- Subscribe to BBC Science Focus Magazine
- Previous Issues
- Future tech
- Everyday science
- Planet Earth
- Newsletters

Everything you need to know about space travel (almost)
We're a long way from home...
Paul Parsons
When did we first start exploring space?
The first human-made object to go into space was a German V2 missile , launched on a test flight in 1942. Although uncrewed, it reached an altitude of 189km (117 miles).
Former Nazi rocket scientists were later recruited by both America and Russia (often at gunpoint in the latter case), where they were instrumental in developing Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) – rockets capable of carrying nuclear weapons from one side of the planet to the other.
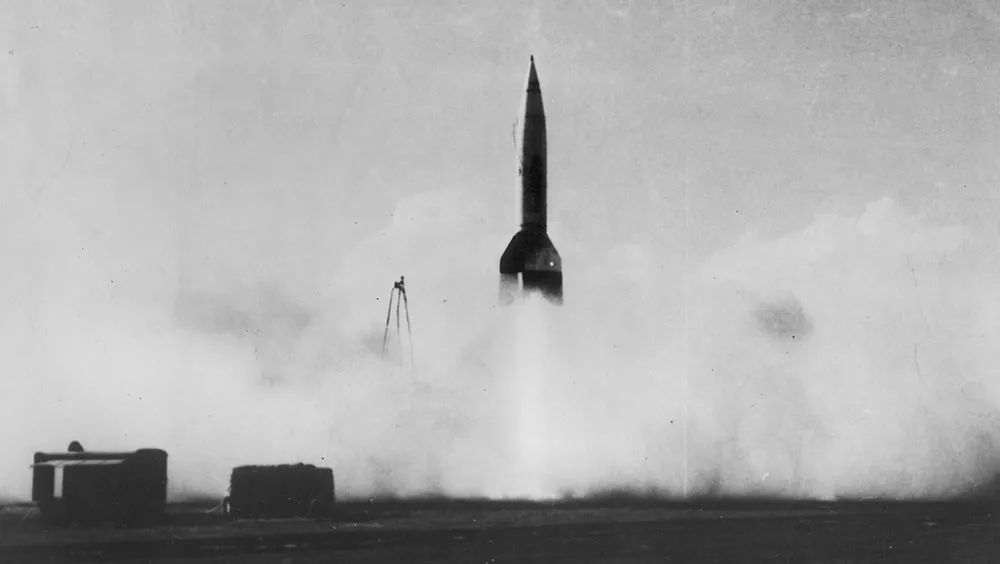

It was these super-missiles that formed the basis for the space programmes of both post-war superpowers. As it happened, Russia was the first to reach Earth orbit, when it launched the uncrewed Sputnik 1 in October 1957, followed a month later by Sputnik 2, carrying the dog Laika – the first live animal in space.
The USA sent its first uncrewed satellite, Explorer 1, into orbit soon after, in January 1958. A slew of robotic spaceflights followed, from both sides of the Atlantic, before Russian cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin piloted Vostok 1 into orbit on 12 April 1961, to become the first human being in space . And from there the space race proper began, culminating in Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin becoming the first people to walk on the Moon as part of NASA's Apollo programme .
Why is space travel important?
Space exploration is the future. It satisfies the human urge to explore and to travel, and in the years and decades to come it could even provide our species with new places to call home – especially relevant now, as Earth becomes increasingly crowded .
Extending our reach into space is also necessary for the advancement of science. Space telescopes like the Hubble Space Telescope and probes to the distant worlds of the Solar System are continually updating, and occasionally revolutionising, our understanding of astronomy and physics.
- Subscribe to the Science Focus Podcast on these services: Acast , iTunes , Stitcher , RSS , Overcast
But there are also some very practical reasons, such as mining asteroids for materials that are extremely rare here on Earth.
One example is the huge reserve of the chemical isotope helium-3 thought to be locked away in the soil on the surface of the Moon . This isotope is a potential fuel for future nuclear fusion reactors – power stations that tap into the same source of energy as the Sun. Unlike other fusion fuels, helium-3 gives off no hard-to-contain and deadly neutron radiation.
However, for this to happen the first challenge to overcome is how to build a base on the Moon. In 2019, China's Chang’e 4 mission marked the beginning of a new space race to conquer the Moon, signalling their intent to build a permanent lunar base , while the NASA Artemis mission plans to build a space station, called Lunar Orbital Platform-Gateway , providing a platform to ferry astronauts to the Moon's surface.
Could humans travel into interstellar space and how would we get there?
It’s entirely feasible that human explorers will visit the furthest reaches of our Solar System. The stars, however, are another matter. Interstellar space is so vast that it takes light – the fastest thing we know of in the Universe – years, centuries and millennia to traverse it. Faster-than-light travel may be possible one day, but is unlikely to become a reality in our lifetimes.
It’s not impossible that humans might one day cross this cosmic gulf, though it won’t be easy. The combustion-powered rocket engines of today certainly aren’t up to the job – they just don’t use fuel efficiently enough. Instead, interstellar spacecraft may create a rocket-like propulsion jet using electric and magnetic fields. This so-called ‘ ion drive ’ technology has already been tested aboard uncrewed Solar System probes.

Another possibility is to push spacecraft off towards the stars using the light from a high-powered laser . A consortium of scientists calling themselves Breakthrough Starshot is already planning to send a flotilla of tiny robotic probes to our nearest star, Proxima Centauri, using just this method.
Though whether human astronauts could survive such punishing acceleration, or the decades-long journey through deep space, remains to be seen.
How do we benefit from space exploration?
Pushing forward the frontiers of science is the stated goal of many space missions . But even the development of space travel technology itself can lead to unintended yet beneficial ‘spin-off’ technologies with some very down-to-earth applications.
Notable spin-offs from the US space programme, NASA, include memory foam mattresses, artificial hearts, and the lubricant spray WD-40. Doubtless, there are many more to come.
Read more about space exploration:
- The next giant leaps: The UK missions getting us to the Moon
- Move over, Mars: why we should look further afield for future human colonies
- Everything you need to know about the Voyager mission
- 6 out-of-this-world experiments recreating space on Earth
Space exploration also instils a sense of wonder, it reminds us that there are issues beyond our humdrum planet and its petty squabbles, and without doubt it helps to inspire each new generation of young scientists. It’s also an insurance policy. We’re now all too aware that global calamities can and do happen – for instance, climate change and the giant asteroid that smashed into the Earth 65 million years ago, leading to the total extinction of the dinosaurs .
The lesson for the human species is that we keep all our eggs in one basket at our peril. On the other hand, a healthy space programme, and the means to travel to other worlds, gives us an out.
Is space travel dangerous?
In short, yes – very. Reaching orbit means accelerating up to around 28,000kph (17,000mph, or 22 times the speed of sound ). If anything goes wrong at that speed, it’s seldom good news.
Then there’s the growing cloud of space junk to contend with in Earth's orbit – defunct satellites, discarded rocket stages and other detritus – all moving just as fast. A five-gram bolt hitting at orbital speed packs as much energy as a 200kg weight dropped from the top of an 18-storey building.

And getting to space is just the start of the danger. The principal hazard once there is cancer-producing radiation – the typical dose from one day in space is equivalent to what you’d receive over an entire year back on Earth, thanks to the planet’s atmosphere and protective magnetic field.
Add to that the icy cold airless vacuum , the need to bring all your own food and water, plus the effects of long-duration weightlessness on bone density, the brain and muscular condition – including that of the heart – and it soon becomes clear that venturing into space really isn’t for the faint-hearted.
When will space travel be available to everyone?
It’s already happening – that is, assuming your pockets are deep enough. The first self-funded ‘space tourist’ was US businessman Dennis Tito, who in 2001 spent a week aboard the International Space Station (ISS) for the cool sum of $20m (£15m).
Virgin Galactic has long been promising to take customers on short sub-orbital hops into space – where passengers get to experience rocket propulsion and several minutes of weightlessness, before gliding back to a runway landing on Earth, all for $250k (£190k). In late July 2020, the company unveiled the finished cabin in its SpaceShipTwo vehicle, suggesting that commercial spaceflights may begin shortly.
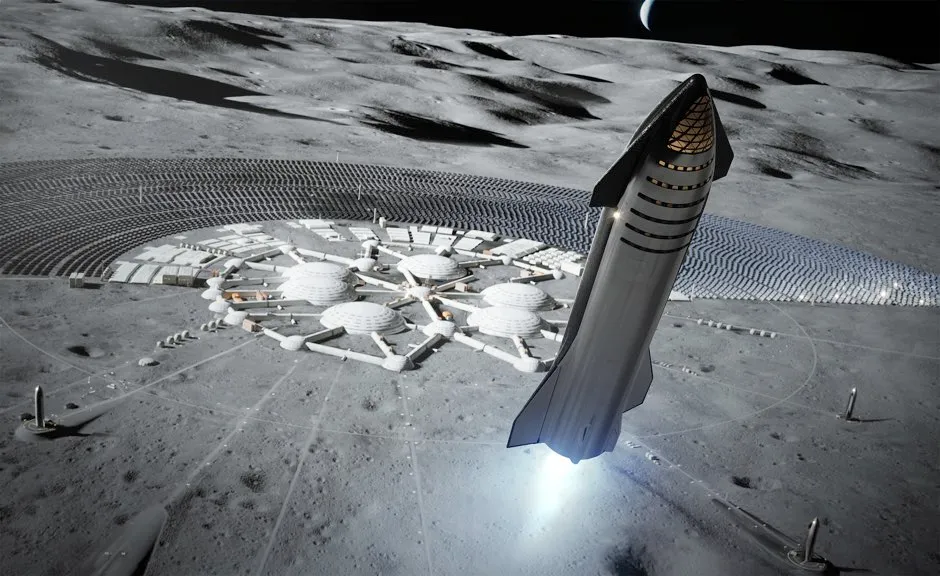
Meanwhile, Elon Musk’s SpaceX , which in May 2020 became the first private company to launch a human crew to Earth orbit aboard the Crew Dragon , plans to offer stays on the ISS for $35k (£27k) per night. SpaceX is now prototyping its huge Starship vehicle , which is designed to take 100 passengers from Earth to as far afield as Mars for around $20k (£15k) per head. Musk stated in January that he hoped to be operating 1,000 Starships by 2050.
10 Short Lessons in Space Travel by Paul Parsons is out now (£9.99, Michael O'Mara)
- Buy now from Amazon UK , Foyles , WH Smith and Wordery
Share this article

- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy policy
- Cookies policy
- Code of conduct
- Magazine subscriptions
- Manage preferences

The future of spaceflight—from orbital vacations to humans on Mars
NASA aims to travel to the moon again—and beyond. Here’s a look at the 21st-century race to send humans into space.
Welcome to the 21st-century space race, one that could potentially lead to 10-minute space vacations, orbiting space hotels , and humans on Mars. Now, instead of warring superpowers battling for dominance in orbit, private companies are competing to make space travel easier and more affordable. This year, SpaceX achieved a major milestone— launching humans to the International Space Station (ISS) from the United States —but additional goalposts are on the star-studded horizon.
Private spaceflight
Private spaceflight is not a new concept . In the United States, commercial companies played a role in the aerospace industry right from the start: Since the 1960s, NASA has relied on private contractors to build spacecraft for every major human spaceflight program, starting with Project Mercury and continuing until the present.
Today, NASA’s Commercial Crew Program is expanding on the agency’s relationship with private companies. Through it, NASA is relying on SpaceX and Boeing to build spacecraft capable of carrying humans into orbit. Once those vehicles are built, both companies retain ownership and control of the craft, and NASA can send astronauts into space for a fraction of the cost of a seat on Russia’s Soyuz spacecraft.
SpaceX, which established a new paradigm by developing reusable rockets , has been running regular cargo resupply missions to the International Space Station since 2012. And in May 2020, the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft carried NASA astronauts Doug Hurley and Bob Behnken to the ISS , becoming the first crewed mission to launch from the United States in nearly a decade. The mission, called Demo-2, is scheduled to return to Earth in August. Boeing is currently developing its Starliner spacecraft and hopes to begin carrying astronauts to the ISS in 2021.
Other companies, such as Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic , are specializing in sub-orbital space tourism. Test launch video from inside the cabin of Blue Origin’s New Shepard shows off breathtaking views of our planet and a relatively calm journey for its first passenger, a test dummy cleverly dubbed “Mannequin Skywalker.” Virgin Galactic is running test flights on its sub-orbital spaceplane , which will offer paying customers roughly six minutes of weightlessness during its journey through Earth’s atmosphere.
With these and other spacecraft in the pipeline, countless dreams of zero-gravity somersaults could soon become a reality—at least for passengers able to pay the hefty sums for the experience.
Early U.S. Spaceflight

Looking to the moon
Moon missions are essential to the exploration of more distant worlds. After a long hiatus from the lunar neighborhood, NASA is again setting its sights on Earth’s nearest celestial neighbor with an ambitious plan to place a space station in lunar orbit sometime in the next decade. Sooner, though, the agency’s Artemis program , a sister to the Apollo missions of the 1960s and 1970s, is aiming to put the first woman (and the next man) on the lunar surface by 2024.
For Hungry Minds
Extended lunar stays build the experience and expertise needed for the long-term space missions required to visit other planets. As well, the moon may also be used as a forward base of operations from which humans learn how to replenish essential supplies, such as rocket fuel and oxygen, by creating them from local material.
You May Also Like

In a first, NASA Mars lander feels shockwaves from meteor impacts

SpaceX takes 4 passengers to orbit—a glimpse at private spaceflight’s future

Why go back to the moon? NASA’s Artemis program has even bigger ambitions
Such skills are crucial for the future expansion of human presence into deeper space, which demands more independence from Earth-based resources. And although humans have visited the moon before, the cratered sphere still harbors its own scientific mysteries to be explored—including the presence and extent of water ice near the moon's south pole, which is one of the top target destinations for space exploration .
NASA is also enlisting the private sector to help it reach the moon. It has awarded three contracts to private companies working on developing human-rated lunar landers—including both Blue Origin and SpaceX. But the backbone of the Artemis program relies on a brand new, state-of-the-art spacecraft called Orion .
Archival Photos of Spaceflight

Currently being built and tested, Orion—like Crew Dragon and Starliner—is a space capsule similar to the spacecraft of the Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo programs, as well as Russia’s Soyuz spacecraft. But the Orion capsule is larger and can accommodate a four-person crew. And even though it has a somewhat retro design, the capsule concept is considered to be safer and more reliable than NASA’s space shuttle—a revolutionary vehicle for its time, but one that couldn’t fly beyond Earth’s orbit and suffered catastrophic failures.
Capsules, on the other hand, offer launch-abort capabilities that can protect astronauts in case of a rocket malfunction. And, their weight and design mean they can also travel beyond Earth’s immediate neighborhood, potentially ferrying humans to the moon, Mars, and beyond.
A new era in spaceflight
By moving into orbit with its Commercial Crew Program and partnering with private companies to reach the lunar surface, NASA hopes to change the economics of spaceflight by increasing competition and driving down costs. If space travel truly does become cheaper and more accessible, it’s possible that private citizens will routinely visit space and gaze upon our blue, watery home world—either from space capsules, space stations, or even space hotels like the inflatable habitats Bigelow Aerospace intends to build .
The United States isn’t the only country with its eyes on the sky. Russia regularly launches humans to the International Space Station aboard its Soyuz spacecraft. China is planning a large, multi-module space station capable of housing three taikonauts, and has already launched two orbiting test vehicles—Tiangong-1 and Tiangong-2, both of which safely burned up in the Earth’s atmosphere after several years in space.
Now, more than a dozen countries have the ability to launch rockets into Earth orbit. A half-dozen space agencies have designed spacecraft that shed the shackles of Earth’s gravity and traveled to the moon or Mars. And if all goes well, the United Arab Emirates will join that list in the summer of 2020 when its Hope spacecraft heads to the red planet . While there are no plans yet to send humans to Mars, these missions—and the discoveries that will come out of them—may help pave the way.
Related Topics
- SPACE EXPLORATION
- SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
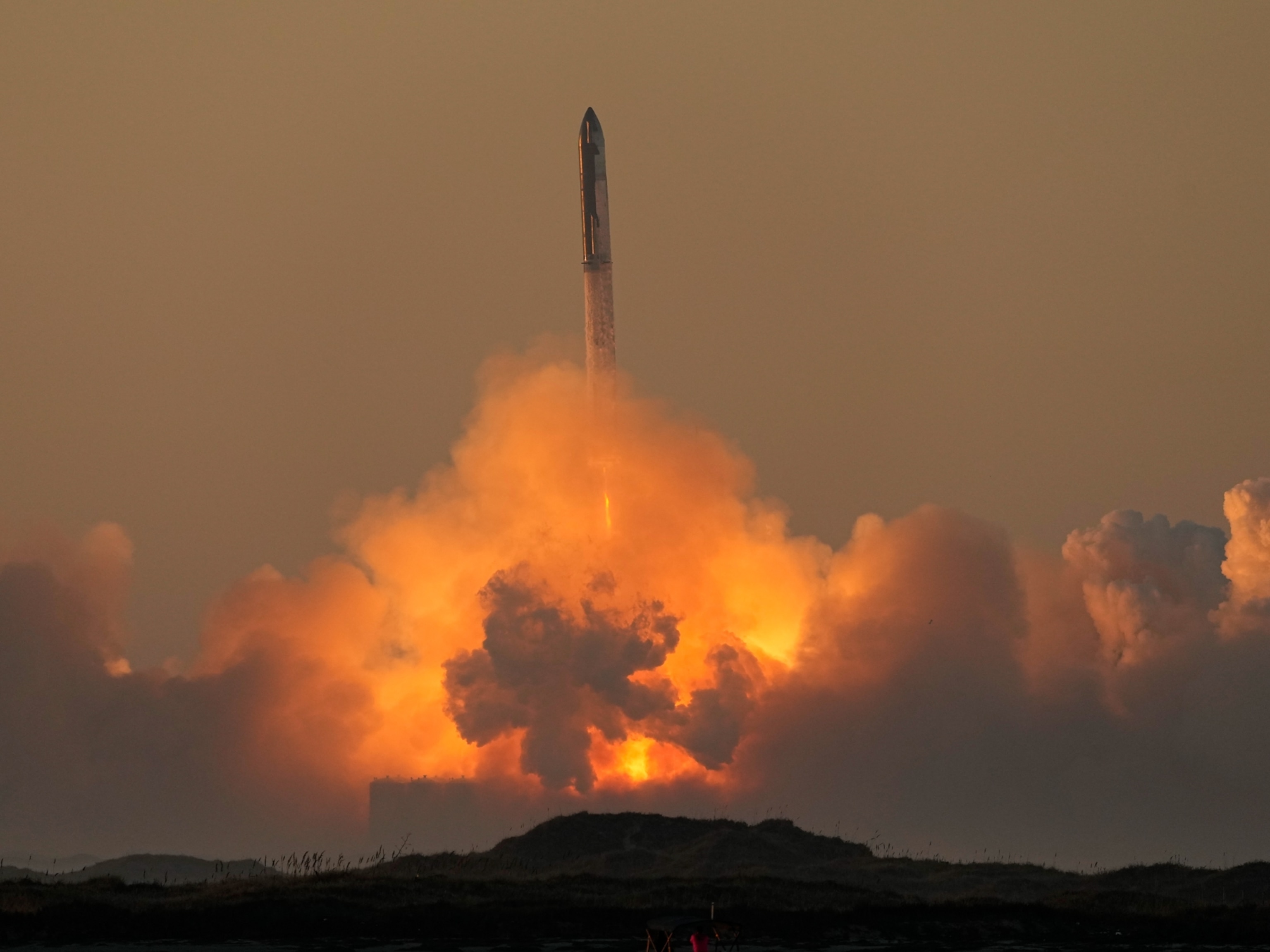

Second SpaceX megarocket launch ends with another explosion. What happens next?

Why did India land near the moon’s south pole?

U.S. returns to the moon as NASA's Odysseus successfully touches down
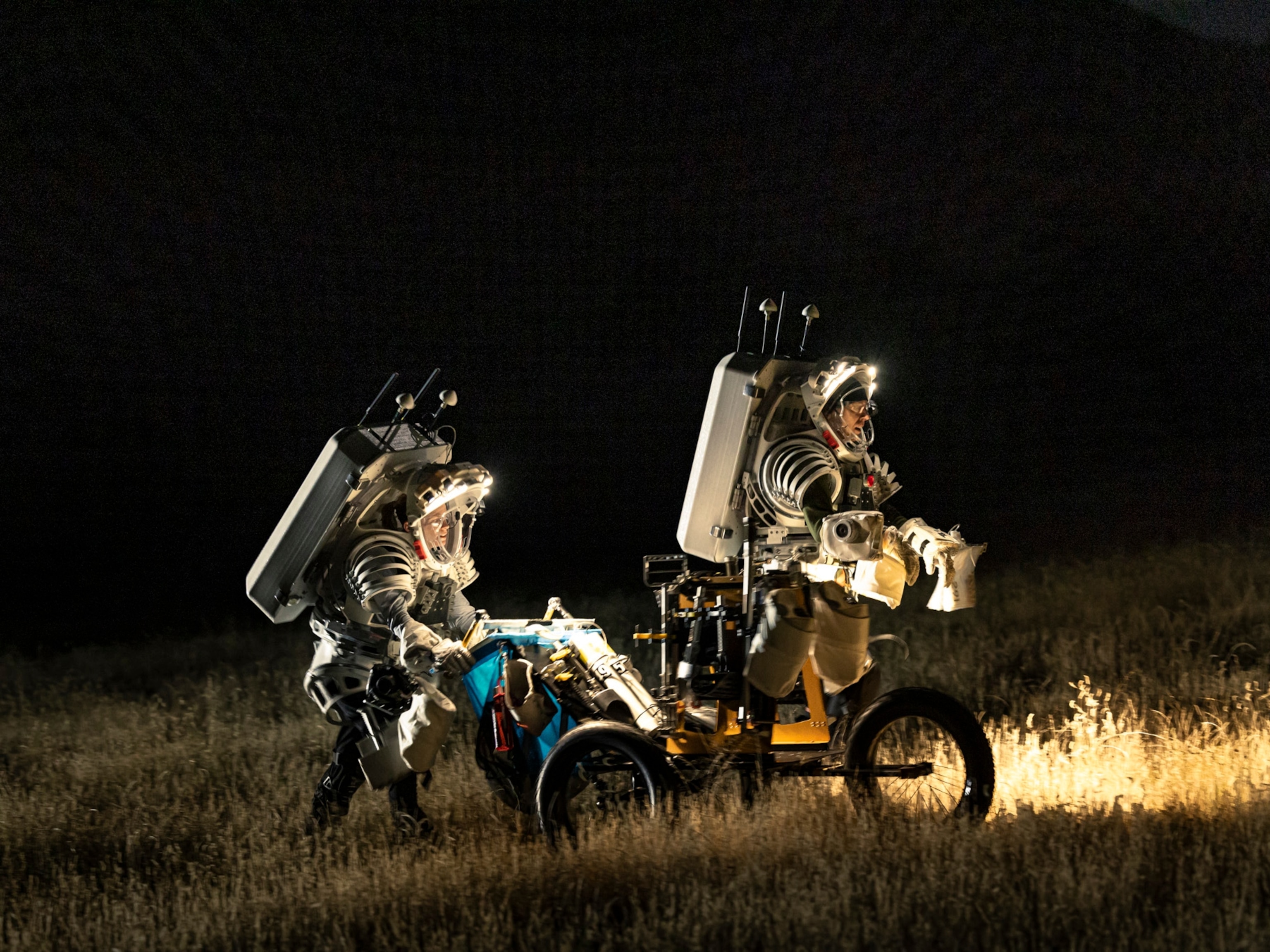

In the Arizona desert, NASA prepares for walking on the moon
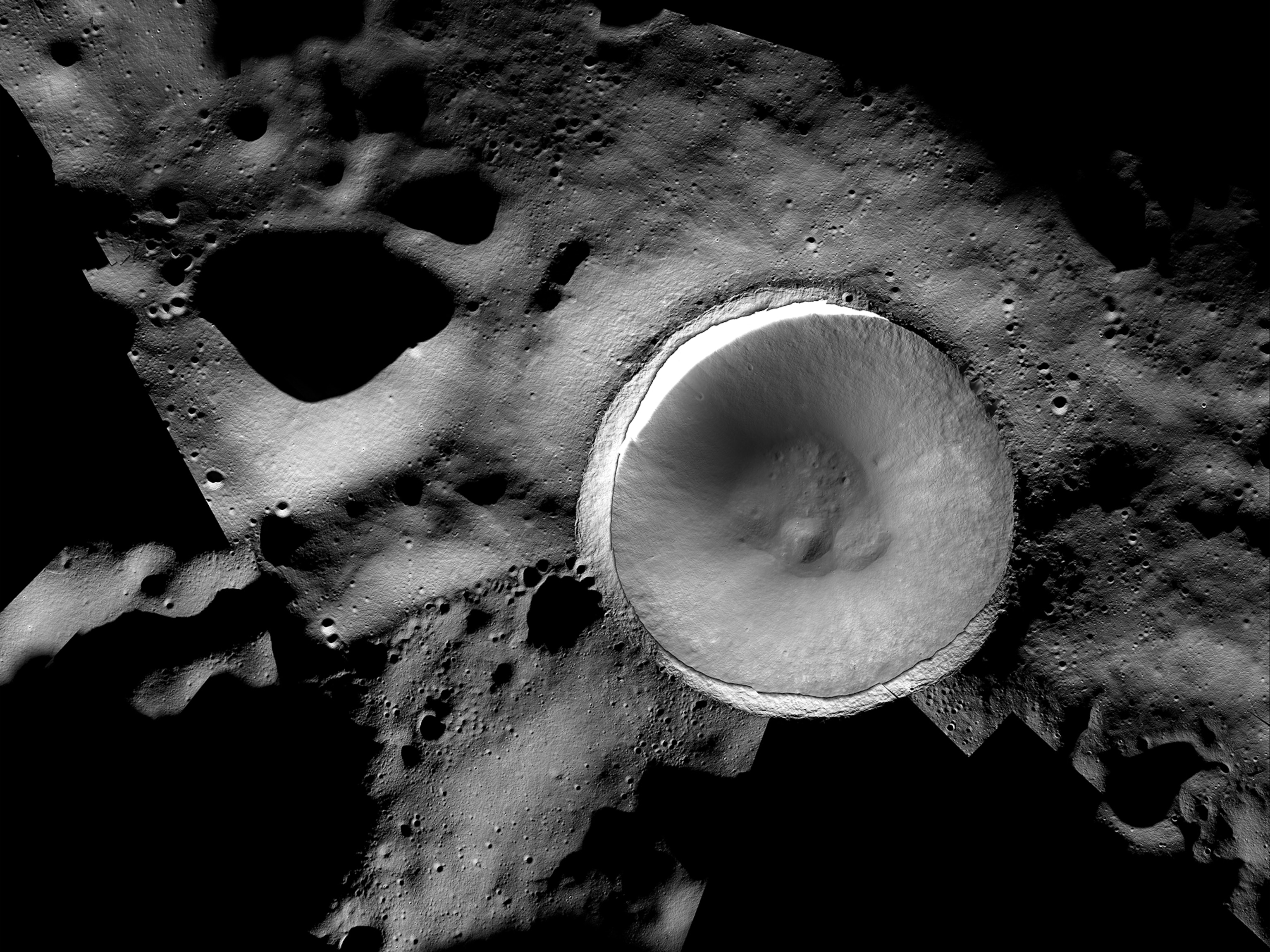

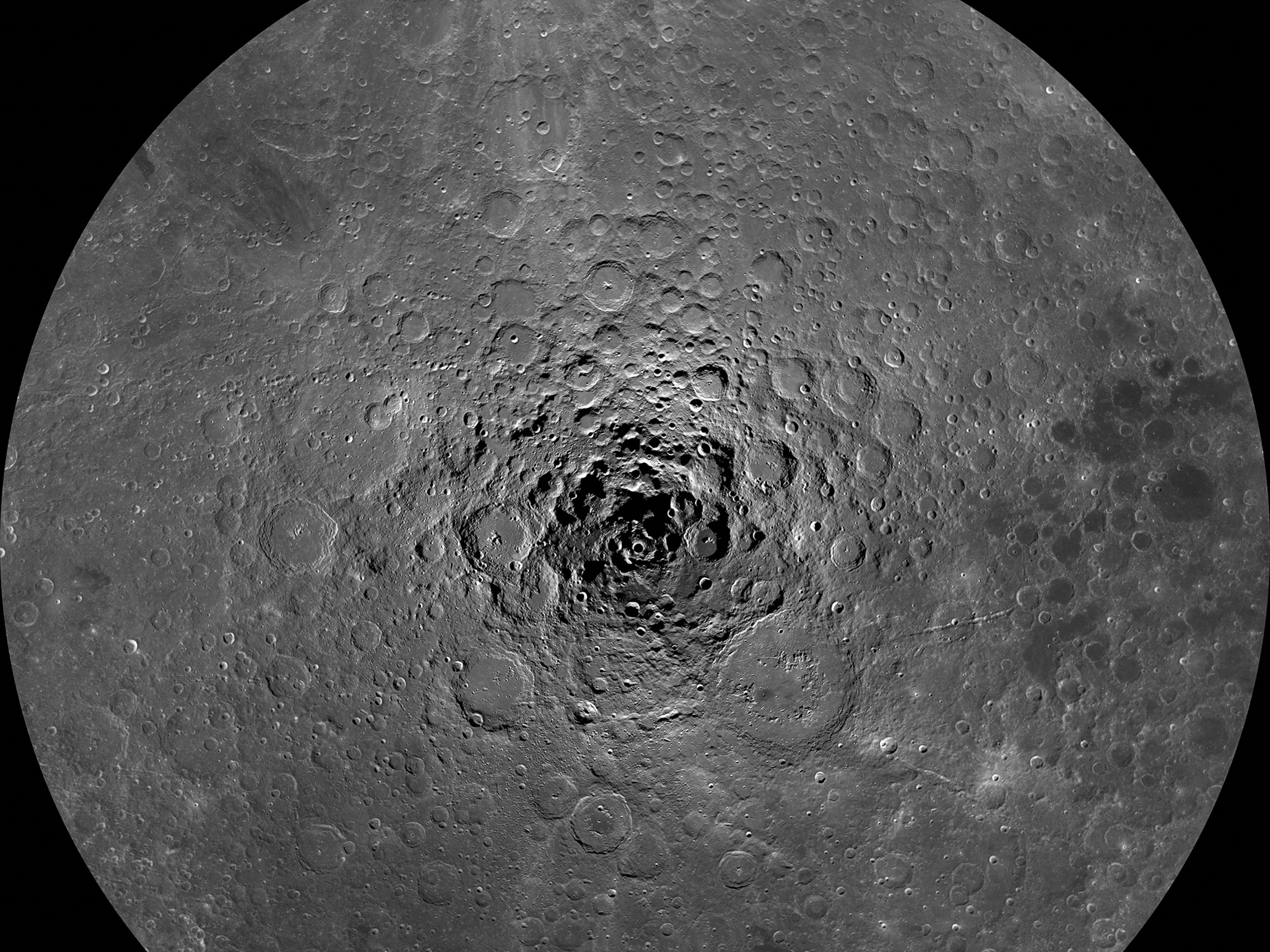
The moon’s darkest corners are a mystery. This image offers a stunning new glimpse.
- Paid Content
- Environment
- Photography
- Perpetual Planet
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved

Solar System Exploration
Join us as we explore our planetary neighborhood: The Sun, planets, moons, and millions of asteroids and comets.
10 THINGS about our solar system
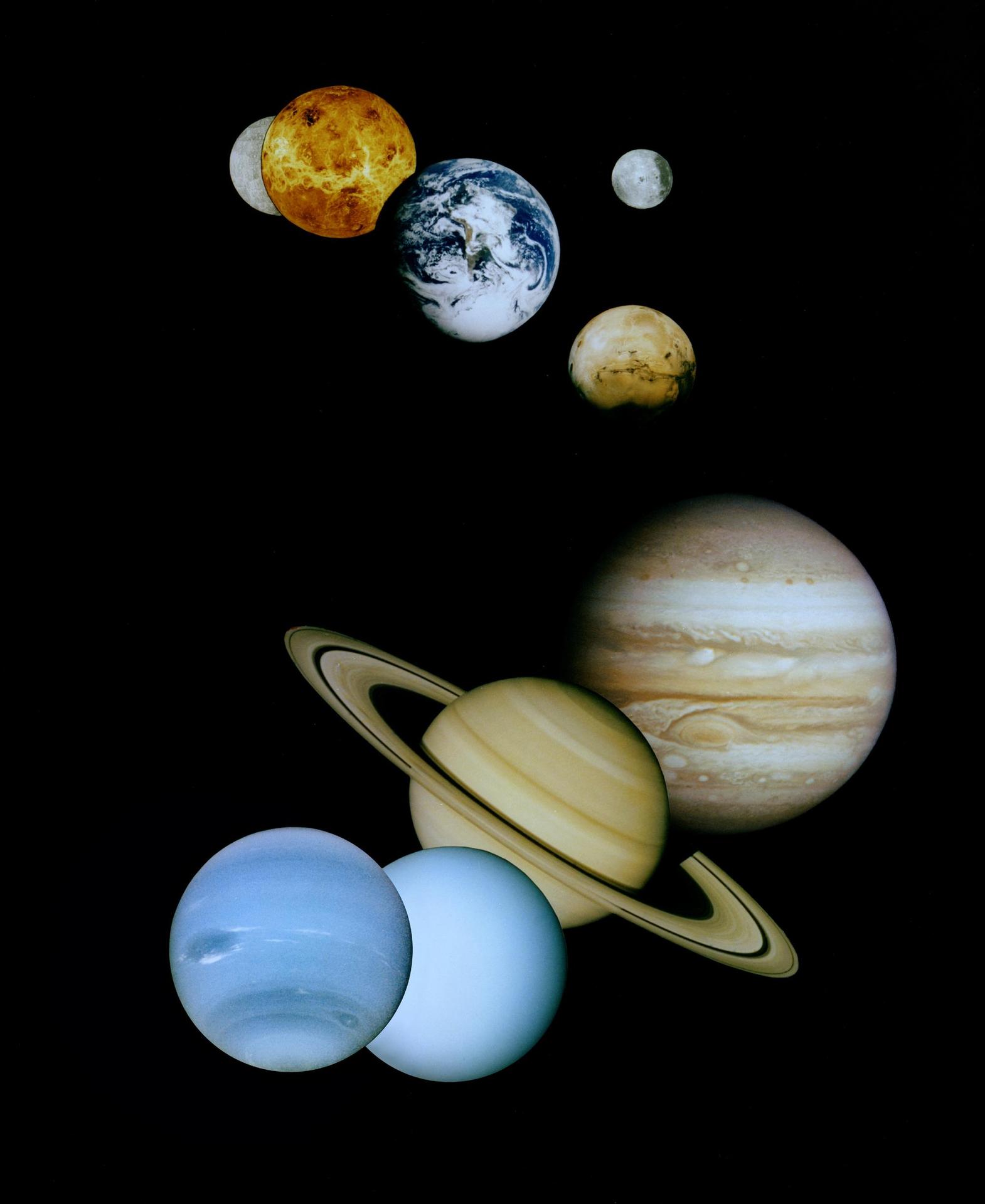

1. Many Worlds
Our solar system has eight planets, and five dwarf planets.

2. Small Worlds, Too
More than 1.3 million asteroids, and about 3,900 comets are in our solar system.

3. Lots of Moons
Our solar system has more than 200 moons.

4. Meet Me in the Milky Way
Our solar system is in one of the Milky Way galaxy’s four spiral arms.

5. A Long Way Around
Our solar system takes about 230 million years to orbit the galactic center.
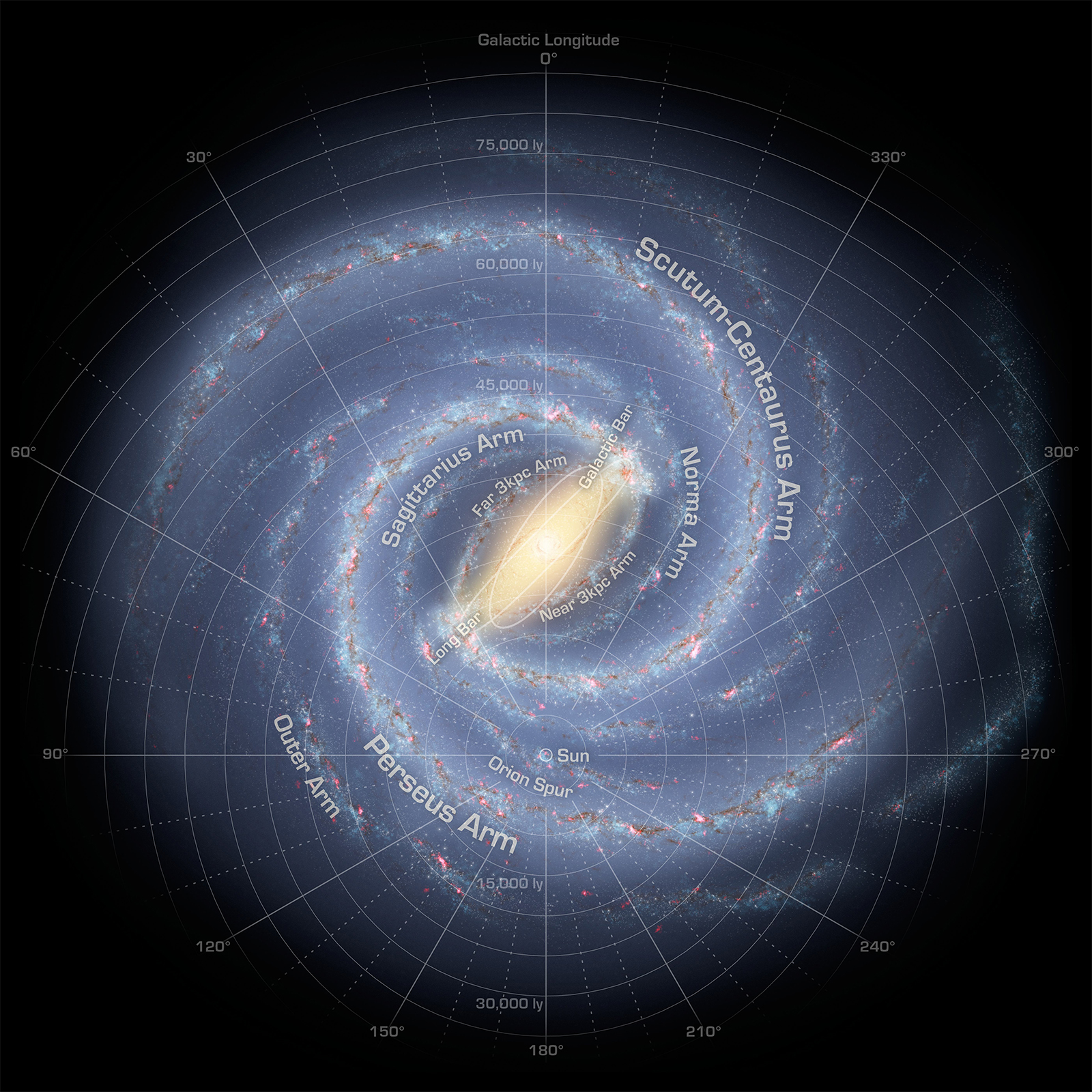
6. Spiraling Through Space
The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy.

7. Room to Breathe
Our solar system has many worlds with many types of atmospheres.
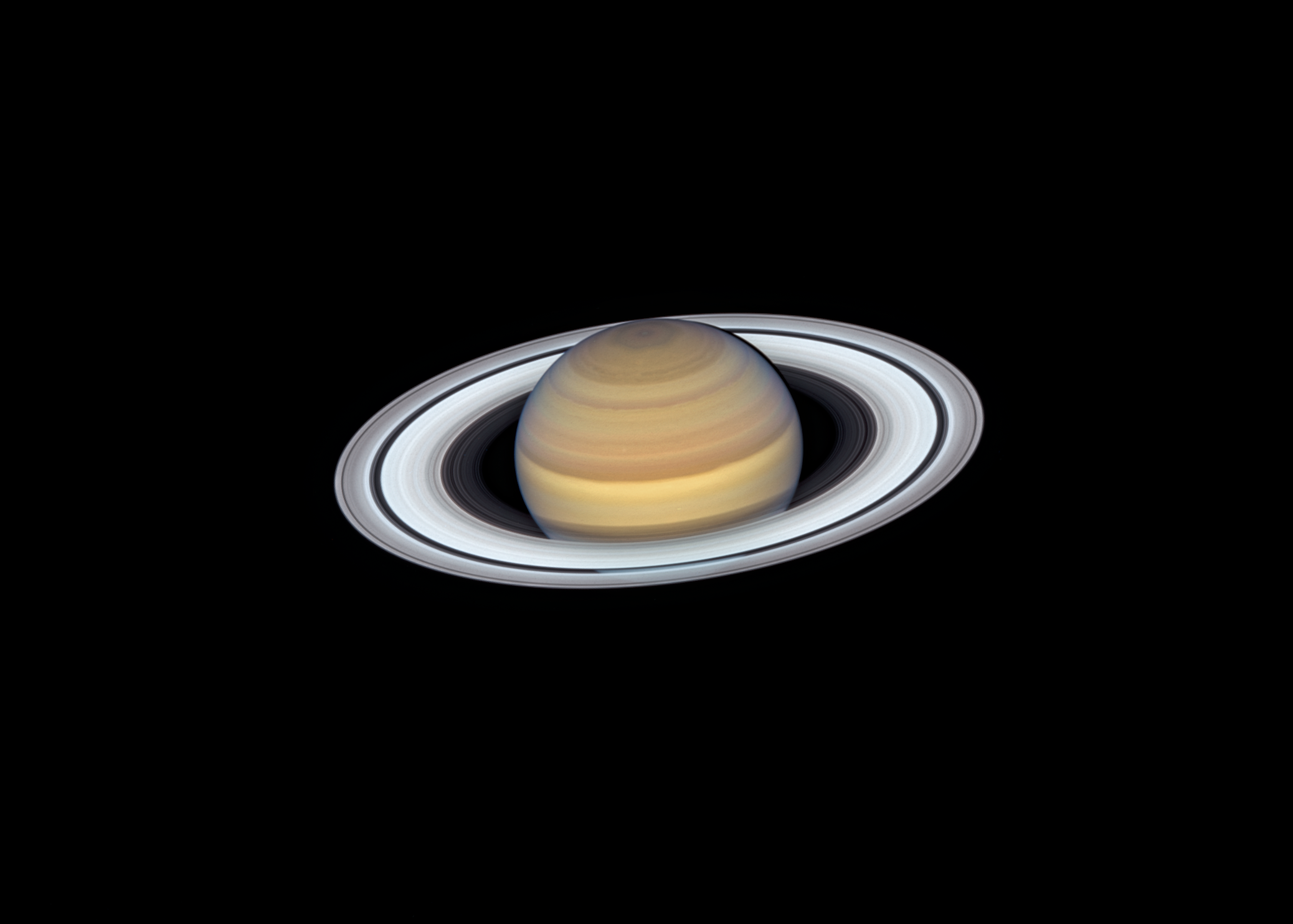
8. Ring Worlds
The four giant planets – and at least one asteroid – have rings.

9. Getting Out There
More than 300 robotic spacecraft have left Earth's orbit, and 24 U.S. astronauts have traveled to the Moon.

10. Life as We Know It
So far, Earth is the only place we've found life in our solar system.
Solar System Overview
The solar system has one star, eight planets, five dwarf planets, at least 290 moons, more than 1.3 million asteroids, and about 3,900 comets. It is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way galaxy called the Orion Arm, or Orion Spur. Our solar system orbits the center of the galaxy at about 515,000 mph (828,000 kph). It takes about 230 million years to complete one orbit around the galactic center.
We call it the solar system because it is made up of our star, the Sun, and everything bound to it by gravity – the planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune; dwarf planets Pluto, Ceres, Makemake, Haumea, and Eris – along with hundreds of moons; and millions of asteroids, comets, and meteoroids.
Why NASA is Going to Europa
Solar System Facts
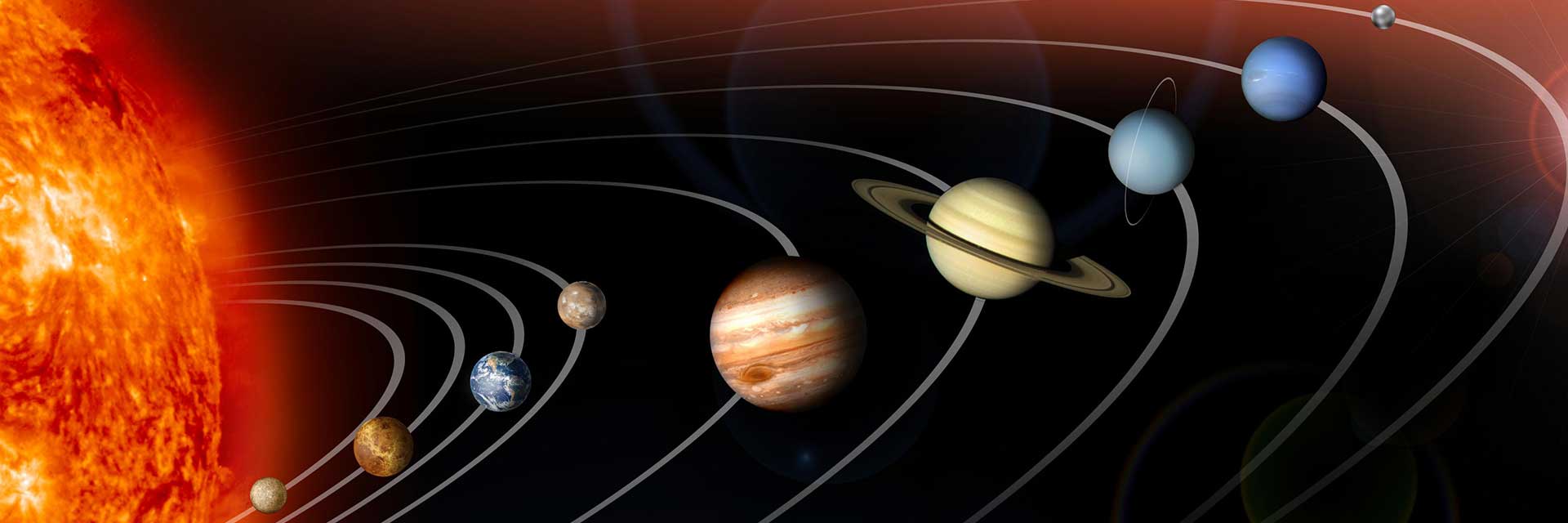
Planet Sizes and Locations

Temperatures Across Our Solar System

Orbits and Kepler's Laws

All About Asteroid Apophis
When is the next full moon.
Our detailed daily guide to the night sky includes full Moon lore, meteor showers, asteroid flybys, and more.

NASA's Eyes
Experience Earth, our solar system, nearby asteroids, the universe, and the spacecraft exploring them with immersive real-time 3D web-based apps. Start exploring your solar system now!
Latest News
NASA “Wildfire Digital Twin” Pioneers New AI Models and Streaming Data Techniques for Forecasting Fire and Smoke

Aurorasaurus Roars During Historic Solar Storm

Webb Cracks Case of Inflated Exoplanet

Hubble Views Cosmic Dust Lanes

Discovery Alert: An Earth-sized World and Its Ultra-cool Star

Hubble Views the Dawn of a Sun-like Star

Binoculars: A Great First Telescope

Hubble Glimpses a Star-Forming Factory
Discover More Topics From NASA
Kuiper Belt

The History of Space Exploration
During the time that has passed since the launching of the first artificial satellite in 1957, astronauts have traveled to the moon, probes have explored the solar system, and instruments in space have discovered thousands of planets around other stars.
Earth Science, Astronomy, Social Studies, U.S. History, World History
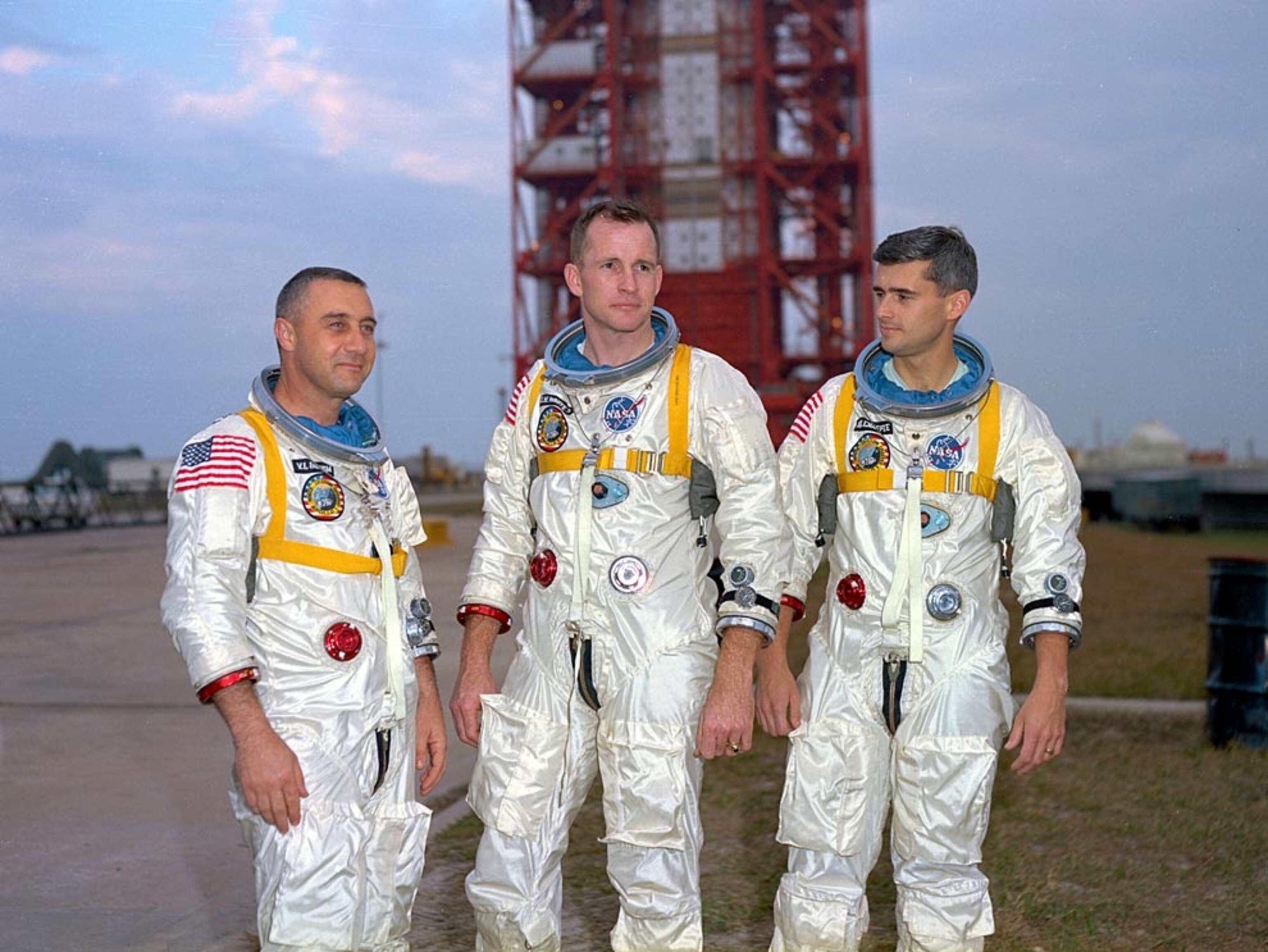
Apollo 11 Astronauts on Moon
A less belligerent, but no less competitive, part of the Cold War was the space race. The Soviet Union bested its rival at nearly every turn, until the U.S. beat them to the finish line by landing astronauts on the moon.
NASA photograph

We human beings have been venturing into space since October 4, 1957, when the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (U.S.S.R.) launched Sputnik, the first artificial satellite to orbit Earth. This happened during the period of political hostility between the Soviet Union and the United States known as the Cold War. For several years, the two superpowers had been competing to develop missiles, called intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), to carry nuclear weapons between continents. In the U.S.S.R., the rocket designer Sergei Korolev had developed the first ICBM, a rocket called the R7, which would begin the space race. This competition came to a head with the launch of Sputnik . Carried atop an R7 rocket, the Sputnik satellite was able to send out beeps from a radio transmitter. After reaching space, Sputnik orbited Earth once every 96 minutes. The radio beeps could be detected on the ground as the satellite passed overhead, so people all around the world knew that it was really in orbit. Realizing that the U.S.S.R. had capabilities that exceeded U.S. technologies that could endanger Americans, the United States grew worried. Then, a month later, on November 3, 1957, the Soviets achieved an even more impressive space venture. This was Sputnik II, a satellite that carried a living creature, a dog named Laika. Prior to the launch of Sputnik, the United States had been working on its own capability to launch a satellite. The United States made two failed attempts to launch a satellite into space before succeeding with a rocket that carried a satellite called Explorer on January 31, 1958. The team that achieved this first U.S. satellite launch consisted largely of German rocket engineers who had once developed ballistic missiles for Nazi Germany. Working for the U.S. Army at the Redstone Arsenal in Huntsville, Alabama, the German rocket engineers were led by Wernher von Braun and had developed the German V2 rocket into a more powerful rocket, called the Jupiter C, or Juno. Explorer carried several instruments into space for conducting science experiments. One instrument was a Geiger counter for detecting cosmic rays. This was for an experiment operated by researcher James Van Allen, which, together with measurements from later satellites, proved the existence of what are now called the Van Allen radiation belts around Earth. In 1958, space exploration activities in the United States were consolidated into a new government agency, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). When it began operations in October of 1958, NASA absorbed what had been called the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), and several other research and military facilities, including the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (the Redstone Arsenal) in Huntsville. The first human in space was the Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin, who made one orbit around Earth on April 12, 1961, on a flight that lasted 108 minutes. A little more than three weeks later, NASA launched astronaut Alan Shepard into space, not on an orbital flight, but on a suborbital trajectory—a flight that goes into space but does not go all the way around Earth. Shepard’s suborbital flight lasted just over 15 minutes. Three weeks later, on May 25, President John F. Kennedy challenged the United States to an ambitious goal, declaring: “I believe that this nation should commit itself to achieving the goal, before the decade is out, of landing a man on the moon and returning him safely to Earth." In addition to launching the first artificial satellite, the first dog in space, and the first human in space, the Soviet Union achieved other space milestones ahead of the United States. These milestones included Luna 2, which became the first human-made object to hit the Moon in 1959. Soon after that, the U.S.S.R. launched Luna 3 . Less than four months after Gagarin’s flight in 1961, a second Soviet human mission orbited a cosmonaut around Earth for a full day. The U.S.S.R. also achieved the first spacewalk and launched the Vostok 6 mission, which made Valentina Tereshkova the first woman to travel to space. During the 1960s, NASA made progress toward President Kennedy’s goal of landing a human on the moon with a program called Project Gemini, in which astronauts tested technology needed for future flights to the moon, and tested their own ability to endure many days in spaceflight. Project Gemini was followed by Project Apollo, which took astronauts into orbit around the moon and to the lunar surface between 1968 and 1972. In 1969, on Apollo11, the United States sent the first astronauts to the Moon, and Neil Armstrong became the first human to set foot on its surface. During the landed missions, astronauts collected samples of rocks and lunar dust that scientists still study to learn about the moon. During the 1960s and 1970s, NASA also launched a series of space probes called Mariner, which studied Venus, Mars, and Mercury. Space stations marked the next phase of space exploration. The first space station in Earth orbit was the Soviet Salyut 1 station, which was launched in 1971. This was followed by NASA’s Skylab space station, the first orbital laboratory in which astronauts and scientists studied Earth and the effects of spaceflight on the human body. During the 1970s, NASA also carried out Project Viking in which two probes landed on Mars, took numerous photographs, examined the chemistry of the Martian surface environment, and tested the Martian dirt (called regolith ) for the presence of microorganisms . Since the Apollo lunar program ended in 1972, human space exploration has been limited to low-Earth orbit, where many countries participate and conduct research on the International Space Station. However, unpiloted probes have traveled throughout our solar system. In recent years, probes have made a range of discoveries, including that a moon of Jupiter, called Europa, and a moon of Saturn, called Enceladus, have oceans under their surface ice that scientists think may harbor life. Meanwhile, instruments in space, such as the Kepler Space Telescope , and instruments on the ground have discovered thousands of exoplanets , planets orbiting other stars. This era of exoplanet discovery began in 1995, and advanced technology now allows instruments in space to characterize the atmospheres of some of these exoplanets.
Articles & Profiles
Media credits.
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
April 17, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

Space Exploration and Satellites
By Edouard Mathieu and Max Roser
Space exploration and the study of outer space have fascinated humans for centuries. In recent decades, we have significantly advanced our understanding of the universe and our place within it. Space travel and exploration have opened up new frontiers and possibilities for humanity, from the first manned mission to the moon in 1969 to the ongoing efforts to send humans to Mars.
In addition to manned missions, we have also sent satellites into orbit around the Earth. These satellites serve various purposes that have revolutionized our lives, including communication, weather forecasting, surveillance, and environmental monitoring.
But, as our presence in space has increased, so has the issue of pollution. Our many launches into space have created debris, including abandoned rocket stages, old satellites, and other discarded equipment. This debris poses a significant risk to future space exploration, as it can collide with and damage functioning satellites or even endanger astronauts on space missions. This is an ongoing challenge that will require continued research and innovation to solve.
This page provides data and visualizations on space exploration, satellites, space pollution, and astronomical research.
Interactive Charts on Space Exploration and Satellites
Cite this work.
Our articles and data visualizations rely on work from many different people and organizations. When citing this topic page, please also cite the underlying data sources. This topic page can be cited as:
BibTeX citation
Reuse this work freely
All visualizations, data, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license . You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
The data produced by third parties and made available by Our World in Data is subject to the license terms from the original third-party authors. We will always indicate the original source of the data in our documentation, so you should always check the license of any such third-party data before use and redistribution.
All of our charts can be embedded in any site.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Manage Your Subscription
- Give a Gift Subscription
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
- Space Travel + Astronomy
13 Things Tourists Should Know Before Traveling to Space, According to Astronauts
We asked the pros for their best tips on handling a first trip to space.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Stefanie-Waldek-7eed18a8c9734cb28c5d887eb583f816.jpg)
For most of human spaceflight history, those lucky enough to reach the stars were professional astronauts hired and trained by government agencies around the world. But since the early 2000s, when seven intrepid travelers paid millions to spend a few days aboard the International Space Station (ISS), space tourism has begun to take off. We're now on the cusp of a new era of space exploration, with commercial companies like Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin launching spacecraft capable of taking paying travelers beyond the Earth's surface.
We spoke with former NASA astronauts Leroy Chiao and Scott Parazynski to get their tips for first-time spaceflight participants. During his 15 years with NASA, Chiao participated in four missions — three aboard the space shuttle and one to the ISS, in which he served as commander. Parazynski worked at NASA for 17 years, flying five shuttle missions throughout his career. Read on to discover what they think aspiring space tourists need to know.
Your only job on the flight will be to kick back, relax, and enjoy the ride.
If you're taking a suborbital flight, which is what companies like Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin have offered, your ride will be a quick up-and-down to reach space, rather than a full orbit of the Earth. The short journey is relatively easy compared to what professional astronauts experience. For starters, you won't need to worry about flying your spacecraft. That's all up to the spaceflight provider. "You won't have any responsibility other than to enjoy the experience — and not kick anyone else in the head," says Parazynski. "Their obligations on the flight are pretty straightforward."
As such, the training programs for suborbital space tourist experiences are relatively minimal, perhaps only a few days in length at most. "The downside of not having a lot of training is that you don't have the confidence that comes from lots of training," says Parazynski. "Contrast that with the training I had on the space shuttle, where we trained for hundreds and hundreds of hours for launching in space. If something were to go awry, we would know exactly what to do and our hearts wouldn't skip a beat."
So, other than learning to place your complete trust in your spaceflight provider, Parazynski recommends talking to people who have flown before in order to ease any nervousness. Chiao agrees: "The best advice I can give on launch — and it's easy to say, harder to do — is to try to relax and enjoy the whole process," he says. "Pay attention during your training, talk to other people who've been there if you can. And actually, you might be surprised — it's quite calm!"
Make sure you’re physically and mentally fit.
"I think people should treat this as their Olympics or Super Bowl. This is a really big life experience, and though you don't need to be an Olympic athlete or a Super Bowl champion to fly in space, it helps to be fit," says Parazynski. After all, your body will be experiencing quite a range of new sensations during your spaceflight."
But it's not just about physical fitness — mental fitness is key, too. "I think through fitness comes mental acuity as well," says Parazynski. "The more you can be engaged in the experience, the more you'll remember of it — it'll be more impactful to you."
The G-forces experienced on launch and reentry are not as intense as you might expect.
If you've ever watched a livestream of an astronaut launch, caught any Hollywood flick about space travel, or ridden Mission: Space at Walt Disney World's Epcot theme park, you know that during launch, astronauts get crushed back into their seats. (And, actually, during reentry, too!) They're experiencing strong G-forces, or a sensation of weight felt during acceleration. It's the same feeling you get when you speed up quickly in a car or zoom through a loop or a sharp curve on a roller coaster, but during a rocket launch, those forces are stronger and more sustained. While the experience might seem a little terrifying, the pros say it's quite manageable.
"The G-forces aren't nearly as bad as they show in the movies," says Chiao. "If you're good enough to be given medical approval to go on a trip like this, you're not going to have any problems handling the G-forces." He also notes that you'll likely go through centrifugal runs during your training to prep for the sensation — you'll be strapped into a spinning machine that lets you experience strong G-forces, just like that spinning amusement park ride where you're pressed against the wall and the floor drops.
But to make launch and reentry as comfortable on your body as possible, you'll want to physically relax your muscles so you don't fight against the G-forces. "If you relax and let your body sink into the launch couch, you're going to tolerate it much better," says Chiao. "If you're rigid, that's where you might hurt yourself. And make sure your limbs and arms are inside of the couch."
To prep for weightlessness, you should book a zero-gravity flight.
While it takes quite a bit of effort (and time and money) to get into space to experience weightlessness, you can actually experience the sensation right here on Earth — or rather, just slightly above it. All you need to do is book a zero-gravity flight , where a plane flies in a series of parabolas (or arch-like shapes) during which passengers experience simulated weightlessness through free fall.
It's physically the same as skydiving or even riding a roller coaster, but in those two instances, your senses tell you you're actually falling. "When you're in a zero-G airplane, the airplane is falling at the same rate you are, so you're floating inside the airplane," says Chiao. "That's what it's like in a spacecraft when you get up into space and the engines cut off."
Through commercial companies like the Zero Gravity Corporation , anyone who can spare the cost of a ticket can experience weightlessness — and anyone who's planning on making a trip to space should definitely give it a go. "If they have the means, they should get on a zero-G flight before they go on a suborbital flight," says Parazynski. "It would take some of the mystery out of 'what am I going to feel like?' and 'how do I move?'"
Learning how to scuba dive is good weightlessness training, too.
While being underwater isn't exactly like floating in space, it's a pretty good way to practice moving around in a weightless environment. In fact, NASA even has a life-sized replica of the ISS set inside a giant pool, so astronauts can train for spacewalks underwater.
"Moving in weightlessness comes to you very quickly when you spend some time underwater," says Parazynski. "Get neutrally buoyant underwater and very gently try and move yourself along the ocean floor or bottom of your pool. It doesn't take a lot of force, but it does take a lot of thought."
Come up with a game plan for your few minutes in space.
On suborbital flights, you're only going to have a few minutes in weightlessness, so you should plan exactly how you want to spend your time up there. Figure out if you'd like to bring a memento like a family photo or college pennant for a fun picture. (U.S. Naval Academy graduates and former astronauts Wally Schirra and Tom Stafford famously put a "Beat Army" sign in the window of their Gemini VI spacecraft, so there's a long tradition of this.) Decide in advance if you want to attempt what spaceflight veterans call "stupid astronaut tricks," like flips or spins. But most importantly, budget time to look out the window.
"The most important thing I would tell future astronauts is to savor the view out the window," says Parazynski. "It's, for lack of a better term, a God's-eye view, and so few people have ever had a chance to see it. It's really a beautiful thing to be hovering in space and looking down at your planet."
Don’t worry about taking your own photos.
"As far as taking photographs, I don't know that I would recommend it," says Chiao. "You're not going to be very good at it, first of all, because it takes a little bit of practice to get used to zero-G. Don't waste that time taking photos. Get your memories, look out those windows, and enjoy the whole experience of being weightless." Plus, given the price tag of these spaceflights, we're pretty sure that your operator will provide you with photos and videos of your journey anyway.
When you get into zero gravity, you might feel a little dizzy.
The body functions a bit differently when you remove gravity from the equation for a sustained period of time, and side effects may include dizziness and nausea. "You're going to feel full-headed because there's no longer gravity pulling fluid down into your legs," says Chiao. "And so all that fluid comes up into your torso, and you can feel it right away. It feels kind of like you're standing on your head."
But the good news is, on suborbital flights you might be able to avoid the worst of it. "The adrenaline and excitement are going to make you do OK at first, and by the time you might start feeling bad, it's time to strap back in and come back down," says Chiao.
If you’re spending a few days in space, be prepared for some bumps and bruises.
On a suborbital flight, you won't have a ton of time in space, so you won't really have to worry about acclimating to zero gravity. However, some private spaceflight companies are looking to send their clients up into orbit for longer stays and there are even talks of a space hotel within Voyager Station . If you're going to spend a few days or even a few weeks up in space, you're probably going to bump your head more than once, no matter how much you've trained for the experience.
"It's really funny watching rookie astronauts the first day or two up on a mission," says Parazynski. "We called them the bull in a china shop. They push off with full force and they crack their skull or bang their knee."
You’re also going to make a mess.
Doing routine tasks like brushing your teeth (you can't just spit your toothpaste into a sink), clipping your fingernails (you don't want them floating off into your space station), and going to the bathroom (have you ever thought about how to use a toilet without gravity?) are all very different experiences in weightlessness. Inevitably, you might have a few mishaps early on in your trip.
"Just sitting down for a meal, you put your fork down, and it's gone in 30 seconds," says Parazynski. "You may find it two days later in the cabin air cleaner because that's where the air currents have taken it." Luckily, a lost fork is an easy mess to clean up — and the situation can be prevented by tethering it down. Other messes are a different story.
"As far as using the restroom, that's what you need to pay attention to during your training. The toilet is not particularly simple and you have to be careful," says Chiao. (In case you were wondering, space toilets use airflow to guide things where they're supposed to go.) "But be prepared to make some messes," says Chiao. "And everybody has to clean up their own mess."
If you’re going to do a spacewalk, the stakes are much higher for you and your crew.
If you want to zip around space with a jetpack like George Clooney in "Gravity," sorry, but chances are that's not going to happen any time soon. Most private astronauts will be safely tucked inside their craft for the duration of their flight.
Unlike suborbital flights, future orbital flights with a spacewalk will require extensive training, given that spacewalks are inherently more dangerous than simply riding in a vessel. "If you're careless with your tethers and you float off into the void, there's not a whole lot anyone can come do for you," says Parazynski. It's possible that a crewmate may be able to head out to rescue you, but then you're endangering their life as well. "It's paramount for a spacewalker to think not just about their own health and well-being and their experience, but also that of their crewmates," he says.
If you’re in a capsule, be prepared for a bumpy landing.
While the only way up to space is by rocket, there are two ways to come back down: via a winged vehicle, like the space shuttle or Virgin Galactic's SpaceShipTwo, or a capsule, like Apollo, Soyuz, and Blue Origin's New Shepard. The experiences are quite different, as winged vehicles land like an airplane on a runway, whereas capsules descend beneath parachutes onto land or water. While both experience a range of G-forces during reentry, capsules have a bit of a rougher ride, particularly at the very end.
"When the parachute comes out, you can expect to get jostled around a fair amount, so that can be disorienting," says Chiao. "Then, whether you're hitting the water or the ground, you're gonna get a good bump. There are shock-absorbing mechanisms, of course, that make it not too big a deal. But on Soyuz, you smack the ground pretty darn hard. It was kind of surprising!"
It’ll be worth every penny.
Sure, it's going to cost a small fortune to go into space as a tourist — for now, that's somewhere in the ballpark of several hundred thousand dollars for a suborbital flight and millions of dollars for longer-duration orbital stays. But ask any astronaut, and they're sure to tell you it'll be worth the investment.
"What I would tell prospective astronauts is that it's going to change their lives forever," says Parazynski. "It's a perspective that can't be captured in emotion on film. Even in 3D IMAX, there's no way to capture the way it's going to make you feel, the connectedness you feel to planet Earth, and the awe you have when you look out into the universe."
Related Articles
MIT Technology Review
- Newsletters
What’s next in space
The moon, private space travel, and the wider solar system will all have major missions over the next 12 months.
- Jonathan O'Callaghan archive page

We’re going back to the moon—again—in 2023. Multiple uncrewed landings are planned for the next 12 months, spurred on by a renewed effort in the US to return humans to the lunar surface later this decade. Both private space companies and national agencies are set to make the 240,000-mile trek to our celestial neighbor, where they will test landing capabilities, look for usable water ice , and more.
Previous years were “all about Mars,” says Jill Stuart, a space policy expert from the London School of Economics in the UK. “Now we’ve shifted back to the moon.”
That is not all 2023 has in store. We’re also likely to see significant strides made in private human spaceflight, including the first-ever commercial spacewalk, compelling missions heading out into—or back from—other solar system destinations, and new rockets set to take flight.
Here’s what the next year has lined up for space.
Moon landings
A lunar lander will already be on its way when 2023 begins. Launched in December on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, the private spacecraft Hakuto-R, developed by Japanese firm ispace , is on a four-month journey to reach the moon , where it will deploy rovers built by the space agencies of Japan and the United Arab Emirates, among other goals. If successful, Hakuto-R could become the first private mission to land on the moon in March.
We say “could” because two private landers from the US—one from the firm Astrobotic and the other from Intuitive Machines, called Peregrine and Nova-C, respectively—are also set to reach the moon around the same time. Both are NASA-backed missions with various instruments on board to study the lunar environment, part of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payloads Services program, which aims to spur commercial interest in the moon ahead of human missions planned for later this decade under its Artemis program.
The first part of that program, Artemis I, saw an uncrewed Orion spacecraft launch to the moon on NASA’s giant new Space Launch System rocket in November 2022. While the next Artemis mission, a crewed flight around the moon, is not planned until 2024, these next 12 months will lay important groundwork for Artemis by studying the moon’s surface and even looking for water ice that could be a potential target for future human missions, among other goals. “The moon is getting a lot more attention than it has done for many years,” says Jon Cowart, a former NASA human spaceflight manager now at the Aerospace Corporation in the US.
Intuitive Machines has a second lunar landing planned in 2023. Also on the books are landings from the space agencies of India and Japan, with Chandrayaan-3 and SLIM (Smart Lander for Investigating Moon) , respectively. India hopes to launch in August 2023. It will be the country’s second attempt—the first crash-landed on the moon in 2019. A date for SLIM, which will test precision landing on the moon, has not yet been set. Russia reportedly has plans for the moon in 2023 too with its Luna-25 lander, but the status of the mission is unclear.
Private space travel
Since May 2020, SpaceX has been using its Crew Dragon spacecraft to ferry astronauts to space, some to the International Space Station (ISS) under contract with NASA and others on private missions. But SpaceX’s Polaris Dawn mission , currently slated for March 2023, will be a big new step.
Four commercial astronauts, including billionaire Jared Isaacman, who is paying for the flight and also funded SpaceX’s first all-private human spaceflight in 2021, will target a maximum orbit of 1,200 kilometers, higher than any human spacecraft since the Apollo missions. And in a first for commercial human spaceflight, the crew will don spacesuits and venture outside the spacecraft.
“Polaris Dawn is really exciting,” says Laura Forczyk from the space consulting firm Astralytical. “My understanding is that the entire vehicle will be evacuated. Everybody is going to at least stick their heads out.”
The mission may help NASA decide whether a future Crew Dragon mission could be used to service the Hubble Space Telescope, a capability that the agency has been investigating with SpaceX. “We’ll have some idea whether it’s feasible,” says Forczyk.
Two more private missions using Crew Dragon—Axiom-2 and Axiom-3—are planned to head for the ISS in 2023, as well as two NASA flights using Crew Dragon. A competing vehicle from the US firm Boeing is also set to launch with crew for the first time in April 2023, following multiple delays .
Meanwhile, we wait to see if Jeff Bezos’s company Blue Origin will be allowed to launch with humans again. The company has been grounded following an uncrewed launch failure in September 2022. Another private spaceflight pioneer, Virgin Galactic, has been relatively quiet since it launched its founder Sir Richard Branson into space in July 2021.
All these developments in commercial human spaceflight may be overshadowed by the first orbital flight attempt of SpaceX’s massive and reusable Starship rocket, which was undergoing launchpad tests earlier this month and should launch in 2023, if not by the end of 2022.
If successful, the rocket, which would surpass NASA’s Space Launch System as the largest rocket to make it to orbit, could transform our exploration of space . “The ability to take more mass up opens up new opportunities,” says Uma Bruegman, an expert in space strategies at the Aerospace Corporation. That could include, one day, human missions to Mars—or beyond. But there’s a long way to go yet. “It’s definitely an important year [for Starship],” says Cowart. “They’ve got a lot to do.” One of its nearer-term goals will be preparing for the moon—NASA chose Starship’s upper stage as the initial lunar lander for the Artemis program.
Into the solar system
Moons of the solar system’s biggest planet are also on the agenda next year. April 2023 will see a gripping new mission launch from the European Space Agency (ESA) called JUICE, for “Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer.” Scheduled to arrive in orbit at Jupiter in 2031, the spacecraft will perform detailed studies of the Jovian moons Ganymede, Callisto, and Europa, all of which are thought to harbor oceans that could contain life beneath their icy surfaces.
“It’s the first mission that’s fundamentally focused on the icy moons,” says Mark McCaughrean, senior advisor for science and exploration at ESA. “We now know these icy moons have very deep water oceans, and they could have the conditions for life to have developed.”
JUICE will map these oceans with radar instruments, but McCaughrean says it will also be able to look for possible biosignatures on the surface of Europa’s ice, which could rain down from plumes ejected into space from its subsurface ocean.
Later in 2023, ESA is scheduled to see another major mission launch: its Euclid telescope, which was switched from a Russian rocket to a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. The telescope will probe the “dark universe,” observing billions of galaxies over a third of the sky to better understand dark matter and dark energy in the cosmos.
In October, NASA should launch a significant science mission of its own when Psyche takes flight following a delay from 2022. The spacecraft will head to 16 Psyche, an unusual metal-rich asteroid that has never been seen up close.
A number of other intriguing developments are expected in 2023. NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission is scheduled to return to Earth in September with pieces of an asteroid called Bennu, which could offer new insight into the structure and formation of the solar system. Amazon aims to send up the first satellites for Project Kuiper in early 2023, the start of a 3,000-satellite orbiting communications network it hopes will rival SpaceX’s Starlink constellation. And several new rockets are set to launch, including the United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan Centaur rocket (it will carry Astrobotic’s moon lander and some of Amazon's satellites) and possibly Blue Origin’s large New Glenn rocket. Both are heavy-lift rockets that could take many satellites into space.
“There’s a huge swathe of activity,” says Cowart. “I’m very excited about this year.”
Keep Reading
Most popular, how scientists traced a mysterious covid case back to six toilets.
When wastewater surveillance turns into a hunt for a single infected individual, the ethics get tricky.
- Cassandra Willyard archive page

It’s time to retire the term “user”
The proliferation of AI means we need a new word.
- Taylor Majewski archive page
The problem with plug-in hybrids? Their drivers.
Plug-in hybrids are often sold as a transition to EVs, but new data from Europe shows we’re still underestimating the emissions they produce.
- Casey Crownhart archive page
Sam Altman says helpful agents are poised to become AI’s killer function
Open AI’s CEO says we won’t need new hardware or lots more training data to get there.
- James O'Donnell archive page
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from mit technology review.
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.
Thank you for submitting your email!
It looks like something went wrong.
We’re having trouble saving your preferences. Try refreshing this page and updating them one more time. If you continue to get this message, reach out to us at [email protected] with a list of newsletters you’d like to receive.
Voyager 1: Facts about Earth's farthest spacecraft
Voyager 1 continues to explore the cosmos along with its twin probe, Voyager 2.

The Grand Tour
Voyager 1 jupiter flyby, voyager 1 visits saturn and its moons, voyager 1 enters interstellar space, voyager 1's interstellar adventures, additional resources.
Voyager 1 is the first spacecraft to travel beyond the solar system and reach interstellar space .
The probe launched on Sept. 5, 1977 — about two weeks after its twin Voyager 2 — and as of August 2022 is approximately 14.6 billion miles (23.5 billion kilometers) away from our planet, making it Earth 's farthest spacecraft. Voyager 1 is currently zipping through space at around 38,000 mph (17 kilometers per second), according to NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory .
When Voyager 1 launched a mission to explore the outer planets in our solar system nobody knew how important the probe would still be 45 years later The probe has remained operational long past expectations and continues to send information about its journeys back to Earth.
Related: Celebrate 45 years of Voyager with these amazing images of our solar system (gallery)

Elizabeth Howell, Ph.D., is a staff writer in the spaceflight channel since 2022. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years before that, since 2012. Elizabeth's on-site reporting includes two human spaceflight launches from Kazakhstan, three space shuttle missions in Florida, and embedded reporting from a simulated Mars mission in Utah.
Size: Voyager 1's body is about the size of a subcompact car. The boom for its magnetometer instrument extends 42.7 feet (13 meters). Weight (at launch): 1,797 pounds (815 kilograms). Launch date: Sept. 5, 1977
Jupiter flyby date: March 5, 1979
Saturn flyby date: Nov. 12, 1980.
Entered interstellar space: Aug. 25, 2012.
The spacecraft entered interstellar space in August 2012, almost 35 years after its voyage began. The discovery wasn't made official until 2013, however, when scientists had time to review the data sent back from Voyager 1.
Voyager 1 was the second of the twin spacecraft to launch, but it was the first to race by Jupiter and Saturn . The images Voyager 1 sent back have been used in schoolbooks and by many media outlets for a generation. The spacecraft also carries a special record — The Golden Record — that's designed to carry voices and music from Earth out into the cosmos.
According to NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) , Voyager 1 has enough fuel to keep its instruments running until at least 2025. By then, the spacecraft will be approximately 13.8 billion miles (22.1 billion kilometers) away from the sun.
The Voyager missions took advantage of a special alignment of the outer planets that happens just once every 176 years. This alignment allows spacecraft to gravitationally "slingshot" from one planet to the next, making the most efficient use of their limited fuel.
NASA originally planned to send two spacecraft past Jupiter, Saturn and Pluto and two other probes past Jupiter, Uranus and Neptune . Budgetary reasons forced the agency to scale back its plans, but NASA still got a lot out of the two Voyagers it launched.
Voyager 2 flew past Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune , while Voyager 1 focused on Jupiter and Saturn.
Recognizing that the Voyagers would eventually fly to interstellar space, NASA authorized the production of two Golden Records to be placed on board the spacecraft. Sounds ranging from whale calls to the music of Chuck Berry were placed on board, as well as spoken greetings in 55 languages.
The 12-inch-wide (30 centimeters), gold-plated copper disks also included pictorials showing how to operate them and the position of the sun among nearby pulsars (a type of fast-spinning stellar corpse known as a neutron star ), in case extraterrestrials someday stumbled onto the spacecraft and wondered where they came from.
Both spacecraft are powered by three radioisotope thermoelectric generators , devices that convert the heat released by the radioactive decay of plutonium to electricity. Both probes were outfitted with 10 scientific instruments, including a two-camera imaging system, multiple spectrometers, a magnetometer and gear that detects low-energy charged particles and high-energy cosmic rays . Mission team members have also used the Voyagers' communications system to help them study planets and moons, bringing the total number of scientific investigations on each craft to 11.
Voyager 1 almost didn't get off the ground at its launch , as its rocket came within 3.5 seconds of running out of fuel on Sept. 5, 1977.
But the probe made it safely to space and raced past its twin after launch, getting beyond the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter before Voyager 2 did. Voyager 1's first pictures of Jupiter beamed back to Earth in April 1978, when the probe was 165 million miles (266 million kilometers) from home.
According to NASA , each voyager probe has about 3 million times less memory than a mobile phone and transmits data approximately 38,000 times slower than a 5g internet connection.
To NASA's surprise, in March 1979 Voyager 1 spotted a thin ring circling the giant planet. It found two new moons as well — Thebe and Metis. Additionally, Voyager 1 sent back detailed pictures of Jupiter's big Galilean moons ( Io , Europa , Ganymede and Callisto ) as well as Amalthea .
Like the Pioneer spacecraft before it , Voyager's look at Jupiter's moons revealed them to be active worlds of their own. And Voyager 1 made some intriguing discoveries about these natural satellites. For example, Io's many volcanoes and mottled yellow-brown-orange surface showed that, like planets, moons can have active interiors.
Additionally, Voyager 1 sent back photos of Europa showing a relatively smooth surface broken up by lines, hinting at ice and maybe even an ocean underneath. (Subsequent observations and analyses have revealed that Europa likely harbors a huge subsurface ocean of liquid water, which may even be able to support Earth-like life .)
Voyager 1's closest approach to Jupiter was on March 5, 1979, when it came within 174,000 miles (280,000 km) of the turbulent cloud tops. Then it was time for the probe to aim for Saturn.
Scientists only had to wait about a year, until 1980, to get close-up pictures of Saturn. Like Jupiter, the ringed planet turned out to be full of surprises.
One of Voyager 1's targets was the F ring, a thin structure discovered only the year previously by NASA's Pioneer 11 probe. Voyager's higher-resolution camera spotted two new moons, Prometheus and Pandora, whose orbits keep the icy material in the F ring in a defined orbit. It also discovered Atlas and a new ring, the G ring, and took images of several other Saturn moons.
One puzzle for astronomers was Titan , the second-largest moon in the solar system (after Jupiter's Ganymede). Close-up pictures of Titan showed nothing but orange haze, leading to years of speculation about what it was like underneath. It wouldn't be until the mid-2000s that humanity would find out, thanks to photos snapped from beneath the haze by the European Space Agency's Huygens atmospheric probe .
The Saturn encounter marked the end of Voyager 1's primary mission. The focus then shifted to tracking the 1,590-pound (720 kg) craft as it sped toward interstellar space.
Two decades before it notched that milestone, however, Voyager 1 took one of the most iconic photos in spaceflight history. On Feb. 14, 1990, the probe turned back toward Earth and snapped an image of its home planet from 3.7 billion miles (6 billion km) away. The photo shows Earth as a tiny dot suspended in a ray of sunlight.
Voyager 1 took dozens of other photos that day, capturing five other planets and the sun in a multi-image "solar system family portrait." But the Pale Blue Dot picture stands out, reminding us that Earth is a small outpost of life in an incomprehensibly vast universe.
Voyager 1 left the heliosphere — the giant bubble of charged particles that the sun blows around itself — in August 2012, popping free into interstellar space. The discovery was made public in a study published in the journal Science the following year.
The results came to light after a powerful solar eruption was recorded by Voyager 1's plasma wave instrument between April 9 and May 22, 2013. The eruption caused electrons near Voyager 1 to vibrate. From the oscillations, researchers discovered that Voyager 1's surroundings had a higher density than what is found just inside the heliosphere.
It seems contradictory that electron density is higher in interstellar space than it is in the sun's neighborhood. But researchers explained that, at the edge of the heliosphere, the electron density is dramatically low compared with locations near Earth.
Researchers then backtracked through Voyager 1's data and nailed down the official departure date to Aug. 25, 2012. The date was fixed not only by the electron oscillations but also by the spacecraft's measurements of charged solar particles.
On that fateful day — which was the same day that Apollo 11 astronaut Neil Armstrong died — the probe saw a 1,000-fold drop in these particles and a 9% increase in galactic cosmic rays that come from outside the solar system . At that point, Voyager 1 was 11.25 billion miles (18.11 billion km) from the sun, or about 121 astronomical units (AU).
One AU is the average Earth-sun distance — about 93 million miles (150 million km).
You can keep tabs on the Voyager 1's current distance and mission status on this NASA website .
Since flying into interstellar space, Voyager 1 has sent back a variety of valuable information about conditions in this zone of the universe . Its discoveries include showing that cosmic radiation out there is very intense, and demonstrating how charged particles from the sun interact with those emitted by other stars , mission project scientist Ed Stone, of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, told Space.com in September 2017 .
The spacecraft's capabilities continue to astound engineers. In December 2017, for example, NASA announced that Voyager 1 successfully used its backup thrusters to orient itself to "talk" with Earth . The trajectory correction maneuver (TCM) thrusters hadn't been used since November 1980, during Voyager 1's flyby of Saturn. Since then, the spacecraft had primarily used its standard attitude-control thrusters to swing the spacecraft in the right orientation to communicate with Earth.
As the performance of the attitude-control thrusters began to deteriorate, however, NASA decided to test the TCM thrusters — an idea that could extend Voyager 1's operational life. That test ultimately succeeded.
"With these thrusters that are still functional after 37 years without use, we will be able to extend the life of the Voyager 1 spacecraft by two to three years," Voyager project manager Suzanne Dodd, of NASA's Jet Propulsion, Laboratory (JPL) in Southern California, said in a statement in December 2017 .
Mission team members have taken other measures to extend Voyager 1's life as well. For example, they turned off the spacecraft's cameras shortly after the Pale Blue Dot photo was taken to help conserve Voyager 1's limited power supply. (The cameras wouldn't pick up much in the darkness of deep space anyway.) Over the years, the mission team has turned off five other scientific instruments as well, leaving Voyager 1 with four that are still functioning — the Cosmic Ray Subsystem, the Low-Energy Charged Particles instrument, the Magnetometer and the Plasma Wave Subsystem. (Similar measures have been taken with Voyager 2, which currently has five operational instruments .)
The Voyager spacecraft each celebrated 45 years in space in 2022, a monumental milestone for the twin probes.
"Over the last 45 years, the Voyager missions have been integral in providing this knowledge and have helped change our understanding of the sun and its influence in ways no other spacecraft can," says Nicola Fox, director of the Heliophysics Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington, in a NASA statement .
"Today, as both Voyagers explore interstellar space, they are providing humanity with observations of uncharted territory," said Linda Spilker, Voyager's deputy project scientist at JPL in the same NASA statement.
"This is the first time we've been able to directly study how a star, our Sun, interacts with the particles and magnetic fields outside our heliosphere, helping scientists understand the local neighborhood between the stars, upending some of the theories about this region, and providing key information for future missions." Spilker continues.
Voyager 1's next big encounter will take place in 40,000 years when the probe comes within 1.7 light-years of the star AC +79 3888. (The star is roughly 17.5 light-years from Earth.) However, Voyager 1's falling power supply means it will probably stop collecting scientific data around 2025.
You can learn much more about both Voyagers' design, scientific instruments and mission goals at JPL's Voyager site . NASA has lots of in-depth information about the Pale Blue Dot photo, including Carl Sagan's large role in making it happen, here . And if you're interested in the Golden Record, check out this detailed New Yorker piece by Timothy Ferris, who produced the historic artifact. Explore the history of Voyager with this interactive timeline courtesy of NASA.
Bibliography
- Bell, Jim. " The Interstellar Age: Inside the Forty-Year Voyager Mission ," Dutton, 2015.
- Landau, Elizabeth. "The Voyagers in popular culture," Dec. 1, 2017. https://www.nasa.gov/feature/jpl/the-voyagers-in-popular-culture
- PBS, "Voyager: A history in photos." https://www.pbs.org/the-farthest/mission/voyager-history-photos/
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Elizabeth Howell (she/her), Ph.D., is a staff writer in the spaceflight channel since 2022 covering diversity, education and gaming as well. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years before joining full-time. Elizabeth's reporting includes multiple exclusives with the White House and Office of the Vice-President of the United States, an exclusive conversation with aspiring space tourist (and NSYNC bassist) Lance Bass, speaking several times with the International Space Station, witnessing five human spaceflight launches on two continents, flying parabolic, working inside a spacesuit, and participating in a simulated Mars mission. Her latest book, " Why Am I Taller ?", is co-written with astronaut Dave Williams. Elizabeth holds a Ph.D. and M.Sc. in Space Studies from the University of North Dakota, a Bachelor of Journalism from Canada's Carleton University and a Bachelor of History from Canada's Athabasca University. Elizabeth is also a post-secondary instructor in communications and science at several institutions since 2015; her experience includes developing and teaching an astronomy course at Canada's Algonquin College (with Indigenous content as well) to more than 1,000 students since 2020. Elizabeth first got interested in space after watching the movie Apollo 13 in 1996, and still wants to be an astronaut someday. Mastodon: https://qoto.org/@howellspace
- Daisy Dobrijevic Reference Editor
'This was a life-changing experience:' 1st Black astronaut candidate exults after suborbital launch (video)
Blue Origin launches 1st Black astronaut candidate, age 90, and 5 space tourists on New Shepard rocket (video)
We may have just witnessed some of the strongest auroras in 500 years
Most Popular
- 2 'This was a life-changing experience:' 1st Black astronaut candidate exults after suborbital launch (video)
- 3 What did Noa see in the telescope in 'Kingdom of the Planet of the Apes?'
- 4 How to watch bright red star Antares disappear behind the moon on May 23
- 5 Solar storm frenzy of May 2024 was strong enough to affect the deep sea
Passport to Space
How hubble works, the milky way, what is hubble, shoot for the stars.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your California Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell My Info
- National Geographic
- National Geographic Education
- Shop Nat Geo
- Customer Service
- Manage Your Subscription
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
The huge solar storm is keeping power grid and satellite operators on edge

Geoff Brumfiel
Willem Marx

NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this image of solar flares early Saturday afternoon. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration says there have been measurable effects and impacts from the geomagnetic storm. Solar Dynamics Observatory hide caption
NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this image of solar flares early Saturday afternoon. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration says there have been measurable effects and impacts from the geomagnetic storm.
Planet Earth is getting rocked by the biggest solar storm in decades – and the potential effects have those people in charge of power grids, communications systems and satellites on edge.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration says there have been measurable effects and impacts from the geomagnetic storm that has been visible as aurora across vast swathes of the Northern Hemisphere. So far though, NOAA has seen no reports of major damage.

The Picture Show
Photos: see the northern lights from rare, solar storm.
There has been some degradation and loss to communication systems that rely on high-frequency radio waves, NOAA told NPR, as well as some preliminary indications of irregularities in power systems.
"Simply put, the power grid operators have been busy since yesterday working to keep proper, regulated current flowing without disruption," said Shawn Dahl, service coordinator for the Boulder, Co.-based Space Weather Prediction Center at NOAA.
NOAA Issues First Severe Geomagnetic Storm Watch Since 2005

- LISTEN & FOLLOW
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
- Amazon Music
- Amazon Alexa
Your support helps make our show possible and unlocks access to our sponsor-free feed.
"Satellite operators are also busy monitoring spacecraft health due to the S1-S2 storm taking place along with the severe-extreme geomagnetic storm that continues even now," Dahl added, saying some GPS systems have struggled to lock locations and offered incorrect positions.
NOAA's GOES-16 satellite captured a flare erupting occurred around 2 p.m. EDT on May 9, 2024.
As NOAA had warned late Friday, the Earth has been experiencing a G5, or "Extreme," geomagnetic storm . It's the first G5 storm to hit the planet since 2003, when a similar event temporarily knocked out power in part of Sweden and damaged electrical transformers in South Africa.
The NOAA center predicted that this current storm could induce auroras visible as far south as Northern California and Alabama.
Extreme (G5) geomagnetic conditions have been observed! pic.twitter.com/qLsC8GbWus — NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center (@NWSSWPC) May 10, 2024
Around the world on social media, posters put up photos of bright auroras visible in Russia , Scandinavia , the United Kingdom and continental Europe . Some reported seeing the aurora as far south as Mallorca, Spain .
The source of the solar storm is a cluster of sunspots on the sun's surface that is 17 times the diameter of the Earth. The spots are filled with tangled magnetic fields that can act as slingshots, throwing huge quantities of charged particles towards our planet. These events, known as coronal mass ejections, become more common during the peak of the Sun's 11-year solar cycle.
A powerful solar storm is bringing northern lights to unusual places
Usually, they miss the Earth, but this time, NOAA says several have headed directly toward our planet, and the agency predicted that several waves of flares will continue to slam into the Earth over the next few days.
While the storm has proven to be large, predicting the effects from such incidents can be difficult, Dahl said.
Shocking problems
The most disruptive solar storm ever recorded came in 1859. Known as the "Carrington Event," it generated shimmering auroras that were visible as far south as Mexico and Hawaii. It also fried telegraph systems throughout Europe and North America.

Stronger activity on the sun could bring more displays of the northern lights in 2024
While this geomagnetic storm will not be as strong, the world has grown more reliant on electronics and electrical systems. Depending on the orientation of the storm's magnetic field, it could induce unexpected electrical currents in long-distance power lines — those currents could cause safety systems to flip, triggering temporary power outages in some areas.
my cat just experienced the aurora borealis, one of the world's most radiant natural phenomena... and she doesn't care pic.twitter.com/Ee74FpWHFm — PJ (@kickthepj) May 10, 2024
The storm is also likely to disrupt the ionosphere, a section of Earth's atmosphere filled with charged particles. Some long-distance radio transmissions use the ionosphere to "bounce" signals around the globe, and those signals will likely be disrupted. The particles may also refract and otherwise scramble signals from the global positioning system, according to Rob Steenburgh, a space scientist with NOAA. Those effects can linger for a few days after the storm.
Like Dahl, Steenburgh said it's unclear just how bad the disruptions will be. While we are more dependent than ever on GPS, there are also more satellites in orbit. Moreover, the anomalies from the storm are constantly shifting through the ionosphere like ripples in a pool. "Outages, with any luck, should not be prolonged," Steenburgh said.

What Causes The Northern Lights? Scientists Finally Know For Sure
The radiation from the storm could have other undesirable effects. At high altitudes, it could damage satellites, while at low altitudes, it's likely to increase atmospheric drag, causing some satellites to sink toward the Earth.
The changes to orbits wreak havoc, warns Tuija Pulkkinen, chair of the department of climate and space sciences at the University of Michigan. Since the last solar maximum, companies such as SpaceX have launched thousands of satellites into low Earth orbit. Those satellites will now see their orbits unexpectedly changed.
"There's a lot of companies that haven't seen these kind of space weather effects before," she says.
The International Space Station lies within Earth's magnetosphere, so its astronauts should be mostly protected, Steenburgh says.
In a statement, NASA said that astronauts would not take additional measures to protect themselves. "NASA completed a thorough analysis of recent space weather activity and determined it posed no risk to the crew aboard the International Space Station and no additional precautionary measures are needed," the agency said late Friday.

People visit St Mary's lighthouse in Whitley Bay to see the aurora borealis on Friday in Whitley Bay, England. Ian Forsyth/Getty Images hide caption
People visit St Mary's lighthouse in Whitley Bay to see the aurora borealis on Friday in Whitley Bay, England.
While this storm will undoubtedly keep satellite operators and utilities busy over the next few days, individuals don't really need to do much to get ready.
"As far as what the general public should be doing, hopefully they're not having to do anything," Dahl said. "Weather permitting, they may be visible again tonight." He advised that the largest problem could be a brief blackout, so keeping some flashlights and a radio handy might prove helpful.
I took these photos near Ranfurly in Central Otago, New Zealand. Anyone can use them please spread far and wide. :-) https://t.co/NUWpLiqY2S — Dr Andrew Dickson reform/ACC (@AndrewDickson13) May 10, 2024
And don't forget to go outside and look up, adds Steenburgh. This event's aurora is visible much further south than usual.
A faint aurora can be detected by a modern cell phone camera, he adds, so even if you can't see it with your eyes, try taking a photo of the sky.
The aurora "is really the gift from space weather," he says.
- space weather
- solar flares
- solar storm
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
TravelAwaits
Our mission is to serve the 50+ traveler who's ready to cross a few items off their bucket list.
6 Tips For Visiting The Space Needle In Seattle

- Activities and Interests
- Destinations
- Sightseeing
- United States
Rising majestically above the hustle and bustle of Seattle’s Lower Queen Anne neighborhood, the Space Needle is one of the West Coast’s most recognizable landmarks. And when you board one of its glass elevators and soar up to the observation tower, you’ll be treated to sweeping city views. Here are a few tips to help you have an unforgettable experience at this iconic Seattle landmark.
About The Space Needle
Standing at 605 feet tall, the Space Needle has been a must-see attraction since it opened at the 1962 World’s Fair as a symbol of innovation and the future. In 2017, the futuristic structure unveiled a newly renovated, fresh look complete with a glass floor on the observation deck and glass benches tilting outward, providing a unique and thrilling experience for visitors brave enough to sit on them. The exterior of the Space Needle now features glass barriers and glass walls, delivering unobstructed 360-degree views of the city and Puget Sound from the observation deck.

1. Tickets And Visiting Information
When visiting the Space Needle, there are a variety of ticket options to choose from, depending on your preferences and budget. You can buy general admission timed-entry tickets, day/night passes, and combo tickets to visit other Seattle attractions. One of my favorite options is the Seattle CityPASS , a combo ticket with admission to the Seattle Aquarium, the Museum of Pop Culture, and more. Whatever ticket option you choose, I recommend purchasing them in advance to spend more time sightseeing and less time waiting in line.

2. Visiting At Night
Visiting the Space Needle during the day is great, but have you ever experienced its magic at night? As the Sun sets and the city lights up, the Space Needle transforms into a stunning beacon that is the crown jewel of the Seattle skyline. One of my favorite things to do in Seattle at night is head up to the Space Needle about an hour before sunset, grab a drink at The Loupe Lounge , and watch nightfall in the Emerald City.
3. What To Bring
It’s no secret that Seattle is known for its rain. Because you can never predict the weather, bringing a lightweight rain jacket that you can easily stow in a backpack or shoulder bag is a good idea. And although you’ll be whisked to the top at a smooth 10 miles per hour (a 41-second elevator ride), there is still a lot of walking involved when you visit the Space Needle and nearby attractions. Make sure to wear comfortable shoes.
Pro Tip: If you experience dreary weather on your trip to the Emerald City, here are several amazing things to do when it’s raining in Seattle .

4. What To See
Offering 360-degree views of Seattle, the observation deck is the main attraction of the Space Needle. From it, you’ll get a bird’s eye view of the bustling Westlake Center, the picturesque Lake Union, and the quaint neighborhood of West Seattle. And on a clear day, you can even see Mount Rainier in the distance.
If you’re feeling brave, check out the rotating glass floor. Located on the lower level of the observation deck, it’s exactly what it sounds like — a section of the floor that rotates as you walk on it. This thrilling experience will make you feel like you’re walking on air as the transparent floor slowly turns above stunning views of the city below.

5. Best Time To Visit
For the best views, visit the Space Needle on a clear day. This may seem obvious, but with Seattle’s reputation for rainy weather, it’s worth noting. On a clear day, you’ll be able to see for miles and all that sunshine will help you take fantastic photos. For a truly unique experience, plan your visit around sunset. There’s nothing quite like taking in breathtaking views while the sky transforms into a tapestry of oranges, pinks, and purples.
The Space Needle is one of the most popular tourist attractions in Seattle, so it can get pretty crowded, especially on a beautiful sunny day. Expect larger crowds on weekends and during the summer months. Visiting during the week or in the off-season can be a great way to beat the crowds and enjoy a more peaceful experience.
Pro Tip: Here are 100+ Seattle quotes to inspire your travels and help you caption your vacation photos.

6. Things To Do
Once you’ve marveled at the impressive panoramic views from the observation deck, there are several other exciting things to do near the Space Needle. First is Chihuly Garden and Glass showcasing the colorful and imaginative glasswork of Dale Chihuly. His glass sculptures fill gallery rooms with natural light and bring additional beauty to the gardens at the base of the Space Needle. One of my favorite pieces at Chihuly Garden and Glass is the Persian ceiling. Look up and observe an impressive collection of glass sculptures affixed to the ceiling as they create a kaleidoscope of colors on the walls and floor of the white room.
Also nearby is the Museum of Pop Culture, celebrating everything from music to movies to science fiction. This unique, immersive experience includes exhibits dedicated to local musical legends like Jimi Hendrix and Nirvana, plus the Science Fiction and Fantasy Hall of Fame. And don’t forget to pop into “The Sky Church” — a room with one of the largest indoor LED screens in the world — where you can sit back and enjoy music videos and performances on a grand scale.
Pro Tip: Looking for more to see and do in Seattle? Here are 14 ways to spend a long weekend in Washington’s Emerald City.
A visit to the Space Needle offers a historical and architectural experience, breathtaking panoramic views, and exciting nearby attractions. As you plan your trip, remember to take into account the city’s weather, time of day, and other factors to make the most of your experience. With its iconic silhouette and awe-inspiring views, the Space Needle is indeed the crown jewel of the Emerald City and an unmissable part of any Seattle itinerary.

Bitten by the travel bug as a preschooler when her family moved abroad for the first time, Sage Scott is addicted to travel. From her nomadic upbringing in a military family to her personal and professional travels as an adult, Sage has visited all 50 states, lived abroad twice, and explored nearly 30 other countries.
Now settled in America’s Heartland, Sage writes with a midlife traveler’s perspective from Kansas City — the Midwestern cowtown affectionately called the Paris of the Plains and the undisputed Barbecue Capital of the World — and is always in search of new experiences whether in her hometown or halfway around the world.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Comet Fragment Explodes in Dark Skies Over Spain and Portugal
A brilliant flash of blue, green and white on Saturday night came from a shard of an as yet unidentified comet that was moving around 100,000 miles per hour, experts said.

By Robin George Andrews
Robin George Andrews has previously reported on fireball sightings over Northern Europe and Greenland .
On Saturday, revelers across Spain and Portugal ventured into the temperate springtime evening, hoping for a memorable night. None were expecting a visitor from outer space exploding above their heads.
At 11:46 p.m. in Portugal, a fireball streaked across the sky, leaving a smoldering trail of incandescent graffiti in its wake. Footage shared on social media shows jaws dropping as the dark night briefly turns into day, blazing in shades of snowy white, otherworldly green and arctic blue .
Rocky asteroids cause sky-high streaks as they self-destruct in Earth’s atmosphere with some frequency. But over the weekend, the projectile was plunging toward Earth at a remarkable speed — around 100,000 miles per hour, more than twice that expected by a typical asteroid. Experts say it had a strange trajectory, not matching the sort normally taken by nearby space rocks.
That’s because the interloper wasn’t an asteroid. It was a fragment of a comet — an icy object that may have formed at the dawn of the solar system — that lost its battle with our planet’s atmosphere 37 miles above the Atlantic Ocean. None of the object is likely to have made it to the ground, the European Space Agency said.
“It’s an unexpected interplanetary fireworks show,” said Meg Schwamb , a planetary astronomer at Queen’s University Belfast.
It is not rare for comets to create shooting stars. “We have notable meteor showers throughout the year, which are the result of the Earth crossing debris clouds of specific comets,” Dr. Schwamb said. For example, the Perseids , which occur every August, are the result of our world’s sweeping through litter left behind by Comet Swift-Tuttle.
These meteor showers, and the lone shard over the weekend, light up the sky in a similar manner. Air in front of the objects is compressed and heats up, which cooks, erodes, cracks open and obliterates the debris. That destructive process releases light — and, if the projectile is big enough, a powerful shock wave when it surrenders its immense kinetic energy into the sky.
The weekend’s “chunk is likely a bit bigger than a good fraction of the meteors we see during meteor showers, so this just made a bigger light show,” Dr. Schwamb said.
In addition to its flashy performance, the comet fragment’s breakup served as a dry run for experts hoping to defend the planet from large killer asteroids .
One tenet of planetary defense is to find space rocks before they find us; that way, the planet’s protectors can try to do something about them . But the shard over Portugal and Spain was not spied before its demise.
“It would have been great to detect the object prior to colliding with the Earth,” said Juan Luis Cano , a member of the Planetary Defence Office at the European Space Agency.
The worry is that an object just a little larger than Saturday’s missile could again escape detection and explode with lethal effect over an unaware, unwarned city. The meager, 55-foot meteor that exploded above the Russian city of Chelyabinsk in 2013, for example, wasn’t identified before its arrival, either — and its airborne blast, equivalent to nearly 500,000 tons of TNT, caused widespread damage, which injured at least 1,200 people.
But with improved technology on the ground and in space, the hope is that even tiny, harmless objects from around the solar system (like the weekend’s icy visitor, which experts estimate was a few feet across) can be spotted, providing practice for planetary defense researchers searching the heavens for the common but elusive football-field-size rocks that could destroy a city.
Fortunately, a series of next-generation observatories are set to come online in the next few years — including one named after an American astronomer, the Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile , which will spot millions of faint and previously undiscovered asteroids .
For now, the spectacle in Spain and Portugal reminds us that Earth is a participant in the solar system’s never-ending game of planetary billiards, and that working to find as many killer space rocks as possible is a task of the utmost importance.
What’s Up in Space and Astronomy
Keep track of things going on in our solar system and all around the universe..
Never miss an eclipse, a meteor shower, a rocket launch or any other 2024 event that’s out of this world with our space and astronomy calendar .
A dramatic blast from the sun set off the highest-level geomagnetic storm in Earth’s atmosphere, making the northern lights visible around the world .
With the help of Google Cloud, scientists who hunt killer asteroids churned through hundreds of thousands of images of the night sky to reveal 27,500 overlooked space rocks in the solar system .
A celestial image, an Impressionistic swirl of color in the center of the Milky Way, represents a first step toward understanding the role of magnetic fields in the cycle of stellar death and rebirth.
Scientists may have discovered a major flaw in their understanding of dark energy, a mysterious cosmic force . That could be good news for the fate of the universe.
Is Pluto a planet? And what is a planet, anyway? Test your knowledge here .
Northern lights dazzle skygazers as ‘extreme’ solar storm hits Earth
Weather experts warn of potential disruptions to power grids, communications as sun’s outburst continues in coming days.

The most powerful solar storm in more than 20 years has struck Earth’s atmosphere, triggering warnings over the potential disruption to power grids and satellite communications while also producing spectacular celestial light shows in some parts of the world.
The US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), which issued a rare solar storm warning, said the solar outburst reached Earth at about 16:00 GMT on Friday, hours sooner than anticipated.
Keep reading
Total solar eclipse sweeps across north america: eight highlights, photos: mexico, us, canada mesmerised by rare total solar eclipse, total solar eclipse 2024: where, when, and how to watch.
The first of several coronal mass ejections (CMEs), described as the expulsions of plasma and magnetic fields from the sun, was later upgraded by the NOAA to an “extreme” geomagnetic storm.
It was the first solar storm occurrence since the Halloween storms of October 2003, which caused blackouts in Sweden and damaged power infrastructure in South Africa.
More solar expulsions are expected in the coming days, and possibly into next week, according to the NOAA.
The United States agency alerted operators of power plants and spacecraft in orbit to take precautions.
Fluctuating magnetic fields associated with geomagnetic storms induce currents in long wires, including power lines, which can potentially cause blackouts. Long pipelines can also become electrified, leading to engineering problems.
Spacecraft are at risk from high doses of radiation, although the atmosphere prevents this from reaching Earth.
Following one particularly strong peak, the NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center said users of high-frequency radio signals “may experience temporary degradation or complete loss of signal on much of the sunlit side of Earth”.
Unlike solar flares, which travel at the speed of light and reach Earth in about eight minutes, CMEs travel at a steadier pace, with officials putting the current average at 800km (500 miles) per second.
They said that the CMEs emanated from a massive sunspot cluster that is 17 times wider than Earth.
Even pigeons and other species that have internal biological compasses could be affected. Pigeon handlers have noted a reduction in birds coming home during geomagnetic storms, according to US space agency NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
The most powerful geomagnetic storm in recorded history, known as the Carrington Event after British astronomer Richard Carrington, occurred in September 1859.
Extreme (G5) geomagnetic conditions have been observed! pic.twitter.com/qLsC8GbWus — NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center (@NWSSWPC) May 10, 2024
‘Gift from space’
Social media lit up with people posting pictures of auroras from northern Europe and Australasia.
“We’ve just woken the kids to go watch the northern lights in the back garden! Clearly visible with the naked eye,” Iain Mansfield in Hertford, England, told the AFP news agency.
That sense of wonder was shared in Australia’s island state of Tasmania.
“Absolutely biblical skies in Tasmania at 4am this morning,” photographer Sean O’Riordan posted on X alongside a photo.
The storm could also produce northern lights as far south in the United States as Alabama and across northern California, according to the NOAA.
But it was hard to predict and experts stressed it would not be the dramatic curtains of colour normally associated with the Northern Lights, but more like splashes of greenish hues.
“That’s really the gift from space weather – the aurora,” Rob Steenburgh, a scientist with the Space Weather Prediction Center, told The Associated Press news agency.

We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked

How to Maximize the Space in Your Carry-On Luggage

Decluttering expert Monica Fay joins Tampa Bay's Morning Blend to show us how to maximize the space in your carry-on luggage as we head into the summer travel season.
For more information, follow her on Instagram @MsMonicaFay or head to TheBigLetGo.com .
Report a typo
Sign up for the Morning Headlines Newsletter and receive up to date information.
Now signed up to receive the morning headlines newsletter..

Tampa Bay's Morning Blend
Tampa Bay’s Morning Blend is an original, local lifestyle show focused on providing our audience with informative, useful and entertaining content. It features a variety of community organizations, businesses and happenings in the Bay area. It is a marketing-friendly program dedicated to offering businesses the opportunity to showcase their company/products, reach potential customers and gain results.
Grow Your Business With Us! For Sponsor Information: [email protected]
Ukraine war latest: Russian missile ship hit, Kyiv officials say; Putin sacks minister in new sign of shift in strategy
Ukraine says it hit Russian missile ship Tsiklon in Crimea. Meanwhile, analysts say Moscow is seeking to draw out Kyiv's forces - as Putin makes another significant change to his cabinet.
Tuesday 21 May 2024 17:00, UK

- Ukraine hit Russian missile ship, Kyiv officials say
- Putin sacks minister in new sign of shift in war strategy
- European country now pushing to let Ukraine strike deep into Russia with Western weapons
- Russia using 'understaffed and incohesive forces' in bid to draw out Ukrainian troops
- Ukraine says it shot down 28 0f 29 drones in overnight Russian attacks
- Big picture: What you need to know as war enters new week
- Live reporting by Bhvishya Patel
European Union countries say they have reached an agreement to use the profits from frozen Russian assets to provide military support to Ukraine and help rebuild the war-torn country.
The 27-nation EU is holding around €210bn (£179bn) in Russian central bank assets, most of it frozen in Belgium, in retaliation for Moscow's war against Ukraine.
It estimates that the interest on that money could provide around €3bn (£2.56bn) each year.
Ukraine is desperate for more weapons and ammunition as Russia presses its military advantage.
EU headquarters said 90% of the money would be put into a special fund known as the European Peace Facility that many EU countries already use to get reimbursed for arms and ammunition they send to Ukraine.
The other 10% would be put into the EU budget. The programmes that this money funds would help to bolster Ukraine's defence industry or to help with reconstruction, should some countries object to their share being used for military purposes.
A small group of member states, notably Hungary, refuse to supply weapons to Ukraine.
Moldova has signed a security and defence partnership with the European Union, the first country to agree such a deal with the bloc.
EU foreign policy chief Josep Borrell made the announcement today.
It follows Moldova's strong condemnation of Russia's invasion of neighbouring Ukraine.
Led by pro-European President Maia Sandu, Moldova, which lies between Ukraine and NATO and EU member Romania, hopes to join the European Union by 2030.
"This partnership will enhance the country's resilience. It will allow (us) to jointly address common security challenges, make our engagement more effective and explore new areas of cooperation," Mr Borrell wrote on X.
Moldovan Prime Minister Dorin Recean said on the X social media platform that EU accession would be the best "mechanism to ensure peace & stability for Moldova's citizens".
"Until then, the signing of the EU-Moldova Security and Defence Partnership is a step forward, enhancing our peace, security, and prosperity," he wrote.
Moldova gained independence from the Soviet Union in 1991 and its relations with Moscow have deteriorated during Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
As reported here earlier, German's foreign minister has been visiting Ukraine today.
Annalena Baerbock held talks with Volodomry Zelenskyy and spoke to Ukrainian energy minister Herman Halushchenko during an official visit to a thermal power plant that was destroyed by a Russian rocket attack in Ukraine.
Russian forces have wrought major damage with strikes on Ukraine's energy infrastructure since invading in 2022.
Ukraine's military hit the Russian missile ship Tsiklon in Moscow-occupied Crimea on Sunday, the Ukrainian general staff has said.
No further details on the matter but we'll bring you any updates on this as we get them.
Tens of thousands of Russians who fled to Turkey after Moscow's invasion of Ukraine have moved on to other countries in the past year, according to a new report.
Reuters says those who have moved have been squeezed by residency issues and soaring costs, citing data and interviews, including with nine Russian citizens.
Turkey, Russia's Black Sea neighbour - a NATO member - emerged as a magnet for Russians after the invasion in February 2022, with Istanbul and the Mediterranean resort of Antalya both among the preferred options.
Some of them had opposed the invasion, others were trying to shield themselves and their businesses from a wave of Western sanctions imposed on Moscow - including travel bans on Russians to much of Europe.
Some men feared being drafted into the army.
But this month, the number of Russians with Turkish resident permits fell to 96,000, down by more than a third from 154,000 at the end of 2022, official data shows.
Nine Russian citizens who spoke to Reuters said they and others had left partly due to struggles to get residence permits since early 2023. Many have headed to Serbia and Montenegro, among the few European countries where they are welcome.
Russians are also moving on because of soaring costs - Turkish inflation hit 70% last month - along with the difficulty doing basic banking in Turkey as a result of the sanctions.
"You can't predict your future in Turkey," said Dmitri, 46, an IT sector employee who declined to give his surname.
After Vladimir Putin announced a mobilisation in September 2022 to recruit Russian men to fight in Ukraine, Dmitri left Saint Petersburg and reunited with his wife and four-year-old son in Istanbul.
But in January 2023, a text message appeared on his phone saying his residency application was rejected without explanation, he said. Dmitri left Istanbul a month later.
"I had signed a rental contract for one year but had to leave everything behind," he said.
"We moved to Montenegro because it is economically and politically more stable than Turkey."
Turkey's Presidency of Migration Management said all rejected resident-permit applications include a justification in the foreigners' own language under relevant laws, and that applicants are free to pursue legal remedies.
In an email, it said departures of Russians were not only linked to residency permits.
"Several political, economic and sociocultural factors play a role," the government agency said.
One of the various sources of growing tension between the US and Russia has been the subject of the stationing of weapons in space.
Russia vetoed a US-drafted United Nations Security Council resolution last month that called on countries to prevent an arms race in outer space - prompting Washington to suggest Moscow was hiding something.
Then yesterday, a Russian-drafted resolution that called on all countries to prevent "for all time" the placement, threat or use of any weapons in outer space failed.
The draft failed to get the minimum nine votes needed from the 15-member group, with seven voting in favour and seven against, while one abstained.
A veto can only be cast by permanent members the US, Russia, China, Britain or France if a draft gets at least nine votes.
US ambassador Robert Wood told the Security Council before the vote: "We are here today because Russia seeks to distract global attention from its development of a new satellite carrying a nuclear device."
He also accused Russia of launching a satellite last Thursday into low Earth orbit that the US "assesses is likely a counterspace weapon presumably capable of attacking other satellites in low Earth orbit".
Russia's UN ambassador Vassily Nebenzia responded: "I didn't even fully understand what he was talking about."
The 1967 Outer Space Treaty already bars signatories - including Russia and the US - from placing "in orbit around the Earth any objects carrying nuclear weapons or any other kinds of weapons of mass destruction".
Russian foreign ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova today claimed Washington was to blame for the world missing another opportunity to prevent an arms race in outer space.
"The results of the vote on the draft resolution on preventing an arms race in outer space and on space security that Russia submitted to the UN Security Council for examination and China co-authored causes disappointment," she said.
"The United States and its allies acted against our constructive and comprehensive initiative, despite all steps that we made to take into account their proposals (including formulations of the corresponding American-Japanese draft resolution)," the diplomat said in a commentary.
"Another opportunity to prevent an arms race in outer space has, unfortunately, been missed through the fault of the United States and its allies."
The former commander of Russia's 58th army, Ivan Popov, has been arrested on suspicion of "large scale fraud", state-run TASS agency is reporting.
TASS has not provided any details of the investigation into Popov's activities.
We'll bring you more on this story as we get it.
We reported earlier this morning (see 7.29 post) that Ukrainian officials had said their forces shot down 28 out of 29 drones used by Russian forces in an overnight attack on seven regions.
However, at least seven people were injured in a strike in Kharkiv, which also damaged four private residences and 25 trucks and buses.
Footage from the scene shows firefighters battling flames in the wake of the attack.
We reported in our 12.00 post about the visit to Kyiv of Germany's foreign minister, in an effort to lend support to Ukraine's war on Russia.
However, it now appears Germany is set to offer assistance beyond the symbolic, with a source telling Reuters the country plans to ramp up military aid for Ukraine by another €3.8bn (£3.25 billion).
So far, Berlin has earmarked €7.1bn (£5.98bn) for Kyiv with weapons and ammunition this year, but the money has already been almost completely allocated to projects, Bild newspaper reported
It added that Defence Minister Boris Pistorius had asked for the additional funds and Finance Minister Christian Lindner had signalled his backing, pending final approval by parliament in June.
A finance ministry source did not confirm the exact number but added that support for Ukraine would not fail because of the ministry.
According to the report, Mr Pistorius has requested €15bn (£12.82bn) be allocated for military aid for Kyiv in Germany's 2025 budget, which is being negotiated at the moment.
As Russia continues to establish momentum in its offensives around Kharkiv, the war in Ukraine has entered an important phase.
Readers have been sending in their questions to our senior correspondents and military experts for their take on the changing battlefield environment.
Today, Peter asks:
Would US A10 Warthogs make any difference to the war in Ukraine? The US has excess stock and is decommissioning them now. They are cheaper than the F-16s, with a shorter learning curve. I know the US military was against sending some over at the beginning of the war, but now?
Military analyst Sean Bell had this to say:
Thank you, Peter, for this interesting question.
History shows that conducting any form of military action without a credible combat air capability is very difficult. Russia is using its air force assets to pound the Ukrainian frontline, and although Ukraine has used Western surface-to-air missiles to great effect - shooting down around 10% of Russia's fighter jets - the Russian fighter air capability presents a formidable threat to any Ukrainian offensive.
The quickest way to provide Ukraine with the air support it requires would be via a NATO or Western-led no-fly zone. However, to date, there has been limited Western appetite to risk an escalation of the war to a direct conflict between NATO and Russia.
Instead, the West has agreed to provide F-16 fighter jets to Ukraine, but only when they have enough pilots trained to operate these Western aircraft, and when the logistics support and weapons are also available.
Providing Ukraine with an F-16 combat capability has taken time, and it is still not clear when the aircraft and supporting logistics will be deployed into battle, or how the F-16s will be used. One reason the F-16s were selected for Ukraine was their availability - it is the most widely used fighter jet of its generation - as that also means there is a ready supply of spares.
Most important, the F-16 is multirole. It is capable of conducting air defence missions - shooting down enemy aircraft - along with bombing missions, and it has the speed and agility to ensure survivability.
The US A-10 Warthog is an immensely capable aircraft, but it is optimised for Close Air Support - close-proximity support of ground forces. At this role it is very effective, but the platform has no air defence capability, and by modern fighter-jet standards, it is very slow - a third of the speed of many Russian fighters. That would make it very vulnerable to Russian attack if deployed into battle without a comprehensive package of air support.
Once the war is over, Ukraine will need to rebuild its own combat air capability, and might benefit from the A-10's unique capabilities. But for now, the F-16 provides Ukraine with the best prospect of a near-term combat-effective combat air capability.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe.
Aeronautics
Learning Resources
News & events.
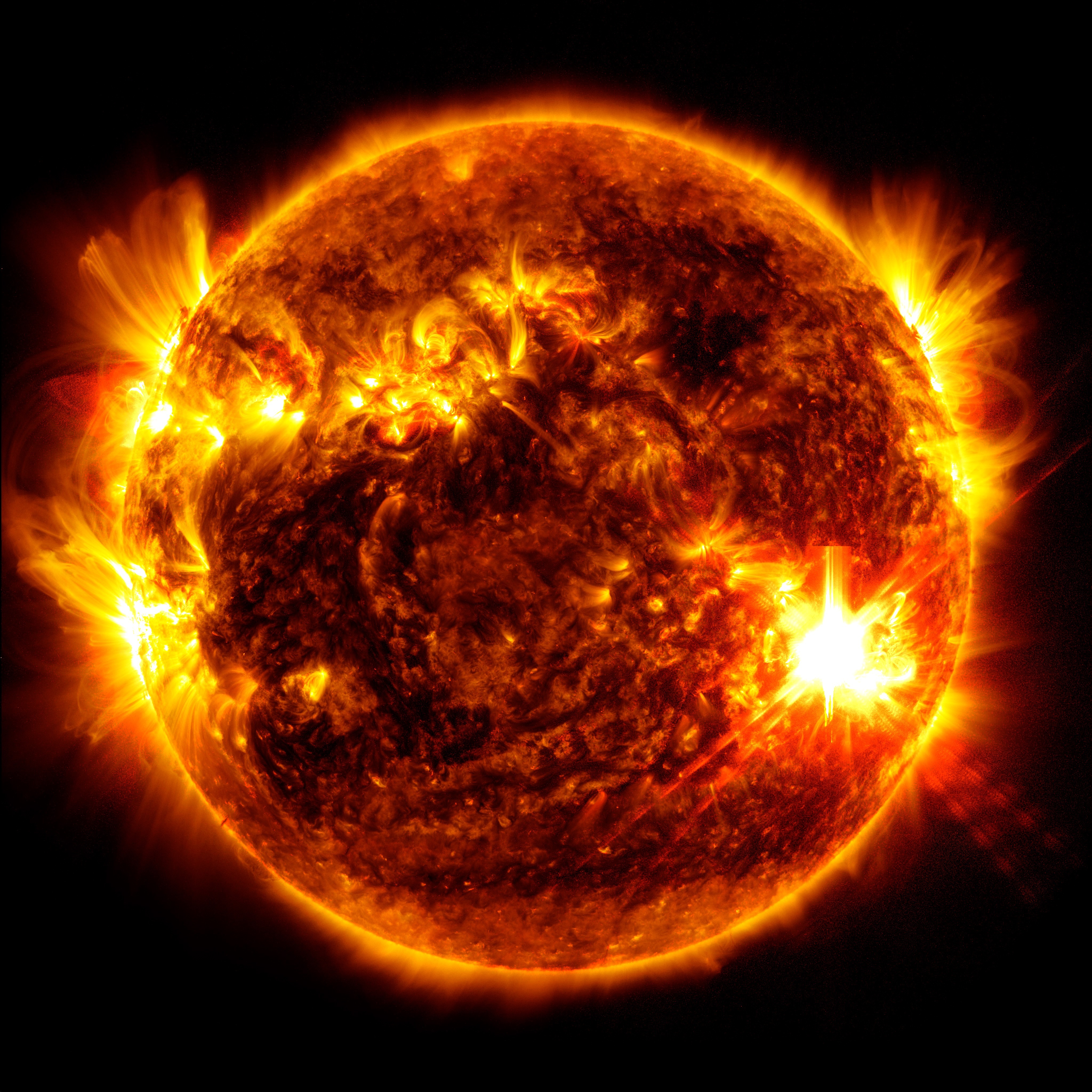

How NASA Tracked the Most Intense Solar Storm in Decades

NASA’s X-59 Passes Milestone Toward Safe First Flight

5 Things to Know About NASA’s Tiny Twin Polar Satellites
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Astronauts Home
- Commercial Space
Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

Welcome Back to Planet Earth, Expedition 70 Crew!

55 Years Ago: Two Months Until the Moon Landing

NASA, Sierra Space Deliver Dream Chaser to Florida for Launch Preparation

Astronaut Exercise
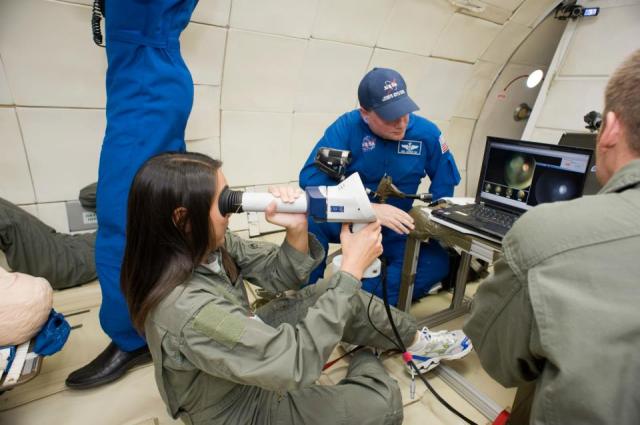

Eleasa Kim: Pioneering CLDP Payload Operations and Cultural Integration
NASA “Wildfire Digital Twin” Pioneers New AI Models and Streaming Data Techniques for Forecasting Fire and Smoke

How ‘Glowing’ Plants Could Help Scientists Predict Flash Drought
NASA’s Juno Provides High-Definition Views of Europa’s Icy Shell
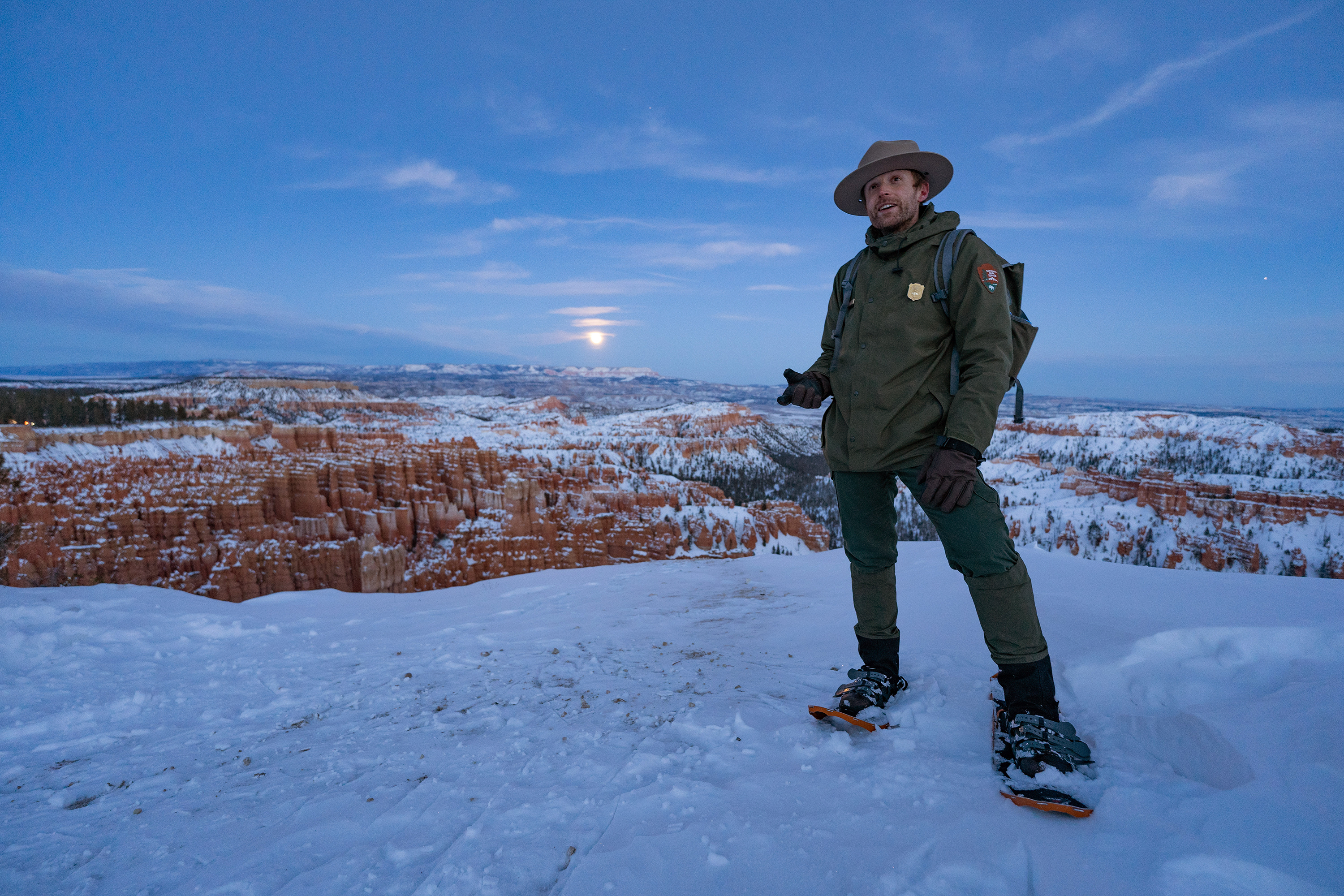

The Next Full Moon is the Flower, Corn, or Corn Planting Moon

Binoculars: A Great First Telescope
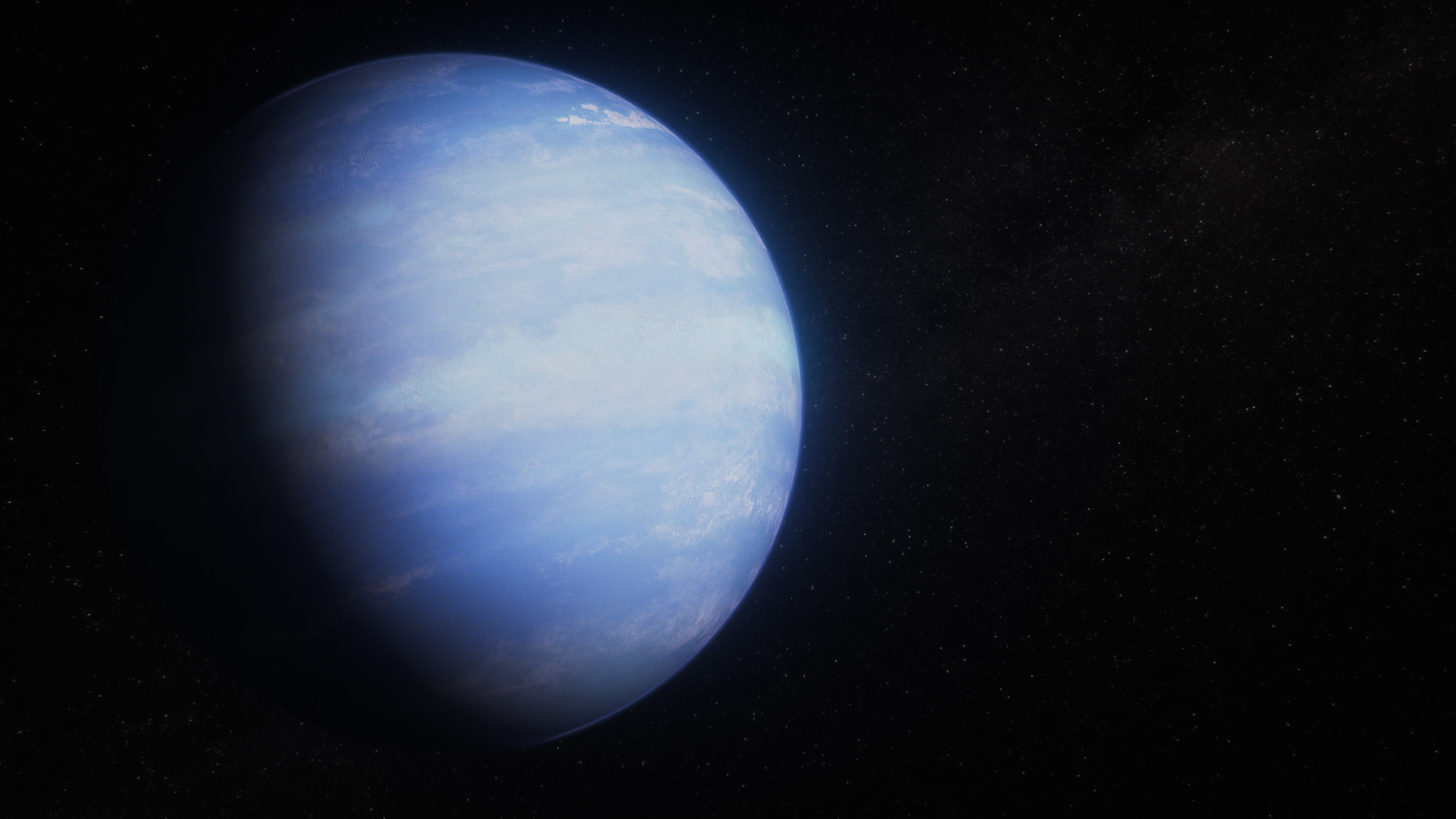
Webb Cracks Case of Inflated Exoplanet
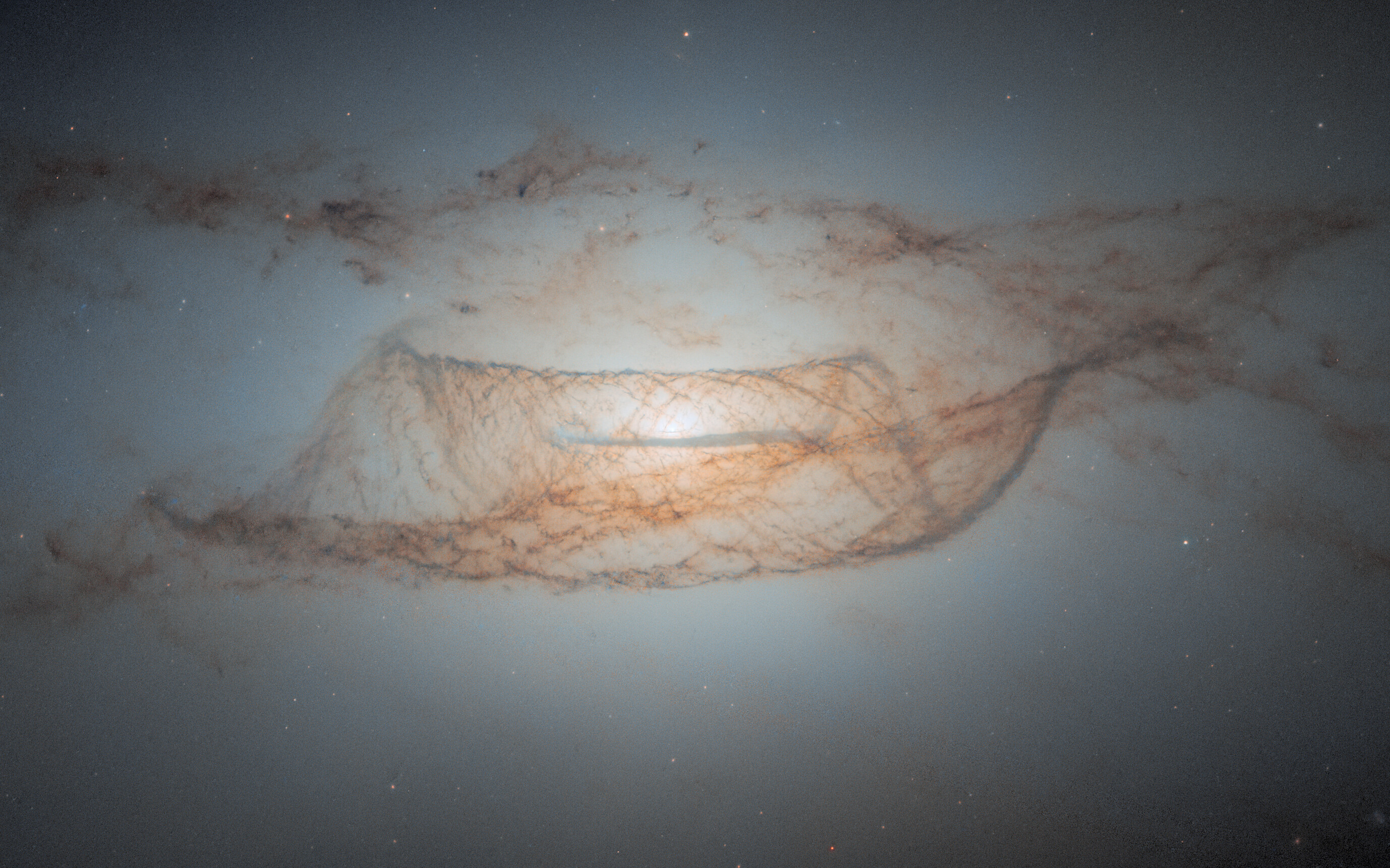

Hubble Views Cosmic Dust Lanes
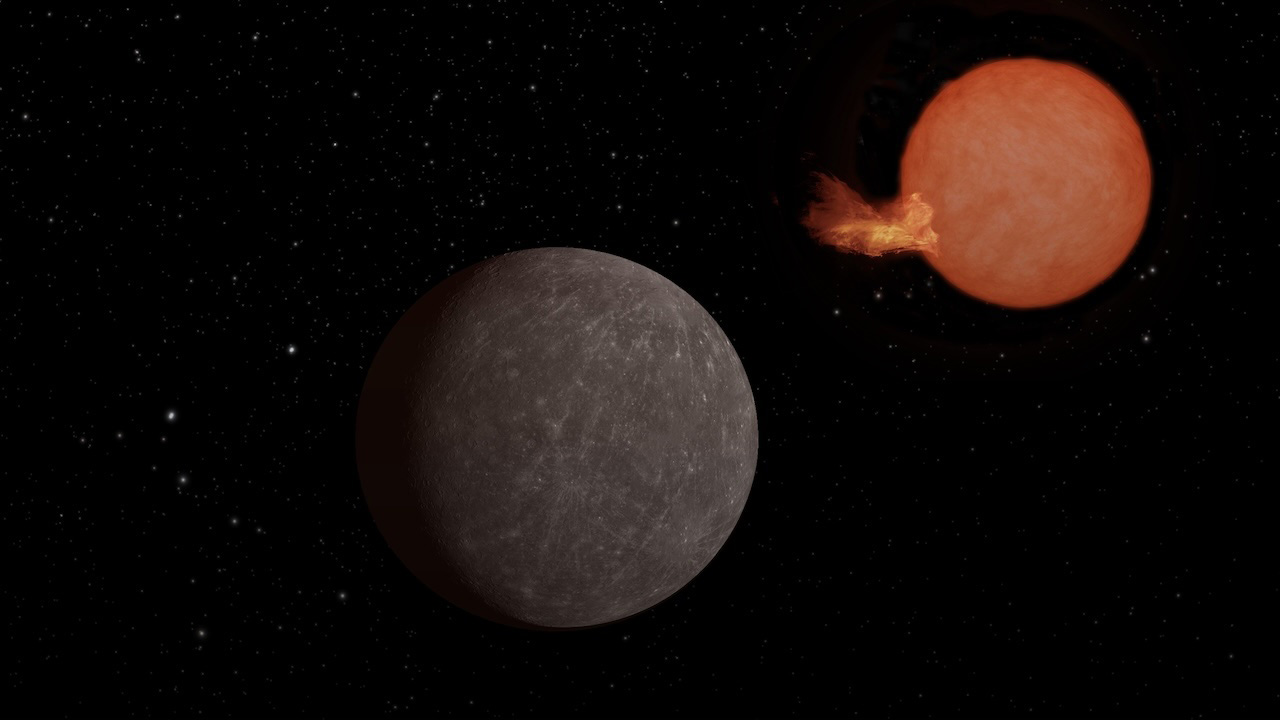

Discovery Alert: An Earth-sized World and Its Ultra-cool Star
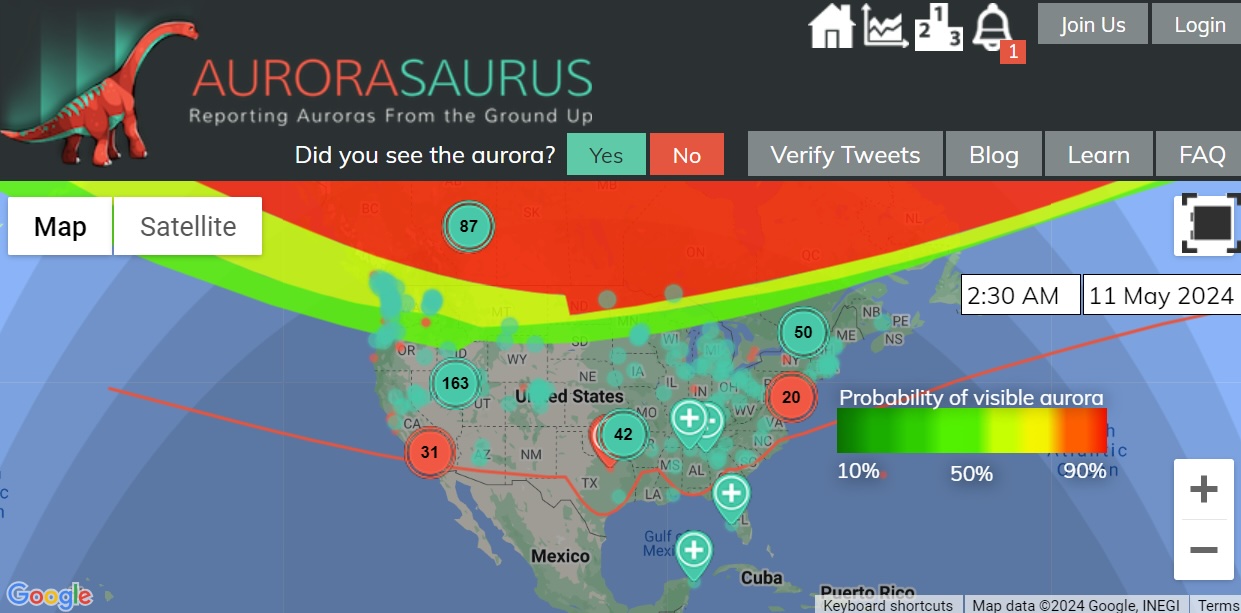
Aurorasaurus Roars During Historic Solar Storm

NASA, Industry to Start Designing More Sustainable Jet Engine Core

Aviary: A New NASA Software Platform for Aircraft Modelling

Tech Today: From Spacesuits to Racing Suits

Tech Today: A NASA-Inspired Bike Helmet with Aerodynamics of a Jet

NASA Challenge Gives Artemis Generation Coders a Chance to Shine

NASA Around the World: Interns Teach Virtual Lessons in Kenya

NASA Names Deputy Station Manager, Operations Integration Manager

Meet NASA Women Behind World’s Largest Flying Laboratory

Diez maneras en que los estudiantes pueden prepararse para ser astronautas

Astronauta de la NASA Marcos Berríos

Resultados científicos revolucionarios en la estación espacial de 2023
Learn more about spaceships and rockets enabled by NASA.

Space Stations
From low Earth orbit to the Moon, these space stations are the ultimate homes away from home.
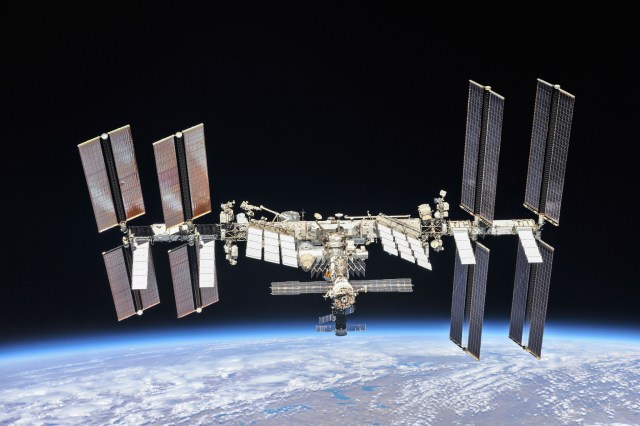

Humanity's home and laboratory off Earth.

Commercial Low Earth Orbit Destinations
The future of off-Earth research.

Humanity's first space station in lunar orbit.
What is a rocket?
A rocket is used to carry a spacecraft from Earth’s surface to space, usually to low Earth orbit or beyond, and is sometimes called a launch vehicle.
Although rockets may appear similar, no two are alike because they are complex devices with millions of pieces and systems that must be calculated and constructed to work together. A rocket is chosen based on the spacecraft’s mission requirements. For example, the farther away from Earth the spacecraft needs to go, the bigger and more powerful the rocket needs to be.

Space Launch System
Combining power and capability, NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and Artemis. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and cargo directly to the Moon in a single launch.

Commercial Crew Rockets
Commercial resupply rockets, more rockets.
These commercial rockets are launching crews to low Earth orbit through partnerships with NASA.
A new generation of rockets capable of carrying astronauts to low Earth orbit and the International Space Station provides expanded utility, additional research time, and broader opportunities for discovery on the orbiting laboratory.
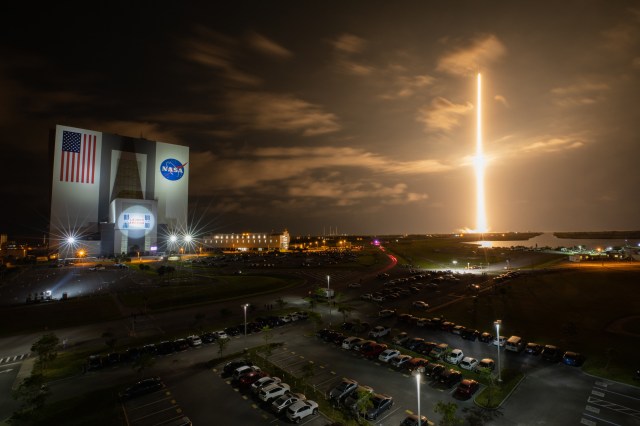

These companies are successfully resupplying the space station.
Safe, reliable, and affordable commercial access low Earth orbit is a critical component of NASA’s path for human exploration. The research being conducted aboard the space station made possible by cargo transportation services also advances NASA’s future deep space exploration objectives.
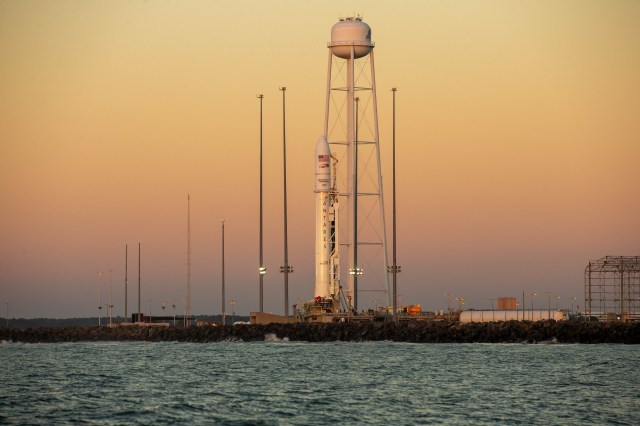

Explore additional uncrewed rockets delivering spacecraft that observe Earth, visit other planets and explore the universe.

What is a spacecraft?
A spacecraft is a vehicle that flies in space. It can carry astronauts, cargo, or instruments to their destination, or it can be the destination. The International Space Station is a spacecraft, just like the smaller vehicles that deliver crew and cargo to it.
Spacecraft launch on rockets and have their own propulsion and navigation systems that take over after they separate from the rocket, propelling them to other worlds in our solar system. Their main purpose lies in transporting payloads — or anything within the vehicle beyond what is essential to operate in space — to their destination. For example, for the Artemis II Moon mission, a human crew and other experiments will be carried aboard the Orion spacecraft.
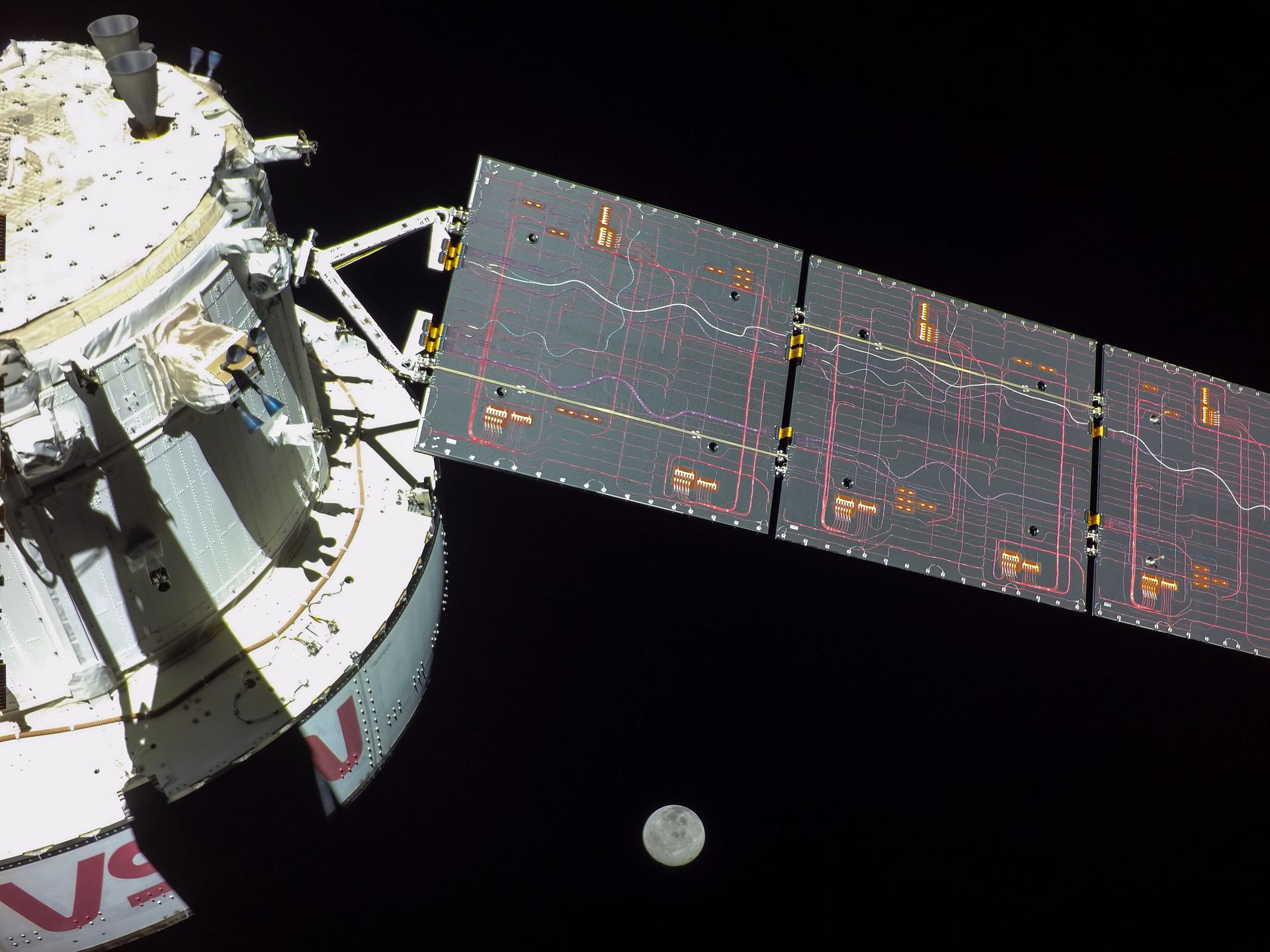

Orion Spacecraft
NASA’s Orion spacecraft is built to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before. On Artemis missions, Orion will serve as the exploration vehicle that will carry the crew to space, provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel, and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion will launch on NASA’s new heavy-lift rocket, the Space Launch System.
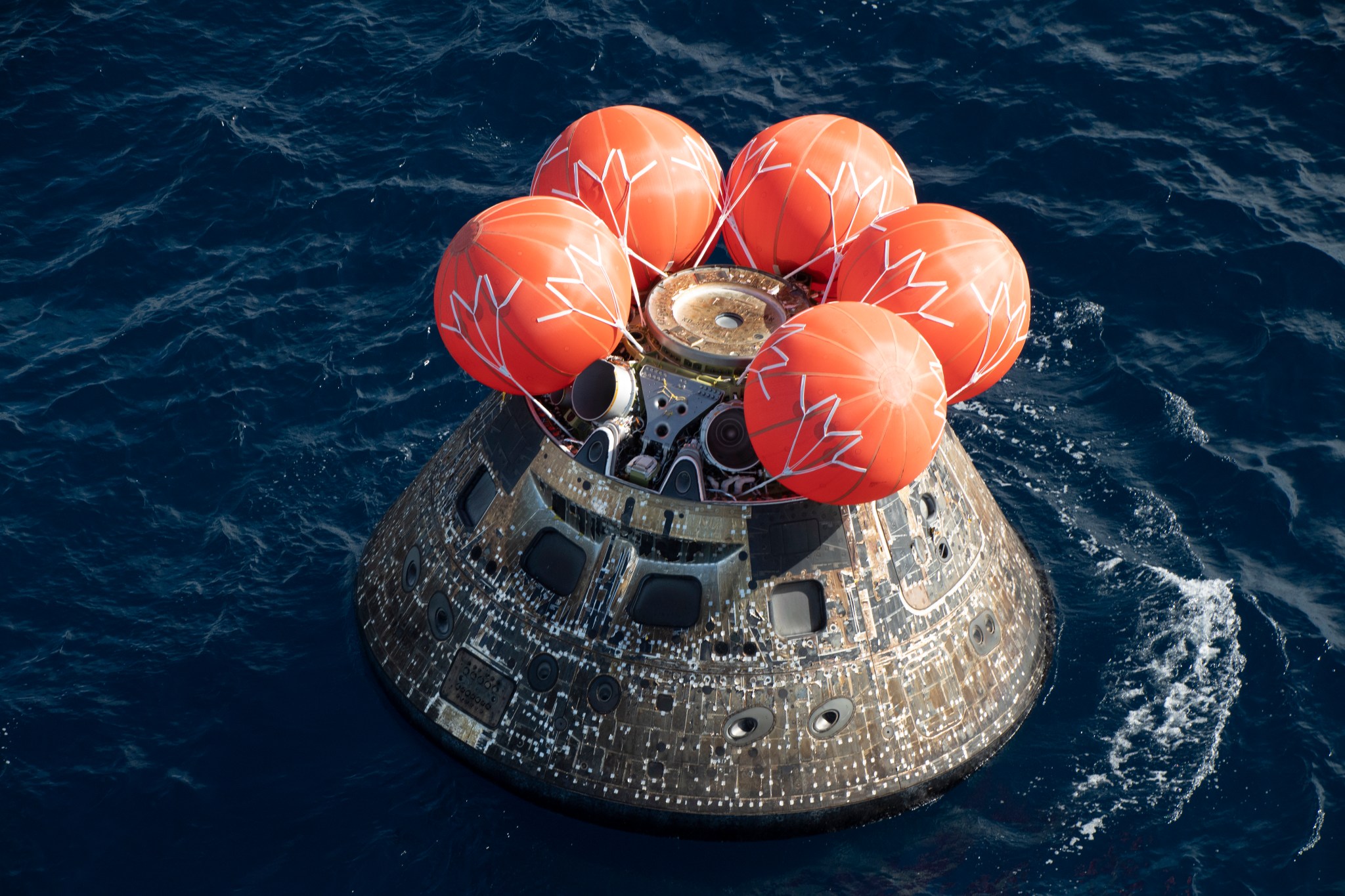

Commercial Cargo Spacecraft
Commercial crew spacecraft.
- International Partners
These spacecraft are carrying cargo and scientific investigations to and from the space station.
Commercial resupply missions are changing the way NASA does business, helping to build a strong American commercial space industry and freeing the agency to focus on developing the next-generation rocket and spacecraft that will allow us to travel farther in space than ever before.

These spacecraft are carrying astronauts to and from the space station.
For more than 22 years, humans have lived and worked on humanity’s home in low Earth orbit. NASA’s Commercial Crew Program is delivering human transportation to and from the International Space Station from the United States through a partnership with American private industry.
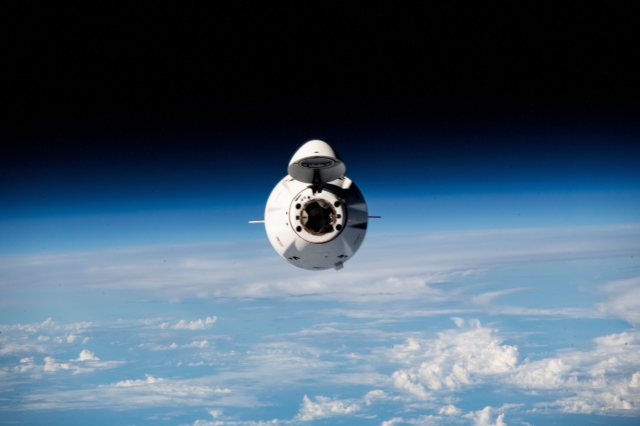

International Partner Rockets and Spacecraft
Exploring low Earth orbit, together.
Partner space agencies provide and operate elements of the International Space Station. The principals are the space agencies of the United States, Russia, Europe, Japan, and Canada.

Ride to the moon?
Human landing systems.
Bringing astronauts from orbit around the Moon onto lunar soil
NASA’s commercial providers, Blue Origin and SpaceX, are building the human landing systems that will carry Artemis astronauts to the lunar surface and back to lunar orbit for their ride home to Earth aboard Orion.
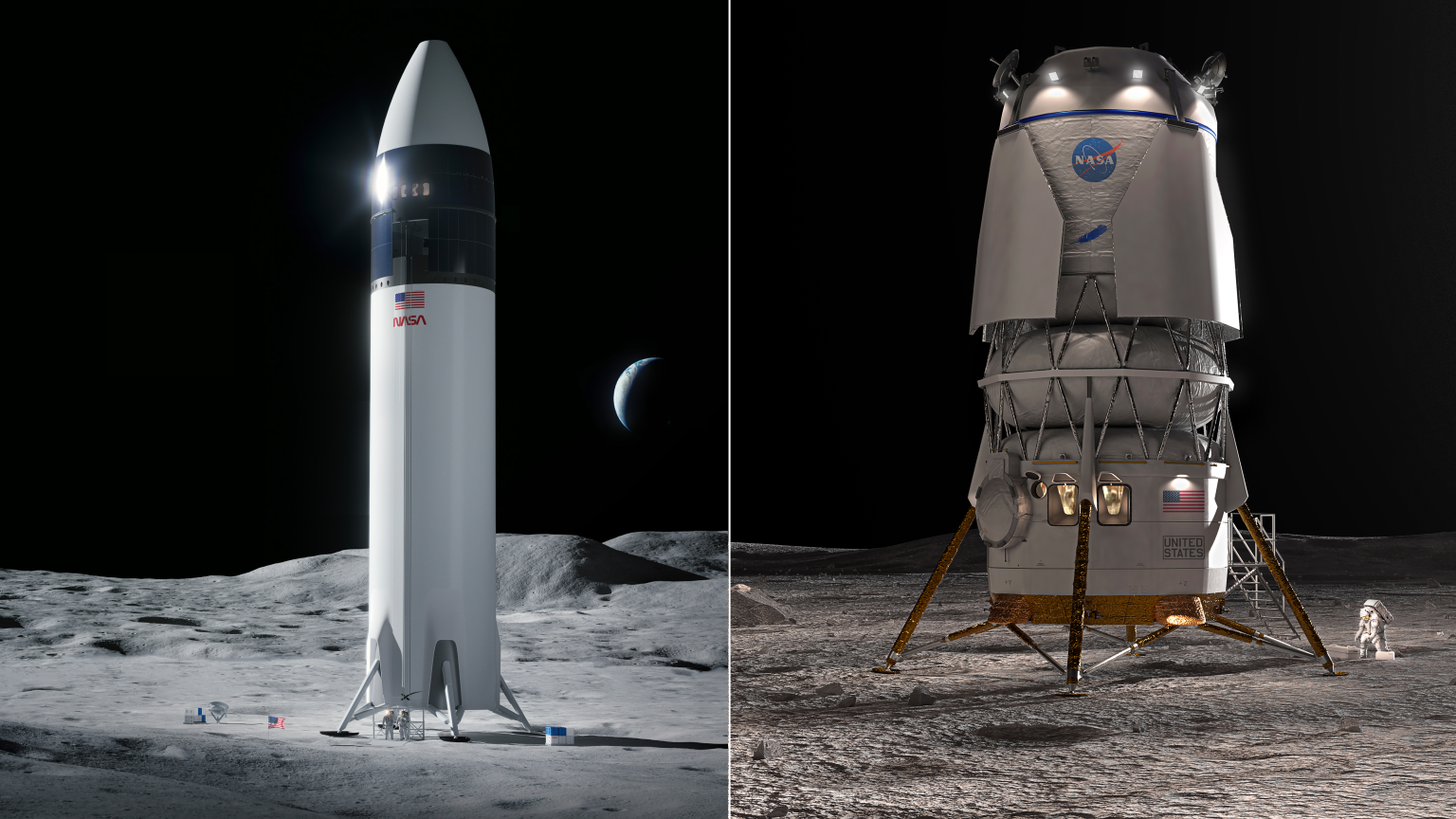
Gateway Deep Space Logistics
As astronauts conduct missions at Gateway and prepare for lunar surface missions, they will need deliveries of critical pressurized and unpressurized cargo, science experiments, and supplies like sample collection materials. In March 2020, NASA announced SpaceX as the first U.S. commercial provider under the Gateway Logistics Services contract to deliver cargo and other supplies to Gateway.
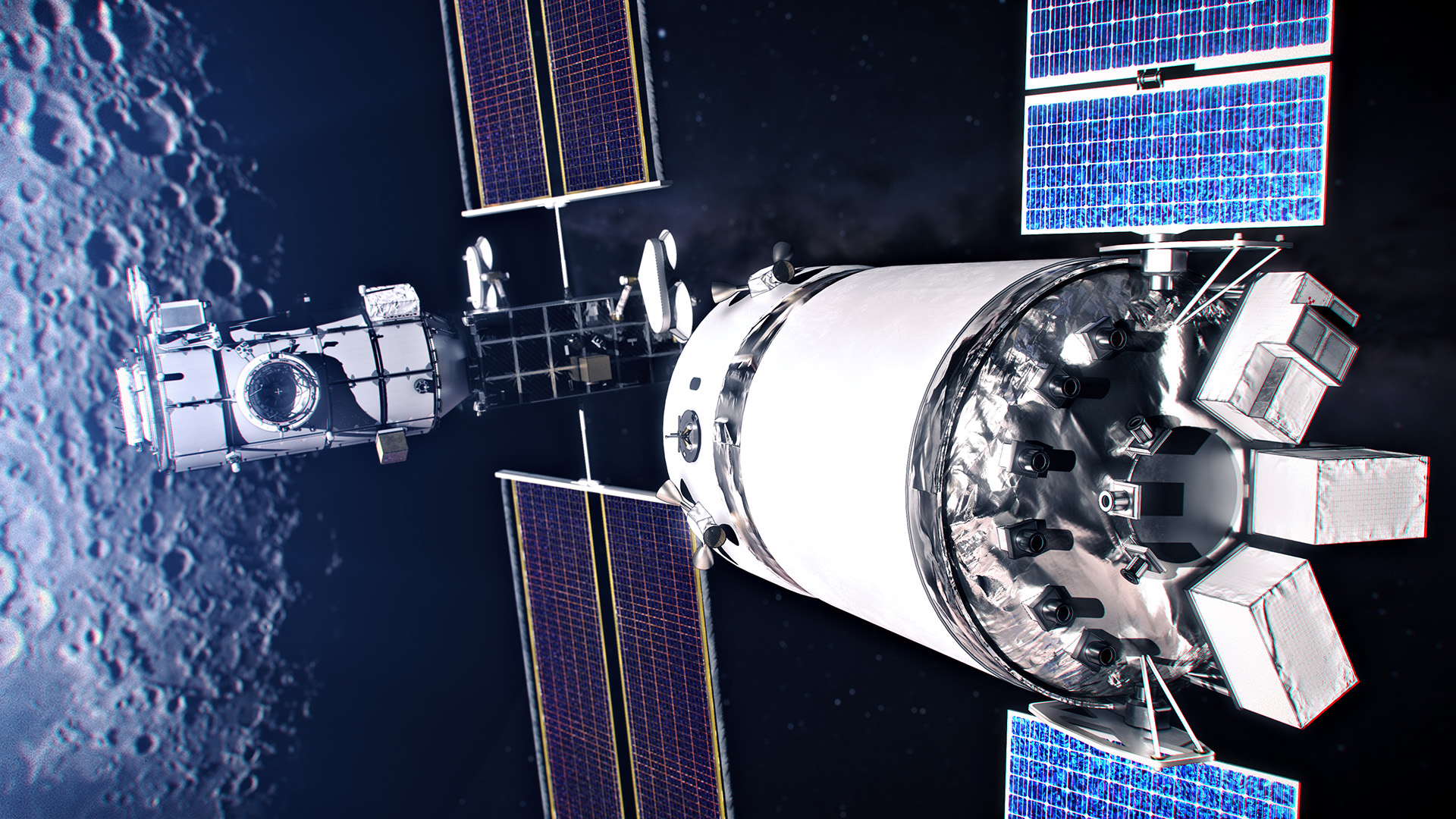

Discover More Topics From NASA


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Everything you need to know about space travel (almost) - BBC Science Focus Magazine.
History of Space Travel. Learn about the history of humans traveling into space. The first earthling to orbit our planet was just two years old, plucked from the streets of Moscow barely more than a week before her historic launch. Her name was Laika. She was a terrier mutt and by all accounts a good dog. Her 1957 flight paved the way for space ...
Space Travel. The path to the Moon, Mars, and beyond requires technologies to get us where we need to go quickly, safely and efficiently. Space travel includes launch and in-space propulsion systems, cryogenic fluid management, and thermal management, as well as navigation and landing systems to get our supplies, equipment, and robotic or human ...
Space exploration, investigation, by means of crewed and uncrewed spacecraft, of the reaches of the universe beyond Earth's atmosphere and the use of the information so gained to increase knowledge of the cosmos and benefit humanity. ... The strong hold that space travel has always had on the imagination may well explain why professional ...
Space exploration is the use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space. [1] While the exploration of space is currently carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration is conducted both by uncrewed robotic space probes and human spaceflight. Space exploration, like its classical form astronomy, is one ...
NASA aims to travel to the moon again—and beyond. Here's a look at the 21st-century race to send humans into space. Private spaceflight is not a new concept. In the United States, commercial ...
Our solar system orbits the center of the galaxy at about 515,000 mph (828,000 kph). It takes about 230 million years to complete one orbit around the galactic center. We call it the solar system because it is made up of our star, the Sun, and everything bound to it by gravity - the planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus ...
In addition to launching the first artificial satellite, the first dog in space, and the first human in space, the Soviet Union achieved other space milestones ahead of the United States. These milestones included Luna 2, which became the first human-made object to hit the Moon in 1959. Soon after that, the U.S.S.R. launched Luna 3.
Space.com is your source for the latest astronomy news and space discoveries, live coverage of space flights and the science of space travel. | Space
The first crewed mission of Boeing's new Starliner spacecraft has been pushed back by an additional four days, to May 25. Human Spaceflight. US Space Force is launching more missions than ever ...
Space travel and exploration have opened up new frontiers and possibilities for humanity, from the first manned mission to the moon in 1969 to the ongoing efforts to send humans to Mars. In addition to manned missions, we have also sent satellites into orbit around the Earth. These satellites serve various purposes that have revolutionized our ...
Stefanie Waldek is a freelance space, travel, and design journalist with expertise in aviation, meteorology, and polar regions. She was a former editor at Architectural Digest, TripAdvisor, and ...
Here's what the next year has lined up for space. Moon landings. A lunar lander will already be on its way when 2023 begins. Launched in December on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, the private ...
Space exploration unites the world to inspire the next generation, make ground-breaking discoveries, and create new opportunities. Technologies and missions we develop for human spaceflight have thousands of applications on Earth, boosting the economy, creating new career paths, and advancing everyday technologies all around us.
Voyager 1 is the first spacecraft to travel beyond the solar system and reach interstellar space . The probe launched on Sept. 5, 1977 — about two weeks after its twin Voyager 2 — and as of ...
NASA One Step Closer to Fueling Space Missions with Plutonium-238. 2 min read. The recent shipment of heat source plutonium-238 from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE's) Oak Ridge National Laboratory to its…. Article.
One of the world's first commercial spaceports designed for orbital missions, launches from Starbase will provide access to destinations in Earth orbit, the Moon, Mars, and beyond. SpaceX designs, manufactures and launches advanced rockets and spacecraft. The company was founded in 2002 to revolutionize space technology, with the ultimate ...
Jason Lyon. By Debra Kamin. May 7, 2022. Ilida Alvarez has dreamed of traveling to space since she was a child. But Ms. Alvarez, a legal-mediation firm owner, is afraid of flying, and she isn't ...
In this episode of "Spaced Out," we break down the inner workings of the most advanced telescope in space—Hubble! Learn about the incredible systems designed to keep Hubble running and how it's affecting the next generation of space telescopes. Now Playing. 3:25.
Reminder to Space-A travelers: Keep in mind there is no guarantee you will be selected for a seat. Space-A travelers must be prepared to cover commercial travel expenses if flight schedules are changed or become unavailable to allow Space-A travel (Per DODI 4515.13, Section 4, Paragraph 4.1.a).
The huge solar storm is keeping power grid and satellite operators on edge. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this image of solar flares early Saturday afternoon. The National Oceanic and ...
5. Best Time To Visit. For the best views, visit the Space Needle on a clear day. This may seem obvious, but with Seattle's reputation for rainy weather, it's worth noting. On a clear day, you'll be able to see for miles and all that sunshine will help you take fantastic photos.
Space exploration unites the world to inspire the next generation, make ground-breaking discoveries, and create new opportunities. Technologies and missions we develop for human spaceflight have thousands of applications on Earth, boosting the economy, creating new career paths, and advancing everyday technologies all around us.
The entitlement is for only one pet (dog or cat) and is limited to $2,000 for an overseas move or $550 for movement within the United States. Travelers using AMC Patriot Express missions will receive a memo receipt for pet travel fees. Please ensure you receive a receipt for your pet's travel fees during check-in for your flight.
None were expecting a visitor from outer space exploding above their heads. At 11:46 p.m. in Portugal, a fireball streaked across the sky, leaving a smoldering trail of incandescent graffiti in ...
Unlike solar flares, which travel at the speed of light and reach Earth in about eight minutes, CMEs travel at a steadier pace, with officials putting the current average at 800km (500 miles) per ...
The wizard will prepare you to apply for a U.S. passport, whether it's your first time applying, you need to renew, or you want to get a passport for your child. Please note that completing the wizard does not entitle you to a U.S. passport, and the U.S. embassy, consulate, or office providing consular services may require you to provide ...
and last updated 4:27 AM, May 21, 2024. Decluttering expert Monica Fay joins Tampa Bay's Morning Blend to show us how to maximize the space in your carry-on luggage as we head into the summer ...
We reported in our 12.00 post about the visit to Kyiv of Germany's foreign minister, in an effort to lend support to Ukraine's war on Russia. However, it now appears Germany is set to offer ...
The International Space Station is a spacecraft, just like the smaller vehicles that deliver crew and cargo to it. Spacecraft launch on rockets and have their own propulsion and navigation systems that take over after they separate from the rocket, propelling them to other worlds in our solar system. Their main purpose lies in transporting ...