 4th in new york city fireworks, best new york marathon hotels, best us tennis open hotels, romantic new york city hotels, new york giants schedule and tickets 2024, new york city events august, nyc concerts shows august, us tennis open tickets * aug 26-sept 8, 2024.
- NYC Restaurant Week
GMA Summer Concert Series
Fall in nyc, new york city events november, new york city events october, new york city events september, new york mets schedule & tickets, new york yankees tickets, fun things to do in new york in fall, macys thanksgiving parade hotel, brooklyn nets tickets schedule, new york rangers tickets 2023-24, popular nyc events, nyc concerts shows september, broadway week * sept 3-15, 2024, latest news, celebs on broadway | r. downey jr, idina, j. parsons, g clooney, denzel ++, new york city events september activities calendar, fall broadway week 2 for 1 tickets on sale, broadway week ticketmaster shows announced, nyc holidays.
- NYC Broadway Week
- Valentines Day in New York City
- Mother’s Day
- Memorial Day NYC
- July 4th NYC
- US Tennis Open
- Labor Day NYC
- Rockettes Christmas Spectacular
- Thanksgiving Day & Parade
- Thanksgiving Parade Hotel
- Thanksgiving Dinner
- Rockefeller Center Christmas Tree
- Christmas in New York City
- New Years Eve
- Ball Drop New Years Eve NYC Hotels
NYC Things to Do
- Things to Do in NYC
- Sample Vacations
Welcome to the NYC Insider Guide . Please enjoy our Insider tips, free maps, where to spend and save your money, secret ways of getting discounts and most importantly, what to book NOW so you don’t miss out! - All the Best, Melissa
© 2008-2024 NYC INSIDER GUIDE , LTD ™. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. CONTENT PROTECTED BY DMCA.
- NYC Travel Itineraries
- Advertising
- Site Policies
This website uses cookies to improve your browsing experience and analyze the use of the website. Learn More

9/11 Memorial and World Trade Center

In this post, we cover the National September 11th Memorial, also known as the 9/11 Memorial.
We provide a map of the memorial and the related sights in the World Trade Center as a whole.
This post has been written with first-hand experience.
We lead daily walking tours, taking visitors to NYC through Ground Zero and the 9/11 Memorial.
Most of our tour guides experienced the World Trade Center before the attacks and this has helped us provide valuable perspective
We also cover hours, security, and other planning tips, including tours you can take, and nearby attractions you may want to see.
- Self-Guided Tour
- Plan Your Visit
- Visiting the 911 Museum
SELF-GUIDED TOUR OF THE 9/11 MEMORIAL AND WORLD TRADE CENTER
The 9/11 Memorial is inside a large public plaza and can be easily accessed from the surrounding streets.
It is open to the public daily from 10 am - 5 pm. There is no cost to visit Ground Zero.
The plaza is sparse and serene. Its openness helps emphasize the focal point of the Memorial which is the Reflecting Pools.
You could also download a more extensive version of this tour as a GPS-enabled audio tour , that was researched, written and recorded by one of our tour guides.
Click on the map for a larger interactive version
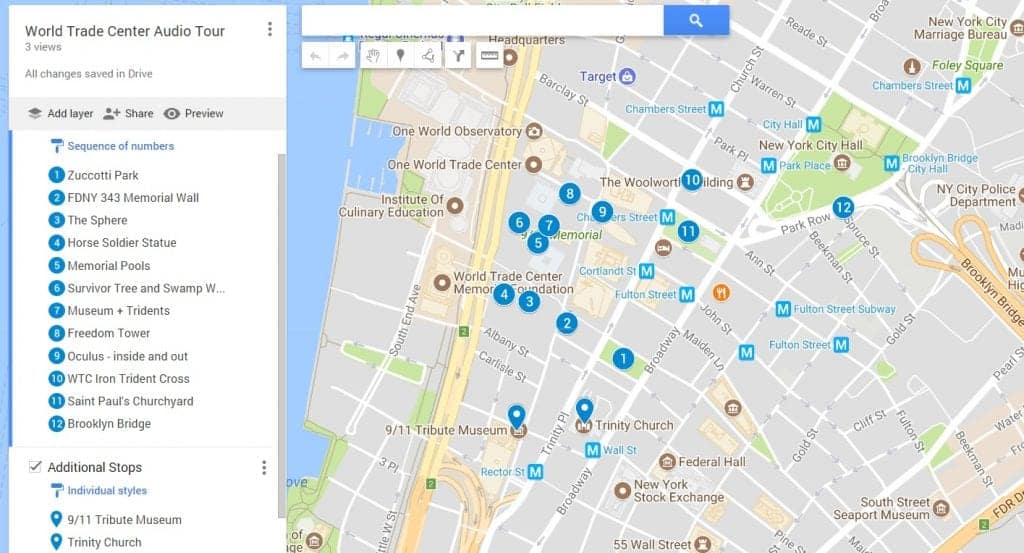
Zuccotti Park
Our self-guided tour begins at Zuccotti Park.
Prior to September 11th, 2001, this park was named Liberty Plaza Park (not to be confused with the new Liberty Park in the memorial).
This was a popular area for workers from the World Trade Center to sit and have lunch or just relax.
The park was damaged by debris from the fallen office towers and was subsequently used as a staging area for the recovery efforts and then later as a place for ceremonies commemorating the events of 9/11 as well as dedications of statues and sculptures.
In the northwest corner (closest to the WTC) sits an everyday man.
The sculpture is called Double Check, and despite the destruction around him, he would survive, a seeming metaphor for the people of NYC and the country.
On a side note, Zuccotti Park would later serve as the center of the Occupy Wall Street protests in 2011.
The FDNY Memorial Wall
Located on Greenwich Street at the corner of Liberty Street, just southeast of the 9/11 Memorial hangs the FDNY Memorial Wall by artist Joe Petrovics.

This 7000-pound (3200 kg) bronze wall is attached to the wall of Engine and Ladder Company 10, the local fire station.
It is a memorial to the 343 active NYC firefighters who lost their lives on September 11th, 2001 + 1 local attorney who was a volunteer firefighter outside of the city.
The 56-foot (17 m) long bas-relief sculpture depicts the World Trade Center towers in flames and scenes of firefighters executing their duties.
For more information on the memorial, please visit http://www.fdnytenhouse.com/ .
Listen to firefighter Lt. Mickey Kross tell his story of surviving the tower collapse ( audio ).
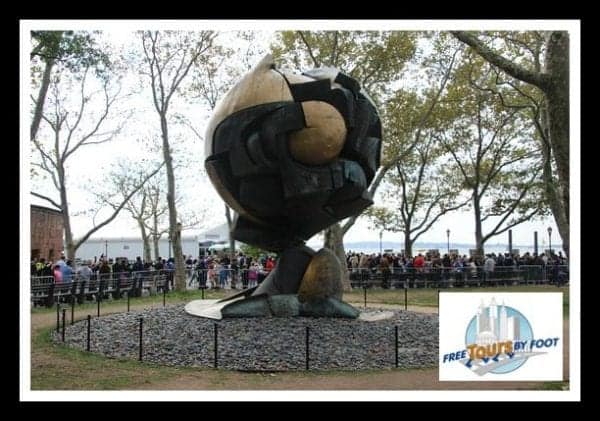
Standing 25’ (8m) tall and comprised of 52 pieces of bronze, weighing 45k lbs (21k kgs), set on a base originally designed to rotate once every 24 hours, the Sphere is certainly an eye-catching sculpture.
Designed by German artist Fritz Koenig to represent world peace through world trade, the Sphere was originally installed in a plaza between the two World Trade Center towers.
Considering its location at Ground Zero during the time of the terrorist attacks of 2001, it survived the devastation battered and bruised but standing.
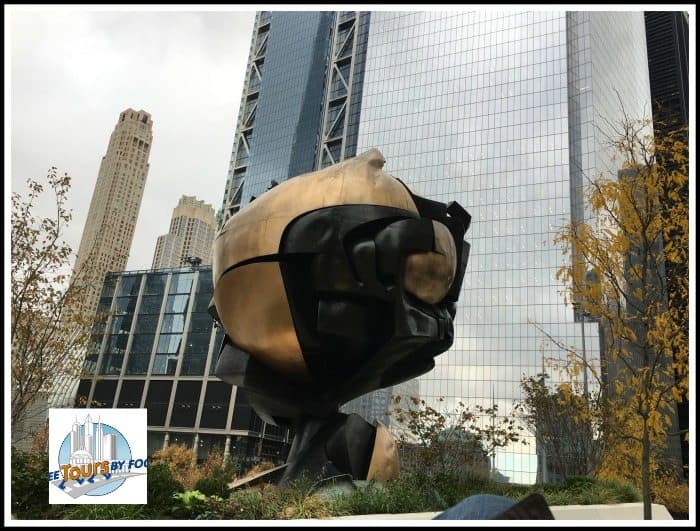

Today, with its eternal flame, it stands as a memorial to the lives lost on that fateful day.
Koenig at first resisted the idea of turning the sculpture into a memorial but later had a change of heart, stating “It was a sculpture, now it’s a monument... it now has a different beauty, one I could never imagine.
It has its own life - different from the one I gave to it.” If you look off to the north, you can see the new towers of the World Trade Center rising day by day.
America's Response Monument
Popularly known as the Horse Soldier Statue, this monument stands on the west end of Liberty Park, just south of the 911 Memorial.
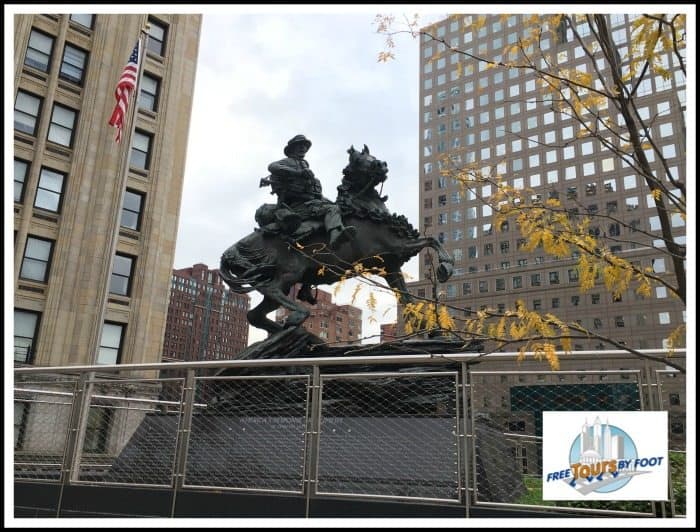

Officially titled America's Response Monument, and subtitled "De Oppresso Libor" (liberate from oppressor), this 18-foot (5.5 m) tall commemorates Task Force Dagger of the Green Berets, U.S. Army Special Forces, who were the vanguard of the American military forces to enter Afghanistan to target Taliban forces just weeks following the 911 attacks.
Due to the difficult terrain where they started, U.S. soldiers were required to operate on horseback.
The statue commemorates all of those beyond first responders who answered the call of duty.
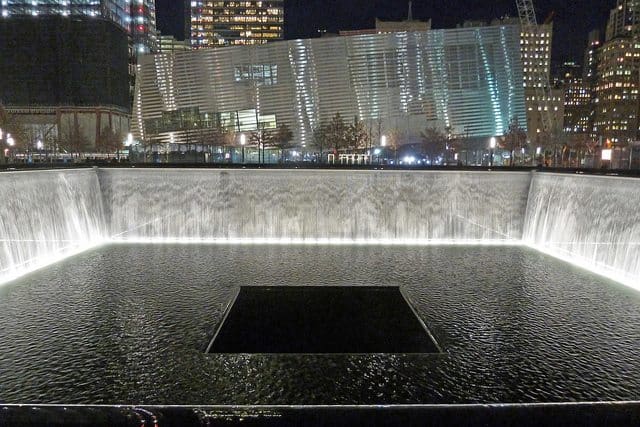
The Waterfalls and Reflecting Pools
These 2 enormous pools with cascading waterfalls, were designed by architect Michael Arad, and titled "Reflecting Absence".
They are set at Ground Zero in the exact footprints of the original North and South World Trade Center Towers, which were destroyed on September 11, 2001.
At 1 acre (4000 m2) in surface area and 32 feet (10 m) deep, these are the largest man-made waterfalls in North America.
The pools are one of the most moving memorials in the world.
These pools represent the void left in the aftermath of the terrorist attacks, both with the loss of life as well as in the soul of the city and the country.
It is nearly impossible to view the pools without experiencing some sort of emotions.
We recommend visiting at twilight or night to see the pools illuminated.

The 911 Memorial honors those who died on 9/11, including those who perished at the World Trade Center, the Pentagon in Washington D.C., and the victims of hijacked Flight 93 that crashed in Pennsylvania.
Also included are the oft-forgotten six victims of the 1993 World Trade Center bombing.
The victims' names are inscribed around the bronze edges of the pools. Instead of being arranged alphabetically, the names are organized by “meaningful adjacencies."
Names are grouped together based on their relationships with other victims, such as co-workers, family members, friends, and even those who commuted together.
As with the voids represented by the pools and waterfalls, so are the names indented.
To find specific names, you can access kiosks in the plaza or download an official 911 Memorial app .
When you are at the pools, you may notice small white roses.
These roses are placed by 911 Memorial staff members at the names of victims who would have celebrated their birthdays today.
One particularly sad statistic is that 13 victims died on their birthday, September 11th.
Swamp White Oaks and The Survivor Tree
Throughout the memorial are several hundred swamp white oak trees, which, according to the 911 Memorial website , were chosen for their durability as well as their variety of heights and leaf colors.
However, there is one particular tree that stands out. Among the rubble of the fallen towers, an 8-foot (2.5 m) Callery pear tree was found alive, but just barely.
Removed from the rubble, the tree was nursed back to health and replanted in the plaza. It has since flourished and has grown to 30 feet in height.
The tree embodies the story of survival and resilience important to the history of the World Trade Center and 9/11.
Download a free Survivor Tree e-book on iTunes .
From the Survivor Tree, walk towards the glass atrium of the museum where you can view the Tridents.
The National September 11th Museum
Read more about the museum here .
Placed inside the Museum, but visible from the Memorial Plaza, are two 70-foot (21 m) high, 50-ton (45 mt) steel beams that were part of the base of the North Tower.
These beams, salvaged from the wreckage of the fallen towers, are known as “tridents” because of their three-pronged tops (from the God Neptune).
The Oculus, designed by Spanish architect, Santiago Calatrava, is a transportation hub that connects the New Jersey PATH Trains to the NYC Subway.
At 800,000 sq. ft (75,000 sq. m), it is the 3rd largest hub in the city and a rival of both Grand Central Terminal and Penn Station, and like those two stations, this structure also houses numerous retail shopping stores.

Originally envisioned as a smaller station, changes to the original plan brought into existence the structure that you see today, which according to Calatrava, was inspired by an image of a girl releasing a bird.
The original plan for this location was to be an area that allowed the morning light of an early rising sun to shine down directly into the memorial pools at approximately the time the planes crashed into the old towers.
Read more about The Oculus here .
The World Trade Center Cross
Just days after the towers' collapse, recovery workers discovered a 17 ft (5 m) tall intersecting beam among the wreckage of Ground Zero that unmistakably resembled a Christian cross.
This cross was installed here on the side of St. Peter's Church as a temporary holding spot before being transferred to the National September 11th Museum.

This transfer was not without controversy, as a national Atheists Association opposed the use of government funds to accommodate the transfer, but they lost.
The court ruled that the cross did not violate constitutional restrictions on church and state.
The current cross was installed in 2011 and was designed by Jon Krawczyk.
Its polish is intended to reflect the sky, crowds, and the emerging World Trade Center.
The new cross is filled with notes, letters, and other symbols of loss.
The image on the left - By James Tourtellotte, U.S. Customs and Border Protection (http://www.cbp.gov/: Gallery, Page) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons.
St. Paul's Chapel
This is the only colonial-era house of worship still standing in New York City and it is also the oldest public building that has been in continuous use since it was built.
It served as an extension of Trinity Church located a few blocks south and included in this tour.
St. Paul's has a sacred and inspirational place in history. George Washington prayed here after his presidential inauguration at the nearby Federal Hall in 1789.
St. Paul's also served as a place of comfort and solace for the rescue workers at the World Trade Center in the days following 9/11.
Despite being located directly across the street from the Twin Towers, St. Paul's survived the tragic events of 9/11 without even a broken window.
The back of the chapel that faced the Towers was shielded by a huge sycamore tree that stood between the chapel and the collapsing buildings.
The tree caught large amounts of falling debris and was uprooted.
The tree's heroic roots have been memorialized by a two-ton bronze sculpture that stands in the courtyard of Trinity Church.
Spend some time inside, as they have small displays commemorating the heroes of September 11th.
THE NATIONAL SEPTEMBER 11th MEMORIAL MUSEUM
Unlike the 911 Memorial, you must purchase tickets to enter the Museum.
Through interactive technology, archives, narratives, and a collection of artifacts, the Museum recounts the events of 9/11.
To see a preview of what your visit will be like, here is a virtual tour of the museum.
Hours : Daily from 9 am to 8 pm. The last entry time is at 7 pm.
Tickets: Tickets are "timed-entry" meaning you must select a specific date and time when you make your purchase. Tickets can be purchased up to three months in advance.
You can purchase tickets by clicking here .
Several tour companies combine a walking tour of the 9/11 Memorial and Ground Zero with tickets to the 9/11 Museum. Learn more .
TIP: Admission to the museum is included for free with the purchase of either the New York Pass, the Explorer Pass, or the CityPass booklet. Read our post comparing the different tourist attractions passes in NYC .
Prices: (Prices below do not reflect the $2 service fee per ticket)
- $28 | Adults
- $22 | Seniors (65 and over)
- $22 | Students (with valid ID)
- $20 | Young Adult (ages 13-17)
- $17 | Youth (Ages 7-12)
- Free Children (Under 6)
- $18 | U.S. Veterans
- Family members of 9/11 victims, 9/11 Rescue and Recovery Workers, and Museum Members receive free entry.
- More info and to book .
Free Mondays
Free admission will be available for all visitors every Monday, from 3:30 pm to 5 pm.
A limited number of advance tickets for these free Mondays will be available online, starting two weeks in advance of each Monday.
A limited number of tickets are available every Monday on a first-come, first-served basis.
Get more details on this cost-saving opportunity at our post, Free Admission 911 Museum .
Join us for our Monday World Trade Center and 911 Memorial Tour from 1 pm to 3 pm, after which you can pick up tickets for free entry.
ONE WORLD TRADE CENTER AND OTHER WTC BUILDINGS
One World Trade Center , nicknamed the “Freedom Tower” is the tallest skyscraper in the Western Hemisphere and, as of 2016, is the 6th tallest in the world.
It’s no coincidence that its height is 1,776 feet.

That number has great significance in American history as it was the year America declared its independence from Great Britain.
The Observatory on the 100th and 101st floors is open and is quite an amazing experience. For information on visiting click on this link: One World Observatory ("Freedom Tower") .
Floors 1-19 are the base of the building with a 65-foot-high (20 meters) public lobby.
Rented office space begins on the 20th Floor and continues to the 64th Floor.
On Floor 65 is a sky lobby and then office floors resume on Floor 65 to Floor 90. Floors 91–99 and 103–104 are mechanical floors.
2 World Trade Center is - after 15 years - still not complete due to many delays in design. The currently agreed-upon design is a 90-story tower standing 1,270 feet tall encompassing 2.8 million square feet.
3 World Trade Center is near completion and will be 80 stories tall rising to 1,079 feet.
The completed and opened 4 World Trade Center is a light, ephemeral vision, facing directly onto the World Trade Center Memorial Plaza.
Rising 977 feet, by Maki and Associates, the 72-story tower is intended to assume a quiet but dignified presence at the site.
7 World Trade Center was completed in 2006 and was the first tower rebuilt after the attacks.
Standing 741 feet and 52 stories tall it sits on the same site as the original 7 World Trade Center.
PLAN YOUR VISIT
Whether to pay their respects or learn more about the event that changed this country, millions of people visit the 9/11 Memorial and Museum each year.
Together they are the country's principal institution of remembrance honoring the victims and memorializing the tragedy of 9/11.
In addition to the memorial itself, there are several monuments and other notable locations nearby that make this one of the most popular sites in NYC.
This section will provide all the details you need to know what to expect, find the memorial, and choose the best time to visit.
Is it Free to Visit the 9/11 Memorial?
The 9/11 Memorial is free to enter. There are no tickets and you do not need to make a reservation.
The only entry cost is for the National September 11th Museum , located on the memorial grounds.
Visiting the 9/11 Memorial is one of the best free things to do in NYC .
How to Get Here
Use this map for specific directions to the 9/11 Memorial.
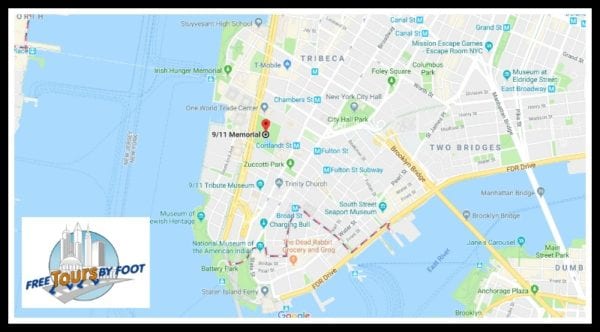
The easiest way to get here is via the subway. The following lines will get you within walking distance of the memorial:
By Subway: • A, C, 1, 2, 3 to Chambers Street • A, C, J, Z, 2, 3, 4, or 5 trains to Fulton Street • 2 or 3 trains to Park Place • E train to World Trade Center • R or 1 train to Rector Street • R train to Cortlandt Street
Be sure to read our guides on navigating the subway and how to purchase a subway MetroCard .
Visitors who plan on using a hop-on-hop-off bus will be happy to know that most services offer stops very close to the 9/11 Memorial.
Alternatively, you can also take a public bus (lines M5, M20 & M22) to get here.
Best Times to Visit
The 9/11 Memorial is free to visit, so you won’t require timed tickets or wait in any lines.
You can come anytime during operational hours, with the exception of rare public events.
9/11 Memorial Plaza Hours
- 8 am - 8 pm
- 7 days a week
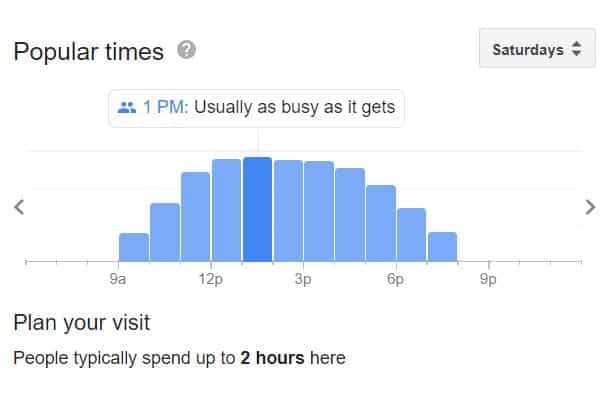
The 9/11 Memorial can get pretty crowded no matter when you come to see it, but there are times when it is easier to get a good look at the site.
If you’re trying to avoid the crowds, you may want to consider coming either as early or late as possible.
Many visitors recommend coming early in the morning, but honestly, crowds never really lessen the experience of a visit.
Alternatively, you may also want to consider coming at night in order to see the memorial light up after dark.
In fact, the memorial is one of our top things to do at night in NYC .
Some visitors indicate that seeing the memorial from 7 pm - 8 pm can be a completely different experience.
NOTE: Night hours are currently limited, likely due to the pandemic.
Even if a crowd does gather to see the landmark at night, chances are it won’t be too difficult to manage.

Additionally, visitors who choose to come on September 11th should keep in mind that the plaza will be closed until later in the day.
Once the sun goes down, two spotlights representing the Twin Towers will light up the night sky.
These lights can be seen up to 60 miles away, but it’s an entirely different experience to be there when this event takes place.
Check our guide below for more details about this activity.

What to Expect
No matter when you come to see the 9/11 Memorial, chances are that you’ll run into large crowds.
Thankfully, there is a lot of space in the area, so you shouldn’t have too much trouble seeing the monument.
How Much Time Do You Need?
Although a quick trip can take anywhere from 15-30 minutes, some guests may want to set aside a little more time to experience the memorial.
There are also several additional monuments nearby that are directly related to the events of 9/11, so you may want to ensure that you have at least 1 hour to see everything.

This is the exact time it will take you to complete our audio walking tour of the memorial and surrounding area.
The 9/11 Museum is located right between the two monuments and you will require tickets for entry.
This location includes several exhibits covering the history before, during, and after the events of September 11th.
For more information, make sure to read our post about visiting the 9/11 Museum .

If you want to take things a step further, you should also consider visiting One World Trade Center.
Located right across the street from the 9/11 Memorial, this is one of the tallest buildings in the world and it has observation decks providing some of the best views in New York City.
Read our post about the Freedom Tower for more details.
Anyone who is considering a trip to the memorial, the museum, and the One World Observatory should set aside at least 5-6 hours for the entire trip.
You’ll also want to purchase tickets in advance to make sure that you can get in when you want and avoid having to wait in line.
If you’re planning on spending the day in this area, consider dropping into Brookfield Place to grab a bite to eat.
This shopping center has a huge food court with several different restaurants to choose from.
TOURS OF THE 9/11 MEMORIAL
There are several options for guided tours and some include admission to the National September 11th Museum and/or One World Observatory as well.
Even if you can’t manage to book a trip with us, there are quite a few affordable options out there, including our anytime audio tour .
Every 9/11 Memorial tour on this list is highly rated and well-received by guests. Most tours are offered daily.
Although these excursions typically include some sensitive historical information, some families really enjoy the experience of visiting this important monument of American history.
Below is a handy calendar of tour availability.
Tours by Foot
We offer several tours as well as anytime GPS tours that include the 911 Memorial as part of the main focus of the tour.
We are one of the highest-rated tour companies in New York City. Read our reviews .
We offer an anytime GPS audio tour of the memorial recorded by one of our tour guides. Here is a sample of the tour.
We also offer a World Trade Center Tour , which focuses on the Memorial and runs Mondays at 1 pm.
We have 4 other tours that include the 911 Memorial and the World Trade Center as a stop on the tour. We have listed them, with the daily tours listed first.
- Lower Manhattan, SoHo, Little Italy, and Chinatown - briefly cover the Memorial. Runs daily at 10 am year-round with occasional afternoon availability.
- Lower Manhattan Tour - this tour briefly covers the Memorial and ends there. It runs Mondays and Fridays at 10 am year-round.
- 911 Memorial and Brooklyn Bridge Night Tour - see the Memorial lit up for a completely different perspective. Currently runs as a private tour only.
- All-in-One Downtown Manhattan - 6-hour tour that briefly covers the Memorial. Runs on Tuesdays and Fridays at 10 am year-round with additional days during the summer months.
NEARBY RELATED SITES
The 9/11 Tribute Museum (permanently closed) at 120 Liberty Street offered visitors a historical timeline and honors the aftermath of rescue and recovery, and shares a personal memorial tribute from 9/11 families.
The Museum was founded by the September 11th Families Association and was not part of the 9/11 Memorial or the National September 11th Museum.
The Museum galleries allowed for an intimate look at the event through films, artifacts, and photos.
Choose a Destination... I want them all PLUS general travel tips. Amsterdam Berlin Boston Charleston Chicago Dubai Lisbon London Los Angeles Miami Nashville New York City New Orleans Paris Philadelphia Prague Rome San Francisco Washington DC
About The Author

Stephen Pickhardt
North america, united kingdom & ireland, middle east & india, asia & oceania.
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Newsletters
- United States
- New York City
- Things To Do
Visiting the 9/11 Memorial in New York City
9/11 memorial, national september 11 memorial museum, 9/11 tribute museum, guided tours, getting there, things to do nearby.
TripSavvy / Winifred Lao
The World Trade Center site is an important place for those who want to pay tribute to the lives lost in the events of 9/11 and gain some perspective regarding that fateful day. The site in lower Manhattan includes an 8-acre memorial plaza dedicated to both the victims and survivors of the terrorist attacks on Sept. 11, 2001, and Feb. 26, 1993.
The 9/11 Memorial opened on Sep. 11, 2011, the 10th anniversary of the attacks. There was a ceremony for victims' families followed by an official opening for the general public the next day.
The 9/11 Memorial includes the names of the nearly 3,000 victims of the 2001 terrorist attack on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon. It also contains the names of the six victims who died in February 1993 after a terrorist bombing at the World Trade Center.
The twin reflecting pools—with the victims' names inscribed on surrounding bronze panels and the country's largest artificial waterfalls cascading down the sides—sit on the original site of the Twin Towers. Surrounding it is a plaza with a grove of nearly 400 North American swamp white oak trees. It is also home to a special Callery pear tree, known as the Survivor Tree , because it flourished again after the 9/11 attacks left it burned and broken.
The memorial site is open to the public with no admission charge. Early morning usually provides the best chance for some peace before the full cacophony of city sounds intrudes. The crowds typically thin out in the evening, and after dark, the water cascading into the reflecting pools turns into a shimmering curtain. The victims' inscriptions appear to be carved in gold.
The 9/11 Memorial Museum opened to the public on May 21, 2014. The museum collection includes more than 23,000 images, 500 hours of video, and 10,000 artifacts. The atrium entrance to the 9/11 Memorial Museum houses two tridents from the steel facade of WTC 1 (the North Tower) that you can see without paying museum admission.
The historical exhibitions cover the events of 9/11 and also explore the global mood leading up to the events of that day and their ongoing significance. The memorial exhibition displays portrait photographs of the 2,977 people who lost their lives that day, with an interactive feature that lets you learn more about the individuals. In Foundation Hall, you can see a wall from the foundation of one of the towers in addition to a 36-foot-tall steel column still covered with the missing posters placed there in the days following the disaster. Rebirth at Ground Zero, an immersive film that follows the rise of the new World Trade Center, also has a permanent home at the museum.
Visitors spend an average of two hours at the museum. Family members of victims enter for free, while visitors can pre-order tickets online or buy them onsite.
The September 11th Families' Association put together the 9/11 Tribute Museum to help those looking to learn about 9/11 with those who survived the event. The displays feature firsthand accounts from survivors and victims' family members, as well as artifacts from the site, many on loan from the families of those lost on 9/11. Since the Tribute Museum opened in 2006, family members, survivors, first responders, and Manhattan residents have been sharing their personal stories on walking tours and in the museum's galleries.
A tour is a good option for those seeking guidance while exploring the WTC site and Ground Zero. You can choose between guided and self-guided tours, making it easier to get oriented and maximizing your time on the grounds.
- Tribute WTC 9/11 Walking Tours : Organized by the nonprofit September 11th Families' Association, these 75-minute tours are led by people who have been directly affected by the events of 9/11. The tour may not be appropriate for visitors under 10 years old.
- Heroes of the World Trade Center Tour : Uncle Sam's New York Tours offers a 2-hour walking tour of the area, including a visit to St. Paul's Chapel, which served as a shelter for the city's rescue personnel during the events of 9/11.
The World Trade Center site is located in lower Manhattan, bound by Vesey Street on the north, Liberty Street on the south, Church Street on the east, and the West Side Highway. You can access 12 subway lines and PATH trains from two convenient transportation hubs near the World Trade Center site.
Lower Manhattan contains many historical sites, including Battery Park, the Ellis Island ferry, and the Statue of Liberty . Wall Street and the New York Stock Exchange anchor New York City's Financial District, and the famed Brooklyn Bridge, one of the country's oldest and most scenic roadway bridges, spans the East River to connect the boroughs of Manhattan and Brooklyn.
Famous chefs and restaurateurs such as Daniel Boulud, Wolfgang Puck, and Danny Meyer operate locations in lower Manhattan, where you can also find city stalwarts such as Delmonico's, P.J. Clarke's, and Nobu.
Related Articles
More related articles.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

How To Visit Ground Zero and 9/11 Memorial Museum in 2024: Tickets, Hours, Tours, and More
Carissa Chesanek Last Updated: October 26, 2023
Ground Zero and The National September 11 Memorial Museum are significant sites in New York City’s history. The historic landmarks honor those who died in the September 11, 2001 terror attacks and the World Trade Center bombing in 1993. But there’s a lot to see and it can be confusing to decide how to plan your trip to these must-see memorials. Here’s how to visit Ground Zero and 9/11 Memorial Museum, with information on tickets, hours, tours, and more
Pro Tip: Bookmark this article as a helpful guide for your visit to Ground Zero, the 9/11 Memorial Museum. You can also use our helpful guide for planning your trip to New York City to see the best sites and eat tasty food.
Ground Zero and 9/11 Memorials: What We’ll Cover
Ground Zero is a large area that’s known as the area where the World Trade Center towers collapsed and many months of cleanup occurred. Here you’ll find the National September 11 Memorial Museum, the 9/11 Memorial Pools, the FDNY Memorial Wall, and the One World Trade Center where you can explore their observation deck at the top of the building. Here’s what we’ll cover in this article:
- One World Trade Center hours and tickets
- 9/11 Memorial hours and tickets
- 9/11 Memorial Museum hours and tickets
- What to see and do
- Ground Zero and 9/11 Memorial tours
- Important facts and history
One World Trade Center: Hours, Tickets, and Directions

One World Trade Center remembers those who lost their lives in the 9/11 terrorist attacks. It is not only the tallest building in the World Trade Center Complex but also in the nation. It’s an impressive sight to view from the outside at 1,776 feet high. However, the inside is also something to see. Here, you’ll find the Oculus subway, Westfield Shops, and restaurants.
While here, check out One World Observatory. It sits at the top of One World Trade Center boasting city views at 102 stories high. And you can try an interactive tour and food from the restaurant and bar.
Admission fee to One World Trade Center: There is no fee to enter the World Trade Center Westfield Shops or Oculus.
Hours: Westfield Shops at the Oculus are open daily, Monday-Saturday from 10 am to 7 pm. Sunday hours are from 11 am to 6 pm.
Admission fee to the One World Observatory: General admission starts at $44 per person.
Hours: The Observatory is currently open Thursday through Monday from 10 am to 9 pm.
Directions: Get here by subway taking the 1 to WTC Cortlandt, the E to World Trade Center, or the R W to Cortlandt. One World Trade Center will be less than a 5-minute walk from the subway station.
Address: 50 Church Street, New York
9/11 Memorial: Hours, Tickets, and Directions

The 9/11 Memorial opened ten years after the September 11th terror attacks as a place for healing. You’ll find the Memorial Pools, Memorial Glade, and Survivor Tree here to visit quietly and reflect on their meaning for this special area.
Admission fee: There is no fee to visit the 9/11 Memorial.
Hours: The 9/11 Memorial is open daily from 10 am – 5 pm.
Directions: Get here by subway taking the 1 to WTC Cortlandt or the E to World Trade Center. The 9/11 Memorial will be less than a 5-minute walk from the subway station.
Address: 180 Greenwich Street, New York
Pro tip: If you are visiting on September 11th, you may be able to see the Tribute in Light ceremony. This art installation projects two beams of light high in the sky resembling the Twin Towers. And you don’t necessarily have to be at the memorial to see it. The installation can be viewed within a 60-mile radius in the Lower Manhattan area.
National September 11 Memorial Museum: Hours, Tickets, and Directions

The 9/11 Memorial Museum reflects on the terror attacks on September 11th and the World Trade Center bombing in 1993. The 110,000 square feet space hosts artifacts and images that tell personal stories of victims, rescue workers, and others impacted.
Admission Fee for the 9/11 Memorial Museum:
- Adults: $29 (A museum tour with admission is $49 per adult)
- Young adults (13-17): $23
- Youths (7-12 years old): $17
- Child (6 and Under): Free
- Seniors 65 and older and college students: $23
- Veterans: $18
Hours: The 9/11 Memorial Museum is open Thursday-Monday from 10 am – 5 pm.
Directions: Get here by subway taking the 1 to WTC Cortlandt or the E to World Trade Center. The 9/11 Memorial Museum will be less than a 5-minute walk from the subway station.
Pro Tip: The 9/11 Memorial Museum offers free admission on Mondays from 3:30 pm to 5 pm. If you’re looking to get free tickets you’ll need to plan ahead and register online here .
Not ready to book a tour? Check out how to spend 3 days in New York .
What To See and Do

There’s a lot to explore and visit around the 9/11 Memorials, and you don’t want to miss anything. Here are the important things to see at each location.
One World Trade Center
- Take a ride on the SkyPod elevator where you’ll experience the New York City skyline through video and illusion.
- One World Explorer interactive iPad guide that lets you learn the history of New York City’s most iconic buildings with a tap of a finger.
9/11 Memorial
- The two Memorial Pools are at the site of the former North and South Towers. Both have two of the largest man-made waterfalls that descend 50 feet. The name of the victims from both 1993 and 2001 (including Flight 93 and the Pentagon) are etched in the bronze wall found alongside the pools.
- The Memorial Glade represents rescue workers and others who were exposed to toxins after the attack and during the long months of cleanup.
- There is also the Callery pear tree that survived the attacks. It was later replanted at the Memorial and named the Survivor Tree.
- The bronze FDNY Memorial Wall, which honors the firefighters who lost their lives on 9/11. It is not in the Memorial but just a short two-minute walk away.

9/11 Memorial Museum
- The FDNY Ladder 3 firetruck that was recovered from the World Trade Center site.
- The memorial exhibition featuring a floor-to-ceiling photo showcase of the victims.
- Artifacts from victims that help shed light on their lives before the bombings.
Ground Zero and 9/11 Memorial Tours
All the guided in-person tours are led by New Yorkers with a connection to 9/11. There are several tours to choose from , including the 90-minute All Access Ground Zero Tour with museum and One World Observatory entry for $109 per adult. Other options include only a guided tour of Ground Zero ($39 per adult), or a tour and entrance to either the museum or One World Observatory ($79 per adult).
There is also the official 9/11 Memorial Audio Guide app ($1.99) with a 40-minute tour discussing the attacks and Memorial design. The audio guide is narrated by a New Yorker who lost a family member on 9/11.
Facts About Ground Zero and the 9/11 Memorials
Though many tourists might be familiar with the events of September 11th, some may not know these important facts about Ground Zero and the 9/11 museum, thanks to the official 9/11 Memorial website and History.com.
- Before the Twin Towers fell they were both over 1,300 feet in height. The North Tower was 1,368 feet high while the South Tower reached 1,362 feet.
- The first plane hit the first tower at 8:45 am at approximately the 80th floor, and the second plane hit the South Tower at 9:03 am at approximately the 60th floor.
- The buildings took roughly ten seconds to collapse to the ground bringing with them about 300,000 tons of steel.
- Almost 3,000 people died in the 9/11 attacks (2,983 total), and 343 of those were firefighters who are also honored at the FDNY Memorial Wall.
- To create the 9/11 Memorial there was an international competition that took place In 2003. The following year, architect Michael Arad and landscape architect Peter Walker were announced the winners with their design titled Reflecting Absence which featured the two pools and white oak trees we see today.
- The Memorial Pools are about the size of one acre each and took ten years to build. The National September 11 Museum opened its doors three years later and continues to be one of the most popular museums to visit in NYC.

Where to Stay in NYC
New York City is the center of the universe to those who adore this iconic city. Choose the best neighborhood to stay in as you plan your upcoming trip to the Big Apple.

Reader Interactions
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Travel Blog
- In The Press
POLICY & TERMS
- Cancellation Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy


By Maria Cramer
North Korea. East Timor. Nagorno-Karabakh, a mountainous enclave that for decades has been a tinderbox for ethnic conflict between Armenians and Azerbaijanis.
They’re not your typical top tourist destinations.
But don’t tell that to Erik Faarlund, the editor of a photography website from Norway, who has visited all three. His next “dream” trip is to tour San Fernando in the Philippines around Easter , when people volunteer to be nailed to a cross to commemorate the suffering of Jesus Christ, a practice discouraged by the Catholic Church.
Mr. Faarlund, whose wife prefers sunning on Mediterranean beaches, said he often travels alone.
“She wonders why on earth I want to go to these places, and I wonder why on earth she goes to the places she goes to,” he said.
Mr. Faarlund, 52, has visited places that fall under a category of travel known as dark tourism , an all-encompassing term that boils down to visiting places associated with death, tragedy and the macabre.
As travel opens up, most people are using their vacation time for the typical goals: to escape reality, relax and recharge. Not so dark tourists, who use their vacation time to plunge deeper into the bleak, even violent corners of the world.
They say going to abandoned nuclear plants or countries where genocides took place is a way to understand the harsh realities of current political turmoil, climate calamities, war and the growing threat of authoritarianism.
“When the whole world is on fire and flooded and no one can afford their energy bills, lying on a beach at a five-star resort feels embarrassing,” said Jodie Joyce, who handles contracts for a genome sequencing company in England and has visited Chernobyl and North Korea .
Mr. Faarlund, who does not see his travels as dark tourism, said he wants to visit places “that function totally differently from the way things are run at home.”
Whatever their motivations, Mr. Faarlund and Ms. Joyce are hardly alone.
Eighty-two percent of American travelers said they have visited at least one dark tourism destination in their lifetime, according to a study published in September by Passport-photo.online, which surveyed more than 900 people. More than half of those surveyed said they preferred visiting “active” or former war zones. About 30 percent said that once the war in Ukraine ends, they wanted to visit the Azovstal steel plant, where Ukrainian soldiers resisted Russian forces for months .
The growing popularity of dark tourism suggests more and more people are resisting vacations that promise escapism, choosing instead to witness firsthand the sites of suffering they have only read about, said Gareth Johnson, a founder of Young Pioneer Tours , which organized trips for Ms. Joyce and Mr. Faarlund.
Tourists, he said, are tired of “getting a sanitized version of the world.”
A pastime that goes back to Gladiator Days
The term “dark tourism” was coined in 1996, by two academics from Scotland, J. John Lennon and Malcolm Foley, who wrote “Dark Tourism: The Attraction to Death and Disaster.”
But people have used their leisure time to witness horror for hundreds of years, said Craig Wight, associate professor of tourism management at Edinburgh Napier University.
“It goes back to the gladiator battles” of ancient Rome, he said. “People coming to watch public hangings. You had tourists sitting comfortably in carriages watching the Battle of Waterloo.”
Professor Wight said the modern dark tourist usually goes to a site defined by tragedy to make a connection to the place, a feeling that is difficult to achieve by just reading about it.
By that definition, anyone can be a dark tourist. A tourist who takes a weekend trip to New York City may visit Ground Zero. Visitors to Boston may drive north to Salem to learn more about the persecution of people accused of witchcraft in the 17th century. Travelers to Germany or Poland might visit a concentration camp. They might have any number of motivations, from honoring victims of genocide to getting a better understanding of history. But in general, a dark tourist is someone who makes a habit of seeking out places that are either tragic, morbid or even dangerous, whether the destinations are local or as far away as Chernobyl.
In recent years, as tour operators have sprung up worldwide promising deep dives into places known for recent tragedy, media attention has followed and so have questions about the intentions of visitors, said Dorina-Maria Buda, a professor of tourism studies at Nottingham Trent University .
Stories of people gawking at neighborhoods in New Orleans destroyed by Hurricane Katrina or posing for selfies at Dachau led to disgust and outrage .
Were people driven to visit these sites out of a “sense of voyeurism or is it a sense of sharing in the pain and showing support?” Professor Buda said.
Most dark tourists are not voyeurs who pose for photos at Auschwitz, said Sian Staudinger, who runs the Austria-based Dark Tourist Trips , which organizes itineraries in the United Kingdom and other parts of Europe and instructs travelers to follow rules like “NO SELFIES!”
“Dark tourists in general ask meaningful questions,” Ms. Staudinger said. “They don’t talk too loud. They don’t laugh. They’re not taking photos at a concentration camp.”
‘Ethically murky territory’
David Farrier , a journalist from New Zealand, spent a year documenting travels to places like Aokigahara , the so-called suicide forest in Japan, the luxury prison Pablo Escobar built for himself in Colombia and McKamey Manor in Tennessee, a notorious haunted house tour where people sign up to be buried alive, submerged in cold water until they feel like they will drown and beaten.
The journey was turned into a show, “Dark Tourist,” that streamed on Netflix in 2018 and was derided by some critics as ghoulish and “sordid.”
Mr. Farrier, 39, said he often questioned the moral implications of his trips.
“It’s very ethically murky territory,” Mr. Farrier said.
But it felt worthwhile to “roll the cameras” on places and rituals that most people want to know about but will never experience, he said.
Visiting places where terrible events unfolded was humbling and helped him confront his fear of death.
He said he felt privileged to have visited most of the places he saw, except McKamey Manor.
“That was deranged,” Mr. Farrier said.
Professor Buda said dark tourists she has interviewed have described feelings of shock and fear at seeing armed soldiers on streets of countries where there is ongoing conflict or that are run by dictatorships.
“When you’re part of a society that is by and large stable and you’ve gotten into an established routine, travel to these places leads you to sort of feel alive,” she said.
But that travel can present real danger.
In 2015, Otto Warmbier , a 21-year-old student from Ohio who traveled with Young Pioneer Tours, was arrested in North Korea after he was accused of stealing a poster off a hotel wall. He was detained for 17 months and was comatose when he was released. He died in 2017, six days after he was brought back to the United States.
The North Korean government said Mr. Warmbier died of botulism but his family said his brain was damaged after he was tortured.
Americans can no longer travel to North Korea unless their passports are validated by the State Department.
A chance to reflect
Even ghost tours — the lighter side of dark tourism — can present dilemmas for tour operators, said Andrea Janes, the owner and founder of Boroughs of the Dead: Macabre New York City Walking Tours.
In 2021, she and her staff questioned whether to restart tours so soon after the pandemic in a city where refrigerated trucks serving as makeshift morgues sat in a marine terminal for months.
They reopened and were surprised when tours booked up fast. People were particularly eager to hear the ghost stories of Roosevelt Island, the site of a shuttered 19th-century hospital where smallpox patients were treated .
“We should have seen as historians that people would want to talk about death in a time of plague,” Ms. Janes said.
Kathy Biehl, who lives in Jefferson Township, N.J., and has gone on a dozen ghost tours with Ms. Janes’s company, recalled taking the tour “Ghosts of the Titanic” along the Hudson River. It was around 2017, when headlines were dominated by President Trump’s tough stance on refugees and immigrants coming into the United States.
Those stories seemed to dovetail with the 100-year-old tales of immigrants trying to make it to New York on a doomed ship, Ms. Biehl said.
It led to “a catharsis” for many on the tour, she said. “People were on the verge of tears over immigration.”
Part of the appeal of dark tourism is its ability to help people process what is happening “as the world gets darker and gloomier,” said Jeffrey S. Podoshen , a professor of marketing at Franklin and Marshall College, who specializes in dark tourism.
“People are trying to understand dark things, trying to understand things like the realities of death, dying and violence,” he said. “They look at this type of tourism as a way to prepare themselves.”
Mr. Faarlund, the photo editor, recalled one trip with his wife and twin sons: a private tour of Cambodia that included a visit to the Killing Fields , where between 1975 and 1979 more than 2 million Cambodians were killed or died of starvation and disease under the Khmer Rouge regime.
His boys, then 14, listened intently to unsparing and brutal stories of the torture center run by the Khmer Rouge. At one point, the boys had to go outside, where they sat quietly for a long time.
“They needed a break,” Mr. Faarlund said. “It was quite mature of them.”
Afterward, they met two of the survivors of the Khmer Rouge, fragile men in their 80s and 90s. The teenagers asked if they could hug them and the men obliged, Mr. Faarlund said.
It was a moving trip that also included visits to temples, among them Angkor Wat in Siem Reap, and meals of frog, oysters and squid at a roadside restaurant.
“They loved it,” Mr. Faarlund said of his family.
Still, he can’t see them coming with him to see people re-enact the crucifixion in the Philippines.
“I don’t think they want to go with me on that one,” Mr. Faarlund said.

52 Places for a Changed World
The 2022 list highlights places around the globe where travelers can be part of the solution.
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram , Twitter and Facebook . And sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to receive expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation. Dreaming up a future getaway or just armchair traveling? Check out our 52 Places for a Changed World for 2022.
Maria Cramer is a reporter on the Travel desk. Please send her tips, questions and complaints about traveling, especially on cruises. More about Maria Cramer
Open Up Your World
Considering a trip, or just some armchair traveling here are some ideas..
52 Places: Why do we travel? For food, culture, adventure, natural beauty? Our 2024 list has all those elements, and more .
D enver, Colo.: The city is undergoing a rebirth , with a newly refreshed Union Station and the gradual reopening of the mile-long, pedestrian-friendly 16th Street Mall to go along with views of the snow-capped Front Range.
La Rioja, Spain: A drive through rolling vineyards will take you to 5 family-run restaurants where you’ll find flavorful, affordable dishes you can linger over for hours.
Seattle, Wash.: Today’s Seattle is ever evolving, filled with colorful neighborhoods that are emblematic of the Emerald City’s natural beauty, vibrant street life , and commitment to both preservation and progress .
Stockholm-Helsinki Ferry: The 16-hour trip between the two northern European cities is a festive summer ritual , with plenty of singing, gambling, limbo contests and maybe a bit too much to drink.
Swim in the Wild: Looking to take a dip in or near a city center? Here are some European urban areas that have successfully opened up waterways for swimmers .
MOST POPULAR
9/11 Ground Zero All Access Tour
Experience the history and hope of ground zero with our all-inclusive tour.
10:30 AM, 1 PM daily
4.5 hours (90 minutes guided)
$114 per adult • $104 per child
$114 per adult
Local experts, worry-free booking, "i got a ride over to manhattan in an ambulance that was heading over from a local hospital, as thousands were crossing the opposite way into brooklyn to escape the chaos...", rob, tour guide, what’s included, st. paul’s chapel.
Only a block from where the Twin Towers collapsed, St. Paul’s Chapel miraculously survived the falling debris. The church was a landmark even then, the city's oldest, continuously used public building. But in the aftermath of 9/11, it became even more — a rescue center for victims, a bulletin board where families posted notices of their missing loved ones, a gathering place for recovery workers. Today, it stands as a living memorial.

9/11 Memorial
Pause to pay your respects at the 9/11 Memorial and learn about its many symbolic elements. One of the most famous of these, Michael Arad’s “Reflecting Absence” is one of the largest man-made waterfalls in the world, pouring endlessly into the empty footprints of the Twin Towers and inscribed with the names of those who died in the attacks.

9/11 Museum
No place covers the events of 9/11 as extensively as this museum. The 9/11 Museum includes firsthand accounts, artifacts, historical records, and more relating to September 11th. Before your self-guided tour of the museum, your guide will tell you about the exhibit to help you prepare. You’ll receive a timed ticket for entry. We recommend allowing two hours to see everything.

Freedom Tower and the One World Observatory
Visit the One World Trade Center, built after the destruction of the World Trade Center. In the Freedom Tower lobby, watch “Voices,” dedicated to the men and women of both the old and new WTC. Next, climb aboard the SkyPod, an elevator that shows you a time-lapse of NYC while whisking you 1,250 feet in the air to the One World Observatory. This three-level observation deck features a theater, interactive displays, dining, and the highest panoramic views in the city.

More at Ground Zero
Each guide's experience of 9/11 is unique, and so is each tour. In addition to the stops above, you may visit other sites at Ground Zero. These include the FDNY Memorial Wall, the Survivor Tree, the Brooks Brothers building that served as a temporary morgue, and the Millennium Hotel, where the FBI thwarted another attack on New York. Your guide may also stop into the Oculus, the grand entrance to the WTC Transportation Hub.

"I was typing a reflection paper due in class that day when my best friend’s mom messaged me on AOL asking to me to look out my dorm room window to see if the World Trade Center was bombed."
Tom, tour guide, video spotlights.

Remembering 9/11

Ground Zero Tour Preview

Worth every penny we paid to get something other than a media-driven, sensational perspective on our history. Tony was there.
I think it was the best tour of all my travels over the past 30 years., you had a wealth of information that was well appreciated by myself and the high school boys that attended., is the tour accessible for wheelchairs and strollers.
Yes, the tour is accessible for both wheelchairs and strollers.
Is the tour appropriate for children?
Yes, our guided tour of Ground Zero is appropriate for all ages. The subject matter is covered sensitively, and we’ve had many families enjoy our tours over the years. Kids 4-12 can join our tour at a reduced rate.
Does this tour cover the 9/11 Museum or Freedom Tower?
Yes, this tour includes admission to the 9/11 Museum and the One World Observatory at Freedom Tower. Your visits to these attractions are self-guided, but your tour guide will prepare you for your visit. We recommend allowing about an hour for Freedom Tower and two hours for the museum, but you may stay as long as you wish at either landmark.
What is the tipping policy?
Tips are always appreciated by our guides but never expected. They should be given if you believe your guide did an outstanding job and want to show your appreciation.
If I miss the tour, can I still get my ticket for the museum or observatory?
Your tour concierge will give you your museum or observatory ticket (or both if you’ve selected both upgrades) when you check in for your tour.
Getting Here
Meeting point.
209 Broadway, New York
Nearest Subways
to Fulton Street — Transit Center, or r to Cortland Street.
Note that traffic may be unpredictable and could cause you to miss the tour.
Tour Ending Point
The guided portion of our tour ends at the 9/11 Memorial (about 4 blocks from the meeting location). Your self-guided visit to the museum and observatory will be after the tour.
Please arrive at least 15 minutes early as we start on time. We can’t guarantee latecomers will be able to catch up and join the group.
When you arrive, just tell the guide your name at check-in. No need to print out anything.
Refunds and Rescheduling
We offer a 100% refund for the guided portion of your tour up to 24 hours before your tour start time. We also offer free rescheduling up to 24 hours before your tour start time. However, attraction tickets cannot be rescheduled or refunded as they’re issued for the time and date provided.
After you’ve rescheduled your tour once, there are no refunds if you decide not to take the tour. You can also transfer or gift your tour to someone else if you wish.
Our tours take place outdoors, rain, snow, or shine. Please check the forecast and dress for the weather. In rare cases of serious inclement weather, we may cancel the tour and offer you the opportunity to reschedule or receive a full refund.
9/11 Ground Zero Tour
A 90-minute guided tour of Ground Zero, featuring stops at St. Paul’s Chapel, the 9/11 Memorial, the FDNY Memorial Wall, and more
$39 per adult €36 per adult £30 per adult C$53 per adult A$59 per adult and $35 per child €32 per child £27 per child C$48 per child A$53 per child

9/11 Ground Zero Tour With 9/11 Museum
Our Ground Zero Tour, which includes the 9/11 Memorial and other sites, plus timed tickets for the 9/11 Museum
$84 per adult €76 per adult £64 per adult C$114 per adult A$126 per adult and $75 per child €68 per child £58 per child C$102 per child A$113 per child

9/11 Ground Zero Tour With Freedom Tower
Our Ground Zero Tour, which includes the 9/11 Memorial, plus admission to the One World Observatory in Freedom Tower

Walking Tour
- 90-minute guided tour of Ground Zero
- 90-minute guided tour of Ground Zero, featuring stops at St. Paul’s Chapel, the 9/11 Memorial, the FDNY Memorial Wall, and more
Tour With 9/11 Museum
Addition to Guided Tour with admission to 9/11 Museum
- Timed ticket for the 9/11 Museum
Tour With Observatory
Addition to Guided Tour with admission to the One World Observatory
- Admission to the One World Observatory at Freedom Tower
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser .
- Guide to Russia
- Experience Russia
Best Places to Visit in Nizhny Novgorod
What are the best places to visit in nizhny novgorod.
- For medieval history : The Novgorod Kremlin, the nucleus of the city and a beacon of Russian power. Visit the fortress’s 13 towers, walk its walls for views of the city and river, and visit the exhibitions inside
- For industrial history : Visit the Open-Air Locomotive Museum to explore steam trains from the first half of the 20th century, or the GAZ History Museum to learn about the Gorky Automobile Factory, where the first Russian tank was created
- For beautiful streets and buildings : Nizhny is a marvel of contrasting architectural styles. Explore Rozhdestvenskaya and Bolshaya Pokrovskaya Streets, admire the State Bank, merchant mansions and Main Fair, and keep an eye out for many quirky statues
- For waterfront relaxation : Explore the Lower and Upper Volga Embankments, admire beautiful views from the Fedorovsky Embankment and cable car, and visit Russia’s longest stairs at the Chkhalov Staircase
- For religious sites : Visit the spectacular Stroganov Church, the more austere Spassky Old Fair Cathedral, the famous Church of the Nativity, and the Pechersky Ascension Monastery, one of the city’s spiritual centres
- For artistic highlights : Visit the State Art Museum’s collection of 15th-20th century European art, and discover the National Centre of Contemporary Art in the Kremlin’s former arsenal For folk culture: See traditional village architecture and learn about folk life at the Shchelokovsky Farm ethnographic museum, and discover the famous folk handicraft, Khokhloma, at the Khokhlomskaya Rospis factory and museum
Founded in 1221, Nizhny Novgorod became one of Russia’s most distinguished political and economic centres. Although a closed Soviet city from 1945 until 1991, today it is the fifth largest city in Russia, a vibrant hub attracting visitors from all over the world. Walk the historical streets and wide embankments, visit cultural and artistic institutions, and learn about the industrial past and folk heritage of one of Russia’s oldest cities. What are the best things to see and do in Nizhny Novgorod?
Learn about Nizhny Novgorod’s medieval history

Address: Ploshad Minina and Pozharskogo, Nizhy Novgorod
Discover Nizhny Novgorod’s industrial history

Address: 1V, Utitsa Gorokhovetskaya, Nizhy Novgorod Opening hours: 09:00 - 17:00 Mon-Sun
For those more interested in four-wheeled vehicles, take a trip to the GAZ History Museum to learn about the Gorky Automobile Plant, a joint venture between the Soviets and Ford and the production site of the first Soviet tank. See over 35,000 exhibits, including cars and military vehicles.
Address: 95, Prospekt Lenina, Nizhy Novgorod Opening hours: 09:00 - 16:00 Mon-Sat
Explore the city streets and architectural marvels

Must-visit spots include the lively Rozhdestvenskaya and Bolshaya Pokrovskaya Streets, home to many restaurants, bars, and historical buildings. Some of Nizhny’s most striking architectural wonders include the State Bank, Rukavishnikov Estate, and the Nizhny Novgorod Fair, an enormous Classicist structure. This building housed the largest fair in the Russian Empire, with thousands of stalls; inside the building today you’ll find exhibitions about the history of Nizhny Novgorod.
Keep an eye out for many interesting statues dotted around Nizhny Novgorod’s streets – in particular the Gromozeka book characters, the Veselaya koza (funny goat), the monument to author Jules Verne in his iconic hot air balloon, and the monument to Minin and Pozharsky, defenders of Moscow against the Poles (whose remains lie in the Kremlin cathedral).
Enjoy the peaceful waterfront

Visit the city’s religious sites

Discover Nizhny Novgorod’s artistic highlights

Address: 3, Kreml, Nizhny Novgorod
At the other end of the artistic spectrum, a visit to the Arsenal National Centre of Contemporary Art is highly recommended. Nizhny’s only museum dedicated to modern art is housed in the former Kremlin arsenal. More than a museum, it is a research and cultural centre dedicated to modern artistic development, offering not just exhibitions but concerts, theatre performances, film nights and more.
Address: 6, Kreml, Nizhny Novgorod
Get a glimpse of Russian folk culture and traditions
Shchelokovsky farm.

Visit this fascinating ethnographic museum to learn about the history of everyday life and folk customs of people living in the Nizhny Novgorod Volga region, and admire the wooden village architecture spanning from the 1600 – 1800s. While there, take a stroll around the surrounding forest and discover its wildlife, protected by local environmental programmes.
Address: 41, Gorbatovskaya Ulitsa, Nizhny Novgorod Opening hours: 10:00 - 17:00 Tue-Sun
Khokhlomskaya Rospis

Address: 18, Ulitsa Chkalova, Semenov, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast Opening hours: 08:00 - 17:00 Mon-Fri
Our travel brands include

Express to Russia
Join us on Facebook
We invite you to become a fan of our company on Facebook and read Russian news and travel stories. To become a fan, click here .
Join our own Russian Travel, Culture and Literature Club on Facebook. The club was created to be a place for everyone with an interest in Russia to get to know each other and share experiences, stories, pictures and advice. To join our club, please follow this link .
We use cookies to improve your experience on our Website, and to facilitate providing you with services available through our Website. To opt out of non-essential cookies, please click here . By continuing to use our Website, you accept our use of cookies, the terms of our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service . I agree
- Trip Planner
- Private Tours
- Small Group Tours
- Two Capitals
- City Breaks
- Trans-Siberian
- River Cruises
- Russia & Beyond
4-star edition of the private 9-day tour of the Russian capitals
5-star edition fo the private 9-day tour of Moscow & St. Petersburg
13-day in-depth discovery of Moscow, Kazan, and St. Petersburg
7-day tour designed to harness the best of the Venice of the North
11-day private discovery of Moscow, St. Petersburg, and the Golden Ring
Your Russia Getaway
Fill out the short trip survey to receive a personalized itinerary from a destination expert.
- Travel guide
- Before you go
- What to see
Russia Trip Planner
Learn about the dos and the don'ts for your amazing trip to Russia
- Our Partners
- Reservation Policies
Rated 9/10 on the Trustpilot review platform
- My itineraries
- Chat with us
- Trip survey
Groups & Agents
- For Suppliers
+1 (888) 744-6056
- North America : +1 (888) 744-6056
- Oceania and Australia : +61261888118
Nizhny Novgorod, Russia
You are here, about nizhny novgorod.
If you are still wondering, whether Nizhny Novgorod travel would be something you'd like to experience, let us help you - it would. This colorful Russian city full of cultural heritage might exceed your expectations since it has something to offer for everyone.
Reasons to Travel to Nizhny Novgorod
Art enthusiasts will surely enjoy the State Gorky Literature Museum which was named after the great Russian author Maxim Gorky. Bet you didn't know that Nizhny Novgorod was his birthplace? Do not worry, now you do.
There are also multiple art galleries and installations such as The Blogger's Bench which provides free Wi-Fi access if you are in the mood of blogging about your experience.
The musician community will not be disappointed as well, as the city has multiple live music bars and cafes open for the public and is often the place where great concerts are staged. If you are not that into art, there are plenty of other places worth putting on your Nizhny Novgorod itinerary, f.e., the grand red-brick Kremlin.
The Cathedral of Archangel Michael, which is actually the only church that has stood the test of time in Kremlin, along with multiple ancient towers is what makes this site a must-see. By the way, the magnificent church of St. Elijah is right around the corner, so make sure to make a little detour during your Nizhny Novgorod tour after seeing the Kremlin.
Another thing you should not miss during your Nizhny Novgorod sightseeing is the panorama of Strelka, overlooking the amazing view of the confluence of the rivers Oka and Volga and also the Fedorovsky Embankment, a perfect place for a stroll in the evening.
If you want to take a look at the scene from a different angle, hop on a boat trip along the two rivers! Nowadays Nizhny Novgorod is the fifth-largest city in the Russian Federation, somehow managing to maintain the unique heritage alongside its cultural versatility, thus looking at pictures is not enough, feel like exploring it yourself?
Best Things to Do in Nizhny Novgorod
- Witness the ancient Novgorod Kremlin
- Get inspired by the scenic panoramas of the Volga River
- Explore diverse museums of Nizhny Novgorod
More About Nizhny Novgorod
- Call us now
- Request a call
- Chat on WhatsApp
- Start Live chat
- Contact via email
Moscow & St. Petersburg Small Group Tours Private Tour Packages Trans-Siberian Trips Russian River Cruises Moscow Tour Packages St. Petersburg Tours All Russia Tours
Why Travel to Russia Best Time to Visit Russia Russian Visa Information Tips Before Traveling Tips on Arrival Russian Currency Moscow Travel Guide Read More in Our Blog
Hermitage Museum Church of the Savior on Blood The Kremlin Sergiev Posad, Golden Ring Kizhi Island The Red Square Siberia Lake Baikal
Fla. Seller of Travel Ref. No. ST39939 All Rights Reserved © 2024 About Us | Testimonials | Our Blog | Terms of Service | Privacy Policy

- Visit Our Blog about Russia to know more about Russian sights, history
- Check out our Russian cities and regions guides
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook to better understand Russia
- Info about getting Russian visa , the main airports , how to rent an apartment
- Our Expert answers your questions about Russia, some tips about sending flowers

Russian regions
- Bashkortostan republic
- Chuvashia republic
- Kirov oblast
- Mari El republic
- Mordovia republic
- Nizhegorodskaya oblast
- Orenburg oblast
- Penza oblast
- Samara oblast
- Saratov oblast
- Tatarstan republic
- Udmurt republic
- Ulyanovsk oblast
- Map of Russia
- All cities and regions
- Blog about Russia
- News from Russia
- How to get a visa
- Flights to Russia
- Russian hotels
- Renting apartments
- Russian currency
- FIFA World Cup 2018
- Submit an article
- Flowers to Russia
- Ask our Expert
Nizhny Novgorod city, Russia
The capital city of Nizhegorodskaya oblast .
Nizhny Novgorod - Overview
Nizhny Novgorod (colloquially often just “Nizhny”; from 1932 to 1990 - Gorky) is a large city located in the center of European Russia, the administrative center of the Volga Federal District and Nizhny Novgorod Oblast.
It is an important economic, industrial, scientific, educational, and cultural center of Russia, the largest transport hub of the Volga Federal District. Nizhny Novgorod is one of the main centers of river tourism in Russia. The historic part of the city is rich in sights and is a popular tourist destination.
The population of Nizhny Novgorod is about 1,234,000 (2022), the area - 411 sq. km.
The phone code - +7 831, the postal codes - 603000-603257.
Nizhny Novgorod city flag
Nizhny novgorod city coat of arms.

Nizhny Novgorod city map, Russia
Nizhny novgorod city latest news and posts from our blog:.
7 January, 2022 / Nikolai Bugrov's Summer Dacha in Volodarsk .
4 December, 2017 / Stadiums and Matches of the World Cup 2018 in Russia .
2 June, 2017 / The Most Beautiful House in Nizhny Novgorod .
13 March, 2016 / Official Look of Host Cities of World Cup 2018 in Russia .
29 September, 2015 / Nizhny Novgorod - the view from above .
More posts..
History of Nizhny Novgorod
Foundation of nizhny novgorod.
During the military campaigns of the Russian princes against the Volga Bulgaria, the place where the Oka River flows into the Volga was used as a gathering point for the Murom and Suzdal troops. In 1220, Grand Duke Yuri Vsevolodovich (the grandson of Prince Yuri Dolgoruky, the founder of Moscow) conducted a successful campaign against the Bulgars. After it, he “decided to strengthen this important place for Rus” and founded a town at the mouth of the Oka.
It was named Novgorod, which literally means “new town”. Later, the adjective “nizhny” (“lower”) was added to the name of the town in the Russian annals. This was probably done in order to distinguish it from the town of Novgorod (present Veliky Novgorod) and other Novgorods that existed at that time.
The founding of Nizhny Novgorod was the beginning of an active expansion of Russian influence in the Mordovian lands. Two white-stone churches were built in the fortress, including the Cathedral of the Archangel (1227) - evidence of the special role that the town had in the system of lands of Vladimir-Suzdal Rus. However, the Mongol invasion stopped further development.
Information about Nizhny Novgorod of the 13th century is extremely scarce. But it is known that after the invasion it revived relatively quickly. Nizhny Novgorod is constantly mentioned in Russian chronicles as a major political and economic center of North-Eastern Rus and a spiritual center of Orthodoxy in the Volga region. The town was often the object of conflicts between Moscow and Tver.
In 1392, the Moscow prince Vasily I received a jarlig for the Nizhny Novgorod Principality and captured Nizhny Novgorod. The final annexation of Nizhny Novgorod to the possessions of Moscow took place in the late 1440s.
More Historical Facts…
Nizhny Novgorod in the 16th-18th centuries
Under Ivan III and Vasily III, the town played the role of a border post and was a gathering place for military campaigns against the Kazan Khanate. In 1508-1515, the stone kremlin was built. After the capture of Kazan by Ivan the Terrible, the border role of Nizhny Novgorod became insignificant. At the same time, Nizhny Novgorod became the center of trade between Russia and the East and a large shipbuilding center.
In September 1611, during the Time of Troubles, the Second People’s Militia was organized in Nizhny Novgorod to fight the Poles who were able to establish control over Moscow. The militia consisted of detachments of townspeople, peasants of the central and northern regions of the Tsardom of Russia. The leaders were the Nizhny Novgorod merchant Kuzma Minin and Prince Dmitry Pozharsky (the monument to them is installed on Red Square in Moscow). In October 1612, the militia was able to completely liberate Moscow.
In the 17th century, a schism occurred in the Orthodox Church under Patriarch Nikon. It led to the formation of numerous settlements of Old Believers in the vicinity of Nizhny Novgorod. In 1695, during his Azov campaign, Peter I arrived in Nizhny Novgorod. In 1719, as a result of his administrative-territorial reforms, the town became the center of a separate Nizhny Novgorod Governorate. In 1722, setting off on the Persian campaign, Nizhny Novgorod was again visited by Peter I. Here he celebrated his 50th birthday.
In 1767, Nizhny Novgorod was visited by Empress Catherine II. During her stay in the town, she met the famous local mechanic and inventor Ivan Kulibin. After her visit, a new regular town plan was approved. The first town theater was built in 1798. Later, it became known as Nikolaevsky, in honor of Emperor Nicholas I.
Nizhny Novgorod in the 19th century
At the turn of the 18th and 19th centuries, Nizhny Novgorod became a major scientific and cultural center of the Russian Empire. In 1811, the population of Nizhny Novgorod was about 14,400 people. In 1817, the Makaryev Fair, the largest fair of the Russian Empire, was moved to the village of Kunavino (one of the districts of today’s Nizhny Novgorod). Before that, it was organized every year near the Makaryevsky Monastery, which burned down a year earlier. From that time on, it began to be called the Nizhny Novgorod Fair. Thanks to it, the rapid economic development of the town and adjacent villages began.
After Emperor Nicholas I visited the town in 1834, the large-scale reconstruction of Nizhny Novgorod began. In 1847, a water supply system appeared in the town and the first fountain was built. Private buildings in the Nizhny Novgorod Kremlin were demolished and new administrative buildings appeared in their place. A lot of new buildings, streets, boulevards, and gardens were built.
In 1849, a large industrial enterprise was founded in the village of Sormovo (another district of today’s Nizhny Novgorod). Later, it became known as the Sormovo plant. It was producing river steamers, various railway cars, steam locomotives, and trams. Thanks to the plant, Sormovo soon turned into a large village of workers. In 1862, the construction of the Moscow-Nizhny Novgorod railway was completed. In 1863, the population of the city was 41,500 people.
In 1896, the city hosted the All-Russian Trade and Industrial Exhibition. The radio receiver of the engineer A.S. Popov, the hyperboloid tower of the engineer V.G. Shukhov were demonstrated at the exhibition, as well as the first Russian car of the Frese and Yakovlev factories.
Nizhny Novgorod in the first half of the 20th century
In 1914, about 111,000 people lived in Nizhny Novgorod. In 1917, during the First World War, the Warsaw Polytechnic Institute was evacuated to this city, on the basis of which the Nizhny Novgorod Polytechnic Institute was created.
On October 7, 1932, Nizhny Novgorod was renamed Gorky due to the 40th anniversary of the literary and social activities of the writer Maxim Gorky. In 1933, the first permanent bridge across the Oka River was built. The railway bridge across the Volga was constructed too. Thanks to this, it became possible to go by rail through Gorky to the Urals and Siberia.
The 1930s were a period of rapid industrialization. In 1932, the largest industrial enterprise in the city was opened - the Gorky Automobile Plant (GAZ), an important object of the Soviet defense industry. In the 1930s-1940s, the city was even referred to as “Russian Detroit”. By 1939, the population of Nizhny Novgorod increased to about 644,000 people.
Every fourth resident of the Gorky region (about 822 thousand people) fought on the fronts of the Second World War. Of these, more than 350 thousand people did not return from the battlefields - they were killed, went missing or died from wounds in hospitals.
In June 1943, three large raids of German bombers were carried out on Gorky. The main target of air strikes was the Gorky Automobile Plant, which as a result was almost completely destroyed. It was rebuilt only in the middle of 1944. Over 500,000 wounded were treated in dozens of hospitals during the war years.
The city was an important center for the production of weapons. During the Second World War, every second Soviet car, every third tank and every fourth artillery piece were produced at Gorky’s plants. In total, about 38 thousand tanks, self-propelled guns, armored vehicles, 43 thousand mortars, 16 thousand aircraft, 22 submarines, 109 thousand cars, more than 85 thousand radio stations, as well as 101 thousand artillery pieces and 1,165 Katyusha multiple rocket launchers were produced in Gorky.
Nizhny Novgorod after the Second World War
In 1946, the first GAZ-M-20 “Pobeda” passenger car and the GAZ-51 truck left the assembly line of the Gorky Automobile Plant. In 1949, the construction of the monumental Chkalov Stairs connecting the Upper Volga and Lower Volga embankments was completed in the historic center of Nizhny Novgorod. On August 4, 1959, the resolution of the Council of Ministers of the USSR “On the closure of the city of Gorky for visiting by foreigners” was issued. In 1962, the population of Gorky exceeded 1 million people.
On January 18, 1970, a radiation accident occurred at the Krasnoe Sormovo plant. During the construction of a nuclear submarine, an unauthorized launch of the reactor took place. After working at prohibitive power for about 10-15 seconds, it partially collapsed. Hundreds of workers were exposed to the radioactive release. In total, over one thousand people took part in the liquidation of the consequences of the accident and were exposed to radiation.
In 1985, a subway was opened in Gorky. In 1980-1986, Andrei Sakharov, a world famous nuclear physicist, Nobel laureate, and activist, was in exile in Gorky to prevent his contacts with foreigners. In the early 1990s, the “closed city” status was lifted and the city became accessible to foreigners. On October 22, 1990, Gorky was renamed back to Nizhny Novgorod. In 1991, the population of the city reached its maximum - 1,445,000 people.
At the end of the 20th century, the information technology sphere began to actively develop in the city. In the 2000s, a transport problem arose because of the insufficient carrying capacity of the Nizhny Novgorod bridges connecting the lower part of the city and the upper one.
In February 2012, the Nizhny Novgorod Volga Aerial Tramway was opened. This 3661-meter-long gondola lift cable car connected Nizhny Novgorod with the town of Bor. Its daily passenger traffic is about 5,000 people. In 2013, the city electric train was launched - an alternative to the subway line from Sormovo to Moskovsky railway station.
Nizhny Novgorod hosted 6 matches of the FIFA World Cup 2018 . A new stadium was built, the old river port was demolished, a new park and embankments were created. Large-scale restoration of old streets and buildings took place, new museums were opened, hotels were built, and parks were reconstructed.
Streets of Nizhny Novgorod

One sunny summer day in Nizhniy Novgorod
Author: Denis Plekhanov

Apartment buildings in Nizhny Novgorod
Author: Eugene Ivanov

On the street in Nizhny Novgorod
Author: Sergey S. Kazenyuk
Nizhny Novgorod - Features
Nizhny Novgorod is located about 425 km east of Moscow, at the confluence of the two largest waterways of the European part of Russia - the Volga and Oka rivers. The city is divided by the Oka into two parts. The length of Nizhny Novgorod along the Oka is 20 km, along the Volga - about 30 km.
The climate in Nizhny Novgorod is moderately continental, with cold, long winters and warm, relatively short summers. The average temperature in January is minus 8.9 degrees Celsius, in July - plus 19.4 degrees Celsius.
A red deer is depicted on the coat of arms and flag of Nizhny Novgorod, which is a symbol of nobility, purity, life, wisdom, and justice. The City Day is celebrated on the 3rd Saturday in August.
In January 2019, Nizhny Novgorod was recognized as the best city in Russia in terms of quality of life. It took first place among Russian cities and 109th in the world in terms of quality of life. The rating was compiled by the site numbeo.com, which specializes in statistics on the cost of living and consumer prices in different countries of the world.
When compiling the rating, the purchasing power of the population, safety, health care, the cost of living, the ratio of real estate prices to the population’s income, traffic congestion, the level of environmental pollution, and climate were taken into account.
The main branches of the local industry are the production of cars and weapons, shipbuilding. Nizhny Novgorod is also one of the IT centers of Russia.
Nizhny Novgorod is a major transport hub. The city has a railway station, a river station, a cargo port, several berths for transshipment of goods. Strigino International Airport named after V.P. Chkalov offers regular flights to such cities as Yekaterinburg, Kazan, Kaliningrad, Moscow, Novosibirsk, Samara, St. Petersburg, Sochi, and a number of others.
Public transport in Nizhny Novgorod plays a very important role in ensuring the life of the city. At the same time, its work is hampered by the distribution of its population on the city’s territory, large daily migrations, a very high concentration of passenger traffic on the bridges across the Oka River, and the lack of an all-encompassing system of high-speed transport. There are municipal buses, fixed-route minibuses, trams, trolleybuses, the city train, and subway.
The tourist potential of Nizhny Novgorod is quite high. According to UNESCO, it is one of the most valuable historical cities in the world. In total, there are more than 600 unique historical, architectural and cultural monuments in Nizhny Novgorod, a variety of museums. The best time to visit Nizhny Novgorod is summer.
One of the alternative ways to visit Nizhny Novgorod is to take a river cruise along the Volga River. Travelers will find exciting excursions and meals in traditional Russian taverns. It will also be interesting to come during one of the many fairs or ethnographic festivals that are held in the city.
Main Attractions of Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Novgorod Kremlin (1508-1515) - a fortress in the historic center of Nizhny Novgorod and its oldest part, the main architectural complex of the city located on the right high bank, at the confluence of the Volga and Oka rivers. To date, all 13 towers of the Nizhny Novgorod Kremlin have been preserved or have been restored. The thickness of the wall at the base reaches 5 meters. There are exhibitions in the towers of the fortress; a section of the wall is open for tourists to visit.
In the past, there were several churches on the territory of the Nizhny Novgorod Kremlin. Today, only the Archangel Michael Cathedral has survived, built no later than the middle of the 16th century and rebuilt in 1628-1631 - the oldest surviving building in the kremlin. There is the grave of Kuzma Minin inside it.
An excellent view of the Volga River and Strelka (the confluence of the Oka and Volga) opens from the walls of the Nizhny Novgorod Kremlin. Here you can also see a collection of military equipment from the Second World War.
Nizhny Novgorod State Art Museum - one of the oldest museums in Russia, the largest museum of fine arts in the Nizhny Novgorod region. The Governor’s Palace on the territory of the Nizhny Novgorod Kremlin houses a permanent exhibition of Russian art and a collection of artistic silver.
In the House of the Merchant and Benefactor D.V. Sirotkin (Verkhnevolzhskaya Embankment, 3), an exposition of Western European art is presented and, separately, the painting by K.E. Makovsky “The appeal of Kuzma Minin to the citizens of Nizhny Novgorod” - one of the largest paintings on a historical theme in Russia (698x594 cm).
Chkalov Stairs (1943-1949) - a monumental staircase in the form of a figure eight in the historic center of Nizhny Novgorod. Connecting the Upper Volga (Verkhnevolzhskaya) and Lower Volga (Nizhnevolzhskaya) embankments, it is one of the longest stairs in Russia. It starts from the observation deck at the monument to Valery Chkalov (the famous Soviet pilot who made the first non-stop flight from the USSR to the USA via the North Pole), next to the St. George Tower of the Nizhny Novgorod Kremlin.
Bolshaya Pokrovskaya Street - the main street of Nizhny Novgorod built up with noble mansions of the past centuries. A large part of Bolshaya Pokrovskaya is reserved for the pedestrian zone and is analogous to the pedestrian Arbat Street in Moscow. There are a lot of historic houses, cafes, souvenir shops, boutiques, monuments, and sculptures here. The length of the street is over 2 km.
The building of the State Bank (Bolshaya Pokrovskaya Street, 26), resembling a medieval palace, is an outstanding architectural monument built in the Russian Revival style in 1911-1913. In the Museum of Old Equipment and Tools (Bolshaya Pokrovskaya Street, 43), you can see unique exhibits, hear their history, and even touch them.
Fedorovsky Embankment - one of the most beautiful embankments in Nizhny Novgorod and the best observation deck in the city. Everything is perfectly visible from this embankment: the old part of the city, the river station with a park, the Kanavinsky bridge - one of the oldest in the city, and, of course, the opposite bank of the Oka River with the Alexander Nevsky Cathedral, the confluence of the Oka and Volga. People also come here to watch the sunset.
Nizhny Novgorod Volga Aerial Tramway . This cable car, 3661 meters long, connects the high right bank of the Volga River, where the historic part of Nizhny Novgorod is located, with the town of Bor. It has the largest unsupported span over the water surface in Europe - 861 meters.
A one way trip during which you can admire the picturesque views of Nizhny Novgorod and the Volga River takes 15 minutes. It is better to use it in good sunny weather, because in windy weather, the movement of the cabins can be stopped. Sennaya Square on Kazanskaya Embankment.
Nizhny Novgorod State Museum of History and Architecture (1875-1877). Also known as the Mansion of S.M. Rukavishnikov, it is an architectural ensemble built in the eclectic style in the historic center of Nizhny Novgorod, one of the most important and famous architectural monuments of this city. Guided tours are held in the premises, allowing you to learn about the life of the former owners of the mansion, as well as look at the historical expositions of different years. Verkhnevolzhskaya Embankment, 7.
Main Palace of Nizhny Novgorod Fair - a luxurious building constructed in the forms of Old Russian architecture of the 17th century. Today, exhibitions of various formats are held here, as well as the multimedia exposition “Russia - my history” dedicated mainly to the history of Nizhny Novgorod starting from the Finno-Ugric peoples. Sovnarkomovskaya Street, 13.
Museum of the History of the Gorky Automobile Plant . The museum houses expositions telling about the history and development of the Gorky Automobile Plant. In total, there are over 40,000 exhibits. Here you can see a collection of Soviet vintage cars, which includes “Chaika”, “Volga”, the truck “GAZ-51”, and a lot of others. Lenina Avenue, 95.
Alexander Nevsky Cathedral (1868-1881) - the most noticeable sight of the lower part of Nizhny Novgorod, which can be seen from all observation decks of the upper city. The church, 87 meters high, was built on the site of the Nizhny Novgorod Fair at the expense of merchants, who wanted to perpetuate the visit of Emperor Alexander II. Strelka Street, 3a.
Church of the Nativity of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1696-1719) - one of the best examples of the Stroganov Baroque, an architectural monument of federal significance. From a distance, this colorful building looks like a sugar gingerbread with “candy” domes and decorated with stone flowers, pears and apples. Rozhdestvenskaya Street, 34.
Pechersky Ascension Monastery - one of the most interesting places in Nizhny Novgorod, where you can feel the spirit of the city. Most of the monastery buildings date back to the first half of the 17th century. A lot of beautiful photographs can be taken here. Privolzhskaya Sloboda Street, 108.
Limpopo Zoo - the first private zoo in Russia. More than 270 species of animals live here, 25 of which are listed in the Red Book of the Russian Federation. It is located on the territory of the Sormovsky Park on an area of 7.1 hectares. Yaroshenko Street, 7b.
Architectural and Ethnographic Museum-Reserve “Shcholokovskiy Khutor” . The exposition of this museum is represented by 16 objects of rural architecture: residential houses, barns, mills and churches of the 17th-19th centuries brought from the northern districts of the Nizhny Novgorod region. The facades of the houses are decorated with traditional relief carvings. In the premises of the houses, interiors with authentic items of peasant life have been restored. Gorbatovskaya Street, 41.
Nizhny Novgorod city of Russia photos
Pictures of nizhny novgorod.

Chkalov Stairs and the Nizhny Novgorod Kremlin
Author: Sergey Bulanov

Alexander Nevsky Cathedral in Nizhny Novgorod
Author: Evgeniy Balashov

Shopping and office center Smart in Nizhny Novgorod
Author: Diman Lazarev
Sights of Nizhny Novgorod

Annunciation Monastery - the oldest monastery in Nizhny Novgorod

Nizhny Novgorod Cathedral Mosque

Church in honor of the icon of the Mother of God Joy of All Who Sorrow in Nizhny Novgorod
The comments of our visitors
- Currently 3.11/5
Rating: 3.1 /5 (267 votes cast)
Sponsored Links:

COMMENTS
Tour Ground Zero with a New Yorker who can share their personal experience of 9/11. Visit the 9/11 Memorial, 9/11 Museum, and the observatory at Freedom Tower. 911 Ground Zero - Tours of 9/11 Memorial, 9/11 Museum Tickets, and One World Observatory Access Included
This tour runs Weds to Mon throughout the year. From $35 per person. Book at Viator.com. Ground Zero 9/11 Memorial Tour. This walking tour is all about seeking the small landmarks around Ground Zero that tell the biggest stories. You'll learn about the heroics of the emergency services at the Firefighter's 9/11 Memorial and stop by St Paul ...
Dark tourism: when tragedy meets tourism
All Access Tour. Includes: 90-minute guided tour of Ground Zero. Timed ticket for the 9/11 Museum. Admission to the One World Observatory at Freedom Tower. $114 per adult. and. $104 per child. Check Availability Learn More.
Born from a 'Day of Terror'. In 2002, the ruins of the World Trade Center in New York attracted 3.6 million visitors; the observation deck from the intact towers used to pull in an average of 1.8 million tourists per year. 'Ground Zero' as the site became known in the aftermath of the terrorist attacks on September 11 2001 appears to be ...
Because of this, she explains, "the architecture of absence is now the model" for most dark tourism sites. Absence is clearly an overriding draw of ground zero, the emptiness representing the physical destruction of two 110-story structures, once the world's most recognizable skyscrapers. The National September 11 Memorial and Museum ...
The Ground Zero Memorial and Museum are officially called the 9/11 Memorial and the 9/11 Memorial Museum.Visiting Ground Zero will likely be difficult for most, if not all, of us, but this incredible tribute to the thousands of heroes lost on and involved in 9/11/01 is a must-do for anyone visiting NYC.. The 9/11 Memorial opened on September 11, 2011 and the 9/11 Memorial Museum opened May 2014.
NYC Ground Zero, 9/11 Memorial, One World Observatory ...
Several tour companies combine a walking tour of the 9/11 Memorial and Ground Zero with tickets to the 9/11 Museum. Learn more. TIP: Admission to the museum is included for free with the purchase of either the New York Pass, the Explorer Pass, or the CityPass booklet. Read our post comparing the different tourist attractions passes in NYC.
NYC 9/11 Memorial and Ground Zero Tour with Museum ...
180 Greenwich St, New York, NY 10007, USA. Get directions. Phone +1 212-312-8800. Visit website. The World Trade Center site is an important place for those who want to pay tribute to the lives lost in the events of 9/11 and gain some perspective regarding that fateful day. The site in lower Manhattan includes an 8-acre memorial plaza dedicated ...
June 13, 2022. Ground Zero is, without doubt, one of the most significant sites in New York City. It's home to the 9/11 Memorial & Museum, plus a collection of brand new buildings that make up the World Trade Center. Taking a guided tour is a great way to experience it. You'll hear firsthand accounts from local guides and get an in-depth ...
How To Visit Ground Zero and 9/11 Memorial Museum in ...
Abstract. This article aims to interrogate the framing of New York's Ground Zero as a 'dark tourist' destination, with particular reference to the entanglement of notions of kitsch in academic discussions of the events of 11 September 2001. What makes Ground Zero contentious, even scandalous, for many scholars is the presence of a ...
Gain a deeper understanding of the events surrounding the attacks on the World Trade Center on September 11, 2001, and the acts of heroism that rallied a nation on this 1.5 hour walking tour of Ground Zero. A certified guide with a personal connection to the events shares firsthand stories as you explore the site of the former World Trade Center and the National 9/11 Memorial, where you can ...
New York City Tourism New York City Hotels New York City Bed and Breakfast New York City Vacation Rentals Flights to New York City New York City Restaurants ... It's certainly understandable why, 23 years later, there are people still referring to it as Ground Zero (it's not a conscious choice & is become less frequently seen here on the ...
Dark Tourism: Destinations of Death, Tragedy and ...
The viewing platform at Ground Zero was initially constructed to manage the thousands of people who traveled to New York in response to the shocking media images of 11 September. However, their desire to escape mediation and touch "the real" had the opposite effect—it transformed Ground Zero into a tourist attraction.
9/11 Ground Zero Tour With Freedom Tower. Our Ground Zero Tour, which includes the 9/11 Memorial, plus admission to the One World Observatory in Freedom Tower. $84 per adult. and. $75 per child. Check Availability Tour Details. Including the 9/11 Memorial, 9/11 Museum, and One World Observatory.
Studies on dark tourism destinations, such as the Auschwitz-Birkenau death camp and the site of 9/11's Ground Zero, have not found such strong tourist moral conflicts as those identified in this ...
Explore Rozhdestvenskaya and Bolshaya Pokrovskaya Streets, admire the State Bank, merchant mansions and Main Fair, and keep an eye out for many quirky statues. Founded in 1221, Nizhny Novgorod became one of Russia's most distinguished political and economic centres. Although a closed Soviet city from 1945 until 1991, today it is the fifth ...
Nizhny Novgorod - Wikipedia
If you are not that into art, there are plenty of other places worth putting on your Nizhny Novgorod itinerary, f.e., the grand red-brick Kremlin. The Cathedral of Archangel Michael, which is actually the only church that has stood the test of time in Kremlin, along with multiple ancient towers is what makes this site a must-see.
Nizhny Novgorod is one of the main centers of river tourism in Russia. The historic part of the city is rich in sights and is a popular tourist destination. The population of Nizhny Novgorod is about 1,234,000 (2022), the area - 411 sq. km. The phone code - +7 831, the postal codes - 603000-603257.